diff options
| author | Android Build Coastguard Worker <android-build-coastguard-worker@google.com> | 2024-02-02 23:47:35 +0000 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | Android Build Coastguard Worker <android-build-coastguard-worker@google.com> | 2024-02-02 23:47:35 +0000 |
| commit | 790cbdbe85f972eada1185fcc5d2d8bbca11d673 (patch) | |
| tree | 03159a0a38f000cb747f4e1128efd557fdf16f72 | |
| parent | 40f29d103e502c161d3c8f64baa141c041ce43ea (diff) | |
| parent | 9ceaceb7129151e8d8bc60979e0292526a59a589 (diff) | |
| download | fmtlib-simpleperf-release.tar.gz | |
Snap for 11400057 from 9ceaceb7129151e8d8bc60979e0292526a59a589 to simpleperf-releasesimpleperf-release
Change-Id: I19e87d8ec253bbce5a7484ee6d9ab2fe75b14290
126 files changed, 54887 insertions, 55184 deletions
diff --git a/.github/dependabot.yml b/.github/dependabot.yml new file mode 100644 index 00000000..55c156a6 --- /dev/null +++ b/.github/dependabot.yml @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ +version: 2 +updates: + - package-ecosystem: "github-actions" # Necessary to update action hashs + directory: "/" + schedule: + interval: "monthly" + # Allow up to 3 opened pull requests for github-actions versions + open-pull-requests-limit: 3 diff --git a/.github/issue_template.md b/.github/issue_template.md new file mode 100644 index 00000000..8e39c5ba --- /dev/null +++ b/.github/issue_template.md @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ +<!-- +Please make sure that the problem reproduces on the current master before +submitting an issue. +If possible please provide a repro on Compiler Explorer: +https://godbolt.org/z/fxccbh53W. +--> diff --git a/.github/pull_request_template.md b/.github/pull_request_template.md new file mode 100644 index 00000000..e8774133 --- /dev/null +++ b/.github/pull_request_template.md @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ +<!-- +Please read the contribution guidelines before submitting a pull request: +https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md. +By submitting this pull request, you agree to license your contribution(s) +under the terms outlined in LICENSE.rst and represent that you have the right +to do so. +--> diff --git a/.github/workflows/cifuzz.yml b/.github/workflows/cifuzz.yml new file mode 100644 index 00000000..f87899d0 --- /dev/null +++ b/.github/workflows/cifuzz.yml @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ +name: CIFuzz +on: [pull_request] + +permissions: + contents: read + +jobs: + Fuzzing: + runs-on: ubuntu-latest + steps: + - name: Build Fuzzers + id: build + uses: google/oss-fuzz/infra/cifuzz/actions/build_fuzzers@master + with: + oss-fuzz-project-name: 'fmt' + dry-run: false + language: c++ + - name: Run Fuzzers + uses: google/oss-fuzz/infra/cifuzz/actions/run_fuzzers@master + with: + oss-fuzz-project-name: 'fmt' + fuzz-seconds: 300 + dry-run: false + language: c++ + - name: Upload Crash + uses: actions/upload-artifact@0b7f8abb1508181956e8e162db84b466c27e18ce # v3.1.2 + if: failure() && steps.build.outcome == 'success' + with: + name: artifacts + path: ./out/artifacts diff --git a/.github/workflows/doc.yml b/.github/workflows/doc.yml new file mode 100644 index 00000000..4055b9f3 --- /dev/null +++ b/.github/workflows/doc.yml @@ -0,0 +1,35 @@ +name: doc + +on: [push, pull_request] + +permissions: + contents: read + +jobs: + build: + # Use Ubuntu 20.04 because doxygen 1.8.13 from Ubuntu 18.04 is broken. + runs-on: ubuntu-20.04 + + steps: + - uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0 + + - name: Add ubuntu mirrors + run: | + # Github Actions caching proxy is at times unreliable + # see https://github.com/actions/runner-images/issues/7048 + printf 'http://azure.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu\tpriority:1\n' | sudo tee /etc/apt/mirrors.txt + curl http://mirrors.ubuntu.com/mirrors.txt | sudo tee --append /etc/apt/mirrors.txt + sudo sed -i 's~http://azure.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/~mirror+file:/etc/apt/mirrors.txt~' /etc/apt/sources.list + + - name: Create Build Environment + run: | + sudo apt update + sudo apt install doxygen python3-virtualenv + sudo npm install -g less clean-css + cmake -E make_directory ${{runner.workspace}}/build + + - name: Build + working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build + env: + KEY: ${{secrets.KEY}} + run: $GITHUB_WORKSPACE/support/build-docs.py diff --git a/.github/workflows/linux.yml b/.github/workflows/linux.yml new file mode 100644 index 00000000..0f30ba63 --- /dev/null +++ b/.github/workflows/linux.yml @@ -0,0 +1,111 @@ +name: linux + +on: [push, pull_request] + +permissions: + contents: read + +jobs: + build: + runs-on: ubuntu-20.04 + strategy: + matrix: + cxx: [g++-4.8, g++-10, clang++-9] + build_type: [Debug, Release] + std: [11] + include: + - cxx: g++-4.8 + install: sudo apt install g++-4.8 + - cxx: g++-8 + build_type: Debug + std: 14 + install: sudo apt install g++-8 + - cxx: g++-8 + build_type: Debug + std: 17 + install: sudo apt install g++-8 + - cxx: g++-9 + build_type: Debug + std: 17 + - cxx: g++-10 + build_type: Debug + std: 17 + - cxx: g++-11 + build_type: Debug + std: 20 + install: sudo apt install g++-11 + - cxx: clang++-8 + build_type: Debug + std: 17 + cxxflags: -stdlib=libc++ + install: sudo apt install clang-8 libc++-8-dev libc++abi-8-dev + - cxx: clang++-9 + install: sudo apt install clang-9 + - cxx: clang++-9 + build_type: Debug + fuzz: -DFMT_FUZZ=ON -DFMT_FUZZ_LINKMAIN=ON + std: 17 + install: sudo apt install clang-9 + - cxx: clang++-11 + build_type: Debug + std: 20 + - cxx: clang++-11 + build_type: Debug + std: 20 + cxxflags: -stdlib=libc++ + install: sudo apt install libc++-11-dev libc++abi-11-dev + - shared: -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON + + steps: + - uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0 + + - name: Set timezone + run: sudo timedatectl set-timezone 'Asia/Yekaterinburg' + + - name: Add repositories for older GCC + run: | + # Below two repos provide GCC 4.8, 5.5 and 6.4 + sudo apt-add-repository 'deb http://azure.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic main' + sudo apt-add-repository 'deb http://azure.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic universe' + # Below two repos additionally update GCC 6 to 6.5 + # sudo apt-add-repository 'deb http://azure.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main' + # sudo apt-add-repository 'deb http://azure.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates universe' + if: ${{ matrix.cxx == 'g++-4.8' }} + + - name: Add ubuntu mirrors + run: | + # Github Actions caching proxy is at times unreliable + # see https://github.com/actions/runner-images/issues/7048 + printf 'http://azure.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu\tpriority:1\n' | sudo tee /etc/apt/mirrors.txt + curl http://mirrors.ubuntu.com/mirrors.txt | sudo tee --append /etc/apt/mirrors.txt + sudo sed -i 's~http://azure.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/~mirror+file:/etc/apt/mirrors.txt~' /etc/apt/sources.list + + - name: Create Build Environment + run: | + sudo apt update + ${{matrix.install}} + sudo apt install locales-all + cmake -E make_directory ${{runner.workspace}}/build + + - name: Configure + working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build + env: + CXX: ${{matrix.cxx}} + CXXFLAGS: ${{matrix.cxxflags}} + run: | + cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${{matrix.build_type}} ${{matrix.fuzz}} ${{matrix.shared}} \ + -DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=${{matrix.std}} -DFMT_DOC=OFF \ + -DCMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET=hidden -DCMAKE_VISIBILITY_INLINES_HIDDEN=ON \ + -DFMT_PEDANTIC=ON -DFMT_WERROR=ON $GITHUB_WORKSPACE + + - name: Build + working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build + run: | + threads=`nproc` + cmake --build . --config ${{matrix.build_type}} --parallel $threads + + - name: Test + working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build + run: ctest -C ${{matrix.build_type}} + env: + CTEST_OUTPUT_ON_FAILURE: True diff --git a/.github/workflows/macos.yml b/.github/workflows/macos.yml new file mode 100644 index 00000000..48d179f6 --- /dev/null +++ b/.github/workflows/macos.yml @@ -0,0 +1,55 @@ +name: macos + +on: [push, pull_request] + +permissions: + contents: read + +jobs: + build: + strategy: + matrix: + os: [macos-11, macos-13] + build_type: [Debug, Release] + std: [11, 17, 20] + exclude: + - { os: macos-11, std: 20 } + - { os: macos-13, std: 11 } + - { os: macos-13, std: 17 } + include: + - shared: -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON + + runs-on: '${{ matrix.os }}' + + steps: + - uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0 + + - name: Set timezone + run: sudo systemsetup -settimezone 'Asia/Yekaterinburg' + + - name: Select Xcode 14.3 (macOS 13) + run: sudo xcode-select -s "/Applications/Xcode_14.3.app" + if: ${{ matrix.os == 'macos-13' }} + + - name: Create Build Environment + run: cmake -E make_directory ${{runner.workspace}}/build + + - name: Configure + working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build + run: | + cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${{matrix.build_type}} ${{matrix.shared}} \ + -DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=${{matrix.std}} \ + -DCMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET=hidden -DCMAKE_VISIBILITY_INLINES_HIDDEN=ON \ + -DFMT_DOC=OFF -DFMT_PEDANTIC=ON -DFMT_WERROR=ON $GITHUB_WORKSPACE + + - name: Build + working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build + run: | + threads=`sysctl -n hw.logicalcpu` + cmake --build . --config ${{matrix.build_type}} --parallel $threads + + - name: Test + working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build + run: ctest -C ${{matrix.build_type}} + env: + CTEST_OUTPUT_ON_FAILURE: True diff --git a/.github/workflows/scorecard.yml b/.github/workflows/scorecard.yml new file mode 100644 index 00000000..33aecd30 --- /dev/null +++ b/.github/workflows/scorecard.yml @@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ +# This workflow uses actions that are not certified by GitHub. They are provided +# by a third-party and are governed by separate terms of service, privacy +# policy, and support documentation. + +name: Scorecard supply-chain security +on: + # For Branch-Protection check. Only the default branch is supported. See + # https://github.com/ossf/scorecard/blob/main/docs/checks.md#branch-protection + branch_protection_rule: + # To guarantee Maintained check is occasionally updated. See + # https://github.com/ossf/scorecard/blob/main/docs/checks.md#maintained + schedule: + - cron: '26 14 * * 5' + push: + branches: [ "master" ] + +# Declare default permissions as read only. +permissions: read-all + +jobs: + analysis: + name: Scorecard analysis + runs-on: ubuntu-latest + permissions: + # Needed to upload the results to code-scanning dashboard. + security-events: write + # Needed to publish results and get a badge (see publish_results below). + id-token: write + + steps: + - name: "Checkout code" + uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0 + with: + persist-credentials: false + + - name: "Run analysis" + uses: ossf/scorecard-action@0864cf19026789058feabb7e87baa5f140aac736 # v2.3.1 + with: + results_file: results.sarif + results_format: sarif + # (Optional) "write" PAT token. Uncomment the `repo_token` line below if: + # - you want to enable the Branch-Protection check on a *public* repository, or + # To create the PAT, follow the steps in https://github.com/ossf/scorecard-action#authentication-with-pat. + # repo_token: ${{ secrets.SCORECARD_TOKEN }} + + # Public repositories: + # - Publish results to OpenSSF REST API for easy access by consumers + # - Allows the repository to include the Scorecard badge. + # - See https://github.com/ossf/scorecard-action#publishing-results. + publish_results: true + + # Upload the results as artifacts (optional). Commenting out will disable uploads of run results in SARIF + # format to the repository Actions tab. + - name: "Upload artifact" + uses: actions/upload-artifact@0b7f8abb1508181956e8e162db84b466c27e18ce # v3.1.2 + with: + name: SARIF file + path: results.sarif + retention-days: 5 + + # Upload the results to GitHub's code scanning dashboard. + - name: "Upload to code-scanning" + uses: github/codeql-action/upload-sarif@74483a38d39275f33fcff5f35b679b5ca4a26a99 # v2.22.5 + with: + sarif_file: results.sarif diff --git a/.github/workflows/windows.yml b/.github/workflows/windows.yml index f66e2bc9..d576abb1 100644 --- a/.github/workflows/windows.yml +++ b/.github/workflows/windows.yml @@ -2,27 +2,49 @@ name: windows on: [push, pull_request] +permissions: + contents: read + jobs: build: runs-on: ${{matrix.os}} strategy: matrix: - # windows-2016 and windows-2019 have MSVC 2017 and 2019 installed - # respectively: https://github.com/actions/virtual-environments. - os: [windows-2016, windows-2019] + # windows-2019 has MSVC 2019 installed; + # windows-2022 has MSVC 2022 installed: + # https://github.com/actions/virtual-environments. + os: [windows-2019] platform: [Win32, x64] + toolset: [v140, v141, v142] + standard: [14, 17, 20] + shared: ["", -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON] build_type: [Debug, Release] + exclude: + - { toolset: v140, standard: 17 } + - { toolset: v140, standard: 20 } + - { toolset: v141, standard: 14 } + - { toolset: v141, standard: 20 } + - { toolset: v142, standard: 14 } + - { platform: Win32, toolset: v140 } + - { platform: Win32, toolset: v141 } + - { platform: Win32, standard: 14 } + - { platform: Win32, standard: 20 } + - { platform: x64, toolset: v140, shared: -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON } + - { platform: x64, toolset: v141, shared: -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON } + - { platform: x64, standard: 14, shared: -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON } + - { platform: x64, standard: 20, shared: -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON } include: - - os: windows-2016 - platform: Win32 + - os: windows-2022 + platform: x64 + toolset: v143 build_type: Debug - shared: -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON - exclude: - - os: windows-2016 - platform: Win32 + standard: 20 steps: - - uses: actions/checkout@v2 + - uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0 + + - name: Set timezone + run: tzutil /s "Ekaterinburg Standard Time" - name: Create Build Environment run: cmake -E make_directory ${{runner.workspace}}/build @@ -32,13 +54,47 @@ jobs: shell: bash working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build run: | - cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${{matrix.build_type}} ${{matrix.shared}} \ - -A ${{matrix.platform}} $GITHUB_WORKSPACE + cmake -A ${{matrix.platform}} -T ${{matrix.toolset}} \ + -DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=${{matrix.standard}} \ + ${{matrix.shared}} -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${{matrix.build_type}} \ + $GITHUB_WORKSPACE - name: Build working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build - run: cmake --build . --config ${{matrix.build_type}} + run: | + $threads = (Get-CimInstance Win32_ComputerSystem).NumberOfLogicalProcessors + cmake --build . --config ${{matrix.build_type}} --parallel $threads - name: Test working-directory: ${{runner.workspace}}/build - run: ctest -C ${{matrix.build_type}} + run: ctest -C ${{matrix.build_type}} -V + env: + CTEST_OUTPUT_ON_FAILURE: True + + mingw: + runs-on: windows-latest + defaults: + run: + shell: msys2 {0} + strategy: + matrix: + sys: [ mingw64, ucrt64 ] + steps: + - name: Set timezone + run: tzutil /s "Ekaterinburg Standard Time" + shell: cmd + - uses: msys2/setup-msys2@7efe20baefed56359985e327d329042cde2434ff # v2 + with: + release: false + msystem: ${{matrix.sys}} + pacboy: cc:p cmake:p ninja:p lld:p + - uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0 + - name: Configure + run: cmake -B ../build -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug + env: { LDFLAGS: -fuse-ld=lld } + - name: Build + run: cmake --build ../build + - name: Test + run: ctest -j `nproc` --test-dir ../build + env: + CTEST_OUTPUT_ON_FAILURE: True @@ -9,6 +9,7 @@ gradle/ gradlew* local.properties build/ +support/.cxx bin/ /_CPack_Packages diff --git a/.travis.yml b/.travis.yml deleted file mode 100644 index ff9d167b..00000000 --- a/.travis.yml +++ /dev/null @@ -1,101 +0,0 @@ -language: cpp -dist: trusty -sudo: false - -os: linux - -git: - depth: 1 - -env: - global: - - secure: |- - a1eovNn4uol9won7ghr67eD3/59oeESN+G9bWE+ecI1V6yRseG9whniGhIpC/YfMW/Qz5I - 5sxSmFjaw9bxCISNwUIrL1O5x2AmRYTnFcXk4dFsUvlZg+WeF/aKyBYCNRM8C2ndbBmtAO - o1F2EwFbiso0EmtzhAPs19ujiVxkLn4= - -matrix: - include: - # Documentation - - env: BUILD=Doc - sudo: required - # g++ 6 on Linux with C++14 - - env: COMPILER=g++-6 BUILD=Debug STANDARD=14 - compiler: gcc - addons: - apt: - update: true - sources: - - ubuntu-toolchain-r-test - packages: - - g++-6 - - env: COMPILER=g++-6 BUILD=Release STANDARD=14 - compiler: gcc - addons: - apt: - update: true - sources: - - ubuntu-toolchain-r-test - packages: - - g++-6 - # g++ 8 on Linux with C++17 - - env: COMPILER=g++-8 BUILD=Debug STANDARD=17 - compiler: gcc - addons: - apt: - update: true - sources: - - ubuntu-toolchain-r-test - packages: - - g++-8 - - env: COMPILER=g++-8 BUILD=Release STANDARD=17 - compiler: gcc - addons: - apt: - update: true - sources: - - ubuntu-toolchain-r-test - packages: - - g++-8 - - # Apple clang on OS X with C++14 - - env: BUILD=Debug STANDARD=14 - compiler: clang - os: osx - - env: BUILD=Release STANDARD=14 - compiler: clang - os: osx - # clang 6.0 on Linux with C++14 (builds the fuzzers as well) - - env: COMPILER=clang++-6.0 BUILD=Debug STANDARD=14 ENABLE_FUZZING=1 - compiler: clang - addons: - apt: - update: true - packages: - - clang-6.0 - sources: - - ubuntu-toolchain-r-test - - llvm-toolchain-trusty - - llvm-toolchain-trusty-6.0 - # clang 4.0 on Linux with C++14 - - env: COMPILER=clang++-4.0 BUILD=Debug STANDARD=11 - compiler: clang - addons: - apt: - update: true - packages: - - clang-4.0 - sources: - - ubuntu-toolchain-r-test - - llvm-toolchain-trusty - - llvm-toolchain-trusty-4.0 - # g++ 4.8 on Linux with C++11 - - env: COMPILER=g++-4.8 BUILD=Debug STANDARD=11 - compiler: gcc - -before_script: - - if [[ "${TRAVIS_OS_NAME}" == "linux" ]]; then export CXX=${COMPILER}; fi - - if [[ "${BUILD}" != "Doc" ]]; then ${CXX} --version; fi - -script: - - support/travis-build.py @@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ license { "legacy_unencumbered", ], license_text: [ - "LICENSE.rst", + "LICENSE", "NOTICE", ], } @@ -115,6 +115,10 @@ cc_library_static { defaults: ["fmtlib-non-test-defaults"], sdk_version: "current", stl: "c++_static", + apex_available: [ + "//apex_available:platform", + "com.android.mediaprovider", + ], } cc_defaults { @@ -146,26 +150,43 @@ cc_defaults { // Most of the fmtlib tests. cc_test { - name: "fmtlib_test", + name: "fmtlib_test_1", defaults: ["fmtlib-test-defaults"], srcs: [ + "test/args-test.cc", "test/chrono-test.cc", "test/color-test.cc", "test/core-test.cc", + "test/enforce-checks-test.cc", "test/format-test.cc", + "test/noexception-test.cc", // Some of the os-test tests deliberately try to do bad things with // file descriptors, but Android's fdsan won't let them. // "test/os-test.cc", - "test/printf-test.cc", - "test/ranges-test.cc", + "test/ranges-odr-test.cc", "test/scan-test.cc", + // Depends on filesystem_error declarations which are not linked. + // "test/std-test.cc", + "test/unicode-test.cc", + "test/xchar-test.cc", ], } // This one needs to be separate because some of the test names overlap with // other tests. cc_test { - name: "fmtlib_ostream_test", + name: "fmtlib_test_2", defaults: ["fmtlib-test-defaults"], - srcs: ["test/ostream-test.cc"], + srcs: [ + "test/ostream-test.cc", + "test/printf-test.cc", + ], +} + +cc_test { + name: "fmtlib_test_3", + defaults: ["fmtlib-test-defaults"], + srcs: [ + "test/ranges-test.cc", + ], } diff --git a/CMakeLists.txt b/CMakeLists.txt index f21cf456..485eb86c 100644 --- a/CMakeLists.txt +++ b/CMakeLists.txt @@ -1,4 +1,4 @@ -cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.1...3.18) +cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8...3.26) # Fallback for using newer policies on CMake <3.12. if(${CMAKE_VERSION} VERSION_LESS 3.12) @@ -7,21 +7,105 @@ endif() # Determine if fmt is built as a subproject (using add_subdirectory) # or if it is the master project. -set(MASTER_PROJECT OFF) -if (CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR STREQUAL CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR) - set(MASTER_PROJECT ON) - message(STATUS "CMake version: ${CMAKE_VERSION}") +if (NOT DEFINED FMT_MASTER_PROJECT) + set(FMT_MASTER_PROJECT OFF) + if (CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR STREQUAL CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR) + set(FMT_MASTER_PROJECT ON) + message(STATUS "CMake version: ${CMAKE_VERSION}") + endif () endif () # Joins arguments and places the results in ${result_var}. function(join result_var) - set(result ) + set(result "") foreach (arg ${ARGN}) set(result "${result}${arg}") endforeach () set(${result_var} "${result}" PARENT_SCOPE) endfunction() +# DEPRECATED! Should be merged into add_module_library. +function(enable_module target) + if (MSVC) + set(BMI ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${target}.ifc) + target_compile_options(${target} + PRIVATE /interface /ifcOutput ${BMI} + INTERFACE /reference fmt=${BMI}) + set_target_properties(${target} PROPERTIES ADDITIONAL_CLEAN_FILES ${BMI}) + set_source_files_properties(${BMI} PROPERTIES GENERATED ON) + endif () +endfunction() + +# Adds a library compiled with C++20 module support. +# `enabled` is a CMake variables that specifies if modules are enabled. +# If modules are disabled `add_module_library` falls back to creating a +# non-modular library. +# +# Usage: +# add_module_library(<name> [sources...] FALLBACK [sources...] [IF enabled]) +function(add_module_library name) + cmake_parse_arguments(AML "" "IF" "FALLBACK" ${ARGN}) + set(sources ${AML_UNPARSED_ARGUMENTS}) + + add_library(${name}) + set_target_properties(${name} PROPERTIES LINKER_LANGUAGE CXX) + + if (NOT ${${AML_IF}}) + # Create a non-modular library. + target_sources(${name} PRIVATE ${AML_FALLBACK}) + return() + endif () + + # Modules require C++20. + target_compile_features(${name} PUBLIC cxx_std_20) + if (CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX) + target_compile_options(${name} PUBLIC -fmodules-ts) + endif () + + # `std` is affected by CMake options and may be higher than C++20. + get_target_property(std ${name} CXX_STANDARD) + + if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang") + set(pcms) + foreach (src ${sources}) + get_filename_component(pcm ${src} NAME_WE) + set(pcm ${pcm}.pcm) + + # Propagate -fmodule-file=*.pcm to targets that link with this library. + target_compile_options( + ${name} PUBLIC -fmodule-file=${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${pcm}) + + # Use an absolute path to prevent target_link_libraries prepending -l + # to it. + set(pcms ${pcms} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${pcm}) + add_custom_command( + OUTPUT ${pcm} + COMMAND ${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER} + -std=c++${std} -x c++-module --precompile -c + -o ${pcm} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/${src} + "-I$<JOIN:$<TARGET_PROPERTY:${name},INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>,;-I>" + # Required by the -I generator expression above. + COMMAND_EXPAND_LISTS + DEPENDS ${src}) + endforeach () + + # Add .pcm files as sources to make sure they are built before the library. + set(sources) + foreach (pcm ${pcms}) + get_filename_component(pcm_we ${pcm} NAME_WE) + set(obj ${pcm_we}.o) + # Use an absolute path to prevent target_link_libraries prepending -l. + set(sources ${sources} ${pcm} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${obj}) + add_custom_command( + OUTPUT ${obj} + COMMAND ${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER} $<TARGET_PROPERTY:${name},COMPILE_OPTIONS> + -c -o ${obj} ${pcm} + DEPENDS ${pcm}) + endforeach () + endif () + target_sources(${name} PRIVATE ${sources}) +endfunction() + include(CMakeParseArguments) # Sets a cache variable with a docstring joined from multiple arguments: @@ -44,7 +128,7 @@ endfunction() # Set the default CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE to Release. # This should be done before the project command since the latter can set # CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE itself (it does so for nmake). -if (MASTER_PROJECT AND NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE) +if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE) set_verbose(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release CACHE STRING "Choose the type of build, options are: None(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS or " "CMAKE_C_FLAGS used) Debug Release RelWithDebInfo MinSizeRel.") @@ -61,12 +145,27 @@ option(FMT_WERROR "Halt the compilation with an error on compiler warnings." OFF) # Options that control generation of various targets. -option(FMT_DOC "Generate the doc target." ${MASTER_PROJECT}) -option(FMT_INSTALL "Generate the install target." ${MASTER_PROJECT}) -option(FMT_TEST "Generate the test target." ${MASTER_PROJECT}) +option(FMT_DOC "Generate the doc target." ${FMT_MASTER_PROJECT}) +option(FMT_INSTALL "Generate the install target." ON) +option(FMT_TEST "Generate the test target." ${FMT_MASTER_PROJECT}) option(FMT_FUZZ "Generate the fuzz target." OFF) option(FMT_CUDA_TEST "Generate the cuda-test target." OFF) option(FMT_OS "Include core requiring OS (Windows/Posix) " ON) +option(FMT_MODULE "Build a module instead of a traditional library." OFF) +option(FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS "Expose headers with marking them as system." OFF) + +if (FMT_TEST AND FMT_MODULE) + # The tests require {fmt} to be compiled as traditional library + message(STATUS "Testing is incompatible with build mode 'module'.") +endif () +set(FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE "") +if (FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS) + set(FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE SYSTEM) +endif () +if(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME STREQUAL "MSDOS") + set(FMT_TEST OFF) + message(STATUS "MSDOS is incompatible with gtest") +endif() # Get version from core.h file(READ include/fmt/core.h core_h) @@ -84,23 +183,26 @@ message(STATUS "Version: ${FMT_VERSION}") message(STATUS "Build type: ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}") if (NOT CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY) - set(CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/bin) + set(CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/bin) endif () set(CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${CMAKE_MODULE_PATH} "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/support/cmake") -include(cxx14) include(CheckCXXCompilerFlag) include(JoinPaths) -list(FIND CMAKE_CXX_COMPILE_FEATURES "cxx_variadic_templates" index) -if (${index} GREATER -1) - # Use cxx_variadic_templates instead of more appropriate cxx_std_11 for - # compatibility with older CMake versions. - set(FMT_REQUIRED_FEATURES cxx_variadic_templates) +if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND NOT DEFINED CMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET) + set_verbose(CMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET hidden CACHE STRING + "Preset for the export of private symbols") + set_property(CACHE CMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET PROPERTY STRINGS + hidden default) +endif () + +if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND NOT DEFINED CMAKE_VISIBILITY_INLINES_HIDDEN) + set_verbose(CMAKE_VISIBILITY_INLINES_HIDDEN ON CACHE BOOL + "Whether to add a compile flag to hide symbols of inline functions") endif () -message(STATUS "Required features: ${FMT_REQUIRED_FEATURES}") if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "GNU") set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS -pedantic-errors -Wall -Wextra -pedantic @@ -110,16 +212,16 @@ if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "GNU") -Wcast-align -Wctor-dtor-privacy -Wdisabled-optimization -Winvalid-pch -Woverloaded-virtual - -Wconversion -Wswitch-enum -Wundef + -Wconversion -Wundef -Wno-ctor-dtor-privacy -Wno-format-nonliteral) if (NOT CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 4.6) - set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS} -Wnoexcept + set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS} -Wno-dangling-else -Wno-unused-local-typedefs) endif () if (NOT CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 5.0) set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS} -Wdouble-promotion -Wtrampolines -Wzero-as-null-pointer-constant -Wuseless-cast - -Wvector-operation-performance -Wsized-deallocation) + -Wvector-operation-performance -Wsized-deallocation -Wshadow) endif () if (NOT CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 6.0) set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS} -Wshift-overflow=2 @@ -130,7 +232,8 @@ endif () if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang") set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS -Wall -Wextra -pedantic -Wconversion -Wundef - -Wdeprecated -Wweak-vtables) + -Wdeprecated -Wweak-vtables -Wshadow + -Wno-gnu-zero-variadic-macro-arguments) check_cxx_compiler_flag(-Wzero-as-null-pointer-constant HAS_NULLPTR_WARNING) if (HAS_NULLPTR_WARNING) set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS} @@ -144,7 +247,7 @@ if (MSVC) set(WERROR_FLAG /WX) endif () -if (MASTER_PROJECT AND CMAKE_GENERATOR MATCHES "Visual Studio") +if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND CMAKE_GENERATOR MATCHES "Visual Studio") # If Microsoft SDK is installed create script run-msbuild.bat that # calls SetEnv.cmd to set up build environment and runs msbuild. # It is useful when building Visual Studio projects with the SDK @@ -162,18 +265,6 @@ if (MASTER_PROJECT AND CMAKE_GENERATOR MATCHES "Visual Studio") ${CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM} -p:FrameworkPathOverride=\"${netfxpath}\" %*") endif () -set(strtod_l_headers stdlib.h) -if (APPLE) - set(strtod_l_headers ${strtod_l_headers} xlocale.h) -endif () - -include(CheckSymbolExists) -if (WIN32) - check_symbol_exists(_strtod_l "${strtod_l_headers}" HAVE_STRTOD_L) -else () - check_symbol_exists(strtod_l "${strtod_l_headers}" HAVE_STRTOD_L) -endif () - function(add_headers VAR) set(headers ${${VAR}}) foreach (header ${ARGN}) @@ -183,26 +274,20 @@ function(add_headers VAR) endfunction() # Define the fmt library, its includes and the needed defines. -add_headers(FMT_HEADERS chrono.h color.h compile.h core.h format.h format-inl.h - locale.h os.h ostream.h posix.h printf.h ranges.h) +add_headers(FMT_HEADERS args.h chrono.h color.h compile.h core.h format.h + format-inl.h os.h ostream.h printf.h ranges.h std.h + xchar.h) +set(FMT_SOURCES src/format.cc) if (FMT_OS) - set(FMT_SOURCES src/format.cc src/os.cc) -else() - set(FMT_SOURCES src/format.cc) + set(FMT_SOURCES ${FMT_SOURCES} src/os.cc) endif () -add_library(fmt ${FMT_SOURCES} ${FMT_HEADERS} README.rst ChangeLog.rst) +add_module_library(fmt src/fmt.cc FALLBACK + ${FMT_SOURCES} ${FMT_HEADERS} README.rst ChangeLog.md + IF FMT_MODULE) add_library(fmt::fmt ALIAS fmt) - -if (HAVE_STRTOD_L) - target_compile_definitions(fmt PUBLIC FMT_LOCALE) -endif () - -if (MINGW) - check_cxx_compiler_flag("Wa,-mbig-obj" FMT_HAS_MBIG_OBJ) - if (${FMT_HAS_MBIG_OBJ}) - target_compile_options(fmt PUBLIC "-Wa,-mbig-obj") - endif() +if (FMT_MODULE) + enable_module(fmt) endif () if (FMT_WERROR) @@ -212,9 +297,13 @@ if (FMT_PEDANTIC) target_compile_options(fmt PRIVATE ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}) endif () -target_compile_features(fmt INTERFACE ${FMT_REQUIRED_FEATURES}) +if (cxx_std_11 IN_LIST CMAKE_CXX_COMPILE_FEATURES) + target_compile_features(fmt PUBLIC cxx_std_11) +else () + message(WARNING "Feature cxx_std_11 is unknown for the CXX compiler") +endif () -target_include_directories(fmt PUBLIC +target_include_directories(fmt ${FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE} PUBLIC $<BUILD_INTERFACE:${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include> $<INSTALL_INTERFACE:${FMT_INC_DIR}>) @@ -222,7 +311,16 @@ set(FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX d CACHE STRING "Debug library postfix.") set_target_properties(fmt PROPERTIES VERSION ${FMT_VERSION} SOVERSION ${CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_MAJOR} - DEBUG_POSTFIX "${FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX}") + PUBLIC_HEADER "${FMT_HEADERS}" + DEBUG_POSTFIX "${FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX}" + + # Workaround for Visual Studio 2017: + # Ensure the .pdb is created with the same name and in the same directory + # as the .lib. Newer VS versions already do this by default, but there is no + # harm in setting it for those too. Ignored by other generators. + COMPILE_PDB_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY "${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}" + COMPILE_PDB_NAME "fmt" + COMPILE_PDB_NAME_DEBUG "fmt${FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX}") # Set FMT_LIB_NAME for pkg-config fmt.pc. We cannot use the OUTPUT_NAME target # property because it's not set by default. @@ -232,13 +330,7 @@ if (CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE STREQUAL "Debug") endif () if (BUILD_SHARED_LIBS) - if (UNIX AND NOT APPLE AND NOT ${CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME} MATCHES "SunOS" AND - NOT EMSCRIPTEN) - # Fix rpmlint warning: - # unused-direct-shlib-dependency /usr/lib/libformat.so.1.1.0 /lib/libm.so.6. - target_link_libraries(fmt -Wl,--as-needed) - endif () - target_compile_definitions(fmt PRIVATE FMT_EXPORT INTERFACE FMT_SHARED) + target_compile_definitions(fmt PRIVATE FMT_LIB_EXPORT INTERFACE FMT_SHARED) endif () if (FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST) target_compile_definitions(fmt PUBLIC FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST) @@ -248,9 +340,9 @@ add_library(fmt-header-only INTERFACE) add_library(fmt::fmt-header-only ALIAS fmt-header-only) target_compile_definitions(fmt-header-only INTERFACE FMT_HEADER_ONLY=1) -target_compile_features(fmt-header-only INTERFACE ${FMT_REQUIRED_FEATURES}) +target_compile_features(fmt-header-only INTERFACE cxx_std_11) -target_include_directories(fmt-header-only INTERFACE +target_include_directories(fmt-header-only ${FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE} INTERFACE $<BUILD_INTERFACE:${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include> $<INSTALL_INTERFACE:${FMT_INC_DIR}>) @@ -270,7 +362,7 @@ if (FMT_INSTALL) "Installation directory for libraries, a relative path that " "will be joined to ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX} or an absolute path.") - set_verbose(FMT_PKGCONFIG_DIR ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}/pkgconfig CACHE PATH + set_verbose(FMT_PKGCONFIG_DIR ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}/pkgconfig CACHE STRING "Installation directory for pkgconfig (.pc) files, a relative " "path that will be joined with ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX} or an " "absolute path.") @@ -294,6 +386,14 @@ if (FMT_INSTALL) INSTALL_DESTINATION ${FMT_CMAKE_DIR}) set(INSTALL_TARGETS fmt fmt-header-only) + + # Install the library and headers. + install(TARGETS ${INSTALL_TARGETS} EXPORT ${targets_export_name} + LIBRARY DESTINATION ${FMT_LIB_DIR} + ARCHIVE DESTINATION ${FMT_LIB_DIR} + PUBLIC_HEADER DESTINATION "${FMT_INC_DIR}/fmt" + RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_BINDIR}) + # Use a namespace because CMake provides better diagnostics for namespaced # imported targets. export(TARGETS ${INSTALL_TARGETS} NAMESPACE fmt:: @@ -306,15 +406,6 @@ if (FMT_INSTALL) install(EXPORT ${targets_export_name} DESTINATION ${FMT_CMAKE_DIR} NAMESPACE fmt::) - # Install the library and headers. - install(TARGETS ${INSTALL_TARGETS} EXPORT ${targets_export_name} - LIBRARY DESTINATION ${FMT_LIB_DIR} - ARCHIVE DESTINATION ${FMT_LIB_DIR} - RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_BINDIR}) - - install(FILES $<TARGET_PDB_FILE:${INSTALL_TARGETS}> - DESTINATION ${FMT_LIB_DIR} OPTIONAL) - install(FILES ${FMT_HEADERS} DESTINATION "${FMT_INC_DIR}/fmt") install(FILES "${pkgconfig}" DESTINATION "${FMT_PKGCONFIG_DIR}") endif () @@ -340,7 +431,7 @@ if (FMT_FUZZ) endif () set(gitignore ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/.gitignore) -if (MASTER_PROJECT AND EXISTS ${gitignore}) +if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND EXISTS ${gitignore}) # Get the list of ignored files from .gitignore. file (STRINGS ${gitignore} lines) list(REMOVE_ITEM lines /doc/html) diff --git a/ChangeLog.md b/ChangeLog.md new file mode 100644 index 00000000..2e51d107 --- /dev/null +++ b/ChangeLog.md @@ -0,0 +1,5282 @@ +# 10.1.1 - 2023-08-28 + +- Added formatters for `std::atomic` and `atomic_flag` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3574, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3594). + Thanks @wangzw and @AlexGuteniev. +- Fixed an error about partial specialization of `formatter<string>` + after instantiation when compiled with gcc and C++20 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3584). +- Fixed compilation as a C++20 module with gcc and clang + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3587, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3597, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3605). + Thanks @MathewBensonCode. +- Made `fmt::to_string` work with types that have `format_as` + overloads (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3575). + Thanks @phprus. +- Made `formatted_size` work with integral format specifiers at + compile time (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3591). + Thanks @elbeno. +- Fixed a warning about the `no_unique_address` attribute on clang-cl + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3599). Thanks @lukester1975. +- Improved compatibility with the legacy GBK encoding + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3598, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3599). Thanks @YuHuanTin. +- Added OpenSSF Scorecard analysis + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3530, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3571). Thanks @joycebrum. +- Updated CI dependencies + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3591, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3592, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3593, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3602). + +# 10.1.0 - 2023-08-12 + +- Optimized format string compilation resulting in up to 40% speed up + in compiled `format_to` and \~4x speed up in compiled `format_to_n` + on a concatenation benchmark + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3133, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3484). + + {fmt} 10.0: + + --------------------------------------------------------- + Benchmark Time CPU Iterations + --------------------------------------------------------- + BM_format_to 78.9 ns 78.9 ns 8881746 + BM_format_to_n 568 ns 568 ns 1232089 + + {fmt} 10.1: + + --------------------------------------------------------- + Benchmark Time CPU Iterations + --------------------------------------------------------- + BM_format_to 54.9 ns 54.9 ns 12727944 + BM_format_to_n 133 ns 133 ns 5257795 + +- Optimized storage of an empty allocator in `basic_memory_buffer` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3485). Thanks @Minty-Meeo. + +- Added formatters for proxy references to elements of + `std::vector<bool>` and `std::bitset<N>` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3567, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3570). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/zYb79Pvn8)): + + ```c++ + #include <vector> + #include <fmt/std.h> + + int main() { + auto v = std::vector<bool>{true}; + fmt::print("{}", v[0]); + } + ``` + + Thanks @phprus and @felix642. + +- Fixed an ambiguous formatter specialization for containers that look + like container adaptors such as `boost::flat_set` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3556, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3561). Thanks @5chmidti. + +- Fixed compilation when formatting durations not convertible from + `std::chrono::seconds` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3430). Thanks @patlkli. + +- Made the `formatter` specialization for `char*` const-correct + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3432). Thanks @timsong-cpp. + +- Made `{}` and `{:}` handled consistently during compile-time checks + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3526). + +- Disallowed passing temporaries to `make_format_args` to improve API + safety by preventing dangling references. + +- Improved the compile-time error for unformattable types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3478). Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Improved the floating-point formatter + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3448, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3450). + Thanks @florimond-collette. + +- Fixed handling of precision for `long double` larger than 64 bits. + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3539, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3564). + +- Made floating-point and chrono tests less platform-dependent + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3337, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3433, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3434). Thanks @phprus. + +- Removed the remnants of the Grisu floating-point formatter that has + been replaced by Dragonbox in earlier versions. + +- Added `throw_format_error` to the public API + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3551). Thanks @mjerabek. + +- Made `FMT_THROW` assert even if assertions are disabled when + compiling with exceptions disabled + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3418, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3439). Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Made `format_as` and `std::filesystem::path` formatter work with + exotic code unit types. + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3457, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3476). Thanks @gix and @hmbj. + +- Added support for the `?` format specifier to + `std::filesystem::path` and made the default unescaped for + consistency with strings. + +- Deprecated the wide stream overload of `printf`. + +- Removed unused `basic_printf_parse_context`. + +- Improved RTTI detection used when formatting exceptions + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3468). Thanks @danakj. + +- Improved compatibility with VxWorks7 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3467). Thanks @wenshan1. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3174, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3423, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3454, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3458, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3461, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3487, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3515). + Thanks @zencatalyst, @rlalik and @mikecrowe. + +- Improved build and CI configurations + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3449, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3451, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3452, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3453, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3459, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3481, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3486, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3489, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3496, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3517, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3523, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3563). + Thanks @joycebrum, @glebm, @phprus, @petrmanek, @setoye and @abouvier. + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3408, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3424, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3444, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3446, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3475, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3482, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3492, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3493, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3508, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3509, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3533, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3542, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3543, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3540, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3544, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3548, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3549, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3550, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3552). + Thanks @adesitter, @hmbj, @Minty-Meeo, @phprus, @TobiSchluter, + @kieranclancy, @alexeedm, @jurihock, @Ozomahtli and @razaqq. + +# 10.0.0 - 2023-05-09 + +- Replaced Grisu with a new floating-point formatting algorithm for + given precision (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3262, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2750, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3269, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3276). The new algorithm + is based on Dragonbox already used for the shortest representation + and gives substantial performance improvement: + +  + + - Red: new algorithm + - Green: new algorithm with `FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX` defined + to 1 + - Blue: old algorithm + + Thanks @jk-jeon. + +- Replaced `snprintf`-based hex float formatter with an internal + implementation (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3179, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3203). This removes the + last usage of `s(n)printf` in {fmt}. Thanks @phprus. + +- Fixed alignment of floating-point numbers with localization + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3263, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3272). Thanks @ShawnZhong. + +- Made handling of `#` consistent with `std::format`. + +- Improved C++20 module support + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3134, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3254, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3386, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3387, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3388, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3392, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3397, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3399, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3400). + Thanks @laitingsheng, @Orvid and @DanielaE. + +- Switched to the [modules CMake library](https://github.com/vitaut/modules) + which allows building {fmt} as a C++20 module with clang: + + CXX=clang++ cmake -DFMT_MODULE=ON . + make + +- Made `format_as` work with any user-defined type and not just enums. + For example ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/b7rqhq5Kh)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/format.h> + + struct floaty_mc_floatface { + double value; + }; + + auto format_as(floaty_mc_floatface f) { return f.value; } + + int main() { + fmt::print("{:8}\n", floaty_mc_floatface{0.42}); // prints " 0.42" + } + ``` + +- Removed deprecated implicit conversions for enums and conversions to + primitive types for compatibility with `std::format` and to prevent + potential ODR violations. Use `format_as` instead. + +- Added support for fill, align and width to the time point formatter + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3237, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3260, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3275). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/rKP6MGz6c)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + + int main() { + // prints " 2023" + fmt::print("{:>8%Y}\n", std::chrono::system_clock::now()); + } + ``` + + Thanks @ShawnZhong. + +- Implemented formatting of subseconds + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2207, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3117, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3115, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3143, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3144, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3349). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/45738oGEo)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + + int main() { + // prints 01.234567 + fmt::print("{:%S}\n", std::chrono::microseconds(1234567)); + } + ``` + + Thanks @patrickroocks @phprus and @BRevzin. + +- Added precision support to `%S` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3148). Thanks @SappyJoy + +- Added support for `std::utc_time` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3098, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3110). Thanks @patrickroocks. + +- Switched formatting of `std::chrono::system_clock` from local time + to UTC for compatibility with the standard + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3199, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3230). Thanks @ned14. + +- Added support for `%Ez` and `%Oz` to chrono formatters. + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3220, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3222). Thanks @phprus. + +- Improved validation of format specifiers for `std::chrono::duration` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3219, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3232). Thanks @ShawnZhong. + +- Fixed formatting of time points before the epoch + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3117, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3261). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/f7bcznb3W)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + + int main() { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::from_time_t(0) - + std::chrono::milliseconds(250); + fmt::print("{:%S}\n", t); // prints 59.750000000 + } + ``` + + Thanks @ShawnZhong. + +- Experimental: implemented glibc extension for padding seconds, + minutes and hours + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2959, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3271). Thanks @ShawnZhong. + +- Added a formatter for `std::exception` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2977, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3012, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3062, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3076, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3119). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/8xoWGs9e4)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/std.h> + #include <vector> + + int main() { + try { + std::vector<bool>().at(0); + } catch(const std::exception& e) { + fmt::print("{}", e); + } + } + ``` + + prints: + + vector<bool>::_M_range_check: __n (which is 0) >= this->size() (which is 0) + + on libstdc++. Thanks @zach2good and @phprus. + +- Moved `std::error_code` formatter from `fmt/os.h` to `fmt/std.h`. + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3125). Thanks @phprus. + +- Added formatters for standard container adapters: + `std::priority_queue`, `std::queue` and `std::stack` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3215, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3279). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/74h1xY9qK)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/ranges.h> + #include <stack> + #include <vector> + + int main() { + auto s = std::stack<bool, std::vector<bool>>(); + for (auto b: {true, false, true}) s.push(b); + fmt::print("{}\n", s); // prints [true, false, true] + } + ``` + + Thanks @ShawnZhong. + +- Added a formatter for `std::optional` to `fmt/std.h`. + Thanks @tom-huntington. + +- Fixed formatting of valueless by exception variants + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3347). Thanks @TheOmegaCarrot. + +- Made `fmt::ptr` accept `unique_ptr` with a custom deleter + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3177). Thanks @hmbj. + +- Fixed formatting of noncopyable ranges and nested ranges of chars + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3158 + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3286, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3290). Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Fixed issues with formatting of paths and ranges of paths + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3319, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3321 + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3322). Thanks @phprus. + +- Improved handling of invalid Unicode in paths. + +- Enabled compile-time checks on Apple clang 14 and later + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3331). Thanks @cloyce. + +- Improved compile-time checks of named arguments + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3105, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3214). Thanks @rbrich. + +- Fixed formatting when both alignment and `0` are given + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3236, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3248). Thanks @ShawnZhong. + +- Improved Unicode support in the experimental file API on Windows + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3234, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3293). Thanks @Fros1er. + +- Unified UTF transcoding + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3416). Thanks @phprus. + +- Added support for UTF-8 digit separators via an experimental locale + facet (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1861). For + example ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/f7bcznb3W)): + + ```c++ + auto loc = std::locale( + std::locale(), new fmt::format_facet<std::locale>("’")); + auto s = fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 1000); + ``` + + where `’` is U+2019 used as a digit separator in the de_CH locale. + +- Added an overload of `formatted_size` that takes a locale + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3084, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3087). Thanks @gerboengels. + +- Removed the deprecated `FMT_DEPRECATED_OSTREAM`. + +- Fixed a UB when using a null `std::string_view` with + `fmt::to_string` or format string compilation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3241, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3244). Thanks @phprus. + +- Added `starts_with` to the fallback `string_view` implementation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3080). Thanks @phprus. + +- Added `fmt::basic_format_string::get()` for compatibility with + `basic_format_string` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3111). Thanks @huangqinjin. + +- Added `println` for compatibility with C++23 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3267). Thanks @ShawnZhong. + +- Renamed the `FMT_EXPORT` macro for shared library usage to + `FMT_LIB_EXPORT`. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3108, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3169, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3243). + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3404). + Thanks @Cleroth and @Vertexwahn. + +- Improved build configuration and tests + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3118, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3120, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3188, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3189, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3198, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3205, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3207, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3210, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3240, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3256, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3264, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3299, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3302, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3312, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3317, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3328, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3333, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3369, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3373, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3395, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3406, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3411). + Thanks @dimztimz, @phprus, @DavidKorczynski, @ChrisThrasher, + @FrancoisCarouge, @kennyweiss, @luzpaz, @codeinred, @Mixaill, @joycebrum, + @kevinhwang and @Vertexwahn. + +- Fixed a regression in handling empty format specifiers after a colon + (`{:}`) (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3086). Thanks @oxidase. + +- Worked around a broken implementation of + `std::is_constant_evaluated` in some versions of libstdc++ on clang + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3247, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3281). Thanks @phprus. + +- Fixed formatting of volatile variables + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3068). + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3057, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3066, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3072, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3082, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3091, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3092, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3093, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3095, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3096, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3097, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3128, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3129, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3137, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3139, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3140, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3142, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3149, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3150, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3154, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3163, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3178, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3184, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3196, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3204, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3206, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3208, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3213, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3216, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3224, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3226, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3228, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3229, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3259, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3274, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3287, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3288, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3292, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3295, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3296, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3298, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3325, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3326, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3334, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3342, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3343, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3351, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3352, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3362, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3365, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3366, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3374, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3377, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3378, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3381, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3398, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3413, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3415). + Thanks @phprus, @gsjaardema, @NewbieOrange, @EngineLessCC, @asmaloney, + @HazardyKnusperkeks, @sergiud, @Youw, @thesmurph, @czudziakm, + @Roman-Koshelev, @chronoxor, @ShawnZhong, @russelltg, @glebm, @tmartin-gh, + @Zhaojun-Liu, @louiswins and @mogemimi. + +# 9.1.0 - 2022-08-27 + +- `fmt::formatted_size` now works at compile time + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3026). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/1MW5rMdf8)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/compile.h> + + int main() { + using namespace fmt::literals; + constexpr size_t n = fmt::formatted_size("{}"_cf, 42); + fmt::print("{}\n", n); // prints 2 + } + ``` + + Thanks @marksantaniello. + +- Fixed handling of invalid UTF-8 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3038, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3044, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3056). + Thanks @phprus and @skeeto. + +- Improved Unicode support in `ostream` overloads of `print` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2994, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3001, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3025). Thanks @dimztimz. + +- Fixed handling of the sign specifier in localized formatting on + systems with 32-bit `wchar_t` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3041). + +- Added support for wide streams to `fmt::streamed` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2994). Thanks @phprus. + +- Added the `n` specifier that disables the output of delimiters when + formatting ranges (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2981, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2983). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/roKqGdj8c)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/ranges.h> + #include <vector> + + int main() { + auto v = std::vector{1, 2, 3}; + fmt::print("{:n}\n", v); // prints 1, 2, 3 + } + ``` + + Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Worked around problematic `std::string_view` constructors introduced + in C++23 (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3030, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3050). Thanks @strega-nil-ms. + +- Improve handling (exclusion) of recursive ranges + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2968, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2974). Thanks @Dani-Hub. + +- Improved error reporting in format string compilation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3055). + +- Improved the implementation of + [Dragonbox](https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox), the algorithm + used for the default floating-point formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2984). Thanks @jk-jeon. + +- Fixed issues with floating-point formatting on exotic platforms. + +- Improved the implementation of chrono formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3010). Thanks @phprus. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2966, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3009, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3020, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3037). + Thanks @mwinterb, @jcelerier and @remiburtin. + +- Improved build configuration + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2991, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2995, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3004, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3007, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3040). + Thanks @dimztimz and @hwhsu1231. + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2969, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2971, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2975, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2982, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2985, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2988, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2989, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3000, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3006, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3014, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3015, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3021, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3023, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3024, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3029, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3043, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3052, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3053, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/3054). + Thanks @h-friederich, @dimztimz, @olupton, @bernhardmgruber and @phprus. + +# 9.0.0 - 2022-07-04 + +- Switched to the internal floating point formatter for all decimal + presentation formats. In particular this results in consistent + rounding on all platforms and removing the `s[n]printf` fallback for + decimal FP formatting. + +- Compile-time floating point formatting no longer requires the + header-only mode. For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/G37PTeG3b)): + + ```c++ + #include <array> + #include <fmt/compile.h> + + consteval auto compile_time_dtoa(double value) -> std::array<char, 10> { + auto result = std::array<char, 10>(); + fmt::format_to(result.data(), FMT_COMPILE("{}"), value); + return result; + } + + constexpr auto answer = compile_time_dtoa(0.42); + ``` + + works with the default settings. + +- Improved the implementation of + [Dragonbox](https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox), the algorithm + used for the default floating-point formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2713, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2750). Thanks @jk-jeon. + +- Made `fmt::to_string` work with `__float128`. This uses the internal + FP formatter and works even on system without `__float128` support + in `[s]printf`. + +- Disabled automatic `std::ostream` insertion operator (`operator<<`) + discovery when `fmt/ostream.h` is included to prevent ODR + violations. You can get the old behavior by defining + `FMT_DEPRECATED_OSTREAM` but this will be removed in the next major + release. Use `fmt::streamed` or `fmt::ostream_formatter` to enable + formatting via `std::ostream` instead. + +- Added `fmt::ostream_formatter` that can be used to write `formatter` + specializations that perform formatting via `std::ostream`. For + example ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/5sEc5qMsf)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/ostream.h> + + struct date { + int year, month, day; + + friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const date& d) { + return os << d.year << '-' << d.month << '-' << d.day; + } + }; + + template <> struct fmt::formatter<date> : ostream_formatter {}; + + std::string s = fmt::format("The date is {}", date{2012, 12, 9}); + // s == "The date is 2012-12-9" + ``` + +- Added the `fmt::streamed` function that takes an object and formats + it via `std::ostream`. For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/5G3346G1f)): + + ```c++ + #include <thread> + #include <fmt/ostream.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("Current thread id: {}\n", + fmt::streamed(std::this_thread::get_id())); + } + ``` + + Note that `fmt/std.h` provides a `formatter` specialization for + `std::thread::id` so you don\'t need to format it via + `std::ostream`. + +- Deprecated implicit conversions of unscoped enums to integers for + consistency with scoped enums. + +- Added an argument-dependent lookup based `format_as` extension API + to simplify formatting of enums. + +- Added experimental `std::variant` formatting support + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2941). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/KG9z6cq68)): + + ```c++ + #include <variant> + #include <fmt/std.h> + + int main() { + auto v = std::variant<int, std::string>(42); + fmt::print("{}\n", v); + } + ``` + + prints: + + variant(42) + + Thanks @jehelset. + +- Added experimental `std::filesystem::path` formatting support + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2865, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2902, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2917, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2918). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/o44dMexEb)): + + ```c++ + #include <filesystem> + #include <fmt/std.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("There is no place like {}.", std::filesystem::path("/home")); + } + ``` + + prints: + + There is no place like "/home". + + Thanks @phprus. + +- Added a `std::thread::id` formatter to `fmt/std.h`. For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/j1azbYf3E)): + + ```c++ + #include <thread> + #include <fmt/std.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("Current thread id: {}\n", std::this_thread::get_id()); + } + ``` + +- Added `fmt::styled` that applies a text style to an individual + argument (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2793). For + example ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/vWGW7v5M6)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + #include <fmt/color.h> + + int main() { + auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); + fmt::print( + "[{}] {}: {}\n", + fmt::styled(now, fmt::emphasis::bold), + fmt::styled("error", fg(fmt::color::red)), + "something went wrong"); + } + ``` + + prints + +  + + Thanks @rbrugo. + +- Made `fmt::print` overload for text styles correctly handle UTF-8 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2681, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2701). Thanks @AlexGuteniev. + +- Fixed Unicode handling when writing to an ostream. + +- Added support for nested specifiers to range formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2673). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/xd3Gj38cf)): + + ```c++ + #include <vector> + #include <fmt/ranges.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{::#x}\n", std::vector{10, 20, 30}); + } + ``` + + prints `[0xa, 0x14, 0x1e]`. + + Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Implemented escaping of wide strings in ranges + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2904). Thanks @phprus. + +- Added support for ranges with `begin` / `end` found via the + argument-dependent lookup + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2807). Thanks @rbrugo. + +- Fixed formatting of certain kinds of ranges of ranges + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2787). Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Fixed handling of maps with element types other than `std::pair` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2944). Thanks @BrukerJWD. + +- Made tuple formatter enabled only if elements are formattable + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2939, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2940). Thanks @jehelset. + +- Made `fmt::join` compatible with format string compilation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2719, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2720). Thanks @phprus. + +- Made compile-time checks work with named arguments of custom types + and `std::ostream` `print` overloads + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2816, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2817, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2819). Thanks @timsong-cpp. + +- Removed `make_args_checked` because it is no longer needed for + compile-time checks + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2760). Thanks @phprus. + +- Removed the following deprecated APIs: `_format`, `arg_join`, the + `format_to` overload that takes a memory buffer, `[v]fprintf` that + takes an `ostream`. + +- Removed the deprecated implicit conversion of `[const] signed char*` + and `[const] unsigned char*` to C strings. + +- Removed the deprecated `fmt/locale.h`. + +- Replaced the deprecated `fileno()` with `descriptor()` in + `buffered_file`. + +- Moved `to_string_view` to the `detail` namespace since it\'s an + implementation detail. + +- Made access mode of a created file consistent with `fopen` by + setting `S_IWGRP` and `S_IWOTH` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2733). Thanks @arogge. + +- Removed a redundant buffer resize when formatting to `std::ostream` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2842, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2843). Thanks @jcelerier. + +- Made precision computation for strings consistent with width + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2888). + +- Fixed handling of locale separators in floating point formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2830). + +- Made sign specifiers work with `__int128_t` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2773). + +- Improved support for systems such as CHERI with extra data stored in + pointers (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2932). + Thanks @davidchisnall. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2706, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2712, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2789, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2803, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2805, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2815, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2924). + Thanks @BRevzin, @Pokechu22, @setoye, @rtobar, @rbrugo, @anoonD and + @leha-bot. + +- Improved build configuration + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2766, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2772, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2836, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2852, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2907, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2913, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2914). + Thanks @kambala-decapitator, @mattiasljungstrom, @kieselnb, @nathannaveen + and @Vertexwahn. + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2408, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2507, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2697, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2715, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2717, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2722, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2724, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2725, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2726, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2728, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2732, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2738, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2742, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2744, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2745, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2746, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2754, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2755, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2757, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2758, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2761, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2762, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2763, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2765, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2769, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2770, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2771, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2777, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2779, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2782, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2783, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2794, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2796, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2797, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2801, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2802, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2808, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2818, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2819, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2829, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2835, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2848, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2860, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2861, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2882, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2886, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2891, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2892, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2895, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2896, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2903, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2906, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2908, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2909, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2920, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2922, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2927, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2929, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2936, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2937, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2938, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2951, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2954, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2957, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2958, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2960). + Thanks @matrackif @Tobi823, @ivan-volnov, @VasiliPupkin256, + @federico-busato, @barcharcraz, @jk-jeon, @HazardyKnusperkeks, @dalboris, + @seanm, @gsjaardema, @timsong-cpp, @seanm, @frithrah, @chronoxor, @Agga, + @madmaxoft, @JurajX, @phprus and @Dani-Hub. + +# 8.1.1 - 2022-01-06 + +- Restored ABI compatibility with version 8.0.x + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2695, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2696). Thanks @saraedum. +- Fixed chrono formatting on big endian systems + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2698, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2699). + Thanks @phprus and @xvitaly. +- Fixed a linkage error with mingw + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2691, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2692). Thanks @rbberger. + +# 8.1.0 - 2022-01-02 + +- Optimized chrono formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2500, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2537, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2541, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2544, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2550, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2551, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2576, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2577, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2586, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2591, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2594, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2602, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2617, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2628, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2633, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2670, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2671). + + Processing of some specifiers such as `%z` and `%Y` is now up to + 10-20 times faster, for example on GCC 11 with libstdc++: + + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + Benchmark Before After + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + FMTFormatter_z 261 ns 26.3 ns + FMTFormatterCompile_z 246 ns 11.6 ns + FMTFormatter_Y 263 ns 26.1 ns + FMTFormatterCompile_Y 244 ns 10.5 ns + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + + Thanks @phprus and @toughengineer. + +- Implemented subsecond formatting for chrono durations + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2623). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/es7vWTETe)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{:%S}", std::chrono::milliseconds(1234)); + } + ``` + + prints \"01.234\". + + Thanks @matrackif. + +- Fixed handling of precision 0 when formatting chrono durations + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2587, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2588). Thanks @lukester1975. + +- Fixed an overflow on invalid inputs in the `tm` formatter + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2564). Thanks @phprus. + +- Added `fmt::group_digits` that formats integers with a non-localized + digit separator (comma) for groups of three digits. For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/TxGxG9Poq)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/format.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{} dollars", fmt::group_digits(1000000)); + } + ``` + + prints \"1,000,000 dollars\". + +- Added support for faint, conceal, reverse and blink text styles + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2394): + + <https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/147710227-c68f5317-f8fa-42c3-9123-7c4ba3c398cb.mp4> + + Thanks @benit8 and @data-man. + +- Added experimental support for compile-time floating point + formatting (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2426, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2470). It is currently + limited to the header-only mode. Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Added UDL-based named argument support to compile-time format string + checks (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2640, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2649). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/ohGbbvonv)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/format.h> + + int main() { + using namespace fmt::literals; + fmt::print("{answer:s}", "answer"_a=42); + } + ``` + + gives a compile-time error on compilers with C++20 `consteval` and + non-type template parameter support (gcc 10+) because `s` is not a + valid format specifier for an integer. + + Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Implemented escaping of string range elements. For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/rKvM1vKf3)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/ranges.h> + #include <vector> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{}", std::vector<std::string>{"\naan"}); + } + ``` + + is now printed as: + + ["\naan"] + + instead of: + + [" + aan"] + +- Added an experimental `?` specifier for escaping strings. + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2674). Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Switched to JSON-like representation of maps and sets for + consistency with Python\'s `str.format`. For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/seKjoY9W5)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/ranges.h> + #include <map> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{}", std::map<std::string, int>{{"answer", 42}}); + } + ``` + + is now printed as: + + {"answer": 42} + +- Extended `fmt::join` to support C++20-only ranges + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2549). Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Optimized handling of non-const-iterable ranges and implemented + initial support for non-const-formattable types. + +- Disabled implicit conversions of scoped enums to integers that was + accidentally introduced in earlier versions + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1841). + +- Deprecated implicit conversion of `[const] signed char*` and + `[const] unsigned char*` to C strings. + +- Deprecated `_format`, a legacy UDL-based format API + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2646). Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Marked `format`, `formatted_size` and `to_string` as `[[nodiscard]]` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2612). @0x8000-0000. + +- Added missing diagnostic when trying to format function and member + pointers as well as objects convertible to pointers which is + explicitly disallowed + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2598, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2609, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2610). Thanks @AlexGuteniev. + +- Optimized writing to a contiguous buffer with `format_to_n` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2489). Thanks @Roman-Koshelev. + +- Optimized writing to non-`char` buffers + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2477). Thanks @Roman-Koshelev. + +- Decimal point is now localized when using the `L` specifier. + +- Improved floating point formatter implementation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2498, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2499). Thanks @Roman-Koshelev. + +- Fixed handling of very large precision in fixed format + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2616). + +- Made a table of cached powers used in FP formatting static + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2509). Thanks @jk-jeon. + +- Resolved a lookup ambiguity with C++20 format-related functions due + to ADL (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2639, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2641). Thanks @mkurdej. + +- Removed unnecessary inline namespace qualification + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2642, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2643). Thanks @mkurdej. + +- Implemented argument forwarding in `format_to_n` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2462, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2463). Thanks @owent. + +- Fixed handling of implicit conversions in `fmt::to_string` and + format string compilation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2565). + +- Changed the default access mode of files created by + `fmt::output_file` to `-rw-r--r--` for consistency with `fopen` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2530). + +- Make `fmt::ostream::flush` public + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2435). + +- Improved C++14/17 attribute detection + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2615). Thanks @AlexGuteniev. + +- Improved `consteval` detection for MSVC + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2559). Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2406, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2446, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2493, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2513, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2515, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2522, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2562, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2575, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2606, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2620, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2676). + Thanks @sobolevn, @UnePierre, @zhsj, @phprus, @ericcurtin and @Lounarok. + +- Improved fuzzers and added a fuzzer for chrono timepoint formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2461, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2469). @pauldreik, + +- Added the `FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS` CMake option setting which marks + {fmt}\'s headers as system. It can be used to suppress warnings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2644, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2651). Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Added the Bazel build system support + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2505, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2516). Thanks @Vertexwahn. + +- Improved build configuration and tests + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2437, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2558, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2648, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2650, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2663, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2677). + Thanks @DanielaE, @alexezeder and @phprus. + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2353, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2356, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2399, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2408, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2414, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2427, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2432, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2442, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2434, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2439, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2447, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2450, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2455, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2465, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2472, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2474, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2476, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2478, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2479, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2481, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2482, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2483, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2490, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2491, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2510, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2518, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2528, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2529, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2539, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2540, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2545, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2555, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2557, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2570, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2573, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2582, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2605, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2611, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2647, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2627, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2630, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2635, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2638, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2653, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2654, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2661, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2664, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2684). + Thanks @DanielaE, @mwinterb, @cdacamar, @TrebledJ, @bodomartin, @cquammen, + @white238, @mmarkeloff, @palacaze, @jcelerier, @mborn-adi, @BrukerJWD, + @spyridon97, @phprus, @oliverlee, @joshessman-llnl, @akohlmey, @timkalu, + @olupton, @Acretock, @alexezeder, @andrewcorrigan, @lucpelletier and + @HazardyKnusperkeks. + +# 8.0.1 - 2021-07-02 + +- Fixed the version number in the inline namespace + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2374). +- Added a missing presentation type check for `std::string` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2402). +- Fixed a linkage error when mixing code built with clang and gcc + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2377). +- Fixed documentation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2396, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2403, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2406). Thanks @mkurdej. +- Removed dead code in FP formatter ( + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2398). Thanks @javierhonduco. +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2351, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2359, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2365, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2368, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2370, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2376, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2381, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2382, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2386, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2389, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2395, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2397, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2400, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2401, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2407). + Thanks @zx2c4, @AidanSun05, @mattiasljungstrom, @joemmett, @erengy, + @patlkli, @gsjaardema and @phprus. + +# 8.0.0 - 2021-06-21 + +- Enabled compile-time format string checks by default. For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/sMxcohGjz)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{:d}", "I am not a number"); + } + ``` + + gives a compile-time error on compilers with C++20 `consteval` + support (gcc 10+, clang 11+) because `d` is not a valid format + specifier for a string. + + To pass a runtime string wrap it in `fmt::runtime`: + + ```c++ + fmt::print(fmt::runtime("{:d}"), "I am not a number"); + ``` + +- Added compile-time formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2019, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2044, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2056, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2072, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2075, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2078, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2129, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2326). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/Mxx9d89jM)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/compile.h> + + consteval auto compile_time_itoa(int value) -> std::array<char, 10> { + auto result = std::array<char, 10>(); + fmt::format_to(result.data(), FMT_COMPILE("{}"), value); + return result; + } + + constexpr auto answer = compile_time_itoa(42); + ``` + + Most of the formatting functionality is available at compile time + with a notable exception of floating-point numbers and pointers. + Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Optimized handling of format specifiers during format string + compilation. For example, hexadecimal formatting (`"{:x}"`) is now + 3-7x faster than before when using `format_to` with format string + compilation and a stack-allocated buffer + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1944). + + Before (7.1.3): + + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + Benchmark Time CPU Iterations + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + FMTCompileOld/0 15.5 ns 15.5 ns 43302898 + FMTCompileOld/42 16.6 ns 16.6 ns 43278267 + FMTCompileOld/273123 18.7 ns 18.6 ns 37035861 + FMTCompileOld/9223372036854775807 19.4 ns 19.4 ns 35243000 + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + + After (8.x): + + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + Benchmark Time CPU Iterations + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + FMTCompileNew/0 1.99 ns 1.99 ns 360523686 + FMTCompileNew/42 2.33 ns 2.33 ns 279865664 + FMTCompileNew/273123 3.72 ns 3.71 ns 190230315 + FMTCompileNew/9223372036854775807 5.28 ns 5.26 ns 130711631 + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + + It is even faster than `std::to_chars` from libc++ compiled with + clang on macOS: + + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + Benchmark Time CPU Iterations + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + ToChars/0 4.42 ns 4.41 ns 160196630 + ToChars/42 5.00 ns 4.98 ns 140735201 + ToChars/273123 7.26 ns 7.24 ns 95784130 + ToChars/9223372036854775807 8.77 ns 8.75 ns 75872534 + ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- + + In other cases, especially involving `std::string` construction, the + speed up is usually lower because handling format specifiers takes a + smaller fraction of the total time. + +- Added the `_cf` user-defined literal to represent a compiled format + string. It can be used instead of the `FMT_COMPILE` macro + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2043, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2242): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/compile.h> + + using namespace fmt::literals; + auto s = fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); // 🙁 not modern + auto s = fmt::format("{}"_cf, 42); // 🙂 modern as hell + ``` + + It requires compiler support for class types in non-type template + parameters (a C++20 feature) which is available in GCC 9.3+. + Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Format string compilation now requires `format` functions of + `formatter` specializations for user-defined types to be `const`: + + ```c++ + template <> struct fmt::formatter<my_type>: formatter<string_view> { + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(my_type obj, FormatContext& ctx) const { // Note const here. + // ... + } + }; + ``` + +- Added UDL-based named argument support to format string compilation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2243, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2281). For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/compile.h> + + using namespace fmt::literals; + auto s = fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{answer}"), "answer"_a = 42); + ``` + + Here the argument named \"answer\" is resolved at compile time with + no runtime overhead. Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Added format string compilation support to `fmt::print` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2280, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2304). Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Added initial support for compiling {fmt} as a C++20 module + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2235, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2240, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2260, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2282, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2283, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2288, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2298, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2306, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2307, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2309, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2318, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2324, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2332, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2340). Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Made symbols private by default reducing shared library size + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2301). For example + there was a \~15% reported reduction on one platform. Thanks @sergiud. + +- Optimized includes making the result of preprocessing `fmt/format.h` + \~20% smaller with libstdc++/C++20 and slightly improving build + times (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1998). + +- Added support of ranges with non-const `begin` / `end` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1953). Thanks @kitegi. + +- Added support of `std::byte` and other formattable types to + `fmt::join` (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1981, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2040, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2050, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2262). For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/format.h> + #include <cstddef> + #include <vector> + + int main() { + auto bytes = std::vector{std::byte(4), std::byte(2)}; + fmt::print("{}", fmt::join(bytes, "")); + } + ``` + + prints \"42\". + + Thanks @kamibo. + +- Implemented the default format for `std::chrono::system_clock` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2319, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2345). For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{}", std::chrono::system_clock::now()); + } + ``` + + prints \"2021-06-18 15:22:00\" (the output depends on the current + date and time). Thanks @sunmy2019. + +- Made more chrono specifiers locale independent by default. Use the + `'L'` specifier to get localized formatting. For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + + int main() { + std::locale::global(std::locale("ru_RU.UTF-8")); + auto monday = std::chrono::weekday(1); + fmt::print("{}\n", monday); // prints "Mon" + fmt::print("{:L}\n", monday); // prints "пн" + } + ``` + +- Improved locale handling in chrono formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2337, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2349, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2350). Thanks @phprus. + +- Deprecated `fmt/locale.h` moving the formatting functions that take + a locale to `fmt/format.h` (`char`) and `fmt/xchar` (other + overloads). This doesn\'t introduce a dependency on `<locale>` so + there is virtually no compile time effect. + +- Deprecated an undocumented `format_to` overload that takes + `basic_memory_buffer`. + +- Made parameter order in `vformat_to` consistent with `format_to` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2327). + +- Added support for time points with arbitrary durations + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2208). For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + + int main() { + using tp = std::chrono::time_point< + std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::seconds>; + fmt::print("{:%S}", tp(std::chrono::seconds(42))); + } + ``` + + prints \"42\". + +- Formatting floating-point numbers no longer produces trailing zeros + by default for consistency with `std::format`. For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{0:.3}", 1.1); + } + ``` + + prints \"1.1\". Use the `'#'` specifier to keep trailing zeros. + +- Dropped a limit on the number of elements in a range and replaced + `{}` with `[]` as range delimiters for consistency with Python\'s + `str.format`. + +- The `'L'` specifier for locale-specific numeric formatting can now + be combined with presentation specifiers as in `std::format`. For + example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + #include <locale> + + int main() { + std::locale::global(std::locale("fr_FR.UTF-8")); + fmt::print("{0:.2Lf}", 0.42); + } + ``` + + prints \"0,42\". The deprecated `'n'` specifier has been removed. + +- Made the `0` specifier ignored for infinity and NaN + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2305, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2310). Thanks @Liedtke. + +- Made the hexfloat formatting use the right alignment by default + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2308, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2317). Thanks @Liedtke. + +- Removed the deprecated numeric alignment (`'='`). Use the `'0'` + specifier instead. + +- Removed the deprecated `fmt/posix.h` header that has been replaced + with `fmt/os.h`. + +- Removed the deprecated `format_to_n_context`, `format_to_n_args` and + `make_format_to_n_args`. They have been replaced with + `format_context`, `` format_args` and ``make_format_args\`\` + respectively. + +- Moved `wchar_t`-specific functions and types to `fmt/xchar.h`. You + can define `FMT_DEPRECATED_INCLUDE_XCHAR` to automatically include + `fmt/xchar.h` from `fmt/format.h` but this will be disabled in the + next major release. + +- Fixed handling of the `'+'` specifier in localized formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2133). + +- Added support for the `'s'` format specifier that gives textual + representation of `bool` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2094, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2109). For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{:s}", true); + } + ``` + + prints \"true\". Thanks @powercoderlol. + +- Made `fmt::ptr` work with function pointers + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2131). For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/format.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("My main: {}\n", fmt::ptr(main)); + } + ``` + + Thanks @mikecrowe. + +- The undocumented support for specializing `formatter` for pointer + types has been removed. + +- Fixed `fmt::formatted_size` with format string compilation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2141, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2161). Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Fixed handling of empty format strings during format string + compilation (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2042): + + ```c++ + auto s = fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("")); + ``` + + Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Fixed handling of enums in `fmt::to_string` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2036). + +- Improved width computation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2033, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2091). For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{:-<10}{}\n", "你好", "世界"); + fmt::print("{:-<10}{}\n", "hello", "world"); + } + ``` + + prints + +  + + on a modern terminal. + +- The experimental fast output stream (`fmt::ostream`) is now + truncated by default for consistency with `fopen` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2018). For example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/os.h> + + int main() { + fmt::ostream out1 = fmt::output_file("guide"); + out1.print("Zaphod"); + out1.close(); + fmt::ostream out2 = fmt::output_file("guide"); + out2.print("Ford"); + } + ``` + + writes \"Ford\" to the file \"guide\". To preserve the old file + content if any pass `fmt::file::WRONLY | fmt::file::CREATE` flags to + `fmt::output_file`. + +- Fixed moving of `fmt::ostream` that holds buffered data + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2197, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2198). Thanks @vtta. + +- Replaced the `fmt::system_error` exception with a function of the + same name that constructs `std::system_error` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2266). + +- Replaced the `fmt::windows_error` exception with a function of the + same name that constructs `std::system_error` with the category + returned by `fmt::system_category()` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2274, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2275). The latter is + similar to `std::sytem_category` but correctly handles UTF-8. + Thanks @phprus. + +- Replaced `fmt::error_code` with `std::error_code` and made it + formattable (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2269, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2270, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2273). Thanks @phprus. + +- Added speech synthesis support + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2206). + +- Made `format_to` work with a memory buffer that has a custom + allocator (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2300). + Thanks @voxmea. + +- Added `Allocator::max_size` support to `basic_memory_buffer`. + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1960). Thanks @phprus. + +- Added wide string support to `fmt::join` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2236). Thanks @crbrz. + +- Made iterators passed to `formatter` specializations via a format + context satisfy C++20 `std::output_iterator` requirements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2156, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2158, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2195, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2204). Thanks @randomnetcat. + +- Optimized the `printf` implementation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1982, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1984, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2016, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2164). + Thanks @rimathia and @moiwi. + +- Improved detection of `constexpr` `char_traits` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2246, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2257). Thanks @phprus. + +- Fixed writing to `stdout` when it is redirected to `NUL` on Windows + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2080). + +- Fixed exception propagation from iterators + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2097). + +- Improved `strftime` error handling + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2238, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2244). Thanks @yumeyao. + +- Stopped using deprecated GCC UDL template extension. + +- Added `fmt/args.h` to the install target + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2096). + +- Error messages are now passed to assert when exceptions are disabled + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2145). Thanks @NobodyXu. + +- Added the `FMT_MASTER_PROJECT` CMake option to control build and + install targets when {fmt} is included via `add_subdirectory` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2098, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2100). + Thanks @randomizedthinking. + +- Improved build configuration + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2026, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2122). + Thanks @luncliff and @ibaned. + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1947, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1959, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1963, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1965, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1966, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1974, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1975, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1990, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2000, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2001, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2002, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2004, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2006, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2009, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2010, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2038, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2039, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2047, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2053, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2059, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2065, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2067, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2068, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2073, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2103, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2105, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2106, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2107, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2116, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2117, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2118, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2119, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2127, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2128, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2140, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2142, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2143, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2144, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2147, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2148, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2149, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2152, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2160, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2170, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2175, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2176, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2177, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2178, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2179, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2180, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2181, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2183, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2184, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2185, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2186, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2187, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2190, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2192, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2194, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2205, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2210, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2211, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2215, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2216, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2218, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2220, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2228, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2229, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2230, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2233, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2239, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2248, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2252, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2253, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2255, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2261, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2278, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2284, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2287, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2289, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2290, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2293, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2295, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2296, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2297, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2311, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2313, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2315, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2320, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2321, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2323, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2328, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2329, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2333, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2338, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2341). + Thanks @darklukee, @fagg, @killerbot242, @jgopel, @yeswalrus, @Finkman, + @HazardyKnusperkeks, @dkavolis, @concatime, @chronoxor, @summivox, @yNeo, + @Apache-HB, @alexezeder, @toojays, @Brainy0207, @vadz, @imsherlock, @phprus, + @white238, @yafshar, @BillyDonahue, @jstaahl, @denchat, @DanielaE, + @ilyakurdyukov, @ilmai, @JessyDL, @sergiud, @mwinterb, @sven-herrmann, + @jmelas, @twoixter, @crbrz and @upsj. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1986, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2051, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2057, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2081, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2084, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2312). + Thanks @imba-tjd, @0x416c69 and @mordante. + +- Continuous integration and test improvements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1969, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1991, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2020, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2110, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2114, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2196, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2217, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2247, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2256, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2336, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/2346). + Thanks @jgopel, @alexezeder and @DanielaE. + +# 7.1.3 - 2020-11-24 + +- Fixed handling of buffer boundaries in `format_to_n` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1996, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2029). +- Fixed linkage errors when linking with a shared library + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2011). +- Reintroduced ostream support to range formatters + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2014). +- Worked around an issue with mixing std versions in gcc + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2017). + +# 7.1.2 - 2020-11-04 + +- Fixed floating point formatting with large precision + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1976). + +# 7.1.1 - 2020-11-01 + +- Fixed ABI compatibility with 7.0.x + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1961). +- Added the `FMT_ARM_ABI_COMPATIBILITY` macro to work around ABI + incompatibility between GCC and Clang on ARM + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1919). +- Worked around a SFINAE bug in GCC 8 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1957). +- Fixed linkage errors when building with GCC\'s LTO + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1955). +- Fixed a compilation error when building without `__builtin_clz` or + equivalent (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1968). + Thanks @tohammer. +- Fixed a sign conversion warning + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1964). Thanks @OptoCloud. + +# 7.1.0 - 2020-10-25 + +- Switched from + [Grisu3](https://www.cs.tufts.edu/~nr/cs257/archive/florian-loitsch/printf.pdf) + to [Dragonbox](https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox) for the default + floating-point formatting which gives the shortest decimal + representation with round-trip guarantee and correct rounding + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1882, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1887, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1894). This makes {fmt} + up to 20-30x faster than common implementations of + `std::ostringstream` and `sprintf` on + [dtoa-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark) and + faster than double-conversion and Ryū: + +  + + It is possible to get even better performance at the cost of larger + binary size by compiling with the `FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX` + macro set to 1. + + Thanks @jk-jeon. + +- Added an experimental unsynchronized file output API which, together + with [format string + compilation](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#compile-api), can give + [5-9 times speed up compared to + fprintf](https://www.zverovich.net/2020/08/04/optimal-file-buffer-size.html) + on common platforms ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/nsTcG8)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/os.h> + + int main() { + auto f = fmt::output_file("guide"); + f.print("The answer is {}.", 42); + } + ``` + +- Added a formatter for `std::chrono::time_point<system_clock>` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1819, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1837). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/c4M6fh)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + + int main() { + auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); + fmt::print("The time is {:%H:%M:%S}.\n", now); + } + ``` + + Thanks @adamburgess. + +- Added support for ranges with non-const `begin`/`end` to `fmt::join` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1784, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1786). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/jP63Tv)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/ranges.h> + #include <range/v3/view/filter.hpp> + + int main() { + using std::literals::string_literals::operator""s; + auto strs = std::array{"a"s, "bb"s, "ccc"s}; + auto range = strs | ranges::views::filter( + [] (const std::string &x) { return x.size() != 2; } + ); + fmt::print("{}\n", fmt::join(range, "")); + } + ``` + + prints \"accc\". + + Thanks @tonyelewis. + +- Added a `memory_buffer::append` overload that takes a range + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1806). Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Improved handling of single code units in `FMT_COMPILE`. For + example: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/compile.h> + + char* f(char* buf) { + return fmt::format_to(buf, FMT_COMPILE("x{}"), 42); + } + ``` + + compiles to just ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/5vncz3)): + + ```asm + _Z1fPc: + movb $120, (%rdi) + xorl %edx, %edx + cmpl $42, _ZN3fmt2v76detail10basic_dataIvE23zero_or_powers_of_10_32E+8(%rip) + movl $3, %eax + seta %dl + subl %edx, %eax + movzwl _ZN3fmt2v76detail10basic_dataIvE6digitsE+84(%rip), %edx + cltq + addq %rdi, %rax + movw %dx, -2(%rax) + ret + ``` + + Here a single `mov` instruction writes `'x'` (`$120`) to the output + buffer. + +- Added dynamic width support to format string compilation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1809). + +- Improved error reporting for unformattable types: now you\'ll get + the type name directly in the error message instead of the note: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + struct how_about_no {}; + + int main() { + fmt::print("{}", how_about_no()); + } + ``` + + Error ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/GoxM4e)): + + `fmt/core.h:1438:3: error: static_assert failed due to requirement 'fmt::v7::formattable<how_about_no>()' "Cannot format an argument. To make type T formattable provide a formatter<T> specialization: https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#udt" ...` + +- Added the + [make_args_checked](https://fmt.dev/7.1.0/api.html#argument-lists) + function template that allows you to write formatting functions with + compile-time format string checks and avoid binary code bloat + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/PEf9qr)): + + ```c++ + void vlog(const char* file, int line, fmt::string_view format, + fmt::format_args args) { + fmt::print("{}: {}: ", file, line); + fmt::vprint(format, args); + } + + template <typename S, typename... Args> + void log(const char* file, int line, const S& format, Args&&... args) { + vlog(file, line, format, + fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format, args...)); + } + + #define MY_LOG(format, ...) \ + log(__FILE__, __LINE__, FMT_STRING(format), __VA_ARGS__) + + MY_LOG("invalid squishiness: {}", 42); + ``` + +- Replaced `snprintf` fallback with a faster internal IEEE 754 `float` + and `double` formatter for arbitrary precision. For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/dPhWvj)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{:.500}\n", 4.9406564584124654E-324); + } + ``` + + prints + + `4.9406564584124654417656879286822137236505980261432476442558568250067550727020875186529983636163599237979656469544571773092665671035593979639877479601078187812630071319031140452784581716784898210368871863605699873072305000638740915356498438731247339727316961514003171538539807412623856559117102665855668676818703956031062493194527159149245532930545654440112748012970999954193198940908041656332452475714786901472678015935523861155013480352649347201937902681071074917033322268447533357208324319360923829e-324`. + +- Made `format_to_n` and `formatted_size` part of the [core + API](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#core-api) + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/sPjY1K)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + char buffer[10]; + auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "{}", 42); + } + ``` + +- Added `fmt::format_to_n` overload with format string compilation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1764, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1767, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1869). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/93h86q)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/compile.h> + + int main() { + char buffer[8]; + fmt::format_to_n(buffer, sizeof(buffer), FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); + } + ``` + + Thanks @Kurkin and @alexezeder. + +- Added `fmt::format_to` overload that take `text_style` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1593, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1842, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1843). For example + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/91153r)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/color.h> + + int main() { + std::string out; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), + fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red), + "The answer is {}.", 42); + } + ``` + + Thanks @Naios. + +- Made the `'#'` specifier emit trailing zeros in addition to the + decimal point (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1797). + For example ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/bhdcW9)): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{:#.2g}", 0.5); + } + ``` + + prints `0.50`. + +- Changed the default floating point format to not include `.0` for + consistency with `std::format` and `std::to_chars` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1893, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1943). It is possible + to get the decimal point and trailing zero with the `#` specifier. + +- Fixed an issue with floating-point formatting that could result in + addition of a non-significant trailing zero in rare cases e.g. + `1.00e-34` instead of `1.0e-34` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1873, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1917). + +- Made `fmt::to_string` fallback on `ostream` insertion operator if + the `formatter` specialization is not provided + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1815, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1829). Thanks @alexezeder. + +- Added support for the append mode to the experimental file API and + improved `fcntl.h` detection. + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1847, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1848). Thanks @t-wiser. + +- Fixed handling of types that have both an implicit conversion + operator and an overloaded `ostream` insertion operator + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1766). + +- Fixed a slicing issue in an internal iterator type + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1822). Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Fixed an issue in locale-specific integer formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1927). + +- Fixed handling of exotic code unit types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1870, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1932). + +- Improved `FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1878). Thanks @jk-jeon. + +- Removed dependency on `windows.h` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1900). Thanks @bernd5. + +- Optimized counting of decimal digits on MSVC + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1890). Thanks @mwinterb. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1772, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1775, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1792, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1838, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1888, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1918, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1939). + Thanks @leolchat, @pepsiman, @Klaim, @ravijanjam, @francesco-st and @udnaan. + +- Added the `FMT_REDUCE_INT_INSTANTIATIONS` CMake option that reduces + the binary code size at the cost of some integer formatting + performance. This can be useful for extremely memory-constrained + embedded systems + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1778, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1781). Thanks @kammce. + +- Added the `FMT_USE_INLINE_NAMESPACES` macro to control usage of + inline namespaces + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1945). Thanks @darklukee. + +- Improved build configuration + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1760, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1770, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1779, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1783, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1823). + Thanks @dvetutnev, @xvitaly, @tambry, @medithe and @martinwuehrer. + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1790, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1802, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1808, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1810, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1811, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1812, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1814, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1816, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1817, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1818, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1825, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1836, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1855, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1856, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1860, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1877, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1879, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1880, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1896, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1897, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1898, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1904, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1908, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1911, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1912, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1928, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1929, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1935, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1937, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1942, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1949). + Thanks @TheQwertiest, @medithe, @martinwuehrer, @n16h7hunt3r, @Othereum, + @gsjaardema, @AlexanderLanin, @gcerretani, @chronoxor, @noizefloor, + @akohlmey, @jk-jeon, @rimathia, @rglarix, @moiwi, @heckad, @MarcDirven. + @BartSiwek and @darklukee. + +# 7.0.3 - 2020-08-06 + +- Worked around broken `numeric_limits` for 128-bit integers + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1787). +- Added error reporting on missing named arguments + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1796). +- Stopped using 128-bit integers with clang-cl + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1800). Thanks @Kingcom. +- Fixed issues in locale-specific integer formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1782, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1801). + +# 7.0.2 - 2020-07-29 + +- Worked around broken `numeric_limits` for 128-bit integers + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1725). +- Fixed compatibility with CMake 3.4 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1779). +- Fixed handling of digit separators in locale-specific formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1782). + +# 7.0.1 - 2020-07-07 + +- Updated the inline version namespace name. +- Worked around a gcc bug in mangling of alias templates + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1753). +- Fixed a linkage error on Windows + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1757). Thanks @Kurkin. +- Fixed minor issues with the documentation. + +# 7.0.0 - 2020-07-05 + +- Reduced the library size. For example, on macOS a stripped test + binary statically linked with {fmt} [shrank from \~368k to less than + 100k](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/05/21/reducing-library-size.html). + +- Added a simpler and more efficient [format string compilation + API](https://fmt.dev/7.0.0/api.html#compile-api): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/compile.h> + + // Converts 42 into std::string using the most efficient method and no + // runtime format string processing. + std::string s = fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); + ``` + + The old `fmt::compile` API is now deprecated. + +- Optimized integer formatting: `format_to` with format string + compilation and a stack-allocated buffer is now [faster than + to_chars on both libc++ and + libstdc++](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html). + +- Optimized handling of small format strings. For example, + + ```c++ + fmt::format("Result: {}: ({},{},{},{})", str1, str2, str3, str4, str5) + ``` + + is now \~40% faster + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1685). + +- Applied extern templates to improve compile times when using the + core API and `fmt/format.h` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1452). For example, + on macOS with clang the compile time of a test translation unit + dropped from 2.3s to 0.3s with `-O2` and from 0.6s to 0.3s with the + default settings (`-O0`). + + Before (`-O2`): + + % time c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 -O2 + c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 -O2 2.22s user 0.08s system 99% cpu 2.311 total + + After (`-O2`): + + % time c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 -O2 + c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 -O2 0.26s user 0.04s system 98% cpu 0.303 total + + Before (default): + + % time c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 + c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 0.53s user 0.06s system 98% cpu 0.601 total + + After (default): + + % time c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 + c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 0.24s user 0.06s system 98% cpu 0.301 total + + It is still recommended to use `fmt/core.h` instead of + `fmt/format.h` but the compile time difference is now smaller. + Thanks @alex3d for the suggestion. + +- Named arguments are now stored on stack (no dynamic memory + allocations) and the compiled code is more compact and efficient. + For example + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("The answer is {answer}\n", fmt::arg("answer", 42)); + } + ``` + + compiles to just ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/z/NcfEp_)) + + ```asm + .LC0: + .string "answer" + .LC1: + .string "The answer is {answer}\n" + main: + sub rsp, 56 + mov edi, OFFSET FLAT:.LC1 + mov esi, 23 + movabs rdx, 4611686018427387905 + lea rax, [rsp+32] + lea rcx, [rsp+16] + mov QWORD PTR [rsp+8], 1 + mov QWORD PTR [rsp], rax + mov DWORD PTR [rsp+16], 42 + mov QWORD PTR [rsp+32], OFFSET FLAT:.LC0 + mov DWORD PTR [rsp+40], 0 + call fmt::v6::vprint(fmt::v6::basic_string_view<char>, + fmt::v6::format_args) + xor eax, eax + add rsp, 56 + ret + + .L.str.1: + .asciz "answer" + ``` + +- Implemented compile-time checks for dynamic width and precision + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1614): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/format.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print(FMT_STRING("{0:{1}}"), 42); + } + ``` + + now gives a compilation error because argument 1 doesn\'t exist: + + In file included from test.cc:1: + include/fmt/format.h:2726:27: error: constexpr variable 'invalid_format' must be + initialized by a constant expression + FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL bool invalid_format = + ^ + ... + include/fmt/core.h:569:26: note: in call to + '&checker(s, {}).context_->on_error(&"argument not found"[0])' + if (id >= num_args_) on_error("argument not found"); + ^ + +- Added sentinel support to `fmt::join` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1689) + + ```c++ + struct zstring_sentinel {}; + bool operator==(const char* p, zstring_sentinel) { return *p == '\0'; } + bool operator!=(const char* p, zstring_sentinel) { return *p != '\0'; } + + struct zstring { + const char* p; + const char* begin() const { return p; } + zstring_sentinel end() const { return {}; } + }; + + auto s = fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(zstring{"hello"}, "_")); + // s == "h_e_l_l_o" + ``` + + Thanks @BRevzin. + +- Added support for named arguments, `clear` and `reserve` to + `dynamic_format_arg_store` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1655, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1663, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1674, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1677). Thanks @vsolontsov-ll. + +- Added support for the `'c'` format specifier to integral types for + compatibility with `std::format` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1652). + +- Replaced the `'n'` format specifier with `'L'` for compatibility + with `std::format` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1624). The `'n'` + specifier can be enabled via the `FMT_DEPRECATED_N_SPECIFIER` macro. + +- The `'='` format specifier is now disabled by default for + compatibility with `std::format`. It can be enabled via the + `FMT_DEPRECATED_NUMERIC_ALIGN` macro. + +- Removed the following deprecated APIs: + + - `FMT_STRING_ALIAS` and `fmt` macros - replaced by `FMT_STRING` + - `fmt::basic_string_view::char_type` - replaced by + `fmt::basic_string_view::value_type` + - `convert_to_int` + - `format_arg_store::types` + - `*parse_context` - replaced by `*format_parse_context` + - `FMT_DEPRECATED_INCLUDE_OS` + - `FMT_DEPRECATED_PERCENT` - incompatible with `std::format` + - `*writer` - replaced by compiled format API + +- Renamed the `internal` namespace to `detail` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1538). The former is + still provided as an alias if the `FMT_USE_INTERNAL` macro is + defined. + +- Improved compatibility between `fmt::printf` with the standard specs + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1595, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1682, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1683, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1687, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1699). Thanks @rimathia. + +- Fixed handling of `operator<<` overloads that use `copyfmt` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1666). + +- Added the `FMT_OS` CMake option to control inclusion of OS-specific + APIs in the fmt target. This can be useful for embedded platforms + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1654, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1656). Thanks @kwesolowski. + +- Replaced `FUZZING_BUILD_MODE_UNSAFE_FOR_PRODUCTION` with the + `FMT_FUZZ` macro to prevent interfering with fuzzing of projects + using {fmt} (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1650). + Thanks @asraa. + +- Fixed compatibility with emscripten + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1636, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1637). Thanks @ArthurSonzogni. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/704, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1643, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1660, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1681, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1691, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1706, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1714, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1721, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1739, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1740, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1741, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1751). + Thanks @senior7515, @lsr0, @puetzk, @fpelliccioni, Alexey Kuzmenko, @jelly, + @claremacrae, @jiapengwen, @gsjaardema and @alexey-milovidov. + +- Implemented various build configuration fixes and improvements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1603, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1657, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1702, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1728). + Thanks @scramsby, @jtojnar, @orivej and @flagarde. + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1616, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1620, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1622, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1625, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1627, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1628, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1629, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1631, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1633, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1649, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1658, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1661, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1667, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1668, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1669, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1692, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1696, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1697, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1707, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1712, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1716, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1722, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1724, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1729, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1738, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1742, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1743, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1744, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1747, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1750). + Thanks @gsjaardema, @gabime, @johnor, @Kurkin, @invexed, @peterbell10, + @daixtrose, @petrutlucian94, @Neargye, @ambitslix, @gabime, @erthink, + @tohammer and @0x8000-0000. + +# 6.2.1 - 2020-05-09 + +- Fixed ostream support in `sprintf` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1631). +- Fixed type detection when using implicit conversion to `string_view` + and ostream `operator<<` inconsistently + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1662). + +# 6.2.0 - 2020-04-05 + +- Improved error reporting when trying to format an object of a + non-formattable type: + + ```c++ + fmt::format("{}", S()); + ``` + + now gives: + + include/fmt/core.h:1015:5: error: static_assert failed due to requirement + 'formattable' "Cannot format argument. To make type T formattable provide a + formatter<T> specialization: + https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#formatting-user-defined-types" + static_assert( + ^ + ... + note: in instantiation of function template specialization + 'fmt::v6::format<char [3], S, char>' requested here + fmt::format("{}", S()); + ^ + + if `S` is not formattable. + +- Reduced the library size by \~10%. + +- Always print decimal point if `#` is specified + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1476, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1498): + + ```c++ + fmt::print("{:#.0f}", 42.0); + ``` + + now prints `42.` + +- Implemented the `'L'` specifier for locale-specific numeric + formatting to improve compatibility with `std::format`. The `'n'` + specifier is now deprecated and will be removed in the next major + release. + +- Moved OS-specific APIs such as `windows_error` from `fmt/format.h` + to `fmt/os.h`. You can define `FMT_DEPRECATED_INCLUDE_OS` to + automatically include `fmt/os.h` from `fmt/format.h` for + compatibility but this will be disabled in the next major release. + +- Added precision overflow detection in floating-point formatting. + +- Implemented detection of invalid use of `fmt::arg`. + +- Used `type_identity` to block unnecessary template argument + deduction. Thanks Tim Song. + +- Improved UTF-8 handling + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1109): + + ```c++ + fmt::print("┌{0:─^{2}}┐\n" + "│{1: ^{2}}│\n" + "└{0:─^{2}}┘\n", "", "Привет, мир!", 20); + ``` + + now prints: + + ┌────────────────────┐ + │ Привет, мир! │ + └────────────────────┘ + + on systems that support Unicode. + +- Added experimental dynamic argument storage + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1170, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1584): + + ```c++ + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + store.push_back("answer"); + store.push_back(42); + fmt::vprint("The {} is {}.\n", store); + ``` + + prints: + + The answer is 42. + + Thanks @vsolontsov-ll. + +- Made `fmt::join` accept `initializer_list` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1591). Thanks @Rapotkinnik. + +- Fixed handling of empty tuples + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1588). + +- Fixed handling of output iterators in `format_to_n` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1506). + +- Fixed formatting of `std::chrono::duration` types to wide output + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1533). Thanks @zeffy. + +- Added const `begin` and `end` overload to buffers + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1553). Thanks @dominicpoeschko. + +- Added the ability to disable floating-point formatting via + `FMT_USE_FLOAT`, `FMT_USE_DOUBLE` and `FMT_USE_LONG_DOUBLE` macros + for extremely memory-constrained embedded system + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1590). Thanks @albaguirre. + +- Made `FMT_STRING` work with `constexpr` `string_view` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1589). Thanks @scramsby. + +- Implemented a minor optimization in the format string parser + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1560). Thanks @IkarusDeveloper. + +- Improved attribute detection + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1469, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1475, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1576). + Thanks @federico-busato, @chronoxor and @refnum. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1481, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1523). + Thanks @JackBoosY and @imba-tjd. + +- Fixed symbol visibility on Linux when compiling with + `-fvisibility=hidden` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1535). Thanks @milianw. + +- Implemented various build configuration fixes and improvements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1264, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1460, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1534, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1536, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1545, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1546, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1566, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1582, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1597, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1598). + Thanks @ambitslix, @jwillikers and @stac47. + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1433, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1461, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1470, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1480, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1485, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1492, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1493, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1504, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1505, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1512, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1515, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1516, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1518, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1519, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1520, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1521, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1522, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1524, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1530, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1531, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1532, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1539, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1547, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1548, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1554, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1567, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1568, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1569, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1571, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1573, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1575, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1581, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1583, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1586, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1587, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1594, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1596, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1604, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1606, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1607, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1609). + Thanks @marti4d, @iPherian, @parkertomatoes, @gsjaardema, @chronoxor, + @DanielaE, @torsten48, @tohammer, @lefticus, @ryusakki, @adnsv, @fghzxm, + @refnum, @pramodk, @Spirrwell and @scramsby. + +# 6.1.2 - 2019-12-11 + +- Fixed ABI compatibility with `libfmt.so.6.0.0` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1471). +- Fixed handling types convertible to `std::string_view` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1451). Thanks @denizevrenci. +- Made CUDA test an opt-in enabled via the `FMT_CUDA_TEST` CMake + option. +- Fixed sign conversion warnings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1440). Thanks @0x8000-0000. + +# 6.1.1 - 2019-12-04 + +- Fixed shared library build on Windows + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1443, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1445, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1446, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1450). + Thanks @egorpugin and @bbolli. +- Added a missing decimal point in exponent notation with trailing + zeros. +- Removed deprecated `format_arg_store::TYPES`. + +# 6.1.0 - 2019-12-01 + +- {fmt} now formats IEEE 754 `float` and `double` using the shortest + decimal representation with correct rounding by default: + + ```c++ + #include <cmath> + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + fmt::print("{}", M_PI); + } + ``` + + prints `3.141592653589793`. + +- Made the fast binary to decimal floating-point formatter the + default, simplified it and improved performance. {fmt} is now 15 + times faster than libc++\'s `std::ostringstream`, 11 times faster + than `printf` and 10% faster than double-conversion on + [dtoa-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark): + + | Function | Time (ns) | Speedup | + | ------------- | --------: | ------: | + | ostringstream | 1,346.30 | 1.00x | + | ostrstream | 1,195.74 | 1.13x | + | sprintf | 995.08 | 1.35x | + | doubleconv | 99.10 | 13.59x | + | fmt | 88.34 | 15.24x | + +  + +- {fmt} no longer converts `float` arguments to `double`. In + particular this improves the default (shortest) representation of + floats and makes `fmt::format` consistent with `std::format` specs + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1336, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1353, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1360, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1361): + + ```c++ + fmt::print("{}", 0.1f); + ``` + + prints `0.1` instead of `0.10000000149011612`. + + Thanks @orivej. + +- Made floating-point formatting output consistent with + `printf`/iostreams + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1376, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1417). + +- Added support for 128-bit integers + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1287): + + ```c++ + fmt::print("{}", std::numeric_limits<__int128_t>::max()); + ``` + + prints `170141183460469231731687303715884105727`. + + Thanks @denizevrenci. + +- The overload of `print` that takes `text_style` is now atomic, i.e. + the output from different threads doesn\'t interleave + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1351). Thanks @tankiJong. + +- Made compile time in the header-only mode \~20% faster by reducing + the number of template instantiations. `wchar_t` overload of + `vprint` was moved from `fmt/core.h` to `fmt/format.h`. + +- Added an overload of `fmt::join` that works with tuples + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1322, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1330): + + ```c++ + #include <tuple> + #include <fmt/ranges.h> + + int main() { + std::tuple<char, int, float> t{'a', 1, 2.0f}; + fmt::print("{}", t); + } + ``` + + prints `('a', 1, 2.0)`. + + Thanks @jeremyong. + +- Changed formatting of octal zero with prefix from \"00\" to \"0\": + + ```c++ + fmt::print("{:#o}", 0); + ``` + + prints `0`. + +- The locale is now passed to ostream insertion (`<<`) operators + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1406): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/locale.h> + #include <fmt/ostream.h> + + struct S { + double value; + }; + + std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, S s) { + return os << s.value; + } + + int main() { + auto s = fmt::format(std::locale("fr_FR.UTF-8"), "{}", S{0.42}); + // s == "0,42" + } + ``` + + Thanks @dlaugt. + +- Locale-specific number formatting now uses grouping + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1393, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1394). Thanks @skrdaniel. + +- Fixed handling of types with deleted implicit rvalue conversion to + `const char**` (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1421): + + ```c++ + struct mystring { + operator const char*() const&; + operator const char*() &; + operator const char*() const&& = delete; + operator const char*() && = delete; + }; + mystring str; + fmt::print("{}", str); // now compiles + ``` + +- Enums are now mapped to correct underlying types instead of `int` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1286). Thanks @agmt. + +- Enum classes are no longer implicitly converted to `int` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1424). + +- Added `basic_format_parse_context` for consistency with C++20 + `std::format` and deprecated `basic_parse_context`. + +- Fixed handling of UTF-8 in precision + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1389, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1390). Thanks @tajtiattila. + +- {fmt} can now be installed on Linux, macOS and Windows with + [Conda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/) using its + [conda-forge](https://conda-forge.org) + [package](https://github.com/conda-forge/fmt-feedstock) + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1410): + + conda install -c conda-forge fmt + + Thanks @tdegeus. + +- Added a CUDA test (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1285, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1317). + Thanks @luncliff and @risa2000. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1276, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1291, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1296, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1315, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1332, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1337, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1395 + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1418). + Thanks @waywardmonkeys, @pauldreik and @jackoalan. + +- Various code improvements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1358, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1407). + Thanks @orivej and @dpacbach. + +- Fixed compile-time format string checks for user-defined types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1292). + +- Worked around a false positive in `unsigned-integer-overflow` sanitizer + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1377). + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1273, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1278, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1280, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1281, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1288, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1290, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1301, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1305, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1306, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1309, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1312, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1313, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1316, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1319, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1320, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1326, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1328, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1344, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1345, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1347, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1349, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1354, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1362, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1366, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1364, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1370, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1371, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1385, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1388, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1397, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1414, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1416, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1422 + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1427, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1431, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1433). + Thanks @hhb, @gsjaardema, @gabime, @neheb, @vedranmiletic, @dkavolis, + @mwinterb, @orivej, @denizevrenci, @leonklingele, @chronoxor, @kent-tri, + @0x8000-0000 and @marti4d. + +# 6.0.0 - 2019-08-26 + +- Switched to the [MIT license]( + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/5a4b24613ba16cc689977c3b5bd8274a3ba1dd1f/LICENSE.rst) + with an optional exception that allows distributing binary code + without attribution. + +- Floating-point formatting is now locale-independent by default: + + ```c++ + #include <locale> + #include <fmt/core.h> + + int main() { + std::locale::global(std::locale("ru_RU.UTF-8")); + fmt::print("value = {}", 4.2); + } + ``` + + prints \"value = 4.2\" regardless of the locale. + + For locale-specific formatting use the `n` specifier: + + ```c++ + std::locale::global(std::locale("ru_RU.UTF-8")); + fmt::print("value = {:n}", 4.2); + ``` + + prints \"value = 4,2\". + +- Added an experimental Grisu floating-point formatting algorithm + implementation (disabled by default). To enable it compile with the + `FMT_USE_GRISU` macro defined to 1: + + ```c++ + #define FMT_USE_GRISU 1 + #include <fmt/format.h> + + auto s = fmt::format("{}", 4.2); // formats 4.2 using Grisu + ``` + + With Grisu enabled, {fmt} is 13x faster than `std::ostringstream` + (libc++) and 10x faster than `sprintf` on + [dtoa-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark) ([full + results](https://fmt.dev/unknown_mac64_clang10.0.html)): + +  + +- Separated formatting and parsing contexts for consistency with + [C++20 std::format](http://eel.is/c++draft/format), removing the + undocumented `basic_format_context::parse_context()` function. + +- Added [oss-fuzz](https://github.com/google/oss-fuzz) support + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1199). Thanks @pauldreik. + +- `formatter` specializations now always take precedence over + `operator<<` (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/952): + + ```c++ + #include <iostream> + #include <fmt/ostream.h> + + struct S {}; + + std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, S) { + return os << 1; + } + + template <> + struct fmt::formatter<S> : fmt::formatter<int> { + auto format(S, format_context& ctx) { + return formatter<int>::format(2, ctx); + } + }; + + int main() { + std::cout << S() << "\n"; // prints 1 using operator<< + fmt::print("{}\n", S()); // prints 2 using formatter + } + ``` + +- Introduced the experimental `fmt::compile` function that does format + string compilation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/618, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1169, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1171): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/compile.h> + + auto f = fmt::compile<int>("{}"); + std::string s = fmt::format(f, 42); // can be called multiple times to + // format different values + // s == "42" + ``` + + It moves the cost of parsing a format string outside of the format + function which can be beneficial when identically formatting many + objects of the same types. Thanks @stryku. + +- Added experimental `%` format specifier that formats floating-point + values as percentages + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1060, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1069, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1071): + + ```c++ + auto s = fmt::format("{:.1%}", 0.42); // s == "42.0%" + ``` + + Thanks @gawain-bolton. + +- Implemented precision for floating-point durations + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1004, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1012): + + ```c++ + auto s = fmt::format("{:.1}", std::chrono::duration<double>(1.234)); + // s == 1.2s + ``` + + Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Implemented `chrono` format specifiers `%Q` and `%q` that give the + value and the unit respectively + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1019): + + ```c++ + auto value = fmt::format("{:%Q}", 42s); // value == "42" + auto unit = fmt::format("{:%q}", 42s); // unit == "s" + ``` + + Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Fixed handling of dynamic width in chrono formatter: + + ```c++ + auto s = fmt::format("{0:{1}%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345), 12); + // ^ width argument index ^ width + // s == "03:25:45 " + ``` + + Thanks Howard Hinnant. + +- Removed deprecated `fmt/time.h`. Use `fmt/chrono.h` instead. + +- Added `fmt::format` and `fmt::vformat` overloads that take + `text_style` (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/993, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/994): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/color.h> + + std::string message = fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red), + "The answer is {}.", 42); + ``` + + Thanks @Naios. + +- Removed the deprecated color API (`print_colored`). Use the new API, + namely `print` overloads that take `text_style` instead. + +- Made `std::unique_ptr` and `std::shared_ptr` formattable as pointers + via `fmt::ptr` (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1121): + + ```c++ + std::unique_ptr<int> p = ...; + fmt::print("{}", fmt::ptr(p)); // prints p as a pointer + ``` + + Thanks @sighingnow. + +- Made `print` and `vprint` report I/O errors + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1098, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1099). Thanks @BillyDonahue. + +- Marked deprecated APIs with the `[[deprecated]]` attribute and + removed internal uses of deprecated APIs + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1022). Thanks @eliaskosunen. + +- Modernized the codebase using more C++11 features and removing + workarounds. Most importantly, `buffer_context` is now an alias + template, so use `buffer_context<T>` instead of + `buffer_context<T>::type`. These features require GCC 4.8 or later. + +- `formatter` specializations now always take precedence over implicit + conversions to `int` and the undocumented `convert_to_int` trait is + now deprecated. + +- Moved the undocumented `basic_writer`, `writer`, and `wwriter` types + to the `internal` namespace. + +- Removed deprecated `basic_format_context::begin()`. Use `out()` + instead. + +- Disallowed passing the result of `join` as an lvalue to prevent + misuse. + +- Refactored the undocumented structs that represent parsed format + specifiers to simplify the API and allow multibyte fill. + +- Moved SFINAE to template parameters to reduce symbol sizes. + +- Switched to `fputws` for writing wide strings so that it\'s no + longer required to call `_setmode` on Windows + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1229, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1243). Thanks @jackoalan. + +- Improved literal-based API + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1254). Thanks @sylveon. + +- Added support for exotic platforms without `uintptr_t` such as IBM i + (AS/400) which has 128-bit pointers and only 64-bit integers + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1059). + +- Added [Sublime Text syntax highlighting config]( + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/support/C%2B%2B.sublime-syntax) + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1037). Thanks @Kronuz. + +- Added the `FMT_ENFORCE_COMPILE_STRING` macro to enforce the use of + compile-time format strings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1231). Thanks @jackoalan. + +- Stopped setting `CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE` if {fmt} is a subproject + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1081). + +- Various build improvements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1039, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1078, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1091, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1103, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1177). + Thanks @luncliff, @jasonszang, @olafhering, @Lecetem and @pauldreik. + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1049, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1051, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1083, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1113, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1114, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1146, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1180, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1250, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1252, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1265). + Thanks @mikelui, @foonathan, @BillyDonahue, @jwakely, @kaisbe and + @sdebionne. + +- Fixed ambiguous formatter specialization in `fmt/ranges.h` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1123). + +- Fixed formatting of a non-empty `std::filesystem::path` which is an + infinitely deep range of its components + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1268). + +- Fixed handling of general output iterators when formatting + characters (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1056, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1058). Thanks @abolz. + +- Fixed handling of output iterators in `formatter` specialization for + ranges (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1064). + +- Fixed handling of exotic character types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1188). + +- Made chrono formatting work with exceptions disabled + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1062). + +- Fixed DLL visibility issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1134, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1147). Thanks @denchat. + +- Disabled the use of UDL template extension on GCC 9 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1148). + +- Removed misplaced `format` compile-time checks from `printf` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1173). + +- Fixed issues in the experimental floating-point formatter + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1072, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1129, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1153, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1155, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1210, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1222). Thanks @alabuzhev. + +- Fixed bugs discovered by fuzzing or during fuzzing integration + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1124, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1127, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1132, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1135, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1136, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1141, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1142, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1178, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1179, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1194). Thanks @pauldreik. + +- Fixed building tests on FreeBSD and Hurd + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1043). Thanks @jackyf. + +- Fixed various warnings and compilation issues + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/998, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1006, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1008, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1011, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1025, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1027, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1028, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1029, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1030, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1031, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1054, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1063, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1068, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1074, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1075, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1079, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1086, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1088, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1089, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1094, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1101, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1102, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1105, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1107, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1115, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1117, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1118, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1120, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1123, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1139, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1140, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1143, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1144, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1150, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1151, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1152, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1154, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1156, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1159, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1175, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1181, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1186, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1187, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1191, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1197, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1200, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1203, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1205, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1206, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1213, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1214, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1217, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1228, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1230, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1232, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1235, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1236, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1240). + Thanks @DanielaE, @mwinterb, @eliaskosunen, @morinmorin, @ricco19, + @waywardmonkeys, @chronoxor, @remyabel, @pauldreik, @gsjaardema, @rcane, + @mocabe, @denchat, @cjdb, @HazardyKnusperkeks, @vedranmiletic, @jackoalan, + @DaanDeMeyer and @starkmapper. + +# 5.3.0 - 2018-12-28 + +- Introduced experimental chrono formatting support: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/chrono.h> + + int main() { + using namespace std::literals::chrono_literals; + fmt::print("Default format: {} {}\n", 42s, 100ms); + fmt::print("strftime-like format: {:%H:%M:%S}\n", 3h + 15min + 30s); + } + ``` + + prints: + + Default format: 42s 100ms + strftime-like format: 03:15:30 + +- Added experimental support for emphasis (bold, italic, underline, + strikethrough), colored output to a file stream, and improved + colored formatting API + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/961, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/967, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/973): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/color.h> + + int main() { + print(fg(fmt::color::crimson) | fmt::emphasis::bold, + "Hello, {}!\n", "world"); + print(fg(fmt::color::floral_white) | bg(fmt::color::slate_gray) | + fmt::emphasis::underline, "Hello, {}!\n", "мир"); + print(fg(fmt::color::steel_blue) | fmt::emphasis::italic, + "Hello, {}!\n", "世界"); + } + ``` + + prints the following on modern terminals with RGB color support: + +  + + Thanks @Rakete1111. + +- Added support for 4-bit terminal colors + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/968, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/974) + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/color.h> + + int main() { + print(fg(fmt::terminal_color::red), "stop\n"); + } + ``` + + Note that these colors vary by terminal: + + 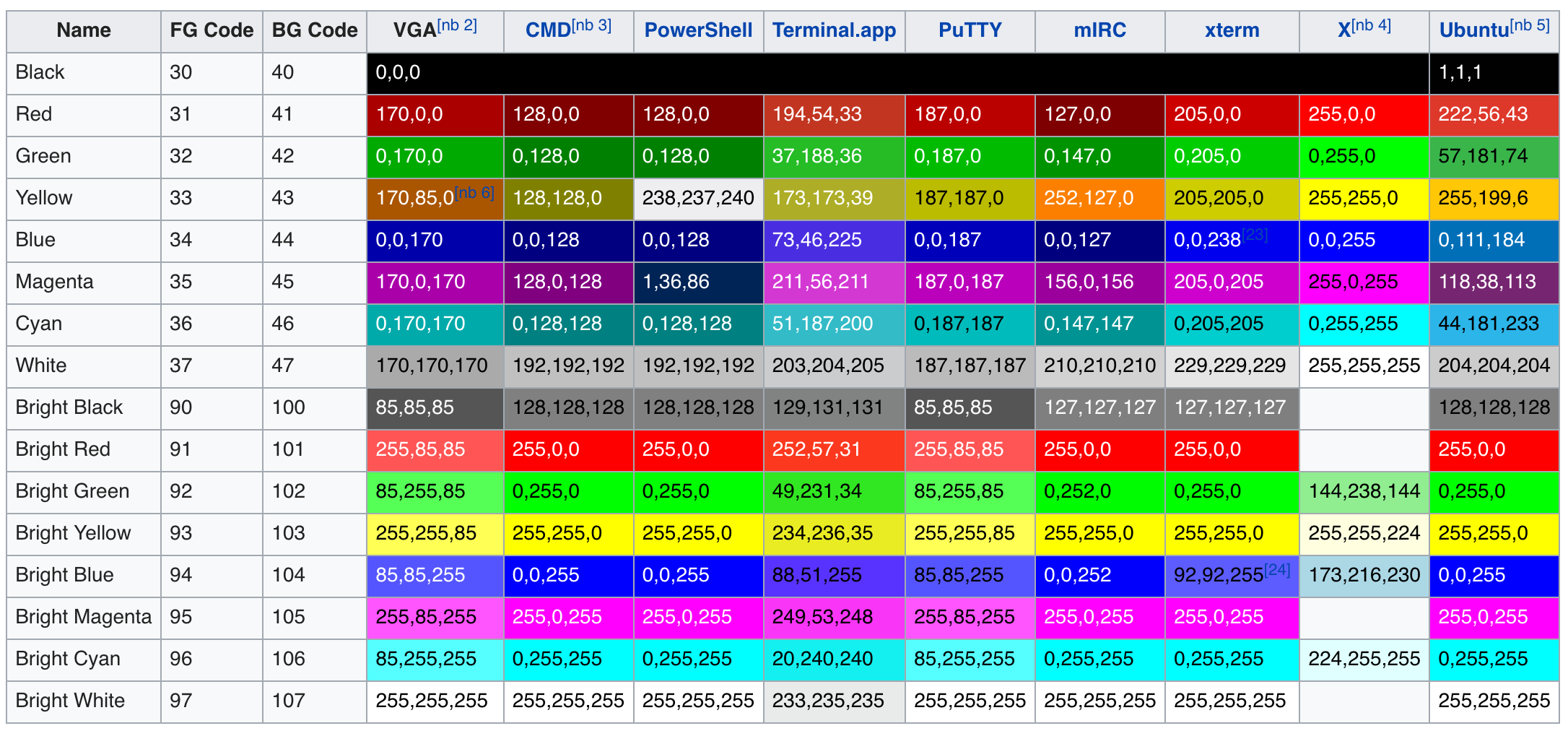 + + Thanks @Rakete1111. + +- Parameterized formatting functions on the type of the format string + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/880, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/881, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/883, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/885, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/897, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/920). Any object of + type `S` that has an overloaded `to_string_view(const S&)` returning + `fmt::string_view` can be used as a format string: + + ```c++ + namespace my_ns { + inline string_view to_string_view(const my_string& s) { + return {s.data(), s.length()}; + } + } + + std::string message = fmt::format(my_string("The answer is {}."), 42); + ``` + + Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Made `std::string_view` work as a format string + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/898): + + ```c++ + auto message = fmt::format(std::string_view("The answer is {}."), 42); + ``` + + Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Added wide string support to compile-time format string checks + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/924): + + ```c++ + print(fmt(L"{:f}"), 42); // compile-time error: invalid type specifier + ``` + + Thanks @XZiar. + +- Made colored print functions work with wide strings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/867): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/color.h> + + int main() { + print(fg(fmt::color::red), L"{}\n", 42); + } + ``` + + Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Introduced experimental Unicode support + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/628, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/891): + + ```c++ + using namespace fmt::literals; + auto s = fmt::format("{:*^5}"_u, "🤡"_u); // s == "**🤡**"_u + ``` + +- Improved locale support: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/locale.h> + + struct numpunct : std::numpunct<char> { + protected: + char do_thousands_sep() const override { return '~'; } + }; + + std::locale loc; + auto s = fmt::format(std::locale(loc, new numpunct()), "{:n}", 1234567); + // s == "1~234~567" + ``` + +- Constrained formatting functions on proper iterator types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/921). Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Added `make_printf_args` and `make_wprintf_args` functions + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/934). Thanks @tnovotny. + +- Deprecated `fmt::visit`, `parse_context`, and `wparse_context`. Use + `fmt::visit_format_arg`, `format_parse_context`, and + `wformat_parse_context` instead. + +- Removed undocumented `basic_fixed_buffer` which has been superseded + by the iterator-based API + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/873, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/902). Thanks @superfunc. + +- Disallowed repeated leading zeros in an argument ID: + + ```c++ + fmt::print("{000}", 42); // error + ``` + +- Reintroduced support for gcc 4.4. + +- Fixed compilation on platforms with exotic `double` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/878). + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/164, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/877, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/901, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/906, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/979). + Thanks @kookjr, @DarkDimius and @HecticSerenity. + +- Added pkgconfig support which makes it easier to consume the library + from meson and other build systems + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/916). Thanks @colemickens. + +- Various build improvements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/909, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/926, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/937, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/953, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/959). + Thanks @tchaikov, @luncliff, @AndreasSchoenle, @hotwatermorning and @Zefz. + +- Improved `string_view` construction performance + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/914). Thanks @gabime. + +- Fixed non-matching char types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/895). Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Fixed `format_to_n` with `std::back_insert_iterator` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/913). Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Fixed locale-dependent formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/905). + +- Fixed various compiler warnings and errors + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/882, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/886, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/933, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/941, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/931, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/943, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/954, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/956, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/962, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/965, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/977, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/983, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/989). + Thanks @Luthaf, @stevenhoving, @christinaa, @lgritz, @DanielaE, + @0x8000-0000 and @liuping1997. + +# 5.2.1 - 2018-09-21 + +- Fixed `visit` lookup issues on gcc 7 & 8 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/870). Thanks @medithe. +- Fixed linkage errors on older gcc. +- Prevented `fmt/range.h` from specializing `fmt::basic_string_view` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/865, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/868). Thanks @hhggit. +- Improved error message when formatting unknown types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/872). Thanks @foonathan. +- Disabled templated user-defined literals when compiled under nvcc + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/875). Thanks @CandyGumdrop. +- Fixed `format_to` formatting to `wmemory_buffer` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/874). + +# 5.2.0 - 2018-09-13 + +- Optimized format string parsing and argument processing which + resulted in up to 5x speed up on long format strings and significant + performance boost on various benchmarks. For example, version 5.2 is + 2.22x faster than 5.1 on decimal integer formatting with `format_to` + (macOS, clang-902.0.39.2): + + | Method | Time, s | Speedup | + | -------------------------- | --------------: | ------: | + | fmt::format 5.1 | 0.58 | | + | fmt::format 5.2 | 0.35 | 1.66x | + | fmt::format_to 5.1 | 0.51 | | + | fmt::format_to 5.2 | 0.23 | 2.22x | + | sprintf | 0.71 | | + | std::to_string | 1.01 | | + | std::stringstream | 1.73 | | + +- Changed the `fmt` macro from opt-out to opt-in to prevent name + collisions. To enable it define the `FMT_STRING_ALIAS` macro to 1 + before including `fmt/format.h`: + + ```c++ + #define FMT_STRING_ALIAS 1 + #include <fmt/format.h> + std::string answer = format(fmt("{}"), 42); + ``` + +- Added compile-time format string checks to `format_to` overload that + takes `fmt::memory_buffer` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/783): + + ```c++ + fmt::memory_buffer buf; + // Compile-time error: invalid type specifier. + fmt::format_to(buf, fmt("{:d}"), "foo"); + ``` + +- Moved experimental color support to `fmt/color.h` and enabled the + new API by default. The old API can be enabled by defining the + `FMT_DEPRECATED_COLORS` macro. + +- Added formatting support for types explicitly convertible to + `fmt::string_view`: + + ```c++ + struct foo { + explicit operator fmt::string_view() const { return "foo"; } + }; + auto s = format("{}", foo()); + ``` + + In particular, this makes formatting function work with + `folly::StringPiece`. + +- Implemented preliminary support for `char*_t` by replacing the + `format` function overloads with a single function template + parameterized on the string type. + +- Added support for dynamic argument lists + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/814, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/819). Thanks @MikePopoloski. + +- Reduced executable size overhead for embedded targets using newlib + nano by making locale dependency optional + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/839). Thanks @teajay-fr. + +- Keep `noexcept` specifier when exceptions are disabled + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/801, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/810). Thanks @qis. + +- Fixed formatting of user-defined types providing `operator<<` with + `format_to_n` (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/806). + Thanks @mkurdej. + +- Fixed dynamic linkage of new symbols + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/808). + +- Fixed global initialization issue + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/807): + + ```c++ + // This works on compilers with constexpr support. + static const std::string answer = fmt::format("{}", 42); + ``` + +- Fixed various compiler warnings and errors + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/804, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/809, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/811, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/822, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/827, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/830, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/838, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/843, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/844, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/851, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/852, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/854). + Thanks @henryiii, @medithe, and @eliasdaler. + +# 5.1.0 - 2018-07-05 + +- Added experimental support for RGB color output enabled with the + `FMT_EXTENDED_COLORS` macro: + + ```c++ + #define FMT_EXTENDED_COLORS + #define FMT_HEADER_ONLY // or compile fmt with FMT_EXTENDED_COLORS defined + #include <fmt/format.h> + + fmt::print(fmt::color::steel_blue, "Some beautiful text"); + ``` + + The old API (the `print_colored` and `vprint_colored` functions and + the `color` enum) is now deprecated. + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/762 + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/767). thanks @Remotion. + +- Added quotes to strings in ranges and tuples + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/766). Thanks @Remotion. + +- Made `format_to` work with `basic_memory_buffer` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/776). + +- Added `vformat_to_n` and `wchar_t` overload of `format_to_n` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/764, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/769). + +- Made `is_range` and `is_tuple_like` part of public (experimental) + API to allow specialization for user-defined types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/751, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/759). Thanks @drrlvn. + +- Added more compilers to continuous integration and increased + `FMT_PEDANTIC` warning levels + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/736). Thanks @eliaskosunen. + +- Fixed compilation with MSVC 2013. + +- Fixed handling of user-defined types in `format_to` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/793). + +- Forced linking of inline `vformat` functions into the library + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/795). + +- Fixed incorrect call to on_align in `'{:}='` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/750). + +- Fixed floating-point formatting to a non-back_insert_iterator with + sign & numeric alignment specified + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/756). + +- Fixed formatting to an array with `format_to_n` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/778). + +- Fixed formatting of more than 15 named arguments + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/754). + +- Fixed handling of compile-time strings when including + `fmt/ostream.h`. (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/768). + +- Fixed various compiler warnings and errors + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/742, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/748, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/752, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/770, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/775, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/779, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/780, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/790, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/792, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/800). + Thanks @Remotion, @gabime, @foonathan, @Dark-Passenger and @0x8000-0000. + +# 5.0.0 - 2018-05-21 + +- Added a requirement for partial C++11 support, most importantly + variadic templates and type traits, and dropped `FMT_VARIADIC_*` + emulation macros. Variadic templates are available since GCC 4.4, + Clang 2.9 and MSVC 18.0 (2013). For older compilers use {fmt} + [version 4.x](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases/tag/4.1.0) + which continues to be maintained and works with C++98 compilers. + +- Renamed symbols to follow standard C++ naming conventions and + proposed a subset of the library for standardization in [P0645R2 + Text Formatting](https://wg21.link/P0645). + +- Implemented `constexpr` parsing of format strings and [compile-time + format string + checks](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#compile-time-format-string-checks). + For example + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/format.h> + + std::string s = format(fmt("{:d}"), "foo"); + ``` + + gives a compile-time error because `d` is an invalid specifier for + strings ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/g/rnCy9Q)): + + ... + <source>:4:19: note: in instantiation of function template specialization 'fmt::v5::format<S, char [4]>' requested here + std::string s = format(fmt("{:d}"), "foo"); + ^ + format.h:1337:13: note: non-constexpr function 'on_error' cannot be used in a constant expression + handler.on_error("invalid type specifier"); + + Compile-time checks require relaxed `constexpr` (C++14 feature) + support. If the latter is not available, checks will be performed at + runtime. + +- Separated format string parsing and formatting in the extension API + to enable compile-time format string processing. For example + + ```c++ + struct Answer {}; + + namespace fmt { + template <> + struct formatter<Answer> { + constexpr auto parse(parse_context& ctx) { + auto it = ctx.begin(); + spec = *it; + if (spec != 'd' && spec != 's') + throw format_error("invalid specifier"); + return ++it; + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(Answer, FormatContext& ctx) { + return spec == 's' ? + format_to(ctx.begin(), "{}", "fourty-two") : + format_to(ctx.begin(), "{}", 42); + } + + char spec = 0; + }; + } + + std::string s = format(fmt("{:x}"), Answer()); + ``` + + gives a compile-time error due to invalid format specifier + ([godbolt](https://godbolt.org/g/2jQ1Dv)): + + ... + <source>:12:45: error: expression '<throw-expression>' is not a constant expression + throw format_error("invalid specifier"); + +- Added [iterator + support](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#output-iterator-support): + + ```c++ + #include <vector> + #include <fmt/format.h> + + std::vector<char> out; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), "{}", 42); + ``` + +- Added the + [format_to_n](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#_CPPv2N3fmt11format_to_nE8OutputItNSt6size_tE11string_viewDpRK4Args) + function that restricts the output to the specified number of + characters (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/298): + + ```c++ + char out[4]; + fmt::format_to_n(out, sizeof(out), "{}", 12345); + // out == "1234" (without terminating '\0') + ``` + +- Added the [formatted_size]( + https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#_CPPv2N3fmt14formatted_sizeE11string_viewDpRK4Args) + function for computing the output size: + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/format.h> + + auto size = fmt::formatted_size("{}", 12345); // size == 5 + ``` + +- Improved compile times by reducing dependencies on standard headers + and providing a lightweight [core + API](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#core-api): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + + fmt::print("The answer is {}.", 42); + ``` + + See [Compile time and code + bloat](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt#compile-time-and-code-bloat). + +- Added the [make_format_args]( + https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#_CPPv2N3fmt16make_format_argsEDpRK4Args) + function for capturing formatting arguments: + + ```c++ + // Prints formatted error message. + void vreport_error(const char *format, fmt::format_args args) { + fmt::print("Error: "); + fmt::vprint(format, args); + } + template <typename... Args> + void report_error(const char *format, const Args & ... args) { + vreport_error(format, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); + } + ``` + +- Added the `make_printf_args` function for capturing `printf` + arguments (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/687, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/694). Thanks @Kronuz. + +- Added prefix `v` to non-variadic functions taking `format_args` to + distinguish them from variadic ones: + + ```c++ + std::string vformat(string_view format_str, format_args args); + + template <typename... Args> + std::string format(string_view format_str, const Args & ... args); + ``` + +- Added experimental support for formatting ranges, containers and + tuple-like types in `fmt/ranges.h` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/735): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/ranges.h> + + std::vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3}; + fmt::print("{}", v); // prints {1, 2, 3} + ``` + + Thanks @Remotion. + +- Implemented `wchar_t` date and time formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/712): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/time.h> + + std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr); + auto s = fmt::format(L"The date is {:%Y-%m-%d}.", *std::localtime(&t)); + ``` + + Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Provided more wide string overloads + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/724). Thanks @DanielaE. + +- Switched from a custom null-terminated string view class to + `string_view` in the format API and provided `fmt::string_view` + which implements a subset of `std::string_view` API for pre-C++17 + systems. + +- Added support for `std::experimental::string_view` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/607): + + ```c++ + #include <fmt/core.h> + #include <experimental/string_view> + + fmt::print("{}", std::experimental::string_view("foo")); + ``` + + Thanks @virgiliofornazin. + +- Allowed mixing named and automatic arguments: + + ```c++ + fmt::format("{} {two}", 1, fmt::arg("two", 2)); + ``` + +- Removed the write API in favor of the [format + API](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#format-api) with compile-time + handling of format strings. + +- Disallowed formatting of multibyte strings into a wide character + target (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/606). + +- Improved documentation + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/515, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/614, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/617, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/661, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/680). + Thanks @ibell, @mihaitodor and @johnthagen. + +- Implemented more efficient handling of large number of format + arguments. + +- Introduced an inline namespace for symbol versioning. + +- Added debug postfix `d` to the `fmt` library name + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/636). + +- Removed unnecessary `fmt/` prefix in includes + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/397). Thanks @chronoxor. + +- Moved `fmt/*.h` to `include/fmt/*.h` to prevent irrelevant files and + directories appearing on the include search paths when fmt is used + as a subproject and moved source files to the `src` directory. + +- Added qmake project file `support/fmt.pro` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/641). Thanks @cowo78. + +- Added Gradle build file `support/build.gradle` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/649). Thanks @luncliff. + +- Removed `FMT_CPPFORMAT` CMake option. + +- Fixed a name conflict with the macro `CHAR_WIDTH` in glibc + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/616). Thanks @aroig. + +- Fixed handling of nested braces in `fmt::join` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/638). + +- Added `SOURCELINK_SUFFIX` for compatibility with Sphinx 1.5 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/497). Thanks @ginggs. + +- Added a missing `inline` in the header-only mode + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/626). Thanks @aroig. + +- Fixed various compiler warnings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/640, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/656, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/679, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/681, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/705, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/715, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/717, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/720, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/723, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/726, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/730, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/739). + Thanks @peterbell10, @LarsGullik, @foonathan, @eliaskosunen, + @christianparpart, @DanielaE and @mwinterb. + +- Worked around an MSVC bug and fixed several warnings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/653). Thanks @alabuzhev. + +- Worked around GCC bug 67371 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/682). + +- Fixed compilation with `-fno-exceptions` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/655). Thanks @chenxiaolong. + +- Made `constexpr remove_prefix` gcc version check tighter + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/648). + +- Renamed internal type enum constants to prevent collision with + poorly written C libraries + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/644). + +- Added detection of `wostream operator<<` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/650). + +- Fixed compilation on OpenBSD + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/660). Thanks @hubslave. + +- Fixed compilation on FreeBSD 12 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/732). Thanks @dankm. + +- Fixed compilation when there is a mismatch between `-std` options + between the library and user code + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/664). + +- Fixed compilation with GCC 7 and `-std=c++11` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/734). + +- Improved generated binary code on GCC 7 and older + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/668). + +- Fixed handling of numeric alignment with no width + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/675). + +- Fixed handling of empty strings in UTF8/16 converters + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/676). Thanks @vgalka-sl. + +- Fixed formatting of an empty `string_view` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/689). + +- Fixed detection of `string_view` on libc++ + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/686). + +- Fixed DLL issues (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/696). + Thanks @sebkoenig. + +- Fixed compile checks for mixing narrow and wide strings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/690). + +- Disabled unsafe implicit conversion to `std::string` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/729). + +- Fixed handling of reused format specs (as in `fmt::join`) for + pointers (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/725). Thanks @mwinterb. + +- Fixed installation of `fmt/ranges.h` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/738). Thanks @sv1990. + +# 4.1.0 - 2017-12-20 + +- Added `fmt::to_wstring()` in addition to `fmt::to_string()` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/559). Thanks @alabuzhev. +- Added support for C++17 `std::string_view` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/571 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/578). + Thanks @thelostt and @mwinterb. +- Enabled stream exceptions to catch errors + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/581). Thanks @crusader-mike. +- Allowed formatting of class hierarchies with `fmt::format_arg()` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/547). Thanks @rollbear. +- Removed limitations on character types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/563). Thanks @Yelnats321. +- Conditionally enabled use of `std::allocator_traits` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/583). Thanks @mwinterb. +- Added support for `const` variadic member function emulation with + `FMT_VARIADIC_CONST` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/591). Thanks @ludekvodicka. +- Various bugfixes: bad overflow check, unsupported implicit type + conversion when determining formatting function, test segfaults + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/551), ill-formed + macros (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/542) and + ambiguous overloads + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/580). Thanks @xylosper. +- Prevented warnings on MSVC + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/605, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/602, and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/545), clang + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/582), GCC + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/573), various + conversion warnings (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/609, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/567, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/553 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/553), and added + `override` and `[[noreturn]]` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/549 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/555). + Thanks @alabuzhev, @virgiliofornazin, @alexanderbock, @yumetodo, @VaderY, + @jpcima, @thelostt and @Manu343726. +- Improved CMake: Used `GNUInstallDirs` to set installation location + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/610) and fixed warnings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/536 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/556). + Thanks @mikecrowe, @evgen231 and @henryiii. + +# 4.0.0 - 2017-06-27 + +- Removed old compatibility headers `cppformat/*.h` and CMake options + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/527). Thanks @maddinat0r. + +- Added `string.h` containing `fmt::to_string()` as alternative to + `std::to_string()` as well as other string writer functionality + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/326 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/441): + + ```c++ + #include "fmt/string.h" + + std::string answer = fmt::to_string(42); + ``` + + Thanks @glebov-andrey. + +- Moved `fmt::printf()` to new `printf.h` header and allowed `%s` as + generic specifier (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/453), + made `%.f` more conformant to regular `printf()` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/490), added custom + writer support (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/476) + and implemented missing custom argument formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/339 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/340): + + ```c++ + #include "fmt/printf.h" + + // %s format specifier can be used with any argument type. + fmt::printf("%s", 42); + ``` + + Thanks @mojoBrendan, @manylegged and @spacemoose. + See also https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/360, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/335 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/331. + +- Added `container.h` containing a `BasicContainerWriter` to write to + containers like `std::vector` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/450). Thanks @polyvertex. + +- Added `fmt::join()` function that takes a range and formats its + elements separated by a given string + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/466): + + ```c++ + #include "fmt/format.h" + + std::vector<double> v = {1.2, 3.4, 5.6}; + // Prints "(+01.20, +03.40, +05.60)". + fmt::print("({:+06.2f})", fmt::join(v.begin(), v.end(), ", ")); + ``` + + Thanks @olivier80. + +- Added support for custom formatting specifications to simplify + customization of built-in formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/444). Thanks @polyvertex. + See also https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/439. + +- Added `fmt::format_system_error()` for error code formatting + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/323 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/526). Thanks @maddinat0r. + +- Added thread-safe `fmt::localtime()` and `fmt::gmtime()` as + replacement for the standard version to `time.h` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/396). Thanks @codicodi. + +- Internal improvements to `NamedArg` and `ArgLists` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/389 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/390). Thanks @chronoxor. + +- Fixed crash due to bug in `FormatBuf` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/493). Thanks @effzeh. See also + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/480 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/491. + +- Fixed handling of wide strings in `fmt::StringWriter`. + +- Improved compiler error messages + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/357). + +- Fixed various warnings and issues with various compilers + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/494, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/499, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/483, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/485, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/482, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/475, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/473 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/414). + Thanks @chronoxor, @zhaohuaxishi, @pkestene, @dschmidt and @0x414c. + +- Improved CMake: targets are now namespaced + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/511 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/513), supported + header-only `printf.h` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/354), fixed issue with + minimal supported library subset + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/418, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/419 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/420). + Thanks @bjoernthiel, @niosHD, @LogicalKnight and @alabuzhev. + +- Improved documentation (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/393). + Thanks @pwm1234. + +# 3.0.2 - 2017-06-14 + +- Added `FMT_VERSION` macro + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/411). +- Used `FMT_NULL` instead of literal `0` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/409). Thanks @alabuzhev. +- Added extern templates for `format_float` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/413). +- Fixed implicit conversion issue + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/507). +- Fixed signbit detection + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/423). +- Fixed naming collision + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/425). +- Fixed missing intrinsic for C++/CLI + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/457). Thanks @calumr. +- Fixed Android detection + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/458). Thanks @Gachapen. +- Use lean `windows.h` if not in header-only mode + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/503). Thanks @Quentin01. +- Fixed issue with CMake exporting C++11 flag + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/455). Thanks @EricWF. +- Fixed issue with nvcc and MSVC compiler bug and MinGW + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/505). +- Fixed DLL issues (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/469 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/502). + Thanks @richardeakin and @AndreasSchoenle. +- Fixed test compilation under FreeBSD + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/433). +- Fixed various warnings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/403, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/410 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/510). + Thanks @Lecetem, @chenhayat and @trozen. +- Worked around a broken `__builtin_clz` in clang with MS codegen + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/519). +- Removed redundant include + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/479). +- Fixed documentation issues. + +# 3.0.1 - 2016-11-01 + +- Fixed handling of thousands separator + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/353). +- Fixed handling of `unsigned char` strings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/373). +- Corrected buffer growth when formatting time + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/367). +- Removed warnings under MSVC and clang + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/318, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/250, also merged + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/385 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/361). + Thanks @jcelerier and @nmoehrle. +- Fixed compilation issues under Android + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/327, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/345 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/381), FreeBSD + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/358), Cygwin + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/388), MinGW + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/355) as well as other + issues (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/350, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/355, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/348, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/402, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/405). + Thanks @dpantele, @hghwng, @arvedarved, @LogicalKnight and @JanHellwig. +- Fixed some documentation issues and extended specification + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/320, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/333, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/347, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/362). Thanks @smellman. + +# 3.0.0 - 2016-05-07 + +- The project has been renamed from C++ Format (cppformat) to fmt for + consistency with the used namespace and macro prefix + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/307). Library headers + are now located in the `fmt` directory: + + ```c++ + #include "fmt/format.h" + ``` + + Including `format.h` from the `cppformat` directory is deprecated + but works via a proxy header which will be removed in the next major + version. + + The documentation is now available at <https://fmt.dev>. + +- Added support for + [strftime](http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/c/strftime)-like + [date and time + formatting](https://fmt.dev/3.0.0/api.html#date-and-time-formatting) + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/283): + + ```c++ + #include "fmt/time.h" + + std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr); + // Prints "The date is 2016-04-29." (with the current date) + fmt::print("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d}.", *std::localtime(&t)); + ``` + +- `std::ostream` support including formatting of user-defined types + that provide overloaded `operator<<` has been moved to + `fmt/ostream.h`: + + ```c++ + #include "fmt/ostream.h" + + class Date { + int year_, month_, day_; + public: + Date(int year, int month, int day) : year_(year), month_(month), day_(day) {} + + friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Date &d) { + return os << d.year_ << '-' << d.month_ << '-' << d.day_; + } + }; + + std::string s = fmt::format("The date is {}", Date(2012, 12, 9)); + // s == "The date is 2012-12-9" + ``` + +- Added support for [custom argument + formatters](https://fmt.dev/3.0.0/api.html#argument-formatters) + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/235). + +- Added support for locale-specific integer formatting with the `n` + specifier (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/305): + + ```c++ + std::setlocale(LC_ALL, "en_US.utf8"); + fmt::print("cppformat: {:n}\n", 1234567); // prints 1,234,567 + ``` + +- Sign is now preserved when formatting an integer with an incorrect + `printf` format specifier + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/265): + + ```c++ + fmt::printf("%lld", -42); // prints -42 + ``` + + Note that it would be an undefined behavior in `std::printf`. + +- Length modifiers such as `ll` are now optional in printf formatting + functions and the correct type is determined automatically + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/255): + + ```c++ + fmt::printf("%d", std::numeric_limits<long long>::max()); + ``` + + Note that it would be an undefined behavior in `std::printf`. + +- Added initial support for custom formatters + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/231). + +- Fixed detection of user-defined literal support on Intel C++ + compiler (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/311, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/312). + Thanks @dean0x7d and @speth. + +- Reduced compile time + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/243, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/249, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/317): + +  + +  + + Thanks @dean0x7d. + +- Compile test fixes (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/313). + Thanks @dean0x7d. + +- Documentation fixes (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/239, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/248, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/252, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/258, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/260, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/301, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/309). + Thanks @ReadmeCritic @Gachapen and @jwilk. + +- Fixed compiler and sanitizer warnings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/244, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/256, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/259, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/263, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/274, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/277, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/286, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/291, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/296, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/308). + Thanks @mwinterb, @pweiskircher and @Naios. + +- Improved compatibility with Windows Store apps + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/280, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/285) Thanks @mwinterb. + +- Added tests of compatibility with older C++ standards + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/273). Thanks @niosHD. + +- Fixed Android build + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/271). Thanks @newnon. + +- Changed `ArgMap` to be backed by a vector instead of a map. + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/261, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/262). Thanks @mwinterb. + +- Added `fprintf` overload that writes to a `std::ostream` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/251). + Thanks @nickhutchinson. + +- Export symbols when building a Windows DLL + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/245). + Thanks @macdems. + +- Fixed compilation on Cygwin + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/304). + +- Implemented a workaround for a bug in Apple LLVM version 4.2 of + clang (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/276). + +- Implemented a workaround for Google Test bug + https://github.com/google/googletest/issues/705 on gcc 6 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/268). Thanks @octoploid. + +- Removed Biicode support because the latter has been discontinued. + +# 2.1.1 - 2016-04-11 + +- The install location for generated CMake files is now configurable + via the `FMT_CMAKE_DIR` CMake variable + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/299). Thanks @niosHD. +- Documentation fixes + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/252). + +# 2.1.0 - 2016-03-21 + +- Project layout and build system improvements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/267): + + - The code have been moved to the `cppformat` directory. Including + `format.h` from the top-level directory is deprecated but works + via a proxy header which will be removed in the next major + version. + - C++ Format CMake targets now have proper interface definitions. + - Installed version of the library now supports the header-only + configuration. + - Targets `doc`, `install`, and `test` are now disabled if C++ + Format is included as a CMake subproject. They can be enabled by + setting `FMT_DOC`, `FMT_INSTALL`, and `FMT_TEST` in the parent + project. + + Thanks @niosHD. + +# 2.0.1 - 2016-03-13 + +- Improved CMake find and package support + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/264). Thanks @niosHD. +- Fix compile error with Android NDK and mingw32 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/241). Thanks @Gachapen. +- Documentation fixes + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/248, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/260). + +# 2.0.0 - 2015-12-01 + +## General + +- \[Breaking\] Named arguments + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/169, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/173, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/174): + + ```c++ + fmt::print("The answer is {answer}.", fmt::arg("answer", 42)); + ``` + + Thanks @jamboree. + +- \[Experimental\] User-defined literals for format and named + arguments (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/204, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/206, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/207): + + ```c++ + using namespace fmt::literals; + fmt::print("The answer is {answer}.", "answer"_a=42); + ``` + + Thanks @dean0x7d. + +- \[Breaking\] Formatting of more than 16 arguments is now supported + when using variadic templates + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/141). Thanks @Shauren. + +- Runtime width specification + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/168): + + ```c++ + fmt::format("{0:{1}}", 42, 5); // gives " 42" + ``` + + Thanks @jamboree. + +- \[Breaking\] Enums are now formatted with an overloaded + `std::ostream` insertion operator (`operator<<`) if available + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/232). + +- \[Breaking\] Changed default `bool` format to textual, \"true\" or + \"false\" (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/170): + + ```c++ + fmt::print("{}", true); // prints "true" + ``` + + To print `bool` as a number use numeric format specifier such as + `d`: + + ```c++ + fmt::print("{:d}", true); // prints "1" + ``` + +- `fmt::printf` and `fmt::sprintf` now support formatting of `bool` + with the `%s` specifier giving textual output, \"true\" or \"false\" + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/223): + + ```c++ + fmt::printf("%s", true); // prints "true" + ``` + + Thanks @LarsGullik. + +- \[Breaking\] `signed char` and `unsigned char` are now formatted as + integers by default + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/217). + +- \[Breaking\] Pointers to C strings can now be formatted with the `p` + specifier (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/223): + + ```c++ + fmt::print("{:p}", "test"); // prints pointer value + ``` + + Thanks @LarsGullik. + +- \[Breaking\] `fmt::printf` and `fmt::sprintf` now print null + pointers as `(nil)` and null strings as `(null)` for consistency + with glibc (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/226). + Thanks @LarsGullik. + +- \[Breaking\] `fmt::(s)printf` now supports formatting of objects of + user-defined types that provide an overloaded `std::ostream` + insertion operator (`operator<<`) + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/201): + + ```c++ + fmt::printf("The date is %s", Date(2012, 12, 9)); + ``` + +- \[Breaking\] The `Buffer` template is now part of the public API and + can be used to implement custom memory buffers + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/140). Thanks @polyvertex. + +- \[Breaking\] Improved compatibility between `BasicStringRef` and + [std::experimental::basic_string_view]( + http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/experimental/basic_string_view) + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/100, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/159, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/183): + + - Comparison operators now compare string content, not pointers + - `BasicStringRef::c_str` replaced by `BasicStringRef::data` + - `BasicStringRef` is no longer assumed to be null-terminated + + References to null-terminated strings are now represented by a new + class, `BasicCStringRef`. + +- Dependency on pthreads introduced by Google Test is now optional + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/185). + +- New CMake options `FMT_DOC`, `FMT_INSTALL` and `FMT_TEST` to control + generation of `doc`, `install` and `test` targets respectively, on + by default (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/197, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/198, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/200). Thanks @maddinat0r. + +- `noexcept` is now used when compiling with MSVC2015 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/215). Thanks @dmkrepo. + +- Added an option to disable use of `windows.h` when + `FMT_USE_WINDOWS_H` is defined as 0 before including `format.h` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/171). Thanks @alfps. + +- \[Breaking\] `windows.h` is now included with `NOMINMAX` unless + `FMT_WIN_MINMAX` is defined. This is done to prevent breaking code + using `std::min` and `std::max` and only affects the header-only + configuration (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/152, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/153, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/154). Thanks @DevO2012. + +- Improved support for custom character types + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/171). Thanks @alfps. + +- Added an option to disable use of IOStreams when `FMT_USE_IOSTREAMS` + is defined as 0 before including `format.h` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/205, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/208). Thanks @JodiTheTigger. + +- Improved detection of `isnan`, `isinf` and `signbit`. + +## Optimization + +- Made formatting of user-defined types more efficient with a custom + stream buffer (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/92, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/230). Thanks @NotImplemented. +- Further improved performance of `fmt::Writer` on integer formatting + and fixed a minor regression. Now it is \~7% faster than + `karma::generate` on Karma\'s benchmark + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/186). +- \[Breaking\] Reduced [compiled code + size](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt#compile-time-and-code-bloat) + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/143, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/149). + +## Distribution + +- \[Breaking\] Headers are now installed in + `${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX}/include/cppformat` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/178). Thanks @jackyf. + +- \[Breaking\] Changed the library name from `format` to `cppformat` + for consistency with the project name and to avoid potential + conflicts (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/178). + Thanks @jackyf. + +- C++ Format is now available in [Debian](https://www.debian.org/) + GNU/Linux + ([stretch](https://packages.debian.org/source/stretch/cppformat), + [sid](https://packages.debian.org/source/sid/cppformat)) and derived + distributions such as + [Ubuntu](https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/cppformat) 15.10 and + later (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/155): + + $ sudo apt-get install libcppformat1-dev + + Thanks @jackyf. + +- [Packages for Fedora and + RHEL](https://admin.fedoraproject.org/pkgdb/package/cppformat/) are + now available. Thanks Dave Johansen. + +- C++ Format can now be installed via [Homebrew](http://brew.sh/) on + OS X (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/157): + + $ brew install cppformat + + Thanks @ortho and Anatoliy Bulukin. + +## Documentation + +- Migrated from ReadTheDocs to GitHub Pages for better responsiveness + and reliability (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/128). + New documentation address is <http://cppformat.github.io/>. +- Added [Building thedocumentation]( + https://fmt.dev/2.0.0/usage.html#building-the-documentation) + section to the documentation. +- Documentation build script is now compatible with Python 3 and newer + pip versions. (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/189, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/209). + Thanks @JodiTheTigger and @xentec. +- Documentation fixes and improvements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/36, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/75, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/125, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/160, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/161, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/162, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/165, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/210). + Thanks @syohex. +- Fixed out-of-tree documentation build + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/177). Thanks @jackyf. + +## Fixes + +- Fixed `initializer_list` detection + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/136). Thanks @Gachapen. + +- \[Breaking\] Fixed formatting of enums with numeric format + specifiers in `fmt::(s)printf` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/131, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/139): + + ```c++ + enum { ANSWER = 42 }; + fmt::printf("%d", ANSWER); + ``` + + Thanks @Naios. + +- Improved compatibility with old versions of MinGW + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/129, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/130, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/132). Thanks @cstamford. + +- Fixed a compile error on MSVC with disabled exceptions + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/144). + +- Added a workaround for broken implementation of variadic templates + in MSVC2012 (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/148). + +- Placed the anonymous namespace within `fmt` namespace for the + header-only configuration (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/171). + Thanks @alfps. + +- Fixed issues reported by Coverity Scan + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/187, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/192). + +- Implemented a workaround for a name lookup bug in MSVC2010 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/188). + +- Fixed compiler warnings + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/95, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/96, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/114, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/135, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/142, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/145, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/146, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/158, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/163, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/175, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/190, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/191, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/194, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/196, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/216, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/218, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/220, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/229, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/233, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/234, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/236, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/281, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/289). + Thanks @seanmiddleditch, @dixlorenz, @CarterLi, @Naios, @fmatthew5876, + @LevskiWeng, @rpopescu, @gabime, @cubicool, @jkflying, @LogicalKnight, + @inguin and @Jopie64. + +- Fixed portability issues (mostly causing test failures) on ARM, + ppc64, ppc64le, s390x and SunOS 5.11 i386 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/138, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/179, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/180, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/202, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/225, [Red Hat Bugzilla + Bug 1260297](https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1260297)). + Thanks @Naios, @jackyf and Dave Johansen. + +- Fixed a name conflict with macro `free` defined in `crtdbg.h` when + `_CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC` is set (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/211). + +- Fixed shared library build on OS X + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/212). Thanks @dean0x7d. + +- Fixed an overload conflict on MSVC when `/Zc:wchar_t-` option is + specified (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/214). + Thanks @slavanap. + +- Improved compatibility with MSVC 2008 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/236). Thanks @Jopie64. + +- Improved compatibility with bcc32 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/227). + +- Fixed `static_assert` detection on Clang + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/228). Thanks @dean0x7d. + +# 1.1.0 - 2015-03-06 + +- Added `BasicArrayWriter`, a class template that provides operations + for formatting and writing data into a fixed-size array + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/105 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/122): + + ```c++ + char buffer[100]; + fmt::ArrayWriter w(buffer); + w.write("The answer is {}", 42); + ``` + +- Added [0 A.D.](http://play0ad.com/) and [PenUltima Online + (POL)](http://www.polserver.com/) to the list of notable projects + using C++ Format. + +- C++ Format now uses MSVC intrinsics for better formatting performance + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/115, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/116, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/118 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/121). Previously these + optimizations where only used on GCC and Clang. + Thanks @CarterLi and @objectx. + +- CMake install target + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/119). Thanks @TrentHouliston. + + You can now install C++ Format with `make install` command. + +- Improved [Biicode](http://www.biicode.com/) support + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/98 and + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/104). + Thanks @MariadeAnton and @franramirez688. + +- Improved support for building with [Android NDK]( + https://developer.android.com/tools/sdk/ndk/index.html) + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/107). Thanks @newnon. + + The [android-ndk-example](https://github.com/fmtlib/android-ndk-example) + repository provides and example of using C++ Format with Android NDK: + +  + +- Improved documentation of `SystemError` and `WindowsError` + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/54). + +- Various code improvements + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/110, + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/111 + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/112). Thanks @CarterLi. + +- Improved compile-time errors when formatting wide into narrow + strings (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/117). + +- Fixed `BasicWriter::write` without formatting arguments when C++11 + support is disabled + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/109). + +- Fixed header-only build on OS X with GCC 4.9 + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/124). + +- Fixed packaging issues (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/94). + +- Added [changelog](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/ChangeLog.md) + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/103). + +# 1.0.0 - 2015-02-05 + +- Add support for a header-only configuration when `FMT_HEADER_ONLY` + is defined before including `format.h`: + + ```c++ + #define FMT_HEADER_ONLY + #include "format.h" + ``` + +- Compute string length in the constructor of `BasicStringRef` instead + of the `size` method + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/79). This eliminates + size computation for string literals on reasonable optimizing + compilers. + +- Fix formatting of types with overloaded `operator <<` for + `std::wostream` (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/86): + + ```c++ + fmt::format(L"The date is {0}", Date(2012, 12, 9)); + ``` + +- Fix linkage of tests on Arch Linux + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/89). + +- Allow precision specifier for non-float arguments + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/90): + + ```c++ + fmt::print("{:.3}\n", "Carpet"); // prints "Car" + ``` + +- Fix build on Android NDK (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/93). + +- Improvements to documentation build procedure. + +- Remove `FMT_SHARED` CMake variable in favor of standard [BUILD_SHARED_LIBS]( + http://www.cmake.org/cmake/help/v3.0/variable/BUILD_SHARED_LIBS.html). + +- Fix error handling in `fmt::fprintf`. + +- Fix a number of warnings. + +# 0.12.0 - 2014-10-25 + +- \[Breaking\] Improved separation between formatting and buffer + management. `Writer` is now a base class that cannot be instantiated + directly. The new `MemoryWriter` class implements the default buffer + management with small allocations done on stack. So `fmt::Writer` + should be replaced with `fmt::MemoryWriter` in variable + declarations. + + Old code: + + ```c++ + fmt::Writer w; + ``` + + New code: + + ```c++ + fmt::MemoryWriter w; + ``` + + If you pass `fmt::Writer` by reference, you can continue to do so: + + ```c++ + void f(fmt::Writer &w); + ``` + + This doesn\'t affect the formatting API. + +- Support for custom memory allocators + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/69) + +- Formatting functions now accept [signed char]{.title-ref} and + [unsigned char]{.title-ref} strings as arguments + (https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/73): + + ```c++ + auto s = format("GLSL version: {}", glGetString(GL_VERSION)); + ``` + +- Reduced code bloat. According to the new [benchmark + results](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt#compile-time-and-code-bloat), + cppformat is close to `printf` and by the order of magnitude better + than Boost Format in terms of compiled code size. + +- Improved appearance of the documentation on mobile by using the + [Sphinx Bootstrap + theme](http://ryan-roemer.github.io/sphinx-bootstrap-theme/): + + | Old | New | + | --- | --- | + |  |  | + +# 0.11.0 - 2014-08-21 + +- Safe printf implementation with a POSIX extension for positional + arguments: + + ```c++ + fmt::printf("Elapsed time: %.2f seconds", 1.23); + fmt::printf("%1$s, %3$d %2$s", weekday, month, day); + ``` + +- Arguments of `char` type can now be formatted as integers (Issue + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/55): + + ```c++ + fmt::format("0x{0:02X}", 'a'); + ``` + +- Deprecated parts of the API removed. + +- The library is now built and tested on MinGW with Appveyor in + addition to existing test platforms Linux/GCC, OS X/Clang, + Windows/MSVC. + +# 0.10.0 - 2014-07-01 + +**Improved API** + +- All formatting methods are now implemented as variadic functions + instead of using `operator<<` for feeding arbitrary arguments into a + temporary formatter object. This works both with C++11 where + variadic templates are used and with older standards where variadic + functions are emulated by providing lightweight wrapper functions + defined with the `FMT_VARIADIC` macro. You can use this macro for + defining your own portable variadic functions: + + ```c++ + void report_error(const char *format, const fmt::ArgList &args) { + fmt::print("Error: {}"); + fmt::print(format, args); + } + FMT_VARIADIC(void, report_error, const char *) + + report_error("file not found: {}", path); + ``` + + Apart from a more natural syntax, this also improves performance as + there is no need to construct temporary formatter objects and + control arguments\' lifetimes. Because the wrapper functions are + very lightweight, this doesn\'t cause code bloat even in pre-C++11 + mode. + +- Simplified common case of formatting an `std::string`. Now it + requires a single function call: + + ```c++ + std::string s = format("The answer is {}.", 42); + ``` + + Previously it required 2 function calls: + + ```c++ + std::string s = str(Format("The answer is {}.") << 42); + ``` + + Instead of unsafe `c_str` function, `fmt::Writer` should be used + directly to bypass creation of `std::string`: + + ```c++ + fmt::Writer w; + w.write("The answer is {}.", 42); + w.c_str(); // returns a C string + ``` + + This doesn\'t do dynamic memory allocation for small strings and is + less error prone as the lifetime of the string is the same as for + `std::string::c_str` which is well understood (hopefully). + +- Improved consistency in naming functions that are a part of the + public API. Now all public functions are lowercase following the + standard library conventions. Previously it was a combination of + lowercase and CapitalizedWords. Issue + https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/50. + +- Old functions are marked as deprecated and will be removed in the + next release. + +**Other Changes** + +- Experimental support for printf format specifications (work in + progress): + + ```c++ + fmt::printf("The answer is %d.", 42); + std::string s = fmt::sprintf("Look, a %s!", "string"); + ``` + +- Support for hexadecimal floating point format specifiers `a` and + `A`: + + ```c++ + print("{:a}", -42.0); // Prints -0x1.5p+5 + print("{:A}", -42.0); // Prints -0X1.5P+5 + ``` + +- CMake option `FMT_SHARED` that specifies whether to build format as + a shared library (off by default). + +# 0.9.0 - 2014-05-13 + +- More efficient implementation of variadic formatting functions. + +- `Writer::Format` now has a variadic overload: + + ```c++ + Writer out; + out.Format("Look, I'm {}!", "variadic"); + ``` + +- For efficiency and consistency with other overloads, variadic + overload of the `Format` function now returns `Writer` instead of + `std::string`. Use the `str` function to convert it to + `std::string`: + + ```c++ + std::string s = str(Format("Look, I'm {}!", "variadic")); + ``` + +- Replaced formatter actions with output sinks: `NoAction` -\> + `NullSink`, `Write` -\> `FileSink`, `ColorWriter` -\> + `ANSITerminalSink`. This improves naming consistency and shouldn\'t + affect client code unless these classes are used directly which + should be rarely needed. + +- Added `ThrowSystemError` function that formats a message and throws + `SystemError` containing the formatted message and system-specific + error description. For example, the following code + + ```c++ + FILE *f = fopen(filename, "r"); + if (!f) + ThrowSystemError(errno, "Failed to open file '{}'") << filename; + ``` + + will throw `SystemError` exception with description \"Failed to open + file \'\<filename\>\': No such file or directory\" if file doesn\'t + exist. + +- Support for AppVeyor continuous integration platform. + +- `Format` now throws `SystemError` in case of I/O errors. + +- Improve test infrastructure. Print functions are now tested by + redirecting the output to a pipe. + +# 0.8.0 - 2014-04-14 + +- Initial release diff --git a/ChangeLog.rst b/ChangeLog.rst deleted file mode 100644 index 9c171af0..00000000 --- a/ChangeLog.rst +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3665 +0,0 @@ -7.1.3 - 2020-11-24 ------------------- - -* Fixed handling of buffer boundaries in ``format_to_n`` - (`#1996 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1996>`_, - `#2029 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2029>`_). - -* Fixed linkage errors when linking with a shared library - (`#2011 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2011>`_). - -* Reintroduced ostream support to range formatters - (`#2014 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2014>`_). - -* Worked around an issue with mixing std versions in gcc - (`#2017 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2017>`_). - -7.1.2 - 2020-11-04 ------------------- - -* Fixed floating point formatting with large precision - (`#1976 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1976>`_). - -7.1.1 - 2020-11-01 ------------------- - -* Fixed ABI compatibility with 7.0.x - (`#1961 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1961>`_). - -* Added the ``FMT_ARM_ABI_COMPATIBILITY`` macro to work around ABI - incompatibility between GCC and Clang on ARM - (`#1919 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1919>`_). - -* Worked around a SFINAE bug in GCC 8 - (`#1957 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1957>`_). - -* Fixed linkage errors when building with GCC's LTO - (`#1955 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1955>`_). - -* Fixed a compilation error when building without ``__builtin_clz`` or equivalent - (`#1968 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1968>`_). - Thanks `@tohammer (Tobias Hammer) <https://github.com/tohammer>`_. - -* Fixed a sign conversion warning - (`#1964 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1964>`_). - Thanks `@OptoCloud <https://github.com/OptoCloud>`_. - -7.1.0 - 2020-10-25 ------------------- - -* Switched from `Grisu3 - <https://www.cs.tufts.edu/~nr/cs257/archive/florian-loitsch/printf.pdf>`_ - to `Dragonbox <https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox>`_ for the default - floating-point formatting which gives the shortest decimal representation - with round-trip guarantee and correct rounding - (`#1882 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1882>`_, - `#1887 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1887>`_, - `#1894 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1894>`_). This makes {fmt} up to - 20-30x faster than common implementations of ``std::ostringstream`` and - ``sprintf`` on `dtoa-benchmark <https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark>`_ - and faster than double-conversion and Ryū: - - .. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/ - 95684665-11719600-0ba8-11eb-8e5b-972ff4e49428.png - - It is possible to get even better performance at the cost of larger binary - size by compiling with the ``FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX`` macro set to 1. - - Thanks `@jk-jeon (Junekey Jeon) <https://github.com/jk-jeon>`_. - -* Added an experimental unsynchronized file output API which, together with - `format string compilation <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#compile-api>`_, - can give `5-9 times speed up compared to fprintf - <https://www.zverovich.net/2020/08/04/optimal-file-buffer-size.html>`_ - on common platforms (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/nsTcG8>`__): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/os.h> - - int main() { - auto f = fmt::output_file("guide"); - f.print("The answer is {}.", 42); - } - -* Added a formatter for ``std::chrono::time_point<system_clock>`` - (`#1819 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1819>`_, - `#1837 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1837>`_). For example - (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/c4M6fh>`__): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/chrono.h> - - int main() { - auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); - fmt::print("The time is {:%H:%M:%S}.\n", now); - } - - Thanks `@adamburgess (Adam Burgess) <https://github.com/adamburgess>`_. - -* Added support for ranges with non-const ``begin``/``end`` to ``fmt::join`` - (`#1784 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1784>`_, - `#1786 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1786>`_). For example - (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/jP63Tv>`__): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/ranges.h> - #include <range/v3/view/filter.hpp> - - int main() { - using std::literals::string_literals::operator""s; - auto strs = std::array{"a"s, "bb"s, "ccc"s}; - auto range = strs | ranges::views::filter( - [] (const std::string &x) { return x.size() != 2; } - ); - fmt::print("{}\n", fmt::join(range, "")); - } - - prints "accc". - - Thanks `@tonyelewis (Tony E Lewis) <https://github.com/tonyelewis>`_. - -* Added a ``memory_buffer::append`` overload that takes a range - (`#1806 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1806>`_). - Thanks `@BRevzin (Barry Revzin) <https://github.com/BRevzin>`_. - -* Improved handling of single code units in ``FMT_COMPILE``. For example: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/compile.h> - - char* f(char* buf) { - return fmt::format_to(buf, FMT_COMPILE("x{}"), 42); - } - - compiles to just (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/5vncz3>`__): - - .. code:: asm - - _Z1fPc: - movb $120, (%rdi) - xorl %edx, %edx - cmpl $42, _ZN3fmt2v76detail10basic_dataIvE23zero_or_powers_of_10_32E+8(%rip) - movl $3, %eax - seta %dl - subl %edx, %eax - movzwl _ZN3fmt2v76detail10basic_dataIvE6digitsE+84(%rip), %edx - cltq - addq %rdi, %rax - movw %dx, -2(%rax) - ret - - Here a single ``mov`` instruction writes ``'x'`` (``$120``) to the output - buffer. - -* Added dynamic width support to format string compilation - (`#1809 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1809>`_). - -* Improved error reporting for unformattable types: now you'll get the type name - directly in the error message instead of the note: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/core.h> - - struct how_about_no {}; - - int main() { - fmt::print("{}", how_about_no()); - } - - Error (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/GoxM4e>`__): - - ``fmt/core.h:1438:3: error: static_assert failed due to requirement - 'fmt::v7::formattable<how_about_no>()' "Cannot format an argument. - To make type T formattable provide a formatter<T> specialization: - https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#udt" - ...`` - -* Added the `make_args_checked <https://fmt.dev/7.1.0/api.html#argument-lists>`_ - function template that allows you to write formatting functions with - compile-time format string checks and avoid binary code bloat - (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/PEf9qr>`__): - - .. code:: c++ - - void vlog(const char* file, int line, fmt::string_view format, - fmt::format_args args) { - fmt::print("{}: {}: ", file, line); - fmt::vprint(format, args); - } - - template <typename S, typename... Args> - void log(const char* file, int line, const S& format, Args&&... args) { - vlog(file, line, format, - fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format, args...)); - } - - #define MY_LOG(format, ...) \ - log(__FILE__, __LINE__, FMT_STRING(format), __VA_ARGS__) - - MY_LOG("invalid squishiness: {}", 42); - -* Replaced ``snprintf`` fallback with a faster internal IEEE 754 ``float`` and - ``double`` formatter for arbitrary precision. For example - (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/dPhWvj>`__): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/core.h> - - int main() { - fmt::print("{:.500}\n", 4.9406564584124654E-324); - } - - prints - - ``4.9406564584124654417656879286822137236505980261432476442558568250067550727020875186529983636163599237979656469544571773092665671035593979639877479601078187812630071319031140452784581716784898210368871863605699873072305000638740915356498438731247339727316961514003171538539807412623856559117102665855668676818703956031062493194527159149245532930545654440112748012970999954193198940908041656332452475714786901472678015935523861155013480352649347201937902681071074917033322268447533357208324319360923829e-324``. - -* Made ``format_to_n`` and ``formatted_size`` part of the `core API - <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#core-api>`__ - (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/sPjY1K>`__): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/core.h> - - int main() { - char buffer[10]; - auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "{}", 42); - } - -* Added ``fmt::format_to_n`` overload with format string compilation - (`#1764 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1764>`_, - `#1767 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1767>`_, - `#1869 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1869>`_). For example - (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/93h86q>`__): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/compile.h> - - int main() { - char buffer[8]; - fmt::format_to_n(buffer, sizeof(buffer), FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); - } - - Thanks `@Kurkin (Dmitry Kurkin) <https://github.com/Kurkin>`_, - `@alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov) <https://github.com/alexezeder>`_. - -* Added ``fmt::format_to`` overload that take ``text_style`` - (`#1593 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1593>`_, - `#1842 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1842>`_, - `#1843 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1843>`_). For example - (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/91153r>`__): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/color.h> - - int main() { - std::string out; - fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), - fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red), - "The answer is {}.", 42); - } - - Thanks `@Naios (Denis Blank) <https://github.com/Naios>`_. - -* Made the ``#`` specifier emit trailing zeros in addition to the decimal point - (`#1797 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1797>`_). For example - (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/bhdcW9>`__): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/core.h> - - int main() { - fmt::print("{:#.2g}", 0.5); - } - - prints ``0.50``. - -* Changed the default floating point format to not include ``.0`` for - consistency with ``std::format`` and ``std::to_chars`` - (`#1893 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1893>`_, - `#1943 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1943>`_). It is possible to get - the decimal point and trailing zero with the ``#`` specifier. - -* Fixed an issue with floating-point formatting that could result in addition of - a non-significant trailing zero in rare cases e.g. ``1.00e-34`` instead of - ``1.0e-34`` (`#1873 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1873>`_, - `#1917 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1917>`_). - -* Made ``fmt::to_string`` fallback on ``ostream`` insertion operator if - the ``formatter`` specialization is not provided - (`#1815 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1815>`_, - `#1829 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1829>`_). - Thanks `@alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov) <https://github.com/alexezeder>`_. - -* Added support for the append mode to the experimental file API and - improved ``fcntl.h`` detection. - (`#1847 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1847>`_, - `#1848 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1848>`_). - Thanks `@t-wiser <https://github.com/t-wiser>`_. - -* Fixed handling of types that have both an implicit conversion operator and - an overloaded ``ostream`` insertion operator - (`#1766 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1766>`_). - -* Fixed a slicing issue in an internal iterator type - (`#1822 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1822>`_). - Thanks `@BRevzin (Barry Revzin) <https://github.com/BRevzin>`_. - -* Fixed an issue in locale-specific integer formatting - (`#1927 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1927>`_). - -* Fixed handling of exotic code unit types - (`#1870 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1870>`_, - `#1932 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1932>`_). - -* Improved ``FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE`` - (`#1878 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1878>`_). - Thanks `@jk-jeon (Junekey Jeon) <https://github.com/jk-jeon>`_. - -* Removed dependency on ``windows.h`` - (`#1900 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1900>`_). - Thanks `@bernd5 (Bernd Baumanns) <https://github.com/bernd5>`_. - -* Optimized counting of decimal digits on MSVC - (`#1890 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1890>`_). - Thanks `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_. - -* Improved documentation - (`#1772 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1772>`_, - `#1775 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1775>`_, - `#1792 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1792>`_, - `#1838 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1838>`_, - `#1888 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1888>`_, - `#1918 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1918>`_, - `#1939 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1939>`_). - Thanks `@leolchat (Léonard Gérard) <https://github.com/leolchat>`_, - `@pepsiman (Malcolm Parsons) <https://github.com/pepsiman>`_, - `@Klaim (Joël Lamotte) <https://github.com/Klaim>`_, - `@ravijanjam (Ravi J) <https://github.com/ravijanjam>`_, - `@francesco-st <https://github.com/francesco-st>`_, - `@udnaan (Adnan) <https://github.com/udnaan>`_. - -* Added the ``FMT_REDUCE_INT_INSTANTIATIONS`` CMake option that reduces the - binary code size at the cost of some integer formatting performance. This can - be useful for extremely memory-constrained embedded systems - (`#1778 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1778>`_, - `#1781 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1781>`_). - Thanks `@kammce (Khalil Estell) <https://github.com/kammce>`_. - -* Added the ``FMT_USE_INLINE_NAMESPACES`` macro to control usage of inline - namespaces (`#1945 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1945>`_). - Thanks `@darklukee <https://github.com/darklukee>`_. - -* Improved build configuration - (`#1760 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1760>`_, - `#1770 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1770>`_, - `#1779 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1779>`_, - `#1783 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1783>`_, - `#1823 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1823>`_). - Thanks `@dvetutnev (Dmitriy Vetutnev) <https://github.com/dvetutnev>`_, - `@xvitaly (Vitaly Zaitsev) <https://github.com/xvitaly>`_, - `@tambry (Raul Tambre) <https://github.com/tambry>`_, - `@medithe <https://github.com/medithe>`_, - `@martinwuehrer (Martin Wührer) <https://github.com/martinwuehrer>`_. - -* Fixed various warnings and compilation issues - (`#1790 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1790>`_, - `#1802 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1802>`_, - `#1808 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1808>`_, - `#1810 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1810>`_, - `#1811 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1811>`_, - `#1812 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1812>`_, - `#1814 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1814>`_, - `#1816 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1816>`_, - `#1817 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1817>`_, - `#1818 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1818>`_, - `#1825 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1825>`_, - `#1836 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1836>`_, - `#1855 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1855>`_, - `#1856 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1856>`_, - `#1860 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1860>`_, - `#1877 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1877>`_, - `#1879 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1879>`_, - `#1880 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1880>`_, - `#1896 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1896>`_, - `#1897 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1897>`_, - `#1898 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1898>`_, - `#1904 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1904>`_, - `#1908 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1908>`_, - `#1911 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1911>`_, - `#1912 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1912>`_, - `#1928 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1928>`_, - `#1929 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1929>`_, - `#1935 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1935>`_ - `#1937 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1937>`_, - `#1942 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1942>`_, - `#1949 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1949>`_). - Thanks `@TheQwertiest <https://github.com/TheQwertiest>`_, - `@medithe <https://github.com/medithe>`_, - `@martinwuehrer (Martin Wührer) <https://github.com/martinwuehrer>`_, - `@n16h7hunt3r <https://github.com/n16h7hunt3r>`_, - `@Othereum (Seokjin Lee) <https://github.com/Othereum>`_, - `@gsjaardema (Greg Sjaardema) <https://github.com/gsjaardema>`_, - `@AlexanderLanin (Alexander Lanin) <https://github.com/AlexanderLanin>`_, - `@gcerretani (Giovanni Cerretani) <https://github.com/gcerretani>`_, - `@chronoxor (Ivan Shynkarenka) <https://github.com/chronoxor>`_, - `@noizefloor (Jan Schwers) <https://github.com/noizefloor>`_, - `@akohlmey (Axel Kohlmeyer) <https://github.com/akohlmey>`_, - `@jk-jeon (Junekey Jeon) <https://github.com/jk-jeon>`_, - `@rimathia <https://github.com/rimathia>`_, - `@rglarix (Riccardo Ghetta (larix)) <https://github.com/rglarix>`_, - `@moiwi <https://github.com/moiwi>`_, - `@heckad (Kazantcev Andrey) <https://github.com/heckad>`_, - `@MarcDirven <https://github.com/MarcDirven>`_. - `@BartSiwek (Bart Siwek) <https://github.com/BartSiwek>`_, - `@darklukee <https://github.com/darklukee>`_. - -7.0.3 - 2020-08-06 ------------------- - -* Worked around broken ``numeric_limits`` for 128-bit integers - (`#1787 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1787>`_). - -* Added error reporting on missing named arguments - (`#1796 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1796>`_). - -* Stopped using 128-bit integers with clang-cl - (`#1800 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1800>`_). - Thanks `@Kingcom <https://github.com/Kingcom>`_. - -* Fixed issues in locale-specific integer formatting - (`#1782 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1782>`_, - `#1801 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1801>`_). - -7.0.2 - 2020-07-29 ------------------- - -* Worked around broken ``numeric_limits`` for 128-bit integers - (`#1725 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1725>`_). - -* Fixed compatibility with CMake 3.4 - (`#1779 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1779>`_). - -* Fixed handling of digit separators in locale-specific formatting - (`#1782 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1782>`_). - -7.0.1 - 2020-07-07 ------------------- - -* Updated the inline version namespace name. - -* Worked around a gcc bug in mangling of alias templates - (`#1753 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1753>`_). - -* Fixed a linkage error on Windows - (`#1757 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1757>`_). - Thanks `@Kurkin (Dmitry Kurkin) <https://github.com/Kurkin>`_. - -* Fixed minor issues with the documentation. - -7.0.0 - 2020-07-05 ------------------- - -* Reduced the library size. For example, on macOS a stripped test binary - statically linked with {fmt} `shrank from ~368k to less than 100k - <http://www.zverovich.net/2020/05/21/reducing-library-size.html>`_. - -* Added a simpler and more efficient `format string compilation API - <https://fmt.dev/7.0.0/api.html#compile-api>`_: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/compile.h> - - // Converts 42 into std::string using the most efficient method and no - // runtime format string processing. - std::string s = fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); - - The old ``fmt::compile`` API is now deprecated. - -* Optimized integer formatting: ``format_to`` with format string compilation - and a stack-allocated buffer is now `faster than to_chars on both - libc++ and libstdc++ - <http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html>`_. - -* Optimized handling of small format strings. For example, - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::format("Result: {}: ({},{},{},{})", str1, str2, str3, str4, str5) - - is now ~40% faster (`#1685 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1685>`_). - -* Applied extern templates to improve compile times when using the core API - and ``fmt/format.h`` (`#1452 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1452>`_). - For example, on macOS with clang the compile time of a test translation unit - dropped from 2.3s to 0.3s with ``-O2`` and from 0.6s to 0.3s with the default - settings (``-O0``). - - Before (``-O2``):: - - % time c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 -O2 - c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 -O2 2.22s user 0.08s system 99% cpu 2.311 total - - After (``-O2``):: - - % time c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 -O2 - c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 -O2 0.26s user 0.04s system 98% cpu 0.303 total - - Before (default):: - - % time c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 - c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 0.53s user 0.06s system 98% cpu 0.601 total - - After (default):: - - % time c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 - c++ -c test.cc -I include -std=c++17 0.24s user 0.06s system 98% cpu 0.301 total - - It is still recommended to use ``fmt/core.h`` instead of ``fmt/format.h`` but - the compile time difference is now smaller. Thanks - `@alex3d <https://github.com/alex3d>`_ for the suggestion. - -* Named arguments are now stored on stack (no dynamic memory allocations) and - the compiled code is more compact and efficient. For example - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/core.h> - - int main() { - fmt::print("The answer is {answer}\n", fmt::arg("answer", 42)); - } - - compiles to just (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/z/NcfEp_>`__) - - .. code:: asm - - .LC0: - .string "answer" - .LC1: - .string "The answer is {answer}\n" - main: - sub rsp, 56 - mov edi, OFFSET FLAT:.LC1 - mov esi, 23 - movabs rdx, 4611686018427387905 - lea rax, [rsp+32] - lea rcx, [rsp+16] - mov QWORD PTR [rsp+8], 1 - mov QWORD PTR [rsp], rax - mov DWORD PTR [rsp+16], 42 - mov QWORD PTR [rsp+32], OFFSET FLAT:.LC0 - mov DWORD PTR [rsp+40], 0 - call fmt::v6::vprint(fmt::v6::basic_string_view<char>, - fmt::v6::format_args) - xor eax, eax - add rsp, 56 - ret - - .L.str.1: - .asciz "answer" - -* Implemented compile-time checks for dynamic width and precision - (`#1614 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1614>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/format.h> - - int main() { - fmt::print(FMT_STRING("{0:{1}}"), 42); - } - - now gives a compilation error because argument 1 doesn't exist:: - - In file included from test.cc:1: - include/fmt/format.h:2726:27: error: constexpr variable 'invalid_format' must be - initialized by a constant expression - FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL bool invalid_format = - ^ - ... - include/fmt/core.h:569:26: note: in call to - '&checker(s, {}).context_->on_error(&"argument not found"[0])' - if (id >= num_args_) on_error("argument not found"); - ^ - -* Added sentinel support to ``fmt::join`` - (`#1689 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1689>`_) - - .. code:: c++ - - struct zstring_sentinel {}; - bool operator==(const char* p, zstring_sentinel) { return *p == '\0'; } - bool operator!=(const char* p, zstring_sentinel) { return *p != '\0'; } - - struct zstring { - const char* p; - const char* begin() const { return p; } - zstring_sentinel end() const { return {}; } - }; - - auto s = fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(zstring{"hello"}, "_")); - // s == "h_e_l_l_o" - - Thanks `@BRevzin (Barry Revzin) <https://github.com/BRevzin>`_. - -* Added support for named arguments, ``clear`` and ``reserve`` to - ``dynamic_format_arg_store`` - (`#1655 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1655>`_, - `#1663 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1663>`_, - `#1674 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1674>`_, - `#1677 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1677>`_). - Thanks `@vsolontsov-ll (Vladimir Solontsov) - <https://github.com/vsolontsov-ll>`_. - -* Added support for the ``'c'`` format specifier to integral types for - compatibility with ``std::format`` - (`#1652 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1652>`_). - -* Replaced the ``'n'`` format specifier with ``'L'`` for compatibility with - ``std::format`` (`#1624 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1624>`_). - The ``'n'`` specifier can be enabled via the ``FMT_DEPRECATED_N_SPECIFIER`` - macro. - -* The ``'='`` format specifier is now disabled by default for compatibility with - ``std::format``. It can be enabled via the ``FMT_DEPRECATED_NUMERIC_ALIGN`` - macro. - -* Removed the following deprecated APIs: - - * ``FMT_STRING_ALIAS`` and ``fmt`` macros - replaced by ``FMT_STRING`` - * ``fmt::basic_string_view::char_type`` - replaced by - ``fmt::basic_string_view::value_type`` - * ``convert_to_int`` - * ``format_arg_store::types`` - * ``*parse_context`` - replaced by ``*format_parse_context`` - * ``FMT_DEPRECATED_INCLUDE_OS`` - * ``FMT_DEPRECATED_PERCENT`` - incompatible with ``std::format`` - * ``*writer`` - replaced by compiled format API - -* Renamed the ``internal`` namespace to ``detail`` - (`#1538 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1538>`_). The former is still - provided as an alias if the ``FMT_USE_INTERNAL`` macro is defined. - -* Improved compatibility between ``fmt::printf`` with the standard specs - (`#1595 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1595>`_, - `#1682 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1682>`_, - `#1683 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1683>`_, - `#1687 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1687>`_, - `#1699 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1699>`_). - Thanks `@rimathia <https://github.com/rimathia>`_. - -* Fixed handling of ``operator<<`` overloads that use ``copyfmt`` - (`#1666 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1666>`_). - -* Added the ``FMT_OS`` CMake option to control inclusion of OS-specific APIs - in the fmt target. This can be useful for embedded platforms - (`#1654 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1654>`_, - `#1656 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1656>`_). - Thanks `@kwesolowski (Krzysztof Wesolowski) - <https://github.com/kwesolowski>`_. - -* Replaced ``FUZZING_BUILD_MODE_UNSAFE_FOR_PRODUCTION`` with the ``FMT_FUZZ`` - macro to prevent interferring with fuzzing of projects using {fmt} - (`#1650 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1650>`_). - Thanks `@asraa (Asra Ali) <https://github.com/asraa>`_. - -* Fixed compatibility with emscripten - (`#1636 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1636>`_, - `#1637 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1637>`_). - Thanks `@ArthurSonzogni (Arthur Sonzogni) - <https://github.com/ArthurSonzogni>`_. - -* Improved documentation - (`#704 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/704>`_, - `#1643 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1643>`_, - `#1660 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1660>`_, - `#1681 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1681>`_, - `#1691 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1691>`_, - `#1706 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1706>`_, - `#1714 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1714>`_, - `#1721 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1721>`_, - `#1739 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1739>`_, - `#1740 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1740>`_, - `#1741 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1741>`_, - `#1751 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1751>`_). - Thanks `@senior7515 (Alexander Gallego) <https://github.com/senior7515>`_, - `@lsr0 (Lindsay Roberts) <https://github.com/lsr0>`_, - `@puetzk (Kevin Puetz) <https://github.com/puetzk>`_, - `@fpelliccioni (Fernando Pelliccioni) <https://github.com/fpelliccioni>`_, - Alexey Kuzmenko, `@jelly (jelle van der Waa) <https://github.com/jelly>`_, - `@claremacrae (Clare Macrae) <https://github.com/claremacrae>`_, - `@jiapengwen (文佳鹏) <https://github.com/jiapengwen>`_, - `@gsjaardema (Greg Sjaardema) <https://github.com/gsjaardema>`_, - `@alexey-milovidov <https://github.com/alexey-milovidov>`_. - -* Implemented various build configuration fixes and improvements - (`#1603 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1603>`_, - `#1657 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1657>`_, - `#1702 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1702>`_, - `#1728 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1728>`_). - Thanks `@scramsby (Scott Ramsby) <https://github.com/scramsby>`_, - `@jtojnar (Jan Tojnar) <https://github.com/jtojnar>`_, - `@orivej (Orivej Desh) <https://github.com/orivej>`_, - `@flagarde <https://github.com/flagarde>`_. - -* Fixed various warnings and compilation issues - (`#1616 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1616>`_, - `#1620 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1620>`_, - `#1622 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1622>`_, - `#1625 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1625>`_, - `#1627 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1627>`_, - `#1628 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1628>`_, - `#1629 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1629>`_, - `#1631 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1631>`_, - `#1633 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1633>`_, - `#1649 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1649>`_, - `#1658 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1658>`_, - `#1661 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1661>`_, - `#1667 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1667>`_, - `#1668 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1668>`_, - `#1669 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1669>`_, - `#1692 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1692>`_, - `#1696 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1696>`_, - `#1697 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1697>`_, - `#1707 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1707>`_, - `#1712 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1712>`_, - `#1716 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1716>`_, - `#1722 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1722>`_, - `#1724 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1724>`_, - `#1729 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1729>`_, - `#1738 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1738>`_, - `#1742 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1742>`_, - `#1743 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1743>`_, - `#1744 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1744>`_, - `#1747 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1747>`_, - `#1750 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1750>`_). - Thanks `@gsjaardema (Greg Sjaardema) <https://github.com/gsjaardema>`_, - `@gabime (Gabi Melman) <https://github.com/gabime>`_, - `@johnor (Johan) <https://github.com/johnor>`_, - `@Kurkin (Dmitry Kurkin) <https://github.com/Kurkin>`_, - `@invexed (James Beach) <https://github.com/invexed>`_, - `@peterbell10 <https://github.com/peterbell10>`_, - `@daixtrose (Markus Werle) <https://github.com/daixtrose>`_, - `@petrutlucian94 (Lucian Petrut) <https://github.com/petrutlucian94>`_, - `@Neargye (Daniil Goncharov) <https://github.com/Neargye>`_, - `@ambitslix (Attila M. Szilagyi) <https://github.com/ambitslix>`_, - `@gabime (Gabi Melman) <https://github.com/gabime>`_, - `@erthink (Leonid Yuriev) <https://github.com/erthink>`_, - `@tohammer (Tobias Hammer) <https://github.com/tohammer>`_, - `@0x8000-0000 (Florin Iucha) <https://github.com/0x8000-0000>`_. - -6.2.1 - 2020-05-09 ------------------- - -* Fixed ostream support in ``sprintf`` - (`#1631 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1631>`_). - -* Fixed type detection when using implicit conversion to ``string_view`` and - ostream ``operator<<`` inconsistently - (`#1662 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1662>`_). - -6.2.0 - 2020-04-05 ------------------- - -* Improved error reporting when trying to format an object of a non-formattable - type: - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::format("{}", S()); - - now gives:: - - include/fmt/core.h:1015:5: error: static_assert failed due to requirement - 'formattable' "Cannot format argument. To make type T formattable provide a - formatter<T> specialization: - https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#formatting-user-defined-types" - static_assert( - ^ - ... - note: in instantiation of function template specialization - 'fmt::v6::format<char [3], S, char>' requested here - fmt::format("{}", S()); - ^ - - if ``S`` is not formattable. - -* Reduced the library size by ~10%. - -* Always print decimal point if ``#`` is specified - (`#1476 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1476>`_, - `#1498 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1498>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("{:#.0f}", 42.0); - - now prints ``42.`` - -* Implemented the ``'L'`` specifier for locale-specific numeric formatting to - improve compatibility with ``std::format``. The ``'n'`` specifier is now - deprecated and will be removed in the next major release. - -* Moved OS-specific APIs such as ``windows_error`` from ``fmt/format.h`` to - ``fmt/os.h``. You can define ``FMT_DEPRECATED_INCLUDE_OS`` to automatically - include ``fmt/os.h`` from ``fmt/format.h`` for compatibility but this will be - disabled in the next major release. - -* Added precision overflow detection in floating-point formatting. - -* Implemented detection of invalid use of ``fmt::arg``. - -* Used ``type_identity`` to block unnecessary template argument deduction. - Thanks Tim Song. - -* Improved UTF-8 handling - (`#1109 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1109>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("┌{0:─^{2}}┐\n" - "│{1: ^{2}}│\n" - "└{0:─^{2}}┘\n", "", "Привет, мир!", 20); - - now prints:: - - ┌────────────────────┐ - │ Привет, мир! │ - └────────────────────┘ - - on systems that support Unicode. - -* Added experimental dynamic argument storage - (`#1170 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1170>`_, - `#1584 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1584>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - store.push_back("answer"); - store.push_back(42); - fmt::vprint("The {} is {}.\n", store); - - prints:: - - The answer is 42. - - Thanks `@vsolontsov-ll (Vladimir Solontsov) - <https://github.com/vsolontsov-ll>`_. - -* Made ``fmt::join`` accept ``initializer_list`` - (`#1591 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1591>`_). - Thanks `@Rapotkinnik (Nikolay Rapotkin) <https://github.com/Rapotkinnik>`_. - -* Fixed handling of empty tuples - (`#1588 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1588>`_). - -* Fixed handling of output iterators in ``format_to_n`` - (`#1506 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1506>`_). - -* Fixed formatting of ``std::chrono::duration`` types to wide output - (`#1533 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1533>`_). - Thanks `@zeffy (pilao) <https://github.com/zeffy>`_. - -* Added const ``begin`` and ``end`` overload to buffers - (`#1553 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1553>`_). - Thanks `@dominicpoeschko <https://github.com/dominicpoeschko>`_. - -* Added the ability to disable floating-point formatting via ``FMT_USE_FLOAT``, - ``FMT_USE_DOUBLE`` and ``FMT_USE_LONG_DOUBLE`` macros for extremely - memory-constrained embedded system - (`#1590 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1590>`_). - Thanks `@albaguirre (Alberto Aguirre) <https://github.com/albaguirre>`_. - -* Made ``FMT_STRING`` work with ``constexpr`` ``string_view`` - (`#1589 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1589>`_). - Thanks `@scramsby (Scott Ramsby) <https://github.com/scramsby>`_. - -* Implemented a minor optimization in the format string parser - (`#1560 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1560>`_). - Thanks `@IkarusDeveloper <https://github.com/IkarusDeveloper>`_. - -* Improved attribute detection - (`#1469 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1469>`_, - `#1475 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1475>`_, - `#1576 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1576>`_). - Thanks `@federico-busato (Federico) <https://github.com/federico-busato>`_, - `@chronoxor (Ivan Shynkarenka) <https://github.com/chronoxor>`_, - `@refnum <https://github.com/refnum>`_. - -* Improved documentation - (`#1481 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1481>`_, - `#1523 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1523>`_). - Thanks `@JackBoosY (Jack·Boos·Yu) <https://github.com/JackBoosY>`_, - `@imba-tjd (谭九鼎) <https://github.com/imba-tjd>`_. - -* Fixed symbol visibility on Linux when compiling with ``-fvisibility=hidden`` - (`#1535 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1535>`_). - Thanks `@milianw (Milian Wolff) <https://github.com/milianw>`_. - -* Implemented various build configuration fixes and improvements - (`#1264 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1264>`_, - `#1460 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1460>`_, - `#1534 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1534>`_, - `#1536 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1536>`_, - `#1545 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1545>`_, - `#1546 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1546>`_, - `#1566 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1566>`_, - `#1582 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1582>`_, - `#1597 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1597>`_, - `#1598 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1598>`_). - Thanks `@ambitslix (Attila M. Szilagyi) <https://github.com/ambitslix>`_, - `@jwillikers (Jordan Williams) <https://github.com/jwillikers>`_, - `@stac47 (Laurent Stacul) <https://github.com/stac47>`_. - -* Fixed various warnings and compilation issues - (`#1433 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1433>`_, - `#1461 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1461>`_, - `#1470 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1470>`_, - `#1480 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1480>`_, - `#1485 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1485>`_, - `#1492 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1492>`_, - `#1493 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1493>`_, - `#1504 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1504>`_, - `#1505 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1505>`_, - `#1512 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1512>`_, - `#1515 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1515>`_, - `#1516 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1516>`_, - `#1518 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1518>`_, - `#1519 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1519>`_, - `#1520 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1520>`_, - `#1521 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1521>`_, - `#1522 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1522>`_, - `#1524 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1524>`_, - `#1530 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1530>`_, - `#1531 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1531>`_, - `#1532 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1532>`_, - `#1539 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1539>`_, - `#1547 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1547>`_, - `#1548 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1548>`_, - `#1554 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1554>`_, - `#1567 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1567>`_, - `#1568 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1568>`_, - `#1569 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1569>`_, - `#1571 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1571>`_, - `#1573 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1573>`_, - `#1575 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1575>`_, - `#1581 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1581>`_, - `#1583 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1583>`_, - `#1586 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1586>`_, - `#1587 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1587>`_, - `#1594 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1594>`_, - `#1596 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1596>`_, - `#1604 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1604>`_, - `#1606 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1606>`_, - `#1607 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1607>`_, - `#1609 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1609>`_). - Thanks `@marti4d (Chris Martin) <https://github.com/marti4d>`_, - `@iPherian <https://github.com/iPherian>`_, - `@parkertomatoes <https://github.com/parkertomatoes>`_, - `@gsjaardema (Greg Sjaardema) <https://github.com/gsjaardema>`_, - `@chronoxor (Ivan Shynkarenka) <https://github.com/chronoxor>`_, - `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_, - `@torsten48 <https://github.com/torsten48>`_, - `@tohammer (Tobias Hammer) <https://github.com/tohammer>`_, - `@lefticus (Jason Turner) <https://github.com/lefticus>`_, - `@ryusakki (Haise) <https://github.com/ryusakki>`_, - `@adnsv (Alex Denisov) <https://github.com/adnsv>`_, - `@fghzxm <https://github.com/fghzxm>`_, - `@refnum <https://github.com/refnum>`_, - `@pramodk (Pramod Kumbhar) <https://github.com/pramodk>`_, - `@Spirrwell <https://github.com/Spirrwell>`_, - `@scramsby (Scott Ramsby) <https://github.com/scramsby>`_. - -6.1.2 - 2019-12-11 ------------------- - -* Fixed ABI compatibility with ``libfmt.so.6.0.0`` - (`#1471 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1471>`_). - -* Fixed handling types convertible to ``std::string_view`` - (`#1451 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1451>`_). - Thanks `@denizevrenci (Deniz Evrenci) <https://github.com/denizevrenci>`_. - -* Made CUDA test an opt-in enabled via the ``FMT_CUDA_TEST`` CMake option. - -* Fixed sign conversion warnings - (`#1440 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1440>`_). - Thanks `@0x8000-0000 (Florin Iucha) <https://github.com/0x8000-0000>`_. - -6.1.1 - 2019-12-04 ------------------- - -* Fixed shared library build on Windows - (`#1443 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1443>`_, - `#1445 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1445>`_, - `#1446 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1446>`_, - `#1450 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1450>`_). - Thanks `@egorpugin (Egor Pugin) <https://github.com/egorpugin>`_, - `@bbolli (Beat Bolli) <https://github.com/bbolli>`_. - -* Added a missing decimal point in exponent notation with trailing zeros. - -* Removed deprecated ``format_arg_store::TYPES``. - -6.1.0 - 2019-12-01 ------------------- - -* {fmt} now formats IEEE 754 ``float`` and ``double`` using the shortest decimal - representation with correct rounding by default: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <cmath> - #include <fmt/core.h> - - int main() { - fmt::print("{}", M_PI); - } - - prints ``3.141592653589793``. - -* Made the fast binary to decimal floating-point formatter the default, - simplified it and improved performance. {fmt} is now 15 times faster than - libc++'s ``std::ostringstream``, 11 times faster than ``printf`` and 10% - faster than double-conversion on `dtoa-benchmark - <https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark>`_: - - ================== ========= ======= - Function Time (ns) Speedup - ================== ========= ======= - ostringstream 1,346.30 1.00x - ostrstream 1,195.74 1.13x - sprintf 995.08 1.35x - doubleconv 99.10 13.59x - fmt 88.34 15.24x - ================== ========= ======= - - .. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/ - 69767160-cdaca400-112f-11ea-9fc5-347c9f83caad.png - -* {fmt} no longer converts ``float`` arguments to ``double``. In particular this - improves the default (shortest) representation of floats and makes - ``fmt::format`` consistent with ``std::format`` specs - (`#1336 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1336>`_, - `#1353 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1353>`_, - `#1360 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1360>`_, - `#1361 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1361>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("{}", 0.1f); - - prints ``0.1`` instead of ``0.10000000149011612``. - - Thanks `@orivej (Orivej Desh) <https://github.com/orivej>`_. - -* Made floating-point formatting output consistent with ``printf``/iostreams - (`#1376 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1376>`_, - `#1417 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1417>`_). - -* Added support for 128-bit integers - (`#1287 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1287>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("{}", std::numeric_limits<__int128_t>::max()); - - prints ``170141183460469231731687303715884105727``. - - Thanks `@denizevrenci (Deniz Evrenci) <https://github.com/denizevrenci>`_. - -* The overload of ``print`` that takes ``text_style`` is now atomic, i.e. the - output from different threads doesn't interleave - (`#1351 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1351>`_). - Thanks `@tankiJong (Tanki Zhang) <https://github.com/tankiJong>`_. - -* Made compile time in the header-only mode ~20% faster by reducing the number - of template instantiations. ``wchar_t`` overload of ``vprint`` was moved from - ``fmt/core.h`` to ``fmt/format.h``. - -* Added an overload of ``fmt::join`` that works with tuples - (`#1322 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1322>`_, - `#1330 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1330>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <tuple> - #include <fmt/ranges.h> - - int main() { - std::tuple<char, int, float> t{'a', 1, 2.0f}; - fmt::print("{}", t); - } - - prints ``('a', 1, 2.0)``. - - Thanks `@jeremyong (Jeremy Ong) <https://github.com/jeremyong>`_. - -* Changed formatting of octal zero with prefix from "00" to "0": - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("{:#o}", 0); - - prints ``0``. - -* The locale is now passed to ostream insertion (``<<``) operators - (`#1406 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1406>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/locale.h> - #include <fmt/ostream.h> - - struct S { - double value; - }; - - std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, S s) { - return os << s.value; - } - - int main() { - auto s = fmt::format(std::locale("fr_FR.UTF-8"), "{}", S{0.42}); - // s == "0,42" - } - - Thanks `@dlaugt (Daniel Laügt) <https://github.com/dlaugt>`_. - -* Locale-specific number formatting now uses grouping - (`#1393 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1393>`_ - `#1394 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1394>`_). - Thanks `@skrdaniel <https://github.com/skrdaniel>`_. - -* Fixed handling of types with deleted implicit rvalue conversion to - ``const char**`` (`#1421 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1421>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - struct mystring { - operator const char*() const&; - operator const char*() &; - operator const char*() const&& = delete; - operator const char*() && = delete; - }; - mystring str; - fmt::print("{}", str); // now compiles - -* Enums are now mapped to correct underlying types instead of ``int`` - (`#1286 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1286>`_). - Thanks `@agmt (Egor Seredin) <https://github.com/agmt>`_. - -* Enum classes are no longer implicitly converted to ``int`` - (`#1424 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1424>`_). - -* Added ``basic_format_parse_context`` for consistency with C++20 - ``std::format`` and deprecated ``basic_parse_context``. - -* Fixed handling of UTF-8 in precision - (`#1389 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1389>`_, - `#1390 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1390>`_). - Thanks `@tajtiattila (Attila Tajti) <https://github.com/tajtiattila>`_. - -* {fmt} can now be installed on Linux, macOS and Windows with - `Conda <https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/>`__ using its - `conda-forge <https://conda-forge.org>`__ - `package <https://github.com/conda-forge/fmt-feedstock>`__ - (`#1410 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1410>`_):: - - conda install -c conda-forge fmt - - Thanks `@tdegeus (Tom de Geus) <https://github.com/tdegeus>`_. - -* Added a CUDA test (`#1285 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1285>`_, - `#1317 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1317>`_). - Thanks `@luncliff (Park DongHa) <https://github.com/luncliff>`_ and - `@risa2000 <https://github.com/risa2000>`_. - -* Improved documentation (`#1276 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1276>`_, - `#1291 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1291>`_, - `#1296 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1296>`_, - `#1315 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1315>`_, - `#1332 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1332>`_, - `#1337 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1337>`_, - `#1395 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1395>`_ - `#1418 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1418>`_). - Thanks - `@waywardmonkeys (Bruce Mitchener) <https://github.com/waywardmonkeys>`_, - `@pauldreik (Paul Dreik) <https://github.com/pauldreik>`_, - `@jackoalan (Jack Andersen) <https://github.com/jackoalan>`_. - -* Various code improvements - (`#1358 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1358>`_, - `#1407 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1407>`_). - Thanks `@orivej (Orivej Desh) <https://github.com/orivej>`_, - `@dpacbach (David P. Sicilia) <https://github.com/dpacbach>`_, - -* Fixed compile-time format string checks for user-defined types - (`#1292 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1292>`_). - -* Worked around a false positive in ``unsigned-integer-overflow`` sanitizer - (`#1377 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1377>`_). - -* Fixed various warnings and compilation issues - (`#1273 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1273>`_, - `#1278 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1278>`_, - `#1280 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1280>`_, - `#1281 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1281>`_, - `#1288 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1288>`_, - `#1290 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1290>`_, - `#1301 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1301>`_, - `#1305 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1305>`_, - `#1306 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1306>`_, - `#1309 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1309>`_, - `#1312 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1312>`_, - `#1313 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1313>`_, - `#1316 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1316>`_, - `#1319 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1319>`_, - `#1320 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1320>`_, - `#1326 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1326>`_, - `#1328 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1328>`_, - `#1344 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1344>`_, - `#1345 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1345>`_, - `#1347 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1347>`_, - `#1349 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1349>`_, - `#1354 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1354>`_, - `#1362 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1362>`_, - `#1366 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1366>`_, - `#1364 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1364>`_, - `#1370 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1370>`_, - `#1371 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1371>`_, - `#1385 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1385>`_, - `#1388 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1388>`_, - `#1397 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1397>`_, - `#1414 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1414>`_, - `#1416 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1416>`_, - `#1422 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1422>`_ - `#1427 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1427>`_, - `#1431 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1431>`_, - `#1433 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1433>`_). - Thanks `@hhb <https://github.com/hhb>`_, - `@gsjaardema (Greg Sjaardema) <https://github.com/gsjaardema>`_, - `@gabime (Gabi Melman) <https://github.com/gabime>`_, - `@neheb (Rosen Penev) <https://github.com/neheb>`_, - `@vedranmiletic (Vedran Miletić) <https://github.com/vedranmiletic>`_, - `@dkavolis (Daumantas Kavolis) <https://github.com/dkavolis>`_, - `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_, - `@orivej (Orivej Desh) <https://github.com/orivej>`_, - `@denizevrenci (Deniz Evrenci) <https://github.com/denizevrenci>`_ - `@leonklingele <https://github.com/leonklingele>`_, - `@chronoxor (Ivan Shynkarenka) <https://github.com/chronoxor>`_, - `@kent-tri <https://github.com/kent-tri>`_, - `@0x8000-0000 (Florin Iucha) <https://github.com/0x8000-0000>`_, - `@marti4d (Chris Martin) <https://github.com/marti4d>`_. - -6.0.0 - 2019-08-26 ------------------- - -* Switched to the `MIT license - <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/5a4b24613ba16cc689977c3b5bd8274a3ba1dd1f/LICENSE.rst>`_ - with an optional exception that allows distributing binary code without - attribution. - -* Floating-point formatting is now locale-independent by default: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <locale> - #include <fmt/core.h> - - int main() { - std::locale::global(std::locale("ru_RU.UTF-8")); - fmt::print("value = {}", 4.2); - } - - prints "value = 4.2" regardless of the locale. - - For locale-specific formatting use the ``n`` specifier: - - .. code:: c++ - - std::locale::global(std::locale("ru_RU.UTF-8")); - fmt::print("value = {:n}", 4.2); - - prints "value = 4,2". - -* Added an experimental Grisu floating-point formatting algorithm - implementation (disabled by default). To enable it compile with the - ``FMT_USE_GRISU`` macro defined to 1: - - .. code:: c++ - - #define FMT_USE_GRISU 1 - #include <fmt/format.h> - - auto s = fmt::format("{}", 4.2); // formats 4.2 using Grisu - - With Grisu enabled, {fmt} is 13x faster than ``std::ostringstream`` (libc++) - and 10x faster than ``sprintf`` on `dtoa-benchmark - <https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark>`_ (`full results - <https://fmt.dev/unknown_mac64_clang10.0.html>`_): - - .. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/ - 54883977-9fe8c000-4e28-11e9-8bde-272d122e7c52.jpg - -* Separated formatting and parsing contexts for consistency with - `C++20 std::format <http://eel.is/c++draft/format>`_, removing the - undocumented ``basic_format_context::parse_context()`` function. - -* Added `oss-fuzz <https://github.com/google/oss-fuzz>`_ support - (`#1199 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1199>`_). - Thanks `@pauldreik (Paul Dreik) <https://github.com/pauldreik>`_. - -* ``formatter`` specializations now always take precedence over ``operator<<`` - (`#952 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/952>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <iostream> - #include <fmt/ostream.h> - - struct S {}; - - std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, S) { - return os << 1; - } - - template <> - struct fmt::formatter<S> : fmt::formatter<int> { - auto format(S, format_context& ctx) { - return formatter<int>::format(2, ctx); - } - }; - - int main() { - std::cout << S() << "\n"; // prints 1 using operator<< - fmt::print("{}\n", S()); // prints 2 using formatter - } - -* Introduced the experimental ``fmt::compile`` function that does format string - compilation (`#618 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/618>`_, - `#1169 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1169>`_, - `#1171 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1171>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/compile.h> - - auto f = fmt::compile<int>("{}"); - std::string s = fmt::format(f, 42); // can be called multiple times to - // format different values - // s == "42" - - It moves the cost of parsing a format string outside of the format function - which can be beneficial when identically formatting many objects of the same - types. Thanks `@stryku (Mateusz Janek) <https://github.com/stryku>`_. - -* Added experimental ``%`` format specifier that formats floating-point values - as percentages (`#1060 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1060>`_, - `#1069 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1069>`_, - `#1071 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1071>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - auto s = fmt::format("{:.1%}", 0.42); // s == "42.0%" - - Thanks `@gawain-bolton (Gawain Bolton) <https://github.com/gawain-bolton>`_. - -* Implemented precision for floating-point durations - (`#1004 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1004>`_, - `#1012 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1012>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - auto s = fmt::format("{:.1}", std::chrono::duration<double>(1.234)); - // s == 1.2s - - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Implemented ``chrono`` format specifiers ``%Q`` and ``%q`` that give the value - and the unit respectively (`#1019 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1019>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - auto value = fmt::format("{:%Q}", 42s); // value == "42" - auto unit = fmt::format("{:%q}", 42s); // unit == "s" - - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Fixed handling of dynamic width in chrono formatter: - - .. code:: c++ - - auto s = fmt::format("{0:{1}%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345), 12); - // ^ width argument index ^ width - // s == "03:25:45 " - - Thanks Howard Hinnant. - -* Removed deprecated ``fmt/time.h``. Use ``fmt/chrono.h`` instead. - -* Added ``fmt::format`` and ``fmt::vformat`` overloads that take ``text_style`` - (`#993 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/993>`_, - `#994 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/994>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/color.h> - - std::string message = fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red), - "The answer is {}.", 42); - - Thanks `@Naios (Denis Blank) <https://github.com/Naios>`_. - -* Removed the deprecated color API (``print_colored``). Use the new API, namely - ``print`` overloads that take ``text_style`` instead. - -* Made ``std::unique_ptr`` and ``std::shared_ptr`` formattable as pointers via - ``fmt::ptr`` (`#1121 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1121>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - std::unique_ptr<int> p = ...; - fmt::print("{}", fmt::ptr(p)); // prints p as a pointer - - Thanks `@sighingnow (Tao He) <https://github.com/sighingnow>`_. - -* Made ``print`` and ``vprint`` report I/O errors - (`#1098 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1098>`_, - `#1099 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1099>`_). - Thanks `@BillyDonahue (Billy Donahue) <https://github.com/BillyDonahue>`_. - -* Marked deprecated APIs with the ``[[deprecated]]`` attribute and removed - internal uses of deprecated APIs - (`#1022 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1022>`_). - Thanks `@eliaskosunen (Elias Kosunen) <https://github.com/eliaskosunen>`_. - -* Modernized the codebase using more C++11 features and removing workarounds. - Most importantly, ``buffer_context`` is now an alias template, so - use ``buffer_context<T>`` instead of ``buffer_context<T>::type``. - These features require GCC 4.8 or later. - -* ``formatter`` specializations now always take precedence over implicit - conversions to ``int`` and the undocumented ``convert_to_int`` trait - is now deprecated. - -* Moved the undocumented ``basic_writer``, ``writer``, and ``wwriter`` types - to the ``internal`` namespace. - -* Removed deprecated ``basic_format_context::begin()``. Use ``out()`` instead. - -* Disallowed passing the result of ``join`` as an lvalue to prevent misuse. - -* Refactored the undocumented structs that represent parsed format specifiers - to simplify the API and allow multibyte fill. - -* Moved SFINAE to template parameters to reduce symbol sizes. - -* Switched to ``fputws`` for writing wide strings so that it's no longer - required to call ``_setmode`` on Windows - (`#1229 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1229>`_, - `#1243 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1243>`_). - Thanks `@jackoalan (Jack Andersen) <https://github.com/jackoalan>`_. - -* Improved literal-based API - (`#1254 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1254>`_). - Thanks `@sylveon (Charles Milette) <https://github.com/sylveon>`_. - -* Added support for exotic platforms without ``uintptr_t`` such as IBM i - (AS/400) which has 128-bit pointers and only 64-bit integers - (`#1059 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1059>`_). - -* Added `Sublime Text syntax highlighting config - <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/support/C%2B%2B.sublime-syntax>`_ - (`#1037 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1037>`_). - Thanks `@Kronuz (Germán Méndez Bravo) <https://github.com/Kronuz>`_. - -* Added the ``FMT_ENFORCE_COMPILE_STRING`` macro to enforce the use of - compile-time format strings - (`#1231 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1231>`_). - Thanks `@jackoalan (Jack Andersen) <https://github.com/jackoalan>`_. - -* Stopped setting ``CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE`` if {fmt} is a subproject - (`#1081 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1081>`_). - -* Various build improvements - (`#1039 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1039>`_, - `#1078 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1078>`_, - `#1091 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1091>`_, - `#1103 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1103>`_, - `#1177 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1177>`_). - Thanks `@luncliff (Park DongHa) <https://github.com/luncliff>`_, - `@jasonszang (Jason Shuo Zang) <https://github.com/jasonszang>`_, - `@olafhering (Olaf Hering) <https://github.com/olafhering>`_, - `@Lecetem <https://github.com/Lectem>`_, - `@pauldreik (Paul Dreik) <https://github.com/pauldreik>`_. - -* Improved documentation - (`#1049 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1049>`_, - `#1051 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1051>`_, - `#1083 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1083>`_, - `#1113 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1113>`_, - `#1114 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1114>`_, - `#1146 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1146>`_, - `#1180 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1180>`_, - `#1250 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1250>`_, - `#1252 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1252>`_, - `#1265 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1265>`_). - Thanks `@mikelui (Michael Lui) <https://github.com/mikelui>`_, - `@foonathan (Jonathan Müller) <https://github.com/foonathan>`_, - `@BillyDonahue (Billy Donahue) <https://github.com/BillyDonahue>`_, - `@jwakely (Jonathan Wakely) <https://github.com/jwakely>`_, - `@kaisbe (Kais Ben Salah) <https://github.com/kaisbe>`_, - `@sdebionne (Samuel Debionne) <https://github.com/sdebionne>`_. - -* Fixed ambiguous formatter specialization in ``fmt/ranges.h`` - (`#1123 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1123>`_). - -* Fixed formatting of a non-empty ``std::filesystem::path`` which is an - infinitely deep range of its components - (`#1268 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1268>`_). - -* Fixed handling of general output iterators when formatting characters - (`#1056 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1056>`_, - `#1058 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1058>`_). - Thanks `@abolz (Alexander Bolz) <https://github.com/abolz>`_. - -* Fixed handling of output iterators in ``formatter`` specialization for - ranges (`#1064 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1064>`_). - -* Fixed handling of exotic character types - (`#1188 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1188>`_). - -* Made chrono formatting work with exceptions disabled - (`#1062 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1062>`_). - -* Fixed DLL visibility issues - (`#1134 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1134>`_, - `#1147 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1147>`_). - Thanks `@denchat <https://github.com/denchat>`_. - -* Disabled the use of UDL template extension on GCC 9 - (`#1148 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1148>`_). - -* Removed misplaced ``format`` compile-time checks from ``printf`` - (`#1173 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1173>`_). - -* Fixed issues in the experimental floating-point formatter - (`#1072 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1072>`_, - `#1129 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1129>`_, - `#1153 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1153>`_, - `#1155 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1155>`_, - `#1210 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1210>`_, - `#1222 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1222>`_). - Thanks `@alabuzhev (Alex Alabuzhev) <https://github.com/alabuzhev>`_. - -* Fixed bugs discovered by fuzzing or during fuzzing integration - (`#1124 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1124>`_, - `#1127 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1127>`_, - `#1132 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1132>`_, - `#1135 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1135>`_, - `#1136 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1136>`_, - `#1141 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1141>`_, - `#1142 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1142>`_, - `#1178 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1178>`_, - `#1179 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1179>`_, - `#1194 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1194>`_). - Thanks `@pauldreik (Paul Dreik) <https://github.com/pauldreik>`_. - -* Fixed building tests on FreeBSD and Hurd - (`#1043 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1043>`_). - Thanks `@jackyf (Eugene V. Lyubimkin) <https://github.com/jackyf>`_. - -* Fixed various warnings and compilation issues - (`#998 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/998>`_, - `#1006 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1006>`_, - `#1008 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1008>`_, - `#1011 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1011>`_, - `#1025 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1025>`_, - `#1027 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1027>`_, - `#1028 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1028>`_, - `#1029 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1029>`_, - `#1030 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1030>`_, - `#1031 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1031>`_, - `#1054 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1054>`_, - `#1063 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1063>`_, - `#1068 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1068>`_, - `#1074 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1074>`_, - `#1075 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1075>`_, - `#1079 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1079>`_, - `#1086 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1086>`_, - `#1088 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1088>`_, - `#1089 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1089>`_, - `#1094 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1094>`_, - `#1101 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1101>`_, - `#1102 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1102>`_, - `#1105 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1105>`_, - `#1107 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1107>`_, - `#1115 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1115>`_, - `#1117 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1117>`_, - `#1118 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1118>`_, - `#1120 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1120>`_, - `#1123 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1123>`_, - `#1139 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1139>`_, - `#1140 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1140>`_, - `#1143 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1143>`_, - `#1144 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1144>`_, - `#1150 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1150>`_, - `#1151 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1151>`_, - `#1152 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1152>`_, - `#1154 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1154>`_, - `#1156 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1156>`_, - `#1159 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1159>`_, - `#1175 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1175>`_, - `#1181 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1181>`_, - `#1186 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1186>`_, - `#1187 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1187>`_, - `#1191 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1191>`_, - `#1197 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1197>`_, - `#1200 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1200>`_, - `#1203 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1203>`_, - `#1205 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1205>`_, - `#1206 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1206>`_, - `#1213 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1213>`_, - `#1214 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1214>`_, - `#1217 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1217>`_, - `#1228 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1228>`_, - `#1230 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1230>`_, - `#1232 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1232>`_, - `#1235 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1235>`_, - `#1236 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/1236>`_, - `#1240 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/1240>`_). - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_, - `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_, - `@eliaskosunen (Elias Kosunen) <https://github.com/eliaskosunen>`_, - `@morinmorin <https://github.com/morinmorin>`_, - `@ricco19 (Brian Ricciardelli) <https://github.com/ricco19>`_, - `@waywardmonkeys (Bruce Mitchener) <https://github.com/waywardmonkeys>`_, - `@chronoxor (Ivan Shynkarenka) <https://github.com/chronoxor>`_, - `@remyabel <https://github.com/remyabel>`_, - `@pauldreik (Paul Dreik) <https://github.com/pauldreik>`_, - `@gsjaardema (Greg Sjaardema) <https://github.com/gsjaardema>`_, - `@rcane (Ronny Krüger) <https://github.com/rcane>`_, - `@mocabe <https://github.com/mocabe>`_, - `@denchat <https://github.com/denchat>`_, - `@cjdb (Christopher Di Bella) <https://github.com/cjdb>`_, - `@HazardyKnusperkeks (Björn Schäpers) <https://github.com/HazardyKnusperkeks>`_, - `@vedranmiletic (Vedran Miletić) <https://github.com/vedranmiletic>`_, - `@jackoalan (Jack Andersen) <https://github.com/jackoalan>`_, - `@DaanDeMeyer (Daan De Meyer) <https://github.com/DaanDeMeyer>`_, - `@starkmapper (Mark Stapper) <https://github.com/starkmapper>`_. - -5.3.0 - 2018-12-28 ------------------- - -* Introduced experimental chrono formatting support: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/chrono.h> - - int main() { - using namespace std::literals::chrono_literals; - fmt::print("Default format: {} {}\n", 42s, 100ms); - fmt::print("strftime-like format: {:%H:%M:%S}\n", 3h + 15min + 30s); - } - - prints:: - - Default format: 42s 100ms - strftime-like format: 03:15:30 - -* Added experimental support for emphasis (bold, italic, underline, - strikethrough), colored output to a file stream, and improved colored - formatting API - (`#961 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/961>`_, - `#967 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/967>`_, - `#973 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/973>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/color.h> - - int main() { - print(fg(fmt::color::crimson) | fmt::emphasis::bold, - "Hello, {}!\n", "world"); - print(fg(fmt::color::floral_white) | bg(fmt::color::slate_gray) | - fmt::emphasis::underline, "Hello, {}!\n", "мир"); - print(fg(fmt::color::steel_blue) | fmt::emphasis::italic, - "Hello, {}!\n", "世界"); - } - - prints the following on modern terminals with RGB color support: - - .. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/ - 50405788-b66e7500-076e-11e9-9592-7324d1f951d8.png - - Thanks `@Rakete1111 (Nicolas) <https://github.com/Rakete1111>`_. - -* Added support for 4-bit terminal colors - (`#968 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/968>`_, - `#974 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/974>`_) - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/color.h> - - int main() { - print(fg(fmt::terminal_color::red), "stop\n"); - } - - Note that these colors vary by terminal: - - .. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/ - 50405925-dbfc7e00-0770-11e9-9b85-333fab0af9ac.png - - Thanks `@Rakete1111 (Nicolas) <https://github.com/Rakete1111>`_. - -* Parameterized formatting functions on the type of the format string - (`#880 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/880>`_, - `#881 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/881>`_, - `#883 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/883>`_, - `#885 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/885>`_, - `#897 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/897>`_, - `#920 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/920>`_). - Any object of type ``S`` that has an overloaded ``to_string_view(const S&)`` - returning ``fmt::string_view`` can be used as a format string: - - .. code:: c++ - - namespace my_ns { - inline string_view to_string_view(const my_string& s) { - return {s.data(), s.length()}; - } - } - - std::string message = fmt::format(my_string("The answer is {}."), 42); - - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Made ``std::string_view`` work as a format string - (`#898 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/898>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - auto message = fmt::format(std::string_view("The answer is {}."), 42); - - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Added wide string support to compile-time format string checks - (`#924 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/924>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - print(fmt(L"{:f}"), 42); // compile-time error: invalid type specifier - - Thanks `@XZiar <https://github.com/XZiar>`_. - -* Made colored print functions work with wide strings - (`#867 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/867>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/color.h> - - int main() { - print(fg(fmt::color::red), L"{}\n", 42); - } - - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Introduced experimental Unicode support - (`#628 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/628>`_, - `#891 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/891>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - using namespace fmt::literals; - auto s = fmt::format("{:*^5}"_u, "🤡"_u); // s == "**🤡**"_u - -* Improved locale support: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/locale.h> - - struct numpunct : std::numpunct<char> { - protected: - char do_thousands_sep() const override { return '~'; } - }; - - std::locale loc; - auto s = fmt::format(std::locale(loc, new numpunct()), "{:n}", 1234567); - // s == "1~234~567" - -* Constrained formatting functions on proper iterator types - (`#921 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/921>`_). - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Added ``make_printf_args`` and ``make_wprintf_args`` functions - (`#934 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/934>`_). - Thanks `@tnovotny <https://github.com/tnovotny>`_. - -* Deprecated ``fmt::visit``, ``parse_context``, and ``wparse_context``. - Use ``fmt::visit_format_arg``, ``format_parse_context``, and - ``wformat_parse_context`` instead. - -* Removed undocumented ``basic_fixed_buffer`` which has been superseded by the - iterator-based API - (`#873 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/873>`_, - `#902 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/902>`_). - Thanks `@superfunc (hollywood programmer) <https://github.com/superfunc>`_. - -* Disallowed repeated leading zeros in an argument ID: - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("{000}", 42); // error - -* Reintroduced support for gcc 4.4. - -* Fixed compilation on platforms with exotic ``double`` - (`#878 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/878>`_). - -* Improved documentation - (`#164 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/164>`_, - `#877 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/877>`_, - `#901 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/901>`_, - `#906 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/906>`_, - `#979 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/979>`_). - Thanks `@kookjr (Mathew Cucuzella) <https://github.com/kookjr>`_, - `@DarkDimius (Dmitry Petrashko) <https://github.com/DarkDimius>`_, - `@HecticSerenity <https://github.com/HecticSerenity>`_. - -* Added pkgconfig support which makes it easier to consume the library from - meson and other build systems - (`#916 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/916>`_). - Thanks `@colemickens (Cole Mickens) <https://github.com/colemickens>`_. - -* Various build improvements - (`#909 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/909>`_, - `#926 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/926>`_, - `#937 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/937>`_, - `#953 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/953>`_, - `#959 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/959>`_). - Thanks `@tchaikov (Kefu Chai) <https://github.com/tchaikov>`_, - `@luncliff (Park DongHa) <https://github.com/luncliff>`_, - `@AndreasSchoenle (Andreas Schönle) <https://github.com/AndreasSchoenle>`_, - `@hotwatermorning <https://github.com/hotwatermorning>`_, - `@Zefz (JohanJansen) <https://github.com/Zefz>`_. - -* Improved ``string_view`` construction performance - (`#914 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/914>`_). - Thanks `@gabime (Gabi Melman) <https://github.com/gabime>`_. - -* Fixed non-matching char types - (`#895 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/895>`_). - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Fixed ``format_to_n`` with ``std::back_insert_iterator`` - (`#913 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/913>`_). - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Fixed locale-dependent formatting - (`#905 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/905>`_). - -* Fixed various compiler warnings and errors - (`#882 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/882>`_, - `#886 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/886>`_, - `#933 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/933>`_, - `#941 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/941>`_, - `#931 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/931>`_, - `#943 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/943>`_, - `#954 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/954>`_, - `#956 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/956>`_, - `#962 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/962>`_, - `#965 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/965>`_, - `#977 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/977>`_, - `#983 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/983>`_, - `#989 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/989>`_). - Thanks `@Luthaf (Guillaume Fraux) <https://github.com/Luthaf>`_, - `@stevenhoving (Steven Hoving) <https://github.com/stevenhoving>`_, - `@christinaa (Kristina Brooks) <https://github.com/christinaa>`_, - `@lgritz (Larry Gritz) <https://github.com/lgritz>`_, - `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_, - `@0x8000-0000 (Sign Bit) <https://github.com/0x8000-0000>`_, - `@liuping1997 <https://github.com/liuping1997>`_. - -5.2.1 - 2018-09-21 ------------------- - -* Fixed ``visit`` lookup issues on gcc 7 & 8 - (`#870 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/870>`_). - Thanks `@medithe <https://github.com/medithe>`_. - -* Fixed linkage errors on older gcc. - -* Prevented ``fmt/range.h`` from specializing ``fmt::basic_string_view`` - (`#865 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/865>`_, - `#868 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/868>`_). - Thanks `@hhggit (dual) <https://github.com/hhggit>`_. - -* Improved error message when formatting unknown types - (`#872 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/872>`_). - Thanks `@foonathan (Jonathan Müller) <https://github.com/foonathan>`_, - -* Disabled templated user-defined literals when compiled under nvcc - (`#875 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/875>`_). - Thanks `@CandyGumdrop (Candy Gumdrop) <https://github.com/CandyGumdrop>`_, - -* Fixed ``format_to`` formatting to ``wmemory_buffer`` - (`#874 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/874>`_). - -5.2.0 - 2018-09-13 ------------------- - -* Optimized format string parsing and argument processing which resulted in up - to 5x speed up on long format strings and significant performance boost on - various benchmarks. For example, version 5.2 is 2.22x faster than 5.1 on - decimal integer formatting with ``format_to`` (macOS, clang-902.0.39.2): - - ================== ======= ======= - Method Time, s Speedup - ================== ======= ======= - fmt::format 5.1 0.58 - fmt::format 5.2 0.35 1.66x - fmt::format_to 5.1 0.51 - fmt::format_to 5.2 0.23 2.22x - sprintf 0.71 - std::to_string 1.01 - std::stringstream 1.73 - ================== ======= ======= - -* Changed the ``fmt`` macro from opt-out to opt-in to prevent name collisions. - To enable it define the ``FMT_STRING_ALIAS`` macro to 1 before including - ``fmt/format.h``: - - .. code:: c++ - - #define FMT_STRING_ALIAS 1 - #include <fmt/format.h> - std::string answer = format(fmt("{}"), 42); - -* Added compile-time format string checks to ``format_to`` overload that takes - ``fmt::memory_buffer`` (`#783 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/783>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::memory_buffer buf; - // Compile-time error: invalid type specifier. - fmt::format_to(buf, fmt("{:d}"), "foo"); - -* Moved experimental color support to ``fmt/color.h`` and enabled the - new API by default. The old API can be enabled by defining the - ``FMT_DEPRECATED_COLORS`` macro. - -* Added formatting support for types explicitly convertible to - ``fmt::string_view``: - - .. code:: c++ - - struct foo { - explicit operator fmt::string_view() const { return "foo"; } - }; - auto s = format("{}", foo()); - - In particular, this makes formatting function work with - ``folly::StringPiece``. - -* Implemented preliminary support for ``char*_t`` by replacing the ``format`` - function overloads with a single function template parameterized on the string - type. - -* Added support for dynamic argument lists - (`#814 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/814>`_, - `#819 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/819>`_). - Thanks `@MikePopoloski (Michael Popoloski) - <https://github.com/MikePopoloski>`_. - -* Reduced executable size overhead for embedded targets using newlib nano by - making locale dependency optional - (`#839 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/839>`_). - Thanks `@teajay-fr (Thomas Benard) <https://github.com/teajay-fr>`_. - -* Keep ``noexcept`` specifier when exceptions are disabled - (`#801 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/801>`_, - `#810 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/810>`_). - Thanks `@qis (Alexej Harm) <https://github.com/qis>`_. - -* Fixed formatting of user-defined types providing ``operator<<`` with - ``format_to_n`` - (`#806 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/806>`_). - Thanks `@mkurdej (Marek Kurdej) <https://github.com/mkurdej>`_. - -* Fixed dynamic linkage of new symbols - (`#808 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/808>`_). - -* Fixed global initialization issue - (`#807 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/807>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - // This works on compilers with constexpr support. - static const std::string answer = fmt::format("{}", 42); - -* Fixed various compiler warnings and errors - (`#804 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/804>`_, - `#809 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/809>`_, - `#811 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/811>`_, - `#822 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/822>`_, - `#827 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/827>`_, - `#830 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/830>`_, - `#838 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/838>`_, - `#843 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/843>`_, - `#844 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/844>`_, - `#851 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/851>`_, - `#852 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/852>`_, - `#854 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/854>`_). - Thanks `@henryiii (Henry Schreiner) <https://github.com/henryiii>`_, - `@medithe <https://github.com/medithe>`_, and - `@eliasdaler (Elias Daler) <https://github.com/eliasdaler>`_. - -5.1.0 - 2018-07-05 ------------------- - -* Added experimental support for RGB color output enabled with - the ``FMT_EXTENDED_COLORS`` macro: - - .. code:: c++ - - #define FMT_EXTENDED_COLORS - #define FMT_HEADER_ONLY // or compile fmt with FMT_EXTENDED_COLORS defined - #include <fmt/format.h> - - fmt::print(fmt::color::steel_blue, "Some beautiful text"); - - The old API (the ``print_colored`` and ``vprint_colored`` functions and the - ``color`` enum) is now deprecated. - (`#762 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/762>`_ - `#767 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/767>`_). - thanks `@Remotion (Remo) <https://github.com/Remotion>`_. - -* Added quotes to strings in ranges and tuples - (`#766 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/766>`_). - Thanks `@Remotion (Remo) <https://github.com/Remotion>`_. - -* Made ``format_to`` work with ``basic_memory_buffer`` - (`#776 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/776>`_). - -* Added ``vformat_to_n`` and ``wchar_t`` overload of ``format_to_n`` - (`#764 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/764>`_, - `#769 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/769>`_). - -* Made ``is_range`` and ``is_tuple_like`` part of public (experimental) API - to allow specialization for user-defined types - (`#751 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/751>`_, - `#759 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/759>`_). - Thanks `@drrlvn (Dror Levin) <https://github.com/drrlvn>`_. - -* Added more compilers to continuous integration and increased ``FMT_PEDANTIC`` - warning levels - (`#736 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/736>`_). - Thanks `@eliaskosunen (Elias Kosunen) <https://github.com/eliaskosunen>`_. - -* Fixed compilation with MSVC 2013. - -* Fixed handling of user-defined types in ``format_to`` - (`#793 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/793>`_). - -* Forced linking of inline ``vformat`` functions into the library - (`#795 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/795>`_). - -* Fixed incorrect call to on_align in ``'{:}='`` - (`#750 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/750>`_). - -* Fixed floating-point formatting to a non-back_insert_iterator with sign & - numeric alignment specified - (`#756 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/756>`_). - -* Fixed formatting to an array with ``format_to_n`` - (`#778 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/778>`_). - -* Fixed formatting of more than 15 named arguments - (`#754 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/754>`_). - -* Fixed handling of compile-time strings when including ``fmt/ostream.h``. - (`#768 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/768>`_). - -* Fixed various compiler warnings and errors - (`#742 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/742>`_, - `#748 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/748>`_, - `#752 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/752>`_, - `#770 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/770>`_, - `#775 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/775>`_, - `#779 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/779>`_, - `#780 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/780>`_, - `#790 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/790>`_, - `#792 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/792>`_, - `#800 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/800>`_). - Thanks `@Remotion (Remo) <https://github.com/Remotion>`_, - `@gabime (Gabi Melman) <https://github.com/gabime>`_, - `@foonathan (Jonathan Müller) <https://github.com/foonathan>`_, - `@Dark-Passenger (Dhruv Paranjape) <https://github.com/Dark-Passenger>`_, and - `@0x8000-0000 (Sign Bit) <https://github.com/0x8000-0000>`_. - -5.0.0 - 2018-05-21 ------------------- - -* Added a requirement for partial C++11 support, most importantly variadic - templates and type traits, and dropped ``FMT_VARIADIC_*`` emulation macros. - Variadic templates are available since GCC 4.4, Clang 2.9 and MSVC 18.0 (2013). - For older compilers use {fmt} `version 4.x - <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases/tag/4.1.0>`_ which continues to be - maintained and works with C++98 compilers. - -* Renamed symbols to follow standard C++ naming conventions and proposed a subset - of the library for standardization in `P0645R2 Text Formatting - <https://wg21.link/P0645>`_. - -* Implemented ``constexpr`` parsing of format strings and `compile-time format - string checks - <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#compile-time-format-string-checks>`_. For - example - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/format.h> - - std::string s = format(fmt("{:d}"), "foo"); - - gives a compile-time error because ``d`` is an invalid specifier for strings - (`godbolt <https://godbolt.org/g/rnCy9Q>`__):: - - ... - <source>:4:19: note: in instantiation of function template specialization 'fmt::v5::format<S, char [4]>' requested here - std::string s = format(fmt("{:d}"), "foo"); - ^ - format.h:1337:13: note: non-constexpr function 'on_error' cannot be used in a constant expression - handler.on_error("invalid type specifier"); - - Compile-time checks require relaxed ``constexpr`` (C++14 feature) support. If - the latter is not available, checks will be performed at runtime. - -* Separated format string parsing and formatting in the extension API to enable - compile-time format string processing. For example - - .. code:: c++ - - struct Answer {}; - - namespace fmt { - template <> - struct formatter<Answer> { - constexpr auto parse(parse_context& ctx) { - auto it = ctx.begin(); - spec = *it; - if (spec != 'd' && spec != 's') - throw format_error("invalid specifier"); - return ++it; - } - - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(Answer, FormatContext& ctx) { - return spec == 's' ? - format_to(ctx.begin(), "{}", "fourty-two") : - format_to(ctx.begin(), "{}", 42); - } - - char spec = 0; - }; - } - - std::string s = format(fmt("{:x}"), Answer()); - - gives a compile-time error due to invalid format specifier (`godbolt - <https://godbolt.org/g/2jQ1Dv>`__):: - - ... - <source>:12:45: error: expression '<throw-expression>' is not a constant expression - throw format_error("invalid specifier"); - -* Added `iterator support - <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#output-iterator-support>`_: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <vector> - #include <fmt/format.h> - - std::vector<char> out; - fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), "{}", 42); - -* Added the `format_to_n - <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#_CPPv2N3fmt11format_to_nE8OutputItNSt6size_tE11string_viewDpRK4Args>`_ - function that restricts the output to the specified number of characters - (`#298 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/298>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - char out[4]; - fmt::format_to_n(out, sizeof(out), "{}", 12345); - // out == "1234" (without terminating '\0') - -* Added the `formatted_size - <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#_CPPv2N3fmt14formatted_sizeE11string_viewDpRK4Args>`_ - function for computing the output size: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/format.h> - - auto size = fmt::formatted_size("{}", 12345); // size == 5 - -* Improved compile times by reducing dependencies on standard headers and - providing a lightweight `core API <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#core-api>`_: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/core.h> - - fmt::print("The answer is {}.", 42); - - See `Compile time and code bloat - <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt#compile-time-and-code-bloat>`_. - -* Added the `make_format_args - <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#_CPPv2N3fmt16make_format_argsEDpRK4Args>`_ - function for capturing formatting arguments: - - .. code:: c++ - - // Prints formatted error message. - void vreport_error(const char *format, fmt::format_args args) { - fmt::print("Error: "); - fmt::vprint(format, args); - } - template <typename... Args> - void report_error(const char *format, const Args & ... args) { - vreport_error(format, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); - } - -* Added the ``make_printf_args`` function for capturing ``printf`` arguments - (`#687 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/687>`_, - `#694 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/694>`_). - Thanks `@Kronuz (Germán Méndez Bravo) <https://github.com/Kronuz>`_. - -* Added prefix ``v`` to non-variadic functions taking ``format_args`` to - distinguish them from variadic ones: - - .. code:: c++ - - std::string vformat(string_view format_str, format_args args); - - template <typename... Args> - std::string format(string_view format_str, const Args & ... args); - -* Added experimental support for formatting ranges, containers and tuple-like - types in ``fmt/ranges.h`` (`#735 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/735>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/ranges.h> - - std::vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3}; - fmt::print("{}", v); // prints {1, 2, 3} - - Thanks `@Remotion (Remo) <https://github.com/Remotion>`_. - -* Implemented ``wchar_t`` date and time formatting - (`#712 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/712>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/time.h> - - std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr); - auto s = fmt::format(L"The date is {:%Y-%m-%d}.", *std::localtime(&t)); - - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Provided more wide string overloads - (`#724 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/724>`_). - Thanks `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_. - -* Switched from a custom null-terminated string view class to ``string_view`` - in the format API and provided ``fmt::string_view`` which implements a subset - of ``std::string_view`` API for pre-C++17 systems. - -* Added support for ``std::experimental::string_view`` - (`#607 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/607>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include <fmt/core.h> - #include <experimental/string_view> - - fmt::print("{}", std::experimental::string_view("foo")); - - Thanks `@virgiliofornazin (Virgilio Alexandre Fornazin) - <https://github.com/virgiliofornazin>`__. - -* Allowed mixing named and automatic arguments: - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::format("{} {two}", 1, fmt::arg("two", 2)); - -* Removed the write API in favor of the `format API - <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#format-api>`_ with compile-time handling of - format strings. - -* Disallowed formatting of multibyte strings into a wide character target - (`#606 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/606>`_). - -* Improved documentation - (`#515 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/515>`_, - `#614 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/614>`_, - `#617 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/617>`_, - `#661 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/661>`_, - `#680 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/680>`_). - Thanks `@ibell (Ian Bell) <https://github.com/ibell>`_, - `@mihaitodor (Mihai Todor) <https://github.com/mihaitodor>`_, and - `@johnthagen <https://github.com/johnthagen>`_. - -* Implemented more efficient handling of large number of format arguments. - -* Introduced an inline namespace for symbol versioning. - -* Added debug postfix ``d`` to the ``fmt`` library name - (`#636 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/636>`_). - -* Removed unnecessary ``fmt/`` prefix in includes - (`#397 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/397>`_). - Thanks `@chronoxor (Ivan Shynkarenka) <https://github.com/chronoxor>`_. - -* Moved ``fmt/*.h`` to ``include/fmt/*.h`` to prevent irrelevant files and - directories appearing on the include search paths when fmt is used as a - subproject and moved source files to the ``src`` directory. - -* Added qmake project file ``support/fmt.pro`` - (`#641 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/641>`_). - Thanks `@cowo78 (Giuseppe Corbelli) <https://github.com/cowo78>`_. - -* Added Gradle build file ``support/build.gradle`` - (`#649 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/649>`_). - Thanks `@luncliff (Park DongHa) <https://github.com/luncliff>`_. - -* Removed ``FMT_CPPFORMAT`` CMake option. - -* Fixed a name conflict with the macro ``CHAR_WIDTH`` in glibc - (`#616 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/616>`_). - Thanks `@aroig (Abdó Roig-Maranges) <https://github.com/aroig>`_. - -* Fixed handling of nested braces in ``fmt::join`` - (`#638 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/638>`_). - -* Added ``SOURCELINK_SUFFIX`` for compatibility with Sphinx 1.5 - (`#497 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/497>`_). - Thanks `@ginggs (Graham Inggs) <https://github.com/ginggs>`_. - -* Added a missing ``inline`` in the header-only mode - (`#626 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/626>`_). - Thanks `@aroig (Abdó Roig-Maranges) <https://github.com/aroig>`_. - -* Fixed various compiler warnings - (`#640 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/640>`_, - `#656 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/656>`_, - `#679 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/679>`_, - `#681 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/681>`_, - `#705 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/705>`__, - `#715 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/715>`_, - `#717 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/717>`_, - `#720 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/720>`_, - `#723 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/723>`_, - `#726 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/726>`_, - `#730 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/730>`_, - `#739 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/739>`_). - Thanks `@peterbell10 <https://github.com/peterbell10>`_, - `@LarsGullik <https://github.com/LarsGullik>`_, - `@foonathan (Jonathan Müller) <https://github.com/foonathan>`_, - `@eliaskosunen (Elias Kosunen) <https://github.com/eliaskosunen>`_, - `@christianparpart (Christian Parpart) <https://github.com/christianparpart>`_, - `@DanielaE (Daniela Engert) <https://github.com/DanielaE>`_, - and `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_. - -* Worked around an MSVC bug and fixed several warnings - (`#653 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/653>`_). - Thanks `@alabuzhev (Alex Alabuzhev) <https://github.com/alabuzhev>`_. - -* Worked around GCC bug 67371 - (`#682 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/682>`_). - -* Fixed compilation with ``-fno-exceptions`` - (`#655 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/655>`_). - Thanks `@chenxiaolong (Andrew Gunnerson) <https://github.com/chenxiaolong>`_. - -* Made ``constexpr remove_prefix`` gcc version check tighter - (`#648 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/648>`_). - -* Renamed internal type enum constants to prevent collision with poorly written - C libraries (`#644 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/644>`_). - -* Added detection of ``wostream operator<<`` - (`#650 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/650>`_). - -* Fixed compilation on OpenBSD - (`#660 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/660>`_). - Thanks `@hubslave <https://github.com/hubslave>`_. - -* Fixed compilation on FreeBSD 12 - (`#732 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/732>`_). - Thanks `@dankm <https://github.com/dankm>`_. - -* Fixed compilation when there is a mismatch between ``-std`` options between - the library and user code - (`#664 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/664>`_). - -* Fixed compilation with GCC 7 and ``-std=c++11`` - (`#734 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/734>`_). - -* Improved generated binary code on GCC 7 and older - (`#668 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/668>`_). - -* Fixed handling of numeric alignment with no width - (`#675 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/675>`_). - -* Fixed handling of empty strings in UTF8/16 converters - (`#676 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/676>`_). - Thanks `@vgalka-sl (Vasili Galka) <https://github.com/vgalka-sl>`_. - -* Fixed formatting of an empty ``string_view`` - (`#689 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/689>`_). - -* Fixed detection of ``string_view`` on libc++ - (`#686 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/686>`_). - -* Fixed DLL issues (`#696 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/696>`_). - Thanks `@sebkoenig <https://github.com/sebkoenig>`_. - -* Fixed compile checks for mixing narrow and wide strings - (`#690 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/690>`_). - -* Disabled unsafe implicit conversion to ``std::string`` - (`#729 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/729>`_). - -* Fixed handling of reused format specs (as in ``fmt::join``) for pointers - (`#725 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/725>`_). - Thanks `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_. - -* Fixed installation of ``fmt/ranges.h`` - (`#738 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/738>`_). - Thanks `@sv1990 <https://github.com/sv1990>`_. - -4.1.0 - 2017-12-20 ------------------- - -* Added ``fmt::to_wstring()`` in addition to ``fmt::to_string()`` - (`#559 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/559>`_). - Thanks `@alabuzhev (Alex Alabuzhev) <https://github.com/alabuzhev>`_. - -* Added support for C++17 ``std::string_view`` - (`#571 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/571>`_ and - `#578 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/578>`_). - Thanks `@thelostt (Mário Feroldi) <https://github.com/thelostt>`_ and - `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_. - -* Enabled stream exceptions to catch errors - (`#581 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/581>`_). - Thanks `@crusader-mike <https://github.com/crusader-mike>`_. - -* Allowed formatting of class hierarchies with ``fmt::format_arg()`` - (`#547 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/547>`_). - Thanks `@rollbear (Björn Fahller) <https://github.com/rollbear>`_. - -* Removed limitations on character types - (`#563 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/563>`_). - Thanks `@Yelnats321 (Elnar Dakeshov) <https://github.com/Yelnats321>`_. - -* Conditionally enabled use of ``std::allocator_traits`` - (`#583 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/583>`_). - Thanks `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_. - -* Added support for ``const`` variadic member function emulation with - ``FMT_VARIADIC_CONST`` (`#591 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/591>`_). - Thanks `@ludekvodicka (Ludek Vodicka) <https://github.com/ludekvodicka>`_. - -* Various bugfixes: bad overflow check, unsupported implicit type conversion - when determining formatting function, test segfaults - (`#551 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/551>`_), ill-formed macros - (`#542 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/542>`_) and ambiguous overloads - (`#580 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/580>`_). - Thanks `@xylosper (Byoung-young Lee) <https://github.com/xylosper>`_. - -* Prevented warnings on MSVC (`#605 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/605>`_, - `#602 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/602>`_, and - `#545 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/545>`_), - clang (`#582 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/582>`_), - GCC (`#573 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/573>`_), - various conversion warnings (`#609 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/609>`_, - `#567 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/567>`_, - `#553 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/553>`_ and - `#553 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/553>`_), and added ``override`` and - ``[[noreturn]]`` (`#549 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/549>`_ and - `#555 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/555>`_). - Thanks `@alabuzhev (Alex Alabuzhev) <https://github.com/alabuzhev>`_, - `@virgiliofornazin (Virgilio Alexandre Fornazin) - <https://gihtub.com/virgiliofornazin>`_, - `@alexanderbock (Alexander Bock) <https://github.com/alexanderbock>`_, - `@yumetodo <https://github.com/yumetodo>`_, - `@VaderY (Császár Mátyás) <https://github.com/VaderY>`_, - `@jpcima (JP Cimalando) <https://github.com/jpcima>`_, - `@thelostt (Mário Feroldi) <https://github.com/thelostt>`_, and - `@Manu343726 (Manu Sánchez) <https://github.com/Manu343726>`_. - -* Improved CMake: Used ``GNUInstallDirs`` to set installation location - (`#610 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/610>`_) and fixed warnings - (`#536 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/536>`_ and - `#556 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/556>`_). - Thanks `@mikecrowe (Mike Crowe) <https://github.com/mikecrowe>`_, - `@evgen231 <https://github.com/evgen231>`_ and - `@henryiii (Henry Schreiner) <https://github.com/henryiii>`_. - -4.0.0 - 2017-06-27 ------------------- - -* Removed old compatibility headers ``cppformat/*.h`` and CMake options - (`#527 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/527>`_). - Thanks `@maddinat0r (Alex Martin) <https://github.com/maddinat0r>`_. - -* Added ``string.h`` containing ``fmt::to_string()`` as alternative to - ``std::to_string()`` as well as other string writer functionality - (`#326 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/326>`_ and - `#441 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/441>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include "fmt/string.h" - - std::string answer = fmt::to_string(42); - - Thanks to `@glebov-andrey (Andrey Glebov) - <https://github.com/glebov-andrey>`_. - -* Moved ``fmt::printf()`` to new ``printf.h`` header and allowed ``%s`` as - generic specifier (`#453 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/453>`_), - made ``%.f`` more conformant to regular ``printf()`` - (`#490 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/490>`_), added custom writer - support (`#476 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/476>`_) and implemented - missing custom argument formatting - (`#339 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/339>`_ and - `#340 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/340>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include "fmt/printf.h" - - // %s format specifier can be used with any argument type. - fmt::printf("%s", 42); - - Thanks `@mojoBrendan <https://github.com/mojoBrendan>`_, - `@manylegged (Arthur Danskin) <https://github.com/manylegged>`_ and - `@spacemoose (Glen Stark) <https://github.com/spacemoose>`_. - See also `#360 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/360>`_, - `#335 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/335>`_ and - `#331 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/331>`_. - -* Added ``container.h`` containing a ``BasicContainerWriter`` - to write to containers like ``std::vector`` - (`#450 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/450>`_). - Thanks `@polyvertex (Jean-Charles Lefebvre) <https://github.com/polyvertex>`_. - -* Added ``fmt::join()`` function that takes a range and formats - its elements separated by a given string - (`#466 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/466>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include "fmt/format.h" - - std::vector<double> v = {1.2, 3.4, 5.6}; - // Prints "(+01.20, +03.40, +05.60)". - fmt::print("({:+06.2f})", fmt::join(v.begin(), v.end(), ", ")); - - Thanks `@olivier80 <https://github.com/olivier80>`_. - -* Added support for custom formatting specifications to simplify customization - of built-in formatting (`#444 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/444>`_). - Thanks `@polyvertex (Jean-Charles Lefebvre) <https://github.com/polyvertex>`_. - See also `#439 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/439>`_. - -* Added ``fmt::format_system_error()`` for error code formatting - (`#323 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/323>`_ and - `#526 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/526>`_). - Thanks `@maddinat0r (Alex Martin) <https://github.com/maddinat0r>`_. - -* Added thread-safe ``fmt::localtime()`` and ``fmt::gmtime()`` - as replacement for the standard version to ``time.h`` - (`#396 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/396>`_). - Thanks `@codicodi <https://github.com/codicodi>`_. - -* Internal improvements to ``NamedArg`` and ``ArgLists`` - (`#389 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/389>`_ and - `#390 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/390>`_). - Thanks `@chronoxor <https://github.com/chronoxor>`_. - -* Fixed crash due to bug in ``FormatBuf`` - (`#493 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/493>`_). - Thanks `@effzeh <https://github.com/effzeh>`_. See also - `#480 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/480>`_ and - `#491 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/491>`_. - -* Fixed handling of wide strings in ``fmt::StringWriter``. - -* Improved compiler error messages - (`#357 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/357>`_). - -* Fixed various warnings and issues with various compilers - (`#494 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/494>`_, - `#499 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/499>`_, - `#483 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/483>`_, - `#485 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/485>`_, - `#482 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/482>`_, - `#475 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/475>`_, - `#473 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/473>`_ and - `#414 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/414>`_). - Thanks `@chronoxor <https://github.com/chronoxor>`_, - `@zhaohuaxishi <https://github.com/zhaohuaxishi>`_, - `@pkestene (Pierre Kestener) <https://github.com/pkestene>`_, - `@dschmidt (Dominik Schmidt) <https://github.com/dschmidt>`_ and - `@0x414c (Alexey Gorishny) <https://github.com/0x414c>`_ . - -* Improved CMake: targets are now namespaced - (`#511 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/511>`_ and - `#513 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/513>`_), supported header-only - ``printf.h`` (`#354 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/354>`_), fixed issue - with minimal supported library subset - (`#418 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/418>`_, - `#419 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/419>`_ and - `#420 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/420>`_). - Thanks `@bjoernthiel (Bjoern Thiel) <https://github.com/bjoernthiel>`_, - `@niosHD (Mario Werner) <https://github.com/niosHD>`_, - `@LogicalKnight (Sean LK) <https://github.com/LogicalKnight>`_ and - `@alabuzhev (Alex Alabuzhev) <https://github.com/alabuzhev>`_. - -* Improved documentation. Thanks to - `@pwm1234 (Phil) <https://github.com/pwm1234>`_ for - `#393 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/393>`_. - -3.0.2 - 2017-06-14 ------------------- - -* Added ``FMT_VERSION`` macro - (`#411 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/411>`_). - -* Used ``FMT_NULL`` instead of literal ``0`` - (`#409 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/409>`_). - Thanks `@alabuzhev (Alex Alabuzhev) <https://github.com/alabuzhev>`_. - -* Added extern templates for ``format_float`` - (`#413 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/413>`_). - -* Fixed implicit conversion issue - (`#507 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/507>`_). - -* Fixed signbit detection (`#423 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/423>`_). - -* Fixed naming collision (`#425 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/425>`_). - -* Fixed missing intrinsic for C++/CLI - (`#457 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/457>`_). - Thanks `@calumr (Calum Robinson) <https://github.com/calumr>`_ - -* Fixed Android detection (`#458 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/458>`_). - Thanks `@Gachapen (Magnus Bjerke Vik) <https://github.com/Gachapen>`_. - -* Use lean ``windows.h`` if not in header-only mode - (`#503 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/503>`_). - Thanks `@Quentin01 (Quentin Buathier) <https://github.com/Quentin01>`_. - -* Fixed issue with CMake exporting C++11 flag - (`#445 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/455>`_). - Thanks `@EricWF (Eric) <https://github.com/EricWF>`_. - -* Fixed issue with nvcc and MSVC compiler bug and MinGW - (`#505 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/505>`_). - -* Fixed DLL issues (`#469 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/469>`_ and - `#502 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/502>`_). - Thanks `@richardeakin (Richard Eakin) <https://github.com/richardeakin>`_ and - `@AndreasSchoenle (Andreas Schönle) <https://github.com/AndreasSchoenle>`_. - -* Fixed test compilation under FreeBSD - (`#433 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/433>`_). - -* Fixed various warnings (`#403 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/403>`_, - `#410 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/410>`_ and - `#510 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/510>`_). - Thanks `@Lecetem <https://github.com/Lectem>`_, - `@chenhayat (Chen Hayat) <https://github.com/chenhayat>`_ and - `@trozen <https://github.com/trozen>`_. - -* Worked around a broken ``__builtin_clz`` in clang with MS codegen - (`#519 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/519>`_). - -* Removed redundant include - (`#479 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/479>`_). - -* Fixed documentation issues. - -3.0.1 - 2016-11-01 ------------------- -* Fixed handling of thousands separator - (`#353 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/353>`_). - -* Fixed handling of ``unsigned char`` strings - (`#373 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/373>`_). - -* Corrected buffer growth when formatting time - (`#367 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/367>`_). - -* Removed warnings under MSVC and clang - (`#318 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/318>`_, - `#250 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/250>`_, also merged - `#385 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/385>`_ and - `#361 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/361>`_). - Thanks `@jcelerier (Jean-Michaël Celerier) <https://github.com/jcelerier>`_ - and `@nmoehrle (Nils Moehrle) <https://github.com/nmoehrle>`_. - -* Fixed compilation issues under Android - (`#327 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/327>`_, - `#345 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/345>`_ and - `#381 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/381>`_), - FreeBSD (`#358 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/358>`_), - Cygwin (`#388 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/388>`_), - MinGW (`#355 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/355>`_) as well as other - issues (`#350 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/350>`_, - `#366 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/355>`_, - `#348 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/348>`_, - `#402 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/402>`_, - `#405 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/405>`_). - Thanks to `@dpantele (Dmitry) <https://github.com/dpantele>`_, - `@hghwng (Hugh Wang) <https://github.com/hghwng>`_, - `@arvedarved (Tilman Keskinöz) <https://github.com/arvedarved>`_, - `@LogicalKnight (Sean) <https://github.com/LogicalKnight>`_ and - `@JanHellwig (Jan Hellwig) <https://github.com/janhellwig>`_. - -* Fixed some documentation issues and extended specification - (`#320 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/320>`_, - `#333 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/333>`_, - `#347 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/347>`_, - `#362 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/362>`_). - Thanks to `@smellman (Taro Matsuzawa aka. btm) - <https://github.com/smellman>`_. - -3.0.0 - 2016-05-07 ------------------- - -* The project has been renamed from C++ Format (cppformat) to fmt for - consistency with the used namespace and macro prefix - (`#307 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/307>`_). - Library headers are now located in the ``fmt`` directory: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include "fmt/format.h" - - Including ``format.h`` from the ``cppformat`` directory is deprecated - but works via a proxy header which will be removed in the next major version. - - The documentation is now available at https://fmt.dev. - -* Added support for `strftime <http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/c/strftime>`_-like - `date and time formatting <https://fmt.dev/3.0.0/api.html#date-and-time-formatting>`_ - (`#283 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/283>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - #include "fmt/time.h" - - std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr); - // Prints "The date is 2016-04-29." (with the current date) - fmt::print("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d}.", *std::localtime(&t)); - -* ``std::ostream`` support including formatting of user-defined types that provide - overloaded ``operator<<`` has been moved to ``fmt/ostream.h``: - - .. code:: c++ - - #include "fmt/ostream.h" - - class Date { - int year_, month_, day_; - public: - Date(int year, int month, int day) : year_(year), month_(month), day_(day) {} - - friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Date &d) { - return os << d.year_ << '-' << d.month_ << '-' << d.day_; - } - }; - - std::string s = fmt::format("The date is {}", Date(2012, 12, 9)); - // s == "The date is 2012-12-9" - -* Added support for `custom argument formatters - <https://fmt.dev/3.0.0/api.html#argument-formatters>`_ - (`#235 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/235>`_). - -* Added support for locale-specific integer formatting with the ``n`` specifier - (`#305 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/305>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - std::setlocale(LC_ALL, "en_US.utf8"); - fmt::print("cppformat: {:n}\n", 1234567); // prints 1,234,567 - -* Sign is now preserved when formatting an integer with an incorrect ``printf`` - format specifier (`#265 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/265>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::printf("%lld", -42); // prints -42 - - Note that it would be an undefined behavior in ``std::printf``. - -* Length modifiers such as ``ll`` are now optional in printf formatting - functions and the correct type is determined automatically - (`#255 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/255>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::printf("%d", std::numeric_limits<long long>::max()); - - Note that it would be an undefined behavior in ``std::printf``. - -* Added initial support for custom formatters - (`#231 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/231>`_). - -* Fixed detection of user-defined literal support on Intel C++ compiler - (`#311 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/311>`_, - `#312 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/312>`_). - Thanks to `@dean0x7d (Dean Moldovan) <https://github.com/dean0x7d>`_ and - `@speth (Ray Speth) <https://github.com/speth>`_. - -* Reduced compile time - (`#243 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/243>`_, - `#249 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/249>`_, - `#317 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/317>`_): - - .. image:: https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/4831417/11614060/ - b9e826d2-9c36-11e5-8666-d4131bf503ef.png - - .. image:: https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/4831417/11614080/ - 6ac903cc-9c37-11e5-8165-26df6efae364.png - - Thanks to `@dean0x7d (Dean Moldovan) <https://github.com/dean0x7d>`_. - -* Compile test fixes (`#313 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/313>`_). - Thanks to `@dean0x7d (Dean Moldovan) <https://github.com/dean0x7d>`_. - -* Documentation fixes (`#239 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/239>`_, - `#248 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/248>`_, - `#252 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/252>`_, - `#258 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/258>`_, - `#260 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/260>`_, - `#301 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/301>`_, - `#309 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/309>`_). - Thanks to `@ReadmeCritic <https://github.com/ReadmeCritic>`_ - `@Gachapen (Magnus Bjerke Vik) <https://github.com/Gachapen>`_ and - `@jwilk (Jakub Wilk) <https://github.com/jwilk>`_. - -* Fixed compiler and sanitizer warnings - (`#244 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/244>`_, - `#256 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/256>`_, - `#259 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/259>`_, - `#263 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/263>`_, - `#274 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/274>`_, - `#277 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/277>`_, - `#286 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/286>`_, - `#291 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/291>`_, - `#296 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/296>`_, - `#308 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/308>`_) - Thanks to `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_, - `@pweiskircher (Patrik Weiskircher) <https://github.com/pweiskircher>`_, - `@Naios <https://github.com/Naios>`_. - -* Improved compatibility with Windows Store apps - (`#280 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/280>`_, - `#285 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/285>`_) - Thanks to `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_. - -* Added tests of compatibility with older C++ standards - (`#273 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/273>`_). - Thanks to `@niosHD <https://github.com/niosHD>`_. - -* Fixed Android build (`#271 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/271>`_). - Thanks to `@newnon <https://github.com/newnon>`_. - -* Changed ``ArgMap`` to be backed by a vector instead of a map. - (`#261 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/261>`_, - `#262 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/262>`_). - Thanks to `@mwinterb <https://github.com/mwinterb>`_. - -* Added ``fprintf`` overload that writes to a ``std::ostream`` - (`#251 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/251>`_). - Thanks to `nickhutchinson (Nicholas Hutchinson) <https://github.com/nickhutchinson>`_. - -* Export symbols when building a Windows DLL - (`#245 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/245>`_). - Thanks to `macdems (Maciek Dems) <https://github.com/macdems>`_. - -* Fixed compilation on Cygwin (`#304 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/304>`_). - -* Implemented a workaround for a bug in Apple LLVM version 4.2 of clang - (`#276 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/276>`_). - -* Implemented a workaround for Google Test bug - `#705 <https://github.com/google/googletest/issues/705>`_ on gcc 6 - (`#268 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/268>`_). - Thanks to `octoploid <https://github.com/octoploid>`_. - -* Removed Biicode support because the latter has been discontinued. - -2.1.1 - 2016-04-11 ------------------- - -* The install location for generated CMake files is now configurable via - the ``FMT_CMAKE_DIR`` CMake variable - (`#299 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/299>`_). - Thanks to `@niosHD <https://github.com/niosHD>`_. - -* Documentation fixes (`#252 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/252>`_). - -2.1.0 - 2016-03-21 ------------------- - -* Project layout and build system improvements - (`#267 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/267>`_): - - * The code have been moved to the ``cppformat`` directory. - Including ``format.h`` from the top-level directory is deprecated - but works via a proxy header which will be removed in the next - major version. - - * C++ Format CMake targets now have proper interface definitions. - - * Installed version of the library now supports the header-only - configuration. - - * Targets ``doc``, ``install``, and ``test`` are now disabled if C++ Format - is included as a CMake subproject. They can be enabled by setting - ``FMT_DOC``, ``FMT_INSTALL``, and ``FMT_TEST`` in the parent project. - - Thanks to `@niosHD <https://github.com/niosHD>`_. - -2.0.1 - 2016-03-13 ------------------- - -* Improved CMake find and package support - (`#264 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/264>`_). - Thanks to `@niosHD <https://github.com/niosHD>`_. - -* Fix compile error with Android NDK and mingw32 - (`#241 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/241>`_). - Thanks to `@Gachapen (Magnus Bjerke Vik) <https://github.com/Gachapen>`_. - -* Documentation fixes - (`#248 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/248>`_, - `#260 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/260>`_). - -2.0.0 - 2015-12-01 ------------------- - -General -~~~~~~~ - -* [Breaking] Named arguments - (`#169 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/169>`_, - `#173 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/173>`_, - `#174 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/174>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("The answer is {answer}.", fmt::arg("answer", 42)); - - Thanks to `@jamboree <https://github.com/jamboree>`_. - -* [Experimental] User-defined literals for format and named arguments - (`#204 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/204>`_, - `#206 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/206>`_, - `#207 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/207>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - using namespace fmt::literals; - fmt::print("The answer is {answer}.", "answer"_a=42); - - Thanks to `@dean0x7d (Dean Moldovan) <https://github.com/dean0x7d>`_. - -* [Breaking] Formatting of more than 16 arguments is now supported when using - variadic templates - (`#141 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/141>`_). - Thanks to `@Shauren <https://github.com/Shauren>`_. - -* Runtime width specification - (`#168 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/168>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::format("{0:{1}}", 42, 5); // gives " 42" - - Thanks to `@jamboree <https://github.com/jamboree>`_. - -* [Breaking] Enums are now formatted with an overloaded ``std::ostream`` insertion - operator (``operator<<``) if available - (`#232 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/232>`_). - -* [Breaking] Changed default ``bool`` format to textual, "true" or "false" - (`#170 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/170>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("{}", true); // prints "true" - - To print ``bool`` as a number use numeric format specifier such as ``d``: - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("{:d}", true); // prints "1" - -* ``fmt::printf`` and ``fmt::sprintf`` now support formatting of ``bool`` with the - ``%s`` specifier giving textual output, "true" or "false" - (`#223 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/223>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::printf("%s", true); // prints "true" - - Thanks to `@LarsGullik <https://github.com/LarsGullik>`_. - -* [Breaking] ``signed char`` and ``unsigned char`` are now formatted as integers by default - (`#217 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/217>`_). - -* [Breaking] Pointers to C strings can now be formatted with the ``p`` specifier - (`#223 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/223>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("{:p}", "test"); // prints pointer value - - Thanks to `@LarsGullik <https://github.com/LarsGullik>`_. - -* [Breaking] ``fmt::printf`` and ``fmt::sprintf`` now print null pointers as ``(nil)`` - and null strings as ``(null)`` for consistency with glibc - (`#226 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/226>`_). - Thanks to `@LarsGullik <https://github.com/LarsGullik>`_. - -* [Breaking] ``fmt::(s)printf`` now supports formatting of objects of user-defined types - that provide an overloaded ``std::ostream`` insertion operator (``operator<<``) - (`#201 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/201>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::printf("The date is %s", Date(2012, 12, 9)); - -* [Breaking] The ``Buffer`` template is now part of the public API and can be used - to implement custom memory buffers - (`#140 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/140>`_). - Thanks to `@polyvertex (Jean-Charles Lefebvre) <https://github.com/polyvertex>`_. - -* [Breaking] Improved compatibility between ``BasicStringRef`` and - `std::experimental::basic_string_view - <http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/experimental/basic_string_view>`_ - (`#100 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/100>`_, - `#159 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/159>`_, - `#183 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/183>`_): - - - Comparison operators now compare string content, not pointers - - ``BasicStringRef::c_str`` replaced by ``BasicStringRef::data`` - - ``BasicStringRef`` is no longer assumed to be null-terminated - - References to null-terminated strings are now represented by a new class, - ``BasicCStringRef``. - -* Dependency on pthreads introduced by Google Test is now optional - (`#185 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/185>`_). - -* New CMake options ``FMT_DOC``, ``FMT_INSTALL`` and ``FMT_TEST`` to control - generation of ``doc``, ``install`` and ``test`` targets respectively, on by default - (`#197 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/197>`_, - `#198 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/198>`_, - `#200 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/200>`_). - Thanks to `@maddinat0r (Alex Martin) <https://github.com/maddinat0r>`_. - -* ``noexcept`` is now used when compiling with MSVC2015 - (`#215 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/215>`_). - Thanks to `@dmkrepo (Dmitriy) <https://github.com/dmkrepo>`_. - -* Added an option to disable use of ``windows.h`` when ``FMT_USE_WINDOWS_H`` - is defined as 0 before including ``format.h`` - (`#171 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/171>`_). - Thanks to `@alfps (Alf P. Steinbach) <https://github.com/alfps>`_. - -* [Breaking] ``windows.h`` is now included with ``NOMINMAX`` unless - ``FMT_WIN_MINMAX`` is defined. This is done to prevent breaking code using - ``std::min`` and ``std::max`` and only affects the header-only configuration - (`#152 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/152>`_, - `#153 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/153>`_, - `#154 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/154>`_). - Thanks to `@DevO2012 <https://github.com/DevO2012>`_. - -* Improved support for custom character types - (`#171 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/171>`_). - Thanks to `@alfps (Alf P. Steinbach) <https://github.com/alfps>`_. - -* Added an option to disable use of IOStreams when ``FMT_USE_IOSTREAMS`` - is defined as 0 before including ``format.h`` - (`#205 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/205>`_, - `#208 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/208>`_). - Thanks to `@JodiTheTigger <https://github.com/JodiTheTigger>`_. - -* Improved detection of ``isnan``, ``isinf`` and ``signbit``. - -Optimization -~~~~~~~~~~~~ - -* Made formatting of user-defined types more efficient with a custom stream buffer - (`#92 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/92>`_, - `#230 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/230>`_). - Thanks to `@NotImplemented <https://github.com/NotImplemented>`_. - -* Further improved performance of ``fmt::Writer`` on integer formatting - and fixed a minor regression. Now it is ~7% faster than ``karma::generate`` - on Karma's benchmark - (`#186 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/186>`_). - -* [Breaking] Reduced `compiled code size - <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt#compile-time-and-code-bloat>`_ - (`#143 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/143>`_, - `#149 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/149>`_). - -Distribution -~~~~~~~~~~~~ - -* [Breaking] Headers are now installed in - ``${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX}/include/cppformat`` - (`#178 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/178>`_). - Thanks to `@jackyf (Eugene V. Lyubimkin) <https://github.com/jackyf>`_. - -* [Breaking] Changed the library name from ``format`` to ``cppformat`` - for consistency with the project name and to avoid potential conflicts - (`#178 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/178>`_). - Thanks to `@jackyf (Eugene V. Lyubimkin) <https://github.com/jackyf>`_. - -* C++ Format is now available in `Debian <https://www.debian.org/>`_ GNU/Linux - (`stretch <https://packages.debian.org/source/stretch/cppformat>`_, - `sid <https://packages.debian.org/source/sid/cppformat>`_) and - derived distributions such as - `Ubuntu <https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/cppformat>`_ 15.10 and later - (`#155 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/155>`_):: - - $ sudo apt-get install libcppformat1-dev - - Thanks to `@jackyf (Eugene V. Lyubimkin) <https://github.com/jackyf>`_. - -* `Packages for Fedora and RHEL <https://admin.fedoraproject.org/pkgdb/package/cppformat/>`_ - are now available. Thanks to Dave Johansen. - -* C++ Format can now be installed via `Homebrew <http://brew.sh/>`_ on OS X - (`#157 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/157>`_):: - - $ brew install cppformat - - Thanks to `@ortho <https://github.com/ortho>`_, Anatoliy Bulukin. - -Documentation -~~~~~~~~~~~~~ - -* Migrated from ReadTheDocs to GitHub Pages for better responsiveness - and reliability - (`#128 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/128>`_). - New documentation address is http://cppformat.github.io/. - - -* Added `Building the documentation - <https://fmt.dev/2.0.0/usage.html#building-the-documentation>`_ - section to the documentation. - -* Documentation build script is now compatible with Python 3 and newer pip versions. - (`#189 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/189>`_, - `#209 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/209>`_). - Thanks to `@JodiTheTigger <https://github.com/JodiTheTigger>`_ and - `@xentec <https://github.com/xentec>`_. - -* Documentation fixes and improvements - (`#36 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/36>`_, - `#75 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/75>`_, - `#125 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/125>`_, - `#160 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/160>`_, - `#161 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/161>`_, - `#162 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/162>`_, - `#165 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/165>`_, - `#210 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/210>`_). - Thanks to `@syohex (Syohei YOSHIDA) <https://github.com/syohex>`_ and - bug reporters. - -* Fixed out-of-tree documentation build - (`#177 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/177>`_). - Thanks to `@jackyf (Eugene V. Lyubimkin) <https://github.com/jackyf>`_. - -Fixes -~~~~~ - -* Fixed ``initializer_list`` detection - (`#136 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/136>`_). - Thanks to `@Gachapen (Magnus Bjerke Vik) <https://github.com/Gachapen>`_. - -* [Breaking] Fixed formatting of enums with numeric format specifiers in - ``fmt::(s)printf`` - (`#131 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/131>`_, - `#139 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/139>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - enum { ANSWER = 42 }; - fmt::printf("%d", ANSWER); - - Thanks to `@Naios <https://github.com/Naios>`_. - -* Improved compatibility with old versions of MinGW - (`#129 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/129>`_, - `#130 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/130>`_, - `#132 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/132>`_). - Thanks to `@cstamford (Christopher Stamford) <https://github.com/cstamford>`_. - -* Fixed a compile error on MSVC with disabled exceptions - (`#144 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/144>`_). - -* Added a workaround for broken implementation of variadic templates in MSVC2012 - (`#148 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/148>`_). - -* Placed the anonymous namespace within ``fmt`` namespace for the header-only - configuration - (`#171 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/171>`_). - Thanks to `@alfps (Alf P. Steinbach) <https://github.com/alfps>`_. - -* Fixed issues reported by Coverity Scan - (`#187 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/187>`_, - `#192 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/192>`_). - -* Implemented a workaround for a name lookup bug in MSVC2010 - (`#188 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/188>`_). - -* Fixed compiler warnings - (`#95 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/95>`_, - `#96 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/96>`_, - `#114 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/114>`_, - `#135 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/135>`_, - `#142 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/142>`_, - `#145 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/145>`_, - `#146 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/146>`_, - `#158 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/158>`_, - `#163 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/163>`_, - `#175 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/175>`_, - `#190 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/190>`_, - `#191 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/191>`_, - `#194 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/194>`_, - `#196 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/196>`_, - `#216 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/216>`_, - `#218 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/218>`_, - `#220 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/220>`_, - `#229 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/229>`_, - `#233 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/233>`_, - `#234 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/234>`_, - `#236 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/236>`_, - `#281 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/281>`_, - `#289 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/289>`_). - Thanks to `@seanmiddleditch (Sean Middleditch) <https://github.com/seanmiddleditch>`_, - `@dixlorenz (Dix Lorenz) <https://github.com/dixlorenz>`_, - `@CarterLi (李通洲) <https://github.com/CarterLi>`_, - `@Naios <https://github.com/Naios>`_, - `@fmatthew5876 (Matthew Fioravante) <https://github.com/fmatthew5876>`_, - `@LevskiWeng (Levski Weng) <https://github.com/LevskiWeng>`_, - `@rpopescu <https://github.com/rpopescu>`_, - `@gabime (Gabi Melman) <https://github.com/gabime>`_, - `@cubicool (Jeremy Moles) <https://github.com/cubicool>`_, - `@jkflying (Julian Kent) <https://github.com/jkflying>`_, - `@LogicalKnight (Sean L) <https://github.com/LogicalKnight>`_, - `@inguin (Ingo van Lil) <https://github.com/inguin>`_ and - `@Jopie64 (Johan) <https://github.com/Jopie64>`_. - -* Fixed portability issues (mostly causing test failures) on ARM, ppc64, ppc64le, - s390x and SunOS 5.11 i386 - (`#138 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/138>`_, - `#179 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/179>`_, - `#180 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/180>`_, - `#202 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/202>`_, - `#225 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/225>`_, - `Red Hat Bugzilla Bug 1260297 <https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1260297>`_). - Thanks to `@Naios <https://github.com/Naios>`_, - `@jackyf (Eugene V. Lyubimkin) <https://github.com/jackyf>`_ and Dave Johansen. - -* Fixed a name conflict with macro ``free`` defined in - ``crtdbg.h`` when ``_CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC`` is set - (`#211 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/211>`_). - -* Fixed shared library build on OS X - (`#212 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/212>`_). - Thanks to `@dean0x7d (Dean Moldovan) <https://github.com/dean0x7d>`_. - -* Fixed an overload conflict on MSVC when ``/Zc:wchar_t-`` option is specified - (`#214 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/214>`_). - Thanks to `@slavanap (Vyacheslav Napadovsky) <https://github.com/slavanap>`_. - -* Improved compatibility with MSVC 2008 - (`#236 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/236>`_). - Thanks to `@Jopie64 (Johan) <https://github.com/Jopie64>`_. - -* Improved compatibility with bcc32 - (`#227 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/227>`_). - -* Fixed ``static_assert`` detection on Clang - (`#228 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/228>`_). - Thanks to `@dean0x7d (Dean Moldovan) <https://github.com/dean0x7d>`_. - -1.1.0 - 2015-03-06 ------------------- - -* Added ``BasicArrayWriter``, a class template that provides operations for - formatting and writing data into a fixed-size array - (`#105 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/105>`_ and - `#122 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/122>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - char buffer[100]; - fmt::ArrayWriter w(buffer); - w.write("The answer is {}", 42); - -* Added `0 A.D. <http://play0ad.com/>`_ and `PenUltima Online (POL) - <http://www.polserver.com/>`_ to the list of notable projects using C++ Format. - -* C++ Format now uses MSVC intrinsics for better formatting performance - (`#115 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/115>`_, - `#116 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/116>`_, - `#118 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/118>`_ and - `#121 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/121>`_). - Previously these optimizations where only used on GCC and Clang. - Thanks to `@CarterLi <https://github.com/CarterLi>`_ and - `@objectx <https://github.com/objectx>`_. - -* CMake install target (`#119 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/119>`_). - Thanks to `@TrentHouliston <https://github.com/TrentHouliston>`_. - - You can now install C++ Format with ``make install`` command. - -* Improved `Biicode <http://www.biicode.com/>`_ support - (`#98 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/98>`_ and - `#104 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/104>`_). Thanks to - `@MariadeAnton <https://github.com/MariadeAnton>`_ and - `@franramirez688 <https://github.com/franramirez688>`_. - -* Improved support for building with `Android NDK - <https://developer.android.com/tools/sdk/ndk/index.html>`_ - (`#107 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/107>`_). - Thanks to `@newnon <https://github.com/newnon>`_. - - The `android-ndk-example <https://github.com/fmtlib/android-ndk-example>`_ - repository provides and example of using C++ Format with Android NDK: - - .. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fmtlib/android-ndk-example/ - master/screenshot.png - -* Improved documentation of ``SystemError`` and ``WindowsError`` - (`#54 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/54>`_). - -* Various code improvements - (`#110 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/110>`_, - `#111 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/111>`_ - `#112 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/pull/112>`_). - Thanks to `@CarterLi <https://github.com/CarterLi>`_. - -* Improved compile-time errors when formatting wide into narrow strings - (`#117 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/117>`_). - -* Fixed ``BasicWriter::write`` without formatting arguments when C++11 support - is disabled (`#109 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/109>`_). - -* Fixed header-only build on OS X with GCC 4.9 - (`#124 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/124>`_). - -* Fixed packaging issues (`#94 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/94>`_). - -* Added `changelog <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/ChangeLog.rst>`_ - (`#103 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/103>`_). - -1.0.0 - 2015-02-05 ------------------- - -* Add support for a header-only configuration when ``FMT_HEADER_ONLY`` is - defined before including ``format.h``: - - .. code:: c++ - - #define FMT_HEADER_ONLY - #include "format.h" - -* Compute string length in the constructor of ``BasicStringRef`` - instead of the ``size`` method - (`#79 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/79>`_). - This eliminates size computation for string literals on reasonable optimizing - compilers. - -* Fix formatting of types with overloaded ``operator <<`` for ``std::wostream`` - (`#86 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/86>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::format(L"The date is {0}", Date(2012, 12, 9)); - -* Fix linkage of tests on Arch Linux - (`#89 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/89>`_). - -* Allow precision specifier for non-float arguments - (`#90 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/90>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::print("{:.3}\n", "Carpet"); // prints "Car" - -* Fix build on Android NDK - (`#93 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/93>`_) - -* Improvements to documentation build procedure. - -* Remove ``FMT_SHARED`` CMake variable in favor of standard `BUILD_SHARED_LIBS - <http://www.cmake.org/cmake/help/v3.0/variable/BUILD_SHARED_LIBS.html>`_. - -* Fix error handling in ``fmt::fprintf``. - -* Fix a number of warnings. - -0.12.0 - 2014-10-25 -------------------- - -* [Breaking] Improved separation between formatting and buffer management. - ``Writer`` is now a base class that cannot be instantiated directly. - The new ``MemoryWriter`` class implements the default buffer management - with small allocations done on stack. So ``fmt::Writer`` should be replaced - with ``fmt::MemoryWriter`` in variable declarations. - - Old code: - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::Writer w; - - New code: - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::MemoryWriter w; - - If you pass ``fmt::Writer`` by reference, you can continue to do so: - - .. code:: c++ - - void f(fmt::Writer &w); - - This doesn't affect the formatting API. - -* Support for custom memory allocators - (`#69 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/69>`_) - -* Formatting functions now accept `signed char` and `unsigned char` strings as - arguments (`#73 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/73>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - auto s = format("GLSL version: {}", glGetString(GL_VERSION)); - -* Reduced code bloat. According to the new `benchmark results - <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt#compile-time-and-code-bloat>`_, - cppformat is close to ``printf`` and by the order of magnitude better than - Boost Format in terms of compiled code size. - -* Improved appearance of the documentation on mobile by using the `Sphinx - Bootstrap theme <http://ryan-roemer.github.io/sphinx-bootstrap-theme/>`_: - - .. |old| image:: https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/576385/4792130/ - cd256436-5de3-11e4-9a62-c077d0c2b003.png - - .. |new| image:: https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/576385/4792131/ - cd29896c-5de3-11e4-8f59-cac952942bf0.png - - +-------+-------+ - | Old | New | - +-------+-------+ - | |old| | |new| | - +-------+-------+ - -0.11.0 - 2014-08-21 -------------------- - -* Safe printf implementation with a POSIX extension for positional arguments: - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::printf("Elapsed time: %.2f seconds", 1.23); - fmt::printf("%1$s, %3$d %2$s", weekday, month, day); - -* Arguments of ``char`` type can now be formatted as integers - (Issue `#55 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/55>`_): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::format("0x{0:02X}", 'a'); - -* Deprecated parts of the API removed. - -* The library is now built and tested on MinGW with Appveyor in addition to - existing test platforms Linux/GCC, OS X/Clang, Windows/MSVC. - -0.10.0 - 2014-07-01 -------------------- - -**Improved API** - -* All formatting methods are now implemented as variadic functions instead - of using ``operator<<`` for feeding arbitrary arguments into a temporary - formatter object. This works both with C++11 where variadic templates are - used and with older standards where variadic functions are emulated by - providing lightweight wrapper functions defined with the ``FMT_VARIADIC`` - macro. You can use this macro for defining your own portable variadic - functions: - - .. code:: c++ - - void report_error(const char *format, const fmt::ArgList &args) { - fmt::print("Error: {}"); - fmt::print(format, args); - } - FMT_VARIADIC(void, report_error, const char *) - - report_error("file not found: {}", path); - - Apart from a more natural syntax, this also improves performance as there - is no need to construct temporary formatter objects and control arguments' - lifetimes. Because the wrapper functions are very lightweight, this doesn't - cause code bloat even in pre-C++11 mode. - -* Simplified common case of formatting an ``std::string``. Now it requires a - single function call: - - .. code:: c++ - - std::string s = format("The answer is {}.", 42); - - Previously it required 2 function calls: - - .. code:: c++ - - std::string s = str(Format("The answer is {}.") << 42); - - Instead of unsafe ``c_str`` function, ``fmt::Writer`` should be used directly - to bypass creation of ``std::string``: - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::Writer w; - w.write("The answer is {}.", 42); - w.c_str(); // returns a C string - - This doesn't do dynamic memory allocation for small strings and is less error - prone as the lifetime of the string is the same as for ``std::string::c_str`` - which is well understood (hopefully). - -* Improved consistency in naming functions that are a part of the public API. - Now all public functions are lowercase following the standard library - conventions. Previously it was a combination of lowercase and - CapitalizedWords. - Issue `#50 <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/50>`_. - -* Old functions are marked as deprecated and will be removed in the next - release. - -**Other Changes** - -* Experimental support for printf format specifications (work in progress): - - .. code:: c++ - - fmt::printf("The answer is %d.", 42); - std::string s = fmt::sprintf("Look, a %s!", "string"); - -* Support for hexadecimal floating point format specifiers ``a`` and ``A``: - - .. code:: c++ - - print("{:a}", -42.0); // Prints -0x1.5p+5 - print("{:A}", -42.0); // Prints -0X1.5P+5 - -* CMake option ``FMT_SHARED`` that specifies whether to build format as a - shared library (off by default). - -0.9.0 - 2014-05-13 ------------------- - -* More efficient implementation of variadic formatting functions. - -* ``Writer::Format`` now has a variadic overload: - - .. code:: c++ - - Writer out; - out.Format("Look, I'm {}!", "variadic"); - -* For efficiency and consistency with other overloads, variadic overload of - the ``Format`` function now returns ``Writer`` instead of ``std::string``. - Use the ``str`` function to convert it to ``std::string``: - - .. code:: c++ - - std::string s = str(Format("Look, I'm {}!", "variadic")); - -* Replaced formatter actions with output sinks: ``NoAction`` -> ``NullSink``, - ``Write`` -> ``FileSink``, ``ColorWriter`` -> ``ANSITerminalSink``. - This improves naming consistency and shouldn't affect client code unless - these classes are used directly which should be rarely needed. - -* Added ``ThrowSystemError`` function that formats a message and throws - ``SystemError`` containing the formatted message and system-specific error - description. For example, the following code - - .. code:: c++ - - FILE *f = fopen(filename, "r"); - if (!f) - ThrowSystemError(errno, "Failed to open file '{}'") << filename; - - will throw ``SystemError`` exception with description - "Failed to open file '<filename>': No such file or directory" if file - doesn't exist. - -* Support for AppVeyor continuous integration platform. - -* ``Format`` now throws ``SystemError`` in case of I/O errors. - -* Improve test infrastructure. Print functions are now tested by redirecting - the output to a pipe. - -0.8.0 - 2014-04-14 ------------------- - -* Initial release @@ -1,4 +1,4 @@ -Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich and {fmt} contributors Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the @@ -1,5 +1,5 @@ name: "fmtlib" -description: "{fmt} is an open-source formatting library for C++. It can be used as a safe and fast alternative to (s)printf and iostreams." +description: "{fmt} is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams." third_party { url { type: HOMEPAGE @@ -9,11 +9,11 @@ third_party { type: GIT value: "https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt.git" } - version: "7.1.3" + version: "10.1.1" license_type: NOTICE last_upgrade_date { year: 2020 - month: 11 - day: 25 + month: 12 + day: 7 } } @@ -1,11 +1,16 @@ -{fmt} -===== +.. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/ + 576385/156254208-f5b743a9-88cf-439d-b0c0-923d53e8d551.png + :width: 25% + :alt: {fmt} + +.. image:: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/workflows/linux/badge.svg + :target: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Alinux -.. image:: https://travis-ci.org/fmtlib/fmt.png?branch=master - :target: https://travis-ci.org/fmtlib/fmt +.. image:: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/workflows/macos/badge.svg + :target: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Amacos -.. image:: https://ci.appveyor.com/api/projects/status/ehjkiefde6gucy1v - :target: https://ci.appveyor.com/project/vitaut/fmt +.. image:: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/workflows/windows/badge.svg + :target: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Awindows .. image:: https://oss-fuzz-build-logs.storage.googleapis.com/badges/fmt.svg :alt: fmt is continuously fuzzed at oss-fuzz @@ -17,15 +22,19 @@ :alt: Ask questions at StackOverflow with the tag fmt :target: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt +.. image:: https://api.securityscorecards.dev/projects/github.com/fmtlib/fmt/badge + :target: https://securityscorecards.dev/viewer/?uri=github.com/fmtlib/fmt + **{fmt}** is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams. -If you like this project, please consider donating to BYSOL, -an initiative to help victims of political repressions in Belarus: -https://www.facebook.com/donate/759400044849707/108388587646909/. +If you like this project, please consider donating to one of the funds that +help victims of the war in Ukraine: https://www.stopputin.net/. `Documentation <https://fmt.dev>`__ +`Cheat Sheets <https://hackingcpp.com/cpp/libs/fmt.html>`__ + Q&A: ask questions on `StackOverflow with the tag fmt <https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt>`_. @@ -37,11 +46,14 @@ Features * Simple `format API <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html>`_ with positional arguments for localization * Implementation of `C++20 std::format - <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/format>`__ + <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/format>`__ and `C++23 std::print + <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/io/print>`__ * `Format string syntax <https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html>`_ similar to Python's `format <https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format>`_ * Fast IEEE 754 floating-point formatter with correct rounding, shortness and - round-trip guarantees + round-trip guarantees using the `Dragonbox <https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox>`_ + algorithm +* Portable Unicode support * Safe `printf implementation <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#printf-formatting>`_ including the POSIX extension for positional arguments @@ -58,7 +70,7 @@ Features <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/tree/master/test>`_ and is `continuously fuzzed <https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?colspec=ID%20Type%20 Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20Summary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1>`_ -* Safety: the library is fully type safe, errors in format strings can be +* Safety: the library is fully type-safe, errors in format strings can be reported at compile time, automatic memory management prevents buffer overflow errors * Ease of use: small self-contained code base, no external dependencies, @@ -68,7 +80,7 @@ Features consistent output across platforms and support for older compilers * Clean warning-free codebase even on high warning levels such as ``-Wall -Wextra -pedantic`` -* Locale-independence by default +* Locale independence by default * Optional header-only configuration enabled with the ``FMT_HEADER_ONLY`` macro See the `documentation <https://fmt.dev>`_ for more details. @@ -81,7 +93,7 @@ Examples .. code:: c++ #include <fmt/core.h> - + int main() { fmt::print("Hello, world!\n"); } @@ -117,7 +129,7 @@ Output:: Default format: 42s 100ms strftime-like format: 03:15:30 -**Print a container** (`run <https://godbolt.org/z/MjsY7c>`_) +**Print a container** (`run <https://godbolt.org/z/MxM1YqjE7>`_) .. code:: c++ @@ -131,16 +143,16 @@ Output:: Output:: - {1, 2, 3} + [1, 2, 3] **Check a format string at compile time** .. code:: c++ - std::string s = fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{:d}"), "don't panic"); + std::string s = fmt::format("{:d}", "I am not a number"); -This gives a compile-time error because ``d`` is an invalid format specifier for -a string. +This gives a compile-time error in C++20 because ``d`` is an invalid format +specifier for a string. **Write a file from a single thread** @@ -166,15 +178,15 @@ This can be `5 to 9 times faster than fprintf fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::crimson) | fmt::emphasis::bold, "Hello, {}!\n", "world"); fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::floral_white) | bg(fmt::color::slate_gray) | - fmt::emphasis::underline, "Hello, {}!\n", "мир"); + fmt::emphasis::underline, "Olá, {}!\n", "Mundo"); fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::steel_blue) | fmt::emphasis::italic, - "Hello, {}!\n", "世界"); + "你好{}!\n", "世界"); } -Output on a modern terminal: +Output on a modern terminal with Unicode support: -.. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/ - 576385/88485597-d312f600-cf2b-11ea-9cbe-61f535a86e28.png +.. image:: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/assets/ + 576385/2a93c904-d6fa-4aa6-b453-2618e1c327d7 Benchmarks ---------- @@ -185,24 +197,24 @@ Speed tests ================= ============= =========== Library Method Run Time, s ================= ============= =========== -libc printf 1.04 -libc++ std::ostream 3.05 -{fmt} 6.1.1 fmt::print 0.75 -Boost Format 1.67 boost::format 7.24 -Folly Format folly::format 2.23 +libc printf 0.91 +libc++ std::ostream 2.49 +{fmt} 9.1 fmt::print 0.74 +Boost Format 1.80 boost::format 6.26 +Folly Format folly::format 1.87 ================= ============= =========== -{fmt} is the fastest of the benchmarked methods, ~35% faster than ``printf``. +{fmt} is the fastest of the benchmarked methods, ~20% faster than ``printf``. The above results were generated by building ``tinyformat_test.cpp`` on macOS -10.14.6 with ``clang++ -O3 -DNDEBUG -DSPEED_TEST -DHAVE_FORMAT``, and taking the +12.6.1 with ``clang++ -O3 -DNDEBUG -DSPEED_TEST -DHAVE_FORMAT``, and taking the best of three runs. In the test, the format string ``"%0.10f:%04d:%+g:%s:%p:%c:%%\n"`` or equivalent is filled 2,000,000 times with output sent to ``/dev/null``; for further details refer to the `source -<https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/tinyformat_test.cpp>`_. +<https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/src/tinyformat-test.cc>`_. {fmt} is up to 20-30x faster than ``std::ostringstream`` and ``sprintf`` on -floating-point formatting (`dtoa-benchmark <https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark>`_) +IEEE754 ``float`` and ``double`` formatting (`dtoa-benchmark <https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark>`_) and faster than `double-conversion <https://github.com/google/double-conversion>`_ and `ryu <https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu>`_: @@ -218,7 +230,7 @@ The script `bloat-test.py from `format-benchmark <https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark>`_ tests compile time and code bloat for nontrivial projects. It generates 100 translation units and uses ``printf()`` or its alternative -five times in each to simulate a medium sized project. The resulting +five times in each to simulate a medium-sized project. The resulting executable size and compile time (Apple LLVM version 8.1.0 (clang-802.0.42), macOS Sierra, best of three) is shown in the following tables. @@ -239,7 +251,7 @@ As you can see, {fmt} has 60% less overhead in terms of resulting binary code size compared to iostreams and comes pretty close to ``printf``. Boost Format and Folly Format have the largest overheads. -``printf+string`` is the same as ``printf`` but with extra ``<string>`` +``printf+string`` is the same as ``printf`` but with an extra ``<string>`` include to measure the overhead of the latter. **Non-optimized build** @@ -255,14 +267,14 @@ Boost Format 54.1 365 303 Folly Format 79.9 445 430 ============= =============== ==================== ================== -``libc``, ``lib(std)c++`` and ``libfmt`` are all linked as shared libraries to +``libc``, ``lib(std)c++``, and ``libfmt`` are all linked as shared libraries to compare formatting function overhead only. Boost Format is a header-only library so it doesn't provide any linkage options. Running the tests ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ -Please refer to `Building the library`__ for the instructions on how to build +Please refer to `Building the library`__ for instructions on how to build the library and run the unit tests. __ https://fmt.dev/latest/usage.html#building-the-library @@ -284,6 +296,16 @@ or the bloat test:: $ make bloat-test +Migrating code +-------------- + +`clang-tidy <https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/>`_ v17 (not yet +released) provides the `modernize-use-std-print +<https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/checks/modernize/use-std-print.html>`_ +check that is capable of converting occurrences of ``printf`` and +``fprintf`` to ``fmt::print`` if configured to do so. (By default it +converts to ``std::print``.) + Projects using this library --------------------------- @@ -294,23 +316,25 @@ Projects using this library an open-source library for mathematical programming * `Aseprite <https://github.com/aseprite/aseprite>`_: - animated sprite editor & pixel art tool + animated sprite editor & pixel art tool * `AvioBook <https://www.aviobook.aero/en>`_: a comprehensive aircraft operations suite - + * `Blizzard Battle.net <https://battle.net/>`_: an online gaming platform - + * `Celestia <https://celestia.space/>`_: real-time 3D visualization of space * `Ceph <https://ceph.com/>`_: a scalable distributed storage system * `ccache <https://ccache.dev/>`_: a compiler cache -* `ClickHouse <https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse>`_: analytical database +* `ClickHouse <https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse>`_: an analytical database management system -* `CUAUV <http://cuauv.org/>`_: Cornell University's autonomous underwater +* `Contour <https://github.com/contour-terminal/contour/>`_: a modern terminal emulator + +* `CUAUV <https://cuauv.org/>`_: Cornell University's autonomous underwater vehicle * `Drake <https://drake.mit.edu/>`_: a planning, control, and analysis toolbox @@ -321,8 +345,18 @@ Projects using this library * `FiveM <https://fivem.net/>`_: a modification framework for GTA V +* `fmtlog <https://github.com/MengRao/fmtlog>`_: a performant fmtlib-style + logging library with latency in nanoseconds + * `Folly <https://github.com/facebook/folly>`_: Facebook open-source library +* `GemRB <https://gemrb.org/>`_: a portable open-source implementation of + Bioware’s Infinity Engine + +* `Grand Mountain Adventure + <https://store.steampowered.com/app/1247360/Grand_Mountain_Adventure/>`_: + a beautiful open-world ski & snowboarding game + * `HarpyWar/pvpgn <https://github.com/pvpgn/pvpgn-server>`_: Player vs Player Gaming Network with tweaks @@ -335,6 +369,10 @@ Projects using this library * `Knuth <https://kth.cash/>`_: high-performance Bitcoin full-node +* `libunicode <https://github.com/contour-terminal/libunicode/>`_: a modern C++17 Unicode library + +* `MariaDB <https://mariadb.org/>`_: relational database management system + * `Microsoft Verona <https://github.com/microsoft/verona>`_: research programming language for concurrent ownership @@ -354,7 +392,7 @@ Projects using this library * `quasardb <https://www.quasardb.net/>`_: a distributed, high-performance, associative database - + * `Quill <https://github.com/odygrd/quill>`_: asynchronous low-latency logging library * `QKW <https://github.com/ravijanjam/qkw>`_: generalizing aliasing to simplify @@ -364,7 +402,7 @@ Projects using this library proxy * `redpanda <https://vectorized.io/redpanda>`_: a 10x faster Kafka® replacement - for mission critical systems written in C++ + for mission-critical systems written in C++ * `rpclib <http://rpclib.net/>`_: a modern C++ msgpack-RPC server and client library @@ -388,6 +426,9 @@ Projects using this library * `TrinityCore <https://github.com/TrinityCore/TrinityCore>`_: open-source MMORPG framework +* `🐙 userver framework <https://userver.tech/>`_: open-source asynchronous + framework with a rich set of abstractions and database drivers + * `Windows Terminal <https://github.com/microsoft/terminal>`_: the new Windows terminal @@ -445,16 +486,16 @@ error handling is awkward. Boost Format ~~~~~~~~~~~~ -This is a very powerful library which supports both ``printf``-like format +This is a very powerful library that supports both ``printf``-like format strings and positional arguments. Its main drawback is performance. According to -various, benchmarks it is much slower than other methods considered here. Boost +various benchmarks, it is much slower than other methods considered here. Boost Format also has excessive build times and severe code bloat issues (see `Benchmarks`_). FastFormat ~~~~~~~~~~ -This is an interesting library which is fast, safe and has positional arguments. +This is an interesting library that is fast, safe, and has positional arguments. However, it has significant limitations, citing its author: Three features that have no hope of being accommodated within the @@ -470,7 +511,7 @@ restrictive for using it in some projects. Boost Spirit.Karma ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ -This is not really a formatting library but I decided to include it here for +This is not a formatting library but I decided to include it here for completeness. As iostreams, it suffers from the problem of mixing verbatim text with arguments. The library is pretty fast, but slower on integer formatting than ``fmt::format_to`` with format string compilation on Karma's own benchmark, @@ -481,7 +522,7 @@ License ------- {fmt} is distributed under the MIT `license -<https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE.rst>`_. +<https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE>`_. Documentation License --------------------- @@ -489,7 +530,7 @@ Documentation License The `Format String Syntax <https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html>`_ section in the documentation is based on the one from Python `string module documentation <https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html#module-string>`_. -For this reason the documentation is distributed under the Python Software +For this reason, the documentation is distributed under the Python Software Foundation license available in `doc/python-license.txt <https://raw.github.com/fmtlib/fmt/master/doc/python-license.txt>`_. It only applies if you distribute the documentation of {fmt}. @@ -498,9 +539,15 @@ Maintainers ----------- The {fmt} library is maintained by Victor Zverovich (`vitaut -<https://github.com/vitaut>`_) and Jonathan Müller (`foonathan -<https://github.com/foonathan>`_) with contributions from many other people. +<https://github.com/vitaut>`_) with contributions from many other people. See `Contributors <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/graphs/contributors>`_ and `Releases <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases>`_ for some of the names. Let us know if your contribution is not listed or mentioned incorrectly and we'll make it right. + +Security Policy +--------------- + +To report a security issue, please disclose it at `security advisory <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/security/advisories/new>`_. + +This project is maintained by a team of volunteers on a reasonable-effort basis. As such, please give us at least 90 days to work on a fix before public exposure. diff --git a/TEST_MAPPING b/TEST_MAPPING index c001ee4f..fa4f8a2a 100644 --- a/TEST_MAPPING +++ b/TEST_MAPPING @@ -1,18 +1,24 @@ { - "presubmit": [ + "postsubmit": [ { - "name": "fmtlib_test" + "name": "fmtlib_test_1" }, { - "name": "fmtlib_ostream_test" + "name": "fmtlib_test_2" + }, + { + "name": "fmtlib_test_3" } ], - "hwasan-presubmit": [ + "hwasan-postsubmit": [ + { + "name": "fmtlib_test_1" + }, { - "name": "fmtlib_test" + "name": "fmtlib_test_2" }, { - "name": "fmtlib_ostream_test" + "name": "fmtlib_test_3" } ] } diff --git a/doc/CMakeLists.txt b/doc/CMakeLists.txt index 06848450..fd9f4d1e 100644 --- a/doc/CMakeLists.txt +++ b/doc/CMakeLists.txt @@ -1,10 +1,19 @@ -find_program(DOXYGEN doxygen) +find_program(DOXYGEN doxygen + PATHS "$ENV{ProgramFiles}/doxygen/bin" + "$ENV{ProgramFiles\(x86\)}/doxygen/bin") if (NOT DOXYGEN) message(STATUS "Target 'doc' disabled (requires doxygen)") return () endif () -find_package(PythonInterp QUIET REQUIRED) +# Find the Python interpreter and set the PYTHON_EXECUTABLE variable. +if (CMAKE_VERSION VERSION_LESS 3.12) + # This logic is deprecated in CMake after 3.12. + find_package(PythonInterp QUIET REQUIRED) +else () + find_package(Python QUIET REQUIRED) + set(PYTHON_EXECUTABLE ${Python_EXECUTABLE}) +endif () add_custom_target(doc COMMAND ${PYTHON_EXECUTABLE} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/build.py diff --git a/doc/_static/bootstrap.min.js b/doc/_static/bootstrap.min.js index c8f82e59..c35e1da1 100644 --- a/doc/_static/bootstrap.min.js +++ b/doc/_static/bootstrap.min.js @@ -1,7 +1,7 @@ /*! - * Bootstrap v3.3.4 (http://getbootstrap.com) - * Copyright 2011-2015 Twitter, Inc. - * Licensed under MIT (https://github.com/twbs/bootstrap/blob/master/LICENSE) - */ -if("undefined"==typeof jQuery)throw new Error("Bootstrap's JavaScript requires jQuery");+function(a){"use strict";var b=a.fn.jquery.split(" ")[0].split(".");if(b[0]<2&&b[1]<9||1==b[0]&&9==b[1]&&b[2]<1)throw new Error("Bootstrap's JavaScript requires jQuery version 1.9.1 or higher")}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(){var a=document.createElement("bootstrap"),b={WebkitTransition:"webkitTransitionEnd",MozTransition:"transitionend",OTransition:"oTransitionEnd otransitionend",transition:"transitionend"};for(var c in b)if(void 0!==a.style[c])return{end:b[c]};return!1}a.fn.emulateTransitionEnd=function(b){var c=!1,d=this;a(this).one("bsTransitionEnd",function(){c=!0});var e=function(){c||a(d).trigger(a.support.transition.end)};return setTimeout(e,b),this},a(function(){a.support.transition=b(),a.support.transition&&(a.event.special.bsTransitionEnd={bindType:a.support.transition.end,delegateType:a.support.transition.end,handle:function(b){return a(b.target).is(this)?b.handleObj.handler.apply(this,arguments):void 0}})})}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b){return this.each(function(){var c=a(this),e=c.data("bs.alert");e||c.data("bs.alert",e=new d(this)),"string"==typeof b&&e[b].call(c)})}var c='[data-dismiss="alert"]',d=function(b){a(b).on("click",c,this.close)};d.VERSION="3.3.4",d.TRANSITION_DURATION=150,d.prototype.close=function(b){function c(){g.detach().trigger("closed.bs.alert").remove()}var e=a(this),f=e.attr("data-target");f||(f=e.attr("href"),f=f&&f.replace(/.*(?=#[^\s]*$)/,""));var g=a(f);b&&b.preventDefault(),g.length||(g=e.closest(".alert")),g.trigger(b=a.Event("close.bs.alert")),b.isDefaultPrevented()||(g.removeClass("in"),a.support.transition&&g.hasClass("fade")?g.one("bsTransitionEnd",c).emulateTransitionEnd(d.TRANSITION_DURATION):c())};var e=a.fn.alert;a.fn.alert=b,a.fn.alert.Constructor=d,a.fn.alert.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.alert=e,this},a(document).on("click.bs.alert.data-api",c,d.prototype.close)}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b){return this.each(function(){var d=a(this),e=d.data("bs.button"),f="object"==typeof b&&b;e||d.data("bs.button",e=new c(this,f)),"toggle"==b?e.toggle():b&&e.setState(b)})}var c=function(b,d){this.$element=a(b),this.options=a.extend({},c.DEFAULTS,d),this.isLoading=!1};c.VERSION="3.3.4",c.DEFAULTS={loadingText:"loading..."},c.prototype.setState=function(b){var c="disabled",d=this.$element,e=d.is("input")?"val":"html",f=d.data();b+="Text",null==f.resetText&&d.data("resetText",d[e]()),setTimeout(a.proxy(function(){d[e](null==f[b]?this.options[b]:f[b]),"loadingText"==b?(this.isLoading=!0,d.addClass(c).attr(c,c)):this.isLoading&&(this.isLoading=!1,d.removeClass(c).removeAttr(c))},this),0)},c.prototype.toggle=function(){var a=!0,b=this.$element.closest('[data-toggle="buttons"]');if(b.length){var c=this.$element.find("input");"radio"==c.prop("type")&&(c.prop("checked")&&this.$element.hasClass("active")?a=!1:b.find(".active").removeClass("active")),a&&c.prop("checked",!this.$element.hasClass("active")).trigger("change")}else this.$element.attr("aria-pressed",!this.$element.hasClass("active"));a&&this.$element.toggleClass("active")};var d=a.fn.button;a.fn.button=b,a.fn.button.Constructor=c,a.fn.button.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.button=d,this},a(document).on("click.bs.button.data-api",'[data-toggle^="button"]',function(c){var d=a(c.target);d.hasClass("btn")||(d=d.closest(".btn")),b.call(d,"toggle"),c.preventDefault()}).on("focus.bs.button.data-api blur.bs.button.data-api",'[data-toggle^="button"]',function(b){a(b.target).closest(".btn").toggleClass("focus",/^focus(in)?$/.test(b.type))})}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b){return this.each(function(){var d=a(this),e=d.data("bs.carousel"),f=a.extend({},c.DEFAULTS,d.data(),"object"==typeof b&&b),g="string"==typeof b?b:f.slide;e||d.data("bs.carousel",e=new c(this,f)),"number"==typeof b?e.to(b):g?e[g]():f.interval&&e.pause().cycle()})}var c=function(b,c){this.$element=a(b),this.$indicators=this.$element.find(".carousel-indicators"),this.options=c,this.paused=null,this.sliding=null,this.interval=null,this.$active=null,this.$items=null,this.options.keyboard&&this.$element.on("keydown.bs.carousel",a.proxy(this.keydown,this)),"hover"==this.options.pause&&!("ontouchstart"in document.documentElement)&&this.$element.on("mouseenter.bs.carousel",a.proxy(this.pause,this)).on("mouseleave.bs.carousel",a.proxy(this.cycle,this))};c.VERSION="3.3.4",c.TRANSITION_DURATION=600,c.DEFAULTS={interval:5e3,pause:"hover",wrap:!0,keyboard:!0},c.prototype.keydown=function(a){if(!/input|textarea/i.test(a.target.tagName)){switch(a.which){case 37:this.prev();break;case 39:this.next();break;default:return}a.preventDefault()}},c.prototype.cycle=function(b){return b||(this.paused=!1),this.interval&&clearInterval(this.interval),this.options.interval&&!this.paused&&(this.interval=setInterval(a.proxy(this.next,this),this.options.interval)),this},c.prototype.getItemIndex=function(a){return this.$items=a.parent().children(".item"),this.$items.index(a||this.$active)},c.prototype.getItemForDirection=function(a,b){var c=this.getItemIndex(b),d="prev"==a&&0===c||"next"==a&&c==this.$items.length-1;if(d&&!this.options.wrap)return b;var e="prev"==a?-1:1,f=(c+e)%this.$items.length;return this.$items.eq(f)},c.prototype.to=function(a){var b=this,c=this.getItemIndex(this.$active=this.$element.find(".item.active"));return a>this.$items.length-1||0>a?void 0:this.sliding?this.$element.one("slid.bs.carousel",function(){b.to(a)}):c==a?this.pause().cycle():this.slide(a>c?"next":"prev",this.$items.eq(a))},c.prototype.pause=function(b){return b||(this.paused=!0),this.$element.find(".next, .prev").length&&a.support.transition&&(this.$element.trigger(a.support.transition.end),this.cycle(!0)),this.interval=clearInterval(this.interval),this},c.prototype.next=function(){return this.sliding?void 0:this.slide("next")},c.prototype.prev=function(){return this.sliding?void 0:this.slide("prev")},c.prototype.slide=function(b,d){var e=this.$element.find(".item.active"),f=d||this.getItemForDirection(b,e),g=this.interval,h="next"==b?"left":"right",i=this;if(f.hasClass("active"))return this.sliding=!1;var j=f[0],k=a.Event("slide.bs.carousel",{relatedTarget:j,direction:h});if(this.$element.trigger(k),!k.isDefaultPrevented()){if(this.sliding=!0,g&&this.pause(),this.$indicators.length){this.$indicators.find(".active").removeClass("active");var l=a(this.$indicators.children()[this.getItemIndex(f)]);l&&l.addClass("active")}var m=a.Event("slid.bs.carousel",{relatedTarget:j,direction:h});return a.support.transition&&this.$element.hasClass("slide")?(f.addClass(b),f[0].offsetWidth,e.addClass(h),f.addClass(h),e.one("bsTransitionEnd",function(){f.removeClass([b,h].join(" ")).addClass("active"),e.removeClass(["active",h].join(" ")),i.sliding=!1,setTimeout(function(){i.$element.trigger(m)},0)}).emulateTransitionEnd(c.TRANSITION_DURATION)):(e.removeClass("active"),f.addClass("active"),this.sliding=!1,this.$element.trigger(m)),g&&this.cycle(),this}};var d=a.fn.carousel;a.fn.carousel=b,a.fn.carousel.Constructor=c,a.fn.carousel.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.carousel=d,this};var e=function(c){var d,e=a(this),f=a(e.attr("data-target")||(d=e.attr("href"))&&d.replace(/.*(?=#[^\s]+$)/,""));if(f.hasClass("carousel")){var g=a.extend({},f.data(),e.data()),h=e.attr("data-slide-to");h&&(g.interval=!1),b.call(f,g),h&&f.data("bs.carousel").to(h),c.preventDefault()}};a(document).on("click.bs.carousel.data-api","[data-slide]",e).on("click.bs.carousel.data-api","[data-slide-to]",e),a(window).on("load",function(){a('[data-ride="carousel"]').each(function(){var c=a(this);b.call(c,c.data())})})}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b){var c,d=b.attr("data-target")||(c=b.attr("href"))&&c.replace(/.*(?=#[^\s]+$)/,"");return a(d)}function c(b){return this.each(function(){var c=a(this),e=c.data("bs.collapse"),f=a.extend({},d.DEFAULTS,c.data(),"object"==typeof b&&b);!e&&f.toggle&&/show|hide/.test(b)&&(f.toggle=!1),e||c.data("bs.collapse",e=new d(this,f)),"string"==typeof b&&e[b]()})}var d=function(b,c){this.$element=a(b),this.options=a.extend({},d.DEFAULTS,c),this.$trigger=a('[data-toggle="collapse"][href="#'+b.id+'"],[data-toggle="collapse"][data-target="#'+b.id+'"]'),this.transitioning=null,this.options.parent?this.$parent=this.getParent():this.addAriaAndCollapsedClass(this.$element,this.$trigger),this.options.toggle&&this.toggle()};d.VERSION="3.3.4",d.TRANSITION_DURATION=350,d.DEFAULTS={toggle:!0},d.prototype.dimension=function(){var a=this.$element.hasClass("width");return a?"width":"height"},d.prototype.show=function(){if(!this.transitioning&&!this.$element.hasClass("in")){var b,e=this.$parent&&this.$parent.children(".panel").children(".in, .collapsing");if(!(e&&e.length&&(b=e.data("bs.collapse"),b&&b.transitioning))){var f=a.Event("show.bs.collapse");if(this.$element.trigger(f),!f.isDefaultPrevented()){e&&e.length&&(c.call(e,"hide"),b||e.data("bs.collapse",null));var g=this.dimension();this.$element.removeClass("collapse").addClass("collapsing")[g](0).attr("aria-expanded",!0),this.$trigger.removeClass("collapsed").attr("aria-expanded",!0),this.transitioning=1;var h=function(){this.$element.removeClass("collapsing").addClass("collapse in")[g](""),this.transitioning=0,this.$element.trigger("shown.bs.collapse")};if(!a.support.transition)return h.call(this);var i=a.camelCase(["scroll",g].join("-"));this.$element.one("bsTransitionEnd",a.proxy(h,this)).emulateTransitionEnd(d.TRANSITION_DURATION)[g](this.$element[0][i])}}}},d.prototype.hide=function(){if(!this.transitioning&&this.$element.hasClass("in")){var b=a.Event("hide.bs.collapse");if(this.$element.trigger(b),!b.isDefaultPrevented()){var c=this.dimension();this.$element[c](this.$element[c]())[0].offsetHeight,this.$element.addClass("collapsing").removeClass("collapse in").attr("aria-expanded",!1),this.$trigger.addClass("collapsed").attr("aria-expanded",!1),this.transitioning=1;var e=function(){this.transitioning=0,this.$element.removeClass("collapsing").addClass("collapse").trigger("hidden.bs.collapse")};return a.support.transition?void this.$element[c](0).one("bsTransitionEnd",a.proxy(e,this)).emulateTransitionEnd(d.TRANSITION_DURATION):e.call(this)}}},d.prototype.toggle=function(){this[this.$element.hasClass("in")?"hide":"show"]()},d.prototype.getParent=function(){return a(this.options.parent).find('[data-toggle="collapse"][data-parent="'+this.options.parent+'"]').each(a.proxy(function(c,d){var e=a(d);this.addAriaAndCollapsedClass(b(e),e)},this)).end()},d.prototype.addAriaAndCollapsedClass=function(a,b){var c=a.hasClass("in");a.attr("aria-expanded",c),b.toggleClass("collapsed",!c).attr("aria-expanded",c)};var e=a.fn.collapse;a.fn.collapse=c,a.fn.collapse.Constructor=d,a.fn.collapse.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.collapse=e,this},a(document).on("click.bs.collapse.data-api",'[data-toggle="collapse"]',function(d){var e=a(this);e.attr("data-target")||d.preventDefault();var f=b(e),g=f.data("bs.collapse"),h=g?"toggle":e.data();c.call(f,h)})}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b){b&&3===b.which||(a(e).remove(),a(f).each(function(){var d=a(this),e=c(d),f={relatedTarget:this};e.hasClass("open")&&(e.trigger(b=a.Event("hide.bs.dropdown",f)),b.isDefaultPrevented()||(d.attr("aria-expanded","false"),e.removeClass("open").trigger("hidden.bs.dropdown",f)))}))}function c(b){var c=b.attr("data-target");c||(c=b.attr("href"),c=c&&/#[A-Za-z]/.test(c)&&c.replace(/.*(?=#[^\s]*$)/,""));var d=c&&a(c);return d&&d.length?d:b.parent()}function d(b){return this.each(function(){var c=a(this),d=c.data("bs.dropdown");d||c.data("bs.dropdown",d=new g(this)),"string"==typeof b&&d[b].call(c)})}var e=".dropdown-backdrop",f='[data-toggle="dropdown"]',g=function(b){a(b).on("click.bs.dropdown",this.toggle)};g.VERSION="3.3.4",g.prototype.toggle=function(d){var e=a(this);if(!e.is(".disabled, :disabled")){var f=c(e),g=f.hasClass("open");if(b(),!g){"ontouchstart"in document.documentElement&&!f.closest(".navbar-nav").length&&a('<div class="dropdown-backdrop"/>').insertAfter(a(this)).on("click",b);var h={relatedTarget:this};if(f.trigger(d=a.Event("show.bs.dropdown",h)),d.isDefaultPrevented())return;e.trigger("focus").attr("aria-expanded","true"),f.toggleClass("open").trigger("shown.bs.dropdown",h)}return!1}},g.prototype.keydown=function(b){if(/(38|40|27|32)/.test(b.which)&&!/input|textarea/i.test(b.target.tagName)){var d=a(this);if(b.preventDefault(),b.stopPropagation(),!d.is(".disabled, :disabled")){var e=c(d),g=e.hasClass("open");if(!g&&27!=b.which||g&&27==b.which)return 27==b.which&&e.find(f).trigger("focus"),d.trigger("click");var h=" li:not(.disabled):visible a",i=e.find('[role="menu"]'+h+', [role="listbox"]'+h);if(i.length){var j=i.index(b.target);38==b.which&&j>0&&j--,40==b.which&&j<i.length-1&&j++,~j||(j=0),i.eq(j).trigger("focus")}}}};var h=a.fn.dropdown;a.fn.dropdown=d,a.fn.dropdown.Constructor=g,a.fn.dropdown.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.dropdown=h,this},a(document).on("click.bs.dropdown.data-api",b).on("click.bs.dropdown.data-api",".dropdown form",function(a){a.stopPropagation()}).on("click.bs.dropdown.data-api",f,g.prototype.toggle).on("keydown.bs.dropdown.data-api",f,g.prototype.keydown).on("keydown.bs.dropdown.data-api",'[role="menu"]',g.prototype.keydown).on("keydown.bs.dropdown.data-api",'[role="listbox"]',g.prototype.keydown)}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b,d){return this.each(function(){var e=a(this),f=e.data("bs.modal"),g=a.extend({},c.DEFAULTS,e.data(),"object"==typeof b&&b);f||e.data("bs.modal",f=new c(this,g)),"string"==typeof b?f[b](d):g.show&&f.show(d)})}var c=function(b,c){this.options=c,this.$body=a(document.body),this.$element=a(b),this.$dialog=this.$element.find(".modal-dialog"),this.$backdrop=null,this.isShown=null,this.originalBodyPad=null,this.scrollbarWidth=0,this.ignoreBackdropClick=!1,this.options.remote&&this.$element.find(".modal-content").load(this.options.remote,a.proxy(function(){this.$element.trigger("loaded.bs.modal")},this))};c.VERSION="3.3.4",c.TRANSITION_DURATION=300,c.BACKDROP_TRANSITION_DURATION=150,c.DEFAULTS={backdrop:!0,keyboard:!0,show:!0},c.prototype.toggle=function(a){return this.isShown?this.hide():this.show(a)},c.prototype.show=function(b){var d=this,e=a.Event("show.bs.modal",{relatedTarget:b});this.$element.trigger(e),this.isShown||e.isDefaultPrevented()||(this.isShown=!0,this.checkScrollbar(),this.setScrollbar(),this.$body.addClass("modal-open"),this.escape(),this.resize(),this.$element.on("click.dismiss.bs.modal",'[data-dismiss="modal"]',a.proxy(this.hide,this)),this.$dialog.on("mousedown.dismiss.bs.modal",function(){d.$element.one("mouseup.dismiss.bs.modal",function(b){a(b.target).is(d.$element)&&(d.ignoreBackdropClick=!0)})}),this.backdrop(function(){var e=a.support.transition&&d.$element.hasClass("fade");d.$element.parent().length||d.$element.appendTo(d.$body),d.$element.show().scrollTop(0),d.adjustDialog(),e&&d.$element[0].offsetWidth,d.$element.addClass("in").attr("aria-hidden",!1),d.enforceFocus();var f=a.Event("shown.bs.modal",{relatedTarget:b});e?d.$dialog.one("bsTransitionEnd",function(){d.$element.trigger("focus").trigger(f)}).emulateTransitionEnd(c.TRANSITION_DURATION):d.$element.trigger("focus").trigger(f)}))},c.prototype.hide=function(b){b&&b.preventDefault(),b=a.Event("hide.bs.modal"),this.$element.trigger(b),this.isShown&&!b.isDefaultPrevented()&&(this.isShown=!1,this.escape(),this.resize(),a(document).off("focusin.bs.modal"),this.$element.removeClass("in").attr("aria-hidden",!0).off("click.dismiss.bs.modal").off("mouseup.dismiss.bs.modal"),this.$dialog.off("mousedown.dismiss.bs.modal"),a.support.transition&&this.$element.hasClass("fade")?this.$element.one("bsTransitionEnd",a.proxy(this.hideModal,this)).emulateTransitionEnd(c.TRANSITION_DURATION):this.hideModal())},c.prototype.enforceFocus=function(){a(document).off("focusin.bs.modal").on("focusin.bs.modal",a.proxy(function(a){this.$element[0]===a.target||this.$element.has(a.target).length||this.$element.trigger("focus")},this))},c.prototype.escape=function(){this.isShown&&this.options.keyboard?this.$element.on("keydown.dismiss.bs.modal",a.proxy(function(a){27==a.which&&this.hide()},this)):this.isShown||this.$element.off("keydown.dismiss.bs.modal")},c.prototype.resize=function(){this.isShown?a(window).on("resize.bs.modal",a.proxy(this.handleUpdate,this)):a(window).off("resize.bs.modal")},c.prototype.hideModal=function(){var a=this;this.$element.hide(),this.backdrop(function(){a.$body.removeClass("modal-open"),a.resetAdjustments(),a.resetScrollbar(),a.$element.trigger("hidden.bs.modal")})},c.prototype.removeBackdrop=function(){this.$backdrop&&this.$backdrop.remove(),this.$backdrop=null},c.prototype.backdrop=function(b){var d=this,e=this.$element.hasClass("fade")?"fade":"";if(this.isShown&&this.options.backdrop){var f=a.support.transition&&e;if(this.$backdrop=a('<div class="modal-backdrop '+e+'" />').appendTo(this.$body),this.$element.on("click.dismiss.bs.modal",a.proxy(function(a){return this.ignoreBackdropClick?void(this.ignoreBackdropClick=!1):void(a.target===a.currentTarget&&("static"==this.options.backdrop?this.$element[0].focus():this.hide()))},this)),f&&this.$backdrop[0].offsetWidth,this.$backdrop.addClass("in"),!b)return;f?this.$backdrop.one("bsTransitionEnd",b).emulateTransitionEnd(c.BACKDROP_TRANSITION_DURATION):b()}else if(!this.isShown&&this.$backdrop){this.$backdrop.removeClass("in");var g=function(){d.removeBackdrop(),b&&b()};a.support.transition&&this.$element.hasClass("fade")?this.$backdrop.one("bsTransitionEnd",g).emulateTransitionEnd(c.BACKDROP_TRANSITION_DURATION):g()}else b&&b()},c.prototype.handleUpdate=function(){this.adjustDialog()},c.prototype.adjustDialog=function(){var a=this.$element[0].scrollHeight>document.documentElement.clientHeight;this.$element.css({paddingLeft:!this.bodyIsOverflowing&&a?this.scrollbarWidth:"",paddingRight:this.bodyIsOverflowing&&!a?this.scrollbarWidth:""})},c.prototype.resetAdjustments=function(){this.$element.css({paddingLeft:"",paddingRight:""})},c.prototype.checkScrollbar=function(){var a=window.innerWidth;if(!a){var b=document.documentElement.getBoundingClientRect();a=b.right-Math.abs(b.left)}this.bodyIsOverflowing=document.body.clientWidth<a,this.scrollbarWidth=this.measureScrollbar()},c.prototype.setScrollbar=function(){var a=parseInt(this.$body.css("padding-right")||0,10);this.originalBodyPad=document.body.style.paddingRight||"",this.bodyIsOverflowing&&this.$body.css("padding-right",a+this.scrollbarWidth)},c.prototype.resetScrollbar=function(){this.$body.css("padding-right",this.originalBodyPad)},c.prototype.measureScrollbar=function(){var a=document.createElement("div");a.className="modal-scrollbar-measure",this.$body.append(a);var b=a.offsetWidth-a.clientWidth;return this.$body[0].removeChild(a),b};var d=a.fn.modal;a.fn.modal=b,a.fn.modal.Constructor=c,a.fn.modal.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.modal=d,this},a(document).on("click.bs.modal.data-api",'[data-toggle="modal"]',function(c){var d=a(this),e=d.attr("href"),f=a(d.attr("data-target")||e&&e.replace(/.*(?=#[^\s]+$)/,"")),g=f.data("bs.modal")?"toggle":a.extend({remote:!/#/.test(e)&&e},f.data(),d.data());d.is("a")&&c.preventDefault(),f.one("show.bs.modal",function(a){a.isDefaultPrevented()||f.one("hidden.bs.modal",function(){d.is(":visible")&&d.trigger("focus")})}),b.call(f,g,this)})}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b){return this.each(function(){var d=a(this),e=d.data("bs.tooltip"),f="object"==typeof b&&b;(e||!/destroy|hide/.test(b))&&(e||d.data("bs.tooltip",e=new c(this,f)),"string"==typeof b&&e[b]())})}var c=function(a,b){this.type=null,this.options=null,this.enabled=null,this.timeout=null,this.hoverState=null,this.$element=null,this.init("tooltip",a,b)};c.VERSION="3.3.4",c.TRANSITION_DURATION=150,c.DEFAULTS={animation:!0,placement:"top",selector:!1,template:'<div class="tooltip" role="tooltip"><div class="tooltip-arrow"></div><div class="tooltip-inner"></div></div>',trigger:"hover focus",title:"",delay:0,html:!1,container:!1,viewport:{selector:"body",padding:0}},c.prototype.init=function(b,c,d){if(this.enabled=!0,this.type=b,this.$element=a(c),this.options=this.getOptions(d),this.$viewport=this.options.viewport&&a(this.options.viewport.selector||this.options.viewport),this.$element[0]instanceof document.constructor&&!this.options.selector)throw new Error("`selector` option must be specified when initializing "+this.type+" on the window.document object!");for(var e=this.options.trigger.split(" "),f=e.length;f--;){var g=e[f];if("click"==g)this.$element.on("click."+this.type,this.options.selector,a.proxy(this.toggle,this));else if("manual"!=g){var h="hover"==g?"mouseenter":"focusin",i="hover"==g?"mouseleave":"focusout";this.$element.on(h+"."+this.type,this.options.selector,a.proxy(this.enter,this)),this.$element.on(i+"."+this.type,this.options.selector,a.proxy(this.leave,this))}}this.options.selector?this._options=a.extend({},this.options,{trigger:"manual",selector:""}):this.fixTitle()},c.prototype.getDefaults=function(){return c.DEFAULTS},c.prototype.getOptions=function(b){return b=a.extend({},this.getDefaults(),this.$element.data(),b),b.delay&&"number"==typeof b.delay&&(b.delay={show:b.delay,hide:b.delay}),b},c.prototype.getDelegateOptions=function(){var b={},c=this.getDefaults();return this._options&&a.each(this._options,function(a,d){c[a]!=d&&(b[a]=d)}),b},c.prototype.enter=function(b){var c=b instanceof this.constructor?b:a(b.currentTarget).data("bs."+this.type);return c&&c.$tip&&c.$tip.is(":visible")?void(c.hoverState="in"):(c||(c=new this.constructor(b.currentTarget,this.getDelegateOptions()),a(b.currentTarget).data("bs."+this.type,c)),clearTimeout(c.timeout),c.hoverState="in",c.options.delay&&c.options.delay.show?void(c.timeout=setTimeout(function(){"in"==c.hoverState&&c.show()},c.options.delay.show)):c.show())},c.prototype.leave=function(b){var c=b instanceof this.constructor?b:a(b.currentTarget).data("bs."+this.type);return c||(c=new this.constructor(b.currentTarget,this.getDelegateOptions()),a(b.currentTarget).data("bs."+this.type,c)),clearTimeout(c.timeout),c.hoverState="out",c.options.delay&&c.options.delay.hide?void(c.timeout=setTimeout(function(){"out"==c.hoverState&&c.hide()},c.options.delay.hide)):c.hide()},c.prototype.show=function(){var b=a.Event("show.bs."+this.type);if(this.hasContent()&&this.enabled){this.$element.trigger(b);var d=a.contains(this.$element[0].ownerDocument.documentElement,this.$element[0]);if(b.isDefaultPrevented()||!d)return;var e=this,f=this.tip(),g=this.getUID(this.type);this.setContent(),f.attr("id",g),this.$element.attr("aria-describedby",g),this.options.animation&&f.addClass("fade");var h="function"==typeof this.options.placement?this.options.placement.call(this,f[0],this.$element[0]):this.options.placement,i=/\s?auto?\s?/i,j=i.test(h);j&&(h=h.replace(i,"")||"top"),f.detach().css({top:0,left:0,display:"block"}).addClass(h).data("bs."+this.type,this),this.options.container?f.appendTo(this.options.container):f.insertAfter(this.$element);var k=this.getPosition(),l=f[0].offsetWidth,m=f[0].offsetHeight;if(j){var n=h,o=this.options.container?a(this.options.container):this.$element.parent(),p=this.getPosition(o);h="bottom"==h&&k.bottom+m>p.bottom?"top":"top"==h&&k.top-m<p.top?"bottom":"right"==h&&k.right+l>p.width?"left":"left"==h&&k.left-l<p.left?"right":h,f.removeClass(n).addClass(h)}var q=this.getCalculatedOffset(h,k,l,m);this.applyPlacement(q,h);var r=function(){var a=e.hoverState;e.$element.trigger("shown.bs."+e.type),e.hoverState=null,"out"==a&&e.leave(e)};a.support.transition&&this.$tip.hasClass("fade")?f.one("bsTransitionEnd",r).emulateTransitionEnd(c.TRANSITION_DURATION):r()}},c.prototype.applyPlacement=function(b,c){var d=this.tip(),e=d[0].offsetWidth,f=d[0].offsetHeight,g=parseInt(d.css("margin-top"),10),h=parseInt(d.css("margin-left"),10);isNaN(g)&&(g=0),isNaN(h)&&(h=0),b.top=b.top+g,b.left=b.left+h,a.offset.setOffset(d[0],a.extend({using:function(a){d.css({top:Math.round(a.top),left:Math.round(a.left)})}},b),0),d.addClass("in");var i=d[0].offsetWidth,j=d[0].offsetHeight;"top"==c&&j!=f&&(b.top=b.top+f-j);var k=this.getViewportAdjustedDelta(c,b,i,j);k.left?b.left+=k.left:b.top+=k.top;var l=/top|bottom/.test(c),m=l?2*k.left-e+i:2*k.top-f+j,n=l?"offsetWidth":"offsetHeight";d.offset(b),this.replaceArrow(m,d[0][n],l)},c.prototype.replaceArrow=function(a,b,c){this.arrow().css(c?"left":"top",50*(1-a/b)+"%").css(c?"top":"left","")},c.prototype.setContent=function(){var a=this.tip(),b=this.getTitle();a.find(".tooltip-inner")[this.options.html?"html":"text"](b),a.removeClass("fade in top bottom left right")},c.prototype.hide=function(b){function d(){"in"!=e.hoverState&&f.detach(),e.$element.removeAttr("aria-describedby").trigger("hidden.bs."+e.type),b&&b()}var e=this,f=a(this.$tip),g=a.Event("hide.bs."+this.type);return this.$element.trigger(g),g.isDefaultPrevented()?void 0:(f.removeClass("in"),a.support.transition&&f.hasClass("fade")?f.one("bsTransitionEnd",d).emulateTransitionEnd(c.TRANSITION_DURATION):d(),this.hoverState=null,this)},c.prototype.fixTitle=function(){var a=this.$element;(a.attr("title")||"string"!=typeof a.attr("data-original-title"))&&a.attr("data-original-title",a.attr("title")||"").attr("title","")},c.prototype.hasContent=function(){return this.getTitle()},c.prototype.getPosition=function(b){b=b||this.$element;var c=b[0],d="BODY"==c.tagName,e=c.getBoundingClientRect();null==e.width&&(e=a.extend({},e,{width:e.right-e.left,height:e.bottom-e.top}));var f=d?{top:0,left:0}:b.offset(),g={scroll:d?document.documentElement.scrollTop||document.body.scrollTop:b.scrollTop()},h=d?{width:a(window).width(),height:a(window).height()}:null;return a.extend({},e,g,h,f)},c.prototype.getCalculatedOffset=function(a,b,c,d){return"bottom"==a?{top:b.top+b.height,left:b.left+b.width/2-c/2}:"top"==a?{top:b.top-d,left:b.left+b.width/2-c/2}:"left"==a?{top:b.top+b.height/2-d/2,left:b.left-c}:{top:b.top+b.height/2-d/2,left:b.left+b.width}},c.prototype.getViewportAdjustedDelta=function(a,b,c,d){var e={top:0,left:0};if(!this.$viewport)return e;var f=this.options.viewport&&this.options.viewport.padding||0,g=this.getPosition(this.$viewport);if(/right|left/.test(a)){var h=b.top-f-g.scroll,i=b.top+f-g.scroll+d;h<g.top?e.top=g.top-h:i>g.top+g.height&&(e.top=g.top+g.height-i)}else{var j=b.left-f,k=b.left+f+c;j<g.left?e.left=g.left-j:k>g.width&&(e.left=g.left+g.width-k)}return e},c.prototype.getTitle=function(){var a,b=this.$element,c=this.options;return a=b.attr("data-original-title")||("function"==typeof c.title?c.title.call(b[0]):c.title)},c.prototype.getUID=function(a){do a+=~~(1e6*Math.random());while(document.getElementById(a));return a},c.prototype.tip=function(){return this.$tip=this.$tip||a(this.options.template)},c.prototype.arrow=function(){return this.$arrow=this.$arrow||this.tip().find(".tooltip-arrow")},c.prototype.enable=function(){this.enabled=!0},c.prototype.disable=function(){this.enabled=!1},c.prototype.toggleEnabled=function(){this.enabled=!this.enabled},c.prototype.toggle=function(b){var c=this;b&&(c=a(b.currentTarget).data("bs."+this.type),c||(c=new this.constructor(b.currentTarget,this.getDelegateOptions()),a(b.currentTarget).data("bs."+this.type,c))),c.tip().hasClass("in")?c.leave(c):c.enter(c)},c.prototype.destroy=function(){var a=this;clearTimeout(this.timeout),this.hide(function(){a.$element.off("."+a.type).removeData("bs."+a.type)})};var d=a.fn.tooltip;a.fn.tooltip=b,a.fn.tooltip.Constructor=c,a.fn.tooltip.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.tooltip=d,this}}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b){return this.each(function(){var d=a(this),e=d.data("bs.popover"),f="object"==typeof b&&b;(e||!/destroy|hide/.test(b))&&(e||d.data("bs.popover",e=new c(this,f)),"string"==typeof b&&e[b]())})}var c=function(a,b){this.init("popover",a,b)};if(!a.fn.tooltip)throw new Error("Popover requires tooltip.js");c.VERSION="3.3.4",c.DEFAULTS=a.extend({},a.fn.tooltip.Constructor.DEFAULTS,{placement:"right",trigger:"click",content:"",template:'<div class="popover" role="tooltip"><div class="arrow"></div><h3 class="popover-title"></h3><div class="popover-content"></div></div>'}),c.prototype=a.extend({},a.fn.tooltip.Constructor.prototype),c.prototype.constructor=c,c.prototype.getDefaults=function(){return c.DEFAULTS},c.prototype.setContent=function(){var a=this.tip(),b=this.getTitle(),c=this.getContent();a.find(".popover-title")[this.options.html?"html":"text"](b),a.find(".popover-content").children().detach().end()[this.options.html?"string"==typeof c?"html":"append":"text"](c),a.removeClass("fade top bottom left right in"),a.find(".popover-title").html()||a.find(".popover-title").hide()},c.prototype.hasContent=function(){return this.getTitle()||this.getContent()},c.prototype.getContent=function(){var a=this.$element,b=this.options;return a.attr("data-content")||("function"==typeof b.content?b.content.call(a[0]):b.content)},c.prototype.arrow=function(){return this.$arrow=this.$arrow||this.tip().find(".arrow")};var d=a.fn.popover;a.fn.popover=b,a.fn.popover.Constructor=c,a.fn.popover.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.popover=d,this}}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(c,d){this.$body=a(document.body),this.$scrollElement=a(a(c).is(document.body)?window:c),this.options=a.extend({},b.DEFAULTS,d),this.selector=(this.options.target||"")+" .nav li > a",this.offsets=[],this.targets=[],this.activeTarget=null,this.scrollHeight=0,this.$scrollElement.on("scroll.bs.scrollspy",a.proxy(this.process,this)),this.refresh(),this.process()}function c(c){return this.each(function(){var d=a(this),e=d.data("bs.scrollspy"),f="object"==typeof c&&c;e||d.data("bs.scrollspy",e=new b(this,f)),"string"==typeof c&&e[c]()})}b.VERSION="3.3.4",b.DEFAULTS={offset:10},b.prototype.getScrollHeight=function(){return this.$scrollElement[0].scrollHeight||Math.max(this.$body[0].scrollHeight,document.documentElement.scrollHeight)},b.prototype.refresh=function(){var b=this,c="offset",d=0;this.offsets=[],this.targets=[],this.scrollHeight=this.getScrollHeight(),a.isWindow(this.$scrollElement[0])||(c="position",d=this.$scrollElement.scrollTop()),this.$body.find(this.selector).map(function(){var b=a(this),e=b.data("target")||b.attr("href"),f=/^#./.test(e)&&a(e);return f&&f.length&&f.is(":visible")&&[[f[c]().top+d,e]]||null}).sort(function(a,b){return a[0]-b[0]}).each(function(){b.offsets.push(this[0]),b.targets.push(this[1])})},b.prototype.process=function(){var a,b=this.$scrollElement.scrollTop()+this.options.offset,c=this.getScrollHeight(),d=this.options.offset+c-this.$scrollElement.height(),e=this.offsets,f=this.targets,g=this.activeTarget;if(this.scrollHeight!=c&&this.refresh(),b>=d)return g!=(a=f[f.length-1])&&this.activate(a);if(g&&b<e[0])return this.activeTarget=null,this.clear();for(a=e.length;a--;)g!=f[a]&&b>=e[a]&&(void 0===e[a+1]||b<e[a+1])&&this.activate(f[a])},b.prototype.activate=function(b){this.activeTarget=b,this.clear();var c=this.selector+'[data-target="'+b+'"],'+this.selector+'[href="'+b+'"]',d=a(c).parents("li").addClass("active");d.parent(".dropdown-menu").length&&(d=d.closest("li.dropdown").addClass("active")),d.trigger("activate.bs.scrollspy")},b.prototype.clear=function(){a(this.selector).parentsUntil(this.options.target,".active").removeClass("active")};var d=a.fn.scrollspy;a.fn.scrollspy=c,a.fn.scrollspy.Constructor=b,a.fn.scrollspy.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.scrollspy=d,this},a(window).on("load.bs.scrollspy.data-api",function(){a('[data-spy="scroll"]').each(function(){var b=a(this);c.call(b,b.data())})})}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b){return this.each(function(){var d=a(this),e=d.data("bs.tab");e||d.data("bs.tab",e=new c(this)),"string"==typeof b&&e[b]()})}var c=function(b){this.element=a(b)};c.VERSION="3.3.4",c.TRANSITION_DURATION=150,c.prototype.show=function(){var b=this.element,c=b.closest("ul:not(.dropdown-menu)"),d=b.data("target");if(d||(d=b.attr("href"),d=d&&d.replace(/.*(?=#[^\s]*$)/,"")),!b.parent("li").hasClass("active")){ -var e=c.find(".active:last a"),f=a.Event("hide.bs.tab",{relatedTarget:b[0]}),g=a.Event("show.bs.tab",{relatedTarget:e[0]});if(e.trigger(f),b.trigger(g),!g.isDefaultPrevented()&&!f.isDefaultPrevented()){var h=a(d);this.activate(b.closest("li"),c),this.activate(h,h.parent(),function(){e.trigger({type:"hidden.bs.tab",relatedTarget:b[0]}),b.trigger({type:"shown.bs.tab",relatedTarget:e[0]})})}}},c.prototype.activate=function(b,d,e){function f(){g.removeClass("active").find("> .dropdown-menu > .active").removeClass("active").end().find('[data-toggle="tab"]').attr("aria-expanded",!1),b.addClass("active").find('[data-toggle="tab"]').attr("aria-expanded",!0),h?(b[0].offsetWidth,b.addClass("in")):b.removeClass("fade"),b.parent(".dropdown-menu").length&&b.closest("li.dropdown").addClass("active").end().find('[data-toggle="tab"]').attr("aria-expanded",!0),e&&e()}var g=d.find("> .active"),h=e&&a.support.transition&&(g.length&&g.hasClass("fade")||!!d.find("> .fade").length);g.length&&h?g.one("bsTransitionEnd",f).emulateTransitionEnd(c.TRANSITION_DURATION):f(),g.removeClass("in")};var d=a.fn.tab;a.fn.tab=b,a.fn.tab.Constructor=c,a.fn.tab.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.tab=d,this};var e=function(c){c.preventDefault(),b.call(a(this),"show")};a(document).on("click.bs.tab.data-api",'[data-toggle="tab"]',e).on("click.bs.tab.data-api",'[data-toggle="pill"]',e)}(jQuery),+function(a){"use strict";function b(b){return this.each(function(){var d=a(this),e=d.data("bs.affix"),f="object"==typeof b&&b;e||d.data("bs.affix",e=new c(this,f)),"string"==typeof b&&e[b]()})}var c=function(b,d){this.options=a.extend({},c.DEFAULTS,d),this.$target=a(this.options.target).on("scroll.bs.affix.data-api",a.proxy(this.checkPosition,this)).on("click.bs.affix.data-api",a.proxy(this.checkPositionWithEventLoop,this)),this.$element=a(b),this.affixed=null,this.unpin=null,this.pinnedOffset=null,this.checkPosition()};c.VERSION="3.3.4",c.RESET="affix affix-top affix-bottom",c.DEFAULTS={offset:0,target:window},c.prototype.getState=function(a,b,c,d){var e=this.$target.scrollTop(),f=this.$element.offset(),g=this.$target.height();if(null!=c&&"top"==this.affixed)return c>e?"top":!1;if("bottom"==this.affixed)return null!=c?e+this.unpin<=f.top?!1:"bottom":a-d>=e+g?!1:"bottom";var h=null==this.affixed,i=h?e:f.top,j=h?g:b;return null!=c&&c>=e?"top":null!=d&&i+j>=a-d?"bottom":!1},c.prototype.getPinnedOffset=function(){if(this.pinnedOffset)return this.pinnedOffset;this.$element.removeClass(c.RESET).addClass("affix");var a=this.$target.scrollTop(),b=this.$element.offset();return this.pinnedOffset=b.top-a},c.prototype.checkPositionWithEventLoop=function(){setTimeout(a.proxy(this.checkPosition,this),1)},c.prototype.checkPosition=function(){if(this.$element.is(":visible")){var b=this.$element.height(),d=this.options.offset,e=d.top,f=d.bottom,g=a(document.body).height();"object"!=typeof d&&(f=e=d),"function"==typeof e&&(e=d.top(this.$element)),"function"==typeof f&&(f=d.bottom(this.$element));var h=this.getState(g,b,e,f);if(this.affixed!=h){null!=this.unpin&&this.$element.css("top","");var i="affix"+(h?"-"+h:""),j=a.Event(i+".bs.affix");if(this.$element.trigger(j),j.isDefaultPrevented())return;this.affixed=h,this.unpin="bottom"==h?this.getPinnedOffset():null,this.$element.removeClass(c.RESET).addClass(i).trigger(i.replace("affix","affixed")+".bs.affix")}"bottom"==h&&this.$element.offset({top:g-b-f})}};var d=a.fn.affix;a.fn.affix=b,a.fn.affix.Constructor=c,a.fn.affix.noConflict=function(){return a.fn.affix=d,this},a(window).on("load",function(){a('[data-spy="affix"]').each(function(){var c=a(this),d=c.data();d.offset=d.offset||{},null!=d.offsetBottom&&(d.offset.bottom=d.offsetBottom),null!=d.offsetTop&&(d.offset.top=d.offsetTop),b.call(c,d)})})}(jQuery);
\ No newline at end of file + * Bootstrap v5.3.2 (https://getbootstrap.com/) + * Copyright 2011-2023 The Bootstrap Authors (https://github.com/twbs/bootstrap/graphs/contributors) + * Licensed under MIT (https://github.com/twbs/bootstrap/blob/main/LICENSE) + */ +!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e(require("@popperjs/core")):"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(["@popperjs/core"],e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).bootstrap=e(t.Popper)}(this,(function(t){"use strict";function e(t){const e=Object.create(null,{[Symbol.toStringTag]:{value:"Module"}});if(t)for(const i in t)if("default"!==i){const s=Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(t,i);Object.defineProperty(e,i,s.get?s:{enumerable:!0,get:()=>t[i]})}return e.default=t,Object.freeze(e)}const i=e(t),s=new Map,n={set(t,e,i){s.has(t)||s.set(t,new Map);const n=s.get(t);n.has(e)||0===n.size?n.set(e,i):console.error(`Bootstrap doesn't allow more than one instance per element. Bound instance: ${Array.from(n.keys())[0]}.`)},get:(t,e)=>s.has(t)&&s.get(t).get(e)||null,remove(t,e){if(!s.has(t))return;const i=s.get(t);i.delete(e),0===i.size&&s.delete(t)}},o="transitionend",r=t=>(t&&window.CSS&&window.CSS.escape&&(t=t.replace(/#([^\s"#']+)/g,((t,e)=>`#${CSS.escape(e)}`))),t),a=t=>{t.dispatchEvent(new Event(o))},l=t=>!(!t||"object"!=typeof t)&&(void 0!==t.jquery&&(t=t[0]),void 0!==t.nodeType),c=t=>l(t)?t.jquery?t[0]:t:"string"==typeof t&&t.length>0?document.querySelector(r(t)):null,h=t=>{if(!l(t)||0===t.getClientRects().length)return!1;const e="visible"===getComputedStyle(t).getPropertyValue("visibility"),i=t.closest("details:not([open])");if(!i)return e;if(i!==t){const e=t.closest("summary");if(e&&e.parentNode!==i)return!1;if(null===e)return!1}return e},d=t=>!t||t.nodeType!==Node.ELEMENT_NODE||!!t.classList.contains("disabled")||(void 0!==t.disabled?t.disabled:t.hasAttribute("disabled")&&"false"!==t.getAttribute("disabled")),u=t=>{if(!document.documentElement.attachShadow)return null;if("function"==typeof t.getRootNode){const e=t.getRootNode();return e instanceof ShadowRoot?e:null}return t instanceof ShadowRoot?t:t.parentNode?u(t.parentNode):null},_=()=>{},g=t=>{t.offsetHeight},f=()=>window.jQuery&&!document.body.hasAttribute("data-bs-no-jquery")?window.jQuery:null,m=[],p=()=>"rtl"===document.documentElement.dir,b=t=>{var e;e=()=>{const e=f();if(e){const i=t.NAME,s=e.fn[i];e.fn[i]=t.jQueryInterface,e.fn[i].Constructor=t,e.fn[i].noConflict=()=>(e.fn[i]=s,t.jQueryInterface)}},"loading"===document.readyState?(m.length||document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",(()=>{for(const t of m)t()})),m.push(e)):e()},v=(t,e=[],i=t)=>"function"==typeof t?t(...e):i,y=(t,e,i=!0)=>{if(!i)return void v(t);const s=(t=>{if(!t)return 0;let{transitionDuration:e,transitionDelay:i}=window.getComputedStyle(t);const s=Number.parseFloat(e),n=Number.parseFloat(i);return s||n?(e=e.split(",")[0],i=i.split(",")[0],1e3*(Number.parseFloat(e)+Number.parseFloat(i))):0})(e)+5;let n=!1;const r=({target:i})=>{i===e&&(n=!0,e.removeEventListener(o,r),v(t))};e.addEventListener(o,r),setTimeout((()=>{n||a(e)}),s)},w=(t,e,i,s)=>{const n=t.length;let o=t.indexOf(e);return-1===o?!i&&s?t[n-1]:t[0]:(o+=i?1:-1,s&&(o=(o+n)%n),t[Math.max(0,Math.min(o,n-1))])},A=/[^.]*(?=\..*)\.|.*/,E=/\..*/,C=/::\d+$/,T={};let k=1;const $={mouseenter:"mouseover",mouseleave:"mouseout"},S=new Set(["click","dblclick","mouseup","mousedown","contextmenu","mousewheel","DOMMouseScroll","mouseover","mouseout","mousemove","selectstart","selectend","keydown","keypress","keyup","orientationchange","touchstart","touchmove","touchend","touchcancel","pointerdown","pointermove","pointerup","pointerleave","pointercancel","gesturestart","gesturechange","gestureend","focus","blur","change","reset","select","submit","focusin","focusout","load","unload","beforeunload","resize","move","DOMContentLoaded","readystatechange","error","abort","scroll"]);function L(t,e){return e&&`${e}::${k++}`||t.uidEvent||k++}function O(t){const e=L(t);return t.uidEvent=e,T[e]=T[e]||{},T[e]}function I(t,e,i=null){return Object.values(t).find((t=>t.callable===e&&t.delegationSelector===i))}function D(t,e,i){const s="string"==typeof e,n=s?i:e||i;let o=M(t);return S.has(o)||(o=t),[s,n,o]}function N(t,e,i,s,n){if("string"!=typeof e||!t)return;let[o,r,a]=D(e,i,s);if(e in $){const t=t=>function(e){if(!e.relatedTarget||e.relatedTarget!==e.delegateTarget&&!e.delegateTarget.contains(e.relatedTarget))return t.call(this,e)};r=t(r)}const l=O(t),c=l[a]||(l[a]={}),h=I(c,r,o?i:null);if(h)return void(h.oneOff=h.oneOff&&n);const d=L(r,e.replace(A,"")),u=o?function(t,e,i){return function s(n){const o=t.querySelectorAll(e);for(let{target:r}=n;r&&r!==this;r=r.parentNode)for(const a of o)if(a===r)return F(n,{delegateTarget:r}),s.oneOff&&j.off(t,n.type,e,i),i.apply(r,[n])}}(t,i,r):function(t,e){return function i(s){return F(s,{delegateTarget:t}),i.oneOff&&j.off(t,s.type,e),e.apply(t,[s])}}(t,r);u.delegationSelector=o?i:null,u.callable=r,u.oneOff=n,u.uidEvent=d,c[d]=u,t.addEventListener(a,u,o)}function P(t,e,i,s,n){const o=I(e[i],s,n);o&&(t.removeEventListener(i,o,Boolean(n)),delete e[i][o.uidEvent])}function x(t,e,i,s){const n=e[i]||{};for(const[o,r]of Object.entries(n))o.includes(s)&&P(t,e,i,r.callable,r.delegationSelector)}function M(t){return t=t.replace(E,""),$[t]||t}const j={on(t,e,i,s){N(t,e,i,s,!1)},one(t,e,i,s){N(t,e,i,s,!0)},off(t,e,i,s){if("string"!=typeof e||!t)return;const[n,o,r]=D(e,i,s),a=r!==e,l=O(t),c=l[r]||{},h=e.startsWith(".");if(void 0===o){if(h)for(const i of Object.keys(l))x(t,l,i,e.slice(1));for(const[i,s]of Object.entries(c)){const n=i.replace(C,"");a&&!e.includes(n)||P(t,l,r,s.callable,s.delegationSelector)}}else{if(!Object.keys(c).length)return;P(t,l,r,o,n?i:null)}},trigger(t,e,i){if("string"!=typeof e||!t)return null;const s=f();let n=null,o=!0,r=!0,a=!1;e!==M(e)&&s&&(n=s.Event(e,i),s(t).trigger(n),o=!n.isPropagationStopped(),r=!n.isImmediatePropagationStopped(),a=n.isDefaultPrevented());const l=F(new Event(e,{bubbles:o,cancelable:!0}),i);return a&&l.preventDefault(),r&&t.dispatchEvent(l),l.defaultPrevented&&n&&n.preventDefault(),l}};function F(t,e={}){for(const[i,s]of Object.entries(e))try{t[i]=s}catch(e){Object.defineProperty(t,i,{configurable:!0,get:()=>s})}return t}function z(t){if("true"===t)return!0;if("false"===t)return!1;if(t===Number(t).toString())return Number(t);if(""===t||"null"===t)return null;if("string"!=typeof t)return t;try{return JSON.parse(decodeURIComponent(t))}catch(e){return t}}function H(t){return t.replace(/[A-Z]/g,(t=>`-${t.toLowerCase()}`))}const B={setDataAttribute(t,e,i){t.setAttribute(`data-bs-${H(e)}`,i)},removeDataAttribute(t,e){t.removeAttribute(`data-bs-${H(e)}`)},getDataAttributes(t){if(!t)return{};const e={},i=Object.keys(t.dataset).filter((t=>t.startsWith("bs")&&!t.startsWith("bsConfig")));for(const s of i){let i=s.replace(/^bs/,"");i=i.charAt(0).toLowerCase()+i.slice(1,i.length),e[i]=z(t.dataset[s])}return e},getDataAttribute:(t,e)=>z(t.getAttribute(`data-bs-${H(e)}`))};class q{static get Default(){return{}}static get DefaultType(){return{}}static get NAME(){throw new Error('You have to implement the static method "NAME", for each component!')}_getConfig(t){return t=this._mergeConfigObj(t),t=this._configAfterMerge(t),this._typeCheckConfig(t),t}_configAfterMerge(t){return t}_mergeConfigObj(t,e){const i=l(e)?B.getDataAttribute(e,"config"):{};return{...this.constructor.Default,..."object"==typeof i?i:{},...l(e)?B.getDataAttributes(e):{},..."object"==typeof t?t:{}}}_typeCheckConfig(t,e=this.constructor.DefaultType){for(const[s,n]of Object.entries(e)){const e=t[s],o=l(e)?"element":null==(i=e)?`${i}`:Object.prototype.toString.call(i).match(/\s([a-z]+)/i)[1].toLowerCase();if(!new RegExp(n).test(o))throw new TypeError(`${this.constructor.NAME.toUpperCase()}: Option "${s}" provided type "${o}" but expected type "${n}".`)}var i}}class W extends q{constructor(t,e){super(),(t=c(t))&&(this._element=t,this._config=this._getConfig(e),n.set(this._element,this.constructor.DATA_KEY,this))}dispose(){n.remove(this._element,this.constructor.DATA_KEY),j.off(this._element,this.constructor.EVENT_KEY);for(const t of Object.getOwnPropertyNames(this))this[t]=null}_queueCallback(t,e,i=!0){y(t,e,i)}_getConfig(t){return t=this._mergeConfigObj(t,this._element),t=this._configAfterMerge(t),this._typeCheckConfig(t),t}static getInstance(t){return n.get(c(t),this.DATA_KEY)}static getOrCreateInstance(t,e={}){return this.getInstance(t)||new this(t,"object"==typeof e?e:null)}static get VERSION(){return"5.3.2"}static get DATA_KEY(){return`bs.${this.NAME}`}static get EVENT_KEY(){return`.${this.DATA_KEY}`}static eventName(t){return`${t}${this.EVENT_KEY}`}}const R=t=>{let e=t.getAttribute("data-bs-target");if(!e||"#"===e){let i=t.getAttribute("href");if(!i||!i.includes("#")&&!i.startsWith("."))return null;i.includes("#")&&!i.startsWith("#")&&(i=`#${i.split("#")[1]}`),e=i&&"#"!==i?r(i.trim()):null}return e},K={find:(t,e=document.documentElement)=>[].concat(...Element.prototype.querySelectorAll.call(e,t)),findOne:(t,e=document.documentElement)=>Element.prototype.querySelector.call(e,t),children:(t,e)=>[].concat(...t.children).filter((t=>t.matches(e))),parents(t,e){const i=[];let s=t.parentNode.closest(e);for(;s;)i.push(s),s=s.parentNode.closest(e);return i},prev(t,e){let i=t.previousElementSibling;for(;i;){if(i.matches(e))return[i];i=i.previousElementSibling}return[]},next(t,e){let i=t.nextElementSibling;for(;i;){if(i.matches(e))return[i];i=i.nextElementSibling}return[]},focusableChildren(t){const e=["a","button","input","textarea","select","details","[tabindex]",'[contenteditable="true"]'].map((t=>`${t}:not([tabindex^="-"])`)).join(",");return this.find(e,t).filter((t=>!d(t)&&h(t)))},getSelectorFromElement(t){const e=R(t);return e&&K.findOne(e)?e:null},getElementFromSelector(t){const e=R(t);return e?K.findOne(e):null},getMultipleElementsFromSelector(t){const e=R(t);return e?K.find(e):[]}},V=(t,e="hide")=>{const i=`click.dismiss${t.EVENT_KEY}`,s=t.NAME;j.on(document,i,`[data-bs-dismiss="${s}"]`,(function(i){if(["A","AREA"].includes(this.tagName)&&i.preventDefault(),d(this))return;const n=K.getElementFromSelector(this)||this.closest(`.${s}`);t.getOrCreateInstance(n)[e]()}))},Q=".bs.alert",X=`close${Q}`,Y=`closed${Q}`;class U extends W{static get NAME(){return"alert"}close(){if(j.trigger(this._element,X).defaultPrevented)return;this._element.classList.remove("show");const t=this._element.classList.contains("fade");this._queueCallback((()=>this._destroyElement()),this._element,t)}_destroyElement(){this._element.remove(),j.trigger(this._element,Y),this.dispose()}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=U.getOrCreateInstance(this);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===e[t]||t.startsWith("_")||"constructor"===t)throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);e[t](this)}}))}}V(U,"close"),b(U);const G='[data-bs-toggle="button"]';class J extends W{static get NAME(){return"button"}toggle(){this._element.setAttribute("aria-pressed",this._element.classList.toggle("active"))}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=J.getOrCreateInstance(this);"toggle"===t&&e[t]()}))}}j.on(document,"click.bs.button.data-api",G,(t=>{t.preventDefault();const e=t.target.closest(G);J.getOrCreateInstance(e).toggle()})),b(J);const Z=".bs.swipe",tt=`touchstart${Z}`,et=`touchmove${Z}`,it=`touchend${Z}`,st=`pointerdown${Z}`,nt=`pointerup${Z}`,ot={endCallback:null,leftCallback:null,rightCallback:null},rt={endCallback:"(function|null)",leftCallback:"(function|null)",rightCallback:"(function|null)"};class at extends q{constructor(t,e){super(),this._element=t,t&&at.isSupported()&&(this._config=this._getConfig(e),this._deltaX=0,this._supportPointerEvents=Boolean(window.PointerEvent),this._initEvents())}static get Default(){return ot}static get DefaultType(){return rt}static get NAME(){return"swipe"}dispose(){j.off(this._element,Z)}_start(t){this._supportPointerEvents?this._eventIsPointerPenTouch(t)&&(this._deltaX=t.clientX):this._deltaX=t.touches[0].clientX}_end(t){this._eventIsPointerPenTouch(t)&&(this._deltaX=t.clientX-this._deltaX),this._handleSwipe(),v(this._config.endCallback)}_move(t){this._deltaX=t.touches&&t.touches.length>1?0:t.touches[0].clientX-this._deltaX}_handleSwipe(){const t=Math.abs(this._deltaX);if(t<=40)return;const e=t/this._deltaX;this._deltaX=0,e&&v(e>0?this._config.rightCallback:this._config.leftCallback)}_initEvents(){this._supportPointerEvents?(j.on(this._element,st,(t=>this._start(t))),j.on(this._element,nt,(t=>this._end(t))),this._element.classList.add("pointer-event")):(j.on(this._element,tt,(t=>this._start(t))),j.on(this._element,et,(t=>this._move(t))),j.on(this._element,it,(t=>this._end(t))))}_eventIsPointerPenTouch(t){return this._supportPointerEvents&&("pen"===t.pointerType||"touch"===t.pointerType)}static isSupported(){return"ontouchstart"in document.documentElement||navigator.maxTouchPoints>0}}const lt=".bs.carousel",ct=".data-api",ht="next",dt="prev",ut="left",_t="right",gt=`slide${lt}`,ft=`slid${lt}`,mt=`keydown${lt}`,pt=`mouseenter${lt}`,bt=`mouseleave${lt}`,vt=`dragstart${lt}`,yt=`load${lt}${ct}`,wt=`click${lt}${ct}`,At="carousel",Et="active",Ct=".active",Tt=".carousel-item",kt=Ct+Tt,$t={ArrowLeft:_t,ArrowRight:ut},St={interval:5e3,keyboard:!0,pause:"hover",ride:!1,touch:!0,wrap:!0},Lt={interval:"(number|boolean)",keyboard:"boolean",pause:"(string|boolean)",ride:"(boolean|string)",touch:"boolean",wrap:"boolean"};class Ot extends W{constructor(t,e){super(t,e),this._interval=null,this._activeElement=null,this._isSliding=!1,this.touchTimeout=null,this._swipeHelper=null,this._indicatorsElement=K.findOne(".carousel-indicators",this._element),this._addEventListeners(),this._config.ride===At&&this.cycle()}static get Default(){return St}static get DefaultType(){return Lt}static get NAME(){return"carousel"}next(){this._slide(ht)}nextWhenVisible(){!document.hidden&&h(this._element)&&this.next()}prev(){this._slide(dt)}pause(){this._isSliding&&a(this._element),this._clearInterval()}cycle(){this._clearInterval(),this._updateInterval(),this._interval=setInterval((()=>this.nextWhenVisible()),this._config.interval)}_maybeEnableCycle(){this._config.ride&&(this._isSliding?j.one(this._element,ft,(()=>this.cycle())):this.cycle())}to(t){const e=this._getItems();if(t>e.length-1||t<0)return;if(this._isSliding)return void j.one(this._element,ft,(()=>this.to(t)));const i=this._getItemIndex(this._getActive());if(i===t)return;const s=t>i?ht:dt;this._slide(s,e[t])}dispose(){this._swipeHelper&&this._swipeHelper.dispose(),super.dispose()}_configAfterMerge(t){return t.defaultInterval=t.interval,t}_addEventListeners(){this._config.keyboard&&j.on(this._element,mt,(t=>this._keydown(t))),"hover"===this._config.pause&&(j.on(this._element,pt,(()=>this.pause())),j.on(this._element,bt,(()=>this._maybeEnableCycle()))),this._config.touch&&at.isSupported()&&this._addTouchEventListeners()}_addTouchEventListeners(){for(const t of K.find(".carousel-item img",this._element))j.on(t,vt,(t=>t.preventDefault()));const t={leftCallback:()=>this._slide(this._directionToOrder(ut)),rightCallback:()=>this._slide(this._directionToOrder(_t)),endCallback:()=>{"hover"===this._config.pause&&(this.pause(),this.touchTimeout&&clearTimeout(this.touchTimeout),this.touchTimeout=setTimeout((()=>this._maybeEnableCycle()),500+this._config.interval))}};this._swipeHelper=new at(this._element,t)}_keydown(t){if(/input|textarea/i.test(t.target.tagName))return;const e=$t[t.key];e&&(t.preventDefault(),this._slide(this._directionToOrder(e)))}_getItemIndex(t){return this._getItems().indexOf(t)}_setActiveIndicatorElement(t){if(!this._indicatorsElement)return;const e=K.findOne(Ct,this._indicatorsElement);e.classList.remove(Et),e.removeAttribute("aria-current");const i=K.findOne(`[data-bs-slide-to="${t}"]`,this._indicatorsElement);i&&(i.classList.add(Et),i.setAttribute("aria-current","true"))}_updateInterval(){const t=this._activeElement||this._getActive();if(!t)return;const e=Number.parseInt(t.getAttribute("data-bs-interval"),10);this._config.interval=e||this._config.defaultInterval}_slide(t,e=null){if(this._isSliding)return;const i=this._getActive(),s=t===ht,n=e||w(this._getItems(),i,s,this._config.wrap);if(n===i)return;const o=this._getItemIndex(n),r=e=>j.trigger(this._element,e,{relatedTarget:n,direction:this._orderToDirection(t),from:this._getItemIndex(i),to:o});if(r(gt).defaultPrevented)return;if(!i||!n)return;const a=Boolean(this._interval);this.pause(),this._isSliding=!0,this._setActiveIndicatorElement(o),this._activeElement=n;const l=s?"carousel-item-start":"carousel-item-end",c=s?"carousel-item-next":"carousel-item-prev";n.classList.add(c),g(n),i.classList.add(l),n.classList.add(l),this._queueCallback((()=>{n.classList.remove(l,c),n.classList.add(Et),i.classList.remove(Et,c,l),this._isSliding=!1,r(ft)}),i,this._isAnimated()),a&&this.cycle()}_isAnimated(){return this._element.classList.contains("slide")}_getActive(){return K.findOne(kt,this._element)}_getItems(){return K.find(Tt,this._element)}_clearInterval(){this._interval&&(clearInterval(this._interval),this._interval=null)}_directionToOrder(t){return p()?t===ut?dt:ht:t===ut?ht:dt}_orderToDirection(t){return p()?t===dt?ut:_t:t===dt?_t:ut}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=Ot.getOrCreateInstance(this,t);if("number"!=typeof t){if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===e[t]||t.startsWith("_")||"constructor"===t)throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);e[t]()}}else e.to(t)}))}}j.on(document,wt,"[data-bs-slide], [data-bs-slide-to]",(function(t){const e=K.getElementFromSelector(this);if(!e||!e.classList.contains(At))return;t.preventDefault();const i=Ot.getOrCreateInstance(e),s=this.getAttribute("data-bs-slide-to");return s?(i.to(s),void i._maybeEnableCycle()):"next"===B.getDataAttribute(this,"slide")?(i.next(),void i._maybeEnableCycle()):(i.prev(),void i._maybeEnableCycle())})),j.on(window,yt,(()=>{const t=K.find('[data-bs-ride="carousel"]');for(const e of t)Ot.getOrCreateInstance(e)})),b(Ot);const It=".bs.collapse",Dt=`show${It}`,Nt=`shown${It}`,Pt=`hide${It}`,xt=`hidden${It}`,Mt=`click${It}.data-api`,jt="show",Ft="collapse",zt="collapsing",Ht=`:scope .${Ft} .${Ft}`,Bt='[data-bs-toggle="collapse"]',qt={parent:null,toggle:!0},Wt={parent:"(null|element)",toggle:"boolean"};class Rt extends W{constructor(t,e){super(t,e),this._isTransitioning=!1,this._triggerArray=[];const i=K.find(Bt);for(const t of i){const e=K.getSelectorFromElement(t),i=K.find(e).filter((t=>t===this._element));null!==e&&i.length&&this._triggerArray.push(t)}this._initializeChildren(),this._config.parent||this._addAriaAndCollapsedClass(this._triggerArray,this._isShown()),this._config.toggle&&this.toggle()}static get Default(){return qt}static get DefaultType(){return Wt}static get NAME(){return"collapse"}toggle(){this._isShown()?this.hide():this.show()}show(){if(this._isTransitioning||this._isShown())return;let t=[];if(this._config.parent&&(t=this._getFirstLevelChildren(".collapse.show, .collapse.collapsing").filter((t=>t!==this._element)).map((t=>Rt.getOrCreateInstance(t,{toggle:!1})))),t.length&&t[0]._isTransitioning)return;if(j.trigger(this._element,Dt).defaultPrevented)return;for(const e of t)e.hide();const e=this._getDimension();this._element.classList.remove(Ft),this._element.classList.add(zt),this._element.style[e]=0,this._addAriaAndCollapsedClass(this._triggerArray,!0),this._isTransitioning=!0;const i=`scroll${e[0].toUpperCase()+e.slice(1)}`;this._queueCallback((()=>{this._isTransitioning=!1,this._element.classList.remove(zt),this._element.classList.add(Ft,jt),this._element.style[e]="",j.trigger(this._element,Nt)}),this._element,!0),this._element.style[e]=`${this._element[i]}px`}hide(){if(this._isTransitioning||!this._isShown())return;if(j.trigger(this._element,Pt).defaultPrevented)return;const t=this._getDimension();this._element.style[t]=`${this._element.getBoundingClientRect()[t]}px`,g(this._element),this._element.classList.add(zt),this._element.classList.remove(Ft,jt);for(const t of this._triggerArray){const e=K.getElementFromSelector(t);e&&!this._isShown(e)&&this._addAriaAndCollapsedClass([t],!1)}this._isTransitioning=!0,this._element.style[t]="",this._queueCallback((()=>{this._isTransitioning=!1,this._element.classList.remove(zt),this._element.classList.add(Ft),j.trigger(this._element,xt)}),this._element,!0)}_isShown(t=this._element){return t.classList.contains(jt)}_configAfterMerge(t){return t.toggle=Boolean(t.toggle),t.parent=c(t.parent),t}_getDimension(){return this._element.classList.contains("collapse-horizontal")?"width":"height"}_initializeChildren(){if(!this._config.parent)return;const t=this._getFirstLevelChildren(Bt);for(const e of t){const t=K.getElementFromSelector(e);t&&this._addAriaAndCollapsedClass([e],this._isShown(t))}}_getFirstLevelChildren(t){const e=K.find(Ht,this._config.parent);return K.find(t,this._config.parent).filter((t=>!e.includes(t)))}_addAriaAndCollapsedClass(t,e){if(t.length)for(const i of t)i.classList.toggle("collapsed",!e),i.setAttribute("aria-expanded",e)}static jQueryInterface(t){const e={};return"string"==typeof t&&/show|hide/.test(t)&&(e.toggle=!1),this.each((function(){const i=Rt.getOrCreateInstance(this,e);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===i[t])throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);i[t]()}}))}}j.on(document,Mt,Bt,(function(t){("A"===t.target.tagName||t.delegateTarget&&"A"===t.delegateTarget.tagName)&&t.preventDefault();for(const t of K.getMultipleElementsFromSelector(this))Rt.getOrCreateInstance(t,{toggle:!1}).toggle()})),b(Rt);const Kt="dropdown",Vt=".bs.dropdown",Qt=".data-api",Xt="ArrowUp",Yt="ArrowDown",Ut=`hide${Vt}`,Gt=`hidden${Vt}`,Jt=`show${Vt}`,Zt=`shown${Vt}`,te=`click${Vt}${Qt}`,ee=`keydown${Vt}${Qt}`,ie=`keyup${Vt}${Qt}`,se="show",ne='[data-bs-toggle="dropdown"]:not(.disabled):not(:disabled)',oe=`${ne}.${se}`,re=".dropdown-menu",ae=p()?"top-end":"top-start",le=p()?"top-start":"top-end",ce=p()?"bottom-end":"bottom-start",he=p()?"bottom-start":"bottom-end",de=p()?"left-start":"right-start",ue=p()?"right-start":"left-start",_e={autoClose:!0,boundary:"clippingParents",display:"dynamic",offset:[0,2],popperConfig:null,reference:"toggle"},ge={autoClose:"(boolean|string)",boundary:"(string|element)",display:"string",offset:"(array|string|function)",popperConfig:"(null|object|function)",reference:"(string|element|object)"};class fe extends W{constructor(t,e){super(t,e),this._popper=null,this._parent=this._element.parentNode,this._menu=K.next(this._element,re)[0]||K.prev(this._element,re)[0]||K.findOne(re,this._parent),this._inNavbar=this._detectNavbar()}static get Default(){return _e}static get DefaultType(){return ge}static get NAME(){return Kt}toggle(){return this._isShown()?this.hide():this.show()}show(){if(d(this._element)||this._isShown())return;const t={relatedTarget:this._element};if(!j.trigger(this._element,Jt,t).defaultPrevented){if(this._createPopper(),"ontouchstart"in document.documentElement&&!this._parent.closest(".navbar-nav"))for(const t of[].concat(...document.body.children))j.on(t,"mouseover",_);this._element.focus(),this._element.setAttribute("aria-expanded",!0),this._menu.classList.add(se),this._element.classList.add(se),j.trigger(this._element,Zt,t)}}hide(){if(d(this._element)||!this._isShown())return;const t={relatedTarget:this._element};this._completeHide(t)}dispose(){this._popper&&this._popper.destroy(),super.dispose()}update(){this._inNavbar=this._detectNavbar(),this._popper&&this._popper.update()}_completeHide(t){if(!j.trigger(this._element,Ut,t).defaultPrevented){if("ontouchstart"in document.documentElement)for(const t of[].concat(...document.body.children))j.off(t,"mouseover",_);this._popper&&this._popper.destroy(),this._menu.classList.remove(se),this._element.classList.remove(se),this._element.setAttribute("aria-expanded","false"),B.removeDataAttribute(this._menu,"popper"),j.trigger(this._element,Gt,t)}}_getConfig(t){if("object"==typeof(t=super._getConfig(t)).reference&&!l(t.reference)&&"function"!=typeof t.reference.getBoundingClientRect)throw new TypeError(`${Kt.toUpperCase()}: Option "reference" provided type "object" without a required "getBoundingClientRect" method.`);return t}_createPopper(){if(void 0===i)throw new TypeError("Bootstrap's dropdowns require Popper (https://popper.js.org)");let t=this._element;"parent"===this._config.reference?t=this._parent:l(this._config.reference)?t=c(this._config.reference):"object"==typeof this._config.reference&&(t=this._config.reference);const e=this._getPopperConfig();this._popper=i.createPopper(t,this._menu,e)}_isShown(){return this._menu.classList.contains(se)}_getPlacement(){const t=this._parent;if(t.classList.contains("dropend"))return de;if(t.classList.contains("dropstart"))return ue;if(t.classList.contains("dropup-center"))return"top";if(t.classList.contains("dropdown-center"))return"bottom";const e="end"===getComputedStyle(this._menu).getPropertyValue("--bs-position").trim();return t.classList.contains("dropup")?e?le:ae:e?he:ce}_detectNavbar(){return null!==this._element.closest(".navbar")}_getOffset(){const{offset:t}=this._config;return"string"==typeof t?t.split(",").map((t=>Number.parseInt(t,10))):"function"==typeof t?e=>t(e,this._element):t}_getPopperConfig(){const t={placement:this._getPlacement(),modifiers:[{name:"preventOverflow",options:{boundary:this._config.boundary}},{name:"offset",options:{offset:this._getOffset()}}]};return(this._inNavbar||"static"===this._config.display)&&(B.setDataAttribute(this._menu,"popper","static"),t.modifiers=[{name:"applyStyles",enabled:!1}]),{...t,...v(this._config.popperConfig,[t])}}_selectMenuItem({key:t,target:e}){const i=K.find(".dropdown-menu .dropdown-item:not(.disabled):not(:disabled)",this._menu).filter((t=>h(t)));i.length&&w(i,e,t===Yt,!i.includes(e)).focus()}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=fe.getOrCreateInstance(this,t);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===e[t])throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);e[t]()}}))}static clearMenus(t){if(2===t.button||"keyup"===t.type&&"Tab"!==t.key)return;const e=K.find(oe);for(const i of e){const e=fe.getInstance(i);if(!e||!1===e._config.autoClose)continue;const s=t.composedPath(),n=s.includes(e._menu);if(s.includes(e._element)||"inside"===e._config.autoClose&&!n||"outside"===e._config.autoClose&&n)continue;if(e._menu.contains(t.target)&&("keyup"===t.type&&"Tab"===t.key||/input|select|option|textarea|form/i.test(t.target.tagName)))continue;const o={relatedTarget:e._element};"click"===t.type&&(o.clickEvent=t),e._completeHide(o)}}static dataApiKeydownHandler(t){const e=/input|textarea/i.test(t.target.tagName),i="Escape"===t.key,s=[Xt,Yt].includes(t.key);if(!s&&!i)return;if(e&&!i)return;t.preventDefault();const n=this.matches(ne)?this:K.prev(this,ne)[0]||K.next(this,ne)[0]||K.findOne(ne,t.delegateTarget.parentNode),o=fe.getOrCreateInstance(n);if(s)return t.stopPropagation(),o.show(),void o._selectMenuItem(t);o._isShown()&&(t.stopPropagation(),o.hide(),n.focus())}}j.on(document,ee,ne,fe.dataApiKeydownHandler),j.on(document,ee,re,fe.dataApiKeydownHandler),j.on(document,te,fe.clearMenus),j.on(document,ie,fe.clearMenus),j.on(document,te,ne,(function(t){t.preventDefault(),fe.getOrCreateInstance(this).toggle()})),b(fe);const me="backdrop",pe="show",be=`mousedown.bs.${me}`,ve={className:"modal-backdrop",clickCallback:null,isAnimated:!1,isVisible:!0,rootElement:"body"},ye={className:"string",clickCallback:"(function|null)",isAnimated:"boolean",isVisible:"boolean",rootElement:"(element|string)"};class we extends q{constructor(t){super(),this._config=this._getConfig(t),this._isAppended=!1,this._element=null}static get Default(){return ve}static get DefaultType(){return ye}static get NAME(){return me}show(t){if(!this._config.isVisible)return void v(t);this._append();const e=this._getElement();this._config.isAnimated&&g(e),e.classList.add(pe),this._emulateAnimation((()=>{v(t)}))}hide(t){this._config.isVisible?(this._getElement().classList.remove(pe),this._emulateAnimation((()=>{this.dispose(),v(t)}))):v(t)}dispose(){this._isAppended&&(j.off(this._element,be),this._element.remove(),this._isAppended=!1)}_getElement(){if(!this._element){const t=document.createElement("div");t.className=this._config.className,this._config.isAnimated&&t.classList.add("fade"),this._element=t}return this._element}_configAfterMerge(t){return t.rootElement=c(t.rootElement),t}_append(){if(this._isAppended)return;const t=this._getElement();this._config.rootElement.append(t),j.on(t,be,(()=>{v(this._config.clickCallback)})),this._isAppended=!0}_emulateAnimation(t){y(t,this._getElement(),this._config.isAnimated)}}const Ae=".bs.focustrap",Ee=`focusin${Ae}`,Ce=`keydown.tab${Ae}`,Te="backward",ke={autofocus:!0,trapElement:null},$e={autofocus:"boolean",trapElement:"element"};class Se extends q{constructor(t){super(),this._config=this._getConfig(t),this._isActive=!1,this._lastTabNavDirection=null}static get Default(){return ke}static get DefaultType(){return $e}static get NAME(){return"focustrap"}activate(){this._isActive||(this._config.autofocus&&this._config.trapElement.focus(),j.off(document,Ae),j.on(document,Ee,(t=>this._handleFocusin(t))),j.on(document,Ce,(t=>this._handleKeydown(t))),this._isActive=!0)}deactivate(){this._isActive&&(this._isActive=!1,j.off(document,Ae))}_handleFocusin(t){const{trapElement:e}=this._config;if(t.target===document||t.target===e||e.contains(t.target))return;const i=K.focusableChildren(e);0===i.length?e.focus():this._lastTabNavDirection===Te?i[i.length-1].focus():i[0].focus()}_handleKeydown(t){"Tab"===t.key&&(this._lastTabNavDirection=t.shiftKey?Te:"forward")}}const Le=".fixed-top, .fixed-bottom, .is-fixed, .sticky-top",Oe=".sticky-top",Ie="padding-right",De="margin-right";class Ne{constructor(){this._element=document.body}getWidth(){const t=document.documentElement.clientWidth;return Math.abs(window.innerWidth-t)}hide(){const t=this.getWidth();this._disableOverFlow(),this._setElementAttributes(this._element,Ie,(e=>e+t)),this._setElementAttributes(Le,Ie,(e=>e+t)),this._setElementAttributes(Oe,De,(e=>e-t))}reset(){this._resetElementAttributes(this._element,"overflow"),this._resetElementAttributes(this._element,Ie),this._resetElementAttributes(Le,Ie),this._resetElementAttributes(Oe,De)}isOverflowing(){return this.getWidth()>0}_disableOverFlow(){this._saveInitialAttribute(this._element,"overflow"),this._element.style.overflow="hidden"}_setElementAttributes(t,e,i){const s=this.getWidth();this._applyManipulationCallback(t,(t=>{if(t!==this._element&&window.innerWidth>t.clientWidth+s)return;this._saveInitialAttribute(t,e);const n=window.getComputedStyle(t).getPropertyValue(e);t.style.setProperty(e,`${i(Number.parseFloat(n))}px`)}))}_saveInitialAttribute(t,e){const i=t.style.getPropertyValue(e);i&&B.setDataAttribute(t,e,i)}_resetElementAttributes(t,e){this._applyManipulationCallback(t,(t=>{const i=B.getDataAttribute(t,e);null!==i?(B.removeDataAttribute(t,e),t.style.setProperty(e,i)):t.style.removeProperty(e)}))}_applyManipulationCallback(t,e){if(l(t))e(t);else for(const i of K.find(t,this._element))e(i)}}const Pe=".bs.modal",xe=`hide${Pe}`,Me=`hidePrevented${Pe}`,je=`hidden${Pe}`,Fe=`show${Pe}`,ze=`shown${Pe}`,He=`resize${Pe}`,Be=`click.dismiss${Pe}`,qe=`mousedown.dismiss${Pe}`,We=`keydown.dismiss${Pe}`,Re=`click${Pe}.data-api`,Ke="modal-open",Ve="show",Qe="modal-static",Xe={backdrop:!0,focus:!0,keyboard:!0},Ye={backdrop:"(boolean|string)",focus:"boolean",keyboard:"boolean"};class Ue extends W{constructor(t,e){super(t,e),this._dialog=K.findOne(".modal-dialog",this._element),this._backdrop=this._initializeBackDrop(),this._focustrap=this._initializeFocusTrap(),this._isShown=!1,this._isTransitioning=!1,this._scrollBar=new Ne,this._addEventListeners()}static get Default(){return Xe}static get DefaultType(){return Ye}static get NAME(){return"modal"}toggle(t){return this._isShown?this.hide():this.show(t)}show(t){this._isShown||this._isTransitioning||j.trigger(this._element,Fe,{relatedTarget:t}).defaultPrevented||(this._isShown=!0,this._isTransitioning=!0,this._scrollBar.hide(),document.body.classList.add(Ke),this._adjustDialog(),this._backdrop.show((()=>this._showElement(t))))}hide(){this._isShown&&!this._isTransitioning&&(j.trigger(this._element,xe).defaultPrevented||(this._isShown=!1,this._isTransitioning=!0,this._focustrap.deactivate(),this._element.classList.remove(Ve),this._queueCallback((()=>this._hideModal()),this._element,this._isAnimated())))}dispose(){j.off(window,Pe),j.off(this._dialog,Pe),this._backdrop.dispose(),this._focustrap.deactivate(),super.dispose()}handleUpdate(){this._adjustDialog()}_initializeBackDrop(){return new we({isVisible:Boolean(this._config.backdrop),isAnimated:this._isAnimated()})}_initializeFocusTrap(){return new Se({trapElement:this._element})}_showElement(t){document.body.contains(this._element)||document.body.append(this._element),this._element.style.display="block",this._element.removeAttribute("aria-hidden"),this._element.setAttribute("aria-modal",!0),this._element.setAttribute("role","dialog"),this._element.scrollTop=0;const e=K.findOne(".modal-body",this._dialog);e&&(e.scrollTop=0),g(this._element),this._element.classList.add(Ve),this._queueCallback((()=>{this._config.focus&&this._focustrap.activate(),this._isTransitioning=!1,j.trigger(this._element,ze,{relatedTarget:t})}),this._dialog,this._isAnimated())}_addEventListeners(){j.on(this._element,We,(t=>{"Escape"===t.key&&(this._config.keyboard?this.hide():this._triggerBackdropTransition())})),j.on(window,He,(()=>{this._isShown&&!this._isTransitioning&&this._adjustDialog()})),j.on(this._element,qe,(t=>{j.one(this._element,Be,(e=>{this._element===t.target&&this._element===e.target&&("static"!==this._config.backdrop?this._config.backdrop&&this.hide():this._triggerBackdropTransition())}))}))}_hideModal(){this._element.style.display="none",this._element.setAttribute("aria-hidden",!0),this._element.removeAttribute("aria-modal"),this._element.removeAttribute("role"),this._isTransitioning=!1,this._backdrop.hide((()=>{document.body.classList.remove(Ke),this._resetAdjustments(),this._scrollBar.reset(),j.trigger(this._element,je)}))}_isAnimated(){return this._element.classList.contains("fade")}_triggerBackdropTransition(){if(j.trigger(this._element,Me).defaultPrevented)return;const t=this._element.scrollHeight>document.documentElement.clientHeight,e=this._element.style.overflowY;"hidden"===e||this._element.classList.contains(Qe)||(t||(this._element.style.overflowY="hidden"),this._element.classList.add(Qe),this._queueCallback((()=>{this._element.classList.remove(Qe),this._queueCallback((()=>{this._element.style.overflowY=e}),this._dialog)}),this._dialog),this._element.focus())}_adjustDialog(){const t=this._element.scrollHeight>document.documentElement.clientHeight,e=this._scrollBar.getWidth(),i=e>0;if(i&&!t){const t=p()?"paddingLeft":"paddingRight";this._element.style[t]=`${e}px`}if(!i&&t){const t=p()?"paddingRight":"paddingLeft";this._element.style[t]=`${e}px`}}_resetAdjustments(){this._element.style.paddingLeft="",this._element.style.paddingRight=""}static jQueryInterface(t,e){return this.each((function(){const i=Ue.getOrCreateInstance(this,t);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===i[t])throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);i[t](e)}}))}}j.on(document,Re,'[data-bs-toggle="modal"]',(function(t){const e=K.getElementFromSelector(this);["A","AREA"].includes(this.tagName)&&t.preventDefault(),j.one(e,Fe,(t=>{t.defaultPrevented||j.one(e,je,(()=>{h(this)&&this.focus()}))}));const i=K.findOne(".modal.show");i&&Ue.getInstance(i).hide(),Ue.getOrCreateInstance(e).toggle(this)})),V(Ue),b(Ue);const Ge=".bs.offcanvas",Je=".data-api",Ze=`load${Ge}${Je}`,ti="show",ei="showing",ii="hiding",si=".offcanvas.show",ni=`show${Ge}`,oi=`shown${Ge}`,ri=`hide${Ge}`,ai=`hidePrevented${Ge}`,li=`hidden${Ge}`,ci=`resize${Ge}`,hi=`click${Ge}${Je}`,di=`keydown.dismiss${Ge}`,ui={backdrop:!0,keyboard:!0,scroll:!1},_i={backdrop:"(boolean|string)",keyboard:"boolean",scroll:"boolean"};class gi extends W{constructor(t,e){super(t,e),this._isShown=!1,this._backdrop=this._initializeBackDrop(),this._focustrap=this._initializeFocusTrap(),this._addEventListeners()}static get Default(){return ui}static get DefaultType(){return _i}static get NAME(){return"offcanvas"}toggle(t){return this._isShown?this.hide():this.show(t)}show(t){this._isShown||j.trigger(this._element,ni,{relatedTarget:t}).defaultPrevented||(this._isShown=!0,this._backdrop.show(),this._config.scroll||(new Ne).hide(),this._element.setAttribute("aria-modal",!0),this._element.setAttribute("role","dialog"),this._element.classList.add(ei),this._queueCallback((()=>{this._config.scroll&&!this._config.backdrop||this._focustrap.activate(),this._element.classList.add(ti),this._element.classList.remove(ei),j.trigger(this._element,oi,{relatedTarget:t})}),this._element,!0))}hide(){this._isShown&&(j.trigger(this._element,ri).defaultPrevented||(this._focustrap.deactivate(),this._element.blur(),this._isShown=!1,this._element.classList.add(ii),this._backdrop.hide(),this._queueCallback((()=>{this._element.classList.remove(ti,ii),this._element.removeAttribute("aria-modal"),this._element.removeAttribute("role"),this._config.scroll||(new Ne).reset(),j.trigger(this._element,li)}),this._element,!0)))}dispose(){this._backdrop.dispose(),this._focustrap.deactivate(),super.dispose()}_initializeBackDrop(){const t=Boolean(this._config.backdrop);return new we({className:"offcanvas-backdrop",isVisible:t,isAnimated:!0,rootElement:this._element.parentNode,clickCallback:t?()=>{"static"!==this._config.backdrop?this.hide():j.trigger(this._element,ai)}:null})}_initializeFocusTrap(){return new Se({trapElement:this._element})}_addEventListeners(){j.on(this._element,di,(t=>{"Escape"===t.key&&(this._config.keyboard?this.hide():j.trigger(this._element,ai))}))}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=gi.getOrCreateInstance(this,t);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===e[t]||t.startsWith("_")||"constructor"===t)throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);e[t](this)}}))}}j.on(document,hi,'[data-bs-toggle="offcanvas"]',(function(t){const e=K.getElementFromSelector(this);if(["A","AREA"].includes(this.tagName)&&t.preventDefault(),d(this))return;j.one(e,li,(()=>{h(this)&&this.focus()}));const i=K.findOne(si);i&&i!==e&&gi.getInstance(i).hide(),gi.getOrCreateInstance(e).toggle(this)})),j.on(window,Ze,(()=>{for(const t of K.find(si))gi.getOrCreateInstance(t).show()})),j.on(window,ci,(()=>{for(const t of K.find("[aria-modal][class*=show][class*=offcanvas-]"))"fixed"!==getComputedStyle(t).position&&gi.getOrCreateInstance(t).hide()})),V(gi),b(gi);const fi={"*":["class","dir","id","lang","role",/^aria-[\w-]*$/i],a:["target","href","title","rel"],area:[],b:[],br:[],col:[],code:[],div:[],em:[],hr:[],h1:[],h2:[],h3:[],h4:[],h5:[],h6:[],i:[],img:["src","srcset","alt","title","width","height"],li:[],ol:[],p:[],pre:[],s:[],small:[],span:[],sub:[],sup:[],strong:[],u:[],ul:[]},mi=new Set(["background","cite","href","itemtype","longdesc","poster","src","xlink:href"]),pi=/^(?!javascript:)(?:[a-z0-9+.-]+:|[^&:/?#]*(?:[/?#]|$))/i,bi=(t,e)=>{const i=t.nodeName.toLowerCase();return e.includes(i)?!mi.has(i)||Boolean(pi.test(t.nodeValue)):e.filter((t=>t instanceof RegExp)).some((t=>t.test(i)))},vi={allowList:fi,content:{},extraClass:"",html:!1,sanitize:!0,sanitizeFn:null,template:"<div></div>"},yi={allowList:"object",content:"object",extraClass:"(string|function)",html:"boolean",sanitize:"boolean",sanitizeFn:"(null|function)",template:"string"},wi={entry:"(string|element|function|null)",selector:"(string|element)"};class Ai extends q{constructor(t){super(),this._config=this._getConfig(t)}static get Default(){return vi}static get DefaultType(){return yi}static get NAME(){return"TemplateFactory"}getContent(){return Object.values(this._config.content).map((t=>this._resolvePossibleFunction(t))).filter(Boolean)}hasContent(){return this.getContent().length>0}changeContent(t){return this._checkContent(t),this._config.content={...this._config.content,...t},this}toHtml(){const t=document.createElement("div");t.innerHTML=this._maybeSanitize(this._config.template);for(const[e,i]of Object.entries(this._config.content))this._setContent(t,i,e);const e=t.children[0],i=this._resolvePossibleFunction(this._config.extraClass);return i&&e.classList.add(...i.split(" ")),e}_typeCheckConfig(t){super._typeCheckConfig(t),this._checkContent(t.content)}_checkContent(t){for(const[e,i]of Object.entries(t))super._typeCheckConfig({selector:e,entry:i},wi)}_setContent(t,e,i){const s=K.findOne(i,t);s&&((e=this._resolvePossibleFunction(e))?l(e)?this._putElementInTemplate(c(e),s):this._config.html?s.innerHTML=this._maybeSanitize(e):s.textContent=e:s.remove())}_maybeSanitize(t){return this._config.sanitize?function(t,e,i){if(!t.length)return t;if(i&&"function"==typeof i)return i(t);const s=(new window.DOMParser).parseFromString(t,"text/html"),n=[].concat(...s.body.querySelectorAll("*"));for(const t of n){const i=t.nodeName.toLowerCase();if(!Object.keys(e).includes(i)){t.remove();continue}const s=[].concat(...t.attributes),n=[].concat(e["*"]||[],e[i]||[]);for(const e of s)bi(e,n)||t.removeAttribute(e.nodeName)}return s.body.innerHTML}(t,this._config.allowList,this._config.sanitizeFn):t}_resolvePossibleFunction(t){return v(t,[this])}_putElementInTemplate(t,e){if(this._config.html)return e.innerHTML="",void e.append(t);e.textContent=t.textContent}}const Ei=new Set(["sanitize","allowList","sanitizeFn"]),Ci="fade",Ti="show",ki=".modal",$i="hide.bs.modal",Si="hover",Li="focus",Oi={AUTO:"auto",TOP:"top",RIGHT:p()?"left":"right",BOTTOM:"bottom",LEFT:p()?"right":"left"},Ii={allowList:fi,animation:!0,boundary:"clippingParents",container:!1,customClass:"",delay:0,fallbackPlacements:["top","right","bottom","left"],html:!1,offset:[0,6],placement:"top",popperConfig:null,sanitize:!0,sanitizeFn:null,selector:!1,template:'<div class="tooltip" role="tooltip"><div class="tooltip-arrow"></div><div class="tooltip-inner"></div></div>',title:"",trigger:"hover focus"},Di={allowList:"object",animation:"boolean",boundary:"(string|element)",container:"(string|element|boolean)",customClass:"(string|function)",delay:"(number|object)",fallbackPlacements:"array",html:"boolean",offset:"(array|string|function)",placement:"(string|function)",popperConfig:"(null|object|function)",sanitize:"boolean",sanitizeFn:"(null|function)",selector:"(string|boolean)",template:"string",title:"(string|element|function)",trigger:"string"};class Ni extends W{constructor(t,e){if(void 0===i)throw new TypeError("Bootstrap's tooltips require Popper (https://popper.js.org)");super(t,e),this._isEnabled=!0,this._timeout=0,this._isHovered=null,this._activeTrigger={},this._popper=null,this._templateFactory=null,this._newContent=null,this.tip=null,this._setListeners(),this._config.selector||this._fixTitle()}static get Default(){return Ii}static get DefaultType(){return Di}static get NAME(){return"tooltip"}enable(){this._isEnabled=!0}disable(){this._isEnabled=!1}toggleEnabled(){this._isEnabled=!this._isEnabled}toggle(){this._isEnabled&&(this._activeTrigger.click=!this._activeTrigger.click,this._isShown()?this._leave():this._enter())}dispose(){clearTimeout(this._timeout),j.off(this._element.closest(ki),$i,this._hideModalHandler),this._element.getAttribute("data-bs-original-title")&&this._element.setAttribute("title",this._element.getAttribute("data-bs-original-title")),this._disposePopper(),super.dispose()}show(){if("none"===this._element.style.display)throw new Error("Please use show on visible elements");if(!this._isWithContent()||!this._isEnabled)return;const t=j.trigger(this._element,this.constructor.eventName("show")),e=(u(this._element)||this._element.ownerDocument.documentElement).contains(this._element);if(t.defaultPrevented||!e)return;this._disposePopper();const i=this._getTipElement();this._element.setAttribute("aria-describedby",i.getAttribute("id"));const{container:s}=this._config;if(this._element.ownerDocument.documentElement.contains(this.tip)||(s.append(i),j.trigger(this._element,this.constructor.eventName("inserted"))),this._popper=this._createPopper(i),i.classList.add(Ti),"ontouchstart"in document.documentElement)for(const t of[].concat(...document.body.children))j.on(t,"mouseover",_);this._queueCallback((()=>{j.trigger(this._element,this.constructor.eventName("shown")),!1===this._isHovered&&this._leave(),this._isHovered=!1}),this.tip,this._isAnimated())}hide(){if(this._isShown()&&!j.trigger(this._element,this.constructor.eventName("hide")).defaultPrevented){if(this._getTipElement().classList.remove(Ti),"ontouchstart"in document.documentElement)for(const t of[].concat(...document.body.children))j.off(t,"mouseover",_);this._activeTrigger.click=!1,this._activeTrigger[Li]=!1,this._activeTrigger[Si]=!1,this._isHovered=null,this._queueCallback((()=>{this._isWithActiveTrigger()||(this._isHovered||this._disposePopper(),this._element.removeAttribute("aria-describedby"),j.trigger(this._element,this.constructor.eventName("hidden")))}),this.tip,this._isAnimated())}}update(){this._popper&&this._popper.update()}_isWithContent(){return Boolean(this._getTitle())}_getTipElement(){return this.tip||(this.tip=this._createTipElement(this._newContent||this._getContentForTemplate())),this.tip}_createTipElement(t){const e=this._getTemplateFactory(t).toHtml();if(!e)return null;e.classList.remove(Ci,Ti),e.classList.add(`bs-${this.constructor.NAME}-auto`);const i=(t=>{do{t+=Math.floor(1e6*Math.random())}while(document.getElementById(t));return t})(this.constructor.NAME).toString();return e.setAttribute("id",i),this._isAnimated()&&e.classList.add(Ci),e}setContent(t){this._newContent=t,this._isShown()&&(this._disposePopper(),this.show())}_getTemplateFactory(t){return this._templateFactory?this._templateFactory.changeContent(t):this._templateFactory=new Ai({...this._config,content:t,extraClass:this._resolvePossibleFunction(this._config.customClass)}),this._templateFactory}_getContentForTemplate(){return{".tooltip-inner":this._getTitle()}}_getTitle(){return this._resolvePossibleFunction(this._config.title)||this._element.getAttribute("data-bs-original-title")}_initializeOnDelegatedTarget(t){return this.constructor.getOrCreateInstance(t.delegateTarget,this._getDelegateConfig())}_isAnimated(){return this._config.animation||this.tip&&this.tip.classList.contains(Ci)}_isShown(){return this.tip&&this.tip.classList.contains(Ti)}_createPopper(t){const e=v(this._config.placement,[this,t,this._element]),s=Oi[e.toUpperCase()];return i.createPopper(this._element,t,this._getPopperConfig(s))}_getOffset(){const{offset:t}=this._config;return"string"==typeof t?t.split(",").map((t=>Number.parseInt(t,10))):"function"==typeof t?e=>t(e,this._element):t}_resolvePossibleFunction(t){return v(t,[this._element])}_getPopperConfig(t){const e={placement:t,modifiers:[{name:"flip",options:{fallbackPlacements:this._config.fallbackPlacements}},{name:"offset",options:{offset:this._getOffset()}},{name:"preventOverflow",options:{boundary:this._config.boundary}},{name:"arrow",options:{element:`.${this.constructor.NAME}-arrow`}},{name:"preSetPlacement",enabled:!0,phase:"beforeMain",fn:t=>{this._getTipElement().setAttribute("data-popper-placement",t.state.placement)}}]};return{...e,...v(this._config.popperConfig,[e])}}_setListeners(){const t=this._config.trigger.split(" ");for(const e of t)if("click"===e)j.on(this._element,this.constructor.eventName("click"),this._config.selector,(t=>{this._initializeOnDelegatedTarget(t).toggle()}));else if("manual"!==e){const t=e===Si?this.constructor.eventName("mouseenter"):this.constructor.eventName("focusin"),i=e===Si?this.constructor.eventName("mouseleave"):this.constructor.eventName("focusout");j.on(this._element,t,this._config.selector,(t=>{const e=this._initializeOnDelegatedTarget(t);e._activeTrigger["focusin"===t.type?Li:Si]=!0,e._enter()})),j.on(this._element,i,this._config.selector,(t=>{const e=this._initializeOnDelegatedTarget(t);e._activeTrigger["focusout"===t.type?Li:Si]=e._element.contains(t.relatedTarget),e._leave()}))}this._hideModalHandler=()=>{this._element&&this.hide()},j.on(this._element.closest(ki),$i,this._hideModalHandler)}_fixTitle(){const t=this._element.getAttribute("title");t&&(this._element.getAttribute("aria-label")||this._element.textContent.trim()||this._element.setAttribute("aria-label",t),this._element.setAttribute("data-bs-original-title",t),this._element.removeAttribute("title"))}_enter(){this._isShown()||this._isHovered?this._isHovered=!0:(this._isHovered=!0,this._setTimeout((()=>{this._isHovered&&this.show()}),this._config.delay.show))}_leave(){this._isWithActiveTrigger()||(this._isHovered=!1,this._setTimeout((()=>{this._isHovered||this.hide()}),this._config.delay.hide))}_setTimeout(t,e){clearTimeout(this._timeout),this._timeout=setTimeout(t,e)}_isWithActiveTrigger(){return Object.values(this._activeTrigger).includes(!0)}_getConfig(t){const e=B.getDataAttributes(this._element);for(const t of Object.keys(e))Ei.has(t)&&delete e[t];return t={...e,..."object"==typeof t&&t?t:{}},t=this._mergeConfigObj(t),t=this._configAfterMerge(t),this._typeCheckConfig(t),t}_configAfterMerge(t){return t.container=!1===t.container?document.body:c(t.container),"number"==typeof t.delay&&(t.delay={show:t.delay,hide:t.delay}),"number"==typeof t.title&&(t.title=t.title.toString()),"number"==typeof t.content&&(t.content=t.content.toString()),t}_getDelegateConfig(){const t={};for(const[e,i]of Object.entries(this._config))this.constructor.Default[e]!==i&&(t[e]=i);return t.selector=!1,t.trigger="manual",t}_disposePopper(){this._popper&&(this._popper.destroy(),this._popper=null),this.tip&&(this.tip.remove(),this.tip=null)}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=Ni.getOrCreateInstance(this,t);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===e[t])throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);e[t]()}}))}}b(Ni);const Pi={...Ni.Default,content:"",offset:[0,8],placement:"right",template:'<div class="popover" role="tooltip"><div class="popover-arrow"></div><h3 class="popover-header"></h3><div class="popover-body"></div></div>',trigger:"click"},xi={...Ni.DefaultType,content:"(null|string|element|function)"};class Mi extends Ni{static get Default(){return Pi}static get DefaultType(){return xi}static get NAME(){return"popover"}_isWithContent(){return this._getTitle()||this._getContent()}_getContentForTemplate(){return{".popover-header":this._getTitle(),".popover-body":this._getContent()}}_getContent(){return this._resolvePossibleFunction(this._config.content)}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=Mi.getOrCreateInstance(this,t);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===e[t])throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);e[t]()}}))}}b(Mi);const ji=".bs.scrollspy",Fi=`activate${ji}`,zi=`click${ji}`,Hi=`load${ji}.data-api`,Bi="active",qi="[href]",Wi=".nav-link",Ri=`${Wi}, .nav-item > ${Wi}, .list-group-item`,Ki={offset:null,rootMargin:"0px 0px -25%",smoothScroll:!1,target:null,threshold:[.1,.5,1]},Vi={offset:"(number|null)",rootMargin:"string",smoothScroll:"boolean",target:"element",threshold:"array"};class Qi extends W{constructor(t,e){super(t,e),this._targetLinks=new Map,this._observableSections=new Map,this._rootElement="visible"===getComputedStyle(this._element).overflowY?null:this._element,this._activeTarget=null,this._observer=null,this._previousScrollData={visibleEntryTop:0,parentScrollTop:0},this.refresh()}static get Default(){return Ki}static get DefaultType(){return Vi}static get NAME(){return"scrollspy"}refresh(){this._initializeTargetsAndObservables(),this._maybeEnableSmoothScroll(),this._observer?this._observer.disconnect():this._observer=this._getNewObserver();for(const t of this._observableSections.values())this._observer.observe(t)}dispose(){this._observer.disconnect(),super.dispose()}_configAfterMerge(t){return t.target=c(t.target)||document.body,t.rootMargin=t.offset?`${t.offset}px 0px -30%`:t.rootMargin,"string"==typeof t.threshold&&(t.threshold=t.threshold.split(",").map((t=>Number.parseFloat(t)))),t}_maybeEnableSmoothScroll(){this._config.smoothScroll&&(j.off(this._config.target,zi),j.on(this._config.target,zi,qi,(t=>{const e=this._observableSections.get(t.target.hash);if(e){t.preventDefault();const i=this._rootElement||window,s=e.offsetTop-this._element.offsetTop;if(i.scrollTo)return void i.scrollTo({top:s,behavior:"smooth"});i.scrollTop=s}})))}_getNewObserver(){const t={root:this._rootElement,threshold:this._config.threshold,rootMargin:this._config.rootMargin};return new IntersectionObserver((t=>this._observerCallback(t)),t)}_observerCallback(t){const e=t=>this._targetLinks.get(`#${t.target.id}`),i=t=>{this._previousScrollData.visibleEntryTop=t.target.offsetTop,this._process(e(t))},s=(this._rootElement||document.documentElement).scrollTop,n=s>=this._previousScrollData.parentScrollTop;this._previousScrollData.parentScrollTop=s;for(const o of t){if(!o.isIntersecting){this._activeTarget=null,this._clearActiveClass(e(o));continue}const t=o.target.offsetTop>=this._previousScrollData.visibleEntryTop;if(n&&t){if(i(o),!s)return}else n||t||i(o)}}_initializeTargetsAndObservables(){this._targetLinks=new Map,this._observableSections=new Map;const t=K.find(qi,this._config.target);for(const e of t){if(!e.hash||d(e))continue;const t=K.findOne(decodeURI(e.hash),this._element);h(t)&&(this._targetLinks.set(decodeURI(e.hash),e),this._observableSections.set(e.hash,t))}}_process(t){this._activeTarget!==t&&(this._clearActiveClass(this._config.target),this._activeTarget=t,t.classList.add(Bi),this._activateParents(t),j.trigger(this._element,Fi,{relatedTarget:t}))}_activateParents(t){if(t.classList.contains("dropdown-item"))K.findOne(".dropdown-toggle",t.closest(".dropdown")).classList.add(Bi);else for(const e of K.parents(t,".nav, .list-group"))for(const t of K.prev(e,Ri))t.classList.add(Bi)}_clearActiveClass(t){t.classList.remove(Bi);const e=K.find(`${qi}.${Bi}`,t);for(const t of e)t.classList.remove(Bi)}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=Qi.getOrCreateInstance(this,t);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===e[t]||t.startsWith("_")||"constructor"===t)throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);e[t]()}}))}}j.on(window,Hi,(()=>{for(const t of K.find('[data-bs-spy="scroll"]'))Qi.getOrCreateInstance(t)})),b(Qi);const Xi=".bs.tab",Yi=`hide${Xi}`,Ui=`hidden${Xi}`,Gi=`show${Xi}`,Ji=`shown${Xi}`,Zi=`click${Xi}`,ts=`keydown${Xi}`,es=`load${Xi}`,is="ArrowLeft",ss="ArrowRight",ns="ArrowUp",os="ArrowDown",rs="Home",as="End",ls="active",cs="fade",hs="show",ds=".dropdown-toggle",us=`:not(${ds})`,_s='[data-bs-toggle="tab"], [data-bs-toggle="pill"], [data-bs-toggle="list"]',gs=`.nav-link${us}, .list-group-item${us}, [role="tab"]${us}, ${_s}`,fs=`.${ls}[data-bs-toggle="tab"], .${ls}[data-bs-toggle="pill"], .${ls}[data-bs-toggle="list"]`;class ms extends W{constructor(t){super(t),this._parent=this._element.closest('.list-group, .nav, [role="tablist"]'),this._parent&&(this._setInitialAttributes(this._parent,this._getChildren()),j.on(this._element,ts,(t=>this._keydown(t))))}static get NAME(){return"tab"}show(){const t=this._element;if(this._elemIsActive(t))return;const e=this._getActiveElem(),i=e?j.trigger(e,Yi,{relatedTarget:t}):null;j.trigger(t,Gi,{relatedTarget:e}).defaultPrevented||i&&i.defaultPrevented||(this._deactivate(e,t),this._activate(t,e))}_activate(t,e){t&&(t.classList.add(ls),this._activate(K.getElementFromSelector(t)),this._queueCallback((()=>{"tab"===t.getAttribute("role")?(t.removeAttribute("tabindex"),t.setAttribute("aria-selected",!0),this._toggleDropDown(t,!0),j.trigger(t,Ji,{relatedTarget:e})):t.classList.add(hs)}),t,t.classList.contains(cs)))}_deactivate(t,e){t&&(t.classList.remove(ls),t.blur(),this._deactivate(K.getElementFromSelector(t)),this._queueCallback((()=>{"tab"===t.getAttribute("role")?(t.setAttribute("aria-selected",!1),t.setAttribute("tabindex","-1"),this._toggleDropDown(t,!1),j.trigger(t,Ui,{relatedTarget:e})):t.classList.remove(hs)}),t,t.classList.contains(cs)))}_keydown(t){if(![is,ss,ns,os,rs,as].includes(t.key))return;t.stopPropagation(),t.preventDefault();const e=this._getChildren().filter((t=>!d(t)));let i;if([rs,as].includes(t.key))i=e[t.key===rs?0:e.length-1];else{const s=[ss,os].includes(t.key);i=w(e,t.target,s,!0)}i&&(i.focus({preventScroll:!0}),ms.getOrCreateInstance(i).show())}_getChildren(){return K.find(gs,this._parent)}_getActiveElem(){return this._getChildren().find((t=>this._elemIsActive(t)))||null}_setInitialAttributes(t,e){this._setAttributeIfNotExists(t,"role","tablist");for(const t of e)this._setInitialAttributesOnChild(t)}_setInitialAttributesOnChild(t){t=this._getInnerElement(t);const e=this._elemIsActive(t),i=this._getOuterElement(t);t.setAttribute("aria-selected",e),i!==t&&this._setAttributeIfNotExists(i,"role","presentation"),e||t.setAttribute("tabindex","-1"),this._setAttributeIfNotExists(t,"role","tab"),this._setInitialAttributesOnTargetPanel(t)}_setInitialAttributesOnTargetPanel(t){const e=K.getElementFromSelector(t);e&&(this._setAttributeIfNotExists(e,"role","tabpanel"),t.id&&this._setAttributeIfNotExists(e,"aria-labelledby",`${t.id}`))}_toggleDropDown(t,e){const i=this._getOuterElement(t);if(!i.classList.contains("dropdown"))return;const s=(t,s)=>{const n=K.findOne(t,i);n&&n.classList.toggle(s,e)};s(ds,ls),s(".dropdown-menu",hs),i.setAttribute("aria-expanded",e)}_setAttributeIfNotExists(t,e,i){t.hasAttribute(e)||t.setAttribute(e,i)}_elemIsActive(t){return t.classList.contains(ls)}_getInnerElement(t){return t.matches(gs)?t:K.findOne(gs,t)}_getOuterElement(t){return t.closest(".nav-item, .list-group-item")||t}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=ms.getOrCreateInstance(this);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===e[t]||t.startsWith("_")||"constructor"===t)throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);e[t]()}}))}}j.on(document,Zi,_s,(function(t){["A","AREA"].includes(this.tagName)&&t.preventDefault(),d(this)||ms.getOrCreateInstance(this).show()})),j.on(window,es,(()=>{for(const t of K.find(fs))ms.getOrCreateInstance(t)})),b(ms);const ps=".bs.toast",bs=`mouseover${ps}`,vs=`mouseout${ps}`,ys=`focusin${ps}`,ws=`focusout${ps}`,As=`hide${ps}`,Es=`hidden${ps}`,Cs=`show${ps}`,Ts=`shown${ps}`,ks="hide",$s="show",Ss="showing",Ls={animation:"boolean",autohide:"boolean",delay:"number"},Os={animation:!0,autohide:!0,delay:5e3};class Is extends W{constructor(t,e){super(t,e),this._timeout=null,this._hasMouseInteraction=!1,this._hasKeyboardInteraction=!1,this._setListeners()}static get Default(){return Os}static get DefaultType(){return Ls}static get NAME(){return"toast"}show(){j.trigger(this._element,Cs).defaultPrevented||(this._clearTimeout(),this._config.animation&&this._element.classList.add("fade"),this._element.classList.remove(ks),g(this._element),this._element.classList.add($s,Ss),this._queueCallback((()=>{this._element.classList.remove(Ss),j.trigger(this._element,Ts),this._maybeScheduleHide()}),this._element,this._config.animation))}hide(){this.isShown()&&(j.trigger(this._element,As).defaultPrevented||(this._element.classList.add(Ss),this._queueCallback((()=>{this._element.classList.add(ks),this._element.classList.remove(Ss,$s),j.trigger(this._element,Es)}),this._element,this._config.animation)))}dispose(){this._clearTimeout(),this.isShown()&&this._element.classList.remove($s),super.dispose()}isShown(){return this._element.classList.contains($s)}_maybeScheduleHide(){this._config.autohide&&(this._hasMouseInteraction||this._hasKeyboardInteraction||(this._timeout=setTimeout((()=>{this.hide()}),this._config.delay)))}_onInteraction(t,e){switch(t.type){case"mouseover":case"mouseout":this._hasMouseInteraction=e;break;case"focusin":case"focusout":this._hasKeyboardInteraction=e}if(e)return void this._clearTimeout();const i=t.relatedTarget;this._element===i||this._element.contains(i)||this._maybeScheduleHide()}_setListeners(){j.on(this._element,bs,(t=>this._onInteraction(t,!0))),j.on(this._element,vs,(t=>this._onInteraction(t,!1))),j.on(this._element,ys,(t=>this._onInteraction(t,!0))),j.on(this._element,ws,(t=>this._onInteraction(t,!1)))}_clearTimeout(){clearTimeout(this._timeout),this._timeout=null}static jQueryInterface(t){return this.each((function(){const e=Is.getOrCreateInstance(this,t);if("string"==typeof t){if(void 0===e[t])throw new TypeError(`No method named "${t}"`);e[t](this)}}))}}return V(Is),b(Is),{Alert:U,Button:J,Carousel:Ot,Collapse:Rt,Dropdown:fe,Modal:Ue,Offcanvas:gi,Popover:Mi,ScrollSpy:Qi,Tab:ms,Toast:Is,Tooltip:Ni}})); +//# sourceMappingURL=bootstrap.min.js.map
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/doc/api.rst b/doc/api.rst index 9b6c0f3c..8b8b19c8 100644 --- a/doc/api.rst +++ b/doc/api.rst @@ -6,18 +6,20 @@ API Reference The {fmt} library API consists of the following parts: -* :ref:`fmt/core.h <core-api>`: the core API providing argument handling - facilities and a lightweight subset of formatting functions -* :ref:`fmt/format.h <format-api>`: the full format API providing compile-time - format string checks, wide string, output iterator and user-defined type - support -* :ref:`fmt/ranges.h <ranges-api>`: additional formatting support for ranges - and tuples +* :ref:`fmt/core.h <core-api>`: the core API providing main formatting functions + for ``char``/UTF-8 with C++20 compile-time checks and minimal dependencies +* :ref:`fmt/format.h <format-api>`: the full format API providing additional + formatting functions and locale support +* :ref:`fmt/ranges.h <ranges-api>`: formatting of ranges and tuples * :ref:`fmt/chrono.h <chrono-api>`: date and time formatting +* :ref:`fmt/std.h <std-api>`: formatters for standard library types * :ref:`fmt/compile.h <compile-api>`: format string compilation * :ref:`fmt/color.h <color-api>`: terminal color and text style +* :ref:`fmt/os.h <os-api>`: system APIs * :ref:`fmt/ostream.h <ostream-api>`: ``std::ostream`` support +* :ref:`fmt/args.h <args-api>`: dynamic argument lists * :ref:`fmt/printf.h <printf-api>`: ``printf`` formatting +* :ref:`fmt/xchar.h <xchar-api>`: optional ``wchar_t`` support All functions and types provided by the library reside in namespace ``fmt`` and macros have prefix ``FMT_``. @@ -27,227 +29,207 @@ macros have prefix ``FMT_``. Core API ======== -``fmt/core.h`` defines the core API which provides argument handling facilities -and a lightweight subset of formatting functions. In the header-only mode -include ``fmt/format.h`` instead of ``fmt/core.h``. +``fmt/core.h`` defines the core API which provides main formatting functions +for ``char``/UTF-8 with C++20 compile-time checks. It has minimal include +dependencies for better compile times. This header is only beneficial when +using {fmt} as a library (the default) and not in the header-only mode. +It also provides ``formatter`` specializations for built-in and string types. The following functions use :ref:`format string syntax <syntax>` similar to that of Python's `str.format -<http://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format>`_. -They take *format_str* and *args* as arguments. +<https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format>`_. +They take *fmt* and *args* as arguments. -*format_str* is a format string that contains literal text and replacement -fields surrounded by braces ``{}``. The fields are replaced with formatted -arguments in the resulting string. A function taking *format_str* doesn't -participate in an overload resolution if the latter is not a string. +*fmt* is a format string that contains literal text and replacement fields +surrounded by braces ``{}``. The fields are replaced with formatted arguments +in the resulting string. `~fmt::format_string` is a format string which can be +implicitly constructed from a string literal or a ``constexpr`` string and is +checked at compile time in C++20. To pass a runtime format string wrap it in +`fmt::runtime`. *args* is an argument list representing objects to be formatted. -.. _format: - -.. doxygenfunction:: format(const S&, Args&&...) -.. doxygenfunction:: vformat(const S&, basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>>) - -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::format_to(OutputIt, const S&, Args&&...) -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::format_to_n(OutputIt, size_t, const S&, const Args&...) -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::formatted_size(string_view, Args&&...) - -.. _print: - -.. doxygenfunction:: print(const S&, Args&&...) -.. doxygenfunction:: vprint(string_view, format_args) +I/O errors are reported as `std::system_error +<https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/error/system_error>`_ exceptions unless +specified otherwise. -.. doxygenfunction:: print(std::FILE *, const S&, Args&&...) -.. doxygenfunction:: vprint(std::FILE *, string_view, format_args) - -Named Arguments ---------------- +.. _format: -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::arg(const S&, const T&) +.. doxygenfunction:: format(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> std::string +.. doxygenfunction:: vformat(string_view fmt, format_args args) -> std::string -Named arguments are not supported in compile-time checks at the moment. +.. doxygenfunction:: format_to(OutputIt out, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> OutputIt +.. doxygenfunction:: format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> format_to_n_result<OutputIt> +.. doxygenfunction:: formatted_size(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> size_t -Argument Lists --------------- +.. doxygenstruct:: fmt::format_to_n_result + :members: -You can create your own formatting function with compile-time checks and small -binary footprint, for example (https://godbolt.org/z/oba4Mc): +.. _print: -.. code:: c++ +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::print(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::vprint(string_view fmt, format_args args) - #include <fmt/format.h> +.. doxygenfunction:: print(std::FILE *f, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) +.. doxygenfunction:: vprint(std::FILE *f, string_view fmt, format_args args) - void vlog(const char* file, int line, fmt::string_view format, - fmt::format_args args) { - fmt::print("{}: {}: ", file, line); - fmt::vprint(format, args); - } +Compile-Time Format String Checks +--------------------------------- - template <typename S, typename... Args> - void log(const char* file, int line, const S& format, Args&&... args) { - vlog(file, line, format, - fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format, args...)); - } +Compile-time format string checks are enabled by default on compilers +that support C++20 ``consteval``. On older compilers you can use the +:ref:`FMT_STRING <legacy-checks>`: macro defined in ``fmt/format.h`` instead. - #define MY_LOG(format, ...) \ - log(__FILE__, __LINE__, FMT_STRING(format), __VA_ARGS__) +Unused arguments are allowed as in Python's `str.format` and ordinary functions. - MY_LOG("invalid squishiness: {}", 42); +.. doxygenclass:: fmt::basic_format_string + :members: -Note that ``vlog`` is not parameterized on argument types which improves compile -times and reduces binary code size compared to a fully parameterized version. +.. doxygentypedef:: fmt::format_string -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::make_args_checked(const S&, const remove_reference_t<Args>&...) +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::runtime(string_view) -> runtime_format_string<> -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::make_format_args(const Args&...) +.. _udt: -.. doxygenclass:: fmt::format_arg_store - :members: +Formatting User-Defined Types +----------------------------- -.. doxygenclass:: fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store - :members: +The {fmt} library provides formatters for many standard C++ types. +See :ref:`fmt/ranges.h <ranges-api>` for ranges and tuples including standard +containers such as ``std::vector``, :ref:`fmt/chrono.h <chrono-api>` for date +and time formatting and :ref:`fmt/std.h <std-api>` for other standard library +types. -.. doxygenclass:: fmt::basic_format_args - :members: +There are two ways to make a user-defined type formattable: providing a +``format_as`` function or specializing the ``formatter`` struct template. -.. doxygenstruct:: fmt::format_args +Use ``format_as`` if you want to make your type formattable as some other type +with the same format specifiers. The ``format_as`` function should take an +object of your type and return an object of a formattable type. It should be +defined in the same namespace as your type. -.. doxygenclass:: fmt::basic_format_arg - :members: +Example (https://godbolt.org/z/nvME4arz8):: -Compatibility -------------- + #include <fmt/format.h> -.. doxygenclass:: fmt::basic_string_view - :members: + namespace kevin_namespacy { + enum class film { + house_of_cards, american_beauty, se7en = 7 + }; + auto format_as(film f) { return fmt::underlying(f); } + } -.. doxygentypedef:: fmt::string_view -.. doxygentypedef:: fmt::wstring_view + int main() { + fmt::print("{}\n", kevin_namespacy::film::se7en); // prints "7" + } -Locale ------- +Using specialization is more complex but gives you full control over parsing and +formatting. To use this method specialize the ``formatter`` struct template for +your type and implement ``parse`` and ``format`` methods. -All formatting is locale-independent by default. Use the ``'L'`` format -specifier to insert the appropriate number separator characters from the -locale:: +The recommended way of defining a formatter is by reusing an existing one via +inheritance or composition. This way you can support standard format specifiers +without implementing them yourself. For example:: + // color.h: #include <fmt/core.h> - #include <locale> - std::locale::global(std::locale("en_US.UTF-8")); - auto s = fmt::format("{:L}", 1000000); // s == "1,000,000" + enum class color {red, green, blue}; -.. _format-api: + template <> struct fmt::formatter<color>: formatter<string_view> { + // parse is inherited from formatter<string_view>. -Format API -========== + auto format(color c, format_context& ctx) const; + }; -``fmt/format.h`` defines the full format API providing compile-time format -string checks, wide string, output iterator and user-defined type support. + // color.cc: + #include "color.h" + #include <fmt/format.h> -Compile-time Format String Checks ---------------------------------- + auto fmt::formatter<color>::format(color c, format_context& ctx) const { + string_view name = "unknown"; + switch (c) { + case color::red: name = "red"; break; + case color::green: name = "green"; break; + case color::blue: name = "blue"; break; + } + return formatter<string_view>::format(name, ctx); + } -Compile-time checks are enabled when using ``FMT_STRING``. They support built-in -and string types as well as user-defined types with ``constexpr`` ``parse`` -functions in their ``formatter`` specializations. +Note that ``formatter<string_view>::format`` is defined in ``fmt/format.h`` so +it has to be included in the source file. Since ``parse`` is inherited from +``formatter<string_view>`` it will recognize all string format specifications, +for example -.. doxygendefine:: FMT_STRING +.. code-block:: c++ -.. _udt: + fmt::format("{:>10}", color::blue) -Formatting User-defined Types ------------------------------ +will return ``" blue"``. + +The experimental ``nested_formatter`` provides an easy way applying a formatter +to one or more subobjects. -To make a user-defined type formattable, specialize the ``formatter<T>`` struct -template and implement ``parse`` and ``format`` methods:: +For example:: #include <fmt/format.h> - struct point { double x, y; }; + struct point { + double x, y; + }; template <> - struct fmt::formatter<point> { - // Presentation format: 'f' - fixed, 'e' - exponential. - char presentation = 'f'; - - // Parses format specifications of the form ['f' | 'e']. - constexpr auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) { - // auto parse(format_parse_context &ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) // c++11 - // [ctx.begin(), ctx.end()) is a character range that contains a part of - // the format string starting from the format specifications to be parsed, - // e.g. in - // - // fmt::format("{:f} - point of interest", point{1, 2}); - // - // the range will contain "f} - point of interest". The formatter should - // parse specifiers until '}' or the end of the range. In this example - // the formatter should parse the 'f' specifier and return an iterator - // pointing to '}'. - - // Parse the presentation format and store it in the formatter: - auto it = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end(); - if (it != end && (*it == 'f' || *it == 'e')) presentation = *it++; - - // Check if reached the end of the range: - if (it != end && *it != '}') - throw format_error("invalid format"); - - // Return an iterator past the end of the parsed range: - return it; - } - - // Formats the point p using the parsed format specification (presentation) - // stored in this formatter. - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(const point& p, FormatContext& ctx) { - // auto format(const point &p, FormatContext &ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) // c++11 - // ctx.out() is an output iterator to write to. - return format_to( - ctx.out(), - presentation == 'f' ? "({:.1f}, {:.1f})" : "({:.1e}, {:.1e})", - p.x, p.y); + struct fmt::formatter<point> : nested_formatter<double> { + auto format(point p, format_context& ctx) const { + return write_padded(ctx, [=](auto out) { + return format_to(out, "({}, {})", nested(p.x), nested(p.y)); + }); } }; -Then you can pass objects of type ``point`` to any formatting function:: - - point p = {1, 2}; - std::string s = fmt::format("{:f}", p); - // s == "(1.0, 2.0)" - -You can also reuse existing formatters via inheritance or composition, for -example:: - - enum class color {red, green, blue}; + int main() { + fmt::print("[{:>20.2f}]", point{1, 2}); + } - template <> struct fmt::formatter<color>: formatter<string_view> { - // parse is inherited from formatter<string_view>. - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(color c, FormatContext& ctx) { - string_view name = "unknown"; - switch (c) { - case color::red: name = "red"; break; - case color::green: name = "green"; break; - case color::blue: name = "blue"; break; - } - return formatter<string_view>::format(name, ctx); - } +prints:: + + [ (1.00, 2.00)] + +Notice that fill, align and width are applied to the whole object which is the +recommended behavior while the remaining specifiers apply to elements. + +In general the formatter has the following form:: + + template <> struct fmt::formatter<T> { + // Parses format specifiers and stores them in the formatter. + // + // [ctx.begin(), ctx.end()) is a, possibly empty, character range that + // contains a part of the format string starting from the format + // specifications to be parsed, e.g. in + // + // fmt::format("{:f} continued", ...); + // + // the range will contain "f} continued". The formatter should parse + // specifiers until '}' or the end of the range. In this example the + // formatter should parse the 'f' specifier and return an iterator + // pointing to '}'. + constexpr auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) + -> format_parse_context::iterator; + + // Formats value using the parsed format specification stored in this + // formatter and writes the output to ctx.out(). + auto format(const T& value, format_context& ctx) const + -> format_context::iterator; }; -Since ``parse`` is inherited from ``formatter<string_view>`` it will recognize -all string format specifications, for example - -.. code-block:: c++ - - fmt::format("{:>10}", color::blue) - -will return ``" blue"``. +It is recommended to at least support fill, align and width that apply to the +whole object and have the same semantics as in standard formatters. You can also write a formatter for a hierarchy of classes:: + // demo.h: #include <type_traits> - #include <fmt/format.h> + #include <fmt/core.h> struct A { virtual ~A() {} @@ -261,62 +243,130 @@ You can also write a formatter for a hierarchy of classes:: template <typename T> struct fmt::formatter<T, std::enable_if_t<std::is_base_of<A, T>::value, char>> : fmt::formatter<std::string> { - template <typename FormatCtx> - auto format(const A& a, FormatCtx& ctx) { + auto format(const A& a, format_context& ctx) const { return fmt::formatter<std::string>::format(a.name(), ctx); } }; + // demo.cc: + #include "demo.h" + #include <fmt/format.h> + int main() { B b; A& a = b; fmt::print("{}", a); // prints "B" } -If a type provides both a ``formatter`` specialization and an implicit -conversion to a formattable type, the specialization takes precedence over the -conversion. +Providing both a ``formatter`` specialization and a ``format_as`` overload is +disallowed. + +Named Arguments +--------------- + +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::arg(const S&, const T&) + +Named arguments are not supported in compile-time checks at the moment. + +Argument Lists +-------------- + +You can create your own formatting function with compile-time checks and small +binary footprint, for example (https://godbolt.org/z/vajfWEG4b): + +.. code:: c++ + + #include <fmt/core.h> + + void vlog(const char* file, int line, fmt::string_view format, + fmt::format_args args) { + fmt::print("{}: {}: ", file, line); + fmt::vprint(format, args); + } + + template <typename... T> + void log(const char* file, int line, fmt::format_string<T...> format, T&&... args) { + vlog(file, line, format, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); + } + + #define MY_LOG(format, ...) log(__FILE__, __LINE__, format, __VA_ARGS__) + + MY_LOG("invalid squishiness: {}", 42); + +Note that ``vlog`` is not parameterized on argument types which improves compile +times and reduces binary code size compared to a fully parameterized version. + +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::make_format_args(const Args&...) + +.. doxygenclass:: fmt::format_arg_store + :members: + +.. doxygenclass:: fmt::basic_format_args + :members: + +.. doxygentypedef:: fmt::format_args + +.. doxygenclass:: fmt::basic_format_arg + :members: .. doxygenclass:: fmt::basic_format_parse_context :members: -Output Iterator Support ------------------------ +.. doxygenclass:: fmt::basic_format_context + :members: -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::format_to(OutputIt, const S&, Args&&...) -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::format_to_n(OutputIt, size_t, const S&, const Args&...) -.. doxygenstruct:: fmt::format_to_n_result +.. doxygentypedef:: fmt::format_context + +.. _args-api: + +Dynamic Argument Lists +---------------------- + +The header ``fmt/args.h`` provides ``dynamic_format_arg_store``, a builder-like +API that can be used to construct format argument lists dynamically. + +.. doxygenclass:: fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store + :members: + +Compatibility +------------- + +.. doxygenclass:: fmt::basic_string_view :members: -Literal-based API +.. doxygentypedef:: fmt::string_view + +.. _format-api: + +Format API +========== + +``fmt/format.h`` defines the full format API providing additional formatting +functions and locale support. + +Literal-Based API ----------------- The following user-defined literals are defined in ``fmt/format.h``. -.. doxygenfunction:: operator""_format(const char *, size_t) - -.. doxygenfunction:: operator""_a(const char *, size_t) +.. doxygenfunction:: operator""_a() Utilities --------- -.. doxygenstruct:: fmt::is_char - -.. doxygentypedef:: fmt::char_t +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::ptr(T p) -> const void* +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::ptr(const std::unique_ptr<T, Deleter> &p) -> const void* +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::ptr(const std::shared_ptr<T> &p) -> const void* -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::ptr(const T *) -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::ptr(const std::unique_ptr<T>&) -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::ptr(const std::shared_ptr<T>&) +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::underlying(Enum e) -> typename std::underlying_type<Enum>::type -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::to_string(const T&) +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::to_string(const T &value) -> std::string -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::to_wstring(const T&) +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::join(Range &&range, string_view sep) -> join_view<detail::iterator_t<Range>, detail::sentinel_t<Range>> -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::to_string_view(const Char *) +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::join(It begin, Sentinel end, string_view sep) -> join_view<It, Sentinel> -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::join(Range&&, string_view) - -.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::join(It, Sentinel, string_view) +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::group_digits(T value) -> group_digits_view<T> .. doxygenclass:: fmt::detail::buffer :members: @@ -328,18 +378,14 @@ Utilities System Errors ------------- -fmt does not use ``errno`` to communicate errors to the user, but it may call -system functions which set ``errno``. Users should not make any assumptions about -the value of ``errno`` being preserved by library functions. +{fmt} does not use ``errno`` to communicate errors to the user, but it may call +system functions which set ``errno``. Users should not make any assumptions +about the value of ``errno`` being preserved by library functions. -.. doxygenclass:: fmt::system_error - :members: +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::system_error .. doxygenfunction:: fmt::format_system_error -.. doxygenclass:: fmt::windows_error - :members: - Custom Allocators ----------------- @@ -358,8 +404,8 @@ allocator:: custom_string vformat(custom_allocator alloc, fmt::string_view format_str, fmt::format_args args) { - custom_memory_buffer buf(alloc); - fmt::vformat_to(buf, format_str, args); + auto buf = custom_memory_buffer(alloc); + fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(buf), format_str, args); return custom_string(buf.data(), buf.size(), alloc); } @@ -375,10 +421,45 @@ normally don't do any allocations for built-in and string types except for non-default floating-point formatting that occasionally falls back on ``sprintf``. +Locale +------ + +All formatting is locale-independent by default. Use the ``'L'`` format +specifier to insert the appropriate number separator characters from the +locale:: + + #include <fmt/core.h> + #include <locale> + + std::locale::global(std::locale("en_US.UTF-8")); + auto s = fmt::format("{:L}", 1000000); // s == "1,000,000" + +``fmt/format.h`` provides the following overloads of formatting functions that +take ``std::locale`` as a parameter. The locale type is a template parameter to +avoid the expensive ``<locale>`` include. + +.. doxygenfunction:: format(const Locale& loc, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> std::string +.. doxygenfunction:: format_to(OutputIt out, const Locale& loc, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> OutputIt +.. doxygenfunction:: formatted_size(const Locale& loc, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> size_t + +.. _legacy-checks: + +Legacy Compile-Time Format String Checks +---------------------------------------- + +``FMT_STRING`` enables compile-time checks on older compilers. It requires C++14 +or later and is a no-op in C++11. + +.. doxygendefine:: FMT_STRING + +To force the use of legacy compile-time checks, define the preprocessor variable +``FMT_ENFORCE_COMPILE_STRING``. When set, functions accepting ``FMT_STRING`` +will fail to compile with regular strings. + .. _ranges-api: -Ranges and Tuple Formatting -=========================== +Range and Tuple Formatting +========================== The library also supports convenient formatting of ranges and tuples:: @@ -405,43 +486,121 @@ Using ``fmt::join``, you can separate tuple elements with a custom separator:: Date and Time Formatting ======================== -The library supports `strftime -<http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/c/strftime>`_-like date and time -formatting:: +``fmt/chrono.h`` provides formatters for + +* `std::chrono::duration <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/duration>`_ +* `std::chrono::time_point + <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/time_point>`_ +* `std::tm <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/c/tm>`_ + +The format syntax is described in :ref:`chrono-specs`. + +**Example**:: #include <fmt/chrono.h> - std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr); - // Prints "The date is 2016-04-29." (with the current date) - fmt::print("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d}.", fmt::localtime(t)); + int main() { + std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr); + + // Prints "The date is 2020-11-07." (with the current date): + fmt::print("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d}.", fmt::localtime(t)); + + using namespace std::literals::chrono_literals; + + // Prints "Default format: 42s 100ms": + fmt::print("Default format: {} {}\n", 42s, 100ms); + + // Prints "strftime-like format: 03:15:30": + fmt::print("strftime-like format: {:%H:%M:%S}\n", 3h + 15min + 30s); + } + +.. doxygenfunction:: localtime(std::time_t time) + +.. doxygenfunction:: gmtime(std::time_t time) + +.. _std-api: + +Standard Library Types Formatting +================================= + +``fmt/std.h`` provides formatters for: + +* `std::filesystem::path <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/filesystem/path>`_ +* `std::thread::id <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/thread/id>`_ +* `std::monostate <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/variant/monostate>`_ +* `std::variant <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/variant/variant>`_ +* `std::optional <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/optional>`_ -The format string syntax is described in the documentation of -`strftime <http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/c/strftime>`_. +Formatting Variants +------------------- + +A ``std::variant`` is only formattable if every variant alternative is formattable, and requires the +``__cpp_lib_variant`` `library feature <https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/feature_test>`_. + +**Example**:: + + #include <fmt/std.h> + + std::variant<char, float> v0{'x'}; + // Prints "variant('x')" + fmt::print("{}", v0); + + std::variant<std::monostate, char> v1; + // Prints "variant(monostate)" .. _compile-api: -Format string compilation +Format String Compilation ========================= -``fmt/compile.h`` provides format string compilation support when using -``FMT_COMPILE``. Format strings are parsed, checked and converted -into efficient formatting code at compile-time. -This supports arguments of built-in and string types as well as user-defined types -with ``constexpr`` ``parse`` functions in their ``formatter`` specializations. +``fmt/compile.h`` provides format string compilation enabled via the +``FMT_COMPILE`` macro or the ``_cf`` user-defined literal. Format strings +marked with ``FMT_COMPILE`` or ``_cf`` are parsed, checked and converted into +efficient formatting code at compile-time. This supports arguments of built-in +and string types as well as user-defined types with ``format`` functions taking +the format context type as a template parameter in their ``formatter`` +specializations. For example:: + + template <> struct fmt::formatter<point> { + constexpr auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx); + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const point& p, FormatContext& ctx) const; + }; + Format string compilation can generate more binary code compared to the default API and is only recommended in places where formatting is a performance bottleneck. .. doxygendefine:: FMT_COMPILE +.. doxygenfunction:: operator""_cf() + .. _color-api: -Terminal color and text style +Terminal Color and Text Style ============================= ``fmt/color.h`` provides support for terminal color and text style output. -.. doxygenfunction:: print(const text_style&, const S&, const Args&...) +.. doxygenfunction:: print(const text_style &ts, const S &format_str, const Args&... args) + +.. doxygenfunction:: fg(detail::color_type) + +.. doxygenfunction:: bg(detail::color_type) + +.. doxygenfunction:: styled(const T& value, text_style ts) + +.. _os-api: + +System APIs +=========== + +.. doxygenclass:: fmt::ostream + :members: + +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::windows_error + :members: .. _ostream-api: @@ -449,24 +608,28 @@ Terminal color and text style ======================== ``fmt/ostream.h`` provides ``std::ostream`` support including formatting of -user-defined types that have overloaded ``operator<<``:: +user-defined types that have an overloaded insertion operator (``operator<<``). +In order to make a type formattable via ``std::ostream`` you should provide a +``formatter`` specialization inherited from ``ostream_formatter``:: #include <fmt/ostream.h> - class date { - int year_, month_, day_; - public: - date(int year, int month, int day): year_(year), month_(month), day_(day) {} + struct date { + int year, month, day; friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const date& d) { - return os << d.year_ << '-' << d.month_ << '-' << d.day_; + return os << d.year << '-' << d.month << '-' << d.day; } }; - std::string s = fmt::format("The date is {}", date(2012, 12, 9)); + template <> struct fmt::formatter<date> : ostream_formatter {}; + + std::string s = fmt::format("The date is {}", date{2012, 12, 9}); // s == "The date is 2012-12-9" -.. doxygenfunction:: print(std::basic_ostream<Char>&, const S&, Args&&...) +.. doxygenfunction:: streamed(const T &) + +.. doxygenfunction:: print(std::ostream &os, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) .. _printf-api: @@ -475,18 +638,32 @@ user-defined types that have overloaded ``operator<<``:: The header ``fmt/printf.h`` provides ``printf``-like formatting functionality. The following functions use `printf format string syntax -<http://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/009695399/functions/fprintf.html>`_ with +<https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/009695399/functions/fprintf.html>`_ with the POSIX extension for positional arguments. Unlike their standard counterparts, the ``fmt`` functions are type-safe and throw an exception if an argument type doesn't match its format specification. -.. doxygenfunction:: printf(const S&, const Args&...) +.. doxygenfunction:: printf(string_view fmt, const T&... args) -> int + +.. doxygenfunction:: fprintf(std::FILE *f, const S &fmt, const T&... args) -> int -.. doxygenfunction:: fprintf(std::FILE *, const S&, const Args&...) +.. doxygenfunction:: sprintf(const S&, const T&...) + +.. _xchar-api: + +``wchar_t`` Support +=================== + +The optional header ``fmt/xchar.h`` provides support for ``wchar_t`` and exotic +character types. + +.. doxygenstruct:: fmt::is_char + +.. doxygentypedef:: fmt::wstring_view -.. doxygenfunction:: fprintf(std::basic_ostream<Char>&, const S&, const Args&...) +.. doxygentypedef:: fmt::wformat_context -.. doxygenfunction:: sprintf(const S&, const Args&...) +.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::to_wstring(const T &value) Compatibility with C++20 ``std::format`` ======================================== @@ -497,9 +674,6 @@ differences: * Names are defined in the ``fmt`` namespace instead of ``std`` to avoid collisions with standard library implementations. -* The ``'L'`` format specifier cannot be combined with presentation specifiers - yet. * Width calculation doesn't use grapheme clusterization. The latter has been implemented in a separate branch but hasn't been integrated yet. -* Chrono formatting doesn't support C++20 date types since they are not provided - by standard library implementations. +* Most C++20 chrono types are not supported yet. diff --git a/doc/basic-bootstrap/layout.html b/doc/basic-bootstrap/layout.html index a257b03d..5519c4b5 100644 --- a/doc/basic-bootstrap/layout.html +++ b/doc/basic-bootstrap/layout.html @@ -90,12 +90,14 @@ VERSION: '{{ release|e }}', COLLAPSE_INDEX: false, FILE_SUFFIX: '{{ '' if no_search_suffix else file_suffix }}', + LINK_SUFFIX: '{{ link_suffix }}', + SOURCELINK_SUFFIX: '{{ sourcelink_suffix }}', HAS_SOURCE: {{ has_source|lower }}, SOURCELINK_SUFFIX: '{{ sourcelink_suffix }}' }; </script> {%- for scriptfile in script_files %} - <script type="text/javascript" src="{{ pathto(scriptfile, 1) }}"></script> + {{ js_tag(scriptfile) }} {%- endfor %} {%- endmacro %} diff --git a/doc/build.py b/doc/build.py index 4651756e..bd10aa84 100755 --- a/doc/build.py +++ b/doc/build.py @@ -1,52 +1,38 @@ -#!/usr/bin/env python +#!/usr/bin/env python3 # Build the documentation. -from __future__ import print_function -import errno, os, shutil, sys, tempfile -from subprocess import check_call, check_output, CalledProcessError, Popen, PIPE -from distutils.version import LooseVersion +import errno, os, re, sys +from subprocess import check_call, CalledProcessError, Popen, PIPE, STDOUT -versions = ['1.0.0', '1.1.0', '2.0.0', '3.0.2', '4.0.0', '4.1.0', '5.0.0', '5.1.0', '5.2.0', '5.2.1', '5.3.0', '6.0.0', '6.1.0', '6.1.1', '6.1.2', '6.2.0', '6.2.1', '7.0.0', '7.0.1', '7.0.2', '7.0.3', '7.1.0', '7.1.1', '7.1.2', '7.1.3'] +versions = ['1.0.0', '1.1.0', '2.0.0', '3.0.2', '4.0.0', '4.1.0', '5.0.0', '5.1.0', '5.2.0', '5.2.1', '5.3.0', '6.0.0', '6.1.0', '6.1.1', '6.1.2', '6.2.0', '6.2.1', '7.0.0', '7.0.1', '7.0.2', '7.0.3', '7.1.0', '7.1.1', '7.1.2', '7.1.3', '8.0.0', '8.0.1', '8.1.0', '8.1.1', '9.0.0', '9.1.0', '10.0.0', '10.1.0', '10.1.1', '10.1.1'] -def pip_install(package, commit=None, **kwargs): - "Install package using pip." - if commit: - package = 'git+https://github.com/{0}.git@{1}'.format(package, commit) - print('Installing {0}'.format(package)) - check_call(['pip', 'install', package]) +class Pip: + def __init__(self, venv_dir): + self.path = os.path.join(venv_dir, 'bin', 'pip') -def create_build_env(dirname='virtualenv'): + def install(self, package, commit=None): + "Install package using pip." + if commit: + package = 'git+https://github.com/{0}.git@{1}'.format(package, commit) + print('Installing {0}'.format(package)) + check_call([self.path, 'install', package]) + +def create_build_env(venv_dir='virtualenv'): # Create virtualenv. - if not os.path.exists(dirname): - check_call(['virtualenv', dirname]) - import sysconfig - scripts_dir = os.path.basename(sysconfig.get_path('scripts')) - activate_this_file = os.path.join(dirname, scripts_dir, 'activate_this.py') - with open(activate_this_file) as f: - exec(f.read(), dict(__file__=activate_this_file)) - # Import get_distribution after activating virtualenv to get info about - # the correct packages. - from pkg_resources import get_distribution, DistributionNotFound - # Upgrade pip because installation of sphinx with pip 1.1 available on Travis - # is broken (see #207) and it doesn't support the show command. - pip_version = get_distribution('pip').version - if LooseVersion(pip_version) < LooseVersion('1.5.4'): - print("Updating pip") - check_call(['pip', 'install', '--upgrade', 'pip']) - # Upgrade distribute because installation of sphinx with distribute 0.6.24 - # available on Travis is broken (see #207). - try: - distribute_version = get_distribution('distribute').version - if LooseVersion(distribute_version) <= LooseVersion('0.6.24'): - print("Updating distribute") - check_call(['pip', 'install', '--upgrade', 'distribute']) - except DistributionNotFound: - pass + if not os.path.exists(venv_dir): + check_call(['python3', '-m', 'venv', venv_dir]) # Install Sphinx and Breathe. Require the exact version of Sphinx which is # compatible with Breathe. - pip_install('sphinx-doc/sphinx', '12b83372ac9316e8cbe86e7fed889296a4cc29ee') - pip_install('michaeljones/breathe', - '129222318f7c8f865d2631e7da7b033567e7f56a') + pip = Pip(venv_dir) + pip.install('wheel') + pip.install('six') + # See: https://github.com/sphinx-doc/sphinx/issues/9777 + pip.install('docutils==0.17.1') + # Jinja2 >= 3.1 incompatible with sphinx 3.3.0 + # See: https://github.com/sphinx-doc/sphinx/issues/10291 + pip.install('Jinja2<3.1') + pip.install('sphinx-doc/sphinx', 'v3.3.0') + pip.install('michaeljones/breathe', 'v4.25.0') def build_docs(version='dev', **kwargs): doc_dir = kwargs.get('doc_dir', os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))) @@ -55,16 +41,17 @@ def build_docs(version='dev', **kwargs): 'include_dir', os.path.join(os.path.dirname(doc_dir), 'include', 'fmt')) # Build docs. cmd = ['doxygen', '-'] - p = Popen(cmd, stdin=PIPE) + p = Popen(cmd, stdin=PIPE, stdout=PIPE, stderr=STDOUT) doxyxml_dir = os.path.join(work_dir, 'doxyxml') - p.communicate(input=r''' + out, _ = p.communicate(input=r''' PROJECT_NAME = fmt GENERATE_LATEX = NO GENERATE_MAN = NO GENERATE_RTF = NO CASE_SENSE_NAMES = NO - INPUT = {0}/chrono.h {0}/color.h {0}/core.h {0}/compile.h \ - {0}/format.h {0}/os.h {0}/ostream.h {0}/printf.h + INPUT = {0}/args.h {0}/chrono.h {0}/color.h {0}/core.h \ + {0}/compile.h {0}/format.h {0}/os.h {0}/ostream.h \ + {0}/printf.h {0}/xchar.h QUIET = YES JAVADOC_AUTOBRIEF = YES AUTOLINK_SUPPORT = NO @@ -75,29 +62,49 @@ def build_docs(version='dev', **kwargs): ALIASES += "endrst=\endverbatim" MACRO_EXPANSION = YES PREDEFINED = _WIN32=1 \ + __linux__=1 \ + FMT_ENABLE_IF(...)= \ FMT_USE_VARIADIC_TEMPLATES=1 \ FMT_USE_RVALUE_REFERENCES=1 \ FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS=1 \ FMT_USE_ALIAS_TEMPLATES=1 \ + FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS=1 \ FMT_API= \ "FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE=namespace fmt {{" \ "FMT_END_NAMESPACE=}}" \ "FMT_STRING_ALIAS=1" \ - "FMT_ENABLE_IF(B)=" + "FMT_VARIADIC(...)=" \ + "FMT_VARIADIC_W(...)=" \ + "FMT_DOC=1" EXCLUDE_SYMBOLS = fmt::formatter fmt::printf_formatter fmt::arg_join \ fmt::basic_format_arg::handle '''.format(include_dir, doxyxml_dir).encode('UTF-8')) + out = out.decode('utf-8') + internal_symbols = [ + 'fmt::detail::.*', + 'basic_data<>', + 'fmt::type_identity' + ] + noisy_warnings = [ + 'warning: (Compound|Member .* of class) (' + '|'.join(internal_symbols) + \ + ') is not documented.', + 'warning: Internal inconsistency: .* does not belong to any container!' + ] + for w in noisy_warnings: + out = re.sub('.*' + w + '\n', '', out) + print(out) if p.returncode != 0: raise CalledProcessError(p.returncode, cmd) + html_dir = os.path.join(work_dir, 'html') main_versions = reversed(versions[-3:]) - check_call(['sphinx-build', + check_call([os.path.join(work_dir, 'virtualenv', 'bin', 'sphinx-build'), '-Dbreathe_projects.format=' + os.path.abspath(doxyxml_dir), '-Dversion=' + version, '-Drelease=' + version, '-Aversion=' + version, '-Aversions=' + ','.join(main_versions), '-b', 'html', doc_dir, html_dir]) try: - check_call(['lessc', '--clean-css', + check_call(['lessc', '--verbose', '--clean-css', '--include-path=' + os.path.join(doc_dir, 'bootstrap'), os.path.join(doc_dir, 'fmt.less'), os.path.join(html_dir, '_static', 'fmt.css')]) diff --git a/doc/fmt.less b/doc/fmt.less index 55c716b8..3a97b9fd 100644 --- a/doc/fmt.less +++ b/doc/fmt.less @@ -56,6 +56,11 @@ div.sphinxsidebar { padding: 0; } +// Override center alignment in tables. +td { + text-align: left; +} + p.rubric { margin-top: 10px; } diff --git a/doc/index.rst b/doc/index.rst index 58f29295..8d55c7a1 100644 --- a/doc/index.rst +++ b/doc/index.rst @@ -26,21 +26,23 @@ is safer, simpler and several times `faster <https://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html>`_ than common standard library implementations. The `format string syntax <syntax.html>`_ is similar to the one used by -`str.format <http://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format>`_ in +`str.format <https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format>`_ in Python: .. code:: c++ - fmt::format("The answer is {}.", 42); + std::string s = fmt::format("The answer is {}.", 42); The ``fmt::format`` function returns a string "The answer is 42.". You can use ``fmt::memory_buffer`` to avoid constructing ``std::string``: .. code:: c++ - fmt::memory_buffer out; - format_to(out, "For a moment, {} happened.", "nothing"); - out.data(); // returns a pointer to the formatted data + auto out = fmt::memory_buffer(); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), + "For a moment, {} happened.", "nothing"); + auto data = out.data(); // pointer to the formatted data + auto size = out.size(); // size of the formatted data The ``fmt::print`` function performs formatting and writes the result to a stream: @@ -99,7 +101,7 @@ The code format(FMT_STRING("The answer is {:d}"), "forty-two"); reports a compile-time error on compilers that support relaxed ``constexpr``. -See `here <api.html#c.fmt>`_ for details. +See `here <api.html#compile-time-format-string-checks>`_ for details. The following code @@ -108,16 +110,10 @@ The following code fmt::format("Cyrillic letter {}", L'\x42e'); produces a compile-time error because wide character ``L'\x42e'`` cannot be -formatted into a narrow string. You can use a wide format string instead: - -.. code:: c++ - - fmt::format(L"Cyrillic letter {}", L'\x42e'); - -For comparison, writing a wide character to ``std::ostream`` results in -its numeric value being written to the stream (i.e. 1070 instead of letter 'ю' -which is represented by ``L'\x42e'`` if we use Unicode) which is rarely -desirable. +formatted into a narrow string. For comparison, writing a wide character to +``std::ostream`` results in its numeric value being written to the stream +(i.e. 1070 instead of letter 'ю' which is represented by ``L'\x42e'`` if we +use Unicode) which is rarely desirable. Compact Binary Code ------------------- @@ -166,7 +162,7 @@ The library is highly portable and relies only on a small set of C++11 features: * deleted functions * alias templates -These are available in GCC 4.8, Clang 3.0, MSVC 19.0 (2015) and more recent +These are available in GCC 4.8, Clang 3.4, MSVC 19.0 (2015) and more recent compiler version. For older compilers use {fmt} `version 4.x <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases/tag/4.1.0>`_ which is maintained and only requires C++98. @@ -190,11 +186,13 @@ just three header files and no external dependencies. A permissive MIT `license <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt#license>`_ allows using the library both in open-source and commercial projects. +`Learn more... <contents.html>`_ + .. raw:: html <a class="btn btn-success" href="https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt">GitHub Repository</a> <div class="section footer"> - <iframe src="http://ghbtns.com/github-btn.html?user=fmtlib&repo=fmt&type=watch&count=true" + <iframe src="https://ghbtns.com/github-btn.html?user=fmtlib&repo=fmt&type=watch&count=true" class="github-btn" width="100" height="20"></iframe> </div> diff --git a/doc/syntax.rst b/doc/syntax.rst index 8265f702..74b64c5a 100644 --- a/doc/syntax.rst +++ b/doc/syntax.rst @@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ literal text, it can be escaped by doubling: ``{{`` and ``}}``. The grammar for a replacement field is as follows: .. productionlist:: sf - replacement_field: "{" [`arg_id`] [":" `format_spec`] "}" + replacement_field: "{" [`arg_id`] [":" (`format_spec` | `chrono_format_spec`)] "}" arg_id: `integer` | `identifier` integer: `digit`+ digit: "0"..."9" @@ -27,8 +27,8 @@ The grammar for a replacement field is as follows: In less formal terms, the replacement field can start with an *arg_id* that specifies the argument whose value is to be formatted and inserted into the output instead of the replacement field. -The *arg_id* is optionally followed by a *format_spec*, which is preceded -by a colon ``':'``. These specify a non-default format for the replacement value. +The *arg_id* is optionally followed by a *format_spec*, which is preceded by a +colon ``':'``. These specify a non-default format for the replacement value. See also the :ref:`formatspec` section. @@ -75,14 +75,14 @@ although some of the formatting options are only supported by the numeric types. The general form of a *standard format specifier* is: .. productionlist:: sf - format_spec: [[`fill`]`align`][`sign`]["#"]["0"][`width`]["." `precision`][`type`] + format_spec: [[`fill`]`align`][`sign`]["#"]["0"][`width`]["." `precision`]["L"][`type`] fill: <a character other than '{' or '}'> align: "<" | ">" | "^" sign: "+" | "-" | " " width: `integer` | "{" [`arg_id`] "}" precision: `integer` | "{" [`arg_id`] "}" - type: `int_type` | "a" | "A" | "c" | "e" | "E" | "f" | "F" | "g" | "G" | "L" | "p" | "s" - int_type: "b" | "B" | "d" | "o" | "x" | "X" + type: "a" | "A" | "b" | "B" | "c" | "d" | "e" | "E" | "f" | "F" | "g" | "G" | + : "o" | "p" | "s" | "x" | "X" The *fill* character can be any Unicode code point other than ``'{'`` or ``'}'``. The presence of a fill character is signaled by the character following @@ -109,21 +109,21 @@ Note that unless a minimum field width is defined, the field width will always be the same size as the data to fill it, so that the alignment option has no meaning in this case. -The *sign* option is only valid for number types, and can be one of the -following: - -+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ -| Option | Meaning | -+=========+==========================================================+ -| ``'+'`` | indicates that a sign should be used for both | -| | positive as well as negative numbers. | -+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ -| ``'-'`` | indicates that a sign should be used only for negative | -| | numbers (this is the default behavior). | -+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ -| space | indicates that a leading space should be used on | -| | positive numbers, and a minus sign on negative numbers. | -+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ +The *sign* option is only valid for floating point and signed integer types, +and can be one of the following: + ++---------+------------------------------------------------------------+ +| Option | Meaning | ++=========+============================================================+ +| ``'+'`` | indicates that a sign should be used for both | +| | nonnegative as well as negative numbers. | ++---------+------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'-'`` | indicates that a sign should be used only for negative | +| | numbers (this is the default behavior). | ++---------+------------------------------------------------------------+ +| space | indicates that a leading space should be used on | +| | nonnegative numbers, and a minus sign on negative numbers. | ++---------+------------------------------------------------------------+ The ``'#'`` option causes the "alternate form" to be used for the conversion. The alternate form is defined differently for different @@ -161,7 +161,11 @@ displayed after the decimal point for a floating-point value formatted with value formatted with ``'g'`` or ``'G'``. For non-number types the field indicates the maximum field size - in other words, how many characters will be used from the field content. The *precision* is not allowed for integer, -character, Boolean, and pointer values. +character, Boolean, and pointer values. Note that a C string must be +null-terminated even if precision is specified. + +The ``'L'`` option uses the current locale setting to insert the appropriate +number separator characters. This option is only valid for numeric types. Finally, the *type* determines how the data should be presented. @@ -200,6 +204,8 @@ The available integer presentation types are: | | ``'#'`` option with this type adds the prefix ``"0B"`` | | | to the output value. | +---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'c'`` | Character format. Outputs the number as a character. | ++---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ | ``'d'`` | Decimal integer. Outputs the number in base 10. | +---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ | ``'o'`` | Octal format. Outputs the number in base 8. | @@ -214,10 +220,6 @@ The available integer presentation types are: | | ``'#'`` option with this type adds the prefix ``"0X"`` | | | to the output value. | +---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ -| ``'L'`` | Locale-specific format. This is the same as ``'d'``, | -| | except that it uses the current locale setting to insert | -| | the appropriate number separator characters. | -+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ | none | The same as ``'d'``. | +---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ @@ -261,14 +263,8 @@ The available presentation types for floating-point values are: | | ``'E'`` if the number gets too large. The | | | representations of infinity and NaN are uppercased, too. | +---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ -| ``'L'`` | Locale-specific format. This is the same as ``'g'``, | -| | except that it uses the current locale setting to insert | -| | the appropriate number separator characters. | -+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ -| none | Similar to ``'g'``, except that fixed-point notation, | -| | when used, has at least one digit past the decimal | -| | point. The default precision is as high as needed to | -| | represent the particular value. | +| none | Similar to ``'g'``, except that the default precision is | +| | as high as needed to represent the particular value. | +---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ .. ifconfig:: False @@ -303,6 +299,212 @@ The available presentation types for pointers are: | none | The same as ``'p'``. | +---------+----------------------------------------------------------+ +.. _chrono-specs: + +Chrono Format Specifications +============================ + +Format specifications for chrono duration and time point types as well as +``std::tm`` have the following syntax: + +.. productionlist:: sf + chrono_format_spec: [[`fill`]`align`][`width`]["." `precision`][`chrono_specs`] + chrono_specs: [`chrono_specs`] `conversion_spec` | `chrono_specs` `literal_char` + conversion_spec: "%" [`modifier`] `chrono_type` + literal_char: <a character other than '{', '}' or '%'> + modifier: "E" | "O" + chrono_type: "a" | "A" | "b" | "B" | "c" | "C" | "d" | "D" | "e" | "F" | + : "g" | "G" | "h" | "H" | "I" | "j" | "m" | "M" | "n" | "p" | + : "q" | "Q" | "r" | "R" | "S" | "t" | "T" | "u" | "U" | "V" | + : "w" | "W" | "x" | "X" | "y" | "Y" | "z" | "Z" | "%" + +Literal chars are copied unchanged to the output. Precision is valid only for +``std::chrono::duration`` types with a floating-point representation type. + +The available presentation types (*chrono_type*) are: + ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| Type | Meaning | ++=========+====================================================================+ +| ``'a'`` | The abbreviated weekday name, e.g. "Sat". If the value does not | +| | contain a valid weekday, an exception of type ``format_error`` is | +| | thrown. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'A'`` | The full weekday name, e.g. "Saturday". If the value does not | +| | contain a valid weekday, an exception of type ``format_error`` is | +| | thrown. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'b'`` | The abbreviated month name, e.g. "Nov". If the value does not | +| | contain a valid month, an exception of type ``format_error`` is | +| | thrown. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'B'`` | The full month name, e.g. "November". If the value does not | +| | contain a valid month, an exception of type ``format_error`` is | +| | thrown. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'c'`` | The date and time representation, e.g. "Sat Nov 12 22:04:00 1955". | +| | The modified command ``%Ec`` produces the locale's alternate date | +| | and time representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'C'`` | The year divided by 100 using floored division, e.g. "55". If the | +| | result is a single decimal digit, it is prefixed with 0. | +| | The modified command ``%EC`` produces the locale's alternative | +| | representation of the century. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'d'`` | The day of month as a decimal number. If the result is a single | +| | decimal digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command ``%Od`` | +| | produces the locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'D'`` | Equivalent to ``%m/%d/%y``, e.g. "11/12/55". | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'e'`` | The day of month as a decimal number. If the result is a single | +| | decimal digit, it is prefixed with a space. The modified command | +| | ``%Oe`` produces the locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'F'`` | Equivalent to ``%Y-%m-%d``, e.g. "1955-11-12". | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'g'`` | The last two decimal digits of the ISO week-based year. If the | +| | result is a single digit it is prefixed by 0. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'G'`` | The ISO week-based year as a decimal number. If the result is less | +| | than four digits it is left-padded with 0 to four digits. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'h'`` | Equivalent to ``%b``, e.g. "Nov". | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'H'`` | The hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number. If the result is a | +| | single digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command ``%OH`` | +| | produces the locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'I'`` | The hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number. If the result is a | +| | single digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command ``%OI`` | +| | produces the locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'j'`` | If the type being formatted is a specialization of duration, the | +| | decimal number of days without padding. Otherwise, the day of the | +| | year as a decimal number. Jan 1 is 001. If the result is less than | +| | three digits, it is left-padded with 0 to three digits. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'m'`` | The month as a decimal number. Jan is 01. If the result is a | +| | single digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command ``%Om`` | +| | produces the locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'M'`` | The minute as a decimal number. If the result is a single digit, | +| | it is prefixed with 0. The modified command ``%OM`` produces the | +| | locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'n'`` | A new-line character. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'p'`` | The AM/PM designations associated with a 12-hour clock. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'q'`` | The duration's unit suffix. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'Q'`` | The duration's numeric value (as if extracted via ``.count()``). | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'r'`` | The 12-hour clock time, e.g. "10:04:00 PM". | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'R'`` | Equivalent to ``%H:%M``, e.g. "22:04". | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'S'`` | Seconds as a decimal number. If the number of seconds is less than | +| | 10, the result is prefixed with 0. If the precision of the input | +| | cannot be exactly represented with seconds, then the format is a | +| | decimal floating-point number with a fixed format and a precision | +| | matching that of the precision of the input (or to a microseconds | +| | precision if the conversion to floating-point decimal seconds | +| | cannot be made within 18 fractional digits). The character for the | +| | decimal point is localized according to the locale. The modified | +| | command ``%OS`` produces the locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'t'`` | A horizontal-tab character. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'T'`` | Equivalent to ``%H:%M:%S``. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'u'`` | The ISO weekday as a decimal number (1-7), where Monday is 1. The | +| | modified command ``%Ou`` produces the locale's alternative | +| | representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'U'`` | The week number of the year as a decimal number. The first Sunday | +| | of the year is the first day of week 01. Days of the same year | +| | prior to that are in week 00. If the result is a single digit, it | +| | is prefixed with 0. The modified command ``%OU`` produces the | +| | locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'V'`` | The ISO week-based week number as a decimal number. If the result | +| | is a single digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command | +| | ``%OV`` produces the locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'w'`` | The weekday as a decimal number (0-6), where Sunday is 0. | +| | The modified command ``%Ow`` produces the locale's alternative | +| | representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'W'`` | The week number of the year as a decimal number. The first Monday | +| | of the year is the first day of week 01. Days of the same year | +| | prior to that are in week 00. If the result is a single digit, it | +| | is prefixed with 0. The modified command ``%OW`` produces the | +| | locale's alternative representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'x'`` | The date representation, e.g. "11/12/55". The modified command | +| | ``%Ex`` produces the locale's alternate date representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'X'`` | The time representation, e.g. "10:04:00". The modified command | +| | ``%EX`` produces the locale's alternate time representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'y'`` | The last two decimal digits of the year. If the result is a single | +| | digit it is prefixed by 0. The modified command ``%Oy`` produces | +| | the locale's alternative representation. The modified command | +| | ``%Ey`` produces the locale's alternative representation of offset | +| | from ``%EC`` (year only). | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'Y'`` | The year as a decimal number. If the result is less than four | +| | digits it is left-padded with 0 to four digits. The modified | +| | command ``%EY`` produces the locale's alternative full year | +| | representation. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'z'`` | The offset from UTC in the ISO 8601:2004 format. For example -0430 | +| | refers to 4 hours 30 minutes behind UTC. If the offset is zero, | +| | +0000 is used. The modified commands ``%Ez`` and ``%Oz`` insert a | +| | ``:`` between the hours and minutes: -04:30. If the offset | +| | information is not available, an exception of type | +| | ``format_error`` is thrown. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'Z'`` | The time zone abbreviation. If the time zone abbreviation is not | +| | available, an exception of type ``format_error`` is thrown. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ +| ``'%'`` | A % character. | ++---------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ + +Specifiers that have a calendaric component such as ``'d'`` (the day of month) +are valid only for ``std::tm`` and time points but not durations. + +.. range-specs: + +Range Format Specifications +=========================== + +Format specifications for range types have the following syntax: + +.. productionlist:: sf + range_format_spec: [":" [`underlying_spec`]] + +The `underlying_spec` is parsed based on the formatter of the range's +reference type. + +By default, a range of characters or strings is printed escaped and quoted. But +if any `underlying_spec` is provided (even if it is empty), then the characters +or strings are printed according to the provided specification. + +Examples:: + + fmt::format("{}", std::vector{10, 20, 30}); + // Result: [10, 20, 30] + fmt::format("{::#x}", std::vector{10, 20, 30}); + // Result: [0xa, 0x14, 0x1e] + fmt::format("{}", vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}); + // Result: ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'] + fmt::format("{::}", vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}); + // Result: [h, e, l, l, o] + fmt::format("{::d}", vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}); + // Result: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111] + .. _formatexamples: Format Examples @@ -391,7 +593,7 @@ Using type-specific formatting:: auto t = tm(); t.tm_year = 2010 - 1900; - t.tm_mon = 6; + t.tm_mon = 7; t.tm_mday = 4; t.tm_hour = 12; t.tm_min = 15; @@ -401,7 +603,7 @@ Using type-specific formatting:: Using the comma as a thousands separator:: - #include <fmt/locale.h> + #include <fmt/format.h> auto s = fmt::format(std::locale("en_US.UTF-8"), "{:L}", 1234567890); // s == "1,234,567,890" diff --git a/doc/usage.rst b/doc/usage.rst index 435afd53..717fd1cd 100644 --- a/doc/usage.rst +++ b/doc/usage.rst @@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ Building the Library The included `CMake build script`__ can be used to build the fmt library on a wide range of platforms. CMake is freely available for -download from http://www.cmake.org/download/. +download from https://www.cmake.org/download/. __ https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/CMakeLists.txt @@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ To build a `shared library`__ set the ``BUILD_SHARED_LIBS`` CMake variable to cmake -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=TRUE ... -__ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Library_%28computing%29#Shared_libraries +__ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Library_%28computing%29#Shared_libraries To build a `static library` with position independent code (required if the main @@ -134,6 +134,44 @@ For ``build2`` newcomers or to get more details and use cases, you can read the ``build2`` `toolchain introduction <https://build2.org/build2-toolchain/doc/build2-toolchain-intro.xhtml>`_. +Usage with Meson +================ + +`Meson's WrapDB <https://mesonbuild.com/Wrapdb-projects.html>` includes a ``fmt`` +package, which repackages fmt to be built by Meson as a subproject. + +**Usage:** + +- Install the ``fmt`` subproject from the WrapDB by running:: + + meson wrap install fmt + + from the root of your project. + +- In your project's ``meson.build`` file, add an entry for the new subproject:: + + fmt = subproject('fmt') + fmt_dep = fmt.get_variable('fmt_dep') + +- Include the new dependency object to link with fmt:: + + my_build_target = executable('name', 'src/main.cc', dependencies: [fmt_dep]) + +**Options:** + +If desired, ``fmt`` may be built as a static library, or as a header-only +library. + +For a static build, use the following subproject definition:: + + fmt = subproject('fmt', default_options: 'default_library=static') + fmt_dep = fmt.get_variable('fmt_dep') + +For the header-only version, use:: + + fmt = subproject('fmt') + fmt_dep = fmt.get_variable('fmt_header_only_dep') + Building the Documentation ========================== @@ -202,11 +240,11 @@ For an example of using fmt with Android NDK, see the `android-ndk-example <https://github.com/fmtlib/android-ndk-example>`_ repository. -__ https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/Android.mk +__ https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/support/Android.mk Homebrew ======== -fmt can be installed on OS X using `Homebrew <http://brew.sh/>`_:: +fmt can be installed on OS X using `Homebrew <https://brew.sh/>`_:: brew install fmt diff --git a/include/fmt/args.h b/include/fmt/args.h new file mode 100644 index 00000000..2d684e7c --- /dev/null +++ b/include/fmt/args.h @@ -0,0 +1,234 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - dynamic argument lists +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#ifndef FMT_ARGS_H_ +#define FMT_ARGS_H_ + +#include <functional> // std::reference_wrapper +#include <memory> // std::unique_ptr +#include <vector> + +#include "core.h" + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE + +namespace detail { + +template <typename T> struct is_reference_wrapper : std::false_type {}; +template <typename T> +struct is_reference_wrapper<std::reference_wrapper<T>> : std::true_type {}; + +template <typename T> const T& unwrap(const T& v) { return v; } +template <typename T> const T& unwrap(const std::reference_wrapper<T>& v) { + return static_cast<const T&>(v); +} + +class dynamic_arg_list { + // Workaround for clang's -Wweak-vtables. Unlike for regular classes, for + // templates it doesn't complain about inability to deduce single translation + // unit for placing vtable. So storage_node_base is made a fake template. + template <typename = void> struct node { + virtual ~node() = default; + std::unique_ptr<node<>> next; + }; + + template <typename T> struct typed_node : node<> { + T value; + + template <typename Arg> + FMT_CONSTEXPR typed_node(const Arg& arg) : value(arg) {} + + template <typename Char> + FMT_CONSTEXPR typed_node(const basic_string_view<Char>& arg) + : value(arg.data(), arg.size()) {} + }; + + std::unique_ptr<node<>> head_; + + public: + template <typename T, typename Arg> const T& push(const Arg& arg) { + auto new_node = std::unique_ptr<typed_node<T>>(new typed_node<T>(arg)); + auto& value = new_node->value; + new_node->next = std::move(head_); + head_ = std::move(new_node); + return value; + } +}; +} // namespace detail + +/** + \rst + A dynamic version of `fmt::format_arg_store`. + It's equipped with a storage to potentially temporary objects which lifetimes + could be shorter than the format arguments object. + + It can be implicitly converted into `~fmt::basic_format_args` for passing + into type-erased formatting functions such as `~fmt::vformat`. + \endrst + */ +template <typename Context> +class dynamic_format_arg_store +#if FMT_GCC_VERSION && FMT_GCC_VERSION < 409 + // Workaround a GCC template argument substitution bug. + : public basic_format_args<Context> +#endif +{ + private: + using char_type = typename Context::char_type; + + template <typename T> struct need_copy { + static constexpr detail::type mapped_type = + detail::mapped_type_constant<T, Context>::value; + + enum { + value = !(detail::is_reference_wrapper<T>::value || + std::is_same<T, basic_string_view<char_type>>::value || + std::is_same<T, detail::std_string_view<char_type>>::value || + (mapped_type != detail::type::cstring_type && + mapped_type != detail::type::string_type && + mapped_type != detail::type::custom_type)) + }; + }; + + template <typename T> + using stored_type = conditional_t< + std::is_convertible<T, std::basic_string<char_type>>::value && + !detail::is_reference_wrapper<T>::value, + std::basic_string<char_type>, T>; + + // Storage of basic_format_arg must be contiguous. + std::vector<basic_format_arg<Context>> data_; + std::vector<detail::named_arg_info<char_type>> named_info_; + + // Storage of arguments not fitting into basic_format_arg must grow + // without relocation because items in data_ refer to it. + detail::dynamic_arg_list dynamic_args_; + + friend class basic_format_args<Context>; + + unsigned long long get_types() const { + return detail::is_unpacked_bit | data_.size() | + (named_info_.empty() + ? 0ULL + : static_cast<unsigned long long>(detail::has_named_args_bit)); + } + + const basic_format_arg<Context>* data() const { + return named_info_.empty() ? data_.data() : data_.data() + 1; + } + + template <typename T> void emplace_arg(const T& arg) { + data_.emplace_back(detail::make_arg<Context>(arg)); + } + + template <typename T> + void emplace_arg(const detail::named_arg<char_type, T>& arg) { + if (named_info_.empty()) { + constexpr const detail::named_arg_info<char_type>* zero_ptr{nullptr}; + data_.insert(data_.begin(), {zero_ptr, 0}); + } + data_.emplace_back(detail::make_arg<Context>(detail::unwrap(arg.value))); + auto pop_one = [](std::vector<basic_format_arg<Context>>* data) { + data->pop_back(); + }; + std::unique_ptr<std::vector<basic_format_arg<Context>>, decltype(pop_one)> + guard{&data_, pop_one}; + named_info_.push_back({arg.name, static_cast<int>(data_.size() - 2u)}); + data_[0].value_.named_args = {named_info_.data(), named_info_.size()}; + guard.release(); + } + + public: + constexpr dynamic_format_arg_store() = default; + + /** + \rst + Adds an argument into the dynamic store for later passing to a formatting + function. + + Note that custom types and string types (but not string views) are copied + into the store dynamically allocating memory if necessary. + + **Example**:: + + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + store.push_back(42); + store.push_back("abc"); + store.push_back(1.5f); + std::string result = fmt::vformat("{} and {} and {}", store); + \endrst + */ + template <typename T> void push_back(const T& arg) { + if (detail::const_check(need_copy<T>::value)) + emplace_arg(dynamic_args_.push<stored_type<T>>(arg)); + else + emplace_arg(detail::unwrap(arg)); + } + + /** + \rst + Adds a reference to the argument into the dynamic store for later passing to + a formatting function. + + **Example**:: + + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + char band[] = "Rolling Stones"; + store.push_back(std::cref(band)); + band[9] = 'c'; // Changing str affects the output. + std::string result = fmt::vformat("{}", store); + // result == "Rolling Scones" + \endrst + */ + template <typename T> void push_back(std::reference_wrapper<T> arg) { + static_assert( + need_copy<T>::value, + "objects of built-in types and string views are always copied"); + emplace_arg(arg.get()); + } + + /** + Adds named argument into the dynamic store for later passing to a formatting + function. ``std::reference_wrapper`` is supported to avoid copying of the + argument. The name is always copied into the store. + */ + template <typename T> + void push_back(const detail::named_arg<char_type, T>& arg) { + const char_type* arg_name = + dynamic_args_.push<std::basic_string<char_type>>(arg.name).c_str(); + if (detail::const_check(need_copy<T>::value)) { + emplace_arg( + fmt::arg(arg_name, dynamic_args_.push<stored_type<T>>(arg.value))); + } else { + emplace_arg(fmt::arg(arg_name, arg.value)); + } + } + + /** Erase all elements from the store */ + void clear() { + data_.clear(); + named_info_.clear(); + dynamic_args_ = detail::dynamic_arg_list(); + } + + /** + \rst + Reserves space to store at least *new_cap* arguments including + *new_cap_named* named arguments. + \endrst + */ + void reserve(size_t new_cap, size_t new_cap_named) { + FMT_ASSERT(new_cap >= new_cap_named, + "Set of arguments includes set of named arguments"); + data_.reserve(new_cap); + named_info_.reserve(new_cap_named); + } +}; + +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +#endif // FMT_ARGS_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/chrono.h b/include/fmt/chrono.h index 1a3b8d5e..7bd4206d 100644 --- a/include/fmt/chrono.h +++ b/include/fmt/chrono.h @@ -8,16 +8,52 @@ #ifndef FMT_CHRONO_H_ #define FMT_CHRONO_H_ +#include <algorithm> #include <chrono> +#include <cmath> // std::isfinite +#include <cstring> // std::memcpy #include <ctime> +#include <iterator> #include <locale> -#include <sstream> +#include <ostream> +#include <type_traits> #include "format.h" -#include "locale.h" FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +// Check if std::chrono::local_t is available. +#ifndef FMT_USE_LOCAL_TIME +# ifdef __cpp_lib_chrono +# define FMT_USE_LOCAL_TIME (__cpp_lib_chrono >= 201907L) +# else +# define FMT_USE_LOCAL_TIME 0 +# endif +#endif + +// Check if std::chrono::utc_timestamp is available. +#ifndef FMT_USE_UTC_TIME +# ifdef __cpp_lib_chrono +# define FMT_USE_UTC_TIME (__cpp_lib_chrono >= 201907L) +# else +# define FMT_USE_UTC_TIME 0 +# endif +#endif + +// Enable tzset. +#ifndef FMT_USE_TZSET +// UWP doesn't provide _tzset. +# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE("winapifamily.h") +# include <winapifamily.h> +# endif +# if defined(_WIN32) && (!defined(WINAPI_FAMILY) || \ + (WINAPI_FAMILY == WINAPI_FAMILY_DESKTOP_APP)) +# define FMT_USE_TZSET 1 +# else +# define FMT_USE_TZSET 0 +# endif +#endif + // Enable safe chrono durations, unless explicitly disabled. #ifndef FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST # define FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST 1 @@ -44,7 +80,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR To lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec) { static_assert(T::is_integer, "To must be integral"); // A and B are both signed, or both unsigned. - if (F::digits <= T::digits) { + if (detail::const_check(F::digits <= T::digits)) { // From fits in To without any problem. } else { // From does not always fit in To, resort to a dynamic check. @@ -79,14 +115,15 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR To lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec) { return {}; } // From is positive. Can it always fit in To? - if (F::digits > T::digits && + if (detail::const_check(F::digits > T::digits) && from > static_cast<From>(detail::max_value<To>())) { ec = 1; return {}; } } - if (!F::is_signed && T::is_signed && F::digits >= T::digits && + if (detail::const_check(!F::is_signed && T::is_signed && + F::digits >= T::digits) && from > static_cast<From>(detail::max_value<To>())) { ec = 1; return {}; @@ -184,7 +221,8 @@ To safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from, } const auto min1 = (std::numeric_limits<IntermediateRep>::min)() / Factor::num; - if (count < min1) { + if (detail::const_check(!std::is_unsigned<IntermediateRep>::value) && + count < min1) { ec = 1; return {}; } @@ -243,7 +281,7 @@ To safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from, } // multiply with Factor::num without overflow or underflow - if (Factor::num != 1) { + if (detail::const_check(Factor::num != 1)) { constexpr auto max1 = detail::max_value<IntermediateRep>() / static_cast<IntermediateRep>(Factor::num); if (count > max1) { @@ -260,7 +298,7 @@ To safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from, } // this can't go wrong, right? den>0 is checked earlier. - if (Factor::den != 1) { + if (detail::const_check(Factor::den != 1)) { using common_t = typename std::common_type<IntermediateRep, intmax_t>::type; count /= static_cast<common_t>(Factor::den); } @@ -282,13 +320,125 @@ To safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from, #define FMT_NOMACRO namespace detail { +template <typename T = void> struct null {}; inline null<> localtime_r FMT_NOMACRO(...) { return null<>(); } inline null<> localtime_s(...) { return null<>(); } inline null<> gmtime_r(...) { return null<>(); } inline null<> gmtime_s(...) { return null<>(); } + +inline const std::locale& get_classic_locale() { + static const auto& locale = std::locale::classic(); + return locale; +} + +template <typename CodeUnit> struct codecvt_result { + static constexpr const size_t max_size = 32; + CodeUnit buf[max_size]; + CodeUnit* end; +}; + +template <typename CodeUnit> +void write_codecvt(codecvt_result<CodeUnit>& out, string_view in_buf, + const std::locale& loc) { +#if FMT_CLANG_VERSION +# pragma clang diagnostic push +# pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wdeprecated" + auto& f = std::use_facet<std::codecvt<CodeUnit, char, std::mbstate_t>>(loc); +# pragma clang diagnostic pop +#else + auto& f = std::use_facet<std::codecvt<CodeUnit, char, std::mbstate_t>>(loc); +#endif + auto mb = std::mbstate_t(); + const char* from_next = nullptr; + auto result = f.in(mb, in_buf.begin(), in_buf.end(), from_next, + std::begin(out.buf), std::end(out.buf), out.end); + if (result != std::codecvt_base::ok) + FMT_THROW(format_error("failed to format time")); +} + +template <typename OutputIt> +auto write_encoded_tm_str(OutputIt out, string_view in, const std::locale& loc) + -> OutputIt { + if (detail::is_utf8() && loc != get_classic_locale()) { + // char16_t and char32_t codecvts are broken in MSVC (linkage errors) and + // gcc-4. +#if FMT_MSC_VERSION != 0 || \ + (defined(__GLIBCXX__) && !defined(_GLIBCXX_USE_DUAL_ABI)) + // The _GLIBCXX_USE_DUAL_ABI macro is always defined in libstdc++ from gcc-5 + // and newer. + using code_unit = wchar_t; +#else + using code_unit = char32_t; +#endif + + using unit_t = codecvt_result<code_unit>; + unit_t unit; + write_codecvt(unit, in, loc); + // In UTF-8 is used one to four one-byte code units. + auto u = + to_utf8<code_unit, basic_memory_buffer<char, unit_t::max_size * 4>>(); + if (!u.convert({unit.buf, to_unsigned(unit.end - unit.buf)})) + FMT_THROW(format_error("failed to format time")); + return copy_str<char>(u.c_str(), u.c_str() + u.size(), out); + } + return copy_str<char>(in.data(), in.data() + in.size(), out); +} + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value)> +auto write_tm_str(OutputIt out, string_view sv, const std::locale& loc) + -> OutputIt { + codecvt_result<Char> unit; + write_codecvt(unit, sv, loc); + return copy_str<Char>(unit.buf, unit.end, out); +} + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<Char, char>::value)> +auto write_tm_str(OutputIt out, string_view sv, const std::locale& loc) + -> OutputIt { + return write_encoded_tm_str(out, sv, loc); +} + +template <typename Char> +inline void do_write(buffer<Char>& buf, const std::tm& time, + const std::locale& loc, char format, char modifier) { + auto&& format_buf = formatbuf<std::basic_streambuf<Char>>(buf); + auto&& os = std::basic_ostream<Char>(&format_buf); + os.imbue(loc); + using iterator = std::ostreambuf_iterator<Char>; + const auto& facet = std::use_facet<std::time_put<Char, iterator>>(loc); + auto end = facet.put(os, os, Char(' '), &time, format, modifier); + if (end.failed()) FMT_THROW(format_error("failed to format time")); +} + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value)> +auto write(OutputIt out, const std::tm& time, const std::locale& loc, + char format, char modifier = 0) -> OutputIt { + auto&& buf = get_buffer<Char>(out); + do_write<Char>(buf, time, loc, format, modifier); + return get_iterator(buf, out); +} + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<Char, char>::value)> +auto write(OutputIt out, const std::tm& time, const std::locale& loc, + char format, char modifier = 0) -> OutputIt { + auto&& buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); + do_write<char>(buf, time, loc, format, modifier); + return write_encoded_tm_str(out, string_view(buf.data(), buf.size()), loc); +} + } // namespace detail -// Thread-safe replacement for std::localtime +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT + +/** + Converts given time since epoch as ``std::time_t`` value into calendar time, + expressed in local time. Unlike ``std::localtime``, this function is + thread-safe on most platforms. + */ inline std::tm localtime(std::time_t time) { struct dispatcher { std::time_t time_; @@ -310,7 +460,7 @@ inline std::tm localtime(std::time_t time) { bool fallback(int res) { return res == 0; } -#if !FMT_MSC_VER +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION bool fallback(detail::null<>) { using namespace fmt::detail; std::tm* tm = std::localtime(&time_); @@ -325,12 +475,19 @@ inline std::tm localtime(std::time_t time) { return lt.tm_; } -inline std::tm localtime( - std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock> time_point) { - return localtime(std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(time_point)); +#if FMT_USE_LOCAL_TIME +template <typename Duration> +inline auto localtime(std::chrono::local_time<Duration> time) -> std::tm { + return localtime(std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t( + std::chrono::current_zone()->to_sys(time))); } +#endif -// Thread-safe replacement for std::gmtime +/** + Converts given time since epoch as ``std::time_t`` value into calendar time, + expressed in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Unlike ``std::gmtime``, this + function is thread-safe on most platforms. + */ inline std::tm gmtime(std::time_t time) { struct dispatcher { std::time_t time_; @@ -352,7 +509,7 @@ inline std::tm gmtime(std::time_t time) { bool fallback(int res) { return res == 0; } -#if !FMT_MSC_VER +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION bool fallback(detail::null<>) { std::tm* tm = std::gmtime(&time_); if (tm) tm_ = *tm; @@ -360,7 +517,7 @@ inline std::tm gmtime(std::time_t time) { } #endif }; - dispatcher gt(time); + auto gt = dispatcher(time); // Too big time values may be unsupported. if (!gt.run()) FMT_THROW(format_error("time_t value out of range")); return gt.tm_; @@ -372,95 +529,64 @@ inline std::tm gmtime( } namespace detail { -inline size_t strftime(char* str, size_t count, const char* format, - const std::tm* time) { - return std::strftime(str, count, format, time); -} -inline size_t strftime(wchar_t* str, size_t count, const wchar_t* format, - const std::tm* time) { - return std::wcsftime(str, count, format, time); -} -} // namespace detail - -template <typename Char> -struct formatter<std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock>, Char> - : formatter<std::tm, Char> { - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock> val, - FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - std::tm time = localtime(val); - return formatter<std::tm, Char>::format(time, ctx); - } -}; - -template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::tm, Char> { - template <typename ParseContext> - auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - auto it = ctx.begin(); - if (it != ctx.end() && *it == ':') ++it; - auto end = it; - while (end != ctx.end() && *end != '}') ++end; - tm_format.reserve(detail::to_unsigned(end - it + 1)); - tm_format.append(it, end); - tm_format.push_back('\0'); - return end; - } - - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(const std::tm& tm, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buf; - size_t start = buf.size(); - for (;;) { - size_t size = buf.capacity() - start; - size_t count = detail::strftime(&buf[start], size, &tm_format[0], &tm); - if (count != 0) { - buf.resize(start + count); - break; - } - if (size >= tm_format.size() * 256) { - // If the buffer is 256 times larger than the format string, assume - // that `strftime` gives an empty result. There doesn't seem to be a - // better way to distinguish the two cases: - // https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/367 - break; - } - const size_t MIN_GROWTH = 10; - buf.reserve(buf.capacity() + (size > MIN_GROWTH ? size : MIN_GROWTH)); - } - return std::copy(buf.begin(), buf.end(), ctx.out()); +// Writes two-digit numbers a, b and c separated by sep to buf. +// The method by Pavel Novikov based on +// https://johnnylee-sde.github.io/Fast-unsigned-integer-to-time-string/. +inline void write_digit2_separated(char* buf, unsigned a, unsigned b, + unsigned c, char sep) { + unsigned long long digits = + a | (b << 24) | (static_cast<unsigned long long>(c) << 48); + // Convert each value to BCD. + // We have x = a * 10 + b and we want to convert it to BCD y = a * 16 + b. + // The difference is + // y - x = a * 6 + // a can be found from x: + // a = floor(x / 10) + // then + // y = x + a * 6 = x + floor(x / 10) * 6 + // floor(x / 10) is (x * 205) >> 11 (needs 16 bits). + digits += (((digits * 205) >> 11) & 0x000f00000f00000f) * 6; + // Put low nibbles to high bytes and high nibbles to low bytes. + digits = ((digits & 0x00f00000f00000f0) >> 4) | + ((digits & 0x000f00000f00000f) << 8); + auto usep = static_cast<unsigned long long>(sep); + // Add ASCII '0' to each digit byte and insert separators. + digits |= 0x3030003030003030 | (usep << 16) | (usep << 40); + + constexpr const size_t len = 8; + if (const_check(is_big_endian())) { + char tmp[len]; + std::memcpy(tmp, &digits, len); + std::reverse_copy(tmp, tmp + len, buf); + } else { + std::memcpy(buf, &digits, len); } +} - basic_memory_buffer<Char> tm_format; -}; - -namespace detail { -template <typename Period> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units() { +template <typename Period> FMT_CONSTEXPR inline const char* get_units() { + if (std::is_same<Period, std::atto>::value) return "as"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::femto>::value) return "fs"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::pico>::value) return "ps"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::nano>::value) return "ns"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::micro>::value) return "µs"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::milli>::value) return "ms"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::centi>::value) return "cs"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::deci>::value) return "ds"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::ratio<1>>::value) return "s"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::deca>::value) return "das"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::hecto>::value) return "hs"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::kilo>::value) return "ks"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::mega>::value) return "Ms"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::giga>::value) return "Gs"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::tera>::value) return "Ts"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::peta>::value) return "Ps"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::exa>::value) return "Es"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::ratio<60>>::value) return "min"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::ratio<3600>>::value) return "h"; + if (std::is_same<Period, std::ratio<86400>>::value) return "d"; return nullptr; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::atto>() { return "as"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::femto>() { return "fs"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::pico>() { return "ps"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::nano>() { return "ns"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::micro>() { return "µs"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::milli>() { return "ms"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::centi>() { return "cs"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::deci>() { return "ds"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::ratio<1>>() { return "s"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::deca>() { return "das"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::hecto>() { return "hs"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::kilo>() { return "ks"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::mega>() { return "Ms"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::giga>() { return "Gs"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::tera>() { return "Ts"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::peta>() { return "Ps"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::exa>() { return "Es"; } -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::ratio<60>>() { - return "m"; -} -template <> FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* get_units<std::ratio<3600>>() { - return "h"; -} enum class numeric_system { standard, @@ -468,12 +594,39 @@ enum class numeric_system { alternative }; +// Glibc extensions for formatting numeric values. +enum class pad_type { + unspecified, + // Do not pad a numeric result string. + none, + // Pad a numeric result string with zeros even if the conversion specifier + // character uses space-padding by default. + zero, + // Pad a numeric result string with spaces. + space, +}; + +template <typename OutputIt> +auto write_padding(OutputIt out, pad_type pad, int width) -> OutputIt { + if (pad == pad_type::none) return out; + return std::fill_n(out, width, pad == pad_type::space ? ' ' : '0'); +} + +template <typename OutputIt> +auto write_padding(OutputIt out, pad_type pad) -> OutputIt { + if (pad != pad_type::none) *out++ = pad == pad_type::space ? ' ' : '0'; + return out; +} + // Parses a put_time-like format string and invokes handler actions. template <typename Char, typename Handler> FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, const Char* end, Handler&& handler) { + if (begin == end || *begin == '}') return begin; + if (*begin != '%') FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format")); auto ptr = begin; + pad_type pad = pad_type::unspecified; while (ptr != end) { auto c = *ptr; if (c == '}') break; @@ -484,6 +637,22 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, if (begin != ptr) handler.on_text(begin, ptr); ++ptr; // consume '%' if (ptr == end) FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format")); + c = *ptr; + switch (c) { + case '_': + pad = pad_type::space; + ++ptr; + break; + case '-': + pad = pad_type::none; + ++ptr; + break; + case '0': + pad = pad_type::zero; + ++ptr; + break; + } + if (ptr == end) FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format")); c = *ptr++; switch (c) { case '%': @@ -499,6 +668,22 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, handler.on_text(tab, tab + 1); break; } + // Year: + case 'Y': + handler.on_year(numeric_system::standard); + break; + case 'y': + handler.on_short_year(numeric_system::standard); + break; + case 'C': + handler.on_century(numeric_system::standard); + break; + case 'G': + handler.on_iso_week_based_year(); + break; + case 'g': + handler.on_iso_week_based_short_year(); + break; // Day of the week: case 'a': handler.on_abbr_weekday(); @@ -514,23 +699,46 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, break; // Month: case 'b': + case 'h': handler.on_abbr_month(); break; case 'B': handler.on_full_month(); break; + case 'm': + handler.on_dec_month(numeric_system::standard); + break; + // Day of the year/month: + case 'U': + handler.on_dec0_week_of_year(numeric_system::standard); + break; + case 'W': + handler.on_dec1_week_of_year(numeric_system::standard); + break; + case 'V': + handler.on_iso_week_of_year(numeric_system::standard); + break; + case 'j': + handler.on_day_of_year(); + break; + case 'd': + handler.on_day_of_month(numeric_system::standard); + break; + case 'e': + handler.on_day_of_month_space(numeric_system::standard); + break; // Hour, minute, second: case 'H': - handler.on_24_hour(numeric_system::standard); + handler.on_24_hour(numeric_system::standard, pad); break; case 'I': - handler.on_12_hour(numeric_system::standard); + handler.on_12_hour(numeric_system::standard, pad); break; case 'M': - handler.on_minute(numeric_system::standard); + handler.on_minute(numeric_system::standard, pad); break; case 'S': - handler.on_second(numeric_system::standard); + handler.on_second(numeric_system::standard, pad); break; // Other: case 'c': @@ -567,7 +775,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, handler.on_duration_unit(); break; case 'z': - handler.on_utc_offset(); + handler.on_utc_offset(numeric_system::standard); break; case 'Z': handler.on_tz_name(); @@ -577,6 +785,15 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, if (ptr == end) FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format")); c = *ptr++; switch (c) { + case 'Y': + handler.on_year(numeric_system::alternative); + break; + case 'y': + handler.on_offset_year(); + break; + case 'C': + handler.on_century(numeric_system::alternative); + break; case 'c': handler.on_datetime(numeric_system::alternative); break; @@ -586,6 +803,9 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, case 'X': handler.on_loc_time(numeric_system::alternative); break; + case 'z': + handler.on_utc_offset(numeric_system::alternative); + break; default: FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format")); } @@ -595,6 +815,27 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, if (ptr == end) FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format")); c = *ptr++; switch (c) { + case 'y': + handler.on_short_year(numeric_system::alternative); + break; + case 'm': + handler.on_dec_month(numeric_system::alternative); + break; + case 'U': + handler.on_dec0_week_of_year(numeric_system::alternative); + break; + case 'W': + handler.on_dec1_week_of_year(numeric_system::alternative); + break; + case 'V': + handler.on_iso_week_of_year(numeric_system::alternative); + break; + case 'd': + handler.on_day_of_month(numeric_system::alternative); + break; + case 'e': + handler.on_day_of_month_space(numeric_system::alternative); + break; case 'w': handler.on_dec0_weekday(numeric_system::alternative); break; @@ -602,16 +843,19 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, handler.on_dec1_weekday(numeric_system::alternative); break; case 'H': - handler.on_24_hour(numeric_system::alternative); + handler.on_24_hour(numeric_system::alternative, pad); break; case 'I': - handler.on_12_hour(numeric_system::alternative); + handler.on_12_hour(numeric_system::alternative, pad); break; case 'M': - handler.on_minute(numeric_system::alternative); + handler.on_minute(numeric_system::alternative, pad); break; case 'S': - handler.on_second(numeric_system::alternative); + handler.on_second(numeric_system::alternative, pad); + break; + case 'z': + handler.on_utc_offset(numeric_system::alternative); break; default: FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format")); @@ -626,67 +870,734 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, return ptr; } -struct chrono_format_checker { - FMT_NORETURN void report_no_date() { FMT_THROW(format_error("no date")); } - - template <typename Char> void on_text(const Char*, const Char*) {} - FMT_NORETURN void on_abbr_weekday() { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_full_weekday() { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_dec0_weekday(numeric_system) { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_dec1_weekday(numeric_system) { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_abbr_month() { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_full_month() { report_no_date(); } - void on_24_hour(numeric_system) {} - void on_12_hour(numeric_system) {} - void on_minute(numeric_system) {} - void on_second(numeric_system) {} - FMT_NORETURN void on_datetime(numeric_system) { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_loc_date(numeric_system) { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_loc_time(numeric_system) { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_us_date() { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_iso_date() { report_no_date(); } - void on_12_hour_time() {} - void on_24_hour_time() {} - void on_iso_time() {} - void on_am_pm() {} - void on_duration_value() {} - void on_duration_unit() {} - FMT_NORETURN void on_utc_offset() { report_no_date(); } - FMT_NORETURN void on_tz_name() { report_no_date(); } +template <typename Derived> struct null_chrono_spec_handler { + FMT_CONSTEXPR void unsupported() { + static_cast<Derived*>(this)->unsupported(); + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_year(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_short_year(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_offset_year() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_century(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_week_based_year() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_week_based_short_year() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_abbr_weekday() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_full_weekday() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec0_weekday(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec1_weekday(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_abbr_month() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_full_month() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec_month(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec0_week_of_year(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec1_week_of_year(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_week_of_year(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_day_of_year() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_day_of_month(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_day_of_month_space(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_24_hour(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_12_hour(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_minute(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_second(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_datetime(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_loc_date(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_loc_time(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_us_date() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_date() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_12_hour_time() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_24_hour_time() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_time() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_am_pm() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_duration_value() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_duration_unit() { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_utc_offset(numeric_system) { unsupported(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_tz_name() { unsupported(); } }; -template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> -inline bool isnan(T) { - return false; +struct tm_format_checker : null_chrono_spec_handler<tm_format_checker> { + FMT_NORETURN void unsupported() { FMT_THROW(format_error("no format")); } + + template <typename Char> + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const Char*, const Char*) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_year(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_short_year(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_offset_year() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_century(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_week_based_year() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_week_based_short_year() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_abbr_weekday() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_full_weekday() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec0_weekday(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec1_weekday(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_abbr_month() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_full_month() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec_month(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec0_week_of_year(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec1_week_of_year(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_week_of_year(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_day_of_year() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_day_of_month(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_day_of_month_space(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_24_hour(numeric_system, pad_type) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_12_hour(numeric_system, pad_type) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_minute(numeric_system, pad_type) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_second(numeric_system, pad_type) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_datetime(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_loc_date(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_loc_time(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_us_date() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_date() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_12_hour_time() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_24_hour_time() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_time() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_am_pm() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_utc_offset(numeric_system) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_tz_name() {} +}; + +inline const char* tm_wday_full_name(int wday) { + static constexpr const char* full_name_list[] = { + "Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", + "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"}; + return wday >= 0 && wday <= 6 ? full_name_list[wday] : "?"; } -template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value)> -inline bool isnan(T value) { - return std::isnan(value); +inline const char* tm_wday_short_name(int wday) { + static constexpr const char* short_name_list[] = {"Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", + "Thu", "Fri", "Sat"}; + return wday >= 0 && wday <= 6 ? short_name_list[wday] : "???"; } -template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> -inline bool isfinite(T) { - return true; +inline const char* tm_mon_full_name(int mon) { + static constexpr const char* full_name_list[] = { + "January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", + "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"}; + return mon >= 0 && mon <= 11 ? full_name_list[mon] : "?"; } -template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value)> -inline bool isfinite(T value) { - return std::isfinite(value); +inline const char* tm_mon_short_name(int mon) { + static constexpr const char* short_name_list[] = { + "Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun", + "Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec", + }; + return mon >= 0 && mon <= 11 ? short_name_list[mon] : "???"; } -// Converts value to int and checks that it's in the range [0, upper). -template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> -inline int to_nonnegative_int(T value, int upper) { - FMT_ASSERT(value >= 0 && value <= upper, "invalid value"); - (void)upper; - return static_cast<int>(value); +template <typename T, typename = void> +struct has_member_data_tm_gmtoff : std::false_type {}; +template <typename T> +struct has_member_data_tm_gmtoff<T, void_t<decltype(T::tm_gmtoff)>> + : std::true_type {}; + +template <typename T, typename = void> +struct has_member_data_tm_zone : std::false_type {}; +template <typename T> +struct has_member_data_tm_zone<T, void_t<decltype(T::tm_zone)>> + : std::true_type {}; + +#if FMT_USE_TZSET +inline void tzset_once() { + static bool init = []() -> bool { + _tzset(); + return true; + }(); + ignore_unused(init); } -template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)> -inline int to_nonnegative_int(T value, int upper) { - FMT_ASSERT( - std::isnan(value) || (value >= 0 && value <= static_cast<T>(upper)), - "invalid value"); +#endif + +// Converts value to Int and checks that it's in the range [0, upper). +template <typename T, typename Int, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> +inline Int to_nonnegative_int(T value, Int upper) { + FMT_ASSERT(std::is_unsigned<Int>::value || + (value >= 0 && to_unsigned(value) <= to_unsigned(upper)), + "invalid value"); (void)upper; - return static_cast<int>(value); + return static_cast<Int>(value); +} +template <typename T, typename Int, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)> +inline Int to_nonnegative_int(T value, Int upper) { + if (value < 0 || value > static_cast<T>(upper)) + FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid value")); + return static_cast<Int>(value); +} + +constexpr long long pow10(std::uint32_t n) { + return n == 0 ? 1 : 10 * pow10(n - 1); +} + +// Counts the number of fractional digits in the range [0, 18] according to the +// C++20 spec. If more than 18 fractional digits are required then returns 6 for +// microseconds precision. +template <long long Num, long long Den, int N = 0, + bool Enabled = (N < 19) && (Num <= max_value<long long>() / 10)> +struct count_fractional_digits { + static constexpr int value = + Num % Den == 0 ? N : count_fractional_digits<Num * 10, Den, N + 1>::value; +}; + +// Base case that doesn't instantiate any more templates +// in order to avoid overflow. +template <long long Num, long long Den, int N> +struct count_fractional_digits<Num, Den, N, false> { + static constexpr int value = (Num % Den == 0) ? N : 6; +}; + +// Format subseconds which are given as an integer type with an appropriate +// number of digits. +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename Duration> +void write_fractional_seconds(OutputIt& out, Duration d, int precision = -1) { + constexpr auto num_fractional_digits = + count_fractional_digits<Duration::period::num, + Duration::period::den>::value; + + using subsecond_precision = std::chrono::duration< + typename std::common_type<typename Duration::rep, + std::chrono::seconds::rep>::type, + std::ratio<1, detail::pow10(num_fractional_digits)>>; + + const auto fractional = + d - std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(d); + const auto subseconds = + std::chrono::treat_as_floating_point< + typename subsecond_precision::rep>::value + ? fractional.count() + : std::chrono::duration_cast<subsecond_precision>(fractional).count(); + auto n = static_cast<uint32_or_64_or_128_t<long long>>(subseconds); + const int num_digits = detail::count_digits(n); + + int leading_zeroes = (std::max)(0, num_fractional_digits - num_digits); + if (precision < 0) { + FMT_ASSERT(!std::is_floating_point<typename Duration::rep>::value, ""); + if (std::ratio_less<typename subsecond_precision::period, + std::chrono::seconds::period>::value) { + *out++ = '.'; + out = std::fill_n(out, leading_zeroes, '0'); + out = format_decimal<Char>(out, n, num_digits).end; + } + } else { + *out++ = '.'; + leading_zeroes = (std::min)(leading_zeroes, precision); + out = std::fill_n(out, leading_zeroes, '0'); + int remaining = precision - leading_zeroes; + if (remaining != 0 && remaining < num_digits) { + n /= to_unsigned(detail::pow10(to_unsigned(num_digits - remaining))); + out = format_decimal<Char>(out, n, remaining).end; + return; + } + out = format_decimal<Char>(out, n, num_digits).end; + remaining -= num_digits; + out = std::fill_n(out, remaining, '0'); + } +} + +// Format subseconds which are given as a floating point type with an +// appropriate number of digits. We cannot pass the Duration here, as we +// explicitly need to pass the Rep value in the chrono_formatter. +template <typename Duration> +void write_floating_seconds(memory_buffer& buf, Duration duration, + int num_fractional_digits = -1) { + using rep = typename Duration::rep; + FMT_ASSERT(std::is_floating_point<rep>::value, ""); + + auto val = duration.count(); + + if (num_fractional_digits < 0) { + // For `std::round` with fallback to `round`: + // On some toolchains `std::round` is not available (e.g. GCC 6). + using namespace std; + num_fractional_digits = + count_fractional_digits<Duration::period::num, + Duration::period::den>::value; + if (num_fractional_digits < 6 && static_cast<rep>(round(val)) != val) + num_fractional_digits = 6; + } + + format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), FMT_STRING("{:.{}f}"), + std::fmod(val * static_cast<rep>(Duration::period::num) / + static_cast<rep>(Duration::period::den), + static_cast<rep>(60)), + num_fractional_digits); +} + +template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, + typename Duration = std::chrono::seconds> +class tm_writer { + private: + static constexpr int days_per_week = 7; + + const std::locale& loc_; + const bool is_classic_; + OutputIt out_; + const Duration* subsecs_; + const std::tm& tm_; + + auto tm_sec() const noexcept -> int { + FMT_ASSERT(tm_.tm_sec >= 0 && tm_.tm_sec <= 61, ""); + return tm_.tm_sec; + } + auto tm_min() const noexcept -> int { + FMT_ASSERT(tm_.tm_min >= 0 && tm_.tm_min <= 59, ""); + return tm_.tm_min; + } + auto tm_hour() const noexcept -> int { + FMT_ASSERT(tm_.tm_hour >= 0 && tm_.tm_hour <= 23, ""); + return tm_.tm_hour; + } + auto tm_mday() const noexcept -> int { + FMT_ASSERT(tm_.tm_mday >= 1 && tm_.tm_mday <= 31, ""); + return tm_.tm_mday; + } + auto tm_mon() const noexcept -> int { + FMT_ASSERT(tm_.tm_mon >= 0 && tm_.tm_mon <= 11, ""); + return tm_.tm_mon; + } + auto tm_year() const noexcept -> long long { return 1900ll + tm_.tm_year; } + auto tm_wday() const noexcept -> int { + FMT_ASSERT(tm_.tm_wday >= 0 && tm_.tm_wday <= 6, ""); + return tm_.tm_wday; + } + auto tm_yday() const noexcept -> int { + FMT_ASSERT(tm_.tm_yday >= 0 && tm_.tm_yday <= 365, ""); + return tm_.tm_yday; + } + + auto tm_hour12() const noexcept -> int { + const auto h = tm_hour(); + const auto z = h < 12 ? h : h - 12; + return z == 0 ? 12 : z; + } + + // POSIX and the C Standard are unclear or inconsistent about what %C and %y + // do if the year is negative or exceeds 9999. Use the convention that %C + // concatenated with %y yields the same output as %Y, and that %Y contains at + // least 4 characters, with more only if necessary. + auto split_year_lower(long long year) const noexcept -> int { + auto l = year % 100; + if (l < 0) l = -l; // l in [0, 99] + return static_cast<int>(l); + } + + // Algorithm: + // https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_week_date#Calculating_the_week_number_from_a_month_and_day_of_the_month_or_ordinal_date + auto iso_year_weeks(long long curr_year) const noexcept -> int { + const auto prev_year = curr_year - 1; + const auto curr_p = + (curr_year + curr_year / 4 - curr_year / 100 + curr_year / 400) % + days_per_week; + const auto prev_p = + (prev_year + prev_year / 4 - prev_year / 100 + prev_year / 400) % + days_per_week; + return 52 + ((curr_p == 4 || prev_p == 3) ? 1 : 0); + } + auto iso_week_num(int tm_yday, int tm_wday) const noexcept -> int { + return (tm_yday + 11 - (tm_wday == 0 ? days_per_week : tm_wday)) / + days_per_week; + } + auto tm_iso_week_year() const noexcept -> long long { + const auto year = tm_year(); + const auto w = iso_week_num(tm_yday(), tm_wday()); + if (w < 1) return year - 1; + if (w > iso_year_weeks(year)) return year + 1; + return year; + } + auto tm_iso_week_of_year() const noexcept -> int { + const auto year = tm_year(); + const auto w = iso_week_num(tm_yday(), tm_wday()); + if (w < 1) return iso_year_weeks(year - 1); + if (w > iso_year_weeks(year)) return 1; + return w; + } + + void write1(int value) { + *out_++ = static_cast<char>('0' + to_unsigned(value) % 10); + } + void write2(int value) { + const char* d = digits2(to_unsigned(value) % 100); + *out_++ = *d++; + *out_++ = *d; + } + void write2(int value, pad_type pad) { + unsigned int v = to_unsigned(value) % 100; + if (v >= 10) { + const char* d = digits2(v); + *out_++ = *d++; + *out_++ = *d; + } else { + out_ = detail::write_padding(out_, pad); + *out_++ = static_cast<char>('0' + v); + } + } + + void write_year_extended(long long year) { + // At least 4 characters. + int width = 4; + if (year < 0) { + *out_++ = '-'; + year = 0 - year; + --width; + } + uint32_or_64_or_128_t<long long> n = to_unsigned(year); + const int num_digits = count_digits(n); + if (width > num_digits) out_ = std::fill_n(out_, width - num_digits, '0'); + out_ = format_decimal<Char>(out_, n, num_digits).end; + } + void write_year(long long year) { + if (year >= 0 && year < 10000) { + write2(static_cast<int>(year / 100)); + write2(static_cast<int>(year % 100)); + } else { + write_year_extended(year); + } + } + + void write_utc_offset(long offset, numeric_system ns) { + if (offset < 0) { + *out_++ = '-'; + offset = -offset; + } else { + *out_++ = '+'; + } + offset /= 60; + write2(static_cast<int>(offset / 60)); + if (ns != numeric_system::standard) *out_++ = ':'; + write2(static_cast<int>(offset % 60)); + } + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(has_member_data_tm_gmtoff<T>::value)> + void format_utc_offset_impl(const T& tm, numeric_system ns) { + write_utc_offset(tm.tm_gmtoff, ns); + } + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!has_member_data_tm_gmtoff<T>::value)> + void format_utc_offset_impl(const T& tm, numeric_system ns) { +#if defined(_WIN32) && defined(_UCRT) +# if FMT_USE_TZSET + tzset_once(); +# endif + long offset = 0; + _get_timezone(&offset); + if (tm.tm_isdst) { + long dstbias = 0; + _get_dstbias(&dstbias); + offset += dstbias; + } + write_utc_offset(-offset, ns); +#else + if (ns == numeric_system::standard) return format_localized('z'); + + // Extract timezone offset from timezone conversion functions. + std::tm gtm = tm; + std::time_t gt = std::mktime(>m); + std::tm ltm = gmtime(gt); + std::time_t lt = std::mktime(<m); + long offset = gt - lt; + write_utc_offset(offset, ns); +#endif + } + + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(has_member_data_tm_zone<T>::value)> + void format_tz_name_impl(const T& tm) { + if (is_classic_) + out_ = write_tm_str<Char>(out_, tm.tm_zone, loc_); + else + format_localized('Z'); + } + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!has_member_data_tm_zone<T>::value)> + void format_tz_name_impl(const T&) { + format_localized('Z'); + } + + void format_localized(char format, char modifier = 0) { + out_ = write<Char>(out_, tm_, loc_, format, modifier); + } + + public: + tm_writer(const std::locale& loc, OutputIt out, const std::tm& tm, + const Duration* subsecs = nullptr) + : loc_(loc), + is_classic_(loc_ == get_classic_locale()), + out_(out), + subsecs_(subsecs), + tm_(tm) {} + + OutputIt out() const { return out_; } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const Char* begin, const Char* end) { + out_ = copy_str<Char>(begin, end, out_); + } + + void on_abbr_weekday() { + if (is_classic_) + out_ = write(out_, tm_wday_short_name(tm_wday())); + else + format_localized('a'); + } + void on_full_weekday() { + if (is_classic_) + out_ = write(out_, tm_wday_full_name(tm_wday())); + else + format_localized('A'); + } + void on_dec0_weekday(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) return write1(tm_wday()); + format_localized('w', 'O'); + } + void on_dec1_weekday(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) { + auto wday = tm_wday(); + write1(wday == 0 ? days_per_week : wday); + } else { + format_localized('u', 'O'); + } + } + + void on_abbr_month() { + if (is_classic_) + out_ = write(out_, tm_mon_short_name(tm_mon())); + else + format_localized('b'); + } + void on_full_month() { + if (is_classic_) + out_ = write(out_, tm_mon_full_name(tm_mon())); + else + format_localized('B'); + } + + void on_datetime(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_) { + on_abbr_weekday(); + *out_++ = ' '; + on_abbr_month(); + *out_++ = ' '; + on_day_of_month_space(numeric_system::standard); + *out_++ = ' '; + on_iso_time(); + *out_++ = ' '; + on_year(numeric_system::standard); + } else { + format_localized('c', ns == numeric_system::standard ? '\0' : 'E'); + } + } + void on_loc_date(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_) + on_us_date(); + else + format_localized('x', ns == numeric_system::standard ? '\0' : 'E'); + } + void on_loc_time(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_) + on_iso_time(); + else + format_localized('X', ns == numeric_system::standard ? '\0' : 'E'); + } + void on_us_date() { + char buf[8]; + write_digit2_separated(buf, to_unsigned(tm_mon() + 1), + to_unsigned(tm_mday()), + to_unsigned(split_year_lower(tm_year())), '/'); + out_ = copy_str<Char>(std::begin(buf), std::end(buf), out_); + } + void on_iso_date() { + auto year = tm_year(); + char buf[10]; + size_t offset = 0; + if (year >= 0 && year < 10000) { + copy2(buf, digits2(static_cast<size_t>(year / 100))); + } else { + offset = 4; + write_year_extended(year); + year = 0; + } + write_digit2_separated(buf + 2, static_cast<unsigned>(year % 100), + to_unsigned(tm_mon() + 1), to_unsigned(tm_mday()), + '-'); + out_ = copy_str<Char>(std::begin(buf) + offset, std::end(buf), out_); + } + + void on_utc_offset(numeric_system ns) { format_utc_offset_impl(tm_, ns); } + void on_tz_name() { format_tz_name_impl(tm_); } + + void on_year(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) + return write_year(tm_year()); + format_localized('Y', 'E'); + } + void on_short_year(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) + return write2(split_year_lower(tm_year())); + format_localized('y', 'O'); + } + void on_offset_year() { + if (is_classic_) return write2(split_year_lower(tm_year())); + format_localized('y', 'E'); + } + + void on_century(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) { + auto year = tm_year(); + auto upper = year / 100; + if (year >= -99 && year < 0) { + // Zero upper on negative year. + *out_++ = '-'; + *out_++ = '0'; + } else if (upper >= 0 && upper < 100) { + write2(static_cast<int>(upper)); + } else { + out_ = write<Char>(out_, upper); + } + } else { + format_localized('C', 'E'); + } + } + + void on_dec_month(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) + return write2(tm_mon() + 1); + format_localized('m', 'O'); + } + + void on_dec0_week_of_year(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) + return write2((tm_yday() + days_per_week - tm_wday()) / days_per_week); + format_localized('U', 'O'); + } + void on_dec1_week_of_year(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) { + auto wday = tm_wday(); + write2((tm_yday() + days_per_week - + (wday == 0 ? (days_per_week - 1) : (wday - 1))) / + days_per_week); + } else { + format_localized('W', 'O'); + } + } + void on_iso_week_of_year(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) + return write2(tm_iso_week_of_year()); + format_localized('V', 'O'); + } + + void on_iso_week_based_year() { write_year(tm_iso_week_year()); } + void on_iso_week_based_short_year() { + write2(split_year_lower(tm_iso_week_year())); + } + + void on_day_of_year() { + auto yday = tm_yday() + 1; + write1(yday / 100); + write2(yday % 100); + } + void on_day_of_month(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) return write2(tm_mday()); + format_localized('d', 'O'); + } + void on_day_of_month_space(numeric_system ns) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) { + auto mday = to_unsigned(tm_mday()) % 100; + const char* d2 = digits2(mday); + *out_++ = mday < 10 ? ' ' : d2[0]; + *out_++ = d2[1]; + } else { + format_localized('e', 'O'); + } + } + + void on_24_hour(numeric_system ns, pad_type pad) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) + return write2(tm_hour(), pad); + format_localized('H', 'O'); + } + void on_12_hour(numeric_system ns, pad_type pad) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) + return write2(tm_hour12(), pad); + format_localized('I', 'O'); + } + void on_minute(numeric_system ns, pad_type pad) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) + return write2(tm_min(), pad); + format_localized('M', 'O'); + } + + void on_second(numeric_system ns, pad_type pad) { + if (is_classic_ || ns == numeric_system::standard) { + write2(tm_sec(), pad); + if (subsecs_) { + if (std::is_floating_point<typename Duration::rep>::value) { + auto buf = memory_buffer(); + write_floating_seconds(buf, *subsecs_); + if (buf.size() > 1) { + // Remove the leading "0", write something like ".123". + out_ = std::copy(buf.begin() + 1, buf.end(), out_); + } + } else { + write_fractional_seconds<Char>(out_, *subsecs_); + } + } + } else { + // Currently no formatting of subseconds when a locale is set. + format_localized('S', 'O'); + } + } + + void on_12_hour_time() { + if (is_classic_) { + char buf[8]; + write_digit2_separated(buf, to_unsigned(tm_hour12()), + to_unsigned(tm_min()), to_unsigned(tm_sec()), ':'); + out_ = copy_str<Char>(std::begin(buf), std::end(buf), out_); + *out_++ = ' '; + on_am_pm(); + } else { + format_localized('r'); + } + } + void on_24_hour_time() { + write2(tm_hour()); + *out_++ = ':'; + write2(tm_min()); + } + void on_iso_time() { + on_24_hour_time(); + *out_++ = ':'; + on_second(numeric_system::standard, pad_type::unspecified); + } + + void on_am_pm() { + if (is_classic_) { + *out_++ = tm_hour() < 12 ? 'A' : 'P'; + *out_++ = 'M'; + } else { + format_localized('p'); + } + } + + // These apply to chrono durations but not tm. + void on_duration_value() {} + void on_duration_unit() {} +}; + +struct chrono_format_checker : null_chrono_spec_handler<chrono_format_checker> { + bool has_precision_integral = false; + + FMT_NORETURN void unsupported() { FMT_THROW(format_error("no date")); } + + template <typename Char> + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const Char*, const Char*) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_24_hour(numeric_system, pad_type) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_12_hour(numeric_system, pad_type) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_minute(numeric_system, pad_type) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_second(numeric_system, pad_type) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_12_hour_time() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_24_hour_time() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_iso_time() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_am_pm() {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_duration_value() const { + if (has_precision_integral) { + FMT_THROW(format_error("precision not allowed for this argument type")); + } + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_duration_unit() {} +}; + +template <typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value&& has_isfinite<T>::value)> +inline bool isfinite(T) { + return true; } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> @@ -743,26 +1654,22 @@ inline std::chrono::duration<Rep, std::milli> get_milliseconds( #endif } -template <typename Rep, typename Period, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<Rep>::value)> -inline std::chrono::duration<Rep, std::milli> get_milliseconds( - std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period> d) { - using common_type = typename std::common_type<Rep, std::intmax_t>::type; - auto ms = mod(d.count() * static_cast<common_type>(Period::num) / - static_cast<common_type>(Period::den) * 1000, - 1000); - return std::chrono::duration<Rep, std::milli>(static_cast<Rep>(ms)); +template <typename Char, typename Rep, typename OutputIt, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<Rep>::value)> +OutputIt format_duration_value(OutputIt out, Rep val, int) { + return write<Char>(out, val); } -template <typename Char, typename Rep, typename OutputIt> +template <typename Char, typename Rep, typename OutputIt, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<Rep>::value)> OutputIt format_duration_value(OutputIt out, Rep val, int precision) { - const Char pr_f[] = {'{', ':', '.', '{', '}', 'f', '}', 0}; - if (precision >= 0) return format_to(out, pr_f, val, precision); - const Char fp_f[] = {'{', ':', 'g', '}', 0}; - const Char format[] = {'{', '}', 0}; - return format_to(out, std::is_floating_point<Rep>::value ? fp_f : format, - val); + auto specs = format_specs<Char>(); + specs.precision = precision; + specs.type = precision >= 0 ? presentation_type::fixed_lower + : presentation_type::general_lower; + return write<Char>(out, val, specs); } + template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> OutputIt copy_unit(string_view unit, OutputIt out, Char) { return std::copy(unit.begin(), unit.end(), out); @@ -780,18 +1687,44 @@ template <typename Char, typename Period, typename OutputIt> OutputIt format_duration_unit(OutputIt out) { if (const char* unit = get_units<Period>()) return copy_unit(string_view(unit), out, Char()); - const Char num_f[] = {'[', '{', '}', ']', 's', 0}; - if (const_check(Period::den == 1)) return format_to(out, num_f, Period::num); - const Char num_def_f[] = {'[', '{', '}', '/', '{', '}', ']', 's', 0}; - return format_to(out, num_def_f, Period::num, Period::den); + *out++ = '['; + out = write<Char>(out, Period::num); + if (const_check(Period::den != 1)) { + *out++ = '/'; + out = write<Char>(out, Period::den); + } + *out++ = ']'; + *out++ = 's'; + return out; } +class get_locale { + private: + union { + std::locale locale_; + }; + bool has_locale_ = false; + + public: + get_locale(bool localized, locale_ref loc) : has_locale_(localized) { + if (localized) + ::new (&locale_) std::locale(loc.template get<std::locale>()); + } + ~get_locale() { + if (has_locale_) locale_.~locale(); + } + operator const std::locale&() const { + return has_locale_ ? locale_ : get_classic_locale(); + } +}; + template <typename FormatContext, typename OutputIt, typename Rep, typename Period> struct chrono_formatter { FormatContext& context; OutputIt out; int precision; + bool localized = false; // rep is unsigned to avoid overflow. using rep = conditional_t<std::is_integral<Rep>::value && sizeof(Rep) < sizeof(int), @@ -803,9 +1736,10 @@ struct chrono_formatter { bool negative; using char_type = typename FormatContext::char_type; + using tm_writer_type = tm_writer<OutputIt, char_type>; - explicit chrono_formatter(FormatContext& ctx, OutputIt o, - std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period> d) + chrono_formatter(FormatContext& ctx, OutputIt o, + std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period> d) : context(ctx), out(o), val(static_cast<rep>(d.count())), @@ -870,13 +1804,15 @@ struct chrono_formatter { } } - void write(Rep value, int width) { + void write(Rep value, int width, pad_type pad = pad_type::unspecified) { write_sign(); if (isnan(value)) return write_nan(); uint32_or_64_or_128_t<int> n = to_unsigned(to_nonnegative_int(value, max_value<int>())); int num_digits = detail::count_digits(n); - if (width > num_digits) out = std::fill_n(out, width - num_digits, '0'); + if (width > num_digits) { + out = detail::write_padding(out, pad, width - num_digits); + } out = format_decimal<char_type>(out, n, num_digits).end; } @@ -884,15 +1820,13 @@ struct chrono_formatter { void write_pinf() { std::copy_n("inf", 3, out); } void write_ninf() { std::copy_n("-inf", 4, out); } - void format_localized(const tm& time, char format, char modifier = 0) { + template <typename Callback, typename... Args> + void format_tm(const tm& time, Callback cb, Args... args) { if (isnan(val)) return write_nan(); - auto locale = context.locale().template get<std::locale>(); - auto& facet = std::use_facet<std::time_put<char_type>>(locale); - std::basic_ostringstream<char_type> os; - os.imbue(locale); - facet.put(os, os, ' ', &time, format, modifier); - auto str = os.str(); - std::copy(str.begin(), str.end(), out); + get_locale loc(localized, context.locale()); + auto w = tm_writer_type(loc, out, time); + (w.*cb)(args...); + out = w.out(); } void on_text(const char_type* begin, const char_type* end) { @@ -911,64 +1845,77 @@ struct chrono_formatter { void on_loc_time(numeric_system) {} void on_us_date() {} void on_iso_date() {} - void on_utc_offset() {} + void on_utc_offset(numeric_system) {} void on_tz_name() {} - - void on_24_hour(numeric_system ns) { + void on_year(numeric_system) {} + void on_short_year(numeric_system) {} + void on_offset_year() {} + void on_century(numeric_system) {} + void on_iso_week_based_year() {} + void on_iso_week_based_short_year() {} + void on_dec_month(numeric_system) {} + void on_dec0_week_of_year(numeric_system) {} + void on_dec1_week_of_year(numeric_system) {} + void on_iso_week_of_year(numeric_system) {} + void on_day_of_year() {} + void on_day_of_month(numeric_system) {} + void on_day_of_month_space(numeric_system) {} + + void on_24_hour(numeric_system ns, pad_type pad) { if (handle_nan_inf()) return; - if (ns == numeric_system::standard) return write(hour(), 2); + if (ns == numeric_system::standard) return write(hour(), 2, pad); auto time = tm(); time.tm_hour = to_nonnegative_int(hour(), 24); - format_localized(time, 'H', 'O'); + format_tm(time, &tm_writer_type::on_24_hour, ns, pad); } - void on_12_hour(numeric_system ns) { + void on_12_hour(numeric_system ns, pad_type pad) { if (handle_nan_inf()) return; - if (ns == numeric_system::standard) return write(hour12(), 2); + if (ns == numeric_system::standard) return write(hour12(), 2, pad); auto time = tm(); time.tm_hour = to_nonnegative_int(hour12(), 12); - format_localized(time, 'I', 'O'); + format_tm(time, &tm_writer_type::on_12_hour, ns, pad); } - void on_minute(numeric_system ns) { + void on_minute(numeric_system ns, pad_type pad) { if (handle_nan_inf()) return; - if (ns == numeric_system::standard) return write(minute(), 2); + if (ns == numeric_system::standard) return write(minute(), 2, pad); auto time = tm(); time.tm_min = to_nonnegative_int(minute(), 60); - format_localized(time, 'M', 'O'); + format_tm(time, &tm_writer_type::on_minute, ns, pad); } - void on_second(numeric_system ns) { + void on_second(numeric_system ns, pad_type pad) { if (handle_nan_inf()) return; if (ns == numeric_system::standard) { - write(second(), 2); -#if FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST - // convert rep->Rep - using duration_rep = std::chrono::duration<rep, Period>; - using duration_Rep = std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period>; - auto tmpval = fmt_safe_duration_cast<duration_Rep>(duration_rep{val}); -#else - auto tmpval = std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period>(val); -#endif - auto ms = get_milliseconds(tmpval); - if (ms != std::chrono::milliseconds(0)) { - *out++ = '.'; - write(ms.count(), 3); + if (std::is_floating_point<rep>::value) { + auto buf = memory_buffer(); + write_floating_seconds(buf, std::chrono::duration<rep, Period>(val), + precision); + if (negative) *out++ = '-'; + if (buf.size() < 2 || buf[1] == '.') { + out = detail::write_padding(out, pad); + } + out = std::copy(buf.begin(), buf.end(), out); + } else { + write(second(), 2, pad); + write_fractional_seconds<char_type>( + out, std::chrono::duration<rep, Period>(val), precision); } return; } auto time = tm(); time.tm_sec = to_nonnegative_int(second(), 60); - format_localized(time, 'S', 'O'); + format_tm(time, &tm_writer_type::on_second, ns, pad); } void on_12_hour_time() { if (handle_nan_inf()) return; - format_localized(time(), 'r'); + format_tm(time(), &tm_writer_type::on_12_hour_time); } void on_24_hour_time() { @@ -987,12 +1934,12 @@ struct chrono_formatter { on_24_hour_time(); *out++ = ':'; if (handle_nan_inf()) return; - write(second(), 2); + on_second(numeric_system::standard, pad_type::unspecified); } void on_am_pm() { if (handle_nan_inf()) return; - format_localized(time(), 'p'); + format_tm(time(), &tm_writer_type::on_am_pm); } void on_duration_value() { @@ -1005,114 +1952,256 @@ struct chrono_formatter { out = format_duration_unit<char_type, Period>(out); } }; + } // namespace detail -template <typename Rep, typename Period, typename Char> -struct formatter<std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period>, Char> { +#if defined(__cpp_lib_chrono) && __cpp_lib_chrono >= 201907 +using weekday = std::chrono::weekday; +#else +// A fallback version of weekday. +class weekday { private: - basic_format_specs<Char> specs; - int precision; - using arg_ref_type = detail::arg_ref<Char>; - arg_ref_type width_ref; - arg_ref_type precision_ref; - mutable basic_string_view<Char> format_str; - using duration = std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period>; - - struct spec_handler { - formatter& f; - basic_format_parse_context<Char>& context; - basic_string_view<Char> format_str; - - template <typename Id> FMT_CONSTEXPR arg_ref_type make_arg_ref(Id arg_id) { - context.check_arg_id(arg_id); - return arg_ref_type(arg_id); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR arg_ref_type make_arg_ref(basic_string_view<Char> arg_id) { - context.check_arg_id(arg_id); - return arg_ref_type(arg_id); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR arg_ref_type make_arg_ref(detail::auto_id) { - return arg_ref_type(context.next_arg_id()); - } - - void on_error(const char* msg) { FMT_THROW(format_error(msg)); } - void on_fill(basic_string_view<Char> fill) { f.specs.fill = fill; } - void on_align(align_t align) { f.specs.align = align; } - void on_width(int width) { f.specs.width = width; } - void on_precision(int _precision) { f.precision = _precision; } - void end_precision() {} + unsigned char value; - template <typename Id> void on_dynamic_width(Id arg_id) { - f.width_ref = make_arg_ref(arg_id); - } + public: + weekday() = default; + explicit constexpr weekday(unsigned wd) noexcept + : value(static_cast<unsigned char>(wd != 7 ? wd : 0)) {} + constexpr unsigned c_encoding() const noexcept { return value; } +}; - template <typename Id> void on_dynamic_precision(Id arg_id) { - f.precision_ref = make_arg_ref(arg_id); - } - }; +class year_month_day {}; +#endif - using iterator = typename basic_format_parse_context<Char>::iterator; - struct parse_range { - iterator begin; - iterator end; - }; +// A rudimentary weekday formatter. +template <typename Char> struct formatter<weekday, Char> { + private: + bool localized = false; - FMT_CONSTEXPR parse_range do_parse(basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx) { + public: + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx) + -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { auto begin = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end(); - if (begin == end || *begin == '}') return {begin, begin}; - spec_handler handler{*this, ctx, format_str}; - begin = detail::parse_align(begin, end, handler); - if (begin == end) return {begin, begin}; - begin = detail::parse_width(begin, end, handler); - if (begin == end) return {begin, begin}; - if (*begin == '.') { - if (std::is_floating_point<Rep>::value) - begin = detail::parse_precision(begin, end, handler); - else - handler.on_error("precision not allowed for this argument type"); + if (begin != end && *begin == 'L') { + ++begin; + localized = true; } - end = parse_chrono_format(begin, end, detail::chrono_format_checker()); - return {begin, end}; + return begin; } - public: - formatter() : precision(-1) {} + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(weekday wd, FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto time = std::tm(); + time.tm_wday = static_cast<int>(wd.c_encoding()); + detail::get_locale loc(localized, ctx.locale()); + auto w = detail::tm_writer<decltype(ctx.out()), Char>(loc, ctx.out(), time); + w.on_abbr_weekday(); + return w.out(); + } +}; +template <typename Rep, typename Period, typename Char> +struct formatter<std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period>, Char> { + private: + format_specs<Char> specs_; + detail::arg_ref<Char> width_ref_; + detail::arg_ref<Char> precision_ref_; + bool localized_ = false; + basic_string_view<Char> format_str_; + + public: FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - auto range = do_parse(ctx); - format_str = basic_string_view<Char>( - &*range.begin, detail::to_unsigned(range.end - range.begin)); - return range.end; + auto it = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end(); + if (it == end || *it == '}') return it; + + it = detail::parse_align(it, end, specs_); + if (it == end) return it; + + it = detail::parse_dynamic_spec(it, end, specs_.width, width_ref_, ctx); + if (it == end) return it; + + auto checker = detail::chrono_format_checker(); + if (*it == '.') { + checker.has_precision_integral = !std::is_floating_point<Rep>::value; + it = detail::parse_precision(it, end, specs_.precision, precision_ref_, + ctx); + } + if (it != end && *it == 'L') { + localized_ = true; + ++it; + } + end = detail::parse_chrono_format(it, end, checker); + format_str_ = {it, detail::to_unsigned(end - it)}; + return end; } template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(const duration& d, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - auto begin = format_str.begin(), end = format_str.end(); + auto format(std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period> d, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto specs = specs_; + auto precision = specs.precision; + specs.precision = -1; + auto begin = format_str_.begin(), end = format_str_.end(); // As a possible future optimization, we could avoid extra copying if width // is not specified. - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buf; + auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); auto out = std::back_inserter(buf); - detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs.width, width_ref, + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs.width, width_ref_, ctx); detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>(precision, - precision_ref, ctx); + precision_ref_, ctx); if (begin == end || *begin == '}') { out = detail::format_duration_value<Char>(out, d.count(), precision); detail::format_duration_unit<Char, Period>(out); } else { - detail::chrono_formatter<FormatContext, decltype(out), Rep, Period> f( - ctx, out, d); + using chrono_formatter = + detail::chrono_formatter<FormatContext, decltype(out), Rep, Period>; + auto f = chrono_formatter(ctx, out, d); f.precision = precision; - parse_chrono_format(begin, end, f); + f.localized = localized_; + detail::parse_chrono_format(begin, end, f); + } + return detail::write( + ctx.out(), basic_string_view<Char>(buf.data(), buf.size()), specs); + } +}; + +template <typename Char, typename Duration> +struct formatter<std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration>, + Char> : formatter<std::tm, Char> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR formatter() { + this->format_str_ = detail::string_literal<Char, '%', 'F', ' ', '%', 'T'>{}; + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration> val, + FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + using period = typename Duration::period; + if (detail::const_check( + period::num != 1 || period::den != 1 || + std::is_floating_point<typename Duration::rep>::value)) { + const auto epoch = val.time_since_epoch(); + auto subsecs = std::chrono::duration_cast<Duration>( + epoch - std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(epoch)); + + if (subsecs.count() < 0) { + auto second = + std::chrono::duration_cast<Duration>(std::chrono::seconds(1)); + if (epoch.count() < ((Duration::min)() + second).count()) + FMT_THROW(format_error("duration is too small")); + subsecs += second; + val -= second; + } + + return formatter<std::tm, Char>::do_format( + gmtime(std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(val)), ctx, + &subsecs); + } + + return formatter<std::tm, Char>::format( + gmtime(std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(val)), ctx); + } +}; + +#if FMT_USE_LOCAL_TIME +template <typename Char, typename Duration> +struct formatter<std::chrono::local_time<Duration>, Char> + : formatter<std::tm, Char> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR formatter() { + this->format_str_ = detail::string_literal<Char, '%', 'F', ' ', '%', 'T'>{}; + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(std::chrono::local_time<Duration> val, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + using period = typename Duration::period; + if (period::num != 1 || period::den != 1 || + std::is_floating_point<typename Duration::rep>::value) { + const auto epoch = val.time_since_epoch(); + const auto subsecs = std::chrono::duration_cast<Duration>( + epoch - std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(epoch)); + + return formatter<std::tm, Char>::do_format( + localtime(std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(val)), + ctx, &subsecs); } + + return formatter<std::tm, Char>::format( + localtime(std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(val)), + ctx); + } +}; +#endif + +#if FMT_USE_UTC_TIME +template <typename Char, typename Duration> +struct formatter<std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::utc_clock, Duration>, + Char> + : formatter<std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration>, + Char> { + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::utc_clock, Duration> val, + FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return formatter< + std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration>, + Char>::format(std::chrono::utc_clock::to_sys(val), ctx); + } +}; +#endif + +template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::tm, Char> { + private: + format_specs<Char> specs_; + detail::arg_ref<Char> width_ref_; + + protected: + basic_string_view<Char> format_str_; + + template <typename FormatContext, typename Duration> + auto do_format(const std::tm& tm, FormatContext& ctx, + const Duration* subsecs) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto specs = specs_; + auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); + auto out = std::back_inserter(buf); + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs.width, width_ref_, + ctx); + + auto loc_ref = ctx.locale(); + detail::get_locale loc(static_cast<bool>(loc_ref), loc_ref); + auto w = + detail::tm_writer<decltype(out), Char, Duration>(loc, out, tm, subsecs); + detail::parse_chrono_format(format_str_.begin(), format_str_.end(), w); return detail::write( ctx.out(), basic_string_view<Char>(buf.data(), buf.size()), specs); } + + public: + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx) + -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + auto it = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end(); + if (it == end || *it == '}') return it; + + it = detail::parse_align(it, end, specs_); + if (it == end) return it; + + it = detail::parse_dynamic_spec(it, end, specs_.width, width_ref_, ctx); + if (it == end) return it; + + end = detail::parse_chrono_format(it, end, detail::tm_format_checker()); + // Replace the default format_str only if the new spec is not empty. + if (end != it) format_str_ = {it, detail::to_unsigned(end - it)}; + return end; + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const std::tm& tm, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return do_format<FormatContext, std::chrono::seconds>(tm, ctx, nullptr); + } }; +FMT_END_EXPORT FMT_END_NAMESPACE #endif // FMT_CHRONO_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/color.h b/include/fmt/color.h index 94e3419d..57b7f578 100644 --- a/include/fmt/color.h +++ b/include/fmt/color.h @@ -11,6 +11,7 @@ #include "format.h" FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT enum class color : uint32_t { alice_blue = 0xF0F8FF, // rgb(240,248,255) @@ -177,9 +178,13 @@ enum class terminal_color : uint8_t { enum class emphasis : uint8_t { bold = 1, - italic = 1 << 1, - underline = 1 << 2, - strikethrough = 1 << 3 + faint = 1 << 1, + italic = 1 << 2, + underline = 1 << 3, + blink = 1 << 4, + reverse = 1 << 5, + conceal = 1 << 6, + strikethrough = 1 << 7, }; // rgb is a struct for red, green and blue colors. @@ -202,17 +207,16 @@ namespace detail { // color is a struct of either a rgb color or a terminal color. struct color_type { - FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type() FMT_NOEXCEPT : is_rgb(), value{} {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type(color rgb_color) FMT_NOEXCEPT : is_rgb(true), - value{} { + FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type() noexcept : is_rgb(), value{} {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type(color rgb_color) noexcept : is_rgb(true), value{} { value.rgb_color = static_cast<uint32_t>(rgb_color); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type(rgb rgb_color) FMT_NOEXCEPT : is_rgb(true), value{} { + FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type(rgb rgb_color) noexcept : is_rgb(true), value{} { value.rgb_color = (static_cast<uint32_t>(rgb_color.r) << 16) | (static_cast<uint32_t>(rgb_color.g) << 8) | rgb_color.b; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type(terminal_color term_color) FMT_NOEXCEPT : is_rgb(), - value{} { + FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type(terminal_color term_color) noexcept + : is_rgb(), value{} { value.term_color = static_cast<uint8_t>(term_color); } bool is_rgb; @@ -223,13 +227,11 @@ struct color_type { }; } // namespace detail -// Experimental text formatting support. +/** A text style consisting of foreground and background colors and emphasis. */ class text_style { public: - FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style(emphasis em = emphasis()) FMT_NOEXCEPT - : set_foreground_color(), - set_background_color(), - ems(em) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style(emphasis em = emphasis()) noexcept + : set_foreground_color(), set_background_color(), ems(em) {} FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style& operator|=(const text_style& rhs) { if (!set_foreground_color) { @@ -260,63 +262,32 @@ class text_style { return lhs |= rhs; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style& operator&=(const text_style& rhs) { - if (!set_foreground_color) { - set_foreground_color = rhs.set_foreground_color; - foreground_color = rhs.foreground_color; - } else if (rhs.set_foreground_color) { - if (!foreground_color.is_rgb || !rhs.foreground_color.is_rgb) - FMT_THROW(format_error("can't AND a terminal color")); - foreground_color.value.rgb_color &= rhs.foreground_color.value.rgb_color; - } - - if (!set_background_color) { - set_background_color = rhs.set_background_color; - background_color = rhs.background_color; - } else if (rhs.set_background_color) { - if (!background_color.is_rgb || !rhs.background_color.is_rgb) - FMT_THROW(format_error("can't AND a terminal color")); - background_color.value.rgb_color &= rhs.background_color.value.rgb_color; - } - - ems = static_cast<emphasis>(static_cast<uint8_t>(ems) & - static_cast<uint8_t>(rhs.ems)); - return *this; - } - - friend FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style operator&(text_style lhs, - const text_style& rhs) { - return lhs &= rhs; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_foreground() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { + FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_foreground() const noexcept { return set_foreground_color; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_background() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { + FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_background() const noexcept { return set_background_color; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_emphasis() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { + FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_emphasis() const noexcept { return static_cast<uint8_t>(ems) != 0; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::color_type get_foreground() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { + FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::color_type get_foreground() const noexcept { FMT_ASSERT(has_foreground(), "no foreground specified for this style"); return foreground_color; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::color_type get_background() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { + FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::color_type get_background() const noexcept { FMT_ASSERT(has_background(), "no background specified for this style"); return background_color; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR emphasis get_emphasis() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { + FMT_CONSTEXPR emphasis get_emphasis() const noexcept { FMT_ASSERT(has_emphasis(), "no emphasis specified for this style"); return ems; } private: FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style(bool is_foreground, - detail::color_type text_color) FMT_NOEXCEPT - : set_foreground_color(), - set_background_color(), - ems() { + detail::color_type text_color) noexcept + : set_foreground_color(), set_background_color(), ems() { if (is_foreground) { foreground_color = text_color; set_foreground_color = true; @@ -326,10 +297,9 @@ class text_style { } } - friend FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL text_style fg(detail::color_type foreground) - FMT_NOEXCEPT; - friend FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL text_style bg(detail::color_type background) - FMT_NOEXCEPT; + friend FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style fg(detail::color_type foreground) noexcept; + + friend FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style bg(detail::color_type background) noexcept; detail::color_type foreground_color; detail::color_type background_color; @@ -338,15 +308,17 @@ class text_style { emphasis ems; }; -FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style fg(detail::color_type foreground) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return text_style(/*is_foreground=*/true, foreground); +/** Creates a text style from the foreground (text) color. */ +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline text_style fg(detail::color_type foreground) noexcept { + return text_style(true, foreground); } -FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style bg(detail::color_type background) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return text_style(/*is_foreground=*/false, background); +/** Creates a text style from the background color. */ +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline text_style bg(detail::color_type background) noexcept { + return text_style(false, background); } -FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style operator|(emphasis lhs, emphasis rhs) FMT_NOEXCEPT { +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline text_style operator|(emphasis lhs, emphasis rhs) noexcept { return text_style(lhs) | rhs; } @@ -354,11 +326,11 @@ namespace detail { template <typename Char> struct ansi_color_escape { FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape(detail::color_type text_color, - const char* esc) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const char* esc) noexcept { // If we have a terminal color, we need to output another escape code // sequence. if (!text_color.is_rgb) { - bool is_background = esc == detail::data::background_color; + bool is_background = esc == string_view("\x1b[48;2;"); uint32_t value = text_color.value.term_color; // Background ASCII codes are the same as the foreground ones but with // 10 more. @@ -389,17 +361,19 @@ template <typename Char> struct ansi_color_escape { to_esc(color.b, buffer + 15, 'm'); buffer[19] = static_cast<Char>(0); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape(emphasis em) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - uint8_t em_codes[4] = {}; - uint8_t em_bits = static_cast<uint8_t>(em); - if (em_bits & static_cast<uint8_t>(emphasis::bold)) em_codes[0] = 1; - if (em_bits & static_cast<uint8_t>(emphasis::italic)) em_codes[1] = 3; - if (em_bits & static_cast<uint8_t>(emphasis::underline)) em_codes[2] = 4; - if (em_bits & static_cast<uint8_t>(emphasis::strikethrough)) - em_codes[3] = 9; + FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape(emphasis em) noexcept { + uint8_t em_codes[num_emphases] = {}; + if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::bold)) em_codes[0] = 1; + if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::faint)) em_codes[1] = 2; + if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::italic)) em_codes[2] = 3; + if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::underline)) em_codes[3] = 4; + if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::blink)) em_codes[4] = 5; + if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::reverse)) em_codes[5] = 7; + if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::conceal)) em_codes[6] = 8; + if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::strikethrough)) em_codes[7] = 9; size_t index = 0; - for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { + for (size_t i = 0; i < num_emphases; ++i) { if (!em_codes[i]) continue; buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('\x1b'); buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('['); @@ -408,66 +382,56 @@ template <typename Char> struct ansi_color_escape { } buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>(0); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR operator const Char*() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return buffer; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR operator const Char*() const noexcept { return buffer; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* begin() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return buffer; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* end() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { + FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* begin() const noexcept { return buffer; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS const Char* end() const noexcept { return buffer + std::char_traits<Char>::length(buffer); } private: - Char buffer[7u + 3u * 4u + 1u]; + static constexpr size_t num_emphases = 8; + Char buffer[7u + 3u * num_emphases + 1u]; static FMT_CONSTEXPR void to_esc(uint8_t c, Char* out, - char delimiter) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + char delimiter) noexcept { out[0] = static_cast<Char>('0' + c / 100); out[1] = static_cast<Char>('0' + c / 10 % 10); out[2] = static_cast<Char>('0' + c % 10); out[3] = static_cast<Char>(delimiter); } + static FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_emphasis(emphasis em, emphasis mask) noexcept { + return static_cast<uint8_t>(em) & static_cast<uint8_t>(mask); + } }; template <typename Char> FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape<Char> make_foreground_color( - detail::color_type foreground) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return ansi_color_escape<Char>(foreground, detail::data::foreground_color); + detail::color_type foreground) noexcept { + return ansi_color_escape<Char>(foreground, "\x1b[38;2;"); } template <typename Char> FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape<Char> make_background_color( - detail::color_type background) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return ansi_color_escape<Char>(background, detail::data::background_color); + detail::color_type background) noexcept { + return ansi_color_escape<Char>(background, "\x1b[48;2;"); } template <typename Char> -FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape<Char> make_emphasis(emphasis em) FMT_NOEXCEPT { +FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape<Char> make_emphasis(emphasis em) noexcept { return ansi_color_escape<Char>(em); } -template <typename Char> -inline void fputs(const Char* chars, FILE* stream) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - std::fputs(chars, stream); -} - -template <> -inline void fputs<wchar_t>(const wchar_t* chars, FILE* stream) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - std::fputws(chars, stream); -} - -template <typename Char> inline void reset_color(FILE* stream) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - fputs(detail::data::reset_color, stream); -} - -template <> inline void reset_color<wchar_t>(FILE* stream) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - fputs(detail::data::wreset_color, stream); +template <typename Char> inline void reset_color(buffer<Char>& buffer) { + auto reset_color = string_view("\x1b[0m"); + buffer.append(reset_color.begin(), reset_color.end()); } -template <typename Char> -inline void reset_color(buffer<Char>& buffer) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - const char* begin = data::reset_color; - const char* end = begin + sizeof(data::reset_color) - 1; - buffer.append(begin, end); -} +template <typename T> struct styled_arg : detail::view { + const T& value; + text_style style; + styled_arg(const T& v, text_style s) : value(v), style(s) {} +}; template <typename Char> void vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, const text_style& ts, @@ -489,18 +453,25 @@ void vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, const text_style& ts, auto background = detail::make_background_color<Char>(ts.get_background()); buf.append(background.begin(), background.end()); } - detail::vformat_to(buf, format_str, args); + detail::vformat_to(buf, format_str, args, {}); if (has_style) detail::reset_color<Char>(buf); } + } // namespace detail -template <typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>> -void vprint(std::FILE* f, const text_style& ts, const S& format, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buf; - detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, to_string_view(format), args); - buf.push_back(Char(0)); - detail::fputs(buf.data(), f); +inline void vprint(std::FILE* f, const text_style& ts, string_view fmt, + format_args args) { + // Legacy wide streams are not supported. + auto buf = memory_buffer(); + detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, fmt, args); + if (detail::is_utf8()) { + detail::print(f, string_view(buf.begin(), buf.size())); + return; + } + buf.push_back('\0'); + int result = std::fputs(buf.data(), f); + if (result < 0) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot write to file"))); } /** @@ -519,15 +490,19 @@ template <typename S, typename... Args, void print(std::FILE* f, const text_style& ts, const S& format_str, const Args&... args) { vprint(f, ts, format_str, - fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...)); + fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<char_t<S>>>(args...)); } /** + \rst Formats a string and prints it to stdout using ANSI escape sequences to specify text formatting. - Example: + + **Example**:: + fmt::print(fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red), "Elapsed time: {0:.2f} seconds", 1.23); + \endrst */ template <typename S, typename... Args, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_string<S>::value)> @@ -540,7 +515,7 @@ inline std::basic_string<Char> vformat( const text_style& ts, const S& format_str, basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { basic_memory_buffer<Char> buf; - detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, to_string_view(format_str), args); + detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, detail::to_string_view(format_str), args); return fmt::to_string(buf); } @@ -559,8 +534,8 @@ inline std::basic_string<Char> vformat( template <typename S, typename... Args, typename Char = char_t<S>> inline std::basic_string<Char> format(const text_style& ts, const S& format_str, const Args&... args) { - return vformat(ts, to_string_view(format_str), - fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...)); + return fmt::vformat(ts, detail::to_string_view(format_str), + fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<Char>>(args...)); } /** @@ -571,9 +546,9 @@ template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, OutputIt vformat_to( OutputIt out, const text_style& ts, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - decltype(detail::get_buffer<Char>(out)) buf(detail::get_buffer_init(out)); + auto&& buf = detail::get_buffer<Char>(out); detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, format_str, args); - return detail::get_iterator(buf); + return detail::get_iterator(buf, out); } /** @@ -594,10 +569,65 @@ template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args, inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const text_style& ts, const S& format_str, Args&&... args) -> typename std::enable_if<enable, OutputIt>::type { - return vformat_to(out, ts, to_string_view(format_str), - fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...)); + return vformat_to(out, ts, detail::to_string_view(format_str), + fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<char_t<S>>>(args...)); +} + +template <typename T, typename Char> +struct formatter<detail::styled_arg<T>, Char> : formatter<T, Char> { + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const detail::styled_arg<T>& arg, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + const auto& ts = arg.style; + const auto& value = arg.value; + auto out = ctx.out(); + + bool has_style = false; + if (ts.has_emphasis()) { + has_style = true; + auto emphasis = detail::make_emphasis<Char>(ts.get_emphasis()); + out = std::copy(emphasis.begin(), emphasis.end(), out); + } + if (ts.has_foreground()) { + has_style = true; + auto foreground = + detail::make_foreground_color<Char>(ts.get_foreground()); + out = std::copy(foreground.begin(), foreground.end(), out); + } + if (ts.has_background()) { + has_style = true; + auto background = + detail::make_background_color<Char>(ts.get_background()); + out = std::copy(background.begin(), background.end(), out); + } + out = formatter<T, Char>::format(value, ctx); + if (has_style) { + auto reset_color = string_view("\x1b[0m"); + out = std::copy(reset_color.begin(), reset_color.end(), out); + } + return out; + } +}; + +/** + \rst + Returns an argument that will be formatted using ANSI escape sequences, + to be used in a formatting function. + + **Example**:: + + fmt::print("Elapsed time: {0:.2f} seconds", + fmt::styled(1.23, fmt::fg(fmt::color::green) | + fmt::bg(fmt::color::blue))); + \endrst + */ +template <typename T> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto styled(const T& value, text_style ts) + -> detail::styled_arg<remove_cvref_t<T>> { + return detail::styled_arg<remove_cvref_t<T>>{value, ts}; } +FMT_END_EXPORT FMT_END_NAMESPACE #endif // FMT_COLOR_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/compile.h b/include/fmt/compile.h index 3a33b020..a4c7e495 100644 --- a/include/fmt/compile.h +++ b/include/fmt/compile.h @@ -8,13 +8,17 @@ #ifndef FMT_COMPILE_H_ #define FMT_COMPILE_H_ -#include <vector> - #include "format.h" FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE namespace detail { +template <typename Char, typename InputIt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline counting_iterator copy_str(InputIt begin, InputIt end, + counting_iterator it) { + return it + (end - begin); +} + // A compile-time string which is compiled into fast formatting code. class compiled_string {}; @@ -34,336 +38,30 @@ struct is_compiled_string : std::is_base_of<compiled_string, S> {}; std::string s = fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); \endrst */ -#define FMT_COMPILE(s) FMT_STRING_IMPL(s, fmt::detail::compiled_string) - -template <typename T, typename... Tail> -const T& first(const T& value, const Tail&...) { - return value; -} - -// Part of a compiled format string. It can be either literal text or a -// replacement field. -template <typename Char> struct format_part { - enum class kind { arg_index, arg_name, text, replacement }; - - struct replacement { - arg_ref<Char> arg_id; - dynamic_format_specs<Char> specs; - }; - - kind part_kind; - union value { - int arg_index; - basic_string_view<Char> str; - replacement repl; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR value(int index = 0) : arg_index(index) {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR value(basic_string_view<Char> s) : str(s) {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR value(replacement r) : repl(r) {} - } val; - // Position past the end of the argument id. - const Char* arg_id_end = nullptr; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR format_part(kind k = kind::arg_index, value v = {}) - : part_kind(k), val(v) {} - - static FMT_CONSTEXPR format_part make_arg_index(int index) { - return format_part(kind::arg_index, index); - } - static FMT_CONSTEXPR format_part make_arg_name(basic_string_view<Char> name) { - return format_part(kind::arg_name, name); - } - static FMT_CONSTEXPR format_part make_text(basic_string_view<Char> text) { - return format_part(kind::text, text); - } - static FMT_CONSTEXPR format_part make_replacement(replacement repl) { - return format_part(kind::replacement, repl); - } -}; - -template <typename Char> struct part_counter { - unsigned num_parts = 0; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const Char* begin, const Char* end) { - if (begin != end) ++num_parts; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id() { return ++num_parts, 0; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(int) { return ++num_parts, 0; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(basic_string_view<Char>) { - return ++num_parts, 0; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_replacement_field(int, const Char*) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* on_format_specs(int, const Char* begin, - const Char* end) { - // Find the matching brace. - unsigned brace_counter = 0; - for (; begin != end; ++begin) { - if (*begin == '{') { - ++brace_counter; - } else if (*begin == '}') { - if (brace_counter == 0u) break; - --brace_counter; - } - } - return begin; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char*) {} -}; - -// Counts the number of parts in a format string. -template <typename Char> -FMT_CONSTEXPR unsigned count_parts(basic_string_view<Char> format_str) { - part_counter<Char> counter; - parse_format_string<true>(format_str, counter); - return counter.num_parts; -} - -template <typename Char, typename PartHandler> -class format_string_compiler : public error_handler { - private: - using part = format_part<Char>; - - PartHandler handler_; - part part_; - basic_string_view<Char> format_str_; - basic_format_parse_context<Char> parse_context_; - - public: - FMT_CONSTEXPR format_string_compiler(basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - PartHandler handler) - : handler_(handler), - format_str_(format_str), - parse_context_(format_str) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const Char* begin, const Char* end) { - if (begin != end) - handler_(part::make_text({begin, to_unsigned(end - begin)})); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id() { - part_ = part::make_arg_index(parse_context_.next_arg_id()); - return 0; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(int id) { - parse_context_.check_arg_id(id); - part_ = part::make_arg_index(id); - return 0; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(basic_string_view<Char> id) { - part_ = part::make_arg_name(id); - return 0; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_replacement_field(int, const Char* ptr) { - part_.arg_id_end = ptr; - handler_(part_); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* on_format_specs(int, const Char* begin, - const Char* end) { - auto repl = typename part::replacement(); - dynamic_specs_handler<basic_format_parse_context<Char>> handler( - repl.specs, parse_context_); - auto it = parse_format_specs(begin, end, handler); - if (*it != '}') on_error("missing '}' in format string"); - repl.arg_id = part_.part_kind == part::kind::arg_index - ? arg_ref<Char>(part_.val.arg_index) - : arg_ref<Char>(part_.val.str); - auto part = part::make_replacement(repl); - part.arg_id_end = begin; - handler_(part); - return it; - } -}; - -// Compiles a format string and invokes handler(part) for each parsed part. -template <bool IS_CONSTEXPR, typename Char, typename PartHandler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR void compile_format_string(basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - PartHandler handler) { - parse_format_string<IS_CONSTEXPR>( - format_str, - format_string_compiler<Char, PartHandler>(format_str, handler)); -} - -template <typename OutputIt, typename Context, typename Id> -void format_arg( - basic_format_parse_context<typename Context::char_type>& parse_ctx, - Context& ctx, Id arg_id) { - ctx.advance_to(visit_format_arg( - arg_formatter<OutputIt, typename Context::char_type>(ctx, &parse_ctx), - ctx.arg(arg_id))); -} - -// vformat_to is defined in a subnamespace to prevent ADL. -namespace cf { -template <typename Context, typename OutputIt, typename CompiledFormat> -auto vformat_to(OutputIt out, CompiledFormat& cf, - basic_format_args<Context> args) -> typename Context::iterator { - using char_type = typename Context::char_type; - basic_format_parse_context<char_type> parse_ctx( - to_string_view(cf.format_str_)); - Context ctx(out, args); - - const auto& parts = cf.parts(); - for (auto part_it = std::begin(parts); part_it != std::end(parts); - ++part_it) { - const auto& part = *part_it; - const auto& value = part.val; - - using format_part_t = format_part<char_type>; - switch (part.part_kind) { - case format_part_t::kind::text: { - const auto text = value.str; - auto output = ctx.out(); - auto&& it = reserve(output, text.size()); - it = std::copy_n(text.begin(), text.size(), it); - ctx.advance_to(output); - break; - } - - case format_part_t::kind::arg_index: - advance_to(parse_ctx, part.arg_id_end); - detail::format_arg<OutputIt>(parse_ctx, ctx, value.arg_index); - break; - - case format_part_t::kind::arg_name: - advance_to(parse_ctx, part.arg_id_end); - detail::format_arg<OutputIt>(parse_ctx, ctx, value.str); - break; - - case format_part_t::kind::replacement: { - const auto& arg_id_value = value.repl.arg_id.val; - const auto arg = value.repl.arg_id.kind == arg_id_kind::index - ? ctx.arg(arg_id_value.index) - : ctx.arg(arg_id_value.name); - - auto specs = value.repl.specs; - - handle_dynamic_spec<width_checker>(specs.width, specs.width_ref, ctx); - handle_dynamic_spec<precision_checker>(specs.precision, - specs.precision_ref, ctx); - - error_handler h; - numeric_specs_checker<error_handler> checker(h, arg.type()); - if (specs.align == align::numeric) checker.require_numeric_argument(); - if (specs.sign != sign::none) checker.check_sign(); - if (specs.alt) checker.require_numeric_argument(); - if (specs.precision >= 0) checker.check_precision(); - - advance_to(parse_ctx, part.arg_id_end); - ctx.advance_to( - visit_format_arg(arg_formatter<OutputIt, typename Context::char_type>( - ctx, nullptr, &specs), - arg)); - break; - } - } - } - return ctx.out(); -} -} // namespace cf - -struct basic_compiled_format {}; - -template <typename S, typename = void> -struct compiled_format_base : basic_compiled_format { - using char_type = char_t<S>; - using parts_container = std::vector<detail::format_part<char_type>>; - - parts_container compiled_parts; - - explicit compiled_format_base(basic_string_view<char_type> format_str) { - compile_format_string<false>(format_str, - [this](const format_part<char_type>& part) { - compiled_parts.push_back(part); - }); - } - - const parts_container& parts() const { return compiled_parts; } -}; - -template <typename Char, unsigned N> struct format_part_array { - format_part<Char> data[N] = {}; - FMT_CONSTEXPR format_part_array() = default; -}; - -template <typename Char, unsigned N> -FMT_CONSTEXPR format_part_array<Char, N> compile_to_parts( - basic_string_view<Char> format_str) { - format_part_array<Char, N> parts; - unsigned counter = 0; - // This is not a lambda for compatibility with older compilers. - struct { - format_part<Char>* parts; - unsigned* counter; - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(const format_part<Char>& part) { - parts[(*counter)++] = part; - } - } collector{parts.data, &counter}; - compile_format_string<true>(format_str, collector); - if (counter < N) { - parts.data[counter] = - format_part<Char>::make_text(basic_string_view<Char>()); - } - return parts; -} - -template <typename T> constexpr const T& constexpr_max(const T& a, const T& b) { - return (a < b) ? b : a; -} - -template <typename S> -struct compiled_format_base<S, enable_if_t<is_compile_string<S>::value>> - : basic_compiled_format { - using char_type = char_t<S>; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR explicit compiled_format_base(basic_string_view<char_type>) {} - -// Workaround for old compilers. Format string compilation will not be -// performed there anyway. -#if FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const unsigned num_format_parts = - constexpr_max(count_parts(to_string_view(S())), 1u); +#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) && defined(__cpp_return_type_deduction) +# define FMT_COMPILE(s) \ + FMT_STRING_IMPL(s, fmt::detail::compiled_string, explicit) #else - static const unsigned num_format_parts = 1; +# define FMT_COMPILE(s) FMT_STRING(s) #endif - using parts_container = format_part<char_type>[num_format_parts]; - - const parts_container& parts() const { - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const auto compiled_parts = - compile_to_parts<char_type, num_format_parts>( - detail::to_string_view(S())); - return compiled_parts.data; +#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS +template <typename Char, size_t N, + fmt::detail_exported::fixed_string<Char, N> Str> +struct udl_compiled_string : compiled_string { + using char_type = Char; + explicit constexpr operator basic_string_view<char_type>() const { + return {Str.data, N - 1}; } }; +#endif -template <typename S, typename... Args> -class compiled_format : private compiled_format_base<S> { - public: - using typename compiled_format_base<S>::char_type; - - private: - basic_string_view<char_type> format_str_; - - template <typename Context, typename OutputIt, typename CompiledFormat> - friend auto cf::vformat_to(OutputIt out, CompiledFormat& cf, - basic_format_args<Context> args) -> - typename Context::iterator; - - public: - compiled_format() = delete; - explicit constexpr compiled_format(basic_string_view<char_type> format_str) - : compiled_format_base<S>(format_str), format_str_(format_str) {} -}; +template <typename T, typename... Tail> +const T& first(const T& value, const Tail&...) { + return value; +} -#ifdef __cpp_if_constexpr +#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) && defined(__cpp_return_type_deduction) template <typename... Args> struct type_list {}; // Returns a reference to the argument at index N from [first, rest...]. @@ -374,13 +72,20 @@ constexpr const auto& get([[maybe_unused]] const T& first, if constexpr (N == 0) return first; else - return get<N - 1>(rest...); + return detail::get<N - 1>(rest...); +} + +template <typename Char, typename... Args> +constexpr int get_arg_index_by_name(basic_string_view<Char> name, + type_list<Args...>) { + return get_arg_index_by_name<Args...>(name); } template <int N, typename> struct get_type_impl; template <int N, typename... Args> struct get_type_impl<N, type_list<Args...>> { - using type = remove_cvref_t<decltype(get<N>(std::declval<Args>()...))>; + using type = + remove_cvref_t<decltype(detail::get<N>(std::declval<Args>()...))>; }; template <int N, typename T> @@ -393,7 +98,7 @@ template <typename Char> struct text { using char_type = Char; template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args> - OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&...) const { + constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&...) const { return write<Char>(out, data); } }; @@ -412,11 +117,23 @@ template <typename Char> struct code_unit { using char_type = Char; template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args> - OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&...) const { - return write<Char>(out, value); + constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&...) const { + *out++ = value; + return out; } }; +// This ensures that the argument type is convertible to `const T&`. +template <typename T, int N, typename... Args> +constexpr const T& get_arg_checked(const Args&... args) { + const auto& arg = detail::get<N>(args...); + if constexpr (detail::is_named_arg<remove_cvref_t<decltype(arg)>>()) { + return arg.value; + } else { + return arg; + } +} + template <typename Char> struct is_compiled_format<code_unit<Char>> : std::true_type {}; @@ -425,9 +142,12 @@ template <typename Char, typename T, int N> struct field { using char_type = Char; template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args> - OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&... args) const { - // This ensures that the argument type is convertile to `const T&`. - const T& arg = get<N>(args...); + constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&... args) const { + const T& arg = get_arg_checked<T, N>(args...); + if constexpr (std::is_convertible_v<T, basic_string_view<Char>>) { + auto s = basic_string_view<Char>(arg); + return copy_str<Char>(s.begin(), s.end(), out); + } return write<Char>(out, arg); } }; @@ -435,19 +155,50 @@ template <typename Char, typename T, int N> struct field { template <typename Char, typename T, int N> struct is_compiled_format<field<Char, T, N>> : std::true_type {}; +// A replacement field that refers to argument with name. +template <typename Char> struct runtime_named_field { + using char_type = Char; + basic_string_view<Char> name; + + template <typename OutputIt, typename T> + constexpr static bool try_format_argument( + OutputIt& out, + // [[maybe_unused]] due to unused-but-set-parameter warning in GCC 7,8,9 + [[maybe_unused]] basic_string_view<Char> arg_name, const T& arg) { + if constexpr (is_named_arg<typename std::remove_cv<T>::type>::value) { + if (arg_name == arg.name) { + out = write<Char>(out, arg.value); + return true; + } + } + return false; + } + + template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args> + constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&... args) const { + bool found = (try_format_argument(out, name, args) || ...); + if (!found) { + FMT_THROW(format_error("argument with specified name is not found")); + } + return out; + } +}; + +template <typename Char> +struct is_compiled_format<runtime_named_field<Char>> : std::true_type {}; + // A replacement field that refers to argument N and has format specifiers. template <typename Char, typename T, int N> struct spec_field { using char_type = Char; - mutable formatter<T, Char> fmt; + formatter<T, Char> fmt; template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args> - OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&... args) const { - // This ensures that the argument type is convertile to `const T&`. - const T& arg = get<N>(args...); + constexpr FMT_INLINE OutputIt format(OutputIt out, + const Args&... args) const { const auto& vargs = - make_format_args<basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>>(args...); + fmt::make_format_args<basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>>(args...); basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char> ctx(out, vargs); - return fmt.format(arg, ctx); + return fmt.format(get_arg_checked<T, N>(args...), ctx); } }; @@ -460,7 +211,7 @@ template <typename L, typename R> struct concat { using char_type = typename L::char_type; template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args> - OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&... args) const { + constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&... args) const { out = lhs.format(out, args...); return rhs.format(out, args...); } @@ -508,14 +259,83 @@ template <typename T, typename Char> struct parse_specs_result { int next_arg_id; }; +enum { manual_indexing_id = -1 }; + template <typename T, typename Char> constexpr parse_specs_result<T, Char> parse_specs(basic_string_view<Char> str, - size_t pos, int arg_id) { + size_t pos, int next_arg_id) { str.remove_prefix(pos); - auto ctx = basic_format_parse_context<Char>(str, {}, arg_id + 1); + auto ctx = + compile_parse_context<Char>(str, max_value<int>(), nullptr, next_arg_id); auto f = formatter<T, Char>(); auto end = f.parse(ctx); - return {f, pos + (end - str.data()) + 1, ctx.next_arg_id()}; + return {f, pos + fmt::detail::to_unsigned(end - str.data()), + next_arg_id == 0 ? manual_indexing_id : ctx.next_arg_id()}; +} + +template <typename Char> struct arg_id_handler { + arg_ref<Char> arg_id; + + constexpr int on_auto() { + FMT_ASSERT(false, "handler cannot be used with automatic indexing"); + return 0; + } + constexpr int on_index(int id) { + arg_id = arg_ref<Char>(id); + return 0; + } + constexpr int on_name(basic_string_view<Char> id) { + arg_id = arg_ref<Char>(id); + return 0; + } +}; + +template <typename Char> struct parse_arg_id_result { + arg_ref<Char> arg_id; + const Char* arg_id_end; +}; + +template <int ID, typename Char> +constexpr auto parse_arg_id(const Char* begin, const Char* end) { + auto handler = arg_id_handler<Char>{arg_ref<Char>{}}; + auto arg_id_end = parse_arg_id(begin, end, handler); + return parse_arg_id_result<Char>{handler.arg_id, arg_id_end}; +} + +template <typename T, typename Enable = void> struct field_type { + using type = remove_cvref_t<T>; +}; + +template <typename T> +struct field_type<T, enable_if_t<detail::is_named_arg<T>::value>> { + using type = remove_cvref_t<decltype(T::value)>; +}; + +template <typename T, typename Args, size_t END_POS, int ARG_INDEX, int NEXT_ID, + typename S> +constexpr auto parse_replacement_field_then_tail(S format_str) { + using char_type = typename S::char_type; + constexpr auto str = basic_string_view<char_type>(format_str); + constexpr char_type c = END_POS != str.size() ? str[END_POS] : char_type(); + if constexpr (c == '}') { + return parse_tail<Args, END_POS + 1, NEXT_ID>( + field<char_type, typename field_type<T>::type, ARG_INDEX>(), + format_str); + } else if constexpr (c != ':') { + FMT_THROW(format_error("expected ':'")); + } else { + constexpr auto result = parse_specs<typename field_type<T>::type>( + str, END_POS + 1, NEXT_ID == manual_indexing_id ? 0 : NEXT_ID); + if constexpr (result.end >= str.size() || str[result.end] != '}') { + FMT_THROW(format_error("expected '}'")); + return 0; + } else { + return parse_tail<Args, result.end + 1, result.next_arg_id>( + spec_field<char_type, typename field_type<T>::type, ARG_INDEX>{ + result.fmt}, + format_str); + } + } } // Compiles a non-empty format string and returns the compiled representation @@ -523,27 +343,57 @@ constexpr parse_specs_result<T, Char> parse_specs(basic_string_view<Char> str, template <typename Args, size_t POS, int ID, typename S> constexpr auto compile_format_string(S format_str) { using char_type = typename S::char_type; - constexpr basic_string_view<char_type> str = format_str; + constexpr auto str = basic_string_view<char_type>(format_str); if constexpr (str[POS] == '{') { - if (POS + 1 == str.size()) - throw format_error("unmatched '{' in format string"); + if constexpr (POS + 1 == str.size()) + FMT_THROW(format_error("unmatched '{' in format string")); if constexpr (str[POS + 1] == '{') { return parse_tail<Args, POS + 2, ID>(make_text(str, POS, 1), format_str); - } else if constexpr (str[POS + 1] == '}') { - using type = get_type<ID, Args>; - return parse_tail<Args, POS + 2, ID + 1>(field<char_type, type, ID>(), - format_str); - } else if constexpr (str[POS + 1] == ':') { - using type = get_type<ID, Args>; - constexpr auto result = parse_specs<type>(str, POS + 2, ID); - return parse_tail<Args, result.end, result.next_arg_id>( - spec_field<char_type, type, ID>{result.fmt}, format_str); + } else if constexpr (str[POS + 1] == '}' || str[POS + 1] == ':') { + static_assert(ID != manual_indexing_id, + "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); + constexpr auto next_id = + ID != manual_indexing_id ? ID + 1 : manual_indexing_id; + return parse_replacement_field_then_tail<get_type<ID, Args>, Args, + POS + 1, ID, next_id>( + format_str); } else { - return unknown_format(); + constexpr auto arg_id_result = + parse_arg_id<ID>(str.data() + POS + 1, str.data() + str.size()); + constexpr auto arg_id_end_pos = arg_id_result.arg_id_end - str.data(); + constexpr char_type c = + arg_id_end_pos != str.size() ? str[arg_id_end_pos] : char_type(); + static_assert(c == '}' || c == ':', "missing '}' in format string"); + if constexpr (arg_id_result.arg_id.kind == arg_id_kind::index) { + static_assert( + ID == manual_indexing_id || ID == 0, + "cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing"); + constexpr auto arg_index = arg_id_result.arg_id.val.index; + return parse_replacement_field_then_tail<get_type<arg_index, Args>, + Args, arg_id_end_pos, + arg_index, manual_indexing_id>( + format_str); + } else if constexpr (arg_id_result.arg_id.kind == arg_id_kind::name) { + constexpr auto arg_index = + get_arg_index_by_name(arg_id_result.arg_id.val.name, Args{}); + if constexpr (arg_index >= 0) { + constexpr auto next_id = + ID != manual_indexing_id ? ID + 1 : manual_indexing_id; + return parse_replacement_field_then_tail< + decltype(get_type<arg_index, Args>::value), Args, arg_id_end_pos, + arg_index, next_id>(format_str); + } else if constexpr (c == '}') { + return parse_tail<Args, arg_id_end_pos + 1, ID>( + runtime_named_field<char_type>{arg_id_result.arg_id.val.name}, + format_str); + } else if constexpr (c == ':') { + return unknown_format(); // no type info for specs parsing + } + } } } else if constexpr (str[POS] == '}') { - if (POS + 1 == str.size()) - throw format_error("unmatched '}' in format string"); + if constexpr (POS + 1 == str.size()) + FMT_THROW(format_error("unmatched '}' in format string")); return parse_tail<Args, POS + 2, ID>(make_text(str, POS, 1), format_str); } else { constexpr auto end = parse_text(str, POS + 1); @@ -558,144 +408,127 @@ constexpr auto compile_format_string(S format_str) { } template <typename... Args, typename S, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_compile_string<S>::value || - detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)> + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)> constexpr auto compile(S format_str) { - constexpr basic_string_view<typename S::char_type> str = format_str; + constexpr auto str = basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>(format_str); if constexpr (str.size() == 0) { return detail::make_text(str, 0, 0); } else { constexpr auto result = detail::compile_format_string<detail::type_list<Args...>, 0, 0>( format_str); - if constexpr (std::is_same<remove_cvref_t<decltype(result)>, - detail::unknown_format>()) { - return detail::compiled_format<S, Args...>(to_string_view(format_str)); - } else { - return result; - } + return result; } } -#else -template <typename... Args, typename S, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_compile_string<S>::value)> -constexpr auto compile(S format_str) -> detail::compiled_format<S, Args...> { - return detail::compiled_format<S, Args...>(to_string_view(format_str)); -} -#endif // __cpp_if_constexpr - -// Compiles the format string which must be a string literal. -template <typename... Args, typename Char, size_t N> -auto compile(const Char (&format_str)[N]) - -> detail::compiled_format<const Char*, Args...> { - return detail::compiled_format<const Char*, Args...>( - basic_string_view<Char>(format_str, N - 1)); -} +#endif // defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) && defined(__cpp_return_type_deduction) } // namespace detail -// DEPRECATED! use FMT_COMPILE instead. -template <typename... Args> -FMT_DEPRECATED auto compile(const Args&... args) - -> decltype(detail::compile(args...)) { - return detail::compile(args...); -} +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT -#if FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR -# ifdef __cpp_if_constexpr +#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) && defined(__cpp_return_type_deduction) template <typename CompiledFormat, typename... Args, typename Char = typename CompiledFormat::char_type, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_format<CompiledFormat>::value)> FMT_INLINE std::basic_string<Char> format(const CompiledFormat& cf, const Args&... args) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - cf.format(detail::buffer_appender<Char>(buffer), args...); - return to_string(buffer); + auto s = std::basic_string<Char>(); + cf.format(std::back_inserter(s), args...); + return s; } template <typename OutputIt, typename CompiledFormat, typename... Args, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_format<CompiledFormat>::value)> -OutputIt format_to(OutputIt out, const CompiledFormat& cf, - const Args&... args) { +constexpr FMT_INLINE OutputIt format_to(OutputIt out, const CompiledFormat& cf, + const Args&... args) { return cf.format(out, args...); } -# endif // __cpp_if_constexpr -#endif // FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR - -template <typename CompiledFormat, typename... Args, - typename Char = typename CompiledFormat::char_type, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_base_of<detail::basic_compiled_format, - CompiledFormat>::value)> -std::basic_string<Char> format(const CompiledFormat& cf, const Args&... args) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - using context = buffer_context<Char>; - detail::cf::vformat_to<context>(detail::buffer_appender<Char>(buffer), cf, - make_format_args<context>(args...)); - return to_string(buffer); -} template <typename S, typename... Args, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)> FMT_INLINE std::basic_string<typename S::char_type> format(const S&, Args&&... args) { -#ifdef __cpp_if_constexpr if constexpr (std::is_same<typename S::char_type, char>::value) { - constexpr basic_string_view<typename S::char_type> str = S(); - if (str.size() == 2 && str[0] == '{' && str[1] == '}') - return fmt::to_string(detail::first(args...)); + constexpr auto str = basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>(S()); + if constexpr (str.size() == 2 && str[0] == '{' && str[1] == '}') { + const auto& first = detail::first(args...); + if constexpr (detail::is_named_arg< + remove_cvref_t<decltype(first)>>::value) { + return fmt::to_string(first.value); + } else { + return fmt::to_string(first); + } + } } -#endif constexpr auto compiled = detail::compile<Args...>(S()); - return format(compiled, std::forward<Args>(args)...); + if constexpr (std::is_same<remove_cvref_t<decltype(compiled)>, + detail::unknown_format>()) { + return fmt::format( + static_cast<basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>>(S()), + std::forward<Args>(args)...); + } else { + return fmt::format(compiled, std::forward<Args>(args)...); + } } -template <typename OutputIt, typename CompiledFormat, typename... Args, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_base_of<detail::basic_compiled_format, - CompiledFormat>::value)> -OutputIt format_to(OutputIt out, const CompiledFormat& cf, - const Args&... args) { - using char_type = typename CompiledFormat::char_type; - using context = format_context_t<OutputIt, char_type>; - return detail::cf::vformat_to<context>(out, cf, - make_format_args<context>(args...)); +template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR OutputIt format_to(OutputIt out, const S&, Args&&... args) { + constexpr auto compiled = detail::compile<Args...>(S()); + if constexpr (std::is_same<remove_cvref_t<decltype(compiled)>, + detail::unknown_format>()) { + return fmt::format_to( + out, static_cast<basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>>(S()), + std::forward<Args>(args)...); + } else { + return fmt::format_to(out, compiled, std::forward<Args>(args)...); + } } +#endif template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)> -OutputIt format_to(OutputIt out, const S&, const Args&... args) { - constexpr auto compiled = detail::compile<Args...>(S()); - return format_to(out, compiled, args...); +format_to_n_result<OutputIt> format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, + const S& format_str, Args&&... args) { + using traits = detail::fixed_buffer_traits; + auto buf = detail::iterator_buffer<OutputIt, char, traits>(out, n); + format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), format_str, std::forward<Args>(args)...); + return {buf.out(), buf.count()}; } -template <typename OutputIt, typename CompiledFormat, typename... Args> -auto format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, const CompiledFormat& cf, - const Args&... args) -> - typename std::enable_if< - detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, - typename CompiledFormat::char_type>::value && - std::is_base_of<detail::basic_compiled_format, - CompiledFormat>::value, - format_to_n_result<OutputIt>>::type { - auto it = - format_to(detail::truncating_iterator<OutputIt>(out, n), cf, args...); - return {it.base(), it.count()}; +template <typename S, typename... Args, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 size_t formatted_size(const S& format_str, + const Args&... args) { + return fmt::format_to(detail::counting_iterator(), format_str, args...) + .count(); } -template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args, +template <typename S, typename... Args, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)> -format_to_n_result<OutputIt> format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, const S&, - const Args&... args) { - constexpr auto compiled = detail::compile<Args...>(S()); - auto it = format_to(detail::truncating_iterator<OutputIt>(out, n), compiled, - args...); - return {it.base(), it.count()}; +void print(std::FILE* f, const S& format_str, const Args&... args) { + memory_buffer buffer; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buffer), format_str, args...); + detail::print(f, {buffer.data(), buffer.size()}); } -template <typename CompiledFormat, typename... Args> -size_t formatted_size(const CompiledFormat& cf, const Args&... args) { - return format_to(detail::counting_iterator(), cf, args...).count(); +template <typename S, typename... Args, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)> +void print(const S& format_str, const Args&... args) { + print(stdout, format_str, args...); } +#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS +inline namespace literals { +template <detail_exported::fixed_string Str> constexpr auto operator""_cf() { + using char_t = remove_cvref_t<decltype(Str.data[0])>; + return detail::udl_compiled_string<char_t, sizeof(Str.data) / sizeof(char_t), + Str>(); +} +} // namespace literals +#endif + +FMT_END_EXPORT FMT_END_NAMESPACE #endif // FMT_COMPILE_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/core.h b/include/fmt/core.h index 0a81e0cc..18ebada2 100644 --- a/include/fmt/core.h +++ b/include/fmt/core.h @@ -1,4 +1,4 @@ -// Formatting library for C++ - the core API +// Formatting library for C++ - the core API for char/UTF-8 // // Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich // All rights reserved. @@ -8,54 +8,60 @@ #ifndef FMT_CORE_H_ #define FMT_CORE_H_ -#include <cstdio> // std::FILE -#include <cstring> -#include <functional> +#include <cstddef> // std::byte +#include <cstdio> // std::FILE +#include <cstring> // std::strlen #include <iterator> -#include <memory> +#include <limits> +#include <memory> // std::addressof #include <string> #include <type_traits> -#include <vector> // The fmt library version in the form major * 10000 + minor * 100 + patch. -#define FMT_VERSION 70103 +#define FMT_VERSION 100101 -#ifdef __clang__ +#if defined(__clang__) && !defined(__ibmxl__) # define FMT_CLANG_VERSION (__clang_major__ * 100 + __clang_minor__) #else # define FMT_CLANG_VERSION 0 #endif -#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) +#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) && !defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) && \ + !defined(__NVCOMPILER) # define FMT_GCC_VERSION (__GNUC__ * 100 + __GNUC_MINOR__) #else # define FMT_GCC_VERSION 0 #endif -#if defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) -# define FMT_ICC_VERSION __INTEL_COMPILER -#else -# define FMT_ICC_VERSION 0 +#ifndef FMT_GCC_PRAGMA +// Workaround _Pragma bug https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=59884. +# if FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 504 +# define FMT_GCC_PRAGMA(arg) _Pragma(arg) +# else +# define FMT_GCC_PRAGMA(arg) +# endif #endif -#if __cplusplus >= 201103L || defined(__GXX_EXPERIMENTAL_CXX0X__) -# define FMT_HAS_GXX_CXX11 FMT_GCC_VERSION +#ifdef __ICL +# define FMT_ICC_VERSION __ICL +#elif defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) +# define FMT_ICC_VERSION __INTEL_COMPILER #else -# define FMT_HAS_GXX_CXX11 0 +# define FMT_ICC_VERSION 0 #endif -#ifdef __NVCC__ -# define FMT_NVCC __NVCC__ +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# define FMT_MSC_VERSION _MSC_VER +# define FMT_MSC_WARNING(...) __pragma(warning(__VA_ARGS__)) #else -# define FMT_NVCC 0 +# define FMT_MSC_VERSION 0 +# define FMT_MSC_WARNING(...) #endif -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# define FMT_MSC_VER _MSC_VER -# define FMT_SUPPRESS_MSC_WARNING(n) __pragma(warning(suppress : n)) +#ifdef _MSVC_LANG +# define FMT_CPLUSPLUS _MSVC_LANG #else -# define FMT_MSC_VER 0 -# define FMT_SUPPRESS_MSC_WARNING(n) +# define FMT_CPLUSPLUS __cplusplus #endif #ifdef __has_feature @@ -64,8 +70,7 @@ # define FMT_HAS_FEATURE(x) 0 #endif -#if defined(__has_include) && !defined(__INTELLISENSE__) && \ - (!FMT_ICC_VERSION || FMT_ICC_VERSION >= 1600) +#if defined(__has_include) || FMT_ICC_VERSION >= 1600 || FMT_MSC_VERSION > 1900 # define FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(x) __has_include(x) #else # define FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(x) 0 @@ -78,98 +83,78 @@ #endif #define FMT_HAS_CPP14_ATTRIBUTE(attribute) \ - (__cplusplus >= 201402L && FMT_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(attribute)) + (FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201402L && FMT_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(attribute)) #define FMT_HAS_CPP17_ATTRIBUTE(attribute) \ - (__cplusplus >= 201703L && FMT_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(attribute)) + (FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L && FMT_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(attribute)) // Check if relaxed C++14 constexpr is supported. // GCC doesn't allow throw in constexpr until version 6 (bug 67371). #ifndef FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR -# define FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR \ - (FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_relaxed_constexpr) || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1910 || \ - (FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 600 && __cplusplus >= 201402L)) && \ - !FMT_NVCC && !FMT_ICC_VERSION +# if (FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_relaxed_constexpr) || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1912 || \ + (FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 600 && FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201402L)) && \ + !FMT_ICC_VERSION && (!defined(__NVCC__) || FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L) +# define FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR 1 +# else +# define FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR 0 +# endif #endif #if FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR # define FMT_CONSTEXPR constexpr -# define FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL constexpr #else -# define FMT_CONSTEXPR inline -# define FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL +# define FMT_CONSTEXPR #endif -#ifndef FMT_OVERRIDE -# if FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_override_control) || \ - (FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 408 && FMT_HAS_GXX_CXX11) || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1900 -# define FMT_OVERRIDE override -# else -# define FMT_OVERRIDE +#if ((FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L) && \ + (!defined(_GLIBCXX_RELEASE) || _GLIBCXX_RELEASE > 9)) || \ + (FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201709L && FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 1002) +# define FMT_CONSTEXPR20 constexpr +#else +# define FMT_CONSTEXPR20 +#endif + +// Check if constexpr std::char_traits<>::{compare,length} are supported. +#if defined(__GLIBCXX__) +# if FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L && defined(_GLIBCXX_RELEASE) && \ + _GLIBCXX_RELEASE >= 7 // GCC 7+ libstdc++ has _GLIBCXX_RELEASE. +# define FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS constexpr # endif +#elif defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION) && FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L && \ + _LIBCPP_VERSION >= 4000 +# define FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS constexpr +#elif FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1914 && FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L +# define FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS constexpr +#endif +#ifndef FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS +# define FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS #endif // Check if exceptions are disabled. #ifndef FMT_EXCEPTIONS # if (defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__EXCEPTIONS)) || \ - FMT_MSC_VER && !_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + (FMT_MSC_VERSION && !_HAS_EXCEPTIONS) # define FMT_EXCEPTIONS 0 # else # define FMT_EXCEPTIONS 1 # endif #endif -// Define FMT_USE_NOEXCEPT to make fmt use noexcept (C++11 feature). -#ifndef FMT_USE_NOEXCEPT -# define FMT_USE_NOEXCEPT 0 -#endif - -#if FMT_USE_NOEXCEPT || FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_noexcept) || \ - (FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 408 && FMT_HAS_GXX_CXX11) || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1900 -# define FMT_DETECTED_NOEXCEPT noexcept -# define FMT_HAS_CXX11_NOEXCEPT 1 -#else -# define FMT_DETECTED_NOEXCEPT throw() -# define FMT_HAS_CXX11_NOEXCEPT 0 -#endif - -#ifndef FMT_NOEXCEPT -# if FMT_EXCEPTIONS || FMT_HAS_CXX11_NOEXCEPT -# define FMT_NOEXCEPT FMT_DETECTED_NOEXCEPT -# else -# define FMT_NOEXCEPT -# endif -#endif - -// [[noreturn]] is disabled on MSVC and NVCC because of bogus unreachable code -// warnings. -#if FMT_EXCEPTIONS && FMT_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(noreturn) && !FMT_MSC_VER && \ - !FMT_NVCC +// Disable [[noreturn]] on MSVC/NVCC because of bogus unreachable code warnings. +#if FMT_EXCEPTIONS && FMT_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(noreturn) && !FMT_MSC_VERSION && \ + !defined(__NVCC__) # define FMT_NORETURN [[noreturn]] #else # define FMT_NORETURN #endif -#ifndef FMT_DEPRECATED -# if FMT_HAS_CPP14_ATTRIBUTE(deprecated) || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1900 -# define FMT_DEPRECATED [[deprecated]] +#ifndef FMT_NODISCARD +# if FMT_HAS_CPP17_ATTRIBUTE(nodiscard) +# define FMT_NODISCARD [[nodiscard]] # else -# if (defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__LCC__)) || defined(__clang__) -# define FMT_DEPRECATED __attribute__((deprecated)) -# elif FMT_MSC_VER -# define FMT_DEPRECATED __declspec(deprecated) -# else -# define FMT_DEPRECATED /* deprecated */ -# endif +# define FMT_NODISCARD # endif #endif -// Workaround broken [[deprecated]] in the Intel, PGI and NVCC compilers. -#if FMT_ICC_VERSION || defined(__PGI) || FMT_NVCC -# define FMT_DEPRECATED_ALIAS -#else -# define FMT_DEPRECATED_ALIAS FMT_DEPRECATED -#endif - #ifndef FMT_INLINE # if FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_CLANG_VERSION # define FMT_INLINE inline __attribute__((always_inline)) @@ -178,86 +163,100 @@ # endif #endif -#ifndef FMT_USE_INLINE_NAMESPACES -# if FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_inline_namespaces) || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 404 || \ - (FMT_MSC_VER >= 1900 && !_MANAGED) -# define FMT_USE_INLINE_NAMESPACES 1 -# else -# define FMT_USE_INLINE_NAMESPACES 0 -# endif +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# define FMT_UNCHECKED_ITERATOR(It) \ + using _Unchecked_type = It // Mark iterator as checked. +#else +# define FMT_UNCHECKED_ITERATOR(It) using unchecked_type = It #endif #ifndef FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -# if FMT_USE_INLINE_NAMESPACES -# define FMT_INLINE_NAMESPACE inline namespace -# define FMT_END_NAMESPACE \ - } \ - } -# else -# define FMT_INLINE_NAMESPACE namespace -# define FMT_END_NAMESPACE \ - } \ - using namespace v7; \ - } -# endif # define FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE \ namespace fmt { \ - FMT_INLINE_NAMESPACE v7 { + inline namespace v10 { +# define FMT_END_NAMESPACE \ + } \ + } +#endif + +#ifndef FMT_EXPORT +# define FMT_EXPORT +# define FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT +# define FMT_END_EXPORT +#endif + +#if FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_CLANG_VERSION +# define FMT_VISIBILITY(value) __attribute__((visibility(value))) +#else +# define FMT_VISIBILITY(value) #endif #if !defined(FMT_HEADER_ONLY) && defined(_WIN32) -# define FMT_CLASS_API FMT_SUPPRESS_MSC_WARNING(4275) -# ifdef FMT_EXPORT +# if defined(FMT_LIB_EXPORT) # define FMT_API __declspec(dllexport) -# define FMT_EXTERN_TEMPLATE_API FMT_API -# define FMT_EXPORTED # elif defined(FMT_SHARED) # define FMT_API __declspec(dllimport) -# define FMT_EXTERN_TEMPLATE_API FMT_API # endif -#else -# define FMT_CLASS_API +#elif defined(FMT_LIB_EXPORT) || defined(FMT_SHARED) +# define FMT_API FMT_VISIBILITY("default") #endif #ifndef FMT_API # define FMT_API #endif -#ifndef FMT_EXTERN_TEMPLATE_API -# define FMT_EXTERN_TEMPLATE_API -#endif -#ifndef FMT_INSTANTIATION_DEF_API -# define FMT_INSTANTIATION_DEF_API FMT_API -#endif - -#ifndef FMT_HEADER_ONLY -# define FMT_EXTERN extern -#else -# define FMT_EXTERN -#endif // libc++ supports string_view in pre-c++17. -#if (FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<string_view>) && \ - (__cplusplus > 201402L || defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION))) || \ - (defined(_MSVC_LANG) && _MSVC_LANG > 201402L && _MSC_VER >= 1910) +#if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<string_view>) && \ + (FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L || defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION)) # include <string_view> # define FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW -#elif FMT_HAS_INCLUDE("experimental/string_view") && __cplusplus >= 201402L +#elif FMT_HAS_INCLUDE("experimental/string_view") && FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201402L # include <experimental/string_view> # define FMT_USE_EXPERIMENTAL_STRING_VIEW #endif #ifndef FMT_UNICODE -# define FMT_UNICODE !FMT_MSC_VER +# define FMT_UNICODE !FMT_MSC_VERSION +#endif + +#ifndef FMT_CONSTEVAL +# if ((FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 1000 || FMT_CLANG_VERSION >= 1101) && \ + (!defined(__apple_build_version__) || \ + __apple_build_version__ >= 14000029L) && \ + FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L) || \ + (defined(__cpp_consteval) && \ + (!FMT_MSC_VERSION || _MSC_FULL_VER >= 193030704)) +// consteval is broken in MSVC before VS2022 and Apple clang before 14. +# define FMT_CONSTEVAL consteval +# define FMT_HAS_CONSTEVAL +# else +# define FMT_CONSTEVAL +# endif +#endif + +#ifndef FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS +# if defined(__cpp_nontype_template_args) && \ + ((FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 903 && FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201709L) || \ + __cpp_nontype_template_args >= 201911L) && \ + !defined(__NVCOMPILER) && !defined(__LCC__) +# define FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS 1 +# else +# define FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS 0 +# endif #endif -#if FMT_UNICODE && FMT_MSC_VER -# pragma execution_character_set("utf-8") + +// Enable minimal optimizations for more compact code in debug mode. +FMT_GCC_PRAGMA("GCC push_options") +#if !defined(__OPTIMIZE__) && !defined(__NVCOMPILER) && !defined(__LCC__) && \ + !defined(__CUDACC__) +FMT_GCC_PRAGMA("GCC optimize(\"Og\")") #endif FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE // Implementations of enable_if_t and other metafunctions for older systems. -template <bool B, class T = void> +template <bool B, typename T = void> using enable_if_t = typename std::enable_if<B, T>::type; -template <bool B, class T, class F> +template <bool B, typename T, typename F> using conditional_t = typename std::conditional<B, T, F>::type; template <bool B> using bool_constant = std::integral_constant<bool, B>; template <typename T> @@ -266,33 +265,82 @@ template <typename T> using remove_const_t = typename std::remove_const<T>::type; template <typename T> using remove_cvref_t = typename std::remove_cv<remove_reference_t<T>>::type; -template <typename T> struct type_identity { using type = T; }; +template <typename T> struct type_identity { + using type = T; +}; template <typename T> using type_identity_t = typename type_identity<T>::type; +template <typename T> +using underlying_t = typename std::underlying_type<T>::type; + +// Checks whether T is a container with contiguous storage. +template <typename T> struct is_contiguous : std::false_type {}; +template <typename Char> +struct is_contiguous<std::basic_string<Char>> : std::true_type {}; -struct monostate {}; +struct monostate { + constexpr monostate() {} +}; // An enable_if helper to be used in template parameters which results in much // shorter symbols: https://godbolt.org/z/sWw4vP. Extra parentheses are needed // to workaround a bug in MSVC 2019 (see #1140 and #1186). -#define FMT_ENABLE_IF(...) enable_if_t<(__VA_ARGS__), int> = 0 +#ifdef FMT_DOC +# define FMT_ENABLE_IF(...) +#else +# define FMT_ENABLE_IF(...) fmt::enable_if_t<(__VA_ARGS__), int> = 0 +#endif + +// This is defined in core.h instead of format.h to avoid injecting in std. +// It is a template to avoid undesirable implicit conversions to std::byte. +#ifdef __cpp_lib_byte +template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<T, std::byte>::value)> +inline auto format_as(T b) -> unsigned char { + return static_cast<unsigned char>(b); +} +#endif namespace detail { +// Suppresses "unused variable" warnings with the method described in +// https://herbsutter.com/2009/10/18/mailbag-shutting-up-compiler-warnings/. +// (void)var does not work on many Intel compilers. +template <typename... T> FMT_CONSTEXPR void ignore_unused(const T&...) {} + +constexpr FMT_INLINE auto is_constant_evaluated( + bool default_value = false) noexcept -> bool { +// Workaround for incompatibility between libstdc++ consteval-based +// std::is_constant_evaluated() implementation and clang-14. +// https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3247 +#if FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L && defined(_GLIBCXX_RELEASE) && \ + _GLIBCXX_RELEASE >= 12 && \ + (FMT_CLANG_VERSION >= 1400 && FMT_CLANG_VERSION < 1500) + ignore_unused(default_value); + return __builtin_is_constant_evaluated(); +#elif defined(__cpp_lib_is_constant_evaluated) + ignore_unused(default_value); + return std::is_constant_evaluated(); +#else + return default_value; +#endif +} -// A helper function to suppress "conditional expression is constant" warnings. -template <typename T> constexpr T const_check(T value) { return value; } +// Suppresses "conditional expression is constant" warnings. +template <typename T> constexpr FMT_INLINE auto const_check(T value) -> T { + return value; +} FMT_NORETURN FMT_API void assert_fail(const char* file, int line, const char* message); #ifndef FMT_ASSERT # ifdef NDEBUG -// FMT_ASSERT is not empty to avoid -Werror=empty-body. -# define FMT_ASSERT(condition, message) ((void)0) +// FMT_ASSERT is not empty to avoid -Wempty-body. +# define FMT_ASSERT(condition, message) \ + fmt::detail::ignore_unused((condition), (message)) # else # define FMT_ASSERT(condition, message) \ ((condition) /* void() fails with -Winvalid-constexpr on clang 4.0.1 */ \ ? (void)0 \ - : ::fmt::detail::assert_fail(__FILE__, __LINE__, (message))) + : fmt::detail::assert_fail(__FILE__, __LINE__, (message))) # endif #endif @@ -307,44 +355,42 @@ template <typename T> struct std_string_view {}; #ifdef FMT_USE_INT128 // Do nothing. -#elif defined(__SIZEOF_INT128__) && !FMT_NVCC && \ - !(FMT_CLANG_VERSION && FMT_MSC_VER) +#elif defined(__SIZEOF_INT128__) && !defined(__NVCC__) && \ + !(FMT_CLANG_VERSION && FMT_MSC_VERSION) # define FMT_USE_INT128 1 -using int128_t = __int128_t; -using uint128_t = __uint128_t; +using int128_opt = __int128_t; // An optional native 128-bit integer. +using uint128_opt = __uint128_t; +template <typename T> inline auto convert_for_visit(T value) -> T { + return value; +} #else # define FMT_USE_INT128 0 #endif #if !FMT_USE_INT128 -struct int128_t {}; -struct uint128_t {}; +enum class int128_opt {}; +enum class uint128_opt {}; +// Reduce template instantiations. +template <typename T> auto convert_for_visit(T) -> monostate { return {}; } #endif // Casts a nonnegative integer to unsigned. template <typename Int> -FMT_CONSTEXPR typename std::make_unsigned<Int>::type to_unsigned(Int value) { - FMT_ASSERT(value >= 0, "negative value"); +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto to_unsigned(Int value) -> + typename std::make_unsigned<Int>::type { + FMT_ASSERT(std::is_unsigned<Int>::value || value >= 0, "negative value"); return static_cast<typename std::make_unsigned<Int>::type>(value); } -FMT_SUPPRESS_MSC_WARNING(4566) constexpr unsigned char micro[] = "\u00B5"; +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto is_utf8() -> bool { + FMT_MSC_WARNING(suppress : 4566) constexpr unsigned char section[] = "\u00A7"; -template <typename Char> constexpr bool is_unicode() { - return FMT_UNICODE || sizeof(Char) != 1 || - (sizeof(micro) == 3 && micro[0] == 0xC2 && micro[1] == 0xB5); + // Avoid buggy sign extensions in MSVC's constant evaluation mode (#2297). + using uchar = unsigned char; + return FMT_UNICODE || (sizeof(section) == 3 && uchar(section[0]) == 0xC2 && + uchar(section[1]) == 0xA7); } - -#ifdef __cpp_char8_t -using char8_type = char8_t; -#else -enum char8_type : unsigned char {}; -#endif } // namespace detail -#ifdef FMT_USE_INTERNAL -namespace internal = detail; // DEPRECATED -#endif - /** An implementation of ``std::basic_string_view`` for pre-C++17. It provides a subset of the API. ``fmt::basic_string_view`` is used for format strings even @@ -352,6 +398,7 @@ namespace internal = detail; // DEPRECATED compiled with a different ``-std`` option than the client code (which is not recommended). */ +FMT_EXPORT template <typename Char> class basic_string_view { private: const Char* data_; @@ -361,12 +408,11 @@ template <typename Char> class basic_string_view { using value_type = Char; using iterator = const Char*; - constexpr basic_string_view() FMT_NOEXCEPT : data_(nullptr), size_(0) {} + constexpr basic_string_view() noexcept : data_(nullptr), size_(0) {} /** Constructs a string reference object from a C string and a size. */ - constexpr basic_string_view(const Char* s, size_t count) FMT_NOEXCEPT - : data_(s), - size_(count) {} + constexpr basic_string_view(const Char* s, size_t count) noexcept + : data_(s), size_(count) {} /** \rst @@ -374,42 +420,58 @@ template <typename Char> class basic_string_view { the size with ``std::char_traits<Char>::length``. \endrst */ -#if __cplusplus >= 201703L // C++17's char_traits::length() is constexpr. - FMT_CONSTEXPR -#endif + FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS + FMT_INLINE basic_string_view(const Char* s) - : data_(s), size_(std::char_traits<Char>::length(s)) {} + : data_(s), + size_(detail::const_check(std::is_same<Char, char>::value && + !detail::is_constant_evaluated(true)) + ? std::strlen(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(s)) + : std::char_traits<Char>::length(s)) {} /** Constructs a string reference from a ``std::basic_string`` object. */ template <typename Traits, typename Alloc> FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_string_view( - const std::basic_string<Char, Traits, Alloc>& s) FMT_NOEXCEPT - : data_(s.data()), - size_(s.size()) {} + const std::basic_string<Char, Traits, Alloc>& s) noexcept + : data_(s.data()), size_(s.size()) {} template <typename S, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same< S, detail::std_string_view<Char>>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_string_view(S s) FMT_NOEXCEPT : data_(s.data()), - size_(s.size()) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_string_view(S s) noexcept + : data_(s.data()), size_(s.size()) {} /** Returns a pointer to the string data. */ - constexpr const Char* data() const { return data_; } + constexpr auto data() const noexcept -> const Char* { return data_; } /** Returns the string size. */ - constexpr size_t size() const { return size_; } + constexpr auto size() const noexcept -> size_t { return size_; } - constexpr iterator begin() const { return data_; } - constexpr iterator end() const { return data_ + size_; } + constexpr auto begin() const noexcept -> iterator { return data_; } + constexpr auto end() const noexcept -> iterator { return data_ + size_; } - constexpr const Char& operator[](size_t pos) const { return data_[pos]; } + constexpr auto operator[](size_t pos) const noexcept -> const Char& { + return data_[pos]; + } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void remove_prefix(size_t n) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR void remove_prefix(size_t n) noexcept { data_ += n; size_ -= n; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS bool starts_with( + basic_string_view<Char> sv) const noexcept { + return size_ >= sv.size_ && + std::char_traits<Char>::compare(data_, sv.data_, sv.size_) == 0; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS bool starts_with(Char c) const noexcept { + return size_ >= 1 && std::char_traits<Char>::eq(*data_, c); + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS bool starts_with(const Char* s) const { + return starts_with(basic_string_view<Char>(s)); + } + // Lexicographically compare this string reference to other. - int compare(basic_string_view other) const { + FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS auto compare(basic_string_view other) const -> int { size_t str_size = size_ < other.size_ ? size_ : other.size_; int result = std::char_traits<Char>::compare(data_, other.data_, str_size); if (result == 0) @@ -417,97 +479,77 @@ template <typename Char> class basic_string_view { return result; } - friend bool operator==(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS friend auto operator==(basic_string_view lhs, + basic_string_view rhs) + -> bool { return lhs.compare(rhs) == 0; } - friend bool operator!=(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) { + friend auto operator!=(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) -> bool { return lhs.compare(rhs) != 0; } - friend bool operator<(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) { + friend auto operator<(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) -> bool { return lhs.compare(rhs) < 0; } - friend bool operator<=(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) { + friend auto operator<=(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) -> bool { return lhs.compare(rhs) <= 0; } - friend bool operator>(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) { + friend auto operator>(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) -> bool { return lhs.compare(rhs) > 0; } - friend bool operator>=(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) { + friend auto operator>=(basic_string_view lhs, basic_string_view rhs) -> bool { return lhs.compare(rhs) >= 0; } }; +FMT_EXPORT using string_view = basic_string_view<char>; -using wstring_view = basic_string_view<wchar_t>; /** Specifies if ``T`` is a character type. Can be specialized by users. */ +FMT_EXPORT template <typename T> struct is_char : std::false_type {}; template <> struct is_char<char> : std::true_type {}; -template <> struct is_char<wchar_t> : std::true_type {}; -template <> struct is_char<detail::char8_type> : std::true_type {}; -template <> struct is_char<char16_t> : std::true_type {}; -template <> struct is_char<char32_t> : std::true_type {}; -/** - \rst - Returns a string view of `s`. In order to add custom string type support to - {fmt} provide an overload of `to_string_view` for it in the same namespace as - the type for the argument-dependent lookup to work. +namespace detail { - **Example**:: +// A base class for compile-time strings. +struct compile_string {}; + +template <typename S> +struct is_compile_string : std::is_base_of<compile_string, S> {}; - namespace my_ns { - inline string_view to_string_view(const my_string& s) { - return {s.data(), s.length()}; - } - } - std::string message = fmt::format(my_string("The answer is {}"), 42); - \endrst - */ template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_char<Char>::value)> -inline basic_string_view<Char> to_string_view(const Char* s) { +FMT_INLINE auto to_string_view(const Char* s) -> basic_string_view<Char> { return s; } - template <typename Char, typename Traits, typename Alloc> -inline basic_string_view<Char> to_string_view( - const std::basic_string<Char, Traits, Alloc>& s) { +inline auto to_string_view(const std::basic_string<Char, Traits, Alloc>& s) + -> basic_string_view<Char> { return s; } - template <typename Char> -inline basic_string_view<Char> to_string_view(basic_string_view<Char> s) { +constexpr auto to_string_view(basic_string_view<Char> s) + -> basic_string_view<Char> { return s; } - template <typename Char, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_empty<detail::std_string_view<Char>>::value)> -inline basic_string_view<Char> to_string_view(detail::std_string_view<Char> s) { + FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_empty<std_string_view<Char>>::value)> +inline auto to_string_view(std_string_view<Char> s) -> basic_string_view<Char> { return s; } - -// A base class for compile-time strings. It is defined in the fmt namespace to -// make formatting functions visible via ADL, e.g. format(FMT_STRING("{}"), 42). -struct compile_string {}; - -template <typename S> -struct is_compile_string : std::is_base_of<compile_string, S> {}; - template <typename S, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_compile_string<S>::value)> -constexpr basic_string_view<typename S::char_type> to_string_view(const S& s) { - return s; +constexpr auto to_string_view(const S& s) + -> basic_string_view<typename S::char_type> { + return basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>(s); } - -namespace detail { void to_string_view(...); -using fmt::v7::to_string_view; // Specifies whether S is a string type convertible to fmt::basic_string_view. // It should be a constexpr function but MSVC 2017 fails to compile it in // enable_if and MSVC 2015 fails to compile it as an alias template. +// ADL is intentionally disabled as to_string_view is not an extension point. template <typename S> -struct is_string : std::is_class<decltype(to_string_view(std::declval<S>()))> { -}; +struct is_string + : std::is_class<decltype(detail::to_string_view(std::declval<S>()))> {}; template <typename S, typename = void> struct char_t_impl {}; template <typename S> struct char_t_impl<S, enable_if_t<is_string<S>::value>> { @@ -515,27 +557,95 @@ template <typename S> struct char_t_impl<S, enable_if_t<is_string<S>::value>> { using type = typename result::value_type; }; -// Reports a compile-time error if S is not a valid format string. -template <typename..., typename S, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_compile_string<S>::value)> -FMT_INLINE void check_format_string(const S&) { -#ifdef FMT_ENFORCE_COMPILE_STRING - static_assert(is_compile_string<S>::value, - "FMT_ENFORCE_COMPILE_STRING requires all format strings to use " - "FMT_STRING."); -#endif +enum class type { + none_type, + // Integer types should go first, + int_type, + uint_type, + long_long_type, + ulong_long_type, + int128_type, + uint128_type, + bool_type, + char_type, + last_integer_type = char_type, + // followed by floating-point types. + float_type, + double_type, + long_double_type, + last_numeric_type = long_double_type, + cstring_type, + string_type, + pointer_type, + custom_type +}; + +// Maps core type T to the corresponding type enum constant. +template <typename T, typename Char> +struct type_constant : std::integral_constant<type, type::custom_type> {}; + +#define FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(Type, constant) \ + template <typename Char> \ + struct type_constant<Type, Char> \ + : std::integral_constant<type, type::constant> {} + +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(int, int_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(unsigned, uint_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(long long, long_long_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(unsigned long long, ulong_long_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(int128_opt, int128_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(uint128_opt, uint128_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(bool, bool_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(Char, char_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(float, float_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(double, double_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(long double, long_double_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(const Char*, cstring_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(basic_string_view<Char>, string_type); +FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(const void*, pointer_type); + +constexpr bool is_integral_type(type t) { + return t > type::none_type && t <= type::last_integer_type; } -template <typename..., typename S, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_compile_string<S>::value)> -void check_format_string(S); +constexpr bool is_arithmetic_type(type t) { + return t > type::none_type && t <= type::last_numeric_type; +} + +constexpr auto set(type rhs) -> int { return 1 << static_cast<int>(rhs); } +constexpr auto in(type t, int set) -> bool { + return ((set >> static_cast<int>(t)) & 1) != 0; +} + +// Bitsets of types. +enum { + sint_set = + set(type::int_type) | set(type::long_long_type) | set(type::int128_type), + uint_set = set(type::uint_type) | set(type::ulong_long_type) | + set(type::uint128_type), + bool_set = set(type::bool_type), + char_set = set(type::char_type), + float_set = set(type::float_type) | set(type::double_type) | + set(type::long_double_type), + string_set = set(type::string_type), + cstring_set = set(type::cstring_type), + pointer_set = set(type::pointer_type) +}; + +FMT_NORETURN FMT_API void throw_format_error(const char* message); struct error_handler { constexpr error_handler() = default; - constexpr error_handler(const error_handler&) = default; // This function is intentionally not constexpr to give a compile-time error. - FMT_NORETURN FMT_API void on_error(const char* message); + FMT_NORETURN void on_error(const char* message) { + throw_format_error(message); + } }; } // namespace detail +/** Throws ``format_error`` with a given message. */ +using detail::throw_format_error; + /** String's character type. */ template <typename S> using char_t = typename detail::char_t_impl<S>::type; @@ -543,43 +653,37 @@ template <typename S> using char_t = typename detail::char_t_impl<S>::type; \rst Parsing context consisting of a format string range being parsed and an argument counter for automatic indexing. - - You can use one of the following type aliases for common character types: - - +-----------------------+-------------------------------------+ - | Type | Definition | - +=======================+=====================================+ - | format_parse_context | basic_format_parse_context<char> | - +-----------------------+-------------------------------------+ - | wformat_parse_context | basic_format_parse_context<wchar_t> | - +-----------------------+-------------------------------------+ + You can use the ``format_parse_context`` type alias for ``char`` instead. \endrst */ -template <typename Char, typename ErrorHandler = detail::error_handler> -class basic_format_parse_context : private ErrorHandler { +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename Char> class basic_format_parse_context { private: basic_string_view<Char> format_str_; int next_arg_id_; + FMT_CONSTEXPR void do_check_arg_id(int id); + public: using char_type = Char; - using iterator = typename basic_string_view<Char>::iterator; + using iterator = const Char*; explicit constexpr basic_format_parse_context( - basic_string_view<Char> format_str, ErrorHandler eh = {}, - int next_arg_id = 0) - : ErrorHandler(eh), format_str_(format_str), next_arg_id_(next_arg_id) {} + basic_string_view<Char> format_str, int next_arg_id = 0) + : format_str_(format_str), next_arg_id_(next_arg_id) {} /** Returns an iterator to the beginning of the format string range being parsed. */ - constexpr iterator begin() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return format_str_.begin(); } + constexpr auto begin() const noexcept -> iterator { + return format_str_.begin(); + } /** Returns an iterator past the end of the format string range being parsed. */ - constexpr iterator end() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return format_str_.end(); } + constexpr auto end() const noexcept -> iterator { return format_str_.end(); } /** Advances the begin iterator to ``it``. */ FMT_CONSTEXPR void advance_to(iterator it) { @@ -590,72 +694,105 @@ class basic_format_parse_context : private ErrorHandler { Reports an error if using the manual argument indexing; otherwise returns the next argument index and switches to the automatic indexing. */ - FMT_CONSTEXPR int next_arg_id() { - // Don't check if the argument id is valid to avoid overhead and because it - // will be checked during formatting anyway. - if (next_arg_id_ >= 0) return next_arg_id_++; - on_error("cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); - return 0; + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto next_arg_id() -> int { + if (next_arg_id_ < 0) { + detail::throw_format_error( + "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); + return 0; + } + int id = next_arg_id_++; + do_check_arg_id(id); + return id; } /** Reports an error if using the automatic argument indexing; otherwise switches to the manual indexing. */ - FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_arg_id(int) { - if (next_arg_id_ > 0) - on_error("cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing"); - else - next_arg_id_ = -1; + FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_arg_id(int id) { + if (next_arg_id_ > 0) { + detail::throw_format_error( + "cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing"); + return; + } + next_arg_id_ = -1; + do_check_arg_id(id); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_arg_id(basic_string_view<Char>) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { - ErrorHandler::on_error(message); - } - - constexpr ErrorHandler error_handler() const { return *this; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_dynamic_spec(int arg_id); }; +FMT_EXPORT using format_parse_context = basic_format_parse_context<char>; -using wformat_parse_context = basic_format_parse_context<wchar_t>; -template <typename Context> class basic_format_arg; -template <typename Context> class basic_format_args; -template <typename Context> class dynamic_format_arg_store; +namespace detail { +// A parse context with extra data used only in compile-time checks. +template <typename Char> +class compile_parse_context : public basic_format_parse_context<Char> { + private: + int num_args_; + const type* types_; + using base = basic_format_parse_context<Char>; -// A formatter for objects of type T. -template <typename T, typename Char = char, typename Enable = void> -struct formatter { - // A deleted default constructor indicates a disabled formatter. - formatter() = delete; -}; + public: + explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR compile_parse_context( + basic_string_view<Char> format_str, int num_args, const type* types, + int next_arg_id = 0) + : base(format_str, next_arg_id), num_args_(num_args), types_(types) {} -// Specifies if T has an enabled formatter specialization. A type can be -// formattable even if it doesn't have a formatter e.g. via a conversion. -template <typename T, typename Context> -using has_formatter = - std::is_constructible<typename Context::template formatter_type<T>>; + constexpr auto num_args() const -> int { return num_args_; } + constexpr auto arg_type(int id) const -> type { return types_[id]; } -// Checks whether T is a container with contiguous storage. -template <typename T> struct is_contiguous : std::false_type {}; -template <typename Char> -struct is_contiguous<std::basic_string<Char>> : std::true_type {}; + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto next_arg_id() -> int { + int id = base::next_arg_id(); + if (id >= num_args_) throw_format_error("argument not found"); + return id; + } -namespace detail { + FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_arg_id(int id) { + base::check_arg_id(id); + if (id >= num_args_) throw_format_error("argument not found"); + } + using base::check_arg_id; + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_dynamic_spec(int arg_id) { + detail::ignore_unused(arg_id); +#if !defined(__LCC__) + if (arg_id < num_args_ && types_ && !is_integral_type(types_[arg_id])) + throw_format_error("width/precision is not integer"); +#endif + } +}; // Extracts a reference to the container from back_insert_iterator. template <typename Container> -inline Container& get_container(std::back_insert_iterator<Container> it) { - using bi_iterator = std::back_insert_iterator<Container>; - struct accessor : bi_iterator { - accessor(bi_iterator iter) : bi_iterator(iter) {} - using bi_iterator::container; +inline auto get_container(std::back_insert_iterator<Container> it) + -> Container& { + using base = std::back_insert_iterator<Container>; + struct accessor : base { + accessor(base b) : base(b) {} + using base::container; }; return *accessor(it).container; } +template <typename Char, typename InputIt, typename OutputIt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto copy_str(InputIt begin, InputIt end, OutputIt out) + -> OutputIt { + while (begin != end) *out++ = static_cast<Char>(*begin++); + return out; +} + +template <typename Char, typename T, typename U, + FMT_ENABLE_IF( + std::is_same<remove_const_t<T>, U>::value&& is_char<U>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto copy_str(T* begin, T* end, U* out) -> U* { + if (is_constant_evaluated()) return copy_str<Char, T*, U*>(begin, end, out); + auto size = to_unsigned(end - begin); + if (size > 0) memcpy(out, begin, size * sizeof(U)); + return out + size; +} + /** \rst A contiguous memory buffer with an optional growing ability. It is an internal @@ -670,24 +807,23 @@ template <typename T> class buffer { protected: // Don't initialize ptr_ since it is not accessed to save a few cycles. - FMT_SUPPRESS_MSC_WARNING(26495) - buffer(size_t sz) FMT_NOEXCEPT : size_(sz), capacity_(sz) {} + FMT_MSC_WARNING(suppress : 26495) + buffer(size_t sz) noexcept : size_(sz), capacity_(sz) {} - buffer(T* p = nullptr, size_t sz = 0, size_t cap = 0) FMT_NOEXCEPT - : ptr_(p), - size_(sz), - capacity_(cap) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 buffer(T* p = nullptr, size_t sz = 0, size_t cap = 0) noexcept + : ptr_(p), size_(sz), capacity_(cap) {} - ~buffer() = default; + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 ~buffer() = default; + buffer(buffer&&) = default; /** Sets the buffer data and capacity. */ - void set(T* buf_data, size_t buf_capacity) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + FMT_CONSTEXPR void set(T* buf_data, size_t buf_capacity) noexcept { ptr_ = buf_data; capacity_ = buf_capacity; } /** Increases the buffer capacity to hold at least *capacity* elements. */ - virtual void grow(size_t capacity) = 0; + virtual FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void grow(size_t capacity) = 0; public: using value_type = T; @@ -696,30 +832,28 @@ template <typename T> class buffer { buffer(const buffer&) = delete; void operator=(const buffer&) = delete; - T* begin() FMT_NOEXCEPT { return ptr_; } - T* end() FMT_NOEXCEPT { return ptr_ + size_; } + FMT_INLINE auto begin() noexcept -> T* { return ptr_; } + FMT_INLINE auto end() noexcept -> T* { return ptr_ + size_; } - const T* begin() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return ptr_; } - const T* end() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return ptr_ + size_; } + FMT_INLINE auto begin() const noexcept -> const T* { return ptr_; } + FMT_INLINE auto end() const noexcept -> const T* { return ptr_ + size_; } /** Returns the size of this buffer. */ - size_t size() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return size_; } + constexpr auto size() const noexcept -> size_t { return size_; } /** Returns the capacity of this buffer. */ - size_t capacity() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return capacity_; } - - /** Returns a pointer to the buffer data. */ - T* data() FMT_NOEXCEPT { return ptr_; } + constexpr auto capacity() const noexcept -> size_t { return capacity_; } - /** Returns a pointer to the buffer data. */ - const T* data() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return ptr_; } + /** Returns a pointer to the buffer data (not null-terminated). */ + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto data() noexcept -> T* { return ptr_; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto data() const noexcept -> const T* { return ptr_; } /** Clears this buffer. */ void clear() { size_ = 0; } // Tries resizing the buffer to contain *count* elements. If T is a POD type // the new elements may not be initialized. - void try_resize(size_t count) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void try_resize(size_t count) { try_reserve(count); size_ = count <= capacity_ ? count : capacity_; } @@ -728,11 +862,11 @@ template <typename T> class buffer { // capacity by a smaller amount than requested but guarantees there is space // for at least one additional element either by increasing the capacity or by // flushing the buffer if it is full. - void try_reserve(size_t new_capacity) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void try_reserve(size_t new_capacity) { if (new_capacity > capacity_) grow(new_capacity); } - void push_back(const T& value) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void push_back(const T& value) { try_reserve(size_ + 1); ptr_[size_++] = value; } @@ -740,16 +874,19 @@ template <typename T> class buffer { /** Appends data to the end of the buffer. */ template <typename U> void append(const U* begin, const U* end); - template <typename I> T& operator[](I index) { return ptr_[index]; } - template <typename I> const T& operator[](I index) const { + template <typename Idx> FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator[](Idx index) -> T& { + return ptr_[index]; + } + template <typename Idx> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator[](Idx index) const -> const T& { return ptr_[index]; } }; struct buffer_traits { explicit buffer_traits(size_t) {} - size_t count() const { return 0; } - size_t limit(size_t size) { return size; } + auto count() const -> size_t { return 0; } + auto limit(size_t size) -> size_t { return size; } }; class fixed_buffer_traits { @@ -759,8 +896,8 @@ class fixed_buffer_traits { public: explicit fixed_buffer_traits(size_t limit) : limit_(limit) {} - size_t count() const { return count_; } - size_t limit(size_t size) { + auto count() const -> size_t { return count_; } + auto limit(size_t size) -> size_t { size_t n = limit_ > count_ ? limit_ - count_ : 0; count_ += size; return size < n ? size : n; @@ -776,33 +913,84 @@ class iterator_buffer final : public Traits, public buffer<T> { T data_[buffer_size]; protected: - void grow(size_t) final FMT_OVERRIDE { + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void grow(size_t) override { if (this->size() == buffer_size) flush(); } - void flush(); + + void flush() { + auto size = this->size(); + this->clear(); + out_ = copy_str<T>(data_, data_ + this->limit(size), out_); + } public: explicit iterator_buffer(OutputIt out, size_t n = buffer_size) - : Traits(n), - buffer<T>(data_, 0, buffer_size), - out_(out) {} + : Traits(n), buffer<T>(data_, 0, buffer_size), out_(out) {} + iterator_buffer(iterator_buffer&& other) + : Traits(other), buffer<T>(data_, 0, buffer_size), out_(other.out_) {} + ~iterator_buffer() { flush(); } + + auto out() -> OutputIt { + flush(); + return out_; + } + auto count() const -> size_t { return Traits::count() + this->size(); } +}; + +template <typename T> +class iterator_buffer<T*, T, fixed_buffer_traits> final + : public fixed_buffer_traits, + public buffer<T> { + private: + T* out_; + enum { buffer_size = 256 }; + T data_[buffer_size]; + + protected: + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void grow(size_t) override { + if (this->size() == this->capacity()) flush(); + } + + void flush() { + size_t n = this->limit(this->size()); + if (this->data() == out_) { + out_ += n; + this->set(data_, buffer_size); + } + this->clear(); + } + + public: + explicit iterator_buffer(T* out, size_t n = buffer_size) + : fixed_buffer_traits(n), buffer<T>(out, 0, n), out_(out) {} + iterator_buffer(iterator_buffer&& other) + : fixed_buffer_traits(other), + buffer<T>(std::move(other)), + out_(other.out_) { + if (this->data() != out_) { + this->set(data_, buffer_size); + this->clear(); + } + } ~iterator_buffer() { flush(); } - OutputIt out() { + auto out() -> T* { flush(); return out_; } - size_t count() const { return Traits::count() + this->size(); } + auto count() const -> size_t { + return fixed_buffer_traits::count() + this->size(); + } }; template <typename T> class iterator_buffer<T*, T> final : public buffer<T> { protected: - void grow(size_t) final FMT_OVERRIDE {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void grow(size_t) override {} public: explicit iterator_buffer(T* out, size_t = 0) : buffer<T>(out, 0, ~size_t()) {} - T* out() { return &*this->end(); } + auto out() -> T* { return &*this->end(); } }; // A buffer that writes to a container with the contiguous storage. @@ -815,7 +1003,7 @@ class iterator_buffer<std::back_insert_iterator<Container>, Container& container_; protected: - void grow(size_t capacity) final FMT_OVERRIDE { + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void grow(size_t capacity) override { container_.resize(capacity); this->set(&container_[0], capacity); } @@ -825,7 +1013,8 @@ class iterator_buffer<std::back_insert_iterator<Container>, : buffer<typename Container::value_type>(c.size()), container_(c) {} explicit iterator_buffer(std::back_insert_iterator<Container> out, size_t = 0) : iterator_buffer(get_container(out)) {} - std::back_insert_iterator<Container> out() { + + auto out() -> std::back_insert_iterator<Container> { return std::back_inserter(container_); } }; @@ -838,7 +1027,7 @@ template <typename T = char> class counting_buffer final : public buffer<T> { size_t count_ = 0; protected: - void grow(size_t) final FMT_OVERRIDE { + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void grow(size_t) override { if (this->size() != buffer_size) return; count_ += this->size(); this->clear(); @@ -847,61 +1036,106 @@ template <typename T = char> class counting_buffer final : public buffer<T> { public: counting_buffer() : buffer<T>(data_, 0, buffer_size) {} - size_t count() { return count_ + this->size(); } + auto count() -> size_t { return count_ + this->size(); } +}; +} // namespace detail + +template <typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR void basic_format_parse_context<Char>::do_check_arg_id(int id) { + // Argument id is only checked at compile-time during parsing because + // formatting has its own validation. + if (detail::is_constant_evaluated() && + (!FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 1200)) { + using context = detail::compile_parse_context<Char>; + if (id >= static_cast<context*>(this)->num_args()) + detail::throw_format_error("argument not found"); + } +} + +template <typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR void basic_format_parse_context<Char>::check_dynamic_spec( + int arg_id) { + if (detail::is_constant_evaluated() && + (!FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 1200)) { + using context = detail::compile_parse_context<Char>; + static_cast<context*>(this)->check_dynamic_spec(arg_id); + } +} + +FMT_EXPORT template <typename Context> class basic_format_arg; +FMT_EXPORT template <typename Context> class basic_format_args; +FMT_EXPORT template <typename Context> class dynamic_format_arg_store; + +// A formatter for objects of type T. +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename T, typename Char = char, typename Enable = void> +struct formatter { + // A deleted default constructor indicates a disabled formatter. + formatter() = delete; }; -// An output iterator that appends to the buffer. +// Specifies if T has an enabled formatter specialization. A type can be +// formattable even if it doesn't have a formatter e.g. via a conversion. +template <typename T, typename Context> +using has_formatter = + std::is_constructible<typename Context::template formatter_type<T>>; + +// An output iterator that appends to a buffer. // It is used to reduce symbol sizes for the common case. -template <typename T> -class buffer_appender : public std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<T>> { - using base = std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<T>>; +class appender : public std::back_insert_iterator<detail::buffer<char>> { + using base = std::back_insert_iterator<detail::buffer<char>>; public: - explicit buffer_appender(buffer<T>& buf) : base(buf) {} - buffer_appender(base it) : base(it) {} + using std::back_insert_iterator<detail::buffer<char>>::back_insert_iterator; + appender(base it) noexcept : base(it) {} + FMT_UNCHECKED_ITERATOR(appender); - buffer_appender& operator++() { - base::operator++(); - return *this; - } - - buffer_appender operator++(int) { - buffer_appender tmp = *this; - ++*this; - return tmp; - } + auto operator++() noexcept -> appender& { return *this; } + auto operator++(int) noexcept -> appender { return *this; } }; -// Maps an output iterator into a buffer. -template <typename T, typename OutputIt> -iterator_buffer<OutputIt, T> get_buffer(OutputIt); -template <typename T> buffer<T>& get_buffer(buffer_appender<T>); +namespace detail { -template <typename OutputIt> OutputIt get_buffer_init(OutputIt out) { - return out; +template <typename Context, typename T> +constexpr auto has_const_formatter_impl(T*) + -> decltype(typename Context::template formatter_type<T>().format( + std::declval<const T&>(), std::declval<Context&>()), + true) { + return true; +} +template <typename Context> +constexpr auto has_const_formatter_impl(...) -> bool { + return false; +} +template <typename T, typename Context> +constexpr auto has_const_formatter() -> bool { + return has_const_formatter_impl<Context>(static_cast<T*>(nullptr)); +} + +template <typename T> +using buffer_appender = conditional_t<std::is_same<T, char>::value, appender, + std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<T>>>; + +// Maps an output iterator to a buffer. +template <typename T, typename OutputIt> +auto get_buffer(OutputIt out) -> iterator_buffer<OutputIt, T> { + return iterator_buffer<OutputIt, T>(out); } -template <typename T> buffer<T>& get_buffer_init(buffer_appender<T> out) { +template <typename T, typename Buf, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_base_of<buffer<char>, Buf>::value)> +auto get_buffer(std::back_insert_iterator<Buf> out) -> buffer<char>& { return get_container(out); } -template <typename Buffer> -auto get_iterator(Buffer& buf) -> decltype(buf.out()) { +template <typename Buf, typename OutputIt> +FMT_INLINE auto get_iterator(Buf& buf, OutputIt) -> decltype(buf.out()) { return buf.out(); } -template <typename T> buffer_appender<T> get_iterator(buffer<T>& buf) { - return buffer_appender<T>(buf); +template <typename T, typename OutputIt> +auto get_iterator(buffer<T>&, OutputIt out) -> OutputIt { + return out; } -template <typename T, typename Char = char, typename Enable = void> -struct fallback_formatter { - fallback_formatter() = delete; -}; - -// Specifies if T has an enabled fallback_formatter specialization. -template <typename T, typename Context> -using has_fallback_formatter = - std::is_constructible<fallback_formatter<T, typename Context::char_type>>; - struct view {}; template <typename Char, typename T> struct named_arg : view { @@ -925,8 +1159,8 @@ struct arg_data { template <typename... U> arg_data(const U&... init) : args_{T(named_args_, NUM_NAMED_ARGS), init...} {} arg_data(const arg_data& other) = delete; - const T* args() const { return args_ + 1; } - named_arg_info<Char>* named_args() { return named_args_; } + auto args() const -> const T* { return args_ + 1; } + auto named_args() -> named_arg_info<Char>* { return named_args_; } }; template <typename T, typename Char, size_t NUM_ARGS> @@ -935,99 +1169,58 @@ struct arg_data<T, Char, NUM_ARGS, 0> { T args_[NUM_ARGS != 0 ? NUM_ARGS : +1]; template <typename... U> - FMT_INLINE arg_data(const U&... init) : args_{init...} {} - FMT_INLINE const T* args() const { return args_; } - FMT_INLINE std::nullptr_t named_args() { return nullptr; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE arg_data(const U&... init) : args_{init...} {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto args() const -> const T* { return args_; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto named_args() -> std::nullptr_t { + return nullptr; + } }; template <typename Char> inline void init_named_args(named_arg_info<Char>*, int, int) {} -template <typename Char, typename T, typename... Tail> +template <typename T> struct is_named_arg : std::false_type {}; +template <typename T> struct is_statically_named_arg : std::false_type {}; + +template <typename T, typename Char> +struct is_named_arg<named_arg<Char, T>> : std::true_type {}; + +template <typename Char, typename T, typename... Tail, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_named_arg<T>::value)> void init_named_args(named_arg_info<Char>* named_args, int arg_count, int named_arg_count, const T&, const Tail&... args) { init_named_args(named_args, arg_count + 1, named_arg_count, args...); } -template <typename Char, typename T, typename... Tail> +template <typename Char, typename T, typename... Tail, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_named_arg<T>::value)> void init_named_args(named_arg_info<Char>* named_args, int arg_count, - int named_arg_count, const named_arg<Char, T>& arg, - const Tail&... args) { + int named_arg_count, const T& arg, const Tail&... args) { named_args[named_arg_count++] = {arg.name, arg_count}; init_named_args(named_args, arg_count + 1, named_arg_count, args...); } template <typename... Args> -FMT_INLINE void init_named_args(std::nullptr_t, int, int, const Args&...) {} +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE void init_named_args(std::nullptr_t, int, int, + const Args&...) {} -template <typename T> struct is_named_arg : std::false_type {}; - -template <typename T, typename Char> -struct is_named_arg<named_arg<Char, T>> : std::true_type {}; - -template <bool B = false> constexpr size_t count() { return B ? 1 : 0; } -template <bool B1, bool B2, bool... Tail> constexpr size_t count() { +template <bool B = false> constexpr auto count() -> size_t { return B ? 1 : 0; } +template <bool B1, bool B2, bool... Tail> constexpr auto count() -> size_t { return (B1 ? 1 : 0) + count<B2, Tail...>(); } -template <typename... Args> constexpr size_t count_named_args() { +template <typename... Args> constexpr auto count_named_args() -> size_t { return count<is_named_arg<Args>::value...>(); } -enum class type { - none_type, - // Integer types should go first, - int_type, - uint_type, - long_long_type, - ulong_long_type, - int128_type, - uint128_type, - bool_type, - char_type, - last_integer_type = char_type, - // followed by floating-point types. - float_type, - double_type, - long_double_type, - last_numeric_type = long_double_type, - cstring_type, - string_type, - pointer_type, - custom_type -}; - -// Maps core type T to the corresponding type enum constant. -template <typename T, typename Char> -struct type_constant : std::integral_constant<type, type::custom_type> {}; - -#define FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(Type, constant) \ - template <typename Char> \ - struct type_constant<Type, Char> \ - : std::integral_constant<type, type::constant> {} - -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(int, int_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(unsigned, uint_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(long long, long_long_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(unsigned long long, ulong_long_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(int128_t, int128_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(uint128_t, uint128_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(bool, bool_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(Char, char_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(float, float_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(double, double_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(long double, long_double_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(const Char*, cstring_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(basic_string_view<Char>, string_type); -FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(const void*, pointer_type); - -constexpr bool is_integral_type(type t) { - return t > type::none_type && t <= type::last_integer_type; +template <typename... Args> +constexpr auto count_statically_named_args() -> size_t { + return count<is_statically_named_arg<Args>::value...>(); } -constexpr bool is_arithmetic_type(type t) { - return t > type::none_type && t <= type::last_numeric_type; -} +struct unformattable {}; +struct unformattable_char : unformattable {}; +struct unformattable_pointer : unformattable {}; template <typename Char> struct string_value { const Char* data; @@ -1041,8 +1234,8 @@ template <typename Char> struct named_arg_value { template <typename Context> struct custom_value { using parse_context = typename Context::parse_context_type; - const void* value; - void (*format)(const void* arg, parse_context& parse_ctx, Context& ctx); + void* value; + void (*format)(void* arg, parse_context& parse_ctx, Context& ctx); }; // A formatting argument value. @@ -1051,12 +1244,13 @@ template <typename Context> class value { using char_type = typename Context::char_type; union { + monostate no_value; int int_value; unsigned uint_value; long long long_long_value; unsigned long long ulong_long_value; - int128_t int128_value; - uint128_t uint128_value; + int128_opt int128_value; + uint128_opt uint128_value; bool bool_value; char_type char_value; float float_value; @@ -1068,19 +1262,23 @@ template <typename Context> class value { named_arg_value<char_type> named_args; }; - constexpr FMT_INLINE value(int val = 0) : int_value(val) {} + constexpr FMT_INLINE value() : no_value() {} + constexpr FMT_INLINE value(int val) : int_value(val) {} constexpr FMT_INLINE value(unsigned val) : uint_value(val) {} - FMT_INLINE value(long long val) : long_long_value(val) {} - FMT_INLINE value(unsigned long long val) : ulong_long_value(val) {} - FMT_INLINE value(int128_t val) : int128_value(val) {} - FMT_INLINE value(uint128_t val) : uint128_value(val) {} - FMT_INLINE value(float val) : float_value(val) {} - FMT_INLINE value(double val) : double_value(val) {} + constexpr FMT_INLINE value(long long val) : long_long_value(val) {} + constexpr FMT_INLINE value(unsigned long long val) : ulong_long_value(val) {} + FMT_INLINE value(int128_opt val) : int128_value(val) {} + FMT_INLINE value(uint128_opt val) : uint128_value(val) {} + constexpr FMT_INLINE value(float val) : float_value(val) {} + constexpr FMT_INLINE value(double val) : double_value(val) {} FMT_INLINE value(long double val) : long_double_value(val) {} - FMT_INLINE value(bool val) : bool_value(val) {} - FMT_INLINE value(char_type val) : char_value(val) {} - FMT_INLINE value(const char_type* val) { string.data = val; } - FMT_INLINE value(basic_string_view<char_type> val) { + constexpr FMT_INLINE value(bool val) : bool_value(val) {} + constexpr FMT_INLINE value(char_type val) : char_value(val) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE value(const char_type* val) { + string.data = val; + if (is_constant_evaluated()) string.size = {}; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE value(basic_string_view<char_type> val) { string.data = val.data(); string.size = val.size(); } @@ -1088,149 +1286,194 @@ template <typename Context> class value { FMT_INLINE value(const named_arg_info<char_type>* args, size_t size) : named_args{args, size} {} - template <typename T> FMT_INLINE value(const T& val) { - custom.value = &val; + template <typename T> FMT_CONSTEXPR20 FMT_INLINE value(T& val) { + using value_type = remove_const_t<T>; + custom.value = const_cast<value_type*>(std::addressof(val)); // Get the formatter type through the context to allow different contexts // have different extension points, e.g. `formatter<T>` for `format` and // `printf_formatter<T>` for `printf`. custom.format = format_custom_arg< - T, conditional_t<has_formatter<T, Context>::value, - typename Context::template formatter_type<T>, - fallback_formatter<T, char_type>>>; + value_type, typename Context::template formatter_type<value_type>>; } + value(unformattable); + value(unformattable_char); + value(unformattable_pointer); private: // Formats an argument of a custom type, such as a user-defined class. template <typename T, typename Formatter> - static void format_custom_arg(const void* arg, + static void format_custom_arg(void* arg, typename Context::parse_context_type& parse_ctx, Context& ctx) { - Formatter f; + auto f = Formatter(); parse_ctx.advance_to(f.parse(parse_ctx)); - ctx.advance_to(f.format(*static_cast<const T*>(arg), ctx)); + using qualified_type = + conditional_t<has_const_formatter<T, Context>(), const T, T>; + ctx.advance_to(f.format(*static_cast<qualified_type*>(arg), ctx)); } }; -template <typename Context, typename T> -FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_format_arg<Context> make_arg(const T& value); - // To minimize the number of types we need to deal with, long is translated // either to int or to long long depending on its size. enum { long_short = sizeof(long) == sizeof(int) }; using long_type = conditional_t<long_short, int, long long>; using ulong_type = conditional_t<long_short, unsigned, unsigned long long>; -struct unformattable {}; +template <typename T> struct format_as_result { + template <typename U, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_enum<U>::value || std::is_class<U>::value)> + static auto map(U*) -> decltype(format_as(std::declval<U>())); + static auto map(...) -> void; + + using type = decltype(map(static_cast<T*>(nullptr))); +}; +template <typename T> using format_as_t = typename format_as_result<T>::type; + +template <typename T> +struct has_format_as + : bool_constant<!std::is_same<format_as_t<T>, void>::value> {}; // Maps formatting arguments to core types. +// arg_mapper reports errors by returning unformattable instead of using +// static_assert because it's used in the is_formattable trait. template <typename Context> struct arg_mapper { using char_type = typename Context::char_type; - FMT_CONSTEXPR int map(signed char val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR unsigned map(unsigned char val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR int map(short val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR unsigned map(unsigned short val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR int map(int val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR unsigned map(unsigned val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR long_type map(long val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR ulong_type map(unsigned long val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR long long map(long long val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR unsigned long long map(unsigned long long val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR int128_t map(int128_t val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR uint128_t map(uint128_t val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR bool map(bool val) { return val; } - - template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_char<T>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR char_type map(T val) { - static_assert( - std::is_same<T, char>::value || std::is_same<T, char_type>::value, - "mixing character types is disallowed"); + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(signed char val) -> int { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(unsigned char val) -> unsigned { + return val; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(short val) -> int { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(unsigned short val) -> unsigned { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(int val) -> int { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(unsigned val) -> unsigned { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(long val) -> long_type { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(unsigned long val) -> ulong_type { + return val; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(long long val) -> long long { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(unsigned long long val) + -> unsigned long long { + return val; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(int128_opt val) -> int128_opt { + return val; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(uint128_opt val) -> uint128_opt { + return val; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(bool val) -> bool { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR float map(float val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR double map(double val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR long double map(long double val) { return val; } + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<T, char>::value || + std::is_same<T, char_type>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(T val) -> char_type { + return val; + } + template <typename T, enable_if_t<(std::is_same<T, wchar_t>::value || +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t + std::is_same<T, char8_t>::value || +#endif + std::is_same<T, char16_t>::value || + std::is_same<T, char32_t>::value) && + !std::is_same<T, char_type>::value, + int> = 0> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(T) -> unformattable_char { + return {}; + } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const char_type* map(char_type* val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const char_type* map(const char_type* val) { return val; } - template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_string<T>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_string_view<char_type> map(const T& val) { - static_assert(std::is_same<char_type, char_t<T>>::value, - "mixing character types is disallowed"); + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(float val) -> float { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(double val) -> double { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(long double val) -> long double { + return val; + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(char_type* val) -> const char_type* { + return val; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const char_type* val) -> const char_type* { + return val; + } + template <typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_string<T>::value && !std::is_pointer<T>::value && + std::is_same<char_type, char_t<T>>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const T& val) + -> basic_string_view<char_type> { return to_string_view(val); } template <typename T, - FMT_ENABLE_IF( - std::is_constructible<basic_string_view<char_type>, T>::value && - !is_string<T>::value && !has_formatter<T, Context>::value && - !has_fallback_formatter<T, Context>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_string_view<char_type> map(const T& val) { - return basic_string_view<char_type>(val); + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_string<T>::value && !std::is_pointer<T>::value && + !std::is_same<char_type, char_t<T>>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const T&) -> unformattable_char { + return {}; + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(void* val) -> const void* { return val; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const void* val) -> const void* { + return val; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(std::nullptr_t val) -> const void* { + return val; } + + // Use SFINAE instead of a const T* parameter to avoid a conflict with the + // array overload. template < typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF( - std::is_constructible<std_string_view<char_type>, T>::value && - !std::is_constructible<basic_string_view<char_type>, T>::value && - !is_string<T>::value && !has_formatter<T, Context>::value && - !has_fallback_formatter<T, Context>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_string_view<char_type> map(const T& val) { - return std_string_view<char_type>(val); - } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* map(const signed char* val) { - static_assert(std::is_same<char_type, char>::value, "invalid string type"); - return reinterpret_cast<const char*>(val); - } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* map(const unsigned char* val) { - static_assert(std::is_same<char_type, char>::value, "invalid string type"); - return reinterpret_cast<const char*>(val); - } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* map(signed char* val) { - const auto* const_val = val; - return map(const_val); - } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* map(unsigned char* val) { - const auto* const_val = val; - return map(const_val); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR const void* map(void* val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const void* map(const void* val) { return val; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const void* map(std::nullptr_t val) { return val; } - template <typename T> FMT_CONSTEXPR int map(const T*) { - // Formatting of arbitrary pointers is disallowed. If you want to output - // a pointer cast it to "void *" or "const void *". In particular, this - // forbids formatting of "[const] volatile char *" which is printed as bool - // by iostreams. - static_assert(!sizeof(T), "formatting of non-void pointers is disallowed"); - return 0; + std::is_pointer<T>::value || std::is_member_pointer<T>::value || + std::is_function<typename std::remove_pointer<T>::type>::value || + (std::is_array<T>::value && + !std::is_convertible<T, const char_type*>::value))> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto map(const T&) -> unformattable_pointer { + return {}; } - template <typename T, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_enum<T>::value && - !has_formatter<T, Context>::value && - !has_fallback_formatter<T, Context>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR auto map(const T& val) - -> decltype(std::declval<arg_mapper>().map( - static_cast<typename std::underlying_type<T>::type>(val))) { - return map(static_cast<typename std::underlying_type<T>::type>(val)); + template <typename T, std::size_t N, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<T, wchar_t>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const T (&values)[N]) -> const T (&)[N] { + return values; } - template <typename T, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_string<T>::value && !is_char<T>::value && - (has_formatter<T, Context>::value || - has_fallback_formatter<T, Context>::value))> - FMT_CONSTEXPR const T& map(const T& val) { + + // Only map owning types because mapping views can be unsafe. + template <typename T, typename U = format_as_t<T>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_arithmetic<U>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const T& val) -> decltype(this->map(U())) { + return map(format_as(val)); + } + + template <typename T, typename U = remove_const_t<T>> + struct formattable : bool_constant<has_const_formatter<U, Context>() || + (has_formatter<U, Context>::value && + !std::is_const<T>::value)> {}; + + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(formattable<T>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto do_map(T& val) -> T& { return val; } + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!formattable<T>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto do_map(T&) -> unformattable { + return {}; + } + + template <typename T, typename U = remove_const_t<T>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF((std::is_class<U>::value || std::is_enum<U>::value || + std::is_union<U>::value) && + !is_string<U>::value && !is_char<U>::value && + !is_named_arg<U>::value && + !std::is_arithmetic<format_as_t<U>>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(T& val) -> decltype(this->do_map(val)) { + return do_map(val); + } - template <typename T> - FMT_CONSTEXPR auto map(const named_arg<char_type, T>& val) - -> decltype(std::declval<arg_mapper>().map(val.value)) { - return map(val.value); + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_named_arg<T>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const T& named_arg) + -> decltype(this->map(named_arg.value)) { + return map(named_arg.value); } - unformattable map(...) { return {}; } + auto map(...) -> unformattable { return {}; } }; // A type constant after applying arg_mapper<Context>. @@ -1244,7 +1487,122 @@ enum { packed_arg_bits = 4 }; enum { max_packed_args = 62 / packed_arg_bits }; enum : unsigned long long { is_unpacked_bit = 1ULL << 63 }; enum : unsigned long long { has_named_args_bit = 1ULL << 62 }; + +template <typename Char, typename InputIt> +auto copy_str(InputIt begin, InputIt end, appender out) -> appender { + get_container(out).append(begin, end); + return out; +} +template <typename Char, typename InputIt> +auto copy_str(InputIt begin, InputIt end, + std::back_insert_iterator<std::string> out) + -> std::back_insert_iterator<std::string> { + get_container(out).append(begin, end); + return out; +} + +template <typename Char, typename R, typename OutputIt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto copy_str(R&& rng, OutputIt out) -> OutputIt { + return detail::copy_str<Char>(rng.begin(), rng.end(), out); +} + +#if FMT_GCC_VERSION && FMT_GCC_VERSION < 500 +// A workaround for gcc 4.8 to make void_t work in a SFINAE context. +template <typename...> struct void_t_impl { + using type = void; +}; +template <typename... T> using void_t = typename void_t_impl<T...>::type; +#else +template <typename...> using void_t = void; +#endif + +template <typename It, typename T, typename Enable = void> +struct is_output_iterator : std::false_type {}; + +template <typename It, typename T> +struct is_output_iterator< + It, T, + void_t<typename std::iterator_traits<It>::iterator_category, + decltype(*std::declval<It>() = std::declval<T>())>> + : std::true_type {}; + +template <typename It> struct is_back_insert_iterator : std::false_type {}; +template <typename Container> +struct is_back_insert_iterator<std::back_insert_iterator<Container>> + : std::true_type {}; + +// A type-erased reference to an std::locale to avoid a heavy <locale> include. +class locale_ref { + private: + const void* locale_; // A type-erased pointer to std::locale. + + public: + constexpr FMT_INLINE locale_ref() : locale_(nullptr) {} + template <typename Locale> explicit locale_ref(const Locale& loc); + + explicit operator bool() const noexcept { return locale_ != nullptr; } + + template <typename Locale> auto get() const -> Locale; +}; + +template <typename> constexpr auto encode_types() -> unsigned long long { + return 0; +} + +template <typename Context, typename Arg, typename... Args> +constexpr auto encode_types() -> unsigned long long { + return static_cast<unsigned>(mapped_type_constant<Arg, Context>::value) | + (encode_types<Context, Args...>() << packed_arg_bits); +} + +#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) +// This type is intentionally undefined, only used for errors +template <typename T, typename Char> struct type_is_unformattable_for; +#endif + +template <bool PACKED, typename Context, typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(PACKED)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto make_arg(T& val) -> value<Context> { + using arg_type = remove_cvref_t<decltype(arg_mapper<Context>().map(val))>; + + constexpr bool formattable_char = + !std::is_same<arg_type, unformattable_char>::value; + static_assert(formattable_char, "Mixing character types is disallowed."); + + // Formatting of arbitrary pointers is disallowed. If you want to format a + // pointer cast it to `void*` or `const void*`. In particular, this forbids + // formatting of `[const] volatile char*` printed as bool by iostreams. + constexpr bool formattable_pointer = + !std::is_same<arg_type, unformattable_pointer>::value; + static_assert(formattable_pointer, + "Formatting of non-void pointers is disallowed."); + + constexpr bool formattable = !std::is_same<arg_type, unformattable>::value; +#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) + if constexpr (!formattable) { + type_is_unformattable_for<T, typename Context::char_type> _; + } +#endif + static_assert( + formattable, + "Cannot format an argument. To make type T formattable provide a " + "formatter<T> specialization: https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#udt"); + return {arg_mapper<Context>().map(val)}; +} + +template <typename Context, typename T> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto make_arg(T& val) -> basic_format_arg<Context> { + auto arg = basic_format_arg<Context>(); + arg.type_ = mapped_type_constant<T, Context>::value; + arg.value_ = make_arg<true, Context>(val); + return arg; +} + +template <bool PACKED, typename Context, typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!PACKED)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto make_arg(T& val) -> basic_format_arg<Context> { + return make_arg<Context>(val); +} } // namespace detail +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT // A formatting argument. It is a trivially copyable/constructible type to // allow storage in basic_memory_buffer. @@ -1254,8 +1612,8 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_arg { detail::type type_; template <typename ContextType, typename T> - friend FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_format_arg<ContextType> detail::make_arg( - const T& value); + friend FMT_CONSTEXPR auto detail::make_arg(T& value) + -> basic_format_arg<ContextType>; template <typename Visitor, typename Ctx> friend FMT_CONSTEXPR auto visit_format_arg(Visitor&& vis, @@ -1289,14 +1647,16 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_arg { constexpr basic_format_arg() : type_(detail::type::none_type) {} - constexpr explicit operator bool() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { + constexpr explicit operator bool() const noexcept { return type_ != detail::type::none_type; } - detail::type type() const { return type_; } + auto type() const -> detail::type { return type_; } - bool is_integral() const { return detail::is_integral_type(type_); } - bool is_arithmetic() const { return detail::is_arithmetic_type(type_); } + auto is_integral() const -> bool { return detail::is_integral_type(type_); } + auto is_arithmetic() const -> bool { + return detail::is_arithmetic_type(type_); + } }; /** @@ -1306,10 +1666,10 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_arg { ``vis(value)`` will be called with the value of type ``double``. \endrst */ +// DEPRECATED! template <typename Visitor, typename Context> -FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL FMT_INLINE auto visit_format_arg( +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto visit_format_arg( Visitor&& vis, const basic_format_arg<Context>& arg) -> decltype(vis(0)) { - using char_type = typename Context::char_type; switch (arg.type_) { case detail::type::none_type: break; @@ -1321,16 +1681,10 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL FMT_INLINE auto visit_format_arg( return vis(arg.value_.long_long_value); case detail::type::ulong_long_type: return vis(arg.value_.ulong_long_value); -#if FMT_USE_INT128 case detail::type::int128_type: - return vis(arg.value_.int128_value); + return vis(detail::convert_for_visit(arg.value_.int128_value)); case detail::type::uint128_type: - return vis(arg.value_.uint128_value); -#else - case detail::type::int128_type: - case detail::type::uint128_type: - break; -#endif + return vis(detail::convert_for_visit(arg.value_.uint128_value)); case detail::type::bool_type: return vis(arg.value_.bool_value); case detail::type::char_type: @@ -1344,8 +1698,8 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL FMT_INLINE auto visit_format_arg( case detail::type::cstring_type: return vis(arg.value_.string.data); case detail::type::string_type: - return vis(basic_string_view<char_type>(arg.value_.string.data, - arg.value_.string.size)); + using sv = basic_string_view<typename Context::char_type>; + return vis(sv(arg.value_.string.data, arg.value_.string.size)); case detail::type::pointer_type: return vis(arg.value_.pointer); case detail::type::custom_type: @@ -1354,144 +1708,8 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL FMT_INLINE auto visit_format_arg( return vis(monostate()); } -template <typename T> struct formattable : std::false_type {}; - -namespace detail { - -// A workaround for gcc 4.8 to make void_t work in a SFINAE context. -template <typename... Ts> struct void_t_impl { using type = void; }; -template <typename... Ts> -using void_t = typename detail::void_t_impl<Ts...>::type; - -template <typename It, typename T, typename Enable = void> -struct is_output_iterator : std::false_type {}; - -template <typename It, typename T> -struct is_output_iterator< - It, T, - void_t<typename std::iterator_traits<It>::iterator_category, - decltype(*std::declval<It>() = std::declval<T>())>> - : std::true_type {}; - -template <typename OutputIt> -struct is_back_insert_iterator : std::false_type {}; -template <typename Container> -struct is_back_insert_iterator<std::back_insert_iterator<Container>> - : std::true_type {}; - -template <typename OutputIt> -struct is_contiguous_back_insert_iterator : std::false_type {}; -template <typename Container> -struct is_contiguous_back_insert_iterator<std::back_insert_iterator<Container>> - : is_contiguous<Container> {}; -template <typename Char> -struct is_contiguous_back_insert_iterator<buffer_appender<Char>> - : std::true_type {}; - -// A type-erased reference to an std::locale to avoid heavy <locale> include. -class locale_ref { - private: - const void* locale_; // A type-erased pointer to std::locale. - - public: - locale_ref() : locale_(nullptr) {} - template <typename Locale> explicit locale_ref(const Locale& loc); - - explicit operator bool() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return locale_ != nullptr; } - - template <typename Locale> Locale get() const; -}; - -template <typename> constexpr unsigned long long encode_types() { return 0; } - -template <typename Context, typename Arg, typename... Args> -constexpr unsigned long long encode_types() { - return static_cast<unsigned>(mapped_type_constant<Arg, Context>::value) | - (encode_types<Context, Args...>() << packed_arg_bits); -} - -template <typename Context, typename T> -FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_format_arg<Context> make_arg(const T& value) { - basic_format_arg<Context> arg; - arg.type_ = mapped_type_constant<T, Context>::value; - arg.value_ = arg_mapper<Context>().map(value); - return arg; -} - -template <typename T> int check(unformattable) { - static_assert( - formattable<T>(), - "Cannot format an argument. To make type T formattable provide a " - "formatter<T> specialization: https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#udt"); - return 0; -} -template <typename T, typename U> inline const U& check(const U& val) { - return val; -} - -// The type template parameter is there to avoid an ODR violation when using -// a fallback formatter in one translation unit and an implicit conversion in -// another (not recommended). -template <bool IS_PACKED, typename Context, type, typename T, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(IS_PACKED)> -inline value<Context> make_arg(const T& val) { - return check<T>(arg_mapper<Context>().map(val)); -} - -template <bool IS_PACKED, typename Context, type, typename T, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(!IS_PACKED)> -inline basic_format_arg<Context> make_arg(const T& value) { - return make_arg<Context>(value); -} - -template <typename T> struct is_reference_wrapper : std::false_type {}; -template <typename T> -struct is_reference_wrapper<std::reference_wrapper<T>> : std::true_type {}; - -template <typename T> const T& unwrap(const T& v) { return v; } -template <typename T> const T& unwrap(const std::reference_wrapper<T>& v) { - return static_cast<const T&>(v); -} - -class dynamic_arg_list { - // Workaround for clang's -Wweak-vtables. Unlike for regular classes, for - // templates it doesn't complain about inability to deduce single translation - // unit for placing vtable. So storage_node_base is made a fake template. - template <typename = void> struct node { - virtual ~node() = default; - std::unique_ptr<node<>> next; - }; - - template <typename T> struct typed_node : node<> { - T value; - - template <typename Arg> - FMT_CONSTEXPR typed_node(const Arg& arg) : value(arg) {} - - template <typename Char> - FMT_CONSTEXPR typed_node(const basic_string_view<Char>& arg) - : value(arg.data(), arg.size()) {} - }; - - std::unique_ptr<node<>> head_; - - public: - template <typename T, typename Arg> const T& push(const Arg& arg) { - auto new_node = std::unique_ptr<typed_node<T>>(new typed_node<T>(arg)); - auto& value = new_node->value; - new_node->next = std::move(head_); - head_ = std::move(new_node); - return value; - } -}; -} // namespace detail - // Formatting context. template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> class basic_format_context { - public: - /** The character type for the output. */ - using char_type = Char; - private: OutputIt out_; basic_format_args<basic_format_context> args_; @@ -1500,48 +1718,56 @@ template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> class basic_format_context { public: using iterator = OutputIt; using format_arg = basic_format_arg<basic_format_context>; + using format_args = basic_format_args<basic_format_context>; using parse_context_type = basic_format_parse_context<Char>; - template <typename T> using formatter_type = formatter<T, char_type>; + template <typename T> using formatter_type = formatter<T, Char>; + /** The character type for the output. */ + using char_type = Char; + + basic_format_context(basic_format_context&&) = default; basic_format_context(const basic_format_context&) = delete; void operator=(const basic_format_context&) = delete; /** - Constructs a ``basic_format_context`` object. References to the arguments are - stored in the object so make sure they have appropriate lifetimes. + Constructs a ``basic_format_context`` object. References to the arguments + are stored in the object so make sure they have appropriate lifetimes. */ - basic_format_context(OutputIt out, - basic_format_args<basic_format_context> ctx_args, - detail::locale_ref loc = detail::locale_ref()) + constexpr basic_format_context(OutputIt out, format_args ctx_args, + detail::locale_ref loc = {}) : out_(out), args_(ctx_args), loc_(loc) {} - format_arg arg(int id) const { return args_.get(id); } - format_arg arg(basic_string_view<char_type> name) { return args_.get(name); } - int arg_id(basic_string_view<char_type> name) { return args_.get_id(name); } - const basic_format_args<basic_format_context>& args() const { return args_; } + constexpr auto arg(int id) const -> format_arg { return args_.get(id); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto arg(basic_string_view<Char> name) -> format_arg { + return args_.get(name); + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto arg_id(basic_string_view<Char> name) -> int { + return args_.get_id(name); + } + auto args() const -> const format_args& { return args_; } - detail::error_handler error_handler() { return {}; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto error_handler() -> detail::error_handler { return {}; } void on_error(const char* message) { error_handler().on_error(message); } // Returns an iterator to the beginning of the output range. - iterator out() { return out_; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto out() -> iterator { return out_; } // Advances the begin iterator to ``it``. void advance_to(iterator it) { if (!detail::is_back_insert_iterator<iterator>()) out_ = it; } - detail::locale_ref locale() { return loc_; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto locale() -> detail::locale_ref { return loc_; } }; template <typename Char> using buffer_context = basic_format_context<detail::buffer_appender<Char>, Char>; using format_context = buffer_context<char>; -using wformat_context = buffer_context<wchar_t>; -// Workaround an alias issue: https://stackoverflow.com/q/62767544/471164. -#define FMT_BUFFER_CONTEXT(Char) \ - basic_format_context<detail::buffer_appender<Char>, Char> +template <typename T, typename Char = char> +using is_formattable = bool_constant<!std::is_base_of< + detail::unformattable, decltype(detail::arg_mapper<buffer_context<Char>>() + .map(std::declval<T&>()))>::value>; /** \rst @@ -1559,7 +1785,7 @@ class format_arg_store { private: static const size_t num_args = sizeof...(Args); - static const size_t num_named_args = detail::count_named_args<Args...>(); + static constexpr size_t num_named_args = detail::count_named_args<Args...>(); static const bool is_packed = num_args <= detail::max_packed_args; using value_type = conditional_t<is_packed, detail::value<Context>, @@ -1579,15 +1805,15 @@ class format_arg_store : 0); public: - format_arg_store(const Args&... args) + template <typename... T> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE format_arg_store(T&... args) : #if FMT_GCC_VERSION && FMT_GCC_VERSION < 409 basic_format_args<Context>(*this), #endif - data_{detail::make_arg< - is_packed, Context, - detail::mapped_type_constant<Args, Context>::value>(args)...} { - detail::init_named_args(data_.named_args(), 0, 0, args...); + data_{detail::make_arg<is_packed, Context>(args)...} { + if (detail::const_check(num_named_args != 0)) + detail::init_named_args(data_.named_args(), 0, 0, args...); } }; @@ -1595,41 +1821,22 @@ class format_arg_store \rst Constructs a `~fmt::format_arg_store` object that contains references to arguments and can be implicitly converted to `~fmt::format_args`. `Context` - can be omitted in which case it defaults to `~fmt::context`. + can be omitted in which case it defaults to `~fmt::format_context`. See `~fmt::arg` for lifetime considerations. \endrst */ -template <typename Context = format_context, typename... Args> -inline format_arg_store<Context, Args...> make_format_args( - const Args&... args) { - return {args...}; -} - -/** - \rst - Constructs a `~fmt::format_arg_store` object that contains references - to arguments and can be implicitly converted to `~fmt::format_args`. - If ``format_str`` is a compile-time string then `make_args_checked` checks - its validity at compile time. - \endrst - */ -template <typename... Args, typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline auto make_args_checked(const S& format_str, - const remove_reference_t<Args>&... args) - -> format_arg_store<buffer_context<Char>, remove_reference_t<Args>...> { - static_assert( - detail::count<( - std::is_base_of<detail::view, remove_reference_t<Args>>::value && - std::is_reference<Args>::value)...>() == 0, - "passing views as lvalues is disallowed"); - detail::check_format_string<Args...>(format_str); +// Arguments are taken by lvalue references to avoid some lifetime issues. +template <typename Context = format_context, typename... T> +constexpr auto make_format_args(T&... args) + -> format_arg_store<Context, remove_cvref_t<T>...> { return {args...}; } /** \rst - Returns a named argument to be used in a formatting function. It should only - be used in a call to a formatting function. + Returns a named argument to be used in a formatting function. + It should only be used in a call to a formatting function or + `dynamic_format_arg_store::push_back`. **Example**:: @@ -1637,183 +1844,11 @@ inline auto make_args_checked(const S& format_str, \endrst */ template <typename Char, typename T> -inline detail::named_arg<Char, T> arg(const Char* name, const T& arg) { +inline auto arg(const Char* name, const T& arg) -> detail::named_arg<Char, T> { static_assert(!detail::is_named_arg<T>(), "nested named arguments"); return {name, arg}; } - -/** - \rst - A dynamic version of `fmt::format_arg_store`. - It's equipped with a storage to potentially temporary objects which lifetimes - could be shorter than the format arguments object. - - It can be implicitly converted into `~fmt::basic_format_args` for passing - into type-erased formatting functions such as `~fmt::vformat`. - \endrst - */ -template <typename Context> -class dynamic_format_arg_store -#if FMT_GCC_VERSION && FMT_GCC_VERSION < 409 - // Workaround a GCC template argument substitution bug. - : public basic_format_args<Context> -#endif -{ - private: - using char_type = typename Context::char_type; - - template <typename T> struct need_copy { - static constexpr detail::type mapped_type = - detail::mapped_type_constant<T, Context>::value; - - enum { - value = !(detail::is_reference_wrapper<T>::value || - std::is_same<T, basic_string_view<char_type>>::value || - std::is_same<T, detail::std_string_view<char_type>>::value || - (mapped_type != detail::type::cstring_type && - mapped_type != detail::type::string_type && - mapped_type != detail::type::custom_type)) - }; - }; - - template <typename T> - using stored_type = conditional_t<detail::is_string<T>::value, - std::basic_string<char_type>, T>; - - // Storage of basic_format_arg must be contiguous. - std::vector<basic_format_arg<Context>> data_; - std::vector<detail::named_arg_info<char_type>> named_info_; - - // Storage of arguments not fitting into basic_format_arg must grow - // without relocation because items in data_ refer to it. - detail::dynamic_arg_list dynamic_args_; - - friend class basic_format_args<Context>; - - unsigned long long get_types() const { - return detail::is_unpacked_bit | data_.size() | - (named_info_.empty() - ? 0ULL - : static_cast<unsigned long long>(detail::has_named_args_bit)); - } - - const basic_format_arg<Context>* data() const { - return named_info_.empty() ? data_.data() : data_.data() + 1; - } - - template <typename T> void emplace_arg(const T& arg) { - data_.emplace_back(detail::make_arg<Context>(arg)); - } - - template <typename T> - void emplace_arg(const detail::named_arg<char_type, T>& arg) { - if (named_info_.empty()) { - constexpr const detail::named_arg_info<char_type>* zero_ptr{nullptr}; - data_.insert(data_.begin(), {zero_ptr, 0}); - } - data_.emplace_back(detail::make_arg<Context>(detail::unwrap(arg.value))); - auto pop_one = [](std::vector<basic_format_arg<Context>>* data) { - data->pop_back(); - }; - std::unique_ptr<std::vector<basic_format_arg<Context>>, decltype(pop_one)> - guard{&data_, pop_one}; - named_info_.push_back({arg.name, static_cast<int>(data_.size() - 2u)}); - data_[0].value_.named_args = {named_info_.data(), named_info_.size()}; - guard.release(); - } - - public: - /** - \rst - Adds an argument into the dynamic store for later passing to a formatting - function. - - Note that custom types and string types (but not string views) are copied - into the store dynamically allocating memory if necessary. - - **Example**:: - - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - store.push_back(42); - store.push_back("abc"); - store.push_back(1.5f); - std::string result = fmt::vformat("{} and {} and {}", store); - \endrst - */ - template <typename T> void push_back(const T& arg) { - if (detail::const_check(need_copy<T>::value)) - emplace_arg(dynamic_args_.push<stored_type<T>>(arg)); - else - emplace_arg(detail::unwrap(arg)); - } - - /** - \rst - Adds a reference to the argument into the dynamic store for later passing to - a formatting function. Supports named arguments wrapped in - ``std::reference_wrapper`` via ``std::ref()``/``std::cref()``. - - **Example**:: - - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - char str[] = "1234567890"; - store.push_back(std::cref(str)); - int a1_val{42}; - auto a1 = fmt::arg("a1_", a1_val); - store.push_back(std::cref(a1)); - - // Changing str affects the output but only for string and custom types. - str[0] = 'X'; - - std::string result = fmt::vformat("{} and {a1_}"); - assert(result == "X234567890 and 42"); - \endrst - */ - template <typename T> void push_back(std::reference_wrapper<T> arg) { - static_assert( - detail::is_named_arg<typename std::remove_cv<T>::type>::value || - need_copy<T>::value, - "objects of built-in types and string views are always copied"); - emplace_arg(arg.get()); - } - - /** - Adds named argument into the dynamic store for later passing to a formatting - function. ``std::reference_wrapper`` is supported to avoid copying of the - argument. - */ - template <typename T> - void push_back(const detail::named_arg<char_type, T>& arg) { - const char_type* arg_name = - dynamic_args_.push<std::basic_string<char_type>>(arg.name).c_str(); - if (detail::const_check(need_copy<T>::value)) { - emplace_arg( - fmt::arg(arg_name, dynamic_args_.push<stored_type<T>>(arg.value))); - } else { - emplace_arg(fmt::arg(arg_name, arg.value)); - } - } - - /** Erase all elements from the store */ - void clear() { - data_.clear(); - named_info_.clear(); - dynamic_args_ = detail::dynamic_arg_list(); - } - - /** - \rst - Reserves space to store at least *new_cap* arguments including - *new_cap_named* named arguments. - \endrst - */ - void reserve(size_t new_cap, size_t new_cap_named) { - FMT_ASSERT(new_cap >= new_cap_named, - "Set of arguments includes set of named arguments"); - data_.reserve(new_cap); - named_info_.reserve(new_cap_named); - } -}; +FMT_END_EXPORT /** \rst @@ -1822,7 +1857,7 @@ class dynamic_format_arg_store ``vformat``:: void vlog(string_view format_str, format_args args); // OK - format_args args = make_format_args(42); // Error: dangling reference + format_args args = make_format_args(); // Error: dangling reference \endrst */ template <typename Context> class basic_format_args { @@ -1846,25 +1881,27 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_args { const format_arg* args_; }; - bool is_packed() const { return (desc_ & detail::is_unpacked_bit) == 0; } - bool has_named_args() const { + constexpr auto is_packed() const -> bool { + return (desc_ & detail::is_unpacked_bit) == 0; + } + auto has_named_args() const -> bool { return (desc_ & detail::has_named_args_bit) != 0; } - detail::type type(int index) const { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto type(int index) const -> detail::type { int shift = index * detail::packed_arg_bits; unsigned int mask = (1 << detail::packed_arg_bits) - 1; return static_cast<detail::type>((desc_ >> shift) & mask); } - basic_format_args(unsigned long long desc, - const detail::value<Context>* values) + constexpr FMT_INLINE basic_format_args(unsigned long long desc, + const detail::value<Context>* values) : desc_(desc), values_(values) {} - basic_format_args(unsigned long long desc, const format_arg* args) + constexpr basic_format_args(unsigned long long desc, const format_arg* args) : desc_(desc), args_(args) {} public: - basic_format_args() : desc_(0) {} + constexpr basic_format_args() : desc_(0), args_(nullptr) {} /** \rst @@ -1872,8 +1909,10 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_args { \endrst */ template <typename... Args> - FMT_INLINE basic_format_args(const format_arg_store<Context, Args...>& store) - : basic_format_args(store.desc, store.data_.args()) {} + constexpr FMT_INLINE basic_format_args( + const format_arg_store<Context, Args...>& store) + : basic_format_args(format_arg_store<Context, Args...>::desc, + store.data_.args()) {} /** \rst @@ -1881,7 +1920,8 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_args { `~fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store`. \endrst */ - FMT_INLINE basic_format_args(const dynamic_format_arg_store<Context>& store) + constexpr FMT_INLINE basic_format_args( + const dynamic_format_arg_store<Context>& store) : basic_format_args(store.get_types(), store.data()) {} /** @@ -1889,12 +1929,12 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_args { Constructs a `basic_format_args` object from a dynamic set of arguments. \endrst */ - basic_format_args(const format_arg* args, int count) + constexpr basic_format_args(const format_arg* args, int count) : basic_format_args(detail::is_unpacked_bit | detail::to_unsigned(count), args) {} /** Returns the argument with the specified id. */ - format_arg get(int id) const { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get(int id) const -> format_arg { format_arg arg; if (!is_packed()) { if (id < max_size()) arg = args_[id]; @@ -1907,12 +1947,14 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_args { return arg; } - template <typename Char> format_arg get(basic_string_view<Char> name) const { + template <typename Char> + auto get(basic_string_view<Char> name) const -> format_arg { int id = get_id(name); return id >= 0 ? get(id) : format_arg(); } - template <typename Char> int get_id(basic_string_view<Char> name) const { + template <typename Char> + auto get_id(basic_string_view<Char> name) const -> int { if (!has_named_args()) return -1; const auto& named_args = (is_packed() ? values_[-1] : args_[-1].value_).named_args; @@ -1922,49 +1964,732 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_args { return -1; } - int max_size() const { + auto max_size() const -> int { unsigned long long max_packed = detail::max_packed_args; return static_cast<int>(is_packed() ? max_packed : desc_ & ~detail::is_unpacked_bit); } }; -#ifdef FMT_ARM_ABI_COMPATIBILITY /** An alias to ``basic_format_args<format_context>``. */ -// Separate types would result in shorter symbols but break ABI compatibility +// A separate type would result in shorter symbols but break ABI compatibility // between clang and gcc on ARM (#1919). -using format_args = basic_format_args<format_context>; -using wformat_args = basic_format_args<wformat_context>; +FMT_EXPORT using format_args = basic_format_args<format_context>; + +// We cannot use enum classes as bit fields because of a gcc bug, so we put them +// in namespaces instead (https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=61414). +// Additionally, if an underlying type is specified, older gcc incorrectly warns +// that the type is too small. Both bugs are fixed in gcc 9.3. +#if FMT_GCC_VERSION && FMT_GCC_VERSION < 903 +# define FMT_ENUM_UNDERLYING_TYPE(type) #else -// DEPRECATED! These are kept for ABI compatibility. -// It is a separate type rather than an alias to make symbols readable. -struct format_args : basic_format_args<format_context> { - template <typename... Args> - FMT_INLINE format_args(const Args&... args) : basic_format_args(args...) {} +# define FMT_ENUM_UNDERLYING_TYPE(type) : type +#endif +namespace align { +enum type FMT_ENUM_UNDERLYING_TYPE(unsigned char){none, left, right, center, + numeric}; +} +using align_t = align::type; +namespace sign { +enum type FMT_ENUM_UNDERLYING_TYPE(unsigned char){none, minus, plus, space}; +} +using sign_t = sign::type; + +namespace detail { + +// Workaround an array initialization issue in gcc 4.8. +template <typename Char> struct fill_t { + private: + enum { max_size = 4 }; + Char data_[max_size] = {Char(' '), Char(0), Char(0), Char(0)}; + unsigned char size_ = 1; + + public: + FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator=(basic_string_view<Char> s) { + auto size = s.size(); + FMT_ASSERT(size <= max_size, "invalid fill"); + for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i) data_[i] = s[i]; + size_ = static_cast<unsigned char>(size); + } + + constexpr auto size() const -> size_t { return size_; } + constexpr auto data() const -> const Char* { return data_; } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator[](size_t index) -> Char& { return data_[index]; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator[](size_t index) const -> const Char& { + return data_[index]; + } }; -struct wformat_args : basic_format_args<wformat_context> { - using basic_format_args::basic_format_args; +} // namespace detail + +enum class presentation_type : unsigned char { + none, + dec, // 'd' + oct, // 'o' + hex_lower, // 'x' + hex_upper, // 'X' + bin_lower, // 'b' + bin_upper, // 'B' + hexfloat_lower, // 'a' + hexfloat_upper, // 'A' + exp_lower, // 'e' + exp_upper, // 'E' + fixed_lower, // 'f' + fixed_upper, // 'F' + general_lower, // 'g' + general_upper, // 'G' + chr, // 'c' + string, // 's' + pointer, // 'p' + debug // '?' +}; + +// Format specifiers for built-in and string types. +template <typename Char = char> struct format_specs { + int width; + int precision; + presentation_type type; + align_t align : 4; + sign_t sign : 3; + bool alt : 1; // Alternate form ('#'). + bool localized : 1; + detail::fill_t<Char> fill; + + constexpr format_specs() + : width(0), + precision(-1), + type(presentation_type::none), + align(align::none), + sign(sign::none), + alt(false), + localized(false) {} }; -#endif namespace detail { -template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value)> -std::basic_string<Char> vformat( - basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args); +enum class arg_id_kind { none, index, name }; + +// An argument reference. +template <typename Char> struct arg_ref { + FMT_CONSTEXPR arg_ref() : kind(arg_id_kind::none), val() {} + + FMT_CONSTEXPR explicit arg_ref(int index) + : kind(arg_id_kind::index), val(index) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR explicit arg_ref(basic_string_view<Char> name) + : kind(arg_id_kind::name), val(name) {} + + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator=(int idx) -> arg_ref& { + kind = arg_id_kind::index; + val.index = idx; + return *this; + } + + arg_id_kind kind; + union value { + FMT_CONSTEXPR value(int idx = 0) : index(idx) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR value(basic_string_view<Char> n) : name(n) {} + + int index; + basic_string_view<Char> name; + } val; +}; + +// Format specifiers with width and precision resolved at formatting rather +// than parsing time to allow reusing the same parsed specifiers with +// different sets of arguments (precompilation of format strings). +template <typename Char = char> +struct dynamic_format_specs : format_specs<Char> { + arg_ref<Char> width_ref; + arg_ref<Char> precision_ref; +}; + +// Converts a character to ASCII. Returns '\0' on conversion failure. +template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<Char>::value)> +constexpr auto to_ascii(Char c) -> char { + return c <= 0xff ? static_cast<char>(c) : '\0'; +} +template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_enum<Char>::value)> +constexpr auto to_ascii(Char c) -> char { + return c <= 0xff ? static_cast<char>(c) : '\0'; +} + +// Returns the number of code units in a code point or 1 on error. +template <typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto code_point_length(const Char* begin) -> int { + if (const_check(sizeof(Char) != 1)) return 1; + auto c = static_cast<unsigned char>(*begin); + return static_cast<int>((0x3a55000000000000ull >> (2 * (c >> 3))) & 0x3) + 1; +} + +// Return the result via the out param to workaround gcc bug 77539. +template <bool IS_CONSTEXPR, typename T, typename Ptr = const T*> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto find(Ptr first, Ptr last, T value, Ptr& out) -> bool { + for (out = first; out != last; ++out) { + if (*out == value) return true; + } + return false; +} + +template <> +inline auto find<false, char>(const char* first, const char* last, char value, + const char*& out) -> bool { + out = static_cast<const char*>( + std::memchr(first, value, to_unsigned(last - first))); + return out != nullptr; +} + +// Parses the range [begin, end) as an unsigned integer. This function assumes +// that the range is non-empty and the first character is a digit. +template <typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_nonnegative_int(const Char*& begin, const Char* end, + int error_value) noexcept -> int { + FMT_ASSERT(begin != end && '0' <= *begin && *begin <= '9', ""); + unsigned value = 0, prev = 0; + auto p = begin; + do { + prev = value; + value = value * 10 + unsigned(*p - '0'); + ++p; + } while (p != end && '0' <= *p && *p <= '9'); + auto num_digits = p - begin; + begin = p; + if (num_digits <= std::numeric_limits<int>::digits10) + return static_cast<int>(value); + // Check for overflow. + const unsigned max = to_unsigned((std::numeric_limits<int>::max)()); + return num_digits == std::numeric_limits<int>::digits10 + 1 && + prev * 10ull + unsigned(p[-1] - '0') <= max + ? static_cast<int>(value) + : error_value; +} + +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto parse_align(char c) -> align_t { + switch (c) { + case '<': + return align::left; + case '>': + return align::right; + case '^': + return align::center; + } + return align::none; +} + +template <typename Char> constexpr auto is_name_start(Char c) -> bool { + return ('a' <= c && c <= 'z') || ('A' <= c && c <= 'Z') || c == '_'; +} + +template <typename Char, typename Handler> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto do_parse_arg_id(const Char* begin, const Char* end, + Handler&& handler) -> const Char* { + Char c = *begin; + if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') { + int index = 0; + constexpr int max = (std::numeric_limits<int>::max)(); + if (c != '0') + index = parse_nonnegative_int(begin, end, max); + else + ++begin; + if (begin == end || (*begin != '}' && *begin != ':')) + throw_format_error("invalid format string"); + else + handler.on_index(index); + return begin; + } + if (!is_name_start(c)) { + throw_format_error("invalid format string"); + return begin; + } + auto it = begin; + do { + ++it; + } while (it != end && (is_name_start(*it) || ('0' <= *it && *it <= '9'))); + handler.on_name({begin, to_unsigned(it - begin)}); + return it; +} + +template <typename Char, typename Handler> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto parse_arg_id(const Char* begin, const Char* end, + Handler&& handler) -> const Char* { + FMT_ASSERT(begin != end, ""); + Char c = *begin; + if (c != '}' && c != ':') return do_parse_arg_id(begin, end, handler); + handler.on_auto(); + return begin; +} + +template <typename Char> struct dynamic_spec_id_handler { + basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx; + arg_ref<Char>& ref; + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_auto() { + int id = ctx.next_arg_id(); + ref = arg_ref<Char>(id); + ctx.check_dynamic_spec(id); + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_index(int id) { + ref = arg_ref<Char>(id); + ctx.check_arg_id(id); + ctx.check_dynamic_spec(id); + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_name(basic_string_view<Char> id) { + ref = arg_ref<Char>(id); + ctx.check_arg_id(id); + } +}; + +// Parses [integer | "{" [arg_id] "}"]. +template <typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_dynamic_spec(const Char* begin, const Char* end, + int& value, arg_ref<Char>& ref, + basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx) + -> const Char* { + FMT_ASSERT(begin != end, ""); + if ('0' <= *begin && *begin <= '9') { + int val = parse_nonnegative_int(begin, end, -1); + if (val != -1) + value = val; + else + throw_format_error("number is too big"); + } else if (*begin == '{') { + ++begin; + auto handler = dynamic_spec_id_handler<Char>{ctx, ref}; + if (begin != end) begin = parse_arg_id(begin, end, handler); + if (begin != end && *begin == '}') return ++begin; + throw_format_error("invalid format string"); + } + return begin; +} + +template <typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_precision(const Char* begin, const Char* end, + int& value, arg_ref<Char>& ref, + basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx) + -> const Char* { + ++begin; + if (begin == end || *begin == '}') { + throw_format_error("invalid precision"); + return begin; + } + return parse_dynamic_spec(begin, end, value, ref, ctx); +} + +enum class state { start, align, sign, hash, zero, width, precision, locale }; + +// Parses standard format specifiers. +template <typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto parse_format_specs( + const Char* begin, const Char* end, dynamic_format_specs<Char>& specs, + basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx, type arg_type) -> const Char* { + auto c = '\0'; + if (end - begin > 1) { + auto next = to_ascii(begin[1]); + c = parse_align(next) == align::none ? to_ascii(*begin) : '\0'; + } else { + if (begin == end) return begin; + c = to_ascii(*begin); + } + + struct { + state current_state = state::start; + FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(state s, bool valid = true) { + if (current_state >= s || !valid) + throw_format_error("invalid format specifier"); + current_state = s; + } + } enter_state; + + using pres = presentation_type; + constexpr auto integral_set = sint_set | uint_set | bool_set | char_set; + struct { + const Char*& begin; + dynamic_format_specs<Char>& specs; + type arg_type; + + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(pres pres_type, int set) -> const Char* { + if (!in(arg_type, set)) { + if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin; + throw_format_error("invalid format specifier"); + } + specs.type = pres_type; + return begin + 1; + } + } parse_presentation_type{begin, specs, arg_type}; + + for (;;) { + switch (c) { + case '<': + case '>': + case '^': + enter_state(state::align); + specs.align = parse_align(c); + ++begin; + break; + case '+': + case '-': + case ' ': + if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin; + enter_state(state::sign, in(arg_type, sint_set | float_set)); + switch (c) { + case '+': + specs.sign = sign::plus; + break; + case '-': + specs.sign = sign::minus; + break; + case ' ': + specs.sign = sign::space; + break; + } + ++begin; + break; + case '#': + if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin; + enter_state(state::hash, is_arithmetic_type(arg_type)); + specs.alt = true; + ++begin; + break; + case '0': + enter_state(state::zero); + if (!is_arithmetic_type(arg_type)) { + if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin; + throw_format_error("format specifier requires numeric argument"); + } + if (specs.align == align::none) { + // Ignore 0 if align is specified for compatibility with std::format. + specs.align = align::numeric; + specs.fill[0] = Char('0'); + } + ++begin; + break; + case '1': + case '2': + case '3': + case '4': + case '5': + case '6': + case '7': + case '8': + case '9': + case '{': + enter_state(state::width); + begin = parse_dynamic_spec(begin, end, specs.width, specs.width_ref, ctx); + break; + case '.': + if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin; + enter_state(state::precision, + in(arg_type, float_set | string_set | cstring_set)); + begin = parse_precision(begin, end, specs.precision, specs.precision_ref, + ctx); + break; + case 'L': + if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin; + enter_state(state::locale, is_arithmetic_type(arg_type)); + specs.localized = true; + ++begin; + break; + case 'd': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::dec, integral_set); + case 'o': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::oct, integral_set); + case 'x': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::hex_lower, integral_set); + case 'X': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::hex_upper, integral_set); + case 'b': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::bin_lower, integral_set); + case 'B': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::bin_upper, integral_set); + case 'a': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::hexfloat_lower, float_set); + case 'A': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::hexfloat_upper, float_set); + case 'e': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::exp_lower, float_set); + case 'E': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::exp_upper, float_set); + case 'f': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::fixed_lower, float_set); + case 'F': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::fixed_upper, float_set); + case 'g': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::general_lower, float_set); + case 'G': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::general_upper, float_set); + case 'c': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::chr, integral_set); + case 's': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::string, + bool_set | string_set | cstring_set); + case 'p': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::pointer, pointer_set | cstring_set); + case '?': + return parse_presentation_type(pres::debug, + char_set | string_set | cstring_set); + case '}': + return begin; + default: { + if (*begin == '}') return begin; + // Parse fill and alignment. + auto fill_end = begin + code_point_length(begin); + if (end - fill_end <= 0) { + throw_format_error("invalid format specifier"); + return begin; + } + if (*begin == '{') { + throw_format_error("invalid fill character '{'"); + return begin; + } + auto align = parse_align(to_ascii(*fill_end)); + enter_state(state::align, align != align::none); + specs.fill = {begin, to_unsigned(fill_end - begin)}; + specs.align = align; + begin = fill_end + 1; + } + } + if (begin == end) return begin; + c = to_ascii(*begin); + } +} + +template <typename Char, typename Handler> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_replacement_field(const Char* begin, const Char* end, + Handler&& handler) -> const Char* { + struct id_adapter { + Handler& handler; + int arg_id; + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_auto() { arg_id = handler.on_arg_id(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_index(int id) { arg_id = handler.on_arg_id(id); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_name(basic_string_view<Char> id) { + arg_id = handler.on_arg_id(id); + } + }; + + ++begin; + if (begin == end) return handler.on_error("invalid format string"), end; + if (*begin == '}') { + handler.on_replacement_field(handler.on_arg_id(), begin); + } else if (*begin == '{') { + handler.on_text(begin, begin + 1); + } else { + auto adapter = id_adapter{handler, 0}; + begin = parse_arg_id(begin, end, adapter); + Char c = begin != end ? *begin : Char(); + if (c == '}') { + handler.on_replacement_field(adapter.arg_id, begin); + } else if (c == ':') { + begin = handler.on_format_specs(adapter.arg_id, begin + 1, end); + if (begin == end || *begin != '}') + return handler.on_error("unknown format specifier"), end; + } else { + return handler.on_error("missing '}' in format string"), end; + } + } + return begin + 1; +} + +template <bool IS_CONSTEXPR, typename Char, typename Handler> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE void parse_format_string( + basic_string_view<Char> format_str, Handler&& handler) { + auto begin = format_str.data(); + auto end = begin + format_str.size(); + if (end - begin < 32) { + // Use a simple loop instead of memchr for small strings. + const Char* p = begin; + while (p != end) { + auto c = *p++; + if (c == '{') { + handler.on_text(begin, p - 1); + begin = p = parse_replacement_field(p - 1, end, handler); + } else if (c == '}') { + if (p == end || *p != '}') + return handler.on_error("unmatched '}' in format string"); + handler.on_text(begin, p); + begin = ++p; + } + } + handler.on_text(begin, end); + return; + } + struct writer { + FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(const Char* from, const Char* to) { + if (from == to) return; + for (;;) { + const Char* p = nullptr; + if (!find<IS_CONSTEXPR>(from, to, Char('}'), p)) + return handler_.on_text(from, to); + ++p; + if (p == to || *p != '}') + return handler_.on_error("unmatched '}' in format string"); + handler_.on_text(from, p); + from = p + 1; + } + } + Handler& handler_; + } write = {handler}; + while (begin != end) { + // Doing two passes with memchr (one for '{' and another for '}') is up to + // 2.5x faster than the naive one-pass implementation on big format strings. + const Char* p = begin; + if (*begin != '{' && !find<IS_CONSTEXPR>(begin + 1, end, Char('{'), p)) + return write(begin, end); + write(begin, p); + begin = parse_replacement_field(p, end, handler); + } +} -FMT_API std::string vformat(string_view format_str, format_args args); +template <typename T, bool = is_named_arg<T>::value> struct strip_named_arg { + using type = T; +}; +template <typename T> struct strip_named_arg<T, true> { + using type = remove_cvref_t<decltype(T::value)>; +}; +template <typename T, typename ParseContext> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_format_specs(ParseContext& ctx) + -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + using char_type = typename ParseContext::char_type; + using context = buffer_context<char_type>; + using mapped_type = conditional_t< + mapped_type_constant<T, context>::value != type::custom_type, + decltype(arg_mapper<context>().map(std::declval<const T&>())), + typename strip_named_arg<T>::type>; +#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) + if constexpr (std::is_default_constructible< + formatter<mapped_type, char_type>>::value) { + return formatter<mapped_type, char_type>().parse(ctx); + } else { + type_is_unformattable_for<T, char_type> _; + return ctx.begin(); + } +#else + return formatter<mapped_type, char_type>().parse(ctx); +#endif +} + +// Checks char specs and returns true iff the presentation type is char-like. template <typename Char> -void vformat_to( - buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - basic_format_args<FMT_BUFFER_CONTEXT(type_identity_t<Char>)> args, - detail::locale_ref loc = {}); +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto check_char_specs(const format_specs<Char>& specs) -> bool { + if (specs.type != presentation_type::none && + specs.type != presentation_type::chr && + specs.type != presentation_type::debug) { + return false; + } + if (specs.align == align::numeric || specs.sign != sign::none || specs.alt) + throw_format_error("invalid format specifier for char"); + return true; +} -template <typename Char, typename Args, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value)> -inline void vprint_mojibake(std::FILE*, basic_string_view<Char>, const Args&) {} +#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS +template <int N, typename T, typename... Args, typename Char> +constexpr auto get_arg_index_by_name(basic_string_view<Char> name) -> int { + if constexpr (is_statically_named_arg<T>()) { + if (name == T::name) return N; + } + if constexpr (sizeof...(Args) > 0) + return get_arg_index_by_name<N + 1, Args...>(name); + (void)name; // Workaround an MSVC bug about "unused" parameter. + return -1; +} +#endif + +template <typename... Args, typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_arg_index_by_name(basic_string_view<Char> name) -> int { +#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS + if constexpr (sizeof...(Args) > 0) + return get_arg_index_by_name<0, Args...>(name); +#endif + (void)name; + return -1; +} + +template <typename Char, typename... Args> class format_string_checker { + private: + using parse_context_type = compile_parse_context<Char>; + static constexpr int num_args = sizeof...(Args); + + // Format specifier parsing function. + // In the future basic_format_parse_context will replace compile_parse_context + // here and will use is_constant_evaluated and downcasting to access the data + // needed for compile-time checks: https://godbolt.org/z/GvWzcTjh1. + using parse_func = const Char* (*)(parse_context_type&); + + type types_[num_args > 0 ? static_cast<size_t>(num_args) : 1]; + parse_context_type context_; + parse_func parse_funcs_[num_args > 0 ? static_cast<size_t>(num_args) : 1]; + + public: + explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR format_string_checker(basic_string_view<Char> fmt) + : types_{mapped_type_constant<Args, buffer_context<Char>>::value...}, + context_(fmt, num_args, types_), + parse_funcs_{&parse_format_specs<Args, parse_context_type>...} {} + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const Char*, const Char*) {} + + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id() -> int { return context_.next_arg_id(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id(int id) -> int { + return context_.check_arg_id(id), id; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id(basic_string_view<Char> id) -> int { +#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS + auto index = get_arg_index_by_name<Args...>(id); + if (index < 0) on_error("named argument is not found"); + return index; +#else + (void)id; + on_error("compile-time checks for named arguments require C++20 support"); + return 0; +#endif + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_replacement_field(int id, const Char* begin) { + on_format_specs(id, begin, begin); // Call parse() on empty specs. + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_format_specs(int id, const Char* begin, const Char*) + -> const Char* { + context_.advance_to(begin); + // id >= 0 check is a workaround for gcc 10 bug (#2065). + return id >= 0 && id < num_args ? parse_funcs_[id](context_) : begin; + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { + throw_format_error(message); + } +}; + +// Reports a compile-time error if S is not a valid format string. +template <typename..., typename S, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_compile_string<S>::value)> +FMT_INLINE void check_format_string(const S&) { +#ifdef FMT_ENFORCE_COMPILE_STRING + static_assert(is_compile_string<S>::value, + "FMT_ENFORCE_COMPILE_STRING requires all format strings to use " + "FMT_STRING."); +#endif +} +template <typename... Args, typename S, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_compile_string<S>::value)> +void check_format_string(S format_str) { + using char_t = typename S::char_type; + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto s = basic_string_view<char_t>(format_str); + using checker = format_string_checker<char_t, remove_cvref_t<Args>...>; + FMT_CONSTEXPR bool error = (parse_format_string<true>(s, checker(s)), true); + ignore_unused(error); +} + +template <typename Char = char> struct vformat_args { + using type = basic_format_args< + basic_format_context<std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<Char>>, Char>>; +}; +template <> struct vformat_args<char> { + using type = format_args; +}; + +// Use vformat_args and avoid type_identity to keep symbols short. +template <typename Char> +void vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> fmt, + typename vformat_args<Char>::type args, locale_ref loc = {}); FMT_API void vprint_mojibake(std::FILE*, string_view, format_args); #ifndef _WIN32 @@ -1972,37 +2697,140 @@ inline void vprint_mojibake(std::FILE*, string_view, format_args) {} #endif } // namespace detail +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT + +// A formatter specialization for natively supported types. +template <typename T, typename Char> +struct formatter<T, Char, + enable_if_t<detail::type_constant<T, Char>::value != + detail::type::custom_type>> { + private: + detail::dynamic_format_specs<Char> specs_; + + public: + template <typename ParseContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> const Char* { + auto type = detail::type_constant<T, Char>::value; + auto end = + detail::parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), specs_, ctx, type); + if (type == detail::type::char_type) detail::check_char_specs(specs_); + return end; + } + + template <detail::type U = detail::type_constant<T, Char>::value, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(U == detail::type::string_type || + U == detail::type::cstring_type || + U == detail::type::char_type)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_debug_format(bool set = true) { + specs_.type = set ? presentation_type::debug : presentation_type::none; + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto format(const T& val, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()); +}; + +template <typename Char = char> struct runtime_format_string { + basic_string_view<Char> str; +}; + +/** A compile-time format string. */ +template <typename Char, typename... Args> class basic_format_string { + private: + basic_string_view<Char> str_; + + public: + template <typename S, + FMT_ENABLE_IF( + std::is_convertible<const S&, basic_string_view<Char>>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEVAL FMT_INLINE basic_format_string(const S& s) : str_(s) { + static_assert( + detail::count< + (std::is_base_of<detail::view, remove_reference_t<Args>>::value && + std::is_reference<Args>::value)...>() == 0, + "passing views as lvalues is disallowed"); +#ifdef FMT_HAS_CONSTEVAL + if constexpr (detail::count_named_args<Args...>() == + detail::count_statically_named_args<Args...>()) { + using checker = + detail::format_string_checker<Char, remove_cvref_t<Args>...>; + detail::parse_format_string<true>(str_, checker(s)); + } +#else + detail::check_format_string<Args...>(s); +#endif + } + basic_format_string(runtime_format_string<Char> fmt) : str_(fmt.str) {} + + FMT_INLINE operator basic_string_view<Char>() const { return str_; } + FMT_INLINE auto get() const -> basic_string_view<Char> { return str_; } +}; + +#if FMT_GCC_VERSION && FMT_GCC_VERSION < 409 +// Workaround broken conversion on older gcc. +template <typename...> using format_string = string_view; +inline auto runtime(string_view s) -> string_view { return s; } +#else +template <typename... Args> +using format_string = basic_format_string<char, type_identity_t<Args>...>; +/** + \rst + Creates a runtime format string. + + **Example**:: + + // Check format string at runtime instead of compile-time. + fmt::print(fmt::runtime("{:d}"), "I am not a number"); + \endrst + */ +inline auto runtime(string_view s) -> runtime_format_string<> { return {{s}}; } +#endif + +FMT_API auto vformat(string_view fmt, format_args args) -> std::string; + +/** + \rst + Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``fmt`` and returns the result + as a string. + + **Example**:: + + #include <fmt/core.h> + std::string message = fmt::format("The answer is {}.", 42); + \endrst +*/ +template <typename... T> +FMT_NODISCARD FMT_INLINE auto format(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) + -> std::string { + return vformat(fmt, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); +} + /** Formats a string and writes the output to ``out``. */ -// GCC 8 and earlier cannot handle std::back_insert_iterator<Container> with -// vformat_to<ArgFormatter>(...) overload, so SFINAE on iterator type instead. -template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>, - bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value> -auto vformat_to(OutputIt out, const S& format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) - -> typename std::enable_if<enable, OutputIt>::type { - decltype(detail::get_buffer<Char>(out)) buf(detail::get_buffer_init(out)); - detail::vformat_to(buf, to_string_view(format_str), args); - return detail::get_iterator(buf); +template <typename OutputIt, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char>::value)> +auto vformat_to(OutputIt out, string_view fmt, format_args args) -> OutputIt { + auto&& buf = detail::get_buffer<char>(out); + detail::vformat_to(buf, fmt, args, {}); + return detail::get_iterator(buf, out); } /** \rst - Formats arguments, writes the result to the output iterator ``out`` and returns - the iterator past the end of the output range. + Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``fmt``, writes the result to + the output iterator ``out`` and returns the iterator past the end of the output + range. `format_to` does not append a terminating null character. **Example**:: - std::vector<char> out; + auto out = std::vector<char>(); fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), "{}", 42); \endrst */ -// We cannot use FMT_ENABLE_IF because of a bug in gcc 8.3. -template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args, - bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char_t<S>>::value> -inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const S& format_str, Args&&... args) -> - typename std::enable_if<enable, OutputIt>::type { - const auto& vargs = fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...); - return vformat_to(out, to_string_view(format_str), vargs); +template <typename OutputIt, typename... T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char>::value)> +FMT_INLINE auto format_to(OutputIt out, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) + -> OutputIt { + return vformat_to(out, fmt, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); } template <typename OutputIt> struct format_to_n_result { @@ -2012,111 +2840,100 @@ template <typename OutputIt> struct format_to_n_result { size_t size; }; -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename... Args, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value)> -inline format_to_n_result<OutputIt> vformat_to_n( - OutputIt out, size_t n, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - detail::iterator_buffer<OutputIt, Char, detail::fixed_buffer_traits> buf(out, - n); - detail::vformat_to(buf, format_str, args); +template <typename OutputIt, typename... T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char>::value)> +auto vformat_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, string_view fmt, format_args args) + -> format_to_n_result<OutputIt> { + using traits = detail::fixed_buffer_traits; + auto buf = detail::iterator_buffer<OutputIt, char, traits>(out, n); + detail::vformat_to(buf, fmt, args, {}); return {buf.out(), buf.count()}; } /** - \rst - Formats arguments, writes up to ``n`` characters of the result to the output - iterator ``out`` and returns the total output size and the iterator past the - end of the output range. - \endrst + \rst + Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``fmt``, writes up to ``n`` + characters of the result to the output iterator ``out`` and returns the total + (not truncated) output size and the iterator past the end of the output range. + `format_to_n` does not append a terminating null character. + \endrst */ -template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args, - bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char_t<S>>::value> -inline auto format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, const S& format_str, - const Args&... args) -> - typename std::enable_if<enable, format_to_n_result<OutputIt>>::type { - const auto& vargs = fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...); - return vformat_to_n(out, n, to_string_view(format_str), vargs); +template <typename OutputIt, typename... T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char>::value)> +FMT_INLINE auto format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, format_string<T...> fmt, + T&&... args) -> format_to_n_result<OutputIt> { + return vformat_to_n(out, n, fmt, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); } -/** - Returns the number of characters in the output of - ``format(format_str, args...)``. - */ -template <typename... Args> -inline size_t formatted_size(string_view format_str, Args&&... args) { - const auto& vargs = fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...); - detail::counting_buffer<> buf; - detail::vformat_to(buf, format_str, vargs); +/** Returns the number of chars in the output of ``format(fmt, args...)``. */ +template <typename... T> +FMT_NODISCARD FMT_INLINE auto formatted_size(format_string<T...> fmt, + T&&... args) -> size_t { + auto buf = detail::counting_buffer<>(); + detail::vformat_to<char>(buf, fmt, fmt::make_format_args(args...), {}); return buf.count(); } -template <typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>> -FMT_INLINE std::basic_string<Char> vformat( - const S& format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - return detail::vformat(to_string_view(format_str), args); -} +FMT_API void vprint(string_view fmt, format_args args); +FMT_API void vprint(std::FILE* f, string_view fmt, format_args args); /** \rst - Formats arguments and returns the result as a string. + Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``fmt`` and writes the output + to ``stdout``. **Example**:: - #include <fmt/core.h> - std::string message = fmt::format("The answer is {}", 42); + fmt::print("Elapsed time: {0:.2f} seconds", 1.23); \endrst -*/ -// Pass char_t as a default template parameter instead of using -// std::basic_string<char_t<S>> to reduce the symbol size. -template <typename S, typename... Args, typename Char = char_t<S>> -FMT_INLINE std::basic_string<Char> format(const S& format_str, Args&&... args) { - const auto& vargs = fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...); - return detail::vformat(to_string_view(format_str), vargs); + */ +template <typename... T> +FMT_INLINE void print(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + const auto& vargs = fmt::make_format_args(args...); + return detail::is_utf8() ? vprint(fmt, vargs) + : detail::vprint_mojibake(stdout, fmt, vargs); } -FMT_API void vprint(string_view, format_args); -FMT_API void vprint(std::FILE*, string_view, format_args); - /** \rst - Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``format_str`` and writes the - output to the file ``f``. Strings are assumed to be Unicode-encoded unless the - ``FMT_UNICODE`` macro is set to 0. + Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``fmt`` and writes the + output to the file ``f``. **Example**:: fmt::print(stderr, "Don't {}!", "panic"); \endrst */ -template <typename S, typename... Args, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline void print(std::FILE* f, const S& format_str, Args&&... args) { - const auto& vargs = fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...); - return detail::is_unicode<Char>() - ? vprint(f, to_string_view(format_str), vargs) - : detail::vprint_mojibake(f, to_string_view(format_str), vargs); +template <typename... T> +FMT_INLINE void print(std::FILE* f, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + const auto& vargs = fmt::make_format_args(args...); + return detail::is_utf8() ? vprint(f, fmt, vargs) + : detail::vprint_mojibake(f, fmt, vargs); } /** - \rst - Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``format_str`` and writes - the output to ``stdout``. Strings are assumed to be Unicode-encoded unless - the ``FMT_UNICODE`` macro is set to 0. - - **Example**:: + Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``fmt`` and writes the + output to the file ``f`` followed by a newline. + */ +template <typename... T> +FMT_INLINE void println(std::FILE* f, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + return fmt::print(f, "{}\n", fmt::format(fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...)); +} - fmt::print("Elapsed time: {0:.2f} seconds", 1.23); - \endrst +/** + Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``fmt`` and writes the output + to ``stdout`` followed by a newline. */ -template <typename S, typename... Args, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline void print(const S& format_str, Args&&... args) { - const auto& vargs = fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...); - return detail::is_unicode<Char>() - ? vprint(to_string_view(format_str), vargs) - : detail::vprint_mojibake(stdout, to_string_view(format_str), - vargs); +template <typename... T> +FMT_INLINE void println(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + return fmt::println(stdout, fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...); } + +FMT_END_EXPORT +FMT_GCC_PRAGMA("GCC pop_options") FMT_END_NAMESPACE +#ifdef FMT_HEADER_ONLY +# include "format.h" +#endif #endif // FMT_CORE_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/format-inl.h b/include/fmt/format-inl.h index 8f2fe735..5f8c83a2 100644 --- a/include/fmt/format-inl.h +++ b/include/fmt/format-inl.h @@ -8,30 +8,22 @@ #ifndef FMT_FORMAT_INL_H_ #define FMT_FORMAT_INL_H_ -#include <cassert> -#include <cctype> +#include <algorithm> +#include <cerrno> // errno #include <climits> #include <cmath> -#include <cstdarg> -#include <cstring> // std::memmove -#include <cwchar> #include <exception> #ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR # include <locale> #endif -#ifdef _WIN32 +#if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(FMT_WINDOWS_NO_WCHAR) # include <io.h> // _isatty #endif #include "format.h" -// Dummy implementations of strerror_r and strerror_s called if corresponding -// system functions are not available. -inline fmt::detail::null<> strerror_r(int, char*, ...) { return {}; } -inline fmt::detail::null<> strerror_s(char*, size_t, ...) { return {}; } - FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE namespace detail { @@ -44,91 +36,12 @@ FMT_FUNC void assert_fail(const char* file, int line, const char* message) { std::terminate(); } -#ifndef _MSC_VER -# define FMT_SNPRINTF snprintf -#else // _MSC_VER -inline int fmt_snprintf(char* buffer, size_t size, const char* format, ...) { - va_list args; - va_start(args, format); - int result = vsnprintf_s(buffer, size, _TRUNCATE, format, args); - va_end(args); - return result; -} -# define FMT_SNPRINTF fmt_snprintf -#endif // _MSC_VER - -// A portable thread-safe version of strerror. -// Sets buffer to point to a string describing the error code. -// This can be either a pointer to a string stored in buffer, -// or a pointer to some static immutable string. -// Returns one of the following values: -// 0 - success -// ERANGE - buffer is not large enough to store the error message -// other - failure -// Buffer should be at least of size 1. -inline int safe_strerror(int error_code, char*& buffer, - size_t buffer_size) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(buffer != nullptr && buffer_size != 0, "invalid buffer"); - - class dispatcher { - private: - int error_code_; - char*& buffer_; - size_t buffer_size_; - - // A noop assignment operator to avoid bogus warnings. - void operator=(const dispatcher&) {} - - // Handle the result of XSI-compliant version of strerror_r. - int handle(int result) { - // glibc versions before 2.13 return result in errno. - return result == -1 ? errno : result; - } - - // Handle the result of GNU-specific version of strerror_r. - FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED - int handle(char* message) { - // If the buffer is full then the message is probably truncated. - if (message == buffer_ && strlen(buffer_) == buffer_size_ - 1) - return ERANGE; - buffer_ = message; - return 0; - } - - // Handle the case when strerror_r is not available. - FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED - int handle(detail::null<>) { - return fallback(strerror_s(buffer_, buffer_size_, error_code_)); - } - - // Fallback to strerror_s when strerror_r is not available. - FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED - int fallback(int result) { - // If the buffer is full then the message is probably truncated. - return result == 0 && strlen(buffer_) == buffer_size_ - 1 ? ERANGE - : result; - } - -#if !FMT_MSC_VER - // Fallback to strerror if strerror_r and strerror_s are not available. - int fallback(detail::null<>) { - errno = 0; - buffer_ = strerror(error_code_); - return errno; - } -#endif - - public: - dispatcher(int err_code, char*& buf, size_t buf_size) - : error_code_(err_code), buffer_(buf), buffer_size_(buf_size) {} - - int run() { return handle(strerror_r(error_code_, buffer_, buffer_size_)); } - }; - return dispatcher(error_code, buffer, buffer_size).run(); +FMT_FUNC void throw_format_error(const char* message) { + FMT_THROW(format_error(message)); } FMT_FUNC void format_error_code(detail::buffer<char>& out, int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + string_view message) noexcept { // Report error code making sure that the output fits into // inline_buffer_size to avoid dynamic memory allocation and potential // bad_alloc. @@ -145,31 +58,28 @@ FMT_FUNC void format_error_code(detail::buffer<char>& out, int error_code, error_code_size += detail::to_unsigned(detail::count_digits(abs_value)); auto it = buffer_appender<char>(out); if (message.size() <= inline_buffer_size - error_code_size) - format_to(it, "{}{}", message, SEP); - format_to(it, "{}{}", ERROR_STR, error_code); - assert(out.size() <= inline_buffer_size); + format_to(it, FMT_STRING("{}{}"), message, SEP); + format_to(it, FMT_STRING("{}{}"), ERROR_STR, error_code); + FMT_ASSERT(out.size() <= inline_buffer_size, ""); } FMT_FUNC void report_error(format_func func, int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const char* message) noexcept { memory_buffer full_message; func(full_message, error_code, message); // Don't use fwrite_fully because the latter may throw. - (void)std::fwrite(full_message.data(), full_message.size(), 1, stderr); - std::fputc('\n', stderr); + if (std::fwrite(full_message.data(), full_message.size(), 1, stderr) > 0) + std::fputc('\n', stderr); } // A wrapper around fwrite that throws on error. -inline void fwrite_fully(const void* ptr, size_t size, size_t count, - FILE* stream) { - size_t written = std::fwrite(ptr, size, count, stream); - if (written < count) FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot write to file")); +inline void fwrite_fully(const void* ptr, size_t count, FILE* stream) { + size_t written = std::fwrite(ptr, 1, count, stream); + if (written < count) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot write to file"))); } -} // namespace detail - -#if !defined(FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR) -namespace detail { +#ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR template <typename Locale> locale_ref::locale_ref(const Locale& loc) : locale_(&loc) { static_assert(std::is_same<Locale, std::locale>::value, ""); @@ -180,1698 +90,252 @@ template <typename Locale> Locale locale_ref::get() const { return locale_ ? *static_cast<const std::locale*>(locale_) : std::locale(); } -template <typename Char> FMT_FUNC std::string grouping_impl(locale_ref loc) { - return std::use_facet<std::numpunct<Char>>(loc.get<std::locale>()).grouping(); -} -template <typename Char> FMT_FUNC Char thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref loc) { - return std::use_facet<std::numpunct<Char>>(loc.get<std::locale>()) - .thousands_sep(); +template <typename Char> +FMT_FUNC auto thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref loc) -> thousands_sep_result<Char> { + auto& facet = std::use_facet<std::numpunct<Char>>(loc.get<std::locale>()); + auto grouping = facet.grouping(); + auto thousands_sep = grouping.empty() ? Char() : facet.thousands_sep(); + return {std::move(grouping), thousands_sep}; } template <typename Char> FMT_FUNC Char decimal_point_impl(locale_ref loc) { return std::use_facet<std::numpunct<Char>>(loc.get<std::locale>()) .decimal_point(); } -} // namespace detail #else template <typename Char> -FMT_FUNC std::string detail::grouping_impl(locale_ref) { - return "\03"; -} -template <typename Char> FMT_FUNC Char detail::thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref) { - return FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR; +FMT_FUNC auto thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref) -> thousands_sep_result<Char> { + return {"\03", FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR}; } -template <typename Char> FMT_FUNC Char detail::decimal_point_impl(locale_ref) { +template <typename Char> FMT_FUNC Char decimal_point_impl(locale_ref) { return '.'; } #endif -FMT_API FMT_FUNC format_error::~format_error() FMT_NOEXCEPT = default; -FMT_API FMT_FUNC system_error::~system_error() FMT_NOEXCEPT = default; - -FMT_FUNC void system_error::init(int err_code, string_view format_str, - format_args args) { - error_code_ = err_code; - memory_buffer buffer; - format_system_error(buffer, err_code, vformat(format_str, args)); - std::runtime_error& base = *this; - base = std::runtime_error(to_string(buffer)); +FMT_FUNC auto write_loc(appender out, loc_value value, + const format_specs<>& specs, locale_ref loc) -> bool { +#ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR + auto locale = loc.get<std::locale>(); + // We cannot use the num_put<char> facet because it may produce output in + // a wrong encoding. + using facet = format_facet<std::locale>; + if (std::has_facet<facet>(locale)) + return std::use_facet<facet>(locale).put(out, value, specs); + return facet(locale).put(out, value, specs); +#endif + return false; } +} // namespace detail -namespace detail { +template <typename Locale> typename Locale::id format_facet<Locale>::id; -template <> FMT_FUNC int count_digits<4>(detail::fallback_uintptr n) { - // fallback_uintptr is always stored in little endian. - int i = static_cast<int>(sizeof(void*)) - 1; - while (i > 0 && n.value[i] == 0) --i; - auto char_digits = std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::digits / 4; - return i >= 0 ? i * char_digits + count_digits<4, unsigned>(n.value[i]) : 1; +#ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR +template <typename Locale> format_facet<Locale>::format_facet(Locale& loc) { + auto& numpunct = std::use_facet<std::numpunct<char>>(loc); + grouping_ = numpunct.grouping(); + if (!grouping_.empty()) separator_ = std::string(1, numpunct.thousands_sep()); } -template <typename T> -const typename basic_data<T>::digit_pair basic_data<T>::digits[] = { - {'0', '0'}, {'0', '1'}, {'0', '2'}, {'0', '3'}, {'0', '4'}, {'0', '5'}, - {'0', '6'}, {'0', '7'}, {'0', '8'}, {'0', '9'}, {'1', '0'}, {'1', '1'}, - {'1', '2'}, {'1', '3'}, {'1', '4'}, {'1', '5'}, {'1', '6'}, {'1', '7'}, - {'1', '8'}, {'1', '9'}, {'2', '0'}, {'2', '1'}, {'2', '2'}, {'2', '3'}, - {'2', '4'}, {'2', '5'}, {'2', '6'}, {'2', '7'}, {'2', '8'}, {'2', '9'}, - {'3', '0'}, {'3', '1'}, {'3', '2'}, {'3', '3'}, {'3', '4'}, {'3', '5'}, - {'3', '6'}, {'3', '7'}, {'3', '8'}, {'3', '9'}, {'4', '0'}, {'4', '1'}, - {'4', '2'}, {'4', '3'}, {'4', '4'}, {'4', '5'}, {'4', '6'}, {'4', '7'}, - {'4', '8'}, {'4', '9'}, {'5', '0'}, {'5', '1'}, {'5', '2'}, {'5', '3'}, - {'5', '4'}, {'5', '5'}, {'5', '6'}, {'5', '7'}, {'5', '8'}, {'5', '9'}, - {'6', '0'}, {'6', '1'}, {'6', '2'}, {'6', '3'}, {'6', '4'}, {'6', '5'}, - {'6', '6'}, {'6', '7'}, {'6', '8'}, {'6', '9'}, {'7', '0'}, {'7', '1'}, - {'7', '2'}, {'7', '3'}, {'7', '4'}, {'7', '5'}, {'7', '6'}, {'7', '7'}, - {'7', '8'}, {'7', '9'}, {'8', '0'}, {'8', '1'}, {'8', '2'}, {'8', '3'}, - {'8', '4'}, {'8', '5'}, {'8', '6'}, {'8', '7'}, {'8', '8'}, {'8', '9'}, - {'9', '0'}, {'9', '1'}, {'9', '2'}, {'9', '3'}, {'9', '4'}, {'9', '5'}, - {'9', '6'}, {'9', '7'}, {'9', '8'}, {'9', '9'}}; - -template <typename T> -const char basic_data<T>::hex_digits[] = "0123456789abcdef"; - -#define FMT_POWERS_OF_10(factor) \ - factor * 10, (factor)*100, (factor)*1000, (factor)*10000, (factor)*100000, \ - (factor)*1000000, (factor)*10000000, (factor)*100000000, \ - (factor)*1000000000 - -template <typename T> -const uint64_t basic_data<T>::powers_of_10_64[] = { - 1, FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1), FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1000000000ULL), - 10000000000000000000ULL}; - -template <typename T> -const uint32_t basic_data<T>::zero_or_powers_of_10_32[] = {0, - FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1)}; -template <typename T> -const uint64_t basic_data<T>::zero_or_powers_of_10_64[] = { - 0, FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1), FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1000000000ULL), - 10000000000000000000ULL}; - -template <typename T> -const uint32_t basic_data<T>::zero_or_powers_of_10_32_new[] = { - 0, 0, FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1)}; - -template <typename T> -const uint64_t basic_data<T>::zero_or_powers_of_10_64_new[] = { - 0, 0, FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1), FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1000000000ULL), - 10000000000000000000ULL}; - -// Normalized 64-bit significands of pow(10, k), for k = -348, -340, ..., 340. -// These are generated by support/compute-powers.py. -template <typename T> -const uint64_t basic_data<T>::grisu_pow10_significands[] = { - 0xfa8fd5a0081c0288, 0xbaaee17fa23ebf76, 0x8b16fb203055ac76, - 0xcf42894a5dce35ea, 0x9a6bb0aa55653b2d, 0xe61acf033d1a45df, - 0xab70fe17c79ac6ca, 0xff77b1fcbebcdc4f, 0xbe5691ef416bd60c, - 0x8dd01fad907ffc3c, 0xd3515c2831559a83, 0x9d71ac8fada6c9b5, - 0xea9c227723ee8bcb, 0xaecc49914078536d, 0x823c12795db6ce57, - 0xc21094364dfb5637, 0x9096ea6f3848984f, 0xd77485cb25823ac7, - 0xa086cfcd97bf97f4, 0xef340a98172aace5, 0xb23867fb2a35b28e, - 0x84c8d4dfd2c63f3b, 0xc5dd44271ad3cdba, 0x936b9fcebb25c996, - 0xdbac6c247d62a584, 0xa3ab66580d5fdaf6, 0xf3e2f893dec3f126, - 0xb5b5ada8aaff80b8, 0x87625f056c7c4a8b, 0xc9bcff6034c13053, - 0x964e858c91ba2655, 0xdff9772470297ebd, 0xa6dfbd9fb8e5b88f, - 0xf8a95fcf88747d94, 0xb94470938fa89bcf, 0x8a08f0f8bf0f156b, - 0xcdb02555653131b6, 0x993fe2c6d07b7fac, 0xe45c10c42a2b3b06, - 0xaa242499697392d3, 0xfd87b5f28300ca0e, 0xbce5086492111aeb, - 0x8cbccc096f5088cc, 0xd1b71758e219652c, 0x9c40000000000000, - 0xe8d4a51000000000, 0xad78ebc5ac620000, 0x813f3978f8940984, - 0xc097ce7bc90715b3, 0x8f7e32ce7bea5c70, 0xd5d238a4abe98068, - 0x9f4f2726179a2245, 0xed63a231d4c4fb27, 0xb0de65388cc8ada8, - 0x83c7088e1aab65db, 0xc45d1df942711d9a, 0x924d692ca61be758, - 0xda01ee641a708dea, 0xa26da3999aef774a, 0xf209787bb47d6b85, - 0xb454e4a179dd1877, 0x865b86925b9bc5c2, 0xc83553c5c8965d3d, - 0x952ab45cfa97a0b3, 0xde469fbd99a05fe3, 0xa59bc234db398c25, - 0xf6c69a72a3989f5c, 0xb7dcbf5354e9bece, 0x88fcf317f22241e2, - 0xcc20ce9bd35c78a5, 0x98165af37b2153df, 0xe2a0b5dc971f303a, - 0xa8d9d1535ce3b396, 0xfb9b7cd9a4a7443c, 0xbb764c4ca7a44410, - 0x8bab8eefb6409c1a, 0xd01fef10a657842c, 0x9b10a4e5e9913129, - 0xe7109bfba19c0c9d, 0xac2820d9623bf429, 0x80444b5e7aa7cf85, - 0xbf21e44003acdd2d, 0x8e679c2f5e44ff8f, 0xd433179d9c8cb841, - 0x9e19db92b4e31ba9, 0xeb96bf6ebadf77d9, 0xaf87023b9bf0ee6b, -}; - -// Binary exponents of pow(10, k), for k = -348, -340, ..., 340, corresponding -// to significands above. -template <typename T> -const int16_t basic_data<T>::grisu_pow10_exponents[] = { - -1220, -1193, -1166, -1140, -1113, -1087, -1060, -1034, -1007, -980, -954, - -927, -901, -874, -847, -821, -794, -768, -741, -715, -688, -661, - -635, -608, -582, -555, -529, -502, -475, -449, -422, -396, -369, - -343, -316, -289, -263, -236, -210, -183, -157, -130, -103, -77, - -50, -24, 3, 30, 56, 83, 109, 136, 162, 189, 216, - 242, 269, 295, 322, 348, 375, 402, 428, 455, 481, 508, - 534, 561, 588, 614, 641, 667, 694, 720, 747, 774, 800, - 827, 853, 880, 907, 933, 960, 986, 1013, 1039, 1066}; - -template <typename T> -const divtest_table_entry<uint32_t> basic_data<T>::divtest_table_for_pow5_32[] = - {{0x00000001, 0xffffffff}, {0xcccccccd, 0x33333333}, - {0xc28f5c29, 0x0a3d70a3}, {0x26e978d5, 0x020c49ba}, - {0x3afb7e91, 0x0068db8b}, {0x0bcbe61d, 0x0014f8b5}, - {0x68c26139, 0x000431bd}, {0xae8d46a5, 0x0000d6bf}, - {0x22e90e21, 0x00002af3}, {0x3a2e9c6d, 0x00000897}, - {0x3ed61f49, 0x000001b7}}; - -template <typename T> -const divtest_table_entry<uint64_t> basic_data<T>::divtest_table_for_pow5_64[] = - {{0x0000000000000001, 0xffffffffffffffff}, - {0xcccccccccccccccd, 0x3333333333333333}, - {0x8f5c28f5c28f5c29, 0x0a3d70a3d70a3d70}, - {0x1cac083126e978d5, 0x020c49ba5e353f7c}, - {0xd288ce703afb7e91, 0x0068db8bac710cb2}, - {0x5d4e8fb00bcbe61d, 0x0014f8b588e368f0}, - {0x790fb65668c26139, 0x000431bde82d7b63}, - {0xe5032477ae8d46a5, 0x0000d6bf94d5e57a}, - {0xc767074b22e90e21, 0x00002af31dc46118}, - {0x8e47ce423a2e9c6d, 0x0000089705f4136b}, - {0x4fa7f60d3ed61f49, 0x000001b7cdfd9d7b}, - {0x0fee64690c913975, 0x00000057f5ff85e5}, - {0x3662e0e1cf503eb1, 0x000000119799812d}, - {0xa47a2cf9f6433fbd, 0x0000000384b84d09}, - {0x54186f653140a659, 0x00000000b424dc35}, - {0x7738164770402145, 0x0000000024075f3d}, - {0xe4a4d1417cd9a041, 0x000000000734aca5}, - {0xc75429d9e5c5200d, 0x000000000170ef54}, - {0xc1773b91fac10669, 0x000000000049c977}, - {0x26b172506559ce15, 0x00000000000ec1e4}, - {0xd489e3a9addec2d1, 0x000000000002f394}, - {0x90e860bb892c8d5d, 0x000000000000971d}, - {0x502e79bf1b6f4f79, 0x0000000000001e39}, - {0xdcd618596be30fe5, 0x000000000000060b}}; - -template <typename T> -const uint64_t basic_data<T>::dragonbox_pow10_significands_64[] = { - 0x81ceb32c4b43fcf5, 0xa2425ff75e14fc32, 0xcad2f7f5359a3b3f, - 0xfd87b5f28300ca0e, 0x9e74d1b791e07e49, 0xc612062576589ddb, - 0xf79687aed3eec552, 0x9abe14cd44753b53, 0xc16d9a0095928a28, - 0xf1c90080baf72cb2, 0x971da05074da7bef, 0xbce5086492111aeb, - 0xec1e4a7db69561a6, 0x9392ee8e921d5d08, 0xb877aa3236a4b44a, - 0xe69594bec44de15c, 0x901d7cf73ab0acda, 0xb424dc35095cd810, - 0xe12e13424bb40e14, 0x8cbccc096f5088cc, 0xafebff0bcb24aaff, - 0xdbe6fecebdedd5bf, 0x89705f4136b4a598, 0xabcc77118461cefd, - 0xd6bf94d5e57a42bd, 0x8637bd05af6c69b6, 0xa7c5ac471b478424, - 0xd1b71758e219652c, 0x83126e978d4fdf3c, 0xa3d70a3d70a3d70b, - 0xcccccccccccccccd, 0x8000000000000000, 0xa000000000000000, - 0xc800000000000000, 0xfa00000000000000, 0x9c40000000000000, - 0xc350000000000000, 0xf424000000000000, 0x9896800000000000, - 0xbebc200000000000, 0xee6b280000000000, 0x9502f90000000000, - 0xba43b74000000000, 0xe8d4a51000000000, 0x9184e72a00000000, - 0xb5e620f480000000, 0xe35fa931a0000000, 0x8e1bc9bf04000000, - 0xb1a2bc2ec5000000, 0xde0b6b3a76400000, 0x8ac7230489e80000, - 0xad78ebc5ac620000, 0xd8d726b7177a8000, 0x878678326eac9000, - 0xa968163f0a57b400, 0xd3c21bcecceda100, 0x84595161401484a0, - 0xa56fa5b99019a5c8, 0xcecb8f27f4200f3a, 0x813f3978f8940984, - 0xa18f07d736b90be5, 0xc9f2c9cd04674ede, 0xfc6f7c4045812296, - 0x9dc5ada82b70b59d, 0xc5371912364ce305, 0xf684df56c3e01bc6, - 0x9a130b963a6c115c, 0xc097ce7bc90715b3, 0xf0bdc21abb48db20, - 0x96769950b50d88f4, 0xbc143fa4e250eb31, 0xeb194f8e1ae525fd, - 0x92efd1b8d0cf37be, 0xb7abc627050305ad, 0xe596b7b0c643c719, - 0x8f7e32ce7bea5c6f, 0xb35dbf821ae4f38b, 0xe0352f62a19e306e}; - -template <typename T> -const uint128_wrapper basic_data<T>::dragonbox_pow10_significands_128[] = { -#if FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX - {0xff77b1fcbebcdc4f, 0x25e8e89c13bb0f7b}, - {0x9faacf3df73609b1, 0x77b191618c54e9ad}, - {0xc795830d75038c1d, 0xd59df5b9ef6a2418}, - {0xf97ae3d0d2446f25, 0x4b0573286b44ad1e}, - {0x9becce62836ac577, 0x4ee367f9430aec33}, - {0xc2e801fb244576d5, 0x229c41f793cda740}, - {0xf3a20279ed56d48a, 0x6b43527578c11110}, - {0x9845418c345644d6, 0x830a13896b78aaaa}, - {0xbe5691ef416bd60c, 0x23cc986bc656d554}, - {0xedec366b11c6cb8f, 0x2cbfbe86b7ec8aa9}, - {0x94b3a202eb1c3f39, 0x7bf7d71432f3d6aa}, - {0xb9e08a83a5e34f07, 0xdaf5ccd93fb0cc54}, - {0xe858ad248f5c22c9, 0xd1b3400f8f9cff69}, - {0x91376c36d99995be, 0x23100809b9c21fa2}, - {0xb58547448ffffb2d, 0xabd40a0c2832a78b}, - {0xe2e69915b3fff9f9, 0x16c90c8f323f516d}, - {0x8dd01fad907ffc3b, 0xae3da7d97f6792e4}, - {0xb1442798f49ffb4a, 0x99cd11cfdf41779d}, - {0xdd95317f31c7fa1d, 0x40405643d711d584}, - {0x8a7d3eef7f1cfc52, 0x482835ea666b2573}, - {0xad1c8eab5ee43b66, 0xda3243650005eed0}, - {0xd863b256369d4a40, 0x90bed43e40076a83}, - {0x873e4f75e2224e68, 0x5a7744a6e804a292}, - {0xa90de3535aaae202, 0x711515d0a205cb37}, - {0xd3515c2831559a83, 0x0d5a5b44ca873e04}, - {0x8412d9991ed58091, 0xe858790afe9486c3}, - {0xa5178fff668ae0b6, 0x626e974dbe39a873}, - {0xce5d73ff402d98e3, 0xfb0a3d212dc81290}, - {0x80fa687f881c7f8e, 0x7ce66634bc9d0b9a}, - {0xa139029f6a239f72, 0x1c1fffc1ebc44e81}, - {0xc987434744ac874e, 0xa327ffb266b56221}, - {0xfbe9141915d7a922, 0x4bf1ff9f0062baa9}, - {0x9d71ac8fada6c9b5, 0x6f773fc3603db4aa}, - {0xc4ce17b399107c22, 0xcb550fb4384d21d4}, - {0xf6019da07f549b2b, 0x7e2a53a146606a49}, - {0x99c102844f94e0fb, 0x2eda7444cbfc426e}, - {0xc0314325637a1939, 0xfa911155fefb5309}, - {0xf03d93eebc589f88, 0x793555ab7eba27cb}, - {0x96267c7535b763b5, 0x4bc1558b2f3458df}, - {0xbbb01b9283253ca2, 0x9eb1aaedfb016f17}, - {0xea9c227723ee8bcb, 0x465e15a979c1cadd}, - {0x92a1958a7675175f, 0x0bfacd89ec191eca}, - {0xb749faed14125d36, 0xcef980ec671f667c}, - {0xe51c79a85916f484, 0x82b7e12780e7401b}, - {0x8f31cc0937ae58d2, 0xd1b2ecb8b0908811}, - {0xb2fe3f0b8599ef07, 0x861fa7e6dcb4aa16}, - {0xdfbdcece67006ac9, 0x67a791e093e1d49b}, - {0x8bd6a141006042bd, 0xe0c8bb2c5c6d24e1}, - {0xaecc49914078536d, 0x58fae9f773886e19}, - {0xda7f5bf590966848, 0xaf39a475506a899f}, - {0x888f99797a5e012d, 0x6d8406c952429604}, - {0xaab37fd7d8f58178, 0xc8e5087ba6d33b84}, - {0xd5605fcdcf32e1d6, 0xfb1e4a9a90880a65}, - {0x855c3be0a17fcd26, 0x5cf2eea09a550680}, - {0xa6b34ad8c9dfc06f, 0xf42faa48c0ea481f}, - {0xd0601d8efc57b08b, 0xf13b94daf124da27}, - {0x823c12795db6ce57, 0x76c53d08d6b70859}, - {0xa2cb1717b52481ed, 0x54768c4b0c64ca6f}, - {0xcb7ddcdda26da268, 0xa9942f5dcf7dfd0a}, - {0xfe5d54150b090b02, 0xd3f93b35435d7c4d}, - {0x9efa548d26e5a6e1, 0xc47bc5014a1a6db0}, - {0xc6b8e9b0709f109a, 0x359ab6419ca1091c}, - {0xf867241c8cc6d4c0, 0xc30163d203c94b63}, - {0x9b407691d7fc44f8, 0x79e0de63425dcf1e}, - {0xc21094364dfb5636, 0x985915fc12f542e5}, - {0xf294b943e17a2bc4, 0x3e6f5b7b17b2939e}, - {0x979cf3ca6cec5b5a, 0xa705992ceecf9c43}, - {0xbd8430bd08277231, 0x50c6ff782a838354}, - {0xece53cec4a314ebd, 0xa4f8bf5635246429}, - {0x940f4613ae5ed136, 0x871b7795e136be9a}, - {0xb913179899f68584, 0x28e2557b59846e40}, - {0xe757dd7ec07426e5, 0x331aeada2fe589d0}, - {0x9096ea6f3848984f, 0x3ff0d2c85def7622}, - {0xb4bca50b065abe63, 0x0fed077a756b53aa}, - {0xe1ebce4dc7f16dfb, 0xd3e8495912c62895}, - {0x8d3360f09cf6e4bd, 0x64712dd7abbbd95d}, - {0xb080392cc4349dec, 0xbd8d794d96aacfb4}, - {0xdca04777f541c567, 0xecf0d7a0fc5583a1}, - {0x89e42caaf9491b60, 0xf41686c49db57245}, - {0xac5d37d5b79b6239, 0x311c2875c522ced6}, - {0xd77485cb25823ac7, 0x7d633293366b828c}, - {0x86a8d39ef77164bc, 0xae5dff9c02033198}, - {0xa8530886b54dbdeb, 0xd9f57f830283fdfd}, - {0xd267caa862a12d66, 0xd072df63c324fd7c}, - {0x8380dea93da4bc60, 0x4247cb9e59f71e6e}, - {0xa46116538d0deb78, 0x52d9be85f074e609}, - {0xcd795be870516656, 0x67902e276c921f8c}, - {0x806bd9714632dff6, 0x00ba1cd8a3db53b7}, - {0xa086cfcd97bf97f3, 0x80e8a40eccd228a5}, - {0xc8a883c0fdaf7df0, 0x6122cd128006b2ce}, - {0xfad2a4b13d1b5d6c, 0x796b805720085f82}, - {0x9cc3a6eec6311a63, 0xcbe3303674053bb1}, - {0xc3f490aa77bd60fc, 0xbedbfc4411068a9d}, - {0xf4f1b4d515acb93b, 0xee92fb5515482d45}, - {0x991711052d8bf3c5, 0x751bdd152d4d1c4b}, - {0xbf5cd54678eef0b6, 0xd262d45a78a0635e}, - {0xef340a98172aace4, 0x86fb897116c87c35}, - {0x9580869f0e7aac0e, 0xd45d35e6ae3d4da1}, - {0xbae0a846d2195712, 0x8974836059cca10a}, - {0xe998d258869facd7, 0x2bd1a438703fc94c}, - {0x91ff83775423cc06, 0x7b6306a34627ddd0}, - {0xb67f6455292cbf08, 0x1a3bc84c17b1d543}, - {0xe41f3d6a7377eeca, 0x20caba5f1d9e4a94}, - {0x8e938662882af53e, 0x547eb47b7282ee9d}, - {0xb23867fb2a35b28d, 0xe99e619a4f23aa44}, - {0xdec681f9f4c31f31, 0x6405fa00e2ec94d5}, - {0x8b3c113c38f9f37e, 0xde83bc408dd3dd05}, - {0xae0b158b4738705e, 0x9624ab50b148d446}, - {0xd98ddaee19068c76, 0x3badd624dd9b0958}, - {0x87f8a8d4cfa417c9, 0xe54ca5d70a80e5d7}, - {0xa9f6d30a038d1dbc, 0x5e9fcf4ccd211f4d}, - {0xd47487cc8470652b, 0x7647c32000696720}, - {0x84c8d4dfd2c63f3b, 0x29ecd9f40041e074}, - {0xa5fb0a17c777cf09, 0xf468107100525891}, - {0xcf79cc9db955c2cc, 0x7182148d4066eeb5}, - {0x81ac1fe293d599bf, 0xc6f14cd848405531}, - {0xa21727db38cb002f, 0xb8ada00e5a506a7d}, - {0xca9cf1d206fdc03b, 0xa6d90811f0e4851d}, - {0xfd442e4688bd304a, 0x908f4a166d1da664}, - {0x9e4a9cec15763e2e, 0x9a598e4e043287ff}, - {0xc5dd44271ad3cdba, 0x40eff1e1853f29fe}, - {0xf7549530e188c128, 0xd12bee59e68ef47d}, - {0x9a94dd3e8cf578b9, 0x82bb74f8301958cf}, - {0xc13a148e3032d6e7, 0xe36a52363c1faf02}, - {0xf18899b1bc3f8ca1, 0xdc44e6c3cb279ac2}, - {0x96f5600f15a7b7e5, 0x29ab103a5ef8c0ba}, - {0xbcb2b812db11a5de, 0x7415d448f6b6f0e8}, - {0xebdf661791d60f56, 0x111b495b3464ad22}, - {0x936b9fcebb25c995, 0xcab10dd900beec35}, - {0xb84687c269ef3bfb, 0x3d5d514f40eea743}, - {0xe65829b3046b0afa, 0x0cb4a5a3112a5113}, - {0x8ff71a0fe2c2e6dc, 0x47f0e785eaba72ac}, - {0xb3f4e093db73a093, 0x59ed216765690f57}, - {0xe0f218b8d25088b8, 0x306869c13ec3532d}, - {0x8c974f7383725573, 0x1e414218c73a13fc}, - {0xafbd2350644eeacf, 0xe5d1929ef90898fb}, - {0xdbac6c247d62a583, 0xdf45f746b74abf3a}, - {0x894bc396ce5da772, 0x6b8bba8c328eb784}, - {0xab9eb47c81f5114f, 0x066ea92f3f326565}, - {0xd686619ba27255a2, 0xc80a537b0efefebe}, - {0x8613fd0145877585, 0xbd06742ce95f5f37}, - {0xa798fc4196e952e7, 0x2c48113823b73705}, - {0xd17f3b51fca3a7a0, 0xf75a15862ca504c6}, - {0x82ef85133de648c4, 0x9a984d73dbe722fc}, - {0xa3ab66580d5fdaf5, 0xc13e60d0d2e0ebbb}, - {0xcc963fee10b7d1b3, 0x318df905079926a9}, - {0xffbbcfe994e5c61f, 0xfdf17746497f7053}, - {0x9fd561f1fd0f9bd3, 0xfeb6ea8bedefa634}, - {0xc7caba6e7c5382c8, 0xfe64a52ee96b8fc1}, - {0xf9bd690a1b68637b, 0x3dfdce7aa3c673b1}, - {0x9c1661a651213e2d, 0x06bea10ca65c084f}, - {0xc31bfa0fe5698db8, 0x486e494fcff30a63}, - {0xf3e2f893dec3f126, 0x5a89dba3c3efccfb}, - {0x986ddb5c6b3a76b7, 0xf89629465a75e01d}, - {0xbe89523386091465, 0xf6bbb397f1135824}, - {0xee2ba6c0678b597f, 0x746aa07ded582e2d}, - {0x94db483840b717ef, 0xa8c2a44eb4571cdd}, - {0xba121a4650e4ddeb, 0x92f34d62616ce414}, - {0xe896a0d7e51e1566, 0x77b020baf9c81d18}, - {0x915e2486ef32cd60, 0x0ace1474dc1d122f}, - {0xb5b5ada8aaff80b8, 0x0d819992132456bb}, - {0xe3231912d5bf60e6, 0x10e1fff697ed6c6a}, - {0x8df5efabc5979c8f, 0xca8d3ffa1ef463c2}, - {0xb1736b96b6fd83b3, 0xbd308ff8a6b17cb3}, - {0xddd0467c64bce4a0, 0xac7cb3f6d05ddbdf}, - {0x8aa22c0dbef60ee4, 0x6bcdf07a423aa96c}, - {0xad4ab7112eb3929d, 0x86c16c98d2c953c7}, - {0xd89d64d57a607744, 0xe871c7bf077ba8b8}, - {0x87625f056c7c4a8b, 0x11471cd764ad4973}, - {0xa93af6c6c79b5d2d, 0xd598e40d3dd89bd0}, - {0xd389b47879823479, 0x4aff1d108d4ec2c4}, - {0x843610cb4bf160cb, 0xcedf722a585139bb}, - {0xa54394fe1eedb8fe, 0xc2974eb4ee658829}, - {0xce947a3da6a9273e, 0x733d226229feea33}, - {0x811ccc668829b887, 0x0806357d5a3f5260}, - {0xa163ff802a3426a8, 0xca07c2dcb0cf26f8}, - {0xc9bcff6034c13052, 0xfc89b393dd02f0b6}, - {0xfc2c3f3841f17c67, 0xbbac2078d443ace3}, - {0x9d9ba7832936edc0, 0xd54b944b84aa4c0e}, - {0xc5029163f384a931, 0x0a9e795e65d4df12}, - {0xf64335bcf065d37d, 0x4d4617b5ff4a16d6}, - {0x99ea0196163fa42e, 0x504bced1bf8e4e46}, - {0xc06481fb9bcf8d39, 0xe45ec2862f71e1d7}, - {0xf07da27a82c37088, 0x5d767327bb4e5a4d}, - {0x964e858c91ba2655, 0x3a6a07f8d510f870}, - {0xbbe226efb628afea, 0x890489f70a55368c}, - {0xeadab0aba3b2dbe5, 0x2b45ac74ccea842f}, - {0x92c8ae6b464fc96f, 0x3b0b8bc90012929e}, - {0xb77ada0617e3bbcb, 0x09ce6ebb40173745}, - {0xe55990879ddcaabd, 0xcc420a6a101d0516}, - {0x8f57fa54c2a9eab6, 0x9fa946824a12232e}, - {0xb32df8e9f3546564, 0x47939822dc96abfa}, - {0xdff9772470297ebd, 0x59787e2b93bc56f8}, - {0x8bfbea76c619ef36, 0x57eb4edb3c55b65b}, - {0xaefae51477a06b03, 0xede622920b6b23f2}, - {0xdab99e59958885c4, 0xe95fab368e45ecee}, - {0x88b402f7fd75539b, 0x11dbcb0218ebb415}, - {0xaae103b5fcd2a881, 0xd652bdc29f26a11a}, - {0xd59944a37c0752a2, 0x4be76d3346f04960}, - {0x857fcae62d8493a5, 0x6f70a4400c562ddc}, - {0xa6dfbd9fb8e5b88e, 0xcb4ccd500f6bb953}, - {0xd097ad07a71f26b2, 0x7e2000a41346a7a8}, - {0x825ecc24c873782f, 0x8ed400668c0c28c9}, - {0xa2f67f2dfa90563b, 0x728900802f0f32fb}, - {0xcbb41ef979346bca, 0x4f2b40a03ad2ffba}, - {0xfea126b7d78186bc, 0xe2f610c84987bfa9}, - {0x9f24b832e6b0f436, 0x0dd9ca7d2df4d7ca}, - {0xc6ede63fa05d3143, 0x91503d1c79720dbc}, - {0xf8a95fcf88747d94, 0x75a44c6397ce912b}, - {0x9b69dbe1b548ce7c, 0xc986afbe3ee11abb}, - {0xc24452da229b021b, 0xfbe85badce996169}, - {0xf2d56790ab41c2a2, 0xfae27299423fb9c4}, - {0x97c560ba6b0919a5, 0xdccd879fc967d41b}, - {0xbdb6b8e905cb600f, 0x5400e987bbc1c921}, - {0xed246723473e3813, 0x290123e9aab23b69}, - {0x9436c0760c86e30b, 0xf9a0b6720aaf6522}, - {0xb94470938fa89bce, 0xf808e40e8d5b3e6a}, - {0xe7958cb87392c2c2, 0xb60b1d1230b20e05}, - {0x90bd77f3483bb9b9, 0xb1c6f22b5e6f48c3}, - {0xb4ecd5f01a4aa828, 0x1e38aeb6360b1af4}, - {0xe2280b6c20dd5232, 0x25c6da63c38de1b1}, - {0x8d590723948a535f, 0x579c487e5a38ad0f}, - {0xb0af48ec79ace837, 0x2d835a9df0c6d852}, - {0xdcdb1b2798182244, 0xf8e431456cf88e66}, - {0x8a08f0f8bf0f156b, 0x1b8e9ecb641b5900}, - {0xac8b2d36eed2dac5, 0xe272467e3d222f40}, - {0xd7adf884aa879177, 0x5b0ed81dcc6abb10}, - {0x86ccbb52ea94baea, 0x98e947129fc2b4ea}, - {0xa87fea27a539e9a5, 0x3f2398d747b36225}, - {0xd29fe4b18e88640e, 0x8eec7f0d19a03aae}, - {0x83a3eeeef9153e89, 0x1953cf68300424ad}, - {0xa48ceaaab75a8e2b, 0x5fa8c3423c052dd8}, - {0xcdb02555653131b6, 0x3792f412cb06794e}, - {0x808e17555f3ebf11, 0xe2bbd88bbee40bd1}, - {0xa0b19d2ab70e6ed6, 0x5b6aceaeae9d0ec5}, - {0xc8de047564d20a8b, 0xf245825a5a445276}, - {0xfb158592be068d2e, 0xeed6e2f0f0d56713}, - {0x9ced737bb6c4183d, 0x55464dd69685606c}, - {0xc428d05aa4751e4c, 0xaa97e14c3c26b887}, - {0xf53304714d9265df, 0xd53dd99f4b3066a9}, - {0x993fe2c6d07b7fab, 0xe546a8038efe402a}, - {0xbf8fdb78849a5f96, 0xde98520472bdd034}, - {0xef73d256a5c0f77c, 0x963e66858f6d4441}, - {0x95a8637627989aad, 0xdde7001379a44aa9}, - {0xbb127c53b17ec159, 0x5560c018580d5d53}, - {0xe9d71b689dde71af, 0xaab8f01e6e10b4a7}, - {0x9226712162ab070d, 0xcab3961304ca70e9}, - {0xb6b00d69bb55c8d1, 0x3d607b97c5fd0d23}, - {0xe45c10c42a2b3b05, 0x8cb89a7db77c506b}, - {0x8eb98a7a9a5b04e3, 0x77f3608e92adb243}, - {0xb267ed1940f1c61c, 0x55f038b237591ed4}, - {0xdf01e85f912e37a3, 0x6b6c46dec52f6689}, - {0x8b61313bbabce2c6, 0x2323ac4b3b3da016}, - {0xae397d8aa96c1b77, 0xabec975e0a0d081b}, - {0xd9c7dced53c72255, 0x96e7bd358c904a22}, - {0x881cea14545c7575, 0x7e50d64177da2e55}, - {0xaa242499697392d2, 0xdde50bd1d5d0b9ea}, - {0xd4ad2dbfc3d07787, 0x955e4ec64b44e865}, - {0x84ec3c97da624ab4, 0xbd5af13bef0b113f}, - {0xa6274bbdd0fadd61, 0xecb1ad8aeacdd58f}, - {0xcfb11ead453994ba, 0x67de18eda5814af3}, - {0x81ceb32c4b43fcf4, 0x80eacf948770ced8}, - {0xa2425ff75e14fc31, 0xa1258379a94d028e}, - {0xcad2f7f5359a3b3e, 0x096ee45813a04331}, - {0xfd87b5f28300ca0d, 0x8bca9d6e188853fd}, - {0x9e74d1b791e07e48, 0x775ea264cf55347e}, - {0xc612062576589dda, 0x95364afe032a819e}, - {0xf79687aed3eec551, 0x3a83ddbd83f52205}, - {0x9abe14cd44753b52, 0xc4926a9672793543}, - {0xc16d9a0095928a27, 0x75b7053c0f178294}, - {0xf1c90080baf72cb1, 0x5324c68b12dd6339}, - {0x971da05074da7bee, 0xd3f6fc16ebca5e04}, - {0xbce5086492111aea, 0x88f4bb1ca6bcf585}, - {0xec1e4a7db69561a5, 0x2b31e9e3d06c32e6}, - {0x9392ee8e921d5d07, 0x3aff322e62439fd0}, - {0xb877aa3236a4b449, 0x09befeb9fad487c3}, - {0xe69594bec44de15b, 0x4c2ebe687989a9b4}, - {0x901d7cf73ab0acd9, 0x0f9d37014bf60a11}, - {0xb424dc35095cd80f, 0x538484c19ef38c95}, - {0xe12e13424bb40e13, 0x2865a5f206b06fba}, - {0x8cbccc096f5088cb, 0xf93f87b7442e45d4}, - {0xafebff0bcb24aafe, 0xf78f69a51539d749}, - {0xdbe6fecebdedd5be, 0xb573440e5a884d1c}, - {0x89705f4136b4a597, 0x31680a88f8953031}, - {0xabcc77118461cefc, 0xfdc20d2b36ba7c3e}, - {0xd6bf94d5e57a42bc, 0x3d32907604691b4d}, - {0x8637bd05af6c69b5, 0xa63f9a49c2c1b110}, - {0xa7c5ac471b478423, 0x0fcf80dc33721d54}, - {0xd1b71758e219652b, 0xd3c36113404ea4a9}, - {0x83126e978d4fdf3b, 0x645a1cac083126ea}, - {0xa3d70a3d70a3d70a, 0x3d70a3d70a3d70a4}, - {0xcccccccccccccccc, 0xcccccccccccccccd}, - {0x8000000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xa000000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xc800000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xfa00000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x9c40000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xc350000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xf424000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x9896800000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xbebc200000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xee6b280000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x9502f90000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xba43b74000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xe8d4a51000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x9184e72a00000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xb5e620f480000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xe35fa931a0000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x8e1bc9bf04000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xb1a2bc2ec5000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xde0b6b3a76400000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x8ac7230489e80000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xad78ebc5ac620000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xd8d726b7177a8000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x878678326eac9000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xa968163f0a57b400, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xd3c21bcecceda100, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x84595161401484a0, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xa56fa5b99019a5c8, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0xcecb8f27f4200f3a, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x813f3978f8940984, 0x4000000000000000}, - {0xa18f07d736b90be5, 0x5000000000000000}, - {0xc9f2c9cd04674ede, 0xa400000000000000}, - {0xfc6f7c4045812296, 0x4d00000000000000}, - {0x9dc5ada82b70b59d, 0xf020000000000000}, - {0xc5371912364ce305, 0x6c28000000000000}, - {0xf684df56c3e01bc6, 0xc732000000000000}, - {0x9a130b963a6c115c, 0x3c7f400000000000}, - {0xc097ce7bc90715b3, 0x4b9f100000000000}, - {0xf0bdc21abb48db20, 0x1e86d40000000000}, - {0x96769950b50d88f4, 0x1314448000000000}, - {0xbc143fa4e250eb31, 0x17d955a000000000}, - {0xeb194f8e1ae525fd, 0x5dcfab0800000000}, - {0x92efd1b8d0cf37be, 0x5aa1cae500000000}, - {0xb7abc627050305ad, 0xf14a3d9e40000000}, - {0xe596b7b0c643c719, 0x6d9ccd05d0000000}, - {0x8f7e32ce7bea5c6f, 0xe4820023a2000000}, - {0xb35dbf821ae4f38b, 0xdda2802c8a800000}, - {0xe0352f62a19e306e, 0xd50b2037ad200000}, - {0x8c213d9da502de45, 0x4526f422cc340000}, - {0xaf298d050e4395d6, 0x9670b12b7f410000}, - {0xdaf3f04651d47b4c, 0x3c0cdd765f114000}, - {0x88d8762bf324cd0f, 0xa5880a69fb6ac800}, - {0xab0e93b6efee0053, 0x8eea0d047a457a00}, - {0xd5d238a4abe98068, 0x72a4904598d6d880}, - {0x85a36366eb71f041, 0x47a6da2b7f864750}, - {0xa70c3c40a64e6c51, 0x999090b65f67d924}, - {0xd0cf4b50cfe20765, 0xfff4b4e3f741cf6d}, - {0x82818f1281ed449f, 0xbff8f10e7a8921a4}, - {0xa321f2d7226895c7, 0xaff72d52192b6a0d}, - {0xcbea6f8ceb02bb39, 0x9bf4f8a69f764490}, - {0xfee50b7025c36a08, 0x02f236d04753d5b4}, - {0x9f4f2726179a2245, 0x01d762422c946590}, - {0xc722f0ef9d80aad6, 0x424d3ad2b7b97ef5}, - {0xf8ebad2b84e0d58b, 0xd2e0898765a7deb2}, - {0x9b934c3b330c8577, 0x63cc55f49f88eb2f}, - {0xc2781f49ffcfa6d5, 0x3cbf6b71c76b25fb}, - {0xf316271c7fc3908a, 0x8bef464e3945ef7a}, - {0x97edd871cfda3a56, 0x97758bf0e3cbb5ac}, - {0xbde94e8e43d0c8ec, 0x3d52eeed1cbea317}, - {0xed63a231d4c4fb27, 0x4ca7aaa863ee4bdd}, - {0x945e455f24fb1cf8, 0x8fe8caa93e74ef6a}, - {0xb975d6b6ee39e436, 0xb3e2fd538e122b44}, - {0xe7d34c64a9c85d44, 0x60dbbca87196b616}, - {0x90e40fbeea1d3a4a, 0xbc8955e946fe31cd}, - {0xb51d13aea4a488dd, 0x6babab6398bdbe41}, - {0xe264589a4dcdab14, 0xc696963c7eed2dd1}, - {0x8d7eb76070a08aec, 0xfc1e1de5cf543ca2}, - {0xb0de65388cc8ada8, 0x3b25a55f43294bcb}, - {0xdd15fe86affad912, 0x49ef0eb713f39ebe}, - {0x8a2dbf142dfcc7ab, 0x6e3569326c784337}, - {0xacb92ed9397bf996, 0x49c2c37f07965404}, - {0xd7e77a8f87daf7fb, 0xdc33745ec97be906}, - {0x86f0ac99b4e8dafd, 0x69a028bb3ded71a3}, - {0xa8acd7c0222311bc, 0xc40832ea0d68ce0c}, - {0xd2d80db02aabd62b, 0xf50a3fa490c30190}, - {0x83c7088e1aab65db, 0x792667c6da79e0fa}, - {0xa4b8cab1a1563f52, 0x577001b891185938}, - {0xcde6fd5e09abcf26, 0xed4c0226b55e6f86}, - {0x80b05e5ac60b6178, 0x544f8158315b05b4}, - {0xa0dc75f1778e39d6, 0x696361ae3db1c721}, - {0xc913936dd571c84c, 0x03bc3a19cd1e38e9}, - {0xfb5878494ace3a5f, 0x04ab48a04065c723}, - {0x9d174b2dcec0e47b, 0x62eb0d64283f9c76}, - {0xc45d1df942711d9a, 0x3ba5d0bd324f8394}, - {0xf5746577930d6500, 0xca8f44ec7ee36479}, - {0x9968bf6abbe85f20, 0x7e998b13cf4e1ecb}, - {0xbfc2ef456ae276e8, 0x9e3fedd8c321a67e}, - {0xefb3ab16c59b14a2, 0xc5cfe94ef3ea101e}, - {0x95d04aee3b80ece5, 0xbba1f1d158724a12}, - {0xbb445da9ca61281f, 0x2a8a6e45ae8edc97}, - {0xea1575143cf97226, 0xf52d09d71a3293bd}, - {0x924d692ca61be758, 0x593c2626705f9c56}, - {0xb6e0c377cfa2e12e, 0x6f8b2fb00c77836c}, - {0xe498f455c38b997a, 0x0b6dfb9c0f956447}, - {0x8edf98b59a373fec, 0x4724bd4189bd5eac}, - {0xb2977ee300c50fe7, 0x58edec91ec2cb657}, - {0xdf3d5e9bc0f653e1, 0x2f2967b66737e3ed}, - {0x8b865b215899f46c, 0xbd79e0d20082ee74}, - {0xae67f1e9aec07187, 0xecd8590680a3aa11}, - {0xda01ee641a708de9, 0xe80e6f4820cc9495}, - {0x884134fe908658b2, 0x3109058d147fdcdd}, - {0xaa51823e34a7eede, 0xbd4b46f0599fd415}, - {0xd4e5e2cdc1d1ea96, 0x6c9e18ac7007c91a}, - {0x850fadc09923329e, 0x03e2cf6bc604ddb0}, - {0xa6539930bf6bff45, 0x84db8346b786151c}, - {0xcfe87f7cef46ff16, 0xe612641865679a63}, - {0x81f14fae158c5f6e, 0x4fcb7e8f3f60c07e}, - {0xa26da3999aef7749, 0xe3be5e330f38f09d}, - {0xcb090c8001ab551c, 0x5cadf5bfd3072cc5}, - {0xfdcb4fa002162a63, 0x73d9732fc7c8f7f6}, - {0x9e9f11c4014dda7e, 0x2867e7fddcdd9afa}, - {0xc646d63501a1511d, 0xb281e1fd541501b8}, - {0xf7d88bc24209a565, 0x1f225a7ca91a4226}, - {0x9ae757596946075f, 0x3375788de9b06958}, - {0xc1a12d2fc3978937, 0x0052d6b1641c83ae}, - {0xf209787bb47d6b84, 0xc0678c5dbd23a49a}, - {0x9745eb4d50ce6332, 0xf840b7ba963646e0}, - {0xbd176620a501fbff, 0xb650e5a93bc3d898}, - {0xec5d3fa8ce427aff, 0xa3e51f138ab4cebe}, - {0x93ba47c980e98cdf, 0xc66f336c36b10137}, - {0xb8a8d9bbe123f017, 0xb80b0047445d4184}, - {0xe6d3102ad96cec1d, 0xa60dc059157491e5}, - {0x9043ea1ac7e41392, 0x87c89837ad68db2f}, - {0xb454e4a179dd1877, 0x29babe4598c311fb}, - {0xe16a1dc9d8545e94, 0xf4296dd6fef3d67a}, - {0x8ce2529e2734bb1d, 0x1899e4a65f58660c}, - {0xb01ae745b101e9e4, 0x5ec05dcff72e7f8f}, - {0xdc21a1171d42645d, 0x76707543f4fa1f73}, - {0x899504ae72497eba, 0x6a06494a791c53a8}, - {0xabfa45da0edbde69, 0x0487db9d17636892}, - {0xd6f8d7509292d603, 0x45a9d2845d3c42b6}, - {0x865b86925b9bc5c2, 0x0b8a2392ba45a9b2}, - {0xa7f26836f282b732, 0x8e6cac7768d7141e}, - {0xd1ef0244af2364ff, 0x3207d795430cd926}, - {0x8335616aed761f1f, 0x7f44e6bd49e807b8}, - {0xa402b9c5a8d3a6e7, 0x5f16206c9c6209a6}, - {0xcd036837130890a1, 0x36dba887c37a8c0f}, - {0x802221226be55a64, 0xc2494954da2c9789}, - {0xa02aa96b06deb0fd, 0xf2db9baa10b7bd6c}, - {0xc83553c5c8965d3d, 0x6f92829494e5acc7}, - {0xfa42a8b73abbf48c, 0xcb772339ba1f17f9}, - {0x9c69a97284b578d7, 0xff2a760414536efb}, - {0xc38413cf25e2d70d, 0xfef5138519684aba}, - {0xf46518c2ef5b8cd1, 0x7eb258665fc25d69}, - {0x98bf2f79d5993802, 0xef2f773ffbd97a61}, - {0xbeeefb584aff8603, 0xaafb550ffacfd8fa}, - {0xeeaaba2e5dbf6784, 0x95ba2a53f983cf38}, - {0x952ab45cfa97a0b2, 0xdd945a747bf26183}, - {0xba756174393d88df, 0x94f971119aeef9e4}, - {0xe912b9d1478ceb17, 0x7a37cd5601aab85d}, - {0x91abb422ccb812ee, 0xac62e055c10ab33a}, - {0xb616a12b7fe617aa, 0x577b986b314d6009}, - {0xe39c49765fdf9d94, 0xed5a7e85fda0b80b}, - {0x8e41ade9fbebc27d, 0x14588f13be847307}, - {0xb1d219647ae6b31c, 0x596eb2d8ae258fc8}, - {0xde469fbd99a05fe3, 0x6fca5f8ed9aef3bb}, - {0x8aec23d680043bee, 0x25de7bb9480d5854}, - {0xada72ccc20054ae9, 0xaf561aa79a10ae6a}, - {0xd910f7ff28069da4, 0x1b2ba1518094da04}, - {0x87aa9aff79042286, 0x90fb44d2f05d0842}, - {0xa99541bf57452b28, 0x353a1607ac744a53}, - {0xd3fa922f2d1675f2, 0x42889b8997915ce8}, - {0x847c9b5d7c2e09b7, 0x69956135febada11}, - {0xa59bc234db398c25, 0x43fab9837e699095}, - {0xcf02b2c21207ef2e, 0x94f967e45e03f4bb}, - {0x8161afb94b44f57d, 0x1d1be0eebac278f5}, - {0xa1ba1ba79e1632dc, 0x6462d92a69731732}, - {0xca28a291859bbf93, 0x7d7b8f7503cfdcfe}, - {0xfcb2cb35e702af78, 0x5cda735244c3d43e}, - {0x9defbf01b061adab, 0x3a0888136afa64a7}, - {0xc56baec21c7a1916, 0x088aaa1845b8fdd0}, - {0xf6c69a72a3989f5b, 0x8aad549e57273d45}, - {0x9a3c2087a63f6399, 0x36ac54e2f678864b}, - {0xc0cb28a98fcf3c7f, 0x84576a1bb416a7dd}, - {0xf0fdf2d3f3c30b9f, 0x656d44a2a11c51d5}, - {0x969eb7c47859e743, 0x9f644ae5a4b1b325}, - {0xbc4665b596706114, 0x873d5d9f0dde1fee}, - {0xeb57ff22fc0c7959, 0xa90cb506d155a7ea}, - {0x9316ff75dd87cbd8, 0x09a7f12442d588f2}, - {0xb7dcbf5354e9bece, 0x0c11ed6d538aeb2f}, - {0xe5d3ef282a242e81, 0x8f1668c8a86da5fa}, - {0x8fa475791a569d10, 0xf96e017d694487bc}, - {0xb38d92d760ec4455, 0x37c981dcc395a9ac}, - {0xe070f78d3927556a, 0x85bbe253f47b1417}, - {0x8c469ab843b89562, 0x93956d7478ccec8e}, - {0xaf58416654a6babb, 0x387ac8d1970027b2}, - {0xdb2e51bfe9d0696a, 0x06997b05fcc0319e}, - {0x88fcf317f22241e2, 0x441fece3bdf81f03}, - {0xab3c2fddeeaad25a, 0xd527e81cad7626c3}, - {0xd60b3bd56a5586f1, 0x8a71e223d8d3b074}, - {0x85c7056562757456, 0xf6872d5667844e49}, - {0xa738c6bebb12d16c, 0xb428f8ac016561db}, - {0xd106f86e69d785c7, 0xe13336d701beba52}, - {0x82a45b450226b39c, 0xecc0024661173473}, - {0xa34d721642b06084, 0x27f002d7f95d0190}, - {0xcc20ce9bd35c78a5, 0x31ec038df7b441f4}, - {0xff290242c83396ce, 0x7e67047175a15271}, - {0x9f79a169bd203e41, 0x0f0062c6e984d386}, - {0xc75809c42c684dd1, 0x52c07b78a3e60868}, - {0xf92e0c3537826145, 0xa7709a56ccdf8a82}, - {0x9bbcc7a142b17ccb, 0x88a66076400bb691}, - {0xc2abf989935ddbfe, 0x6acff893d00ea435}, - {0xf356f7ebf83552fe, 0x0583f6b8c4124d43}, - {0x98165af37b2153de, 0xc3727a337a8b704a}, - {0xbe1bf1b059e9a8d6, 0x744f18c0592e4c5c}, - {0xeda2ee1c7064130c, 0x1162def06f79df73}, - {0x9485d4d1c63e8be7, 0x8addcb5645ac2ba8}, - {0xb9a74a0637ce2ee1, 0x6d953e2bd7173692}, - {0xe8111c87c5c1ba99, 0xc8fa8db6ccdd0437}, - {0x910ab1d4db9914a0, 0x1d9c9892400a22a2}, - {0xb54d5e4a127f59c8, 0x2503beb6d00cab4b}, - {0xe2a0b5dc971f303a, 0x2e44ae64840fd61d}, - {0x8da471a9de737e24, 0x5ceaecfed289e5d2}, - {0xb10d8e1456105dad, 0x7425a83e872c5f47}, - {0xdd50f1996b947518, 0xd12f124e28f77719}, - {0x8a5296ffe33cc92f, 0x82bd6b70d99aaa6f}, - {0xace73cbfdc0bfb7b, 0x636cc64d1001550b}, - {0xd8210befd30efa5a, 0x3c47f7e05401aa4e}, - {0x8714a775e3e95c78, 0x65acfaec34810a71}, - {0xa8d9d1535ce3b396, 0x7f1839a741a14d0d}, - {0xd31045a8341ca07c, 0x1ede48111209a050}, - {0x83ea2b892091e44d, 0x934aed0aab460432}, - {0xa4e4b66b68b65d60, 0xf81da84d5617853f}, - {0xce1de40642e3f4b9, 0x36251260ab9d668e}, - {0x80d2ae83e9ce78f3, 0xc1d72b7c6b426019}, - {0xa1075a24e4421730, 0xb24cf65b8612f81f}, - {0xc94930ae1d529cfc, 0xdee033f26797b627}, - {0xfb9b7cd9a4a7443c, 0x169840ef017da3b1}, - {0x9d412e0806e88aa5, 0x8e1f289560ee864e}, - {0xc491798a08a2ad4e, 0xf1a6f2bab92a27e2}, - {0xf5b5d7ec8acb58a2, 0xae10af696774b1db}, - {0x9991a6f3d6bf1765, 0xacca6da1e0a8ef29}, - {0xbff610b0cc6edd3f, 0x17fd090a58d32af3}, - {0xeff394dcff8a948e, 0xddfc4b4cef07f5b0}, - {0x95f83d0a1fb69cd9, 0x4abdaf101564f98e}, - {0xbb764c4ca7a4440f, 0x9d6d1ad41abe37f1}, - {0xea53df5fd18d5513, 0x84c86189216dc5ed}, - {0x92746b9be2f8552c, 0x32fd3cf5b4e49bb4}, - {0xb7118682dbb66a77, 0x3fbc8c33221dc2a1}, - {0xe4d5e82392a40515, 0x0fabaf3feaa5334a}, - {0x8f05b1163ba6832d, 0x29cb4d87f2a7400e}, - {0xb2c71d5bca9023f8, 0x743e20e9ef511012}, - {0xdf78e4b2bd342cf6, 0x914da9246b255416}, - {0x8bab8eefb6409c1a, 0x1ad089b6c2f7548e}, - {0xae9672aba3d0c320, 0xa184ac2473b529b1}, - {0xda3c0f568cc4f3e8, 0xc9e5d72d90a2741e}, - {0x8865899617fb1871, 0x7e2fa67c7a658892}, - {0xaa7eebfb9df9de8d, 0xddbb901b98feeab7}, - {0xd51ea6fa85785631, 0x552a74227f3ea565}, - {0x8533285c936b35de, 0xd53a88958f87275f}, - {0xa67ff273b8460356, 0x8a892abaf368f137}, - {0xd01fef10a657842c, 0x2d2b7569b0432d85}, - {0x8213f56a67f6b29b, 0x9c3b29620e29fc73}, - {0xa298f2c501f45f42, 0x8349f3ba91b47b8f}, - {0xcb3f2f7642717713, 0x241c70a936219a73}, - {0xfe0efb53d30dd4d7, 0xed238cd383aa0110}, - {0x9ec95d1463e8a506, 0xf4363804324a40aa}, - {0xc67bb4597ce2ce48, 0xb143c6053edcd0d5}, - {0xf81aa16fdc1b81da, 0xdd94b7868e94050a}, - {0x9b10a4e5e9913128, 0xca7cf2b4191c8326}, - {0xc1d4ce1f63f57d72, 0xfd1c2f611f63a3f0}, - {0xf24a01a73cf2dccf, 0xbc633b39673c8cec}, - {0x976e41088617ca01, 0xd5be0503e085d813}, - {0xbd49d14aa79dbc82, 0x4b2d8644d8a74e18}, - {0xec9c459d51852ba2, 0xddf8e7d60ed1219e}, - {0x93e1ab8252f33b45, 0xcabb90e5c942b503}, - {0xb8da1662e7b00a17, 0x3d6a751f3b936243}, - {0xe7109bfba19c0c9d, 0x0cc512670a783ad4}, - {0x906a617d450187e2, 0x27fb2b80668b24c5}, - {0xb484f9dc9641e9da, 0xb1f9f660802dedf6}, - {0xe1a63853bbd26451, 0x5e7873f8a0396973}, - {0x8d07e33455637eb2, 0xdb0b487b6423e1e8}, - {0xb049dc016abc5e5f, 0x91ce1a9a3d2cda62}, - {0xdc5c5301c56b75f7, 0x7641a140cc7810fb}, - {0x89b9b3e11b6329ba, 0xa9e904c87fcb0a9d}, - {0xac2820d9623bf429, 0x546345fa9fbdcd44}, - {0xd732290fbacaf133, 0xa97c177947ad4095}, - {0x867f59a9d4bed6c0, 0x49ed8eabcccc485d}, - {0xa81f301449ee8c70, 0x5c68f256bfff5a74}, - {0xd226fc195c6a2f8c, 0x73832eec6fff3111}, - {0x83585d8fd9c25db7, 0xc831fd53c5ff7eab}, - {0xa42e74f3d032f525, 0xba3e7ca8b77f5e55}, - {0xcd3a1230c43fb26f, 0x28ce1bd2e55f35eb}, - {0x80444b5e7aa7cf85, 0x7980d163cf5b81b3}, - {0xa0555e361951c366, 0xd7e105bcc332621f}, - {0xc86ab5c39fa63440, 0x8dd9472bf3fefaa7}, - {0xfa856334878fc150, 0xb14f98f6f0feb951}, - {0x9c935e00d4b9d8d2, 0x6ed1bf9a569f33d3}, - {0xc3b8358109e84f07, 0x0a862f80ec4700c8}, - {0xf4a642e14c6262c8, 0xcd27bb612758c0fa}, - {0x98e7e9cccfbd7dbd, 0x8038d51cb897789c}, - {0xbf21e44003acdd2c, 0xe0470a63e6bd56c3}, - {0xeeea5d5004981478, 0x1858ccfce06cac74}, - {0x95527a5202df0ccb, 0x0f37801e0c43ebc8}, - {0xbaa718e68396cffd, 0xd30560258f54e6ba}, - {0xe950df20247c83fd, 0x47c6b82ef32a2069}, - {0x91d28b7416cdd27e, 0x4cdc331d57fa5441}, - {0xb6472e511c81471d, 0xe0133fe4adf8e952}, - {0xe3d8f9e563a198e5, 0x58180fddd97723a6}, - {0x8e679c2f5e44ff8f, 0x570f09eaa7ea7648}, - {0xb201833b35d63f73, 0x2cd2cc6551e513da}, - {0xde81e40a034bcf4f, 0xf8077f7ea65e58d1}, - {0x8b112e86420f6191, 0xfb04afaf27faf782}, - {0xadd57a27d29339f6, 0x79c5db9af1f9b563}, - {0xd94ad8b1c7380874, 0x18375281ae7822bc}, - {0x87cec76f1c830548, 0x8f2293910d0b15b5}, - {0xa9c2794ae3a3c69a, 0xb2eb3875504ddb22}, - {0xd433179d9c8cb841, 0x5fa60692a46151eb}, - {0x849feec281d7f328, 0xdbc7c41ba6bcd333}, - {0xa5c7ea73224deff3, 0x12b9b522906c0800}, - {0xcf39e50feae16bef, 0xd768226b34870a00}, - {0x81842f29f2cce375, 0xe6a1158300d46640}, - {0xa1e53af46f801c53, 0x60495ae3c1097fd0}, - {0xca5e89b18b602368, 0x385bb19cb14bdfc4}, - {0xfcf62c1dee382c42, 0x46729e03dd9ed7b5}, - {0x9e19db92b4e31ba9, 0x6c07a2c26a8346d1}, - {0xc5a05277621be293, 0xc7098b7305241885}, - {0xf70867153aa2db38, 0xb8cbee4fc66d1ea7} -#else - {0xff77b1fcbebcdc4f, 0x25e8e89c13bb0f7b}, - {0xce5d73ff402d98e3, 0xfb0a3d212dc81290}, - {0xa6b34ad8c9dfc06f, 0xf42faa48c0ea481f}, - {0x86a8d39ef77164bc, 0xae5dff9c02033198}, - {0xd98ddaee19068c76, 0x3badd624dd9b0958}, - {0xafbd2350644eeacf, 0xe5d1929ef90898fb}, - {0x8df5efabc5979c8f, 0xca8d3ffa1ef463c2}, - {0xe55990879ddcaabd, 0xcc420a6a101d0516}, - {0xb94470938fa89bce, 0xf808e40e8d5b3e6a}, - {0x95a8637627989aad, 0xdde7001379a44aa9}, - {0xf1c90080baf72cb1, 0x5324c68b12dd6339}, - {0xc350000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, - {0x9dc5ada82b70b59d, 0xf020000000000000}, - {0xfee50b7025c36a08, 0x02f236d04753d5b4}, - {0xcde6fd5e09abcf26, 0xed4c0226b55e6f86}, - {0xa6539930bf6bff45, 0x84db8346b786151c}, - {0x865b86925b9bc5c2, 0x0b8a2392ba45a9b2}, - {0xd910f7ff28069da4, 0x1b2ba1518094da04}, - {0xaf58416654a6babb, 0x387ac8d1970027b2}, - {0x8da471a9de737e24, 0x5ceaecfed289e5d2}, - {0xe4d5e82392a40515, 0x0fabaf3feaa5334a}, - {0xb8da1662e7b00a17, 0x3d6a751f3b936243}, - {0x95527a5202df0ccb, 0x0f37801e0c43ebc8} -#endif -}; - -#if !FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX -template <typename T> -const uint64_t basic_data<T>::powers_of_5_64[] = { - 0x0000000000000001, 0x0000000000000005, 0x0000000000000019, - 0x000000000000007d, 0x0000000000000271, 0x0000000000000c35, - 0x0000000000003d09, 0x000000000001312d, 0x000000000005f5e1, - 0x00000000001dcd65, 0x00000000009502f9, 0x0000000002e90edd, - 0x000000000e8d4a51, 0x0000000048c27395, 0x000000016bcc41e9, - 0x000000071afd498d, 0x0000002386f26fc1, 0x000000b1a2bc2ec5, - 0x000003782dace9d9, 0x00001158e460913d, 0x000056bc75e2d631, - 0x0001b1ae4d6e2ef5, 0x000878678326eac9, 0x002a5a058fc295ed, - 0x00d3c21bcecceda1, 0x0422ca8b0a00a425, 0x14adf4b7320334b9}; - -template <typename T> -const uint32_t basic_data<T>::dragonbox_pow10_recovery_errors[] = { - 0x50001400, 0x54044100, 0x54014555, 0x55954415, 0x54115555, 0x00000001, - 0x50000000, 0x00104000, 0x54010004, 0x05004001, 0x55555544, 0x41545555, - 0x54040551, 0x15445545, 0x51555514, 0x10000015, 0x00101100, 0x01100015, - 0x00000000, 0x00000000, 0x00000000, 0x00000000, 0x04450514, 0x45414110, - 0x55555145, 0x50544050, 0x15040155, 0x11054140, 0x50111514, 0x11451454, - 0x00400541, 0x00000000, 0x55555450, 0x10056551, 0x10054011, 0x55551014, - 0x69514555, 0x05151109, 0x00155555}; -#endif - -template <typename T> -const char basic_data<T>::foreground_color[] = "\x1b[38;2;"; -template <typename T> -const char basic_data<T>::background_color[] = "\x1b[48;2;"; -template <typename T> const char basic_data<T>::reset_color[] = "\x1b[0m"; -template <typename T> const wchar_t basic_data<T>::wreset_color[] = L"\x1b[0m"; -template <typename T> const char basic_data<T>::signs[] = {0, '-', '+', ' '}; -template <typename T> -const char basic_data<T>::left_padding_shifts[] = {31, 31, 0, 1, 0}; -template <typename T> -const char basic_data<T>::right_padding_shifts[] = {0, 31, 0, 1, 0}; - -template <typename T> struct bits { - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const int value = - static_cast<int>(sizeof(T) * std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::digits); -}; - -class fp; -template <int SHIFT = 0> fp normalize(fp value); - -// Lower (upper) boundary is a value half way between a floating-point value -// and its predecessor (successor). Boundaries have the same exponent as the -// value so only significands are stored. -struct boundaries { - uint64_t lower; - uint64_t upper; -}; - -// A handmade floating-point number f * pow(2, e). -class fp { - private: - using significand_type = uint64_t; - - template <typename Float> - using is_supported_float = bool_constant<sizeof(Float) == sizeof(uint64_t) || - sizeof(Float) == sizeof(uint32_t)>; - - public: - significand_type f; - int e; - - // All sizes are in bits. - // Subtract 1 to account for an implicit most significant bit in the - // normalized form. - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const int double_significand_size = - std::numeric_limits<double>::digits - 1; - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const uint64_t implicit_bit = - 1ULL << double_significand_size; - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const int significand_size = - bits<significand_type>::value; - - fp() : f(0), e(0) {} - fp(uint64_t f_val, int e_val) : f(f_val), e(e_val) {} - - // Constructs fp from an IEEE754 double. It is a template to prevent compile - // errors on platforms where double is not IEEE754. - template <typename Double> explicit fp(Double d) { assign(d); } - - // Assigns d to this and return true iff predecessor is closer than successor. - template <typename Float, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_supported_float<Float>::value)> - bool assign(Float d) { - // Assume float is in the format [sign][exponent][significand]. - using limits = std::numeric_limits<Float>; - const int float_significand_size = limits::digits - 1; - const int exponent_size = - bits<Float>::value - float_significand_size - 1; // -1 for sign - const uint64_t float_implicit_bit = 1ULL << float_significand_size; - const uint64_t significand_mask = float_implicit_bit - 1; - const uint64_t exponent_mask = (~0ULL >> 1) & ~significand_mask; - const int exponent_bias = (1 << exponent_size) - limits::max_exponent - 1; - constexpr bool is_double = sizeof(Float) == sizeof(uint64_t); - auto u = bit_cast<conditional_t<is_double, uint64_t, uint32_t>>(d); - f = u & significand_mask; - int biased_e = - static_cast<int>((u & exponent_mask) >> float_significand_size); - // Predecessor is closer if d is a normalized power of 2 (f == 0) other than - // the smallest normalized number (biased_e > 1). - bool is_predecessor_closer = f == 0 && biased_e > 1; - if (biased_e != 0) - f += float_implicit_bit; - else - biased_e = 1; // Subnormals use biased exponent 1 (min exponent). - e = biased_e - exponent_bias - float_significand_size; - return is_predecessor_closer; - } - - template <typename Float, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_supported_float<Float>::value)> - bool assign(Float) { - *this = fp(); - return false; - } -}; - -// Normalizes the value converted from double and multiplied by (1 << SHIFT). -template <int SHIFT> fp normalize(fp value) { - // Handle subnormals. - const auto shifted_implicit_bit = fp::implicit_bit << SHIFT; - while ((value.f & shifted_implicit_bit) == 0) { - value.f <<= 1; - --value.e; - } - // Subtract 1 to account for hidden bit. - const auto offset = - fp::significand_size - fp::double_significand_size - SHIFT - 1; - value.f <<= offset; - value.e -= offset; - return value; +template <> +FMT_API FMT_FUNC auto format_facet<std::locale>::do_put( + appender out, loc_value val, const format_specs<>& specs) const -> bool { + return val.visit( + detail::loc_writer<>{out, specs, separator_, grouping_, decimal_point_}); } - -inline bool operator==(fp x, fp y) { return x.f == y.f && x.e == y.e; } - -// Computes lhs * rhs / pow(2, 64) rounded to nearest with half-up tie breaking. -inline uint64_t multiply(uint64_t lhs, uint64_t rhs) { -#if FMT_USE_INT128 - auto product = static_cast<__uint128_t>(lhs) * rhs; - auto f = static_cast<uint64_t>(product >> 64); - return (static_cast<uint64_t>(product) & (1ULL << 63)) != 0 ? f + 1 : f; -#else - // Multiply 32-bit parts of significands. - uint64_t mask = (1ULL << 32) - 1; - uint64_t a = lhs >> 32, b = lhs & mask; - uint64_t c = rhs >> 32, d = rhs & mask; - uint64_t ac = a * c, bc = b * c, ad = a * d, bd = b * d; - // Compute mid 64-bit of result and round. - uint64_t mid = (bd >> 32) + (ad & mask) + (bc & mask) + (1U << 31); - return ac + (ad >> 32) + (bc >> 32) + (mid >> 32); #endif -} -inline fp operator*(fp x, fp y) { return {multiply(x.f, y.f), x.e + y.e + 64}; } - -// Returns a cached power of 10 `c_k = c_k.f * pow(2, c_k.e)` such that its -// (binary) exponent satisfies `min_exponent <= c_k.e <= min_exponent + 28`. -inline fp get_cached_power(int min_exponent, int& pow10_exponent) { - const int shift = 32; - const auto significand = static_cast<int64_t>(data::log10_2_significand); - int index = static_cast<int>( - ((min_exponent + fp::significand_size - 1) * (significand >> shift) + - ((int64_t(1) << shift) - 1)) // ceil - >> 32 // arithmetic shift - ); - // Decimal exponent of the first (smallest) cached power of 10. - const int first_dec_exp = -348; - // Difference between 2 consecutive decimal exponents in cached powers of 10. - const int dec_exp_step = 8; - index = (index - first_dec_exp - 1) / dec_exp_step + 1; - pow10_exponent = first_dec_exp + index * dec_exp_step; - return {data::grisu_pow10_significands[index], - data::grisu_pow10_exponents[index]}; +FMT_FUNC std::system_error vsystem_error(int error_code, string_view fmt, + format_args args) { + auto ec = std::error_code(error_code, std::generic_category()); + return std::system_error(ec, vformat(fmt, args)); } -// A simple accumulator to hold the sums of terms in bigint::square if uint128_t -// is not available. -struct accumulator { - uint64_t lower; - uint64_t upper; - - accumulator() : lower(0), upper(0) {} - explicit operator uint32_t() const { return static_cast<uint32_t>(lower); } - - void operator+=(uint64_t n) { - lower += n; - if (lower < n) ++upper; - } - void operator>>=(int shift) { - assert(shift == 32); - (void)shift; - lower = (upper << 32) | (lower >> 32); - upper >>= 32; - } -}; - -class bigint { - private: - // A bigint is stored as an array of bigits (big digits), with bigit at index - // 0 being the least significant one. - using bigit = uint32_t; - using double_bigit = uint64_t; - enum { bigits_capacity = 32 }; - basic_memory_buffer<bigit, bigits_capacity> bigits_; - int exp_; - - bigit operator[](int index) const { return bigits_[to_unsigned(index)]; } - bigit& operator[](int index) { return bigits_[to_unsigned(index)]; } - - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const int bigit_bits = bits<bigit>::value; - - friend struct formatter<bigint>; - - void subtract_bigits(int index, bigit other, bigit& borrow) { - auto result = static_cast<double_bigit>((*this)[index]) - other - borrow; - (*this)[index] = static_cast<bigit>(result); - borrow = static_cast<bigit>(result >> (bigit_bits * 2 - 1)); - } - - void remove_leading_zeros() { - int num_bigits = static_cast<int>(bigits_.size()) - 1; - while (num_bigits > 0 && (*this)[num_bigits] == 0) --num_bigits; - bigits_.resize(to_unsigned(num_bigits + 1)); - } - - // Computes *this -= other assuming aligned bigints and *this >= other. - void subtract_aligned(const bigint& other) { - FMT_ASSERT(other.exp_ >= exp_, "unaligned bigints"); - FMT_ASSERT(compare(*this, other) >= 0, ""); - bigit borrow = 0; - int i = other.exp_ - exp_; - for (size_t j = 0, n = other.bigits_.size(); j != n; ++i, ++j) - subtract_bigits(i, other.bigits_[j], borrow); - while (borrow > 0) subtract_bigits(i, 0, borrow); - remove_leading_zeros(); - } - - void multiply(uint32_t value) { - const double_bigit wide_value = value; - bigit carry = 0; - for (size_t i = 0, n = bigits_.size(); i < n; ++i) { - double_bigit result = bigits_[i] * wide_value + carry; - bigits_[i] = static_cast<bigit>(result); - carry = static_cast<bigit>(result >> bigit_bits); - } - if (carry != 0) bigits_.push_back(carry); - } - - void multiply(uint64_t value) { - const bigit mask = ~bigit(0); - const double_bigit lower = value & mask; - const double_bigit upper = value >> bigit_bits; - double_bigit carry = 0; - for (size_t i = 0, n = bigits_.size(); i < n; ++i) { - double_bigit result = bigits_[i] * lower + (carry & mask); - carry = - bigits_[i] * upper + (result >> bigit_bits) + (carry >> bigit_bits); - bigits_[i] = static_cast<bigit>(result); - } - while (carry != 0) { - bigits_.push_back(carry & mask); - carry >>= bigit_bits; - } - } - - public: - bigint() : exp_(0) {} - explicit bigint(uint64_t n) { assign(n); } - ~bigint() { assert(bigits_.capacity() <= bigits_capacity); } - - bigint(const bigint&) = delete; - void operator=(const bigint&) = delete; - - void assign(const bigint& other) { - auto size = other.bigits_.size(); - bigits_.resize(size); - auto data = other.bigits_.data(); - std::copy(data, data + size, make_checked(bigits_.data(), size)); - exp_ = other.exp_; - } - - void assign(uint64_t n) { - size_t num_bigits = 0; - do { - bigits_[num_bigits++] = n & ~bigit(0); - n >>= bigit_bits; - } while (n != 0); - bigits_.resize(num_bigits); - exp_ = 0; - } - - int num_bigits() const { return static_cast<int>(bigits_.size()) + exp_; } - - FMT_NOINLINE bigint& operator<<=(int shift) { - assert(shift >= 0); - exp_ += shift / bigit_bits; - shift %= bigit_bits; - if (shift == 0) return *this; - bigit carry = 0; - for (size_t i = 0, n = bigits_.size(); i < n; ++i) { - bigit c = bigits_[i] >> (bigit_bits - shift); - bigits_[i] = (bigits_[i] << shift) + carry; - carry = c; - } - if (carry != 0) bigits_.push_back(carry); - return *this; - } - - template <typename Int> bigint& operator*=(Int value) { - FMT_ASSERT(value > 0, ""); - multiply(uint32_or_64_or_128_t<Int>(value)); - return *this; - } - - friend int compare(const bigint& lhs, const bigint& rhs) { - int num_lhs_bigits = lhs.num_bigits(), num_rhs_bigits = rhs.num_bigits(); - if (num_lhs_bigits != num_rhs_bigits) - return num_lhs_bigits > num_rhs_bigits ? 1 : -1; - int i = static_cast<int>(lhs.bigits_.size()) - 1; - int j = static_cast<int>(rhs.bigits_.size()) - 1; - int end = i - j; - if (end < 0) end = 0; - for (; i >= end; --i, --j) { - bigit lhs_bigit = lhs[i], rhs_bigit = rhs[j]; - if (lhs_bigit != rhs_bigit) return lhs_bigit > rhs_bigit ? 1 : -1; - } - if (i != j) return i > j ? 1 : -1; - return 0; - } - - // Returns compare(lhs1 + lhs2, rhs). - friend int add_compare(const bigint& lhs1, const bigint& lhs2, - const bigint& rhs) { - int max_lhs_bigits = (std::max)(lhs1.num_bigits(), lhs2.num_bigits()); - int num_rhs_bigits = rhs.num_bigits(); - if (max_lhs_bigits + 1 < num_rhs_bigits) return -1; - if (max_lhs_bigits > num_rhs_bigits) return 1; - auto get_bigit = [](const bigint& n, int i) -> bigit { - return i >= n.exp_ && i < n.num_bigits() ? n[i - n.exp_] : 0; - }; - double_bigit borrow = 0; - int min_exp = (std::min)((std::min)(lhs1.exp_, lhs2.exp_), rhs.exp_); - for (int i = num_rhs_bigits - 1; i >= min_exp; --i) { - double_bigit sum = - static_cast<double_bigit>(get_bigit(lhs1, i)) + get_bigit(lhs2, i); - bigit rhs_bigit = get_bigit(rhs, i); - if (sum > rhs_bigit + borrow) return 1; - borrow = rhs_bigit + borrow - sum; - if (borrow > 1) return -1; - borrow <<= bigit_bits; - } - return borrow != 0 ? -1 : 0; - } - - // Assigns pow(10, exp) to this bigint. - void assign_pow10(int exp) { - assert(exp >= 0); - if (exp == 0) return assign(1); - // Find the top bit. - int bitmask = 1; - while (exp >= bitmask) bitmask <<= 1; - bitmask >>= 1; - // pow(10, exp) = pow(5, exp) * pow(2, exp). First compute pow(5, exp) by - // repeated squaring and multiplication. - assign(5); - bitmask >>= 1; - while (bitmask != 0) { - square(); - if ((exp & bitmask) != 0) *this *= 5; - bitmask >>= 1; - } - *this <<= exp; // Multiply by pow(2, exp) by shifting. - } - - void square() { - basic_memory_buffer<bigit, bigits_capacity> n(std::move(bigits_)); - int num_bigits = static_cast<int>(bigits_.size()); - int num_result_bigits = 2 * num_bigits; - bigits_.resize(to_unsigned(num_result_bigits)); - using accumulator_t = conditional_t<FMT_USE_INT128, uint128_t, accumulator>; - auto sum = accumulator_t(); - for (int bigit_index = 0; bigit_index < num_bigits; ++bigit_index) { - // Compute bigit at position bigit_index of the result by adding - // cross-product terms n[i] * n[j] such that i + j == bigit_index. - for (int i = 0, j = bigit_index; j >= 0; ++i, --j) { - // Most terms are multiplied twice which can be optimized in the future. - sum += static_cast<double_bigit>(n[i]) * n[j]; - } - (*this)[bigit_index] = static_cast<bigit>(sum); - sum >>= bits<bigit>::value; // Compute the carry. - } - // Do the same for the top half. - for (int bigit_index = num_bigits; bigit_index < num_result_bigits; - ++bigit_index) { - for (int j = num_bigits - 1, i = bigit_index - j; i < num_bigits;) - sum += static_cast<double_bigit>(n[i++]) * n[j--]; - (*this)[bigit_index] = static_cast<bigit>(sum); - sum >>= bits<bigit>::value; - } - --num_result_bigits; - remove_leading_zeros(); - exp_ *= 2; - } - - // If this bigint has a bigger exponent than other, adds trailing zero to make - // exponents equal. This simplifies some operations such as subtraction. - void align(const bigint& other) { - int exp_difference = exp_ - other.exp_; - if (exp_difference <= 0) return; - int num_bigits = static_cast<int>(bigits_.size()); - bigits_.resize(to_unsigned(num_bigits + exp_difference)); - for (int i = num_bigits - 1, j = i + exp_difference; i >= 0; --i, --j) - bigits_[j] = bigits_[i]; - std::uninitialized_fill_n(bigits_.data(), exp_difference, 0); - exp_ -= exp_difference; - } - - // Divides this bignum by divisor, assigning the remainder to this and - // returning the quotient. - int divmod_assign(const bigint& divisor) { - FMT_ASSERT(this != &divisor, ""); - if (compare(*this, divisor) < 0) return 0; - FMT_ASSERT(divisor.bigits_[divisor.bigits_.size() - 1u] != 0, ""); - align(divisor); - int quotient = 0; - do { - subtract_aligned(divisor); - ++quotient; - } while (compare(*this, divisor) >= 0); - return quotient; - } -}; +namespace detail { -enum class round_direction { unknown, up, down }; - -// Given the divisor (normally a power of 10), the remainder = v % divisor for -// some number v and the error, returns whether v should be rounded up, down, or -// whether the rounding direction can't be determined due to error. -// error should be less than divisor / 2. -inline round_direction get_round_direction(uint64_t divisor, uint64_t remainder, - uint64_t error) { - FMT_ASSERT(remainder < divisor, ""); // divisor - remainder won't overflow. - FMT_ASSERT(error < divisor, ""); // divisor - error won't overflow. - FMT_ASSERT(error < divisor - error, ""); // error * 2 won't overflow. - // Round down if (remainder + error) * 2 <= divisor. - if (remainder <= divisor - remainder && error * 2 <= divisor - remainder * 2) - return round_direction::down; - // Round up if (remainder - error) * 2 >= divisor. - if (remainder >= error && - remainder - error >= divisor - (remainder - error)) { - return round_direction::up; - } - return round_direction::unknown; +template <typename F> inline bool operator==(basic_fp<F> x, basic_fp<F> y) { + return x.f == y.f && x.e == y.e; } -namespace digits { -enum result { - more, // Generate more digits. - done, // Done generating digits. - error // Digit generation cancelled due to an error. -}; +// Compilers should be able to optimize this into the ror instruction. +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline uint32_t rotr(uint32_t n, uint32_t r) noexcept { + r &= 31; + return (n >> r) | (n << (32 - r)); } - -// Generates output using the Grisu digit-gen algorithm. -// error: the size of the region (lower, upper) outside of which numbers -// definitely do not round to value (Delta in Grisu3). -template <typename Handler> -FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE digits::result grisu_gen_digits(fp value, uint64_t error, - int& exp, Handler& handler) { - const fp one(1ULL << -value.e, value.e); - // The integral part of scaled value (p1 in Grisu) = value / one. It cannot be - // zero because it contains a product of two 64-bit numbers with MSB set (due - // to normalization) - 1, shifted right by at most 60 bits. - auto integral = static_cast<uint32_t>(value.f >> -one.e); - FMT_ASSERT(integral != 0, ""); - FMT_ASSERT(integral == value.f >> -one.e, ""); - // The fractional part of scaled value (p2 in Grisu) c = value % one. - uint64_t fractional = value.f & (one.f - 1); - exp = count_digits(integral); // kappa in Grisu. - // Divide by 10 to prevent overflow. - auto result = handler.on_start(data::powers_of_10_64[exp - 1] << -one.e, - value.f / 10, error * 10, exp); - if (result != digits::more) return result; - // Generate digits for the integral part. This can produce up to 10 digits. - do { - uint32_t digit = 0; - auto divmod_integral = [&](uint32_t divisor) { - digit = integral / divisor; - integral %= divisor; - }; - // This optimization by Milo Yip reduces the number of integer divisions by - // one per iteration. - switch (exp) { - case 10: - divmod_integral(1000000000); - break; - case 9: - divmod_integral(100000000); - break; - case 8: - divmod_integral(10000000); - break; - case 7: - divmod_integral(1000000); - break; - case 6: - divmod_integral(100000); - break; - case 5: - divmod_integral(10000); - break; - case 4: - divmod_integral(1000); - break; - case 3: - divmod_integral(100); - break; - case 2: - divmod_integral(10); - break; - case 1: - digit = integral; - integral = 0; - break; - default: - FMT_ASSERT(false, "invalid number of digits"); - } - --exp; - auto remainder = (static_cast<uint64_t>(integral) << -one.e) + fractional; - result = handler.on_digit(static_cast<char>('0' + digit), - data::powers_of_10_64[exp] << -one.e, remainder, - error, exp, true); - if (result != digits::more) return result; - } while (exp > 0); - // Generate digits for the fractional part. - for (;;) { - fractional *= 10; - error *= 10; - char digit = static_cast<char>('0' + (fractional >> -one.e)); - fractional &= one.f - 1; - --exp; - result = handler.on_digit(digit, one.f, fractional, error, exp, false); - if (result != digits::more) return result; - } +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline uint64_t rotr(uint64_t n, uint32_t r) noexcept { + r &= 63; + return (n >> r) | (n << (64 - r)); } -// The fixed precision digit handler. -struct fixed_handler { - char* buf; - int size; - int precision; - int exp10; - bool fixed; - - digits::result on_start(uint64_t divisor, uint64_t remainder, uint64_t error, - int& exp) { - // Non-fixed formats require at least one digit and no precision adjustment. - if (!fixed) return digits::more; - // Adjust fixed precision by exponent because it is relative to decimal - // point. - precision += exp + exp10; - // Check if precision is satisfied just by leading zeros, e.g. - // format("{:.2f}", 0.001) gives "0.00" without generating any digits. - if (precision > 0) return digits::more; - if (precision < 0) return digits::done; - auto dir = get_round_direction(divisor, remainder, error); - if (dir == round_direction::unknown) return digits::error; - buf[size++] = dir == round_direction::up ? '1' : '0'; - return digits::done; - } - - digits::result on_digit(char digit, uint64_t divisor, uint64_t remainder, - uint64_t error, int, bool integral) { - FMT_ASSERT(remainder < divisor, ""); - buf[size++] = digit; - if (!integral && error >= remainder) return digits::error; - if (size < precision) return digits::more; - if (!integral) { - // Check if error * 2 < divisor with overflow prevention. - // The check is not needed for the integral part because error = 1 - // and divisor > (1 << 32) there. - if (error >= divisor || error >= divisor - error) return digits::error; - } else { - FMT_ASSERT(error == 1 && divisor > 2, ""); - } - auto dir = get_round_direction(divisor, remainder, error); - if (dir != round_direction::up) - return dir == round_direction::down ? digits::done : digits::error; - ++buf[size - 1]; - for (int i = size - 1; i > 0 && buf[i] > '9'; --i) { - buf[i] = '0'; - ++buf[i - 1]; - } - if (buf[0] > '9') { - buf[0] = '1'; - if (fixed) - buf[size++] = '0'; - else - ++exp10; - } - return digits::done; - } -}; - // Implementation of Dragonbox algorithm: https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox. namespace dragonbox { -// Computes 128-bit result of multiplication of two 64-bit unsigned integers. -FMT_SAFEBUFFERS inline uint128_wrapper umul128(uint64_t x, - uint64_t y) FMT_NOEXCEPT { -#if FMT_USE_INT128 - return static_cast<uint128_t>(x) * static_cast<uint128_t>(y); -#elif defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_X64) - uint128_wrapper result; - result.low_ = _umul128(x, y, &result.high_); - return result; -#else - const uint64_t mask = (uint64_t(1) << 32) - uint64_t(1); - - uint64_t a = x >> 32; - uint64_t b = x & mask; - uint64_t c = y >> 32; - uint64_t d = y & mask; - - uint64_t ac = a * c; - uint64_t bc = b * c; - uint64_t ad = a * d; - uint64_t bd = b * d; - - uint64_t intermediate = (bd >> 32) + (ad & mask) + (bc & mask); - - return {ac + (intermediate >> 32) + (ad >> 32) + (bc >> 32), - (intermediate << 32) + (bd & mask)}; -#endif -} - -// Computes upper 64 bits of multiplication of two 64-bit unsigned integers. -FMT_SAFEBUFFERS inline uint64_t umul128_upper64(uint64_t x, - uint64_t y) FMT_NOEXCEPT { -#if FMT_USE_INT128 - auto p = static_cast<uint128_t>(x) * static_cast<uint128_t>(y); - return static_cast<uint64_t>(p >> 64); -#elif defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_X64) - return __umulh(x, y); -#else - return umul128(x, y).high(); -#endif -} - -// Computes upper 64 bits of multiplication of a 64-bit unsigned integer and a -// 128-bit unsigned integer. -FMT_SAFEBUFFERS inline uint64_t umul192_upper64(uint64_t x, uint128_wrapper y) - FMT_NOEXCEPT { - uint128_wrapper g0 = umul128(x, y.high()); - g0 += umul128_upper64(x, y.low()); - return g0.high(); -} - -// Computes upper 32 bits of multiplication of a 32-bit unsigned integer and a +// Computes upper 64 bits of multiplication of a 32-bit unsigned integer and a // 64-bit unsigned integer. -inline uint32_t umul96_upper32(uint32_t x, uint64_t y) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return static_cast<uint32_t>(umul128_upper64(x, y)); +inline uint64_t umul96_upper64(uint32_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept { + return umul128_upper64(static_cast<uint64_t>(x) << 32, y); } -// Computes middle 64 bits of multiplication of a 64-bit unsigned integer and a +// Computes lower 128 bits of multiplication of a 64-bit unsigned integer and a // 128-bit unsigned integer. -FMT_SAFEBUFFERS inline uint64_t umul192_middle64(uint64_t x, uint128_wrapper y) - FMT_NOEXCEPT { - uint64_t g01 = x * y.high(); - uint64_t g10 = umul128_upper64(x, y.low()); - return g01 + g10; +inline uint128_fallback umul192_lower128(uint64_t x, + uint128_fallback y) noexcept { + uint64_t high = x * y.high(); + uint128_fallback high_low = umul128(x, y.low()); + return {high + high_low.high(), high_low.low()}; } // Computes lower 64 bits of multiplication of a 32-bit unsigned integer and a // 64-bit unsigned integer. -inline uint64_t umul96_lower64(uint32_t x, uint64_t y) FMT_NOEXCEPT { +inline uint64_t umul96_lower64(uint32_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept { return x * y; } -// Computes floor(log10(pow(2, e))) for e in [-1700, 1700] using the method from -// https://fmt.dev/papers/Grisu-Exact.pdf#page=5, section 3.4. -inline int floor_log10_pow2(int e) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(e <= 1700 && e >= -1700, "too large exponent"); - const int shift = 22; - return (e * static_cast<int>(data::log10_2_significand >> (64 - shift))) >> - shift; -} - // Various fast log computations. -inline int floor_log2_pow10(int e) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(e <= 1233 && e >= -1233, "too large exponent"); - const uint64_t log2_10_integer_part = 3; - const uint64_t log2_10_fractional_digits = 0x5269e12f346e2bf9; - const int shift_amount = 19; - return (e * static_cast<int>( - (log2_10_integer_part << shift_amount) | - (log2_10_fractional_digits >> (64 - shift_amount)))) >> - shift_amount; -} -inline int floor_log10_pow2_minus_log10_4_over_3(int e) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(e <= 1700 && e >= -1700, "too large exponent"); - const uint64_t log10_4_over_3_fractional_digits = 0x1ffbfc2bbc780375; - const int shift_amount = 22; - return (e * static_cast<int>(data::log10_2_significand >> - (64 - shift_amount)) - - static_cast<int>(log10_4_over_3_fractional_digits >> - (64 - shift_amount))) >> - shift_amount; +inline int floor_log10_pow2_minus_log10_4_over_3(int e) noexcept { + FMT_ASSERT(e <= 2936 && e >= -2985, "too large exponent"); + return (e * 631305 - 261663) >> 21; } -// Returns true iff x is divisible by pow(2, exp). -inline bool divisible_by_power_of_2(uint32_t x, int exp) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(exp >= 1, ""); - FMT_ASSERT(x != 0, ""); -#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CTZ - return FMT_BUILTIN_CTZ(x) >= exp; -#else - return exp < num_bits<uint32_t>() && x == ((x >> exp) << exp); -#endif -} -inline bool divisible_by_power_of_2(uint64_t x, int exp) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(exp >= 1, ""); - FMT_ASSERT(x != 0, ""); -#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CTZLL - return FMT_BUILTIN_CTZLL(x) >= exp; -#else - return exp < num_bits<uint64_t>() && x == ((x >> exp) << exp); -#endif -} +FMT_INLINE_VARIABLE constexpr struct { + uint32_t divisor; + int shift_amount; +} div_small_pow10_infos[] = {{10, 16}, {100, 16}}; -// Returns true iff x is divisible by pow(5, exp). -inline bool divisible_by_power_of_5(uint32_t x, int exp) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(exp <= 10, "too large exponent"); - return x * data::divtest_table_for_pow5_32[exp].mod_inv <= - data::divtest_table_for_pow5_32[exp].max_quotient; -} -inline bool divisible_by_power_of_5(uint64_t x, int exp) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(exp <= 23, "too large exponent"); - return x * data::divtest_table_for_pow5_64[exp].mod_inv <= - data::divtest_table_for_pow5_64[exp].max_quotient; -} - -// Replaces n by floor(n / pow(5, N)) returning true if and only if n is -// divisible by pow(5, N). -// Precondition: n <= 2 * pow(5, N + 1). +// Replaces n by floor(n / pow(10, N)) returning true if and only if n is +// divisible by pow(10, N). +// Precondition: n <= pow(10, N + 1). template <int N> -bool check_divisibility_and_divide_by_pow5(uint32_t& n) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - static constexpr struct { - uint32_t magic_number; - int bits_for_comparison; - uint32_t threshold; - int shift_amount; - } infos[] = {{0xcccd, 16, 0x3333, 18}, {0xa429, 8, 0x0a, 20}}; - constexpr auto info = infos[N - 1]; - n *= info.magic_number; - const uint32_t comparison_mask = (1u << info.bits_for_comparison) - 1; - bool result = (n & comparison_mask) <= info.threshold; +bool check_divisibility_and_divide_by_pow10(uint32_t& n) noexcept { + // The numbers below are chosen such that: + // 1. floor(n/d) = floor(nm / 2^k) where d=10 or d=100, + // 2. nm mod 2^k < m if and only if n is divisible by d, + // where m is magic_number, k is shift_amount + // and d is divisor. + // + // Item 1 is a common technique of replacing division by a constant with + // multiplication, see e.g. "Division by Invariant Integers Using + // Multiplication" by Granlund and Montgomery (1994). magic_number (m) is set + // to ceil(2^k/d) for large enough k. + // The idea for item 2 originates from Schubfach. + constexpr auto info = div_small_pow10_infos[N - 1]; + FMT_ASSERT(n <= info.divisor * 10, "n is too large"); + constexpr uint32_t magic_number = + (1u << info.shift_amount) / info.divisor + 1; + n *= magic_number; + const uint32_t comparison_mask = (1u << info.shift_amount) - 1; + bool result = (n & comparison_mask) < magic_number; n >>= info.shift_amount; return result; } // Computes floor(n / pow(10, N)) for small n and N. // Precondition: n <= pow(10, N + 1). -template <int N> uint32_t small_division_by_pow10(uint32_t n) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - static constexpr struct { - uint32_t magic_number; - int shift_amount; - uint32_t divisor_times_10; - } infos[] = {{0xcccd, 19, 100}, {0xa3d8, 22, 1000}}; - constexpr auto info = infos[N - 1]; - FMT_ASSERT(n <= info.divisor_times_10, "n is too large"); - return n * info.magic_number >> info.shift_amount; +template <int N> uint32_t small_division_by_pow10(uint32_t n) noexcept { + constexpr auto info = div_small_pow10_infos[N - 1]; + FMT_ASSERT(n <= info.divisor * 10, "n is too large"); + constexpr uint32_t magic_number = + (1u << info.shift_amount) / info.divisor + 1; + return (n * magic_number) >> info.shift_amount; } // Computes floor(n / 10^(kappa + 1)) (float) -inline uint32_t divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(uint32_t n) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return n / float_info<float>::big_divisor; +inline uint32_t divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(uint32_t n) noexcept { + // 1374389535 = ceil(2^37/100) + return static_cast<uint32_t>((static_cast<uint64_t>(n) * 1374389535) >> 37); } // Computes floor(n / 10^(kappa + 1)) (double) -inline uint64_t divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(uint64_t n) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return umul128_upper64(n, 0x83126e978d4fdf3c) >> 9; +inline uint64_t divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(uint64_t n) noexcept { + // 2361183241434822607 = ceil(2^(64+7)/1000) + return umul128_upper64(n, 2361183241434822607ull) >> 7; } // Various subroutines using pow10 cache -template <class T> struct cache_accessor; +template <typename T> struct cache_accessor; template <> struct cache_accessor<float> { using carrier_uint = float_info<float>::carrier_uint; using cache_entry_type = uint64_t; - static uint64_t get_cached_power(int k) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + static uint64_t get_cached_power(int k) noexcept { FMT_ASSERT(k >= float_info<float>::min_k && k <= float_info<float>::max_k, "k is out of range"); - return data::dragonbox_pow10_significands_64[k - float_info<float>::min_k]; - } + static constexpr const uint64_t pow10_significands[] = { + 0x81ceb32c4b43fcf5, 0xa2425ff75e14fc32, 0xcad2f7f5359a3b3f, + 0xfd87b5f28300ca0e, 0x9e74d1b791e07e49, 0xc612062576589ddb, + 0xf79687aed3eec552, 0x9abe14cd44753b53, 0xc16d9a0095928a28, + 0xf1c90080baf72cb2, 0x971da05074da7bef, 0xbce5086492111aeb, + 0xec1e4a7db69561a6, 0x9392ee8e921d5d08, 0xb877aa3236a4b44a, + 0xe69594bec44de15c, 0x901d7cf73ab0acda, 0xb424dc35095cd810, + 0xe12e13424bb40e14, 0x8cbccc096f5088cc, 0xafebff0bcb24aaff, + 0xdbe6fecebdedd5bf, 0x89705f4136b4a598, 0xabcc77118461cefd, + 0xd6bf94d5e57a42bd, 0x8637bd05af6c69b6, 0xa7c5ac471b478424, + 0xd1b71758e219652c, 0x83126e978d4fdf3c, 0xa3d70a3d70a3d70b, + 0xcccccccccccccccd, 0x8000000000000000, 0xa000000000000000, + 0xc800000000000000, 0xfa00000000000000, 0x9c40000000000000, + 0xc350000000000000, 0xf424000000000000, 0x9896800000000000, + 0xbebc200000000000, 0xee6b280000000000, 0x9502f90000000000, + 0xba43b74000000000, 0xe8d4a51000000000, 0x9184e72a00000000, + 0xb5e620f480000000, 0xe35fa931a0000000, 0x8e1bc9bf04000000, + 0xb1a2bc2ec5000000, 0xde0b6b3a76400000, 0x8ac7230489e80000, + 0xad78ebc5ac620000, 0xd8d726b7177a8000, 0x878678326eac9000, + 0xa968163f0a57b400, 0xd3c21bcecceda100, 0x84595161401484a0, + 0xa56fa5b99019a5c8, 0xcecb8f27f4200f3a, 0x813f3978f8940985, + 0xa18f07d736b90be6, 0xc9f2c9cd04674edf, 0xfc6f7c4045812297, + 0x9dc5ada82b70b59e, 0xc5371912364ce306, 0xf684df56c3e01bc7, + 0x9a130b963a6c115d, 0xc097ce7bc90715b4, 0xf0bdc21abb48db21, + 0x96769950b50d88f5, 0xbc143fa4e250eb32, 0xeb194f8e1ae525fe, + 0x92efd1b8d0cf37bf, 0xb7abc627050305ae, 0xe596b7b0c643c71a, + 0x8f7e32ce7bea5c70, 0xb35dbf821ae4f38c, 0xe0352f62a19e306f}; + return pow10_significands[k - float_info<float>::min_k]; + } + + struct compute_mul_result { + carrier_uint result; + bool is_integer; + }; + struct compute_mul_parity_result { + bool parity; + bool is_integer; + }; - static carrier_uint compute_mul(carrier_uint u, - const cache_entry_type& cache) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return umul96_upper32(u, cache); + static compute_mul_result compute_mul( + carrier_uint u, const cache_entry_type& cache) noexcept { + auto r = umul96_upper64(u, cache); + return {static_cast<carrier_uint>(r >> 32), + static_cast<carrier_uint>(r) == 0}; } static uint32_t compute_delta(const cache_entry_type& cache, - int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return static_cast<uint32_t>(cache >> (64 - 1 - beta_minus_1)); + int beta) noexcept { + return static_cast<uint32_t>(cache >> (64 - 1 - beta)); } - static bool compute_mul_parity(carrier_uint two_f, - const cache_entry_type& cache, - int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(beta_minus_1 >= 1, ""); - FMT_ASSERT(beta_minus_1 < 64, ""); + static compute_mul_parity_result compute_mul_parity( + carrier_uint two_f, const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept { + FMT_ASSERT(beta >= 1, ""); + FMT_ASSERT(beta < 64, ""); - return ((umul96_lower64(two_f, cache) >> (64 - beta_minus_1)) & 1) != 0; + auto r = umul96_lower64(two_f, cache); + return {((r >> (64 - beta)) & 1) != 0, + static_cast<uint32_t>(r >> (32 - beta)) == 0}; } static carrier_uint compute_left_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case( - const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept { return static_cast<carrier_uint>( - (cache - (cache >> (float_info<float>::significand_bits + 2))) >> - (64 - float_info<float>::significand_bits - 1 - beta_minus_1)); + (cache - (cache >> (num_significand_bits<float>() + 2))) >> + (64 - num_significand_bits<float>() - 1 - beta)); } static carrier_uint compute_right_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case( - const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept { return static_cast<carrier_uint>( - (cache + (cache >> (float_info<float>::significand_bits + 1))) >> - (64 - float_info<float>::significand_bits - 1 - beta_minus_1)); + (cache + (cache >> (num_significand_bits<float>() + 1))) >> + (64 - num_significand_bits<float>() - 1 - beta)); } static carrier_uint compute_round_up_for_shorter_interval_case( - const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept { return (static_cast<carrier_uint>( - cache >> - (64 - float_info<float>::significand_bits - 2 - beta_minus_1)) + + cache >> (64 - num_significand_bits<float>() - 2 - beta)) + 1) / 2; } @@ -1879,16 +343,690 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<float> { template <> struct cache_accessor<double> { using carrier_uint = float_info<double>::carrier_uint; - using cache_entry_type = uint128_wrapper; + using cache_entry_type = uint128_fallback; - static uint128_wrapper get_cached_power(int k) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + static uint128_fallback get_cached_power(int k) noexcept { FMT_ASSERT(k >= float_info<double>::min_k && k <= float_info<double>::max_k, "k is out of range"); + static constexpr const uint128_fallback pow10_significands[] = { #if FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX - return data::dragonbox_pow10_significands_128[k - - float_info<double>::min_k]; + {0xff77b1fcbebcdc4f, 0x25e8e89c13bb0f7b}, + {0x9faacf3df73609b1, 0x77b191618c54e9ad}, + {0xc795830d75038c1d, 0xd59df5b9ef6a2418}, + {0xf97ae3d0d2446f25, 0x4b0573286b44ad1e}, + {0x9becce62836ac577, 0x4ee367f9430aec33}, + {0xc2e801fb244576d5, 0x229c41f793cda740}, + {0xf3a20279ed56d48a, 0x6b43527578c11110}, + {0x9845418c345644d6, 0x830a13896b78aaaa}, + {0xbe5691ef416bd60c, 0x23cc986bc656d554}, + {0xedec366b11c6cb8f, 0x2cbfbe86b7ec8aa9}, + {0x94b3a202eb1c3f39, 0x7bf7d71432f3d6aa}, + {0xb9e08a83a5e34f07, 0xdaf5ccd93fb0cc54}, + {0xe858ad248f5c22c9, 0xd1b3400f8f9cff69}, + {0x91376c36d99995be, 0x23100809b9c21fa2}, + {0xb58547448ffffb2d, 0xabd40a0c2832a78b}, + {0xe2e69915b3fff9f9, 0x16c90c8f323f516d}, + {0x8dd01fad907ffc3b, 0xae3da7d97f6792e4}, + {0xb1442798f49ffb4a, 0x99cd11cfdf41779d}, + {0xdd95317f31c7fa1d, 0x40405643d711d584}, + {0x8a7d3eef7f1cfc52, 0x482835ea666b2573}, + {0xad1c8eab5ee43b66, 0xda3243650005eed0}, + {0xd863b256369d4a40, 0x90bed43e40076a83}, + {0x873e4f75e2224e68, 0x5a7744a6e804a292}, + {0xa90de3535aaae202, 0x711515d0a205cb37}, + {0xd3515c2831559a83, 0x0d5a5b44ca873e04}, + {0x8412d9991ed58091, 0xe858790afe9486c3}, + {0xa5178fff668ae0b6, 0x626e974dbe39a873}, + {0xce5d73ff402d98e3, 0xfb0a3d212dc81290}, + {0x80fa687f881c7f8e, 0x7ce66634bc9d0b9a}, + {0xa139029f6a239f72, 0x1c1fffc1ebc44e81}, + {0xc987434744ac874e, 0xa327ffb266b56221}, + {0xfbe9141915d7a922, 0x4bf1ff9f0062baa9}, + {0x9d71ac8fada6c9b5, 0x6f773fc3603db4aa}, + {0xc4ce17b399107c22, 0xcb550fb4384d21d4}, + {0xf6019da07f549b2b, 0x7e2a53a146606a49}, + {0x99c102844f94e0fb, 0x2eda7444cbfc426e}, + {0xc0314325637a1939, 0xfa911155fefb5309}, + {0xf03d93eebc589f88, 0x793555ab7eba27cb}, + {0x96267c7535b763b5, 0x4bc1558b2f3458df}, + {0xbbb01b9283253ca2, 0x9eb1aaedfb016f17}, + {0xea9c227723ee8bcb, 0x465e15a979c1cadd}, + {0x92a1958a7675175f, 0x0bfacd89ec191eca}, + {0xb749faed14125d36, 0xcef980ec671f667c}, + {0xe51c79a85916f484, 0x82b7e12780e7401b}, + {0x8f31cc0937ae58d2, 0xd1b2ecb8b0908811}, + {0xb2fe3f0b8599ef07, 0x861fa7e6dcb4aa16}, + {0xdfbdcece67006ac9, 0x67a791e093e1d49b}, + {0x8bd6a141006042bd, 0xe0c8bb2c5c6d24e1}, + {0xaecc49914078536d, 0x58fae9f773886e19}, + {0xda7f5bf590966848, 0xaf39a475506a899f}, + {0x888f99797a5e012d, 0x6d8406c952429604}, + {0xaab37fd7d8f58178, 0xc8e5087ba6d33b84}, + {0xd5605fcdcf32e1d6, 0xfb1e4a9a90880a65}, + {0x855c3be0a17fcd26, 0x5cf2eea09a550680}, + {0xa6b34ad8c9dfc06f, 0xf42faa48c0ea481f}, + {0xd0601d8efc57b08b, 0xf13b94daf124da27}, + {0x823c12795db6ce57, 0x76c53d08d6b70859}, + {0xa2cb1717b52481ed, 0x54768c4b0c64ca6f}, + {0xcb7ddcdda26da268, 0xa9942f5dcf7dfd0a}, + {0xfe5d54150b090b02, 0xd3f93b35435d7c4d}, + {0x9efa548d26e5a6e1, 0xc47bc5014a1a6db0}, + {0xc6b8e9b0709f109a, 0x359ab6419ca1091c}, + {0xf867241c8cc6d4c0, 0xc30163d203c94b63}, + {0x9b407691d7fc44f8, 0x79e0de63425dcf1e}, + {0xc21094364dfb5636, 0x985915fc12f542e5}, + {0xf294b943e17a2bc4, 0x3e6f5b7b17b2939e}, + {0x979cf3ca6cec5b5a, 0xa705992ceecf9c43}, + {0xbd8430bd08277231, 0x50c6ff782a838354}, + {0xece53cec4a314ebd, 0xa4f8bf5635246429}, + {0x940f4613ae5ed136, 0x871b7795e136be9a}, + {0xb913179899f68584, 0x28e2557b59846e40}, + {0xe757dd7ec07426e5, 0x331aeada2fe589d0}, + {0x9096ea6f3848984f, 0x3ff0d2c85def7622}, + {0xb4bca50b065abe63, 0x0fed077a756b53aa}, + {0xe1ebce4dc7f16dfb, 0xd3e8495912c62895}, + {0x8d3360f09cf6e4bd, 0x64712dd7abbbd95d}, + {0xb080392cc4349dec, 0xbd8d794d96aacfb4}, + {0xdca04777f541c567, 0xecf0d7a0fc5583a1}, + {0x89e42caaf9491b60, 0xf41686c49db57245}, + {0xac5d37d5b79b6239, 0x311c2875c522ced6}, + {0xd77485cb25823ac7, 0x7d633293366b828c}, + {0x86a8d39ef77164bc, 0xae5dff9c02033198}, + {0xa8530886b54dbdeb, 0xd9f57f830283fdfd}, + {0xd267caa862a12d66, 0xd072df63c324fd7c}, + {0x8380dea93da4bc60, 0x4247cb9e59f71e6e}, + {0xa46116538d0deb78, 0x52d9be85f074e609}, + {0xcd795be870516656, 0x67902e276c921f8c}, + {0x806bd9714632dff6, 0x00ba1cd8a3db53b7}, + {0xa086cfcd97bf97f3, 0x80e8a40eccd228a5}, + {0xc8a883c0fdaf7df0, 0x6122cd128006b2ce}, + {0xfad2a4b13d1b5d6c, 0x796b805720085f82}, + {0x9cc3a6eec6311a63, 0xcbe3303674053bb1}, + {0xc3f490aa77bd60fc, 0xbedbfc4411068a9d}, + {0xf4f1b4d515acb93b, 0xee92fb5515482d45}, + {0x991711052d8bf3c5, 0x751bdd152d4d1c4b}, + {0xbf5cd54678eef0b6, 0xd262d45a78a0635e}, + {0xef340a98172aace4, 0x86fb897116c87c35}, + {0x9580869f0e7aac0e, 0xd45d35e6ae3d4da1}, + {0xbae0a846d2195712, 0x8974836059cca10a}, + {0xe998d258869facd7, 0x2bd1a438703fc94c}, + {0x91ff83775423cc06, 0x7b6306a34627ddd0}, + {0xb67f6455292cbf08, 0x1a3bc84c17b1d543}, + {0xe41f3d6a7377eeca, 0x20caba5f1d9e4a94}, + {0x8e938662882af53e, 0x547eb47b7282ee9d}, + {0xb23867fb2a35b28d, 0xe99e619a4f23aa44}, + {0xdec681f9f4c31f31, 0x6405fa00e2ec94d5}, + {0x8b3c113c38f9f37e, 0xde83bc408dd3dd05}, + {0xae0b158b4738705e, 0x9624ab50b148d446}, + {0xd98ddaee19068c76, 0x3badd624dd9b0958}, + {0x87f8a8d4cfa417c9, 0xe54ca5d70a80e5d7}, + {0xa9f6d30a038d1dbc, 0x5e9fcf4ccd211f4d}, + {0xd47487cc8470652b, 0x7647c32000696720}, + {0x84c8d4dfd2c63f3b, 0x29ecd9f40041e074}, + {0xa5fb0a17c777cf09, 0xf468107100525891}, + {0xcf79cc9db955c2cc, 0x7182148d4066eeb5}, + {0x81ac1fe293d599bf, 0xc6f14cd848405531}, + {0xa21727db38cb002f, 0xb8ada00e5a506a7d}, + {0xca9cf1d206fdc03b, 0xa6d90811f0e4851d}, + {0xfd442e4688bd304a, 0x908f4a166d1da664}, + {0x9e4a9cec15763e2e, 0x9a598e4e043287ff}, + {0xc5dd44271ad3cdba, 0x40eff1e1853f29fe}, + {0xf7549530e188c128, 0xd12bee59e68ef47d}, + {0x9a94dd3e8cf578b9, 0x82bb74f8301958cf}, + {0xc13a148e3032d6e7, 0xe36a52363c1faf02}, + {0xf18899b1bc3f8ca1, 0xdc44e6c3cb279ac2}, + {0x96f5600f15a7b7e5, 0x29ab103a5ef8c0ba}, + {0xbcb2b812db11a5de, 0x7415d448f6b6f0e8}, + {0xebdf661791d60f56, 0x111b495b3464ad22}, + {0x936b9fcebb25c995, 0xcab10dd900beec35}, + {0xb84687c269ef3bfb, 0x3d5d514f40eea743}, + {0xe65829b3046b0afa, 0x0cb4a5a3112a5113}, + {0x8ff71a0fe2c2e6dc, 0x47f0e785eaba72ac}, + {0xb3f4e093db73a093, 0x59ed216765690f57}, + {0xe0f218b8d25088b8, 0x306869c13ec3532d}, + {0x8c974f7383725573, 0x1e414218c73a13fc}, + {0xafbd2350644eeacf, 0xe5d1929ef90898fb}, + {0xdbac6c247d62a583, 0xdf45f746b74abf3a}, + {0x894bc396ce5da772, 0x6b8bba8c328eb784}, + {0xab9eb47c81f5114f, 0x066ea92f3f326565}, + {0xd686619ba27255a2, 0xc80a537b0efefebe}, + {0x8613fd0145877585, 0xbd06742ce95f5f37}, + {0xa798fc4196e952e7, 0x2c48113823b73705}, + {0xd17f3b51fca3a7a0, 0xf75a15862ca504c6}, + {0x82ef85133de648c4, 0x9a984d73dbe722fc}, + {0xa3ab66580d5fdaf5, 0xc13e60d0d2e0ebbb}, + {0xcc963fee10b7d1b3, 0x318df905079926a9}, + {0xffbbcfe994e5c61f, 0xfdf17746497f7053}, + {0x9fd561f1fd0f9bd3, 0xfeb6ea8bedefa634}, + {0xc7caba6e7c5382c8, 0xfe64a52ee96b8fc1}, + {0xf9bd690a1b68637b, 0x3dfdce7aa3c673b1}, + {0x9c1661a651213e2d, 0x06bea10ca65c084f}, + {0xc31bfa0fe5698db8, 0x486e494fcff30a63}, + {0xf3e2f893dec3f126, 0x5a89dba3c3efccfb}, + {0x986ddb5c6b3a76b7, 0xf89629465a75e01d}, + {0xbe89523386091465, 0xf6bbb397f1135824}, + {0xee2ba6c0678b597f, 0x746aa07ded582e2d}, + {0x94db483840b717ef, 0xa8c2a44eb4571cdd}, + {0xba121a4650e4ddeb, 0x92f34d62616ce414}, + {0xe896a0d7e51e1566, 0x77b020baf9c81d18}, + {0x915e2486ef32cd60, 0x0ace1474dc1d122f}, + {0xb5b5ada8aaff80b8, 0x0d819992132456bb}, + {0xe3231912d5bf60e6, 0x10e1fff697ed6c6a}, + {0x8df5efabc5979c8f, 0xca8d3ffa1ef463c2}, + {0xb1736b96b6fd83b3, 0xbd308ff8a6b17cb3}, + {0xddd0467c64bce4a0, 0xac7cb3f6d05ddbdf}, + {0x8aa22c0dbef60ee4, 0x6bcdf07a423aa96c}, + {0xad4ab7112eb3929d, 0x86c16c98d2c953c7}, + {0xd89d64d57a607744, 0xe871c7bf077ba8b8}, + {0x87625f056c7c4a8b, 0x11471cd764ad4973}, + {0xa93af6c6c79b5d2d, 0xd598e40d3dd89bd0}, + {0xd389b47879823479, 0x4aff1d108d4ec2c4}, + {0x843610cb4bf160cb, 0xcedf722a585139bb}, + {0xa54394fe1eedb8fe, 0xc2974eb4ee658829}, + {0xce947a3da6a9273e, 0x733d226229feea33}, + {0x811ccc668829b887, 0x0806357d5a3f5260}, + {0xa163ff802a3426a8, 0xca07c2dcb0cf26f8}, + {0xc9bcff6034c13052, 0xfc89b393dd02f0b6}, + {0xfc2c3f3841f17c67, 0xbbac2078d443ace3}, + {0x9d9ba7832936edc0, 0xd54b944b84aa4c0e}, + {0xc5029163f384a931, 0x0a9e795e65d4df12}, + {0xf64335bcf065d37d, 0x4d4617b5ff4a16d6}, + {0x99ea0196163fa42e, 0x504bced1bf8e4e46}, + {0xc06481fb9bcf8d39, 0xe45ec2862f71e1d7}, + {0xf07da27a82c37088, 0x5d767327bb4e5a4d}, + {0x964e858c91ba2655, 0x3a6a07f8d510f870}, + {0xbbe226efb628afea, 0x890489f70a55368c}, + {0xeadab0aba3b2dbe5, 0x2b45ac74ccea842f}, + {0x92c8ae6b464fc96f, 0x3b0b8bc90012929e}, + {0xb77ada0617e3bbcb, 0x09ce6ebb40173745}, + {0xe55990879ddcaabd, 0xcc420a6a101d0516}, + {0x8f57fa54c2a9eab6, 0x9fa946824a12232e}, + {0xb32df8e9f3546564, 0x47939822dc96abfa}, + {0xdff9772470297ebd, 0x59787e2b93bc56f8}, + {0x8bfbea76c619ef36, 0x57eb4edb3c55b65b}, + {0xaefae51477a06b03, 0xede622920b6b23f2}, + {0xdab99e59958885c4, 0xe95fab368e45ecee}, + {0x88b402f7fd75539b, 0x11dbcb0218ebb415}, + {0xaae103b5fcd2a881, 0xd652bdc29f26a11a}, + {0xd59944a37c0752a2, 0x4be76d3346f04960}, + {0x857fcae62d8493a5, 0x6f70a4400c562ddc}, + {0xa6dfbd9fb8e5b88e, 0xcb4ccd500f6bb953}, + {0xd097ad07a71f26b2, 0x7e2000a41346a7a8}, + {0x825ecc24c873782f, 0x8ed400668c0c28c9}, + {0xa2f67f2dfa90563b, 0x728900802f0f32fb}, + {0xcbb41ef979346bca, 0x4f2b40a03ad2ffba}, + {0xfea126b7d78186bc, 0xe2f610c84987bfa9}, + {0x9f24b832e6b0f436, 0x0dd9ca7d2df4d7ca}, + {0xc6ede63fa05d3143, 0x91503d1c79720dbc}, + {0xf8a95fcf88747d94, 0x75a44c6397ce912b}, + {0x9b69dbe1b548ce7c, 0xc986afbe3ee11abb}, + {0xc24452da229b021b, 0xfbe85badce996169}, + {0xf2d56790ab41c2a2, 0xfae27299423fb9c4}, + {0x97c560ba6b0919a5, 0xdccd879fc967d41b}, + {0xbdb6b8e905cb600f, 0x5400e987bbc1c921}, + {0xed246723473e3813, 0x290123e9aab23b69}, + {0x9436c0760c86e30b, 0xf9a0b6720aaf6522}, + {0xb94470938fa89bce, 0xf808e40e8d5b3e6a}, + {0xe7958cb87392c2c2, 0xb60b1d1230b20e05}, + {0x90bd77f3483bb9b9, 0xb1c6f22b5e6f48c3}, + {0xb4ecd5f01a4aa828, 0x1e38aeb6360b1af4}, + {0xe2280b6c20dd5232, 0x25c6da63c38de1b1}, + {0x8d590723948a535f, 0x579c487e5a38ad0f}, + {0xb0af48ec79ace837, 0x2d835a9df0c6d852}, + {0xdcdb1b2798182244, 0xf8e431456cf88e66}, + {0x8a08f0f8bf0f156b, 0x1b8e9ecb641b5900}, + {0xac8b2d36eed2dac5, 0xe272467e3d222f40}, + {0xd7adf884aa879177, 0x5b0ed81dcc6abb10}, + {0x86ccbb52ea94baea, 0x98e947129fc2b4ea}, + {0xa87fea27a539e9a5, 0x3f2398d747b36225}, + {0xd29fe4b18e88640e, 0x8eec7f0d19a03aae}, + {0x83a3eeeef9153e89, 0x1953cf68300424ad}, + {0xa48ceaaab75a8e2b, 0x5fa8c3423c052dd8}, + {0xcdb02555653131b6, 0x3792f412cb06794e}, + {0x808e17555f3ebf11, 0xe2bbd88bbee40bd1}, + {0xa0b19d2ab70e6ed6, 0x5b6aceaeae9d0ec5}, + {0xc8de047564d20a8b, 0xf245825a5a445276}, + {0xfb158592be068d2e, 0xeed6e2f0f0d56713}, + {0x9ced737bb6c4183d, 0x55464dd69685606c}, + {0xc428d05aa4751e4c, 0xaa97e14c3c26b887}, + {0xf53304714d9265df, 0xd53dd99f4b3066a9}, + {0x993fe2c6d07b7fab, 0xe546a8038efe402a}, + {0xbf8fdb78849a5f96, 0xde98520472bdd034}, + {0xef73d256a5c0f77c, 0x963e66858f6d4441}, + {0x95a8637627989aad, 0xdde7001379a44aa9}, + {0xbb127c53b17ec159, 0x5560c018580d5d53}, + {0xe9d71b689dde71af, 0xaab8f01e6e10b4a7}, + {0x9226712162ab070d, 0xcab3961304ca70e9}, + {0xb6b00d69bb55c8d1, 0x3d607b97c5fd0d23}, + {0xe45c10c42a2b3b05, 0x8cb89a7db77c506b}, + {0x8eb98a7a9a5b04e3, 0x77f3608e92adb243}, + {0xb267ed1940f1c61c, 0x55f038b237591ed4}, + {0xdf01e85f912e37a3, 0x6b6c46dec52f6689}, + {0x8b61313bbabce2c6, 0x2323ac4b3b3da016}, + {0xae397d8aa96c1b77, 0xabec975e0a0d081b}, + {0xd9c7dced53c72255, 0x96e7bd358c904a22}, + {0x881cea14545c7575, 0x7e50d64177da2e55}, + {0xaa242499697392d2, 0xdde50bd1d5d0b9ea}, + {0xd4ad2dbfc3d07787, 0x955e4ec64b44e865}, + {0x84ec3c97da624ab4, 0xbd5af13bef0b113f}, + {0xa6274bbdd0fadd61, 0xecb1ad8aeacdd58f}, + {0xcfb11ead453994ba, 0x67de18eda5814af3}, + {0x81ceb32c4b43fcf4, 0x80eacf948770ced8}, + {0xa2425ff75e14fc31, 0xa1258379a94d028e}, + {0xcad2f7f5359a3b3e, 0x096ee45813a04331}, + {0xfd87b5f28300ca0d, 0x8bca9d6e188853fd}, + {0x9e74d1b791e07e48, 0x775ea264cf55347e}, + {0xc612062576589dda, 0x95364afe032a819e}, + {0xf79687aed3eec551, 0x3a83ddbd83f52205}, + {0x9abe14cd44753b52, 0xc4926a9672793543}, + {0xc16d9a0095928a27, 0x75b7053c0f178294}, + {0xf1c90080baf72cb1, 0x5324c68b12dd6339}, + {0x971da05074da7bee, 0xd3f6fc16ebca5e04}, + {0xbce5086492111aea, 0x88f4bb1ca6bcf585}, + {0xec1e4a7db69561a5, 0x2b31e9e3d06c32e6}, + {0x9392ee8e921d5d07, 0x3aff322e62439fd0}, + {0xb877aa3236a4b449, 0x09befeb9fad487c3}, + {0xe69594bec44de15b, 0x4c2ebe687989a9b4}, + {0x901d7cf73ab0acd9, 0x0f9d37014bf60a11}, + {0xb424dc35095cd80f, 0x538484c19ef38c95}, + {0xe12e13424bb40e13, 0x2865a5f206b06fba}, + {0x8cbccc096f5088cb, 0xf93f87b7442e45d4}, + {0xafebff0bcb24aafe, 0xf78f69a51539d749}, + {0xdbe6fecebdedd5be, 0xb573440e5a884d1c}, + {0x89705f4136b4a597, 0x31680a88f8953031}, + {0xabcc77118461cefc, 0xfdc20d2b36ba7c3e}, + {0xd6bf94d5e57a42bc, 0x3d32907604691b4d}, + {0x8637bd05af6c69b5, 0xa63f9a49c2c1b110}, + {0xa7c5ac471b478423, 0x0fcf80dc33721d54}, + {0xd1b71758e219652b, 0xd3c36113404ea4a9}, + {0x83126e978d4fdf3b, 0x645a1cac083126ea}, + {0xa3d70a3d70a3d70a, 0x3d70a3d70a3d70a4}, + {0xcccccccccccccccc, 0xcccccccccccccccd}, + {0x8000000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xa000000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xc800000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xfa00000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x9c40000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xc350000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xf424000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x9896800000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xbebc200000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xee6b280000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x9502f90000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xba43b74000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xe8d4a51000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x9184e72a00000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xb5e620f480000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xe35fa931a0000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x8e1bc9bf04000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xb1a2bc2ec5000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xde0b6b3a76400000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x8ac7230489e80000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xad78ebc5ac620000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xd8d726b7177a8000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x878678326eac9000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xa968163f0a57b400, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xd3c21bcecceda100, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x84595161401484a0, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xa56fa5b99019a5c8, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0xcecb8f27f4200f3a, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x813f3978f8940984, 0x4000000000000000}, + {0xa18f07d736b90be5, 0x5000000000000000}, + {0xc9f2c9cd04674ede, 0xa400000000000000}, + {0xfc6f7c4045812296, 0x4d00000000000000}, + {0x9dc5ada82b70b59d, 0xf020000000000000}, + {0xc5371912364ce305, 0x6c28000000000000}, + {0xf684df56c3e01bc6, 0xc732000000000000}, + {0x9a130b963a6c115c, 0x3c7f400000000000}, + {0xc097ce7bc90715b3, 0x4b9f100000000000}, + {0xf0bdc21abb48db20, 0x1e86d40000000000}, + {0x96769950b50d88f4, 0x1314448000000000}, + {0xbc143fa4e250eb31, 0x17d955a000000000}, + {0xeb194f8e1ae525fd, 0x5dcfab0800000000}, + {0x92efd1b8d0cf37be, 0x5aa1cae500000000}, + {0xb7abc627050305ad, 0xf14a3d9e40000000}, + {0xe596b7b0c643c719, 0x6d9ccd05d0000000}, + {0x8f7e32ce7bea5c6f, 0xe4820023a2000000}, + {0xb35dbf821ae4f38b, 0xdda2802c8a800000}, + {0xe0352f62a19e306e, 0xd50b2037ad200000}, + {0x8c213d9da502de45, 0x4526f422cc340000}, + {0xaf298d050e4395d6, 0x9670b12b7f410000}, + {0xdaf3f04651d47b4c, 0x3c0cdd765f114000}, + {0x88d8762bf324cd0f, 0xa5880a69fb6ac800}, + {0xab0e93b6efee0053, 0x8eea0d047a457a00}, + {0xd5d238a4abe98068, 0x72a4904598d6d880}, + {0x85a36366eb71f041, 0x47a6da2b7f864750}, + {0xa70c3c40a64e6c51, 0x999090b65f67d924}, + {0xd0cf4b50cfe20765, 0xfff4b4e3f741cf6d}, + {0x82818f1281ed449f, 0xbff8f10e7a8921a5}, + {0xa321f2d7226895c7, 0xaff72d52192b6a0e}, + {0xcbea6f8ceb02bb39, 0x9bf4f8a69f764491}, + {0xfee50b7025c36a08, 0x02f236d04753d5b5}, + {0x9f4f2726179a2245, 0x01d762422c946591}, + {0xc722f0ef9d80aad6, 0x424d3ad2b7b97ef6}, + {0xf8ebad2b84e0d58b, 0xd2e0898765a7deb3}, + {0x9b934c3b330c8577, 0x63cc55f49f88eb30}, + {0xc2781f49ffcfa6d5, 0x3cbf6b71c76b25fc}, + {0xf316271c7fc3908a, 0x8bef464e3945ef7b}, + {0x97edd871cfda3a56, 0x97758bf0e3cbb5ad}, + {0xbde94e8e43d0c8ec, 0x3d52eeed1cbea318}, + {0xed63a231d4c4fb27, 0x4ca7aaa863ee4bde}, + {0x945e455f24fb1cf8, 0x8fe8caa93e74ef6b}, + {0xb975d6b6ee39e436, 0xb3e2fd538e122b45}, + {0xe7d34c64a9c85d44, 0x60dbbca87196b617}, + {0x90e40fbeea1d3a4a, 0xbc8955e946fe31ce}, + {0xb51d13aea4a488dd, 0x6babab6398bdbe42}, + {0xe264589a4dcdab14, 0xc696963c7eed2dd2}, + {0x8d7eb76070a08aec, 0xfc1e1de5cf543ca3}, + {0xb0de65388cc8ada8, 0x3b25a55f43294bcc}, + {0xdd15fe86affad912, 0x49ef0eb713f39ebf}, + {0x8a2dbf142dfcc7ab, 0x6e3569326c784338}, + {0xacb92ed9397bf996, 0x49c2c37f07965405}, + {0xd7e77a8f87daf7fb, 0xdc33745ec97be907}, + {0x86f0ac99b4e8dafd, 0x69a028bb3ded71a4}, + {0xa8acd7c0222311bc, 0xc40832ea0d68ce0d}, + {0xd2d80db02aabd62b, 0xf50a3fa490c30191}, + {0x83c7088e1aab65db, 0x792667c6da79e0fb}, + {0xa4b8cab1a1563f52, 0x577001b891185939}, + {0xcde6fd5e09abcf26, 0xed4c0226b55e6f87}, + {0x80b05e5ac60b6178, 0x544f8158315b05b5}, + {0xa0dc75f1778e39d6, 0x696361ae3db1c722}, + {0xc913936dd571c84c, 0x03bc3a19cd1e38ea}, + {0xfb5878494ace3a5f, 0x04ab48a04065c724}, + {0x9d174b2dcec0e47b, 0x62eb0d64283f9c77}, + {0xc45d1df942711d9a, 0x3ba5d0bd324f8395}, + {0xf5746577930d6500, 0xca8f44ec7ee3647a}, + {0x9968bf6abbe85f20, 0x7e998b13cf4e1ecc}, + {0xbfc2ef456ae276e8, 0x9e3fedd8c321a67f}, + {0xefb3ab16c59b14a2, 0xc5cfe94ef3ea101f}, + {0x95d04aee3b80ece5, 0xbba1f1d158724a13}, + {0xbb445da9ca61281f, 0x2a8a6e45ae8edc98}, + {0xea1575143cf97226, 0xf52d09d71a3293be}, + {0x924d692ca61be758, 0x593c2626705f9c57}, + {0xb6e0c377cfa2e12e, 0x6f8b2fb00c77836d}, + {0xe498f455c38b997a, 0x0b6dfb9c0f956448}, + {0x8edf98b59a373fec, 0x4724bd4189bd5ead}, + {0xb2977ee300c50fe7, 0x58edec91ec2cb658}, + {0xdf3d5e9bc0f653e1, 0x2f2967b66737e3ee}, + {0x8b865b215899f46c, 0xbd79e0d20082ee75}, + {0xae67f1e9aec07187, 0xecd8590680a3aa12}, + {0xda01ee641a708de9, 0xe80e6f4820cc9496}, + {0x884134fe908658b2, 0x3109058d147fdcde}, + {0xaa51823e34a7eede, 0xbd4b46f0599fd416}, + {0xd4e5e2cdc1d1ea96, 0x6c9e18ac7007c91b}, + {0x850fadc09923329e, 0x03e2cf6bc604ddb1}, + {0xa6539930bf6bff45, 0x84db8346b786151d}, + {0xcfe87f7cef46ff16, 0xe612641865679a64}, + {0x81f14fae158c5f6e, 0x4fcb7e8f3f60c07f}, + {0xa26da3999aef7749, 0xe3be5e330f38f09e}, + {0xcb090c8001ab551c, 0x5cadf5bfd3072cc6}, + {0xfdcb4fa002162a63, 0x73d9732fc7c8f7f7}, + {0x9e9f11c4014dda7e, 0x2867e7fddcdd9afb}, + {0xc646d63501a1511d, 0xb281e1fd541501b9}, + {0xf7d88bc24209a565, 0x1f225a7ca91a4227}, + {0x9ae757596946075f, 0x3375788de9b06959}, + {0xc1a12d2fc3978937, 0x0052d6b1641c83af}, + {0xf209787bb47d6b84, 0xc0678c5dbd23a49b}, + {0x9745eb4d50ce6332, 0xf840b7ba963646e1}, + {0xbd176620a501fbff, 0xb650e5a93bc3d899}, + {0xec5d3fa8ce427aff, 0xa3e51f138ab4cebf}, + {0x93ba47c980e98cdf, 0xc66f336c36b10138}, + {0xb8a8d9bbe123f017, 0xb80b0047445d4185}, + {0xe6d3102ad96cec1d, 0xa60dc059157491e6}, + {0x9043ea1ac7e41392, 0x87c89837ad68db30}, + {0xb454e4a179dd1877, 0x29babe4598c311fc}, + {0xe16a1dc9d8545e94, 0xf4296dd6fef3d67b}, + {0x8ce2529e2734bb1d, 0x1899e4a65f58660d}, + {0xb01ae745b101e9e4, 0x5ec05dcff72e7f90}, + {0xdc21a1171d42645d, 0x76707543f4fa1f74}, + {0x899504ae72497eba, 0x6a06494a791c53a9}, + {0xabfa45da0edbde69, 0x0487db9d17636893}, + {0xd6f8d7509292d603, 0x45a9d2845d3c42b7}, + {0x865b86925b9bc5c2, 0x0b8a2392ba45a9b3}, + {0xa7f26836f282b732, 0x8e6cac7768d7141f}, + {0xd1ef0244af2364ff, 0x3207d795430cd927}, + {0x8335616aed761f1f, 0x7f44e6bd49e807b9}, + {0xa402b9c5a8d3a6e7, 0x5f16206c9c6209a7}, + {0xcd036837130890a1, 0x36dba887c37a8c10}, + {0x802221226be55a64, 0xc2494954da2c978a}, + {0xa02aa96b06deb0fd, 0xf2db9baa10b7bd6d}, + {0xc83553c5c8965d3d, 0x6f92829494e5acc8}, + {0xfa42a8b73abbf48c, 0xcb772339ba1f17fa}, + {0x9c69a97284b578d7, 0xff2a760414536efc}, + {0xc38413cf25e2d70d, 0xfef5138519684abb}, + {0xf46518c2ef5b8cd1, 0x7eb258665fc25d6a}, + {0x98bf2f79d5993802, 0xef2f773ffbd97a62}, + {0xbeeefb584aff8603, 0xaafb550ffacfd8fb}, + {0xeeaaba2e5dbf6784, 0x95ba2a53f983cf39}, + {0x952ab45cfa97a0b2, 0xdd945a747bf26184}, + {0xba756174393d88df, 0x94f971119aeef9e5}, + {0xe912b9d1478ceb17, 0x7a37cd5601aab85e}, + {0x91abb422ccb812ee, 0xac62e055c10ab33b}, + {0xb616a12b7fe617aa, 0x577b986b314d600a}, + {0xe39c49765fdf9d94, 0xed5a7e85fda0b80c}, + {0x8e41ade9fbebc27d, 0x14588f13be847308}, + {0xb1d219647ae6b31c, 0x596eb2d8ae258fc9}, + {0xde469fbd99a05fe3, 0x6fca5f8ed9aef3bc}, + {0x8aec23d680043bee, 0x25de7bb9480d5855}, + {0xada72ccc20054ae9, 0xaf561aa79a10ae6b}, + {0xd910f7ff28069da4, 0x1b2ba1518094da05}, + {0x87aa9aff79042286, 0x90fb44d2f05d0843}, + {0xa99541bf57452b28, 0x353a1607ac744a54}, + {0xd3fa922f2d1675f2, 0x42889b8997915ce9}, + {0x847c9b5d7c2e09b7, 0x69956135febada12}, + {0xa59bc234db398c25, 0x43fab9837e699096}, + {0xcf02b2c21207ef2e, 0x94f967e45e03f4bc}, + {0x8161afb94b44f57d, 0x1d1be0eebac278f6}, + {0xa1ba1ba79e1632dc, 0x6462d92a69731733}, + {0xca28a291859bbf93, 0x7d7b8f7503cfdcff}, + {0xfcb2cb35e702af78, 0x5cda735244c3d43f}, + {0x9defbf01b061adab, 0x3a0888136afa64a8}, + {0xc56baec21c7a1916, 0x088aaa1845b8fdd1}, + {0xf6c69a72a3989f5b, 0x8aad549e57273d46}, + {0x9a3c2087a63f6399, 0x36ac54e2f678864c}, + {0xc0cb28a98fcf3c7f, 0x84576a1bb416a7de}, + {0xf0fdf2d3f3c30b9f, 0x656d44a2a11c51d6}, + {0x969eb7c47859e743, 0x9f644ae5a4b1b326}, + {0xbc4665b596706114, 0x873d5d9f0dde1fef}, + {0xeb57ff22fc0c7959, 0xa90cb506d155a7eb}, + {0x9316ff75dd87cbd8, 0x09a7f12442d588f3}, + {0xb7dcbf5354e9bece, 0x0c11ed6d538aeb30}, + {0xe5d3ef282a242e81, 0x8f1668c8a86da5fb}, + {0x8fa475791a569d10, 0xf96e017d694487bd}, + {0xb38d92d760ec4455, 0x37c981dcc395a9ad}, + {0xe070f78d3927556a, 0x85bbe253f47b1418}, + {0x8c469ab843b89562, 0x93956d7478ccec8f}, + {0xaf58416654a6babb, 0x387ac8d1970027b3}, + {0xdb2e51bfe9d0696a, 0x06997b05fcc0319f}, + {0x88fcf317f22241e2, 0x441fece3bdf81f04}, + {0xab3c2fddeeaad25a, 0xd527e81cad7626c4}, + {0xd60b3bd56a5586f1, 0x8a71e223d8d3b075}, + {0x85c7056562757456, 0xf6872d5667844e4a}, + {0xa738c6bebb12d16c, 0xb428f8ac016561dc}, + {0xd106f86e69d785c7, 0xe13336d701beba53}, + {0x82a45b450226b39c, 0xecc0024661173474}, + {0xa34d721642b06084, 0x27f002d7f95d0191}, + {0xcc20ce9bd35c78a5, 0x31ec038df7b441f5}, + {0xff290242c83396ce, 0x7e67047175a15272}, + {0x9f79a169bd203e41, 0x0f0062c6e984d387}, + {0xc75809c42c684dd1, 0x52c07b78a3e60869}, + {0xf92e0c3537826145, 0xa7709a56ccdf8a83}, + {0x9bbcc7a142b17ccb, 0x88a66076400bb692}, + {0xc2abf989935ddbfe, 0x6acff893d00ea436}, + {0xf356f7ebf83552fe, 0x0583f6b8c4124d44}, + {0x98165af37b2153de, 0xc3727a337a8b704b}, + {0xbe1bf1b059e9a8d6, 0x744f18c0592e4c5d}, + {0xeda2ee1c7064130c, 0x1162def06f79df74}, + {0x9485d4d1c63e8be7, 0x8addcb5645ac2ba9}, + {0xb9a74a0637ce2ee1, 0x6d953e2bd7173693}, + {0xe8111c87c5c1ba99, 0xc8fa8db6ccdd0438}, + {0x910ab1d4db9914a0, 0x1d9c9892400a22a3}, + {0xb54d5e4a127f59c8, 0x2503beb6d00cab4c}, + {0xe2a0b5dc971f303a, 0x2e44ae64840fd61e}, + {0x8da471a9de737e24, 0x5ceaecfed289e5d3}, + {0xb10d8e1456105dad, 0x7425a83e872c5f48}, + {0xdd50f1996b947518, 0xd12f124e28f7771a}, + {0x8a5296ffe33cc92f, 0x82bd6b70d99aaa70}, + {0xace73cbfdc0bfb7b, 0x636cc64d1001550c}, + {0xd8210befd30efa5a, 0x3c47f7e05401aa4f}, + {0x8714a775e3e95c78, 0x65acfaec34810a72}, + {0xa8d9d1535ce3b396, 0x7f1839a741a14d0e}, + {0xd31045a8341ca07c, 0x1ede48111209a051}, + {0x83ea2b892091e44d, 0x934aed0aab460433}, + {0xa4e4b66b68b65d60, 0xf81da84d56178540}, + {0xce1de40642e3f4b9, 0x36251260ab9d668f}, + {0x80d2ae83e9ce78f3, 0xc1d72b7c6b42601a}, + {0xa1075a24e4421730, 0xb24cf65b8612f820}, + {0xc94930ae1d529cfc, 0xdee033f26797b628}, + {0xfb9b7cd9a4a7443c, 0x169840ef017da3b2}, + {0x9d412e0806e88aa5, 0x8e1f289560ee864f}, + {0xc491798a08a2ad4e, 0xf1a6f2bab92a27e3}, + {0xf5b5d7ec8acb58a2, 0xae10af696774b1dc}, + {0x9991a6f3d6bf1765, 0xacca6da1e0a8ef2a}, + {0xbff610b0cc6edd3f, 0x17fd090a58d32af4}, + {0xeff394dcff8a948e, 0xddfc4b4cef07f5b1}, + {0x95f83d0a1fb69cd9, 0x4abdaf101564f98f}, + {0xbb764c4ca7a4440f, 0x9d6d1ad41abe37f2}, + {0xea53df5fd18d5513, 0x84c86189216dc5ee}, + {0x92746b9be2f8552c, 0x32fd3cf5b4e49bb5}, + {0xb7118682dbb66a77, 0x3fbc8c33221dc2a2}, + {0xe4d5e82392a40515, 0x0fabaf3feaa5334b}, + {0x8f05b1163ba6832d, 0x29cb4d87f2a7400f}, + {0xb2c71d5bca9023f8, 0x743e20e9ef511013}, + {0xdf78e4b2bd342cf6, 0x914da9246b255417}, + {0x8bab8eefb6409c1a, 0x1ad089b6c2f7548f}, + {0xae9672aba3d0c320, 0xa184ac2473b529b2}, + {0xda3c0f568cc4f3e8, 0xc9e5d72d90a2741f}, + {0x8865899617fb1871, 0x7e2fa67c7a658893}, + {0xaa7eebfb9df9de8d, 0xddbb901b98feeab8}, + {0xd51ea6fa85785631, 0x552a74227f3ea566}, + {0x8533285c936b35de, 0xd53a88958f872760}, + {0xa67ff273b8460356, 0x8a892abaf368f138}, + {0xd01fef10a657842c, 0x2d2b7569b0432d86}, + {0x8213f56a67f6b29b, 0x9c3b29620e29fc74}, + {0xa298f2c501f45f42, 0x8349f3ba91b47b90}, + {0xcb3f2f7642717713, 0x241c70a936219a74}, + {0xfe0efb53d30dd4d7, 0xed238cd383aa0111}, + {0x9ec95d1463e8a506, 0xf4363804324a40ab}, + {0xc67bb4597ce2ce48, 0xb143c6053edcd0d6}, + {0xf81aa16fdc1b81da, 0xdd94b7868e94050b}, + {0x9b10a4e5e9913128, 0xca7cf2b4191c8327}, + {0xc1d4ce1f63f57d72, 0xfd1c2f611f63a3f1}, + {0xf24a01a73cf2dccf, 0xbc633b39673c8ced}, + {0x976e41088617ca01, 0xd5be0503e085d814}, + {0xbd49d14aa79dbc82, 0x4b2d8644d8a74e19}, + {0xec9c459d51852ba2, 0xddf8e7d60ed1219f}, + {0x93e1ab8252f33b45, 0xcabb90e5c942b504}, + {0xb8da1662e7b00a17, 0x3d6a751f3b936244}, + {0xe7109bfba19c0c9d, 0x0cc512670a783ad5}, + {0x906a617d450187e2, 0x27fb2b80668b24c6}, + {0xb484f9dc9641e9da, 0xb1f9f660802dedf7}, + {0xe1a63853bbd26451, 0x5e7873f8a0396974}, + {0x8d07e33455637eb2, 0xdb0b487b6423e1e9}, + {0xb049dc016abc5e5f, 0x91ce1a9a3d2cda63}, + {0xdc5c5301c56b75f7, 0x7641a140cc7810fc}, + {0x89b9b3e11b6329ba, 0xa9e904c87fcb0a9e}, + {0xac2820d9623bf429, 0x546345fa9fbdcd45}, + {0xd732290fbacaf133, 0xa97c177947ad4096}, + {0x867f59a9d4bed6c0, 0x49ed8eabcccc485e}, + {0xa81f301449ee8c70, 0x5c68f256bfff5a75}, + {0xd226fc195c6a2f8c, 0x73832eec6fff3112}, + {0x83585d8fd9c25db7, 0xc831fd53c5ff7eac}, + {0xa42e74f3d032f525, 0xba3e7ca8b77f5e56}, + {0xcd3a1230c43fb26f, 0x28ce1bd2e55f35ec}, + {0x80444b5e7aa7cf85, 0x7980d163cf5b81b4}, + {0xa0555e361951c366, 0xd7e105bcc3326220}, + {0xc86ab5c39fa63440, 0x8dd9472bf3fefaa8}, + {0xfa856334878fc150, 0xb14f98f6f0feb952}, + {0x9c935e00d4b9d8d2, 0x6ed1bf9a569f33d4}, + {0xc3b8358109e84f07, 0x0a862f80ec4700c9}, + {0xf4a642e14c6262c8, 0xcd27bb612758c0fb}, + {0x98e7e9cccfbd7dbd, 0x8038d51cb897789d}, + {0xbf21e44003acdd2c, 0xe0470a63e6bd56c4}, + {0xeeea5d5004981478, 0x1858ccfce06cac75}, + {0x95527a5202df0ccb, 0x0f37801e0c43ebc9}, + {0xbaa718e68396cffd, 0xd30560258f54e6bb}, + {0xe950df20247c83fd, 0x47c6b82ef32a206a}, + {0x91d28b7416cdd27e, 0x4cdc331d57fa5442}, + {0xb6472e511c81471d, 0xe0133fe4adf8e953}, + {0xe3d8f9e563a198e5, 0x58180fddd97723a7}, + {0x8e679c2f5e44ff8f, 0x570f09eaa7ea7649}, + {0xb201833b35d63f73, 0x2cd2cc6551e513db}, + {0xde81e40a034bcf4f, 0xf8077f7ea65e58d2}, + {0x8b112e86420f6191, 0xfb04afaf27faf783}, + {0xadd57a27d29339f6, 0x79c5db9af1f9b564}, + {0xd94ad8b1c7380874, 0x18375281ae7822bd}, + {0x87cec76f1c830548, 0x8f2293910d0b15b6}, + {0xa9c2794ae3a3c69a, 0xb2eb3875504ddb23}, + {0xd433179d9c8cb841, 0x5fa60692a46151ec}, + {0x849feec281d7f328, 0xdbc7c41ba6bcd334}, + {0xa5c7ea73224deff3, 0x12b9b522906c0801}, + {0xcf39e50feae16bef, 0xd768226b34870a01}, + {0x81842f29f2cce375, 0xe6a1158300d46641}, + {0xa1e53af46f801c53, 0x60495ae3c1097fd1}, + {0xca5e89b18b602368, 0x385bb19cb14bdfc5}, + {0xfcf62c1dee382c42, 0x46729e03dd9ed7b6}, + {0x9e19db92b4e31ba9, 0x6c07a2c26a8346d2}, + {0xc5a05277621be293, 0xc7098b7305241886}, + {0xf70867153aa2db38, 0xb8cbee4fc66d1ea8}, + {0x9a65406d44a5c903, 0x737f74f1dc043329}, + {0xc0fe908895cf3b44, 0x505f522e53053ff3}, + {0xf13e34aabb430a15, 0x647726b9e7c68ff0}, + {0x96c6e0eab509e64d, 0x5eca783430dc19f6}, + {0xbc789925624c5fe0, 0xb67d16413d132073}, + {0xeb96bf6ebadf77d8, 0xe41c5bd18c57e890}, + {0x933e37a534cbaae7, 0x8e91b962f7b6f15a}, + {0xb80dc58e81fe95a1, 0x723627bbb5a4adb1}, + {0xe61136f2227e3b09, 0xcec3b1aaa30dd91d}, + {0x8fcac257558ee4e6, 0x213a4f0aa5e8a7b2}, + {0xb3bd72ed2af29e1f, 0xa988e2cd4f62d19e}, + {0xe0accfa875af45a7, 0x93eb1b80a33b8606}, + {0x8c6c01c9498d8b88, 0xbc72f130660533c4}, + {0xaf87023b9bf0ee6a, 0xeb8fad7c7f8680b5}, + {0xdb68c2ca82ed2a05, 0xa67398db9f6820e2} #else + {0xff77b1fcbebcdc4f, 0x25e8e89c13bb0f7b}, + {0xce5d73ff402d98e3, 0xfb0a3d212dc81290}, + {0xa6b34ad8c9dfc06f, 0xf42faa48c0ea481f}, + {0x86a8d39ef77164bc, 0xae5dff9c02033198}, + {0xd98ddaee19068c76, 0x3badd624dd9b0958}, + {0xafbd2350644eeacf, 0xe5d1929ef90898fb}, + {0x8df5efabc5979c8f, 0xca8d3ffa1ef463c2}, + {0xe55990879ddcaabd, 0xcc420a6a101d0516}, + {0xb94470938fa89bce, 0xf808e40e8d5b3e6a}, + {0x95a8637627989aad, 0xdde7001379a44aa9}, + {0xf1c90080baf72cb1, 0x5324c68b12dd6339}, + {0xc350000000000000, 0x0000000000000000}, + {0x9dc5ada82b70b59d, 0xf020000000000000}, + {0xfee50b7025c36a08, 0x02f236d04753d5b5}, + {0xcde6fd5e09abcf26, 0xed4c0226b55e6f87}, + {0xa6539930bf6bff45, 0x84db8346b786151d}, + {0x865b86925b9bc5c2, 0x0b8a2392ba45a9b3}, + {0xd910f7ff28069da4, 0x1b2ba1518094da05}, + {0xaf58416654a6babb, 0x387ac8d1970027b3}, + {0x8da471a9de737e24, 0x5ceaecfed289e5d3}, + {0xe4d5e82392a40515, 0x0fabaf3feaa5334b}, + {0xb8da1662e7b00a17, 0x3d6a751f3b936244}, + {0x95527a5202df0ccb, 0x0f37801e0c43ebc9}, + {0xf13e34aabb430a15, 0x647726b9e7c68ff0} +#endif + }; + +#if FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX + return pow10_significands[k - float_info<double>::min_k]; +#else + static constexpr const uint64_t powers_of_5_64[] = { + 0x0000000000000001, 0x0000000000000005, 0x0000000000000019, + 0x000000000000007d, 0x0000000000000271, 0x0000000000000c35, + 0x0000000000003d09, 0x000000000001312d, 0x000000000005f5e1, + 0x00000000001dcd65, 0x00000000009502f9, 0x0000000002e90edd, + 0x000000000e8d4a51, 0x0000000048c27395, 0x000000016bcc41e9, + 0x000000071afd498d, 0x0000002386f26fc1, 0x000000b1a2bc2ec5, + 0x000003782dace9d9, 0x00001158e460913d, 0x000056bc75e2d631, + 0x0001b1ae4d6e2ef5, 0x000878678326eac9, 0x002a5a058fc295ed, + 0x00d3c21bcecceda1, 0x0422ca8b0a00a425, 0x14adf4b7320334b9}; + static const int compression_ratio = 27; // Compute base index. @@ -1897,8 +1035,7 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<double> { int offset = k - kb; // Get base cache. - uint128_wrapper base_cache = - data::dragonbox_pow10_significands_128[cache_index]; + uint128_fallback base_cache = pow10_significands[cache_index]; if (offset == 0) return base_cache; // Compute the required amount of bit-shift. @@ -1906,10 +1043,9 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<double> { FMT_ASSERT(alpha > 0 && alpha < 64, "shifting error detected"); // Try to recover the real cache. - uint64_t pow5 = data::powers_of_5_64[offset]; - uint128_wrapper recovered_cache = umul128(base_cache.high(), pow5); - uint128_wrapper middle_low = - umul128(base_cache.low() - (kb < 0 ? 1u : 0u), pow5); + uint64_t pow5 = powers_of_5_64[offset]; + uint128_fallback recovered_cache = umul128(base_cache.high(), pow5); + uint128_fallback middle_low = umul128(base_cache.low(), pow5); recovered_cache += middle_low.high(); @@ -1917,228 +1053,153 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<double> { uint64_t middle_to_low = recovered_cache.low() << (64 - alpha); recovered_cache = - uint128_wrapper{(recovered_cache.low() >> alpha) | high_to_middle, - ((middle_low.low() >> alpha) | middle_to_low)}; - - if (kb < 0) recovered_cache += 1; - - // Get error. - int error_idx = (k - float_info<double>::min_k) / 16; - uint32_t error = (data::dragonbox_pow10_recovery_errors[error_idx] >> - ((k - float_info<double>::min_k) % 16) * 2) & - 0x3; - - // Add the error back. - FMT_ASSERT(recovered_cache.low() + error >= recovered_cache.low(), ""); - return {recovered_cache.high(), recovered_cache.low() + error}; + uint128_fallback{(recovered_cache.low() >> alpha) | high_to_middle, + ((middle_low.low() >> alpha) | middle_to_low)}; + FMT_ASSERT(recovered_cache.low() + 1 != 0, ""); + return {recovered_cache.high(), recovered_cache.low() + 1}; #endif } - static carrier_uint compute_mul(carrier_uint u, - const cache_entry_type& cache) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return umul192_upper64(u, cache); + struct compute_mul_result { + carrier_uint result; + bool is_integer; + }; + struct compute_mul_parity_result { + bool parity; + bool is_integer; + }; + + static compute_mul_result compute_mul( + carrier_uint u, const cache_entry_type& cache) noexcept { + auto r = umul192_upper128(u, cache); + return {r.high(), r.low() == 0}; } static uint32_t compute_delta(cache_entry_type const& cache, - int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return static_cast<uint32_t>(cache.high() >> (64 - 1 - beta_minus_1)); + int beta) noexcept { + return static_cast<uint32_t>(cache.high() >> (64 - 1 - beta)); } - static bool compute_mul_parity(carrier_uint two_f, - const cache_entry_type& cache, - int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - FMT_ASSERT(beta_minus_1 >= 1, ""); - FMT_ASSERT(beta_minus_1 < 64, ""); + static compute_mul_parity_result compute_mul_parity( + carrier_uint two_f, const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept { + FMT_ASSERT(beta >= 1, ""); + FMT_ASSERT(beta < 64, ""); - return ((umul192_middle64(two_f, cache) >> (64 - beta_minus_1)) & 1) != 0; + auto r = umul192_lower128(two_f, cache); + return {((r.high() >> (64 - beta)) & 1) != 0, + ((r.high() << beta) | (r.low() >> (64 - beta))) == 0}; } static carrier_uint compute_left_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case( - const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept { return (cache.high() - - (cache.high() >> (float_info<double>::significand_bits + 2))) >> - (64 - float_info<double>::significand_bits - 1 - beta_minus_1); + (cache.high() >> (num_significand_bits<double>() + 2))) >> + (64 - num_significand_bits<double>() - 1 - beta); } static carrier_uint compute_right_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case( - const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept { return (cache.high() + - (cache.high() >> (float_info<double>::significand_bits + 1))) >> - (64 - float_info<double>::significand_bits - 1 - beta_minus_1); + (cache.high() >> (num_significand_bits<double>() + 1))) >> + (64 - num_significand_bits<double>() - 1 - beta); } static carrier_uint compute_round_up_for_shorter_interval_case( - const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta_minus_1) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return ((cache.high() >> - (64 - float_info<double>::significand_bits - 2 - beta_minus_1)) + + const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept { + return ((cache.high() >> (64 - num_significand_bits<double>() - 2 - beta)) + 1) / 2; } }; -// Various integer checks -template <class T> -bool is_left_endpoint_integer_shorter_interval(int exponent) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return exponent >= - float_info< - T>::case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_lower_threshold && - exponent <= - float_info<T>::case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_upper_threshold; -} -template <class T> -bool is_endpoint_integer(typename float_info<T>::carrier_uint two_f, - int exponent, int minus_k) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - if (exponent < float_info<T>::case_fc_pm_half_lower_threshold) return false; - // For k >= 0. - if (exponent <= float_info<T>::case_fc_pm_half_upper_threshold) return true; - // For k < 0. - if (exponent > float_info<T>::divisibility_check_by_5_threshold) return false; - return divisible_by_power_of_5(two_f, minus_k); +FMT_FUNC uint128_fallback get_cached_power(int k) noexcept { + return cache_accessor<double>::get_cached_power(k); } -template <class T> -bool is_center_integer(typename float_info<T>::carrier_uint two_f, int exponent, - int minus_k) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - // Exponent for 5 is negative. - if (exponent > float_info<T>::divisibility_check_by_5_threshold) return false; - if (exponent > float_info<T>::case_fc_upper_threshold) - return divisible_by_power_of_5(two_f, minus_k); - // Both exponents are nonnegative. - if (exponent >= float_info<T>::case_fc_lower_threshold) return true; - // Exponent for 2 is negative. - return divisible_by_power_of_2(two_f, minus_k - exponent + 1); +// Various integer checks +template <typename T> +bool is_left_endpoint_integer_shorter_interval(int exponent) noexcept { + const int case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_lower_threshold = 2; + const int case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_upper_threshold = 3; + return exponent >= case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_lower_threshold && + exponent <= case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_upper_threshold; } // Remove trailing zeros from n and return the number of zeros removed (float) -FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE int remove_trailing_zeros(uint32_t& n) FMT_NOEXCEPT { -#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CTZ - int t = FMT_BUILTIN_CTZ(n); -#else - int t = ctz(n); -#endif - if (t > float_info<float>::max_trailing_zeros) - t = float_info<float>::max_trailing_zeros; - - const uint32_t mod_inv1 = 0xcccccccd; - const uint32_t max_quotient1 = 0x33333333; - const uint32_t mod_inv2 = 0xc28f5c29; - const uint32_t max_quotient2 = 0x0a3d70a3; - - int s = 0; - for (; s < t - 1; s += 2) { - if (n * mod_inv2 > max_quotient2) break; - n *= mod_inv2; - } - if (s < t && n * mod_inv1 <= max_quotient1) { - n *= mod_inv1; - ++s; +FMT_INLINE int remove_trailing_zeros(uint32_t& n, int s = 0) noexcept { + FMT_ASSERT(n != 0, ""); + // Modular inverse of 5 (mod 2^32): (mod_inv_5 * 5) mod 2^32 = 1. + constexpr uint32_t mod_inv_5 = 0xcccccccd; + constexpr uint32_t mod_inv_25 = 0xc28f5c29; // = mod_inv_5 * mod_inv_5 + + while (true) { + auto q = rotr(n * mod_inv_25, 2); + if (q > max_value<uint32_t>() / 100) break; + n = q; + s += 2; + } + auto q = rotr(n * mod_inv_5, 1); + if (q <= max_value<uint32_t>() / 10) { + n = q; + s |= 1; } - n >>= s; return s; } // Removes trailing zeros and returns the number of zeros removed (double) -FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE int remove_trailing_zeros(uint64_t& n) FMT_NOEXCEPT { -#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CTZLL - int t = FMT_BUILTIN_CTZLL(n); -#else - int t = ctzll(n); -#endif - if (t > float_info<double>::max_trailing_zeros) - t = float_info<double>::max_trailing_zeros; - // Divide by 10^8 and reduce to 32-bits - // Since ret_value.significand <= (2^64 - 1) / 1000 < 10^17, - // both of the quotient and the r should fit in 32-bits - - const uint32_t mod_inv1 = 0xcccccccd; - const uint32_t max_quotient1 = 0x33333333; - const uint64_t mod_inv8 = 0xc767074b22e90e21; - const uint64_t max_quotient8 = 0x00002af31dc46118; - - // If the number is divisible by 1'0000'0000, work with the quotient - if (t >= 8) { - auto quotient_candidate = n * mod_inv8; - - if (quotient_candidate <= max_quotient8) { - auto quotient = static_cast<uint32_t>(quotient_candidate >> 8); - - int s = 8; - for (; s < t; ++s) { - if (quotient * mod_inv1 > max_quotient1) break; - quotient *= mod_inv1; - } - quotient >>= (s - 8); - n = quotient; - return s; - } - } +FMT_INLINE int remove_trailing_zeros(uint64_t& n) noexcept { + FMT_ASSERT(n != 0, ""); - // Otherwise, work with the remainder - auto quotient = static_cast<uint32_t>(n / 100000000); - auto remainder = static_cast<uint32_t>(n - 100000000 * quotient); + // This magic number is ceil(2^90 / 10^8). + constexpr uint64_t magic_number = 12379400392853802749ull; + auto nm = umul128(n, magic_number); - if (t == 0 || remainder * mod_inv1 > max_quotient1) { - return 0; + // Is n is divisible by 10^8? + if ((nm.high() & ((1ull << (90 - 64)) - 1)) == 0 && nm.low() < magic_number) { + // If yes, work with the quotient... + auto n32 = static_cast<uint32_t>(nm.high() >> (90 - 64)); + // ... and use the 32 bit variant of the function + int s = remove_trailing_zeros(n32, 8); + n = n32; + return s; } - remainder *= mod_inv1; - if (t == 1 || remainder * mod_inv1 > max_quotient1) { - n = (remainder >> 1) + quotient * 10000000ull; - return 1; - } - remainder *= mod_inv1; - - if (t == 2 || remainder * mod_inv1 > max_quotient1) { - n = (remainder >> 2) + quotient * 1000000ull; - return 2; - } - remainder *= mod_inv1; + // If n is not divisible by 10^8, work with n itself. + constexpr uint64_t mod_inv_5 = 0xcccccccccccccccd; + constexpr uint64_t mod_inv_25 = 0x8f5c28f5c28f5c29; // mod_inv_5 * mod_inv_5 - if (t == 3 || remainder * mod_inv1 > max_quotient1) { - n = (remainder >> 3) + quotient * 100000ull; - return 3; - } - remainder *= mod_inv1; - - if (t == 4 || remainder * mod_inv1 > max_quotient1) { - n = (remainder >> 4) + quotient * 10000ull; - return 4; - } - remainder *= mod_inv1; - - if (t == 5 || remainder * mod_inv1 > max_quotient1) { - n = (remainder >> 5) + quotient * 1000ull; - return 5; + int s = 0; + while (true) { + auto q = rotr(n * mod_inv_25, 2); + if (q > max_value<uint64_t>() / 100) break; + n = q; + s += 2; } - remainder *= mod_inv1; - - if (t == 6 || remainder * mod_inv1 > max_quotient1) { - n = (remainder >> 6) + quotient * 100ull; - return 6; + auto q = rotr(n * mod_inv_5, 1); + if (q <= max_value<uint64_t>() / 10) { + n = q; + s |= 1; } - remainder *= mod_inv1; - n = (remainder >> 7) + quotient * 10ull; - return 7; + return s; } // The main algorithm for shorter interval case -template <class T> -FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE FMT_SAFEBUFFERS decimal_fp<T> shorter_interval_case( - int exponent) FMT_NOEXCEPT { +template <typename T> +FMT_INLINE decimal_fp<T> shorter_interval_case(int exponent) noexcept { decimal_fp<T> ret_value; // Compute k and beta const int minus_k = floor_log10_pow2_minus_log10_4_over_3(exponent); - const int beta_minus_1 = exponent + floor_log2_pow10(-minus_k); + const int beta = exponent + floor_log2_pow10(-minus_k); // Compute xi and zi using cache_entry_type = typename cache_accessor<T>::cache_entry_type; const cache_entry_type cache = cache_accessor<T>::get_cached_power(-minus_k); auto xi = cache_accessor<T>::compute_left_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case( - cache, beta_minus_1); + cache, beta); auto zi = cache_accessor<T>::compute_right_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case( - cache, beta_minus_1); + cache, beta); // If the left endpoint is not an integer, increase it if (!is_left_endpoint_integer_shorter_interval<T>(exponent)) ++xi; @@ -2155,8 +1216,8 @@ FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE FMT_SAFEBUFFERS decimal_fp<T> shorter_interval_case( // Otherwise, compute the round-up of y ret_value.significand = - cache_accessor<T>::compute_round_up_for_shorter_interval_case( - cache, beta_minus_1); + cache_accessor<T>::compute_round_up_for_shorter_interval_case(cache, + beta); ret_value.exponent = minus_k; // When tie occurs, choose one of them according to the rule @@ -2171,8 +1232,7 @@ FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE FMT_SAFEBUFFERS decimal_fp<T> shorter_interval_case( return ret_value; } -template <typename T> -FMT_SAFEBUFFERS decimal_fp<T> to_decimal(T x) FMT_NOEXCEPT { +template <typename T> decimal_fp<T> to_decimal(T x) noexcept { // Step 1: integer promotion & Schubfach multiplier calculation. using carrier_uint = typename float_info<T>::carrier_uint; @@ -2181,23 +1241,25 @@ FMT_SAFEBUFFERS decimal_fp<T> to_decimal(T x) FMT_NOEXCEPT { // Extract significand bits and exponent bits. const carrier_uint significand_mask = - (static_cast<carrier_uint>(1) << float_info<T>::significand_bits) - 1; + (static_cast<carrier_uint>(1) << num_significand_bits<T>()) - 1; carrier_uint significand = (br & significand_mask); - int exponent = static_cast<int>((br & exponent_mask<T>()) >> - float_info<T>::significand_bits); + int exponent = + static_cast<int>((br & exponent_mask<T>()) >> num_significand_bits<T>()); if (exponent != 0) { // Check if normal. - exponent += float_info<T>::exponent_bias - float_info<T>::significand_bits; + exponent -= exponent_bias<T>() + num_significand_bits<T>(); // Shorter interval case; proceed like Schubfach. + // In fact, when exponent == 1 and significand == 0, the interval is + // regular. However, it can be shown that the end-results are anyway same. if (significand == 0) return shorter_interval_case<T>(exponent); - significand |= - (static_cast<carrier_uint>(1) << float_info<T>::significand_bits); + significand |= (static_cast<carrier_uint>(1) << num_significand_bits<T>()); } else { // Subnormal case; the interval is always regular. if (significand == 0) return {0, 0}; - exponent = float_info<T>::min_exponent - float_info<T>::significand_bits; + exponent = + std::numeric_limits<T>::min_exponent - num_significand_bits<T>() - 1; } const bool include_left_endpoint = (significand % 2 == 0); @@ -2206,485 +1268,125 @@ FMT_SAFEBUFFERS decimal_fp<T> to_decimal(T x) FMT_NOEXCEPT { // Compute k and beta. const int minus_k = floor_log10_pow2(exponent) - float_info<T>::kappa; const cache_entry_type cache = cache_accessor<T>::get_cached_power(-minus_k); - const int beta_minus_1 = exponent + floor_log2_pow10(-minus_k); + const int beta = exponent + floor_log2_pow10(-minus_k); - // Compute zi and deltai + // Compute zi and deltai. // 10^kappa <= deltai < 10^(kappa + 1) - const uint32_t deltai = cache_accessor<T>::compute_delta(cache, beta_minus_1); + const uint32_t deltai = cache_accessor<T>::compute_delta(cache, beta); const carrier_uint two_fc = significand << 1; - const carrier_uint two_fr = two_fc | 1; - const carrier_uint zi = - cache_accessor<T>::compute_mul(two_fr << beta_minus_1, cache); - // Step 2: Try larger divisor; remove trailing zeros if necessary + // For the case of binary32, the result of integer check is not correct for + // 29711844 * 2^-82 + // = 6.1442653300000000008655037797566933477355632930994033813476... * 10^-18 + // and 29711844 * 2^-81 + // = 1.2288530660000000001731007559513386695471126586198806762695... * 10^-17, + // and they are the unique counterexamples. However, since 29711844 is even, + // this does not cause any problem for the endpoints calculations; it can only + // cause a problem when we need to perform integer check for the center. + // Fortunately, with these inputs, that branch is never executed, so we are + // fine. + const typename cache_accessor<T>::compute_mul_result z_mul = + cache_accessor<T>::compute_mul((two_fc | 1) << beta, cache); + + // Step 2: Try larger divisor; remove trailing zeros if necessary. // Using an upper bound on zi, we might be able to optimize the division - // better than the compiler; we are computing zi / big_divisor here + // better than the compiler; we are computing zi / big_divisor here. decimal_fp<T> ret_value; - ret_value.significand = divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(zi); - uint32_t r = static_cast<uint32_t>(zi - float_info<T>::big_divisor * - ret_value.significand); + ret_value.significand = divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(z_mul.result); + uint32_t r = static_cast<uint32_t>(z_mul.result - float_info<T>::big_divisor * + ret_value.significand); - if (r > deltai) { - goto small_divisor_case_label; - } else if (r < deltai) { - // Exclude the right endpoint if necessary - if (r == 0 && !include_right_endpoint && - is_endpoint_integer<T>(two_fr, exponent, minus_k)) { + if (r < deltai) { + // Exclude the right endpoint if necessary. + if (r == 0 && (z_mul.is_integer & !include_right_endpoint)) { --ret_value.significand; r = float_info<T>::big_divisor; goto small_divisor_case_label; } + } else if (r > deltai) { + goto small_divisor_case_label; } else { - // r == deltai; compare fractional parts - // Check conditions in the order different from the paper - // to take advantage of short-circuiting - const carrier_uint two_fl = two_fc - 1; - if ((!include_left_endpoint || - !is_endpoint_integer<T>(two_fl, exponent, minus_k)) && - !cache_accessor<T>::compute_mul_parity(two_fl, cache, beta_minus_1)) { + // r == deltai; compare fractional parts. + const typename cache_accessor<T>::compute_mul_parity_result x_mul = + cache_accessor<T>::compute_mul_parity(two_fc - 1, cache, beta); + + if (!(x_mul.parity | (x_mul.is_integer & include_left_endpoint))) goto small_divisor_case_label; - } } ret_value.exponent = minus_k + float_info<T>::kappa + 1; - // We may need to remove trailing zeros + // We may need to remove trailing zeros. ret_value.exponent += remove_trailing_zeros(ret_value.significand); return ret_value; - // Step 3: Find the significand with the smaller divisor + // Step 3: Find the significand with the smaller divisor. small_divisor_case_label: ret_value.significand *= 10; ret_value.exponent = minus_k + float_info<T>::kappa; - const uint32_t mask = (1u << float_info<T>::kappa) - 1; - auto dist = r - (deltai / 2) + (float_info<T>::small_divisor / 2); - - // Is dist divisible by 2^kappa? - if ((dist & mask) == 0) { - const bool approx_y_parity = - ((dist ^ (float_info<T>::small_divisor / 2)) & 1) != 0; - dist >>= float_info<T>::kappa; - - // Is dist divisible by 5^kappa? - if (check_divisibility_and_divide_by_pow5<float_info<T>::kappa>(dist)) { - ret_value.significand += dist; - - // Check z^(f) >= epsilon^(f) - // We have either yi == zi - epsiloni or yi == (zi - epsiloni) - 1, - // where yi == zi - epsiloni if and only if z^(f) >= epsilon^(f) - // Since there are only 2 possibilities, we only need to care about the - // parity. Also, zi and r should have the same parity since the divisor - // is an even number - if (cache_accessor<T>::compute_mul_parity(two_fc, cache, beta_minus_1) != - approx_y_parity) { - --ret_value.significand; - } else { - // If z^(f) >= epsilon^(f), we might have a tie - // when z^(f) == epsilon^(f), or equivalently, when y is an integer - if (is_center_integer<T>(two_fc, exponent, minus_k)) { - ret_value.significand = ret_value.significand % 2 == 0 - ? ret_value.significand - : ret_value.significand - 1; - } - } - } - // Is dist not divisible by 5^kappa? - else { - ret_value.significand += dist; - } - } - // Is dist not divisible by 2^kappa? - else { - // Since we know dist is small, we might be able to optimize the division - // better than the compiler; we are computing dist / small_divisor here - ret_value.significand += - small_division_by_pow10<float_info<T>::kappa>(dist); - } + uint32_t dist = r - (deltai / 2) + (float_info<T>::small_divisor / 2); + const bool approx_y_parity = + ((dist ^ (float_info<T>::small_divisor / 2)) & 1) != 0; + + // Is dist divisible by 10^kappa? + const bool divisible_by_small_divisor = + check_divisibility_and_divide_by_pow10<float_info<T>::kappa>(dist); + + // Add dist / 10^kappa to the significand. + ret_value.significand += dist; + + if (!divisible_by_small_divisor) return ret_value; + + // Check z^(f) >= epsilon^(f). + // We have either yi == zi - epsiloni or yi == (zi - epsiloni) - 1, + // where yi == zi - epsiloni if and only if z^(f) >= epsilon^(f). + // Since there are only 2 possibilities, we only need to care about the + // parity. Also, zi and r should have the same parity since the divisor + // is an even number. + const auto y_mul = cache_accessor<T>::compute_mul_parity(two_fc, cache, beta); + + // If z^(f) >= epsilon^(f), we might have a tie when z^(f) == epsilon^(f), + // or equivalently, when y is an integer. + if (y_mul.parity != approx_y_parity) + --ret_value.significand; + else if (y_mul.is_integer & (ret_value.significand % 2 != 0)) + --ret_value.significand; return ret_value; } } // namespace dragonbox - -// Formats value using a variation of the Fixed-Precision Positive -// Floating-Point Printout ((FPP)^2) algorithm by Steele & White: -// https://fmt.dev/p372-steele.pdf. -template <typename Double> -void fallback_format(Double d, int num_digits, bool binary32, buffer<char>& buf, - int& exp10) { - bigint numerator; // 2 * R in (FPP)^2. - bigint denominator; // 2 * S in (FPP)^2. - // lower and upper are differences between value and corresponding boundaries. - bigint lower; // (M^- in (FPP)^2). - bigint upper_store; // upper's value if different from lower. - bigint* upper = nullptr; // (M^+ in (FPP)^2). - fp value; - // Shift numerator and denominator by an extra bit or two (if lower boundary - // is closer) to make lower and upper integers. This eliminates multiplication - // by 2 during later computations. - const bool is_predecessor_closer = - binary32 ? value.assign(static_cast<float>(d)) : value.assign(d); - int shift = is_predecessor_closer ? 2 : 1; - uint64_t significand = value.f << shift; - if (value.e >= 0) { - numerator.assign(significand); - numerator <<= value.e; - lower.assign(1); - lower <<= value.e; - if (shift != 1) { - upper_store.assign(1); - upper_store <<= value.e + 1; - upper = &upper_store; - } - denominator.assign_pow10(exp10); - denominator <<= shift; - } else if (exp10 < 0) { - numerator.assign_pow10(-exp10); - lower.assign(numerator); - if (shift != 1) { - upper_store.assign(numerator); - upper_store <<= 1; - upper = &upper_store; - } - numerator *= significand; - denominator.assign(1); - denominator <<= shift - value.e; - } else { - numerator.assign(significand); - denominator.assign_pow10(exp10); - denominator <<= shift - value.e; - lower.assign(1); - if (shift != 1) { - upper_store.assign(1ULL << 1); - upper = &upper_store; - } - } - // Invariant: value == (numerator / denominator) * pow(10, exp10). - if (num_digits < 0) { - // Generate the shortest representation. - if (!upper) upper = &lower; - bool even = (value.f & 1) == 0; - num_digits = 0; - char* data = buf.data(); - for (;;) { - int digit = numerator.divmod_assign(denominator); - bool low = compare(numerator, lower) - even < 0; // numerator <[=] lower. - // numerator + upper >[=] pow10: - bool high = add_compare(numerator, *upper, denominator) + even > 0; - data[num_digits++] = static_cast<char>('0' + digit); - if (low || high) { - if (!low) { - ++data[num_digits - 1]; - } else if (high) { - int result = add_compare(numerator, numerator, denominator); - // Round half to even. - if (result > 0 || (result == 0 && (digit % 2) != 0)) - ++data[num_digits - 1]; - } - buf.try_resize(to_unsigned(num_digits)); - exp10 -= num_digits - 1; - return; - } - numerator *= 10; - lower *= 10; - if (upper != &lower) *upper *= 10; - } - } - // Generate the given number of digits. - exp10 -= num_digits - 1; - if (num_digits == 0) { - buf.try_resize(1); - denominator *= 10; - buf[0] = add_compare(numerator, numerator, denominator) > 0 ? '1' : '0'; - return; - } - buf.try_resize(to_unsigned(num_digits)); - for (int i = 0; i < num_digits - 1; ++i) { - int digit = numerator.divmod_assign(denominator); - buf[i] = static_cast<char>('0' + digit); - numerator *= 10; - } - int digit = numerator.divmod_assign(denominator); - auto result = add_compare(numerator, numerator, denominator); - if (result > 0 || (result == 0 && (digit % 2) != 0)) { - if (digit == 9) { - const auto overflow = '0' + 10; - buf[num_digits - 1] = overflow; - // Propagate the carry. - for (int i = num_digits - 1; i > 0 && buf[i] == overflow; --i) { - buf[i] = '0'; - ++buf[i - 1]; - } - if (buf[0] == overflow) { - buf[0] = '1'; - ++exp10; - } - return; - } - ++digit; - } - buf[num_digits - 1] = static_cast<char>('0' + digit); -} - -template <typename T> -int format_float(T value, int precision, float_specs specs, buffer<char>& buf) { - static_assert(!std::is_same<T, float>::value, ""); - FMT_ASSERT(value >= 0, "value is negative"); - - const bool fixed = specs.format == float_format::fixed; - if (value <= 0) { // <= instead of == to silence a warning. - if (precision <= 0 || !fixed) { - buf.push_back('0'); - return 0; - } - buf.try_resize(to_unsigned(precision)); - std::uninitialized_fill_n(buf.data(), precision, '0'); - return -precision; - } - - if (!specs.use_grisu) return snprintf_float(value, precision, specs, buf); - - if (precision < 0) { - // Use Dragonbox for the shortest format. - if (specs.binary32) { - auto dec = dragonbox::to_decimal(static_cast<float>(value)); - write<char>(buffer_appender<char>(buf), dec.significand); - return dec.exponent; - } - auto dec = dragonbox::to_decimal(static_cast<double>(value)); - write<char>(buffer_appender<char>(buf), dec.significand); - return dec.exponent; - } - - // Use Grisu + Dragon4 for the given precision: - // https://www.cs.tufts.edu/~nr/cs257/archive/florian-loitsch/printf.pdf. - int exp = 0; - const int min_exp = -60; // alpha in Grisu. - int cached_exp10 = 0; // K in Grisu. - fp normalized = normalize(fp(value)); - const auto cached_pow = get_cached_power( - min_exp - (normalized.e + fp::significand_size), cached_exp10); - normalized = normalized * cached_pow; - // Limit precision to the maximum possible number of significant digits in an - // IEEE754 double because we don't need to generate zeros. - const int max_double_digits = 767; - if (precision > max_double_digits) precision = max_double_digits; - fixed_handler handler{buf.data(), 0, precision, -cached_exp10, fixed}; - if (grisu_gen_digits(normalized, 1, exp, handler) == digits::error) { - exp += handler.size - cached_exp10 - 1; - fallback_format(value, handler.precision, specs.binary32, buf, exp); - } else { - exp += handler.exp10; - buf.try_resize(to_unsigned(handler.size)); - } - if (!fixed && !specs.showpoint) { - // Remove trailing zeros. - auto num_digits = buf.size(); - while (num_digits > 0 && buf[num_digits - 1] == '0') { - --num_digits; - ++exp; - } - buf.try_resize(num_digits); - } - return exp; -} // namespace detail - -template <typename T> -int snprintf_float(T value, int precision, float_specs specs, - buffer<char>& buf) { - // Buffer capacity must be non-zero, otherwise MSVC's vsnprintf_s will fail. - FMT_ASSERT(buf.capacity() > buf.size(), "empty buffer"); - static_assert(!std::is_same<T, float>::value, ""); - - // Subtract 1 to account for the difference in precision since we use %e for - // both general and exponent format. - if (specs.format == float_format::general || - specs.format == float_format::exp) - precision = (precision >= 0 ? precision : 6) - 1; - - // Build the format string. - enum { max_format_size = 7 }; // The longest format is "%#.*Le". - char format[max_format_size]; - char* format_ptr = format; - *format_ptr++ = '%'; - if (specs.showpoint && specs.format == float_format::hex) *format_ptr++ = '#'; - if (precision >= 0) { - *format_ptr++ = '.'; - *format_ptr++ = '*'; - } - if (std::is_same<T, long double>()) *format_ptr++ = 'L'; - *format_ptr++ = specs.format != float_format::hex - ? (specs.format == float_format::fixed ? 'f' : 'e') - : (specs.upper ? 'A' : 'a'); - *format_ptr = '\0'; - - // Format using snprintf. - auto offset = buf.size(); - for (;;) { - auto begin = buf.data() + offset; - auto capacity = buf.capacity() - offset; -#ifdef FMT_FUZZ - if (precision > 100000) - throw std::runtime_error( - "fuzz mode - avoid large allocation inside snprintf"); -#endif - // Suppress the warning about a nonliteral format string. - // Cannot use auto because of a bug in MinGW (#1532). - int (*snprintf_ptr)(char*, size_t, const char*, ...) = FMT_SNPRINTF; - int result = precision >= 0 - ? snprintf_ptr(begin, capacity, format, precision, value) - : snprintf_ptr(begin, capacity, format, value); - if (result < 0) { - // The buffer will grow exponentially. - buf.try_reserve(buf.capacity() + 1); - continue; - } - auto size = to_unsigned(result); - // Size equal to capacity means that the last character was truncated. - if (size >= capacity) { - buf.try_reserve(size + offset + 1); // Add 1 for the terminating '\0'. - continue; - } - auto is_digit = [](char c) { return c >= '0' && c <= '9'; }; - if (specs.format == float_format::fixed) { - if (precision == 0) { - buf.try_resize(size); - return 0; - } - // Find and remove the decimal point. - auto end = begin + size, p = end; - do { - --p; - } while (is_digit(*p)); - int fraction_size = static_cast<int>(end - p - 1); - std::memmove(p, p + 1, to_unsigned(fraction_size)); - buf.try_resize(size - 1); - return -fraction_size; - } - if (specs.format == float_format::hex) { - buf.try_resize(size + offset); - return 0; - } - // Find and parse the exponent. - auto end = begin + size, exp_pos = end; - do { - --exp_pos; - } while (*exp_pos != 'e'); - char sign = exp_pos[1]; - assert(sign == '+' || sign == '-'); - int exp = 0; - auto p = exp_pos + 2; // Skip 'e' and sign. - do { - assert(is_digit(*p)); - exp = exp * 10 + (*p++ - '0'); - } while (p != end); - if (sign == '-') exp = -exp; - int fraction_size = 0; - if (exp_pos != begin + 1) { - // Remove trailing zeros. - auto fraction_end = exp_pos - 1; - while (*fraction_end == '0') --fraction_end; - // Move the fractional part left to get rid of the decimal point. - fraction_size = static_cast<int>(fraction_end - begin - 1); - std::memmove(begin + 1, begin + 2, to_unsigned(fraction_size)); - } - buf.try_resize(to_unsigned(fraction_size) + offset + 1); - return exp - fraction_size; - } -} - -// A public domain branchless UTF-8 decoder by Christopher Wellons: -// https://github.com/skeeto/branchless-utf8 -/* Decode the next character, c, from buf, reporting errors in e. - * - * Since this is a branchless decoder, four bytes will be read from the - * buffer regardless of the actual length of the next character. This - * means the buffer _must_ have at least three bytes of zero padding - * following the end of the data stream. - * - * Errors are reported in e, which will be non-zero if the parsed - * character was somehow invalid: invalid byte sequence, non-canonical - * encoding, or a surrogate half. - * - * The function returns a pointer to the next character. When an error - * occurs, this pointer will be a guess that depends on the particular - * error, but it will always advance at least one byte. - */ -inline const char* utf8_decode(const char* buf, uint32_t* c, int* e) { - static const int masks[] = {0x00, 0x7f, 0x1f, 0x0f, 0x07}; - static const uint32_t mins[] = {4194304, 0, 128, 2048, 65536}; - static const int shiftc[] = {0, 18, 12, 6, 0}; - static const int shifte[] = {0, 6, 4, 2, 0}; - - int len = code_point_length(buf); - const char* next = buf + len; - - // Assume a four-byte character and load four bytes. Unused bits are - // shifted out. - auto s = reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(buf); - *c = uint32_t(s[0] & masks[len]) << 18; - *c |= uint32_t(s[1] & 0x3f) << 12; - *c |= uint32_t(s[2] & 0x3f) << 6; - *c |= uint32_t(s[3] & 0x3f) << 0; - *c >>= shiftc[len]; - - // Accumulate the various error conditions. - *e = (*c < mins[len]) << 6; // non-canonical encoding - *e |= ((*c >> 11) == 0x1b) << 7; // surrogate half? - *e |= (*c > 0x10FFFF) << 8; // out of range? - *e |= (s[1] & 0xc0) >> 2; - *e |= (s[2] & 0xc0) >> 4; - *e |= (s[3]) >> 6; - *e ^= 0x2a; // top two bits of each tail byte correct? - *e >>= shifte[len]; - - return next; -} - -struct stringifier { - template <typename T> FMT_INLINE std::string operator()(T value) const { - return to_string(value); - } - std::string operator()(basic_format_arg<format_context>::handle h) const { - memory_buffer buf; - format_parse_context parse_ctx({}); - format_context format_ctx(buffer_appender<char>(buf), {}, {}); - h.format(parse_ctx, format_ctx); - return to_string(buf); - } -}; } // namespace detail template <> struct formatter<detail::bigint> { - format_parse_context::iterator parse(format_parse_context& ctx) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) + -> format_parse_context::iterator { return ctx.begin(); } - format_context::iterator format(const detail::bigint& n, - format_context& ctx) { + auto format(const detail::bigint& n, format_context& ctx) const + -> format_context::iterator { auto out = ctx.out(); bool first = true; for (auto i = n.bigits_.size(); i > 0; --i) { auto value = n.bigits_[i - 1u]; if (first) { - out = format_to(out, "{:x}", value); + out = format_to(out, FMT_STRING("{:x}"), value); first = false; continue; } - out = format_to(out, "{:08x}", value); + out = format_to(out, FMT_STRING("{:08x}"), value); } if (n.exp_ > 0) - out = format_to(out, "p{}", n.exp_ * detail::bigint::bigit_bits); + out = format_to(out, FMT_STRING("p{}"), + n.exp_ * detail::bigint::bigit_bits); return out; } }; FMT_FUNC detail::utf8_to_utf16::utf8_to_utf16(string_view s) { - auto transcode = [this](const char* p) { - auto cp = uint32_t(); - auto error = 0; - p = utf8_decode(p, &cp, &error); - if (error != 0) FMT_THROW(std::runtime_error("invalid utf8")); + for_each_codepoint(s, [this](uint32_t cp, string_view) { + if (cp == invalid_code_point) FMT_THROW(std::runtime_error("invalid utf8")); if (cp <= 0xFFFF) { buffer_.push_back(static_cast<wchar_t>(cp)); } else { @@ -2692,110 +1394,272 @@ FMT_FUNC detail::utf8_to_utf16::utf8_to_utf16(string_view s) { buffer_.push_back(static_cast<wchar_t>(0xD800 + (cp >> 10))); buffer_.push_back(static_cast<wchar_t>(0xDC00 + (cp & 0x3FF))); } - return p; - }; - auto p = s.data(); - const size_t block_size = 4; // utf8_decode always reads blocks of 4 chars. - if (s.size() >= block_size) { - for (auto end = p + s.size() - block_size + 1; p < end;) p = transcode(p); - } - if (auto num_chars_left = s.data() + s.size() - p) { - char buf[2 * block_size - 1] = {}; - memcpy(buf, p, to_unsigned(num_chars_left)); - p = buf; - do { - p = transcode(p); - } while (p - buf < num_chars_left); - } + return true; + }); buffer_.push_back(0); } FMT_FUNC void format_system_error(detail::buffer<char>& out, int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const char* message) noexcept { FMT_TRY { - memory_buffer buf; - buf.resize(inline_buffer_size); - for (;;) { - char* system_message = &buf[0]; - int result = - detail::safe_strerror(error_code, system_message, buf.size()); - if (result == 0) { - format_to(detail::buffer_appender<char>(out), "{}: {}", message, - system_message); - return; - } - if (result != ERANGE) - break; // Can't get error message, report error code instead. - buf.resize(buf.size() * 2); - } + auto ec = std::error_code(error_code, std::generic_category()); + write(std::back_inserter(out), std::system_error(ec, message).what()); + return; } FMT_CATCH(...) {} format_error_code(out, error_code, message); } -FMT_FUNC void detail::error_handler::on_error(const char* message) { - FMT_THROW(format_error(message)); -} - FMT_FUNC void report_system_error(int error_code, - fmt::string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const char* message) noexcept { report_error(format_system_error, error_code, message); } -FMT_FUNC std::string detail::vformat(string_view format_str, format_args args) { - if (format_str.size() == 2 && equal2(format_str.data(), "{}")) { - auto arg = args.get(0); - if (!arg) error_handler().on_error("argument not found"); - return visit_format_arg(stringifier(), arg); - } - memory_buffer buffer; - detail::vformat_to(buffer, format_str, args); +FMT_FUNC std::string vformat(string_view fmt, format_args args) { + // Don't optimize the "{}" case to keep the binary size small and because it + // can be better optimized in fmt::format anyway. + auto buffer = memory_buffer(); + detail::vformat_to(buffer, fmt, args); return to_string(buffer); } -#ifdef _WIN32 namespace detail { +#if !defined(_WIN32) || defined(FMT_WINDOWS_NO_WCHAR) +FMT_FUNC bool write_console(int, string_view) { return false; } +#else using dword = conditional_t<sizeof(long) == 4, unsigned long, unsigned>; extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) int __stdcall WriteConsoleW( // void*, const void*, dword, dword*, void*); -} // namespace detail + +FMT_FUNC bool write_console(int fd, string_view text) { + auto u16 = utf8_to_utf16(text); + return WriteConsoleW(reinterpret_cast<void*>(_get_osfhandle(fd)), u16.c_str(), + static_cast<dword>(u16.size()), nullptr, nullptr) != 0; +} #endif -FMT_FUNC void vprint(std::FILE* f, string_view format_str, format_args args) { - memory_buffer buffer; - detail::vformat_to(buffer, format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<char>>(args)); #ifdef _WIN32 - auto fd = _fileno(f); +// Print assuming legacy (non-Unicode) encoding. +FMT_FUNC void vprint_mojibake(std::FILE* f, string_view fmt, format_args args) { + auto buffer = memory_buffer(); + detail::vformat_to(buffer, fmt, args); + fwrite_fully(buffer.data(), buffer.size(), f); +} +#endif + +FMT_FUNC void print(std::FILE* f, string_view text) { +#ifdef _WIN32 + int fd = _fileno(f); if (_isatty(fd)) { - detail::utf8_to_utf16 u16(string_view(buffer.data(), buffer.size())); - auto written = detail::dword(); - if (!detail::WriteConsoleW(reinterpret_cast<void*>(_get_osfhandle(fd)), - u16.c_str(), static_cast<uint32_t>(u16.size()), - &written, nullptr)) { - FMT_THROW(format_error("failed to write to console")); - } - return; + std::fflush(f); + if (write_console(fd, text)) return; } #endif - detail::fwrite_fully(buffer.data(), 1, buffer.size(), f); + fwrite_fully(text.data(), text.size(), f); } +} // namespace detail -#ifdef _WIN32 -// Print assuming legacy (non-Unicode) encoding. -FMT_FUNC void detail::vprint_mojibake(std::FILE* f, string_view format_str, - format_args args) { - memory_buffer buffer; - detail::vformat_to(buffer, format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<char>>(args)); - fwrite_fully(buffer.data(), 1, buffer.size(), f); +FMT_FUNC void vprint(std::FILE* f, string_view fmt, format_args args) { + auto buffer = memory_buffer(); + detail::vformat_to(buffer, fmt, args); + detail::print(f, {buffer.data(), buffer.size()}); } -#endif -FMT_FUNC void vprint(string_view format_str, format_args args) { - vprint(stdout, format_str, args); +FMT_FUNC void vprint(string_view fmt, format_args args) { + vprint(stdout, fmt, args); } +namespace detail { + +struct singleton { + unsigned char upper; + unsigned char lower_count; +}; + +inline auto is_printable(uint16_t x, const singleton* singletons, + size_t singletons_size, + const unsigned char* singleton_lowers, + const unsigned char* normal, size_t normal_size) + -> bool { + auto upper = x >> 8; + auto lower_start = 0; + for (size_t i = 0; i < singletons_size; ++i) { + auto s = singletons[i]; + auto lower_end = lower_start + s.lower_count; + if (upper < s.upper) break; + if (upper == s.upper) { + for (auto j = lower_start; j < lower_end; ++j) { + if (singleton_lowers[j] == (x & 0xff)) return false; + } + } + lower_start = lower_end; + } + + auto xsigned = static_cast<int>(x); + auto current = true; + for (size_t i = 0; i < normal_size; ++i) { + auto v = static_cast<int>(normal[i]); + auto len = (v & 0x80) != 0 ? (v & 0x7f) << 8 | normal[++i] : v; + xsigned -= len; + if (xsigned < 0) break; + current = !current; + } + return current; +} + +// This code is generated by support/printable.py. +FMT_FUNC auto is_printable(uint32_t cp) -> bool { + static constexpr singleton singletons0[] = { + {0x00, 1}, {0x03, 5}, {0x05, 6}, {0x06, 3}, {0x07, 6}, {0x08, 8}, + {0x09, 17}, {0x0a, 28}, {0x0b, 25}, {0x0c, 20}, {0x0d, 16}, {0x0e, 13}, + {0x0f, 4}, {0x10, 3}, {0x12, 18}, {0x13, 9}, {0x16, 1}, {0x17, 5}, + {0x18, 2}, {0x19, 3}, {0x1a, 7}, {0x1c, 2}, {0x1d, 1}, {0x1f, 22}, + {0x20, 3}, {0x2b, 3}, {0x2c, 2}, {0x2d, 11}, {0x2e, 1}, {0x30, 3}, + {0x31, 2}, {0x32, 1}, {0xa7, 2}, {0xa9, 2}, {0xaa, 4}, {0xab, 8}, + {0xfa, 2}, {0xfb, 5}, {0xfd, 4}, {0xfe, 3}, {0xff, 9}, + }; + static constexpr unsigned char singletons0_lower[] = { + 0xad, 0x78, 0x79, 0x8b, 0x8d, 0xa2, 0x30, 0x57, 0x58, 0x8b, 0x8c, 0x90, + 0x1c, 0x1d, 0xdd, 0x0e, 0x0f, 0x4b, 0x4c, 0xfb, 0xfc, 0x2e, 0x2f, 0x3f, + 0x5c, 0x5d, 0x5f, 0xb5, 0xe2, 0x84, 0x8d, 0x8e, 0x91, 0x92, 0xa9, 0xb1, + 0xba, 0xbb, 0xc5, 0xc6, 0xc9, 0xca, 0xde, 0xe4, 0xe5, 0xff, 0x00, 0x04, + 0x11, 0x12, 0x29, 0x31, 0x34, 0x37, 0x3a, 0x3b, 0x3d, 0x49, 0x4a, 0x5d, + 0x84, 0x8e, 0x92, 0xa9, 0xb1, 0xb4, 0xba, 0xbb, 0xc6, 0xca, 0xce, 0xcf, + 0xe4, 0xe5, 0x00, 0x04, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x11, 0x12, 0x29, 0x31, 0x34, 0x3a, + 0x3b, 0x45, 0x46, 0x49, 0x4a, 0x5e, 0x64, 0x65, 0x84, 0x91, 0x9b, 0x9d, + 0xc9, 0xce, 0xcf, 0x0d, 0x11, 0x29, 0x45, 0x49, 0x57, 0x64, 0x65, 0x8d, + 0x91, 0xa9, 0xb4, 0xba, 0xbb, 0xc5, 0xc9, 0xdf, 0xe4, 0xe5, 0xf0, 0x0d, + 0x11, 0x45, 0x49, 0x64, 0x65, 0x80, 0x84, 0xb2, 0xbc, 0xbe, 0xbf, 0xd5, + 0xd7, 0xf0, 0xf1, 0x83, 0x85, 0x8b, 0xa4, 0xa6, 0xbe, 0xbf, 0xc5, 0xc7, + 0xce, 0xcf, 0xda, 0xdb, 0x48, 0x98, 0xbd, 0xcd, 0xc6, 0xce, 0xcf, 0x49, + 0x4e, 0x4f, 0x57, 0x59, 0x5e, 0x5f, 0x89, 0x8e, 0x8f, 0xb1, 0xb6, 0xb7, + 0xbf, 0xc1, 0xc6, 0xc7, 0xd7, 0x11, 0x16, 0x17, 0x5b, 0x5c, 0xf6, 0xf7, + 0xfe, 0xff, 0x80, 0x0d, 0x6d, 0x71, 0xde, 0xdf, 0x0e, 0x0f, 0x1f, 0x6e, + 0x6f, 0x1c, 0x1d, 0x5f, 0x7d, 0x7e, 0xae, 0xaf, 0xbb, 0xbc, 0xfa, 0x16, + 0x17, 0x1e, 0x1f, 0x46, 0x47, 0x4e, 0x4f, 0x58, 0x5a, 0x5c, 0x5e, 0x7e, + 0x7f, 0xb5, 0xc5, 0xd4, 0xd5, 0xdc, 0xf0, 0xf1, 0xf5, 0x72, 0x73, 0x8f, + 0x74, 0x75, 0x96, 0x2f, 0x5f, 0x26, 0x2e, 0x2f, 0xa7, 0xaf, 0xb7, 0xbf, + 0xc7, 0xcf, 0xd7, 0xdf, 0x9a, 0x40, 0x97, 0x98, 0x30, 0x8f, 0x1f, 0xc0, + 0xc1, 0xce, 0xff, 0x4e, 0x4f, 0x5a, 0x5b, 0x07, 0x08, 0x0f, 0x10, 0x27, + 0x2f, 0xee, 0xef, 0x6e, 0x6f, 0x37, 0x3d, 0x3f, 0x42, 0x45, 0x90, 0x91, + 0xfe, 0xff, 0x53, 0x67, 0x75, 0xc8, 0xc9, 0xd0, 0xd1, 0xd8, 0xd9, 0xe7, + 0xfe, 0xff, + }; + static constexpr singleton singletons1[] = { + {0x00, 6}, {0x01, 1}, {0x03, 1}, {0x04, 2}, {0x08, 8}, {0x09, 2}, + {0x0a, 5}, {0x0b, 2}, {0x0e, 4}, {0x10, 1}, {0x11, 2}, {0x12, 5}, + {0x13, 17}, {0x14, 1}, {0x15, 2}, {0x17, 2}, {0x19, 13}, {0x1c, 5}, + {0x1d, 8}, {0x24, 1}, {0x6a, 3}, {0x6b, 2}, {0xbc, 2}, {0xd1, 2}, + {0xd4, 12}, {0xd5, 9}, {0xd6, 2}, {0xd7, 2}, {0xda, 1}, {0xe0, 5}, + {0xe1, 2}, {0xe8, 2}, {0xee, 32}, {0xf0, 4}, {0xf8, 2}, {0xf9, 2}, + {0xfa, 2}, {0xfb, 1}, + }; + static constexpr unsigned char singletons1_lower[] = { + 0x0c, 0x27, 0x3b, 0x3e, 0x4e, 0x4f, 0x8f, 0x9e, 0x9e, 0x9f, 0x06, 0x07, + 0x09, 0x36, 0x3d, 0x3e, 0x56, 0xf3, 0xd0, 0xd1, 0x04, 0x14, 0x18, 0x36, + 0x37, 0x56, 0x57, 0x7f, 0xaa, 0xae, 0xaf, 0xbd, 0x35, 0xe0, 0x12, 0x87, + 0x89, 0x8e, 0x9e, 0x04, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x11, 0x12, 0x29, 0x31, 0x34, 0x3a, + 0x45, 0x46, 0x49, 0x4a, 0x4e, 0x4f, 0x64, 0x65, 0x5c, 0xb6, 0xb7, 0x1b, + 0x1c, 0x07, 0x08, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x14, 0x17, 0x36, 0x39, 0x3a, 0xa8, 0xa9, + 0xd8, 0xd9, 0x09, 0x37, 0x90, 0x91, 0xa8, 0x07, 0x0a, 0x3b, 0x3e, 0x66, + 0x69, 0x8f, 0x92, 0x6f, 0x5f, 0xee, 0xef, 0x5a, 0x62, 0x9a, 0x9b, 0x27, + 0x28, 0x55, 0x9d, 0xa0, 0xa1, 0xa3, 0xa4, 0xa7, 0xa8, 0xad, 0xba, 0xbc, + 0xc4, 0x06, 0x0b, 0x0c, 0x15, 0x1d, 0x3a, 0x3f, 0x45, 0x51, 0xa6, 0xa7, + 0xcc, 0xcd, 0xa0, 0x07, 0x19, 0x1a, 0x22, 0x25, 0x3e, 0x3f, 0xc5, 0xc6, + 0x04, 0x20, 0x23, 0x25, 0x26, 0x28, 0x33, 0x38, 0x3a, 0x48, 0x4a, 0x4c, + 0x50, 0x53, 0x55, 0x56, 0x58, 0x5a, 0x5c, 0x5e, 0x60, 0x63, 0x65, 0x66, + 0x6b, 0x73, 0x78, 0x7d, 0x7f, 0x8a, 0xa4, 0xaa, 0xaf, 0xb0, 0xc0, 0xd0, + 0xae, 0xaf, 0x79, 0xcc, 0x6e, 0x6f, 0x93, + }; + static constexpr unsigned char normal0[] = { + 0x00, 0x20, 0x5f, 0x22, 0x82, 0xdf, 0x04, 0x82, 0x44, 0x08, 0x1b, 0x04, + 0x06, 0x11, 0x81, 0xac, 0x0e, 0x80, 0xab, 0x35, 0x28, 0x0b, 0x80, 0xe0, + 0x03, 0x19, 0x08, 0x01, 0x04, 0x2f, 0x04, 0x34, 0x04, 0x07, 0x03, 0x01, + 0x07, 0x06, 0x07, 0x11, 0x0a, 0x50, 0x0f, 0x12, 0x07, 0x55, 0x07, 0x03, + 0x04, 0x1c, 0x0a, 0x09, 0x03, 0x08, 0x03, 0x07, 0x03, 0x02, 0x03, 0x03, + 0x03, 0x0c, 0x04, 0x05, 0x03, 0x0b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x0e, 0x15, 0x05, 0x3a, + 0x03, 0x11, 0x07, 0x06, 0x05, 0x10, 0x07, 0x57, 0x07, 0x02, 0x07, 0x15, + 0x0d, 0x50, 0x04, 0x43, 0x03, 0x2d, 0x03, 0x01, 0x04, 0x11, 0x06, 0x0f, + 0x0c, 0x3a, 0x04, 0x1d, 0x25, 0x5f, 0x20, 0x6d, 0x04, 0x6a, 0x25, 0x80, + 0xc8, 0x05, 0x82, 0xb0, 0x03, 0x1a, 0x06, 0x82, 0xfd, 0x03, 0x59, 0x07, + 0x15, 0x0b, 0x17, 0x09, 0x14, 0x0c, 0x14, 0x0c, 0x6a, 0x06, 0x0a, 0x06, + 0x1a, 0x06, 0x59, 0x07, 0x2b, 0x05, 0x46, 0x0a, 0x2c, 0x04, 0x0c, 0x04, + 0x01, 0x03, 0x31, 0x0b, 0x2c, 0x04, 0x1a, 0x06, 0x0b, 0x03, 0x80, 0xac, + 0x06, 0x0a, 0x06, 0x21, 0x3f, 0x4c, 0x04, 0x2d, 0x03, 0x74, 0x08, 0x3c, + 0x03, 0x0f, 0x03, 0x3c, 0x07, 0x38, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x05, 0x82, 0xff, 0x11, + 0x18, 0x08, 0x2f, 0x11, 0x2d, 0x03, 0x20, 0x10, 0x21, 0x0f, 0x80, 0x8c, + 0x04, 0x82, 0x97, 0x19, 0x0b, 0x15, 0x88, 0x94, 0x05, 0x2f, 0x05, 0x3b, + 0x07, 0x02, 0x0e, 0x18, 0x09, 0x80, 0xb3, 0x2d, 0x74, 0x0c, 0x80, 0xd6, + 0x1a, 0x0c, 0x05, 0x80, 0xff, 0x05, 0x80, 0xdf, 0x0c, 0xee, 0x0d, 0x03, + 0x84, 0x8d, 0x03, 0x37, 0x09, 0x81, 0x5c, 0x14, 0x80, 0xb8, 0x08, 0x80, + 0xcb, 0x2a, 0x38, 0x03, 0x0a, 0x06, 0x38, 0x08, 0x46, 0x08, 0x0c, 0x06, + 0x74, 0x0b, 0x1e, 0x03, 0x5a, 0x04, 0x59, 0x09, 0x80, 0x83, 0x18, 0x1c, + 0x0a, 0x16, 0x09, 0x4c, 0x04, 0x80, 0x8a, 0x06, 0xab, 0xa4, 0x0c, 0x17, + 0x04, 0x31, 0xa1, 0x04, 0x81, 0xda, 0x26, 0x07, 0x0c, 0x05, 0x05, 0x80, + 0xa5, 0x11, 0x81, 0x6d, 0x10, 0x78, 0x28, 0x2a, 0x06, 0x4c, 0x04, 0x80, + 0x8d, 0x04, 0x80, 0xbe, 0x03, 0x1b, 0x03, 0x0f, 0x0d, + }; + static constexpr unsigned char normal1[] = { + 0x5e, 0x22, 0x7b, 0x05, 0x03, 0x04, 0x2d, 0x03, 0x66, 0x03, 0x01, 0x2f, + 0x2e, 0x80, 0x82, 0x1d, 0x03, 0x31, 0x0f, 0x1c, 0x04, 0x24, 0x09, 0x1e, + 0x05, 0x2b, 0x05, 0x44, 0x04, 0x0e, 0x2a, 0x80, 0xaa, 0x06, 0x24, 0x04, + 0x24, 0x04, 0x28, 0x08, 0x34, 0x0b, 0x01, 0x80, 0x90, 0x81, 0x37, 0x09, + 0x16, 0x0a, 0x08, 0x80, 0x98, 0x39, 0x03, 0x63, 0x08, 0x09, 0x30, 0x16, + 0x05, 0x21, 0x03, 0x1b, 0x05, 0x01, 0x40, 0x38, 0x04, 0x4b, 0x05, 0x2f, + 0x04, 0x0a, 0x07, 0x09, 0x07, 0x40, 0x20, 0x27, 0x04, 0x0c, 0x09, 0x36, + 0x03, 0x3a, 0x05, 0x1a, 0x07, 0x04, 0x0c, 0x07, 0x50, 0x49, 0x37, 0x33, + 0x0d, 0x33, 0x07, 0x2e, 0x08, 0x0a, 0x81, 0x26, 0x52, 0x4e, 0x28, 0x08, + 0x2a, 0x56, 0x1c, 0x14, 0x17, 0x09, 0x4e, 0x04, 0x1e, 0x0f, 0x43, 0x0e, + 0x19, 0x07, 0x0a, 0x06, 0x48, 0x08, 0x27, 0x09, 0x75, 0x0b, 0x3f, 0x41, + 0x2a, 0x06, 0x3b, 0x05, 0x0a, 0x06, 0x51, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x10, 0x03, + 0x05, 0x80, 0x8b, 0x62, 0x1e, 0x48, 0x08, 0x0a, 0x80, 0xa6, 0x5e, 0x22, + 0x45, 0x0b, 0x0a, 0x06, 0x0d, 0x13, 0x39, 0x07, 0x0a, 0x36, 0x2c, 0x04, + 0x10, 0x80, 0xc0, 0x3c, 0x64, 0x53, 0x0c, 0x48, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x46, 0x45, + 0x1b, 0x48, 0x08, 0x53, 0x1d, 0x39, 0x81, 0x07, 0x46, 0x0a, 0x1d, 0x03, + 0x47, 0x49, 0x37, 0x03, 0x0e, 0x08, 0x0a, 0x06, 0x39, 0x07, 0x0a, 0x81, + 0x36, 0x19, 0x80, 0xb7, 0x01, 0x0f, 0x32, 0x0d, 0x83, 0x9b, 0x66, 0x75, + 0x0b, 0x80, 0xc4, 0x8a, 0xbc, 0x84, 0x2f, 0x8f, 0xd1, 0x82, 0x47, 0xa1, + 0xb9, 0x82, 0x39, 0x07, 0x2a, 0x04, 0x02, 0x60, 0x26, 0x0a, 0x46, 0x0a, + 0x28, 0x05, 0x13, 0x82, 0xb0, 0x5b, 0x65, 0x4b, 0x04, 0x39, 0x07, 0x11, + 0x40, 0x05, 0x0b, 0x02, 0x0e, 0x97, 0xf8, 0x08, 0x84, 0xd6, 0x2a, 0x09, + 0xa2, 0xf7, 0x81, 0x1f, 0x31, 0x03, 0x11, 0x04, 0x08, 0x81, 0x8c, 0x89, + 0x04, 0x6b, 0x05, 0x0d, 0x03, 0x09, 0x07, 0x10, 0x93, 0x60, 0x80, 0xf6, + 0x0a, 0x73, 0x08, 0x6e, 0x17, 0x46, 0x80, 0x9a, 0x14, 0x0c, 0x57, 0x09, + 0x19, 0x80, 0x87, 0x81, 0x47, 0x03, 0x85, 0x42, 0x0f, 0x15, 0x85, 0x50, + 0x2b, 0x80, 0xd5, 0x2d, 0x03, 0x1a, 0x04, 0x02, 0x81, 0x70, 0x3a, 0x05, + 0x01, 0x85, 0x00, 0x80, 0xd7, 0x29, 0x4c, 0x04, 0x0a, 0x04, 0x02, 0x83, + 0x11, 0x44, 0x4c, 0x3d, 0x80, 0xc2, 0x3c, 0x06, 0x01, 0x04, 0x55, 0x05, + 0x1b, 0x34, 0x02, 0x81, 0x0e, 0x2c, 0x04, 0x64, 0x0c, 0x56, 0x0a, 0x80, + 0xae, 0x38, 0x1d, 0x0d, 0x2c, 0x04, 0x09, 0x07, 0x02, 0x0e, 0x06, 0x80, + 0x9a, 0x83, 0xd8, 0x08, 0x0d, 0x03, 0x0d, 0x03, 0x74, 0x0c, 0x59, 0x07, + 0x0c, 0x14, 0x0c, 0x04, 0x38, 0x08, 0x0a, 0x06, 0x28, 0x08, 0x22, 0x4e, + 0x81, 0x54, 0x0c, 0x15, 0x03, 0x03, 0x05, 0x07, 0x09, 0x19, 0x07, 0x07, + 0x09, 0x03, 0x0d, 0x07, 0x29, 0x80, 0xcb, 0x25, 0x0a, 0x84, 0x06, + }; + auto lower = static_cast<uint16_t>(cp); + if (cp < 0x10000) { + return is_printable(lower, singletons0, + sizeof(singletons0) / sizeof(*singletons0), + singletons0_lower, normal0, sizeof(normal0)); + } + if (cp < 0x20000) { + return is_printable(lower, singletons1, + sizeof(singletons1) / sizeof(*singletons1), + singletons1_lower, normal1, sizeof(normal1)); + } + if (0x2a6de <= cp && cp < 0x2a700) return false; + if (0x2b735 <= cp && cp < 0x2b740) return false; + if (0x2b81e <= cp && cp < 0x2b820) return false; + if (0x2cea2 <= cp && cp < 0x2ceb0) return false; + if (0x2ebe1 <= cp && cp < 0x2f800) return false; + if (0x2fa1e <= cp && cp < 0x30000) return false; + if (0x3134b <= cp && cp < 0xe0100) return false; + if (0xe01f0 <= cp && cp < 0x110000) return false; + return cp < 0x110000; +} + +} // namespace detail + FMT_END_NAMESPACE #endif // FMT_FORMAT_INL_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/format.h b/include/fmt/format.h index 1a037b02..c8e1c46d 100644 --- a/include/fmt/format.h +++ b/include/fmt/format.h @@ -1,60 +1,103 @@ /* - Formatting library for C++ - - Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich - - Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining - a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the - "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including - without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, - distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to - permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to - the following conditions: - - The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be - included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software. - - THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, - EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF - MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND - NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE - LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION - OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION - WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE. - - --- Optional exception to the license --- - - As an exception, if, as a result of your compiling your source code, portions - of this Software are embedded into a machine-executable object form of such - source code, you may redistribute such embedded portions in such object form - without including the above copyright and permission notices. + Formatting library for C++ + + Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich + + Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining + a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the + "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including + without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, + distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to + permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to + the following conditions: + + The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be + included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software. + + THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, + EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF + MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND + NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE + LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION + OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION + WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE. + + --- Optional exception to the license --- + + As an exception, if, as a result of your compiling your source code, portions + of this Software are embedded into a machine-executable object form of such + source code, you may redistribute such embedded portions in such object form + without including the above copyright and permission notices. */ #ifndef FMT_FORMAT_H_ #define FMT_FORMAT_H_ -#include <algorithm> -#include <cerrno> -#include <cmath> -#include <cstdint> -#include <limits> -#include <memory> -#include <stdexcept> +#include <cmath> // std::signbit +#include <cstdint> // uint32_t +#include <cstring> // std::memcpy +#include <initializer_list> // std::initializer_list +#include <limits> // std::numeric_limits +#include <memory> // std::uninitialized_copy +#include <stdexcept> // std::runtime_error +#include <system_error> // std::system_error + +#ifdef __cpp_lib_bit_cast +# include <bit> // std::bitcast +#endif #include "core.h" -#ifdef __INTEL_COMPILER -# define FMT_ICC_VERSION __INTEL_COMPILER -#elif defined(__ICL) -# define FMT_ICC_VERSION __ICL +#if defined __cpp_inline_variables && __cpp_inline_variables >= 201606L +# define FMT_INLINE_VARIABLE inline #else -# define FMT_ICC_VERSION 0 +# define FMT_INLINE_VARIABLE #endif -#ifdef __NVCC__ -# define FMT_CUDA_VERSION (__CUDACC_VER_MAJOR__ * 100 + __CUDACC_VER_MINOR__) +#if FMT_HAS_CPP17_ATTRIBUTE(fallthrough) +# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH [[fallthrough]] +#elif defined(__clang__) +# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH [[clang::fallthrough]] +#elif FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 700 && \ + (!defined(__EDG_VERSION__) || __EDG_VERSION__ >= 520) +# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH [[gnu::fallthrough]] #else -# define FMT_CUDA_VERSION 0 +# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH +#endif + +#ifndef FMT_DEPRECATED +# if FMT_HAS_CPP14_ATTRIBUTE(deprecated) || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1900 +# define FMT_DEPRECATED [[deprecated]] +# else +# if (defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__LCC__)) || defined(__clang__) +# define FMT_DEPRECATED __attribute__((deprecated)) +# elif FMT_MSC_VERSION +# define FMT_DEPRECATED __declspec(deprecated) +# else +# define FMT_DEPRECATED /* deprecated */ +# endif +# endif +#endif + +#ifndef FMT_NO_UNIQUE_ADDRESS +# if FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L +# if FMT_HAS_CPP_ATTRIBUTE(no_unique_address) +# define FMT_NO_UNIQUE_ADDRESS [[no_unique_address]] +// VS2019 v16.10 and later except clang-cl (https://reviews.llvm.org/D110485) +# elif (FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1929) && !FMT_CLANG_VERSION +# define FMT_NO_UNIQUE_ADDRESS [[msvc::no_unique_address]] +# endif +# endif +#endif +#ifndef FMT_NO_UNIQUE_ADDRESS +# define FMT_NO_UNIQUE_ADDRESS +#endif + +// Visibility when compiled as a shared library/object. +#if defined(FMT_LIB_EXPORT) || defined(FMT_SHARED) +# define FMT_SO_VISIBILITY(value) FMT_VISIBILITY(value) +#else +# define FMT_SO_VISIBILITY(value) #endif #ifdef __has_builtin @@ -69,35 +112,9 @@ # define FMT_NOINLINE #endif -#if __cplusplus == 201103L || __cplusplus == 201402L -# if defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) || defined(__PGI) -# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH -# elif defined(__clang__) -# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH [[clang::fallthrough]] -# elif FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 700 && \ - (!defined(__EDG_VERSION__) || __EDG_VERSION__ >= 520) -# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH [[gnu::fallthrough]] -# else -# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH -# endif -#elif FMT_HAS_CPP17_ATTRIBUTE(fallthrough) || \ - (defined(_MSVC_LANG) && _MSVC_LANG >= 201703L) -# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH [[fallthrough]] -#else -# define FMT_FALLTHROUGH -#endif - -#ifndef FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED -# if FMT_HAS_CPP17_ATTRIBUTE(maybe_unused) -# define FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED [[maybe_unused]] -# else -# define FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED -# endif -#endif - #ifndef FMT_THROW # if FMT_EXCEPTIONS -# if FMT_MSC_VER || FMT_NVCC +# if FMT_MSC_VERSION || defined(__NVCC__) FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE namespace detail { template <typename Exception> inline void do_throw(const Exception& x) { @@ -113,11 +130,8 @@ FMT_END_NAMESPACE # define FMT_THROW(x) throw x # endif # else -# define FMT_THROW(x) \ - do { \ - static_cast<void>(sizeof(x)); \ - FMT_ASSERT(false, ""); \ - } while (false) +# define FMT_THROW(x) \ + ::fmt::detail::assert_fail(__FILE__, __LINE__, (x).what()) # endif #endif @@ -129,10 +143,21 @@ FMT_END_NAMESPACE # define FMT_CATCH(x) if (false) #endif +#ifndef FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED +# if FMT_HAS_CPP17_ATTRIBUTE(maybe_unused) +# define FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED [[maybe_unused]] +# else +# define FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED +# endif +#endif + #ifndef FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS // EDG based compilers (Intel, NVIDIA, Elbrus, etc), GCC and MSVC support UDLs. -# if (FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_user_literals) || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 407 || \ - FMT_MSC_VER >= 1900) && \ +// +// GCC before 4.9 requires a space in `operator"" _a` which is invalid in later +// compiler versions. +# if (FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_user_literals) || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 409 || \ + FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1900) && \ (!defined(__EDG_VERSION__) || __EDG_VERSION__ >= /* UDL feature */ 480) # define FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS 1 # else @@ -140,117 +165,101 @@ FMT_END_NAMESPACE # endif #endif -#ifndef FMT_USE_UDL_TEMPLATE -// EDG frontend based compilers (icc, nvcc, PGI, etc) and GCC < 6.4 do not -// properly support UDL templates and GCC >= 9 warns about them. -# if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS && \ - (!defined(__EDG_VERSION__) || __EDG_VERSION__ >= 501) && \ - ((FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 604 && __cplusplus >= 201402L) || \ - FMT_CLANG_VERSION >= 304) && \ - !defined(__PGI) && !defined(__NVCC__) -# define FMT_USE_UDL_TEMPLATE 1 -# else -# define FMT_USE_UDL_TEMPLATE 0 -# endif -#endif - -#ifndef FMT_USE_FLOAT -# define FMT_USE_FLOAT 1 -#endif - -#ifndef FMT_USE_DOUBLE -# define FMT_USE_DOUBLE 1 -#endif - -#ifndef FMT_USE_LONG_DOUBLE -# define FMT_USE_LONG_DOUBLE 1 -#endif - // Defining FMT_REDUCE_INT_INSTANTIATIONS to 1, will reduce the number of -// int_writer template instances to just one by only using the largest integer -// type. This results in a reduction in binary size but will cause a decrease in -// integer formatting performance. +// integer formatter template instantiations to just one by only using the +// largest integer type. This results in a reduction in binary size but will +// cause a decrease in integer formatting performance. #if !defined(FMT_REDUCE_INT_INSTANTIATIONS) # define FMT_REDUCE_INT_INSTANTIATIONS 0 #endif // __builtin_clz is broken in clang with Microsoft CodeGen: -// https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/519 -#if (FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_clz)) && !FMT_MSC_VER -# define FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ(n) __builtin_clz(n) -#endif -#if (FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_clzll)) && !FMT_MSC_VER -# define FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL(n) __builtin_clzll(n) -#endif -#if (FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_ctz)) -# define FMT_BUILTIN_CTZ(n) __builtin_ctz(n) +// https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/519. +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION +# if FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_clz) || FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_ICC_VERSION +# define FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ(n) __builtin_clz(n) +# endif +# if FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_clzll) || FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_ICC_VERSION +# define FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL(n) __builtin_clzll(n) +# endif #endif -#if (FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_ctzll)) -# define FMT_BUILTIN_CTZLL(n) __builtin_ctzll(n) + +// __builtin_ctz is broken in Intel Compiler Classic on Windows: +// https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/2510. +#ifndef __ICL +# if FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_ctz) || FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_ICC_VERSION || \ + defined(__NVCOMPILER) +# define FMT_BUILTIN_CTZ(n) __builtin_ctz(n) +# endif +# if FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_ctzll) || FMT_GCC_VERSION || \ + FMT_ICC_VERSION || defined(__NVCOMPILER) +# define FMT_BUILTIN_CTZLL(n) __builtin_ctzll(n) +# endif #endif -#if FMT_MSC_VER +#if FMT_MSC_VERSION # include <intrin.h> // _BitScanReverse[64], _BitScanForward[64], _umul128 #endif // Some compilers masquerade as both MSVC and GCC-likes or otherwise support // __builtin_clz and __builtin_clzll, so only define FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ using the // MSVC intrinsics if the clz and clzll builtins are not available. -#if FMT_MSC_VER && !defined(FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL) && \ - !defined(FMT_BUILTIN_CTZLL) && !defined(_MANAGED) +#if FMT_MSC_VERSION && !defined(FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL) && \ + !defined(FMT_BUILTIN_CTZLL) FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE namespace detail { // Avoid Clang with Microsoft CodeGen's -Wunknown-pragmas warning. -# ifndef __clang__ +# if !defined(__clang__) # pragma intrinsic(_BitScanForward) # pragma intrinsic(_BitScanReverse) -# endif -# if defined(_WIN64) && !defined(__clang__) -# pragma intrinsic(_BitScanForward64) -# pragma intrinsic(_BitScanReverse64) +# if defined(_WIN64) +# pragma intrinsic(_BitScanForward64) +# pragma intrinsic(_BitScanReverse64) +# endif # endif -inline int clz(uint32_t x) { +inline auto clz(uint32_t x) -> int { unsigned long r = 0; _BitScanReverse(&r, x); FMT_ASSERT(x != 0, ""); // Static analysis complains about using uninitialized data // "r", but the only way that can happen is if "x" is 0, // which the callers guarantee to not happen. - FMT_SUPPRESS_MSC_WARNING(6102) + FMT_MSC_WARNING(suppress : 6102) return 31 ^ static_cast<int>(r); } # define FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ(n) detail::clz(n) -inline int clzll(uint64_t x) { +inline auto clzll(uint64_t x) -> int { unsigned long r = 0; # ifdef _WIN64 _BitScanReverse64(&r, x); # else // Scan the high 32 bits. - if (_BitScanReverse(&r, static_cast<uint32_t>(x >> 32))) return 63 ^ (r + 32); + if (_BitScanReverse(&r, static_cast<uint32_t>(x >> 32))) + return 63 ^ static_cast<int>(r + 32); // Scan the low 32 bits. _BitScanReverse(&r, static_cast<uint32_t>(x)); # endif FMT_ASSERT(x != 0, ""); - FMT_SUPPRESS_MSC_WARNING(6102) // Suppress a bogus static analysis warning. + FMT_MSC_WARNING(suppress : 6102) // Suppress a bogus static analysis warning. return 63 ^ static_cast<int>(r); } # define FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL(n) detail::clzll(n) -inline int ctz(uint32_t x) { +inline auto ctz(uint32_t x) -> int { unsigned long r = 0; _BitScanForward(&r, x); FMT_ASSERT(x != 0, ""); - FMT_SUPPRESS_MSC_WARNING(6102) // Suppress a bogus static analysis warning. + FMT_MSC_WARNING(suppress : 6102) // Suppress a bogus static analysis warning. return static_cast<int>(r); } # define FMT_BUILTIN_CTZ(n) detail::ctz(n) -inline int ctzll(uint64_t x) { +inline auto ctzll(uint64_t x) -> int { unsigned long r = 0; FMT_ASSERT(x != 0, ""); - FMT_SUPPRESS_MSC_WARNING(6102) // Suppress a bogus static analysis warning. + FMT_MSC_WARNING(suppress : 6102) // Suppress a bogus static analysis warning. # ifdef _WIN64 _BitScanForward64(&r, x); # else @@ -267,76 +276,277 @@ inline int ctzll(uint64_t x) { FMT_END_NAMESPACE #endif -// Enable the deprecated numeric alignment. -#ifndef FMT_DEPRECATED_NUMERIC_ALIGN -# define FMT_DEPRECATED_NUMERIC_ALIGN 0 -#endif - FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE + +template <typename...> struct disjunction : std::false_type {}; +template <typename P> struct disjunction<P> : P {}; +template <typename P1, typename... Pn> +struct disjunction<P1, Pn...> + : conditional_t<bool(P1::value), P1, disjunction<Pn...>> {}; + +template <typename...> struct conjunction : std::true_type {}; +template <typename P> struct conjunction<P> : P {}; +template <typename P1, typename... Pn> +struct conjunction<P1, Pn...> + : conditional_t<bool(P1::value), conjunction<Pn...>, P1> {}; + namespace detail { -// An equivalent of `*reinterpret_cast<Dest*>(&source)` that doesn't have -// undefined behavior (e.g. due to type aliasing). -// Example: uint64_t d = bit_cast<uint64_t>(2.718); -template <typename Dest, typename Source> -inline Dest bit_cast(const Source& source) { - static_assert(sizeof(Dest) == sizeof(Source), "size mismatch"); - Dest dest; - std::memcpy(&dest, &source, sizeof(dest)); - return dest; +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline void abort_fuzzing_if(bool condition) { + ignore_unused(condition); +#ifdef FMT_FUZZ + if (condition) throw std::runtime_error("fuzzing limit reached"); +#endif +} + +template <typename CharT, CharT... C> struct string_literal { + static constexpr CharT value[sizeof...(C)] = {C...}; + constexpr operator basic_string_view<CharT>() const { + return {value, sizeof...(C)}; + } +}; + +#if FMT_CPLUSPLUS < 201703L +template <typename CharT, CharT... C> +constexpr CharT string_literal<CharT, C...>::value[sizeof...(C)]; +#endif + +template <typename Streambuf> class formatbuf : public Streambuf { + private: + using char_type = typename Streambuf::char_type; + using streamsize = decltype(std::declval<Streambuf>().sputn(nullptr, 0)); + using int_type = typename Streambuf::int_type; + using traits_type = typename Streambuf::traits_type; + + buffer<char_type>& buffer_; + + public: + explicit formatbuf(buffer<char_type>& buf) : buffer_(buf) {} + + protected: + // The put area is always empty. This makes the implementation simpler and has + // the advantage that the streambuf and the buffer are always in sync and + // sputc never writes into uninitialized memory. A disadvantage is that each + // call to sputc always results in a (virtual) call to overflow. There is no + // disadvantage here for sputn since this always results in a call to xsputn. + + auto overflow(int_type ch) -> int_type override { + if (!traits_type::eq_int_type(ch, traits_type::eof())) + buffer_.push_back(static_cast<char_type>(ch)); + return ch; + } + + auto xsputn(const char_type* s, streamsize count) -> streamsize override { + buffer_.append(s, s + count); + return count; + } +}; + +// Implementation of std::bit_cast for pre-C++20. +template <typename To, typename From, FMT_ENABLE_IF(sizeof(To) == sizeof(From))> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto bit_cast(const From& from) -> To { +#ifdef __cpp_lib_bit_cast + if (is_constant_evaluated()) return std::bit_cast<To>(from); +#endif + auto to = To(); + // The cast suppresses a bogus -Wclass-memaccess on GCC. + std::memcpy(static_cast<void*>(&to), &from, sizeof(to)); + return to; } -inline bool is_big_endian() { - const auto u = 1u; +inline auto is_big_endian() -> bool { +#ifdef _WIN32 + return false; +#elif defined(__BIG_ENDIAN__) + return true; +#elif defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && defined(__ORDER_BIG_ENDIAN__) + return __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_BIG_ENDIAN__; +#else struct bytes { - char data[sizeof(u)]; + char data[sizeof(int)]; }; - return bit_cast<bytes>(u).data[0] == 0; + return bit_cast<bytes>(1).data[0] == 0; +#endif } -// A fallback implementation of uintptr_t for systems that lack it. -struct fallback_uintptr { - unsigned char value[sizeof(void*)]; +class uint128_fallback { + private: + uint64_t lo_, hi_; - fallback_uintptr() = default; - explicit fallback_uintptr(const void* p) { - *this = bit_cast<fallback_uintptr>(p); - if (is_big_endian()) { - for (size_t i = 0, j = sizeof(void*) - 1; i < j; ++i, --j) - std::swap(value[i], value[j]); + public: + constexpr uint128_fallback(uint64_t hi, uint64_t lo) : lo_(lo), hi_(hi) {} + constexpr uint128_fallback(uint64_t value = 0) : lo_(value), hi_(0) {} + + constexpr uint64_t high() const noexcept { return hi_; } + constexpr uint64_t low() const noexcept { return lo_; } + + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> + constexpr explicit operator T() const { + return static_cast<T>(lo_); + } + + friend constexpr auto operator==(const uint128_fallback& lhs, + const uint128_fallback& rhs) -> bool { + return lhs.hi_ == rhs.hi_ && lhs.lo_ == rhs.lo_; + } + friend constexpr auto operator!=(const uint128_fallback& lhs, + const uint128_fallback& rhs) -> bool { + return !(lhs == rhs); + } + friend constexpr auto operator>(const uint128_fallback& lhs, + const uint128_fallback& rhs) -> bool { + return lhs.hi_ != rhs.hi_ ? lhs.hi_ > rhs.hi_ : lhs.lo_ > rhs.lo_; + } + friend constexpr auto operator|(const uint128_fallback& lhs, + const uint128_fallback& rhs) + -> uint128_fallback { + return {lhs.hi_ | rhs.hi_, lhs.lo_ | rhs.lo_}; + } + friend constexpr auto operator&(const uint128_fallback& lhs, + const uint128_fallback& rhs) + -> uint128_fallback { + return {lhs.hi_ & rhs.hi_, lhs.lo_ & rhs.lo_}; + } + friend constexpr auto operator~(const uint128_fallback& n) + -> uint128_fallback { + return {~n.hi_, ~n.lo_}; + } + friend auto operator+(const uint128_fallback& lhs, + const uint128_fallback& rhs) -> uint128_fallback { + auto result = uint128_fallback(lhs); + result += rhs; + return result; + } + friend auto operator*(const uint128_fallback& lhs, uint32_t rhs) + -> uint128_fallback { + FMT_ASSERT(lhs.hi_ == 0, ""); + uint64_t hi = (lhs.lo_ >> 32) * rhs; + uint64_t lo = (lhs.lo_ & ~uint32_t()) * rhs; + uint64_t new_lo = (hi << 32) + lo; + return {(hi >> 32) + (new_lo < lo ? 1 : 0), new_lo}; + } + friend auto operator-(const uint128_fallback& lhs, uint64_t rhs) + -> uint128_fallback { + return {lhs.hi_ - (lhs.lo_ < rhs ? 1 : 0), lhs.lo_ - rhs}; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator>>(int shift) const -> uint128_fallback { + if (shift == 64) return {0, hi_}; + if (shift > 64) return uint128_fallback(0, hi_) >> (shift - 64); + return {hi_ >> shift, (hi_ << (64 - shift)) | (lo_ >> shift)}; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator<<(int shift) const -> uint128_fallback { + if (shift == 64) return {lo_, 0}; + if (shift > 64) return uint128_fallback(lo_, 0) << (shift - 64); + return {hi_ << shift | (lo_ >> (64 - shift)), (lo_ << shift)}; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator>>=(int shift) -> uint128_fallback& { + return *this = *this >> shift; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator+=(uint128_fallback n) { + uint64_t new_lo = lo_ + n.lo_; + uint64_t new_hi = hi_ + n.hi_ + (new_lo < lo_ ? 1 : 0); + FMT_ASSERT(new_hi >= hi_, ""); + lo_ = new_lo; + hi_ = new_hi; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator&=(uint128_fallback n) { + lo_ &= n.lo_; + hi_ &= n.hi_; + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 uint128_fallback& operator+=(uint64_t n) noexcept { + if (is_constant_evaluated()) { + lo_ += n; + hi_ += (lo_ < n ? 1 : 0); + return *this; } +#if FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_addcll) && !defined(__ibmxl__) + unsigned long long carry; + lo_ = __builtin_addcll(lo_, n, 0, &carry); + hi_ += carry; +#elif FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_ia32_addcarryx_u64) && !defined(__ibmxl__) + unsigned long long result; + auto carry = __builtin_ia32_addcarryx_u64(0, lo_, n, &result); + lo_ = result; + hi_ += carry; +#elif defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_X64) + auto carry = _addcarry_u64(0, lo_, n, &lo_); + _addcarry_u64(carry, hi_, 0, &hi_); +#else + lo_ += n; + hi_ += (lo_ < n ? 1 : 0); +#endif + return *this; } }; + +using uint128_t = conditional_t<FMT_USE_INT128, uint128_opt, uint128_fallback>; + #ifdef UINTPTR_MAX using uintptr_t = ::uintptr_t; -inline uintptr_t to_uintptr(const void* p) { return bit_cast<uintptr_t>(p); } #else -using uintptr_t = fallback_uintptr; -inline fallback_uintptr to_uintptr(const void* p) { - return fallback_uintptr(p); -} +using uintptr_t = uint128_t; #endif // Returns the largest possible value for type T. Same as // std::numeric_limits<T>::max() but shorter and not affected by the max macro. -template <typename T> constexpr T max_value() { +template <typename T> constexpr auto max_value() -> T { return (std::numeric_limits<T>::max)(); } -template <typename T> constexpr int num_bits() { +template <typename T> constexpr auto num_bits() -> int { return std::numeric_limits<T>::digits; } // std::numeric_limits<T>::digits may return 0 for 128-bit ints. -template <> constexpr int num_bits<int128_t>() { return 128; } -template <> constexpr int num_bits<uint128_t>() { return 128; } -template <> constexpr int num_bits<fallback_uintptr>() { - return static_cast<int>(sizeof(void*) * - std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::digits); +template <> constexpr auto num_bits<int128_opt>() -> int { return 128; } +template <> constexpr auto num_bits<uint128_t>() -> int { return 128; } + +// A heterogeneous bit_cast used for converting 96-bit long double to uint128_t +// and 128-bit pointers to uint128_fallback. +template <typename To, typename From, FMT_ENABLE_IF(sizeof(To) > sizeof(From))> +inline auto bit_cast(const From& from) -> To { + constexpr auto size = static_cast<int>(sizeof(From) / sizeof(unsigned)); + struct data_t { + unsigned value[static_cast<unsigned>(size)]; + } data = bit_cast<data_t>(from); + auto result = To(); + if (const_check(is_big_endian())) { + for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) + result = (result << num_bits<unsigned>()) | data.value[i]; + } else { + for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; --i) + result = (result << num_bits<unsigned>()) | data.value[i]; + } + return result; +} + +template <typename UInt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 inline auto countl_zero_fallback(UInt n) -> int { + int lz = 0; + constexpr UInt msb_mask = static_cast<UInt>(1) << (num_bits<UInt>() - 1); + for (; (n & msb_mask) == 0; n <<= 1) lz++; + return lz; +} + +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 inline auto countl_zero(uint32_t n) -> int { +#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ + if (!is_constant_evaluated()) return FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ(n); +#endif + return countl_zero_fallback(n); +} + +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 inline auto countl_zero(uint64_t n) -> int { +#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL + if (!is_constant_evaluated()) return FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL(n); +#endif + return countl_zero_fallback(n); } FMT_INLINE void assume(bool condition) { (void)condition; -#if FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_assume) +#if FMT_HAS_BUILTIN(__builtin_assume) && !FMT_ICC_VERSION __builtin_assume(condition); +#elif FMT_GCC_VERSION + if (!condition) __builtin_unreachable(); #endif } @@ -346,53 +556,51 @@ using iterator_t = decltype(std::begin(std::declval<T&>())); template <typename T> using sentinel_t = decltype(std::end(std::declval<T&>())); // A workaround for std::string not having mutable data() until C++17. -template <typename Char> inline Char* get_data(std::basic_string<Char>& s) { +template <typename Char> +inline auto get_data(std::basic_string<Char>& s) -> Char* { return &s[0]; } template <typename Container> -inline typename Container::value_type* get_data(Container& c) { +inline auto get_data(Container& c) -> typename Container::value_type* { return c.data(); } -#if defined(_SECURE_SCL) && _SECURE_SCL -// Make a checked iterator to avoid MSVC warnings. -template <typename T> using checked_ptr = stdext::checked_array_iterator<T*>; -template <typename T> checked_ptr<T> make_checked(T* p, size_t size) { - return {p, size}; -} -#else -template <typename T> using checked_ptr = T*; -template <typename T> inline T* make_checked(T* p, size_t) { return p; } -#endif - +// Attempts to reserve space for n extra characters in the output range. +// Returns a pointer to the reserved range or a reference to it. template <typename Container, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_contiguous<Container>::value)> -#if FMT_CLANG_VERSION +#if FMT_CLANG_VERSION >= 307 && !FMT_ICC_VERSION __attribute__((no_sanitize("undefined"))) #endif -inline checked_ptr<typename Container::value_type> -reserve(std::back_insert_iterator<Container> it, size_t n) { +inline auto +reserve(std::back_insert_iterator<Container> it, size_t n) -> + typename Container::value_type* { Container& c = get_container(it); size_t size = c.size(); c.resize(size + n); - return make_checked(get_data(c) + size, n); + return get_data(c) + size; } template <typename T> -inline buffer_appender<T> reserve(buffer_appender<T> it, size_t n) { +inline auto reserve(buffer_appender<T> it, size_t n) -> buffer_appender<T> { buffer<T>& buf = get_container(it); buf.try_reserve(buf.size() + n); return it; } -template <typename Iterator> inline Iterator& reserve(Iterator& it, size_t) { +template <typename Iterator> +constexpr auto reserve(Iterator& it, size_t) -> Iterator& { return it; } +template <typename OutputIt> +using reserve_iterator = + remove_reference_t<decltype(reserve(std::declval<OutputIt&>(), 0))>; + template <typename T, typename OutputIt> -constexpr T* to_pointer(OutputIt, size_t) { +constexpr auto to_pointer(OutputIt, size_t) -> T* { return nullptr; } -template <typename T> T* to_pointer(buffer_appender<T> it, size_t n) { +template <typename T> auto to_pointer(buffer_appender<T> it, size_t n) -> T* { buffer<T>& buf = get_container(it); auto size = buf.size(); if (buf.capacity() < size + n) return nullptr; @@ -401,195 +609,262 @@ template <typename T> T* to_pointer(buffer_appender<T> it, size_t n) { } template <typename Container, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_contiguous<Container>::value)> -inline std::back_insert_iterator<Container> base_iterator( - std::back_insert_iterator<Container>& it, - checked_ptr<typename Container::value_type>) { +inline auto base_iterator(std::back_insert_iterator<Container> it, + typename Container::value_type*) + -> std::back_insert_iterator<Container> { return it; } template <typename Iterator> -inline Iterator base_iterator(Iterator, Iterator it) { +constexpr auto base_iterator(Iterator, Iterator it) -> Iterator { return it; } -// An output iterator that counts the number of objects written to it and -// discards them. -class counting_iterator { - private: - size_t count_; - - public: - using iterator_category = std::output_iterator_tag; - using difference_type = std::ptrdiff_t; - using pointer = void; - using reference = void; - using _Unchecked_type = counting_iterator; // Mark iterator as checked. - - struct value_type { - template <typename T> void operator=(const T&) {} - }; - - counting_iterator() : count_(0) {} - - size_t count() const { return count_; } - - counting_iterator& operator++() { - ++count_; - return *this; - } - counting_iterator operator++(int) { - auto it = *this; - ++*this; - return it; - } - - friend counting_iterator operator+(counting_iterator it, difference_type n) { - it.count_ += static_cast<size_t>(n); - return it; - } - - value_type operator*() const { return {}; } -}; - -template <typename OutputIt> class truncating_iterator_base { - protected: - OutputIt out_; - size_t limit_; - size_t count_; - - truncating_iterator_base(OutputIt out, size_t limit) - : out_(out), limit_(limit), count_(0) {} - - public: - using iterator_category = std::output_iterator_tag; - using value_type = typename std::iterator_traits<OutputIt>::value_type; - using difference_type = void; - using pointer = void; - using reference = void; - using _Unchecked_type = - truncating_iterator_base; // Mark iterator as checked. - - OutputIt base() const { return out_; } - size_t count() const { return count_; } -}; - -// An output iterator that truncates the output and counts the number of objects -// written to it. -template <typename OutputIt, - typename Enable = typename std::is_void< - typename std::iterator_traits<OutputIt>::value_type>::type> -class truncating_iterator; - -template <typename OutputIt> -class truncating_iterator<OutputIt, std::false_type> - : public truncating_iterator_base<OutputIt> { - mutable typename truncating_iterator_base<OutputIt>::value_type blackhole_; - - public: - using value_type = typename truncating_iterator_base<OutputIt>::value_type; - - truncating_iterator(OutputIt out, size_t limit) - : truncating_iterator_base<OutputIt>(out, limit) {} - - truncating_iterator& operator++() { - if (this->count_++ < this->limit_) ++this->out_; - return *this; +// <algorithm> is spectacularly slow to compile in C++20 so use a simple fill_n +// instead (#1998). +template <typename OutputIt, typename Size, typename T> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto fill_n(OutputIt out, Size count, const T& value) + -> OutputIt { + for (Size i = 0; i < count; ++i) *out++ = value; + return out; +} +template <typename T, typename Size> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto fill_n(T* out, Size count, char value) -> T* { + if (is_constant_evaluated()) { + return fill_n<T*, Size, T>(out, count, value); } + std::memset(out, value, to_unsigned(count)); + return out + count; +} - truncating_iterator operator++(int) { - auto it = *this; - ++*this; - return it; - } +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +using char8_type = char8_t; +#else +enum char8_type : unsigned char {}; +#endif - value_type& operator*() const { - return this->count_ < this->limit_ ? *this->out_ : blackhole_; +template <typename OutChar, typename InputIt, typename OutputIt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_NOINLINE auto copy_str_noinline(InputIt begin, InputIt end, + OutputIt out) -> OutputIt { + return copy_str<OutChar>(begin, end, out); +} + +// A public domain branchless UTF-8 decoder by Christopher Wellons: +// https://github.com/skeeto/branchless-utf8 +/* Decode the next character, c, from s, reporting errors in e. + * + * Since this is a branchless decoder, four bytes will be read from the + * buffer regardless of the actual length of the next character. This + * means the buffer _must_ have at least three bytes of zero padding + * following the end of the data stream. + * + * Errors are reported in e, which will be non-zero if the parsed + * character was somehow invalid: invalid byte sequence, non-canonical + * encoding, or a surrogate half. + * + * The function returns a pointer to the next character. When an error + * occurs, this pointer will be a guess that depends on the particular + * error, but it will always advance at least one byte. + */ +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto utf8_decode(const char* s, uint32_t* c, int* e) + -> const char* { + constexpr const int masks[] = {0x00, 0x7f, 0x1f, 0x0f, 0x07}; + constexpr const uint32_t mins[] = {4194304, 0, 128, 2048, 65536}; + constexpr const int shiftc[] = {0, 18, 12, 6, 0}; + constexpr const int shifte[] = {0, 6, 4, 2, 0}; + + int len = "\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\1\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\2\2\2\2\3\3\4" + [static_cast<unsigned char>(*s) >> 3]; + // Compute the pointer to the next character early so that the next + // iteration can start working on the next character. Neither Clang + // nor GCC figure out this reordering on their own. + const char* next = s + len + !len; + + using uchar = unsigned char; + + // Assume a four-byte character and load four bytes. Unused bits are + // shifted out. + *c = uint32_t(uchar(s[0]) & masks[len]) << 18; + *c |= uint32_t(uchar(s[1]) & 0x3f) << 12; + *c |= uint32_t(uchar(s[2]) & 0x3f) << 6; + *c |= uint32_t(uchar(s[3]) & 0x3f) << 0; + *c >>= shiftc[len]; + + // Accumulate the various error conditions. + *e = (*c < mins[len]) << 6; // non-canonical encoding + *e |= ((*c >> 11) == 0x1b) << 7; // surrogate half? + *e |= (*c > 0x10FFFF) << 8; // out of range? + *e |= (uchar(s[1]) & 0xc0) >> 2; + *e |= (uchar(s[2]) & 0xc0) >> 4; + *e |= uchar(s[3]) >> 6; + *e ^= 0x2a; // top two bits of each tail byte correct? + *e >>= shifte[len]; + + return next; +} + +constexpr FMT_INLINE_VARIABLE uint32_t invalid_code_point = ~uint32_t(); + +// Invokes f(cp, sv) for every code point cp in s with sv being the string view +// corresponding to the code point. cp is invalid_code_point on error. +template <typename F> +FMT_CONSTEXPR void for_each_codepoint(string_view s, F f) { + auto decode = [f](const char* buf_ptr, const char* ptr) { + auto cp = uint32_t(); + auto error = 0; + auto end = utf8_decode(buf_ptr, &cp, &error); + bool result = f(error ? invalid_code_point : cp, + string_view(ptr, error ? 1 : to_unsigned(end - buf_ptr))); + return result ? (error ? buf_ptr + 1 : end) : nullptr; + }; + auto p = s.data(); + const size_t block_size = 4; // utf8_decode always reads blocks of 4 chars. + if (s.size() >= block_size) { + for (auto end = p + s.size() - block_size + 1; p < end;) { + p = decode(p, p); + if (!p) return; + } } -}; - -template <typename OutputIt> -class truncating_iterator<OutputIt, std::true_type> - : public truncating_iterator_base<OutputIt> { - public: - truncating_iterator(OutputIt out, size_t limit) - : truncating_iterator_base<OutputIt>(out, limit) {} - - template <typename T> truncating_iterator& operator=(T val) { - if (this->count_++ < this->limit_) *this->out_++ = val; - return *this; + if (auto num_chars_left = s.data() + s.size() - p) { + char buf[2 * block_size - 1] = {}; + copy_str<char>(p, p + num_chars_left, buf); + const char* buf_ptr = buf; + do { + auto end = decode(buf_ptr, p); + if (!end) return; + p += end - buf_ptr; + buf_ptr = end; + } while (buf_ptr - buf < num_chars_left); } - - truncating_iterator& operator++() { return *this; } - truncating_iterator& operator++(int) { return *this; } - truncating_iterator& operator*() { return *this; } -}; +} template <typename Char> -inline size_t count_code_points(basic_string_view<Char> s) { +inline auto compute_width(basic_string_view<Char> s) -> size_t { return s.size(); } -// Counts the number of code points in a UTF-8 string. -inline size_t count_code_points(basic_string_view<char> s) { - const char* data = s.data(); +// Computes approximate display width of a UTF-8 string. +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline size_t compute_width(string_view s) { size_t num_code_points = 0; - for (size_t i = 0, size = s.size(); i != size; ++i) { - if ((data[i] & 0xc0) != 0x80) ++num_code_points; - } + // It is not a lambda for compatibility with C++14. + struct count_code_points { + size_t* count; + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(uint32_t cp, string_view) const -> bool { + *count += detail::to_unsigned( + 1 + + (cp >= 0x1100 && + (cp <= 0x115f || // Hangul Jamo init. consonants + cp == 0x2329 || // LEFT-POINTING ANGLE BRACKET + cp == 0x232a || // RIGHT-POINTING ANGLE BRACKET + // CJK ... Yi except IDEOGRAPHIC HALF FILL SPACE: + (cp >= 0x2e80 && cp <= 0xa4cf && cp != 0x303f) || + (cp >= 0xac00 && cp <= 0xd7a3) || // Hangul Syllables + (cp >= 0xf900 && cp <= 0xfaff) || // CJK Compatibility Ideographs + (cp >= 0xfe10 && cp <= 0xfe19) || // Vertical Forms + (cp >= 0xfe30 && cp <= 0xfe6f) || // CJK Compatibility Forms + (cp >= 0xff00 && cp <= 0xff60) || // Fullwidth Forms + (cp >= 0xffe0 && cp <= 0xffe6) || // Fullwidth Forms + (cp >= 0x20000 && cp <= 0x2fffd) || // CJK + (cp >= 0x30000 && cp <= 0x3fffd) || + // Miscellaneous Symbols and Pictographs + Emoticons: + (cp >= 0x1f300 && cp <= 0x1f64f) || + // Supplemental Symbols and Pictographs: + (cp >= 0x1f900 && cp <= 0x1f9ff)))); + return true; + } + }; + // We could avoid branches by using utf8_decode directly. + for_each_codepoint(s, count_code_points{&num_code_points}); return num_code_points; } -inline size_t count_code_points(basic_string_view<char8_type> s) { - return count_code_points(basic_string_view<char>( - reinterpret_cast<const char*>(s.data()), s.size())); +inline auto compute_width(basic_string_view<char8_type> s) -> size_t { + return compute_width( + string_view(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(s.data()), s.size())); } template <typename Char> -inline size_t code_point_index(basic_string_view<Char> s, size_t n) { +inline auto code_point_index(basic_string_view<Char> s, size_t n) -> size_t { size_t size = s.size(); return n < size ? n : size; } // Calculates the index of the nth code point in a UTF-8 string. -inline size_t code_point_index(basic_string_view<char8_type> s, size_t n) { - const char8_type* data = s.data(); +inline auto code_point_index(string_view s, size_t n) -> size_t { + const char* data = s.data(); size_t num_code_points = 0; for (size_t i = 0, size = s.size(); i != size; ++i) { - if ((data[i] & 0xc0) != 0x80 && ++num_code_points > n) { - return i; - } + if ((data[i] & 0xc0) != 0x80 && ++num_code_points > n) return i; } return s.size(); } -template <typename InputIt, typename OutChar> -using needs_conversion = bool_constant< - std::is_same<typename std::iterator_traits<InputIt>::value_type, - char>::value && - std::is_same<OutChar, char8_type>::value>; - -template <typename OutChar, typename InputIt, typename OutputIt, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(!needs_conversion<InputIt, OutChar>::value)> -OutputIt copy_str(InputIt begin, InputIt end, OutputIt it) { - return std::copy(begin, end, it); +inline auto code_point_index(basic_string_view<char8_type> s, size_t n) + -> size_t { + return code_point_index( + string_view(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(s.data()), s.size()), n); } -template <typename OutChar, typename InputIt, typename OutputIt, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(needs_conversion<InputIt, OutChar>::value)> -OutputIt copy_str(InputIt begin, InputIt end, OutputIt it) { - return std::transform(begin, end, it, - [](char c) { return static_cast<char8_type>(c); }); -} +template <typename T> struct is_integral : std::is_integral<T> {}; +template <> struct is_integral<int128_opt> : std::true_type {}; +template <> struct is_integral<uint128_t> : std::true_type {}; -template <typename Char, typename InputIt> -inline counting_iterator copy_str(InputIt begin, InputIt end, - counting_iterator it) { - return it + (end - begin); -} +template <typename T> +using is_signed = + std::integral_constant<bool, std::numeric_limits<T>::is_signed || + std::is_same<T, int128_opt>::value>; + +template <typename T> +using is_integer = + bool_constant<is_integral<T>::value && !std::is_same<T, bool>::value && + !std::is_same<T, char>::value && + !std::is_same<T, wchar_t>::value>; + +#ifndef FMT_USE_FLOAT +# define FMT_USE_FLOAT 1 +#endif +#ifndef FMT_USE_DOUBLE +# define FMT_USE_DOUBLE 1 +#endif +#ifndef FMT_USE_LONG_DOUBLE +# define FMT_USE_LONG_DOUBLE 1 +#endif + +#ifndef FMT_USE_FLOAT128 +# ifdef __clang__ +// Clang emulates GCC, so it has to appear early. +# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<quadmath.h>) +# define FMT_USE_FLOAT128 1 +# endif +# elif defined(__GNUC__) +// GNU C++: +# if defined(_GLIBCXX_USE_FLOAT128) && !defined(__STRICT_ANSI__) +# define FMT_USE_FLOAT128 1 +# endif +# endif +# ifndef FMT_USE_FLOAT128 +# define FMT_USE_FLOAT128 0 +# endif +#endif + +#if FMT_USE_FLOAT128 +using float128 = __float128; +#else +using float128 = void; +#endif +template <typename T> using is_float128 = std::is_same<T, float128>; + +template <typename T> +using is_floating_point = + bool_constant<std::is_floating_point<T>::value || is_float128<T>::value>; + +template <typename T, bool = std::is_floating_point<T>::value> +struct is_fast_float : bool_constant<std::numeric_limits<T>::is_iec559 && + sizeof(T) <= sizeof(double)> {}; +template <typename T> struct is_fast_float<T, false> : std::false_type {}; template <typename T> -using is_fast_float = bool_constant<std::numeric_limits<T>::is_iec559 && - sizeof(T) <= sizeof(double)>; +using is_double_double = bool_constant<std::numeric_limits<T>::digits == 106>; #ifndef FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX # define FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX 0 @@ -598,24 +873,25 @@ using is_fast_float = bool_constant<std::numeric_limits<T>::is_iec559 && template <typename T> template <typename U> void buffer<T>::append(const U* begin, const U* end) { - do { + while (begin != end) { auto count = to_unsigned(end - begin); try_reserve(size_ + count); auto free_cap = capacity_ - size_; if (free_cap < count) count = free_cap; - std::uninitialized_copy_n(begin, count, make_checked(ptr_ + size_, count)); + std::uninitialized_copy_n(begin, count, ptr_ + size_); size_ += count; begin += count; - } while (begin != end); + } } -template <typename OutputIt, typename T, typename Traits> -void iterator_buffer<OutputIt, T, Traits>::flush() { - out_ = std::copy_n(data_, this->limit(this->size()), out_); - this->clear(); -} +template <typename T, typename Enable = void> +struct is_locale : std::false_type {}; +template <typename T> +struct is_locale<T, void_t<decltype(T::classic())>> : std::true_type {}; } // namespace detail +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT + // The number of characters to store in the basic_memory_buffer object itself // to avoid dynamic memory allocation. enum { inline_buffer_size = 500 }; @@ -625,20 +901,12 @@ enum { inline_buffer_size = 500 }; A dynamically growing memory buffer for trivially copyable/constructible types with the first ``SIZE`` elements stored in the object itself. - You can use one of the following type aliases for common character types: - - +----------------+------------------------------+ - | Type | Definition | - +================+==============================+ - | memory_buffer | basic_memory_buffer<char> | - +----------------+------------------------------+ - | wmemory_buffer | basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t> | - +----------------+------------------------------+ + You can use the ``memory_buffer`` type alias for ``char`` instead. **Example**:: - fmt::memory_buffer out; - format_to(out, "The answer is {}.", 42); + auto out = fmt::memory_buffer(); + format_to(std::back_inserter(out), "The answer is {}.", 42); This will append the following output to the ``out`` object: @@ -655,43 +923,66 @@ class basic_memory_buffer final : public detail::buffer<T> { private: T store_[SIZE]; - // Don't inherit from Allocator avoid generating type_info for it. - Allocator alloc_; + // Don't inherit from Allocator to avoid generating type_info for it. + FMT_NO_UNIQUE_ADDRESS Allocator alloc_; // Deallocate memory allocated by the buffer. - void deallocate() { + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void deallocate() { T* data = this->data(); if (data != store_) alloc_.deallocate(data, this->capacity()); } protected: - void grow(size_t size) final FMT_OVERRIDE; + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void grow(size_t size) override { + detail::abort_fuzzing_if(size > 5000); + const size_t max_size = std::allocator_traits<Allocator>::max_size(alloc_); + size_t old_capacity = this->capacity(); + size_t new_capacity = old_capacity + old_capacity / 2; + if (size > new_capacity) + new_capacity = size; + else if (new_capacity > max_size) + new_capacity = size > max_size ? size : max_size; + T* old_data = this->data(); + T* new_data = + std::allocator_traits<Allocator>::allocate(alloc_, new_capacity); + // Suppress a bogus -Wstringop-overflow in gcc 13.1 (#3481). + detail::assume(this->size() <= new_capacity); + // The following code doesn't throw, so the raw pointer above doesn't leak. + std::uninitialized_copy_n(old_data, this->size(), new_data); + this->set(new_data, new_capacity); + // deallocate must not throw according to the standard, but even if it does, + // the buffer already uses the new storage and will deallocate it in + // destructor. + if (old_data != store_) alloc_.deallocate(old_data, old_capacity); + } public: using value_type = T; using const_reference = const T&; - explicit basic_memory_buffer(const Allocator& alloc = Allocator()) + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 explicit basic_memory_buffer( + const Allocator& alloc = Allocator()) : alloc_(alloc) { this->set(store_, SIZE); + if (detail::is_constant_evaluated()) detail::fill_n(store_, SIZE, T()); } - ~basic_memory_buffer() { deallocate(); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 ~basic_memory_buffer() { deallocate(); } private: // Move data from other to this buffer. - void move(basic_memory_buffer& other) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void move(basic_memory_buffer& other) { alloc_ = std::move(other.alloc_); T* data = other.data(); size_t size = other.size(), capacity = other.capacity(); if (data == other.store_) { this->set(store_, capacity); - std::uninitialized_copy(other.store_, other.store_ + size, - detail::make_checked(store_, capacity)); + detail::copy_str<T>(other.store_, other.store_ + size, store_); } else { this->set(data, capacity); // Set pointer to the inline array so that delete is not called // when deallocating. other.set(other.store_, 0); + other.clear(); } this->resize(size); } @@ -703,14 +994,16 @@ class basic_memory_buffer final : public detail::buffer<T> { of the other object to it. \endrst */ - basic_memory_buffer(basic_memory_buffer&& other) FMT_NOEXCEPT { move(other); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 basic_memory_buffer(basic_memory_buffer&& other) noexcept { + move(other); + } /** \rst Moves the content of the other ``basic_memory_buffer`` object to this one. \endrst */ - basic_memory_buffer& operator=(basic_memory_buffer&& other) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + auto operator=(basic_memory_buffer&& other) noexcept -> basic_memory_buffer& { FMT_ASSERT(this != &other, ""); deallocate(); move(other); @@ -718,13 +1011,13 @@ class basic_memory_buffer final : public detail::buffer<T> { } // Returns a copy of the allocator associated with this buffer. - Allocator get_allocator() const { return alloc_; } + auto get_allocator() const -> Allocator { return alloc_; } /** Resizes the buffer to contain *count* elements. If T is a POD type new elements may not be initialized. */ - void resize(size_t count) { this->try_resize(count); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void resize(size_t count) { this->try_resize(count); } /** Increases the buffer capacity to *new_capacity*. */ void reserve(size_t new_capacity) { this->try_reserve(new_capacity); } @@ -737,71 +1030,121 @@ class basic_memory_buffer final : public detail::buffer<T> { } }; +using memory_buffer = basic_memory_buffer<char>; + template <typename T, size_t SIZE, typename Allocator> -void basic_memory_buffer<T, SIZE, Allocator>::grow(size_t size) { -#ifdef FMT_FUZZ - if (size > 5000) throw std::runtime_error("fuzz mode - won't grow that much"); +struct is_contiguous<basic_memory_buffer<T, SIZE, Allocator>> : std::true_type { +}; + +FMT_END_EXPORT +namespace detail { +FMT_API bool write_console(int fd, string_view text); +FMT_API void print(std::FILE*, string_view); +} // namespace detail + +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT + +// Suppress a misleading warning in older versions of clang. +#if FMT_CLANG_VERSION +# pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wweak-vtables" +#endif + +/** An error reported from a formatting function. */ +class FMT_SO_VISIBILITY("default") format_error : public std::runtime_error { + public: + using std::runtime_error::runtime_error; +}; + +namespace detail_exported { +#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS +template <typename Char, size_t N> struct fixed_string { + constexpr fixed_string(const Char (&str)[N]) { + detail::copy_str<Char, const Char*, Char*>(static_cast<const Char*>(str), + str + N, data); + } + Char data[N] = {}; +}; #endif - size_t old_capacity = this->capacity(); - size_t new_capacity = old_capacity + old_capacity / 2; - if (size > new_capacity) new_capacity = size; - T* old_data = this->data(); - T* new_data = - std::allocator_traits<Allocator>::allocate(alloc_, new_capacity); - // The following code doesn't throw, so the raw pointer above doesn't leak. - std::uninitialized_copy(old_data, old_data + this->size(), - detail::make_checked(new_data, new_capacity)); - this->set(new_data, new_capacity); - // deallocate must not throw according to the standard, but even if it does, - // the buffer already uses the new storage and will deallocate it in - // destructor. - if (old_data != store_) alloc_.deallocate(old_data, old_capacity); + +// Converts a compile-time string to basic_string_view. +template <typename Char, size_t N> +constexpr auto compile_string_to_view(const Char (&s)[N]) + -> basic_string_view<Char> { + // Remove trailing NUL character if needed. Won't be present if this is used + // with a raw character array (i.e. not defined as a string). + return {s, N - (std::char_traits<Char>::to_int_type(s[N - 1]) == 0 ? 1 : 0)}; +} +template <typename Char> +constexpr auto compile_string_to_view(detail::std_string_view<Char> s) + -> basic_string_view<Char> { + return {s.data(), s.size()}; } +} // namespace detail_exported -using memory_buffer = basic_memory_buffer<char>; -using wmemory_buffer = basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t>; +class loc_value { + private: + basic_format_arg<format_context> value_; -template <typename T, size_t SIZE, typename Allocator> -struct is_contiguous<basic_memory_buffer<T, SIZE, Allocator>> : std::true_type { + public: + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!detail::is_float128<T>::value)> + loc_value(T value) : value_(detail::make_arg<format_context>(value)) {} + + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_float128<T>::value)> + loc_value(T) {} + + template <typename Visitor> auto visit(Visitor&& vis) -> decltype(vis(0)) { + return visit_format_arg(vis, value_); + } }; -/** A formatting error such as invalid format string. */ -FMT_CLASS_API -class FMT_API format_error : public std::runtime_error { +// A locale facet that formats values in UTF-8. +// It is parameterized on the locale to avoid the heavy <locale> include. +template <typename Locale> class format_facet : public Locale::facet { + private: + std::string separator_; + std::string grouping_; + std::string decimal_point_; + + protected: + virtual auto do_put(appender out, loc_value val, + const format_specs<>& specs) const -> bool; + public: - explicit format_error(const char* message) : std::runtime_error(message) {} - explicit format_error(const std::string& message) - : std::runtime_error(message) {} - format_error(const format_error&) = default; - format_error& operator=(const format_error&) = default; - format_error(format_error&&) = default; - format_error& operator=(format_error&&) = default; - ~format_error() FMT_NOEXCEPT FMT_OVERRIDE; + static FMT_API typename Locale::id id; + + explicit format_facet(Locale& loc); + explicit format_facet(string_view sep = "", + std::initializer_list<unsigned char> g = {3}, + std::string decimal_point = ".") + : separator_(sep.data(), sep.size()), + grouping_(g.begin(), g.end()), + decimal_point_(decimal_point) {} + + auto put(appender out, loc_value val, const format_specs<>& specs) const + -> bool { + return do_put(out, val, specs); + } }; namespace detail { -template <typename T> -using is_signed = - std::integral_constant<bool, std::numeric_limits<T>::is_signed || - std::is_same<T, int128_t>::value>; - // Returns true if value is negative, false otherwise. // Same as `value < 0` but doesn't produce warnings if T is an unsigned type. template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_signed<T>::value)> -FMT_CONSTEXPR bool is_negative(T value) { +constexpr auto is_negative(T value) -> bool { return value < 0; } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_signed<T>::value)> -FMT_CONSTEXPR bool is_negative(T) { +constexpr auto is_negative(T) -> bool { return false; } -template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value)> -FMT_CONSTEXPR bool is_supported_floating_point(T) { - return (std::is_same<T, float>::value && FMT_USE_FLOAT) || - (std::is_same<T, double>::value && FMT_USE_DOUBLE) || - (std::is_same<T, long double>::value && FMT_USE_LONG_DOUBLE); +template <typename T> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto is_supported_floating_point(T) -> bool { + if (std::is_same<T, float>()) return FMT_USE_FLOAT; + if (std::is_same<T, double>()) return FMT_USE_DOUBLE; + if (std::is_same<T, long double>()) return FMT_USE_LONG_DOUBLE; + return true; } // Smallest of uint32_t, uint64_t, uint128_t that is large enough to @@ -811,121 +1154,33 @@ using uint32_or_64_or_128_t = conditional_t<num_bits<T>() <= 32 && !FMT_REDUCE_INT_INSTANTIATIONS, uint32_t, conditional_t<num_bits<T>() <= 64, uint64_t, uint128_t>>; - -// 128-bit integer type used internally -struct FMT_EXTERN_TEMPLATE_API uint128_wrapper { - uint128_wrapper() = default; - -#if FMT_USE_INT128 - uint128_t internal_; - - uint128_wrapper(uint64_t high, uint64_t low) FMT_NOEXCEPT - : internal_{static_cast<uint128_t>(low) | - (static_cast<uint128_t>(high) << 64)} {} - - uint128_wrapper(uint128_t u) : internal_{u} {} - - uint64_t high() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return uint64_t(internal_ >> 64); } - uint64_t low() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return uint64_t(internal_); } - - uint128_wrapper& operator+=(uint64_t n) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - internal_ += n; - return *this; - } -#else - uint64_t high_; - uint64_t low_; - - uint128_wrapper(uint64_t high, uint64_t low) FMT_NOEXCEPT : high_{high}, - low_{low} {} - - uint64_t high() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return high_; } - uint64_t low() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return low_; } - - uint128_wrapper& operator+=(uint64_t n) FMT_NOEXCEPT { -# if defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_X64) - unsigned char carry = _addcarry_u64(0, low_, n, &low_); - _addcarry_u64(carry, high_, 0, &high_); - return *this; -# else - uint64_t sum = low_ + n; - high_ += (sum < low_ ? 1 : 0); - low_ = sum; - return *this; -# endif - } -#endif -}; - -// Table entry type for divisibility test used internally -template <typename T> struct FMT_EXTERN_TEMPLATE_API divtest_table_entry { - T mod_inv; - T max_quotient; -}; - -// Static data is placed in this class template for the header-only config. -template <typename T = void> struct FMT_EXTERN_TEMPLATE_API basic_data { - static const uint64_t powers_of_10_64[]; - static const uint32_t zero_or_powers_of_10_32_new[]; - static const uint64_t zero_or_powers_of_10_64_new[]; - static const uint64_t grisu_pow10_significands[]; - static const int16_t grisu_pow10_exponents[]; - static const divtest_table_entry<uint32_t> divtest_table_for_pow5_32[]; - static const divtest_table_entry<uint64_t> divtest_table_for_pow5_64[]; - static const uint64_t dragonbox_pow10_significands_64[]; - static const uint128_wrapper dragonbox_pow10_significands_128[]; - // log10(2) = 0x0.4d104d427de7fbcc... - static const uint64_t log10_2_significand = 0x4d104d427de7fbcc; -#if !FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOX - static const uint64_t powers_of_5_64[]; - static const uint32_t dragonbox_pow10_recovery_errors[]; +template <typename T> +using uint64_or_128_t = conditional_t<num_bits<T>() <= 64, uint64_t, uint128_t>; + +#define FMT_POWERS_OF_10(factor) \ + factor * 10, (factor)*100, (factor)*1000, (factor)*10000, (factor)*100000, \ + (factor)*1000000, (factor)*10000000, (factor)*100000000, \ + (factor)*1000000000 + +// Converts value in the range [0, 100) to a string. +constexpr const char* digits2(size_t value) { + // GCC generates slightly better code when value is pointer-size. + return &"0001020304050607080910111213141516171819" + "2021222324252627282930313233343536373839" + "4041424344454647484950515253545556575859" + "6061626364656667686970717273747576777879" + "8081828384858687888990919293949596979899"[value * 2]; +} + +// Sign is a template parameter to workaround a bug in gcc 4.8. +template <typename Char, typename Sign> constexpr Char sign(Sign s) { +#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 604 + static_assert(std::is_same<Sign, sign_t>::value, ""); #endif - // GCC generates slightly better code for pairs than chars. - using digit_pair = char[2]; - static const digit_pair digits[]; - static const char hex_digits[]; - static const char foreground_color[]; - static const char background_color[]; - static const char reset_color[5]; - static const wchar_t wreset_color[5]; - static const char signs[]; - static const char left_padding_shifts[5]; - static const char right_padding_shifts[5]; - - // DEPRECATED! These are for ABI compatibility. - static const uint32_t zero_or_powers_of_10_32[]; - static const uint64_t zero_or_powers_of_10_64[]; -}; - -// Maps bsr(n) to ceil(log10(pow(2, bsr(n) + 1) - 1)). -// This is a function instead of an array to workaround a bug in GCC10 (#1810). -FMT_INLINE uint16_t bsr2log10(int bsr) { - static constexpr uint16_t data[] = { - 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, - 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, - 10, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 13, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 14, 15, 15, - 15, 16, 16, 16, 16, 17, 17, 17, 18, 18, 18, 19, 19, 19, 19, 20}; - return data[bsr]; + return static_cast<Char>("\0-+ "[s]); } -#ifndef FMT_EXPORTED -FMT_EXTERN template struct basic_data<void>; -#endif - -// This is a struct rather than an alias to avoid shadowing warnings in gcc. -struct data : basic_data<> {}; - -#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL -// Returns the number of decimal digits in n. Leading zeros are not counted -// except for n == 0 in which case count_digits returns 1. -inline int count_digits(uint64_t n) { - // https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/digits10 - auto t = bsr2log10(FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL(n | 1) ^ 63); - return t - (n < data::zero_or_powers_of_10_64_new[t]); -} -#else -// Fallback version of count_digits used when __builtin_clz is not available. -inline int count_digits(uint64_t n) { +template <typename T> FMT_CONSTEXPR auto count_digits_fallback(T n) -> int { int count = 1; for (;;) { // Integer division is slow so do it for a group of four digits instead @@ -939,103 +1194,146 @@ inline int count_digits(uint64_t n) { count += 4; } } -#endif - #if FMT_USE_INT128 -inline int count_digits(uint128_t n) { - int count = 1; - for (;;) { - // Integer division is slow so do it for a group of four digits instead - // of for every digit. The idea comes from the talk by Alexandrescu - // "Three Optimization Tips for C++". See speed-test for a comparison. - if (n < 10) return count; - if (n < 100) return count + 1; - if (n < 1000) return count + 2; - if (n < 10000) return count + 3; - n /= 10000U; - count += 4; - } +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto count_digits(uint128_opt n) -> int { + return count_digits_fallback(n); } #endif -// Counts the number of digits in n. BITS = log2(radix). -template <unsigned BITS, typename UInt> inline int count_digits(UInt n) { - int num_digits = 0; - do { - ++num_digits; - } while ((n >>= BITS) != 0); - return num_digits; +#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL +// It is a separate function rather than a part of count_digits to workaround +// the lack of static constexpr in constexpr functions. +inline auto do_count_digits(uint64_t n) -> int { + // This has comparable performance to the version by Kendall Willets + // (https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/digits10) + // but uses smaller tables. + // Maps bsr(n) to ceil(log10(pow(2, bsr(n) + 1) - 1)). + static constexpr uint8_t bsr2log10[] = { + 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, + 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, + 10, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 13, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 14, 15, 15, + 15, 16, 16, 16, 16, 17, 17, 17, 18, 18, 18, 19, 19, 19, 19, 20}; + auto t = bsr2log10[FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL(n | 1) ^ 63]; + static constexpr const uint64_t zero_or_powers_of_10[] = { + 0, 0, FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1U), FMT_POWERS_OF_10(1000000000ULL), + 10000000000000000000ULL}; + return t - (n < zero_or_powers_of_10[t]); } +#endif -template <> int count_digits<4>(detail::fallback_uintptr n); - -#if FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_CLANG_VERSION -# define FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE inline __attribute__((always_inline)) -#elif FMT_MSC_VER -# define FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE __forceinline -#else -# define FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE inline +// Returns the number of decimal digits in n. Leading zeros are not counted +// except for n == 0 in which case count_digits returns 1. +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 inline auto count_digits(uint64_t n) -> int { +#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CLZLL + if (!is_constant_evaluated()) { + return do_count_digits(n); + } #endif + return count_digits_fallback(n); +} -// To suppress unnecessary security cookie checks -#if FMT_MSC_VER && !FMT_CLANG_VERSION -# define FMT_SAFEBUFFERS __declspec(safebuffers) -#else -# define FMT_SAFEBUFFERS +// Counts the number of digits in n. BITS = log2(radix). +template <int BITS, typename UInt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto count_digits(UInt n) -> int { +#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ + if (!is_constant_evaluated() && num_bits<UInt>() == 32) + return (FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ(static_cast<uint32_t>(n) | 1) ^ 31) / BITS + 1; #endif + // Lambda avoids unreachable code warnings from NVHPC. + return [](UInt m) { + int num_digits = 0; + do { + ++num_digits; + } while ((m >>= BITS) != 0); + return num_digits; + }(n); +} #ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ -// Optional version of count_digits for better performance on 32-bit platforms. -inline int count_digits(uint32_t n) { - auto t = bsr2log10(FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ(n | 1) ^ 31); - return t - (n < data::zero_or_powers_of_10_32_new[t]); +// It is a separate function rather than a part of count_digits to workaround +// the lack of static constexpr in constexpr functions. +FMT_INLINE auto do_count_digits(uint32_t n) -> int { +// An optimization by Kendall Willets from https://bit.ly/3uOIQrB. +// This increments the upper 32 bits (log10(T) - 1) when >= T is added. +# define FMT_INC(T) (((sizeof(#T) - 1ull) << 32) - T) + static constexpr uint64_t table[] = { + FMT_INC(0), FMT_INC(0), FMT_INC(0), // 8 + FMT_INC(10), FMT_INC(10), FMT_INC(10), // 64 + FMT_INC(100), FMT_INC(100), FMT_INC(100), // 512 + FMT_INC(1000), FMT_INC(1000), FMT_INC(1000), // 4096 + FMT_INC(10000), FMT_INC(10000), FMT_INC(10000), // 32k + FMT_INC(100000), FMT_INC(100000), FMT_INC(100000), // 256k + FMT_INC(1000000), FMT_INC(1000000), FMT_INC(1000000), // 2048k + FMT_INC(10000000), FMT_INC(10000000), FMT_INC(10000000), // 16M + FMT_INC(100000000), FMT_INC(100000000), FMT_INC(100000000), // 128M + FMT_INC(1000000000), FMT_INC(1000000000), FMT_INC(1000000000), // 1024M + FMT_INC(1000000000), FMT_INC(1000000000) // 4B + }; + auto inc = table[FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ(n | 1) ^ 31]; + return static_cast<int>((n + inc) >> 32); } #endif -template <typename Int> constexpr int digits10() FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return std::numeric_limits<Int>::digits10; +// Optional version of count_digits for better performance on 32-bit platforms. +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 inline auto count_digits(uint32_t n) -> int { +#ifdef FMT_BUILTIN_CLZ + if (!is_constant_evaluated()) { + return do_count_digits(n); + } +#endif + return count_digits_fallback(n); } -template <> constexpr int digits10<int128_t>() FMT_NOEXCEPT { return 38; } -template <> constexpr int digits10<uint128_t>() FMT_NOEXCEPT { return 38; } -template <typename Char> FMT_API std::string grouping_impl(locale_ref loc); -template <typename Char> inline std::string grouping(locale_ref loc) { - return grouping_impl<char>(loc); -} -template <> inline std::string grouping<wchar_t>(locale_ref loc) { - return grouping_impl<wchar_t>(loc); +template <typename Int> constexpr auto digits10() noexcept -> int { + return std::numeric_limits<Int>::digits10; } +template <> constexpr auto digits10<int128_opt>() noexcept -> int { return 38; } +template <> constexpr auto digits10<uint128_t>() noexcept -> int { return 38; } + +template <typename Char> struct thousands_sep_result { + std::string grouping; + Char thousands_sep; +}; -template <typename Char> FMT_API Char thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref loc); -template <typename Char> inline Char thousands_sep(locale_ref loc) { - return Char(thousands_sep_impl<char>(loc)); +template <typename Char> +FMT_API auto thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref loc) -> thousands_sep_result<Char>; +template <typename Char> +inline auto thousands_sep(locale_ref loc) -> thousands_sep_result<Char> { + auto result = thousands_sep_impl<char>(loc); + return {result.grouping, Char(result.thousands_sep)}; } -template <> inline wchar_t thousands_sep(locale_ref loc) { +template <> +inline auto thousands_sep(locale_ref loc) -> thousands_sep_result<wchar_t> { return thousands_sep_impl<wchar_t>(loc); } -template <typename Char> FMT_API Char decimal_point_impl(locale_ref loc); -template <typename Char> inline Char decimal_point(locale_ref loc) { +template <typename Char> +FMT_API auto decimal_point_impl(locale_ref loc) -> Char; +template <typename Char> inline auto decimal_point(locale_ref loc) -> Char { return Char(decimal_point_impl<char>(loc)); } -template <> inline wchar_t decimal_point(locale_ref loc) { +template <> inline auto decimal_point(locale_ref loc) -> wchar_t { return decimal_point_impl<wchar_t>(loc); } // Compares two characters for equality. -template <typename Char> bool equal2(const Char* lhs, const char* rhs) { - return lhs[0] == rhs[0] && lhs[1] == rhs[1]; +template <typename Char> auto equal2(const Char* lhs, const char* rhs) -> bool { + return lhs[0] == Char(rhs[0]) && lhs[1] == Char(rhs[1]); } -inline bool equal2(const char* lhs, const char* rhs) { +inline auto equal2(const char* lhs, const char* rhs) -> bool { return memcmp(lhs, rhs, 2) == 0; } // Copies two characters from src to dst. -template <typename Char> void copy2(Char* dst, const char* src) { +template <typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 FMT_INLINE void copy2(Char* dst, const char* src) { + if (!is_constant_evaluated() && sizeof(Char) == sizeof(char)) { + memcpy(dst, src, 2); + return; + } *dst++ = static_cast<Char>(*src++); *dst = static_cast<Char>(*src); } -FMT_INLINE void copy2(char* dst, const char* src) { memcpy(dst, src, 2); } template <typename Iterator> struct format_decimal_result { Iterator begin; @@ -1046,8 +1344,8 @@ template <typename Iterator> struct format_decimal_result { // buffer of specified size. The caller must ensure that the buffer is large // enough. template <typename Char, typename UInt> -inline format_decimal_result<Char*> format_decimal(Char* out, UInt value, - int size) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto format_decimal(Char* out, UInt value, int size) + -> format_decimal_result<Char*> { FMT_ASSERT(size >= count_digits(value), "invalid digit count"); out += size; Char* end = out; @@ -1056,7 +1354,7 @@ inline format_decimal_result<Char*> format_decimal(Char* out, UInt value, // of for every digit. The idea comes from the talk by Alexandrescu // "Three Optimization Tips for C++". See speed-test for a comparison. out -= 2; - copy2(out, data::digits[value % 100]); + copy2(out, digits2(static_cast<size_t>(value % 100))); value /= 100; } if (value < 10) { @@ -1064,200 +1362,234 @@ inline format_decimal_result<Char*> format_decimal(Char* out, UInt value, return {out, end}; } out -= 2; - copy2(out, data::digits[value]); + copy2(out, digits2(static_cast<size_t>(value))); return {out, end}; } template <typename Char, typename UInt, typename Iterator, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_pointer<remove_cvref_t<Iterator>>::value)> -inline format_decimal_result<Iterator> format_decimal(Iterator out, UInt value, - int size) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto format_decimal(Iterator out, UInt value, int size) + -> format_decimal_result<Iterator> { // Buffer is large enough to hold all digits (digits10 + 1). - Char buffer[digits10<UInt>() + 1]; + Char buffer[digits10<UInt>() + 1] = {}; auto end = format_decimal(buffer, value, size).end; - return {out, detail::copy_str<Char>(buffer, end, out)}; + return {out, detail::copy_str_noinline<Char>(buffer, end, out)}; } template <unsigned BASE_BITS, typename Char, typename UInt> -inline Char* format_uint(Char* buffer, UInt value, int num_digits, - bool upper = false) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto format_uint(Char* buffer, UInt value, int num_digits, + bool upper = false) -> Char* { buffer += num_digits; Char* end = buffer; do { - const char* digits = upper ? "0123456789ABCDEF" : data::hex_digits; - unsigned digit = (value & ((1 << BASE_BITS) - 1)); + const char* digits = upper ? "0123456789ABCDEF" : "0123456789abcdef"; + unsigned digit = static_cast<unsigned>(value & ((1 << BASE_BITS) - 1)); *--buffer = static_cast<Char>(BASE_BITS < 4 ? static_cast<char>('0' + digit) : digits[digit]); } while ((value >>= BASE_BITS) != 0); return end; } -template <unsigned BASE_BITS, typename Char> -Char* format_uint(Char* buffer, detail::fallback_uintptr n, int num_digits, - bool = false) { - auto char_digits = std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::digits / 4; - int start = (num_digits + char_digits - 1) / char_digits - 1; - if (int start_digits = num_digits % char_digits) { - unsigned value = n.value[start--]; - buffer = format_uint<BASE_BITS>(buffer, value, start_digits); - } - for (; start >= 0; --start) { - unsigned value = n.value[start]; - buffer += char_digits; - auto p = buffer; - for (int i = 0; i < char_digits; ++i) { - unsigned digit = (value & ((1 << BASE_BITS) - 1)); - *--p = static_cast<Char>(data::hex_digits[digit]); - value >>= BASE_BITS; - } - } - return buffer; -} - template <unsigned BASE_BITS, typename Char, typename It, typename UInt> -inline It format_uint(It out, UInt value, int num_digits, bool upper = false) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto format_uint(It out, UInt value, int num_digits, + bool upper = false) -> It { if (auto ptr = to_pointer<Char>(out, to_unsigned(num_digits))) { format_uint<BASE_BITS>(ptr, value, num_digits, upper); return out; } // Buffer should be large enough to hold all digits (digits / BASE_BITS + 1). - char buffer[num_bits<UInt>() / BASE_BITS + 1]; + char buffer[num_bits<UInt>() / BASE_BITS + 1] = {}; format_uint<BASE_BITS>(buffer, value, num_digits, upper); - return detail::copy_str<Char>(buffer, buffer + num_digits, out); + return detail::copy_str_noinline<Char>(buffer, buffer + num_digits, out); } // A converter from UTF-8 to UTF-16. class utf8_to_utf16 { private: - wmemory_buffer buffer_; + basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t> buffer_; public: FMT_API explicit utf8_to_utf16(string_view s); - operator wstring_view() const { return {&buffer_[0], size()}; } - size_t size() const { return buffer_.size() - 1; } - const wchar_t* c_str() const { return &buffer_[0]; } - std::wstring str() const { return {&buffer_[0], size()}; } + operator basic_string_view<wchar_t>() const { return {&buffer_[0], size()}; } + auto size() const -> size_t { return buffer_.size() - 1; } + auto c_str() const -> const wchar_t* { return &buffer_[0]; } + auto str() const -> std::wstring { return {&buffer_[0], size()}; } }; -template <typename T = void> struct null {}; +enum class to_utf8_error_policy { abort, replace }; -// Workaround an array initialization issue in gcc 4.8. -template <typename Char> struct fill_t { +// A converter from UTF-16/UTF-32 (host endian) to UTF-8. +template <typename WChar, typename Buffer = memory_buffer> class to_utf8 { private: - enum { max_size = 4 }; - Char data_[max_size] = {Char(' '), Char(0), Char(0), Char(0)}; - unsigned char size_ = 1; + Buffer buffer_; public: - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator=(basic_string_view<Char> s) { - auto size = s.size(); - if (size > max_size) { - FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid fill")); - return; + to_utf8() {} + explicit to_utf8(basic_string_view<WChar> s, + to_utf8_error_policy policy = to_utf8_error_policy::abort) { + static_assert(sizeof(WChar) == 2 || sizeof(WChar) == 4, + "Expect utf16 or utf32"); + if (!convert(s, policy)) + FMT_THROW(std::runtime_error(sizeof(WChar) == 2 ? "invalid utf16" + : "invalid utf32")); + } + operator string_view() const { return string_view(&buffer_[0], size()); } + size_t size() const { return buffer_.size() - 1; } + const char* c_str() const { return &buffer_[0]; } + std::string str() const { return std::string(&buffer_[0], size()); } + + // Performs conversion returning a bool instead of throwing exception on + // conversion error. This method may still throw in case of memory allocation + // error. + bool convert(basic_string_view<WChar> s, + to_utf8_error_policy policy = to_utf8_error_policy::abort) { + if (!convert(buffer_, s, policy)) return false; + buffer_.push_back(0); + return true; + } + static bool convert( + Buffer& buf, basic_string_view<WChar> s, + to_utf8_error_policy policy = to_utf8_error_policy::abort) { + for (auto p = s.begin(); p != s.end(); ++p) { + uint32_t c = static_cast<uint32_t>(*p); + if (sizeof(WChar) == 2 && c >= 0xd800 && c <= 0xdfff) { + // Handle a surrogate pair. + ++p; + if (p == s.end() || (c & 0xfc00) != 0xd800 || (*p & 0xfc00) != 0xdc00) { + if (policy == to_utf8_error_policy::abort) return false; + buf.append(string_view("\xEF\xBF\xBD")); + --p; + } else { + c = (c << 10) + static_cast<uint32_t>(*p) - 0x35fdc00; + } + } else if (c < 0x80) { + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(c)); + } else if (c < 0x800) { + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(0xc0 | (c >> 6))); + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(0x80 | (c & 0x3f))); + } else if ((c >= 0x800 && c <= 0xd7ff) || (c >= 0xe000 && c <= 0xffff)) { + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(0xe0 | (c >> 12))); + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(0x80 | ((c & 0xfff) >> 6))); + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(0x80 | (c & 0x3f))); + } else if (c >= 0x10000 && c <= 0x10ffff) { + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(0xf0 | (c >> 18))); + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(0x80 | ((c & 0x3ffff) >> 12))); + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(0x80 | ((c & 0xfff) >> 6))); + buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(0x80 | (c & 0x3f))); + } else { + return false; + } } - for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i) data_[i] = s[i]; - size_ = static_cast<unsigned char>(size); + return true; } +}; - size_t size() const { return size_; } - const Char* data() const { return data_; } +// Computes 128-bit result of multiplication of two 64-bit unsigned integers. +inline uint128_fallback umul128(uint64_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept { +#if FMT_USE_INT128 + auto p = static_cast<uint128_opt>(x) * static_cast<uint128_opt>(y); + return {static_cast<uint64_t>(p >> 64), static_cast<uint64_t>(p)}; +#elif defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_X64) + auto hi = uint64_t(); + auto lo = _umul128(x, y, &hi); + return {hi, lo}; +#else + const uint64_t mask = static_cast<uint64_t>(max_value<uint32_t>()); - FMT_CONSTEXPR Char& operator[](size_t index) { return data_[index]; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char& operator[](size_t index) const { - return data_[index]; - } -}; -} // namespace detail + uint64_t a = x >> 32; + uint64_t b = x & mask; + uint64_t c = y >> 32; + uint64_t d = y & mask; -// We cannot use enum classes as bit fields because of a gcc bug -// https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=61414. -namespace align { -enum type { none, left, right, center, numeric }; + uint64_t ac = a * c; + uint64_t bc = b * c; + uint64_t ad = a * d; + uint64_t bd = b * d; + + uint64_t intermediate = (bd >> 32) + (ad & mask) + (bc & mask); + + return {ac + (intermediate >> 32) + (ad >> 32) + (bc >> 32), + (intermediate << 32) + (bd & mask)}; +#endif } -using align_t = align::type; -namespace sign { -enum type { none, minus, plus, space }; +namespace dragonbox { +// Computes floor(log10(pow(2, e))) for e in [-2620, 2620] using the method from +// https://fmt.dev/papers/Dragonbox.pdf#page=28, section 6.1. +inline int floor_log10_pow2(int e) noexcept { + FMT_ASSERT(e <= 2620 && e >= -2620, "too large exponent"); + static_assert((-1 >> 1) == -1, "right shift is not arithmetic"); + return (e * 315653) >> 20; } -using sign_t = sign::type; -// Format specifiers for built-in and string types. -template <typename Char> struct basic_format_specs { - int width; - int precision; - char type; - align_t align : 4; - sign_t sign : 3; - bool alt : 1; // Alternate form ('#'). - detail::fill_t<Char> fill; - - constexpr basic_format_specs() - : width(0), - precision(-1), - type(0), - align(align::none), - sign(sign::none), - alt(false) {} -}; +inline int floor_log2_pow10(int e) noexcept { + FMT_ASSERT(e <= 1233 && e >= -1233, "too large exponent"); + return (e * 1741647) >> 19; +} -using format_specs = basic_format_specs<char>; +// Computes upper 64 bits of multiplication of two 64-bit unsigned integers. +inline uint64_t umul128_upper64(uint64_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept { +#if FMT_USE_INT128 + auto p = static_cast<uint128_opt>(x) * static_cast<uint128_opt>(y); + return static_cast<uint64_t>(p >> 64); +#elif defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_X64) + return __umulh(x, y); +#else + return umul128(x, y).high(); +#endif +} -namespace detail { -namespace dragonbox { +// Computes upper 128 bits of multiplication of a 64-bit unsigned integer and a +// 128-bit unsigned integer. +inline uint128_fallback umul192_upper128(uint64_t x, + uint128_fallback y) noexcept { + uint128_fallback r = umul128(x, y.high()); + r += umul128_upper64(x, y.low()); + return r; +} + +FMT_API uint128_fallback get_cached_power(int k) noexcept; // Type-specific information that Dragonbox uses. -template <class T> struct float_info; +template <typename T, typename Enable = void> struct float_info; template <> struct float_info<float> { using carrier_uint = uint32_t; - static const int significand_bits = 23; static const int exponent_bits = 8; - static const int min_exponent = -126; - static const int max_exponent = 127; - static const int exponent_bias = -127; - static const int decimal_digits = 9; static const int kappa = 1; static const int big_divisor = 100; static const int small_divisor = 10; static const int min_k = -31; static const int max_k = 46; - static const int cache_bits = 64; - static const int divisibility_check_by_5_threshold = 39; - static const int case_fc_pm_half_lower_threshold = -1; - static const int case_fc_pm_half_upper_threshold = 6; - static const int case_fc_lower_threshold = -2; - static const int case_fc_upper_threshold = 6; - static const int case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_lower_threshold = 2; - static const int case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_upper_threshold = 3; static const int shorter_interval_tie_lower_threshold = -35; static const int shorter_interval_tie_upper_threshold = -35; - static const int max_trailing_zeros = 7; }; template <> struct float_info<double> { using carrier_uint = uint64_t; - static const int significand_bits = 52; static const int exponent_bits = 11; - static const int min_exponent = -1022; - static const int max_exponent = 1023; - static const int exponent_bias = -1023; - static const int decimal_digits = 17; static const int kappa = 2; static const int big_divisor = 1000; static const int small_divisor = 100; static const int min_k = -292; - static const int max_k = 326; - static const int cache_bits = 128; - static const int divisibility_check_by_5_threshold = 86; - static const int case_fc_pm_half_lower_threshold = -2; - static const int case_fc_pm_half_upper_threshold = 9; - static const int case_fc_lower_threshold = -4; - static const int case_fc_upper_threshold = 9; - static const int case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_lower_threshold = 2; - static const int case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_upper_threshold = 3; + static const int max_k = 341; static const int shorter_interval_tie_lower_threshold = -77; static const int shorter_interval_tie_upper_threshold = -77; - static const int max_trailing_zeros = 16; +}; + +// An 80- or 128-bit floating point number. +template <typename T> +struct float_info<T, enable_if_t<std::numeric_limits<T>::digits == 64 || + std::numeric_limits<T>::digits == 113 || + is_float128<T>::value>> { + using carrier_uint = detail::uint128_t; + static const int exponent_bits = 15; +}; + +// A double-double floating point number. +template <typename T> +struct float_info<T, enable_if_t<is_double_double<T>::value>> { + using carrier_uint = detail::uint128_t; }; template <typename T> struct decimal_fp { @@ -1266,37 +1598,40 @@ template <typename T> struct decimal_fp { int exponent; }; -template <typename T> FMT_API decimal_fp<T> to_decimal(T x) FMT_NOEXCEPT; +template <typename T> FMT_API auto to_decimal(T x) noexcept -> decimal_fp<T>; } // namespace dragonbox -template <typename T> -constexpr typename dragonbox::float_info<T>::carrier_uint exponent_mask() { - using uint = typename dragonbox::float_info<T>::carrier_uint; - return ((uint(1) << dragonbox::float_info<T>::exponent_bits) - 1) - << dragonbox::float_info<T>::significand_bits; +// Returns true iff Float has the implicit bit which is not stored. +template <typename Float> constexpr bool has_implicit_bit() { + // An 80-bit FP number has a 64-bit significand an no implicit bit. + return std::numeric_limits<Float>::digits != 64; } -// A floating-point presentation format. -enum class float_format : unsigned char { - general, // General: exponent notation or fixed point based on magnitude. - exp, // Exponent notation with the default precision of 6, e.g. 1.2e-3. - fixed, // Fixed point with the default precision of 6, e.g. 0.0012. - hex -}; +// Returns the number of significand bits stored in Float. The implicit bit is +// not counted since it is not stored. +template <typename Float> constexpr int num_significand_bits() { + // std::numeric_limits may not support __float128. + return is_float128<Float>() ? 112 + : (std::numeric_limits<Float>::digits - + (has_implicit_bit<Float>() ? 1 : 0)); +} -struct float_specs { - int precision; - float_format format : 8; - sign_t sign : 8; - bool upper : 1; - bool locale : 1; - bool binary32 : 1; - bool use_grisu : 1; - bool showpoint : 1; -}; +template <typename Float> +constexpr auto exponent_mask() -> + typename dragonbox::float_info<Float>::carrier_uint { + using float_uint = typename dragonbox::float_info<Float>::carrier_uint; + return ((float_uint(1) << dragonbox::float_info<Float>::exponent_bits) - 1) + << num_significand_bits<Float>(); +} +template <typename Float> constexpr auto exponent_bias() -> int { + // std::numeric_limits may not support __float128. + return is_float128<Float>() ? 16383 + : std::numeric_limits<Float>::max_exponent - 1; +} // Writes the exponent exp in the form "[+-]d{2,3}" to buffer. -template <typename Char, typename It> It write_exponent(int exp, It it) { +template <typename Char, typename It> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write_exponent(int exp, It it) -> It { FMT_ASSERT(-10000 < exp && exp < 10000, "exponent out of range"); if (exp < 0) { *it++ = static_cast<Char>('-'); @@ -1305,185 +1640,123 @@ template <typename Char, typename It> It write_exponent(int exp, It it) { *it++ = static_cast<Char>('+'); } if (exp >= 100) { - const char* top = data::digits[exp / 100]; + const char* top = digits2(to_unsigned(exp / 100)); if (exp >= 1000) *it++ = static_cast<Char>(top[0]); *it++ = static_cast<Char>(top[1]); exp %= 100; } - const char* d = data::digits[exp]; + const char* d = digits2(to_unsigned(exp)); *it++ = static_cast<Char>(d[0]); *it++ = static_cast<Char>(d[1]); return it; } -template <typename T> -int format_float(T value, int precision, float_specs specs, buffer<char>& buf); - -// Formats a floating-point number with snprintf. -template <typename T> -int snprintf_float(T value, int precision, float_specs specs, - buffer<char>& buf); - -template <typename T> T promote_float(T value) { return value; } -inline double promote_float(float value) { return static_cast<double>(value); } - -template <typename Handler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR void handle_int_type_spec(char spec, Handler&& handler) { - switch (spec) { - case 0: - case 'd': - handler.on_dec(); - break; - case 'x': - case 'X': - handler.on_hex(); - break; - case 'b': - case 'B': - handler.on_bin(); - break; - case 'o': - handler.on_oct(); - break; -#ifdef FMT_DEPRECATED_N_SPECIFIER - case 'n': -#endif - case 'L': - handler.on_num(); - break; - case 'c': - handler.on_chr(); - break; - default: - handler.on_error(); +// A floating-point number f * pow(2, e) where F is an unsigned type. +template <typename F> struct basic_fp { + F f; + int e; + + static constexpr const int num_significand_bits = + static_cast<int>(sizeof(F) * num_bits<unsigned char>()); + + constexpr basic_fp() : f(0), e(0) {} + constexpr basic_fp(uint64_t f_val, int e_val) : f(f_val), e(e_val) {} + + // Constructs fp from an IEEE754 floating-point number. + template <typename Float> FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_fp(Float n) { assign(n); } + + // Assigns n to this and return true iff predecessor is closer than successor. + template <typename Float, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_double_double<Float>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto assign(Float n) -> bool { + static_assert(std::numeric_limits<Float>::digits <= 113, "unsupported FP"); + // Assume Float is in the format [sign][exponent][significand]. + using carrier_uint = typename dragonbox::float_info<Float>::carrier_uint; + const auto num_float_significand_bits = + detail::num_significand_bits<Float>(); + const auto implicit_bit = carrier_uint(1) << num_float_significand_bits; + const auto significand_mask = implicit_bit - 1; + auto u = bit_cast<carrier_uint>(n); + f = static_cast<F>(u & significand_mask); + auto biased_e = static_cast<int>((u & exponent_mask<Float>()) >> + num_float_significand_bits); + // The predecessor is closer if n is a normalized power of 2 (f == 0) + // other than the smallest normalized number (biased_e > 1). + auto is_predecessor_closer = f == 0 && biased_e > 1; + if (biased_e == 0) + biased_e = 1; // Subnormals use biased exponent 1 (min exponent). + else if (has_implicit_bit<Float>()) + f += static_cast<F>(implicit_bit); + e = biased_e - exponent_bias<Float>() - num_float_significand_bits; + if (!has_implicit_bit<Float>()) ++e; + return is_predecessor_closer; + } + + template <typename Float, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_double_double<Float>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto assign(Float n) -> bool { + static_assert(std::numeric_limits<double>::is_iec559, "unsupported FP"); + return assign(static_cast<double>(n)); } -} +}; -template <typename ErrorHandler = error_handler, typename Char> -FMT_CONSTEXPR float_specs parse_float_type_spec( - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs, ErrorHandler&& eh = {}) { - auto result = float_specs(); - result.showpoint = specs.alt; - switch (specs.type) { - case 0: - result.format = float_format::general; - result.showpoint |= specs.precision > 0; - break; - case 'G': - result.upper = true; - FMT_FALLTHROUGH; - case 'g': - result.format = float_format::general; - break; - case 'E': - result.upper = true; - FMT_FALLTHROUGH; - case 'e': - result.format = float_format::exp; - result.showpoint |= specs.precision != 0; - break; - case 'F': - result.upper = true; - FMT_FALLTHROUGH; - case 'f': - result.format = float_format::fixed; - result.showpoint |= specs.precision != 0; - break; - case 'A': - result.upper = true; - FMT_FALLTHROUGH; - case 'a': - result.format = float_format::hex; - break; -#ifdef FMT_DEPRECATED_N_SPECIFIER - case 'n': -#endif - case 'L': - result.locale = true; - break; - default: - eh.on_error("invalid type specifier"); - break; - } - return result; +using fp = basic_fp<unsigned long long>; + +// Normalizes the value converted from double and multiplied by (1 << SHIFT). +template <int SHIFT = 0, typename F> +FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_fp<F> normalize(basic_fp<F> value) { + // Handle subnormals. + const auto implicit_bit = F(1) << num_significand_bits<double>(); + const auto shifted_implicit_bit = implicit_bit << SHIFT; + while ((value.f & shifted_implicit_bit) == 0) { + value.f <<= 1; + --value.e; + } + // Subtract 1 to account for hidden bit. + const auto offset = basic_fp<F>::num_significand_bits - + num_significand_bits<double>() - SHIFT - 1; + value.f <<= offset; + value.e -= offset; + return value; } -template <typename Char, typename Handler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR void handle_char_specs(const basic_format_specs<Char>* specs, - Handler&& handler) { - if (!specs) return handler.on_char(); - if (specs->type && specs->type != 'c') return handler.on_int(); - if (specs->align == align::numeric || specs->sign != sign::none || specs->alt) - handler.on_error("invalid format specifier for char"); - handler.on_char(); +// Computes lhs * rhs / pow(2, 64) rounded to nearest with half-up tie breaking. +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline uint64_t multiply(uint64_t lhs, uint64_t rhs) { +#if FMT_USE_INT128 + auto product = static_cast<__uint128_t>(lhs) * rhs; + auto f = static_cast<uint64_t>(product >> 64); + return (static_cast<uint64_t>(product) & (1ULL << 63)) != 0 ? f + 1 : f; +#else + // Multiply 32-bit parts of significands. + uint64_t mask = (1ULL << 32) - 1; + uint64_t a = lhs >> 32, b = lhs & mask; + uint64_t c = rhs >> 32, d = rhs & mask; + uint64_t ac = a * c, bc = b * c, ad = a * d, bd = b * d; + // Compute mid 64-bit of result and round. + uint64_t mid = (bd >> 32) + (ad & mask) + (bc & mask) + (1U << 31); + return ac + (ad >> 32) + (bc >> 32) + (mid >> 32); +#endif } -template <typename Char, typename Handler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR void handle_cstring_type_spec(Char spec, Handler&& handler) { - if (spec == 0 || spec == 's') - handler.on_string(); - else if (spec == 'p') - handler.on_pointer(); - else - handler.on_error("invalid type specifier"); +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline fp operator*(fp x, fp y) { + return {multiply(x.f, y.f), x.e + y.e + 64}; } -template <typename Char, typename ErrorHandler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_string_type_spec(Char spec, ErrorHandler&& eh) { - if (spec != 0 && spec != 's') eh.on_error("invalid type specifier"); -} +template <typename T, bool doublish = num_bits<T>() == num_bits<double>()> +using convert_float_result = + conditional_t<std::is_same<T, float>::value || doublish, double, T>; -template <typename Char, typename ErrorHandler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_pointer_type_spec(Char spec, ErrorHandler&& eh) { - if (spec != 0 && spec != 'p') eh.on_error("invalid type specifier"); +template <typename T> +constexpr auto convert_float(T value) -> convert_float_result<T> { + return static_cast<convert_float_result<T>>(value); } -template <typename ErrorHandler> class int_type_checker : private ErrorHandler { - public: - FMT_CONSTEXPR explicit int_type_checker(ErrorHandler eh) : ErrorHandler(eh) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dec() {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_hex() {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_bin() {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_oct() {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_num() {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_chr() {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error() { - ErrorHandler::on_error("invalid type specifier"); - } -}; - -template <typename ErrorHandler> -class char_specs_checker : public ErrorHandler { - private: - char type_; - - public: - FMT_CONSTEXPR char_specs_checker(char type, ErrorHandler eh) - : ErrorHandler(eh), type_(type) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_int() { - handle_int_type_spec(type_, int_type_checker<ErrorHandler>(*this)); - } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_char() {} -}; - -template <typename ErrorHandler> -class cstring_type_checker : public ErrorHandler { - public: - FMT_CONSTEXPR explicit cstring_type_checker(ErrorHandler eh) - : ErrorHandler(eh) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_string() {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_pointer() {} -}; - template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -FMT_NOINLINE OutputIt fill(OutputIt it, size_t n, const fill_t<Char>& fill) { +FMT_NOINLINE FMT_CONSTEXPR auto fill(OutputIt it, size_t n, + const fill_t<Char>& fill) -> OutputIt { auto fill_size = fill.size(); - if (fill_size == 1) return std::fill_n(it, n, fill[0]); - for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i) it = std::copy_n(fill.data(), fill_size, it); + if (fill_size == 1) return detail::fill_n(it, n, fill[0]); + auto data = fill.data(); + for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i) + it = copy_str<Char>(data, data + fill_size, it); return it; } @@ -1492,39 +1765,233 @@ FMT_NOINLINE OutputIt fill(OutputIt it, size_t n, const fill_t<Char>& fill) { // width: output display width in (terminal) column positions. template <align::type align = align::left, typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename F> -inline OutputIt write_padded(OutputIt out, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs, size_t size, - size_t width, F&& f) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write_padded(OutputIt out, const format_specs<Char>& specs, + size_t size, size_t width, F&& f) -> OutputIt { static_assert(align == align::left || align == align::right, ""); unsigned spec_width = to_unsigned(specs.width); size_t padding = spec_width > width ? spec_width - width : 0; - auto* shifts = align == align::left ? data::left_padding_shifts - : data::right_padding_shifts; + // Shifts are encoded as string literals because static constexpr is not + // supported in constexpr functions. + auto* shifts = align == align::left ? "\x1f\x1f\x00\x01" : "\x00\x1f\x00\x01"; size_t left_padding = padding >> shifts[specs.align]; + size_t right_padding = padding - left_padding; auto it = reserve(out, size + padding * specs.fill.size()); - it = fill(it, left_padding, specs.fill); + if (left_padding != 0) it = fill(it, left_padding, specs.fill); it = f(it); - it = fill(it, padding - left_padding, specs.fill); + if (right_padding != 0) it = fill(it, right_padding, specs.fill); return base_iterator(out, it); } template <align::type align = align::left, typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename F> -inline OutputIt write_padded(OutputIt out, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs, size_t size, - F&& f) { +constexpr auto write_padded(OutputIt out, const format_specs<Char>& specs, + size_t size, F&& f) -> OutputIt { return write_padded<align>(out, specs, size, size, f); } +template <align::type align = align::left, typename Char, typename OutputIt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write_bytes(OutputIt out, string_view bytes, + const format_specs<Char>& specs) -> OutputIt { + return write_padded<align>( + out, specs, bytes.size(), [bytes](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + const char* data = bytes.data(); + return copy_str<Char>(data, data + bytes.size(), it); + }); +} + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename UIntPtr> +auto write_ptr(OutputIt out, UIntPtr value, const format_specs<Char>* specs) + -> OutputIt { + int num_digits = count_digits<4>(value); + auto size = to_unsigned(num_digits) + size_t(2); + auto write = [=](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + *it++ = static_cast<Char>('0'); + *it++ = static_cast<Char>('x'); + return format_uint<4, Char>(it, value, num_digits); + }; + return specs ? write_padded<align::right>(out, *specs, size, write) + : base_iterator(out, write(reserve(out, size))); +} + +// Returns true iff the code point cp is printable. +FMT_API auto is_printable(uint32_t cp) -> bool; + +inline auto needs_escape(uint32_t cp) -> bool { + return cp < 0x20 || cp == 0x7f || cp == '"' || cp == '\\' || + !is_printable(cp); +} + +template <typename Char> struct find_escape_result { + const Char* begin; + const Char* end; + uint32_t cp; +}; + +template <typename Char> +using make_unsigned_char = + typename conditional_t<std::is_integral<Char>::value, + std::make_unsigned<Char>, + type_identity<uint32_t>>::type; + +template <typename Char> +auto find_escape(const Char* begin, const Char* end) + -> find_escape_result<Char> { + for (; begin != end; ++begin) { + uint32_t cp = static_cast<make_unsigned_char<Char>>(*begin); + if (const_check(sizeof(Char) == 1) && cp >= 0x80) continue; + if (needs_escape(cp)) return {begin, begin + 1, cp}; + } + return {begin, nullptr, 0}; +} + +inline auto find_escape(const char* begin, const char* end) + -> find_escape_result<char> { + if (!is_utf8()) return find_escape<char>(begin, end); + auto result = find_escape_result<char>{end, nullptr, 0}; + for_each_codepoint(string_view(begin, to_unsigned(end - begin)), + [&](uint32_t cp, string_view sv) { + if (needs_escape(cp)) { + result = {sv.begin(), sv.end(), cp}; + return false; + } + return true; + }); + return result; +} + +#define FMT_STRING_IMPL(s, base, explicit) \ + [] { \ + /* Use the hidden visibility as a workaround for a GCC bug (#1973). */ \ + /* Use a macro-like name to avoid shadowing warnings. */ \ + struct FMT_VISIBILITY("hidden") FMT_COMPILE_STRING : base { \ + using char_type FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED = fmt::remove_cvref_t<decltype(s[0])>; \ + FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED FMT_CONSTEXPR explicit \ + operator fmt::basic_string_view<char_type>() const { \ + return fmt::detail_exported::compile_string_to_view<char_type>(s); \ + } \ + }; \ + return FMT_COMPILE_STRING(); \ + }() + +/** + \rst + Constructs a compile-time format string from a string literal *s*. + + **Example**:: + + // A compile-time error because 'd' is an invalid specifier for strings. + std::string s = fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{:d}"), "foo"); + \endrst + */ +#define FMT_STRING(s) FMT_STRING_IMPL(s, fmt::detail::compile_string, ) + +template <size_t width, typename Char, typename OutputIt> +auto write_codepoint(OutputIt out, char prefix, uint32_t cp) -> OutputIt { + *out++ = static_cast<Char>('\\'); + *out++ = static_cast<Char>(prefix); + Char buf[width]; + fill_n(buf, width, static_cast<Char>('0')); + format_uint<4>(buf, cp, width); + return copy_str<Char>(buf, buf + width, out); +} + +template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> +auto write_escaped_cp(OutputIt out, const find_escape_result<Char>& escape) + -> OutputIt { + auto c = static_cast<Char>(escape.cp); + switch (escape.cp) { + case '\n': + *out++ = static_cast<Char>('\\'); + c = static_cast<Char>('n'); + break; + case '\r': + *out++ = static_cast<Char>('\\'); + c = static_cast<Char>('r'); + break; + case '\t': + *out++ = static_cast<Char>('\\'); + c = static_cast<Char>('t'); + break; + case '"': + FMT_FALLTHROUGH; + case '\'': + FMT_FALLTHROUGH; + case '\\': + *out++ = static_cast<Char>('\\'); + break; + default: + if (escape.cp < 0x100) { + return write_codepoint<2, Char>(out, 'x', escape.cp); + } + if (escape.cp < 0x10000) { + return write_codepoint<4, Char>(out, 'u', escape.cp); + } + if (escape.cp < 0x110000) { + return write_codepoint<8, Char>(out, 'U', escape.cp); + } + for (Char escape_char : basic_string_view<Char>( + escape.begin, to_unsigned(escape.end - escape.begin))) { + out = write_codepoint<2, Char>(out, 'x', + static_cast<uint32_t>(escape_char) & 0xFF); + } + return out; + } + *out++ = c; + return out; +} + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> +auto write_escaped_string(OutputIt out, basic_string_view<Char> str) + -> OutputIt { + *out++ = static_cast<Char>('"'); + auto begin = str.begin(), end = str.end(); + do { + auto escape = find_escape(begin, end); + out = copy_str<Char>(begin, escape.begin, out); + begin = escape.end; + if (!begin) break; + out = write_escaped_cp<OutputIt, Char>(out, escape); + } while (begin != end); + *out++ = static_cast<Char>('"'); + return out; +} + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> +auto write_escaped_char(OutputIt out, Char v) -> OutputIt { + Char v_array[1] = {v}; + *out++ = static_cast<Char>('\''); + if ((needs_escape(static_cast<uint32_t>(v)) && v != static_cast<Char>('"')) || + v == static_cast<Char>('\'')) { + out = write_escaped_cp( + out, find_escape_result<Char>{v_array, v_array + 1, static_cast<uint32_t>(v)}); + } else { + *out++ = v; + } + *out++ = static_cast<Char>('\''); + return out; +} + template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write_bytes(OutputIt out, string_view bytes, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs) { - using iterator = remove_reference_t<decltype(reserve(out, 0))>; - return write_padded(out, specs, bytes.size(), [bytes](iterator it) { - const char* data = bytes.data(); - return copy_str<Char>(data, data + bytes.size(), it); +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write_char(OutputIt out, Char value, + const format_specs<Char>& specs) -> OutputIt { + bool is_debug = specs.type == presentation_type::debug; + return write_padded(out, specs, 1, [=](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + if (is_debug) return write_escaped_char(it, value); + *it++ = value; + return it; }); } +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, Char value, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, locale_ref loc = {}) + -> OutputIt { + // char is formatted as unsigned char for consistency across platforms. + using unsigned_type = + conditional_t<std::is_same<Char, char>::value, unsigned char, unsigned>; + return check_char_specs(specs) + ? write_char(out, value, specs) + : write(out, static_cast<unsigned_type>(value), specs, loc); +} // Data for write_int that doesn't depend on output iterator type. It is used to // avoid template code bloat. @@ -1532,9 +1999,9 @@ template <typename Char> struct write_int_data { size_t size; size_t padding; - write_int_data(int num_digits, string_view prefix, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs) - : size(prefix.size() + to_unsigned(num_digits)), padding(0) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR write_int_data(int num_digits, unsigned prefix, + const format_specs<Char>& specs) + : size((prefix >> 24) + to_unsigned(num_digits)), padding(0) { if (specs.align == align::numeric) { auto width = to_unsigned(specs.width); if (width > size) { @@ -1542,7 +2009,7 @@ template <typename Char> struct write_int_data { size = width; } } else if (specs.precision > num_digits) { - size = prefix.size() + to_unsigned(specs.precision); + size = (prefix >> 24) + to_unsigned(specs.precision); padding = to_unsigned(specs.precision - num_digits); } } @@ -1550,183 +2017,478 @@ template <typename Char> struct write_int_data { // Writes an integer in the format // <left-padding><prefix><numeric-padding><digits><right-padding> -// where <digits> are written by f(it). -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename F> -OutputIt write_int(OutputIt out, int num_digits, string_view prefix, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs, F f) { +// where <digits> are written by write_digits(it). +// prefix contains chars in three lower bytes and the size in the fourth byte. +template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename W> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto write_int(OutputIt out, int num_digits, + unsigned prefix, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, + W write_digits) -> OutputIt { + // Slightly faster check for specs.width == 0 && specs.precision == -1. + if ((specs.width | (specs.precision + 1)) == 0) { + auto it = reserve(out, to_unsigned(num_digits) + (prefix >> 24)); + if (prefix != 0) { + for (unsigned p = prefix & 0xffffff; p != 0; p >>= 8) + *it++ = static_cast<Char>(p & 0xff); + } + return base_iterator(out, write_digits(it)); + } auto data = write_int_data<Char>(num_digits, prefix, specs); - using iterator = remove_reference_t<decltype(reserve(out, 0))>; - return write_padded<align::right>(out, specs, data.size, [=](iterator it) { - if (prefix.size() != 0) - it = copy_str<Char>(prefix.begin(), prefix.end(), it); - it = std::fill_n(it, data.padding, static_cast<Char>('0')); - return f(it); - }); + return write_padded<align::right>( + out, specs, data.size, [=](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + for (unsigned p = prefix & 0xffffff; p != 0; p >>= 8) + *it++ = static_cast<Char>(p & 0xff); + it = detail::fill_n(it, data.padding, static_cast<Char>('0')); + return write_digits(it); + }); } -template <typename StrChar, typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, basic_string_view<StrChar> s, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs) { - auto data = s.data(); - auto size = s.size(); - if (specs.precision >= 0 && to_unsigned(specs.precision) < size) - size = code_point_index(s, to_unsigned(specs.precision)); - auto width = specs.width != 0 - ? count_code_points(basic_string_view<StrChar>(data, size)) - : 0; - using iterator = remove_reference_t<decltype(reserve(out, 0))>; - return write_padded(out, specs, size, width, [=](iterator it) { - return copy_str<Char>(data, data + size, it); - }); +template <typename Char> class digit_grouping { + private: + std::string grouping_; + std::basic_string<Char> thousands_sep_; + + struct next_state { + std::string::const_iterator group; + int pos; + }; + next_state initial_state() const { return {grouping_.begin(), 0}; } + + // Returns the next digit group separator position. + int next(next_state& state) const { + if (thousands_sep_.empty()) return max_value<int>(); + if (state.group == grouping_.end()) return state.pos += grouping_.back(); + if (*state.group <= 0 || *state.group == max_value<char>()) + return max_value<int>(); + state.pos += *state.group++; + return state.pos; + } + + public: + explicit digit_grouping(locale_ref loc, bool localized = true) { + if (!localized) return; + auto sep = thousands_sep<Char>(loc); + grouping_ = sep.grouping; + if (sep.thousands_sep) thousands_sep_.assign(1, sep.thousands_sep); + } + digit_grouping(std::string grouping, std::basic_string<Char> sep) + : grouping_(std::move(grouping)), thousands_sep_(std::move(sep)) {} + + bool has_separator() const { return !thousands_sep_.empty(); } + + int count_separators(int num_digits) const { + int count = 0; + auto state = initial_state(); + while (num_digits > next(state)) ++count; + return count; + } + + // Applies grouping to digits and write the output to out. + template <typename Out, typename C> + Out apply(Out out, basic_string_view<C> digits) const { + auto num_digits = static_cast<int>(digits.size()); + auto separators = basic_memory_buffer<int>(); + separators.push_back(0); + auto state = initial_state(); + while (int i = next(state)) { + if (i >= num_digits) break; + separators.push_back(i); + } + for (int i = 0, sep_index = static_cast<int>(separators.size() - 1); + i < num_digits; ++i) { + if (num_digits - i == separators[sep_index]) { + out = + copy_str<Char>(thousands_sep_.data(), + thousands_sep_.data() + thousands_sep_.size(), out); + --sep_index; + } + *out++ = static_cast<Char>(digits[to_unsigned(i)]); + } + return out; + } +}; + +// Writes a decimal integer with digit grouping. +template <typename OutputIt, typename UInt, typename Char> +auto write_int(OutputIt out, UInt value, unsigned prefix, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, + const digit_grouping<Char>& grouping) -> OutputIt { + static_assert(std::is_same<uint64_or_128_t<UInt>, UInt>::value, ""); + int num_digits = count_digits(value); + char digits[40]; + format_decimal(digits, value, num_digits); + unsigned size = to_unsigned((prefix != 0 ? 1 : 0) + num_digits + + grouping.count_separators(num_digits)); + return write_padded<align::right>( + out, specs, size, size, [&](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + if (prefix != 0) { + char sign = static_cast<char>(prefix); + *it++ = static_cast<Char>(sign); + } + return grouping.apply(it, string_view(digits, to_unsigned(num_digits))); + }); +} + +// Writes a localized value. +FMT_API auto write_loc(appender out, loc_value value, + const format_specs<>& specs, locale_ref loc) -> bool; +template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> +inline auto write_loc(OutputIt, loc_value, const format_specs<Char>&, + locale_ref) -> bool { + return false; } -// The handle_int_type_spec handler that writes an integer. -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename UInt> struct int_writer { - OutputIt out; - locale_ref locale; - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs; +FMT_CONSTEXPR inline void prefix_append(unsigned& prefix, unsigned value) { + prefix |= prefix != 0 ? value << 8 : value; + prefix += (1u + (value > 0xff ? 1 : 0)) << 24; +} + +template <typename UInt> struct write_int_arg { UInt abs_value; - char prefix[4]; - unsigned prefix_size; - - using iterator = - remove_reference_t<decltype(reserve(std::declval<OutputIt&>(), 0))>; - - string_view get_prefix() const { return string_view(prefix, prefix_size); } - - template <typename Int> - int_writer(OutputIt output, locale_ref loc, Int value, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& s) - : out(output), - locale(loc), - specs(s), - abs_value(static_cast<UInt>(value)), - prefix_size(0) { - static_assert(std::is_same<uint32_or_64_or_128_t<Int>, UInt>::value, ""); - if (is_negative(value)) { - prefix[0] = '-'; - ++prefix_size; - abs_value = 0 - abs_value; - } else if (specs.sign != sign::none && specs.sign != sign::minus) { - prefix[0] = specs.sign == sign::plus ? '+' : ' '; - ++prefix_size; - } + unsigned prefix; +}; + +template <typename T> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto make_write_int_arg(T value, sign_t sign) + -> write_int_arg<uint32_or_64_or_128_t<T>> { + auto prefix = 0u; + auto abs_value = static_cast<uint32_or_64_or_128_t<T>>(value); + if (is_negative(value)) { + prefix = 0x01000000 | '-'; + abs_value = 0 - abs_value; + } else { + constexpr const unsigned prefixes[4] = {0, 0, 0x1000000u | '+', + 0x1000000u | ' '}; + prefix = prefixes[sign]; } + return {abs_value, prefix}; +} - void on_dec() { +template <typename Char = char> struct loc_writer { + buffer_appender<Char> out; + const format_specs<Char>& specs; + std::basic_string<Char> sep; + std::string grouping; + std::basic_string<Char> decimal_point; + + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integer<T>::value)> + auto operator()(T value) -> bool { + auto arg = make_write_int_arg(value, specs.sign); + write_int(out, static_cast<uint64_or_128_t<T>>(arg.abs_value), arg.prefix, + specs, digit_grouping<Char>(grouping, sep)); + return true; + } + + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_integer<T>::value)> + auto operator()(T) -> bool { + return false; + } +}; + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto write_int(OutputIt out, write_int_arg<T> arg, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, + locale_ref) -> OutputIt { + static_assert(std::is_same<T, uint32_or_64_or_128_t<T>>::value, ""); + auto abs_value = arg.abs_value; + auto prefix = arg.prefix; + switch (specs.type) { + case presentation_type::none: + case presentation_type::dec: { auto num_digits = count_digits(abs_value); - out = write_int( - out, num_digits, get_prefix(), specs, [this, num_digits](iterator it) { + return write_int( + out, num_digits, prefix, specs, [=](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { return format_decimal<Char>(it, abs_value, num_digits).end; }); } - - void on_hex() { - if (specs.alt) { - prefix[prefix_size++] = '0'; - prefix[prefix_size++] = specs.type; - } + case presentation_type::hex_lower: + case presentation_type::hex_upper: { + bool upper = specs.type == presentation_type::hex_upper; + if (specs.alt) + prefix_append(prefix, unsigned(upper ? 'X' : 'x') << 8 | '0'); int num_digits = count_digits<4>(abs_value); - out = write_int(out, num_digits, get_prefix(), specs, - [this, num_digits](iterator it) { - return format_uint<4, Char>(it, abs_value, num_digits, - specs.type != 'x'); - }); + return write_int( + out, num_digits, prefix, specs, [=](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + return format_uint<4, Char>(it, abs_value, num_digits, upper); + }); } - - void on_bin() { - if (specs.alt) { - prefix[prefix_size++] = '0'; - prefix[prefix_size++] = static_cast<char>(specs.type); - } + case presentation_type::bin_lower: + case presentation_type::bin_upper: { + bool upper = specs.type == presentation_type::bin_upper; + if (specs.alt) + prefix_append(prefix, unsigned(upper ? 'B' : 'b') << 8 | '0'); int num_digits = count_digits<1>(abs_value); - out = write_int(out, num_digits, get_prefix(), specs, - [this, num_digits](iterator it) { - return format_uint<1, Char>(it, abs_value, num_digits); - }); + return write_int(out, num_digits, prefix, specs, + [=](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + return format_uint<1, Char>(it, abs_value, num_digits); + }); } - - void on_oct() { + case presentation_type::oct: { int num_digits = count_digits<3>(abs_value); - if (specs.alt && specs.precision <= num_digits && abs_value != 0) { - // Octal prefix '0' is counted as a digit, so only add it if precision - // is not greater than the number of digits. - prefix[prefix_size++] = '0'; - } - out = write_int(out, num_digits, get_prefix(), specs, - [this, num_digits](iterator it) { - return format_uint<3, Char>(it, abs_value, num_digits); - }); - } - - enum { sep_size = 1 }; - - void on_num() { - std::string groups = grouping<Char>(locale); - if (groups.empty()) return on_dec(); - auto sep = thousands_sep<Char>(locale); - if (!sep) return on_dec(); - int num_digits = count_digits(abs_value); - int size = num_digits, n = num_digits; - std::string::const_iterator group = groups.cbegin(); - while (group != groups.cend() && n > *group && *group > 0 && - *group != max_value<char>()) { - size += sep_size; - n -= *group; - ++group; + // Octal prefix '0' is counted as a digit, so only add it if precision + // is not greater than the number of digits. + if (specs.alt && specs.precision <= num_digits && abs_value != 0) + prefix_append(prefix, '0'); + return write_int(out, num_digits, prefix, specs, + [=](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + return format_uint<3, Char>(it, abs_value, num_digits); + }); + } + case presentation_type::chr: + return write_char(out, static_cast<Char>(abs_value), specs); + default: + throw_format_error("invalid format specifier"); + } + return out; +} +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_NOINLINE auto write_int_noinline( + OutputIt out, write_int_arg<T> arg, const format_specs<Char>& specs, + locale_ref loc) -> OutputIt { + return write_int(out, arg, specs, loc); +} +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integral<T>::value && + !std::is_same<T, bool>::value && + std::is_same<OutputIt, buffer_appender<Char>>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto write(OutputIt out, T value, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, + locale_ref loc) -> OutputIt { + if (specs.localized && write_loc(out, value, specs, loc)) return out; + return write_int_noinline(out, make_write_int_arg(value, specs.sign), specs, + loc); +} +// An inlined version of write used in format string compilation. +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integral<T>::value && + !std::is_same<T, bool>::value && + !std::is_same<OutputIt, buffer_appender<Char>>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto write(OutputIt out, T value, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, + locale_ref loc) -> OutputIt { + if (specs.localized && write_loc(out, value, specs, loc)) return out; + return write_int(out, make_write_int_arg(value, specs.sign), specs, loc); +} + +// An output iterator that counts the number of objects written to it and +// discards them. +class counting_iterator { + private: + size_t count_; + + public: + using iterator_category = std::output_iterator_tag; + using difference_type = std::ptrdiff_t; + using pointer = void; + using reference = void; + FMT_UNCHECKED_ITERATOR(counting_iterator); + + struct value_type { + template <typename T> FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator=(const T&) {} + }; + + FMT_CONSTEXPR counting_iterator() : count_(0) {} + + FMT_CONSTEXPR size_t count() const { return count_; } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR counting_iterator& operator++() { + ++count_; + return *this; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR counting_iterator operator++(int) { + auto it = *this; + ++*this; + return it; + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR friend counting_iterator operator+(counting_iterator it, + difference_type n) { + it.count_ += static_cast<size_t>(n); + return it; + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR value_type operator*() const { return {}; } +}; + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, basic_string_view<Char> s, + const format_specs<Char>& specs) -> OutputIt { + auto data = s.data(); + auto size = s.size(); + if (specs.precision >= 0 && to_unsigned(specs.precision) < size) + size = code_point_index(s, to_unsigned(specs.precision)); + bool is_debug = specs.type == presentation_type::debug; + size_t width = 0; + if (specs.width != 0) { + if (is_debug) + width = write_escaped_string(counting_iterator{}, s).count(); + else + width = compute_width(basic_string_view<Char>(data, size)); + } + return write_padded(out, specs, size, width, + [=](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + if (is_debug) return write_escaped_string(it, s); + return copy_str<Char>(data, data + size, it); + }); +} +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, + basic_string_view<type_identity_t<Char>> s, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, locale_ref) + -> OutputIt { + return write(out, s, specs); +} +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, const Char* s, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, locale_ref) + -> OutputIt { + return specs.type != presentation_type::pointer + ? write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(s), specs, {}) + : write_ptr<Char>(out, bit_cast<uintptr_t>(s), &specs); +} + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integral<T>::value && + !std::is_same<T, bool>::value && + !std::is_same<T, Char>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, T value) -> OutputIt { + auto abs_value = static_cast<uint32_or_64_or_128_t<T>>(value); + bool negative = is_negative(value); + // Don't do -abs_value since it trips unsigned-integer-overflow sanitizer. + if (negative) abs_value = ~abs_value + 1; + int num_digits = count_digits(abs_value); + auto size = (negative ? 1 : 0) + static_cast<size_t>(num_digits); + auto it = reserve(out, size); + if (auto ptr = to_pointer<Char>(it, size)) { + if (negative) *ptr++ = static_cast<Char>('-'); + format_decimal<Char>(ptr, abs_value, num_digits); + return out; + } + if (negative) *it++ = static_cast<Char>('-'); + it = format_decimal<Char>(it, abs_value, num_digits).end; + return base_iterator(out, it); +} + +// DEPRECATED! +template <typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_align(const Char* begin, const Char* end, + format_specs<Char>& specs) -> const Char* { + FMT_ASSERT(begin != end, ""); + auto align = align::none; + auto p = begin + code_point_length(begin); + if (end - p <= 0) p = begin; + for (;;) { + switch (to_ascii(*p)) { + case '<': + align = align::left; + break; + case '>': + align = align::right; + break; + case '^': + align = align::center; + break; } - if (group == groups.cend()) size += sep_size * ((n - 1) / groups.back()); - char digits[40]; - format_decimal(digits, abs_value, num_digits); - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - size += static_cast<int>(prefix_size); - const auto usize = to_unsigned(size); - buffer.resize(usize); - basic_string_view<Char> s(&sep, sep_size); - // Index of a decimal digit with the least significant digit having index 0. - int digit_index = 0; - group = groups.cbegin(); - auto p = buffer.data() + size - 1; - for (int i = num_digits - 1; i > 0; --i) { - *p-- = static_cast<Char>(digits[i]); - if (*group <= 0 || ++digit_index % *group != 0 || - *group == max_value<char>()) - continue; - if (group + 1 != groups.cend()) { - digit_index = 0; - ++group; + if (align != align::none) { + if (p != begin) { + auto c = *begin; + if (c == '}') return begin; + if (c == '{') { + throw_format_error("invalid fill character '{'"); + return begin; + } + specs.fill = {begin, to_unsigned(p - begin)}; + begin = p + 1; + } else { + ++begin; } - std::uninitialized_copy(s.data(), s.data() + s.size(), - make_checked(p, s.size())); - p -= s.size(); + break; + } else if (p == begin) { + break; } - *p-- = static_cast<Char>(*digits); - if (prefix_size != 0) *p = static_cast<Char>('-'); - auto data = buffer.data(); - out = write_padded<align::right>( - out, specs, usize, usize, - [=](iterator it) { return copy_str<Char>(data, data + size, it); }); + p = begin; } + specs.align = align; + return begin; +} - void on_chr() { *out++ = static_cast<Char>(abs_value); } +// A floating-point presentation format. +enum class float_format : unsigned char { + general, // General: exponent notation or fixed point based on magnitude. + exp, // Exponent notation with the default precision of 6, e.g. 1.2e-3. + fixed, // Fixed point with the default precision of 6, e.g. 0.0012. + hex +}; - FMT_NORETURN void on_error() { - FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid type specifier")); - } +struct float_specs { + int precision; + float_format format : 8; + sign_t sign : 8; + bool upper : 1; + bool locale : 1; + bool binary32 : 1; + bool showpoint : 1; }; +template <typename ErrorHandler = error_handler, typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_float_type_spec(const format_specs<Char>& specs, + ErrorHandler&& eh = {}) + -> float_specs { + auto result = float_specs(); + result.showpoint = specs.alt; + result.locale = specs.localized; + switch (specs.type) { + case presentation_type::none: + result.format = float_format::general; + break; + case presentation_type::general_upper: + result.upper = true; + FMT_FALLTHROUGH; + case presentation_type::general_lower: + result.format = float_format::general; + break; + case presentation_type::exp_upper: + result.upper = true; + FMT_FALLTHROUGH; + case presentation_type::exp_lower: + result.format = float_format::exp; + result.showpoint |= specs.precision != 0; + break; + case presentation_type::fixed_upper: + result.upper = true; + FMT_FALLTHROUGH; + case presentation_type::fixed_lower: + result.format = float_format::fixed; + result.showpoint |= specs.precision != 0; + break; + case presentation_type::hexfloat_upper: + result.upper = true; + FMT_FALLTHROUGH; + case presentation_type::hexfloat_lower: + result.format = float_format::hex; + break; + default: + eh.on_error("invalid format specifier"); + break; + } + return result; +} + template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write_nonfinite(OutputIt out, bool isinf, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs, - const float_specs& fspecs) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto write_nonfinite(OutputIt out, bool isnan, + format_specs<Char> specs, + const float_specs& fspecs) -> OutputIt { auto str = - isinf ? (fspecs.upper ? "INF" : "inf") : (fspecs.upper ? "NAN" : "nan"); + isnan ? (fspecs.upper ? "NAN" : "nan") : (fspecs.upper ? "INF" : "inf"); constexpr size_t str_size = 3; auto sign = fspecs.sign; auto size = str_size + (sign ? 1 : 0); - using iterator = remove_reference_t<decltype(reserve(out, 0))>; - return write_padded(out, specs, size, [=](iterator it) { - if (sign) *it++ = static_cast<Char>(data::signs[sign]); + // Replace '0'-padding with space for non-finite values. + const bool is_zero_fill = + specs.fill.size() == 1 && *specs.fill.data() == static_cast<Char>('0'); + if (is_zero_fill) specs.fill[0] = static_cast<Char>(' '); + return write_padded(out, specs, size, [=](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) { + if (sign) *it++ = detail::sign<Char>(sign); return copy_str<Char>(str, str + str_size, it); }); } @@ -1738,76 +2500,120 @@ struct big_decimal_fp { int exponent; }; -inline int get_significand_size(const big_decimal_fp& fp) { - return fp.significand_size; +constexpr auto get_significand_size(const big_decimal_fp& f) -> int { + return f.significand_size; } template <typename T> -inline int get_significand_size(const dragonbox::decimal_fp<T>& fp) { - return count_digits(fp.significand); +inline auto get_significand_size(const dragonbox::decimal_fp<T>& f) -> int { + return count_digits(f.significand); } template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -inline OutputIt write_significand(OutputIt out, const char* significand, - int& significand_size) { +constexpr auto write_significand(OutputIt out, const char* significand, + int significand_size) -> OutputIt { return copy_str<Char>(significand, significand + significand_size, out); } template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename UInt> -inline OutputIt write_significand(OutputIt out, UInt significand, - int significand_size) { +inline auto write_significand(OutputIt out, UInt significand, + int significand_size) -> OutputIt { return format_decimal<Char>(out, significand, significand_size).end; } +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, typename Grouping> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto write_significand(OutputIt out, T significand, + int significand_size, int exponent, + const Grouping& grouping) -> OutputIt { + if (!grouping.has_separator()) { + out = write_significand<Char>(out, significand, significand_size); + return detail::fill_n(out, exponent, static_cast<Char>('0')); + } + auto buffer = memory_buffer(); + write_significand<char>(appender(buffer), significand, significand_size); + detail::fill_n(appender(buffer), exponent, '0'); + return grouping.apply(out, string_view(buffer.data(), buffer.size())); +} template <typename Char, typename UInt, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<UInt>::value)> -inline Char* write_significand(Char* out, UInt significand, - int significand_size, int integral_size, - Char decimal_point) { +inline auto write_significand(Char* out, UInt significand, int significand_size, + int integral_size, Char decimal_point) -> Char* { if (!decimal_point) return format_decimal(out, significand, significand_size).end; - auto end = format_decimal(out + 1, significand, significand_size).end; - if (integral_size == 1) - out[0] = out[1]; - else - std::copy_n(out + 1, integral_size, out); - out[integral_size] = decimal_point; + out += significand_size + 1; + Char* end = out; + int floating_size = significand_size - integral_size; + for (int i = floating_size / 2; i > 0; --i) { + out -= 2; + copy2(out, digits2(static_cast<std::size_t>(significand % 100))); + significand /= 100; + } + if (floating_size % 2 != 0) { + *--out = static_cast<Char>('0' + significand % 10); + significand /= 10; + } + *--out = decimal_point; + format_decimal(out - integral_size, significand, integral_size); return end; } template <typename OutputIt, typename UInt, typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_pointer<remove_cvref_t<OutputIt>>::value)> -inline OutputIt write_significand(OutputIt out, UInt significand, - int significand_size, int integral_size, - Char decimal_point) { +inline auto write_significand(OutputIt out, UInt significand, + int significand_size, int integral_size, + Char decimal_point) -> OutputIt { // Buffer is large enough to hold digits (digits10 + 1) and a decimal point. Char buffer[digits10<UInt>() + 2]; auto end = write_significand(buffer, significand, significand_size, integral_size, decimal_point); - return detail::copy_str<Char>(buffer, end, out); + return detail::copy_str_noinline<Char>(buffer, end, out); } template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -inline OutputIt write_significand(OutputIt out, const char* significand, - int significand_size, int integral_size, - Char decimal_point) { - out = detail::copy_str<Char>(significand, significand + integral_size, out); +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write_significand(OutputIt out, const char* significand, + int significand_size, int integral_size, + Char decimal_point) -> OutputIt { + out = detail::copy_str_noinline<Char>(significand, + significand + integral_size, out); if (!decimal_point) return out; *out++ = decimal_point; - return detail::copy_str<Char>(significand + integral_size, - significand + significand_size, out); + return detail::copy_str_noinline<Char>(significand + integral_size, + significand + significand_size, out); } -template <typename OutputIt, typename DecimalFP, typename Char> -OutputIt write_float(OutputIt out, const DecimalFP& fp, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs, float_specs fspecs, - Char decimal_point) { - auto significand = fp.significand; - int significand_size = get_significand_size(fp); - static const Char zero = static_cast<Char>('0'); +template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename T, typename Grouping> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto write_significand(OutputIt out, T significand, + int significand_size, int integral_size, + Char decimal_point, + const Grouping& grouping) -> OutputIt { + if (!grouping.has_separator()) { + return write_significand(out, significand, significand_size, integral_size, + decimal_point); + } + auto buffer = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); + write_significand(buffer_appender<Char>(buffer), significand, + significand_size, integral_size, decimal_point); + grouping.apply( + out, basic_string_view<Char>(buffer.data(), to_unsigned(integral_size))); + return detail::copy_str_noinline<Char>(buffer.data() + integral_size, + buffer.end(), out); +} + +template <typename OutputIt, typename DecimalFP, typename Char, + typename Grouping = digit_grouping<Char>> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto do_write_float(OutputIt out, const DecimalFP& f, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, + float_specs fspecs, locale_ref loc) + -> OutputIt { + auto significand = f.significand; + int significand_size = get_significand_size(f); + const Char zero = static_cast<Char>('0'); auto sign = fspecs.sign; size_t size = to_unsigned(significand_size) + (sign ? 1 : 0); - using iterator = remove_reference_t<decltype(reserve(out, 0))>; + using iterator = reserve_iterator<OutputIt>; + + Char decimal_point = + fspecs.locale ? detail::decimal_point<Char>(loc) : static_cast<Char>('.'); - int output_exp = fp.exponent + significand_size - 1; + int output_exp = f.exponent + significand_size - 1; auto use_exp_format = [=]() { if (fspecs.format == float_format::exp) return true; if (fspecs.format != float_format::general) return false; @@ -1820,7 +2626,8 @@ OutputIt write_float(OutputIt out, const DecimalFP& fp, if (use_exp_format()) { int num_zeros = 0; if (fspecs.showpoint) { - num_zeros = (std::max)(fspecs.precision - significand_size, 0); + num_zeros = fspecs.precision - significand_size; + if (num_zeros < 0) num_zeros = 0; size += to_unsigned(num_zeros); } else if (significand_size == 1) { decimal_point = Char(); @@ -1832,11 +2639,11 @@ OutputIt write_float(OutputIt out, const DecimalFP& fp, size += to_unsigned((decimal_point ? 1 : 0) + 2 + exp_digits); char exp_char = fspecs.upper ? 'E' : 'e'; auto write = [=](iterator it) { - if (sign) *it++ = static_cast<Char>(data::signs[sign]); + if (sign) *it++ = detail::sign<Char>(sign); // Insert a decimal point after the first digit and add an exponent. it = write_significand(it, significand, significand_size, 1, decimal_point); - if (num_zeros > 0) it = std::fill_n(it, num_zeros, zero); + if (num_zeros > 0) it = detail::fill_n(it, num_zeros, zero); *it++ = static_cast<Char>(exp_char); return write_exponent<Char>(output_exp, it); }; @@ -1844,36 +2651,38 @@ OutputIt write_float(OutputIt out, const DecimalFP& fp, : base_iterator(out, write(reserve(out, size))); } - int exp = fp.exponent + significand_size; - if (fp.exponent >= 0) { + int exp = f.exponent + significand_size; + if (f.exponent >= 0) { // 1234e5 -> 123400000[.0+] - size += to_unsigned(fp.exponent); + size += to_unsigned(f.exponent); int num_zeros = fspecs.precision - exp; -#ifdef FMT_FUZZ - if (num_zeros > 5000) - throw std::runtime_error("fuzz mode - avoiding excessive cpu use"); -#endif + abort_fuzzing_if(num_zeros > 5000); if (fspecs.showpoint) { - if (num_zeros <= 0 && fspecs.format != float_format::fixed) num_zeros = 1; + ++size; + if (num_zeros <= 0 && fspecs.format != float_format::fixed) num_zeros = 0; if (num_zeros > 0) size += to_unsigned(num_zeros); } + auto grouping = Grouping(loc, fspecs.locale); + size += to_unsigned(grouping.count_separators(exp)); return write_padded<align::right>(out, specs, size, [&](iterator it) { - if (sign) *it++ = static_cast<Char>(data::signs[sign]); - it = write_significand<Char>(it, significand, significand_size); - it = std::fill_n(it, fp.exponent, zero); + if (sign) *it++ = detail::sign<Char>(sign); + it = write_significand<Char>(it, significand, significand_size, + f.exponent, grouping); if (!fspecs.showpoint) return it; *it++ = decimal_point; - return num_zeros > 0 ? std::fill_n(it, num_zeros, zero) : it; + return num_zeros > 0 ? detail::fill_n(it, num_zeros, zero) : it; }); } else if (exp > 0) { // 1234e-2 -> 12.34[0+] int num_zeros = fspecs.showpoint ? fspecs.precision - significand_size : 0; size += 1 + to_unsigned(num_zeros > 0 ? num_zeros : 0); + auto grouping = Grouping(loc, fspecs.locale); + size += to_unsigned(grouping.count_separators(exp)); return write_padded<align::right>(out, specs, size, [&](iterator it) { - if (sign) *it++ = static_cast<Char>(data::signs[sign]); + if (sign) *it++ = detail::sign<Char>(sign); it = write_significand(it, significand, significand_size, exp, - decimal_point); - return num_zeros > 0 ? std::fill_n(it, num_zeros, zero) : it; + decimal_point, grouping); + return num_zeros > 0 ? detail::fill_n(it, num_zeros, zero) : it; }); } // 1234e-6 -> 0.001234 @@ -1882,37 +2691,914 @@ OutputIt write_float(OutputIt out, const DecimalFP& fp, fspecs.precision < num_zeros) { num_zeros = fspecs.precision; } - size += 2 + to_unsigned(num_zeros); + bool pointy = num_zeros != 0 || significand_size != 0 || fspecs.showpoint; + size += 1 + (pointy ? 1 : 0) + to_unsigned(num_zeros); return write_padded<align::right>(out, specs, size, [&](iterator it) { - if (sign) *it++ = static_cast<Char>(data::signs[sign]); + if (sign) *it++ = detail::sign<Char>(sign); *it++ = zero; - if (num_zeros == 0 && significand_size == 0 && !fspecs.showpoint) return it; + if (!pointy) return it; *it++ = decimal_point; - it = std::fill_n(it, num_zeros, zero); + it = detail::fill_n(it, num_zeros, zero); return write_significand<Char>(it, significand, significand_size); }); } -template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value)> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, T value, basic_format_specs<Char> specs, - locale_ref loc = {}) { - if (const_check(!is_supported_floating_point(value))) return out; +template <typename Char> class fallback_digit_grouping { + public: + constexpr fallback_digit_grouping(locale_ref, bool) {} + + constexpr bool has_separator() const { return false; } + + constexpr int count_separators(int) const { return 0; } + + template <typename Out, typename C> + constexpr Out apply(Out out, basic_string_view<C>) const { + return out; + } +}; + +template <typename OutputIt, typename DecimalFP, typename Char> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto write_float(OutputIt out, const DecimalFP& f, + const format_specs<Char>& specs, + float_specs fspecs, locale_ref loc) + -> OutputIt { + if (is_constant_evaluated()) { + return do_write_float<OutputIt, DecimalFP, Char, + fallback_digit_grouping<Char>>(out, f, specs, fspecs, + loc); + } else { + return do_write_float(out, f, specs, fspecs, loc); + } +} + +template <typename T> constexpr bool isnan(T value) { + return !(value >= value); // std::isnan doesn't support __float128. +} + +template <typename T, typename Enable = void> +struct has_isfinite : std::false_type {}; + +template <typename T> +struct has_isfinite<T, enable_if_t<sizeof(std::isfinite(T())) != 0>> + : std::true_type {}; + +template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value&& + has_isfinite<T>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bool isfinite(T value) { + constexpr T inf = T(std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity()); + if (is_constant_evaluated(true)) + return !detail::isnan(value) && value < inf && value > -inf; + return std::isfinite(value); +} +template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!has_isfinite<T>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR bool isfinite(T value) { + T inf = T(std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity()); + // std::isfinite doesn't support __float128. + return !detail::isnan(value) && value < inf && value > -inf; +} + +template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_floating_point<T>::value)> +FMT_INLINE FMT_CONSTEXPR bool signbit(T value) { + if (is_constant_evaluated()) { +#ifdef __cpp_if_constexpr + if constexpr (std::numeric_limits<double>::is_iec559) { + auto bits = detail::bit_cast<uint64_t>(static_cast<double>(value)); + return (bits >> (num_bits<uint64_t>() - 1)) != 0; + } +#endif + } + return std::signbit(static_cast<double>(value)); +} + +inline FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void adjust_precision(int& precision, int exp10) { + // Adjust fixed precision by exponent because it is relative to decimal + // point. + if (exp10 > 0 && precision > max_value<int>() - exp10) + FMT_THROW(format_error("number is too big")); + precision += exp10; +} + +class bigint { + private: + // A bigint is stored as an array of bigits (big digits), with bigit at index + // 0 being the least significant one. + using bigit = uint32_t; + using double_bigit = uint64_t; + enum { bigits_capacity = 32 }; + basic_memory_buffer<bigit, bigits_capacity> bigits_; + int exp_; + + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bigit operator[](int index) const { + return bigits_[to_unsigned(index)]; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bigit& operator[](int index) { + return bigits_[to_unsigned(index)]; + } + + static constexpr const int bigit_bits = num_bits<bigit>(); + + friend struct formatter<bigint>; + + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void subtract_bigits(int index, bigit other, bigit& borrow) { + auto result = static_cast<double_bigit>((*this)[index]) - other - borrow; + (*this)[index] = static_cast<bigit>(result); + borrow = static_cast<bigit>(result >> (bigit_bits * 2 - 1)); + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void remove_leading_zeros() { + int num_bigits = static_cast<int>(bigits_.size()) - 1; + while (num_bigits > 0 && (*this)[num_bigits] == 0) --num_bigits; + bigits_.resize(to_unsigned(num_bigits + 1)); + } + + // Computes *this -= other assuming aligned bigints and *this >= other. + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void subtract_aligned(const bigint& other) { + FMT_ASSERT(other.exp_ >= exp_, "unaligned bigints"); + FMT_ASSERT(compare(*this, other) >= 0, ""); + bigit borrow = 0; + int i = other.exp_ - exp_; + for (size_t j = 0, n = other.bigits_.size(); j != n; ++i, ++j) + subtract_bigits(i, other.bigits_[j], borrow); + while (borrow > 0) subtract_bigits(i, 0, borrow); + remove_leading_zeros(); + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void multiply(uint32_t value) { + const double_bigit wide_value = value; + bigit carry = 0; + for (size_t i = 0, n = bigits_.size(); i < n; ++i) { + double_bigit result = bigits_[i] * wide_value + carry; + bigits_[i] = static_cast<bigit>(result); + carry = static_cast<bigit>(result >> bigit_bits); + } + if (carry != 0) bigits_.push_back(carry); + } + + template <typename UInt, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<UInt, uint64_t>::value || + std::is_same<UInt, uint128_t>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void multiply(UInt value) { + using half_uint = + conditional_t<std::is_same<UInt, uint128_t>::value, uint64_t, uint32_t>; + const int shift = num_bits<half_uint>() - bigit_bits; + const UInt lower = static_cast<half_uint>(value); + const UInt upper = value >> num_bits<half_uint>(); + UInt carry = 0; + for (size_t i = 0, n = bigits_.size(); i < n; ++i) { + UInt result = lower * bigits_[i] + static_cast<bigit>(carry); + carry = (upper * bigits_[i] << shift) + (result >> bigit_bits) + + (carry >> bigit_bits); + bigits_[i] = static_cast<bigit>(result); + } + while (carry != 0) { + bigits_.push_back(static_cast<bigit>(carry)); + carry >>= bigit_bits; + } + } + + template <typename UInt, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<UInt, uint64_t>::value || + std::is_same<UInt, uint128_t>::value)> + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void assign(UInt n) { + size_t num_bigits = 0; + do { + bigits_[num_bigits++] = static_cast<bigit>(n); + n >>= bigit_bits; + } while (n != 0); + bigits_.resize(num_bigits); + exp_ = 0; + } + + public: + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bigint() : exp_(0) {} + explicit bigint(uint64_t n) { assign(n); } + + bigint(const bigint&) = delete; + void operator=(const bigint&) = delete; + + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void assign(const bigint& other) { + auto size = other.bigits_.size(); + bigits_.resize(size); + auto data = other.bigits_.data(); + copy_str<bigit>(data, data + size, bigits_.data()); + exp_ = other.exp_; + } + + template <typename Int> FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void operator=(Int n) { + FMT_ASSERT(n > 0, ""); + assign(uint64_or_128_t<Int>(n)); + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 int num_bigits() const { + return static_cast<int>(bigits_.size()) + exp_; + } + + FMT_NOINLINE FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bigint& operator<<=(int shift) { + FMT_ASSERT(shift >= 0, ""); + exp_ += shift / bigit_bits; + shift %= bigit_bits; + if (shift == 0) return *this; + bigit carry = 0; + for (size_t i = 0, n = bigits_.size(); i < n; ++i) { + bigit c = bigits_[i] >> (bigit_bits - shift); + bigits_[i] = (bigits_[i] << shift) + carry; + carry = c; + } + if (carry != 0) bigits_.push_back(carry); + return *this; + } + + template <typename Int> FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bigint& operator*=(Int value) { + FMT_ASSERT(value > 0, ""); + multiply(uint32_or_64_or_128_t<Int>(value)); + return *this; + } + + friend FMT_CONSTEXPR20 int compare(const bigint& lhs, const bigint& rhs) { + int num_lhs_bigits = lhs.num_bigits(), num_rhs_bigits = rhs.num_bigits(); + if (num_lhs_bigits != num_rhs_bigits) + return num_lhs_bigits > num_rhs_bigits ? 1 : -1; + int i = static_cast<int>(lhs.bigits_.size()) - 1; + int j = static_cast<int>(rhs.bigits_.size()) - 1; + int end = i - j; + if (end < 0) end = 0; + for (; i >= end; --i, --j) { + bigit lhs_bigit = lhs[i], rhs_bigit = rhs[j]; + if (lhs_bigit != rhs_bigit) return lhs_bigit > rhs_bigit ? 1 : -1; + } + if (i != j) return i > j ? 1 : -1; + return 0; + } + + // Returns compare(lhs1 + lhs2, rhs). + friend FMT_CONSTEXPR20 int add_compare(const bigint& lhs1, const bigint& lhs2, + const bigint& rhs) { + auto minimum = [](int a, int b) { return a < b ? a : b; }; + auto maximum = [](int a, int b) { return a > b ? a : b; }; + int max_lhs_bigits = maximum(lhs1.num_bigits(), lhs2.num_bigits()); + int num_rhs_bigits = rhs.num_bigits(); + if (max_lhs_bigits + 1 < num_rhs_bigits) return -1; + if (max_lhs_bigits > num_rhs_bigits) return 1; + auto get_bigit = [](const bigint& n, int i) -> bigit { + return i >= n.exp_ && i < n.num_bigits() ? n[i - n.exp_] : 0; + }; + double_bigit borrow = 0; + int min_exp = minimum(minimum(lhs1.exp_, lhs2.exp_), rhs.exp_); + for (int i = num_rhs_bigits - 1; i >= min_exp; --i) { + double_bigit sum = + static_cast<double_bigit>(get_bigit(lhs1, i)) + get_bigit(lhs2, i); + bigit rhs_bigit = get_bigit(rhs, i); + if (sum > rhs_bigit + borrow) return 1; + borrow = rhs_bigit + borrow - sum; + if (borrow > 1) return -1; + borrow <<= bigit_bits; + } + return borrow != 0 ? -1 : 0; + } + + // Assigns pow(10, exp) to this bigint. + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void assign_pow10(int exp) { + FMT_ASSERT(exp >= 0, ""); + if (exp == 0) return *this = 1; + // Find the top bit. + int bitmask = 1; + while (exp >= bitmask) bitmask <<= 1; + bitmask >>= 1; + // pow(10, exp) = pow(5, exp) * pow(2, exp). First compute pow(5, exp) by + // repeated squaring and multiplication. + *this = 5; + bitmask >>= 1; + while (bitmask != 0) { + square(); + if ((exp & bitmask) != 0) *this *= 5; + bitmask >>= 1; + } + *this <<= exp; // Multiply by pow(2, exp) by shifting. + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void square() { + int num_bigits = static_cast<int>(bigits_.size()); + int num_result_bigits = 2 * num_bigits; + basic_memory_buffer<bigit, bigits_capacity> n(std::move(bigits_)); + bigits_.resize(to_unsigned(num_result_bigits)); + auto sum = uint128_t(); + for (int bigit_index = 0; bigit_index < num_bigits; ++bigit_index) { + // Compute bigit at position bigit_index of the result by adding + // cross-product terms n[i] * n[j] such that i + j == bigit_index. + for (int i = 0, j = bigit_index; j >= 0; ++i, --j) { + // Most terms are multiplied twice which can be optimized in the future. + sum += static_cast<double_bigit>(n[i]) * n[j]; + } + (*this)[bigit_index] = static_cast<bigit>(sum); + sum >>= num_bits<bigit>(); // Compute the carry. + } + // Do the same for the top half. + for (int bigit_index = num_bigits; bigit_index < num_result_bigits; + ++bigit_index) { + for (int j = num_bigits - 1, i = bigit_index - j; i < num_bigits;) + sum += static_cast<double_bigit>(n[i++]) * n[j--]; + (*this)[bigit_index] = static_cast<bigit>(sum); + sum >>= num_bits<bigit>(); + } + remove_leading_zeros(); + exp_ *= 2; + } + + // If this bigint has a bigger exponent than other, adds trailing zero to make + // exponents equal. This simplifies some operations such as subtraction. + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void align(const bigint& other) { + int exp_difference = exp_ - other.exp_; + if (exp_difference <= 0) return; + int num_bigits = static_cast<int>(bigits_.size()); + bigits_.resize(to_unsigned(num_bigits + exp_difference)); + for (int i = num_bigits - 1, j = i + exp_difference; i >= 0; --i, --j) + bigits_[j] = bigits_[i]; + std::uninitialized_fill_n(bigits_.data(), exp_difference, 0u); + exp_ -= exp_difference; + } + + // Divides this bignum by divisor, assigning the remainder to this and + // returning the quotient. + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 int divmod_assign(const bigint& divisor) { + FMT_ASSERT(this != &divisor, ""); + if (compare(*this, divisor) < 0) return 0; + FMT_ASSERT(divisor.bigits_[divisor.bigits_.size() - 1u] != 0, ""); + align(divisor); + int quotient = 0; + do { + subtract_aligned(divisor); + ++quotient; + } while (compare(*this, divisor) >= 0); + return quotient; + } +}; + +// format_dragon flags. +enum dragon { + predecessor_closer = 1, + fixup = 2, // Run fixup to correct exp10 which can be off by one. + fixed = 4, +}; + +// Formats a floating-point number using a variation of the Fixed-Precision +// Positive Floating-Point Printout ((FPP)^2) algorithm by Steele & White: +// https://fmt.dev/papers/p372-steele.pdf. +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 inline void format_dragon(basic_fp<uint128_t> value, + unsigned flags, int num_digits, + buffer<char>& buf, int& exp10) { + bigint numerator; // 2 * R in (FPP)^2. + bigint denominator; // 2 * S in (FPP)^2. + // lower and upper are differences between value and corresponding boundaries. + bigint lower; // (M^- in (FPP)^2). + bigint upper_store; // upper's value if different from lower. + bigint* upper = nullptr; // (M^+ in (FPP)^2). + // Shift numerator and denominator by an extra bit or two (if lower boundary + // is closer) to make lower and upper integers. This eliminates multiplication + // by 2 during later computations. + bool is_predecessor_closer = (flags & dragon::predecessor_closer) != 0; + int shift = is_predecessor_closer ? 2 : 1; + if (value.e >= 0) { + numerator = value.f; + numerator <<= value.e + shift; + lower = 1; + lower <<= value.e; + if (is_predecessor_closer) { + upper_store = 1; + upper_store <<= value.e + 1; + upper = &upper_store; + } + denominator.assign_pow10(exp10); + denominator <<= shift; + } else if (exp10 < 0) { + numerator.assign_pow10(-exp10); + lower.assign(numerator); + if (is_predecessor_closer) { + upper_store.assign(numerator); + upper_store <<= 1; + upper = &upper_store; + } + numerator *= value.f; + numerator <<= shift; + denominator = 1; + denominator <<= shift - value.e; + } else { + numerator = value.f; + numerator <<= shift; + denominator.assign_pow10(exp10); + denominator <<= shift - value.e; + lower = 1; + if (is_predecessor_closer) { + upper_store = 1ULL << 1; + upper = &upper_store; + } + } + int even = static_cast<int>((value.f & 1) == 0); + if (!upper) upper = &lower; + bool shortest = num_digits < 0; + if ((flags & dragon::fixup) != 0) { + if (add_compare(numerator, *upper, denominator) + even <= 0) { + --exp10; + numerator *= 10; + if (num_digits < 0) { + lower *= 10; + if (upper != &lower) *upper *= 10; + } + } + if ((flags & dragon::fixed) != 0) adjust_precision(num_digits, exp10 + 1); + } + // Invariant: value == (numerator / denominator) * pow(10, exp10). + if (shortest) { + // Generate the shortest representation. + num_digits = 0; + char* data = buf.data(); + for (;;) { + int digit = numerator.divmod_assign(denominator); + bool low = compare(numerator, lower) - even < 0; // numerator <[=] lower. + // numerator + upper >[=] pow10: + bool high = add_compare(numerator, *upper, denominator) + even > 0; + data[num_digits++] = static_cast<char>('0' + digit); + if (low || high) { + if (!low) { + ++data[num_digits - 1]; + } else if (high) { + int result = add_compare(numerator, numerator, denominator); + // Round half to even. + if (result > 0 || (result == 0 && (digit % 2) != 0)) + ++data[num_digits - 1]; + } + buf.try_resize(to_unsigned(num_digits)); + exp10 -= num_digits - 1; + return; + } + numerator *= 10; + lower *= 10; + if (upper != &lower) *upper *= 10; + } + } + // Generate the given number of digits. + exp10 -= num_digits - 1; + if (num_digits <= 0) { + denominator *= 10; + auto digit = add_compare(numerator, numerator, denominator) > 0 ? '1' : '0'; + buf.push_back(digit); + return; + } + buf.try_resize(to_unsigned(num_digits)); + for (int i = 0; i < num_digits - 1; ++i) { + int digit = numerator.divmod_assign(denominator); + buf[i] = static_cast<char>('0' + digit); + numerator *= 10; + } + int digit = numerator.divmod_assign(denominator); + auto result = add_compare(numerator, numerator, denominator); + if (result > 0 || (result == 0 && (digit % 2) != 0)) { + if (digit == 9) { + const auto overflow = '0' + 10; + buf[num_digits - 1] = overflow; + // Propagate the carry. + for (int i = num_digits - 1; i > 0 && buf[i] == overflow; --i) { + buf[i] = '0'; + ++buf[i - 1]; + } + if (buf[0] == overflow) { + buf[0] = '1'; + if ((flags & dragon::fixed) != 0) + buf.push_back('0'); + else + ++exp10; + } + return; + } + ++digit; + } + buf[num_digits - 1] = static_cast<char>('0' + digit); +} + +// Formats a floating-point number using the hexfloat format. +template <typename Float, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_double_double<Float>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void format_hexfloat(Float value, int precision, + float_specs specs, buffer<char>& buf) { + // float is passed as double to reduce the number of instantiations and to + // simplify implementation. + static_assert(!std::is_same<Float, float>::value, ""); + + using info = dragonbox::float_info<Float>; + + // Assume Float is in the format [sign][exponent][significand]. + using carrier_uint = typename info::carrier_uint; + + constexpr auto num_float_significand_bits = + detail::num_significand_bits<Float>(); + + basic_fp<carrier_uint> f(value); + f.e += num_float_significand_bits; + if (!has_implicit_bit<Float>()) --f.e; + + constexpr auto num_fraction_bits = + num_float_significand_bits + (has_implicit_bit<Float>() ? 1 : 0); + constexpr auto num_xdigits = (num_fraction_bits + 3) / 4; + + constexpr auto leading_shift = ((num_xdigits - 1) * 4); + const auto leading_mask = carrier_uint(0xF) << leading_shift; + const auto leading_xdigit = + static_cast<uint32_t>((f.f & leading_mask) >> leading_shift); + if (leading_xdigit > 1) f.e -= (32 - countl_zero(leading_xdigit) - 1); + + int print_xdigits = num_xdigits - 1; + if (precision >= 0 && print_xdigits > precision) { + const int shift = ((print_xdigits - precision - 1) * 4); + const auto mask = carrier_uint(0xF) << shift; + const auto v = static_cast<uint32_t>((f.f & mask) >> shift); + + if (v >= 8) { + const auto inc = carrier_uint(1) << (shift + 4); + f.f += inc; + f.f &= ~(inc - 1); + } + + // Check long double overflow + if (!has_implicit_bit<Float>()) { + const auto implicit_bit = carrier_uint(1) << num_float_significand_bits; + if ((f.f & implicit_bit) == implicit_bit) { + f.f >>= 4; + f.e += 4; + } + } + + print_xdigits = precision; + } + + char xdigits[num_bits<carrier_uint>() / 4]; + detail::fill_n(xdigits, sizeof(xdigits), '0'); + format_uint<4>(xdigits, f.f, num_xdigits, specs.upper); + + // Remove zero tail + while (print_xdigits > 0 && xdigits[print_xdigits] == '0') --print_xdigits; + + buf.push_back('0'); + buf.push_back(specs.upper ? 'X' : 'x'); + buf.push_back(xdigits[0]); + if (specs.showpoint || print_xdigits > 0 || print_xdigits < precision) + buf.push_back('.'); + buf.append(xdigits + 1, xdigits + 1 + print_xdigits); + for (; print_xdigits < precision; ++print_xdigits) buf.push_back('0'); + + buf.push_back(specs.upper ? 'P' : 'p'); + + uint32_t abs_e; + if (f.e < 0) { + buf.push_back('-'); + abs_e = static_cast<uint32_t>(-f.e); + } else { + buf.push_back('+'); + abs_e = static_cast<uint32_t>(f.e); + } + format_decimal<char>(appender(buf), abs_e, detail::count_digits(abs_e)); +} + +template <typename Float, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_double_double<Float>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void format_hexfloat(Float value, int precision, + float_specs specs, buffer<char>& buf) { + format_hexfloat(static_cast<double>(value), precision, specs, buf); +} + +constexpr uint32_t fractional_part_rounding_thresholds(int index) { + // For checking rounding thresholds. + // The kth entry is chosen to be the smallest integer such that the + // upper 32-bits of 10^(k+1) times it is strictly bigger than 5 * 10^k. + // It is equal to ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^(k + 1)). + // These are stored in a string literal because we cannot have static arrays + // in constexpr functions and non-static ones are poorly optimized. + return U"\x9999999a\x828f5c29\x80418938\x80068db9\x8000a7c6\x800010c7" + U"\x800001ae\x8000002b"[index]; +} + +template <typename Float> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto format_float(Float value, int precision, float_specs specs, + buffer<char>& buf) -> int { + // float is passed as double to reduce the number of instantiations. + static_assert(!std::is_same<Float, float>::value, ""); + FMT_ASSERT(value >= 0, "value is negative"); + auto converted_value = convert_float(value); + + const bool fixed = specs.format == float_format::fixed; + if (value <= 0) { // <= instead of == to silence a warning. + if (precision <= 0 || !fixed) { + buf.push_back('0'); + return 0; + } + buf.try_resize(to_unsigned(precision)); + fill_n(buf.data(), precision, '0'); + return -precision; + } + + int exp = 0; + bool use_dragon = true; + unsigned dragon_flags = 0; + if (!is_fast_float<Float>() || is_constant_evaluated()) { + const auto inv_log2_10 = 0.3010299956639812; // 1 / log2(10) + using info = dragonbox::float_info<decltype(converted_value)>; + const auto f = basic_fp<typename info::carrier_uint>(converted_value); + // Compute exp, an approximate power of 10, such that + // 10^(exp - 1) <= value < 10^exp or 10^exp <= value < 10^(exp + 1). + // This is based on log10(value) == log2(value) / log2(10) and approximation + // of log2(value) by e + num_fraction_bits idea from double-conversion. + auto e = (f.e + count_digits<1>(f.f) - 1) * inv_log2_10 - 1e-10; + exp = static_cast<int>(e); + if (e > exp) ++exp; // Compute ceil. + dragon_flags = dragon::fixup; + } else if (precision < 0) { + // Use Dragonbox for the shortest format. + if (specs.binary32) { + auto dec = dragonbox::to_decimal(static_cast<float>(value)); + write<char>(buffer_appender<char>(buf), dec.significand); + return dec.exponent; + } + auto dec = dragonbox::to_decimal(static_cast<double>(value)); + write<char>(buffer_appender<char>(buf), dec.significand); + return dec.exponent; + } else { + // Extract significand bits and exponent bits. + using info = dragonbox::float_info<double>; + auto br = bit_cast<uint64_t>(static_cast<double>(value)); + + const uint64_t significand_mask = + (static_cast<uint64_t>(1) << num_significand_bits<double>()) - 1; + uint64_t significand = (br & significand_mask); + int exponent = static_cast<int>((br & exponent_mask<double>()) >> + num_significand_bits<double>()); + + if (exponent != 0) { // Check if normal. + exponent -= exponent_bias<double>() + num_significand_bits<double>(); + significand |= + (static_cast<uint64_t>(1) << num_significand_bits<double>()); + significand <<= 1; + } else { + // Normalize subnormal inputs. + FMT_ASSERT(significand != 0, "zeros should not appear here"); + int shift = countl_zero(significand); + FMT_ASSERT(shift >= num_bits<uint64_t>() - num_significand_bits<double>(), + ""); + shift -= (num_bits<uint64_t>() - num_significand_bits<double>() - 2); + exponent = (std::numeric_limits<double>::min_exponent - + num_significand_bits<double>()) - + shift; + significand <<= shift; + } + + // Compute the first several nonzero decimal significand digits. + // We call the number we get the first segment. + const int k = info::kappa - dragonbox::floor_log10_pow2(exponent); + exp = -k; + const int beta = exponent + dragonbox::floor_log2_pow10(k); + uint64_t first_segment; + bool has_more_segments; + int digits_in_the_first_segment; + { + const auto r = dragonbox::umul192_upper128( + significand << beta, dragonbox::get_cached_power(k)); + first_segment = r.high(); + has_more_segments = r.low() != 0; + + // The first segment can have 18 ~ 19 digits. + if (first_segment >= 1000000000000000000ULL) { + digits_in_the_first_segment = 19; + } else { + // When it is of 18-digits, we align it to 19-digits by adding a bogus + // zero at the end. + digits_in_the_first_segment = 18; + first_segment *= 10; + } + } + + // Compute the actual number of decimal digits to print. + if (fixed) adjust_precision(precision, exp + digits_in_the_first_segment); + + // Use Dragon4 only when there might be not enough digits in the first + // segment. + if (digits_in_the_first_segment > precision) { + use_dragon = false; + + if (precision <= 0) { + exp += digits_in_the_first_segment; + + if (precision < 0) { + // Nothing to do, since all we have are just leading zeros. + buf.try_resize(0); + } else { + // We may need to round-up. + buf.try_resize(1); + if ((first_segment | static_cast<uint64_t>(has_more_segments)) > + 5000000000000000000ULL) { + buf[0] = '1'; + } else { + buf[0] = '0'; + } + } + } // precision <= 0 + else { + exp += digits_in_the_first_segment - precision; + + // When precision > 0, we divide the first segment into three + // subsegments, each with 9, 9, and 0 ~ 1 digits so that each fits + // in 32-bits which usually allows faster calculation than in + // 64-bits. Since some compiler (e.g. MSVC) doesn't know how to optimize + // division-by-constant for large 64-bit divisors, we do it here + // manually. The magic number 7922816251426433760 below is equal to + // ceil(2^(64+32) / 10^10). + const uint32_t first_subsegment = static_cast<uint32_t>( + dragonbox::umul128_upper64(first_segment, 7922816251426433760ULL) >> + 32); + const uint64_t second_third_subsegments = + first_segment - first_subsegment * 10000000000ULL; + + uint64_t prod; + uint32_t digits; + bool should_round_up; + int number_of_digits_to_print = precision > 9 ? 9 : precision; + + // Print a 9-digits subsegment, either the first or the second. + auto print_subsegment = [&](uint32_t subsegment, char* buffer) { + int number_of_digits_printed = 0; + + // If we want to print an odd number of digits from the subsegment, + if ((number_of_digits_to_print & 1) != 0) { + // Convert to 64-bit fixed-point fractional form with 1-digit + // integer part. The magic number 720575941 is a good enough + // approximation of 2^(32 + 24) / 10^8; see + // https://jk-jeon.github.io/posts/2022/12/fixed-precision-formatting/#fixed-length-case + // for details. + prod = ((subsegment * static_cast<uint64_t>(720575941)) >> 24) + 1; + digits = static_cast<uint32_t>(prod >> 32); + *buffer = static_cast<char>('0' + digits); + number_of_digits_printed++; + } + // If we want to print an even number of digits from the + // first_subsegment, + else { + // Convert to 64-bit fixed-point fractional form with 2-digits + // integer part. The magic number 450359963 is a good enough + // approximation of 2^(32 + 20) / 10^7; see + // https://jk-jeon.github.io/posts/2022/12/fixed-precision-formatting/#fixed-length-case + // for details. + prod = ((subsegment * static_cast<uint64_t>(450359963)) >> 20) + 1; + digits = static_cast<uint32_t>(prod >> 32); + copy2(buffer, digits2(digits)); + number_of_digits_printed += 2; + } + + // Print all digit pairs. + while (number_of_digits_printed < number_of_digits_to_print) { + prod = static_cast<uint32_t>(prod) * static_cast<uint64_t>(100); + digits = static_cast<uint32_t>(prod >> 32); + copy2(buffer + number_of_digits_printed, digits2(digits)); + number_of_digits_printed += 2; + } + }; + + // Print first subsegment. + print_subsegment(first_subsegment, buf.data()); + + // Perform rounding if the first subsegment is the last subsegment to + // print. + if (precision <= 9) { + // Rounding inside the subsegment. + // We round-up if: + // - either the fractional part is strictly larger than 1/2, or + // - the fractional part is exactly 1/2 and the last digit is odd. + // We rely on the following observations: + // - If fractional_part >= threshold, then the fractional part is + // strictly larger than 1/2. + // - If the MSB of fractional_part is set, then the fractional part + // must be at least 1/2. + // - When the MSB of fractional_part is set, either + // second_third_subsegments being nonzero or has_more_segments + // being true means there are further digits not printed, so the + // fractional part is strictly larger than 1/2. + if (precision < 9) { + uint32_t fractional_part = static_cast<uint32_t>(prod); + should_round_up = + fractional_part >= fractional_part_rounding_thresholds( + 8 - number_of_digits_to_print) || + ((fractional_part >> 31) & + ((digits & 1) | (second_third_subsegments != 0) | + has_more_segments)) != 0; + } + // Rounding at the subsegment boundary. + // In this case, the fractional part is at least 1/2 if and only if + // second_third_subsegments >= 5000000000ULL, and is strictly larger + // than 1/2 if we further have either second_third_subsegments > + // 5000000000ULL or has_more_segments == true. + else { + should_round_up = second_third_subsegments > 5000000000ULL || + (second_third_subsegments == 5000000000ULL && + ((digits & 1) != 0 || has_more_segments)); + } + } + // Otherwise, print the second subsegment. + else { + // Compilers are not aware of how to leverage the maximum value of + // second_third_subsegments to find out a better magic number which + // allows us to eliminate an additional shift. 1844674407370955162 = + // ceil(2^64/10) < ceil(2^64*(10^9/(10^10 - 1))). + const uint32_t second_subsegment = + static_cast<uint32_t>(dragonbox::umul128_upper64( + second_third_subsegments, 1844674407370955162ULL)); + const uint32_t third_subsegment = + static_cast<uint32_t>(second_third_subsegments) - + second_subsegment * 10; + + number_of_digits_to_print = precision - 9; + print_subsegment(second_subsegment, buf.data() + 9); + + // Rounding inside the subsegment. + if (precision < 18) { + // The condition third_subsegment != 0 implies that the segment was + // of 19 digits, so in this case the third segment should be + // consisting of a genuine digit from the input. + uint32_t fractional_part = static_cast<uint32_t>(prod); + should_round_up = + fractional_part >= fractional_part_rounding_thresholds( + 8 - number_of_digits_to_print) || + ((fractional_part >> 31) & + ((digits & 1) | (third_subsegment != 0) | + has_more_segments)) != 0; + } + // Rounding at the subsegment boundary. + else { + // In this case, the segment must be of 19 digits, thus + // the third subsegment should be consisting of a genuine digit from + // the input. + should_round_up = third_subsegment > 5 || + (third_subsegment == 5 && + ((digits & 1) != 0 || has_more_segments)); + } + } + + // Round-up if necessary. + if (should_round_up) { + ++buf[precision - 1]; + for (int i = precision - 1; i > 0 && buf[i] > '9'; --i) { + buf[i] = '0'; + ++buf[i - 1]; + } + if (buf[0] > '9') { + buf[0] = '1'; + if (fixed) + buf[precision++] = '0'; + else + ++exp; + } + } + buf.try_resize(to_unsigned(precision)); + } + } // if (digits_in_the_first_segment > precision) + else { + // Adjust the exponent for its use in Dragon4. + exp += digits_in_the_first_segment - 1; + } + } + if (use_dragon) { + auto f = basic_fp<uint128_t>(); + bool is_predecessor_closer = specs.binary32 + ? f.assign(static_cast<float>(value)) + : f.assign(converted_value); + if (is_predecessor_closer) dragon_flags |= dragon::predecessor_closer; + if (fixed) dragon_flags |= dragon::fixed; + // Limit precision to the maximum possible number of significant digits in + // an IEEE754 double because we don't need to generate zeros. + const int max_double_digits = 767; + if (precision > max_double_digits) precision = max_double_digits; + format_dragon(f, dragon_flags, precision, buf, exp); + } + if (!fixed && !specs.showpoint) { + // Remove trailing zeros. + auto num_digits = buf.size(); + while (num_digits > 0 && buf[num_digits - 1] == '0') { + --num_digits; + ++exp; + } + buf.try_resize(num_digits); + } + return exp; +} +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto write_float(OutputIt out, T value, + format_specs<Char> specs, locale_ref loc) + -> OutputIt { float_specs fspecs = parse_float_type_spec(specs); fspecs.sign = specs.sign; - if (std::signbit(value)) { // value < 0 is false for NaN so use signbit. + if (detail::signbit(value)) { // value < 0 is false for NaN so use signbit. fspecs.sign = sign::minus; value = -value; } else if (fspecs.sign == sign::minus) { fspecs.sign = sign::none; } - if (!std::isfinite(value)) - return write_nonfinite(out, std::isinf(value), specs, fspecs); + if (!detail::isfinite(value)) + return write_nonfinite(out, detail::isnan(value), specs, fspecs); if (specs.align == align::numeric && fspecs.sign) { auto it = reserve(out, 1); - *it++ = static_cast<Char>(data::signs[fspecs.sign]); + *it++ = detail::sign<Char>(fspecs.sign); out = base_iterator(out, it); fspecs.sign = sign::none; if (specs.width != 0) --specs.width; @@ -1920,489 +3606,222 @@ OutputIt write(OutputIt out, T value, basic_format_specs<Char> specs, memory_buffer buffer; if (fspecs.format == float_format::hex) { - if (fspecs.sign) buffer.push_back(data::signs[fspecs.sign]); - snprintf_float(promote_float(value), specs.precision, fspecs, buffer); - return write_bytes(out, {buffer.data(), buffer.size()}, specs); - } - int precision = specs.precision >= 0 || !specs.type ? specs.precision : 6; + if (fspecs.sign) buffer.push_back(detail::sign<char>(fspecs.sign)); + format_hexfloat(convert_float(value), specs.precision, fspecs, buffer); + return write_bytes<align::right>(out, {buffer.data(), buffer.size()}, + specs); + } + int precision = specs.precision >= 0 || specs.type == presentation_type::none + ? specs.precision + : 6; if (fspecs.format == float_format::exp) { if (precision == max_value<int>()) - FMT_THROW(format_error("number is too big")); + throw_format_error("number is too big"); else ++precision; + } else if (fspecs.format != float_format::fixed && precision == 0) { + precision = 1; } if (const_check(std::is_same<T, float>())) fspecs.binary32 = true; - fspecs.use_grisu = is_fast_float<T>(); - int exp = format_float(promote_float(value), precision, fspecs, buffer); + int exp = format_float(convert_float(value), precision, fspecs, buffer); fspecs.precision = precision; - Char point = - fspecs.locale ? decimal_point<Char>(loc) : static_cast<Char>('.'); - auto fp = big_decimal_fp{buffer.data(), static_cast<int>(buffer.size()), exp}; - return write_float(out, fp, specs, fspecs, point); + auto f = big_decimal_fp{buffer.data(), static_cast<int>(buffer.size()), exp}; + return write_float(out, f, specs, fspecs, loc); } template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_fast_float<T>::value)> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, T value) { + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_floating_point<T>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto write(OutputIt out, T value, format_specs<Char> specs, + locale_ref loc = {}) -> OutputIt { if (const_check(!is_supported_floating_point(value))) return out; + return specs.localized && write_loc(out, value, specs, loc) + ? out + : write_float(out, value, specs, loc); +} - using floaty = conditional_t<std::is_same<T, long double>::value, double, T>; - using uint = typename dragonbox::float_info<floaty>::carrier_uint; - auto bits = bit_cast<uint>(value); +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_fast_float<T>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto write(OutputIt out, T value) -> OutputIt { + if (is_constant_evaluated()) return write(out, value, format_specs<Char>()); + if (const_check(!is_supported_floating_point(value))) return out; auto fspecs = float_specs(); - auto sign_bit = bits & (uint(1) << (num_bits<uint>() - 1)); - if (sign_bit != 0) { + if (detail::signbit(value)) { fspecs.sign = sign::minus; value = -value; } - static const auto specs = basic_format_specs<Char>(); - uint mask = exponent_mask<floaty>(); - if ((bits & mask) == mask) - return write_nonfinite(out, std::isinf(value), specs, fspecs); + constexpr auto specs = format_specs<Char>(); + using floaty = conditional_t<std::is_same<T, long double>::value, double, T>; + using floaty_uint = typename dragonbox::float_info<floaty>::carrier_uint; + floaty_uint mask = exponent_mask<floaty>(); + if ((bit_cast<floaty_uint>(value) & mask) == mask) + return write_nonfinite(out, std::isnan(value), specs, fspecs); auto dec = dragonbox::to_decimal(static_cast<floaty>(value)); - return write_float(out, dec, specs, fspecs, static_cast<Char>('.')); + return write_float(out, dec, specs, fspecs, {}); } template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value && + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_floating_point<T>::value && !is_fast_float<T>::value)> -inline OutputIt write(OutputIt out, T value) { - return write(out, value, basic_format_specs<Char>()); -} - -template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write_char(OutputIt out, Char value, - const basic_format_specs<Char>& specs) { - using iterator = remove_reference_t<decltype(reserve(out, 0))>; - return write_padded(out, specs, 1, [=](iterator it) { - *it++ = value; - return it; - }); -} - -template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename UIntPtr> -OutputIt write_ptr(OutputIt out, UIntPtr value, - const basic_format_specs<Char>* specs) { - int num_digits = count_digits<4>(value); - auto size = to_unsigned(num_digits) + size_t(2); - using iterator = remove_reference_t<decltype(reserve(out, 0))>; - auto write = [=](iterator it) { - *it++ = static_cast<Char>('0'); - *it++ = static_cast<Char>('x'); - return format_uint<4, Char>(it, value, num_digits); - }; - return specs ? write_padded<align::right>(out, *specs, size, write) - : base_iterator(out, write(reserve(out, size))); +inline auto write(OutputIt out, T value) -> OutputIt { + return write(out, value, format_specs<Char>()); } -template <typename T> struct is_integral : std::is_integral<T> {}; -template <> struct is_integral<int128_t> : std::true_type {}; -template <> struct is_integral<uint128_t> : std::true_type {}; - template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, monostate) { +auto write(OutputIt out, monostate, format_specs<Char> = {}, locale_ref = {}) + -> OutputIt { FMT_ASSERT(false, ""); return out; } -template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value)> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, string_view value) { - auto it = reserve(out, value.size()); - it = copy_str<Char>(value.begin(), value.end(), it); - return base_iterator(out, it); -} - template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, basic_string_view<Char> value) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, basic_string_view<Char> value) + -> OutputIt { auto it = reserve(out, value.size()); - it = std::copy(value.begin(), value.end(), it); + it = copy_str_noinline<Char>(value.begin(), value.end(), it); return base_iterator(out, it); } -template <typename Char> -buffer_appender<Char> write(buffer_appender<Char> out, - basic_string_view<Char> value) { - get_container(out).append(value.begin(), value.end()); - return out; +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_string<T>::value)> +constexpr auto write(OutputIt out, const T& value) -> OutputIt { + return write<Char>(out, to_string_view(value)); } -template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integral<T>::value && - !std::is_same<T, bool>::value && - !std::is_same<T, Char>::value)> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, T value) { - auto abs_value = static_cast<uint32_or_64_or_128_t<T>>(value); - bool negative = is_negative(value); - // Don't do -abs_value since it trips unsigned-integer-overflow sanitizer. - if (negative) abs_value = ~abs_value + 1; - int num_digits = count_digits(abs_value); - auto size = (negative ? 1 : 0) + static_cast<size_t>(num_digits); - auto it = reserve(out, size); - if (auto ptr = to_pointer<Char>(it, size)) { - if (negative) *ptr++ = static_cast<Char>('-'); - format_decimal<Char>(ptr, abs_value, num_digits); - return out; - } - if (negative) *it++ = static_cast<Char>('-'); - it = format_decimal<Char>(it, abs_value, num_digits).end; - return base_iterator(out, it); +// FMT_ENABLE_IF() condition separated to workaround an MSVC bug. +template < + typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + bool check = + std::is_enum<T>::value && !std::is_same<T, Char>::value && + mapped_type_constant<T, basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>>::value != + type::custom_type, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(check)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, T value) -> OutputIt { + return write<Char>(out, static_cast<underlying_t<T>>(value)); } -template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, bool value) { - return write<Char>(out, string_view(value ? "true" : "false")); +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<T, bool>::value)> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, T value, + const format_specs<Char>& specs = {}, locale_ref = {}) + -> OutputIt { + return specs.type != presentation_type::none && + specs.type != presentation_type::string + ? write(out, value ? 1 : 0, specs, {}) + : write_bytes(out, value ? "true" : "false", specs); } template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, Char value) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, Char value) -> OutputIt { auto it = reserve(out, 1); *it++ = value; return base_iterator(out, it); } template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, const Char* value) { - if (!value) { - FMT_THROW(format_error("string pointer is null")); - } else { - auto length = std::char_traits<Char>::length(value); - out = write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(value, length)); - } +FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS auto write(OutputIt out, const Char* value) + -> OutputIt { + if (value) return write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(value)); + throw_format_error("string pointer is null"); return out; } -template <typename Char, typename OutputIt> -OutputIt write(OutputIt out, const void* value) { - return write_ptr<Char>(out, to_uintptr(value), nullptr); +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<T, void>::value)> +auto write(OutputIt out, const T* value, const format_specs<Char>& specs = {}, + locale_ref = {}) -> OutputIt { + return write_ptr<Char>(out, bit_cast<uintptr_t>(value), &specs); } -template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T> -auto write(OutputIt out, const T& value) -> typename std::enable_if< - mapped_type_constant<T, basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>>::value == - type::custom_type, - OutputIt>::type { - using context_type = basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>; - using formatter_type = - conditional_t<has_formatter<T, context_type>::value, - typename context_type::template formatter_type<T>, - fallback_formatter<T, Char>>; - context_type ctx(out, {}, {}); - return formatter_type().format(value, ctx); +// A write overload that handles implicit conversions. +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + typename Context = basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, const T& value) -> enable_if_t< + std::is_class<T>::value && !is_string<T>::value && + !is_floating_point<T>::value && !std::is_same<T, Char>::value && + !std::is_same<T, remove_cvref_t<decltype(arg_mapper<Context>().map( + value))>>::value, + OutputIt> { + return write<Char>(out, arg_mapper<Context>().map(value)); +} + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T, + typename Context = basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, const T& value) + -> enable_if_t<mapped_type_constant<T, Context>::value == type::custom_type, + OutputIt> { + auto formatter = typename Context::template formatter_type<T>(); + auto parse_ctx = typename Context::parse_context_type({}); + formatter.parse(parse_ctx); + auto ctx = Context(out, {}, {}); + return formatter.format(value, ctx); } // An argument visitor that formats the argument and writes it via the output // iterator. It's a class and not a generic lambda for compatibility with C++11. -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> struct default_arg_formatter { - using context = basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>; +template <typename Char> struct default_arg_formatter { + using iterator = buffer_appender<Char>; + using context = buffer_context<Char>; - OutputIt out; + iterator out; basic_format_args<context> args; locale_ref loc; - template <typename T> OutputIt operator()(T value) { + template <typename T> auto operator()(T value) -> iterator { return write<Char>(out, value); } - - OutputIt operator()(typename basic_format_arg<context>::handle handle) { + auto operator()(typename basic_format_arg<context>::handle h) -> iterator { basic_format_parse_context<Char> parse_ctx({}); - basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char> format_ctx(out, args, loc); - handle.format(parse_ctx, format_ctx); + context format_ctx(out, args, loc); + h.format(parse_ctx, format_ctx); return format_ctx.out(); } }; -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, - typename ErrorHandler = error_handler> -class arg_formatter_base { - public: - using iterator = OutputIt; - using char_type = Char; - using format_specs = basic_format_specs<Char>; - - private: - iterator out_; - locale_ref locale_; - format_specs* specs_; - - // Attempts to reserve space for n extra characters in the output range. - // Returns a pointer to the reserved range or a reference to out_. - auto reserve(size_t n) -> decltype(detail::reserve(out_, n)) { - return detail::reserve(out_, n); - } - - using reserve_iterator = remove_reference_t<decltype( - detail::reserve(std::declval<iterator&>(), 0))>; - - template <typename T> void write_int(T value, const format_specs& spec) { - using uint_type = uint32_or_64_or_128_t<T>; - int_writer<iterator, Char, uint_type> w(out_, locale_, value, spec); - handle_int_type_spec(spec.type, w); - out_ = w.out; - } - - void write(char value) { - auto&& it = reserve(1); - *it++ = value; - } - - template <typename Ch, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<Ch, Char>::value)> - void write(Ch value) { - out_ = detail::write<Char>(out_, value); - } - - void write(string_view value) { - auto&& it = reserve(value.size()); - it = copy_str<Char>(value.begin(), value.end(), it); - } - void write(wstring_view value) { - static_assert(std::is_same<Char, wchar_t>::value, ""); - auto&& it = reserve(value.size()); - it = std::copy(value.begin(), value.end(), it); - } - - template <typename Ch> - void write(const Ch* s, size_t size, const format_specs& specs) { - auto width = specs.width != 0 - ? count_code_points(basic_string_view<Ch>(s, size)) - : 0; - out_ = write_padded(out_, specs, size, width, [=](reserve_iterator it) { - return copy_str<Char>(s, s + size, it); - }); - } - - template <typename Ch> - void write(basic_string_view<Ch> s, const format_specs& specs = {}) { - out_ = detail::write(out_, s, specs); - } - - void write_pointer(const void* p) { - out_ = write_ptr<char_type>(out_, to_uintptr(p), specs_); - } - - struct char_spec_handler : ErrorHandler { - arg_formatter_base& formatter; - Char value; - - char_spec_handler(arg_formatter_base& f, Char val) - : formatter(f), value(val) {} - - void on_int() { - // char is only formatted as int if there are specs. - formatter.write_int(static_cast<int>(value), *formatter.specs_); - } - void on_char() { - if (formatter.specs_) - formatter.out_ = write_char(formatter.out_, value, *formatter.specs_); - else - formatter.write(value); - } - }; - - struct cstring_spec_handler : error_handler { - arg_formatter_base& formatter; - const Char* value; - - cstring_spec_handler(arg_formatter_base& f, const Char* val) - : formatter(f), value(val) {} - - void on_string() { formatter.write(value); } - void on_pointer() { formatter.write_pointer(value); } - }; - - protected: - iterator out() { return out_; } - format_specs* specs() { return specs_; } - - void write(bool value) { - if (specs_) - write(string_view(value ? "true" : "false"), *specs_); - else - out_ = detail::write<Char>(out_, value); - } - - void write(const Char* value) { - if (!value) { - FMT_THROW(format_error("string pointer is null")); - } else { - auto length = std::char_traits<char_type>::length(value); - basic_string_view<char_type> sv(value, length); - specs_ ? write(sv, *specs_) : write(sv); - } - } - - public: - arg_formatter_base(OutputIt out, format_specs* s, locale_ref loc) - : out_(out), locale_(loc), specs_(s) {} - - iterator operator()(monostate) { - FMT_ASSERT(false, "invalid argument type"); - return out_; - } - - template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integral<T>::value)> - FMT_INLINE iterator operator()(T value) { - if (specs_) - write_int(value, *specs_); - else - out_ = detail::write<Char>(out_, value); - return out_; - } - - iterator operator()(Char value) { - handle_char_specs(specs_, - char_spec_handler(*this, static_cast<Char>(value))); - return out_; - } - - iterator operator()(bool value) { - if (specs_ && specs_->type) return (*this)(value ? 1 : 0); - write(value != 0); - return out_; - } - - template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value)> - iterator operator()(T value) { - auto specs = specs_ ? *specs_ : format_specs(); - if (const_check(is_supported_floating_point(value))) - out_ = detail::write(out_, value, specs, locale_); - else - FMT_ASSERT(false, "unsupported float argument type"); - return out_; - } - - iterator operator()(const Char* value) { - if (!specs_) return write(value), out_; - handle_cstring_type_spec(specs_->type, cstring_spec_handler(*this, value)); - return out_; - } +template <typename Char> struct arg_formatter { + using iterator = buffer_appender<Char>; + using context = buffer_context<Char>; - iterator operator()(basic_string_view<Char> value) { - if (specs_) { - check_string_type_spec(specs_->type, error_handler()); - write(value, *specs_); - } else { - write(value); - } - return out_; - } + iterator out; + const format_specs<Char>& specs; + locale_ref locale; - iterator operator()(const void* value) { - if (specs_) check_pointer_type_spec(specs_->type, error_handler()); - write_pointer(value); - return out_; + template <typename T> + FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto operator()(T value) -> iterator { + return detail::write(out, value, specs, locale); } -}; - -/** The default argument formatter. */ -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -class arg_formatter : public arg_formatter_base<OutputIt, Char> { - private: - using char_type = Char; - using base = arg_formatter_base<OutputIt, Char>; - using context_type = basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>; - - context_type& ctx_; - basic_format_parse_context<char_type>* parse_ctx_; - const Char* ptr_; - - public: - using iterator = typename base::iterator; - using format_specs = typename base::format_specs; - - /** - \rst - Constructs an argument formatter object. - *ctx* is a reference to the formatting context, - *specs* contains format specifier information for standard argument types. - \endrst - */ - explicit arg_formatter( - context_type& ctx, - basic_format_parse_context<char_type>* parse_ctx = nullptr, - format_specs* specs = nullptr, const Char* ptr = nullptr) - : base(ctx.out(), specs, ctx.locale()), - ctx_(ctx), - parse_ctx_(parse_ctx), - ptr_(ptr) {} - - using base::operator(); - - /** Formats an argument of a user-defined type. */ - iterator operator()(typename basic_format_arg<context_type>::handle handle) { - if (ptr_) advance_to(*parse_ctx_, ptr_); - handle.format(*parse_ctx_, ctx_); - return ctx_.out(); + auto operator()(typename basic_format_arg<context>::handle) -> iterator { + // User-defined types are handled separately because they require access + // to the parse context. + return out; } }; -template <typename Char> FMT_CONSTEXPR bool is_name_start(Char c) { - return ('a' <= c && c <= 'z') || ('A' <= c && c <= 'Z') || '_' == c; -} - -// Parses the range [begin, end) as an unsigned integer. This function assumes -// that the range is non-empty and the first character is a digit. -template <typename Char, typename ErrorHandler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR int parse_nonnegative_int(const Char*& begin, const Char* end, - ErrorHandler&& eh) { - FMT_ASSERT(begin != end && '0' <= *begin && *begin <= '9', ""); - unsigned value = 0; - // Convert to unsigned to prevent a warning. - constexpr unsigned max_int = max_value<int>(); - unsigned big = max_int / 10; - do { - // Check for overflow. - if (value > big) { - value = max_int + 1; - break; - } - value = value * 10 + unsigned(*begin - '0'); - ++begin; - } while (begin != end && '0' <= *begin && *begin <= '9'); - if (value > max_int) eh.on_error("number is too big"); - return static_cast<int>(value); -} - -template <typename Context> class custom_formatter { - private: - using char_type = typename Context::char_type; - - basic_format_parse_context<char_type>& parse_ctx_; - Context& ctx_; +template <typename Char> struct custom_formatter { + basic_format_parse_context<Char>& parse_ctx; + buffer_context<Char>& ctx; - public: - explicit custom_formatter(basic_format_parse_context<char_type>& parse_ctx, - Context& ctx) - : parse_ctx_(parse_ctx), ctx_(ctx) {} - - void operator()(typename basic_format_arg<Context>::handle h) const { - h.format(parse_ctx_, ctx_); + void operator()( + typename basic_format_arg<buffer_context<Char>>::handle h) const { + h.format(parse_ctx, ctx); } - template <typename T> void operator()(T) const {} }; -template <typename T> -using is_integer = - bool_constant<is_integral<T>::value && !std::is_same<T, bool>::value && - !std::is_same<T, char>::value && - !std::is_same<T, wchar_t>::value>; - template <typename ErrorHandler> class width_checker { public: explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR width_checker(ErrorHandler& eh) : handler_(eh) {} template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integer<T>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR unsigned long long operator()(T value) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(T value) -> unsigned long long { if (is_negative(value)) handler_.on_error("negative width"); return static_cast<unsigned long long>(value); } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_integer<T>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR unsigned long long operator()(T) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(T) -> unsigned long long { handler_.on_error("width is not integer"); return 0; } @@ -2416,13 +3835,13 @@ template <typename ErrorHandler> class precision_checker { explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR precision_checker(ErrorHandler& eh) : handler_(eh) {} template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integer<T>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR unsigned long long operator()(T value) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(T value) -> unsigned long long { if (is_negative(value)) handler_.on_error("negative precision"); return static_cast<unsigned long long>(value); } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_integer<T>::value)> - FMT_CONSTEXPR unsigned long long operator()(T) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(T) -> unsigned long long { handler_.on_error("precision is not integer"); return 0; } @@ -2431,904 +3850,143 @@ template <typename ErrorHandler> class precision_checker { ErrorHandler& handler_; }; -// A format specifier handler that sets fields in basic_format_specs. -template <typename Char> class specs_setter { - public: - explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR specs_setter(basic_format_specs<Char>& specs) - : specs_(specs) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR specs_setter(const specs_setter& other) - : specs_(other.specs_) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_align(align_t align) { specs_.align = align; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_fill(basic_string_view<Char> fill) { - specs_.fill = fill; - } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_plus() { specs_.sign = sign::plus; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_minus() { specs_.sign = sign::minus; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_space() { specs_.sign = sign::space; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_hash() { specs_.alt = true; } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_zero() { - specs_.align = align::numeric; - specs_.fill[0] = Char('0'); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_width(int width) { specs_.width = width; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_precision(int precision) { - specs_.precision = precision; - } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void end_precision() {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_type(Char type) { - specs_.type = static_cast<char>(type); - } - - protected: - basic_format_specs<Char>& specs_; -}; - -template <typename ErrorHandler> class numeric_specs_checker { - public: - FMT_CONSTEXPR numeric_specs_checker(ErrorHandler& eh, detail::type arg_type) - : error_handler_(eh), arg_type_(arg_type) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void require_numeric_argument() { - if (!is_arithmetic_type(arg_type_)) - error_handler_.on_error("format specifier requires numeric argument"); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_sign() { - require_numeric_argument(); - if (is_integral_type(arg_type_) && arg_type_ != type::int_type && - arg_type_ != type::long_long_type && arg_type_ != type::char_type) { - error_handler_.on_error("format specifier requires signed argument"); - } - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_precision() { - if (is_integral_type(arg_type_) || arg_type_ == type::pointer_type) - error_handler_.on_error("precision not allowed for this argument type"); - } - - private: - ErrorHandler& error_handler_; - detail::type arg_type_; -}; - -// A format specifier handler that checks if specifiers are consistent with the -// argument type. -template <typename Handler> class specs_checker : public Handler { - private: - numeric_specs_checker<Handler> checker_; - - // Suppress an MSVC warning about using this in initializer list. - FMT_CONSTEXPR Handler& error_handler() { return *this; } - - public: - FMT_CONSTEXPR specs_checker(const Handler& handler, detail::type arg_type) - : Handler(handler), checker_(error_handler(), arg_type) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR specs_checker(const specs_checker& other) - : Handler(other), checker_(error_handler(), other.arg_type_) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_align(align_t align) { - if (align == align::numeric) checker_.require_numeric_argument(); - Handler::on_align(align); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_plus() { - checker_.check_sign(); - Handler::on_plus(); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_minus() { - checker_.check_sign(); - Handler::on_minus(); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_space() { - checker_.check_sign(); - Handler::on_space(); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_hash() { - checker_.require_numeric_argument(); - Handler::on_hash(); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_zero() { - checker_.require_numeric_argument(); - Handler::on_zero(); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void end_precision() { checker_.check_precision(); } -}; - template <template <typename> class Handler, typename FormatArg, typename ErrorHandler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR int get_dynamic_spec(FormatArg arg, ErrorHandler eh) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_dynamic_spec(FormatArg arg, ErrorHandler eh) -> int { unsigned long long value = visit_format_arg(Handler<ErrorHandler>(eh), arg); if (value > to_unsigned(max_value<int>())) eh.on_error("number is too big"); return static_cast<int>(value); } -struct auto_id {}; - template <typename Context, typename ID> -FMT_CONSTEXPR typename Context::format_arg get_arg(Context& ctx, ID id) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_arg(Context& ctx, ID id) -> decltype(ctx.arg(id)) { auto arg = ctx.arg(id); if (!arg) ctx.on_error("argument not found"); return arg; } -// The standard format specifier handler with checking. -template <typename ParseContext, typename Context> -class specs_handler : public specs_setter<typename Context::char_type> { - public: - using char_type = typename Context::char_type; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR specs_handler(basic_format_specs<char_type>& specs, - ParseContext& parse_ctx, Context& ctx) - : specs_setter<char_type>(specs), - parse_context_(parse_ctx), - context_(ctx) {} - - template <typename Id> FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_width(Id arg_id) { - this->specs_.width = get_dynamic_spec<width_checker>( - get_arg(arg_id), context_.error_handler()); - } - - template <typename Id> FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_precision(Id arg_id) { - this->specs_.precision = get_dynamic_spec<precision_checker>( - get_arg(arg_id), context_.error_handler()); - } - - void on_error(const char* message) { context_.on_error(message); } - - private: - // This is only needed for compatibility with gcc 4.4. - using format_arg = typename Context::format_arg; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR format_arg get_arg(auto_id) { - return detail::get_arg(context_, parse_context_.next_arg_id()); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR format_arg get_arg(int arg_id) { - parse_context_.check_arg_id(arg_id); - return detail::get_arg(context_, arg_id); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR format_arg get_arg(basic_string_view<char_type> arg_id) { - parse_context_.check_arg_id(arg_id); - return detail::get_arg(context_, arg_id); - } - - ParseContext& parse_context_; - Context& context_; -}; - -enum class arg_id_kind { none, index, name }; - -// An argument reference. -template <typename Char> struct arg_ref { - FMT_CONSTEXPR arg_ref() : kind(arg_id_kind::none), val() {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR explicit arg_ref(int index) - : kind(arg_id_kind::index), val(index) {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR explicit arg_ref(basic_string_view<Char> name) - : kind(arg_id_kind::name), val(name) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR arg_ref& operator=(int idx) { - kind = arg_id_kind::index; - val.index = idx; - return *this; - } - - arg_id_kind kind; - union value { - FMT_CONSTEXPR value(int id = 0) : index{id} {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR value(basic_string_view<Char> n) : name(n) {} - - int index; - basic_string_view<Char> name; - } val; -}; - -// Format specifiers with width and precision resolved at formatting rather -// than parsing time to allow re-using the same parsed specifiers with -// different sets of arguments (precompilation of format strings). -template <typename Char> -struct dynamic_format_specs : basic_format_specs<Char> { - arg_ref<Char> width_ref; - arg_ref<Char> precision_ref; -}; - -// Format spec handler that saves references to arguments representing dynamic -// width and precision to be resolved at formatting time. -template <typename ParseContext> -class dynamic_specs_handler - : public specs_setter<typename ParseContext::char_type> { - public: - using char_type = typename ParseContext::char_type; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR dynamic_specs_handler(dynamic_format_specs<char_type>& specs, - ParseContext& ctx) - : specs_setter<char_type>(specs), specs_(specs), context_(ctx) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR dynamic_specs_handler(const dynamic_specs_handler& other) - : specs_setter<char_type>(other), - specs_(other.specs_), - context_(other.context_) {} - - template <typename Id> FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_width(Id arg_id) { - specs_.width_ref = make_arg_ref(arg_id); - } - - template <typename Id> FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_precision(Id arg_id) { - specs_.precision_ref = make_arg_ref(arg_id); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { - context_.on_error(message); - } - - private: - using arg_ref_type = arg_ref<char_type>; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR arg_ref_type make_arg_ref(int arg_id) { - context_.check_arg_id(arg_id); - return arg_ref_type(arg_id); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR arg_ref_type make_arg_ref(auto_id) { - return arg_ref_type(context_.next_arg_id()); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR arg_ref_type make_arg_ref(basic_string_view<char_type> arg_id) { - context_.check_arg_id(arg_id); - basic_string_view<char_type> format_str( - context_.begin(), to_unsigned(context_.end() - context_.begin())); - return arg_ref_type(arg_id); - } - - dynamic_format_specs<char_type>& specs_; - ParseContext& context_; -}; - -template <typename Char, typename IDHandler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_arg_id(const Char* begin, const Char* end, - IDHandler&& handler) { - FMT_ASSERT(begin != end, ""); - Char c = *begin; - if (c == '}' || c == ':') { - handler(); - return begin; - } - if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') { - int index = 0; - if (c != '0') - index = parse_nonnegative_int(begin, end, handler); - else - ++begin; - if (begin == end || (*begin != '}' && *begin != ':')) - handler.on_error("invalid format string"); - else - handler(index); - return begin; - } - if (!is_name_start(c)) { - handler.on_error("invalid format string"); - return begin; - } - auto it = begin; - do { - ++it; - } while (it != end && (is_name_start(c = *it) || ('0' <= c && c <= '9'))); - handler(basic_string_view<Char>(begin, to_unsigned(it - begin))); - return it; -} - -// Adapts SpecHandler to IDHandler API for dynamic width. -template <typename SpecHandler, typename Char> struct width_adapter { - explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR width_adapter(SpecHandler& h) : handler(h) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()() { handler.on_dynamic_width(auto_id()); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(int id) { handler.on_dynamic_width(id); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(basic_string_view<Char> id) { - handler.on_dynamic_width(id); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { - handler.on_error(message); - } - - SpecHandler& handler; -}; - -// Adapts SpecHandler to IDHandler API for dynamic precision. -template <typename SpecHandler, typename Char> struct precision_adapter { - explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR precision_adapter(SpecHandler& h) : handler(h) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()() { handler.on_dynamic_precision(auto_id()); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(int id) { handler.on_dynamic_precision(id); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(basic_string_view<Char> id) { - handler.on_dynamic_precision(id); - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { - handler.on_error(message); - } - - SpecHandler& handler; -}; - -template <typename Char> -FMT_CONSTEXPR int code_point_length(const Char* begin) { - if (const_check(sizeof(Char) != 1)) return 1; - constexpr char lengths[] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, - 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 0}; - int len = lengths[static_cast<unsigned char>(*begin) >> 3]; - - // Compute the pointer to the next character early so that the next - // iteration can start working on the next character. Neither Clang - // nor GCC figure out this reordering on their own. - return len + !len; -} - -template <typename Char> constexpr bool is_ascii_letter(Char c) { - return (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') || (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z'); -} - -// Converts a character to ASCII. Returns a number > 127 on conversion failure. -template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<Char>::value)> -constexpr Char to_ascii(Char value) { - return value; -} -template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_enum<Char>::value)> -constexpr typename std::underlying_type<Char>::type to_ascii(Char value) { - return value; -} - -// Parses fill and alignment. -template <typename Char, typename Handler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_align(const Char* begin, const Char* end, - Handler&& handler) { - FMT_ASSERT(begin != end, ""); - auto align = align::none; - auto p = begin + code_point_length(begin); - if (p >= end) p = begin; - for (;;) { - switch (to_ascii(*p)) { - case '<': - align = align::left; - break; - case '>': - align = align::right; - break; -#if FMT_DEPRECATED_NUMERIC_ALIGN - case '=': - align = align::numeric; - break; -#endif - case '^': - align = align::center; - break; - } - if (align != align::none) { - if (p != begin) { - auto c = *begin; - if (c == '{') - return handler.on_error("invalid fill character '{'"), begin; - handler.on_fill(basic_string_view<Char>(begin, to_unsigned(p - begin))); - begin = p + 1; - } else - ++begin; - handler.on_align(align); - break; - } else if (p == begin) { - break; - } - p = begin; - } - return begin; -} - -template <typename Char, typename Handler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_width(const Char* begin, const Char* end, - Handler&& handler) { - FMT_ASSERT(begin != end, ""); - if ('0' <= *begin && *begin <= '9') { - handler.on_width(parse_nonnegative_int(begin, end, handler)); - } else if (*begin == '{') { - ++begin; - if (begin != end) - begin = parse_arg_id(begin, end, width_adapter<Handler, Char>(handler)); - if (begin == end || *begin != '}') - return handler.on_error("invalid format string"), begin; - ++begin; - } - return begin; -} - -template <typename Char, typename Handler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_precision(const Char* begin, const Char* end, - Handler&& handler) { - ++begin; - auto c = begin != end ? *begin : Char(); - if ('0' <= c && c <= '9') { - handler.on_precision(parse_nonnegative_int(begin, end, handler)); - } else if (c == '{') { - ++begin; - if (begin != end) { - begin = - parse_arg_id(begin, end, precision_adapter<Handler, Char>(handler)); - } - if (begin == end || *begin++ != '}') - return handler.on_error("invalid format string"), begin; - } else { - return handler.on_error("missing precision specifier"), begin; - } - handler.end_precision(); - return begin; -} - -// Parses standard format specifiers and sends notifications about parsed -// components to handler. -template <typename Char, typename SpecHandler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_format_specs(const Char* begin, const Char* end, - SpecHandler&& handler) { - if (begin == end) return begin; - - begin = parse_align(begin, end, handler); - if (begin == end) return begin; - - // Parse sign. - switch (to_ascii(*begin)) { - case '+': - handler.on_plus(); - ++begin; +template <template <typename> class Handler, typename Context> +FMT_CONSTEXPR void handle_dynamic_spec(int& value, + arg_ref<typename Context::char_type> ref, + Context& ctx) { + switch (ref.kind) { + case arg_id_kind::none: break; - case '-': - handler.on_minus(); - ++begin; + case arg_id_kind::index: + value = detail::get_dynamic_spec<Handler>(get_arg(ctx, ref.val.index), + ctx.error_handler()); break; - case ' ': - handler.on_space(); - ++begin; + case arg_id_kind::name: + value = detail::get_dynamic_spec<Handler>(get_arg(ctx, ref.val.name), + ctx.error_handler()); break; } - if (begin == end) return begin; - - if (*begin == '#') { - handler.on_hash(); - if (++begin == end) return begin; - } - - // Parse zero flag. - if (*begin == '0') { - handler.on_zero(); - if (++begin == end) return begin; - } - - begin = parse_width(begin, end, handler); - if (begin == end) return begin; - - // Parse precision. - if (*begin == '.') { - begin = parse_precision(begin, end, handler); - } - - // Parse type. - if (begin != end && *begin != '}') handler.on_type(*begin++); - return begin; } -// Return the result via the out param to workaround gcc bug 77539. -template <bool IS_CONSTEXPR, typename T, typename Ptr = const T*> -FMT_CONSTEXPR bool find(Ptr first, Ptr last, T value, Ptr& out) { - for (out = first; out != last; ++out) { - if (*out == value) return true; - } - return false; -} - -template <> -inline bool find<false, char>(const char* first, const char* last, char value, - const char*& out) { - out = static_cast<const char*>( - std::memchr(first, value, detail::to_unsigned(last - first))); - return out != nullptr; -} - -template <typename Handler, typename Char> struct id_adapter { - Handler& handler; - int arg_id; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()() { arg_id = handler.on_arg_id(); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(int id) { arg_id = handler.on_arg_id(id); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(basic_string_view<Char> id) { - arg_id = handler.on_arg_id(id); - } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { - handler.on_error(message); - } -}; - -template <typename Char, typename Handler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_replacement_field(const Char* begin, - const Char* end, - Handler&& handler) { - ++begin; - if (begin == end) return handler.on_error("invalid format string"), end; - if (*begin == '}') { - handler.on_replacement_field(handler.on_arg_id(), begin); - } else if (*begin == '{') { - handler.on_text(begin, begin + 1); - } else { - auto adapter = id_adapter<Handler, Char>{handler, 0}; - begin = parse_arg_id(begin, end, adapter); - Char c = begin != end ? *begin : Char(); - if (c == '}') { - handler.on_replacement_field(adapter.arg_id, begin); - } else if (c == ':') { - begin = handler.on_format_specs(adapter.arg_id, begin + 1, end); - if (begin == end || *begin != '}') - return handler.on_error("unknown format specifier"), end; - } else { - return handler.on_error("missing '}' in format string"), end; - } - } - return begin + 1; -} - -template <bool IS_CONSTEXPR, typename Char, typename Handler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL FMT_INLINE void parse_format_string( - basic_string_view<Char> format_str, Handler&& handler) { - auto begin = format_str.data(); - auto end = begin + format_str.size(); - if (end - begin < 32) { - // Use a simple loop instead of memchr for small strings. - const Char* p = begin; - while (p != end) { - auto c = *p++; - if (c == '{') { - handler.on_text(begin, p - 1); - begin = p = parse_replacement_field(p - 1, end, handler); - } else if (c == '}') { - if (p == end || *p != '}') - return handler.on_error("unmatched '}' in format string"); - handler.on_text(begin, p); - begin = ++p; - } - } - handler.on_text(begin, end); - return; - } - struct writer { - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(const Char* pbegin, const Char* pend) { - if (pbegin == pend) return; - for (;;) { - const Char* p = nullptr; - if (!find<IS_CONSTEXPR>(pbegin, pend, '}', p)) - return handler_.on_text(pbegin, pend); - ++p; - if (p == pend || *p != '}') - return handler_.on_error("unmatched '}' in format string"); - handler_.on_text(pbegin, p); - pbegin = p + 1; - } - } - Handler& handler_; - } write{handler}; - while (begin != end) { - // Doing two passes with memchr (one for '{' and another for '}') is up to - // 2.5x faster than the naive one-pass implementation on big format strings. - const Char* p = begin; - if (*begin != '{' && !find<IS_CONSTEXPR>(begin + 1, end, '{', p)) - return write(begin, end); - write(begin, p); - begin = parse_replacement_field(p, end, handler); - } -} - -template <typename T, typename ParseContext> -FMT_CONSTEXPR const typename ParseContext::char_type* parse_format_specs( - ParseContext& ctx) { - using char_type = typename ParseContext::char_type; - using context = buffer_context<char_type>; - using mapped_type = - conditional_t<detail::mapped_type_constant<T, context>::value != - type::custom_type, - decltype(arg_mapper<context>().map(std::declval<T>())), T>; - auto f = conditional_t<has_formatter<mapped_type, context>::value, - formatter<mapped_type, char_type>, - detail::fallback_formatter<T, char_type>>(); - return f.parse(ctx); -} - -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename Context> -struct format_handler : detail::error_handler { - basic_format_parse_context<Char> parse_context; - Context context; - - format_handler(OutputIt out, basic_string_view<Char> str, - basic_format_args<Context> format_args, detail::locale_ref loc) - : parse_context(str), context(out, format_args, loc) {} - - void on_text(const Char* begin, const Char* end) { - auto size = to_unsigned(end - begin); - auto out = context.out(); - auto&& it = reserve(out, size); - it = std::copy_n(begin, size, it); - context.advance_to(out); - } - - int on_arg_id() { return parse_context.next_arg_id(); } - int on_arg_id(int id) { return parse_context.check_arg_id(id), id; } - int on_arg_id(basic_string_view<Char> id) { - int arg_id = context.arg_id(id); - if (arg_id < 0) on_error("argument not found"); - return arg_id; - } - - FMT_INLINE void on_replacement_field(int id, const Char*) { - auto arg = get_arg(context, id); - context.advance_to(visit_format_arg( - default_arg_formatter<OutputIt, Char>{context.out(), context.args(), - context.locale()}, - arg)); - } - - const Char* on_format_specs(int id, const Char* begin, const Char* end) { - auto arg = get_arg(context, id); - if (arg.type() == type::custom_type) { - advance_to(parse_context, begin); - visit_format_arg(custom_formatter<Context>(parse_context, context), arg); - return parse_context.begin(); - } - auto specs = basic_format_specs<Char>(); - if (begin + 1 < end && begin[1] == '}' && is_ascii_letter(*begin)) { - specs.type = static_cast<char>(*begin++); - } else { - using parse_context_t = basic_format_parse_context<Char>; - specs_checker<specs_handler<parse_context_t, Context>> handler( - specs_handler<parse_context_t, Context>(specs, parse_context, - context), - arg.type()); - begin = parse_format_specs(begin, end, handler); - if (begin == end || *begin != '}') - on_error("missing '}' in format string"); - } - context.advance_to(visit_format_arg( - arg_formatter<OutputIt, Char>(context, &parse_context, &specs), arg)); - return begin; - } +#if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS +# if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS +template <typename T, typename Char, size_t N, + fmt::detail_exported::fixed_string<Char, N> Str> +struct statically_named_arg : view { + static constexpr auto name = Str.data; + + const T& value; + statically_named_arg(const T& v) : value(v) {} }; -// A parse context with extra argument id checks. It is only used at compile -// time because adding checks at runtime would introduce substantial overhead -// and would be redundant since argument ids are checked when arguments are -// retrieved anyway. -template <typename Char, typename ErrorHandler = error_handler> -class compile_parse_context - : public basic_format_parse_context<Char, ErrorHandler> { - private: - int num_args_; - using base = basic_format_parse_context<Char, ErrorHandler>; - - public: - explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR compile_parse_context( - basic_string_view<Char> format_str, int num_args = max_value<int>(), - ErrorHandler eh = {}) - : base(format_str, eh), num_args_(num_args) {} +template <typename T, typename Char, size_t N, + fmt::detail_exported::fixed_string<Char, N> Str> +struct is_named_arg<statically_named_arg<T, Char, N, Str>> : std::true_type {}; - FMT_CONSTEXPR int next_arg_id() { - int id = base::next_arg_id(); - if (id >= num_args_) this->on_error("argument not found"); - return id; - } +template <typename T, typename Char, size_t N, + fmt::detail_exported::fixed_string<Char, N> Str> +struct is_statically_named_arg<statically_named_arg<T, Char, N, Str>> + : std::true_type {}; - FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_arg_id(int id) { - base::check_arg_id(id); - if (id >= num_args_) this->on_error("argument not found"); +template <typename Char, size_t N, + fmt::detail_exported::fixed_string<Char, N> Str> +struct udl_arg { + template <typename T> auto operator=(T&& value) const { + return statically_named_arg<T, Char, N, Str>(std::forward<T>(value)); } - using base::check_arg_id; }; +# else +template <typename Char> struct udl_arg { + const Char* str; -template <typename Char, typename ErrorHandler, typename... Args> -class format_string_checker { - public: - explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR format_string_checker( - basic_string_view<Char> format_str, ErrorHandler eh) - : context_(format_str, num_args, eh), - parse_funcs_{&parse_format_specs<Args, parse_context_type>...} {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const Char*, const Char*) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id() { return context_.next_arg_id(); } - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(int id) { return context_.check_arg_id(id), id; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(basic_string_view<Char>) { - on_error("compile-time checks don't support named arguments"); - return 0; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_replacement_field(int, const Char*) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* on_format_specs(int id, const Char* begin, - const Char*) { - advance_to(context_, begin); - return id < num_args ? parse_funcs_[id](context_) : begin; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { - context_.on_error(message); + template <typename T> auto operator=(T&& value) const -> named_arg<Char, T> { + return {str, std::forward<T>(value)}; } - - private: - using parse_context_type = compile_parse_context<Char, ErrorHandler>; - enum { num_args = sizeof...(Args) }; - - // Format specifier parsing function. - using parse_func = const Char* (*)(parse_context_type&); - - parse_context_type context_; - parse_func parse_funcs_[num_args > 0 ? num_args : 1]; }; +# endif +#endif // FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS -// Converts string literals to basic_string_view. -template <typename Char, size_t N> -FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_string_view<Char> compile_string_to_view( - const Char (&s)[N]) { - // Remove trailing null character if needed. Won't be present if this is used - // with raw character array (i.e. not defined as a string). - return {s, - N - ((std::char_traits<Char>::to_int_type(s[N - 1]) == 0) ? 1 : 0)}; -} - -// Converts string_view to basic_string_view. -template <typename Char> -FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_string_view<Char> compile_string_to_view( - const std_string_view<Char>& s) { - return {s.data(), s.size()}; -} - -#define FMT_STRING_IMPL(s, base) \ - [] { \ - /* Use a macro-like name to avoid shadowing warnings. */ \ - struct FMT_COMPILE_STRING : base { \ - using char_type = fmt::remove_cvref_t<decltype(s[0])>; \ - FMT_MAYBE_UNUSED FMT_CONSTEXPR \ - operator fmt::basic_string_view<char_type>() const { \ - return fmt::detail::compile_string_to_view<char_type>(s); \ - } \ - }; \ - return FMT_COMPILE_STRING(); \ - }() - -/** - \rst - Constructs a compile-time format string from a string literal *s*. - - **Example**:: - - // A compile-time error because 'd' is an invalid specifier for strings. - std::string s = fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{:d}"), "foo"); - \endrst - */ -#define FMT_STRING(s) FMT_STRING_IMPL(s, fmt::compile_string) - -template <typename... Args, typename S, - enable_if_t<(is_compile_string<S>::value), int>> -void check_format_string(S format_str) { - FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL auto s = to_string_view(format_str); - using checker = format_string_checker<typename S::char_type, error_handler, - remove_cvref_t<Args>...>; - FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL bool invalid_format = - (parse_format_string<true>(s, checker(s, {})), true); - (void)invalid_format; +template <typename Locale, typename Char> +auto vformat(const Locale& loc, basic_string_view<Char> fmt, + basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) + -> std::basic_string<Char> { + auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); + detail::vformat_to(buf, fmt, args, detail::locale_ref(loc)); + return {buf.data(), buf.size()}; } -template <template <typename> class Handler, typename Context> -void handle_dynamic_spec(int& value, arg_ref<typename Context::char_type> ref, - Context& ctx) { - switch (ref.kind) { - case arg_id_kind::none: - break; - case arg_id_kind::index: - value = detail::get_dynamic_spec<Handler>(ctx.arg(ref.val.index), - ctx.error_handler()); - break; - case arg_id_kind::name: - value = detail::get_dynamic_spec<Handler>(ctx.arg(ref.val.name), - ctx.error_handler()); - break; - } -} - -using format_func = void (*)(detail::buffer<char>&, int, string_view); +using format_func = void (*)(detail::buffer<char>&, int, const char*); FMT_API void format_error_code(buffer<char>& out, int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT; + string_view message) noexcept; FMT_API void report_error(format_func func, int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT; + const char* message) noexcept; } // namespace detail -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -using arg_formatter FMT_DEPRECATED_ALIAS = - detail::arg_formatter<OutputIt, Char>; +FMT_API auto vsystem_error(int error_code, string_view format_str, + format_args args) -> std::system_error; /** - An error returned by an operating system or a language runtime, - for example a file opening error. -*/ -FMT_CLASS_API -class FMT_API system_error : public std::runtime_error { - private: - void init(int err_code, string_view format_str, format_args args); - - protected: - int error_code_; + \rst + Constructs :class:`std::system_error` with a message formatted with + ``fmt::format(fmt, args...)``. + *error_code* is a system error code as given by ``errno``. - system_error() : std::runtime_error(""), error_code_(0) {} + **Example**:: - public: - /** - \rst - Constructs a :class:`fmt::system_error` object with a description - formatted with `fmt::format_system_error`. *message* and additional - arguments passed into the constructor are formatted similarly to - `fmt::format`. - - **Example**:: - - // This throws a system_error with the description - // cannot open file 'madeup': No such file or directory - // or similar (system message may vary). - const char *filename = "madeup"; - std::FILE *file = std::fopen(filename, "r"); - if (!file) - throw fmt::system_error(errno, "cannot open file '{}'", filename); - \endrst - */ - template <typename... Args> - system_error(int error_code, string_view message, const Args&... args) - : std::runtime_error("") { - init(error_code, message, make_format_args(args...)); - } - system_error(const system_error&) = default; - system_error& operator=(const system_error&) = default; - system_error(system_error&&) = default; - system_error& operator=(system_error&&) = default; - ~system_error() FMT_NOEXCEPT FMT_OVERRIDE; - - int error_code() const { return error_code_; } -}; + // This throws std::system_error with the description + // cannot open file 'madeup': No such file or directory + // or similar (system message may vary). + const char* filename = "madeup"; + std::FILE* file = std::fopen(filename, "r"); + if (!file) + throw fmt::system_error(errno, "cannot open file '{}'", filename); + \endrst + */ +template <typename... T> +auto system_error(int error_code, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) + -> std::system_error { + return vsystem_error(error_code, fmt, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); +} /** \rst - Formats an error returned by an operating system or a language runtime, - for example a file opening error, and writes it to *out* in the following - form: + Formats an error message for an error returned by an operating system or a + language runtime, for example a file opening error, and writes it to *out*. + The format is the same as the one used by ``std::system_error(ec, message)`` + where ``ec`` is ``std::error_code(error_code, std::generic_category()})``. + It is implementation-defined but normally looks like: .. parsed-literal:: *<message>*: *<system-message>* - where *<message>* is the passed message and *<system-message>* is - the system message corresponding to the error code. + where *<message>* is the passed message and *<system-message>* is the system + message corresponding to the error code. *error_code* is a system error code as given by ``errno``. - If *error_code* is not a valid error code such as -1, the system message - may look like "Unknown error -1" and is platform-dependent. \endrst */ FMT_API void format_system_error(detail::buffer<char>& out, int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT; + const char* message) noexcept; // Reports a system error without throwing an exception. // Can be used to report errors from destructors. -FMT_API void report_system_error(int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT; +FMT_API void report_system_error(int error_code, const char* message) noexcept; /** Fast integer formatter. */ class format_int { @@ -3339,12 +3997,12 @@ class format_int { mutable char buffer_[buffer_size]; char* str_; - template <typename UInt> char* format_unsigned(UInt value) { + template <typename UInt> auto format_unsigned(UInt value) -> char* { auto n = static_cast<detail::uint32_or_64_or_128_t<UInt>>(value); return detail::format_decimal(buffer_, n, buffer_size - 1).begin; } - template <typename Int> char* format_signed(Int value) { + template <typename Int> auto format_signed(Int value) -> char* { auto abs_value = static_cast<detail::uint32_or_64_or_128_t<Int>>(value); bool negative = value < 0; if (negative) abs_value = 0 - abs_value; @@ -3363,7 +4021,7 @@ class format_int { : str_(format_unsigned(value)) {} /** Returns the number of characters written to the output buffer. */ - size_t size() const { + auto size() const -> size_t { return detail::to_unsigned(buffer_ - str_ + buffer_size - 1); } @@ -3371,13 +4029,13 @@ class format_int { Returns a pointer to the output buffer content. No terminating null character is appended. */ - const char* data() const { return str_; } + auto data() const -> const char* { return str_; } /** Returns a pointer to the output buffer content with terminating null character appended. */ - const char* c_str() const { + auto c_str() const -> const char* { buffer_[buffer_size - 1] = '\0'; return str_; } @@ -3387,209 +4045,39 @@ class format_int { Returns the content of the output buffer as an ``std::string``. \endrst */ - std::string str() const { return std::string(str_, size()); } + auto str() const -> std::string { return std::string(str_, size()); } }; -// A formatter specialization for the core types corresponding to detail::type -// constants. template <typename T, typename Char> -struct formatter<T, Char, - enable_if_t<detail::type_constant<T, Char>::value != - detail::type::custom_type>> { - FMT_CONSTEXPR formatter() = default; - - // Parses format specifiers stopping either at the end of the range or at the - // terminating '}'. - template <typename ParseContext> - FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - using handler_type = detail::dynamic_specs_handler<ParseContext>; - auto type = detail::type_constant<T, Char>::value; - detail::specs_checker<handler_type> handler(handler_type(specs_, ctx), - type); - auto it = parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), handler); - auto eh = ctx.error_handler(); - switch (type) { - case detail::type::none_type: - FMT_ASSERT(false, "invalid argument type"); - break; - case detail::type::int_type: - case detail::type::uint_type: - case detail::type::long_long_type: - case detail::type::ulong_long_type: - case detail::type::int128_type: - case detail::type::uint128_type: - case detail::type::bool_type: - handle_int_type_spec(specs_.type, - detail::int_type_checker<decltype(eh)>(eh)); - break; - case detail::type::char_type: - handle_char_specs( - &specs_, detail::char_specs_checker<decltype(eh)>(specs_.type, eh)); - break; - case detail::type::float_type: - if (detail::const_check(FMT_USE_FLOAT)) - detail::parse_float_type_spec(specs_, eh); - else - FMT_ASSERT(false, "float support disabled"); - break; - case detail::type::double_type: - if (detail::const_check(FMT_USE_DOUBLE)) - detail::parse_float_type_spec(specs_, eh); - else - FMT_ASSERT(false, "double support disabled"); - break; - case detail::type::long_double_type: - if (detail::const_check(FMT_USE_LONG_DOUBLE)) - detail::parse_float_type_spec(specs_, eh); - else - FMT_ASSERT(false, "long double support disabled"); - break; - case detail::type::cstring_type: - detail::handle_cstring_type_spec( - specs_.type, detail::cstring_type_checker<decltype(eh)>(eh)); - break; - case detail::type::string_type: - detail::check_string_type_spec(specs_.type, eh); - break; - case detail::type::pointer_type: - detail::check_pointer_type_spec(specs_.type, eh); - break; - case detail::type::custom_type: - // Custom format specifiers should be checked in parse functions of - // formatter specializations. - break; - } - return it; - } +struct formatter<T, Char, enable_if_t<detail::has_format_as<T>::value>> + : private formatter<detail::format_as_t<T>, Char> { + using base = formatter<detail::format_as_t<T>, Char>; + using base::parse; template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(const T& val, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs_.width, - specs_.width_ref, ctx); - detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>( - specs_.precision, specs_.precision_ref, ctx); - using af = detail::arg_formatter<typename FormatContext::iterator, - typename FormatContext::char_type>; - return visit_format_arg(af(ctx, nullptr, &specs_), - detail::make_arg<FormatContext>(val)); + auto format(const T& value, FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return base::format(format_as(value), ctx); } - - private: - detail::dynamic_format_specs<Char> specs_; }; -#define FMT_FORMAT_AS(Type, Base) \ - template <typename Char> \ - struct formatter<Type, Char> : formatter<Base, Char> { \ - template <typename FormatContext> \ - auto format(Type const& val, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { \ - return formatter<Base, Char>::format(val, ctx); \ - } \ - } +#define FMT_FORMAT_AS(Type, Base) \ + template <typename Char> \ + struct formatter<Type, Char> : formatter<Base, Char> {} FMT_FORMAT_AS(signed char, int); FMT_FORMAT_AS(unsigned char, unsigned); FMT_FORMAT_AS(short, int); FMT_FORMAT_AS(unsigned short, unsigned); -FMT_FORMAT_AS(long, long long); -FMT_FORMAT_AS(unsigned long, unsigned long long); +FMT_FORMAT_AS(long, detail::long_type); +FMT_FORMAT_AS(unsigned long, detail::ulong_type); FMT_FORMAT_AS(Char*, const Char*); FMT_FORMAT_AS(std::basic_string<Char>, basic_string_view<Char>); FMT_FORMAT_AS(std::nullptr_t, const void*); FMT_FORMAT_AS(detail::std_string_view<Char>, basic_string_view<Char>); - -template <typename Char> -struct formatter<void*, Char> : formatter<const void*, Char> { - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(void* val, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - return formatter<const void*, Char>::format(val, ctx); - } -}; +FMT_FORMAT_AS(void*, const void*); template <typename Char, size_t N> -struct formatter<Char[N], Char> : formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char> { - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(const Char* val, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - return formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char>::format(val, ctx); - } -}; - -// A formatter for types known only at run time such as variant alternatives. -// -// Usage: -// using variant = std::variant<int, std::string>; -// template <> -// struct formatter<variant>: dynamic_formatter<> { -// auto format(const variant& v, format_context& ctx) { -// return visit([&](const auto& val) { -// return dynamic_formatter<>::format(val, ctx); -// }, v); -// } -// }; -template <typename Char = char> class dynamic_formatter { - private: - struct null_handler : detail::error_handler { - void on_align(align_t) {} - void on_plus() {} - void on_minus() {} - void on_space() {} - void on_hash() {} - }; - - public: - template <typename ParseContext> - auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - format_str_ = ctx.begin(); - // Checks are deferred to formatting time when the argument type is known. - detail::dynamic_specs_handler<ParseContext> handler(specs_, ctx); - return parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), handler); - } - - template <typename T, typename FormatContext> - auto format(const T& val, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - handle_specs(ctx); - detail::specs_checker<null_handler> checker( - null_handler(), detail::mapped_type_constant<T, FormatContext>::value); - checker.on_align(specs_.align); - switch (specs_.sign) { - case sign::none: - break; - case sign::plus: - checker.on_plus(); - break; - case sign::minus: - checker.on_minus(); - break; - case sign::space: - checker.on_space(); - break; - } - if (specs_.alt) checker.on_hash(); - if (specs_.precision >= 0) checker.end_precision(); - using af = detail::arg_formatter<typename FormatContext::iterator, - typename FormatContext::char_type>; - visit_format_arg(af(ctx, nullptr, &specs_), - detail::make_arg<FormatContext>(val)); - return ctx.out(); - } - - private: - template <typename Context> void handle_specs(Context& ctx) { - detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs_.width, - specs_.width_ref, ctx); - detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>( - specs_.precision, specs_.precision_ref, ctx); - } - - detail::dynamic_format_specs<Char> specs_; - const Char* format_str_; -}; - -template <typename Char, typename ErrorHandler> -FMT_CONSTEXPR void advance_to( - basic_format_parse_context<Char, ErrorHandler>& ctx, const Char* p) { - ctx.advance_to(ctx.begin() + (p - &*ctx.begin())); -} +struct formatter<Char[N], Char> : formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char> {}; /** \rst @@ -3600,14 +4088,40 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR void advance_to( auto s = fmt::format("{}", fmt::ptr(p)); \endrst */ -template <typename T> inline const void* ptr(const T* p) { return p; } -template <typename T> inline const void* ptr(const std::unique_ptr<T>& p) { +template <typename T> auto ptr(T p) -> const void* { + static_assert(std::is_pointer<T>::value, ""); + return detail::bit_cast<const void*>(p); +} +template <typename T, typename Deleter> +auto ptr(const std::unique_ptr<T, Deleter>& p) -> const void* { return p.get(); } -template <typename T> inline const void* ptr(const std::shared_ptr<T>& p) { +template <typename T> auto ptr(const std::shared_ptr<T>& p) -> const void* { return p.get(); } +/** + \rst + Converts ``e`` to the underlying type. + + **Example**:: + + enum class color { red, green, blue }; + auto s = fmt::format("{}", fmt::underlying(color::red)); + \endrst + */ +template <typename Enum> +constexpr auto underlying(Enum e) noexcept -> underlying_t<Enum> { + return static_cast<underlying_t<Enum>>(e); +} + +namespace enums { +template <typename Enum, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_enum<Enum>::value)> +constexpr auto format_as(Enum e) noexcept -> underlying_t<Enum> { + return static_cast<underlying_t<Enum>>(e); +} +} // namespace enums + class bytes { private: string_view data_; @@ -3619,17 +4133,13 @@ class bytes { template <> struct formatter<bytes> { private: - detail::dynamic_format_specs<char> specs_; + detail::dynamic_format_specs<> specs_; public: template <typename ParseContext> - FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - using handler_type = detail::dynamic_specs_handler<ParseContext>; - detail::specs_checker<handler_type> handler(handler_type(specs_, ctx), - detail::type::string_type); - auto it = parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), handler); - detail::check_string_type_spec(specs_.type, ctx.error_handler()); - return it; + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> const char* { + return parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), specs_, ctx, + detail::type::string_type); } template <typename FormatContext> @@ -3642,31 +4152,144 @@ template <> struct formatter<bytes> { } }; -template <typename It, typename Sentinel, typename Char> -struct arg_join : detail::view { +// group_digits_view is not derived from view because it copies the argument. +template <typename T> struct group_digits_view { + T value; +}; + +/** + \rst + Returns a view that formats an integer value using ',' as a locale-independent + thousands separator. + + **Example**:: + + fmt::print("{}", fmt::group_digits(12345)); + // Output: "12,345" + \endrst + */ +template <typename T> auto group_digits(T value) -> group_digits_view<T> { + return {value}; +} + +template <typename T> struct formatter<group_digits_view<T>> : formatter<T> { + private: + detail::dynamic_format_specs<> specs_; + + public: + template <typename ParseContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> const char* { + return parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), specs_, ctx, + detail::type::int_type); + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(group_digits_view<T> t, FormatContext& ctx) + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs_.width, + specs_.width_ref, ctx); + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>( + specs_.precision, specs_.precision_ref, ctx); + return detail::write_int( + ctx.out(), static_cast<detail::uint64_or_128_t<T>>(t.value), 0, specs_, + detail::digit_grouping<char>("\3", ",")); + } +}; + +template <typename T> struct nested_view { + const formatter<T>* fmt; + const T* value; +}; + +template <typename T> struct formatter<nested_view<T>> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> const char* { + return ctx.begin(); + } + auto format(nested_view<T> view, format_context& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return view.fmt->format(*view.value, ctx); + } +}; + +template <typename T> struct nested_formatter { + private: + int width_; + detail::fill_t<char> fill_; + align_t align_ : 4; + formatter<T> formatter_; + + public: + constexpr nested_formatter() : width_(0), align_(align_t::none) {} + + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> const char* { + auto specs = detail::dynamic_format_specs<char>(); + auto it = parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), specs, ctx, + detail::type::none_type); + width_ = specs.width; + fill_ = specs.fill; + align_ = specs.align; + ctx.advance_to(it); + return formatter_.parse(ctx); + } + + template <typename F> + auto write_padded(format_context& ctx, F write) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + if (width_ == 0) return write(ctx.out()); + auto buf = memory_buffer(); + write(std::back_inserter(buf)); + auto specs = format_specs<>(); + specs.width = width_; + specs.fill = fill_; + specs.align = align_; + return detail::write(ctx.out(), string_view(buf.data(), buf.size()), specs); + } + + auto nested(const T& value) const -> nested_view<T> { + return nested_view<T>{&formatter_, &value}; + } +}; + +// DEPRECATED! join_view will be moved to ranges.h. +template <typename It, typename Sentinel, typename Char = char> +struct join_view : detail::view { It begin; Sentinel end; basic_string_view<Char> sep; - arg_join(It b, Sentinel e, basic_string_view<Char> s) + join_view(It b, Sentinel e, basic_string_view<Char> s) : begin(b), end(e), sep(s) {} }; template <typename It, typename Sentinel, typename Char> -struct formatter<arg_join<It, Sentinel, Char>, Char> - : formatter<typename std::iterator_traits<It>::value_type, Char> { +struct formatter<join_view<It, Sentinel, Char>, Char> { + private: + using value_type = +#ifdef __cpp_lib_ranges + std::iter_value_t<It>; +#else + typename std::iterator_traits<It>::value_type; +#endif + formatter<remove_cvref_t<value_type>, Char> value_formatter_; + + public: + template <typename ParseContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> const Char* { + return value_formatter_.parse(ctx); + } + template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(const arg_join<It, Sentinel, Char>& value, FormatContext& ctx) - -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - using base = formatter<typename std::iterator_traits<It>::value_type, Char>; + auto format(const join_view<It, Sentinel, Char>& value, + FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { auto it = value.begin; auto out = ctx.out(); if (it != value.end) { - out = base::format(*it++, ctx); + out = value_formatter_.format(*it, ctx); + ++it; while (it != value.end) { - out = std::copy(value.sep.begin(), value.sep.end(), out); + out = detail::copy_str<Char>(value.sep.begin(), value.sep.end(), out); ctx.advance_to(out); - out = base::format(*it++, ctx); + out = value_formatter_.format(*it, ctx); + ++it; } } return out; @@ -3674,22 +4297,17 @@ struct formatter<arg_join<It, Sentinel, Char>, Char> }; /** - Returns an object that formats the iterator range `[begin, end)` with elements + Returns a view that formats the iterator range `[begin, end)` with elements separated by `sep`. */ template <typename It, typename Sentinel> -arg_join<It, Sentinel, char> join(It begin, Sentinel end, string_view sep) { - return {begin, end, sep}; -} - -template <typename It, typename Sentinel> -arg_join<It, Sentinel, wchar_t> join(It begin, Sentinel end, wstring_view sep) { +auto join(It begin, Sentinel end, string_view sep) -> join_view<It, Sentinel> { return {begin, end, sep}; } /** \rst - Returns an object that formats `range` with elements separated by `sep`. + Returns a view that formats `range` with elements separated by `sep`. **Example**:: @@ -3704,14 +4322,8 @@ arg_join<It, Sentinel, wchar_t> join(It begin, Sentinel end, wstring_view sep) { \endrst */ template <typename Range> -arg_join<detail::iterator_t<Range>, detail::sentinel_t<Range>, char> join( - Range&& range, string_view sep) { - return join(std::begin(range), std::end(range), sep); -} - -template <typename Range> -arg_join<detail::iterator_t<Range>, detail::sentinel_t<Range>, wchar_t> join( - Range&& range, wstring_view sep) { +auto join(Range&& range, string_view sep) + -> join_view<detail::iterator_t<Range>, detail::sentinel_t<Range>> { return join(std::begin(range), std::end(range), sep); } @@ -3726,210 +4338,129 @@ arg_join<detail::iterator_t<Range>, detail::sentinel_t<Range>, wchar_t> join( std::string answer = fmt::to_string(42); \endrst */ -template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)> -inline std::string to_string(const T& value) { - std::string result; - detail::write<char>(std::back_inserter(result), value); - return result; +template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value && + !detail::has_format_as<T>::value)> +inline auto to_string(const T& value) -> std::string { + auto buffer = memory_buffer(); + detail::write<char>(appender(buffer), value); + return {buffer.data(), buffer.size()}; } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> -inline std::string to_string(T value) { - // The buffer should be large enough to store the number including the sign or - // "false" for bool. +FMT_NODISCARD inline auto to_string(T value) -> std::string { + // The buffer should be large enough to store the number including the sign + // or "false" for bool. constexpr int max_size = detail::digits10<T>() + 2; char buffer[max_size > 5 ? static_cast<unsigned>(max_size) : 5]; char* begin = buffer; return std::string(begin, detail::write<char>(begin, value)); } -/** - Converts *value* to ``std::wstring`` using the default format for type *T*. - */ -template <typename T> inline std::wstring to_wstring(const T& value) { - return format(L"{}", value); -} - template <typename Char, size_t SIZE> -std::basic_string<Char> to_string(const basic_memory_buffer<Char, SIZE>& buf) { +FMT_NODISCARD auto to_string(const basic_memory_buffer<Char, SIZE>& buf) + -> std::basic_string<Char> { auto size = buf.size(); detail::assume(size < std::basic_string<Char>().max_size()); return std::basic_string<Char>(buf.data(), size); } +template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value && + detail::has_format_as<T>::value)> +inline auto to_string(const T& value) -> std::string { + return to_string(format_as(value)); +} + +FMT_END_EXPORT + +namespace detail { + template <typename Char> -void detail::vformat_to( - detail::buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args, - detail::locale_ref loc) { - using iterator = typename buffer_context<Char>::iterator; +void vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> fmt, + typename vformat_args<Char>::type args, locale_ref loc) { auto out = buffer_appender<Char>(buf); - if (format_str.size() == 2 && equal2(format_str.data(), "{}")) { + if (fmt.size() == 2 && equal2(fmt.data(), "{}")) { auto arg = args.get(0); if (!arg) error_handler().on_error("argument not found"); - visit_format_arg(default_arg_formatter<iterator, Char>{out, args, loc}, - arg); + visit_format_arg(default_arg_formatter<Char>{out, args, loc}, arg); return; } - format_handler<iterator, Char, buffer_context<Char>> h(out, format_str, args, - loc); - parse_format_string<false>(format_str, h); -} - -#ifndef FMT_HEADER_ONLY -extern template void detail::vformat_to(detail::buffer<char>&, string_view, - basic_format_args<format_context>, - detail::locale_ref); -namespace detail { - -extern template FMT_API std::string grouping_impl<char>(locale_ref loc); -extern template FMT_API std::string grouping_impl<wchar_t>(locale_ref loc); -extern template FMT_API char thousands_sep_impl<char>(locale_ref loc); -extern template FMT_API wchar_t thousands_sep_impl<wchar_t>(locale_ref loc); -extern template FMT_API char decimal_point_impl(locale_ref loc); -extern template FMT_API wchar_t decimal_point_impl(locale_ref loc); -extern template int format_float<double>(double value, int precision, - float_specs specs, buffer<char>& buf); -extern template int format_float<long double>(long double value, int precision, - float_specs specs, - buffer<char>& buf); -int snprintf_float(float value, int precision, float_specs specs, - buffer<char>& buf) = delete; -extern template int snprintf_float<double>(double value, int precision, - float_specs specs, - buffer<char>& buf); -extern template int snprintf_float<long double>(long double value, - int precision, - float_specs specs, - buffer<char>& buf); -} // namespace detail -#endif -template <typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_string<S>::value)> -inline void vformat_to( - detail::buffer<Char>& buf, const S& format_str, - basic_format_args<FMT_BUFFER_CONTEXT(type_identity_t<Char>)> args) { - return detail::vformat_to(buf, to_string_view(format_str), args); -} - -template <typename S, typename... Args, size_t SIZE = inline_buffer_size, - typename Char = enable_if_t<detail::is_string<S>::value, char_t<S>>> -inline typename buffer_context<Char>::iterator format_to( - basic_memory_buffer<Char, SIZE>& buf, const S& format_str, Args&&... args) { - const auto& vargs = fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...); - detail::vformat_to(buf, to_string_view(format_str), vargs); - return detail::buffer_appender<Char>(buf); -} + struct format_handler : error_handler { + basic_format_parse_context<Char> parse_context; + buffer_context<Char> context; -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char = char> -using format_context_t = basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>; + format_handler(buffer_appender<Char> p_out, basic_string_view<Char> str, + basic_format_args<buffer_context<Char>> p_args, + locale_ref p_loc) + : parse_context(str), context(p_out, p_args, p_loc) {} -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char = char> -using format_args_t = basic_format_args<format_context_t<OutputIt, Char>>; - -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char = typename OutputIt::value_type> -using format_to_n_context FMT_DEPRECATED_ALIAS = buffer_context<Char>; - -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char = typename OutputIt::value_type> -using format_to_n_args FMT_DEPRECATED_ALIAS = - basic_format_args<buffer_context<Char>>; - -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename... Args> -FMT_DEPRECATED format_arg_store<buffer_context<Char>, Args...> -make_format_to_n_args(const Args&... args) { - return format_arg_store<buffer_context<Char>, Args...>(args...); -} + void on_text(const Char* begin, const Char* end) { + auto text = basic_string_view<Char>(begin, to_unsigned(end - begin)); + context.advance_to(write<Char>(context.out(), text)); + } -template <typename Char, enable_if_t<(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value), int>> -std::basic_string<Char> detail::vformat( - basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - detail::vformat_to(buffer, format_str, args); - return to_string(buffer); -} + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id() -> int { + return parse_context.next_arg_id(); + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id(int id) -> int { + return parse_context.check_arg_id(id), id; + } + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id(basic_string_view<Char> id) -> int { + int arg_id = context.arg_id(id); + if (arg_id < 0) on_error("argument not found"); + return arg_id; + } -template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<Char, wchar_t>::value)> -void vprint(std::FILE* f, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - wformat_args args) { - wmemory_buffer buffer; - detail::vformat_to(buffer, format_str, args); - buffer.push_back(L'\0'); - if (std::fputws(buffer.data(), f) == -1) - FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot write to file")); -} + FMT_INLINE void on_replacement_field(int id, const Char*) { + auto arg = get_arg(context, id); + context.advance_to(visit_format_arg( + default_arg_formatter<Char>{context.out(), context.args(), + context.locale()}, + arg)); + } -template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<Char, wchar_t>::value)> -void vprint(basic_string_view<Char> format_str, wformat_args args) { - vprint(stdout, format_str, args); + auto on_format_specs(int id, const Char* begin, const Char* end) + -> const Char* { + auto arg = get_arg(context, id); + if (arg.type() == type::custom_type) { + parse_context.advance_to(begin); + visit_format_arg(custom_formatter<Char>{parse_context, context}, arg); + return parse_context.begin(); + } + auto specs = detail::dynamic_format_specs<Char>(); + begin = parse_format_specs(begin, end, specs, parse_context, arg.type()); + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>( + specs.width, specs.width_ref, context); + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>( + specs.precision, specs.precision_ref, context); + if (begin == end || *begin != '}') + on_error("missing '}' in format string"); + auto f = arg_formatter<Char>{context.out(), specs, context.locale()}; + context.advance_to(visit_format_arg(f, arg)); + return begin; + } + }; + detail::parse_format_string<false>(fmt, format_handler(out, fmt, args, loc)); } -#if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS -namespace detail { +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT -# if FMT_USE_UDL_TEMPLATE -template <typename Char, Char... CHARS> class udl_formatter { - public: - template <typename... Args> - std::basic_string<Char> operator()(Args&&... args) const { - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL Char s[] = {CHARS..., '\0'}; - return format(FMT_STRING(s), std::forward<Args>(args)...); - } -}; -# else -template <typename Char> struct udl_formatter { - basic_string_view<Char> str; - - template <typename... Args> - std::basic_string<Char> operator()(Args&&... args) const { - return format(str, std::forward<Args>(args)...); - } -}; -# endif // FMT_USE_UDL_TEMPLATE - -template <typename Char> struct udl_arg { - const Char* str; +#ifndef FMT_HEADER_ONLY +extern template FMT_API void vformat_to(buffer<char>&, string_view, + typename vformat_args<>::type, + locale_ref); +extern template FMT_API auto thousands_sep_impl<char>(locale_ref) + -> thousands_sep_result<char>; +extern template FMT_API auto thousands_sep_impl<wchar_t>(locale_ref) + -> thousands_sep_result<wchar_t>; +extern template FMT_API auto decimal_point_impl(locale_ref) -> char; +extern template FMT_API auto decimal_point_impl(locale_ref) -> wchar_t; +#endif // FMT_HEADER_ONLY - template <typename T> named_arg<Char, T> operator=(T&& value) const { - return {str, std::forward<T>(value)}; - } -}; } // namespace detail +#if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS inline namespace literals { -# if FMT_USE_UDL_TEMPLATE -# pragma GCC diagnostic push -# pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wpedantic" -# if FMT_CLANG_VERSION -# pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wgnu-string-literal-operator-template" -# endif -template <typename Char, Char... CHARS> -FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::udl_formatter<Char, CHARS...> operator""_format() { - return {}; -} -# pragma GCC diagnostic pop -# else -/** - \rst - User-defined literal equivalent of :func:`fmt::format`. - - **Example**:: - - using namespace fmt::literals; - std::string message = "The answer is {}"_format(42); - \endrst - */ -FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::udl_formatter<char> operator"" _format(const char* s, - size_t n) { - return {{s, n}}; -} -FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::udl_formatter<wchar_t> operator"" _format( - const wchar_t* s, size_t n) { - return {{s, n}}; -} -# endif // FMT_USE_UDL_TEMPLATE - /** \rst User-defined literal equivalent of :func:`fmt::arg`. @@ -3940,14 +4471,84 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::udl_formatter<wchar_t> operator"" _format( fmt::print("Elapsed time: {s:.2f} seconds", "s"_a=1.23); \endrst */ -FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::udl_arg<char> operator"" _a(const char* s, size_t) { - return {s}; +# if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS +template <detail_exported::fixed_string Str> constexpr auto operator""_a() { + using char_t = remove_cvref_t<decltype(Str.data[0])>; + return detail::udl_arg<char_t, sizeof(Str.data) / sizeof(char_t), Str>(); } -FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::udl_arg<wchar_t> operator"" _a(const wchar_t* s, size_t) { +# else +constexpr auto operator""_a(const char* s, size_t) -> detail::udl_arg<char> { return {s}; } +# endif } // namespace literals #endif // FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS + +template <typename Locale, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_locale<Locale>::value)> +inline auto vformat(const Locale& loc, string_view fmt, format_args args) + -> std::string { + return detail::vformat(loc, fmt, args); +} + +template <typename Locale, typename... T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_locale<Locale>::value)> +inline auto format(const Locale& loc, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) + -> std::string { + return fmt::vformat(loc, string_view(fmt), fmt::make_format_args(args...)); +} + +template <typename OutputIt, typename Locale, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char>::value&& + detail::is_locale<Locale>::value)> +auto vformat_to(OutputIt out, const Locale& loc, string_view fmt, + format_args args) -> OutputIt { + using detail::get_buffer; + auto&& buf = get_buffer<char>(out); + detail::vformat_to(buf, fmt, args, detail::locale_ref(loc)); + return detail::get_iterator(buf, out); +} + +template <typename OutputIt, typename Locale, typename... T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char>::value&& + detail::is_locale<Locale>::value)> +FMT_INLINE auto format_to(OutputIt out, const Locale& loc, + format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> OutputIt { + return vformat_to(out, loc, fmt, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); +} + +template <typename Locale, typename... T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_locale<Locale>::value)> +FMT_NODISCARD FMT_INLINE auto formatted_size(const Locale& loc, + format_string<T...> fmt, + T&&... args) -> size_t { + auto buf = detail::counting_buffer<>(); + detail::vformat_to<char>(buf, fmt, fmt::make_format_args(args...), + detail::locale_ref(loc)); + return buf.count(); +} + +FMT_END_EXPORT + +template <typename T, typename Char> +template <typename FormatContext> +FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto +formatter<T, Char, + enable_if_t<detail::type_constant<T, Char>::value != + detail::type::custom_type>>::format(const T& val, + FormatContext& ctx) + const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + if (specs_.width_ref.kind != detail::arg_id_kind::none || + specs_.precision_ref.kind != detail::arg_id_kind::none) { + auto specs = specs_; + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs.width, + specs.width_ref, ctx); + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>( + specs.precision, specs.precision_ref, ctx); + return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), val, specs, ctx.locale()); + } + return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), val, specs_, ctx.locale()); +} + FMT_END_NAMESPACE #ifdef FMT_HEADER_ONLY diff --git a/include/fmt/locale.h b/include/fmt/locale.h deleted file mode 100644 index 7301bf92..00000000 --- a/include/fmt/locale.h +++ /dev/null @@ -1,64 +0,0 @@ -// Formatting library for C++ - std::locale support -// -// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich -// All rights reserved. -// -// For the license information refer to format.h. - -#ifndef FMT_LOCALE_H_ -#define FMT_LOCALE_H_ - -#include <locale> - -#include "format.h" - -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE - -namespace detail { -template <typename Char> -std::basic_string<Char> vformat( - const std::locale& loc, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - detail::vformat_to(buffer, format_str, args, detail::locale_ref(loc)); - return fmt::to_string(buffer); -} -} // namespace detail - -template <typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline std::basic_string<Char> vformat( - const std::locale& loc, const S& format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - return detail::vformat(loc, to_string_view(format_str), args); -} - -template <typename S, typename... Args, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline std::basic_string<Char> format(const std::locale& loc, - const S& format_str, Args&&... args) { - return detail::vformat(loc, to_string_view(format_str), - fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...)); -} - -template <typename S, typename OutputIt, typename... Args, - typename Char = char_t<S>, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value)> -inline OutputIt vformat_to( - OutputIt out, const std::locale& loc, const S& format_str, - basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - decltype(detail::get_buffer<Char>(out)) buf(detail::get_buffer_init(out)); - vformat_to(buf, to_string_view(format_str), args, detail::locale_ref(loc)); - return detail::get_iterator(buf); -} - -template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args, - bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char_t<S>>::value> -inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const std::locale& loc, - const S& format_str, Args&&... args) -> - typename std::enable_if<enable, OutputIt>::type { - const auto& vargs = fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...); - return vformat_to(out, loc, to_string_view(format_str), vargs); -} - -FMT_END_NAMESPACE - -#endif // FMT_LOCALE_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/os.h b/include/fmt/os.h index d44ea0c9..2b517cd4 100644 --- a/include/fmt/os.h +++ b/include/fmt/os.h @@ -8,34 +8,33 @@ #ifndef FMT_OS_H_ #define FMT_OS_H_ -#if defined(__MINGW32__) || defined(__CYGWIN__) -// Workaround MinGW bug https://sourceforge.net/p/mingw/bugs/2024/. -# undef __STRICT_ANSI__ -#endif - #include <cerrno> -#include <clocale> // for locale_t #include <cstddef> #include <cstdio> -#include <cstdlib> // for strtod_l +#include <system_error> // std::system_error + +#include "format.h" #if defined __APPLE__ || defined(__FreeBSD__) -# include <xlocale.h> // for LC_NUMERIC_MASK on OS X +# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<xlocale.h>) +# include <xlocale.h> // for LC_NUMERIC_MASK on OS X +# endif #endif -#include "format.h" - +#ifndef FMT_USE_FCNTL // UWP doesn't provide _pipe. -#if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE("winapifamily.h") -# include <winapifamily.h> -#endif -#if (FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<fcntl.h>) || defined(__APPLE__) || \ - defined(__linux__)) && \ - (!defined(WINAPI_FAMILY) || (WINAPI_FAMILY == WINAPI_FAMILY_DESKTOP_APP)) -# include <fcntl.h> // for O_RDONLY -# define FMT_USE_FCNTL 1 -#else -# define FMT_USE_FCNTL 0 +# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE("winapifamily.h") +# include <winapifamily.h> +# endif +# if (FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<fcntl.h>) || defined(__APPLE__) || \ + defined(__linux__)) && \ + (!defined(WINAPI_FAMILY) || \ + (WINAPI_FAMILY == WINAPI_FAMILY_DESKTOP_APP)) +# include <fcntl.h> // for O_RDONLY +# define FMT_USE_FCNTL 1 +# else +# define FMT_USE_FCNTL 0 +# endif #endif #ifndef FMT_POSIX @@ -74,6 +73,7 @@ #define FMT_RETRY(result, expression) FMT_RETRY_VAL(result, expression, -1) FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT /** \rst @@ -122,89 +122,68 @@ template <typename Char> class basic_cstring_view { using cstring_view = basic_cstring_view<char>; using wcstring_view = basic_cstring_view<wchar_t>; -// An error code. -class error_code { - private: - int value_; - - public: - explicit error_code(int value = 0) FMT_NOEXCEPT : value_(value) {} - - int get() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return value_; } -}; - #ifdef _WIN32 -namespace detail { -// A converter from UTF-16 to UTF-8. -// It is only provided for Windows since other systems support UTF-8 natively. -class utf16_to_utf8 { - private: - memory_buffer buffer_; - - public: - utf16_to_utf8() {} - FMT_API explicit utf16_to_utf8(wstring_view s); - operator string_view() const { return string_view(&buffer_[0], size()); } - size_t size() const { return buffer_.size() - 1; } - const char* c_str() const { return &buffer_[0]; } - std::string str() const { return std::string(&buffer_[0], size()); } - - // Performs conversion returning a system error code instead of - // throwing exception on conversion error. This method may still throw - // in case of memory allocation error. - FMT_API int convert(wstring_view s); -}; +FMT_API const std::error_category& system_category() noexcept; +namespace detail { FMT_API void format_windows_error(buffer<char>& out, int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT; -} // namespace detail + const char* message) noexcept; +} -/** A Windows error. */ -class windows_error : public system_error { - private: - FMT_API void init(int error_code, string_view format_str, format_args args); +FMT_API std::system_error vwindows_error(int error_code, string_view format_str, + format_args args); - public: - /** - \rst - Constructs a :class:`fmt::windows_error` object with the description - of the form - - .. parsed-literal:: - *<message>*: *<system-message>* - - where *<message>* is the formatted message and *<system-message>* is the - system message corresponding to the error code. - *error_code* is a Windows error code as given by ``GetLastError``. - If *error_code* is not a valid error code such as -1, the system message - will look like "error -1". - - **Example**:: - - // This throws a windows_error with the description - // cannot open file 'madeup': The system cannot find the file specified. - // or similar (system message may vary). - const char *filename = "madeup"; - LPOFSTRUCT of = LPOFSTRUCT(); - HFILE file = OpenFile(filename, &of, OF_READ); - if (file == HFILE_ERROR) { - throw fmt::windows_error(GetLastError(), - "cannot open file '{}'", filename); - } - \endrst - */ - template <typename... Args> - windows_error(int error_code, string_view message, const Args&... args) { - init(error_code, message, make_format_args(args...)); - } -}; +/** + \rst + Constructs a :class:`std::system_error` object with the description + of the form + + .. parsed-literal:: + *<message>*: *<system-message>* + + where *<message>* is the formatted message and *<system-message>* is the + system message corresponding to the error code. + *error_code* is a Windows error code as given by ``GetLastError``. + If *error_code* is not a valid error code such as -1, the system message + will look like "error -1". + + **Example**:: + + // This throws a system_error with the description + // cannot open file 'madeup': The system cannot find the file specified. + // or similar (system message may vary). + const char *filename = "madeup"; + LPOFSTRUCT of = LPOFSTRUCT(); + HFILE file = OpenFile(filename, &of, OF_READ); + if (file == HFILE_ERROR) { + throw fmt::windows_error(GetLastError(), + "cannot open file '{}'", filename); + } + \endrst +*/ +template <typename... Args> +std::system_error windows_error(int error_code, string_view message, + const Args&... args) { + return vwindows_error(error_code, message, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); +} // Reports a Windows error without throwing an exception. // Can be used to report errors from destructors. -FMT_API void report_windows_error(int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT; +FMT_API void report_windows_error(int error_code, const char* message) noexcept; +#else +inline const std::error_category& system_category() noexcept { + return std::system_category(); +} #endif // _WIN32 +// std::system is not available on some platforms such as iOS (#2248). +#ifdef __OSX__ +template <typename S, typename... Args, typename Char = char_t<S>> +void say(const S& format_str, Args&&... args) { + std::system(format("say \"{}\"", format(format_str, args...)).c_str()); +} +#endif + // A buffered file. class buffered_file { private: @@ -219,13 +198,13 @@ class buffered_file { void operator=(const buffered_file&) = delete; // Constructs a buffered_file object which doesn't represent any file. - buffered_file() FMT_NOEXCEPT : file_(nullptr) {} + buffered_file() noexcept : file_(nullptr) {} // Destroys the object closing the file it represents if any. - FMT_API ~buffered_file() FMT_NOEXCEPT; + FMT_API ~buffered_file() noexcept; public: - buffered_file(buffered_file&& other) FMT_NOEXCEPT : file_(other.file_) { + buffered_file(buffered_file&& other) noexcept : file_(other.file_) { other.file_ = nullptr; } @@ -243,11 +222,9 @@ class buffered_file { FMT_API void close(); // Returns the pointer to a FILE object representing this file. - FILE* get() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return file_; } + FILE* get() const noexcept { return file_; } - // We place parentheses around fileno to workaround a bug in some versions - // of MinGW that define fileno as a macro. - FMT_API int(fileno)() const; + FMT_API int descriptor() const; void vprint(string_view format_str, format_args args) { fmt::vprint(file_, format_str, args); @@ -255,18 +232,18 @@ class buffered_file { template <typename... Args> inline void print(string_view format_str, const Args&... args) { - vprint(format_str, make_format_args(args...)); + vprint(format_str, fmt::make_format_args(args...)); } }; #if FMT_USE_FCNTL // A file. Closed file is represented by a file object with descriptor -1. -// Methods that are not declared with FMT_NOEXCEPT may throw +// Methods that are not declared with noexcept may throw // fmt::system_error in case of failure. Note that some errors such as // closing the file multiple times will cause a crash on Windows rather // than an exception. You can get standard behavior by overriding the // invalid parameter handler with _set_invalid_parameter_handler. -class file { +class FMT_API file { private: int fd_; // File descriptor. @@ -280,22 +257,24 @@ class file { WRONLY = FMT_POSIX(O_WRONLY), // Open for writing only. RDWR = FMT_POSIX(O_RDWR), // Open for reading and writing. CREATE = FMT_POSIX(O_CREAT), // Create if the file doesn't exist. - APPEND = FMT_POSIX(O_APPEND) // Open in append mode. + APPEND = FMT_POSIX(O_APPEND), // Open in append mode. + TRUNC = FMT_POSIX(O_TRUNC) // Truncate the content of the file. }; // Constructs a file object which doesn't represent any file. - file() FMT_NOEXCEPT : fd_(-1) {} + file() noexcept : fd_(-1) {} // Opens a file and constructs a file object representing this file. - FMT_API file(cstring_view path, int oflag); + file(cstring_view path, int oflag); public: file(const file&) = delete; void operator=(const file&) = delete; - file(file&& other) FMT_NOEXCEPT : fd_(other.fd_) { other.fd_ = -1; } + file(file&& other) noexcept : fd_(other.fd_) { other.fd_ = -1; } - file& operator=(file&& other) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + // Move assignment is not noexcept because close may throw. + file& operator=(file&& other) { close(); fd_ = other.fd_; other.fd_ = -1; @@ -303,43 +282,49 @@ class file { } // Destroys the object closing the file it represents if any. - FMT_API ~file() FMT_NOEXCEPT; + ~file() noexcept; // Returns the file descriptor. - int descriptor() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return fd_; } + int descriptor() const noexcept { return fd_; } // Closes the file. - FMT_API void close(); + void close(); // Returns the file size. The size has signed type for consistency with // stat::st_size. - FMT_API long long size() const; + long long size() const; // Attempts to read count bytes from the file into the specified buffer. - FMT_API size_t read(void* buffer, size_t count); + size_t read(void* buffer, size_t count); // Attempts to write count bytes from the specified buffer to the file. - FMT_API size_t write(const void* buffer, size_t count); + size_t write(const void* buffer, size_t count); // Duplicates a file descriptor with the dup function and returns // the duplicate as a file object. - FMT_API static file dup(int fd); + static file dup(int fd); // Makes fd be the copy of this file descriptor, closing fd first if // necessary. - FMT_API void dup2(int fd); + void dup2(int fd); // Makes fd be the copy of this file descriptor, closing fd first if // necessary. - FMT_API void dup2(int fd, error_code& ec) FMT_NOEXCEPT; + void dup2(int fd, std::error_code& ec) noexcept; // Creates a pipe setting up read_end and write_end file objects for reading // and writing respectively. - FMT_API static void pipe(file& read_end, file& write_end); + static void pipe(file& read_end, file& write_end); // Creates a buffered_file object associated with this file and detaches // this file object from the file. - FMT_API buffered_file fdopen(const char* mode); + buffered_file fdopen(const char* mode); + +# if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__) + // Opens a file and constructs a file object representing this file by + // wcstring_view filename. Windows only. + static file open_windows_file(wcstring_view path, int oflag); +# endif }; // Returns the memory page size. @@ -348,6 +333,7 @@ long getpagesize(); namespace detail { struct buffer_size { + buffer_size() = default; size_t value = 0; buffer_size operator=(size_t val) const { auto bs = buffer_size(); @@ -357,14 +343,14 @@ struct buffer_size { }; struct ostream_params { - int oflag = file::WRONLY | file::CREATE; + int oflag = file::WRONLY | file::CREATE | file::TRUNC; size_t buffer_size = BUFSIZ > 32768 ? BUFSIZ : 32768; ostream_params() {} template <typename... T> - ostream_params(T... params, int oflag) : ostream_params(params...) { - this->oflag = oflag; + ostream_params(T... params, int new_oflag) : ostream_params(params...) { + oflag = new_oflag; } template <typename... T> @@ -372,58 +358,88 @@ struct ostream_params { : ostream_params(params...) { this->buffer_size = bs.value; } -}; -} // namespace detail -static constexpr detail::buffer_size buffer_size; +// Intel has a bug that results in failure to deduce a constructor +// for empty parameter packs. +# if defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) && __INTEL_COMPILER < 2000 + ostream_params(int new_oflag) : oflag(new_oflag) {} + ostream_params(detail::buffer_size bs) : buffer_size(bs.value) {} +# endif +}; -// A fast output stream which is not thread-safe. -class ostream final : private detail::buffer<char> { - private: +class file_buffer final : public buffer<char> { file file_; + FMT_API void grow(size_t) override; + + public: + FMT_API file_buffer(cstring_view path, const ostream_params& params); + FMT_API file_buffer(file_buffer&& other); + FMT_API ~file_buffer(); + void flush() { if (size() == 0) return; - file_.write(data(), size()); + file_.write(data(), size() * sizeof(data()[0])); clear(); } - FMT_API void grow(size_t) override final; + void close() { + flush(); + file_.close(); + } +}; + +} // namespace detail + +// Added {} below to work around default constructor error known to +// occur in Xcode versions 7.2.1 and 8.2.1. +constexpr detail::buffer_size buffer_size{}; + +/** A fast output stream which is not thread-safe. */ +class FMT_API ostream { + private: + FMT_MSC_WARNING(suppress : 4251) + detail::file_buffer buffer_; ostream(cstring_view path, const detail::ostream_params& params) - : file_(path, params.oflag) { - set(new char[params.buffer_size], params.buffer_size); - } + : buffer_(path, params) {} public: - ostream(ostream&& other) - : detail::buffer<char>(other.data(), other.size(), other.capacity()), - file_(std::move(other.file_)) { - other.set(nullptr, 0); - } - ~ostream() { - flush(); - delete[] data(); - } + ostream(ostream&& other) : buffer_(std::move(other.buffer_)) {} + + ~ostream(); + + void flush() { buffer_.flush(); } template <typename... T> friend ostream output_file(cstring_view path, T... params); - void close() { - flush(); - file_.close(); - } + void close() { buffer_.close(); } - template <typename S, typename... Args> - void print(const S& format_str, const Args&... args) { - format_to(detail::buffer_appender<char>(*this), format_str, args...); + /** + Formats ``args`` according to specifications in ``fmt`` and writes the + output to the file. + */ + template <typename... T> void print(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + vformat_to(std::back_inserter(buffer_), fmt, + fmt::make_format_args(args...)); } }; /** - Opens a file for writing. Supported parameters passed in `params`: - * ``<integer>``: Output flags (``file::WRONLY | file::CREATE`` by default) + \rst + Opens a file for writing. Supported parameters passed in *params*: + + * ``<integer>``: Flags passed to `open + <https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/007904875/functions/open.html>`_ + (``file::WRONLY | file::CREATE | file::TRUNC`` by default) * ``buffer_size=<integer>``: Output buffer size + + **Example**:: + + auto out = fmt::output_file("guide.txt"); + out.print("Don't {}", "Panic"); + \endrst */ template <typename... T> inline ostream output_file(cstring_view path, T... params) { @@ -431,50 +447,7 @@ inline ostream output_file(cstring_view path, T... params) { } #endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL -#ifdef FMT_LOCALE -// A "C" numeric locale. -class locale { - private: -# ifdef _WIN32 - using locale_t = _locale_t; - - static void freelocale(locale_t loc) { _free_locale(loc); } - - static double strtod_l(const char* nptr, char** endptr, _locale_t loc) { - return _strtod_l(nptr, endptr, loc); - } -# endif - - locale_t locale_; - - public: - using type = locale_t; - locale(const locale&) = delete; - void operator=(const locale&) = delete; - - locale() { -# ifndef _WIN32 - locale_ = FMT_SYSTEM(newlocale(LC_NUMERIC_MASK, "C", nullptr)); -# else - locale_ = _create_locale(LC_NUMERIC, "C"); -# endif - if (!locale_) FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot create locale")); - } - ~locale() { freelocale(locale_); } - - type get() const { return locale_; } - - // Converts string to floating-point number and advances str past the end - // of the parsed input. - double strtod(const char*& str) const { - char* end = nullptr; - double result = strtod_l(str, &end, locale_); - str = end; - return result; - } -}; -using Locale FMT_DEPRECATED_ALIAS = locale; -#endif // FMT_LOCALE +FMT_END_EXPORT FMT_END_NAMESPACE #endif // FMT_OS_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/ostream.h b/include/fmt/ostream.h index 29c58ec1..782ace5c 100644 --- a/include/fmt/ostream.h +++ b/include/fmt/ostream.h @@ -8,87 +8,74 @@ #ifndef FMT_OSTREAM_H_ #define FMT_OSTREAM_H_ -#include <ostream> +#include <fstream> // std::filebuf + +#ifdef _WIN32 +# ifdef __GLIBCXX__ +# include <ext/stdio_filebuf.h> +# include <ext/stdio_sync_filebuf.h> +# endif +# include <io.h> +#endif #include "format.h" FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <typename Char> class basic_printf_parse_context; -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> class basic_printf_context; - namespace detail { -template <class Char> class formatbuf : public std::basic_streambuf<Char> { - private: - using int_type = typename std::basic_streambuf<Char>::int_type; - using traits_type = typename std::basic_streambuf<Char>::traits_type; - - buffer<Char>& buffer_; - - public: - formatbuf(buffer<Char>& buf) : buffer_(buf) {} - - protected: - // The put-area is actually always empty. This makes the implementation - // simpler and has the advantage that the streambuf and the buffer are always - // in sync and sputc never writes into uninitialized memory. The obvious - // disadvantage is that each call to sputc always results in a (virtual) call - // to overflow. There is no disadvantage here for sputn since this always - // results in a call to xsputn. - - int_type overflow(int_type ch = traits_type::eof()) FMT_OVERRIDE { - if (!traits_type::eq_int_type(ch, traits_type::eof())) - buffer_.push_back(static_cast<Char>(ch)); - return ch; - } - - std::streamsize xsputn(const Char* s, std::streamsize count) FMT_OVERRIDE { - buffer_.append(s, s + count); - return count; - } -}; - -struct converter { - template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integral<T>::value)> converter(T); +// Generate a unique explicit instantion in every translation unit using a tag +// type in an anonymous namespace. +namespace { +struct file_access_tag {}; +} // namespace +template <typename Tag, typename BufType, FILE* BufType::*FileMemberPtr> +class file_access { + friend auto get_file(BufType& obj) -> FILE* { return obj.*FileMemberPtr; } }; -template <typename Char> struct test_stream : std::basic_ostream<Char> { - private: - void_t<> operator<<(converter); -}; +#if FMT_MSC_VERSION +template class file_access<file_access_tag, std::filebuf, + &std::filebuf::_Myfile>; +auto get_file(std::filebuf&) -> FILE*; +#endif -// Hide insertion operators for built-in types. -template <typename Char, typename Traits> -void_t<> operator<<(std::basic_ostream<Char, Traits>&, Char); -template <typename Char, typename Traits> -void_t<> operator<<(std::basic_ostream<Char, Traits>&, char); -template <typename Traits> -void_t<> operator<<(std::basic_ostream<char, Traits>&, char); -template <typename Traits> -void_t<> operator<<(std::basic_ostream<char, Traits>&, signed char); -template <typename Traits> -void_t<> operator<<(std::basic_ostream<char, Traits>&, unsigned char); - -// Checks if T has a user-defined operator<< (e.g. not a member of -// std::ostream). -template <typename T, typename Char> class is_streamable { - private: - template <typename U> - static bool_constant<!std::is_same<decltype(std::declval<test_stream<Char>&>() - << std::declval<U>()), - void_t<>>::value> - test(int); - - template <typename> static std::false_type test(...); - - using result = decltype(test<T>(0)); - - public: - static const bool value = result::value; -}; +inline bool write_ostream_unicode(std::ostream& os, fmt::string_view data) { + FILE* f = nullptr; +#if FMT_MSC_VERSION + if (auto* buf = dynamic_cast<std::filebuf*>(os.rdbuf())) + f = get_file(*buf); + else + return false; +#elif defined(_WIN32) && defined(__GLIBCXX__) + auto* rdbuf = os.rdbuf(); + if (auto* sfbuf = dynamic_cast<__gnu_cxx::stdio_sync_filebuf<char>*>(rdbuf)) + f = sfbuf->file(); + else if (auto* fbuf = dynamic_cast<__gnu_cxx::stdio_filebuf<char>*>(rdbuf)) + f = fbuf->file(); + else + return false; +#else + ignore_unused(os, data, f); +#endif +#ifdef _WIN32 + if (f) { + int fd = _fileno(f); + if (_isatty(fd)) { + os.flush(); + return write_console(fd, data); + } + } +#endif + return false; +} +inline bool write_ostream_unicode(std::wostream&, + fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t>) { + return false; +} // Write the content of buf to os. +// It is a separate function rather than a part of vprint to simplify testing. template <typename Char> void write_buffer(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, buffer<Char>& buf) { const Char* buf_data = buf.data(); @@ -106,54 +93,81 @@ void write_buffer(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, buffer<Char>& buf) { template <typename Char, typename T> void format_value(buffer<Char>& buf, const T& value, locale_ref loc = locale_ref()) { - formatbuf<Char> format_buf(buf); - std::basic_ostream<Char> output(&format_buf); + auto&& format_buf = formatbuf<std::basic_streambuf<Char>>(buf); + auto&& output = std::basic_ostream<Char>(&format_buf); #if !defined(FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR) if (loc) output.imbue(loc.get<std::locale>()); #endif output << value; output.exceptions(std::ios_base::failbit | std::ios_base::badbit); - buf.try_resize(buf.size()); } +template <typename T> struct streamed_view { + const T& value; +}; + +} // namespace detail + // Formats an object of type T that has an overloaded ostream operator<<. -template <typename T, typename Char> -struct fallback_formatter<T, Char, enable_if_t<is_streamable<T, Char>::value>> - : private formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char> { - FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx) - -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char>::parse(ctx); - } - template <typename ParseCtx, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same< - ParseCtx, basic_printf_parse_context<Char>>::value)> - auto parse(ParseCtx& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return ctx.begin(); - } +template <typename Char> +struct basic_ostream_formatter : formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char> { + void set_debug_format() = delete; - template <typename OutputIt> - auto format(const T& value, basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>& ctx) + template <typename T, typename OutputIt> + auto format(const T& value, basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>& ctx) const -> OutputIt { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - format_value(buffer, value, ctx.locale()); - basic_string_view<Char> str(buffer.data(), buffer.size()); - return formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char>::format(str, ctx); + auto buffer = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); + detail::format_value(buffer, value, ctx.locale()); + return formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char>::format( + {buffer.data(), buffer.size()}, ctx); } +}; + +using ostream_formatter = basic_ostream_formatter<char>; + +template <typename T, typename Char> +struct formatter<detail::streamed_view<T>, Char> + : basic_ostream_formatter<Char> { template <typename OutputIt> - auto format(const T& value, basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>& ctx) - -> OutputIt { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - format_value(buffer, value, ctx.locale()); - return std::copy(buffer.begin(), buffer.end(), ctx.out()); + auto format(detail::streamed_view<T> view, + basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>& ctx) const -> OutputIt { + return basic_ostream_formatter<Char>::format(view.value, ctx); } }; + +/** + \rst + Returns a view that formats `value` via an ostream ``operator<<``. + + **Example**:: + + fmt::print("Current thread id: {}\n", + fmt::streamed(std::this_thread::get_id())); + \endrst + */ +template <typename T> +constexpr auto streamed(const T& value) -> detail::streamed_view<T> { + return {value}; +} + +namespace detail { + +inline void vprint_directly(std::ostream& os, string_view format_str, + format_args args) { + auto buffer = memory_buffer(); + detail::vformat_to(buffer, format_str, args); + detail::write_buffer(os, buffer); +} + } // namespace detail -template <typename Char> -void vprint(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, +FMT_EXPORT template <typename Char> +void vprint(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, + basic_string_view<type_identity_t<Char>> format_str, basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; + auto buffer = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); detail::vformat_to(buffer, format_str, args); + if (detail::write_ostream_unicode(os, {buffer.data(), buffer.size()})) return; detail::write_buffer(os, buffer); } @@ -166,12 +180,36 @@ void vprint(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, fmt::print(cerr, "Don't {}!", "panic"); \endrst */ -template <typename S, typename... Args, - typename Char = enable_if_t<detail::is_string<S>::value, char_t<S>>> -void print(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, const S& format_str, Args&&... args) { - vprint(os, to_string_view(format_str), - fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format_str, args...)); +FMT_EXPORT template <typename... T> +void print(std::ostream& os, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + const auto& vargs = fmt::make_format_args(args...); + if (detail::is_utf8()) + vprint(os, fmt, vargs); + else + detail::vprint_directly(os, fmt, vargs); } + +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename... Args> +void print(std::wostream& os, + basic_format_string<wchar_t, type_identity_t<Args>...> fmt, + Args&&... args) { + vprint(os, fmt, fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<wchar_t>>(args...)); +} + +FMT_EXPORT template <typename... T> +void println(std::ostream& os, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + fmt::print(os, "{}\n", fmt::format(fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...)); +} + +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename... Args> +void println(std::wostream& os, + basic_format_string<wchar_t, type_identity_t<Args>...> fmt, + Args&&... args) { + print(os, L"{}\n", fmt::format(fmt, std::forward<Args>(args)...)); +} + FMT_END_NAMESPACE #endif // FMT_OSTREAM_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/posix.h b/include/fmt/posix.h deleted file mode 100644 index da19e9d5..00000000 --- a/include/fmt/posix.h +++ /dev/null @@ -1,2 +0,0 @@ -#include "os.h" -#warning "fmt/posix.h is deprecated; use fmt/os.h instead" diff --git a/include/fmt/printf.h b/include/fmt/printf.h index 8c28ac23..07e81577 100644 --- a/include/fmt/printf.h +++ b/include/fmt/printf.h @@ -11,62 +11,106 @@ #include <algorithm> // std::max #include <limits> // std::numeric_limits -#include "ostream.h" +#include "format.h" FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT + +template <typename T> struct printf_formatter { + printf_formatter() = delete; +}; + +template <typename Char> class basic_printf_context { + private: + detail::buffer_appender<Char> out_; + basic_format_args<basic_printf_context> args_; + + static_assert(std::is_same<Char, char>::value || + std::is_same<Char, wchar_t>::value, + "Unsupported code unit type."); + + public: + using char_type = Char; + using parse_context_type = basic_format_parse_context<Char>; + template <typename T> using formatter_type = printf_formatter<T>; + + /** + \rst + Constructs a ``printf_context`` object. References to the arguments are + stored in the context object so make sure they have appropriate lifetimes. + \endrst + */ + basic_printf_context(detail::buffer_appender<Char> out, + basic_format_args<basic_printf_context> args) + : out_(out), args_(args) {} + + auto out() -> detail::buffer_appender<Char> { return out_; } + void advance_to(detail::buffer_appender<Char>) {} + + auto locale() -> detail::locale_ref { return {}; } + + auto arg(int id) const -> basic_format_arg<basic_printf_context> { + return args_.get(id); + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { + detail::error_handler().on_error(message); + } +}; + namespace detail { // Checks if a value fits in int - used to avoid warnings about comparing // signed and unsigned integers. template <bool IsSigned> struct int_checker { - template <typename T> static bool fits_in_int(T value) { + template <typename T> static auto fits_in_int(T value) -> bool { unsigned max = max_value<int>(); return value <= max; } - static bool fits_in_int(bool) { return true; } + static auto fits_in_int(bool) -> bool { return true; } }; template <> struct int_checker<true> { - template <typename T> static bool fits_in_int(T value) { + template <typename T> static auto fits_in_int(T value) -> bool { return value >= (std::numeric_limits<int>::min)() && value <= max_value<int>(); } - static bool fits_in_int(int) { return true; } + static auto fits_in_int(int) -> bool { return true; } }; -class printf_precision_handler { - public: +struct printf_precision_handler { template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> - int operator()(T value) { + auto operator()(T value) -> int { if (!int_checker<std::numeric_limits<T>::is_signed>::fits_in_int(value)) - FMT_THROW(format_error("number is too big")); + throw_format_error("number is too big"); return (std::max)(static_cast<int>(value), 0); } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)> - int operator()(T) { - FMT_THROW(format_error("precision is not integer")); + auto operator()(T) -> int { + throw_format_error("precision is not integer"); return 0; } }; // An argument visitor that returns true iff arg is a zero integer. -class is_zero_int { - public: +struct is_zero_int { template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> - bool operator()(T value) { + auto operator()(T value) -> bool { return value == 0; } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)> - bool operator()(T) { + auto operator()(T) -> bool { return false; } }; template <typename T> struct make_unsigned_or_bool : std::make_unsigned<T> {}; -template <> struct make_unsigned_or_bool<bool> { using type = bool; }; +template <> struct make_unsigned_or_bool<bool> { + using type = bool; +}; template <typename T, typename Context> class arg_converter { private: @@ -90,22 +134,23 @@ template <typename T, typename Context> class arg_converter { if (const_check(sizeof(target_type) <= sizeof(int))) { // Extra casts are used to silence warnings. if (is_signed) { - arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>( - static_cast<int>(static_cast<target_type>(value))); + auto n = static_cast<int>(static_cast<target_type>(value)); + arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>(n); } else { using unsigned_type = typename make_unsigned_or_bool<target_type>::type; - arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>( - static_cast<unsigned>(static_cast<unsigned_type>(value))); + auto n = static_cast<unsigned>(static_cast<unsigned_type>(value)); + arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>(n); } } else { if (is_signed) { // glibc's printf doesn't sign extend arguments of smaller types: // std::printf("%lld", -42); // prints "4294967254" // but we don't have to do the same because it's a UB. - arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>(static_cast<long long>(value)); + auto n = static_cast<long long>(value); + arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>(n); } else { - arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>( - static_cast<typename make_unsigned_or_bool<U>::type>(value)); + auto n = static_cast<typename make_unsigned_or_bool<U>::type>(value); + arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>(n); } } } @@ -133,8 +178,8 @@ template <typename Context> class char_converter { template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> void operator()(T value) { - arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>( - static_cast<typename Context::char_type>(value)); + auto c = static_cast<typename Context::char_type>(value); + arg_ = detail::make_arg<Context>(c); } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)> @@ -144,254 +189,131 @@ template <typename Context> class char_converter { // An argument visitor that return a pointer to a C string if argument is a // string or null otherwise. template <typename Char> struct get_cstring { - template <typename T> const Char* operator()(T) { return nullptr; } - const Char* operator()(const Char* s) { return s; } + template <typename T> auto operator()(T) -> const Char* { return nullptr; } + auto operator()(const Char* s) -> const Char* { return s; } }; // Checks if an argument is a valid printf width specifier and sets // left alignment if it is negative. template <typename Char> class printf_width_handler { private: - using format_specs = basic_format_specs<Char>; - - format_specs& specs_; + format_specs<Char>& specs_; public: - explicit printf_width_handler(format_specs& specs) : specs_(specs) {} + explicit printf_width_handler(format_specs<Char>& specs) : specs_(specs) {} template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)> - unsigned operator()(T value) { + auto operator()(T value) -> unsigned { auto width = static_cast<uint32_or_64_or_128_t<T>>(value); if (detail::is_negative(value)) { specs_.align = align::left; width = 0 - width; } unsigned int_max = max_value<int>(); - if (width > int_max) FMT_THROW(format_error("number is too big")); + if (width > int_max) throw_format_error("number is too big"); return static_cast<unsigned>(width); } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)> - unsigned operator()(T) { - FMT_THROW(format_error("width is not integer")); + auto operator()(T) -> unsigned { + throw_format_error("width is not integer"); return 0; } }; -template <typename Char, typename Context> -void vprintf(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> format, - basic_format_args<Context> args) { - Context(buffer_appender<Char>(buf), format, args).format(); -} -} // namespace detail - -// For printing into memory_buffer. -template <typename Char, typename Context> -FMT_DEPRECATED void printf(detail::buffer<Char>& buf, - basic_string_view<Char> format, - basic_format_args<Context> args) { - return detail::vprintf(buf, format, args); +// Workaround for a bug with the XL compiler when initializing +// printf_arg_formatter's base class. +template <typename Char> +auto make_arg_formatter(buffer_appender<Char> iter, format_specs<Char>& s) + -> arg_formatter<Char> { + return {iter, s, locale_ref()}; } -using detail::vprintf; +// The ``printf`` argument formatter. template <typename Char> -class basic_printf_parse_context : public basic_format_parse_context<Char> { - using basic_format_parse_context<Char>::basic_format_parse_context; -}; -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> class basic_printf_context; - -/** - \rst - The ``printf`` argument formatter. - \endrst - */ -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -class printf_arg_formatter : public detail::arg_formatter_base<OutputIt, Char> { - public: - using iterator = OutputIt; - +class printf_arg_formatter : public arg_formatter<Char> { private: - using char_type = Char; - using base = detail::arg_formatter_base<OutputIt, Char>; - using context_type = basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>; + using base = arg_formatter<Char>; + using context_type = basic_printf_context<Char>; context_type& context_; - void write_null_pointer(char) { - this->specs()->type = 0; - this->write("(nil)"); - } - - void write_null_pointer(wchar_t) { - this->specs()->type = 0; - this->write(L"(nil)"); + void write_null_pointer(bool is_string = false) { + auto s = this->specs; + s.type = presentation_type::none; + write_bytes(this->out, is_string ? "(null)" : "(nil)", s); } public: - using format_specs = typename base::format_specs; + printf_arg_formatter(buffer_appender<Char> iter, format_specs<Char>& s, + context_type& ctx) + : base(make_arg_formatter(iter, s)), context_(ctx) {} - /** - \rst - Constructs an argument formatter object. - *buffer* is a reference to the output buffer and *specs* contains format - specifier information for standard argument types. - \endrst - */ - printf_arg_formatter(iterator iter, format_specs& specs, context_type& ctx) - : base(iter, &specs, detail::locale_ref()), context_(ctx) {} - - template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(fmt::detail::is_integral<T>::value)> - iterator operator()(T value) { - // MSVC2013 fails to compile separate overloads for bool and char_type so - // use std::is_same instead. - if (std::is_same<T, bool>::value) { - format_specs& fmt_specs = *this->specs(); - if (fmt_specs.type != 's') return base::operator()(value ? 1 : 0); - fmt_specs.type = 0; - this->write(value != 0); - } else if (std::is_same<T, char_type>::value) { - format_specs& fmt_specs = *this->specs(); - if (fmt_specs.type && fmt_specs.type != 'c') - return (*this)(static_cast<int>(value)); - fmt_specs.sign = sign::none; - fmt_specs.alt = false; - fmt_specs.fill[0] = ' '; // Ignore '0' flag for char types. - // align::numeric needs to be overwritten here since the '0' flag is - // ignored for non-numeric types - if (fmt_specs.align == align::none || fmt_specs.align == align::numeric) - fmt_specs.align = align::right; - return base::operator()(value); - } else { - return base::operator()(value); + void operator()(monostate value) { base::operator()(value); } + + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_integral<T>::value)> + void operator()(T value) { + // MSVC2013 fails to compile separate overloads for bool and Char so use + // std::is_same instead. + if (!std::is_same<T, Char>::value) { + base::operator()(value); + return; } - return this->out(); + format_specs<Char> fmt_specs = this->specs; + if (fmt_specs.type != presentation_type::none && + fmt_specs.type != presentation_type::chr) { + return (*this)(static_cast<int>(value)); + } + fmt_specs.sign = sign::none; + fmt_specs.alt = false; + fmt_specs.fill[0] = ' '; // Ignore '0' flag for char types. + // align::numeric needs to be overwritten here since the '0' flag is + // ignored for non-numeric types + if (fmt_specs.align == align::none || fmt_specs.align == align::numeric) + fmt_specs.align = align::right; + write<Char>(this->out, static_cast<Char>(value), fmt_specs); } template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value)> - iterator operator()(T value) { - return base::operator()(value); + void operator()(T value) { + base::operator()(value); } /** Formats a null-terminated C string. */ - iterator operator()(const char* value) { + void operator()(const char* value) { if (value) base::operator()(value); - else if (this->specs()->type == 'p') - write_null_pointer(char_type()); else - this->write("(null)"); - return this->out(); + write_null_pointer(this->specs.type != presentation_type::pointer); } /** Formats a null-terminated wide C string. */ - iterator operator()(const wchar_t* value) { + void operator()(const wchar_t* value) { if (value) base::operator()(value); - else if (this->specs()->type == 'p') - write_null_pointer(char_type()); else - this->write(L"(null)"); - return this->out(); - } - - iterator operator()(basic_string_view<char_type> value) { - return base::operator()(value); + write_null_pointer(this->specs.type != presentation_type::pointer); } - iterator operator()(monostate value) { return base::operator()(value); } + void operator()(basic_string_view<Char> value) { base::operator()(value); } /** Formats a pointer. */ - iterator operator()(const void* value) { - if (value) return base::operator()(value); - this->specs()->type = 0; - write_null_pointer(char_type()); - return this->out(); + void operator()(const void* value) { + if (value) + base::operator()(value); + else + write_null_pointer(); } /** Formats an argument of a custom (user-defined) type. */ - iterator operator()(typename basic_format_arg<context_type>::handle handle) { - handle.format(context_.parse_context(), context_); - return this->out(); - } -}; - -template <typename T> struct printf_formatter { - printf_formatter() = delete; - - template <typename ParseContext> - auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return ctx.begin(); + void operator()(typename basic_format_arg<context_type>::handle handle) { + auto parse_ctx = basic_format_parse_context<Char>({}); + handle.format(parse_ctx, context_); } - - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(const T& value, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - detail::format_value(detail::get_container(ctx.out()), value); - return ctx.out(); - } -}; - -/** - This template formats data and writes the output through an output iterator. - */ -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> class basic_printf_context { - public: - /** The character type for the output. */ - using char_type = Char; - using iterator = OutputIt; - using format_arg = basic_format_arg<basic_printf_context>; - using parse_context_type = basic_printf_parse_context<Char>; - template <typename T> using formatter_type = printf_formatter<T>; - - private: - using format_specs = basic_format_specs<char_type>; - - OutputIt out_; - basic_format_args<basic_printf_context> args_; - parse_context_type parse_ctx_; - - static void parse_flags(format_specs& specs, const Char*& it, - const Char* end); - - // Returns the argument with specified index or, if arg_index is -1, the next - // argument. - format_arg get_arg(int arg_index = -1); - - // Parses argument index, flags and width and returns the argument index. - int parse_header(const Char*& it, const Char* end, format_specs& specs); - - public: - /** - \rst - Constructs a ``printf_context`` object. References to the arguments are - stored in the context object so make sure they have appropriate lifetimes. - \endrst - */ - basic_printf_context(OutputIt out, basic_string_view<char_type> format_str, - basic_format_args<basic_printf_context> args) - : out_(out), args_(args), parse_ctx_(format_str) {} - - OutputIt out() { return out_; } - void advance_to(OutputIt it) { out_ = it; } - - detail::locale_ref locale() { return {}; } - - format_arg arg(int id) const { return args_.get(id); } - - parse_context_type& parse_context() { return parse_ctx_; } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { - parse_ctx_.on_error(message); - } - - /** Formats stored arguments and writes the output to the range. */ - template <typename ArgFormatter = printf_arg_formatter<OutputIt, Char>> - OutputIt format(); }; -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -void basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::parse_flags(format_specs& specs, - const Char*& it, - const Char* end) { +template <typename Char> +void parse_flags(format_specs<Char>& specs, const Char*& it, const Char* end) { for (; it != end; ++it) { switch (*it) { case '-': @@ -404,9 +326,7 @@ void basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::parse_flags(format_specs& specs, specs.fill[0] = '0'; break; case ' ': - if (specs.sign != sign::plus) { - specs.sign = sign::space; - } + if (specs.sign != sign::plus) specs.sign = sign::space; break; case '#': specs.alt = true; @@ -417,35 +337,24 @@ void basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::parse_flags(format_specs& specs, } } -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -typename basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::format_arg -basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::get_arg(int arg_index) { - if (arg_index < 0) - arg_index = parse_ctx_.next_arg_id(); - else - parse_ctx_.check_arg_id(--arg_index); - return detail::get_arg(*this, arg_index); -} - -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -int basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::parse_header(const Char*& it, - const Char* end, - format_specs& specs) { +template <typename Char, typename GetArg> +auto parse_header(const Char*& it, const Char* end, format_specs<Char>& specs, + GetArg get_arg) -> int { int arg_index = -1; - char_type c = *it; + Char c = *it; if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') { // Parse an argument index (if followed by '$') or a width possibly // preceded with '0' flag(s). - detail::error_handler eh; - int value = parse_nonnegative_int(it, end, eh); + int value = parse_nonnegative_int(it, end, -1); if (it != end && *it == '$') { // value is an argument index ++it; - arg_index = value; + arg_index = value != -1 ? value : max_value<int>(); } else { if (c == '0') specs.fill[0] = '0'; if (value != 0) { // Nonzero value means that we parsed width and don't need to // parse it or flags again, so return now. + if (value == -1) throw_format_error("number is too big"); specs.width = value; return arg_index; } @@ -455,73 +364,129 @@ int basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::parse_header(const Char*& it, // Parse width. if (it != end) { if (*it >= '0' && *it <= '9') { - detail::error_handler eh; - specs.width = parse_nonnegative_int(it, end, eh); + specs.width = parse_nonnegative_int(it, end, -1); + if (specs.width == -1) throw_format_error("number is too big"); } else if (*it == '*') { ++it; specs.width = static_cast<int>(visit_format_arg( - detail::printf_width_handler<char_type>(specs), get_arg())); + detail::printf_width_handler<Char>(specs), get_arg(-1))); } } return arg_index; } -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -template <typename ArgFormatter> -OutputIt basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::format() { - auto out = this->out(); - const Char* start = parse_ctx_.begin(); - const Char* end = parse_ctx_.end(); +inline auto parse_printf_presentation_type(char c, type t) + -> presentation_type { + using pt = presentation_type; + constexpr auto integral_set = sint_set | uint_set | bool_set | char_set; + switch (c) { + case 'd': + return in(t, integral_set) ? pt::dec : pt::none; + case 'o': + return in(t, integral_set) ? pt::oct : pt::none; + case 'x': + return in(t, integral_set) ? pt::hex_lower : pt::none; + case 'X': + return in(t, integral_set) ? pt::hex_upper : pt::none; + case 'a': + return in(t, float_set) ? pt::hexfloat_lower : pt::none; + case 'A': + return in(t, float_set) ? pt::hexfloat_upper : pt::none; + case 'e': + return in(t, float_set) ? pt::exp_lower : pt::none; + case 'E': + return in(t, float_set) ? pt::exp_upper : pt::none; + case 'f': + return in(t, float_set) ? pt::fixed_lower : pt::none; + case 'F': + return in(t, float_set) ? pt::fixed_upper : pt::none; + case 'g': + return in(t, float_set) ? pt::general_lower : pt::none; + case 'G': + return in(t, float_set) ? pt::general_upper : pt::none; + case 'c': + return in(t, integral_set) ? pt::chr : pt::none; + case 's': + return in(t, string_set | cstring_set) ? pt::string : pt::none; + case 'p': + return in(t, pointer_set | cstring_set) ? pt::pointer : pt::none; + default: + return pt::none; + } +} + +template <typename Char, typename Context> +void vprintf(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> format, + basic_format_args<Context> args) { + using iterator = buffer_appender<Char>; + auto out = iterator(buf); + auto context = basic_printf_context<Char>(out, args); + auto parse_ctx = basic_format_parse_context<Char>(format); + + // Returns the argument with specified index or, if arg_index is -1, the next + // argument. + auto get_arg = [&](int arg_index) { + if (arg_index < 0) + arg_index = parse_ctx.next_arg_id(); + else + parse_ctx.check_arg_id(--arg_index); + return detail::get_arg(context, arg_index); + }; + + const Char* start = parse_ctx.begin(); + const Char* end = parse_ctx.end(); auto it = start; while (it != end) { - char_type c = *it++; - if (c != '%') continue; + if (!find<false, Char>(it, end, '%', it)) { + it = end; // find leaves it == nullptr if it doesn't find '%'. + break; + } + Char c = *it++; if (it != end && *it == c) { - out = std::copy(start, it, out); + write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(start, to_unsigned(it - start))); start = ++it; continue; } - out = std::copy(start, it - 1, out); + write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(start, to_unsigned(it - 1 - start))); - format_specs specs; + auto specs = format_specs<Char>(); specs.align = align::right; // Parse argument index, flags and width. - int arg_index = parse_header(it, end, specs); - if (arg_index == 0) on_error("argument not found"); + int arg_index = parse_header(it, end, specs, get_arg); + if (arg_index == 0) throw_format_error("argument not found"); // Parse precision. if (it != end && *it == '.') { ++it; c = it != end ? *it : 0; if ('0' <= c && c <= '9') { - detail::error_handler eh; - specs.precision = parse_nonnegative_int(it, end, eh); + specs.precision = parse_nonnegative_int(it, end, 0); } else if (c == '*') { ++it; specs.precision = static_cast<int>( - visit_format_arg(detail::printf_precision_handler(), get_arg())); + visit_format_arg(printf_precision_handler(), get_arg(-1))); } else { specs.precision = 0; } } - format_arg arg = get_arg(arg_index); + auto arg = get_arg(arg_index); // For d, i, o, u, x, and X conversion specifiers, if a precision is // specified, the '0' flag is ignored - if (specs.precision >= 0 && arg.is_integral()) - specs.fill[0] = - ' '; // Ignore '0' flag for non-numeric types or if '-' present. - if (specs.precision >= 0 && arg.type() == detail::type::cstring_type) { - auto str = visit_format_arg(detail::get_cstring<Char>(), arg); + if (specs.precision >= 0 && arg.is_integral()) { + // Ignore '0' for non-numeric types or if '-' present. + specs.fill[0] = ' '; + } + if (specs.precision >= 0 && arg.type() == type::cstring_type) { + auto str = visit_format_arg(get_cstring<Char>(), arg); auto str_end = str + specs.precision; auto nul = std::find(str, str_end, Char()); - arg = detail::make_arg<basic_printf_context>(basic_string_view<Char>( - str, - detail::to_unsigned(nul != str_end ? nul - str : specs.precision))); + auto sv = basic_string_view<Char>( + str, to_unsigned(nul != str_end ? nul - str : specs.precision)); + arg = make_arg<basic_printf_context<Char>>(sv); } - if (specs.alt && visit_format_arg(detail::is_zero_int(), arg)) - specs.alt = false; + if (specs.alt && visit_format_arg(is_zero_int(), arg)) specs.alt = false; if (specs.fill[0] == '0') { if (arg.is_arithmetic() && specs.align != align::left) specs.align = align::numeric; @@ -532,8 +497,7 @@ OutputIt basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::format() { // Parse length and convert the argument to the required type. c = it != end ? *it++ : 0; - char_type t = it != end ? *it : 0; - using detail::convert_arg; + Char t = it != end ? *it : 0; switch (c) { case 'h': if (t == 'h') { @@ -572,36 +536,35 @@ OutputIt basic_printf_context<OutputIt, Char>::format() { } // Parse type. - if (it == end) FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format string")); - specs.type = static_cast<char>(*it++); + if (it == end) throw_format_error("invalid format string"); + char type = static_cast<char>(*it++); if (arg.is_integral()) { // Normalize type. - switch (specs.type) { + switch (type) { case 'i': case 'u': - specs.type = 'd'; + type = 'd'; break; case 'c': - visit_format_arg(detail::char_converter<basic_printf_context>(arg), - arg); + visit_format_arg(char_converter<basic_printf_context<Char>>(arg), arg); break; } } + specs.type = parse_printf_presentation_type(type, arg.type()); + if (specs.type == presentation_type::none) + throw_format_error("invalid format specifier"); start = it; // Format argument. - out = visit_format_arg(ArgFormatter(out, specs, *this), arg); + visit_format_arg(printf_arg_formatter<Char>(out, specs, context), arg); } - return std::copy(start, it, out); + write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(start, to_unsigned(it - start))); } +} // namespace detail -template <typename Char> -using basic_printf_context_t = - basic_printf_context<detail::buffer_appender<Char>, Char>; - -using printf_context = basic_printf_context_t<char>; -using wprintf_context = basic_printf_context_t<wchar_t>; +using printf_context = basic_printf_context<char>; +using wprintf_context = basic_printf_context<wchar_t>; using printf_args = basic_format_args<printf_context>; using wprintf_args = basic_format_args<wprintf_context>; @@ -612,31 +575,27 @@ using wprintf_args = basic_format_args<wprintf_context>; arguments and can be implicitly converted to `~fmt::printf_args`. \endrst */ -template <typename... Args> -inline format_arg_store<printf_context, Args...> make_printf_args( - const Args&... args) { +template <typename... T> +inline auto make_printf_args(const T&... args) + -> format_arg_store<printf_context, T...> { return {args...}; } -/** - \rst - Constructs an `~fmt::format_arg_store` object that contains references to - arguments and can be implicitly converted to `~fmt::wprintf_args`. - \endrst - */ -template <typename... Args> -inline format_arg_store<wprintf_context, Args...> make_wprintf_args( - const Args&... args) { +// DEPRECATED! +template <typename... T> +inline auto make_wprintf_args(const T&... args) + -> format_arg_store<wprintf_context, T...> { return {args...}; } -template <typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline std::basic_string<Char> vsprintf( - const S& format, - basic_format_args<basic_printf_context_t<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - vprintf(buffer, to_string_view(format), args); - return to_string(buffer); +template <typename Char> +inline auto vsprintf( + basic_string_view<Char> fmt, + basic_format_args<basic_printf_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) + -> std::basic_string<Char> { + auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); + detail::vprintf(buf, fmt, args); + return to_string(buf); } /** @@ -648,21 +607,22 @@ inline std::basic_string<Char> vsprintf( std::string message = fmt::sprintf("The answer is %d", 42); \endrst */ -template <typename S, typename... Args, +template <typename S, typename... T, typename Char = enable_if_t<detail::is_string<S>::value, char_t<S>>> -inline std::basic_string<Char> sprintf(const S& format, const Args&... args) { - using context = basic_printf_context_t<Char>; - return vsprintf(to_string_view(format), make_format_args<context>(args...)); +inline auto sprintf(const S& fmt, const T&... args) -> std::basic_string<Char> { + return vsprintf(detail::to_string_view(fmt), + fmt::make_format_args<basic_printf_context<Char>>(args...)); } -template <typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline int vfprintf( - std::FILE* f, const S& format, - basic_format_args<basic_printf_context_t<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - vprintf(buffer, to_string_view(format), args); - size_t size = buffer.size(); - return std::fwrite(buffer.data(), sizeof(Char), size, f) < size +template <typename Char> +inline auto vfprintf( + std::FILE* f, basic_string_view<Char> fmt, + basic_format_args<basic_printf_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) + -> int { + auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); + detail::vprintf(buf, fmt, args); + size_t size = buf.size(); + return std::fwrite(buf.data(), sizeof(Char), size, f) < size ? -1 : static_cast<int>(size); } @@ -676,19 +636,18 @@ inline int vfprintf( fmt::fprintf(stderr, "Don't %s!", "panic"); \endrst */ -template <typename S, typename... Args, - typename Char = enable_if_t<detail::is_string<S>::value, char_t<S>>> -inline int fprintf(std::FILE* f, const S& format, const Args&... args) { - using context = basic_printf_context_t<Char>; - return vfprintf(f, to_string_view(format), - make_format_args<context>(args...)); +template <typename S, typename... T, typename Char = char_t<S>> +inline auto fprintf(std::FILE* f, const S& fmt, const T&... args) -> int { + return vfprintf(f, detail::to_string_view(fmt), + fmt::make_format_args<basic_printf_context<Char>>(args...)); } -template <typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline int vprintf( - const S& format, - basic_format_args<basic_printf_context_t<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - return vfprintf(stdout, to_string_view(format), args); +template <typename Char> +FMT_DEPRECATED inline auto vprintf( + basic_string_view<Char> fmt, + basic_format_args<basic_printf_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) + -> int { + return vfprintf(stdout, fmt, args); } /** @@ -700,52 +659,17 @@ inline int vprintf( fmt::printf("Elapsed time: %.2f seconds", 1.23); \endrst */ -template <typename S, typename... Args, - FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_string<S>::value)> -inline int printf(const S& format_str, const Args&... args) { - using context = basic_printf_context_t<char_t<S>>; - return vprintf(to_string_view(format_str), - make_format_args<context>(args...)); -} - -template <typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline int vfprintf( - std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, const S& format, - basic_format_args<basic_printf_context_t<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) { - basic_memory_buffer<Char> buffer; - vprintf(buffer, to_string_view(format), args); - detail::write_buffer(os, buffer); - return static_cast<int>(buffer.size()); +template <typename... T> +inline auto printf(string_view fmt, const T&... args) -> int { + return vfprintf(stdout, fmt, make_printf_args(args...)); } - -/** Formats arguments and writes the output to the range. */ -template <typename ArgFormatter, typename Char, - typename Context = - basic_printf_context<typename ArgFormatter::iterator, Char>> -typename ArgFormatter::iterator vprintf( - detail::buffer<Char>& out, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - basic_format_args<type_identity_t<Context>> args) { - typename ArgFormatter::iterator iter(out); - Context(iter, format_str, args).template format<ArgFormatter>(); - return iter; +template <typename... T> +FMT_DEPRECATED inline auto printf(basic_string_view<wchar_t> fmt, + const T&... args) -> int { + return vfprintf(stdout, fmt, make_wprintf_args(args...)); } -/** - \rst - Prints formatted data to the stream *os*. - - **Example**:: - - fmt::fprintf(cerr, "Don't %s!", "panic"); - \endrst - */ -template <typename S, typename... Args, typename Char = char_t<S>> -inline int fprintf(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, const S& format_str, - const Args&... args) { - using context = basic_printf_context_t<Char>; - return vfprintf(os, to_string_view(format_str), - make_format_args<context>(args...)); -} +FMT_END_EXPORT FMT_END_NAMESPACE #endif // FMT_PRINTF_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/ranges.h b/include/fmt/ranges.h index 632f0494..c0b51aee 100644 --- a/include/fmt/ranges.h +++ b/include/fmt/ranges.h @@ -1,121 +1,180 @@ -// Formatting library for C++ - experimental range support +// Formatting library for C++ - range and tuple support // -// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich and {fmt} contributors // All rights reserved. // // For the license information refer to format.h. -// -// Copyright (c) 2018 - present, Remotion (Igor Schulz) -// All Rights Reserved -// {fmt} support for ranges, containers and types tuple interface. #ifndef FMT_RANGES_H_ #define FMT_RANGES_H_ #include <initializer_list> +#include <tuple> #include <type_traits> #include "format.h" -// output only up to N items from the range. -#ifndef FMT_RANGE_OUTPUT_LENGTH_LIMIT -# define FMT_RANGE_OUTPUT_LENGTH_LIMIT 256 -#endif - FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <typename Char> struct formatting_base { - template <typename ParseContext> - FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return ctx.begin(); - } -}; - -template <typename Char, typename Enable = void> -struct formatting_range : formatting_base<Char> { - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const size_t range_length_limit = - FMT_RANGE_OUTPUT_LENGTH_LIMIT; // output only up to N items from the - // range. - Char prefix; - Char delimiter; - Char postfix; - formatting_range() : prefix('{'), delimiter(','), postfix('}') {} - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const bool add_delimiter_spaces = true; - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const bool add_prepostfix_space = false; -}; - -template <typename Char, typename Enable = void> -struct formatting_tuple : formatting_base<Char> { - Char prefix; - Char delimiter; - Char postfix; - formatting_tuple() : prefix('('), delimiter(','), postfix(')') {} - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const bool add_delimiter_spaces = true; - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const bool add_prepostfix_space = false; -}; - namespace detail { -template <typename RangeT, typename OutputIterator> -OutputIterator copy(const RangeT& range, OutputIterator out) { +template <typename Range, typename OutputIt> +auto copy(const Range& range, OutputIt out) -> OutputIt { for (auto it = range.begin(), end = range.end(); it != end; ++it) *out++ = *it; return out; } -template <typename OutputIterator> -OutputIterator copy(const char* str, OutputIterator out) { +template <typename OutputIt> +auto copy(const char* str, OutputIt out) -> OutputIt { while (*str) *out++ = *str++; return out; } -template <typename OutputIterator> -OutputIterator copy(char ch, OutputIterator out) { +template <typename OutputIt> auto copy(char ch, OutputIt out) -> OutputIt { + *out++ = ch; + return out; +} + +template <typename OutputIt> auto copy(wchar_t ch, OutputIt out) -> OutputIt { *out++ = ch; return out; } -/// Return true value if T has std::string interface, like std::string_view. -template <typename T> class is_like_std_string { +// Returns true if T has a std::string-like interface, like std::string_view. +template <typename T> class is_std_string_like { template <typename U> static auto check(U* p) -> decltype((void)p->find('a'), p->length(), (void)p->data(), int()); template <typename> static void check(...); public: - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const bool value = - is_string<T>::value || !std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value; + static constexpr const bool value = + is_string<T>::value || + std::is_convertible<T, std_string_view<char>>::value || + !std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value; }; template <typename Char> -struct is_like_std_string<fmt::basic_string_view<Char>> : std::true_type {}; +struct is_std_string_like<fmt::basic_string_view<Char>> : std::true_type {}; + +template <typename T> class is_map { + template <typename U> static auto check(U*) -> typename U::mapped_type; + template <typename> static void check(...); + + public: +#ifdef FMT_FORMAT_MAP_AS_LIST // DEPRECATED! + static constexpr const bool value = false; +#else + static constexpr const bool value = + !std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value; +#endif +}; + +template <typename T> class is_set { + template <typename U> static auto check(U*) -> typename U::key_type; + template <typename> static void check(...); + + public: +#ifdef FMT_FORMAT_SET_AS_LIST // DEPRECATED! + static constexpr const bool value = false; +#else + static constexpr const bool value = + !std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value && !is_map<T>::value; +#endif +}; template <typename... Ts> struct conditional_helper {}; template <typename T, typename _ = void> struct is_range_ : std::false_type {}; -#if !FMT_MSC_VER || FMT_MSC_VER > 1800 +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION > 1800 + +# define FMT_DECLTYPE_RETURN(val) \ + ->decltype(val) { return val; } \ + static_assert( \ + true, "") // This makes it so that a semicolon is required after the + // macro, which helps clang-format handle the formatting. + +// C array overload +template <typename T, std::size_t N> +auto range_begin(const T (&arr)[N]) -> const T* { + return arr; +} +template <typename T, std::size_t N> +auto range_end(const T (&arr)[N]) -> const T* { + return arr + N; +} + +template <typename T, typename Enable = void> +struct has_member_fn_begin_end_t : std::false_type {}; + +template <typename T> +struct has_member_fn_begin_end_t<T, void_t<decltype(std::declval<T>().begin()), + decltype(std::declval<T>().end())>> + : std::true_type {}; + +// Member function overload +template <typename T> +auto range_begin(T&& rng) FMT_DECLTYPE_RETURN(static_cast<T&&>(rng).begin()); +template <typename T> +auto range_end(T&& rng) FMT_DECLTYPE_RETURN(static_cast<T&&>(rng).end()); + +// ADL overload. Only participates in overload resolution if member functions +// are not found. +template <typename T> +auto range_begin(T&& rng) + -> enable_if_t<!has_member_fn_begin_end_t<T&&>::value, + decltype(begin(static_cast<T&&>(rng)))> { + return begin(static_cast<T&&>(rng)); +} +template <typename T> +auto range_end(T&& rng) -> enable_if_t<!has_member_fn_begin_end_t<T&&>::value, + decltype(end(static_cast<T&&>(rng)))> { + return end(static_cast<T&&>(rng)); +} + +template <typename T, typename Enable = void> +struct has_const_begin_end : std::false_type {}; +template <typename T, typename Enable = void> +struct has_mutable_begin_end : std::false_type {}; + +template <typename T> +struct has_const_begin_end< + T, + void_t< + decltype(detail::range_begin(std::declval<const remove_cvref_t<T>&>())), + decltype(detail::range_end(std::declval<const remove_cvref_t<T>&>()))>> + : std::true_type {}; + +template <typename T> +struct has_mutable_begin_end< + T, void_t<decltype(detail::range_begin(std::declval<T>())), + decltype(detail::range_end(std::declval<T>())), + // the extra int here is because older versions of MSVC don't + // SFINAE properly unless there are distinct types + int>> : std::true_type {}; + template <typename T> -struct is_range_< - T, conditional_t<false, - conditional_helper<decltype(std::declval<T>().begin()), - decltype(std::declval<T>().end())>, - void>> : std::true_type {}; +struct is_range_<T, void> + : std::integral_constant<bool, (has_const_begin_end<T>::value || + has_mutable_begin_end<T>::value)> {}; +# undef FMT_DECLTYPE_RETURN #endif -/// tuple_size and tuple_element check. +// tuple_size and tuple_element check. template <typename T> class is_tuple_like_ { template <typename U> static auto check(U* p) -> decltype(std::tuple_size<U>::value, int()); template <typename> static void check(...); public: - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const bool value = + static constexpr const bool value = !std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value; }; // Check for integer_sequence -#if defined(__cpp_lib_integer_sequence) || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1900 +#if defined(__cpp_lib_integer_sequence) || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1900 template <typename T, T... N> using integer_sequence = std::integer_sequence<T, N...>; template <size_t... N> using index_sequence = std::index_sequence<N...>; @@ -138,213 +197,493 @@ template <size_t N> using make_index_sequence = make_integer_sequence<size_t, N>; #endif -template <class Tuple, class F, size_t... Is> -void for_each(index_sequence<Is...>, Tuple&& tup, F&& f) FMT_NOEXCEPT { +template <typename T> +using tuple_index_sequence = make_index_sequence<std::tuple_size<T>::value>; + +template <typename T, typename C, bool = is_tuple_like_<T>::value> +class is_tuple_formattable_ { + public: + static constexpr const bool value = false; +}; +template <typename T, typename C> class is_tuple_formattable_<T, C, true> { + template <std::size_t... Is> + static std::true_type check2(index_sequence<Is...>, + integer_sequence<bool, (Is == Is)...>); + static std::false_type check2(...); + template <std::size_t... Is> + static decltype(check2( + index_sequence<Is...>{}, + integer_sequence< + bool, (is_formattable<typename std::tuple_element<Is, T>::type, + C>::value)...>{})) check(index_sequence<Is...>); + + public: + static constexpr const bool value = + decltype(check(tuple_index_sequence<T>{}))::value; +}; + +template <typename Tuple, typename F, size_t... Is> +FMT_CONSTEXPR void for_each(index_sequence<Is...>, Tuple&& t, F&& f) { using std::get; - // using free function get<I>(T) now. - const int _[] = {0, ((void)f(get<Is>(tup)), 0)...}; - (void)_; // blocks warnings + // Using a free function get<Is>(Tuple) now. + const int unused[] = {0, ((void)f(get<Is>(t)), 0)...}; + ignore_unused(unused); } -template <class T> -FMT_CONSTEXPR make_index_sequence<std::tuple_size<T>::value> get_indexes( - T const&) { - return {}; +template <typename Tuple, typename F> +FMT_CONSTEXPR void for_each(Tuple&& t, F&& f) { + for_each(tuple_index_sequence<remove_cvref_t<Tuple>>(), + std::forward<Tuple>(t), std::forward<F>(f)); +} + +template <typename Tuple1, typename Tuple2, typename F, size_t... Is> +void for_each2(index_sequence<Is...>, Tuple1&& t1, Tuple2&& t2, F&& f) { + using std::get; + const int unused[] = {0, ((void)f(get<Is>(t1), get<Is>(t2)), 0)...}; + ignore_unused(unused); } -template <class Tuple, class F> void for_each(Tuple&& tup, F&& f) { - const auto indexes = get_indexes(tup); - for_each(indexes, std::forward<Tuple>(tup), std::forward<F>(f)); +template <typename Tuple1, typename Tuple2, typename F> +void for_each2(Tuple1&& t1, Tuple2&& t2, F&& f) { + for_each2(tuple_index_sequence<remove_cvref_t<Tuple1>>(), + std::forward<Tuple1>(t1), std::forward<Tuple2>(t2), + std::forward<F>(f)); } +namespace tuple { +// Workaround a bug in MSVC 2019 (v140). +template <typename Char, typename... T> +using result_t = std::tuple<formatter<remove_cvref_t<T>, Char>...>; + +using std::get; +template <typename Tuple, typename Char, std::size_t... Is> +auto get_formatters(index_sequence<Is...>) + -> result_t<Char, decltype(get<Is>(std::declval<Tuple>()))...>; +} // namespace tuple + +#if FMT_MSC_VERSION && FMT_MSC_VERSION < 1920 +// Older MSVC doesn't get the reference type correctly for arrays. +template <typename R> struct range_reference_type_impl { + using type = decltype(*detail::range_begin(std::declval<R&>())); +}; + +template <typename T, std::size_t N> struct range_reference_type_impl<T[N]> { + using type = T&; +}; + +template <typename T> +using range_reference_type = typename range_reference_type_impl<T>::type; +#else template <typename Range> -using value_type = remove_cvref_t<decltype(*std::declval<Range>().begin())>; +using range_reference_type = + decltype(*detail::range_begin(std::declval<Range&>())); +#endif -template <typename Arg, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_like_std_string< - typename std::decay<Arg>::type>::value)> -FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* format_str_quoted(bool add_space, const Arg&) { - return add_space ? " {}" : "{}"; -} +// We don't use the Range's value_type for anything, but we do need the Range's +// reference type, with cv-ref stripped. +template <typename Range> +using uncvref_type = remove_cvref_t<range_reference_type<Range>>; -template <typename Arg, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_like_std_string< - typename std::decay<Arg>::type>::value)> -FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* format_str_quoted(bool add_space, const Arg&) { - return add_space ? " \"{}\"" : "\"{}\""; +template <typename Formatter> +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto maybe_set_debug_format(Formatter& f, bool set) + -> decltype(f.set_debug_format(set)) { + f.set_debug_format(set); } +template <typename Formatter> +FMT_CONSTEXPR void maybe_set_debug_format(Formatter&, ...) {} + +// These are not generic lambdas for compatibility with C++11. +template <typename ParseContext> struct parse_empty_specs { + template <typename Formatter> FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(Formatter& f) { + f.parse(ctx); + detail::maybe_set_debug_format(f, true); + } + ParseContext& ctx; +}; +template <typename FormatContext> struct format_tuple_element { + using char_type = typename FormatContext::char_type; + + template <typename T> + void operator()(const formatter<T, char_type>& f, const T& v) { + if (i > 0) + ctx.advance_to(detail::copy_str<char_type>(separator, ctx.out())); + ctx.advance_to(f.format(v, ctx)); + ++i; + } -FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* format_str_quoted(bool add_space, const char*) { - return add_space ? " \"{}\"" : "\"{}\""; -} -FMT_CONSTEXPR const wchar_t* format_str_quoted(bool add_space, const wchar_t*) { - return add_space ? L" \"{}\"" : L"\"{}\""; -} + int i; + FormatContext& ctx; + basic_string_view<char_type> separator; +}; -FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* format_str_quoted(bool add_space, const char) { - return add_space ? " '{}'" : "'{}'"; -} -FMT_CONSTEXPR const wchar_t* format_str_quoted(bool add_space, const wchar_t) { - return add_space ? L" '{}'" : L"'{}'"; -} } // namespace detail template <typename T> struct is_tuple_like { - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const bool value = + static constexpr const bool value = detail::is_tuple_like_<T>::value && !detail::is_range_<T>::value; }; -template <typename TupleT, typename Char> -struct formatter<TupleT, Char, enable_if_t<fmt::is_tuple_like<TupleT>::value>> { +template <typename T, typename C> struct is_tuple_formattable { + static constexpr const bool value = + detail::is_tuple_formattable_<T, C>::value; +}; + +template <typename Tuple, typename Char> +struct formatter<Tuple, Char, + enable_if_t<fmt::is_tuple_like<Tuple>::value && + fmt::is_tuple_formattable<Tuple, Char>::value>> { private: - // C++11 generic lambda for format() - template <typename FormatContext> struct format_each { - template <typename T> void operator()(const T& v) { - if (i > 0) { - if (formatting.add_prepostfix_space) { - *out++ = ' '; - } - out = detail::copy(formatting.delimiter, out); - } - out = format_to(out, - detail::format_str_quoted( - (formatting.add_delimiter_spaces && i > 0), v), - v); - ++i; - } + decltype(detail::tuple::get_formatters<Tuple, Char>( + detail::tuple_index_sequence<Tuple>())) formatters_; - formatting_tuple<Char>& formatting; - size_t& i; - typename std::add_lvalue_reference<decltype( - std::declval<FormatContext>().out())>::type out; - }; + basic_string_view<Char> separator_ = detail::string_literal<Char, ',', ' '>{}; + basic_string_view<Char> opening_bracket_ = + detail::string_literal<Char, '('>{}; + basic_string_view<Char> closing_bracket_ = + detail::string_literal<Char, ')'>{}; public: - formatting_tuple<Char> formatting; + FMT_CONSTEXPR formatter() {} - template <typename ParseContext> - FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return formatting.parse(ctx); + FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_separator(basic_string_view<Char> sep) { + separator_ = sep; } - template <typename FormatContext = format_context> - auto format(const TupleT& values, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - auto out = ctx.out(); - size_t i = 0; - detail::copy(formatting.prefix, out); + FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_brackets(basic_string_view<Char> open, + basic_string_view<Char> close) { + opening_bracket_ = open; + closing_bracket_ = close; + } - detail::for_each(values, format_each<FormatContext>{formatting, i, out}); - if (formatting.add_prepostfix_space) { - *out++ = ' '; - } - detail::copy(formatting.postfix, out); + template <typename ParseContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + auto it = ctx.begin(); + if (it != ctx.end() && *it != '}') + FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format specifier")); + detail::for_each(formatters_, detail::parse_empty_specs<ParseContext>{ctx}); + return it; + } - return ctx.out(); + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const Tuple& value, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + ctx.advance_to(detail::copy_str<Char>(opening_bracket_, ctx.out())); + detail::for_each2( + formatters_, value, + detail::format_tuple_element<FormatContext>{0, ctx, separator_}); + return detail::copy_str<Char>(closing_bracket_, ctx.out()); } }; template <typename T, typename Char> struct is_range { - static FMT_CONSTEXPR_DECL const bool value = - detail::is_range_<T>::value && !detail::is_like_std_string<T>::value && + static constexpr const bool value = + detail::is_range_<T>::value && !detail::is_std_string_like<T>::value && !std::is_convertible<T, std::basic_string<Char>>::value && - !std::is_constructible<detail::std_string_view<Char>, T>::value; + !std::is_convertible<T, detail::std_string_view<Char>>::value; +}; + +namespace detail { +template <typename Context> struct range_mapper { + using mapper = arg_mapper<Context>; + + template <typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(has_formatter<remove_cvref_t<T>, Context>::value)> + static auto map(T&& value) -> T&& { + return static_cast<T&&>(value); + } + template <typename T, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(!has_formatter<remove_cvref_t<T>, Context>::value)> + static auto map(T&& value) + -> decltype(mapper().map(static_cast<T&&>(value))) { + return mapper().map(static_cast<T&&>(value)); + } }; +template <typename Char, typename Element> +using range_formatter_type = + formatter<remove_cvref_t<decltype(range_mapper<buffer_context<Char>>{}.map( + std::declval<Element>()))>, + Char>; + +template <typename R> +using maybe_const_range = + conditional_t<has_const_begin_end<R>::value, const R, R>; + +// Workaround a bug in MSVC 2015 and earlier. +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1910 +template <typename R, typename Char> +struct is_formattable_delayed + : is_formattable<uncvref_type<maybe_const_range<R>>, Char> {}; +#endif +} // namespace detail + +template <typename T, typename Char, typename Enable = void> +struct range_formatter; + template <typename T, typename Char> -struct formatter< +struct range_formatter< T, Char, - enable_if_t<fmt::is_range<T, Char>::value -// Workaround a bug in MSVC 2017 and earlier. -#if !FMT_MSC_VER || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1927 - && - (has_formatter<detail::value_type<T>, format_context>::value || - detail::has_fallback_formatter<detail::value_type<T>, - format_context>::value) -#endif - >> { - formatting_range<Char> formatting; + enable_if_t<conjunction<std::is_same<T, remove_cvref_t<T>>, + is_formattable<T, Char>>::value>> { + private: + detail::range_formatter_type<Char, T> underlying_; + basic_string_view<Char> separator_ = detail::string_literal<Char, ',', ' '>{}; + basic_string_view<Char> opening_bracket_ = + detail::string_literal<Char, '['>{}; + basic_string_view<Char> closing_bracket_ = + detail::string_literal<Char, ']'>{}; + + public: + FMT_CONSTEXPR range_formatter() {} + + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto underlying() -> detail::range_formatter_type<Char, T>& { + return underlying_; + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_separator(basic_string_view<Char> sep) { + separator_ = sep; + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_brackets(basic_string_view<Char> open, + basic_string_view<Char> close) { + opening_bracket_ = open; + closing_bracket_ = close; + } template <typename ParseContext> FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return formatting.parse(ctx); + auto it = ctx.begin(); + auto end = ctx.end(); + + if (it != end && *it == 'n') { + set_brackets({}, {}); + ++it; + } + + if (it != end && *it != '}') { + if (*it != ':') FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format specifier")); + ++it; + } else { + detail::maybe_set_debug_format(underlying_, true); + } + + ctx.advance_to(it); + return underlying_.parse(ctx); } - template <typename FormatContext> - typename FormatContext::iterator format(const T& values, FormatContext& ctx) { - auto out = detail::copy(formatting.prefix, ctx.out()); - size_t i = 0; - auto it = values.begin(); - auto end = values.end(); + template <typename R, typename FormatContext> + auto format(R&& range, FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + detail::range_mapper<buffer_context<Char>> mapper; + auto out = ctx.out(); + out = detail::copy_str<Char>(opening_bracket_, out); + int i = 0; + auto it = detail::range_begin(range); + auto end = detail::range_end(range); for (; it != end; ++it) { - if (i > 0) { - if (formatting.add_prepostfix_space) *out++ = ' '; - out = detail::copy(formatting.delimiter, out); - } - out = format_to(out, - detail::format_str_quoted( - (formatting.add_delimiter_spaces && i > 0), *it), - *it); - if (++i > formatting.range_length_limit) { - out = format_to(out, " ... <other elements>"); - break; - } + if (i > 0) out = detail::copy_str<Char>(separator_, out); + ctx.advance_to(out); + out = underlying_.format(mapper.map(*it), ctx); + ++i; } - if (formatting.add_prepostfix_space) *out++ = ' '; - return detail::copy(formatting.postfix, out); + out = detail::copy_str<Char>(closing_bracket_, out); + return out; } }; -template <typename Char, typename... T> struct tuple_arg_join : detail::view { +enum class range_format { disabled, map, set, sequence, string, debug_string }; + +namespace detail { +template <typename T> +struct range_format_kind_ + : std::integral_constant<range_format, + std::is_same<uncvref_type<T>, T>::value + ? range_format::disabled + : is_map<T>::value ? range_format::map + : is_set<T>::value ? range_format::set + : range_format::sequence> {}; + +template <range_format K, typename R, typename Char, typename Enable = void> +struct range_default_formatter; + +template <range_format K> +using range_format_constant = std::integral_constant<range_format, K>; + +template <range_format K, typename R, typename Char> +struct range_default_formatter< + K, R, Char, + enable_if_t<(K == range_format::sequence || K == range_format::map || + K == range_format::set)>> { + using range_type = detail::maybe_const_range<R>; + range_formatter<detail::uncvref_type<range_type>, Char> underlying_; + + FMT_CONSTEXPR range_default_formatter() { init(range_format_constant<K>()); } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void init(range_format_constant<range_format::set>) { + underlying_.set_brackets(detail::string_literal<Char, '{'>{}, + detail::string_literal<Char, '}'>{}); + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void init(range_format_constant<range_format::map>) { + underlying_.set_brackets(detail::string_literal<Char, '{'>{}, + detail::string_literal<Char, '}'>{}); + underlying_.underlying().set_brackets({}, {}); + underlying_.underlying().set_separator( + detail::string_literal<Char, ':', ' '>{}); + } + + FMT_CONSTEXPR void init(range_format_constant<range_format::sequence>) {} + + template <typename ParseContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return underlying_.parse(ctx); + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(range_type& range, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return underlying_.format(range, ctx); + } +}; +} // namespace detail + +template <typename T, typename Char, typename Enable = void> +struct range_format_kind + : conditional_t< + is_range<T, Char>::value, detail::range_format_kind_<T>, + std::integral_constant<range_format, range_format::disabled>> {}; + +template <typename R, typename Char> +struct formatter< + R, Char, + enable_if_t<conjunction<bool_constant<range_format_kind<R, Char>::value != + range_format::disabled> +// Workaround a bug in MSVC 2015 and earlier. +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1910 + , + detail::is_formattable_delayed<R, Char> +#endif + >::value>> + : detail::range_default_formatter<range_format_kind<R, Char>::value, R, + Char> { +}; + +template <typename Char, typename... T> struct tuple_join_view : detail::view { const std::tuple<T...>& tuple; basic_string_view<Char> sep; - tuple_arg_join(const std::tuple<T...>& t, basic_string_view<Char> s) - : tuple{t}, sep{s} {} + tuple_join_view(const std::tuple<T...>& t, basic_string_view<Char> s) + : tuple(t), sep{s} {} }; +// Define FMT_TUPLE_JOIN_SPECIFIERS to enable experimental format specifiers +// support in tuple_join. It is disabled by default because of issues with +// the dynamic width and precision. +#ifndef FMT_TUPLE_JOIN_SPECIFIERS +# define FMT_TUPLE_JOIN_SPECIFIERS 0 +#endif + template <typename Char, typename... T> -struct formatter<tuple_arg_join<Char, T...>, Char> { +struct formatter<tuple_join_view<Char, T...>, Char> { template <typename ParseContext> FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return ctx.begin(); + return do_parse(ctx, std::integral_constant<size_t, sizeof...(T)>()); } template <typename FormatContext> - typename FormatContext::iterator format( - const tuple_arg_join<Char, T...>& value, FormatContext& ctx) { - return format(value, ctx, detail::make_index_sequence<sizeof...(T)>{}); + auto format(const tuple_join_view<Char, T...>& value, + FormatContext& ctx) const -> typename FormatContext::iterator { + return do_format(value, ctx, + std::integral_constant<size_t, sizeof...(T)>()); } private: - template <typename FormatContext, size_t... N> - typename FormatContext::iterator format( - const tuple_arg_join<Char, T...>& value, FormatContext& ctx, - detail::index_sequence<N...>) { - return format_args(value, ctx, std::get<N>(value.tuple)...); + std::tuple<formatter<typename std::decay<T>::type, Char>...> formatters_; + + template <typename ParseContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto do_parse(ParseContext& ctx, + std::integral_constant<size_t, 0>) + -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + template <typename ParseContext, size_t N> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto do_parse(ParseContext& ctx, + std::integral_constant<size_t, N>) + -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + auto end = ctx.begin(); +#if FMT_TUPLE_JOIN_SPECIFIERS + end = std::get<sizeof...(T) - N>(formatters_).parse(ctx); + if (N > 1) { + auto end1 = do_parse(ctx, std::integral_constant<size_t, N - 1>()); + if (end != end1) + FMT_THROW(format_error("incompatible format specs for tuple elements")); + } +#endif + return end; } template <typename FormatContext> - typename FormatContext::iterator format_args( - const tuple_arg_join<Char, T...>&, FormatContext& ctx) { - // NOTE: for compilers that support C++17, this empty function instantiation - // can be replaced with a constexpr branch in the variadic overload. + auto do_format(const tuple_join_view<Char, T...>&, FormatContext& ctx, + std::integral_constant<size_t, 0>) const -> + typename FormatContext::iterator { return ctx.out(); } - template <typename FormatContext, typename Arg, typename... Args> - typename FormatContext::iterator format_args( - const tuple_arg_join<Char, T...>& value, FormatContext& ctx, - const Arg& arg, const Args&... args) { - using base = formatter<typename std::decay<Arg>::type, Char>; - auto out = ctx.out(); - out = base{}.format(arg, ctx); - if (sizeof...(Args) > 0) { + template <typename FormatContext, size_t N> + auto do_format(const tuple_join_view<Char, T...>& value, FormatContext& ctx, + std::integral_constant<size_t, N>) const -> + typename FormatContext::iterator { + auto out = std::get<sizeof...(T) - N>(formatters_) + .format(std::get<sizeof...(T) - N>(value.tuple), ctx); + if (N > 1) { out = std::copy(value.sep.begin(), value.sep.end(), out); ctx.advance_to(out); - return format_args(value, ctx, args...); + return do_format(value, ctx, std::integral_constant<size_t, N - 1>()); } return out; } }; +namespace detail { +// Check if T has an interface like a container adaptor (e.g. std::stack, +// std::queue, std::priority_queue). +template <typename T> class is_container_adaptor_like { + template <typename U> static auto check(U* p) -> typename U::container_type; + template <typename> static void check(...); + + public: + static constexpr const bool value = + !std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value; +}; + +template <typename Container> struct all { + const Container& c; + auto begin() const -> typename Container::const_iterator { return c.begin(); } + auto end() const -> typename Container::const_iterator { return c.end(); } +}; +} // namespace detail + +template <typename T, typename Char> +struct formatter< + T, Char, + enable_if_t<conjunction<detail::is_container_adaptor_like<T>, + bool_constant<range_format_kind<T, Char>::value == + range_format::disabled>>::value>> + : formatter<detail::all<typename T::container_type>, Char> { + using all = detail::all<typename T::container_type>; + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const T& t, FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + struct getter : T { + static auto get(const T& t) -> all { + return {t.*(&getter::c)}; // Access c through the derived class. + } + }; + return formatter<all>::format(getter::get(t), ctx); + } +}; + +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT + /** \rst Returns an object that formats `tuple` with elements separated by `sep`. @@ -357,14 +696,15 @@ struct formatter<tuple_arg_join<Char, T...>, Char> { \endrst */ template <typename... T> -FMT_CONSTEXPR tuple_arg_join<char, T...> join(const std::tuple<T...>& tuple, - string_view sep) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto join(const std::tuple<T...>& tuple, string_view sep) + -> tuple_join_view<char, T...> { return {tuple, sep}; } template <typename... T> -FMT_CONSTEXPR tuple_arg_join<wchar_t, T...> join(const std::tuple<T...>& tuple, - wstring_view sep) { +FMT_CONSTEXPR auto join(const std::tuple<T...>& tuple, + basic_string_view<wchar_t> sep) + -> tuple_join_view<wchar_t, T...> { return {tuple, sep}; } @@ -380,17 +720,12 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR tuple_arg_join<wchar_t, T...> join(const std::tuple<T...>& tuple, \endrst */ template <typename T> -arg_join<const T*, const T*, char> join(std::initializer_list<T> list, - string_view sep) { - return join(std::begin(list), std::end(list), sep); -} - -template <typename T> -arg_join<const T*, const T*, wchar_t> join(std::initializer_list<T> list, - wstring_view sep) { +auto join(std::initializer_list<T> list, string_view sep) + -> join_view<const T*, const T*> { return join(std::begin(list), std::end(list), sep); } +FMT_END_EXPORT FMT_END_NAMESPACE #endif // FMT_RANGES_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/std.h b/include/fmt/std.h new file mode 100644 index 00000000..4d1f97d2 --- /dev/null +++ b/include/fmt/std.h @@ -0,0 +1,481 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - formatters for standard library types +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#ifndef FMT_STD_H_ +#define FMT_STD_H_ + +#include <atomic> +#include <bitset> +#include <cstdlib> +#include <exception> +#include <memory> +#include <thread> +#include <type_traits> +#include <typeinfo> +#include <utility> +#include <vector> + +#include "format.h" +#include "ostream.h" + +#if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<version>) +# include <version> +#endif +// Checking FMT_CPLUSPLUS for warning suppression in MSVC. +#if FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L +# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<filesystem>) +# include <filesystem> +# endif +# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<variant>) +# include <variant> +# endif +# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<optional>) +# include <optional> +# endif +#endif + +// GCC 4 does not support FMT_HAS_INCLUDE. +#if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<cxxabi.h>) || defined(__GLIBCXX__) +# include <cxxabi.h> +// Android NDK with gabi++ library on some architectures does not implement +// abi::__cxa_demangle(). +# ifndef __GABIXX_CXXABI_H__ +# define FMT_HAS_ABI_CXA_DEMANGLE +# endif +#endif + +// Check if typeid is available. +#ifndef FMT_USE_TYPEID +// __RTTI is for EDG compilers. In MSVC typeid is available without RTTI. +# if defined(__GXX_RTTI) || FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_rtti) || FMT_MSC_VERSION || \ + defined(__INTEL_RTTI__) || defined(__RTTI) +# define FMT_USE_TYPEID 1 +# else +# define FMT_USE_TYPEID 0 +# endif +#endif + +#ifdef __cpp_lib_filesystem +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE + +namespace detail { + +template <typename Char, typename PathChar> auto get_path_string( + const std::filesystem::path& p, const std::basic_string<PathChar>& native) { + if constexpr (std::is_same_v<Char, char> && std::is_same_v<PathChar, wchar_t>) + return to_utf8<wchar_t>(native, to_utf8_error_policy::replace); + else + return p.string<Char>(); +} + +template <typename Char, typename PathChar> +void write_escaped_path(basic_memory_buffer<Char>& quoted, + const std::filesystem::path& p, + const std::basic_string<PathChar>& native) { + if constexpr (std::is_same_v<Char, char> && std::is_same_v<PathChar, wchar_t>) { + auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t>(); + write_escaped_string<wchar_t>(std::back_inserter(buf), native); + bool valid = to_utf8<wchar_t>::convert(quoted, {buf.data(), buf.size()}); + FMT_ASSERT(valid, "invalid utf16"); + } else if constexpr (std::is_same_v<Char, PathChar>) { + write_escaped_string<std::filesystem::path::value_type>( + std::back_inserter(quoted), native); + } else { + write_escaped_string<Char>(std::back_inserter(quoted), p.string<Char>()); + } +} + +} // namespace detail + +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::filesystem::path, Char> { + private: + format_specs<Char> specs_; + detail::arg_ref<Char> width_ref_; + bool debug_ = false; + + public: + FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_debug_format(bool set = true) { debug_ = set; } + + template <typename ParseContext> FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) { + auto it = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end(); + if (it == end) return it; + + it = detail::parse_align(it, end, specs_); + if (it == end) return it; + + it = detail::parse_dynamic_spec(it, end, specs_.width, width_ref_, ctx); + if (it != end && *it == '?') { + debug_ = true; + ++it; + } + return it; + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const std::filesystem::path& p, FormatContext& ctx) const { + auto specs = specs_; + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs.width, width_ref_, + ctx); + if (!debug_) { + auto s = detail::get_path_string<Char>(p, p.native()); + return detail::write(ctx.out(), basic_string_view<Char>(s), specs); + } + auto quoted = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); + detail::write_escaped_path(quoted, p, p.native()); + return detail::write(ctx.out(), + basic_string_view<Char>(quoted.data(), quoted.size()), + specs); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE +#endif + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +FMT_EXPORT +template <std::size_t N, typename Char> +struct formatter<std::bitset<N>, Char> : nested_formatter<string_view> { + private: + // Functor because C++11 doesn't support generic lambdas. + struct writer { + const std::bitset<N>& bs; + + template <typename OutputIt> + FMT_CONSTEXPR OutputIt operator()(OutputIt out) { + for (auto pos = N; pos > 0; --pos) { + out = detail::write<Char>(out, bs[pos - 1] ? Char('1') : Char('0')); + } + + return out; + } + }; + + public: + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const std::bitset<N>& bs, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return write_padded(ctx, writer{bs}); + } +}; + +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename Char> +struct formatter<std::thread::id, Char> : basic_ostream_formatter<Char> {}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +#ifdef __cpp_lib_optional +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename T, typename Char> +struct formatter<std::optional<T>, Char, + std::enable_if_t<is_formattable<T, Char>::value>> { + private: + formatter<T, Char> underlying_; + static constexpr basic_string_view<Char> optional = + detail::string_literal<Char, 'o', 'p', 't', 'i', 'o', 'n', 'a', 'l', + '('>{}; + static constexpr basic_string_view<Char> none = + detail::string_literal<Char, 'n', 'o', 'n', 'e'>{}; + + template <class U> + FMT_CONSTEXPR static auto maybe_set_debug_format(U& u, bool set) + -> decltype(u.set_debug_format(set)) { + u.set_debug_format(set); + } + + template <class U> + FMT_CONSTEXPR static void maybe_set_debug_format(U&, ...) {} + + public: + template <typename ParseContext> FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) { + maybe_set_debug_format(underlying_, true); + return underlying_.parse(ctx); + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(std::optional<T> const& opt, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + if (!opt) return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), none); + + auto out = ctx.out(); + out = detail::write<Char>(out, optional); + ctx.advance_to(out); + out = underlying_.format(*opt, ctx); + return detail::write(out, ')'); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE +#endif // __cpp_lib_optional + +#ifdef __cpp_lib_variant +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +namespace detail { + +template <typename T> +using variant_index_sequence = + std::make_index_sequence<std::variant_size<T>::value>; + +template <typename> struct is_variant_like_ : std::false_type {}; +template <typename... Types> +struct is_variant_like_<std::variant<Types...>> : std::true_type {}; + +// formattable element check. +template <typename T, typename C> class is_variant_formattable_ { + template <std::size_t... Is> + static std::conjunction< + is_formattable<std::variant_alternative_t<Is, T>, C>...> + check(std::index_sequence<Is...>); + + public: + static constexpr const bool value = + decltype(check(variant_index_sequence<T>{}))::value; +}; + +template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T> +auto write_variant_alternative(OutputIt out, const T& v) -> OutputIt { + if constexpr (is_string<T>::value) + return write_escaped_string<Char>(out, detail::to_string_view(v)); + else if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, Char>) + return write_escaped_char(out, v); + else + return write<Char>(out, v); +} + +} // namespace detail + +template <typename T> struct is_variant_like { + static constexpr const bool value = detail::is_variant_like_<T>::value; +}; + +template <typename T, typename C> struct is_variant_formattable { + static constexpr const bool value = + detail::is_variant_formattable_<T, C>::value; +}; + +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::monostate, Char> { + template <typename ParseContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const std::monostate&, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), "monostate"); + } +}; + +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename Variant, typename Char> +struct formatter< + Variant, Char, + std::enable_if_t<std::conjunction_v< + is_variant_like<Variant>, is_variant_formattable<Variant, Char>>>> { + template <typename ParseContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const Variant& value, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto out = ctx.out(); + + out = detail::write<Char>(out, "variant("); + FMT_TRY { + std::visit( + [&](const auto& v) { + out = detail::write_variant_alternative<Char>(out, v); + }, + value); + } + FMT_CATCH(const std::bad_variant_access&) { + detail::write<Char>(out, "valueless by exception"); + } + *out++ = ')'; + return out; + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE +#endif // __cpp_lib_variant + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::error_code, Char> { + template <typename ParseContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto format(const std::error_code& ec, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto out = ctx.out(); + out = detail::write_bytes(out, ec.category().name(), format_specs<Char>()); + out = detail::write<Char>(out, Char(':')); + out = detail::write<Char>(out, ec.value()); + return out; + } +}; + +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename T, typename Char> +struct formatter< + T, Char, + typename std::enable_if<std::is_base_of<std::exception, T>::value>::type> { + private: + bool with_typename_ = false; + + public: + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(basic_format_parse_context<Char>& ctx) + -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + auto it = ctx.begin(); + auto end = ctx.end(); + if (it == end || *it == '}') return it; + if (*it == 't') { + ++it; + with_typename_ = FMT_USE_TYPEID != 0; + } + return it; + } + + template <typename OutputIt> + auto format(const std::exception& ex, + basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>& ctx) const -> OutputIt { + format_specs<Char> spec; + auto out = ctx.out(); + if (!with_typename_) + return detail::write_bytes(out, string_view(ex.what()), spec); + +#if FMT_USE_TYPEID + const std::type_info& ti = typeid(ex); +# ifdef FMT_HAS_ABI_CXA_DEMANGLE + int status = 0; + std::size_t size = 0; + std::unique_ptr<char, decltype(&std::free)> demangled_name_ptr( + abi::__cxa_demangle(ti.name(), nullptr, &size, &status), &std::free); + + string_view demangled_name_view; + if (demangled_name_ptr) { + demangled_name_view = demangled_name_ptr.get(); + + // Normalization of stdlib inline namespace names. + // libc++ inline namespaces. + // std::__1::* -> std::* + // std::__1::__fs::* -> std::* + // libstdc++ inline namespaces. + // std::__cxx11::* -> std::* + // std::filesystem::__cxx11::* -> std::filesystem::* + if (demangled_name_view.starts_with("std::")) { + char* begin = demangled_name_ptr.get(); + char* to = begin + 5; // std:: + for (char *from = to, *end = begin + demangled_name_view.size(); + from < end;) { + // This is safe, because demangled_name is NUL-terminated. + if (from[0] == '_' && from[1] == '_') { + char* next = from + 1; + while (next < end && *next != ':') next++; + if (next[0] == ':' && next[1] == ':') { + from = next + 2; + continue; + } + } + *to++ = *from++; + } + demangled_name_view = {begin, detail::to_unsigned(to - begin)}; + } + } else { + demangled_name_view = string_view(ti.name()); + } + out = detail::write_bytes(out, demangled_name_view, spec); +# elif FMT_MSC_VERSION + string_view demangled_name_view(ti.name()); + if (demangled_name_view.starts_with("class ")) + demangled_name_view.remove_prefix(6); + else if (demangled_name_view.starts_with("struct ")) + demangled_name_view.remove_prefix(7); + out = detail::write_bytes(out, demangled_name_view, spec); +# else + out = detail::write_bytes(out, string_view(ti.name()), spec); +# endif + *out++ = ':'; + *out++ = ' '; + return detail::write_bytes(out, string_view(ex.what()), spec); +#endif + } +}; + +namespace detail { + +template <typename T, typename Enable = void> +struct has_flip : std::false_type {}; + +template <typename T> +struct has_flip<T, void_t<decltype(std::declval<T>().flip())>> + : std::true_type {}; + +template <typename T> struct is_bit_reference_like { + static constexpr const bool value = + std::is_convertible<T, bool>::value && + std::is_nothrow_assignable<T, bool>::value && has_flip<T>::value; +}; + +#ifdef _LIBCPP_VERSION + +// Workaround for libc++ incompatibility with C++ standard. +// According to the Standard, `bitset::operator[] const` returns bool. +template <typename C> +struct is_bit_reference_like<std::__bit_const_reference<C>> { + static constexpr const bool value = true; +}; + +#endif + +} // namespace detail + +// We can't use std::vector<bool, Allocator>::reference and +// std::bitset<N>::reference because the compiler can't deduce Allocator and N +// in partial specialization. +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename BitRef, typename Char> +struct formatter<BitRef, Char, + enable_if_t<detail::is_bit_reference_like<BitRef>::value>> + : formatter<bool, Char> { + template <typename FormatContext> + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto format(const BitRef& v, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return formatter<bool, Char>::format(v, ctx); + } +}; + +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename T, typename Char> +struct formatter<std::atomic<T>, Char, + enable_if_t<is_formattable<T, Char>::value>> + : formatter<T, Char> { + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const std::atomic<T>& v, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return formatter<T, Char>::format(v.load(), ctx); + } +}; + +#ifdef __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test +FMT_EXPORT +template <typename Char> +struct formatter<std::atomic_flag, Char> : formatter<bool, Char> { + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const std::atomic_flag& v, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return formatter<bool, Char>::format(v.test(), ctx); + } +}; +#endif // __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test + +FMT_END_NAMESPACE +#endif // FMT_STD_H_ diff --git a/include/fmt/xchar.h b/include/fmt/xchar.h new file mode 100644 index 00000000..625ec369 --- /dev/null +++ b/include/fmt/xchar.h @@ -0,0 +1,258 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - optional wchar_t and exotic character support +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#ifndef FMT_XCHAR_H_ +#define FMT_XCHAR_H_ + +#include <cwchar> + +#include "format.h" + +#ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR +# include <locale> +#endif + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +namespace detail { + +template <typename T> +using is_exotic_char = bool_constant<!std::is_same<T, char>::value>; + +inline auto write_loc(std::back_insert_iterator<detail::buffer<wchar_t>> out, + loc_value value, const format_specs<wchar_t>& specs, + locale_ref loc) -> bool { +#ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR + auto& numpunct = + std::use_facet<std::numpunct<wchar_t>>(loc.get<std::locale>()); + auto separator = std::wstring(); + auto grouping = numpunct.grouping(); + if (!grouping.empty()) separator = std::wstring(1, numpunct.thousands_sep()); + return value.visit(loc_writer<wchar_t>{out, specs, separator, grouping, {}}); +#endif + return false; +} +} // namespace detail + +FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT + +using wstring_view = basic_string_view<wchar_t>; +using wformat_parse_context = basic_format_parse_context<wchar_t>; +using wformat_context = buffer_context<wchar_t>; +using wformat_args = basic_format_args<wformat_context>; +using wmemory_buffer = basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t>; + +#if FMT_GCC_VERSION && FMT_GCC_VERSION < 409 +// Workaround broken conversion on older gcc. +template <typename... Args> using wformat_string = wstring_view; +inline auto runtime(wstring_view s) -> wstring_view { return s; } +#else +template <typename... Args> +using wformat_string = basic_format_string<wchar_t, type_identity_t<Args>...>; +inline auto runtime(wstring_view s) -> runtime_format_string<wchar_t> { + return {{s}}; +} +#endif + +template <> struct is_char<wchar_t> : std::true_type {}; +template <> struct is_char<detail::char8_type> : std::true_type {}; +template <> struct is_char<char16_t> : std::true_type {}; +template <> struct is_char<char32_t> : std::true_type {}; + +template <typename... T> +constexpr format_arg_store<wformat_context, T...> make_wformat_args( + const T&... args) { + return {args...}; +} + +inline namespace literals { +#if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS && !FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS +constexpr detail::udl_arg<wchar_t> operator"" _a(const wchar_t* s, size_t) { + return {s}; +} +#endif +} // namespace literals + +template <typename It, typename Sentinel> +auto join(It begin, Sentinel end, wstring_view sep) + -> join_view<It, Sentinel, wchar_t> { + return {begin, end, sep}; +} + +template <typename Range> +auto join(Range&& range, wstring_view sep) + -> join_view<detail::iterator_t<Range>, detail::sentinel_t<Range>, + wchar_t> { + return join(std::begin(range), std::end(range), sep); +} + +template <typename T> +auto join(std::initializer_list<T> list, wstring_view sep) + -> join_view<const T*, const T*, wchar_t> { + return join(std::begin(list), std::end(list), sep); +} + +template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value)> +auto vformat(basic_string_view<Char> format_str, + basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) + -> std::basic_string<Char> { + auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>(); + detail::vformat_to(buf, format_str, args); + return to_string(buf); +} + +template <typename... T> +auto format(wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> std::wstring { + return vformat(fmt::wstring_view(fmt), fmt::make_wformat_args(args...)); +} + +// Pass char_t as a default template parameter instead of using +// std::basic_string<char_t<S>> to reduce the symbol size. +template <typename S, typename... T, typename Char = char_t<S>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value && + !std::is_same<Char, wchar_t>::value)> +auto format(const S& format_str, T&&... args) -> std::basic_string<Char> { + return vformat(detail::to_string_view(format_str), + fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<Char>>(args...)); +} + +template <typename Locale, typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_locale<Locale>::value&& + detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)> +inline auto vformat( + const Locale& loc, const S& format_str, + basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) + -> std::basic_string<Char> { + return detail::vformat(loc, detail::to_string_view(format_str), args); +} + +template <typename Locale, typename S, typename... T, typename Char = char_t<S>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_locale<Locale>::value&& + detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)> +inline auto format(const Locale& loc, const S& format_str, T&&... args) + -> std::basic_string<Char> { + return detail::vformat(loc, detail::to_string_view(format_str), + fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<Char>>(args...)); +} + +template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&& + detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)> +auto vformat_to(OutputIt out, const S& format_str, + basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) + -> OutputIt { + auto&& buf = detail::get_buffer<Char>(out); + detail::vformat_to(buf, detail::to_string_view(format_str), args); + return detail::get_iterator(buf, out); +} + +template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... T, + typename Char = char_t<S>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&& + detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)> +inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const S& fmt, T&&... args) -> OutputIt { + return vformat_to(out, detail::to_string_view(fmt), + fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<Char>>(args...)); +} + +template <typename Locale, typename S, typename OutputIt, typename... Args, + typename Char = char_t<S>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&& + detail::is_locale<Locale>::value&& + detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)> +inline auto vformat_to( + OutputIt out, const Locale& loc, const S& format_str, + basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) -> OutputIt { + auto&& buf = detail::get_buffer<Char>(out); + vformat_to(buf, detail::to_string_view(format_str), args, + detail::locale_ref(loc)); + return detail::get_iterator(buf, out); +} + +template < + typename OutputIt, typename Locale, typename S, typename... T, + typename Char = char_t<S>, + bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&& + detail::is_locale<Locale>::value&& detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value> +inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const Locale& loc, const S& format_str, + T&&... args) -> + typename std::enable_if<enable, OutputIt>::type { + return vformat_to(out, loc, detail::to_string_view(format_str), + fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<Char>>(args...)); +} + +template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename... Args, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&& + detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)> +inline auto vformat_to_n( + OutputIt out, size_t n, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, + basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) + -> format_to_n_result<OutputIt> { + using traits = detail::fixed_buffer_traits; + auto buf = detail::iterator_buffer<OutputIt, Char, traits>(out, n); + detail::vformat_to(buf, format_str, args); + return {buf.out(), buf.count()}; +} + +template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... T, + typename Char = char_t<S>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&& + detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)> +inline auto format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, const S& fmt, T&&... args) + -> format_to_n_result<OutputIt> { + return vformat_to_n(out, n, detail::to_string_view(fmt), + fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<Char>>(args...)); +} + +template <typename S, typename... T, typename Char = char_t<S>, + FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)> +inline auto formatted_size(const S& fmt, T&&... args) -> size_t { + auto buf = detail::counting_buffer<Char>(); + detail::vformat_to(buf, detail::to_string_view(fmt), + fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<Char>>(args...)); + return buf.count(); +} + +inline void vprint(std::FILE* f, wstring_view fmt, wformat_args args) { + auto buf = wmemory_buffer(); + detail::vformat_to(buf, fmt, args); + buf.push_back(L'\0'); + if (std::fputws(buf.data(), f) == -1) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot write to file"))); +} + +inline void vprint(wstring_view fmt, wformat_args args) { + vprint(stdout, fmt, args); +} + +template <typename... T> +void print(std::FILE* f, wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + return vprint(f, wstring_view(fmt), fmt::make_wformat_args(args...)); +} + +template <typename... T> void print(wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + return vprint(wstring_view(fmt), fmt::make_wformat_args(args...)); +} + +template <typename... T> +void println(std::FILE* f, wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + return print(f, L"{}\n", fmt::format(fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...)); +} + +template <typename... T> void println(wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) { + return print(L"{}\n", fmt::format(fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...)); +} + +/** + Converts *value* to ``std::wstring`` using the default format for type *T*. + */ +template <typename T> inline auto to_wstring(const T& value) -> std::wstring { + return format(FMT_STRING(L"{}"), value); +} +FMT_END_EXPORT +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +#endif // FMT_XCHAR_H_ diff --git a/pull_request_template.md b/pull_request_template.md deleted file mode 100644 index 548e30f2..00000000 --- a/pull_request_template.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,6 +0,0 @@ -<!-- Please read the contribution guidelines before submitting a pull request. --> -<!-- By submitting this pull request, you agree that your contributions are licensed under the {fmt} license, - and agree to future changes to the licensing. --> -<!-- If you're a first-time contributor, please acknowledge it by leaving the statement below. --> - -I agree that my contributions are licensed under the {fmt} license, and agree to future changes to the licensing. diff --git a/src/fmt.cc b/src/fmt.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..6638bb4a --- /dev/null +++ b/src/fmt.cc @@ -0,0 +1,108 @@ +module; + +// Put all implementation-provided headers into the global module fragment +// to prevent attachment to this module. +#include <algorithm> +#include <cerrno> +#include <chrono> +#include <climits> +#include <cmath> +#include <cstddef> +#include <cstdint> +#include <cstdio> +#include <cstdlib> +#include <cstring> +#include <ctime> +#include <exception> +#include <filesystem> +#include <fstream> +#include <functional> +#include <iterator> +#include <limits> +#include <locale> +#include <memory> +#include <optional> +#include <ostream> +#include <stdexcept> +#include <string> +#include <string_view> +#include <system_error> +#include <thread> +#include <type_traits> +#include <typeinfo> +#include <utility> +#include <variant> +#include <vector> +#include <version> + +#if __has_include(<cxxabi.h>) +# include <cxxabi.h> +#endif +#if defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(__MINGW32__) +# include <intrin.h> +#endif +#if defined __APPLE__ || defined(__FreeBSD__) +# include <xlocale.h> +#endif +#if __has_include(<winapifamily.h>) +# include <winapifamily.h> +#endif +#if (__has_include(<fcntl.h>) || defined(__APPLE__) || \ + defined(__linux__)) && \ + (!defined(WINAPI_FAMILY) || (WINAPI_FAMILY == WINAPI_FAMILY_DESKTOP_APP)) +# include <fcntl.h> +# include <sys/stat.h> +# include <sys/types.h> +# ifndef _WIN32 +# include <unistd.h> +# else +# include <io.h> +# endif +#endif +#ifdef _WIN32 +# if defined(__GLIBCXX__) +# include <ext/stdio_filebuf.h> +# include <ext/stdio_sync_filebuf.h> +# endif +# define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN +# include <windows.h> +#endif + +export module fmt; + +#define FMT_EXPORT export +#define FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT export { +#define FMT_END_EXPORT } + +// If you define FMT_ATTACH_TO_GLOBAL_MODULE +// - all declarations are detached from module 'fmt' +// - the module behaves like a traditional static library, too +// - all library symbols are mangled traditionally +// - you can mix TUs with either importing or #including the {fmt} API +#ifdef FMT_ATTACH_TO_GLOBAL_MODULE +extern "C++" { +#endif + +// All library-provided declarations and definitions must be in the module +// purview to be exported. +#include "fmt/args.h" +#include "fmt/chrono.h" +#include "fmt/color.h" +#include "fmt/compile.h" +#include "fmt/format.h" +#include "fmt/os.h" +#include "fmt/printf.h" +#include "fmt/std.h" +#include "fmt/xchar.h" + +#ifdef FMT_ATTACH_TO_GLOBAL_MODULE +} +#endif + +// gcc doesn't yet implement private module fragments +#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION +module : private; +#endif + +#include "format.cc" +#include "os.cc" diff --git a/src/format.cc b/src/format.cc index 6141d964..391d3a24 100644 --- a/src/format.cc +++ b/src/format.cc @@ -10,90 +10,34 @@ FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE namespace detail { -template <typename T> -int format_float(char* buf, std::size_t size, const char* format, int precision, - T value) { -#ifdef FMT_FUZZ - if (precision > 100000) - throw std::runtime_error( - "fuzz mode - avoid large allocation inside snprintf"); -#endif - // Suppress the warning about nonliteral format string. - int (*snprintf_ptr)(char*, size_t, const char*, ...) = FMT_SNPRINTF; - return precision < 0 ? snprintf_ptr(buf, size, format, value) - : snprintf_ptr(buf, size, format, precision, value); -} - -template FMT_API dragonbox::decimal_fp<float> dragonbox::to_decimal(float x) - FMT_NOEXCEPT; -template FMT_API dragonbox::decimal_fp<double> dragonbox::to_decimal(double x) - FMT_NOEXCEPT; - -// DEPRECATED! This function exists for ABI compatibility. -template <typename Char> -typename basic_format_context<std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<Char>>, - Char>::iterator -vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> format_str, - basic_format_args<basic_format_context< - std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<type_identity_t<Char>>>, - type_identity_t<Char>>> - args) { - using iterator = std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<char>>; - using context = basic_format_context< - std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<type_identity_t<Char>>>, - type_identity_t<Char>>; - auto out = iterator(buf); - format_handler<iterator, Char, context> h(out, format_str, args, {}); - parse_format_string<false>(format_str, h); - return out; -} -template basic_format_context<std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<char>>, - char>::iterator -vformat_to(buffer<char>&, string_view, - basic_format_args<basic_format_context< - std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<type_identity_t<char>>>, - type_identity_t<char>>>); -} // namespace detail - -template struct FMT_INSTANTIATION_DEF_API detail::basic_data<void>; - -// Workaround a bug in MSVC2013 that prevents instantiation of format_float. -int (*instantiate_format_float)(double, int, detail::float_specs, - detail::buffer<char>&) = detail::format_float; +template FMT_API auto dragonbox::to_decimal(float x) noexcept + -> dragonbox::decimal_fp<float>; +template FMT_API auto dragonbox::to_decimal(double x) noexcept + -> dragonbox::decimal_fp<double>; #ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR -template FMT_API detail::locale_ref::locale_ref(const std::locale& loc); -template FMT_API std::locale detail::locale_ref::get<std::locale>() const; +template FMT_API locale_ref::locale_ref(const std::locale& loc); +template FMT_API auto locale_ref::get<std::locale>() const -> std::locale; #endif // Explicit instantiations for char. -template FMT_API std::string detail::grouping_impl<char>(locale_ref); -template FMT_API char detail::thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref); -template FMT_API char detail::decimal_point_impl(locale_ref); - -template FMT_API void detail::buffer<char>::append(const char*, const char*); +template FMT_API auto thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref) + -> thousands_sep_result<char>; +template FMT_API auto decimal_point_impl(locale_ref) -> char; -template FMT_API void detail::vformat_to( - detail::buffer<char>&, string_view, - basic_format_args<FMT_BUFFER_CONTEXT(char)>, detail::locale_ref); +template FMT_API void buffer<char>::append(const char*, const char*); -template FMT_API int detail::snprintf_float(double, int, detail::float_specs, - detail::buffer<char>&); -template FMT_API int detail::snprintf_float(long double, int, - detail::float_specs, - detail::buffer<char>&); -template FMT_API int detail::format_float(double, int, detail::float_specs, - detail::buffer<char>&); -template FMT_API int detail::format_float(long double, int, detail::float_specs, - detail::buffer<char>&); +template FMT_API void vformat_to(buffer<char>&, string_view, + typename vformat_args<>::type, locale_ref); // Explicit instantiations for wchar_t. -template FMT_API std::string detail::grouping_impl<wchar_t>(locale_ref); -template FMT_API wchar_t detail::thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref); -template FMT_API wchar_t detail::decimal_point_impl(locale_ref); +template FMT_API auto thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref) + -> thousands_sep_result<wchar_t>; +template FMT_API auto decimal_point_impl(locale_ref) -> wchar_t; -template FMT_API void detail::buffer<wchar_t>::append(const wchar_t*, - const wchar_t*); +template FMT_API void buffer<wchar_t>::append(const wchar_t*, const wchar_t*); + +} // namespace detail FMT_END_NAMESPACE @@ -18,6 +18,10 @@ # include <sys/stat.h> # include <sys/types.h> +# ifdef _WRS_KERNEL // VxWorks7 kernel +# include <ioLib.h> // getpagesize +# endif + # ifndef _WIN32 # include <unistd.h> # else @@ -25,21 +29,24 @@ # define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN # endif # include <io.h> -# include <windows.h> - -# define O_CREAT _O_CREAT -# define O_TRUNC _O_TRUNC # ifndef S_IRUSR # define S_IRUSR _S_IREAD # endif - # ifndef S_IWUSR # define S_IWUSR _S_IWRITE # endif - -# ifdef __MINGW32__ -# define _SH_DENYNO 0x40 +# ifndef S_IRGRP +# define S_IRGRP 0 +# endif +# ifndef S_IWGRP +# define S_IWGRP 0 +# endif +# ifndef S_IROTH +# define S_IROTH 0 +# endif +# ifndef S_IWOTH +# define S_IWOTH 0 # endif # endif // _WIN32 #endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL @@ -48,14 +55,10 @@ # include <windows.h> #endif -#ifdef fileno -# undef fileno -#endif - namespace { #ifdef _WIN32 // Return type of read and write functions. -using RWResult = int; +using rwresult = int; // On Windows the count argument to read and write is unsigned, so convert // it from size_t preventing integer overflow. @@ -64,7 +67,7 @@ inline unsigned convert_rwcount(std::size_t count) { } #elif FMT_USE_FCNTL // Return type of read and write functions. -using RWResult = ssize_t; +using rwresult = ssize_t; inline std::size_t convert_rwcount(std::size_t count) { return count; } #endif @@ -73,79 +76,91 @@ inline std::size_t convert_rwcount(std::size_t count) { return count; } FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE #ifdef _WIN32 -detail::utf16_to_utf8::utf16_to_utf8(wstring_view s) { - if (int error_code = convert(s)) { - FMT_THROW(windows_error(error_code, - "cannot convert string from UTF-16 to UTF-8")); +namespace detail { + +class system_message { + system_message(const system_message&) = delete; + void operator=(const system_message&) = delete; + + unsigned long result_; + wchar_t* message_; + + static bool is_whitespace(wchar_t c) noexcept { + return c == L' ' || c == L'\n' || c == L'\r' || c == L'\t' || c == L'\0'; } -} -int detail::utf16_to_utf8::convert(wstring_view s) { - if (s.size() > INT_MAX) return ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER; - int s_size = static_cast<int>(s.size()); - if (s_size == 0) { - // WideCharToMultiByte does not support zero length, handle separately. - buffer_.resize(1); - buffer_[0] = 0; - return 0; + public: + explicit system_message(unsigned long error_code) + : result_(0), message_(nullptr) { + result_ = FormatMessageW( + FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | + FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS, + nullptr, error_code, MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), + reinterpret_cast<wchar_t*>(&message_), 0, nullptr); + if (result_ != 0) { + while (result_ != 0 && is_whitespace(message_[result_ - 1])) { + --result_; + } + } + } + ~system_message() { LocalFree(message_); } + explicit operator bool() const noexcept { return result_ != 0; } + operator basic_string_view<wchar_t>() const noexcept { + return basic_string_view<wchar_t>(message_, result_); + } +}; + +class utf8_system_category final : public std::error_category { + public: + const char* name() const noexcept override { return "system"; } + std::string message(int error_code) const override { + auto&& msg = system_message(error_code); + if (msg) { + auto utf8_message = to_utf8<wchar_t>(); + if (utf8_message.convert(msg)) { + return utf8_message.str(); + } + } + return "unknown error"; } +}; + +} // namespace detail - int length = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, 0, s.data(), s_size, nullptr, 0, - nullptr, nullptr); - if (length == 0) return GetLastError(); - buffer_.resize(length + 1); - length = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, 0, s.data(), s_size, &buffer_[0], - length, nullptr, nullptr); - if (length == 0) return GetLastError(); - buffer_[length] = 0; - return 0; +FMT_API const std::error_category& system_category() noexcept { + static const detail::utf8_system_category category; + return category; } -void windows_error::init(int err_code, string_view format_str, - format_args args) { - error_code_ = err_code; - memory_buffer buffer; - detail::format_windows_error(buffer, err_code, vformat(format_str, args)); - std::runtime_error& base = *this; - base = std::runtime_error(to_string(buffer)); +std::system_error vwindows_error(int err_code, string_view format_str, + format_args args) { + auto ec = std::error_code(err_code, system_category()); + return std::system_error(ec, vformat(format_str, args)); } void detail::format_windows_error(detail::buffer<char>& out, int error_code, - string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT { + const char* message) noexcept { FMT_TRY { - wmemory_buffer buf; - buf.resize(inline_buffer_size); - for (;;) { - wchar_t* system_message = &buf[0]; - int result = FormatMessageW( - FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS, nullptr, - error_code, MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), system_message, - static_cast<uint32_t>(buf.size()), nullptr); - if (result != 0) { - utf16_to_utf8 utf8_message; - if (utf8_message.convert(system_message) == ERROR_SUCCESS) { - format_to(buffer_appender<char>(out), "{}: {}", message, - utf8_message); - return; - } - break; + auto&& msg = system_message(error_code); + if (msg) { + auto utf8_message = to_utf8<wchar_t>(); + if (utf8_message.convert(msg)) { + fmt::format_to(appender(out), FMT_STRING("{}: {}"), message, + string_view(utf8_message)); + return; } - if (GetLastError() != ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER) - break; // Can't get error message, report error code instead. - buf.resize(buf.size() * 2); } } FMT_CATCH(...) {} format_error_code(out, error_code, message); } -void report_windows_error(int error_code, - fmt::string_view message) FMT_NOEXCEPT { +void report_windows_error(int error_code, const char* message) noexcept { report_error(detail::format_windows_error, error_code, message); } #endif // _WIN32 -buffered_file::~buffered_file() FMT_NOEXCEPT { +buffered_file::~buffered_file() noexcept { if (file_ && FMT_SYSTEM(fclose(file_)) != 0) report_system_error(errno, "cannot close file"); } @@ -154,39 +169,50 @@ buffered_file::buffered_file(cstring_view filename, cstring_view mode) { FMT_RETRY_VAL(file_, FMT_SYSTEM(fopen(filename.c_str(), mode.c_str())), nullptr); if (!file_) - FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot open file {}", filename.c_str())); + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot open file {}"), + filename.c_str())); } void buffered_file::close() { if (!file_) return; int result = FMT_SYSTEM(fclose(file_)); file_ = nullptr; - if (result != 0) FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot close file")); + if (result != 0) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot close file"))); } -// A macro used to prevent expansion of fileno on broken versions of MinGW. -#define FMT_ARGS - -int buffered_file::fileno() const { - int fd = FMT_POSIX_CALL(fileno FMT_ARGS(file_)); - if (fd == -1) FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot get file descriptor")); +int buffered_file::descriptor() const { +#ifdef fileno // fileno is a macro on OpenBSD so we cannot use FMT_POSIX_CALL. + int fd = fileno(file_); +#else + int fd = FMT_POSIX_CALL(fileno(file_)); +#endif + if (fd == -1) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot get file descriptor"))); return fd; } #if FMT_USE_FCNTL +# ifdef _WIN32 +using mode_t = int; +# endif +constexpr mode_t default_open_mode = + S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH; + file::file(cstring_view path, int oflag) { - int mode = S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR; # if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__) fd_ = -1; - FMT_POSIX_CALL(sopen_s(&fd_, path.c_str(), oflag, _SH_DENYNO, mode)); + auto converted = detail::utf8_to_utf16(string_view(path.c_str())); + *this = file::open_windows_file(converted.c_str(), oflag); # else - FMT_RETRY(fd_, FMT_POSIX_CALL(open(path.c_str(), oflag, mode))); -# endif + FMT_RETRY(fd_, FMT_POSIX_CALL(open(path.c_str(), oflag, default_open_mode))); if (fd_ == -1) - FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot open file {}", path.c_str())); + FMT_THROW( + system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot open file {}"), path.c_str())); +# endif } -file::~file() FMT_NOEXCEPT { +file::~file() noexcept { // Don't retry close in case of EINTR! // See http://linux.derkeiler.com/Mailing-Lists/Kernel/2005-09/3000.html if (fd_ != -1 && FMT_POSIX_CALL(close(fd_)) != 0) @@ -199,7 +225,8 @@ void file::close() { // See http://linux.derkeiler.com/Mailing-Lists/Kernel/2005-09/3000.html int result = FMT_POSIX_CALL(close(fd_)); fd_ = -1; - if (result != 0) FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot close file")); + if (result != 0) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot close file"))); } long long file::size() const { @@ -221,7 +248,7 @@ long long file::size() const { using Stat = struct stat; Stat file_stat = Stat(); if (FMT_POSIX_CALL(fstat(fd_, &file_stat)) == -1) - FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot get file attributes")); + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot get file attributes"))); static_assert(sizeof(long long) >= sizeof(file_stat.st_size), "return type of file::size is not large enough"); return file_stat.st_size; @@ -229,16 +256,18 @@ long long file::size() const { } std::size_t file::read(void* buffer, std::size_t count) { - RWResult result = 0; + rwresult result = 0; FMT_RETRY(result, FMT_POSIX_CALL(read(fd_, buffer, convert_rwcount(count)))); - if (result < 0) FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot read from file")); + if (result < 0) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot read from file"))); return detail::to_unsigned(result); } std::size_t file::write(const void* buffer, std::size_t count) { - RWResult result = 0; + rwresult result = 0; FMT_RETRY(result, FMT_POSIX_CALL(write(fd_, buffer, convert_rwcount(count)))); - if (result < 0) FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot write to file")); + if (result < 0) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot write to file"))); return detail::to_unsigned(result); } @@ -247,7 +276,8 @@ file file::dup(int fd) { // http://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/009695399/functions/dup.html int new_fd = FMT_POSIX_CALL(dup(fd)); if (new_fd == -1) - FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot duplicate file descriptor {}", fd)); + FMT_THROW(system_error( + errno, FMT_STRING("cannot duplicate file descriptor {}"), fd)); return file(new_fd); } @@ -255,15 +285,16 @@ void file::dup2(int fd) { int result = 0; FMT_RETRY(result, FMT_POSIX_CALL(dup2(fd_, fd))); if (result == -1) { - FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot duplicate file descriptor {} to {}", - fd_, fd)); + FMT_THROW(system_error( + errno, FMT_STRING("cannot duplicate file descriptor {} to {}"), fd_, + fd)); } } -void file::dup2(int fd, error_code& ec) FMT_NOEXCEPT { +void file::dup2(int fd, std::error_code& ec) noexcept { int result = 0; FMT_RETRY(result, FMT_POSIX_CALL(dup2(fd_, fd))); - if (result == -1) ec = error_code(errno); + if (result == -1) ec = std::error_code(errno, std::generic_category()); } void file::pipe(file& read_end, file& write_end) { @@ -281,7 +312,8 @@ void file::pipe(file& read_end, file& write_end) { // http://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/009696799/functions/pipe.html int result = FMT_POSIX_CALL(pipe(fds)); # endif - if (result != 0) FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot create pipe")); + if (result != 0) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot create pipe"))); // The following assignments don't throw because read_fd and write_fd // are closed. read_end = file(fds[0]); @@ -295,28 +327,72 @@ buffered_file file::fdopen(const char* mode) { # else FILE* f = FMT_POSIX_CALL(fdopen(fd_, mode)); # endif - if (!f) - FMT_THROW( - system_error(errno, "cannot associate stream with file descriptor")); + if (!f) { + FMT_THROW(system_error( + errno, FMT_STRING("cannot associate stream with file descriptor"))); + } buffered_file bf(f); fd_ = -1; return bf; } +# if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__) +file file::open_windows_file(wcstring_view path, int oflag) { + int fd = -1; + auto err = _wsopen_s(&fd, path.c_str(), oflag, _SH_DENYNO, default_open_mode); + if (fd == -1) { + FMT_THROW(system_error(err, FMT_STRING("cannot open file {}"), + detail::to_utf8<wchar_t>(path.c_str()).c_str())); + } + return file(fd); +} +# endif + +# if !defined(__MSDOS__) long getpagesize() { -# ifdef _WIN32 +# ifdef _WIN32 SYSTEM_INFO si; GetSystemInfo(&si); return si.dwPageSize; -# else +# else +# ifdef _WRS_KERNEL + long size = FMT_POSIX_CALL(getpagesize()); +# else long size = FMT_POSIX_CALL(sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE)); - if (size < 0) FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, "cannot get memory page size")); +# endif + + if (size < 0) + FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot get memory page size"))); return size; -# endif +# endif } +# endif + +namespace detail { -FMT_API void ostream::grow(size_t) { +void file_buffer::grow(size_t) { if (this->size() == this->capacity()) flush(); } + +file_buffer::file_buffer(cstring_view path, + const detail::ostream_params& params) + : file_(path, params.oflag) { + set(new char[params.buffer_size], params.buffer_size); +} + +file_buffer::file_buffer(file_buffer&& other) + : detail::buffer<char>(other.data(), other.size(), other.capacity()), + file_(std::move(other.file_)) { + other.clear(); + other.set(nullptr, 0); +} + +file_buffer::~file_buffer() { + flush(); + delete[] data(); +} +} // namespace detail + +ostream::~ostream() = default; #endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL FMT_END_NAMESPACE diff --git a/support/Vagrantfile b/support/Vagrantfile index f6b5f936..9680a1a1 100644 --- a/support/Vagrantfile +++ b/support/Vagrantfile @@ -13,8 +13,8 @@ Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL apt-get update apt-get install -y g++ make wget git - wget -q https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v3.14.4/cmake-3.14.4-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz - tar xzf cmake-3.14.4-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz - ln -s `pwd`/cmake-3.14.4-Linux-x86_64/bin/cmake /usr/local/bin + wget -q https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v3.26.0/cmake-3.26.0-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz + tar xzf cmake-3.26.0-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz + ln -s `pwd`/cmake-3.26.0-Linux-x86_64/bin/cmake /usr/local/bin SHELL end diff --git a/support/appveyor-build.py b/support/appveyor-build.py deleted file mode 100644 index 65446103..00000000 --- a/support/appveyor-build.py +++ /dev/null @@ -1,43 +0,0 @@ -#!/usr/bin/env python -# Build the project on AppVeyor. - -import os -from subprocess import check_call - -build = os.environ['BUILD'] -config = os.environ['CONFIGURATION'] -platform = os.environ['PLATFORM'] -path = os.environ['PATH'] -image = os.environ['APPVEYOR_BUILD_WORKER_IMAGE'] -jobid = os.environ['APPVEYOR_JOB_ID'] -cmake_command = ['cmake', '-DFMT_PEDANTIC=ON', '-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=' + config, '..'] -if build == 'mingw': - cmake_command.append('-GMinGW Makefiles') - build_command = ['mingw32-make', '-j4'] - test_command = ['mingw32-make', 'test'] - # Remove the path to Git bin directory from $PATH because it breaks - # MinGW config. - path = path.replace(r'C:\Program Files (x86)\Git\bin', '') - os.environ['PATH'] = r'C:\MinGW\bin;' + path -else: - # Add MSBuild 14.0 to PATH as described in - # http://help.appveyor.com/discussions/problems/2229-v140-not-found-on-vs2105rc. - os.environ['PATH'] = r'C:\Program Files (x86)\MSBuild\15.0\Bin;' + path - if image == 'Visual Studio 2019': - generator = 'Visual Studio 16 2019' - if platform == 'x64': - cmake_command.extend(['-A', 'x64']) - else: - if image == 'Visual Studio 2015': - generator = 'Visual Studio 14 2015' - elif image == 'Visual Studio 2017': - generator = 'Visual Studio 15 2017' - if platform == 'x64': - generator += ' Win64' - cmake_command.append('-G' + generator) - build_command = ['cmake', '--build', '.', '--config', config, '--', '/m:4'] - test_command = ['ctest', '-C', config] - -check_call(cmake_command) -check_call(build_command) -check_call(test_command) diff --git a/support/appveyor.yml b/support/appveyor.yml deleted file mode 100644 index f53e4383..00000000 --- a/support/appveyor.yml +++ /dev/null @@ -1,41 +0,0 @@ -configuration: - - Debug - - Release - -clone_depth: 1 - -image: - - Visual Studio 2015 - - Visual Studio 2019 - - Visual Studio 2017 - -platform: - - Win32 - - x64 - -environment: - CTEST_OUTPUT_ON_FAILURE: 1 - MSVC_DEFAULT_OPTIONS: ON - BUILD: msvc - -matrix: - exclude: - - image: Visual Studio 2015 - platform: Win32 - - image: Visual Studio 2019 - platform: Win32 - -before_build: - - mkdir build - - cd build - -build_script: - - python ../support/appveyor-build.py - -on_failure: - - appveyor PushArtifact Testing/Temporary/LastTest.log - - appveyor AddTest test - -# Uncomment this to debug AppVeyor failures. -#on_finish: -# - ps: $blockRdp = $true; iex ((new-object net.webclient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/appveyor/ci/master/scripts/enable-rdp.ps1')) diff --git a/support/bazel/.bazelversion b/support/bazel/.bazelversion new file mode 100644 index 00000000..5e325424 --- /dev/null +++ b/support/bazel/.bazelversion @@ -0,0 +1 @@ +6.1.2 diff --git a/support/bazel/BUILD.bazel b/support/bazel/BUILD.bazel new file mode 100644 index 00000000..29f639be --- /dev/null +++ b/support/bazel/BUILD.bazel @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ +cc_library( + name = "fmt", + srcs = [ + #"src/fmt.cc", # No C++ module support + "src/format.cc", + "src/os.cc", + ], + hdrs = [ + "include/fmt/args.h", + "include/fmt/chrono.h", + "include/fmt/color.h", + "include/fmt/compile.h", + "include/fmt/core.h", + "include/fmt/format.h", + "include/fmt/format-inl.h", + "include/fmt/os.h", + "include/fmt/ostream.h", + "include/fmt/printf.h", + "include/fmt/ranges.h", + "include/fmt/std.h", + "include/fmt/xchar.h", + ], + includes = [ + "include", + ], + strip_include_prefix = "include", + visibility = ["//visibility:public"], +) diff --git a/support/bazel/README.md b/support/bazel/README.md new file mode 100644 index 00000000..4c29febb --- /dev/null +++ b/support/bazel/README.md @@ -0,0 +1,74 @@ +# Bazel support + +To get [Bazel](https://bazel.build/) working with {fmt} you can copy the files `BUILD.bazel`, `WORKSPACE.bazel`, and `.bazelversion` from this folder (`support/bazel`) to the root folder of this project. This way {fmt} gets bazelized and can be used with Bazel (e.g. doing a `bazel build //...` on {fmt}). + +## Using {fmt} as a dependency + +The following minimal example shows how to use {fmt} as a dependency within a Bazel project. + +The following file structure is assumed: + +``` +example +├── BUILD.bazel +├── main.cpp +└── WORKSPACE.bazel +``` + +*main.cpp*: + +```c++ +#include "fmt/core.h" + +int main() { + fmt::print("The answer is {}\n", 42); +} +``` + +The expected output of this example is `The answer is 42`. + +*WORKSPACE.bazel*: + +```python +load("@bazel_tools//tools/build_defs/repo:git.bzl", "git_repository") + +git_repository( + name = "fmt", + branch = "master", + remote = "https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt", + patch_cmds = [ + "mv support/bazel/.bazelversion .bazelversion", + "mv support/bazel/BUILD.bazel BUILD.bazel", + "mv support/bazel/WORKSPACE.bazel WORKSPACE.bazel", + ], + # Windows-related patch commands are only needed in the case MSYS2 is not installed. + # More details about the installation process of MSYS2 on Windows systems can be found here: + # https://docs.bazel.build/versions/main/install-windows.html#installing-compilers-and-language-runtimes + # Even if MSYS2 is installed the Windows related patch commands can still be used. + patch_cmds_win = [ + "Move-Item -Path support/bazel/.bazelversion -Destination .bazelversion", + "Move-Item -Path support/bazel/BUILD.bazel -Destination BUILD.bazel", + "Move-Item -Path support/bazel/WORKSPACE.bazel -Destination WORKSPACE.bazel", + ], +) +``` + +In the *WORKSPACE* file, the {fmt} GitHub repository is fetched. Using the attribute `patch_cmds` the files `BUILD.bazel`, `WORKSPACE.bazel`, and `.bazelversion` are moved to the root of the {fmt} repository. This way the {fmt} repository is recognized as a bazelized workspace. + +*BUILD.bazel*: + +```python +cc_binary( + name = "Demo", + srcs = ["main.cpp"], + deps = ["@fmt"], +) +``` + +The *BUILD* file defines a binary named `Demo` that has a dependency to {fmt}. + +To execute the binary you can run `bazel run //:Demo`. + +# Using Bzlmod + +The [Bazel Central Registry](https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazel-central-registry/tree/main/modules/fmt) also provides support for {fmt}. diff --git a/support/bazel/WORKSPACE.bazel b/support/bazel/WORKSPACE.bazel new file mode 100644 index 00000000..5be77811 --- /dev/null +++ b/support/bazel/WORKSPACE.bazel @@ -0,0 +1 @@ +workspace(name = "fmt") diff --git a/support/build-docs.py b/support/build-docs.py new file mode 100755 index 00000000..f1395cd6 --- /dev/null +++ b/support/build-docs.py @@ -0,0 +1,58 @@ +#!/usr/bin/env python +# Build the documentation in CI. + +from __future__ import print_function +import errno, os, shutil, subprocess, sys, urllib +from subprocess import call, check_call, Popen, PIPE, STDOUT + +def rmtree_if_exists(dir): + try: + shutil.rmtree(dir) + except OSError as e: + if e.errno == errno.ENOENT: + pass + +# Build the docs. +fmt_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))) +sys.path.insert(0, os.path.join(fmt_dir, 'doc')) +import build +build.create_build_env() +html_dir = build.build_docs() + +repo = 'fmtlib.github.io' +branch = os.environ['GITHUB_REF'] +is_ci = 'CI' in os.environ +if is_ci and branch != 'refs/heads/master': + print('Branch: ' + branch) + exit(0) # Ignore non-master branches +if is_ci and 'KEY' not in os.environ: + # Don't update the repo if building in CI from an account that doesn't have + # push access. + print('Skipping update of ' + repo) + exit(0) + +# Clone the fmtlib.github.io repo. +rmtree_if_exists(repo) +git_url = 'https://github.com/' if is_ci else 'git@github.com:' +check_call(['git', 'clone', git_url + 'fmtlib/{}.git'.format(repo)]) + +# Copy docs to the repo. +target_dir = os.path.join(repo, 'dev') +rmtree_if_exists(target_dir) +shutil.copytree(html_dir, target_dir, ignore=shutil.ignore_patterns('.*')) +if is_ci: + check_call(['git', 'config', '--global', 'user.name', 'fmtbot']) + check_call(['git', 'config', '--global', 'user.email', 'viz@fmt.dev']) + +# Push docs to GitHub pages. +check_call(['git', 'add', '--all'], cwd=repo) +if call(['git', 'diff-index', '--quiet', 'HEAD'], cwd=repo): + check_call(['git', 'commit', '-m', 'Update documentation'], cwd=repo) + cmd = 'git push' + if is_ci: + cmd += ' https://$KEY@github.com/fmtlib/fmtlib.github.io.git master' + p = Popen(cmd, shell=True, stdout=PIPE, stderr=STDOUT, cwd=repo) + # Print the output without the key. + print(p.communicate()[0].decode('utf-8').replace(os.environ['KEY'], '$KEY')) + if p.returncode != 0: + raise subprocess.CalledProcessError(p.returncode, cmd) diff --git a/support/build.gradle b/support/build.gradle index 11648da8..c5126d05 100644 --- a/support/build.gradle +++ b/support/build.gradle @@ -1,3 +1,4 @@ +import java.nio.file.Paths // General gradle arguments for root project buildscript { @@ -7,24 +8,25 @@ buildscript { } dependencies { // - // https://developer.android.com/studio/releases/gradle-plugin + // https://developer.android.com/studio/releases/gradle-plugin#updating-gradle // - // Notice that 3.3.0 here is the version of [Android Gradle Plugin] - // Accroding to URL above you will need Gradle 5.0 or higher + // Notice that 4.0.0 here is the version of [Android Gradle Plugin] + // According to URL above you will need Gradle 6.1 or higher // - // If you are using Android Studio, and it is using Gradle's lower - // version, Use the plugin version 3.1.3 ~ 3.2.0 for Gradle 4.4 ~ 4.10 - classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.3.0' + classpath "com.android.tools.build:gradle:4.1.1" } } repositories { google() jcenter() } - -// Output: Shared library (.so) for Android -apply plugin: 'com.android.library' +// Project's root where CMakeLists.txt exists: rootDir/support/.cxx -> rootDir +def rootDir = Paths.get(project.buildDir.getParent()).getParent() +println("rootDir: ${rootDir}") + +// Output: Shared library (.so) for Android +apply plugin: "com.android.library" android { compileSdkVersion 25 // Android 7.0 @@ -41,13 +43,13 @@ android { include "arm64-v8a", "armeabi-v7a", "x86_64" } } + ndkVersion "21.3.6528147" // ANDROID_NDK_HOME is deprecated. Be explicit defaultConfig { minSdkVersion 21 // Android 5.0+ targetSdkVersion 25 // Follow Compile SDK - versionCode 21 // Follow release count - versionName "5.3.0" // Follow Official version - testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner" + versionCode 34 // Follow release count + versionName "7.1.2" // Follow Official version externalNativeBuild { cmake { @@ -56,9 +58,9 @@ android { arguments "-DFMT_TEST=false" // Skip test arguments "-DFMT_DOC=false" // Skip document cppFlags "-std=c++17" + targets "fmt" } } - println("Gradle CMake Plugin: ") println(externalNativeBuild.cmake.cppFlags) println(externalNativeBuild.cmake.arguments) } @@ -69,16 +71,27 @@ android { // neighbor of the top level cmake externalNativeBuild { cmake { - path "../CMakeLists.txt" + version "3.10.0+" + path "${rootDir}/CMakeLists.txt" // buildStagingDirectory "./build" // Custom path for cmake output } - //println(cmake.path) } sourceSets{ // Android Manifest for Gradle main { - manifest.srcFile 'AndroidManifest.xml' + manifest.srcFile "AndroidManifest.xml" + } + } + + // https://developer.android.com/studio/build/native-dependencies#build_system_configuration + buildFeatures { + prefab true + prefabPublishing true + } + prefab { + fmt { + headers "${rootDir}/include" } } } @@ -88,20 +101,32 @@ assemble.doLast // Instead of `ninja install`, Gradle will deploy the files. // We are doing this since FMT is dependent to the ANDROID_STL after build copy { - from 'build/intermediates/cmake' - into '../libs' + from "build/intermediates/cmake" + into "${rootDir}/libs" } // Copy debug binaries copy { - from '../libs/debug/obj' - into '../libs/debug' + from "${rootDir}/libs/debug/obj" + into "${rootDir}/libs/debug" } // Copy Release binaries copy { - from '../libs/release/obj' - into '../libs/release' + from "${rootDir}/libs/release/obj" + into "${rootDir}/libs/release" } // Remove empty directory - delete '../libs/debug/obj' - delete '../libs/release/obj' + delete "${rootDir}/libs/debug/obj" + delete "${rootDir}/libs/release/obj" + + // Copy AAR files. Notice that the aar is named after the folder of this script. + copy { + from "build/outputs/aar/support-release.aar" + into "${rootDir}/libs" + rename "support-release.aar", "fmt-release.aar" + } + copy { + from "build/outputs/aar/support-debug.aar" + into "${rootDir}/libs" + rename "support-debug.aar", "fmt-debug.aar" + } } diff --git a/support/cmake/cxx14.cmake b/support/cmake/cxx14.cmake deleted file mode 100644 index 16ff5754..00000000 --- a/support/cmake/cxx14.cmake +++ /dev/null @@ -1,70 +0,0 @@ -# C++14 feature support detection - -include(CheckCXXSourceCompiles) -include(CheckCXXCompilerFlag) - -if (NOT CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD) - set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11) -endif() -message(STATUS "CXX_STANDARD: ${CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD}") - -if (CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD EQUAL 20) - check_cxx_compiler_flag(-std=c++20 has_std_20_flag) - check_cxx_compiler_flag(-std=c++2a has_std_2a_flag) - - if (has_std_20_flag) - set(CXX_STANDARD_FLAG -std=c++20) - elseif (has_std_2a_flag) - set(CXX_STANDARD_FLAG -std=c++2a) - endif () -elseif (CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD EQUAL 17) - check_cxx_compiler_flag(-std=c++17 has_std_17_flag) - check_cxx_compiler_flag(-std=c++1z has_std_1z_flag) - - if (has_std_17_flag) - set(CXX_STANDARD_FLAG -std=c++17) - elseif (has_std_1z_flag) - set(CXX_STANDARD_FLAG -std=c++1z) - endif () -elseif (CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD EQUAL 14) - check_cxx_compiler_flag(-std=c++14 has_std_14_flag) - check_cxx_compiler_flag(-std=c++1y has_std_1y_flag) - - if (has_std_14_flag) - set(CXX_STANDARD_FLAG -std=c++14) - elseif (has_std_1y_flag) - set(CXX_STANDARD_FLAG -std=c++1y) - endif () -elseif (CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD EQUAL 11) - check_cxx_compiler_flag(-std=c++11 has_std_11_flag) - check_cxx_compiler_flag(-std=c++0x has_std_0x_flag) - - if (has_std_11_flag) - set(CXX_STANDARD_FLAG -std=c++11) - elseif (has_std_0x_flag) - set(CXX_STANDARD_FLAG -std=c++0x) - endif () -endif () - -set(CMAKE_REQUIRED_FLAGS ${CXX_STANDARD_FLAG}) - -# Check if user-defined literals are available -check_cxx_source_compiles(" - void operator\"\" _udl(long double); - int main() {}" - SUPPORTS_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS) -if (NOT SUPPORTS_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS) - set (SUPPORTS_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS OFF) -endif () - -# Check if <variant> is available -set(CMAKE_REQUIRED_FLAGS -std=c++1z) -check_cxx_source_compiles(" - #include <variant> - int main() {}" - FMT_HAS_VARIANT) -if (NOT FMT_HAS_VARIANT) - set (FMT_HAS_VARIANT OFF) -endif () - -set(CMAKE_REQUIRED_FLAGS ) diff --git a/support/cmake/fmt-config.cmake.in b/support/cmake/fmt-config.cmake.in index 71e30286..bc1684f2 100644 --- a/support/cmake/fmt-config.cmake.in +++ b/support/cmake/fmt-config.cmake.in @@ -1,4 +1,7 @@ @PACKAGE_INIT@ -include(${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/@targets_export_name@.cmake) +if (NOT TARGET fmt::fmt) + include(${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/@targets_export_name@.cmake) +endif () + check_required_components(fmt) diff --git a/support/manage.py b/support/manage.py index 9f270669..36f61d9b 100755 --- a/support/manage.py +++ b/support/manage.py @@ -1,4 +1,4 @@ -#!/usr/bin/env python +#!/usr/bin/env python3 """Manage site and releases. @@ -163,6 +163,13 @@ def update_site(env): if version.startswith('7.'): b.data = b.data.replace(', std::size_t', ', size_t') b.data = b.data.replace('join(It, It', 'join(It, Sentinel') + if version.startswith('7.1.'): + b.data = b.data.replace(', std::size_t', ', size_t') + b.data = b.data.replace('join(It, It', 'join(It, Sentinel') + b.data = b.data.replace( + 'fmt::format_to(OutputIt, const S&, Args&&...)', + 'fmt::format_to(OutputIt, const S&, Args&&...) -> ' + + 'typename std::enable_if<enable, OutputIt>::type') b.data = b.data.replace('aa long', 'a long') b.data = b.data.replace('serveral', 'several') if version.startswith('6.2.'): @@ -176,6 +183,12 @@ def update_site(env): with rewrite(index) as b: b.data = b.data.replace( 'doc/latest/index.html#format-string-syntax', 'syntax.html') + # Fix issues in syntax.rst. + index = os.path.join(target_doc_dir, 'syntax.rst') + with rewrite(index) as b: + b.data = b.data.replace( + '..productionlist:: sf\n', '.. productionlist:: sf\n ') + b.data = b.data.replace('Examples:\n', 'Examples::\n') # Build the docs. html_dir = os.path.join(env.build_dir, 'html') if os.path.exists(html_dir): @@ -218,7 +231,7 @@ def release(args): # Convert changelog from RST to GitHub-flavored Markdown and get the # version. - changelog = 'ChangeLog.rst' + changelog = 'ChangeLog.md' changelog_path = os.path.join(fmt_repo.dir, changelog) import rst2md changes, version = rst2md.convert(changelog_path) @@ -233,7 +246,7 @@ def release(args): # Update the version in the changelog. title_len = 0 for line in fileinput.input(changelog_path, inplace=True): - if line.decode('utf-8').startswith(version + ' - TBD'): + if line.startswith(version + ' - TBD'): line = version + ' - ' + datetime.date.today().isoformat() title_len = len(line) line += '\n' @@ -263,9 +276,9 @@ def release(args): # Create a release on GitHub. fmt_repo.push('origin', 'release') - params = {'access_token': os.getenv('FMT_TOKEN')} + auth_headers = {'Authorization': 'token ' + os.getenv('FMT_TOKEN')} r = requests.post('https://api.github.com/repos/fmtlib/fmt/releases', - params=params, + headers=auth_headers, data=json.dumps({'tag_name': version, 'target_commitish': 'release', 'body': changes, 'draft': True})) @@ -276,8 +289,8 @@ def release(args): package = 'fmt-{}.zip'.format(version) r = requests.post( '{}/{}/assets?name={}'.format(uploads_url, id, package), - headers={'Content-Type': 'application/zip'}, - params=params, data=open('build/fmt/' + package, 'rb')) + headers={'Content-Type': 'application/zip'} | auth_headers, + data=open('build/fmt/' + package, 'rb')) if r.status_code != 201: raise Exception('Failed to upload an asset ' + str(r)) diff --git a/support/printable.py b/support/printable.py new file mode 100755 index 00000000..8fa86b30 --- /dev/null +++ b/support/printable.py @@ -0,0 +1,201 @@ +#!/usr/bin/env python3 + +# This script is based on +# https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/master/library/core/src/unicode/printable.py +# distributed under https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/master/LICENSE-MIT. + +# This script uses the following Unicode tables: +# - UnicodeData.txt + + +from collections import namedtuple +import csv +import os +import subprocess + +NUM_CODEPOINTS=0x110000 + +def to_ranges(iter): + current = None + for i in iter: + if current is None or i != current[1] or i in (0x10000, 0x20000): + if current is not None: + yield tuple(current) + current = [i, i + 1] + else: + current[1] += 1 + if current is not None: + yield tuple(current) + +def get_escaped(codepoints): + for c in codepoints: + if (c.class_ or "Cn") in "Cc Cf Cs Co Cn Zl Zp Zs".split() and c.value != ord(' '): + yield c.value + +def get_file(f): + try: + return open(os.path.basename(f)) + except FileNotFoundError: + subprocess.run(["curl", "-O", f], check=True) + return open(os.path.basename(f)) + +Codepoint = namedtuple('Codepoint', 'value class_') + +def get_codepoints(f): + r = csv.reader(f, delimiter=";") + prev_codepoint = 0 + class_first = None + for row in r: + codepoint = int(row[0], 16) + name = row[1] + class_ = row[2] + + if class_first is not None: + if not name.endswith("Last>"): + raise ValueError("Missing Last after First") + + for c in range(prev_codepoint + 1, codepoint): + yield Codepoint(c, class_first) + + class_first = None + if name.endswith("First>"): + class_first = class_ + + yield Codepoint(codepoint, class_) + prev_codepoint = codepoint + + if class_first is not None: + raise ValueError("Missing Last after First") + + for c in range(prev_codepoint + 1, NUM_CODEPOINTS): + yield Codepoint(c, None) + +def compress_singletons(singletons): + uppers = [] # (upper, # items in lowers) + lowers = [] + + for i in singletons: + upper = i >> 8 + lower = i & 0xff + if len(uppers) == 0 or uppers[-1][0] != upper: + uppers.append((upper, 1)) + else: + upper, count = uppers[-1] + uppers[-1] = upper, count + 1 + lowers.append(lower) + + return uppers, lowers + +def compress_normal(normal): + # lengths 0x00..0x7f are encoded as 00, 01, ..., 7e, 7f + # lengths 0x80..0x7fff are encoded as 80 80, 80 81, ..., ff fe, ff ff + compressed = [] # [truelen, (truelenaux), falselen, (falselenaux)] + + prev_start = 0 + for start, count in normal: + truelen = start - prev_start + falselen = count + prev_start = start + count + + assert truelen < 0x8000 and falselen < 0x8000 + entry = [] + if truelen > 0x7f: + entry.append(0x80 | (truelen >> 8)) + entry.append(truelen & 0xff) + else: + entry.append(truelen & 0x7f) + if falselen > 0x7f: + entry.append(0x80 | (falselen >> 8)) + entry.append(falselen & 0xff) + else: + entry.append(falselen & 0x7f) + + compressed.append(entry) + + return compressed + +def print_singletons(uppers, lowers, uppersname, lowersname): + print(" static constexpr singleton {}[] = {{".format(uppersname)) + for u, c in uppers: + print(" {{{:#04x}, {}}},".format(u, c)) + print(" };") + print(" static constexpr unsigned char {}[] = {{".format(lowersname)) + for i in range(0, len(lowers), 8): + print(" {}".format(" ".join("{:#04x},".format(l) for l in lowers[i:i+8]))) + print(" };") + +def print_normal(normal, normalname): + print(" static constexpr unsigned char {}[] = {{".format(normalname)) + for v in normal: + print(" {}".format(" ".join("{:#04x},".format(i) for i in v))) + print(" };") + +def main(): + file = get_file("https://www.unicode.org/Public/UNIDATA/UnicodeData.txt") + + codepoints = get_codepoints(file) + + CUTOFF=0x10000 + singletons0 = [] + singletons1 = [] + normal0 = [] + normal1 = [] + extra = [] + + for a, b in to_ranges(get_escaped(codepoints)): + if a > 2 * CUTOFF: + extra.append((a, b - a)) + elif a == b - 1: + if a & CUTOFF: + singletons1.append(a & ~CUTOFF) + else: + singletons0.append(a) + elif a == b - 2: + if a & CUTOFF: + singletons1.append(a & ~CUTOFF) + singletons1.append((a + 1) & ~CUTOFF) + else: + singletons0.append(a) + singletons0.append(a + 1) + else: + if a >= 2 * CUTOFF: + extra.append((a, b - a)) + elif a & CUTOFF: + normal1.append((a & ~CUTOFF, b - a)) + else: + normal0.append((a, b - a)) + + singletons0u, singletons0l = compress_singletons(singletons0) + singletons1u, singletons1l = compress_singletons(singletons1) + normal0 = compress_normal(normal0) + normal1 = compress_normal(normal1) + + print("""\ +FMT_FUNC auto is_printable(uint32_t cp) -> bool {\ +""") + print_singletons(singletons0u, singletons0l, 'singletons0', 'singletons0_lower') + print_singletons(singletons1u, singletons1l, 'singletons1', 'singletons1_lower') + print_normal(normal0, 'normal0') + print_normal(normal1, 'normal1') + print("""\ + auto lower = static_cast<uint16_t>(cp); + if (cp < 0x10000) { + return is_printable(lower, singletons0, + sizeof(singletons0) / sizeof(*singletons0), + singletons0_lower, normal0, sizeof(normal0)); + } + if (cp < 0x20000) { + return is_printable(lower, singletons1, + sizeof(singletons1) / sizeof(*singletons1), + singletons1_lower, normal1, sizeof(normal1)); + }\ +""") + for a, b in extra: + print(" if (0x{:x} <= cp && cp < 0x{:x}) return false;".format(a, a + b)) + print("""\ + return cp < 0x{:x}; +}}\ +""".format(NUM_CODEPOINTS)) + +if __name__ == '__main__': + main() diff --git a/support/rst2md.py b/support/rst2md.py deleted file mode 100755 index cf170fe2..00000000 --- a/support/rst2md.py +++ /dev/null @@ -1,159 +0,0 @@ -#!/usr/bin/env python -# reStructuredText (RST) to GitHub-flavored Markdown converter - -import re, sys -from docutils import core, nodes, writers - - -def is_github_ref(node): - return re.match('https://github.com/.*/(issues|pull)/.*', node['refuri']) - - -class Translator(nodes.NodeVisitor): - def __init__(self, document): - nodes.NodeVisitor.__init__(self, document) - self.output = '' - self.indent = 0 - self.preserve_newlines = False - - def write(self, text): - self.output += text.replace('\n', '\n' + ' ' * self.indent) - - def visit_document(self, node): - pass - - def depart_document(self, node): - pass - - def visit_section(self, node): - pass - - def depart_section(self, node): - # Skip all sections except the first one. - raise nodes.StopTraversal - - def visit_title(self, node): - self.version = re.match(r'(\d+\.\d+\.\d+).*', node.children[0]).group(1) - raise nodes.SkipChildren - - def visit_title_reference(self, node): - raise Exception(node) - - def depart_title(self, node): - pass - - def visit_Text(self, node): - if not self.preserve_newlines: - node = node.replace('\n', ' ') - self.write(node) - - def depart_Text(self, node): - pass - - def visit_bullet_list(self, node): - pass - - def depart_bullet_list(self, node): - pass - - def visit_list_item(self, node): - self.write('* ') - self.indent += 2 - - def depart_list_item(self, node): - self.indent -= 2 - self.write('\n\n') - - def visit_paragraph(self, node): - pass - - def depart_paragraph(self, node): - pass - - def visit_reference(self, node): - if not is_github_ref(node): - self.write('[') - - def depart_reference(self, node): - if not is_github_ref(node): - self.write('](' + node['refuri'] + ')') - - def visit_target(self, node): - pass - - def depart_target(self, node): - pass - - def visit_literal(self, node): - self.write('`') - - def depart_literal(self, node): - self.write('`') - - def visit_literal_block(self, node): - self.write('\n\n```') - if 'c++' in node['classes']: - self.write('c++') - self.write('\n') - self.preserve_newlines = True - - def depart_literal_block(self, node): - self.write('\n```\n') - self.preserve_newlines = False - - def visit_inline(self, node): - pass - - def depart_inline(self, node): - pass - - def visit_image(self, node): - self.write('') - - def depart_image(self, node): - pass - - def write_row(self, row, widths): - for i, entry in enumerate(row): - text = entry[0][0] if len(entry) > 0 else '' - if i != 0: - self.write('|') - self.write('{:{}}'.format(text, widths[i])) - self.write('\n') - - def visit_table(self, node): - table = node.children[0] - colspecs = table[:-2] - thead = table[-2] - tbody = table[-1] - widths = [int(cs['colwidth']) for cs in colspecs] - sep = '|'.join(['-' * w for w in widths]) + '\n' - self.write('\n\n') - self.write_row(thead[0], widths) - self.write(sep) - for row in tbody: - self.write_row(row, widths) - raise nodes.SkipChildren - - def depart_table(self, node): - pass - -class MDWriter(writers.Writer): - """GitHub-flavored markdown writer""" - - supported = ('md',) - """Formats this writer supports.""" - - def translate(self): - translator = Translator(self.document) - self.document.walkabout(translator) - self.output = (translator.output, translator.version) - - -def convert(rst_path): - """Converts RST file to Markdown.""" - return core.publish_file(source_path=rst_path, writer=MDWriter()) - - -if __name__ == '__main__': - convert(sys.argv[1]) diff --git a/support/travis-build.py b/support/travis-build.py deleted file mode 100755 index 0cf73c84..00000000 --- a/support/travis-build.py +++ /dev/null @@ -1,119 +0,0 @@ -#!/usr/bin/env python -# Build the project on Travis CI. - -from __future__ import print_function -import errno, os, shutil, subprocess, sys, urllib -from subprocess import call, check_call, Popen, PIPE, STDOUT - -def rmtree_if_exists(dir): - try: - shutil.rmtree(dir) - except OSError as e: - if e.errno == errno.ENOENT: - pass - -def makedirs_if_not_exist(dir): - try: - os.makedirs(dir) - except OSError as e: - if e.errno != errno.EEXIST: - raise - -def install_dependencies(): - branch = os.environ['TRAVIS_BRANCH'] - if branch != 'master': - print('Branch: ' + branch) - exit(0) # Ignore non-master branches - check_call('curl -s https://deb.nodesource.com/gpgkey/nodesource.gpg.key ' + - '| sudo apt-key add -', shell=True) - check_call('echo "deb https://deb.nodesource.com/node_0.10 precise main" ' + - '| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.list', shell=True) - check_call(['sudo', 'apt-get', 'update']) - check_call(['sudo', 'apt-get', 'install', 'python-virtualenv', 'nodejs']) - check_call(['sudo', 'npm', 'install', '-g', 'less@2.6.1', 'less-plugin-clean-css']) - deb_file = 'doxygen_1.8.6-2_amd64.deb' - urllib.urlretrieve('http://mirrors.kernel.org/ubuntu/pool/main/d/doxygen/' + - deb_file, deb_file) - check_call(['sudo', 'dpkg', '-i', deb_file]) - -fmt_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))) - -build = os.environ['BUILD'] -if build == 'Doc': - travis = 'TRAVIS' in os.environ - if travis: - install_dependencies() - sys.path.insert(0, os.path.join(fmt_dir, 'doc')) - import build - build.create_build_env() - html_dir = build.build_docs() - repo = 'fmtlib.github.io' - if travis and 'KEY' not in os.environ: - # Don't update the repo if building on Travis from an account that - # doesn't have push access. - print('Skipping update of ' + repo) - exit(0) - # Clone the fmtlib.github.io repo. - rmtree_if_exists(repo) - git_url = 'https://github.com/' if travis else 'git@github.com:' - check_call(['git', 'clone', git_url + 'fmtlib/{}.git'.format(repo)]) - # Copy docs to the repo. - target_dir = os.path.join(repo, 'dev') - rmtree_if_exists(target_dir) - shutil.copytree(html_dir, target_dir, ignore=shutil.ignore_patterns('.*')) - if travis: - check_call(['git', 'config', '--global', 'user.name', 'amplbot']) - check_call(['git', 'config', '--global', 'user.email', 'viz@ampl.com']) - # Push docs to GitHub pages. - check_call(['git', 'add', '--all'], cwd=repo) - if call(['git', 'diff-index', '--quiet', 'HEAD'], cwd=repo): - check_call(['git', 'commit', '-m', 'Update documentation'], cwd=repo) - cmd = 'git push' - if travis: - cmd += ' https://$KEY@github.com/fmtlib/fmtlib.github.io.git master' - p = Popen(cmd, shell=True, stdout=PIPE, stderr=STDOUT, cwd=repo) - # Print the output without the key. - print(p.communicate()[0].replace(os.environ['KEY'], '$KEY')) - if p.returncode != 0: - raise subprocess.CalledProcessError(p.returncode, cmd) - exit(0) - -standard = os.environ['STANDARD'] -install_dir = os.path.join(fmt_dir, "_install") -build_dir = os.path.join(fmt_dir, "_build") -test_build_dir = os.path.join(fmt_dir, "_build_test") - -# Configure the library. -makedirs_if_not_exist(build_dir) -cmake_flags = [ - '-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=' + install_dir, '-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=' + build, - '-DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=' + standard -] - -# Make sure the fuzzers still compile. -main_cmake_flags = list(cmake_flags) -if 'ENABLE_FUZZING' in os.environ: - main_cmake_flags += ['-DFMT_FUZZ=ON', '-DFMT_FUZZ_LINKMAIN=On'] - -check_call(['cmake', '-DFMT_DOC=OFF', '-DFMT_PEDANTIC=ON', '-DFMT_WERROR=ON', fmt_dir] + - main_cmake_flags, cwd=build_dir) - -# Build the library. -check_call(['cmake', '--build','.'], cwd=build_dir) - -# Test the library. -env = os.environ.copy() -env['CTEST_OUTPUT_ON_FAILURE'] = '1' -if call(['make', 'test'], env=env, cwd=build_dir): - with open(os.path.join(build_dir, 'Testing', 'Temporary', 'LastTest.log'), 'r') as f: - print(f.read()) - sys.exit(-1) - -# Install the library. -check_call(['make', 'install'], cwd=build_dir) - -# Test installation. -makedirs_if_not_exist(test_build_dir) -check_call(['cmake', os.path.join(fmt_dir, "test", "find-package-test")] + - cmake_flags, cwd=test_build_dir) -check_call(['make', '-j4'], cwd=test_build_dir) diff --git a/test/CMakeLists.txt b/test/CMakeLists.txt index 7ae5659d..ec97ac29 100644 --- a/test/CMakeLists.txt +++ b/test/CMakeLists.txt @@ -1,80 +1,49 @@ -#------------------------------------------------------------------------------ -# Build the google test library - -# We compile Google Test ourselves instead of using pre-compiled libraries. -# See the Google Test FAQ "Why is it not recommended to install a -# pre-compiled copy of Google Test (for example, into /usr/local)?" -# at http://code.google.com/p/googletest/wiki/FAQ for more details. -add_library(gmock STATIC - gmock-gtest-all.cc gmock/gmock.h gtest/gtest.h gtest/gtest-spi.h) -target_compile_definitions(gmock PUBLIC GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING=1) -target_include_directories(gmock SYSTEM PUBLIC . gmock gtest) - -find_package(Threads) -if (Threads_FOUND) - target_link_libraries(gmock ${CMAKE_THREAD_LIBS_INIT}) -else () - target_compile_definitions(gmock PUBLIC GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD=0) -endif () - -target_compile_definitions(gmock PUBLIC GTEST_LANG_CXX11=0) - -if (MSVC) - # Workaround a bug in implementation of variadic templates in MSVC11. - target_compile_definitions(gmock PUBLIC _VARIADIC_MAX=10) - - # Disable MSVC warnings of _CRT_INSECURE_DEPRECATE functions. - target_compile_definitions(gmock PRIVATE _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS) - if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang") - # Disable MSVC warnings of POSIX functions. - target_compile_options(gmock PUBLIC -Wno-deprecated-declarations) - endif () -endif () - -# GTest doesn't detect <tuple> with clang. -if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID STREQUAL "Clang") - target_compile_definitions(gmock PUBLIC GTEST_USE_OWN_TR1_TUPLE=1) -endif () - -# Silence MSVC tr1 deprecation warning in gmock. -target_compile_definitions(gmock - PUBLIC _SILENCE_TR1_NAMESPACE_DEPRECATION_WARNING=1) +add_subdirectory(gtest) -#------------------------------------------------------------------------------ -# Build the actual library tests +include(CheckSymbolExists) set(TEST_MAIN_SRC test-main.cc gtest-extra.cc gtest-extra.h util.cc) add_library(test-main STATIC ${TEST_MAIN_SRC}) -target_include_directories(test-main SYSTEM PUBLIC gtest gmock) -target_link_libraries(test-main gmock fmt) - -include(CheckCXXCompilerFlag) - -# Workaround GTest bug https://github.com/google/googletest/issues/705. -check_cxx_compiler_flag( - -fno-delete-null-pointer-checks HAVE_FNO_DELETE_NULL_POINTER_CHECKS) -if (HAVE_FNO_DELETE_NULL_POINTER_CHECKS) - target_compile_options(test-main PUBLIC -fno-delete-null-pointer-checks) -endif () - -# Use less strict pedantic flags for the tests because GMock doesn't compile -# cleanly with -pedantic and -std=c++98. -if (CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")) - #set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS -Wall -Wextra -Wno-long-long -Wno-variadic-macros) -endif () +target_include_directories(test-main PUBLIC + $<BUILD_INTERFACE:${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>) +target_link_libraries(test-main gtest fmt) function(add_fmt_executable name) add_executable(${name} ${ARGN}) - if (MINGW) - target_link_libraries(${name} -static-libgcc -static-libstdc++) + # (Wstringop-overflow) - [meta-bug] bogus/missing -Wstringop-overflow warnings + # https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=88443 + # Bogus -Wstringop-overflow warning + # https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=100395 + # [10 Regression] spurious -Wstringop-overflow writing to a trailing array plus offset + # https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=95353 + if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "GNU" AND + NOT CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 7.0) + target_compile_options(${name} PRIVATE -Wno-stringop-overflow) + # The linker flag is needed for LTO. + target_link_libraries(${name} -Wno-stringop-overflow) endif () endfunction() # Adds a test. # Usage: add_fmt_test(name srcs...) function(add_fmt_test name) - add_fmt_executable(${name} ${name}.cc ${ARGN}) - target_link_libraries(${name} test-main) + cmake_parse_arguments(ADD_FMT_TEST "HEADER_ONLY;MODULE" "" "" ${ARGN}) + + set(sources ${name}.cc ${ADD_FMT_TEST_UNPARSED_ARGUMENTS}) + if (ADD_FMT_TEST_HEADER_ONLY) + set(sources ${sources} ${TEST_MAIN_SRC} ../src/os.cc) + set(libs gtest fmt-header-only) + if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang") + set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS} -Wno-weak-vtables) + endif () + elseif (ADD_FMT_TEST_MODULE) + set(libs test-main test-module) + set_source_files_properties(${name}.cc PROPERTIES OBJECT_DEPENDS test-module) + else () + set(libs test-main fmt) + endif () + add_fmt_executable(${name} ${sources}) + target_link_libraries(${name} ${libs}) # Define if certain C++ features can be used. if (FMT_PEDANTIC) @@ -83,10 +52,14 @@ function(add_fmt_test name) if (FMT_WERROR) target_compile_options(${name} PRIVATE ${WERROR_FLAG}) endif () - target_include_directories(${name} SYSTEM PUBLIC gtest gmock) add_test(NAME ${name} COMMAND ${name}) endfunction() +if (FMT_MODULE) + return () +endif () + +add_fmt_test(args-test) add_fmt_test(assert-test) add_fmt_test(chrono-test) add_fmt_test(color-test) @@ -97,14 +70,61 @@ if (MSVC) target_compile_options(format-test PRIVATE /bigobj) endif () if (NOT (MSVC AND BUILD_SHARED_LIBS)) - add_fmt_test(format-impl-test) + add_fmt_test(format-impl-test HEADER_ONLY header-only-test.cc) endif () -add_fmt_test(locale-test) add_fmt_test(ostream-test) add_fmt_test(compile-test) +add_fmt_test(compile-fp-test HEADER_ONLY) +if (MSVC) + # Without this option, MSVC returns 199711L for the __cplusplus macro. + target_compile_options(compile-fp-test PRIVATE /Zc:__cplusplus) +endif() add_fmt_test(printf-test) -add_fmt_test(ranges-test) +add_fmt_test(ranges-test ranges-odr-test.cc) + add_fmt_test(scan-test) +check_symbol_exists(strptime "time.h" HAVE_STRPTIME) +if (HAVE_STRPTIME) + target_compile_definitions(scan-test PRIVATE FMT_HAVE_STRPTIME) +endif () + +add_fmt_test(std-test) +try_compile(compile_result_unused + ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR} + SOURCES ${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/detect-stdfs.cc + OUTPUT_VARIABLE RAWOUTPUT) +string(REGEX REPLACE ".*libfound \"([^\"]*)\".*" "\\1" STDLIBFS "${RAWOUTPUT}") +if (STDLIBFS) + target_link_libraries(std-test ${STDLIBFS}) +endif () +add_fmt_test(unicode-test HEADER_ONLY) +if (MSVC) + target_compile_options(unicode-test PRIVATE /utf-8) +endif () +add_fmt_test(xchar-test) +add_fmt_test(enforce-checks-test) +target_compile_definitions(enforce-checks-test PRIVATE + -DFMT_ENFORCE_COMPILE_STRING) + +if (FMT_MODULE) + # The tests need {fmt} to be compiled as traditional library + # because of visibility of implementation details. + # If module support is present the module tests require a + # test-only module to be built from {fmt} + add_library(test-module OBJECT ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/src/fmt.cc) + target_compile_features(test-module PUBLIC cxx_std_11) + target_include_directories(test-module PUBLIC + $<BUILD_INTERFACE:${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>) + enable_module(test-module) + + add_fmt_test(module-test MODULE test-main.cc) + if (MSVC) + target_compile_options(test-module PRIVATE /utf-8 /Zc:__cplusplus + /Zc:externConstexpr /Zc:inline) + target_compile_options(module-test PRIVATE /utf-8 /Zc:__cplusplus + /Zc:externConstexpr /Zc:inline) + endif () +endif () if (NOT DEFINED MSVC_STATIC_RUNTIME AND MSVC) foreach (flag_var @@ -122,52 +142,28 @@ if (NOT MSVC_STATIC_RUNTIME) posix-mock-test.cc ../src/format.cc ${TEST_MAIN_SRC}) target_include_directories( posix-mock-test PRIVATE ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include) - target_link_libraries(posix-mock-test gmock) - target_include_directories(posix-mock-test SYSTEM PUBLIC gtest gmock) + target_link_libraries(posix-mock-test gtest) if (FMT_PEDANTIC) target_compile_options(posix-mock-test PRIVATE ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}) endif () - if (HAVE_STRTOD_L) - target_compile_definitions(posix-mock-test PRIVATE FMT_LOCALE) - endif () add_test(NAME posix-mock-test COMMAND posix-mock-test) add_fmt_test(os-test) endif () -add_fmt_executable(header-only-test - header-only-test.cc header-only-test2.cc test-main.cc) -target_link_libraries(header-only-test gmock) -target_include_directories(header-only-test SYSTEM PUBLIC gtest gmock) -if (TARGET fmt-header-only) - target_link_libraries(header-only-test fmt-header-only) -else () - target_include_directories( - header-only-test PRIVATE ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include) - target_compile_definitions(header-only-test PRIVATE FMT_HEADER_ONLY=1) -endif () - message(STATUS "FMT_PEDANTIC: ${FMT_PEDANTIC}") if (FMT_PEDANTIC) - # MSVC fails to compile GMock when C++17 is enabled. - if (FMT_HAS_VARIANT AND NOT MSVC) - add_fmt_test(std-format-test) - set_property(TARGET std-format-test PROPERTY CXX_STANDARD 17) - endif () - # Test that the library can be compiled with exceptions disabled. # -fno-exception is broken in icc: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/822. if (NOT CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID STREQUAL "Intel") check_cxx_compiler_flag(-fno-exceptions HAVE_FNO_EXCEPTIONS_FLAG) endif () if (HAVE_FNO_EXCEPTIONS_FLAG) - add_library(noexception-test ../src/format.cc) + add_library(noexception-test ../src/format.cc noexception-test.cc) target_include_directories( noexception-test PRIVATE ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include) target_compile_options(noexception-test PRIVATE -fno-exceptions) - if (FMT_PEDANTIC) - target_compile_options(noexception-test PRIVATE ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}) - endif () + target_compile_options(noexception-test PRIVATE ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}) endif () # Test that the library compiles without locale. @@ -176,7 +172,16 @@ if (FMT_PEDANTIC) nolocale-test PRIVATE ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include) target_compile_definitions( nolocale-test PRIVATE FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR=1) +endif () +# These tests are disabled on Windows because they take too long. +# They are disabled on GCC < 4.9 because it can not parse UDLs without +# a space after `operator""` but that is an incorrect syntax for any more +# modern compiler. +if (FMT_PEDANTIC AND NOT WIN32 AND NOT ( + CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "GNU" AND + CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 4.9)) + # Test if incorrect API usages produce compilation error. add_test(compile-error-test ${CMAKE_CTEST_COMMAND} --build-and-test "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/compile-error-test" @@ -185,14 +190,11 @@ if (FMT_PEDANTIC) --build-makeprogram ${CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM} --build-options "-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER}" + "-DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS=${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS}" "-DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=${CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD}" "-DCXX_STANDARD_FLAG=${CXX_STANDARD_FLAG}" - "-DPEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS=${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}" - "-DSUPPORTS_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS=${SUPPORTS_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS}") -endif () + "-DFMT_DIR=${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}") -# These tests are disabled on Windows because they take too long. -if (FMT_PEDANTIC AND NOT WIN32) # Test if the targets are found from the build directory. add_test(find-package-test ${CMAKE_CTEST_COMMAND} -C ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE} @@ -203,6 +205,7 @@ if (FMT_PEDANTIC AND NOT WIN32) --build-makeprogram ${CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM} --build-options "-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER}" + "-DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS=${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS}" "-DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=${CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD}" "-DFMT_DIR=${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}" "-DPEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS=${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}" @@ -223,6 +226,21 @@ if (FMT_PEDANTIC AND NOT WIN32) "-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}") endif () +# This test are disabled on Windows because it is only *NIX issue. +if (FMT_PEDANTIC AND NOT WIN32) + add_test(static-export-test ${CMAKE_CTEST_COMMAND} + -C ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE} + --build-and-test + "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/static-export-test" + "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/static-export-test" + --build-generator ${CMAKE_GENERATOR} + --build-makeprogram ${CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM} + --build-options + "-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER}" + "-DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=${CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD}" + "-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}") +endif () + # Activate optional CUDA tests if CUDA is found. For version selection see # https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/index.html#cpp14-language-features if (FMT_CUDA_TEST) diff --git a/test/add-subdirectory-test/CMakeLists.txt b/test/add-subdirectory-test/CMakeLists.txt index 9cc4b0e9..362b0494 100644 --- a/test/add-subdirectory-test/CMakeLists.txt +++ b/test/add-subdirectory-test/CMakeLists.txt @@ -1,17 +1,17 @@ -cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.1...3.18) +cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8...3.25) -project(fmt-test) +project(fmt-test CXX) add_subdirectory(../.. fmt) -add_executable(library-test "main.cc") -target_link_libraries(library-test fmt::fmt) -target_compile_options(library-test PRIVATE ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}) +add_executable(library-test main.cc) target_include_directories(library-test PUBLIC SYSTEM .) +target_compile_options(library-test PRIVATE ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}) +target_link_libraries(library-test fmt::fmt) if (TARGET fmt::fmt-header-only) - add_executable(header-only-test "main.cc") - target_link_libraries(header-only-test fmt::fmt-header-only) - target_compile_options(header-only-test PRIVATE ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}) + add_executable(header-only-test main.cc) target_include_directories(header-only-test PUBLIC SYSTEM .) + target_compile_options(header-only-test PRIVATE ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}) + target_link_libraries(header-only-test fmt::fmt-header-only) endif () diff --git a/test/add-subdirectory-test/main.cc b/test/add-subdirectory-test/main.cc index f39f377c..fcdf232e 100644 --- a/test/add-subdirectory-test/main.cc +++ b/test/add-subdirectory-test/main.cc @@ -1,6 +1,5 @@ -#include "fmt/format.h" +#include "fmt/core.h" int main(int argc, char** argv) { - for(int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) - fmt::print("{}: {}\n", i, argv[i]); + for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) fmt::print("{}: {}\n", i, argv[i]); } diff --git a/test/args-test.cc b/test/args-test.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..3ab31335 --- /dev/null +++ b/test/args-test.cc @@ -0,0 +1,186 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - dynamic argument store tests +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#include "fmt/args.h" + +#include <memory> + +#include "gtest/gtest.h" + +TEST(args_test, basic) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + store.push_back(42); + store.push_back("abc1"); + store.push_back(1.5f); + EXPECT_EQ("42 and abc1 and 1.5", fmt::vformat("{} and {} and {}", store)); +} + +TEST(args_test, strings_and_refs) { + // Unfortunately the tests are compiled with old ABI so strings use COW. + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + char str[] = "1234567890"; + store.push_back(str); + store.push_back(std::cref(str)); + store.push_back(fmt::string_view{str}); + str[0] = 'X'; + + auto result = fmt::vformat("{} and {} and {}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("1234567890 and X234567890 and X234567890", result); +} + +struct custom_type { + int i = 0; +}; + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<custom_type> { + auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const custom_type& p, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return fmt::format_to(ctx.out(), "cust={}", p.i); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(args_test, custom_format) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + auto c = custom_type(); + store.push_back(c); + ++c.i; + store.push_back(c); + ++c.i; + store.push_back(std::cref(c)); + ++c.i; + auto result = fmt::vformat("{} and {} and {}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("cust=0 and cust=1 and cust=3", result); +} + +struct to_stringable { + friend fmt::string_view to_string_view(to_stringable) { return {}; } +}; + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<to_stringable> { + auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + auto format(to_stringable, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return ctx.out(); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(args_test, to_string_and_formatter) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + auto s = to_stringable(); + store.push_back(s); + store.push_back(std::cref(s)); + fmt::vformat("", store); +} + +TEST(args_test, named_int) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + store.push_back(fmt::arg("a1", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::vformat("{a1}", store)); +} + +TEST(args_test, named_strings) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + char str[] = "1234567890"; + store.push_back(fmt::arg("a1", str)); + store.push_back(fmt::arg("a2", std::cref(str))); + str[0] = 'X'; + EXPECT_EQ("1234567890 and X234567890", fmt::vformat("{a1} and {a2}", store)); +} + +TEST(args_test, named_arg_by_ref) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + char band[] = "Rolling Stones"; + store.push_back(fmt::arg("band", std::cref(band))); + band[9] = 'c'; // Changing band affects the output. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::vformat("{band}", store), "Rolling Scones"); +} + +TEST(args_test, named_custom_format) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + auto c = custom_type(); + store.push_back(fmt::arg("c1", c)); + ++c.i; + store.push_back(fmt::arg("c2", c)); + ++c.i; + store.push_back(fmt::arg("c_ref", std::cref(c))); + ++c.i; + auto result = fmt::vformat("{c1} and {c2} and {c_ref}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("cust=0 and cust=1 and cust=3", result); +} + +TEST(args_test, clear) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + store.push_back(42); + + auto result = fmt::vformat("{}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("42", result); + + store.push_back(43); + result = fmt::vformat("{} and {}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("42 and 43", result); + + store.clear(); + store.push_back(44); + result = fmt::vformat("{}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("44", result); +} + +TEST(args_test, reserve) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + store.reserve(2, 1); + store.push_back(1.5f); + store.push_back(fmt::arg("a1", 42)); + auto result = fmt::vformat("{a1} and {}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("42 and 1.5", result); +} + +struct copy_throwable { + copy_throwable() {} + copy_throwable(const copy_throwable&) { throw "deal with it"; } +}; + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<copy_throwable> { + auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + auto format(copy_throwable, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return ctx.out(); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(args_test, throw_on_copy) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; + store.push_back(std::string("foo")); + try { + store.push_back(copy_throwable()); + } catch (...) { + } + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::vformat("{}", store), "foo"); +} + +TEST(args_test, move_constructor) { + using store_type = fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context>; + auto store = std::unique_ptr<store_type>(new store_type()); + store->push_back(42); + store->push_back(std::string("foo")); + store->push_back(fmt::arg("a1", "foo")); + auto moved_store = std::move(*store); + store.reset(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::vformat("{} {} {a1}", moved_store), "42 foo foo"); +} diff --git a/test/assert-test.cc b/test/assert-test.cc index 70efa381..c74e617e 100644 --- a/test/assert-test.cc +++ b/test/assert-test.cc @@ -10,9 +10,9 @@ // For the license information refer to format.h. #include "fmt/core.h" -#include "gtest.h" +#include "gtest/gtest.h" -TEST(AssertTest, Fail) { +TEST(assert_test, fail) { #if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH(FMT_ASSERT(false, "don't panic!"), "don't panic!"); #else @@ -20,9 +20,8 @@ TEST(AssertTest, Fail) { #endif } -bool test_condition = false; - -TEST(AssertTest, DanglingElse) { +TEST(assert_test, dangling_else) { + bool test_condition = false; bool executed_else = false; if (test_condition) FMT_ASSERT(true, ""); diff --git a/test/chrono-test.cc b/test/chrono-test.cc index fa383c14..07760688 100644 --- a/test/chrono-test.cc +++ b/test/chrono-test.cc @@ -5,77 +5,235 @@ // // For the license information refer to format.h. -#ifdef WIN32 -# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS -#endif - #include "fmt/chrono.h" -#include <iomanip> +#include <algorithm> +#include <ctime> +#include <vector> + +#include "gtest-extra.h" // EXPECT_THROW_MSG +#include "util.h" // get_locale -#include "gtest-extra.h" +using fmt::runtime; +using testing::Contains; + +#if defined(__MINGW32__) && !defined(_UCRT) +// Only C89 conversion specifiers when using MSVCRT instead of UCRT +# define FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME 0 +#else +# define FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME 1 +#endif -std::tm make_tm() { +auto make_tm() -> std::tm { auto time = std::tm(); time.tm_mday = 1; return time; } -std::tm make_hour(int h) { +auto make_hour(int h) -> std::tm { auto time = make_tm(); time.tm_hour = h; return time; } -std::tm make_minute(int m) { +auto make_minute(int m) -> std::tm { auto time = make_tm(); time.tm_min = m; return time; } -std::tm make_second(int s) { +auto make_second(int s) -> std::tm { auto time = make_tm(); time.tm_sec = s; return time; } -std::string format_tm(const std::tm& time, const char* spec, - const std::locale& loc) { +std::string system_strftime(const std::string& format, const std::tm* timeptr, + std::locale* locptr = nullptr) { + auto loc = locptr ? *locptr : std::locale::classic(); auto& facet = std::use_facet<std::time_put<char>>(loc); std::ostringstream os; os.imbue(loc); - facet.put(os, os, ' ', &time, spec, spec + std::strlen(spec)); + facet.put(os, os, ' ', timeptr, format.c_str(), + format.c_str() + format.size()); +#ifdef _WIN32 + // Workaround a bug in older versions of Universal CRT. + auto str = os.str(); + if (str == "-0000") str = "+0000"; + return str; +#else return os.str(); +#endif +} + +FMT_CONSTEXPR std::tm make_tm(int year, int mon, int mday, int hour, int min, + int sec) { + auto tm = std::tm(); + tm.tm_sec = sec; + tm.tm_min = min; + tm.tm_hour = hour; + tm.tm_mday = mday; + tm.tm_mon = mon - 1; + tm.tm_year = year - 1900; + return tm; } -TEST(TimeTest, Format) { - std::tm tm = std::tm(); +TEST(chrono_test, format_tm) { + auto tm = std::tm(); tm.tm_year = 116; tm.tm_mon = 3; tm.tm_mday = 25; - EXPECT_EQ("The date is 2016-04-25.", - fmt::format("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d}.", tm)); + tm.tm_hour = 11; + tm.tm_min = 22; + tm.tm_sec = 33; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}.", tm), + "The date is 2016-04-25 11:22:33."); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm), "2016"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C}", tm), "20"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C%y}", tm), fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%e}", tm), "25"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%D}", tm), "04/25/16"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%F}", tm), "2016-04-25"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%T}", tm), "11:22:33"); + + // Short year + tm.tm_year = 999 - 1900; + tm.tm_mon = 0; // for %G + tm.tm_mday = 2; // for %G + tm.tm_wday = 3; // for %G + tm.tm_yday = 1; // for %G + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm), "0999"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C%y}", tm), "0999"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%G}", tm), "0999"); + + tm.tm_year = 27 - 1900; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm), "0027"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C%y}", tm), "0027"); + + // Overflow year + tm.tm_year = 2147483647; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm), "2147485547"); + + tm.tm_year = -2147483648; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm), "-2147481748"); + + // for week on the year + // https://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/iso-time.html + std::vector<std::tm> tm_list = { + make_tm(1975, 12, 29, 12, 14, 16), // W01 + make_tm(1977, 1, 2, 12, 14, 16), // W53 + make_tm(1999, 12, 27, 12, 14, 16), // W52 + make_tm(1999, 12, 31, 12, 14, 16), // W52 + make_tm(2000, 1, 1, 12, 14, 16), // W52 + make_tm(2000, 1, 2, 12, 14, 16), // W52 + make_tm(2000, 1, 3, 12, 14, 16) // W1 + }; + +#if !FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME + GTEST_SKIP() << "Skip the rest of this test because it relies on strftime() " + "conforming to C99, but on this platform, MINGW + MSVCRT, " + "the function conforms only to C89."; +#endif + + const std::string iso_week_spec = "%Y-%m-%d: %G %g %V"; + for (auto ctm : tm_list) { + // Calculate tm_yday, tm_wday, etc. + std::time_t t = std::mktime(&ctm); + tm = *std::localtime(&t); + + auto fmt_spec = fmt::format("{{:{}}}", iso_week_spec); + EXPECT_EQ(system_strftime(iso_week_spec, &tm), + fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), tm)); + } + + // Every day from 1970-01-01 + std::time_t time_now = std::time(nullptr); + for (std::time_t t = 6 * 3600; t < time_now; t += 86400) { + tm = *std::localtime(&t); + + auto fmt_spec = fmt::format("{{:{}}}", iso_week_spec); + EXPECT_EQ(system_strftime(iso_week_spec, &tm), + fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), tm)); + } +} + +// MSVC: +// minkernel\crts\ucrt\src\appcrt\time\wcsftime.cpp(971) : Assertion failed: +// timeptr->tm_year >= -1900 && timeptr->tm_year <= 8099 +#ifndef _WIN32 +TEST(chrono_test, format_tm_future) { + auto tm = std::tm(); + tm.tm_year = 10445; // 10000+ years + tm.tm_mon = 3; + tm.tm_mday = 25; + tm.tm_hour = 11; + tm.tm_min = 22; + tm.tm_sec = 33; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}.", tm), + "The date is 12345-04-25 11:22:33."); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm), "12345"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C}", tm), "123"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C%y}", tm), fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%D}", tm), "04/25/45"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%F}", tm), "12345-04-25"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%T}", tm), "11:22:33"); } -TEST(TimeTest, GrowBuffer) { - std::string s = "{:"; +TEST(chrono_test, format_tm_past) { + auto tm = std::tm(); + tm.tm_year = -2001; + tm.tm_mon = 3; + tm.tm_mday = 25; + tm.tm_hour = 11; + tm.tm_min = 22; + tm.tm_sec = 33; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}.", tm), + "The date is -101-04-25 11:22:33."); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm), "-101"); + + // macOS %C - "-1" + // Linux %C - "-2" + // fmt %C - "-1" + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C}", tm), "-1"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C%y}", tm), fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm)); + + // macOS %D - "04/25/01" (%y) + // Linux %D - "04/25/99" (%y) + // fmt %D - "04/25/01" (%y) + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%D}", tm), "04/25/01"); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%F}", tm), "-101-04-25"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%T}", tm), "11:22:33"); + + tm.tm_year = -1901; // -1 + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm), "-001"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C%y}", tm), fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm)); + + tm.tm_year = -1911; // -11 + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm), "-011"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%C%y}", tm), fmt::format("{:%Y}", tm)); +} +#endif + +TEST(chrono_test, grow_buffer) { + auto s = std::string("{:"); for (int i = 0; i < 30; ++i) s += "%c"; s += "}\n"; - std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr); - fmt::format(s, *std::localtime(&t)); + auto t = std::time(nullptr); + (void)fmt::format(fmt::runtime(s), *std::localtime(&t)); } -TEST(TimeTest, FormatToEmptyContainer) { - std::string s; +TEST(chrono_test, format_to_empty_container) { auto time = std::tm(); time.tm_sec = 42; + auto s = std::string(); fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), "{:%S}", time); EXPECT_EQ(s, "42"); } -TEST(TimeTest, EmptyResult) { EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format("{}", std::tm())); } +TEST(chrono_test, empty_result) { EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::tm()), ""); } -static bool EqualTime(const std::tm& lhs, const std::tm& rhs) { +auto equal(const std::tm& lhs, const std::tm& rhs) -> bool { return lhs.tm_sec == rhs.tm_sec && lhs.tm_min == rhs.tm_min && lhs.tm_hour == rhs.tm_hour && lhs.tm_mday == rhs.tm_mday && lhs.tm_mon == rhs.tm_mon && lhs.tm_year == rhs.tm_year && @@ -83,39 +241,188 @@ static bool EqualTime(const std::tm& lhs, const std::tm& rhs) { lhs.tm_isdst == rhs.tm_isdst; } -TEST(TimeTest, LocalTime) { - std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr); - std::tm tm = *std::localtime(&t); - EXPECT_TRUE(EqualTime(tm, fmt::localtime(t))); +TEST(chrono_test, gmtime) { + auto t = std::time(nullptr); + auto tm = *std::gmtime(&t); + EXPECT_TRUE(equal(tm, fmt::gmtime(t))); +} + +template <typename TimePoint> +auto strftime_full_utc(TimePoint tp) -> std::string { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(tp); + auto tm = *std::gmtime(&t); + return system_strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &tm); } -TEST(TimeTest, GMTime) { - std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr); - std::tm tm = *std::gmtime(&t); - EXPECT_TRUE(EqualTime(tm, fmt::gmtime(t))); +TEST(chrono_test, system_clock_time_point) { + auto t1 = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>( + std::chrono::system_clock::now()); + EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_utc(t1), fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_utc(t1), fmt::format("{}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_utc(t1), fmt::format("{:}", t1)); + using time_point = + std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::seconds>; + auto t2 = time_point(std::chrono::seconds(42)); + EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_utc(t2), fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t2)); + + std::vector<std::string> spec_list = { + "%%", "%n", "%t", "%Y", "%EY", "%y", "%Oy", "%Ey", "%C", + "%EC", "%G", "%g", "%b", "%h", "%B", "%m", "%Om", "%U", + "%OU", "%W", "%OW", "%V", "%OV", "%j", "%d", "%Od", "%e", + "%Oe", "%a", "%A", "%w", "%Ow", "%u", "%Ou", "%H", "%OH", + "%I", "%OI", "%M", "%OM", "%S", "%OS", "%x", "%Ex", "%X", + "%EX", "%D", "%F", "%R", "%T", "%p"}; +#ifndef _WIN32 + // Disabled on Windows because these formats are not consistent among + // platforms. + spec_list.insert(spec_list.end(), {"%c", "%Ec", "%r"}); +#elif !FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME + // Only C89 conversion specifiers when using MSVCRT instead of UCRT + spec_list = {"%%", "%Y", "%y", "%b", "%B", "%m", "%U", "%W", "%j", "%d", + "%a", "%A", "%w", "%H", "%I", "%M", "%S", "%x", "%X", "%p"}; +#endif + spec_list.push_back("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"); + + for (const auto& spec : spec_list) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(t1); + auto tm = *std::gmtime(&t); + + auto sys_output = system_strftime(spec, &tm); + + auto fmt_spec = fmt::format("{{:{}}}", spec); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), tm)); + } + + // Timezone formatters tests makes sense for localtime. +#if FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME + spec_list = {"%z", "%Z"}; +#else + spec_list = {"%Z"}; +#endif + for (const auto& spec : spec_list) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(t1); + auto tm = *std::localtime(&t); + + auto sys_output = system_strftime(spec, &tm); + + auto fmt_spec = fmt::format("{{:{}}}", spec); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), tm)); + + if (spec == "%z") { + sys_output.insert(sys_output.end() - 2, 1, ':'); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format("{:%Ez}", tm)); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format("{:%Oz}", tm)); + } + } + + // Separate tests for UTC, since std::time_put can use local time and ignoring + // the timezone in std::tm (if it presents on platform). + if (fmt::detail::has_member_data_tm_zone<std::tm>::value) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(t1); + auto tm = *std::gmtime(&t); + + std::vector<std::string> tz_names = {"GMT", "UTC"}; + EXPECT_THAT(tz_names, Contains(fmt::format("{:%Z}", t1))); + EXPECT_THAT(tz_names, Contains(fmt::format("{:%Z}", tm))); + } + + if (fmt::detail::has_member_data_tm_gmtoff<std::tm>::value) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(t1); + auto tm = *std::gmtime(&t); + + EXPECT_EQ("+0000", fmt::format("{:%z}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ("+0000", fmt::format("{:%z}", tm)); + + EXPECT_EQ("+00:00", fmt::format("{:%Ez}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ("+00:00", fmt::format("{:%Ez}", tm)); + + EXPECT_EQ("+00:00", fmt::format("{:%Oz}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ("+00:00", fmt::format("{:%Oz}", tm)); + } } -TEST(TimeTest, TimePoint) { - std::chrono::system_clock::time_point point = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); +#if FMT_USE_LOCAL_TIME - std::time_t t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(point); - std::tm tm = *std::localtime(&t); - char strftime_output[256]; - std::strftime(strftime_output, sizeof(strftime_output), "It is %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &tm); +TEST(chrono_test, localtime) { + auto t = std::time(nullptr); + auto tm = *std::localtime(&t); + EXPECT_TRUE(equal(tm, fmt::localtime(t))); +} - EXPECT_EQ(strftime_output, fmt::format("It is {:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", point)); +template <typename Duration> +auto strftime_full_local(std::chrono::local_time<Duration> tp) -> std::string { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t( + std::chrono::current_zone()->to_sys(tp)); + auto tm = *std::localtime(&t); + return system_strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &tm); } -#define EXPECT_TIME(spec, time, duration) \ - { \ - std::locale loc("ja_JP.utf8"); \ - EXPECT_EQ(format_tm(time, spec, loc), \ - fmt::format(loc, "{:" spec "}", duration)); \ +TEST(chrono_test, local_system_clock_time_point) { +# ifdef _WIN32 + return; // Not supported on Windows. +# endif + auto t1 = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>( + std::chrono::current_zone()->to_local(std::chrono::system_clock::now())); + EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_local(t1), fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_local(t1), fmt::format("{}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_local(t1), fmt::format("{:}", t1)); + using time_point = std::chrono::local_time<std::chrono::seconds>; + auto t2 = time_point(std::chrono::seconds(86400 + 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_local(t2), fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t2)); + + std::vector<std::string> spec_list = { + "%%", "%n", "%t", "%Y", "%EY", "%y", "%Oy", "%Ey", "%C", + "%EC", "%G", "%g", "%b", "%h", "%B", "%m", "%Om", "%U", + "%OU", "%W", "%OW", "%V", "%OV", "%j", "%d", "%Od", "%e", + "%Oe", "%a", "%A", "%w", "%Ow", "%u", "%Ou", "%H", "%OH", + "%I", "%OI", "%M", "%OM", "%S", "%OS", "%x", "%Ex", "%X", + "%EX", "%D", "%F", "%R", "%T", "%p", "%z", "%Z"}; +# ifndef _WIN32 + // Disabled on Windows because these formats are not consistent among + // platforms. + spec_list.insert(spec_list.end(), {"%c", "%Ec", "%r"}); +# elif !FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME + // Only C89 conversion specifiers when using MSVCRT instead of UCRT + spec_list = {"%%", "%Y", "%y", "%b", "%B", "%m", "%U", "%W", "%j", "%d", "%a", + "%A", "%w", "%H", "%I", "%M", "%S", "%x", "%X", "%p", "%Z"}; +# endif + spec_list.push_back("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"); + + for (const auto& spec : spec_list) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t( + std::chrono::current_zone()->to_sys(t1)); + auto tm = *std::localtime(&t); + + auto sys_output = system_strftime(spec, &tm); + + auto fmt_spec = fmt::format("{{:{}}}", spec); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), tm)); + } + + if (std::find(spec_list.cbegin(), spec_list.cend(), "%z") != + spec_list.cend()) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t( + std::chrono::current_zone()->to_sys(t1)); + auto tm = *std::localtime(&t); + + auto sys_output = system_strftime("%z", &tm); + sys_output.insert(sys_output.end() - 2, 1, ':'); + + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format("{:%Ez}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format("{:%Ez}", tm)); + + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format("{:%Oz}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format("{:%Oz}", tm)); } +} + +#endif // FMT_USE_LOCAL_TIME #ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR -TEST(ChronoTest, FormatDefault) { +TEST(chrono_test, format_default) { EXPECT_EQ("42s", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::seconds(42))); EXPECT_EQ("42as", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::atto>(42))); @@ -147,8 +454,11 @@ TEST(ChronoTest, FormatDefault) { fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::peta>(42))); EXPECT_EQ("42Es", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::exa>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ("42m", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::minutes(42))); + EXPECT_EQ("42min", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::minutes(42))); EXPECT_EQ("42h", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::hours(42))); +# if defined(__cpp_lib_chrono) && __cpp_lib_chrono >= 201907L + EXPECT_EQ("42d", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::days(42))); +# endif EXPECT_EQ( "42[15]s", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<15, 1>>(42))); @@ -157,49 +467,7 @@ TEST(ChronoTest, FormatDefault) { fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<15, 4>>(42))); } -TEST(ChronoTest, FormatWide) { - EXPECT_EQ(L"42s", fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::seconds(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42as", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::atto>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42fs", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::femto>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42ps", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::pico>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42ns", fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::nanoseconds(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42\u00B5s", fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::microseconds(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42ms", fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::milliseconds(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42cs", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::centi>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42ds", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::deci>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42s", fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::seconds(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42das", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::deca>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42hs", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::hecto>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42ks", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::kilo>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42Ms", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::mega>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42Gs", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::giga>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42Ts", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::tera>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42Ps", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::peta>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42Es", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::exa>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42m", fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::minutes(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42h", fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::hours(42))); - EXPECT_EQ( - L"42[15]s", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<15, 1>>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ( - L"42[15/4]s", - fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<15, 4>>(42))); -} - -TEST(ChronoTest, Align) { +TEST(chrono_test, duration_align) { auto s = std::chrono::seconds(42); EXPECT_EQ("42s ", fmt::format("{:5}", s)); EXPECT_EQ("42s ", fmt::format("{:{}}", s, 5)); @@ -215,7 +483,36 @@ TEST(ChronoTest, Align) { fmt::format("{:{}%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345), 12)); } -TEST(ChronoTest, FormatSpecs) { +TEST(chrono_test, tm_align) { + auto t = make_tm(1975, 12, 29, 12, 14, 16); + EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16", fmt::format("{:%F %T}", t)); + EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16 ", fmt::format("{:30%F %T}", t)); + EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16 ", fmt::format("{:{}%F %T}", t, 30)); + EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16 ", fmt::format("{:<30%F %T}", t)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 1975-12-29 12:14:16 ", fmt::format("{:^30%F %T}", t)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 1975-12-29 12:14:16", fmt::format("{:>30%F %T}", t)); + + EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16***********", fmt::format("{:*<30%F %T}", t)); + EXPECT_EQ("*****1975-12-29 12:14:16******", fmt::format("{:*^30%F %T}", t)); + EXPECT_EQ("***********1975-12-29 12:14:16", fmt::format("{:*>30%F %T}", t)); +} + +TEST(chrono_test, tp_align) { + auto tp = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>( + std::chrono::system_clock::from_time_t(0)); + EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000", fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", tp)); + EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000 ", fmt::format("{:15%M:%S}", tp)); + EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000 ", fmt::format("{:{}%M:%S}", tp, 15)); + EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000 ", fmt::format("{:<15%M:%S}", tp)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 00:00.000000 ", fmt::format("{:^15%M:%S}", tp)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 00:00.000000", fmt::format("{:>15%M:%S}", tp)); + + EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000***", fmt::format("{:*<15%M:%S}", tp)); + EXPECT_EQ("*00:00.000000**", fmt::format("{:*^15%M:%S}", tp)); + EXPECT_EQ("***00:00.000000", fmt::format("{:*>15%M:%S}", tp)); +} + +TEST(chrono_test, format_specs) { EXPECT_EQ("%", fmt::format("{:%%}", std::chrono::seconds(0))); EXPECT_EQ("\n", fmt::format("{:%n}", std::chrono::seconds(0))); EXPECT_EQ("\t", fmt::format("{:%t}", std::chrono::seconds(0))); @@ -244,43 +541,68 @@ TEST(ChronoTest, FormatSpecs) { EXPECT_EQ("s", fmt::format("{:%q}", std::chrono::seconds(12345))); } -TEST(ChronoTest, InvalidSpecs) { +TEST(chrono_test, invalid_specs) { auto sec = std::chrono::seconds(0); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%a}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%A}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%c}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%x}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%Ex}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%X}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%EX}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%D}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%F}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%Ec}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%w}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%u}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%b}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%B}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%z}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%Z}", sec), fmt::format_error, "no date"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%Eq}", sec), fmt::format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%a}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%A}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%c}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%x}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%Ex}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%X}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%EX}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%D}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%F}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%Ec}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%w}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%u}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%b}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%B}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%z}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%Z}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "no date"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%Eq}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "invalid format"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%Oq}"), sec), fmt::format_error, "invalid format"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:%Oq}", sec), fmt::format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:abc}"), sec), fmt::format_error, + "invalid format"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:.2f}"), sec), fmt::format_error, "invalid format"); } -TEST(ChronoTest, Locale) { - const char* loc_name = "ja_JP.utf8"; - bool has_locale = false; - std::locale loc; - try { - loc = std::locale(loc_name); - has_locale = true; - } catch (const std::runtime_error&) { - } - if (!has_locale) { - fmt::print("{} locale is missing.\n", loc_name); - return; - } +auto format_tm(const std::tm& time, fmt::string_view spec, + const std::locale& loc) -> std::string { + auto& facet = std::use_facet<std::time_put<char>>(loc); + std::ostringstream os; + os.imbue(loc); + facet.put(os, os, ' ', &time, spec.begin(), spec.end()); + return os.str(); +} + +TEST(chrono_test, locale) { + auto loc = get_locale("ja_JP.utf8"); + if (loc == std::locale::classic()) return; +# define EXPECT_TIME(spec, time, duration) \ + { \ + auto jp_loc = std::locale("ja_JP.utf8"); \ + EXPECT_EQ(format_tm(time, spec, jp_loc), \ + fmt::format(jp_loc, "{:L" spec "}", duration)); \ + } EXPECT_TIME("%OH", make_hour(14), std::chrono::hours(14)); EXPECT_TIME("%OI", make_hour(14), std::chrono::hours(14)); EXPECT_TIME("%OM", make_minute(42), std::chrono::minutes(42)); @@ -294,9 +616,9 @@ TEST(ChronoTest, Locale) { EXPECT_TIME("%p", time, sec); } -typedef std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli> dms; +using dms = std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>; -TEST(ChronoTest, FormatDefaultFP) { +TEST(chrono_test, format_default_fp) { typedef std::chrono::duration<float> fs; EXPECT_EQ("1.234s", fmt::format("{}", fs(1.234))); typedef std::chrono::duration<float, std::milli> fms; @@ -306,24 +628,37 @@ TEST(ChronoTest, FormatDefaultFP) { EXPECT_EQ("1.234ms", fmt::format("{}", dms(1.234))); } -TEST(ChronoTest, FormatPrecision) { - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:.2}", std::chrono::seconds(42)), - fmt::format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); +TEST(chrono_test, format_precision) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{:.2%Q}"), std::chrono::seconds(42)), + fmt::format_error, "precision not allowed for this argument type"); + EXPECT_EQ("1ms", fmt::format("{:.0}", dms(1.234))); EXPECT_EQ("1.2ms", fmt::format("{:.1}", dms(1.234))); EXPECT_EQ("1.23ms", fmt::format("{:.{}}", dms(1.234), 2)); + + EXPECT_EQ("13ms", fmt::format("{:.0}", dms(12.56))); + EXPECT_EQ("12.6ms", fmt::format("{:.1}", dms(12.56))); + EXPECT_EQ("12.56ms", fmt::format("{:.2}", dms(12.56))); } -TEST(ChronoTest, FormatFullSpecs) { +TEST(chrono_test, format_full_specs) { + EXPECT_EQ("1ms ", fmt::format("{:6.0}", dms(1.234))); EXPECT_EQ("1.2ms ", fmt::format("{:6.1}", dms(1.234))); EXPECT_EQ(" 1.23ms", fmt::format("{:>8.{}}", dms(1.234), 2)); EXPECT_EQ(" 1.2ms ", fmt::format("{:^{}.{}}", dms(1.234), 7, 1)); EXPECT_EQ(" 1.23ms ", fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}}", dms(1.234), 2, 8)); EXPECT_EQ("=1.234ms=", fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}}", dms(1.234), 9, 3)); EXPECT_EQ("*1.2340ms*", fmt::format("{:*^10.4}", dms(1.234))); + + EXPECT_EQ("13ms ", fmt::format("{:6.0}", dms(12.56))); + EXPECT_EQ(" 13ms", fmt::format("{:>8.{}}", dms(12.56), 0)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 13ms ", fmt::format("{:^{}.{}}", dms(12.56), 6, 0)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 13ms ", fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}}", dms(12.56), 0, 8)); + EXPECT_EQ("==13ms===", fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}}", dms(12.56), 9, 0)); + EXPECT_EQ("***13ms***", fmt::format("{:*^10.0}", dms(12.56))); } -TEST(ChronoTest, FormatSimpleQq) { +TEST(chrono_test, format_simple_q) { typedef std::chrono::duration<float> fs; EXPECT_EQ("1.234 s", fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", fs(1.234))); typedef std::chrono::duration<float, std::milli> fms; @@ -333,34 +668,42 @@ TEST(ChronoTest, FormatSimpleQq) { EXPECT_EQ("1.234 ms", fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", dms(1.234))); } -TEST(ChronoTest, FormatPrecisionQq) { - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:.2%Q %q}", std::chrono::seconds(42)), - fmt::format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); +TEST(chrono_test, format_precision_q) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{:.2%Q %q}"), std::chrono::seconds(42)), + fmt::format_error, "precision not allowed for this argument type"); EXPECT_EQ("1.2 ms", fmt::format("{:.1%Q %q}", dms(1.234))); EXPECT_EQ("1.23 ms", fmt::format("{:.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 2)); } -TEST(ChronoTest, FormatFullSpecsQq) { +TEST(chrono_test, format_full_specs_q) { + EXPECT_EQ("1 ms ", fmt::format("{:7.0%Q %q}", dms(1.234))); EXPECT_EQ("1.2 ms ", fmt::format("{:7.1%Q %q}", dms(1.234))); EXPECT_EQ(" 1.23 ms", fmt::format("{:>8.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 2)); EXPECT_EQ(" 1.2 ms ", fmt::format("{:^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 8, 1)); EXPECT_EQ(" 1.23 ms ", fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 2, 9)); EXPECT_EQ("=1.234 ms=", fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 10, 3)); EXPECT_EQ("*1.2340 ms*", fmt::format("{:*^11.4%Q %q}", dms(1.234))); + + EXPECT_EQ("13 ms ", fmt::format("{:7.0%Q %q}", dms(12.56))); + EXPECT_EQ(" 13 ms", fmt::format("{:>8.{}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 0)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 13 ms ", fmt::format("{:^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 8, 0)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 13 ms ", fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 0, 9)); + EXPECT_EQ("==13 ms==", fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 9, 0)); + EXPECT_EQ("***13 ms***", fmt::format("{:*^11.0%Q %q}", dms(12.56))); } -TEST(ChronoTest, InvalidWidthId) { - EXPECT_THROW(fmt::format("{:{o}", std::chrono::seconds(0)), +TEST(chrono_test, invalid_width_id) { + EXPECT_THROW((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:{o}"), std::chrono::seconds(0)), fmt::format_error); } -TEST(ChronoTest, InvalidColons) { - EXPECT_THROW(fmt::format("{0}=:{0::", std::chrono::seconds(0)), +TEST(chrono_test, invalid_colons) { + EXPECT_THROW((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0}=:{0::"), std::chrono::seconds(0)), fmt::format_error); } -TEST(ChronoTest, NegativeDurations) { +TEST(chrono_test, negative_durations) { EXPECT_EQ("-12345", fmt::format("{:%Q}", std::chrono::seconds(-12345))); EXPECT_EQ("-03:25:45", fmt::format("{:%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(-12345))); @@ -375,16 +718,13 @@ TEST(ChronoTest, NegativeDurations) { fmt::format("{:%Q}", std::chrono::duration<int>(min))); } -TEST(ChronoTest, SpecialDurations) { - EXPECT_EQ( - "40.", - fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::duration<double>(1e20)).substr(0, 3)); +TEST(chrono_test, special_durations) { + auto value = fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::duration<double>(1e20)); + EXPECT_EQ(value, "40"); auto nan = std::numeric_limits<double>::quiet_NaN(); EXPECT_EQ( "nan nan nan nan nan:nan nan", fmt::format("{:%I %H %M %S %R %r}", std::chrono::duration<double>(nan))); - fmt::format("{:%S}", - std::chrono::duration<float, std::atto>(1.79400457e+31f)); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<float, std::exa>(1)), "1Es"); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<float, std::atto>(1)), @@ -393,6 +733,273 @@ TEST(ChronoTest, SpecialDurations) { "03:33"); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%T}", std::chrono::duration<char, std::mega>{2}), "03:33:20"); + EXPECT_EQ("01.234", + fmt::format("{:.3%S}", std::chrono::duration<float, std::pico>( + 1.234e12))); +} + +TEST(chrono_test, unsigned_duration) { + EXPECT_EQ("42s", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<unsigned>(42))); +} + +TEST(chrono_test, weekday) { + auto loc = get_locale("es_ES.UTF-8"); + std::locale::global(loc); + auto sat = fmt::weekday(6); + + auto tm = std::tm(); + tm.tm_wday = static_cast<int>(sat.c_encoding()); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", sat), "Sat"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%a}", tm), "Sat"); + + if (loc != std::locale::classic()) { + auto saturdays = std::vector<std::string>{"sáb", "sá."}; + EXPECT_THAT(saturdays, Contains(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", sat))); + EXPECT_THAT(saturdays, Contains(fmt::format(loc, "{:%a}", tm))); + } +} + +TEST(chrono_test, cpp20_duration_subsecond_support) { + using attoseconds = std::chrono::duration<long long, std::atto>; + // Check that 18 digits of subsecond precision are supported. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", attoseconds{999999999999999999}), + "00.999999999999999999"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", attoseconds{673231113420148734}), + "00.673231113420148734"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", attoseconds{-673231113420148734}), + "-00.673231113420148734"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::nanoseconds{13420148734}), + "13.420148734"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::nanoseconds{-13420148734}), + "-13.420148734"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::milliseconds{1234}), "01.234"); + // Check subsecond presision modifier. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.6%S}", std::chrono::nanoseconds{1234}), + "00.000001"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.18%S}", std::chrono::nanoseconds{1234}), + "00.000001234000000000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.{}%S}", std::chrono::nanoseconds{1234}, 6), + "00.000001"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.6%S}", std::chrono::milliseconds{1234}), + "01.234000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.6%S}", std::chrono::milliseconds{-1234}), + "-01.234000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.3%S}", std::chrono::seconds{1234}), "34.000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.3%S}", std::chrono::hours{1234}), "00.000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.5%S}", dms(1.234)), "00.00123"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.8%S}", dms(1.234)), "00.00123400"); + { + // Check that {:%H:%M:%S} is equivalent to {:%T}. + auto dur = std::chrono::milliseconds{3601234}; + auto formatted_dur = fmt::format("{:%T}", dur); + EXPECT_EQ(formatted_dur, "01:00:01.234"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%H:%M:%S}", dur), formatted_dur); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.6%H:%M:%S}", dur), "01:00:01.234000"); + } + using nanoseconds_dbl = std::chrono::duration<double, std::nano>; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", nanoseconds_dbl{-123456789}), "-00.123456789"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", nanoseconds_dbl{9123456789}), "09.123456789"); + // Verify that only the seconds part is extracted and printed. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", nanoseconds_dbl{99123456789}), "39.123456789"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", nanoseconds_dbl{99123000000}), "39.123000000"); + { + // Now the hour is printed, and we also test if negative doubles work. + auto dur = nanoseconds_dbl{-99123456789}; + auto formatted_dur = fmt::format("{:%T}", dur); + EXPECT_EQ(formatted_dur, "-00:01:39.123456789"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%H:%M:%S}", dur), formatted_dur); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.3%H:%M:%S}", dur), "-00:01:39.123"); + } + // Check that durations with precision greater than std::chrono::seconds have + // fixed precision, and print zeros even if there is no fractional part. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::microseconds{7000000}), + "07.000000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", + std::chrono::duration<long long, std::ratio<1, 3>>(1)), + "00.333333"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", + std::chrono::duration<long long, std::ratio<1, 7>>(1)), + "00.142857"); + + EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format("{:%S}", + std::chrono::duration<signed char, std::ratio<1, 100>>(0x80)), + "-01.28"); + + EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", + std::chrono::duration<short, std::ratio<1, 100>>(0x8000)), + "-05:27.68"); + + // Check that floating point seconds with ratio<1,1> are printed. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::duration<double>{1.5}), + "01.500000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", std::chrono::duration<double>{-61.25}), + "-01:01.250000"); } #endif // FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR + +// Disable the utc_clock test for windows, as the icu.dll used for tzdb +// (time zone database) is not shipped with many windows versions. +#if FMT_USE_UTC_TIME && !defined(_WIN32) +TEST(chrono_test, utc_clock) { + auto t1 = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); + auto t1_utc = std::chrono::utc_clock::from_sys(t1); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t1), + fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t1_utc)); +} +#endif + +TEST(chrono_test, timestamps_ratios) { + std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::milliseconds> + t1(std::chrono::milliseconds(67890)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", t1), "01:07.890"); + + std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::minutes> + t2(std::chrono::minutes(7)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", t2), "07:00"); + + std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<9>>> + t3(std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<9>>(7)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", t3), "01:03"); + + std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<63>>> + t4(std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<63>>(1)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", t4), "01:03"); +} + +TEST(chrono_test, timestamps_sub_seconds) { + std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::duration<long long, std::ratio<1, 3>>> + t1(std::chrono::duration<long long, std::ratio<1, 3>>(4)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t1), "01.333333"); + + std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 3>>> + t2(std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 3>>(4)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t2), "01.333333"); + + const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::seconds> + t3(std::chrono::seconds(2)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t3), "02"); + + const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::duration<double>> + t4(std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 1>>(9.5)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t4), "09.500000"); + + const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::duration<double>> + t5(std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 1>>(9)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t5), "09"); + + const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::milliseconds> + t6(std::chrono::seconds(1) + std::chrono::milliseconds(120)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t6), "01.120"); + + const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::microseconds> + t7(std::chrono::microseconds(1234567)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t7), "01.234567"); + + const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::nanoseconds> + t8(std::chrono::nanoseconds(123456789)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t8), "00.123456789"); + + const auto t9 = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>( + std::chrono::system_clock::now()); + const auto t9_sec = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(t9); + auto t9_sub_sec_part = fmt::format("{0:09}", (t9 - t9_sec).count()); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}.{}", strftime_full_utc(t9_sec), t9_sub_sec_part), + fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t9)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}.{}", strftime_full_utc(t9_sec), t9_sub_sec_part), + fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %T}", t9)); + + const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::milliseconds> + t10(std::chrono::milliseconds(2000)); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t10), "02.000"); + + { + const auto epoch = std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, + std::chrono::milliseconds>(); + const auto d = std::chrono::milliseconds(250); + + EXPECT_EQ("59.750", fmt::format("{:%S}", epoch - d)); + EXPECT_EQ("00.000", fmt::format("{:%S}", epoch)); + EXPECT_EQ("00.250", fmt::format("{:%S}", epoch + d)); + } +} + +TEST(chrono_test, glibc_extensions) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%0}"), std::chrono::seconds()), + fmt::format_error, "invalid format"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%_}"), std::chrono::seconds()), + fmt::format_error, "invalid format"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:%-}"), std::chrono::seconds()), + fmt::format_error, "invalid format"); + + { + const auto d = std::chrono::hours(1) + std::chrono::minutes(2) + + std::chrono::seconds(3); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%I,%H,%M,%S}", d), "01,01,02,03"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%0I,%0H,%0M,%0S}", d), "01,01,02,03"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%_I,%_H,%_M,%_S}", d), " 1, 1, 2, 3"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%-I,%-H,%-M,%-S}", d), "1,1,2,3"); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%OI,%OH,%OM,%OS}", d), "01,01,02,03"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%0OI,%0OH,%0OM,%0OS}", d), "01,01,02,03"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%_OI,%_OH,%_OM,%_OS}", d), " 1, 1, 2, 3"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%-OI,%-OH,%-OM,%-OS}", d), "1,1,2,3"); + } + + { + const auto tm = make_tm(1970, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%I,%H,%M,%S}", tm), "01,01,02,03"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%0I,%0H,%0M,%0S}", tm), "01,01,02,03"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%_I,%_H,%_M,%_S}", tm), " 1, 1, 2, 3"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%-I,%-H,%-M,%-S}", tm), "1,1,2,3"); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%OI,%OH,%OM,%OS}", tm), "01,01,02,03"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%0OI,%0OH,%0OM,%0OS}", tm), "01,01,02,03"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%_OI,%_OH,%_OM,%_OS}", tm), " 1, 1, 2, 3"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%-OI,%-OH,%-OM,%-OS}", tm), "1,1,2,3"); + } + + { + const auto d = std::chrono::seconds(3) + std::chrono::milliseconds(140); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", d), "03.140"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%0S}", d), "03.140"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%_S}", d), " 3.140"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%-S}", d), "3.140"); + } + + { + const auto d = std::chrono::duration<double>(3.14); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", d), "03.140000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%0S}", d), "03.140000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%_S}", d), " 3.140000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%-S}", d), "3.140000"); + } +} diff --git a/test/color-test.cc b/test/color-test.cc index 30738085..c2ba13a9 100644 --- a/test/color-test.cc +++ b/test/color-test.cc @@ -7,66 +7,29 @@ #include "fmt/color.h" -#include <iterator> -#include <string> -#include <utility> +#include <iterator> // std::back_inserter -#include "gtest-extra.h" +#include "gtest-extra.h" // EXPECT_WRITE -TEST(ColorsTest, ColorsPrint) { - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)), "rgb(255,20,30)"), - "\x1b[38;2;255;020;030mrgb(255,20,30)\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::blue), "blue"), - "\x1b[38;2;000;000;255mblue\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE( - stdout, - fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::blue) | bg(fmt::color::red), "two color"), - "\x1b[38;2;000;000;255m\x1b[48;2;255;000;000mtwo color\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(fmt::emphasis::bold, "bold"), - "\x1b[1mbold\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(fmt::emphasis::italic, "italic"), - "\x1b[3mitalic\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(fmt::emphasis::underline, "underline"), - "\x1b[4munderline\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, - fmt::print(fmt::emphasis::strikethrough, "strikethrough"), - "\x1b[9mstrikethrough\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE( - stdout, - fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::blue) | fmt::emphasis::bold, "blue/bold"), - "\x1b[1m\x1b[38;2;000;000;255mblue/bold\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::print(stderr, fmt::emphasis::bold, "bold error"), - "\x1b[1mbold error\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::print(stderr, fg(fmt::color::blue), "blue log"), - "\x1b[38;2;000;000;255mblue log\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(fmt::text_style(), "hi"), "hi"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(fg(fmt::terminal_color::red), "tred"), - "\x1b[31mtred\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(bg(fmt::terminal_color::cyan), "tcyan"), - "\x1b[46mtcyan\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, - fmt::print(fg(fmt::terminal_color::bright_green), "tbgreen"), - "\x1b[92mtbgreen\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, - fmt::print(bg(fmt::terminal_color::bright_magenta), "tbmagenta"), - "\x1b[105mtbmagenta\x1b[0m"); -} - -TEST(ColorsTest, Format) { +TEST(color_test, format) { EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)), "rgb(255,20,30)"), "\x1b[38;2;255;020;030mrgb(255,20,30)\x1b[0m"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)), L"rgb(255,20,30) wide"), - L"\x1b[38;2;255;020;030mrgb(255,20,30) wide\x1b[0m"); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fg(fmt::color::blue), "blue"), "\x1b[38;2;000;000;255mblue\x1b[0m"); EXPECT_EQ( fmt::format(fg(fmt::color::blue) | bg(fmt::color::red), "two color"), "\x1b[38;2;000;000;255m\x1b[48;2;255;000;000mtwo color\x1b[0m"); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::bold, "bold"), "\x1b[1mbold\x1b[0m"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::faint, "faint"), "\x1b[2mfaint\x1b[0m"); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::italic, "italic"), "\x1b[3mitalic\x1b[0m"); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::underline, "underline"), "\x1b[4munderline\x1b[0m"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::blink, "blink"), "\x1b[5mblink\x1b[0m"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::reverse, "reverse"), + "\x1b[7mreverse\x1b[0m"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::conceal, "conceal"), + "\x1b[8mconceal\x1b[0m"); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::strikethrough, "strikethrough"), "\x1b[9mstrikethrough\x1b[0m"); EXPECT_EQ( @@ -87,13 +50,23 @@ TEST(ColorsTest, Format) { "\x1b[105mtbmagenta\x1b[0m"); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fg(fmt::terminal_color::red), "{}", "foo"), "\x1b[31mfoo\x1b[0m"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}{}", fmt::styled("red", fg(fmt::color::red)), + fmt::styled("bold", fmt::emphasis::bold)), + "\x1b[38;2;255;000;000mred\x1b[0m\x1b[1mbold\x1b[0m"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::styled("bar", fg(fmt::color::blue) | + fmt::emphasis::underline)), + "\x1b[4m\x1b[38;2;000;000;255mbar\x1b[0m"); } -TEST(ColorsTest, FormatToOutAcceptsTextStyle) { - fmt::text_style ts = fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)); - std::string out; - fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), ts, "rgb(255,20,30){}{}{}", 1, 2, 3); - +TEST(color_test, format_to) { + auto out = std::string(); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)), + "rgb(255,20,30){}{}{}", 1, 2, 3); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(out), "\x1b[38;2;255;020;030mrgb(255,20,30)123\x1b[0m"); } + +TEST(color_test, print) { + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)), "rgb(255,20,30)"), + "\x1b[38;2;255;020;030mrgb(255,20,30)\x1b[0m"); +} diff --git a/test/compile-error-test/CMakeLists.txt b/test/compile-error-test/CMakeLists.txt index 8202f279..c4a16068 100644 --- a/test/compile-error-test/CMakeLists.txt +++ b/test/compile-error-test/CMakeLists.txt @@ -1,71 +1,182 @@ # Test if compile errors are produced where necessary. -cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.1...3.18) +cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8...3.25) +project(compile-error-test CXX) -include(CheckCXXSourceCompiles) -include(CheckCXXCompilerFlag) - -set(CMAKE_REQUIRED_INCLUDES ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/../../include) -set(CMAKE_REQUIRED_FLAGS ${CXX_STANDARD_FLAG} ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}) - -function (generate_source result fragment) - set(${result} " - #define FMT_HEADER_ONLY 1 - #include \"fmt/format.h\" - int main() { - ${fragment} - } - " PARENT_SCOPE) -endfunction () +set(fmt_headers " + #include <fmt/format.h> + #include <fmt/xchar.h> + #include <fmt/ostream.h> + #include <iostream> +") -function (expect_compile code) - generate_source(source "${code}") - check_cxx_source_compiles("${source}" compiles) - if (NOT compiles) - set(error_msg "Compile error for: ${code}") - endif () - # Unset the CMake cache variable compiles. Otherwise the compile test will - # just use cached information next time it runs. - unset(compiles CACHE) - if (error_msg) - message(FATAL_ERROR ${error_msg}) - endif () +set(error_test_names "") +set(non_error_test_content "") + +# For error tests (we expect them to produce compilation error): +# * adds a name of test into `error_test_names` list +# * generates a single source file (with the same name) for each test +# For non-error tests (we expect them to compile successfully): +# * adds a code segment as separate function to `non_error_test_content` +function (expect_compile name code_fragment) + cmake_parse_arguments(EXPECT_COMPILE "ERROR" "" "" ${ARGN}) + string(MAKE_C_IDENTIFIER "${name}" test_name) + + if (EXPECT_COMPILE_ERROR) + file(WRITE "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/test/${test_name}.cc" " + ${fmt_headers} + void ${test_name}() { + ${code_fragment} + } + ") + set(error_test_names_copy "${error_test_names}") + list(APPEND error_test_names_copy "${test_name}") + set(error_test_names "${error_test_names_copy}" PARENT_SCOPE) + else() + set(non_error_test_content " + ${non_error_test_content} + void ${test_name}() { + ${code_fragment} + }" PARENT_SCOPE) + endif() endfunction () -function (expect_compile_error code) - generate_source(source "${code}") - check_cxx_source_compiles("${source}" compiles) - if (compiles) - set(error_msg "No compile error for: ${code}") - endif () - # Unset the CMake cache variable compiles. Otherwise the compile test will - # just use cached information next time it runs. - unset(compiles CACHE) - if (error_msg) - message(FATAL_ERROR ${error_msg}) +# Generates a source file for non-error test with `non_error_test_content` and +# CMake project file with all error and single non-error test targets. +function (run_tests) + set(cmake_targets "") + foreach(test_name IN LISTS error_test_names) + set(cmake_targets " + ${cmake_targets} + add_library(test-${test_name} ${test_name}.cc) + target_link_libraries(test-${test_name} PRIVATE fmt::fmt) + ") + endforeach() + + file(WRITE "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/test/non_error_test.cc" " + ${fmt_headers} + ${non_error_test_content} + ") + set(cmake_targets " + ${cmake_targets} + add_library(non-error-test non_error_test.cc) + target_link_libraries(non-error-test PRIVATE fmt::fmt) + ") + + file(WRITE "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/test/CMakeLists.txt" " + cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8...3.25) + project(tests CXX) + add_subdirectory(${FMT_DIR} fmt) + ${cmake_targets} + ") + + set(build_directory "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/test/build") + file(MAKE_DIRECTORY "${build_directory}") + execute_process( + COMMAND + "${CMAKE_COMMAND}" + "-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER}" + "-DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS=${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS}" + "-DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=${CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD}" + "-DCMAKE_GENERATOR=${CMAKE_GENERATOR}" + "-DCMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM=${CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM}" + "-DFMT_DIR=${FMT_DIR}" + "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/test" + WORKING_DIRECTORY "${build_directory}" + RESULT_VARIABLE result_var + OUTPUT_VARIABLE output_var + ERROR_VARIABLE output_var) + if (NOT result_var EQUAL 0) + message(FATAL_ERROR "Unable to configure:\n${output_var}") + endif() + + foreach(test_name IN LISTS error_test_names) + execute_process( + COMMAND + "${CMAKE_COMMAND}" --build "${build_directory}" --target "test-${test_name}" + WORKING_DIRECTORY "${build_directory}" + RESULT_VARIABLE result_var + OUTPUT_VARIABLE output_var + ERROR_QUIET) + if (result_var EQUAL 0) + message(SEND_ERROR "No compile error for \"${test_name}\":\n${output_var}") + endif () + endforeach() + + execute_process( + COMMAND + "${CMAKE_COMMAND}" --build "${build_directory}" --target "non-error-test" + WORKING_DIRECTORY "${build_directory}" + RESULT_VARIABLE result_var + OUTPUT_VARIABLE output_var + ERROR_VARIABLE output_var) + if (NOT result_var EQUAL 0) + message(SEND_ERROR "Compile error for combined non-error test:\n${output_var}") endif () endfunction () + # check if the source file skeleton compiles -expect_compile("") +expect_compile(check "") +expect_compile(check-error "compilation_error" ERROR) # Formatting a wide character with a narrow format string is forbidden. -expect_compile_error("fmt::format(\"{}\", L'a');") +expect_compile(wide-character-narrow-format-string "fmt::format(L\"{}\", L'a');") +expect_compile(wide-character-narrow-format-string-error "fmt::format(\"{}\", L'a');" ERROR) # Formatting a wide string with a narrow format string is forbidden. -expect_compile_error("fmt::format(\"{}\", L\"foo\");") +expect_compile(wide-string-narrow-format-string "fmt::format(L\"{}\", L\"foo\");") +expect_compile(wide-string-narrow-format-string-error "fmt::format(\"{}\", L\"foo\");" ERROR) # Formatting a narrow string with a wide format string is forbidden because # mixing UTF-8 with UTF-16/32 can result in an invalid output. -expect_compile_error("fmt::format(L\"{}\", \"foo\");") +expect_compile(narrow-string-wide-format-string "fmt::format(L\"{}\", L\"foo\");") +expect_compile(narrow-string-wide-format-string-error "fmt::format(L\"{}\", \"foo\");" ERROR) -# Formatting a wide string with a narrow format string is forbidden. -expect_compile_error(" +expect_compile(cast-to-string " + struct S { + operator std::string() const { return std::string(); } + }; + fmt::format(\"{}\", std::string(S())); +") +expect_compile(cast-to-string-error " struct S { operator std::string() const { return std::string(); } }; fmt::format(\"{}\", S()); +" ERROR) + +# Formatting a function +expect_compile(format-function " + void (*f)(); + fmt::format(\"{}\", fmt::ptr(f)); ") +expect_compile(format-function-error " + void (*f)(); + fmt::format(\"{}\", f); +" ERROR) + +# Formatting an unformattable argument should always be a compile time error +expect_compile(format-lots-of-arguments-with-unformattable " + struct E {}; + fmt::format(\"\", 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, E()); +" ERROR) +expect_compile(format-lots-of-arguments-with-function " + void (*f)(); + fmt::format(\"\", 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, f); +" ERROR) + +# Check if user-defined literals are available +include(CheckCXXSourceCompiles) +set(CMAKE_REQUIRED_FLAGS ${CXX_STANDARD_FLAG}) +check_cxx_source_compiles(" + void operator\"\" _udl(long double); + int main() {}" + SUPPORTS_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS) +set(CMAKE_REQUIRED_FLAGS ) +if (NOT SUPPORTS_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS) + set (SUPPORTS_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS OFF) +endif () # Make sure that compiler features detected in the header # match the features detected in CMake. @@ -74,6 +185,57 @@ if (SUPPORTS_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS) else () set(supports_udl 0) endif () -expect_compile("#if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS != ${supports_udl} - # error - #endif") +expect_compile(udl-check " + #if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS != ${supports_udl} + # error + #endif +") + +if (CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD GREATER_EQUAL 20) + # Compile-time argument type check + expect_compile(format-string-number-spec " + #ifdef FMT_HAS_CONSTEVAL + fmt::format(\"{:d}\", 42); + #endif + ") + expect_compile(format-string-number-spec-error " + #ifdef FMT_HAS_CONSTEVAL + fmt::format(\"{:d}\", \"I am not a number\"); + #else + #error + #endif + " ERROR) + expect_compile(print-string-number-spec-error " + #ifdef FMT_HAS_CONSTEVAL + fmt::print(\"{:d}\", \"I am not a number\"); + #else + #error + #endif + " ERROR) + expect_compile(print-stream-string-number-spec-error " + #ifdef FMT_HAS_CONSTEVAL + fmt::print(std::cout, \"{:d}\", \"I am not a number\"); + #else + #error + #endif + " ERROR) + + # Compile-time argument name check + expect_compile(format-string-name " + #if defined(FMT_HAS_CONSTEVAL) && FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS + using namespace fmt::literals; + fmt::print(\"{foo}\", \"foo\"_a=42); + #endif + ") + expect_compile(format-string-name-error " + #if defined(FMT_HAS_CONSTEVAL) && FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS + using namespace fmt::literals; + fmt::print(\"{foo}\", \"bar\"_a=42); + #else + #error + #endif + " ERROR) +endif () + +# Run all tests +run_tests() diff --git a/test/compile-fp-test.cc b/test/compile-fp-test.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..5b46d74b --- /dev/null +++ b/test/compile-fp-test.cc @@ -0,0 +1,63 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - formatting library tests +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#include "fmt/compile.h" +#include "gmock/gmock.h" + +#if defined(__cpp_lib_bit_cast) && __cpp_lib_bit_cast >= 201806 && \ + defined(__cpp_constexpr) && __cpp_constexpr >= 201907 && \ + defined(__cpp_constexpr_dynamic_alloc) && \ + __cpp_constexpr_dynamic_alloc >= 201907 && FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L + +template <size_t max_string_length, typename Char = char> struct test_string { + template <typename T> constexpr bool operator==(const T& rhs) const noexcept { + return fmt::basic_string_view<Char>(rhs).compare(buffer) == 0; + } + Char buffer[max_string_length]{}; +}; + +template <size_t max_string_length, typename Char = char, typename... Args> +consteval auto test_format(auto format, const Args&... args) { + test_string<max_string_length, Char> string{}; + fmt::format_to(string.buffer, format, args...); + return string; +} + +TEST(compile_time_formatting_test, floating_point) { + EXPECT_EQ("0", test_format<2>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 0.0f)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.500000", test_format<11>(FMT_COMPILE("{0:f}"), 392.5f)); + + EXPECT_EQ("0", test_format<2>(FMT_COMPILE("{:}"), 0.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.000000", test_format<9>(FMT_COMPILE("{:f}"), 0.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("0", test_format<2>(FMT_COMPILE("{:g}"), 0.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.65", test_format<7>(FMT_COMPILE("{:}"), 392.65)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.65", test_format<7>(FMT_COMPILE("{:g}"), 392.65)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.65", test_format<7>(FMT_COMPILE("{:G}"), 392.65)); + EXPECT_EQ("4.9014e+06", test_format<11>(FMT_COMPILE("{:g}"), 4.9014e6)); + EXPECT_EQ("-392.650000", test_format<12>(FMT_COMPILE("{:f}"), -392.65)); + EXPECT_EQ("-392.650000", test_format<12>(FMT_COMPILE("{:F}"), -392.65)); + + EXPECT_EQ("3.926500e+02", test_format<13>(FMT_COMPILE("{0:e}"), 392.65)); + EXPECT_EQ("3.926500E+02", test_format<13>(FMT_COMPILE("{0:E}"), 392.65)); + EXPECT_EQ("+0000392.6", test_format<11>(FMT_COMPILE("{0:+010.4g}"), 392.65)); + EXPECT_EQ("9223372036854775808.000000", + test_format<27>(FMT_COMPILE("{:f}"), 9223372036854775807.0)); + + constexpr double nan = std::numeric_limits<double>::quiet_NaN(); + EXPECT_EQ("nan", test_format<4>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), nan)); + EXPECT_EQ("+nan", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{:+}"), nan)); + if (std::signbit(-nan)) + EXPECT_EQ("-nan", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), -nan)); + else + fmt::print("Warning: compiler doesn't handle negative NaN correctly"); + + constexpr double inf = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); + EXPECT_EQ("inf", test_format<4>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), inf)); + EXPECT_EQ("+inf", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{:+}"), inf)); + EXPECT_EQ("-inf", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), -inf)); +} +#endif diff --git a/test/compile-test.cc b/test/compile-test.cc index c0dda50c..d6c7c643 100644 --- a/test/compile-test.cc +++ b/test/compile-test.cc @@ -5,121 +5,68 @@ // // For the license information refer to format.h. -#include <string> -#include <type_traits> +#include "fmt/compile.h" -// Check that fmt/compile.h compiles with windows.h included before it. -#ifdef _WIN32 -# include <windows.h> -#endif +#include <type_traits> -#include "fmt/compile.h" -#include "gmock.h" +#include "fmt/chrono.h" +#include "gmock/gmock.h" #include "gtest-extra.h" -#include "util.h" - -// compiletime_prepared_parts_type_provider is useful only with relaxed -// constexpr. -#if FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR -template <unsigned EXPECTED_PARTS_COUNT, typename Format> -void check_prepared_parts_type(Format format) { - typedef fmt::detail::compiled_format_base<decltype(format)> provider; - typedef fmt::detail::format_part<char> - expected_parts_type[EXPECTED_PARTS_COUNT]; - static_assert(std::is_same<typename provider::parts_container, - expected_parts_type>::value, - "CompileTimePreparedPartsTypeProvider test failed"); -} - -TEST(CompileTest, CompileTimePreparedPartsTypeProvider) { - check_prepared_parts_type<1u>(FMT_STRING("text")); - check_prepared_parts_type<1u>(FMT_STRING("{}")); - check_prepared_parts_type<2u>(FMT_STRING("text{}")); - check_prepared_parts_type<2u>(FMT_STRING("{}text")); - check_prepared_parts_type<3u>(FMT_STRING("text{}text")); - check_prepared_parts_type<3u>(FMT_STRING("{:{}.{}} {:{}}")); - - check_prepared_parts_type<3u>(FMT_STRING("{{{}}}")); // '{', 'argument', '}' - check_prepared_parts_type<2u>(FMT_STRING("text{{")); // 'text', '{' - check_prepared_parts_type<3u>(FMT_STRING("text{{ ")); // 'text', '{', ' ' - check_prepared_parts_type<2u>(FMT_STRING("}}text")); // '}', text - check_prepared_parts_type<2u>(FMT_STRING("text}}text")); // 'text}', 'text' - check_prepared_parts_type<4u>( - FMT_STRING("text{{}}text")); // 'text', '{', '}', 'text' -} -#endif - -TEST(CompileTest, PassStringLiteralFormat) { - const auto prepared = fmt::detail::compile<int>("test {}"); - EXPECT_EQ("test 42", fmt::format(prepared, 42)); - const auto wprepared = fmt::detail::compile<int>(L"test {}"); - EXPECT_EQ(L"test 42", fmt::format(wprepared, 42)); -} -TEST(CompileTest, FormatToArrayOfChars) { - char buffer[32] = {0}; - const auto prepared = fmt::detail::compile<int>("4{}"); - fmt::format_to(fmt::detail::make_checked(buffer, 32), prepared, 2); - EXPECT_EQ(std::string("42"), buffer); - wchar_t wbuffer[32] = {0}; - const auto wprepared = fmt::detail::compile<int>(L"4{}"); - fmt::format_to(fmt::detail::make_checked(wbuffer, 32), wprepared, 2); - EXPECT_EQ(std::wstring(L"42"), wbuffer); +TEST(iterator_test, counting_iterator) { + auto it = fmt::detail::counting_iterator(); + auto prev = it++; + EXPECT_EQ(prev.count(), 0); + EXPECT_EQ(it.count(), 1); + EXPECT_EQ((it + 41).count(), 42); } -TEST(CompileTest, FormatToIterator) { - std::string s(2, ' '); - const auto prepared = fmt::detail::compile<int>("4{}"); - fmt::format_to(s.begin(), prepared, 2); - EXPECT_EQ("42", s); - std::wstring ws(2, L' '); - const auto wprepared = fmt::detail::compile<int>(L"4{}"); - fmt::format_to(ws.begin(), wprepared, 2); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42", ws); +TEST(compile_test, compile_fallback) { + // FMT_COMPILE should fallback on runtime formatting when `if constexpr` is + // not available. + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42)); } -TEST(CompileTest, FormatToN) { - char buf[5]; - auto f = fmt::detail::compile<int>("{:10}"); - auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buf, 5, f, 42); - EXPECT_EQ(result.size, 10); - EXPECT_EQ(result.out, buf + 5); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::string_view(buf, 5), " "); -} +struct type_with_get { + template <int> friend void get(type_with_get); +}; -TEST(CompileTest, FormattedSize) { - auto f = fmt::detail::compile<int>("{:10}"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::formatted_size(f, 42), 10); -} +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<type_with_get> : formatter<int> { + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(type_with_get, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return formatter<int>::format(42, ctx); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(CompileTest, MultipleTypes) { - auto f = fmt::detail::compile<int, int>("{} {}"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(f, 42, 42), "42 42"); +TEST(compile_test, compile_type_with_get) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), type_with_get())); } +#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) && defined(__cpp_return_type_deduction) struct test_formattable {}; FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE template <> struct formatter<test_formattable> : formatter<const char*> { + char word_spec = 'f'; + constexpr auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) { + auto it = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end(); + if (it == end || *it == '}') return it; + if (it != end && (*it == 'f' || *it == 'b')) word_spec = *it++; + if (it != end && *it != '}') throw format_error("invalid format"); + return it; + } template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(test_formattable, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - return formatter<const char*>::format("foo", ctx); + constexpr auto format(test_formattable, FormatContext& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return formatter<const char*>::format(word_spec == 'f' ? "foo" : "bar", + ctx); } }; FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(CompileTest, FormatUserDefinedType) { - auto f = fmt::detail::compile<test_formattable>("{}"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(f, test_formattable()), "foo"); -} - -TEST(CompileTest, EmptyFormatString) { - auto f = fmt::detail::compile<>(""); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(f), ""); -} - -#ifdef __cpp_if_constexpr -TEST(CompileTest, FormatDefault) { +TEST(compile_test, format_default) { EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42)); EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42u)); EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42ll)); @@ -130,22 +77,104 @@ TEST(CompileTest, FormatDefault) { EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), "foo")); EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), std::string("foo"))); EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), test_formattable())); + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", t), fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), t)); +# ifdef __cpp_lib_byte + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), std::byte{42})); +# endif } -TEST(CompileTest, FormatWideString) { +TEST(compile_test, format_wide_string) { EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE(L"{}"), 42)); } -TEST(CompileTest, FormatSpecs) { +TEST(compile_test, format_specs) { EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{:x}"), 0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ("1.2 ms ", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{:7.1%Q %q}"), + std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>(1.234))); +} + +TEST(compile_test, dynamic_format_specs) { + EXPECT_EQ("foo ", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{:{}}"), "foo", 5)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 3.14", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{:{}.{}f}"), 3.141592, 6, 2)); + EXPECT_EQ( + "=1.234ms=", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{:=^{}.{}}"), + std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>(1.234), 9, 3)); +} + +TEST(compile_test, manual_ordering) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{0}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{0:4}"), -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("41 43", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{0} {1}"), 41, 43)); + EXPECT_EQ("41 43", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{1} {0}"), 43, 41)); + EXPECT_EQ("41 43", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{0} {2}"), 41, 42, 43)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 41 43", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{1:{2}} {0:4}"), 43, 41, 4)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 1.2 ms ", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{0} {1:7.1%Q %q}"), 42, + std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>(1.234))); + EXPECT_EQ( + "true 42 42 foo 0x1234 foo", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{0} {1} {2} {3} {4} {5}"), true, 42, 42.0f, + "foo", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x1234), test_formattable())); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE(L"{0}"), 42)); +} + +TEST(compile_test, named) { + auto runtime_named_field_compiled = + fmt::detail::compile<decltype(fmt::arg("arg", 42))>(FMT_COMPILE("{arg}")); + static_assert(std::is_same_v<decltype(runtime_named_field_compiled), + fmt::detail::runtime_named_field<char>>); + + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), fmt::arg("arg", 42))); + EXPECT_EQ("41 43", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{} {}"), fmt::arg("arg", 41), + fmt::arg("arg", 43))); + + EXPECT_EQ("foobar", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{a0}{a1}"), fmt::arg("a0", "foo"), + fmt::arg("a1", "bar"))); + EXPECT_EQ("foobar", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}{a1}"), fmt::arg("a0", "foo"), + fmt::arg("a1", "bar"))); + EXPECT_EQ("foofoo", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{a0}{}"), fmt::arg("a0", "foo"), + fmt::arg("a1", "bar"))); + EXPECT_EQ("foobar", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{0}{a1}"), fmt::arg("a0", "foo"), + fmt::arg("a1", "bar"))); + EXPECT_EQ("foobar", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{a0}{1}"), fmt::arg("a0", "foo"), + fmt::arg("a1", "bar"))); + + EXPECT_EQ("foobar", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}{a1}"), "foo", fmt::arg("a1", "bar"))); + EXPECT_EQ("foobar", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{a0}{a1}"), fmt::arg("a1", "bar"), + fmt::arg("a2", "baz"), fmt::arg("a0", "foo"))); + EXPECT_EQ(" bar foo ", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE(" {foo} {bar} "), fmt::arg("foo", "bar"), + fmt::arg("bar", "foo"))); + + EXPECT_THROW(fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{invalid}"), fmt::arg("valid", 42)), + fmt::format_error); + +# if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS + using namespace fmt::literals; + auto statically_named_field_compiled = + fmt::detail::compile<decltype("arg"_a = 42)>(FMT_COMPILE("{arg}")); + static_assert(std::is_same_v<decltype(statically_named_field_compiled), + fmt::detail::field<char, int, 0>>); + + EXPECT_EQ("41 43", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{a0} {a1}"), "a0"_a = 41, "a1"_a = 43)); + EXPECT_EQ("41 43", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{a1} {a0}"), "a0"_a = 43, "a1"_a = 41)); +# endif } -TEST(CompileTest, DynamicWidth) { - EXPECT_EQ(" 42foo ", - fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{:{}}{:{}}"), 42, 4, "foo", 5)); +TEST(compile_test, join) { + unsigned char data[] = {0x1, 0x2, 0xaf}; + EXPECT_EQ("0102af", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{:02x}"), fmt::join(data, ""))); } -TEST(CompileTest, FormatTo) { +TEST(compile_test, format_to) { char buf[8]; auto end = fmt::format_to(buf, FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); *end = '\0'; @@ -155,7 +184,7 @@ TEST(CompileTest, FormatTo) { EXPECT_STREQ("2a", buf); } -TEST(CompileTest, FormatToNWithCompileMacro) { +TEST(compile_test, format_to_n) { constexpr auto buffer_size = 8; char buffer[buffer_size]; auto res = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, buffer_size, FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); @@ -166,8 +195,180 @@ TEST(CompileTest, FormatToNWithCompileMacro) { EXPECT_STREQ("2a", buffer); } -TEST(CompileTest, TextAndArg) { +# ifdef __cpp_lib_bit_cast +TEST(compile_test, constexpr_formatted_size) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 size_t size = fmt::formatted_size(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); + EXPECT_EQ(size, 2); + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 size_t hex_size = + fmt::formatted_size(FMT_COMPILE("{:x}"), 15); + EXPECT_EQ(hex_size, 1); + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 size_t binary_size = + fmt::formatted_size(FMT_COMPILE("{:b}"), 15); + EXPECT_EQ(binary_size, 4); + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 size_t padded_size = + fmt::formatted_size(FMT_COMPILE("{:*^6}"), 42); + EXPECT_EQ(padded_size, 6); + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 size_t float_size = + fmt::formatted_size(FMT_COMPILE("{:.3}"), 12.345); + EXPECT_EQ(float_size, 4); + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 size_t str_size = + fmt::formatted_size(FMT_COMPILE("{:s}"), "abc"); + EXPECT_EQ(str_size, 3); +} +# endif + +TEST(compile_test, text_and_arg) { EXPECT_EQ(">>>42<<<", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE(">>>{}<<<"), 42)); EXPECT_EQ("42!", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}!"), 42)); } + +TEST(compile_test, unknown_format_fallback) { + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{name:^4}"), fmt::arg("name", 42))); + + std::vector<char> v; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(v), FMT_COMPILE("{name:^4}"), + fmt::arg("name", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", fmt::string_view(v.data(), v.size())); + + char buffer[4]; + auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 4, FMT_COMPILE("{name:^5}"), + fmt::arg("name", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(5u, result.size); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer + 4, result.out); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", fmt::string_view(buffer, 4)); +} + +TEST(compile_test, empty) { EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE(""))); } + +struct to_stringable { + friend fmt::string_view to_string_view(to_stringable) { return {}; } +}; + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<to_stringable> { + auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + template <typename FormatContext> + auto format(const to_stringable&, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return ctx.out(); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(compile_test, to_string_and_formatter) { + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), to_stringable()); +} + +TEST(compile_test, print) { + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(FMT_COMPILE("Don't {}!"), "panic"), + "Don't panic!"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::print(stderr, FMT_COMPILE("Don't {}!"), "panic"), + "Don't panic!"); +} +#endif + +#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS +TEST(compile_test, compile_format_string_literal) { + using namespace fmt::literals; + EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format(""_cf)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{}"_cf, 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(L"{}"_cf, 42)); +} +#endif + +// MSVS 2019 19.29.30145.0 - Support C++20 and OK. +// MSVS 2022 19.32.31332.0 - compile-test.cc(362,3): fatal error C1001: Internal +// compiler error. +// (compiler file +// 'D:\a\_work\1\s\src\vctools\Compiler\CxxFE\sl\p1\c\constexpr\constexpr.cpp', +// line 8635) +#if ((FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L) && \ + (!defined(_GLIBCXX_RELEASE) || _GLIBCXX_RELEASE > 9) && \ + (!FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION < 1930)) || \ + (FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201709L && FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 1002) +template <size_t max_string_length, typename Char = char> struct test_string { + template <typename T> constexpr bool operator==(const T& rhs) const noexcept { + return fmt::basic_string_view<Char>(rhs).compare(buffer) == 0; + } + Char buffer[max_string_length]{}; +}; + +template <size_t max_string_length, typename Char = char, typename... Args> +consteval auto test_format(auto format, const Args&... args) { + test_string<max_string_length, Char> string{}; + fmt::format_to(string.buffer, format, args...); + return string; +} + +TEST(compile_time_formatting_test, bool) { + EXPECT_EQ("true", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), true)); + EXPECT_EQ("false", test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), false)); + EXPECT_EQ("true ", test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{:5}"), true)); + EXPECT_EQ("1", test_format<2>(FMT_COMPILE("{:d}"), true)); +} + +TEST(compile_time_formatting_test, integer) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", test_format<3>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("420", test_format<4>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 420)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 42", test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{} {}"), 42, 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 42", + test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{} {}"), uint32_t{42}, uint64_t{42})); + + EXPECT_EQ("+42", test_format<4>(FMT_COMPILE("{:+}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", test_format<3>(FMT_COMPILE("{:-}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", test_format<4>(FMT_COMPILE("{: }"), 42)); + + EXPECT_EQ("-0042", test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{:05}"), -42)); + + EXPECT_EQ("101010", test_format<7>(FMT_COMPILE("{:b}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("0b101010", test_format<9>(FMT_COMPILE("{:#b}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("0B101010", test_format<9>(FMT_COMPILE("{:#B}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("042", test_format<4>(FMT_COMPILE("{:#o}"), 042)); + EXPECT_EQ("0x4a", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{:#x}"), 0x4a)); + EXPECT_EQ("0X4A", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{:#X}"), 0x4a)); + + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{:5}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{:5}"), 42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{:5}"), 42ull)); + + EXPECT_EQ("42 ", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{:<4}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{:>4}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{:^4}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("**-42", test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{:*>5}"), -42)); +} + +TEST(compile_time_formatting_test, char) { + EXPECT_EQ("c", test_format<2>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 'c')); + + EXPECT_EQ("c ", test_format<4>(FMT_COMPILE("{:3}"), 'c')); + EXPECT_EQ("99", test_format<3>(FMT_COMPILE("{:d}"), 'c')); +} + +TEST(compile_time_formatting_test, string) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", test_format<3>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), "42")); + EXPECT_EQ("The answer is 42", + test_format<17>(FMT_COMPILE("{} is {}"), "The answer", "42")); + + EXPECT_EQ("abc**", test_format<6>(FMT_COMPILE("{:*<5}"), "abc")); + EXPECT_EQ("**🤡**", test_format<9>(FMT_COMPILE("{:*^6}"), "🤡")); +} + +TEST(compile_time_formatting_test, combination) { + EXPECT_EQ("420, true, answer", + test_format<18>(FMT_COMPILE("{}, {}, {}"), 420, true, "answer")); + + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", test_format<5>(FMT_COMPILE("{:{}}"), -42, 4)); +} + +TEST(compile_time_formatting_test, custom_type) { + EXPECT_EQ("foo", test_format<4>(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), test_formattable())); + EXPECT_EQ("bar", test_format<4>(FMT_COMPILE("{:b}"), test_formattable())); +} + +TEST(compile_time_formatting_test, multibyte_fill) { + EXPECT_EQ("жж42", test_format<8>(FMT_COMPILE("{:ж>4}"), 42)); +} #endif diff --git a/test/core-test.cc b/test/core-test.cc index 9d88070d..1d84ffd7 100644 --- a/test/core-test.cc +++ b/test/core-test.cc @@ -5,93 +5,157 @@ // // For the license information refer to format.h. -#include <algorithm> -#include <climits> -#include <cstring> -#include <functional> -#include <iterator> -#include <limits> -#include <memory> -#include <string> -#include <type_traits> - -#include "gmock.h" +// clang-format off #include "test-assert.h" - -// Check if fmt/core.h compiles with windows.h included before it. -#ifdef _WIN32 -# include <windows.h> -#endif +// clang-format on #include "fmt/core.h" -#undef min -#undef max +#include <algorithm> // std::copy_n +#include <climits> // INT_MAX +#include <cstring> // std::strlen +#include <functional> // std::equal_to +#include <iterator> // std::back_insert_iterator +#include <limits> // std::numeric_limits +#include <string> // std::string +#include <type_traits> // std::is_same + +#include "gmock/gmock.h" -using fmt::basic_format_arg; using fmt::string_view; using fmt::detail::buffer; -using fmt::detail::make_arg; -using fmt::detail::value; using testing::_; using testing::Invoke; using testing::Return; -using testing::StrictMock; -struct test_struct {}; +#ifdef FMT_FORMAT_H_ +# error core-test includes format.h +#endif -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <typename Char> struct formatter<test_struct, Char> { - template <typename ParseContext> - auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return ctx.begin(); - } +TEST(string_view_test, value_type) { + static_assert(std::is_same<string_view::value_type, char>::value, ""); +} + +TEST(string_view_test, ctor) { + EXPECT_STREQ("abc", fmt::string_view("abc").data()); + EXPECT_EQ(3u, fmt::string_view("abc").size()); + + EXPECT_STREQ("defg", fmt::string_view(std::string("defg")).data()); + EXPECT_EQ(4u, fmt::string_view(std::string("defg")).size()); +} - auto format(test_struct, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - const Char* test = "test"; - return std::copy_n(test, std::strlen(test), ctx.out()); +TEST(string_view_test, length) { + // Test that string_view::size() returns string length, not buffer size. + char str[100] = "some string"; + EXPECT_EQ(std::strlen(str), string_view(str).size()); + EXPECT_LT(std::strlen(str), sizeof(str)); +} + +// Check string_view's comparison operator. +template <template <typename> class Op> void check_op() { + const char* inputs[] = {"foo", "fop", "fo"}; + size_t num_inputs = sizeof(inputs) / sizeof(*inputs); + for (size_t i = 0; i < num_inputs; ++i) { + for (size_t j = 0; j < num_inputs; ++j) { + string_view lhs(inputs[i]), rhs(inputs[j]); + EXPECT_EQ(Op<int>()(lhs.compare(rhs), 0), Op<string_view>()(lhs, rhs)); + } } -}; -FMT_END_NAMESPACE +} + +TEST(string_view_test, compare) { + EXPECT_EQ(string_view("foo").compare(string_view("foo")), 0); + EXPECT_GT(string_view("fop").compare(string_view("foo")), 0); + EXPECT_LT(string_view("foo").compare(string_view("fop")), 0); + EXPECT_GT(string_view("foo").compare(string_view("fo")), 0); + EXPECT_LT(string_view("fo").compare(string_view("foo")), 0); + + EXPECT_TRUE(string_view("foo").starts_with('f')); + EXPECT_FALSE(string_view("foo").starts_with('o')); + EXPECT_FALSE(string_view().starts_with('o')); + + EXPECT_TRUE(string_view("foo").starts_with("fo")); + EXPECT_TRUE(string_view("foo").starts_with("foo")); + EXPECT_FALSE(string_view("foo").starts_with("fooo")); + EXPECT_FALSE(string_view().starts_with("fooo")); + + check_op<std::equal_to>(); + check_op<std::not_equal_to>(); + check_op<std::less>(); + check_op<std::less_equal>(); + check_op<std::greater>(); + check_op<std::greater_equal>(); +} + +TEST(core_test, is_output_iterator) { + EXPECT_TRUE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<char*, char>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<const char*, char>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::string, char>::value)); + EXPECT_TRUE( + (fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::back_insert_iterator<std::string>, + char>::value)); + EXPECT_TRUE( + (fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::string::iterator, char>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::string::const_iterator, + char>::value)); +} + +TEST(core_test, buffer_appender) { + // back_insert_iterator is not default-constructible before C++20, so + // buffer_appender can only be default-constructible when back_insert_iterator + // is. + static_assert( + std::is_default_constructible< + std::back_insert_iterator<fmt::detail::buffer<char>>>::value == + std::is_default_constructible< + fmt::detail::buffer_appender<char>>::value, + ""); + +#ifdef __cpp_lib_ranges + static_assert(std::output_iterator<fmt::detail::buffer_appender<char>, char>); +#endif +} #if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 470 -TEST(BufferTest, Noncopyable) { +TEST(buffer_test, noncopyable) { EXPECT_FALSE(std::is_copy_constructible<buffer<char>>::value); -# if !FMT_MSC_VER +# if !FMT_MSC_VERSION // std::is_copy_assignable is broken in MSVC2013. EXPECT_FALSE(std::is_copy_assignable<buffer<char>>::value); # endif } -TEST(BufferTest, Nonmoveable) { +TEST(buffer_test, nonmoveable) { EXPECT_FALSE(std::is_move_constructible<buffer<char>>::value); -# if !FMT_MSC_VER +# if !FMT_MSC_VERSION // std::is_move_assignable is broken in MSVC2013. EXPECT_FALSE(std::is_move_assignable<buffer<char>>::value); # endif } #endif -TEST(BufferTest, Indestructible) { +TEST(buffer_test, indestructible) { static_assert(!std::is_destructible<fmt::detail::buffer<int>>(), "buffer's destructor is protected"); } template <typename T> struct mock_buffer final : buffer<T> { - MOCK_METHOD1(do_grow, size_t(size_t capacity)); + MOCK_METHOD(size_t, do_grow, (size_t)); - void grow(size_t capacity) { this->set(this->data(), do_grow(capacity)); } + void grow(size_t capacity) override { + this->set(this->data(), do_grow(capacity)); + } - mock_buffer(T* data = nullptr, size_t capacity = 0) { - this->set(data, capacity); + mock_buffer(T* data = nullptr, size_t buf_capacity = 0) { + this->set(data, buf_capacity); ON_CALL(*this, do_grow(_)).WillByDefault(Invoke([](size_t capacity) { return capacity; })); } }; -TEST(BufferTest, Ctor) { +TEST(buffer_test, ctor) { { mock_buffer<int> buffer; EXPECT_EQ(nullptr, buffer.data()); @@ -115,7 +179,7 @@ TEST(BufferTest, Ctor) { } } -TEST(BufferTest, Access) { +TEST(buffer_test, access) { char data[10]; mock_buffer<char> buffer(data, sizeof(data)); buffer[0] = 11; @@ -126,7 +190,7 @@ TEST(BufferTest, Access) { EXPECT_EQ(42, const_buffer[3]); } -TEST(BufferTest, TryResize) { +TEST(buffer_test, try_resize) { char data[123]; mock_buffer<char> buffer(data, sizeof(data)); buffer[10] = 42; @@ -146,7 +210,7 @@ TEST(BufferTest, TryResize) { buffer.try_resize(200); } -TEST(BufferTest, TryResizePartial) { +TEST(buffer_test, try_resize_partial) { char data[10]; mock_buffer<char> buffer(data, sizeof(data)); EXPECT_CALL(buffer, do_grow(20)).WillOnce(Return(15)); @@ -155,7 +219,7 @@ TEST(BufferTest, TryResizePartial) { EXPECT_EQ(buffer.size(), 15); } -TEST(BufferTest, Clear) { +TEST(buffer_test, clear) { mock_buffer<char> buffer; EXPECT_CALL(buffer, do_grow(20)); buffer.try_resize(20); @@ -164,7 +228,7 @@ TEST(BufferTest, Clear) { EXPECT_EQ(20u, buffer.capacity()); } -TEST(BufferTest, Append) { +TEST(buffer_test, append) { char data[15]; mock_buffer<char> buffer(data, 10); auto test = "test"; @@ -179,7 +243,7 @@ TEST(BufferTest, Append) { EXPECT_EQ(12u, buffer.size()); } -TEST(BufferTest, AppendPartial) { +TEST(buffer_test, append_partial) { char data[10]; mock_buffer<char> buffer(data, sizeof(data)); testing::InSequence seq; @@ -193,7 +257,7 @@ TEST(BufferTest, AppendPartial) { buffer.append(test, test + 15); } -TEST(BufferTest, AppendAllocatesEnoughStorage) { +TEST(buffer_test, append_allocates_enough_storage) { char data[19]; mock_buffer<char> buffer(data, 10); auto test = "abcdefgh"; @@ -202,18 +266,14 @@ TEST(BufferTest, AppendAllocatesEnoughStorage) { buffer.append(test, test + 9); } -TEST(ArgTest, FormatArgs) { - auto args = fmt::format_args(); - EXPECT_FALSE(args.get(1)); -} - struct custom_context { using char_type = char; using parse_context_type = fmt::format_parse_context; + bool called = false; + template <typename T> struct formatter_type { - template <typename ParseContext> - auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(fmt::format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { return ctx.begin(); } @@ -223,31 +283,39 @@ struct custom_context { } }; - bool called; - fmt::format_parse_context ctx; - - fmt::format_parse_context& parse_context() { return ctx; } void advance_to(const char*) {} }; -TEST(ArgTest, MakeValueWithCustomContext) { +struct test_struct {}; + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <typename Char> struct formatter<test_struct, Char> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + auto format(test_struct, format_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto test = string_view("test"); + return std::copy_n(test.data(), test.size(), ctx.out()); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(arg_test, format_args) { + auto args = fmt::format_args(); + EXPECT_FALSE(args.get(1)); +} + +TEST(arg_test, make_value_with_custom_context) { auto t = test_struct(); - fmt::detail::value<custom_context> arg( + auto arg = fmt::detail::value<custom_context>( fmt::detail::arg_mapper<custom_context>().map(t)); - custom_context ctx = {false, fmt::format_parse_context("")}; - arg.custom.format(&t, ctx.parse_context(), ctx); + auto ctx = custom_context(); + auto parse_ctx = fmt::format_parse_context(""); + arg.custom.format(&t, parse_ctx, ctx); EXPECT_TRUE(ctx.called); } -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -namespace detail { -template <typename Char> -bool operator==(custom_value<Char> lhs, custom_value<Char> rhs) { - return lhs.value == rhs.value; -} -} // namespace detail -FMT_END_NAMESPACE - // Use a unique result type to make sure that there are no undesirable // conversions. struct test_result {}; @@ -259,12 +327,12 @@ template <typename T> struct mock_visitor { ON_CALL(*this, visit(_)).WillByDefault(Return(test_result())); } - MOCK_METHOD1_T(visit, test_result(T value)); - MOCK_METHOD0_T(unexpected, void()); + MOCK_METHOD(test_result, visit, (T)); + MOCK_METHOD(void, unexpected, ()); - test_result operator()(T value) { return visit(value); } + auto operator()(T value) -> test_result { return visit(value); } - template <typename U> test_result operator()(U) { + template <typename U> auto operator()(U) -> test_result { unexpected(); return test_result(); } @@ -288,307 +356,216 @@ VISIT_TYPE(long, long long); VISIT_TYPE(unsigned long, unsigned long long); #endif -#define CHECK_ARG_(Char, expected, value) \ - { \ - testing::StrictMock<mock_visitor<decltype(expected)>> visitor; \ - EXPECT_CALL(visitor, visit(expected)); \ - using iterator = std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<Char>>; \ - fmt::visit_format_arg( \ - visitor, make_arg<fmt::basic_format_context<iterator, Char>>(value)); \ +#define CHECK_ARG(Char, expected, value) \ + { \ + testing::StrictMock<mock_visitor<decltype(expected)>> visitor; \ + EXPECT_CALL(visitor, visit(expected)); \ + using iterator = std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<Char>>; \ + auto var = value; \ + fmt::visit_format_arg( \ + visitor, \ + fmt::detail::make_arg<fmt::basic_format_context<iterator, Char>>( \ + var)); \ } -#define CHECK_ARG(value, typename_) \ - { \ - using value_type = decltype(value); \ - typename_ visit_type<value_type>::type expected = value; \ - CHECK_ARG_(char, expected, value) \ - CHECK_ARG_(wchar_t, expected, value) \ +#define CHECK_ARG_SIMPLE(value) \ + { \ + using value_type = decltype(value); \ + typename visit_type<value_type>::type expected = value; \ + CHECK_ARG(char, expected, value) \ + CHECK_ARG(wchar_t, expected, value) \ } -template <typename T> class NumericArgTest : public testing::Test {}; +template <typename T> class numeric_arg_test : public testing::Test {}; -using types = - ::testing::Types<bool, signed char, unsigned char, signed, unsigned short, - int, unsigned, long, unsigned long, long long, - unsigned long long, float, double, long double>; -TYPED_TEST_CASE(NumericArgTest, types); +using test_types = + testing::Types<bool, signed char, unsigned char, short, unsigned short, int, + unsigned, long, unsigned long, long long, unsigned long long, + float, double, long double>; +TYPED_TEST_SUITE(numeric_arg_test, test_types); -template <typename T> -fmt::enable_if_t<std::is_integral<T>::value, T> test_value() { +template <typename T, fmt::enable_if_t<std::is_integral<T>::value, int> = 0> +auto test_value() -> T { return static_cast<T>(42); } -template <typename T> -fmt::enable_if_t<std::is_floating_point<T>::value, T> test_value() { +template <typename T, + fmt::enable_if_t<std::is_floating_point<T>::value, int> = 0> +auto test_value() -> T { return static_cast<T>(4.2); } -TYPED_TEST(NumericArgTest, MakeAndVisit) { - CHECK_ARG(test_value<TypeParam>(), typename); - CHECK_ARG(std::numeric_limits<TypeParam>::min(), typename); - CHECK_ARG(std::numeric_limits<TypeParam>::max(), typename); +TYPED_TEST(numeric_arg_test, make_and_visit) { + CHECK_ARG_SIMPLE(test_value<TypeParam>()); + CHECK_ARG_SIMPLE(std::numeric_limits<TypeParam>::min()); + CHECK_ARG_SIMPLE(std::numeric_limits<TypeParam>::max()); } -TEST(ArgTest, CharArg) { - CHECK_ARG_(char, 'a', 'a'); - CHECK_ARG_(wchar_t, L'a', 'a'); - CHECK_ARG_(wchar_t, L'a', L'a'); -} +TEST(arg_test, char_arg) { CHECK_ARG(char, 'a', 'a'); } -TEST(ArgTest, StringArg) { +TEST(arg_test, string_arg) { char str_data[] = "test"; char* str = str_data; const char* cstr = str; - CHECK_ARG_(char, cstr, str); + CHECK_ARG(char, cstr, str); - auto sref = string_view(str); - CHECK_ARG_(char, sref, std::string(str)); + auto sv = fmt::string_view(str); + CHECK_ARG(char, sv, std::string(str)); } -TEST(ArgTest, WStringArg) { +TEST(arg_test, wstring_arg) { wchar_t str_data[] = L"test"; wchar_t* str = str_data; const wchar_t* cstr = str; - fmt::wstring_view sref(str); - CHECK_ARG_(wchar_t, cstr, str); - CHECK_ARG_(wchar_t, cstr, cstr); - CHECK_ARG_(wchar_t, sref, std::wstring(str)); - CHECK_ARG_(wchar_t, sref, fmt::wstring_view(str)); + auto sv = fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t>(str); + CHECK_ARG(wchar_t, cstr, str); + CHECK_ARG(wchar_t, cstr, cstr); + CHECK_ARG(wchar_t, sv, std::wstring(str)); + CHECK_ARG(wchar_t, sv, fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t>(str)); } -TEST(ArgTest, PointerArg) { +TEST(arg_test, pointer_arg) { void* p = nullptr; const void* cp = nullptr; - CHECK_ARG_(char, cp, p); - CHECK_ARG_(wchar_t, cp, p); - CHECK_ARG(cp, ); + CHECK_ARG(char, cp, p); + CHECK_ARG(wchar_t, cp, p); + CHECK_ARG_SIMPLE(cp); } struct check_custom { - test_result operator()( - fmt::basic_format_arg<fmt::format_context>::handle h) const { + auto operator()(fmt::basic_format_arg<fmt::format_context>::handle h) const + -> test_result { struct test_buffer final : fmt::detail::buffer<char> { char data[10]; test_buffer() : fmt::detail::buffer<char>(data, 0, 10) {} - void grow(size_t) {} + void grow(size_t) override {} } buffer; - fmt::format_parse_context parse_ctx(""); - fmt::format_context ctx{fmt::detail::buffer_appender<char>(buffer), - fmt::format_args()}; + auto parse_ctx = fmt::format_parse_context(""); + auto ctx = fmt::format_context(fmt::detail::buffer_appender<char>(buffer), + fmt::format_args()); h.format(parse_ctx, ctx); EXPECT_EQ("test", std::string(buffer.data, buffer.size())); return test_result(); } }; -TEST(ArgTest, CustomArg) { - test_struct test; +TEST(arg_test, custom_arg) { + auto test = test_struct(); using visitor = mock_visitor<fmt::basic_format_arg<fmt::format_context>::handle>; - testing::StrictMock<visitor> v; + auto&& v = testing::StrictMock<visitor>(); EXPECT_CALL(v, visit(_)).WillOnce(Invoke(check_custom())); - fmt::visit_format_arg(v, make_arg<fmt::format_context>(test)); + fmt::visit_format_arg(v, fmt::detail::make_arg<fmt::format_context>(test)); } -TEST(ArgTest, VisitInvalidArg) { - testing::StrictMock<mock_visitor<fmt::monostate>> visitor; +TEST(arg_test, visit_invalid_arg) { + auto&& visitor = testing::StrictMock<mock_visitor<fmt::monostate>>(); EXPECT_CALL(visitor, visit(_)); - fmt::basic_format_arg<fmt::format_context> arg; + auto arg = fmt::basic_format_arg<fmt::format_context>(); fmt::visit_format_arg(visitor, arg); } -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, Basic) { - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - store.push_back(42); - store.push_back("abc1"); - store.push_back(1.5f); - EXPECT_EQ("42 and abc1 and 1.5", fmt::vformat("{} and {} and {}", store)); -} +#if FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, StringsAndRefs) { - // Unfortunately the tests are compiled with old ABI so strings use COW. - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - char str[] = "1234567890"; - store.push_back(str); - store.push_back(std::cref(str)); - store.push_back(fmt::string_view{str}); - str[0] = 'X'; +enum class arg_id_result { none, empty, index, name }; +struct test_arg_id_handler { + arg_id_result res = arg_id_result::none; + int index = 0; + string_view name; - std::string result = fmt::vformat("{} and {} and {}", store); - EXPECT_EQ("1234567890 and X234567890 and X234567890", result); -} - -struct custom_type { - int i = 0; -}; + constexpr void on_auto() { res = arg_id_result::empty; } -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <> struct formatter<custom_type> { - auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return ctx.begin(); + constexpr void on_index(int i) { + res = arg_id_result::index; + index = i; } - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(const custom_type& p, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - return format_to(ctx.out(), "cust={}", p.i); + constexpr void on_name(string_view n) { + res = arg_id_result::name; + name = n; } }; -FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, CustomFormat) { - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - custom_type c{}; - store.push_back(c); - ++c.i; - store.push_back(c); - ++c.i; - store.push_back(std::cref(c)); - ++c.i; - std::string result = fmt::vformat("{} and {} and {}", store); - EXPECT_EQ("cust=0 and cust=1 and cust=3", result); -} - -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, NamedInt) { - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - store.push_back(fmt::arg("a1", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::vformat("{a1}", store)); -} - -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, NamedStrings) { - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - char str[]{"1234567890"}; - store.push_back(fmt::arg("a1", str)); - store.push_back(fmt::arg("a2", std::cref(str))); - str[0] = 'X'; - EXPECT_EQ("1234567890 and X234567890", fmt::vformat("{a1} and {a2}", store)); -} - -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, NamedArgByRef) { - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - - // Note: fmt::arg() constructs an object which holds a reference - // to its value. It's not an aggregate, so it doesn't extend the - // reference lifetime. As a result, it's a very bad idea passing temporary - // as a named argument value. Only GCC with optimization level >0 - // complains about this. - // - // A real life usecase is when you have both name and value alive - // guarantee their lifetime and thus don't want them to be copied into - // storages. - int a1_val{42}; - auto a1 = fmt::arg("a1_", a1_val); - store.push_back("abc"); - store.push_back(1.5f); - store.push_back(std::cref(a1)); - - std::string result = fmt::vformat("{a1_} and {} and {} and {}", store); - EXPECT_EQ("42 and abc and 1.5 and 42", result); -} - -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, NamedCustomFormat) { - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - custom_type c{}; - store.push_back(fmt::arg("c1", c)); - ++c.i; - store.push_back(fmt::arg("c2", c)); - ++c.i; - store.push_back(fmt::arg("c_ref", std::cref(c))); - ++c.i; - std::string result = fmt::vformat("{c1} and {c2} and {c_ref}", store); - EXPECT_EQ("cust=0 and cust=1 and cust=3", result); -} - -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, Clear) { - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - store.push_back(42); - - std::string result = fmt::vformat("{}", store); - EXPECT_EQ("42", result); - - store.push_back(43); - result = fmt::vformat("{} and {}", store); - EXPECT_EQ("42 and 43", result); - - store.clear(); - store.push_back(44); - result = fmt::vformat("{}", store); - EXPECT_EQ("44", result); -} - -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, Reserve) { - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - store.reserve(2, 1); - store.push_back(1.5f); - store.push_back(fmt::arg("a1", 42)); - std::string result = fmt::vformat("{a1} and {}", store); - EXPECT_EQ("42 and 1.5", result); -} - -struct copy_throwable { - copy_throwable() {} - copy_throwable(const copy_throwable&) { throw "deal with it"; } -}; - -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <> struct formatter<copy_throwable> { - auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return ctx.begin(); - } - auto format(copy_throwable, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - return ctx.out(); - } -}; -FMT_END_NAMESPACE +template <size_t N> +constexpr test_arg_id_handler parse_arg_id(const char (&s)[N]) { + auto h = test_arg_id_handler(); + fmt::detail::parse_arg_id(s, s + N, h); + return h; +} -TEST(FormatDynArgsTest, ThrowOnCopy) { - fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store; - store.push_back(std::string("foo")); - try { - store.push_back(copy_throwable()); - } catch (...) { - } - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::vformat("{}", store), "foo"); +TEST(core_test, constexpr_parse_arg_id) { + static_assert(parse_arg_id(":").res == arg_id_result::empty, ""); + static_assert(parse_arg_id("}").res == arg_id_result::empty, ""); + static_assert(parse_arg_id("42:").res == arg_id_result::index, ""); + static_assert(parse_arg_id("42:").index == 42, ""); + static_assert(parse_arg_id("foo:").res == arg_id_result::name, ""); + static_assert(parse_arg_id("foo:").name.size() == 3, ""); } -TEST(StringViewTest, ValueType) { - static_assert(std::is_same<string_view::value_type, char>::value, ""); +template <size_t N> constexpr auto parse_test_specs(const char (&s)[N]) { + auto ctx = fmt::detail::compile_parse_context<char>(fmt::string_view(s, N), + 43, nullptr); + auto specs = fmt::detail::dynamic_format_specs<>(); + fmt::detail::parse_format_specs(s, s + N - 1, specs, ctx, + fmt::detail::type::float_type); + return specs; } -TEST(StringViewTest, Length) { - // Test that string_view::size() returns string length, not buffer size. - char str[100] = "some string"; - EXPECT_EQ(std::strlen(str), string_view(str).size()); - EXPECT_LT(std::strlen(str), sizeof(str)); +TEST(core_test, constexpr_parse_format_specs) { + static_assert(parse_test_specs("<").align == fmt::align::left, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs("*^").fill[0] == '*', ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs("+").sign == fmt::sign::plus, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs("-").sign == fmt::sign::minus, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs(" ").sign == fmt::sign::space, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs("#").alt, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs("0").align == fmt::align::numeric, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs("L").localized, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs("42").width == 42, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs("{42}").width_ref.val.index == 42, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs(".42").precision == 42, ""); + static_assert(parse_test_specs(".{42}").precision_ref.val.index == 42, ""); + static_assert( + parse_test_specs("f").type == fmt::presentation_type::fixed_lower, ""); } -// Check string_view's comparison operator. -template <template <typename> class Op> void check_op() { - const char* inputs[] = {"foo", "fop", "fo"}; - size_t num_inputs = sizeof(inputs) / sizeof(*inputs); - for (size_t i = 0; i < num_inputs; ++i) { - for (size_t j = 0; j < num_inputs; ++j) { - string_view lhs(inputs[i]), rhs(inputs[j]); - EXPECT_EQ(Op<int>()(lhs.compare(rhs), 0), Op<string_view>()(lhs, rhs)); - } +struct test_format_string_handler { + constexpr void on_text(const char*, const char*) {} + + constexpr auto on_arg_id() -> int { return 0; } + + template <typename T> constexpr auto on_arg_id(T) -> int { return 0; } + + constexpr void on_replacement_field(int, const char*) {} + + constexpr auto on_format_specs(int, const char* begin, const char*) -> const + char* { + return begin; } + + constexpr void on_error(const char*) { error = true; } + + bool error = false; +}; + +template <size_t N> constexpr bool parse_string(const char (&s)[N]) { + auto h = test_format_string_handler(); + fmt::detail::parse_format_string<true>(fmt::string_view(s, N - 1), h); + return !h.error; } -TEST(StringViewTest, Compare) { - EXPECT_EQ(string_view("foo").compare(string_view("foo")), 0); - EXPECT_GT(string_view("fop").compare(string_view("foo")), 0); - EXPECT_LT(string_view("foo").compare(string_view("fop")), 0); - EXPECT_GT(string_view("foo").compare(string_view("fo")), 0); - EXPECT_LT(string_view("fo").compare(string_view("foo")), 0); - check_op<std::equal_to>(); - check_op<std::not_equal_to>(); - check_op<std::less>(); - check_op<std::less_equal>(); - check_op<std::greater>(); - check_op<std::greater_equal>(); +TEST(core_test, constexpr_parse_format_string) { + static_assert(parse_string("foo"), ""); + static_assert(!parse_string("}"), ""); + static_assert(parse_string("{}"), ""); + static_assert(parse_string("{42}"), ""); + static_assert(parse_string("{foo}"), ""); + static_assert(parse_string("{:}"), ""); } +#endif // FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR struct enabled_formatter {}; +struct enabled_ptr_formatter {}; struct disabled_formatter {}; struct disabled_formatter_convertible { operator int() const { return 42; } @@ -596,16 +573,27 @@ struct disabled_formatter_convertible { FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE template <> struct formatter<enabled_formatter> { - auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + auto format(enabled_formatter, format_context& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return ctx.out(); + } +}; + +template <> struct formatter<enabled_ptr_formatter*> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { return ctx.begin(); } - auto format(enabled_formatter, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto format(enabled_ptr_formatter*, format_context& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { return ctx.out(); } }; FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(CoreTest, HasFormatter) { +TEST(core_test, has_formatter) { using fmt::has_formatter; using context = fmt::format_context; static_assert(has_formatter<enabled_formatter, context>::value, ""); @@ -614,139 +602,187 @@ TEST(CoreTest, HasFormatter) { ""); } -struct convertible_to_int { - operator int() const { return 42; } -}; - -struct convertible_to_c_string { - operator const char*() const { return "foo"; } -}; +struct const_formattable {}; +struct nonconst_formattable {}; FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <> struct formatter<convertible_to_int> { - auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { +template <> struct formatter<const_formattable> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { return ctx.begin(); } - auto format(convertible_to_int, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - return std::copy_n("foo", 3, ctx.out()); + + auto format(const const_formattable&, format_context& ctx) + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto test = string_view("test"); + return std::copy_n(test.data(), test.size(), ctx.out()); } }; -template <> struct formatter<convertible_to_c_string> { - auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { +template <> struct formatter<nonconst_formattable> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { return ctx.begin(); } - auto format(convertible_to_c_string, format_context& ctx) + + auto format(nonconst_formattable&, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - return std::copy_n("bar", 3, ctx.out()); + auto test = string_view("test"); + return std::copy_n(test.data(), test.size(), ctx.out()); } }; FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(CoreTest, FormatterOverridesImplicitConversion) { - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", convertible_to_int()), "foo"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", convertible_to_c_string()), "bar"); -} +struct convertible_to_pointer { + operator const int*() const { return nullptr; } +}; -namespace my_ns { -template <typename Char> class my_string { - private: - std::basic_string<Char> s_; +struct convertible_to_pointer_formattable { + operator const int*() const { return nullptr; } +}; - public: - my_string(const Char* s) : s_(s) {} - const Char* data() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return s_.data(); } - size_t length() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return s_.size(); } - operator const Char*() const { return s_.c_str(); } +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<convertible_to_pointer_formattable> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + auto format(convertible_to_pointer_formattable, format_context& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto test = string_view("test"); + return std::copy_n(test.data(), test.size(), ctx.out()); + } }; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE -template <typename Char> -inline fmt::basic_string_view<Char> to_string_view(const my_string<Char>& s) - FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return {s.data(), s.length()}; -} +enum class unformattable_scoped_enum {}; -struct non_string {}; -} // namespace my_ns +TEST(core_test, is_formattable) { + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<wchar_t>::value, ""); +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<char8_t>::value, ""); +#endif + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<char16_t>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<char32_t>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<signed char*>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<unsigned char*>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<const signed char*>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<const unsigned char*>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<const wchar_t*>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<const wchar_t[3]>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t>>::value, + ""); + static_assert(fmt::is_formattable<enabled_formatter>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<enabled_ptr_formatter*>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<disabled_formatter>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<disabled_formatter_convertible>::value, + ""); -template <typename T> class IsStringTest : public testing::Test {}; + static_assert(fmt::is_formattable<const_formattable&>::value, ""); + static_assert(fmt::is_formattable<const const_formattable&>::value, ""); -typedef ::testing::Types<char, wchar_t, char16_t, char32_t> StringCharTypes; -TYPED_TEST_CASE(IsStringTest, StringCharTypes); + static_assert(fmt::is_formattable<nonconst_formattable&>::value, ""); +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1910 + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<const nonconst_formattable&>::value, ""); +#endif -namespace { -template <typename Char> -struct derived_from_string_view : fmt::basic_string_view<Char> {}; -} // namespace + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<convertible_to_pointer>::value, ""); + const auto f = convertible_to_pointer_formattable(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", f), "test"); -TYPED_TEST(IsStringTest, IsString) { - EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<TypeParam*>::value); - EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<const TypeParam*>::value); - EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<TypeParam[2]>::value); - EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<const TypeParam[2]>::value); - EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<std::basic_string<TypeParam>>::value); - EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<fmt::basic_string_view<TypeParam>>::value); - EXPECT_TRUE( - fmt::detail::is_string<derived_from_string_view<TypeParam>>::value); - using string_view = fmt::detail::std_string_view<TypeParam>; - EXPECT_TRUE(std::is_empty<string_view>::value != - fmt::detail::is_string<string_view>::value); - EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<my_ns::my_string<TypeParam>>::value); - EXPECT_FALSE(fmt::detail::is_string<my_ns::non_string>::value); -} + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<void (*)()>::value, ""); -TEST(CoreTest, Format) { - // This should work without including fmt/format.h. -#ifdef FMT_FORMAT_H_ -# error fmt/format.h must not be included in the core test -#endif - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", 42), "42"); + struct s; + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<int(s::*)>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<int (s::*)()>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<unformattable_scoped_enum>::value, ""); + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<unformattable_scoped_enum>::value, ""); } -TEST(CoreTest, FormatTo) { - // This should work without including fmt/format.h. -#ifdef FMT_FORMAT_H_ -# error fmt/format.h must not be included in the core test -#endif - std::string s; +TEST(core_test, format) { EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", 42), "42"); } + +TEST(core_test, format_to) { + auto s = std::string(); fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), "{}", 42); EXPECT_EQ(s, "42"); } -TEST(CoreTest, ToStringViewForeignStrings) { - using namespace my_ns; - EXPECT_EQ(to_string_view(my_string<char>("42")), "42"); - fmt::detail::type type = - fmt::detail::mapped_type_constant<my_string<char>, - fmt::format_context>::value; - EXPECT_EQ(type, fmt::detail::type::string_type); +#ifdef __cpp_lib_byte +TEST(core_test, format_byte) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::byte(42)), "42"); } +#endif -TEST(CoreTest, FormatForeignStrings) { - using namespace my_ns; - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(my_string<char>("{}"), 42), "42"); -} +struct convertible_to_int { + operator int() const { return 42; } +}; + +struct convertible_to_cstring { + operator const char*() const { return "foo"; } +}; -struct implicitly_convertible_to_string { - operator std::string() const { return "foo"; } +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<convertible_to_int> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + auto format(convertible_to_int, format_context& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return std::copy_n("foo", 3, ctx.out()); + } +}; + +template <> struct formatter<convertible_to_cstring> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + auto format(convertible_to_cstring, format_context& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return std::copy_n("bar", 3, ctx.out()); + } }; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(core_test, formatter_overrides_implicit_conversion) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", convertible_to_int()), "foo"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", convertible_to_cstring()), "bar"); +} + +// Test that check is not found by ADL. +template <typename T> void check(T); +TEST(core_test, adl_check) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", test_struct()), "test"); +} struct implicitly_convertible_to_string_view { operator fmt::string_view() const { return "foo"; } }; -TEST(CoreTest, FormatImplicitlyConvertibleToStringView) { - EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format("{}", implicitly_convertible_to_string_view())); +TEST(core_test, no_implicit_conversion_to_string_view) { + EXPECT_FALSE( + fmt::is_formattable<implicitly_convertible_to_string_view>::value); +} + +#ifdef FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW +struct implicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view { + operator std::string_view() const { return "foo"; } +}; + +TEST(core_test, no_implicit_conversion_to_std_string_view) { + EXPECT_FALSE( + fmt::is_formattable<implicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view>::value); } +#endif // std::is_constructible is broken in MSVC until version 2015. -#if !FMT_MSC_VER || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1900 +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1900 struct explicitly_convertible_to_string_view { explicit operator fmt::string_view() const { return "foo"; } }; -TEST(CoreTest, FormatExplicitlyConvertibleToStringView) { - EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format("{}", explicitly_convertible_to_string_view())); +TEST(core_test, format_explicitly_convertible_to_string_view) { + // Types explicitly convertible to string_view are not formattable by + // default because it may introduce ODR violations. + static_assert( + !fmt::is_formattable<explicitly_convertible_to_string_view>::value, ""); } # ifdef FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW @@ -754,20 +790,69 @@ struct explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view { explicit operator std::string_view() const { return "foo"; } }; -TEST(CoreTest, FormatExplicitlyConvertibleToStdStringView) { - EXPECT_EQ("foo", - fmt::format("{}", explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view())); +TEST(core_test, format_explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view) { + // Types explicitly convertible to string_view are not formattable by + // default because it may introduce ODR violations. + static_assert( + !fmt::is_formattable<explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view>::value, + ""); } # endif #endif -struct disabled_rvalue_conversion { - operator const char*() const& { return "foo"; } - operator const char*() & { return "foo"; } - operator const char*() const&& = delete; - operator const char*() && = delete; +namespace adl_test { +template <typename... T> void make_format_args(const T&...) = delete; + +struct string : std::string {}; +} // namespace adl_test + +// Test that formatting functions compile when make_format_args is found by ADL. +TEST(core_test, adl) { + // Only check compilation and don't run the code to avoid polluting the output + // and since the output is tested elsewhere. + if (fmt::detail::const_check(true)) return; + auto s = adl_test::string(); + char buf[10]; + (void)fmt::format("{}", s); + fmt::format_to(buf, "{}", s); + fmt::format_to_n(buf, 10, "{}", s); + (void)fmt::formatted_size("{}", s); + fmt::print("{}", s); + fmt::print(stdout, "{}", s); +} + +TEST(core_test, has_const_formatter) { + EXPECT_TRUE((fmt::detail::has_const_formatter<const_formattable, + fmt::format_context>())); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::has_const_formatter<nonconst_formattable, + fmt::format_context>())); +} + +TEST(core_test, format_nonconst) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", nonconst_formattable()), "test"); +} + +struct its_a_trap { + template <typename T> operator T() const { + auto v = T(); + v.x = 42; + return v; + } +}; + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<its_a_trap> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); + } + + auto format(its_a_trap, format_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto s = string_view("42"); + return std::copy(s.begin(), s.end(), ctx.out()); + } }; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(CoreTest, DisabledRValueConversion) { - EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format("{}", disabled_rvalue_conversion())); +TEST(core_test, trappy_conversion) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", its_a_trap()), "42"); } diff --git a/test/detect-stdfs.cc b/test/detect-stdfs.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..2dc66538 --- /dev/null +++ b/test/detect-stdfs.cc @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - tests of formatters for standard library types +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#include <exception> // _GLIBCXX_RELEASE & _LIBCPP_VERSION + +#if defined(_GLIBCXX_RELEASE) && _GLIBCXX_RELEASE == 8 +# error libfound "stdc++fs" +#elif !defined(__apple_build_version__) && defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION) && \ + _LIBCPP_VERSION >= 7000 && _LIBCPP_VERSION < 9000 +# error libfound "c++fs" +#else +// none if std::filesystem does not require additional libraries +# error libfound "" +#endif diff --git a/test/enforce-checks-test.cc b/test/enforce-checks-test.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..960a7fcd --- /dev/null +++ b/test/enforce-checks-test.cc @@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - formatting library tests +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#include <iterator> +#include <vector> + +#define I 42 // simulate https://en.cppreference.com/w/c/numeric/complex/I +#include "fmt/chrono.h" +#include "fmt/color.h" +#include "fmt/format.h" +#include "fmt/ostream.h" +#include "fmt/ranges.h" +#include "fmt/xchar.h" +#undef I + +// Exercise the API to verify that everything we expect to can compile. +void test_format_api() { + (void)fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), 42); + (void)fmt::format(FMT_STRING(L"{}"), 42); + (void)fmt::format(FMT_STRING("noop")); + + (void)fmt::to_string(42); + (void)fmt::to_wstring(42); + + std::vector<char> out; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), FMT_STRING("{}"), 42); + + char buffer[4]; + fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, FMT_STRING("{}"), 12345); + + wchar_t wbuffer[4]; + fmt::format_to_n(wbuffer, 3, FMT_STRING(L"{}"), 12345); +} + +void test_chrono() { + (void)fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), std::chrono::seconds(42)); + (void)fmt::format(FMT_STRING(L"{}"), std::chrono::seconds(42)); +} + +void test_text_style() { + fmt::print(fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)), FMT_STRING("{}"), "rgb(255,20,30)"); + (void)fmt::format(fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)), FMT_STRING("{}"), + "rgb(255,20,30)"); + + fmt::text_style ts = fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)); + std::string out; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), ts, + FMT_STRING("rgb(255,20,30){}{}{}"), 1, 2, 3); +} + +void test_range() { + std::vector<char> hello = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}; + (void)fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), hello); +} + +int main() { + test_format_api(); + test_chrono(); + test_text_style(); + test_range(); +} diff --git a/test/find-package-test/CMakeLists.txt b/test/find-package-test/CMakeLists.txt index 93d686e6..eb2ea25f 100644 --- a/test/find-package-test/CMakeLists.txt +++ b/test/find-package-test/CMakeLists.txt @@ -1,4 +1,4 @@ -cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.1...3.18) +cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8...3.25) project(fmt-test) diff --git a/test/find-package-test/main.cc b/test/find-package-test/main.cc index f39f377c..911e0e8d 100644 --- a/test/find-package-test/main.cc +++ b/test/find-package-test/main.cc @@ -1,6 +1,5 @@ #include "fmt/format.h" int main(int argc, char** argv) { - for(int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) - fmt::print("{}: {}\n", i, argv[i]); + for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) fmt::print("{}: {}\n", i, argv[i]); } diff --git a/test/format b/test/format deleted file mode 100644 index 76ac5476..00000000 --- a/test/format +++ /dev/null @@ -1,855 +0,0 @@ -// Formatting library for C++ - the standard API implementation -// -// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich -// All rights reserved. -// -// For the license information refer to format.h. - -#ifndef FMT_FORMAT_ -#define FMT_FORMAT_ - -#include <cassert> -#include <variant> -#include "fmt/format.h" - -// This implementation verifies the correctness of the standard API proposed in -// P0645 Text Formatting and is optimized for copy-pasting from the paper, not -// for efficiency or readability. An efficient implementation should not use -// std::variant and should store packed argument type tags separately from -// values in basic_format_args for small number of arguments. - -namespace std { -template<class T> -constexpr bool Integral = is_integral_v<T>; - -template <class O> - using iter_difference_t = ptrdiff_t; -} - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.syn -namespace std { - // [format.error], class format_error - class format_error; - - // [format.formatter], formatter - template<class charT> class basic_format_parse_context; - using format_parse_context = basic_format_parse_context<char>; - using wformat_parse_context = basic_format_parse_context<wchar_t>; - - template<class Out, class charT> class basic_format_context; - using format_context = basic_format_context< - /* unspecified */ fmt::detail::buffer_appender<char>, char>; - using wformat_context = basic_format_context< - /* unspecified */ fmt::detail::buffer_appender<wchar_t>, wchar_t>; - - template<class T, class charT = char> struct formatter { - formatter() = delete; - }; - - // [format.arguments], arguments - template<class Context> class basic_format_arg; - - template<class Visitor, class Context> - /* see below */ auto visit_format_arg(Visitor&& vis, basic_format_arg<Context> arg); - - template<class Context, class... Args> struct format_arg_store; // exposition only - - template<class Context> class basic_format_args; - using format_args = basic_format_args<format_context>; - using wformat_args = basic_format_args<wformat_context>; - - template<class Out, class charT> - using format_args_t = basic_format_args<basic_format_context<Out, charT>>; - - template<class Context = format_context, class... Args> - format_arg_store<Context, Args...> - make_format_args(const Args&... args); - template<class... Args> - format_arg_store<wformat_context, Args...> - make_wformat_args(const Args&... args); - - // [format.functions], formatting functions - template<class... Args> - string format(string_view fmt, const Args&... args); - template<class... Args> - wstring format(wstring_view fmt, const Args&... args); - - string vformat(string_view fmt, format_args args); - wstring vformat(wstring_view fmt, wformat_args args); - - template<class Out, class... Args> - Out format_to(Out out, string_view fmt, const Args&... args); - template<class Out, class... Args> - Out format_to(Out out, wstring_view fmt, const Args&... args); - - template<class Out> - Out vformat_to(Out out, string_view fmt, format_args_t<fmt::type_identity_t<Out>, char> args); - template<class Out> - Out vformat_to(Out out, wstring_view fmt, format_args_t<fmt::type_identity_t<Out>, wchar_t> args); - - template<class Out> - struct format_to_n_result { - Out out; - iter_difference_t<Out> size; - }; - - template<class Out, class... Args> - format_to_n_result<Out> format_to_n(Out out, iter_difference_t<Out> n, - string_view fmt, const Args&... args); - template<class Out, class... Args> - format_to_n_result<Out> format_to_n(Out out, iter_difference_t<Out> n, - wstring_view fmt, const Args&... args); - - template<class... Args> - size_t formatted_size(string_view fmt, const Args&... args); - template<class... Args> - size_t formatted_size(wstring_view fmt, const Args&... args); -} - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.error -namespace std { - class format_error : public runtime_error { - public: - explicit format_error(const string& what_arg) : runtime_error(what_arg) {} - explicit format_error(const char* what_arg) : runtime_error(what_arg) {} - }; -} - -namespace std { -namespace detail { -struct error_handler { - // This function is intentionally not constexpr to give a compile-time error. - void on_error(const char* message) { - throw std::format_error(message); - } -}; -} -} - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.parse_context -namespace std { - template<class charT> - class basic_format_parse_context { - public: - using char_type = charT; - using const_iterator = typename basic_string_view<charT>::const_iterator; - using iterator = const_iterator; - - private: - iterator begin_; // exposition only - iterator end_; // exposition only - enum indexing { unknown, manual, automatic }; // exposition only - indexing indexing_; // exposition only - size_t next_arg_id_; // exposition only - size_t num_args_; // exposition only - - public: - explicit constexpr basic_format_parse_context(basic_string_view<charT> fmt, - size_t num_args = 0) noexcept; - basic_format_parse_context(const basic_format_parse_context&) = delete; - basic_format_parse_context& operator=(const basic_format_parse_context&) = delete; - - constexpr const_iterator begin() const noexcept; - constexpr const_iterator end() const noexcept; - constexpr void advance_to(const_iterator it); - - constexpr size_t next_arg_id(); - constexpr void check_arg_id(size_t id); - - // Implementation detail: - constexpr void check_arg_id(fmt::string_view) {} - detail::error_handler error_handler() const { return {}; } - void on_error(const char* msg) { error_handler().on_error(msg); } - }; -} - -namespace std { -template<class charT> -/* explicit */ constexpr basic_format_parse_context<charT>:: - basic_format_parse_context(basic_string_view<charT> fmt, - size_t num_args) noexcept -: begin_(fmt.begin()), end_(fmt.end()), indexing_(unknown), next_arg_id_(0), num_args_(num_args) {} - -template<class charT> -constexpr typename basic_format_parse_context<charT>::const_iterator basic_format_parse_context<charT>::begin() const noexcept { return begin_; } - -template<class charT> -constexpr typename basic_format_parse_context<charT>::const_iterator basic_format_parse_context<charT>::end() const noexcept { return end_; } - -template<class charT> -constexpr void basic_format_parse_context<charT>::advance_to(typename basic_format_parse_context<charT>::iterator it) { begin_ = it; } - -template<class charT> -constexpr size_t basic_format_parse_context<charT>::next_arg_id() { - if (indexing_ == manual) - throw format_error("manual to automatic indexing"); - if (indexing_ == unknown) - indexing_ = automatic; - return next_arg_id_++; -} - -template<class charT> -constexpr void basic_format_parse_context<charT>::check_arg_id(size_t id) { - // clang doesn't support __builtin_is_constant_evaluated yet - //if (!(!__builtin_is_constant_evaluated() || id < num_args_)) - // throw format_error(invalid index is out of range"); - if (indexing_ == automatic) - throw format_error("automatic to manual indexing"); - if (indexing_ == unknown) - indexing_ = manual; -} -} - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.context -namespace std { - template<class Out, class charT> - class basic_format_context { - basic_format_args<basic_format_context> args_; // exposition only - Out out_; // exposition only - - public: - using iterator = Out; - using char_type = charT; - template<class T> using formatter_type = formatter<T, charT>; - - basic_format_arg<basic_format_context> arg(size_t id) const; - - iterator out(); - void advance_to(iterator it); - - // Implementation details: - using format_arg = basic_format_arg<basic_format_context>; - basic_format_context(Out out, basic_format_args<basic_format_context> args, fmt::detail::locale_ref) - : args_(args), out_(out) {} - detail::error_handler error_handler() const { return {}; } - basic_format_arg<basic_format_context> arg(fmt::basic_string_view<charT>) const { - return {}; // unused: named arguments are not supported yet - } - void on_error(const char* msg) { error_handler().on_error(msg); } - }; -} - -namespace std { -template<class O, class charT> -basic_format_arg<basic_format_context<O, charT>> basic_format_context<O, charT>::arg(size_t id) const { return args_.get(id); } - -template<class O, class charT> -typename basic_format_context<O, charT>::iterator basic_format_context<O, charT>::out() { return out_; } - -template<class O, class charT> -void basic_format_context<O, charT>::advance_to(typename basic_format_context<O, charT>::iterator it) { out_ = it; } -} - -namespace std { -namespace detail { -template <typename T> -constexpr bool is_standard_integer_v = - std::is_same_v<T, signed char> || - std::is_same_v<T, short int> || - std::is_same_v<T, int> || - std::is_same_v<T, long int> || - std::is_same_v<T, long long int>; - -template <typename T> -constexpr bool is_standard_unsigned_integer_v = - std::is_same_v<T, unsigned char> || - std::is_same_v<T, unsigned short int> || - std::is_same_v<T, unsigned int> || - std::is_same_v<T, unsigned long int> || - std::is_same_v<T, unsigned long long int>; - -template <typename T, typename Char> struct formatter; -} -} - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.arg -namespace std { - template<class Context> - class basic_format_arg { - public: - class handle; - - private: - using char_type = typename Context::char_type; // exposition only - - variant<monostate, bool, char_type, - int, unsigned int, long long int, unsigned long long int, - double, long double, - const char_type*, basic_string_view<char_type>, - const void*, handle> value; // exposition only - - template<typename T, - typename = enable_if_t< - std::is_same_v<T, bool> || - std::is_same_v<T, char_type> || - (std::is_same_v<T, char> && std::is_same_v<char_type, wchar_t>) || - detail::is_standard_integer_v<T> || - detail::is_standard_unsigned_integer_v<T> || - sizeof(typename Context::template formatter_type<T>().format(declval<const T&>(), declval<Context&>())) != 0 - >> explicit basic_format_arg(const T& v) noexcept; // exposition only - explicit basic_format_arg(float n) noexcept; // exposition only - explicit basic_format_arg(double n) noexcept; // exposition only - explicit basic_format_arg(long double n) noexcept; // exposition only - explicit basic_format_arg(const char_type* s); // exposition only - - template<class traits> - explicit basic_format_arg( - basic_string_view<char_type, traits> s) noexcept; // exposition only - - template<class traits, class Allocator> - explicit basic_format_arg( - const basic_string<char_type, traits, Allocator>& s) noexcept; // exposition only - - explicit basic_format_arg(nullptr_t) noexcept; // exposition only - - template<class T, typename = enable_if_t<is_void_v<T>>> - explicit basic_format_arg(const T* p) noexcept; // exposition only - - // Fails due to a bug in clang - //template<class Visitor, class Ctx> - // friend auto visit_format_arg(Visitor&& vis, - // basic_format_arg<Ctx> arg); // exposition only - - friend auto get_value(basic_format_arg arg) { - return arg.value; - } - - template <typename T, typename Char> friend struct detail::formatter; - - template<class Ctx, class... Args> - friend format_arg_store<Ctx, Args...> - make_format_args(const Args&... args); // exposition only - - public: - basic_format_arg() noexcept; - - explicit operator bool() const noexcept; - }; -} - -namespace std { -template<class Context> -basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg() noexcept {} - -template<class Context> -template<class T, typename> /* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg(const T& v) noexcept { - if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, bool> || std::is_same_v<T, char_type>) - value = v; - else if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, char> && std::is_same_v<char_type, wchar_t>) - value = static_cast<wchar_t>(v); - else if constexpr (detail::is_standard_integer_v<T> && sizeof(T) <= sizeof(int)) - value = static_cast<int>(v); - else if constexpr (detail::is_standard_unsigned_integer_v<T> && sizeof(T) <= sizeof(unsigned)) - value = static_cast<unsigned>(v); - else if constexpr (detail::is_standard_integer_v<T>) - value = static_cast<long long int>(v); - else if constexpr (detail::is_standard_unsigned_integer_v<T>) - value = static_cast<unsigned long long int>(v); - else if constexpr (sizeof(typename Context::template formatter_type<T>().format(declval<const T&>(), declval<Context&>())) != 0) - value = handle(v); -} - -template<class Context> -/* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg(float n) noexcept - : value(static_cast<double>(n)) {} - -template<class Context> -/* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg(double n) noexcept - : value(n) {} - -template<class Context> -/* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg(long double n) noexcept - : value(n) {} - -template<class Context> -/* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg(const typename basic_format_arg<Context>::char_type* s) - : value(s) { - assert(s != nullptr); -} - -template<class Context> -template<class traits> -/* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg(basic_string_view<char_type, traits> s) noexcept - : value(s) {} - -template<class Context> -template<class traits, class Allocator> -/* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg( - const basic_string<char_type, traits, Allocator>& s) noexcept - : value(basic_string_view<char_type>(s.data(), s.size())) {} - - -template<class Context> -/* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg(nullptr_t) noexcept - : value(static_cast<const void*>(nullptr)) {} - -template<class Context> -template<class T, typename> /* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::basic_format_arg(const T* p) noexcept - : value(p) {} - -template<class Context> -/* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::operator bool() const noexcept { - return !holds_alternative<monostate>(value); -} -} - -namespace std { - template<class Context> - class basic_format_arg<Context>::handle { - const void* ptr_; // exposition only - void (*format_)(basic_format_parse_context<char_type>&, - Context&, const void*); // exposition only - - template<class T> explicit handle(const T& val) noexcept; // exposition only - - friend class basic_format_arg<Context>; // exposition only - - public: - void format(basic_format_parse_context<char_type>&, Context& ctx) const; - }; -} - -namespace std { -template<class Context> -template<class T> /* explicit */ basic_format_arg<Context>::handle::handle(const T& val) noexcept - : ptr_(&val), format_([](basic_format_parse_context<char_type>& parse_ctx, Context& format_ctx, const void* ptr) { - typename Context::template formatter_type<T> f; - parse_ctx.advance_to(f.parse(parse_ctx)); - format_ctx.advance_to(f.format(*static_cast<const T*>(ptr), format_ctx)); - }) {} - -template<class Context> -void basic_format_arg<Context>::handle::format(basic_format_parse_context<char_type>& parse_ctx, Context& format_ctx) const { - format_(parse_ctx, format_ctx, ptr_); -} - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.visit -template<class Visitor, class Context> - auto visit_format_arg(Visitor&& vis, basic_format_arg<Context> arg) { - return visit(vis, get_value(arg)); - } -} - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.store -namespace std { - template<class Context, class... Args> - struct format_arg_store { // exposition only - array<basic_format_arg<Context>, sizeof...(Args)> args; - }; -} - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.basic_args -namespace std { - template<class Context> - class basic_format_args { - size_t size_; // exposition only - const basic_format_arg<Context>* data_; // exposition only - - public: - basic_format_args() noexcept; - - template<class... Args> - basic_format_args(const format_arg_store<Context, Args...>& store) noexcept; - - basic_format_arg<Context> get(size_t i) const noexcept; - }; -} - -namespace std { - -template<class Context> -basic_format_args<Context>::basic_format_args() noexcept : size_(0) {} - -template<class Context> -template<class... Args> - basic_format_args<Context>::basic_format_args(const format_arg_store<Context, Args...>& store) noexcept - : size_(sizeof...(Args)), data_(store.args.data()) {} - -template<class Context> -basic_format_arg<Context> basic_format_args<Context>::get(size_t i) const noexcept { - return i < size_ ? data_[i] : basic_format_arg<Context>(); -} -} - -namespace std { -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.make_args -template<class Context /*= format_context*/, class... Args> - format_arg_store<Context, Args...> make_format_args(const Args&... args) { - return {basic_format_arg<Context>(args)...}; - } - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.make_wargs -template<class... Args> - format_arg_store<wformat_context, Args...> make_wformat_args(const Args&... args) { - return make_format_args<wformat_context>(args...); - } -} - -namespace std { -namespace detail { - -template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> -class arg_formatter - : public fmt::detail::arg_formatter_base<OutputIt, Char, error_handler> { - private: - using char_type = Char; - using base = fmt::detail::arg_formatter_base<OutputIt, Char, error_handler>; - using format_context = std::basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>; - using parse_context = basic_format_parse_context<Char>; - - parse_context* parse_ctx_; - format_context& ctx_; - - public: - using iterator = OutputIt; - using format_specs = typename base::format_specs; - - /** - \rst - Constructs an argument formatter object. - *ctx* is a reference to the formatting context, - *spec* contains format specifier information for standard argument types. - \endrst - */ - arg_formatter(format_context& ctx, parse_context* parse_ctx = nullptr, fmt::format_specs* spec = nullptr) - : base(ctx.out(), spec, {}), parse_ctx_(parse_ctx), ctx_(ctx) {} - - using base::operator(); - - /** Formats an argument of a user-defined type. */ - iterator operator()(typename std::basic_format_arg<format_context>::handle handle) { - handle.format(*parse_ctx_, ctx_); - return this->out(); - } - - iterator operator()(monostate) { - throw format_error(""); - } -}; - -template <typename Context> -inline fmt::detail::type get_type(basic_format_arg<Context> arg) { - return visit_format_arg([&] (auto val) { - using char_type = typename Context::char_type; - using T = decltype(val); - if (std::is_same_v<T, monostate>) - return fmt::detail::type::none_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, bool>) - return fmt::detail::type::bool_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, char_type>) - return fmt::detail::type::char_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, int>) - return fmt::detail::type::int_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, unsigned int>) - return fmt::detail::type::uint_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, long long int>) - return fmt::detail::type::long_long_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, unsigned long long int>) - return fmt::detail::type::ulong_long_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, double>) - return fmt::detail::type::double_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, long double>) - return fmt::detail::type::long_double_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, const char_type*>) - return fmt::detail::type::cstring_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, basic_string_view<char_type>>) - return fmt::detail::type::string_type; - if (std::is_same_v<T, const void*>) - return fmt::detail::type::pointer_type; - assert(get_value(arg).index() == 12); - return fmt::detail::type::custom_type; - }, arg); -} - -template <typename Context> -class custom_formatter { - private: - using parse_context = basic_format_parse_context<typename Context::char_type>; - parse_context& parse_ctx_; - Context& format_ctx_; - - public: - custom_formatter(parse_context& parse_ctx, Context& ctx) : parse_ctx_(parse_ctx), format_ctx_(ctx) {} - - bool operator()(typename basic_format_arg<Context>::handle h) const { - h.format(parse_ctx_, format_ctx_); - return true; - } - - template <typename T> bool operator()(T) const { return false; } -}; - -template <typename ArgFormatter, typename Char, typename Context> -struct format_handler : detail::error_handler { - using iterator = typename ArgFormatter::iterator; - - format_handler(iterator out, basic_string_view<Char> str, - basic_format_args<Context> format_args, - fmt::detail::locale_ref loc) - : parse_ctx(str), context(out, format_args, loc) {} - - void on_text(const Char* begin, const Char* end) { - auto size = fmt::detail::to_unsigned(end - begin); - auto out = context.out(); - auto&& it = fmt::detail::reserve(out, size); - it = std::copy_n(begin, size, it); - context.advance_to(out); - } - - int on_arg_id() { return parse_ctx.next_arg_id(); } - int on_arg_id(unsigned id) { return parse_ctx.check_arg_id(id), id; } - int on_arg_id(fmt::basic_string_view<Char>) { return 0; } - - void on_replacement_field(int id, const Char* p) { - auto arg = context.arg(id); - parse_ctx.advance_to(parse_ctx.begin() + (p - &*parse_ctx.begin())); - custom_formatter<Context> f(parse_ctx, context); - if (!visit_format_arg(f, arg)) - context.advance_to(visit_format_arg(ArgFormatter(context, &parse_ctx), arg)); - } - - const Char* on_format_specs(int id, const Char* begin, const Char* end) { - auto arg = context.arg(id); - parse_ctx.advance_to(parse_ctx.begin() + (begin - &*parse_ctx.begin())); - custom_formatter<Context> f(parse_ctx, context); - if (visit_format_arg(f, arg)) return &*parse_ctx.begin(); - fmt::basic_format_specs<Char> specs; - using fmt::detail::specs_handler; - using parse_context = basic_format_parse_context<Char>; - fmt::detail::specs_checker<specs_handler<parse_context, Context>> handler( - specs_handler<parse_context, Context>(specs, parse_ctx, context), get_type(arg)); - begin = parse_format_specs(begin, end, handler); - if (begin == end || *begin != '}') on_error("missing '}' in format string"); - parse_ctx.advance_to(parse_ctx.begin() + (begin - &*parse_ctx.begin())); - context.advance_to(visit_format_arg(ArgFormatter(context, &parse_ctx, &specs), arg)); - return begin; - } - - basic_format_parse_context<Char> parse_ctx; - Context context; -}; - -template <typename T, typename Char> -struct formatter { - // Parses format specifiers stopping either at the end of the range or at the - // terminating '}'. - template <typename ParseContext> - FMT_CONSTEXPR typename ParseContext::iterator parse(ParseContext& ctx) { - namespace detail = fmt::detail; - typedef detail::dynamic_specs_handler<ParseContext> handler_type; - auto type = detail::mapped_type_constant<T, fmt::buffer_context<Char>>::value; - detail::specs_checker<handler_type> handler(handler_type(specs_, ctx), - type); - auto it = parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), handler); - auto type_spec = specs_.type; - auto eh = ctx.error_handler(); - switch (type) { - case detail::type::none_type: - FMT_ASSERT(false, "invalid argument type"); - break; - case detail::type::int_type: - case detail::type::uint_type: - case detail::type::long_long_type: - case detail::type::ulong_long_type: - case detail::type::bool_type: - handle_int_type_spec(type_spec, - detail::int_type_checker<decltype(eh)>(eh)); - break; - case detail::type::char_type: - handle_char_specs( - &specs_, detail::char_specs_checker<decltype(eh)>(type_spec, eh)); - break; - case detail::type::double_type: - case detail::type::long_double_type: - detail::parse_float_type_spec(specs_, eh); - break; - case detail::type::cstring_type: - detail::handle_cstring_type_spec( - type_spec, detail::cstring_type_checker<decltype(eh)>(eh)); - break; - case detail::type::string_type: - detail::check_string_type_spec(type_spec, eh); - break; - case detail::type::pointer_type: - detail::check_pointer_type_spec(type_spec, eh); - break; - case detail::type::custom_type: - // Custom format specifiers should be checked in parse functions of - // formatter specializations. - break; - } - return it; - } - - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(const T& val, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - fmt::detail::handle_dynamic_spec<fmt::detail::width_checker>( - specs_.width, specs_.width_ref, ctx); - fmt::detail::handle_dynamic_spec<fmt::detail::precision_checker>( - specs_.precision, specs_.precision_ref, ctx); - using af = arg_formatter<typename FormatContext::iterator, - typename FormatContext::char_type>; - return visit_format_arg(af(ctx, nullptr, &specs_), - basic_format_arg<FormatContext>(val)); - } - - private: - fmt::detail::dynamic_format_specs<Char> specs_; -}; -} // namespace detail - -// https://fmt.dev/Text%20Formatting.html#format.functions -template<class... Args> - string format(string_view fmt, const Args&... args) { - return vformat(fmt, make_format_args(args...)); - } - -template<class... Args> - wstring format(wstring_view fmt, const Args&... args) { - return vformat(fmt, make_wformat_args(args...)); - } - -string vformat(string_view fmt, format_args args) { - fmt::memory_buffer mbuf; - fmt::detail::buffer<char>& buf = mbuf; - using af = detail::arg_formatter<fmt::format_context::iterator, char>; - detail::format_handler<af, char, format_context> - h(fmt::detail::buffer_appender<char>(buf), fmt, args, {}); - fmt::detail::parse_format_string<false>(fmt::to_string_view(fmt), h); - return to_string(mbuf); -} - -wstring vformat(wstring_view fmt, wformat_args args); - -template<class Out, class... Args> - Out format_to(Out out, string_view fmt, const Args&... args) { - using context = basic_format_context<Out, decltype(fmt)::value_type>; - return vformat_to(out, fmt, make_format_args<context>(args...)); - } - -template<class Out, class... Args> - Out format_to(Out out, wstring_view fmt, const Args&... args) { - using context = basic_format_context<Out, decltype(fmt)::value_type>; - return vformat_to(out, fmt, make_format_args<context>(args...)); - } - -template<class Out> - Out vformat_to(Out out, string_view fmt, format_args_t<fmt::type_identity_t<Out>, char> args) { - using af = detail::arg_formatter<Out, char>; - detail::format_handler<af, char, basic_format_context<Out, char>> - h(out, fmt, args, {}); - fmt::detail::parse_format_string<false>(fmt::to_string_view(fmt), h); - return h.context.out(); - } - -template<class Out> - Out vformat_to(Out out, wstring_view fmt, format_args_t<fmt::type_identity_t<Out>, wchar_t> args); - -template<class Out, class... Args> - format_to_n_result<Out> format_to_n(Out out, iter_difference_t<Out> n, - string_view fmt, const Args&... args); -template<class Out, class... Args> - format_to_n_result<Out> format_to_n(Out out, iter_difference_t<Out> n, - wstring_view fmt, const Args&... args); - -template<class... Args> - size_t formatted_size(string_view fmt, const Args&... args); -template<class... Args> - size_t formatted_size(wstring_view fmt, const Args&... args); - -#define charT char - -template<> struct formatter<charT, charT> : detail::formatter<charT, charT> {}; - -template<> struct formatter<char, wchar_t>; - -template<> struct formatter<charT*, charT> : detail::formatter<const charT*, charT> {}; - -template<> struct formatter<const charT*, charT> : detail::formatter<const charT*, charT> {}; - -template<size_t N> struct formatter<const charT[N], charT> - : detail::formatter<std::basic_string_view<charT>, charT> {}; - -template<class traits, class Allocator> - struct formatter<basic_string<charT, traits, Allocator>, charT> - : detail::formatter<std::basic_string_view<charT>, charT> {}; - -template<class traits> - struct formatter<basic_string_view<charT, traits>, charT> - : detail::formatter<std::basic_string_view<charT>, charT> {}; - -template <> struct formatter<nullptr_t, charT> : detail::formatter<const void*, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<void*, charT> : detail::formatter<const void*, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<const void*, charT> : detail::formatter<const void*, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<bool, charT> : detail::formatter<bool, charT> {}; - -template <> struct formatter<signed char, charT> : detail::formatter<int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<short, charT> : detail::formatter<int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<int, charT> : detail::formatter<int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<long, charT> - : detail::formatter<std::conditional_t<sizeof(long) == sizeof(int), int, long long>, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<long long, charT> : detail::formatter<long long, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned char, charT> : detail::formatter<unsigned int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned short, charT> : detail::formatter<unsigned int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned int, charT> : detail::formatter<unsigned int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned long, charT> - : detail::formatter<std::conditional_t<sizeof(long) == sizeof(int), unsigned, unsigned long long>, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned long long, charT> : detail::formatter<unsigned long long, charT> {}; - -template <> struct formatter<float, charT> : detail::formatter<double, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<double, charT> : detail::formatter<double, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<long double, charT> : detail::formatter<long double, charT> {}; - -#undef charT - -#define charT wchar_t - -template<> struct formatter<charT, charT> : detail::formatter<charT, charT> {}; - -template<> struct formatter<char, wchar_t> : detail::formatter<charT, charT> {}; - -template<> struct formatter<charT*, charT> : detail::formatter<const charT*, charT> {}; - -template<> struct formatter<const charT*, charT> : detail::formatter<const charT*, charT> {}; - -template<size_t N> struct formatter<const charT[N], charT> - : detail::formatter<std::basic_string_view<charT>, charT> {}; - -template<class traits, class Allocator> - struct formatter<std::basic_string<charT, traits, Allocator>, charT> - : detail::formatter<std::basic_string_view<charT>, charT> {}; - -template<class traits> - struct formatter<std::basic_string_view<charT, traits>, charT> - : detail::formatter<std::basic_string_view<charT>, charT> {}; - -template <> struct formatter<nullptr_t, charT> : detail::formatter<const void*, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<void*, charT> : detail::formatter<const void*, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<const void*, charT> : detail::formatter<const void*, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<bool, charT> : detail::formatter<bool, charT> {}; - -template <> struct formatter<signed char, charT> : detail::formatter<int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<short, charT> : detail::formatter<int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<int, charT> : detail::formatter<int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<long, charT> - : detail::formatter<std::conditional_t<sizeof(long) == sizeof(int), int, long long>, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<long long, charT> : detail::formatter<long long, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned char, charT> : detail::formatter<unsigned int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned short, charT> : detail::formatter<unsigned int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned int, charT> : detail::formatter<unsigned int, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned long, charT> - : detail::formatter<std::conditional_t<sizeof(long) == sizeof(int), unsigned, unsigned long long>, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<unsigned long long, charT> : detail::formatter<unsigned long long, charT> {}; - -template <> struct formatter<float, charT> : detail::formatter<double, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<double, charT> : detail::formatter<double, charT> {}; -template <> struct formatter<long double, charT> : detail::formatter<long double, charT> {}; - -#undef charT - - template<> struct formatter<const wchar_t, char> { - formatter() = delete; - }; -} - -#endif // FMT_FORMAT_ diff --git a/test/format-impl-test.cc b/test/format-impl-test.cc index 1290c077..4d6198b6 100644 --- a/test/format-impl-test.cc +++ b/test/format-impl-test.cc @@ -5,24 +5,16 @@ // // For the license information refer to format.h. -#define FMT_NOEXCEPT -#undef FMT_SHARED -#include "test-assert.h" - -// Include format.cc instead of format.h to test implementation. #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> -#include "../src/format.cc" -#include "fmt/printf.h" -#include "gmock.h" -#include "gtest-extra.h" -#include "util.h" +// clang-format off +#include "test-assert.h" +// clang-format on -#ifdef _WIN32 -# include <windows.h> -# undef max -#endif +#include "fmt/format.h" +#include "gmock/gmock.h" +#include "util.h" using fmt::detail::bigint; using fmt::detail::fp; @@ -31,13 +23,13 @@ using fmt::detail::max_value; static_assert(!std::is_copy_constructible<bigint>::value, ""); static_assert(!std::is_copy_assignable<bigint>::value, ""); -TEST(BigIntTest, Construct) { - EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format("{}", bigint())); - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{}", bigint(0x42))); - EXPECT_EQ("123456789abcedf0", fmt::format("{}", bigint(0x123456789abcedf0))); +TEST(bigint_test, construct) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(bigint()), ""); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(bigint(0x42)), "42"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(bigint(0x123456789abcedf0)), "123456789abcedf0"); } -TEST(BigIntTest, Compare) { +TEST(bigint_test, compare) { bigint n1(42); bigint n2(42); EXPECT_EQ(compare(n1, n2), 0); @@ -51,7 +43,7 @@ TEST(BigIntTest, Compare) { EXPECT_GT(compare(n4, n2), 0); } -TEST(BigIntTest, AddCompare) { +TEST(bigint_test, add_compare) { EXPECT_LT( add_compare(bigint(0xffffffff), bigint(0xffffffff), bigint(1) <<= 64), 0); EXPECT_LT(add_compare(bigint(1) <<= 32, bigint(1), bigint(1) <<= 96), 0); @@ -77,80 +69,73 @@ TEST(BigIntTest, AddCompare) { 0); } -TEST(BigIntTest, ShiftLeft) { +TEST(bigint_test, shift_left) { bigint n(0x42); n <<= 0; - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{}", n)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n), "42"); n <<= 1; - EXPECT_EQ("84", fmt::format("{}", n)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n), "84"); n <<= 25; - EXPECT_EQ("108000000", fmt::format("{}", n)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n), "108000000"); } -TEST(BigIntTest, Multiply) { +TEST(bigint_test, multiply) { bigint n(0x42); EXPECT_THROW(n *= 0, assertion_failure); n *= 1; - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{}", n)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n), "42"); + n *= 2; - EXPECT_EQ("84", fmt::format("{}", n)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n), "84"); n *= 0x12345678; - EXPECT_EQ("962fc95e0", fmt::format("{}", n)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n), "962fc95e0"); + bigint bigmax(max_value<uint32_t>()); bigmax *= max_value<uint32_t>(); - EXPECT_EQ("fffffffe00000001", fmt::format("{}", bigmax)); - bigmax.assign(max_value<uint64_t>()); - bigmax *= max_value<uint64_t>(); - EXPECT_EQ("fffffffffffffffe0000000000000001", fmt::format("{}", bigmax)); -} - -TEST(BigIntTest, Accumulator) { - fmt::detail::accumulator acc; - EXPECT_EQ(acc.lower, 0); - EXPECT_EQ(acc.upper, 0); - acc.upper = 12; - acc.lower = 34; - EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<uint32_t>(acc), 34); - acc += 56; - EXPECT_EQ(acc.lower, 90); - acc += fmt::detail::max_value<uint64_t>(); - EXPECT_EQ(acc.upper, 13); - EXPECT_EQ(acc.lower, 89); - acc >>= 32; - EXPECT_EQ(acc.upper, 0); - EXPECT_EQ(acc.lower, 13 * 0x100000000); -} - -TEST(BigIntTest, Square) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(bigmax), "fffffffe00000001"); + + const auto max64 = max_value<uint64_t>(); + bigmax = max64; + bigmax *= max64; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(bigmax), "fffffffffffffffe0000000000000001"); + + const auto max128 = (fmt::detail::uint128_t(max64) << 64) | max64; + bigmax = max128; + bigmax *= max128; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(bigmax), + "fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffe00000000000000000000000000000001"); +} + +TEST(bigint_test, square) { bigint n0(0); n0.square(); - EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{}", n0)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n0), "0"); bigint n1(0x100); n1.square(); - EXPECT_EQ("10000", fmt::format("{}", n1)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n1), "10000"); bigint n2(0xfffffffff); n2.square(); - EXPECT_EQ("ffffffffe000000001", fmt::format("{}", n2)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n2), "ffffffffe000000001"); bigint n3(max_value<uint64_t>()); n3.square(); - EXPECT_EQ("fffffffffffffffe0000000000000001", fmt::format("{}", n3)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n3), "fffffffffffffffe0000000000000001"); bigint n4; n4.assign_pow10(10); - EXPECT_EQ("2540be400", fmt::format("{}", n4)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n4), "2540be400"); } -TEST(BigIntTest, DivModAssignZeroDivisor) { +TEST(bigint_test, divmod_assign_zero_divisor) { bigint zero(0); EXPECT_THROW(bigint(0).divmod_assign(zero), assertion_failure); EXPECT_THROW(bigint(42).divmod_assign(zero), assertion_failure); } -TEST(BigIntTest, DivModAssignSelf) { +TEST(bigint_test, divmod_assign_self) { bigint n(100); EXPECT_THROW(n.divmod_assign(n), assertion_failure); } -TEST(BigIntTest, DivModAssignUnaligned) { +TEST(bigint_test, divmod_assign_unaligned) { // (42 << 340) / pow(10, 100): bigint n1(42); n1 <<= 340; @@ -158,28 +143,28 @@ TEST(BigIntTest, DivModAssignUnaligned) { n2.assign_pow10(100); int result = n1.divmod_assign(n2); EXPECT_EQ(result, 9406); - EXPECT_EQ("10f8353019583bfc29ffc8f564e1b9f9d819dbb4cf783e4507eca1539220p96", - fmt::format("{}", n1)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n1), + "10f8353019583bfc29ffc8f564e1b9f9d819dbb4cf783e4507eca1539220p96"); } -TEST(BigIntTest, DivModAssign) { +TEST(bigint_test, divmod_assign) { // 100 / 10: bigint n1(100); int result = n1.divmod_assign(bigint(10)); EXPECT_EQ(result, 10); - EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{}", n1)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n1), "0"); // pow(10, 100) / (42 << 320): n1.assign_pow10(100); result = n1.divmod_assign(bigint(42) <<= 320); EXPECT_EQ(result, 111); - EXPECT_EQ("13ad2594c37ceb0b2784c4ce0bf38ace408e211a7caab24308a82e8f10p96", - fmt::format("{}", n1)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n1), + "13ad2594c37ceb0b2784c4ce0bf38ace408e211a7caab24308a82e8f10p96"); // 42 / 100: bigint n2(42); n1.assign_pow10(2); result = n2.divmod_assign(n1); EXPECT_EQ(result, 0); - EXPECT_EQ("2a", fmt::format("{}", n2)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(n2), "2a"); } template <bool is_iec559> void run_double_tests() { @@ -191,18 +176,18 @@ template <> void run_double_tests<true>() { EXPECT_EQ(fp(1.23), fp(0x13ae147ae147aeu, -52)); } -TEST(FPTest, DoubleTests) { +TEST(fp_test, double_tests) { run_double_tests<std::numeric_limits<double>::is_iec559>(); } -TEST(FPTest, Normalize) { +TEST(fp_test, normalize) { const auto v = fp(0xbeef, 42); auto normalized = normalize(v); - EXPECT_EQ(0xbeef000000000000, normalized.f); - EXPECT_EQ(-6, normalized.e); + EXPECT_EQ(normalized.f, 0xbeef000000000000); + EXPECT_EQ(normalized.e, -6); } -TEST(FPTest, Multiply) { +TEST(fp_test, multiply) { auto v = fp(123ULL << 32, 4) * fp(56ULL << 32, 7); EXPECT_EQ(v.f, 123u * 56u); EXPECT_EQ(v.e, 4 + 7 + 64); @@ -211,182 +196,34 @@ TEST(FPTest, Multiply) { EXPECT_EQ(v.e, 4 + 8 + 64); } -TEST(FPTest, GetCachedPower) { - using limits = std::numeric_limits<double>; - for (auto exp = limits::min_exponent; exp <= limits::max_exponent; ++exp) { - int dec_exp = 0; - auto fp = fmt::detail::get_cached_power(exp, dec_exp); - bigint exact, cache(fp.f); - if (dec_exp >= 0) { - exact.assign_pow10(dec_exp); - if (fp.e <= 0) - exact <<= -fp.e; - else - cache <<= fp.e; - exact.align(cache); - cache.align(exact); - auto exact_str = fmt::format("{}", exact); - auto cache_str = fmt::format("{}", cache); - EXPECT_EQ(exact_str.size(), cache_str.size()); - EXPECT_EQ(exact_str.substr(0, 15), cache_str.substr(0, 15)); - int diff = cache_str[15] - exact_str[15]; - if (diff == 1) - EXPECT_GT(exact_str[16], '8'); - else - EXPECT_EQ(diff, 0); - } else { - cache.assign_pow10(-dec_exp); - cache *= fp.f + 1; // Inexact check. - exact.assign(1); - exact <<= -fp.e; - exact.align(cache); - auto exact_str = fmt::format("{}", exact); - auto cache_str = fmt::format("{}", cache); - EXPECT_EQ(exact_str.size(), cache_str.size()); - EXPECT_EQ(exact_str.substr(0, 16), cache_str.substr(0, 16)); - } - } -} - -TEST(FPTest, DragonboxMaxK) { +TEST(fp_test, dragonbox_max_k) { using fmt::detail::dragonbox::floor_log10_pow2; using float_info = fmt::detail::dragonbox::float_info<float>; - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::const_check(float_info::max_k), - float_info::kappa - floor_log10_pow2(float_info::min_exponent - - float_info::significand_bits)); - using double_info = fmt::detail::dragonbox::float_info<double>; EXPECT_EQ( - fmt::detail::const_check(double_info::max_k), - double_info::kappa - floor_log10_pow2(double_info::min_exponent - - double_info::significand_bits)); -} - -TEST(FPTest, GetRoundDirection) { - using fmt::detail::get_round_direction; - using fmt::detail::round_direction; - EXPECT_EQ(round_direction::down, get_round_direction(100, 50, 0)); - EXPECT_EQ(round_direction::up, get_round_direction(100, 51, 0)); - EXPECT_EQ(round_direction::down, get_round_direction(100, 40, 10)); - EXPECT_EQ(round_direction::up, get_round_direction(100, 60, 10)); - for (size_t i = 41; i < 60; ++i) - EXPECT_EQ(round_direction::unknown, get_round_direction(100, i, 10)); - uint64_t max = max_value<uint64_t>(); - EXPECT_THROW(get_round_direction(100, 100, 0), assertion_failure); - EXPECT_THROW(get_round_direction(100, 0, 100), assertion_failure); - EXPECT_THROW(get_round_direction(100, 0, 50), assertion_failure); - // Check that remainder + error doesn't overflow. - EXPECT_EQ(round_direction::up, get_round_direction(max, max - 1, 2)); - // Check that 2 * (remainder + error) doesn't overflow. - EXPECT_EQ(round_direction::unknown, - get_round_direction(max, max / 2 + 1, max / 2)); - // Check that remainder - error doesn't overflow. - EXPECT_EQ(round_direction::unknown, get_round_direction(100, 40, 41)); - // Check that 2 * (remainder - error) doesn't overflow. - EXPECT_EQ(round_direction::up, get_round_direction(max, max - 1, 1)); -} - -TEST(FPTest, FixedHandler) { - struct handler : fmt::detail::fixed_handler { - char buffer[10]; - handler(int prec = 0) : fmt::detail::fixed_handler() { - buf = buffer; - precision = prec; - } - }; - int exp = 0; - handler().on_digit('0', 100, 99, 0, exp, false); - EXPECT_THROW(handler().on_digit('0', 100, 100, 0, exp, false), - assertion_failure); - namespace digits = fmt::detail::digits; - EXPECT_EQ(handler(1).on_digit('0', 100, 10, 10, exp, false), digits::error); - // Check that divisor - error doesn't overflow. - EXPECT_EQ(handler(1).on_digit('0', 100, 10, 101, exp, false), digits::error); - // Check that 2 * error doesn't overflow. - uint64_t max = max_value<uint64_t>(); - EXPECT_EQ(handler(1).on_digit('0', max, 10, max - 1, exp, false), - digits::error); -} - -TEST(FPTest, GrisuFormatCompilesWithNonIEEEDouble) { - fmt::memory_buffer buf; - format_float(0.42, -1, fmt::detail::float_specs(), buf); -} - -template <typename T> struct value_extractor { - T operator()(T value) { return value; } - - template <typename U> FMT_NORETURN T operator()(U) { - throw std::runtime_error(fmt::format("invalid type {}", typeid(U).name())); - } - -#if FMT_USE_INT128 - // Apple Clang does not define typeid for __int128_t and __uint128_t. - FMT_NORETURN T operator()(fmt::detail::int128_t) { - throw std::runtime_error("invalid type __int128_t"); - } - - FMT_NORETURN T operator()(fmt::detail::uint128_t) { - throw std::runtime_error("invalid type __uint128_t"); - } -#endif -}; - -TEST(FormatTest, ArgConverter) { - long long value = max_value<long long>(); - auto arg = fmt::detail::make_arg<fmt::format_context>(value); - fmt::visit_format_arg( - fmt::detail::arg_converter<long long, fmt::format_context>(arg, 'd'), - arg); - EXPECT_EQ(value, fmt::visit_format_arg(value_extractor<long long>(), arg)); -} - -TEST(FormatTest, StrError) { - char* message = nullptr; - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; - EXPECT_ASSERT(fmt::detail::safe_strerror(EDOM, message = nullptr, 0), - "invalid buffer"); - EXPECT_ASSERT(fmt::detail::safe_strerror(EDOM, message = buffer, 0), - "invalid buffer"); - buffer[0] = 'x'; -#if defined(_GNU_SOURCE) && !defined(__COVERITY__) - // Use invalid error code to make sure that safe_strerror returns an error - // message in the buffer rather than a pointer to a static string. - int error_code = -1; -#else - int error_code = EDOM; -#endif - - int result = - fmt::detail::safe_strerror(error_code, message = buffer, BUFFER_SIZE); - EXPECT_EQ(result, 0); - size_t message_size = std::strlen(message); - EXPECT_GE(BUFFER_SIZE - 1u, message_size); - EXPECT_EQ(get_system_error(error_code), message); - - // safe_strerror never uses buffer on MinGW. -#if !defined(__MINGW32__) && !defined(__sun) - result = - fmt::detail::safe_strerror(error_code, message = buffer, message_size); - EXPECT_EQ(ERANGE, result); - result = fmt::detail::safe_strerror(error_code, message = buffer, 1); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, message); // Message should point to buffer. - EXPECT_EQ(ERANGE, result); - EXPECT_STREQ("", message); -#endif + fmt::detail::const_check(float_info::max_k), + float_info::kappa - + floor_log10_pow2(std::numeric_limits<float>::min_exponent - + fmt::detail::num_significand_bits<float>() - 1)); + using double_info = fmt::detail::dragonbox::float_info<double>; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::const_check(double_info::max_k), + double_info::kappa - + floor_log10_pow2( + std::numeric_limits<double>::min_exponent - + 2 * fmt::detail::num_significand_bits<double>() - 1)); } -TEST(FormatTest, FormatErrorCode) { +TEST(format_impl_test, format_error_code) { std::string msg = "error 42", sep = ": "; { - fmt::memory_buffer buffer; - format_to(buffer, "garbage"); + auto buffer = fmt::memory_buffer(); + fmt::format_to(fmt::appender(buffer), "garbage"); fmt::detail::format_error_code(buffer, 42, "test"); - EXPECT_EQ("test: " + msg, to_string(buffer)); + EXPECT_EQ(to_string(buffer), "test: " + msg); } { - fmt::memory_buffer buffer; - std::string prefix(fmt::inline_buffer_size - msg.size() - sep.size() + 1, - 'x'); + auto buffer = fmt::memory_buffer(); + auto prefix = + std::string(fmt::inline_buffer_size - msg.size() - sep.size() + 1, 'x'); fmt::detail::format_error_code(buffer, 42, prefix); EXPECT_EQ(msg, to_string(buffer)); } @@ -395,7 +232,8 @@ TEST(FormatTest, FormatErrorCode) { // Test maximum buffer size. msg = fmt::format("error {}", codes[i]); fmt::memory_buffer buffer; - std::string prefix(fmt::inline_buffer_size - msg.size() - sep.size(), 'x'); + auto prefix = + std::string(fmt::inline_buffer_size - msg.size() - sep.size(), 'x'); fmt::detail::format_error_code(buffer, codes[i], prefix); EXPECT_EQ(prefix + sep + msg, to_string(buffer)); size_t size = fmt::inline_buffer_size; @@ -404,13 +242,13 @@ TEST(FormatTest, FormatErrorCode) { // Test with a message that doesn't fit into the buffer. prefix += 'x'; fmt::detail::format_error_code(buffer, codes[i], prefix); - EXPECT_EQ(msg, to_string(buffer)); + EXPECT_EQ(to_string(buffer), msg); } } -TEST(FormatTest, CountCodePoints) { +TEST(format_impl_test, compute_width) { EXPECT_EQ(4, - fmt::detail::count_code_points( + fmt::detail::compute_width( fmt::basic_string_view<fmt::detail::char8_type>( reinterpret_cast<const fmt::detail::char8_type*>("ёжик")))); } @@ -420,27 +258,226 @@ template <typename Int> void test_count_digits() { for (Int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) EXPECT_EQ(1u, fmt::detail::count_digits(i)); for (Int i = 1, n = 1, end = max_value<Int>() / 10; n <= end; ++i) { n *= 10; - EXPECT_EQ(i, fmt::detail::count_digits(n - 1)); - EXPECT_EQ(i + 1, fmt::detail::count_digits(n)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::count_digits(n - 1), i); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::count_digits(n), i + 1); } } -TEST(UtilTest, CountDigits) { +TEST(format_impl_test, count_digits) { test_count_digits<uint32_t>(); test_count_digits<uint64_t>(); } -TEST(UtilTest, WriteFallbackUIntPtr) { - std::string s; - fmt::detail::write_ptr<char>( - std::back_inserter(s), - fmt::detail::fallback_uintptr(reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface)), nullptr); - EXPECT_EQ(s, "0xface"); +TEST(format_impl_test, countl_zero) { + constexpr auto num_bits = fmt::detail::num_bits<uint32_t>(); + uint32_t n = 1u; + for (int i = 1; i < num_bits - 1; i++) { + n <<= 1; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::countl_zero(n - 1), num_bits - i); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::countl_zero(n), num_bits - i - 1); + } +} + +#if FMT_USE_FLOAT128 +TEST(format_impl_test, write_float128) { + auto s = std::string(); + fmt::detail::write<char>(std::back_inserter(s), __float128(42)); + EXPECT_EQ(s, "42"); +} +#endif + +struct double_double { + double a; + double b; + + explicit constexpr double_double(double a_val = 0, double b_val = 0) + : a(a_val), b(b_val) {} + + operator double() const { return a + b; } + auto operator-() const -> double_double { return double_double(-a, -b); } +}; + +auto format_as(double_double d) -> double { return d; } + +bool operator>=(const double_double& lhs, const double_double& rhs) { + return lhs.a + lhs.b >= rhs.a + rhs.b; +} + +struct slow_float { + float value; + + explicit constexpr slow_float(float val = 0) : value(val) {} + operator float() const { return value; } + auto operator-() const -> slow_float { return slow_float(-value); } +}; + +auto format_as(slow_float f) -> float { return f; } + +namespace std { +template <> struct is_floating_point<double_double> : std::true_type {}; +template <> struct numeric_limits<double_double> { + // is_iec559 is true for double-double in libstdc++. + static constexpr bool is_iec559 = true; + static constexpr int digits = 106; +}; + +template <> struct is_floating_point<slow_float> : std::true_type {}; +template <> struct numeric_limits<slow_float> : numeric_limits<float> {}; +} // namespace std + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +namespace detail { +template <> struct is_fast_float<slow_float> : std::false_type {}; +namespace dragonbox { +template <> struct float_info<slow_float> { + using carrier_uint = uint32_t; + static const int exponent_bits = 8; +}; +} // namespace dragonbox +} // namespace detail +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(format_impl_test, write_double_double) { + auto s = std::string(); + fmt::detail::write<char>(std::back_inserter(s), double_double(42), {}); + // Specializing is_floating_point is broken in MSVC. + if (!FMT_MSC_VERSION) EXPECT_EQ(s, "42"); +} + +TEST(format_impl_test, write_dragon_even) { + auto s = std::string(); + fmt::detail::write<char>(std::back_inserter(s), slow_float(33554450.0f), {}); + // Specializing is_floating_point is broken in MSVC. + if (!FMT_MSC_VERSION) EXPECT_EQ(s, "33554450"); } -#ifdef _WIN32 -TEST(UtilTest, WriteConsoleSignature) { - decltype(WriteConsoleW)* p = fmt::detail::WriteConsoleW; +#if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(FMT_WINDOWS_NO_WCHAR) +# include <windows.h> + +TEST(format_impl_test, write_console_signature) { + decltype(::WriteConsoleW)* p = fmt::detail::WriteConsoleW; (void)p; } #endif + +// A public domain branchless UTF-8 decoder by Christopher Wellons: +// https://github.com/skeeto/branchless-utf8 +constexpr bool unicode_is_surrogate(uint32_t c) { + return c >= 0xD800U && c <= 0xDFFFU; +} + +FMT_CONSTEXPR char* utf8_encode(char* s, uint32_t c) { + if (c >= (1UL << 16)) { + s[0] = static_cast<char>(0xf0 | (c >> 18)); + s[1] = static_cast<char>(0x80 | ((c >> 12) & 0x3f)); + s[2] = static_cast<char>(0x80 | ((c >> 6) & 0x3f)); + s[3] = static_cast<char>(0x80 | ((c >> 0) & 0x3f)); + return s + 4; + } else if (c >= (1UL << 11)) { + s[0] = static_cast<char>(0xe0 | (c >> 12)); + s[1] = static_cast<char>(0x80 | ((c >> 6) & 0x3f)); + s[2] = static_cast<char>(0x80 | ((c >> 0) & 0x3f)); + return s + 3; + } else if (c >= (1UL << 7)) { + s[0] = static_cast<char>(0xc0 | (c >> 6)); + s[1] = static_cast<char>(0x80 | ((c >> 0) & 0x3f)); + return s + 2; + } else { + s[0] = static_cast<char>(c); + return s + 1; + } +} + +// Make sure it can decode every character +TEST(format_impl_test, utf8_decode_decode_all) { + for (uint32_t i = 0; i < 0x10ffff; i++) { + if (!unicode_is_surrogate(i)) { + int e; + uint32_t c; + char buf[8] = {0}; + char* end = utf8_encode(buf, i); + const char* res = fmt::detail::utf8_decode(buf, &c, &e); + EXPECT_EQ(end, res); + EXPECT_EQ(c, i); + EXPECT_EQ(e, 0); + } + } +} + +// Reject everything outside of U+0000..U+10FFFF +TEST(format_impl_test, utf8_decode_out_of_range) { + for (uint32_t i = 0x110000; i < 0x1fffff; i++) { + int e; + uint32_t c; + char buf[8] = {0}; + utf8_encode(buf, i); + const char* end = fmt::detail::utf8_decode(buf, &c, &e); + EXPECT_NE(e, 0); + EXPECT_EQ(end - buf, 4); + } +} + +// Does it reject all surrogate halves? +TEST(format_impl_test, utf8_decode_surrogate_halves) { + for (uint32_t i = 0xd800; i <= 0xdfff; i++) { + int e; + uint32_t c; + char buf[8] = {0}; + utf8_encode(buf, i); + fmt::detail::utf8_decode(buf, &c, &e); + EXPECT_NE(e, 0); + } +} + +// How about non-canonical encodings? +TEST(format_impl_test, utf8_decode_non_canonical_encodings) { + int e; + uint32_t c; + const char* end; + + char buf2[8] = {char(0xc0), char(0xA4)}; + end = fmt::detail::utf8_decode(buf2, &c, &e); + EXPECT_NE(e, 0); // non-canonical len 2 + EXPECT_EQ(end, buf2 + 2); // non-canonical recover 2 + + char buf3[8] = {char(0xe0), char(0x80), char(0xA4)}; + end = fmt::detail::utf8_decode(buf3, &c, &e); + EXPECT_NE(e, 0); // non-canonical len 3 + EXPECT_EQ(end, buf3 + 3); // non-canonical recover 3 + + char buf4[8] = {char(0xf0), char(0x80), char(0x80), char(0xA4)}; + end = fmt::detail::utf8_decode(buf4, &c, &e); + EXPECT_NE(e, 0); // non-canonical encoding len 4 + EXPECT_EQ(end, buf4 + 4); // non-canonical recover 4 +} + +// Let's try some bogus byte sequences +TEST(format_impl_test, utf8_decode_bogus_byte_sequences) { + int e; + uint32_t c; + + // Invalid first byte + char buf0[4] = {char(0xff)}; + auto len = fmt::detail::utf8_decode(buf0, &c, &e) - buf0; + EXPECT_NE(e, 0); // "bogus [ff] 0x%02x U+%04lx", e, (unsigned long)c); + EXPECT_EQ(len, 1); // "bogus [ff] recovery %d", len); + + // Invalid first byte + char buf1[4] = {char(0x80)}; + len = fmt::detail::utf8_decode(buf1, &c, &e) - buf1; + EXPECT_NE(e, 0); // "bogus [80] 0x%02x U+%04lx", e, (unsigned long)c); + EXPECT_EQ(len, 1); // "bogus [80] recovery %d", len); + + // Looks like a two-byte sequence but second byte is wrong + char buf2[4] = {char(0xc0), char(0x0a)}; + len = fmt::detail::utf8_decode(buf2, &c, &e) - buf2; + EXPECT_NE(e, 0); // "bogus [c0 0a] 0x%02x U+%04lx", e, (unsigned long)c + EXPECT_EQ(len, 2); // "bogus [c0 0a] recovery %d", len); +} + +TEST(format_impl_test, to_utf8) { + auto s = std::string("ёжик"); + auto u = fmt::detail::to_utf8<wchar_t>(L"\x0451\x0436\x0438\x043A"); + EXPECT_EQ(s, u.str()); + EXPECT_EQ(s.size(), u.size()); +} diff --git a/test/format-test.cc b/test/format-test.cc index 8ed524cc..9788c246 100644 --- a/test/format-test.cc +++ b/test/format-test.cc @@ -5,111 +5,151 @@ // // For the license information refer to format.h. -#include <stdint.h> - -#include <cctype> -#include <cfloat> -#include <climits> -#include <cmath> -#include <cstring> -#include <list> -#include <memory> -#include <string> - // Check if fmt/format.h compiles with windows.h included before it. #ifdef _WIN32 # include <windows.h> #endif - -// Check if fmt/format.h compiles with the X11 index macro defined. -#define index(x, y) no nice things - +// clang-format off #include "fmt/format.h" +// clang-format on + +#include <stdint.h> // uint32_t -#undef index +#include <climits> // INT_MAX +#include <cmath> // std::signbit +#include <cstring> // std::strlen +#include <iterator> // std::back_inserter +#include <list> // std::list +#include <memory> // std::unique_ptr +#include <type_traits> // std::is_default_constructible -#include "gmock.h" #include "gtest-extra.h" #include "mock-allocator.h" #include "util.h" -#undef ERROR - using fmt::basic_memory_buffer; -using fmt::format; using fmt::format_error; using fmt::memory_buffer; +using fmt::runtime; using fmt::string_view; -using fmt::wmemory_buffer; -using fmt::wstring_view; using fmt::detail::max_value; +using fmt::detail::uint128_fallback; using testing::Return; using testing::StrictMock; -namespace { - -#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 408 -template <typename Char, typename T> bool check_enabled_formatter() { - static_assert(std::is_default_constructible<fmt::formatter<T, Char>>::value, - ""); - return true; -} - -template <typename Char, typename... T> void check_enabled_formatters() { - auto dummy = {check_enabled_formatter<Char, T>()...}; - (void)dummy; -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, TestFormattersEnabled) { - check_enabled_formatters<char, bool, char, signed char, unsigned char, short, - unsigned short, int, unsigned, long, unsigned long, - long long, unsigned long long, float, double, - long double, void*, const void*, char*, const char*, - std::string, std::nullptr_t>(); - check_enabled_formatters<wchar_t, bool, wchar_t, signed char, unsigned char, - short, unsigned short, int, unsigned, long, - unsigned long, long long, unsigned long long, float, - double, long double, void*, const void*, wchar_t*, - const wchar_t*, std::wstring, std::nullptr_t>(); -} +enum { buffer_size = 256 }; + +TEST(uint128_test, ctor) { + auto n = uint128_fallback(); + EXPECT_EQ(n, 0); + n = uint128_fallback(42); + EXPECT_EQ(n, 42); + EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<uint64_t>(n), 42); +} + +TEST(uint128_test, shift) { + auto n = uint128_fallback(42); + n = n << 64; + EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<uint64_t>(n), 0); + n = n >> 64; + EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<uint64_t>(n), 42); + n = n << 62; + EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<uint64_t>(n >> 64), 0xa); + EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<uint64_t>(n), 0x8000000000000000); + n = n >> 62; + EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<uint64_t>(n), 42); + EXPECT_EQ(uint128_fallback(1) << 112, uint128_fallback(0x1000000000000, 0)); + EXPECT_EQ(uint128_fallback(0x1000000000000, 0) >> 112, uint128_fallback(1)); +} + +TEST(uint128_test, minus) { + auto n = uint128_fallback(42); + EXPECT_EQ(n - 2, 40); +} + +TEST(uint128_test, plus_assign) { + auto n = uint128_fallback(32); + n += uint128_fallback(10); + EXPECT_EQ(n, 42); + n = uint128_fallback(max_value<uint64_t>()); + n += uint128_fallback(1); + EXPECT_EQ(n, uint128_fallback(1) << 64); +} + +TEST(uint128_test, multiply) { + auto n = uint128_fallback(2251799813685247); + n = n * 3611864890; + EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<uint64_t>(n >> 64), 440901); +} + +template <typename Float> void check_isfinite() { + using fmt::detail::isfinite; + EXPECT_TRUE(isfinite(Float(0.0))); + EXPECT_TRUE(isfinite(Float(42.0))); + EXPECT_TRUE(isfinite(Float(-42.0))); + EXPECT_TRUE(isfinite(Float(fmt::detail::max_value<double>()))); + // Use double because std::numeric_limits is broken for __float128. + using limits = std::numeric_limits<double>; + FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto result = isfinite(Float(limits::infinity())); + EXPECT_FALSE(result); + EXPECT_FALSE(isfinite(Float(limits::infinity()))); + EXPECT_FALSE(isfinite(Float(-limits::infinity()))); + EXPECT_FALSE(isfinite(Float(limits::quiet_NaN()))); + EXPECT_FALSE(isfinite(Float(-limits::quiet_NaN()))); +} + +TEST(float_test, isfinite) { + check_isfinite<double>(); +#if FMT_USE_FLOAT128 + check_isfinite<fmt::detail::float128>(); #endif - -// Format value using the standard library. -template <typename Char, typename T> -void std_format(const T& value, std::basic_string<Char>& result) { - std::basic_ostringstream<Char> os; - os << value; - result = os.str(); } -#ifdef __MINGW32__ -// Workaround a bug in formatting long double in MinGW. -void std_format(long double value, std::string& result) { - char buffer[100]; - safe_sprintf(buffer, "%Lg", value); - result = buffer; -} -void std_format(long double value, std::wstring& result) { - wchar_t buffer[100]; - swprintf(buffer, L"%Lg", value); - result = buffer; -} +template <typename Float> void check_isnan() { + using fmt::detail::isnan; + EXPECT_FALSE(isnan(Float(0.0))); + EXPECT_FALSE(isnan(Float(42.0))); + EXPECT_FALSE(isnan(Float(-42.0))); + EXPECT_FALSE(isnan(Float(fmt::detail::max_value<double>()))); + // Use double because std::numeric_limits is broken for __float128. + using limits = std::numeric_limits<double>; + EXPECT_FALSE(isnan(Float(limits::infinity()))); + EXPECT_FALSE(isnan(Float(-limits::infinity()))); + EXPECT_TRUE(isnan(Float(limits::quiet_NaN()))); + EXPECT_TRUE(isnan(Float(-limits::quiet_NaN()))); +} + +TEST(float_test, isnan) { + check_isnan<double>(); +#if FMT_USE_FLOAT128 + check_isnan<fmt::detail::float128>(); #endif -} // namespace +} struct uint32_pair { uint32_t u[2]; }; -TEST(UtilTest, BitCast) { +TEST(util_test, bit_cast) { auto s = fmt::detail::bit_cast<uint32_pair>(uint64_t{42}); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::bit_cast<uint64_t>(s), 42ull); - s = fmt::detail::bit_cast<uint32_pair>(uint64_t(~0ull)); + s = fmt::detail::bit_cast<uint32_pair>(~uint64_t{0}); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::bit_cast<uint64_t>(s), ~0ull); } -TEST(UtilTest, Increment) { +// Increment a number in a string. +void increment(char* s) { + for (int i = static_cast<int>(std::strlen(s)) - 1; i >= 0; --i) { + if (s[i] != '9') { + ++s[i]; + break; + } + s[i] = '0'; + } +} + +TEST(util_test, increment) { char s[10] = "123"; increment(s); EXPECT_STREQ("124", s); @@ -123,92 +163,52 @@ TEST(UtilTest, Increment) { EXPECT_STREQ("200", s); } -TEST(UtilTest, ParseNonnegativeInt) { - if (max_value<int>() != static_cast<int>(static_cast<unsigned>(1) << 31)) { - fmt::print("Skipping parse_nonnegative_int test\n"); - return; - } - fmt::string_view s = "10000000000"; +TEST(util_test, parse_nonnegative_int) { + auto s = fmt::string_view("10000000000"); auto begin = s.begin(), end = s.end(); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG( - parse_nonnegative_int(begin, end, fmt::detail::error_handler()), - fmt::format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::parse_nonnegative_int(begin, end, -1), -1); s = "2147483649"; begin = s.begin(); end = s.end(); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG( - parse_nonnegative_int(begin, end, fmt::detail::error_handler()), - fmt::format_error, "number is too big"); -} - -TEST(IteratorTest, CountingIterator) { - fmt::detail::counting_iterator it; - auto prev = it++; - EXPECT_EQ(prev.count(), 0); - EXPECT_EQ(it.count(), 1); - EXPECT_EQ((it + 41).count(), 42); -} - -TEST(IteratorTest, TruncatingIterator) { - char* p = nullptr; - fmt::detail::truncating_iterator<char*> it(p, 3); - auto prev = it++; - EXPECT_EQ(prev.base(), p); - EXPECT_EQ(it.base(), p + 1); -} - -TEST(IteratorTest, TruncatingBackInserter) { - std::string buffer; - auto bi = std::back_inserter(buffer); - fmt::detail::truncating_iterator<decltype(bi)> it(bi, 2); - *it++ = '4'; - *it++ = '2'; - *it++ = '1'; - EXPECT_EQ(buffer.size(), 2); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, "42"); -} - -TEST(IteratorTest, IsOutputIterator) { - EXPECT_TRUE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<char*, char>::value)); - EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<const char*, char>::value)); - EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::string, char>::value)); - EXPECT_TRUE( - (fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::back_insert_iterator<std::string>, - char>::value)); - EXPECT_TRUE( - (fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::string::iterator, char>::value)); - EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::string::const_iterator, - char>::value)); - EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::list<char>, char>::value)); - EXPECT_TRUE(( - fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::list<char>::iterator, char>::value)); - EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<std::list<char>::const_iterator, - char>::value)); - EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::detail::is_output_iterator<uint32_pair, char>::value)); -} - -TEST(MemoryBufferTest, Ctor) { - basic_memory_buffer<char, 123> buffer; - EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<size_t>(0), buffer.size()); - EXPECT_EQ(123u, buffer.capacity()); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::parse_nonnegative_int(begin, end, -1), -1); +} + +TEST(util_test, utf8_to_utf16) { + auto u = fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16("лошадка"); + EXPECT_EQ(L"\x043B\x043E\x0448\x0430\x0434\x043A\x0430", u.str()); + EXPECT_EQ(7, u.size()); + // U+10437 { DESERET SMALL LETTER YEE } + EXPECT_EQ(L"\xD801\xDC37", fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16("𐐷").str()); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16("\xc3\x28"), std::runtime_error, + "invalid utf8"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16(fmt::string_view("л", 1)), + std::runtime_error, "invalid utf8"); + EXPECT_EQ(L"123456", fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16("123456").str()); } -static void check_forwarding(mock_allocator<int>& alloc, - allocator_ref<mock_allocator<int>>& ref) { - int mem; - // Check if value_type is properly defined. - allocator_ref<mock_allocator<int>>::value_type* ptr = &mem; - // Check forwarding. - EXPECT_CALL(alloc, allocate(42)).WillOnce(testing::Return(ptr)); - ref.allocate(42); - EXPECT_CALL(alloc, deallocate(ptr, 42)); - ref.deallocate(ptr, 42); +TEST(util_test, utf8_to_utf16_empty_string) { + auto s = std::string(); + auto u = fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16(s.c_str()); + EXPECT_EQ(L"", u.str()); + EXPECT_EQ(s.size(), u.size()); } -TEST(AllocatorTest, allocator_ref) { +TEST(util_test, allocator_ref) { + using test_allocator_ref = allocator_ref<mock_allocator<int>>; + auto check_forwarding = [](mock_allocator<int>& alloc, + test_allocator_ref& ref) { + int mem; + // Check if value_type is properly defined. + allocator_ref<mock_allocator<int>>::value_type* ptr = &mem; + // Check forwarding. + EXPECT_CALL(alloc, allocate(42)).WillOnce(Return(ptr)); + ref.allocate(42); + EXPECT_CALL(alloc, deallocate(ptr, 42)); + ref.deallocate(ptr, 42); + }; + StrictMock<mock_allocator<int>> alloc; - typedef allocator_ref<mock_allocator<int>> test_allocator_ref; - test_allocator_ref ref(&alloc); + auto ref = test_allocator_ref(&alloc); // Check if allocator_ref forwards to the underlying allocator. check_forwarding(alloc, ref); test_allocator_ref ref2(ref); @@ -219,24 +219,78 @@ TEST(AllocatorTest, allocator_ref) { check_forwarding(alloc, ref3); } -typedef allocator_ref<std::allocator<char>> TestAllocator; +TEST(util_test, format_system_error) { + fmt::memory_buffer message; + fmt::format_system_error(message, EDOM, "test"); + auto ec = std::error_code(EDOM, std::generic_category()); + EXPECT_EQ(to_string(message), std::system_error(ec, "test").what()); + message = fmt::memory_buffer(); -static void check_move_buffer( - const char* str, basic_memory_buffer<char, 5, TestAllocator>& buffer) { - std::allocator<char>* alloc = buffer.get_allocator().get(); - basic_memory_buffer<char, 5, TestAllocator> buffer2(std::move(buffer)); - // Move shouldn't destroy the inline content of the first buffer. - EXPECT_EQ(str, std::string(&buffer[0], buffer.size())); - EXPECT_EQ(str, std::string(&buffer2[0], buffer2.size())); - EXPECT_EQ(5u, buffer2.capacity()); - // Move should transfer allocator. - EXPECT_EQ(nullptr, buffer.get_allocator().get()); - EXPECT_EQ(alloc, buffer2.get_allocator().get()); + // Check if std::allocator throws on allocating max size_t / 2 chars. + size_t max_size = max_value<size_t>() / 2; + bool throws_on_alloc = false; + try { + auto alloc = std::allocator<char>(); + alloc.deallocate(alloc.allocate(max_size), max_size); + } catch (const std::bad_alloc&) { + throws_on_alloc = true; + } + if (!throws_on_alloc) { + fmt::print("warning: std::allocator allocates {} chars\n", max_size); + return; + } +} + +TEST(util_test, system_error) { + auto test_error = fmt::system_error(EDOM, "test"); + auto ec = std::error_code(EDOM, std::generic_category()); + EXPECT_STREQ(test_error.what(), std::system_error(ec, "test").what()); + EXPECT_EQ(test_error.code(), ec); + + auto error = std::system_error(std::error_code()); + try { + throw fmt::system_error(EDOM, "test {}", "error"); + } catch (const std::system_error& e) { + error = e; + } + fmt::memory_buffer message; + fmt::format_system_error(message, EDOM, "test error"); + EXPECT_EQ(error.what(), to_string(message)); + EXPECT_EQ(error.code(), std::error_code(EDOM, std::generic_category())); } -TEST(MemoryBufferTest, MoveCtorInlineBuffer) { - std::allocator<char> alloc; - basic_memory_buffer<char, 5, TestAllocator> buffer((TestAllocator(&alloc))); +TEST(util_test, report_system_error) { + fmt::memory_buffer out; + fmt::format_system_error(out, EDOM, "test error"); + out.push_back('\n'); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::report_system_error(EDOM, "test error"), + to_string(out)); +} + +TEST(memory_buffer_test, ctor) { + basic_memory_buffer<char, 123> buffer; + EXPECT_EQ(static_cast<size_t>(0), buffer.size()); + EXPECT_EQ(123u, buffer.capacity()); +} + +using std_allocator = allocator_ref<std::allocator<char>>; + +TEST(memory_buffer_test, move_ctor_inline_buffer) { + auto check_move_buffer = + [](const char* str, basic_memory_buffer<char, 5, std_allocator>& buffer) { + std::allocator<char>* alloc = buffer.get_allocator().get(); + basic_memory_buffer<char, 5, std_allocator> buffer2(std::move(buffer)); + // Move shouldn't destroy the inline content of the first buffer. + EXPECT_EQ(str, std::string(&buffer[0], buffer.size())); + EXPECT_EQ(str, std::string(&buffer2[0], buffer2.size())); + EXPECT_EQ(5u, buffer2.capacity()); + // Move should transfer allocator. + EXPECT_EQ(nullptr, buffer.get_allocator().get()); + EXPECT_EQ(alloc, buffer2.get_allocator().get()); + }; + + auto alloc = std::allocator<char>(); + basic_memory_buffer<char, 5, std_allocator> buffer((std_allocator(&alloc))); const char test[] = "test"; buffer.append(string_view(test, 4)); check_move_buffer("test", buffer); @@ -246,24 +300,25 @@ TEST(MemoryBufferTest, MoveCtorInlineBuffer) { check_move_buffer("testa", buffer); } -TEST(MemoryBufferTest, MoveCtorDynamicBuffer) { - std::allocator<char> alloc; - basic_memory_buffer<char, 4, TestAllocator> buffer((TestAllocator(&alloc))); +TEST(memory_buffer_test, move_ctor_dynamic_buffer) { + auto alloc = std::allocator<char>(); + basic_memory_buffer<char, 4, std_allocator> buffer((std_allocator(&alloc))); const char test[] = "test"; buffer.append(test, test + 4); const char* inline_buffer_ptr = &buffer[0]; // Adding one more character causes the content to move from the inline to // a dynamically allocated buffer. buffer.push_back('a'); - basic_memory_buffer<char, 4, TestAllocator> buffer2(std::move(buffer)); + basic_memory_buffer<char, 4, std_allocator> buffer2(std::move(buffer)); // Move should rip the guts of the first buffer. - EXPECT_EQ(inline_buffer_ptr, &buffer[0]); - EXPECT_EQ("testa", std::string(&buffer2[0], buffer2.size())); + EXPECT_EQ(&buffer[0], inline_buffer_ptr); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer.size(), 0); + EXPECT_EQ(std::string(&buffer2[0], buffer2.size()), "testa"); EXPECT_GT(buffer2.capacity(), 4u); } -static void check_move_assign_buffer(const char* str, - basic_memory_buffer<char, 5>& buffer) { +void check_move_assign_buffer(const char* str, + basic_memory_buffer<char, 5>& buffer) { basic_memory_buffer<char, 5> buffer2; buffer2 = std::move(buffer); // Move shouldn't destroy the inline content of the first buffer. @@ -272,7 +327,7 @@ static void check_move_assign_buffer(const char* str, EXPECT_EQ(5u, buffer2.capacity()); } -TEST(MemoryBufferTest, MoveAssignment) { +TEST(memory_buffer_test, move_assignment) { basic_memory_buffer<char, 5> buffer; const char test[] = "test"; buffer.append(test, test + 4); @@ -293,7 +348,7 @@ TEST(MemoryBufferTest, MoveAssignment) { EXPECT_GT(buffer2.capacity(), 5u); } -TEST(MemoryBufferTest, Grow) { +TEST(memory_buffer_test, grow) { typedef allocator_ref<mock_allocator<int>> Allocator; mock_allocator<int> alloc; basic_memory_buffer<int, 10, Allocator> buffer((Allocator(&alloc))); @@ -313,15 +368,15 @@ TEST(MemoryBufferTest, Grow) { EXPECT_CALL(alloc, deallocate(mem, 20)); } -TEST(MemoryBufferTest, Allocator) { - typedef allocator_ref<mock_allocator<char>> TestAllocator; - basic_memory_buffer<char, 10, TestAllocator> buffer; +TEST(memory_buffer_test, allocator) { + using test_allocator = allocator_ref<mock_allocator<char>>; + basic_memory_buffer<char, 10, test_allocator> buffer; EXPECT_EQ(nullptr, buffer.get_allocator().get()); StrictMock<mock_allocator<char>> alloc; char mem; { - basic_memory_buffer<char, 10, TestAllocator> buffer2( - (TestAllocator(&alloc))); + basic_memory_buffer<char, 10, test_allocator> buffer2( + (test_allocator(&alloc))); EXPECT_EQ(&alloc, buffer2.get_allocator().get()); size_t size = 2 * fmt::inline_buffer_size; EXPECT_CALL(alloc, allocate(size)).WillOnce(Return(&mem)); @@ -330,21 +385,22 @@ TEST(MemoryBufferTest, Allocator) { } } -TEST(MemoryBufferTest, ExceptionInDeallocate) { - typedef allocator_ref<mock_allocator<char>> TestAllocator; +TEST(memory_buffer_test, exception_in_deallocate) { + using test_allocator = allocator_ref<mock_allocator<char>>; StrictMock<mock_allocator<char>> alloc; - basic_memory_buffer<char, 10, TestAllocator> buffer((TestAllocator(&alloc))); + basic_memory_buffer<char, 10, test_allocator> buffer( + (test_allocator(&alloc))); size_t size = 2 * fmt::inline_buffer_size; - std::vector<char> mem(size); + auto mem = std::vector<char>(size); { EXPECT_CALL(alloc, allocate(size)).WillOnce(Return(&mem[0])); buffer.resize(size); std::fill(&buffer[0], &buffer[0] + size, 'x'); } - std::vector<char> mem2(2 * size); + auto mem2 = std::vector<char>(2 * size); { EXPECT_CALL(alloc, allocate(2 * size)).WillOnce(Return(&mem2[0])); - std::exception e; + auto e = std::exception(); EXPECT_CALL(alloc, deallocate(&mem[0], size)).WillOnce(testing::Throw(e)); EXPECT_THROW(buffer.reserve(2 * size), std::exception); EXPECT_EQ(&mem2[0], &buffer[0]); @@ -354,595 +410,589 @@ TEST(MemoryBufferTest, ExceptionInDeallocate) { EXPECT_CALL(alloc, deallocate(&mem2[0], 2 * size)); } -TEST(UtilTest, UTF8ToUTF16) { - fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16 u("лошадка"); - EXPECT_EQ(L"\x043B\x043E\x0448\x0430\x0434\x043A\x0430", u.str()); - EXPECT_EQ(7, u.size()); - // U+10437 { DESERET SMALL LETTER YEE } - EXPECT_EQ(L"\xD801\xDC37", fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16("𐐷").str()); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16("\xc3\x28"), std::runtime_error, - "invalid utf8"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16(fmt::string_view("л", 1)), - std::runtime_error, "invalid utf8"); - EXPECT_EQ(L"123456", fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16("123456").str()); -} - -TEST(UtilTest, UTF8ToUTF16EmptyString) { - std::string s = ""; - fmt::detail::utf8_to_utf16 u(s.c_str()); - EXPECT_EQ(L"", u.str()); - EXPECT_EQ(s.size(), u.size()); -} - -TEST(UtilTest, FormatSystemError) { - fmt::memory_buffer message; - fmt::format_system_error(message, EDOM, "test"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("test: {}", get_system_error(EDOM)), - to_string(message)); - message = fmt::memory_buffer(); - - // Check if std::allocator throws on allocating max size_t / 2 chars. - size_t max_size = max_value<size_t>() / 2; - bool throws_on_alloc = false; - try { - std::allocator<char> alloc; - alloc.deallocate(alloc.allocate(max_size), max_size); - } catch (const std::bad_alloc&) { - throws_on_alloc = true; +template <typename Allocator, size_t MaxSize> +class max_size_allocator : public Allocator { + public: + using typename Allocator::value_type; + size_t max_size() const noexcept { return MaxSize; } + value_type* allocate(size_t n) { + if (n > max_size()) { + throw std::length_error("size > max_size"); + } + return std::allocator_traits<Allocator>::allocate( + *static_cast<Allocator*>(this), n); } - if (!throws_on_alloc) { - fmt::print("warning: std::allocator allocates {} chars", max_size); - return; + void deallocate(value_type* p, size_t n) { + std::allocator_traits<Allocator>::deallocate(*static_cast<Allocator*>(this), + p, n); } - fmt::format_system_error(message, EDOM, fmt::string_view(nullptr, max_size)); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("error {}", EDOM), to_string(message)); -} - -TEST(UtilTest, SystemError) { - fmt::system_error e(EDOM, "test"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("test: {}", get_system_error(EDOM)), e.what()); - EXPECT_EQ(EDOM, e.error_code()); - - fmt::system_error error(0, ""); - try { - throw fmt::system_error(EDOM, "test {}", "error"); - } catch (const fmt::system_error& e) { - error = e; - } - fmt::memory_buffer message; - fmt::format_system_error(message, EDOM, "test error"); - EXPECT_EQ(to_string(message), error.what()); - EXPECT_EQ(EDOM, error.error_code()); -} +}; -TEST(UtilTest, ReportSystemError) { - fmt::memory_buffer out; - fmt::format_system_error(out, EDOM, "test error"); - out.push_back('\n'); - EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::report_system_error(EDOM, "test error"), - to_string(out)); +TEST(memory_buffer_test, max_size_allocator) { + // 160 = 128 + 32 + using test_allocator = max_size_allocator<std::allocator<char>, 160>; + basic_memory_buffer<char, 10, test_allocator> buffer; + buffer.resize(128); + // new_capacity = 128 + 128/2 = 192 > 160 + buffer.resize(160); // Shouldn't throw. } -TEST(StringViewTest, Ctor) { - EXPECT_STREQ("abc", string_view("abc").data()); - EXPECT_EQ(3u, string_view("abc").size()); - - EXPECT_STREQ("defg", string_view(std::string("defg")).data()); - EXPECT_EQ(4u, string_view(std::string("defg")).size()); +TEST(memory_buffer_test, max_size_allocator_overflow) { + using test_allocator = max_size_allocator<std::allocator<char>, 160>; + basic_memory_buffer<char, 10, test_allocator> buffer; + EXPECT_THROW(buffer.resize(161), std::exception); } -TEST(FormatToTest, FormatWithoutArgs) { - std::string s; - fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), "test"); - EXPECT_EQ("test", s); +TEST(format_test, exception_from_lib) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::throw_format_error("test"), format_error, "test"); } -TEST(FormatToTest, Format) { - std::string s; - fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), "part{0}", 1); - EXPECT_EQ("part1", s); - fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), "part{0}", 2); - EXPECT_EQ("part1part2", s); -} +TEST(format_test, escape) { + EXPECT_EQ("{", fmt::format("{{")); + EXPECT_EQ("before {", fmt::format("before {{")); + EXPECT_EQ("{ after", fmt::format("{{ after")); + EXPECT_EQ("before { after", fmt::format("before {{ after")); -TEST(FormatToTest, WideString) { - std::vector<wchar_t> buf; - fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), L"{}{}", 42, L'\0'); - EXPECT_STREQ(buf.data(), L"42"); -} + EXPECT_EQ("}", fmt::format("}}")); + EXPECT_EQ("before }", fmt::format("before }}")); + EXPECT_EQ("} after", fmt::format("}} after")); + EXPECT_EQ("before } after", fmt::format("before }} after")); -TEST(FormatToTest, FormatToMemoryBuffer) { - fmt::basic_memory_buffer<char, 100> buffer; - fmt::format_to(buffer, "{}", "foo"); - EXPECT_EQ("foo", to_string(buffer)); - fmt::wmemory_buffer wbuffer; - fmt::format_to(wbuffer, L"{}", L"foo"); - EXPECT_EQ(L"foo", to_string(wbuffer)); + EXPECT_EQ("{}", fmt::format("{{}}")); + EXPECT_EQ("{42}", fmt::format("{{{0}}}", 42)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, Escape) { - EXPECT_EQ("{", format("{{")); - EXPECT_EQ("before {", format("before {{")); - EXPECT_EQ("{ after", format("{{ after")); - EXPECT_EQ("before { after", format("before {{ after")); - - EXPECT_EQ("}", format("}}")); - EXPECT_EQ("before }", format("before }}")); - EXPECT_EQ("} after", format("}} after")); - EXPECT_EQ("before } after", format("before }} after")); - - EXPECT_EQ("{}", format("{{}}")); - EXPECT_EQ("{42}", format("{{{0}}}", 42)); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, UnmatchedBraces) { - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{"), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("}"), format_error, "unmatched '}' in format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0{}"), format_error, "invalid format string"); +TEST(format_test, unmatched_braces) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{")), format_error, + "invalid format string"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("}")), format_error, + "unmatched '}' in format string"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0{}")), format_error, + "invalid format string"); } -TEST(FormatterTest, NoArgs) { EXPECT_EQ("test", format("test")); } +TEST(format_test, no_args) { EXPECT_EQ("test", fmt::format("test")); } -TEST(FormatterTest, ArgsInDifferentPositions) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("before 42", format("before {0}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42 after", format("{0} after", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("before 42 after", format("before {0} after", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("answer = 42", format("{0} = {1}", "answer", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42 is the answer", format("{1} is the {0}", "answer", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("abracadabra", format("{0}{1}{0}", "abra", "cad")); +TEST(format_test, args_in_different_positions) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("before 42", fmt::format("before {0}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 after", fmt::format("{0} after", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("before 42 after", fmt::format("before {0} after", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("answer = 42", fmt::format("{0} = {1}", "answer", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 is the answer", fmt::format("{1} is the {0}", "answer", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("abracadabra", fmt::format("{0}{1}{0}", "abra", "cad")); } -TEST(FormatterTest, ArgErrors) { - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{"), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{?}"), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0"), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0}"), format_error, "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{00}", 42), format_error, "invalid format string"); +TEST(format_test, arg_errors) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{")), format_error, + "invalid format string"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{?}")), format_error, + "invalid format string"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0")), format_error, + "invalid format string"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0}")), format_error, + "argument not found"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{00}"), 42), format_error, + "invalid format string"); - char format_str[BUFFER_SIZE]; + char format_str[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(format_str, "{%u", INT_MAX); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str), format_error, "invalid format string"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str)), format_error, + "invalid format string"); safe_sprintf(format_str, "{%u}", INT_MAX); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str), format_error, "argument not found"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str)), format_error, + "argument not found"); safe_sprintf(format_str, "{%u", INT_MAX + 1u); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str)), format_error, + "invalid format string"); safe_sprintf(format_str, "{%u}", INT_MAX + 1u); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str)), format_error, + "argument not found"); } -template <int N> struct TestFormat { - template <typename... Args> - static std::string format(fmt::string_view format_str, const Args&... args) { - return TestFormat<N - 1>::format(format_str, N - 1, args...); +template <int N> struct test_format { + template <typename... T> + static std::string format(fmt::string_view fmt, const T&... args) { + return test_format<N - 1>::format(fmt, N - 1, args...); } }; -template <> struct TestFormat<0> { - template <typename... Args> - static std::string format(fmt::string_view format_str, const Args&... args) { - return fmt::format(format_str, args...); +template <> struct test_format<0> { + template <typename... T> + static std::string format(fmt::string_view fmt, const T&... args) { + return fmt::format(runtime(fmt), args...); } }; -TEST(FormatterTest, ManyArgs) { - EXPECT_EQ("19", TestFormat<20>::format("{19}")); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(TestFormat<20>::format("{20}"), format_error, +TEST(format_test, many_args) { + EXPECT_EQ("19", test_format<20>::format("{19}")); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_format<20>::format("{20}"), format_error, "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(TestFormat<21>::format("{21}"), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_format<21>::format("{21}"), format_error, "argument not found"); - enum { max_packed_args = fmt::detail::max_packed_args }; + using fmt::detail::max_packed_args; std::string format_str = fmt::format("{{{}}}", max_packed_args + 1); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(TestFormat<max_packed_args>::format(format_str), + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_format<max_packed_args>::format(format_str), format_error, "argument not found"); } -TEST(FormatterTest, NamedArg) { - EXPECT_EQ("1/a/A", format("{_1}/{a_}/{A_}", fmt::arg("a_", 'a'), - fmt::arg("A_", "A"), fmt::arg("_1", 1))); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:{width}}", -42, fmt::arg("width", 4))); - EXPECT_EQ("st", format("{0:.{precision}}", "str", fmt::arg("precision", 2))); - EXPECT_EQ("1 2", format("{} {two}", 1, fmt::arg("two", 2))); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{c}", fmt::arg("a", 0), fmt::arg("b", 0), - fmt::arg("c", 42), fmt::arg("d", 0), fmt::arg("e", 0), - fmt::arg("f", 0), fmt::arg("g", 0), fmt::arg("h", 0), - fmt::arg("i", 0), fmt::arg("j", 0), fmt::arg("k", 0), - fmt::arg("l", 0), fmt::arg("m", 0), fmt::arg("n", 0), - fmt::arg("o", 0), fmt::arg("p", 0))); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{a}"), format_error, "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{a}", 42), format_error, "argument not found"); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, AutoArgIndex) { - EXPECT_EQ("abc", format("{}{}{}", 'a', 'b', 'c')); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0}{}", 'a', 'b'), format_error, +TEST(format_test, named_arg) { + EXPECT_EQ("1/a/A", fmt::format("{_1}/{a_}/{A_}", fmt::arg("a_", 'a'), + fmt::arg("A_", "A"), fmt::arg("_1", 1))); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:{width}}", -42, fmt::arg("width", 4))); + EXPECT_EQ("st", + fmt::format("{0:.{precision}}", "str", fmt::arg("precision", 2))); + EXPECT_EQ("1 2", fmt::format("{} {two}", 1, fmt::arg("two", 2))); + EXPECT_EQ("42", + fmt::format("{c}", fmt::arg("a", 0), fmt::arg("b", 0), + fmt::arg("c", 42), fmt::arg("d", 0), fmt::arg("e", 0), + fmt::arg("f", 0), fmt::arg("g", 0), fmt::arg("h", 0), + fmt::arg("i", 0), fmt::arg("j", 0), fmt::arg("k", 0), + fmt::arg("l", 0), fmt::arg("m", 0), fmt::arg("n", 0), + fmt::arg("o", 0), fmt::arg("p", 0))); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{a}")), format_error, + "argument not found"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{a}"), 42), format_error, + "argument not found"); +} + +TEST(format_test, auto_arg_index) { + EXPECT_EQ("abc", fmt::format("{}{}{}", 'a', 'b', 'c')); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0}{}"), 'a', 'b'), format_error, "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{}{0}", 'a', 'b'), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{}{0}"), 'a', 'b'), format_error, "cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing"); - EXPECT_EQ("1.2", format("{:.{}}", 1.2345, 2)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0}:.{}", 1.2345, 2), format_error, + EXPECT_EQ("1.2", fmt::format("{:.{}}", 1.2345, 2)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0}:.{}"), 1.2345, 2), + format_error, "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:.{0}}", 1.2345, 2), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:.{0}}"), 1.2345, 2), + format_error, "cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{}"), format_error, "argument not found"); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, EmptySpecs) { EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:}", 42)); } - -TEST(FormatterTest, LeftAlign) { - EXPECT_EQ("42 ", format("{0:<4}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42 ", format("{0:<4o}", 042)); - EXPECT_EQ("42 ", format("{0:<4x}", 0x42)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", format("{0:<5}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42 ", format("{0:<5}", 42u)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", format("{0:<5}", -42l)); - EXPECT_EQ("42 ", format("{0:<5}", 42ul)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", format("{0:<5}", -42ll)); - EXPECT_EQ("42 ", format("{0:<5}", 42ull)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", format("{0:<5}", -42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", format("{0:<5}", -42.0l)); - EXPECT_EQ("c ", format("{0:<5}", 'c')); - EXPECT_EQ("abc ", format("{0:<5}", "abc")); - EXPECT_EQ("0xface ", format("{0:<8}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface))); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, RightAlign) { - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:>4}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:>4o}", 042)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:>4x}", 0x42)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:>5}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:>5}", 42u)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:>5}", -42l)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:>5}", 42ul)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:>5}", -42ll)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:>5}", 42ull)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:>5}", -42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:>5}", -42.0l)); - EXPECT_EQ(" c", format("{0:>5}", 'c')); - EXPECT_EQ(" abc", format("{0:>5}", "abc")); - EXPECT_EQ(" 0xface", format("{0:>8}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface))); -} - -#if FMT_DEPRECATED_NUMERIC_ALIGN -TEST(FormatterTest, NumericAlign) { EXPECT_EQ("0042", format("{0:=4}", 42)); } -#endif + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{}")), format_error, + "argument not found"); +} -TEST(FormatterTest, CenterAlign) { - EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", format("{0:^5}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", format("{0:^5o}", 042)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", format("{0:^5x}", 0x42)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", format("{0:^5}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", format("{0:^5}", 42u)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", format("{0:^5}", -42l)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", format("{0:^5}", 42ul)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", format("{0:^5}", -42ll)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", format("{0:^5}", 42ull)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", format("{0:^5}", -42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", format("{0:^5}", -42.0l)); - EXPECT_EQ(" c ", format("{0:^5}", 'c')); - EXPECT_EQ(" abc ", format("{0:^6}", "abc")); - EXPECT_EQ(" 0xface ", format("{0:^8}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface))); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, Fill) { - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{<5}", 'c'), format_error, +TEST(format_test, empty_specs) { EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:}", 42)); } + +TEST(format_test, left_align) { + EXPECT_EQ("42 ", fmt::format("{0:<4}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 ", fmt::format("{0:<4o}", 042)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 ", fmt::format("{0:<4x}", 0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", 42u)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", -42l)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", 42ul)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", -42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ("42 ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", 42ull)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", -42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", -42.0l)); + EXPECT_EQ("c ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", 'c')); + EXPECT_EQ("abc ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", "abc")); + EXPECT_EQ("0xface ", fmt::format("{0:<8}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface))); +} + +TEST(format_test, right_align) { + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:>4}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:>4o}", 042)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:>4x}", 0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:>5}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:>5}", 42u)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:>5}", -42l)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:>5}", 42ul)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:>5}", -42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:>5}", 42ull)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:>5}", -42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:>5}", -42.0l)); + EXPECT_EQ(" c", fmt::format("{0:>5}", 'c')); + EXPECT_EQ(" abc", fmt::format("{0:>5}", "abc")); + EXPECT_EQ(" 0xface", fmt::format("{0:>8}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface))); +} + +TEST(format_test, center_align) { + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5o}", 042)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5x}", 0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", 42u)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", -42l)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", 42ul)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", -42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", 42ull)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", -42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", -42.0l)); + EXPECT_EQ(" c ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", 'c')); + EXPECT_EQ(" abc ", fmt::format("{0:^6}", "abc")); + EXPECT_EQ(" 0xface ", fmt::format("{0:^8}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface))); +} + +TEST(format_test, fill) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{<5}"), 'c'), format_error, "invalid fill character '{'"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{<5}}", 'c'), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{<5}}"), 'c'), format_error, "invalid fill character '{'"); - EXPECT_EQ("**42", format("{0:*>4}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("**-42", format("{0:*>5}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ("***42", format("{0:*>5}", 42u)); - EXPECT_EQ("**-42", format("{0:*>5}", -42l)); - EXPECT_EQ("***42", format("{0:*>5}", 42ul)); - EXPECT_EQ("**-42", format("{0:*>5}", -42ll)); - EXPECT_EQ("***42", format("{0:*>5}", 42ull)); - EXPECT_EQ("**-42", format("{0:*>5}", -42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("**-42", format("{0:*>5}", -42.0l)); - EXPECT_EQ("c****", format("{0:*<5}", 'c')); - EXPECT_EQ("abc**", format("{0:*<5}", "abc")); - EXPECT_EQ("**0xface", format("{0:*>8}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface))); - EXPECT_EQ("foo=", format("{:}=", "foo")); - EXPECT_EQ(std::string("\0\0\0*", 4), format(string_view("{:\0>4}", 6), '*')); - EXPECT_EQ("жж42", format("{0:ж>4}", 42)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:\x80\x80\x80\x80\x80>}", 0), format_error, - "missing '}' in format string"); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, PlusSign) { - EXPECT_EQ("+42", format("{0:+}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", format("{0:+}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ("+42", format("{0:+}", 42)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:+}", 42u), format_error, - "format specifier requires signed argument"); - EXPECT_EQ("+42", format("{0:+}", 42l)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:+}", 42ul), format_error, - "format specifier requires signed argument"); - EXPECT_EQ("+42", format("{0:+}", 42ll)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:+}", 42ull), format_error, - "format specifier requires signed argument"); - EXPECT_EQ("+42", format("{0:+}", 42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("+42", format("{0:+}", 42.0l)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:+", 'c'), format_error, - "missing '}' in format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:+}", 'c'), format_error, - "invalid format specifier for char"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:+}", "abc"), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:+}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, MinusSign) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:-}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", format("{0:-}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:-}", 42)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:-}", 42u), format_error, - "format specifier requires signed argument"); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:-}", 42l)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:-}", 42ul), format_error, - "format specifier requires signed argument"); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:-}", 42ll)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:-}", 42ull), format_error, - "format specifier requires signed argument"); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:-}", 42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:-}", 42.0l)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:-", 'c'), format_error, - "missing '}' in format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:-}", 'c'), format_error, - "invalid format specifier for char"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:-}", "abc"), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:-}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, SpaceSign) { - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0: }", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", format("{0: }", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0: }", 42)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0: }", 42u), format_error, - "format specifier requires signed argument"); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0: }", 42l)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0: }", 42ul), format_error, - "format specifier requires signed argument"); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0: }", 42ll)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0: }", 42ull), format_error, - "format specifier requires signed argument"); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0: }", 42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0: }", 42.0l)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0: ", 'c'), format_error, + EXPECT_EQ("**42", fmt::format("{0:*>4}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("**-42", fmt::format("{0:*>5}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("***42", fmt::format("{0:*>5}", 42u)); + EXPECT_EQ("**-42", fmt::format("{0:*>5}", -42l)); + EXPECT_EQ("***42", fmt::format("{0:*>5}", 42ul)); + EXPECT_EQ("**-42", fmt::format("{0:*>5}", -42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ("***42", fmt::format("{0:*>5}", 42ull)); + EXPECT_EQ("**-42", fmt::format("{0:*>5}", -42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("**-42", fmt::format("{0:*>5}", -42.0l)); + EXPECT_EQ("c****", fmt::format("{0:*<5}", 'c')); + EXPECT_EQ("abc**", fmt::format("{0:*<5}", "abc")); + EXPECT_EQ("**0xface", + fmt::format("{0:*>8}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface))); + EXPECT_EQ("foo=", fmt::format("{:}=", "foo")); + EXPECT_EQ(std::string("\0\0\0*", 4), + fmt::format(string_view("{:\0>4}", 6), '*')); + EXPECT_EQ("жж42", fmt::format("{0:ж>4}", 42)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:\x80\x80\x80\x80\x80>}"), 0), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); +} + +TEST(format_test, plus_sign) { + EXPECT_EQ("+42", fmt::format("{0:+}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0:+}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("+42", fmt::format("{0:+}", 42)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:+}"), 42u), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ("+42", fmt::format("{0:+}", 42l)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:+}"), 42ul), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ("+42", fmt::format("{0:+}", 42ll)); +#if FMT_USE_INT128 + EXPECT_EQ("+42", fmt::format("{0:+}", __int128_t(42))); +#endif + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:+}"), 42ull), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ("+42", fmt::format("{0:+}", 42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("+42", fmt::format("{0:+}", 42.0l)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:+}"), 'c'), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:+}"), "abc"), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:+}"), reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); +} + +TEST(format_test, minus_sign) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:-}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0:-}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:-}", 42)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:-}"), 42u), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:-}", 42l)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:-}"), 42ul), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:-}", 42ll)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:-}"), 42ull), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:-}", 42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:-}", 42.0l)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:-}"), 'c'), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:-}"), "abc"), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:-}"), reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); +} + +TEST(format_test, space_sign) { + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0: }", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0: }", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0: }", 42)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0: }"), 42u), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0: }", 42l)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0: }"), 42ul), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0: }", 42ll)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0: }"), 42ull), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0: }", 42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0: }", 42.0l)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0: }"), 'c'), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0: }"), "abc"), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{0: }"), reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); +} + +TEST(format_test, hash_flag) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:#}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0:#}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("0b101010", fmt::format("{0:#b}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("0B101010", fmt::format("{0:#B}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-0b101010", fmt::format("{0:#b}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("0x42", fmt::format("{0:#x}", 0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ("0X42", fmt::format("{0:#X}", 0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-0x42", fmt::format("{0:#x}", -0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0:#o}", 0)); + EXPECT_EQ("042", fmt::format("{0:#o}", 042)); + EXPECT_EQ("-042", fmt::format("{0:#o}", -042)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:#}", 42u)); + EXPECT_EQ("0x42", fmt::format("{0:#x}", 0x42u)); + EXPECT_EQ("042", fmt::format("{0:#o}", 042u)); + + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0:#}", -42l)); + EXPECT_EQ("0x42", fmt::format("{0:#x}", 0x42l)); + EXPECT_EQ("-0x42", fmt::format("{0:#x}", -0x42l)); + EXPECT_EQ("042", fmt::format("{0:#o}", 042l)); + EXPECT_EQ("-042", fmt::format("{0:#o}", -042l)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:#}", 42ul)); + EXPECT_EQ("0x42", fmt::format("{0:#x}", 0x42ul)); + EXPECT_EQ("042", fmt::format("{0:#o}", 042ul)); + + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0:#}", -42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ("0x42", fmt::format("{0:#x}", 0x42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ("-0x42", fmt::format("{0:#x}", -0x42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ("042", fmt::format("{0:#o}", 042ll)); + EXPECT_EQ("-042", fmt::format("{0:#o}", -042ll)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:#}", 42ull)); + EXPECT_EQ("0x42", fmt::format("{0:#x}", 0x42ull)); + EXPECT_EQ("042", fmt::format("{0:#o}", 042ull)); + + EXPECT_EQ("-42.", fmt::format("{0:#}", -42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42.", fmt::format("{0:#}", -42.0l)); + EXPECT_EQ("4.e+01", fmt::format("{:#.0e}", 42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.", fmt::format("{:#.0f}", 0.01)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.50", fmt::format("{:#.2g}", 0.5)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.", fmt::format("{:#.0f}", 0.5)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:#"), 'c'), format_error, "missing '}' in format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0: }", 'c'), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:#}"), 'c'), format_error, "invalid format specifier for char"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0: }", "abc"), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0: }", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, SignNotTruncated) { - wchar_t format_str[] = {L'{', L':', - '+' | (1 << fmt::detail::num_bits<char>()), L'}', 0}; - EXPECT_THROW(format(format_str, 42), format_error); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, HashFlag) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:#}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", format("{0:#}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ("0b101010", format("{0:#b}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("0B101010", format("{0:#B}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("-0b101010", format("{0:#b}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ("0x42", format("{0:#x}", 0x42)); - EXPECT_EQ("0X42", format("{0:#X}", 0x42)); - EXPECT_EQ("-0x42", format("{0:#x}", -0x42)); - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0:#o}", 0)); - EXPECT_EQ("042", format("{0:#o}", 042)); - EXPECT_EQ("-042", format("{0:#o}", -042)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:#}", 42u)); - EXPECT_EQ("0x42", format("{0:#x}", 0x42u)); - EXPECT_EQ("042", format("{0:#o}", 042u)); - - EXPECT_EQ("-42", format("{0:#}", -42l)); - EXPECT_EQ("0x42", format("{0:#x}", 0x42l)); - EXPECT_EQ("-0x42", format("{0:#x}", -0x42l)); - EXPECT_EQ("042", format("{0:#o}", 042l)); - EXPECT_EQ("-042", format("{0:#o}", -042l)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:#}", 42ul)); - EXPECT_EQ("0x42", format("{0:#x}", 0x42ul)); - EXPECT_EQ("042", format("{0:#o}", 042ul)); - - EXPECT_EQ("-42", format("{0:#}", -42ll)); - EXPECT_EQ("0x42", format("{0:#x}", 0x42ll)); - EXPECT_EQ("-0x42", format("{0:#x}", -0x42ll)); - EXPECT_EQ("042", format("{0:#o}", 042ll)); - EXPECT_EQ("-042", format("{0:#o}", -042ll)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:#}", 42ull)); - EXPECT_EQ("0x42", format("{0:#x}", 0x42ull)); - EXPECT_EQ("042", format("{0:#o}", 042ull)); - - EXPECT_EQ("-42.0", format("{0:#}", -42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42.0", format("{0:#}", -42.0l)); - EXPECT_EQ("4.e+01", format("{:#.0e}", 42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.", format("{:#.0f}", 0.01)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.50", format("{:#.2g}", 0.5)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.", format("{:#.0f}", 0.5)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:#", 'c'), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:#}"), "abc"), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:#}"), reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); +} + +TEST(format_test, zero_flag) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:0}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-0042", fmt::format("{0:05}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("00042", fmt::format("{0:05}", 42u)); + EXPECT_EQ("-0042", fmt::format("{0:05}", -42l)); + EXPECT_EQ("00042", fmt::format("{0:05}", 42ul)); + EXPECT_EQ("-0042", fmt::format("{0:05}", -42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ("00042", fmt::format("{0:05}", 42ull)); + EXPECT_EQ("-000042", fmt::format("{0:07}", -42.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("-000042", fmt::format("{0:07}", -42.0l)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:0"), 'c'), format_error, "missing '}' in format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:#}", 'c'), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:05}"), 'c'), format_error, "invalid format specifier for char"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:#}", "abc"), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:#}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:05}"), "abc"), format_error, "format specifier requires numeric argument"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:05}"), reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), + format_error, "format specifier requires numeric argument"); } -TEST(FormatterTest, ZeroFlag) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:0}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("-0042", format("{0:05}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ("00042", format("{0:05}", 42u)); - EXPECT_EQ("-0042", format("{0:05}", -42l)); - EXPECT_EQ("00042", format("{0:05}", 42ul)); - EXPECT_EQ("-0042", format("{0:05}", -42ll)); - EXPECT_EQ("00042", format("{0:05}", 42ull)); - EXPECT_EQ("-000042", format("{0:07}", -42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("-000042", format("{0:07}", -42.0l)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:0", 'c'), format_error, - "missing '}' in format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:05}", 'c'), format_error, - "invalid format specifier for char"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:05}", "abc"), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:05}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x42)), - format_error, "format specifier requires numeric argument"); +TEST(format_test, zero_flag_and_align) { + // If the 0 character and an align option both appear, the 0 character is + // ignored. + EXPECT_EQ("42 ", fmt::format("{0:<05}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42 ", fmt::format("{0:<05}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42 ", fmt::format("{0:^05}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42 ", fmt::format("{0:^05}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:>05}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:>05}", -42)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, Width) { - char format_str[BUFFER_SIZE]; +TEST(format_test, width) { + char format_str[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(format_str, "{0:%u", UINT_MAX); increment(format_str + 3); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0), format_error, + "number is too big"); size_t size = std::strlen(format_str); format_str[size] = '}'; format_str[size + 1] = 0; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0), format_error, + "number is too big"); safe_sprintf(format_str, "{0:%u", INT_MAX + 1u); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0), format_error, + "number is too big"); safe_sprintf(format_str, "{0:%u}", INT_MAX + 1u); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:4}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:5}", 42u)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:6}", -42l)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:7}", 42ul)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:6}", -42ll)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:7}", 42ull)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -1.23", format("{0:8}", -1.23)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -1.23", format("{0:9}", -1.23l)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 0xcafe", format("{0:10}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe))); - EXPECT_EQ("x ", format("{0:11}", 'x')); - EXPECT_EQ("str ", format("{0:12}", "str")); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^5}", "🤡"), "**🤡**"); -} - -template <typename T> inline T const_check(T value) { return value; } - -TEST(FormatterTest, RuntimeWidth) { - char format_str[BUFFER_SIZE]; + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0), format_error, + "number is too big"); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:4}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:5}", 42u)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:6}", -42l)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:7}", 42ul)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:6}", -42ll)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:7}", 42ull)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -1.23", fmt::format("{0:8}", -1.23)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -1.23", fmt::format("{0:9}", -1.23l)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 0xcafe", + fmt::format("{0:10}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe))); + EXPECT_EQ("x ", fmt::format("{0:11}", 'x')); + EXPECT_EQ("str ", fmt::format("{0:12}", "str")); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^6}", "🤡"), "**🤡**"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^8}", "你好"), "**你好**"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:#6}", 42.0), " 42."); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:6c}", static_cast<int>('x')), "x "); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>06.0f}", 0.00884311), " 0"); +} + +TEST(format_test, runtime_width) { + char format_str[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(format_str, "{0:{%u", UINT_MAX); increment(format_str + 4); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0), format_error, + "invalid format string"); size_t size = std::strlen(format_str); format_str[size] = '}'; format_str[size + 1] = 0; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0), format_error, + "argument not found"); format_str[size + 1] = '}'; format_str[size + 2] = 0; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0), format_error, + "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{", 0), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{}", 0), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{"), 0), format_error, + "invalid format string"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{}"), 0), format_error, "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{?}}", 0), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{1}}", 0), format_error, "argument not found"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{?}}"), 0), format_error, + "invalid format string"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{1}}"), 0), format_error, + "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{0:}}", 0), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{0:}}"), 0), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{1}}", 0, -1), format_error, "negative width"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{1}}", 0, (INT_MAX + 1u)), format_error, - "number is too big"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{1}}", 0, -1l), format_error, "negative width"); - if (const_check(sizeof(long) > sizeof(int))) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{1}}"), 0, -1), format_error, + "negative width"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{1}}"), 0, (INT_MAX + 1u)), + format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{1}}"), 0, -1l), format_error, + "negative width"); + if (fmt::detail::const_check(sizeof(long) > sizeof(int))) { long value = INT_MAX; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{1}}", 0, (value + 1)), format_error, - "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{1}}"), 0, (value + 1)), + format_error, "number is too big"); } - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{1}}", 0, (INT_MAX + 1ul)), format_error, - "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{1}}"), 0, (INT_MAX + 1ul)), + format_error, "number is too big"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{1}}", 0, '0'), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{1}}"), 0, '0'), format_error, "width is not integer"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{1}}", 0, 0.0), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:{1}}"), 0, 0.0), format_error, "width is not integer"); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:{1}}", -42, 4)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:{1}}", 42u, 5)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:{1}}", -42l, 6)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:{1}}", 42ul, 7)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -42", format("{0:{1}}", -42ll, 6)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", format("{0:{1}}", 42ull, 7)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -1.23", format("{0:{1}}", -1.23, 8)); - EXPECT_EQ(" -1.23", format("{0:{1}}", -1.23l, 9)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", -42, 4)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", 42u, 5)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", -42l, 6)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", 42ul, 7)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -42", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", -42ll, 6)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 42", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", 42ull, 7)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -1.23", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", -1.23, 8)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -1.23", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", -1.23l, 9)); EXPECT_EQ(" 0xcafe", - format("{0:{1}}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe), 10)); - EXPECT_EQ("x ", format("{0:{1}}", 'x', 11)); - EXPECT_EQ("str ", format("{0:{1}}", "str", 12)); + fmt::format("{0:{1}}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe), 10)); + EXPECT_EQ("x ", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", 'x', 11)); + EXPECT_EQ("str ", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", "str", 12)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:{}}", 42, short(4)), " 42"); } -TEST(FormatterTest, Precision) { - char format_str[BUFFER_SIZE]; +TEST(format_test, precision) { + char format_str[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(format_str, "{0:.%u", UINT_MAX); increment(format_str + 4); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0.0), format_error, + "number is too big"); size_t size = std::strlen(format_str); format_str[size] = '}'; format_str[size + 1] = 0; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0.0), format_error, + "number is too big"); safe_sprintf(format_str, "{0:.%u", INT_MAX + 1u); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0.0), format_error, + "number is too big"); safe_sprintf(format_str, "{0:.%u}", INT_MAX + 1u); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); - - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.", 0), format_error, - "missing precision specifier"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.}", 0), format_error, - "missing precision specifier"); - - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2", 0), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2}", 42), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2f}", 42), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2}", 42u), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2f}", 42u), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2}", 42l), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2f}", 42l), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2}", 42ul), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2f}", 42ul), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2}", 42ll), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2f}", 42ll), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2}", 42ull), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2f}", 42ull), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:3.0}", 'x'), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_EQ("1.2", format("{0:.2}", 1.2345)); - EXPECT_EQ("1.2", format("{0:.2}", 1.2345l)); - EXPECT_EQ("1.2e+56", format("{:.2}", 1.234e56)); - EXPECT_EQ("1e+00", format("{:.0e}", 1.0L)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 0.0e+00", format("{:9.1e}", 0.0)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0.0), format_error, + "number is too big"); + + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:."), 0.0), format_error, + "invalid precision"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.}"), 0.0), format_error, + "invalid precision"); + + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2"), 0), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2}"), 42), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2f}"), 42), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2}"), 42u), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2f}"), 42u), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2}"), 42l), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2f}"), 42l), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2}"), 42ul), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2f}"), 42ul), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2}"), 42ll), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2f}"), 42ll), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2}"), 42ull), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2f}"), 42ull), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:3.0}"), 'x'), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ("1.2", fmt::format("{0:.2}", 1.2345)); + EXPECT_EQ("1.2", fmt::format("{0:.2}", 1.2345l)); + EXPECT_EQ("1.2e+56", fmt::format("{:.2}", 1.234e56)); + EXPECT_EQ("1.1", fmt::format("{0:.3}", 1.1)); + EXPECT_EQ("1e+00", fmt::format("{:.0e}", 1.0L)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 0.0e+00", fmt::format("{:9.1e}", 0.0)); EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format("{:.494}", 4.9406564584124654E-324), "4.9406564584124654417656879286822137236505980261432476442558568250067550" "727020875186529983636163599237979656469544571773092665671035593979639877" "479601078187812630071319031140452784581716784898210368871863605699873072" "305000638740915356498438731247339727316961514003171538539807412623856559" "117102665855668676818703956031062493194527159149245532930545654440112748" "012970999954193198940908041656332452475714786901472678015935523861155013" - "480352649347201937902681071074917033322268447533357208324319361e-324", - format("{:.494}", 4.9406564584124654E-324)); + "480352649347201937902681071074917033322268447533357208324319361e-324"); EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format("{:.1074f}", 1.1125369292536e-308), + "0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000111253692925360019747947051741965785554081512200979" + "355021686109411883779182127659725163430929750364498219730822952552570601" + "152163505899912777129583674906301179059298598412303893909188340988729019" + "014361467448914817838555156840459458527907308695109202499990850735085304" + "478476991912072201449236975063640913461919914396877093174125167509869762" + "482369631100360266123742648159508919592746619553246586039571522788247697" + "156360766271842991667238355464496455107749716934387136380536472531224398" + "559833794807213172371254492216255558078524900147957309382830827524104234" + "530961756787819847850302379672357738807808384667004752163416921762619527" + "462847642037420991432005657440259928195996762610375541867198059294212446" + "81962777939941034720757232455434770912461317493580281734466552734375"); + + std::string outputs[] = { "-0X1.41FE3FFE71C9E000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" @@ -955,155 +1005,191 @@ TEST(FormatterTest, Precision) { "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000P+127", - format("{:.838A}", -2.14001164E+38)); - EXPECT_EQ("123.", format("{:#.0f}", 123.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("1.23", format("{:.02f}", 1.234)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.001", format("{:.1g}", 0.001)); - EXPECT_EQ("1019666400", format("{}", 1019666432.0f)); - EXPECT_EQ("1e+01", format("{:.0e}", 9.5)); + "-0XA.0FF1FFF38E4F0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + "000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000P+124"}; + EXPECT_THAT(outputs, + testing::Contains(fmt::format("{:.838A}", -2.14001164E+38))); + + if (std::numeric_limits<long double>::digits == 64) { + auto ld = (std::numeric_limits<long double>::min)(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.0}", ld), "3e-4932"); + EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format("{:0g}", std::numeric_limits<long double>::denorm_min()), + "3.6452e-4951"); + } + + EXPECT_EQ("123.", fmt::format("{:#.0f}", 123.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("1.23", fmt::format("{:.02f}", 1.234)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.001", fmt::format("{:.1g}", 0.001)); + EXPECT_EQ("1019666400", fmt::format("{}", 1019666432.0f)); + EXPECT_EQ("1e+01", fmt::format("{:.0e}", 9.5)); EXPECT_EQ("1.0e-34", fmt::format("{:.1e}", 1e-34)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe)), - format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.2f}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe)), - format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:.{}e}", 42.0, fmt::detail::max_value<int>()), + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2}"), reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe)), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.2f}"), reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe)), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:.{}e}"), 42.0, + fmt::detail::max_value<int>()), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format("{:.2147483646f}", -2.2121295195081227E+304), + format_error, "number is too big"); - EXPECT_EQ("st", format("{0:.2}", "str")); + EXPECT_EQ("st", fmt::format("{0:.2}", "str")); + EXPECT_EQ("вожык", fmt::format("{0:.5}", "вожыкі")); } -TEST(FormatterTest, RuntimePrecision) { - char format_str[BUFFER_SIZE]; +TEST(format_test, runtime_precision) { + char format_str[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(format_str, "{0:.{%u", UINT_MAX); increment(format_str + 5); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0.0), format_error, + "invalid format string"); size_t size = std::strlen(format_str); format_str[size] = '}'; format_str[size + 1] = 0; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0.0), format_error, + "argument not found"); format_str[size + 1] = '}'; format_str[size + 2] = 0; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, 0), format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 0.0), format_error, + "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{", 0), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{}", 0), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{"), 0.0), format_error, + "invalid format string"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{}"), 0.0), format_error, "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{?}}", 0), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{?}}"), 0.0), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}", 0, 0), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 0), format_error, "argument not found"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}"), 0, 0), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 0.0), format_error, + "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{0:}}", 0), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{0:}}"), 0.0), format_error, "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 0, -1), format_error, - "negative precision"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 0, (INT_MAX + 1u)), format_error, - "number is too big"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 0, -1l), format_error, - "negative precision"); - if (const_check(sizeof(long) > sizeof(int))) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 0.0, -1), + format_error, "negative precision"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 0.0, (INT_MAX + 1u)), + format_error, "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 0.0, -1l), + format_error, "negative precision"); + if (fmt::detail::const_check(sizeof(long) > sizeof(int))) { long value = INT_MAX; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 0, (value + 1)), format_error, - "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 0.0, (value + 1)), + format_error, "number is too big"); } - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 0, (INT_MAX + 1ul)), format_error, - "number is too big"); - - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 0, '0'), format_error, - "precision is not integer"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 0, 0.0), format_error, - "precision is not integer"); - - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 42, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}f}", 42, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 42u, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}f}", 42u, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 42l, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}f}", 42l, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 42ul, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}f}", 42ul, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 42ll, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}f}", 42ll, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", 42ull, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}f}", 42ull, 2), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:3.{1}}", 'x', 0), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_EQ("1.2", format("{0:.{1}}", 1.2345, 2)); - EXPECT_EQ("1.2", format("{1:.{0}}", 2, 1.2345l)); - - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe), 2), - format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:.{1}f}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe), 2), - format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 0.0, (INT_MAX + 1ul)), + format_error, "number is too big"); - EXPECT_EQ("st", format("{0:.{1}}", "str", 2)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 0.0, '0'), + format_error, "precision is not integer"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 0.0, 0.0), + format_error, "precision is not integer"); + + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 42, 2), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}f}"), 42, 2), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 42u, 2), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}f}"), 42u, 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 42l, 2), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}f}"), 42l, 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 42ul, 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}f}"), 42ul, 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 42ll, 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}f}"), 42ll, 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), 42ull, 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}f}"), 42ull, 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:3.{1}}"), 'x', 0), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ("1.2", fmt::format("{0:.{1}}", 1.2345, 2)); + EXPECT_EQ("1.2", fmt::format("{1:.{0}}", 2, 1.2345l)); + + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}}"), + reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe), 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:.{1}f}"), + reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xcafe), 2), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + + EXPECT_EQ("st", fmt::format("{0:.{1}}", "str", 2)); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_bool) { + EXPECT_EQ("true", fmt::format("{}", true)); + EXPECT_EQ("false", fmt::format("{}", false)); + EXPECT_EQ("1", fmt::format("{:d}", true)); + EXPECT_EQ("true ", fmt::format("{:5}", true)); + EXPECT_EQ("true", fmt::format("{:s}", true)); + EXPECT_EQ("false", fmt::format("{:s}", false)); + EXPECT_EQ("false ", fmt::format("{:6s}", false)); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_short) { + short s = 42; + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:d}", s)); + unsigned short us = 42; + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:d}", us)); } template <typename T> void check_unknown_types(const T& value, const char* types, const char*) { - char format_str[BUFFER_SIZE]; - const char* special = ".0123456789}"; + char format_str[buffer_size]; + const char* special = ".0123456789L?}"; for (int i = CHAR_MIN; i <= CHAR_MAX; ++i) { char c = static_cast<char>(i); if (std::strchr(types, c) || std::strchr(special, c) || !c) continue; safe_sprintf(format_str, "{0:10%c}", c); - const char* message = "invalid type specifier"; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format(format_str, value), format_error, message) + const char* message = "invalid format specifier"; + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime(format_str), value), + format_error, message) << format_str << " " << message; } } -TEST(BoolTest, FormatBool) { - EXPECT_EQ("true", format("{}", true)); - EXPECT_EQ("false", format("{}", false)); - EXPECT_EQ("1", format("{:d}", true)); - EXPECT_EQ("true ", format("{:5}", true)); - EXPECT_EQ(L"true", format(L"{}", true)); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatShort) { - short s = 42; - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:d}", s)); - unsigned short us = 42; - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:d}", us)); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatInt) { - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:v", 42), format_error, - "missing '}' in format string"); +TEST(format_test, format_int) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:v"), 42), format_error, + "invalid format specifier"); check_unknown_types(42, "bBdoxXnLc", "integer"); - EXPECT_EQ("x", format("{:c}", static_cast<int>('x'))); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatBin) { - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0:b}", 0)); - EXPECT_EQ("101010", format("{0:b}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("101010", format("{0:b}", 42u)); - EXPECT_EQ("-101010", format("{0:b}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ("11000000111001", format("{0:b}", 12345)); - EXPECT_EQ("10010001101000101011001111000", format("{0:b}", 0x12345678)); - EXPECT_EQ("10010000101010111100110111101111", format("{0:b}", 0x90ABCDEF)); + EXPECT_EQ("x", fmt::format("{:c}", static_cast<int>('x'))); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_bin) { + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0:b}", 0)); + EXPECT_EQ("101010", fmt::format("{0:b}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("101010", fmt::format("{0:b}", 42u)); + EXPECT_EQ("-101010", fmt::format("{0:b}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("11000000111001", fmt::format("{0:b}", 12345)); + EXPECT_EQ("10010001101000101011001111000", fmt::format("{0:b}", 0x12345678)); + EXPECT_EQ("10010000101010111100110111101111", + fmt::format("{0:b}", 0x90ABCDEF)); EXPECT_EQ("11111111111111111111111111111111", - format("{0:b}", max_value<uint32_t>())); + fmt::format("{0:b}", max_value<uint32_t>())); } #if FMT_USE_INT128 @@ -1114,177 +1200,216 @@ constexpr auto int128_min = -int128_max - 1; constexpr auto uint128_max = ~static_cast<__uint128_t>(0); #endif -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatDec) { - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0}", 0)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:d}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0}", 42u)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", format("{0}", -42)); - EXPECT_EQ("12345", format("{0}", 12345)); - EXPECT_EQ("67890", format("{0}", 67890)); +TEST(format_test, format_dec) { + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0}", 0)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42>", fmt::format("{:}>", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:d}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0}", 42u)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0}", -42)); + EXPECT_EQ("12345", fmt::format("{0}", 12345)); + EXPECT_EQ("67890", fmt::format("{0}", 67890)); #if FMT_USE_INT128 - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0}", static_cast<__int128_t>(0))); - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0}", static_cast<__uint128_t>(0))); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0}", static_cast<__int128_t>(0))); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0}", static_cast<__uint128_t>(0))); EXPECT_EQ("9223372036854775808", - format("{0}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MAX) + 1)); + fmt::format("{0}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MAX) + 1)); EXPECT_EQ("-9223372036854775809", - format("{0}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MIN) - 1)); + fmt::format("{0}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MIN) - 1)); EXPECT_EQ("18446744073709551616", - format("{0}", static_cast<__int128_t>(UINT64_MAX) + 1)); + fmt::format("{0}", static_cast<__int128_t>(UINT64_MAX) + 1)); EXPECT_EQ("170141183460469231731687303715884105727", - format("{0}", int128_max)); + fmt::format("{0}", int128_max)); EXPECT_EQ("-170141183460469231731687303715884105728", - format("{0}", int128_min)); + fmt::format("{0}", int128_min)); EXPECT_EQ("340282366920938463463374607431768211455", - format("{0}", uint128_max)); + fmt::format("{0}", uint128_max)); #endif - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; + char buffer[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(buffer, "%d", INT_MIN); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0}", INT_MIN)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0}", INT_MIN)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%d", INT_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0}", INT_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0}", INT_MAX)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%u", UINT_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0}", UINT_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0}", UINT_MAX)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%ld", 0 - static_cast<unsigned long>(LONG_MIN)); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0}", LONG_MIN)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0}", LONG_MIN)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%ld", LONG_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0}", LONG_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0}", LONG_MAX)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%lu", ULONG_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0}", ULONG_MAX)); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatHex) { - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0:x}", 0)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:x}", 0x42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:x}", 0x42u)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", format("{0:x}", -0x42)); - EXPECT_EQ("12345678", format("{0:x}", 0x12345678)); - EXPECT_EQ("90abcdef", format("{0:x}", 0x90abcdef)); - EXPECT_EQ("12345678", format("{0:X}", 0x12345678)); - EXPECT_EQ("90ABCDEF", format("{0:X}", 0x90ABCDEF)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0}", ULONG_MAX)); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_hex) { + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0:x}", 0)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:x}", 0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:x}", 0x42u)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0:x}", -0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ("12345678", fmt::format("{0:x}", 0x12345678)); + EXPECT_EQ("90abcdef", fmt::format("{0:x}", 0x90abcdef)); + EXPECT_EQ("12345678", fmt::format("{0:X}", 0x12345678)); + EXPECT_EQ("90ABCDEF", fmt::format("{0:X}", 0x90ABCDEF)); #if FMT_USE_INT128 - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0:x}", static_cast<__int128_t>(0))); - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0:x}", static_cast<__uint128_t>(0))); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0:x}", static_cast<__int128_t>(0))); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0:x}", static_cast<__uint128_t>(0))); EXPECT_EQ("8000000000000000", - format("{0:x}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MAX) + 1)); + fmt::format("{0:x}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MAX) + 1)); EXPECT_EQ("-8000000000000001", - format("{0:x}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MIN) - 1)); + fmt::format("{0:x}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MIN) - 1)); EXPECT_EQ("10000000000000000", - format("{0:x}", static_cast<__int128_t>(UINT64_MAX) + 1)); - EXPECT_EQ("7fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff", format("{0:x}", int128_max)); - EXPECT_EQ("-80000000000000000000000000000000", format("{0:x}", int128_min)); - EXPECT_EQ("ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff", format("{0:x}", uint128_max)); + fmt::format("{0:x}", static_cast<__int128_t>(UINT64_MAX) + 1)); + EXPECT_EQ("7fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff", + fmt::format("{0:x}", int128_max)); + EXPECT_EQ("-80000000000000000000000000000000", + fmt::format("{0:x}", int128_min)); + EXPECT_EQ("ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff", + fmt::format("{0:x}", uint128_max)); #endif - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; + char buffer[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(buffer, "-%x", 0 - static_cast<unsigned>(INT_MIN)); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:x}", INT_MIN)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:x}", INT_MIN)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%x", INT_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:x}", INT_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:x}", INT_MAX)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%x", UINT_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:x}", UINT_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:x}", UINT_MAX)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "-%lx", 0 - static_cast<unsigned long>(LONG_MIN)); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:x}", LONG_MIN)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:x}", LONG_MIN)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%lx", LONG_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:x}", LONG_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:x}", LONG_MAX)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%lx", ULONG_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:x}", ULONG_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:x}", ULONG_MAX)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatOct) { - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0:o}", 0)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:o}", 042)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0:o}", 042u)); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", format("{0:o}", -042)); - EXPECT_EQ("12345670", format("{0:o}", 012345670)); +TEST(format_test, format_oct) { + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0:o}", 0)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:o}", 042)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:o}", 042u)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0:o}", -042)); + EXPECT_EQ("12345670", fmt::format("{0:o}", 012345670)); #if FMT_USE_INT128 - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0:o}", static_cast<__int128_t>(0))); - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0:o}", static_cast<__uint128_t>(0))); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0:o}", static_cast<__int128_t>(0))); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0:o}", static_cast<__uint128_t>(0))); EXPECT_EQ("1000000000000000000000", - format("{0:o}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MAX) + 1)); + fmt::format("{0:o}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MAX) + 1)); EXPECT_EQ("-1000000000000000000001", - format("{0:o}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MIN) - 1)); + fmt::format("{0:o}", static_cast<__int128_t>(INT64_MIN) - 1)); EXPECT_EQ("2000000000000000000000", - format("{0:o}", static_cast<__int128_t>(UINT64_MAX) + 1)); + fmt::format("{0:o}", static_cast<__int128_t>(UINT64_MAX) + 1)); EXPECT_EQ("1777777777777777777777777777777777777777777", - format("{0:o}", int128_max)); + fmt::format("{0:o}", int128_max)); EXPECT_EQ("-2000000000000000000000000000000000000000000", - format("{0:o}", int128_min)); + fmt::format("{0:o}", int128_min)); EXPECT_EQ("3777777777777777777777777777777777777777777", - format("{0:o}", uint128_max)); + fmt::format("{0:o}", uint128_max)); #endif - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; + char buffer[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(buffer, "-%o", 0 - static_cast<unsigned>(INT_MIN)); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:o}", INT_MIN)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:o}", INT_MIN)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%o", INT_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:o}", INT_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:o}", INT_MAX)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%o", UINT_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:o}", UINT_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:o}", UINT_MAX)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "-%lo", 0 - static_cast<unsigned long>(LONG_MIN)); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:o}", LONG_MIN)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:o}", LONG_MIN)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%lo", LONG_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:o}", LONG_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:o}", LONG_MAX)); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%lo", ULONG_MAX); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:o}", ULONG_MAX)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:o}", ULONG_MAX)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatIntLocale) { - EXPECT_EQ("1234", format("{:L}", 1234)); +TEST(format_test, format_int_locale) { + EXPECT_EQ("1234", fmt::format("{:L}", 1234)); } -struct ConvertibleToLongLong { - operator long long() const { return 1LL << 32; } -}; - -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatConvertibleToLongLong) { - EXPECT_EQ("100000000", format("{:x}", ConvertibleToLongLong())); +TEST(format_test, format_float) { + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{}", 0.0f)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.500000", fmt::format("{0:f}", 392.5f)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatFloat) { - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{}", 0.0f)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.500000", format("{0:f}", 392.5f)); +TEST(format_test, format_double) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", 0.0), "0"); + check_unknown_types(1.2, "eEfFgGaAnL%", "double"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:}", 0.0), "0"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:f}", 0.0), "0.000000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:g}", 0.0), "0"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:}", 392.65), "392.65"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:g}", 392.65), "392.65"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:G}", 392.65), "392.65"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:g}", 4.9014e6), "4.9014e+06"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:f}", 392.65), "392.650000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:F}", 392.65), "392.650000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:L}", 42.0), "42"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:24a}", 4.2f), " 0x1.0cccccp+2"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:24a}", 4.2), " 0x1.0cccccccccccdp+2"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:<24a}", 4.2), "0x1.0cccccccccccdp+2 "); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{0:e}", 392.65), "3.926500e+02"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{0:E}", 392.65), "3.926500E+02"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{0:+010.4g}", 392.65), "+0000392.6"); + char buffer[buffer_size]; + +#if FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L + double xd = 0x1.ffffffffffp+2; + safe_sprintf(buffer, "%.*a", 10, xd); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.10a}", xd), buffer); + safe_sprintf(buffer, "%.*a", 9, xd); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.9a}", xd), buffer); + + if (std::numeric_limits<long double>::digits == 64) { + auto ld = 0xf.ffffffffffp-3l; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:a}", ld), "0xf.ffffffffffp-3"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.10a}", ld), "0xf.ffffffffffp-3"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.9a}", ld), "0x1.000000000p+1"); + } +#endif + + if (fmt::detail::const_check(std::numeric_limits<double>::is_iec559)) { + double d = (std::numeric_limits<double>::min)(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:a}", d), "0x1p-1022"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:#a}", d), "0x1.p-1022"); + + d = (std::numeric_limits<double>::max)(); + safe_sprintf(buffer, "%a", d); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:a}", d), buffer); + + d = std::numeric_limits<double>::denorm_min(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:a}", d), "0x0.0000000000001p-1022"); + } + + if (std::numeric_limits<long double>::digits == 64) { + auto ld = (std::numeric_limits<long double>::min)(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:a}", ld), "0x8p-16385"); + + ld = (std::numeric_limits<long double>::max)(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:a}", ld), "0xf.fffffffffffffffp+16380"); + + ld = std::numeric_limits<long double>::denorm_min(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:a}", ld), "0x0.000000000000001p-16382"); + } + + safe_sprintf(buffer, "%.*a", 10, 4.2); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.10a}", 4.2), buffer); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:a}", -42.0), "-0x1.5p+5"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:A}", -42.0), "-0X1.5P+5"); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:f}", 9223372036854775807.0), + "9223372036854775808.000000"); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatDouble) { - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{}", 0.0)); - check_unknown_types(1.2, "eEfFgGaAnL%", "double"); - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{:}", 0.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.000000", format("{:f}", 0.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{:g}", 0.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.65", format("{:}", 392.65)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.65", format("{:g}", 392.65)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.65", format("{:G}", 392.65)); - EXPECT_EQ("4.9014e+06", format("{:g}", 4.9014e6)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.650000", format("{:f}", 392.65)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.650000", format("{:F}", 392.65)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{:L}", 42.0)); - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; - safe_sprintf(buffer, "%e", 392.65); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:e}", 392.65)); - safe_sprintf(buffer, "%E", 392.65); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:E}", 392.65)); - EXPECT_EQ("+0000392.6", format("{0:+010.4g}", 392.65)); - safe_sprintf(buffer, "%a", -42.0); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{:a}", -42.0)); - safe_sprintf(buffer, "%A", -42.0); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{:A}", -42.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("9223372036854775808.000000", - format("{:f}", 9223372036854775807.0)); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, PrecisionRounding) { - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{:.0f}", 0.0)); - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{:.0f}", 0.01)); - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{:.0f}", 0.1)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.000", format("{:.3f}", 0.00049)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.001", format("{:.3f}", 0.0005)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.001", format("{:.3f}", 0.00149)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.002", format("{:.3f}", 0.0015)); - EXPECT_EQ("1.000", format("{:.3f}", 0.9999)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.00123", format("{:.3}", 0.00123)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.1", format("{:.16g}", 0.1)); +TEST(format_test, precision_rounding) { + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{:.0f}", 0.0)); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{:.0f}", 0.01)); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{:.0f}", 0.1)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.000", fmt::format("{:.3f}", 0.00049)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.001", fmt::format("{:.3f}", 0.0005)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.001", fmt::format("{:.3f}", 0.00149)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.002", fmt::format("{:.3f}", 0.0015)); + EXPECT_EQ("1.000", fmt::format("{:.3f}", 0.9999)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.00123", fmt::format("{:.3}", 0.00123)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.1", fmt::format("{:.16g}", 0.1)); EXPECT_EQ("1", fmt::format("{:.0}", 1.0)); EXPECT_EQ("225.51575035152063720", fmt::format("{:.17f}", 225.51575035152064)); @@ -1292,12 +1417,9 @@ TEST(FormatterTest, PrecisionRounding) { EXPECT_EQ("1.9156918820264798e-56", fmt::format("{}", 1.9156918820264798e-56)); EXPECT_EQ("0.0000", fmt::format("{:.4f}", 7.2809479766055470e-15)); - - // Trigger a rounding error in Grisu by a specially chosen number. - EXPECT_EQ("3788512123356.985352", format("{:f}", 3788512123356.985352)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, PrettifyFloat) { +TEST(format_test, prettify_float) { EXPECT_EQ("0.0001", fmt::format("{}", 1e-4)); EXPECT_EQ("1e-05", fmt::format("{}", 1e-5)); EXPECT_EQ("1000000000000000", fmt::format("{}", 1e15)); @@ -1309,131 +1431,182 @@ TEST(FormatterTest, PrettifyFloat) { EXPECT_EQ("12.34", fmt::format("{}", 1234e-2)); EXPECT_EQ("0.001234", fmt::format("{}", 1234e-6)); EXPECT_EQ("0.1", fmt::format("{}", 0.1f)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.10000000149011612", fmt::format("{}", double(0.1f))); EXPECT_EQ("1.3563156e-19", fmt::format("{}", 1.35631564e-19f)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatNaN) { +TEST(format_test, format_nan) { double nan = std::numeric_limits<double>::quiet_NaN(); - EXPECT_EQ("nan", format("{}", nan)); - EXPECT_EQ("+nan", format("{:+}", nan)); - if (std::signbit(-nan)) - EXPECT_EQ("-nan", format("{}", -nan)); - else + EXPECT_EQ("nan", fmt::format("{}", nan)); + EXPECT_EQ("+nan", fmt::format("{:+}", nan)); + EXPECT_EQ(" +nan", fmt::format("{:+06}", nan)); + EXPECT_EQ("+nan ", fmt::format("{:<+06}", nan)); + EXPECT_EQ(" +nan ", fmt::format("{:^+06}", nan)); + EXPECT_EQ(" +nan", fmt::format("{:>+06}", nan)); + if (std::signbit(-nan)) { + EXPECT_EQ("-nan", fmt::format("{}", -nan)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -nan", fmt::format("{:+06}", -nan)); + } else { fmt::print("Warning: compiler doesn't handle negative NaN correctly"); - EXPECT_EQ(" nan", format("{: }", nan)); - EXPECT_EQ("NAN", format("{:F}", nan)); - EXPECT_EQ("nan ", format("{:<7}", nan)); - EXPECT_EQ(" nan ", format("{:^7}", nan)); - EXPECT_EQ(" nan", format("{:>7}", nan)); + } + EXPECT_EQ(" nan", fmt::format("{: }", nan)); + EXPECT_EQ("NAN", fmt::format("{:F}", nan)); + EXPECT_EQ("nan ", fmt::format("{:<7}", nan)); + EXPECT_EQ(" nan ", fmt::format("{:^7}", nan)); + EXPECT_EQ(" nan", fmt::format("{:>7}", nan)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatInfinity) { +TEST(format_test, format_infinity) { double inf = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); - EXPECT_EQ("inf", format("{}", inf)); - EXPECT_EQ("+inf", format("{:+}", inf)); - EXPECT_EQ("-inf", format("{}", -inf)); - EXPECT_EQ(" inf", format("{: }", inf)); - EXPECT_EQ("INF", format("{:F}", inf)); - EXPECT_EQ("inf ", format("{:<7}", inf)); - EXPECT_EQ(" inf ", format("{:^7}", inf)); - EXPECT_EQ(" inf", format("{:>7}", inf)); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatLongDouble) { - EXPECT_EQ("0", format("{0:}", 0.0l)); - EXPECT_EQ("0.000000", format("{0:f}", 0.0l)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.65", format("{0:}", 392.65l)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.65", format("{0:g}", 392.65l)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.65", format("{0:G}", 392.65l)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.650000", format("{0:f}", 392.65l)); - EXPECT_EQ("392.650000", format("{0:F}", 392.65l)); - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; + EXPECT_EQ("inf", fmt::format("{}", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ("+inf", fmt::format("{:+}", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ("-inf", fmt::format("{}", -inf)); + EXPECT_EQ(" +inf", fmt::format("{:+06}", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ(" -inf", fmt::format("{:+06}", -inf)); + EXPECT_EQ("+inf ", fmt::format("{:<+06}", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ(" +inf ", fmt::format("{:^+06}", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ(" +inf", fmt::format("{:>+06}", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ(" inf", fmt::format("{: }", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ("INF", fmt::format("{:F}", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ("inf ", fmt::format("{:<7}", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ(" inf ", fmt::format("{:^7}", inf)); + EXPECT_EQ(" inf", fmt::format("{:>7}", inf)); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_long_double) { + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{0:}", 0.0l)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.000000", fmt::format("{0:f}", 0.0l)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.0", fmt::format("{:.1f}", 0.000000001l)); + EXPECT_EQ("0.10", fmt::format("{:.2f}", 0.099l)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.65", fmt::format("{0:}", 392.65l)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.65", fmt::format("{0:g}", 392.65l)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.65", fmt::format("{0:G}", 392.65l)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.650000", fmt::format("{0:f}", 392.65l)); + EXPECT_EQ("392.650000", fmt::format("{0:F}", 392.65l)); + char buffer[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(buffer, "%Le", 392.65l); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{0:e}", 392.65l)); - EXPECT_EQ("+0000392.6", format("{0:+010.4g}", 392.64l)); - safe_sprintf(buffer, "%La", 3.31l); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{:a}", 3.31l)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{0:e}", 392.65l)); + EXPECT_EQ("+0000392.6", fmt::format("{0:+010.4g}", 392.64l)); + + auto ld = 3.31l; + if (fmt::detail::is_double_double<decltype(ld)>::value) { + safe_sprintf(buffer, "%a", static_cast<double>(ld)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{:a}", ld)); + } else if (std::numeric_limits<long double>::digits == 64) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:a}", ld), "0xd.3d70a3d70a3d70ap-2"); + } } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatChar) { - const char types[] = "cbBdoxXL"; +TEST(format_test, format_char) { + const char types[] = "cbBdoxX"; check_unknown_types('a', types, "char"); - EXPECT_EQ("a", format("{0}", 'a')); - EXPECT_EQ("z", format("{0:c}", 'z')); - EXPECT_EQ(L"a", format(L"{0}", 'a')); + EXPECT_EQ("a", fmt::format("{0}", 'a')); + EXPECT_EQ("z", fmt::format("{0:c}", 'z')); int n = 'x'; for (const char* type = types + 1; *type; ++type) { std::string format_str = fmt::format("{{:{}}}", *type); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(format_str, n), fmt::format(format_str, 'x')); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(runtime(format_str), n), + fmt::format(runtime(format_str), 'x')) + << format_str; } EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:02X}", n), fmt::format("{:02X}", 'x')); -} -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatVolatileChar) { - volatile char c = 'x'; - EXPECT_EQ("x", format("{}", c)); + EXPECT_EQ("\n", fmt::format("{}", '\n')); + EXPECT_EQ("'\\n'", fmt::format("{:?}", '\n')); + EXPECT_EQ("ff", fmt::format("{:x}", '\xff')); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatUnsignedChar) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{}", static_cast<unsigned char>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{}", static_cast<uint8_t>(42))); +TEST(format_test, format_volatile_char) { + volatile char c = 'x'; + EXPECT_EQ("x", fmt::format("{}", c)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatWChar) { - EXPECT_EQ(L"a", format(L"{0}", L'a')); - // This shouldn't compile: - // format("{}", L'a'); +TEST(format_test, format_unsigned_char) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{}", static_cast<unsigned char>(42))); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{}", static_cast<uint8_t>(42))); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatCString) { +TEST(format_test, format_cstring) { check_unknown_types("test", "sp", "string"); - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{0}", "test")); - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{0:s}", "test")); + EXPECT_EQ("test", fmt::format("{0}", "test")); + EXPECT_EQ("test", fmt::format("{0:s}", "test")); char nonconst[] = "nonconst"; - EXPECT_EQ("nonconst", format("{0}", nonconst)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0}", static_cast<const char*>(nullptr)), - format_error, "string pointer is null"); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatSCharString) { - signed char str[] = "test"; - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{0:s}", str)); - const signed char* const_str = str; - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{0:s}", const_str)); + EXPECT_EQ("nonconst", fmt::format("{0}", nonconst)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("{0}"), static_cast<const char*>(nullptr)), + format_error, "string pointer is null"); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatUCharString) { - unsigned char str[] = "test"; - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{0:s}", str)); - const unsigned char* const_str = str; - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{0:s}", const_str)); - unsigned char* ptr = str; - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{0:s}", ptr)); -} +void function_pointer_test(int, double, std::string) {} -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatPointer) { +TEST(format_test, format_pointer) { check_unknown_types(reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x1234), "p", "pointer"); - EXPECT_EQ("0x0", format("{0}", static_cast<void*>(nullptr))); - EXPECT_EQ("0x1234", format("{0}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x1234))); - EXPECT_EQ("0x1234", format("{0:p}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x1234))); - EXPECT_EQ("0x" + std::string(sizeof(void*) * CHAR_BIT / 4, 'f'), - format("{0}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(~uintptr_t()))); - EXPECT_EQ("0x1234", format("{}", fmt::ptr(reinterpret_cast<int*>(0x1234)))); + EXPECT_EQ("0x0", fmt::format("{0}", static_cast<void*>(nullptr))); + EXPECT_EQ("0x1234", fmt::format("{0}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x1234))); + EXPECT_EQ("0x1234", fmt::format("{0:p}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x1234))); + // On CHERI (or other fat-pointer) systems, the size of a pointer is greater + // than the size an integer that can hold a virtual address. There is no + // portable address-as-an-integer type (yet) in C++, so we use `size_t` as + // the closest equivalent for now. + EXPECT_EQ("0x" + std::string(sizeof(size_t) * CHAR_BIT / 4, 'f'), + fmt::format("{0}", reinterpret_cast<void*>(~uintptr_t()))); + EXPECT_EQ("0x1234", + fmt::format("{}", fmt::ptr(reinterpret_cast<int*>(0x1234)))); std::unique_ptr<int> up(new int(1)); - EXPECT_EQ(format("{}", fmt::ptr(up.get())), format("{}", fmt::ptr(up))); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::ptr(up.get())), + fmt::format("{}", fmt::ptr(up))); + struct custom_deleter { + void operator()(int* p) const { delete p; } + }; + std::unique_ptr<int, custom_deleter> upcd(new int(1)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::ptr(upcd.get())), + fmt::format("{}", fmt::ptr(upcd))); std::shared_ptr<int> sp(new int(1)); - EXPECT_EQ(format("{}", fmt::ptr(sp.get())), format("{}", fmt::ptr(sp))); - EXPECT_EQ("0x0", format("{}", nullptr)); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::ptr(sp.get())), + fmt::format("{}", fmt::ptr(sp))); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::detail::bit_cast<const void*>( + &function_pointer_test)), + fmt::format("{}", fmt::ptr(function_pointer_test))); + EXPECT_EQ("0x0", fmt::format("{}", nullptr)); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatString) { - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{0}", std::string("test"))); +TEST(format_test, write_uintptr_fallback) { + // Test that formatting a pointer by converting it to uint128_fallback works. + // This is needed to support systems without uintptr_t. + auto s = std::string(); + fmt::detail::write_ptr<char>( + std::back_inserter(s), + fmt::detail::bit_cast<fmt::detail::uint128_fallback>( + reinterpret_cast<void*>(0xface)), + nullptr); + EXPECT_EQ(s, "0xface"); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatStringView) { - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{}", string_view("test"))); - EXPECT_EQ("", format("{}", string_view())); +enum class color { red, green, blue }; + +namespace test_ns { +enum class color { red, green, blue }; +using fmt::enums::format_as; +} // namespace test_ns + +TEST(format_test, format_enum_class) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::underlying(color::red)), "0"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", test_ns::color::red), "0"); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_string) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{0}", std::string("test")), "test"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{0}", std::string("test")), "test"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:?}", std::string("test")), "\"test\""); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^10?}", std::string("test")), "**\"test\"**"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:?}", std::string("\test")), "\"\\test\""); + EXPECT_THROW((void)fmt::format(fmt::runtime("{:x}"), std::string("test")), + fmt::format_error); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_string_view) { + EXPECT_EQ("test", fmt::format("{}", string_view("test"))); + EXPECT_EQ("\"t\\nst\"", fmt::format("{:?}", string_view("t\nst"))); + EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format("{}", string_view())); } #ifdef FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW @@ -1447,68 +1620,34 @@ template <> struct formatter<string_viewable> : formatter<std::string_view> { }; FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatStdStringView) { - EXPECT_EQ("test", format("{}", std::string_view("test"))); - EXPECT_EQ("foo", format("{}", string_viewable())); +TEST(format_test, format_std_string_view) { + EXPECT_EQ("test", fmt::format("{}", std::string_view("test"))); + EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format("{}", string_viewable())); } struct explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view { explicit operator std::string_view() const { return "foo"; } }; -namespace fmt { template <> -struct formatter<explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view> +struct fmt::formatter<explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view> : formatter<std::string_view> { - auto format(const explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view& v, - format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - return format_to(ctx.out(), "'{}'", std::string_view(v)); + auto format(explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view v, format_context& ctx) + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return fmt::format_to(ctx.out(), "'{}'", std::string_view(v)); } }; -} // namespace fmt -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatExplicitlyConvertibleToStdStringView) { +TEST(format_test, format_explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view) { EXPECT_EQ("'foo'", fmt::format("{}", explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view())); } #endif -// std::is_constructible is broken in MSVC until version 2015. -#if !FMT_MSC_VER || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1900 -struct explicitly_convertible_to_wstring_view { - explicit operator fmt::wstring_view() const { return L"foo"; } -}; - -TEST(FormatTest, FormatExplicitlyConvertibleToWStringView) { - EXPECT_EQ(L"foo", - fmt::format(L"{}", explicitly_convertible_to_wstring_view())); -} -#endif - -namespace fake_qt { -class QString { - public: - QString(const wchar_t* s) : s_(std::make_shared<std::wstring>(s)) {} - const wchar_t* utf16() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return s_->data(); } - int size() const FMT_NOEXCEPT { return static_cast<int>(s_->size()); } - - private: - std::shared_ptr<std::wstring> s_; -}; - -fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t> to_string_view(const QString& s) FMT_NOEXCEPT { - return {s.utf16(), static_cast<size_t>(s.size())}; -} -} // namespace fake_qt - -TEST(FormatTest, FormatForeignStrings) { - using fake_qt::QString; - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(QString(L"{}"), 42), L"42"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(QString(L"{}"), QString(L"42")), L"42"); -} +class Answer {}; FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <> struct formatter<Date> { +template <> struct formatter<date> { template <typename ParseContext> FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { auto it = ctx.begin(); @@ -1516,22 +1655,13 @@ template <> struct formatter<Date> { return it; } - auto format(const Date& d, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - format_to(ctx.out(), "{}-{}-{}", d.year(), d.month(), d.day()); + auto format(const date& d, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + // Namespace-qualify to avoid ambiguity with std::format_to. + fmt::format_to(ctx.out(), "{}-{}-{}", d.year(), d.month(), d.day()); return ctx.out(); } }; -FMT_END_NAMESPACE - -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatCustom) { - Date date(2012, 12, 9); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::format("{:s}", date), format_error, - "unknown format specifier"); -} - -class Answer {}; -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE template <> struct formatter<Answer> : formatter<int> { template <typename FormatContext> auto format(Answer, FormatContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { @@ -1540,42 +1670,34 @@ template <> struct formatter<Answer> : formatter<int> { }; FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(FormatterTest, CustomFormat) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{0}", Answer())); - EXPECT_EQ("0042", format("{:04}", Answer())); +TEST(format_test, format_custom) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{:s}"), date(2012, 12, 9)), + format_error, "unknown format specifier"); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0}", Answer())); + EXPECT_EQ("0042", fmt::format("{:04}", Answer())); } -TEST(FormatterTest, CustomFormatTo) { +TEST(format_test, format_to_custom) { char buf[10] = {}; - auto end = - &*fmt::format_to(fmt::detail::make_checked(buf, 10), "{}", Answer()); + auto end = fmt::format_to(buf, "{}", Answer()); EXPECT_EQ(end, buf + 2); EXPECT_STREQ(buf, "42"); } -TEST(FormatterTest, WideFormatString) { - EXPECT_EQ(L"42", format(L"{}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ(L"4.2", format(L"{}", 4.2)); - EXPECT_EQ(L"abc", format(L"{}", L"abc")); - EXPECT_EQ(L"z", format(L"{}", L'z')); - EXPECT_THROW(fmt::format(L"{:*\x343E}", 42), fmt::format_error); -} - -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatStringFromSpeedTest) { +TEST(format_test, format_string_from_speed_test) { EXPECT_EQ("1.2340000000:0042:+3.13:str:0x3e8:X:%", - format("{0:0.10f}:{1:04}:{2:+g}:{3}:{4}:{5}:%", 1.234, 42, 3.13, - "str", reinterpret_cast<void*>(1000), 'X')); + fmt::format("{0:0.10f}:{1:04}:{2:+g}:{3}:{4}:{5}:%", 1.234, 42, + 3.13, "str", reinterpret_cast<void*>(1000), 'X')); } -TEST(FormatterTest, FormatExamples) { - std::string message = format("The answer is {}", 42); +TEST(format_test, format_examples) { + std::string message = fmt::format("The answer is {}", 42); EXPECT_EQ("The answer is 42", message); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format(std::string("{}"), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{}", 42)); memory_buffer out; - format_to(out, "The answer is {}.", 42); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), "The answer is {}.", 42); EXPECT_EQ("The answer is 42.", to_string(out)); const char* filename = "nonexistent"; @@ -1591,143 +1713,133 @@ TEST(FormatterTest, FormatExamples) { fclose(f); }, error_code, "Cannot open file 'nonexistent'"); -} -TEST(FormatterTest, Examples) { EXPECT_EQ("First, thou shalt count to three", - format("First, thou shalt count to {0}", "three")); - EXPECT_EQ("Bring me a shrubbery", format("Bring me a {}", "shrubbery")); - EXPECT_EQ("From 1 to 3", format("From {} to {}", 1, 3)); + fmt::format("First, thou shalt count to {0}", "three")); + EXPECT_EQ("Bring me a shrubbery", fmt::format("Bring me a {}", "shrubbery")); + EXPECT_EQ("From 1 to 3", fmt::format("From {} to {}", 1, 3)); - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; + char buffer[buffer_size]; safe_sprintf(buffer, "%03.2f", -1.2); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{:03.2f}", -1.2)); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer, fmt::format("{:03.2f}", -1.2)); - EXPECT_EQ("a, b, c", format("{0}, {1}, {2}", 'a', 'b', 'c')); - EXPECT_EQ("a, b, c", format("{}, {}, {}", 'a', 'b', 'c')); - EXPECT_EQ("c, b, a", format("{2}, {1}, {0}", 'a', 'b', 'c')); - EXPECT_EQ("abracadabra", format("{0}{1}{0}", "abra", "cad")); + EXPECT_EQ("a, b, c", fmt::format("{0}, {1}, {2}", 'a', 'b', 'c')); + EXPECT_EQ("a, b, c", fmt::format("{}, {}, {}", 'a', 'b', 'c')); + EXPECT_EQ("c, b, a", fmt::format("{2}, {1}, {0}", 'a', 'b', 'c')); + EXPECT_EQ("abracadabra", fmt::format("{0}{1}{0}", "abra", "cad")); - EXPECT_EQ("left aligned ", format("{:<30}", "left aligned")); + EXPECT_EQ("left aligned ", + fmt::format("{:<30}", "left aligned")); EXPECT_EQ(" right aligned", - format("{:>30}", "right aligned")); - EXPECT_EQ(" centered ", format("{:^30}", "centered")); - EXPECT_EQ("***********centered***********", format("{:*^30}", "centered")); + fmt::format("{:>30}", "right aligned")); + EXPECT_EQ(" centered ", + fmt::format("{:^30}", "centered")); + EXPECT_EQ("***********centered***********", + fmt::format("{:*^30}", "centered")); - EXPECT_EQ("+3.140000; -3.140000", format("{:+f}; {:+f}", 3.14, -3.14)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 3.140000; -3.140000", format("{: f}; {: f}", 3.14, -3.14)); - EXPECT_EQ("3.140000; -3.140000", format("{:-f}; {:-f}", 3.14, -3.14)); + EXPECT_EQ("+3.140000; -3.140000", fmt::format("{:+f}; {:+f}", 3.14, -3.14)); + EXPECT_EQ(" 3.140000; -3.140000", fmt::format("{: f}; {: f}", 3.14, -3.14)); + EXPECT_EQ("3.140000; -3.140000", fmt::format("{:-f}; {:-f}", 3.14, -3.14)); EXPECT_EQ("int: 42; hex: 2a; oct: 52", - format("int: {0:d}; hex: {0:x}; oct: {0:o}", 42)); + fmt::format("int: {0:d}; hex: {0:x}; oct: {0:o}", 42)); EXPECT_EQ("int: 42; hex: 0x2a; oct: 052", - format("int: {0:d}; hex: {0:#x}; oct: {0:#o}", 42)); + fmt::format("int: {0:d}; hex: {0:#x}; oct: {0:#o}", 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("The answer is 42", format("The answer is {}", 42)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("The answer is {:d}", "forty-two"), format_error, - "invalid type specifier"); - - EXPECT_EQ(L"Cyrillic letter \x42e", format(L"Cyrillic letter {}", L'\x42e')); + EXPECT_EQ("The answer is 42", fmt::format("The answer is {}", 42)); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG( + (void)fmt::format(runtime("The answer is {:d}"), "forty-two"), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); EXPECT_WRITE( stdout, fmt::print("{}", std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity()), "inf"); } -TEST(FormatIntTest, Data) { - fmt::format_int format_int(42); - EXPECT_EQ("42", std::string(format_int.data(), format_int.size())); +TEST(format_test, print) { + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print("Don't {}!", "panic"), "Don't panic!"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::print(stderr, "Don't {}!", "panic"), + "Don't panic!"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::println("Don't {}!", "panic"), "Don't panic!\n"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::println(stderr, "Don't {}!", "panic"), + "Don't panic!\n"); } -TEST(FormatIntTest, FormatInt) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format_int(42).str()); - EXPECT_EQ(2u, fmt::format_int(42).size()); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format_int(-42).str()); - EXPECT_EQ(3u, fmt::format_int(-42).size()); - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format_int(42ul).str()); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format_int(-42l).str()); - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format_int(42ull).str()); - EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format_int(-42ll).str()); - std::ostringstream os; - os << max_value<int64_t>(); - EXPECT_EQ(os.str(), fmt::format_int(max_value<int64_t>()).str()); +TEST(format_test, variadic) { + EXPECT_EQ("abc1", fmt::format("{}c{}", "ab", 1)); } -TEST(FormatTest, Print) { -#if FMT_USE_FCNTL - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print("Don't {}!", "panic"), "Don't panic!"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::print(stderr, "Don't {}!", "panic"), - "Don't panic!"); -#endif - // Check that the wide print overload compiles. - if (fmt::detail::const_check(false)) fmt::print(L"test"); +TEST(format_test, bytes) { + auto s = fmt::format("{:10}", fmt::bytes("ёжик")); + EXPECT_EQ("ёжик ", s); + EXPECT_EQ(10, s.size()); } -TEST(FormatTest, Variadic) { - EXPECT_EQ("abc1", format("{}c{}", "ab", 1)); - EXPECT_EQ(L"abc1", format(L"{}c{}", L"ab", 1)); +TEST(format_test, group_digits_view) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::group_digits(10000000)), "10,000,000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:8}", fmt::group_digits(1000)), " 1,000"); } -TEST(FormatTest, Dynamic) { - typedef fmt::format_context ctx; - std::vector<fmt::basic_format_arg<ctx>> args; - args.emplace_back(fmt::detail::make_arg<ctx>(42)); - args.emplace_back(fmt::detail::make_arg<ctx>("abc1")); - args.emplace_back(fmt::detail::make_arg<ctx>(1.5f)); +#ifdef __cpp_generic_lambdas +struct point { + double x, y; +}; - std::string result = fmt::vformat( - "{} and {} and {}", - fmt::basic_format_args<ctx>(args.data(), static_cast<int>(args.size()))); +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<point> : nested_formatter<double> { + auto format(point p, format_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + return write_padded(ctx, [this, p](auto out) -> decltype(out) { + return fmt::format_to(out, "({}, {})", nested(p.x), nested(p.y)); + }); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE - EXPECT_EQ("42 and abc1 and 1.5", result); +TEST(format_test, nested_formatter) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>16.2f}", point{1, 2}), " (1.00, 2.00)"); } +#endif // __cpp_generic_lambdas -TEST(FormatTest, Bytes) { - auto s = fmt::format("{:10}", fmt::bytes("ёжик")); - EXPECT_EQ("ёжик ", s); - EXPECT_EQ(10, s.size()); -} +enum test_enum { foo, bar }; +auto format_as(test_enum e) -> int { return e; } -TEST(FormatTest, JoinArg) { +TEST(format_test, join) { using fmt::join; int v1[3] = {1, 2, 3}; - std::vector<float> v2; + auto v2 = std::vector<float>(); v2.push_back(1.2f); v2.push_back(3.4f); void* v3[2] = {&v1[0], &v1[1]}; - EXPECT_EQ("(1, 2, 3)", format("({})", join(v1, v1 + 3, ", "))); - EXPECT_EQ("(1)", format("({})", join(v1, v1 + 1, ", "))); - EXPECT_EQ("()", format("({})", join(v1, v1, ", "))); - EXPECT_EQ("(001, 002, 003)", format("({:03})", join(v1, v1 + 3, ", "))); + EXPECT_EQ("(1, 2, 3)", fmt::format("({})", join(v1, v1 + 3, ", "))); + EXPECT_EQ("(1)", fmt::format("({})", join(v1, v1 + 1, ", "))); + EXPECT_EQ("()", fmt::format("({})", join(v1, v1, ", "))); + EXPECT_EQ("(001, 002, 003)", fmt::format("({:03})", join(v1, v1 + 3, ", "))); EXPECT_EQ("(+01.20, +03.40)", - format("({:+06.2f})", join(v2.begin(), v2.end(), ", "))); + fmt::format("({:+06.2f})", join(v2.begin(), v2.end(), ", "))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"(1, 2, 3)", format(L"({})", join(v1, v1 + 3, L", "))); - EXPECT_EQ("1, 2, 3", format("{0:{1}}", join(v1, v1 + 3, ", "), 1)); + EXPECT_EQ("1, 2, 3", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", join(v1, v1 + 3, ", "), 1)); - EXPECT_EQ(format("{}, {}", v3[0], v3[1]), - format("{}", join(v3, v3 + 2, ", "))); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}, {}", v3[0], v3[1]), + fmt::format("{}", join(v3, v3 + 2, ", "))); -#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 405 - EXPECT_EQ("(1, 2, 3)", format("({})", join(v1, ", "))); - EXPECT_EQ("(+01.20, +03.40)", format("({:+06.2f})", join(v2, ", "))); -#endif -} + EXPECT_EQ("(1, 2, 3)", fmt::format("({})", join(v1, ", "))); + EXPECT_EQ("(+01.20, +03.40)", fmt::format("({:+06.2f})", join(v2, ", "))); -template <typename T> std::string str(const T& value) { - return fmt::format("{}", value); + auto v4 = std::vector<test_enum>{foo, bar, foo}; + EXPECT_EQ("0 1 0", fmt::format("{}", join(v4, " "))); } -TEST(StrTest, Convert) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", str(42)); - std::string s = str(Date(2012, 12, 9)); - EXPECT_EQ("2012-12-9", s); +#ifdef __cpp_lib_byte +TEST(format_test, join_bytes) { + auto v = std::vector<std::byte>{std::byte(1), std::byte(2), std::byte(3)}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(v, ", ")), "1, 2, 3"); } +#endif std::string vformat_message(int id, const char* format, fmt::format_args args) { - fmt::memory_buffer buffer; - format_to(buffer, "[{}] ", id); - vformat_to(buffer, format, args); + auto buffer = fmt::memory_buffer(); + fmt::format_to(fmt::appender(buffer), "[{}] ", id); + vformat_to(fmt::appender(buffer), format, args); return to_string(buffer); } @@ -1737,7 +1849,7 @@ std::string format_message(int id, const char* format, const Args&... args) { return vformat_message(id, format, va); } -TEST(FormatTest, FormatMessageExample) { +TEST(format_test, format_message_example) { EXPECT_EQ("[42] something happened", format_message(42, "{} happened", "something")); } @@ -1749,37 +1861,52 @@ void print_error(const char* file, int line, const char* format, fmt::print(format, args...); } -TEST(FormatTest, UnpackedArgs) { +TEST(format_test, unpacked_args) { EXPECT_EQ("0123456789abcdefg", fmt::format("{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}", 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g')); } -struct string_like {}; -fmt::string_view to_string_view(string_like) { return "foo"; } - constexpr char with_null[3] = {'{', '}', '\0'}; constexpr char no_null[2] = {'{', '}'}; +static constexpr const char static_with_null[3] = {'{', '}', '\0'}; +static constexpr const char static_no_null[2] = {'{', '}'}; -TEST(FormatTest, CompileTimeString) { +TEST(format_test, compile_time_string) { + EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("foo"))); EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), 42)); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING(L"{}"), 42)); - EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), string_like())); + +#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS + using namespace fmt::literals; + EXPECT_EQ("foobar", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{foo}{bar}"), "bar"_a = "bar", + "foo"_a = "foo")); + EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format(FMT_STRING(""))); + EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format(FMT_STRING(""), "arg"_a = 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{answer}"), "answer"_a = Answer())); + EXPECT_EQ("1 2", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{} {two}"), 1, "two"_a = 2)); +#endif + + (void)static_with_null; + (void)static_no_null; +#ifndef _MSC_VER + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING(static_with_null), 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING(static_no_null), 42)); +#endif + (void)with_null; (void)no_null; -#if __cplusplus >= 201703L +#if FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING(with_null), 42)); EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING(no_null), 42)); #endif -#if defined(FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW) && __cplusplus >= 201703L +#if defined(FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW) && FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING(std::string_view("{}")), 42)); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING(std::wstring_view(L"{}")), 42)); #endif } -TEST(FormatTest, CustomFormatCompileTimeString) { +TEST(format_test, custom_format_compile_time_string) { EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), Answer())); - Answer answer; + auto answer = Answer(); EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), answer)); char buf[10] = {}; fmt::format_to(buf, FMT_STRING("{}"), answer); @@ -1788,107 +1915,38 @@ TEST(FormatTest, CustomFormatCompileTimeString) { } #if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS -// Passing user-defined literals directly to EXPECT_EQ causes problems -// with macro argument stringification (#) on some versions of GCC. -// Workaround: Assing the UDL result to a variable before the macro. - -using namespace fmt::literals; - -TEST(LiteralsTest, Format) { - auto udl_format = "{}c{}"_format("ab", 1); - EXPECT_EQ(format("{}c{}", "ab", 1), udl_format); - auto udl_format_w = L"{}c{}"_format(L"ab", 1); - EXPECT_EQ(format(L"{}c{}", L"ab", 1), udl_format_w); -} - -TEST(LiteralsTest, NamedArg) { - auto udl_a = format("{first}{second}{first}{third}", "first"_a = "abra", - "second"_a = "cad", "third"_a = 99); - EXPECT_EQ(format("{first}{second}{first}{third}", fmt::arg("first", "abra"), - fmt::arg("second", "cad"), fmt::arg("third", 99)), - udl_a); - auto udl_a_w = format(L"{first}{second}{first}{third}", L"first"_a = L"abra", - L"second"_a = L"cad", L"third"_a = 99); +TEST(format_test, named_arg_udl) { + using namespace fmt::literals; + auto udl_a = fmt::format("{first}{second}{first}{third}", "first"_a = "abra", + "second"_a = "cad", "third"_a = 99); EXPECT_EQ( - format(L"{first}{second}{first}{third}", fmt::arg(L"first", L"abra"), - fmt::arg(L"second", L"cad"), fmt::arg(L"third", 99)), - udl_a_w); -} - -TEST(FormatTest, UdlTemplate) { - EXPECT_EQ("foo", "foo"_format()); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42", "{0:10}"_format(42)); -} + fmt::format("{first}{second}{first}{third}", fmt::arg("first", "abra"), + fmt::arg("second", "cad"), fmt::arg("third", 99)), + udl_a); -TEST(FormatTest, UdlPassUserDefinedObjectAsLvalue) { - Date date(2015, 10, 21); - EXPECT_EQ("2015-10-21", "{}"_format(date)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{answer}", "answer"_a = Answer())); } #endif // FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS -enum TestEnum { A }; - -TEST(FormatTest, Enum) { EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{}", A)); } +TEST(format_test, enum) { EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{}", foo)); } -TEST(FormatTest, FormatterNotSpecialized) { - static_assert( - !fmt::has_formatter<fmt::formatter<TestEnum>, fmt::format_context>::value, - ""); +TEST(format_test, formatter_not_specialized) { + static_assert(!fmt::has_formatter<fmt::formatter<test_enum>, + fmt::format_context>::value, + ""); } #if FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_strong_enums) enum big_enum : unsigned long long { big_enum_value = 5000000000ULL }; +auto format_as(big_enum e) -> unsigned long long { return e; } -TEST(FormatTest, StrongEnum) { +TEST(format_test, strong_enum) { EXPECT_EQ("5000000000", fmt::format("{}", big_enum_value)); } #endif -TEST(FormatTest, NonNullTerminatedFormatString) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", format(string_view("{}foo", 2), 42)); -} - -struct variant { - enum { INT, STRING } type; - explicit variant(int) : type(INT) {} - explicit variant(const char*) : type(STRING) {} -}; - -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <> struct formatter<variant> : dynamic_formatter<> { - auto format(variant value, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - if (value.type == variant::INT) return dynamic_formatter<>::format(42, ctx); - return dynamic_formatter<>::format("foo", ctx); - } -}; -FMT_END_NAMESPACE - -TEST(FormatTest, DynamicFormatter) { - auto num = variant(42); - auto str = variant("foo"); - EXPECT_EQ("42", format("{:d}", num)); - EXPECT_EQ("foo", format("{:s}", str)); - EXPECT_EQ(" 42 foo ", format("{:{}} {:{}}", num, 3, str, 4)); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:{}}", num), format_error, - "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:{0}}", num), format_error, - "cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing"); -#if FMT_DEPRECATED_NUMERIC_ALIGN - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:=}", str), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); -#endif - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:+}", str), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:-}", str), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{: }", str), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:#}", str), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:0}", str), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{:.2}", num), format_error, - "precision not allowed for this argument type"); +TEST(format_test, non_null_terminated_format_string) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(string_view("{}foo", 2), 42)); } namespace adl_test { @@ -1903,23 +1961,29 @@ template <typename, typename OutputIt> void write(OutputIt, foo) = delete; FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE template <> struct formatter<adl_test::fmt::detail::foo> : formatter<std::string> { - template <typename FormatContext> - auto format(adl_test::fmt::detail::foo, FormatContext& ctx) + auto format(adl_test::fmt::detail::foo, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { return formatter<std::string>::format("foo", ctx); } }; FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(FormatTest, ToString) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::to_string(42)); - EXPECT_EQ("0x1234", fmt::to_string(reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x1234))); - EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::to_string(adl_test::fmt::detail::foo())); -} +TEST(format_test, to_string) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(42), "42"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x1234)), "0x1234"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(adl_test::fmt::detail::foo()), "foo"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(foo), "0"); -TEST(FormatTest, ToWString) { EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::to_wstring(42)); } +#if FMT_USE_FLOAT128 + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(__float128(0.5)), "0.5"); +#endif -TEST(FormatTest, OutputIterators) { +#if defined(FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW) && FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(std::string_view()), ""); +#endif +} + +TEST(format_test, output_iterators) { std::list<char> out; fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), "{}", 42); EXPECT_EQ("42", std::string(out.begin(), out.end())); @@ -1928,17 +1992,49 @@ TEST(FormatTest, OutputIterators) { EXPECT_EQ("42", s.str()); } -TEST(FormatTest, FormattedSize) { +TEST(format_test, formatted_size) { EXPECT_EQ(2u, fmt::formatted_size("{}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(2u, fmt::formatted_size(std::locale(), "{}", 42)); } -TEST(FormatTest, FormatTo) { +TEST(format_test, format_to_no_args) { + std::string s; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), "test"); + EXPECT_EQ("test", s); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_to) { + std::string s; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), "part{0}", 1); + EXPECT_EQ("part1", s); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), "part{0}", 2); + EXPECT_EQ("part1part2", s); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_to_memory_buffer) { + auto buf = fmt::basic_memory_buffer<char, 100>(); + fmt::format_to(fmt::appender(buf), "{}", "foo"); + EXPECT_EQ("foo", to_string(buf)); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_to_vector) { std::vector<char> v; fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(v), "{}", "foo"); EXPECT_EQ(string_view(v.data(), v.size()), "foo"); } -TEST(FormatTest, FormatToN) { +struct nongrowing_container { + using value_type = char; + void push_back(char) { throw std::runtime_error("can't take it any more"); } +}; + +TEST(format_test, format_to_propagates_exceptions) { + auto c = nongrowing_container(); + EXPECT_THROW(fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(c), "{}", 42), + std::runtime_error); +} + +TEST(format_test, format_to_n) { char buffer[4]; buffer[3] = 'x'; auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, "{}", 12345); @@ -1974,26 +2070,6 @@ TEST(FormatTest, FormatToN) { EXPECT_EQ("***x", fmt::string_view(buffer, 4)); } -TEST(FormatTest, WideFormatToN) { - wchar_t buffer[4]; - buffer[3] = L'x'; - auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, L"{}", 12345); - EXPECT_EQ(5u, result.size); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer + 3, result.out); - EXPECT_EQ(L"123x", fmt::wstring_view(buffer, 4)); - buffer[0] = L'x'; - buffer[1] = L'x'; - buffer[2] = L'x'; - result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, L"{}", L'A'); - EXPECT_EQ(1u, result.size); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer + 1, result.out); - EXPECT_EQ(L"Axxx", fmt::wstring_view(buffer, 4)); - result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, L"{}{} ", L'B', L'C'); - EXPECT_EQ(3u, result.size); - EXPECT_EQ(buffer + 3, result.out); - EXPECT_EQ(L"BC x", fmt::wstring_view(buffer, 4)); -} - struct test_output_iterator { char* data; @@ -2015,481 +2091,201 @@ struct test_output_iterator { char& operator*() { return *data; } }; -TEST(FormatTest, FormatToNOutputIterator) { +TEST(format_test, format_to_n_output_iterator) { char buf[10] = {}; fmt::format_to_n(test_output_iterator{buf}, 10, "{}", 42); EXPECT_STREQ(buf, "42"); } -#if FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR -struct test_arg_id_handler { - enum result { NONE, EMPTY, INDEX, NAME, ERROR }; - result res = NONE; - int index = 0; - string_view name; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()() { res = EMPTY; } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(int i) { - res = INDEX; - index = i; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(string_view n) { - res = NAME; - name = n; - } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char*) { res = ERROR; } -}; - -template <size_t N> -FMT_CONSTEXPR test_arg_id_handler parse_arg_id(const char (&s)[N]) { - test_arg_id_handler h; - fmt::detail::parse_arg_id(s, s + N, h); - return h; -} - -TEST(FormatTest, ConstexprParseArgID) { - static_assert(parse_arg_id(":").res == test_arg_id_handler::EMPTY, ""); - static_assert(parse_arg_id("}").res == test_arg_id_handler::EMPTY, ""); - static_assert(parse_arg_id("42:").res == test_arg_id_handler::INDEX, ""); - static_assert(parse_arg_id("42:").index == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_arg_id("foo:").res == test_arg_id_handler::NAME, ""); - static_assert(parse_arg_id("foo:").name.size() == 3, ""); - static_assert(parse_arg_id("!").res == test_arg_id_handler::ERROR, ""); -} - -struct test_format_specs_handler { - enum Result { NONE, PLUS, MINUS, SPACE, HASH, ZERO, ERROR }; - Result res = NONE; - - fmt::align_t align = fmt::align::none; - char fill = 0; - int width = 0; - fmt::detail::arg_ref<char> width_ref; - int precision = 0; - fmt::detail::arg_ref<char> precision_ref; - char type = 0; - - // Workaround for MSVC2017 bug that results in "expression did not evaluate - // to a constant" with compiler-generated copy ctor. - FMT_CONSTEXPR test_format_specs_handler() {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR test_format_specs_handler( - const test_format_specs_handler& other) - : res(other.res), - align(other.align), - fill(other.fill), - width(other.width), - width_ref(other.width_ref), - precision(other.precision), - precision_ref(other.precision_ref), - type(other.type) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_align(fmt::align_t a) { align = a; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_fill(fmt::string_view f) { fill = f[0]; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_plus() { res = PLUS; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_minus() { res = MINUS; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_space() { res = SPACE; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_hash() { res = HASH; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_zero() { res = ZERO; } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_width(int w) { width = w; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_width(fmt::detail::auto_id) {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_width(int index) { width_ref = index; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_width(string_view) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_precision(int p) { precision = p; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_precision(fmt::detail::auto_id) {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_precision(int index) { precision_ref = index; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_dynamic_precision(string_view) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void end_precision() {} - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_type(char t) { type = t; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char*) { res = ERROR; } -}; - -template <size_t N> -FMT_CONSTEXPR test_format_specs_handler parse_test_specs(const char (&s)[N]) { - test_format_specs_handler h; - fmt::detail::parse_format_specs(s, s + N, h); - return h; +TEST(format_test, vformat_to) { + using context = fmt::format_context; + int n = 42; + auto args = fmt::make_format_args<context>(n); + auto s = std::string(); + fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(s), "{}", args); + EXPECT_EQ("42", s); + s.clear(); + fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(s), FMT_STRING("{}"), args); + EXPECT_EQ("42", s); } -TEST(FormatTest, ConstexprParseFormatSpecs) { - typedef test_format_specs_handler handler; - static_assert(parse_test_specs("<").align == fmt::align::left, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs("*^").fill == '*', ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs("+").res == handler::PLUS, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs("-").res == handler::MINUS, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs(" ").res == handler::SPACE, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs("#").res == handler::HASH, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs("0").res == handler::ZERO, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs("42").width == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs("{42}").width_ref.val.index == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs(".42").precision == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs(".{42}").precision_ref.val.index == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs("d").type == 'd', ""); - static_assert(parse_test_specs("{<").res == handler::ERROR, ""); +TEST(format_test, char_traits_is_not_ambiguous) { + // Test that we don't inject detail names into the std namespace. + using namespace std; + auto c = char_traits<char>::char_type(); + (void)c; +#if FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201103L + auto s = std::string(); + auto lval = begin(s); + (void)lval; +#endif } -struct test_parse_context { - typedef char char_type; - - FMT_CONSTEXPR int next_arg_id() { return 11; } - template <typename Id> FMT_CONSTEXPR void check_arg_id(Id) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* begin() { return nullptr; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* end() { return nullptr; } - - void on_error(const char*) {} -}; - -struct test_context { - using char_type = char; - using format_arg = fmt::basic_format_arg<test_context>; - using parse_context_type = fmt::format_parse_context; - - template <typename T> struct formatter_type { - typedef fmt::formatter<T, char_type> type; - }; +struct check_back_appender {}; - template <typename Id> - FMT_CONSTEXPR fmt::basic_format_arg<test_context> arg(Id id) { - return fmt::detail::make_arg<test_context>(id); +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<check_back_appender> { + FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { + return ctx.begin(); } - void on_error(const char*) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR test_context error_handler() { return *this; } -}; - -template <size_t N> -FMT_CONSTEXPR fmt::format_specs parse_specs(const char (&s)[N]) { - auto specs = fmt::format_specs(); - auto parse_ctx = test_parse_context(); - auto ctx = test_context(); - fmt::detail::specs_handler<test_parse_context, test_context> h( - specs, parse_ctx, ctx); - parse_format_specs(s, s + N, h); - return specs; -} - -TEST(FormatTest, ConstexprSpecsHandler) { - static_assert(parse_specs("<").align == fmt::align::left, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs("*^").fill[0] == '*', ""); - static_assert(parse_specs("+").sign == fmt::sign::plus, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs("-").sign == fmt::sign::minus, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs(" ").sign == fmt::sign::space, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs("#").alt, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs("0").align == fmt::align::numeric, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs("42").width == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs("{}").width == 11, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs("{22}").width == 22, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs(".42").precision == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs(".{}").precision == 11, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs(".{22}").precision == 22, ""); - static_assert(parse_specs("d").type == 'd', ""); -} - -template <size_t N> -FMT_CONSTEXPR fmt::detail::dynamic_format_specs<char> parse_dynamic_specs( - const char (&s)[N]) { - fmt::detail::dynamic_format_specs<char> specs; - test_parse_context ctx{}; - fmt::detail::dynamic_specs_handler<test_parse_context> h(specs, ctx); - parse_format_specs(s, s + N, h); - return specs; -} - -TEST(FormatTest, ConstexprDynamicSpecsHandler) { - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("<").align == fmt::align::left, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("*^").fill[0] == '*', ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("+").sign == fmt::sign::plus, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("-").sign == fmt::sign::minus, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs(" ").sign == fmt::sign::space, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("#").alt, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("0").align == fmt::align::numeric, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("42").width == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("{}").width_ref.val.index == 11, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("{42}").width_ref.val.index == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs(".42").precision == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs(".{}").precision_ref.val.index == 11, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs(".{42}").precision_ref.val.index == 42, ""); - static_assert(parse_dynamic_specs("d").type == 'd', ""); -} - -template <size_t N> -FMT_CONSTEXPR test_format_specs_handler check_specs(const char (&s)[N]) { - fmt::detail::specs_checker<test_format_specs_handler> checker( - test_format_specs_handler(), fmt::detail::type::double_type); - parse_format_specs(s, s + N, checker); - return checker; -} - -TEST(FormatTest, ConstexprSpecsChecker) { - typedef test_format_specs_handler handler; - static_assert(check_specs("<").align == fmt::align::left, ""); - static_assert(check_specs("*^").fill == '*', ""); - static_assert(check_specs("+").res == handler::PLUS, ""); - static_assert(check_specs("-").res == handler::MINUS, ""); - static_assert(check_specs(" ").res == handler::SPACE, ""); - static_assert(check_specs("#").res == handler::HASH, ""); - static_assert(check_specs("0").res == handler::ZERO, ""); - static_assert(check_specs("42").width == 42, ""); - static_assert(check_specs("{42}").width_ref.val.index == 42, ""); - static_assert(check_specs(".42").precision == 42, ""); - static_assert(check_specs(".{42}").precision_ref.val.index == 42, ""); - static_assert(check_specs("d").type == 'd', ""); - static_assert(check_specs("{<").res == handler::ERROR, ""); -} - -struct test_format_string_handler { - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const char*, const char*) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id() { return 0; } - - template <typename T> FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(T) { return 0; } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_replacement_field(int, const char*) {} - - FMT_CONSTEXPR const char* on_format_specs(int, const char* begin, - const char*) { - return begin; + template <typename Context> + auto format(check_back_appender, Context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + auto out = ctx.out(); + static_assert(std::is_same<decltype(++out), decltype(out)&>::value, + "needs to satisfy weakly_incrementable"); + *out = 'y'; + return ++out; } - - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char*) { error = true; } - - bool error = false; }; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE -template <size_t N> FMT_CONSTEXPR bool parse_string(const char (&s)[N]) { - test_format_string_handler h; - fmt::detail::parse_format_string<true>(fmt::string_view(s, N - 1), h); - return !h.error; +TEST(format_test, back_insert_slicing) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", check_back_appender{}), "y"); } -TEST(FormatTest, ConstexprParseFormatString) { - static_assert(parse_string("foo"), ""); - static_assert(!parse_string("}"), ""); - static_assert(parse_string("{}"), ""); - static_assert(parse_string("{42}"), ""); - static_assert(parse_string("{foo}"), ""); - static_assert(parse_string("{:}"), ""); -} +namespace test { +enum class scoped_enum_as_int {}; +auto format_as(scoped_enum_as_int) -> int { return 42; } -struct test_error_handler { - const char*& error; +enum class scoped_enum_as_string_view {}; +auto format_as(scoped_enum_as_string_view) -> fmt::string_view { return "foo"; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR test_error_handler(const char*& err) : error(err) {} +enum class scoped_enum_as_string {}; +auto format_as(scoped_enum_as_string) -> std::string { return "foo"; } - FMT_CONSTEXPR test_error_handler(const test_error_handler& other) - : error(other.error) {} +struct struct_as_int {}; +auto format_as(struct_as_int) -> int { return 42; } +} // namespace test - FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_error(const char* message) { - if (!error) error = message; - } -}; +TEST(format_test, format_as) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", test::scoped_enum_as_int()), "42"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", test::scoped_enum_as_string_view()), "foo"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", test::scoped_enum_as_string()), "foo"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", test::struct_as_int()), "42"); +} -FMT_CONSTEXPR size_t len(const char* s) { - size_t len = 0; - while (*s++) ++len; - return len; +TEST(format_test, format_as_to_string) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(test::scoped_enum_as_int()), "42"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(test::scoped_enum_as_string_view()), "foo"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(test::scoped_enum_as_string()), "foo"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(test::struct_as_int()), "42"); } -FMT_CONSTEXPR bool equal(const char* s1, const char* s2) { - if (!s1 || !s2) return s1 == s2; - while (*s1 && *s1 == *s2) { - ++s1; - ++s2; - } - return *s1 == *s2; +template <typename Char, typename T> bool check_enabled_formatter() { + static_assert(std::is_default_constructible<fmt::formatter<T, Char>>::value, + ""); + return true; } -template <typename... Args> -FMT_CONSTEXPR bool test_error(const char* fmt, const char* expected_error) { - const char* actual_error = nullptr; - string_view s(fmt, len(fmt)); - fmt::detail::format_string_checker<char, test_error_handler, Args...> checker( - s, test_error_handler(actual_error)); - fmt::detail::parse_format_string<true>(s, checker); - return equal(actual_error, expected_error); -} - -# define EXPECT_ERROR_NOARGS(fmt, error) \ - static_assert(test_error(fmt, error), "") -# define EXPECT_ERROR(fmt, error, ...) \ - static_assert(test_error<__VA_ARGS__>(fmt, error), "") - -TEST(FormatTest, FormatStringErrors) { - EXPECT_ERROR_NOARGS("foo", nullptr); - EXPECT_ERROR_NOARGS("}", "unmatched '}' in format string"); - EXPECT_ERROR("{0:s", "unknown format specifier", Date); -# if !FMT_MSC_VER || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1916 - // This causes an detail compiler error in MSVC2017. - EXPECT_ERROR("{:{<}", "invalid fill character '{'", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:10000000000}", "number is too big", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:.10000000000}", "number is too big", int); - EXPECT_ERROR_NOARGS("{:x}", "argument not found"); -# if FMT_DEPRECATED_NUMERIC_ALIGN - EXPECT_ERROR("{0:=5", "unknown format specifier", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:=}", "format specifier requires numeric argument", - const char*); -# endif - EXPECT_ERROR("{:+}", "format specifier requires numeric argument", - const char*); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:-}", "format specifier requires numeric argument", - const char*); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:#}", "format specifier requires numeric argument", - const char*); - EXPECT_ERROR("{: }", "format specifier requires numeric argument", - const char*); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:0}", "format specifier requires numeric argument", - const char*); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:+}", "format specifier requires signed argument", unsigned); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:-}", "format specifier requires signed argument", unsigned); - EXPECT_ERROR("{: }", "format specifier requires signed argument", unsigned); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:{}}", "argument not found", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:.{}}", "argument not found", double); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:.2}", "precision not allowed for this argument type", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:s}", "invalid type specifier", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:s}", "invalid type specifier", bool); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:s}", "invalid type specifier", char); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:+}", "invalid format specifier for char", char); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:s}", "invalid type specifier", double); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:d}", "invalid type specifier", const char*); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:d}", "invalid type specifier", std::string); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:s}", "invalid type specifier", void*); -# else - fmt::print("warning: constexpr is broken in this version of MSVC\n"); -# endif - EXPECT_ERROR("{foo", "compile-time checks don't support named arguments", - int); - EXPECT_ERROR_NOARGS("{10000000000}", "number is too big"); - EXPECT_ERROR_NOARGS("{0x}", "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_ERROR_NOARGS("{-}", "invalid format string"); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:{0x}}", "invalid format string", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:{-}}", "invalid format string", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:.{0x}}", "invalid format string", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:.{-}}", "invalid format string", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{:.x}", "missing precision specifier", int); - EXPECT_ERROR_NOARGS("{}", "argument not found"); - EXPECT_ERROR("{1}", "argument not found", int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{1}{}", - "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing", int, - int); - EXPECT_ERROR("{}{1}", - "cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing", int, - int); -} - -TEST(FormatTest, VFormatTo) { - typedef fmt::format_context context; - fmt::basic_format_arg<context> arg = fmt::detail::make_arg<context>(42); - fmt::basic_format_args<context> args(&arg, 1); - std::string s; - fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(s), "{}", args); - EXPECT_EQ("42", s); - s.clear(); - fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(s), FMT_STRING("{}"), args); - EXPECT_EQ("42", s); +template <typename Char, typename... T> void check_enabled_formatters() { + auto dummy = {check_enabled_formatter<Char, T>()...}; + (void)dummy; +} - typedef fmt::wformat_context wcontext; - fmt::basic_format_arg<wcontext> warg = fmt::detail::make_arg<wcontext>(42); - fmt::basic_format_args<wcontext> wargs(&warg, 1); - std::wstring w; - fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(w), L"{}", wargs); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42", w); - w.clear(); - fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(w), FMT_STRING(L"{}"), wargs); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42", w); +TEST(format_test, test_formatters_enabled) { + check_enabled_formatters<char, bool, char, signed char, unsigned char, short, + unsigned short, int, unsigned, long, unsigned long, + long long, unsigned long long, float, double, + long double, void*, const void*, char*, const char*, + std::string, std::nullptr_t>(); + check_enabled_formatters<wchar_t, bool, wchar_t, signed char, unsigned char, + short, unsigned short, int, unsigned, long, + unsigned long, long long, unsigned long long, float, + double, long double, void*, const void*, wchar_t*, + const wchar_t*, std::wstring, std::nullptr_t>(); } -template <typename T> static std::string FmtToString(const T& t) { - return fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), t); +TEST(format_int_test, data) { + fmt::format_int format_int(42); + EXPECT_EQ("42", std::string(format_int.data(), format_int.size())); } -TEST(FormatTest, FmtStringInTemplate) { - EXPECT_EQ(FmtToString(1), "1"); - EXPECT_EQ(FmtToString(0), "0"); +TEST(format_int_test, format_int) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format_int(42).str()); + EXPECT_EQ(2u, fmt::format_int(42).size()); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format_int(-42).str()); + EXPECT_EQ(3u, fmt::format_int(-42).size()); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format_int(42ul).str()); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format_int(-42l).str()); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format_int(42ull).str()); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format_int(-42ll).str()); + std::ostringstream os; + os << max_value<int64_t>(); + EXPECT_EQ(os.str(), fmt::format_int(max_value<int64_t>()).str()); } -#endif // FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR +#ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR -TEST(FormatTest, CharTraitsIsNotAmbiguous) { - // Test that we don't inject detail names into the std namespace. - using namespace std; - char_traits<char>::char_type c; - (void)c; -#if __cplusplus >= 201103L - std::string s; - auto lval = begin(s); - (void)lval; -#endif -} +# include <locale> -#if __cplusplus > 201103L -struct custom_char { - int value; - custom_char() = default; +class format_facet : public fmt::format_facet<std::locale> { + protected: + struct int_formatter { + fmt::appender out; - template <typename T> - constexpr custom_char(T val) : value(static_cast<int>(val)) {} + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(fmt::detail::is_integer<T>::value)> + auto operator()(T value) -> bool { + fmt::format_to(out, "[{}]", value); + return true; + } - operator int() const { return value; } -}; + template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!fmt::detail::is_integer<T>::value)> + auto operator()(T) -> bool { + return false; + } + }; -int to_ascii(custom_char c) { return c; } + auto do_put(fmt::appender out, fmt::loc_value val, + const fmt::format_specs<>&) const -> bool override; +}; -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <> struct is_char<custom_char> : std::true_type {}; -FMT_END_NAMESPACE +auto format_facet::do_put(fmt::appender out, fmt::loc_value val, + const fmt::format_specs<>&) const -> bool { + return val.visit(int_formatter{out}); +} -TEST(FormatTest, FormatCustomChar) { - const custom_char format[] = {'{', '}', 0}; - auto result = fmt::format(format, custom_char('x')); - EXPECT_EQ(result.size(), 1); - EXPECT_EQ(result[0], custom_char('x')); +TEST(format_test, format_facet) { + auto loc = std::locale(std::locale(), new format_facet()); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 42), "[42]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", -42), "[-42]"); } -#endif -// Convert a char8_t string to std::string. Otherwise GTest will insist on -// inserting `char8_t` NTBS into a `char` stream which is disabled by P1423. -template <typename S> std::string from_u8str(const S& str) { - return std::string(str.begin(), str.end()); +TEST(format_test, format_facet_separator) { + // U+2019 RIGHT SINGLE QUOTATION MARK is a digit separator in the de_CH + // locale. + auto loc = + std::locale({}, new fmt::format_facet<std::locale>("\xe2\x80\x99")); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 1000), + "1\xe2\x80\x99" + "000"); } -TEST(FormatTest, FormatUTF8Precision) { - using str_type = std::basic_string<fmt::detail::char8_type>; - str_type format(reinterpret_cast<const fmt::detail::char8_type*>(u8"{:.4}")); - str_type str(reinterpret_cast<const fmt::detail::char8_type*>( - u8"caf\u00e9s")); // cafés - auto result = fmt::format(format, str); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::count_code_points(result), 4); - EXPECT_EQ(result.size(), 5); - EXPECT_EQ(from_u8str(result), from_u8str(str.substr(0, 5))); +TEST(format_test, format_facet_grouping) { + auto loc = + std::locale({}, new fmt::format_facet<std::locale>(",", {1, 2, 3})); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 1234567890), "1,234,567,89,0"); } -struct check_back_appender {}; +TEST(format_test, format_named_arg_with_locale) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(std::locale(), "{answer}", fmt::arg("answer", 42)), + "42"); +} -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <> struct formatter<check_back_appender> { - template <typename ParseContext> - auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.begin()) { - return ctx.begin(); - } +#endif // FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR - template <typename Context> - auto format(check_back_appender, Context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { - auto out = ctx.out(); - static_assert(std::is_same<decltype(++out), decltype(out)&>::value, - "needs to satisfy weakly_incrementable"); - *out = 'y'; - return ++out; +struct convertible_to_nonconst_cstring { + operator char*() const { + static char c[] = "bar"; + return c; } }; + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> +struct formatter<convertible_to_nonconst_cstring> : formatter<char*> {}; FMT_END_NAMESPACE -TEST(FormatTest, BackInsertSlicing) { - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", check_back_appender{}), "y"); +TEST(format_test, formatter_nonconst_char) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", convertible_to_nonconst_cstring()), "bar"); } diff --git a/test/fuzzing/CMakeLists.txt b/test/fuzzing/CMakeLists.txt index 2f716d83..afcf9df1 100644 --- a/test/fuzzing/CMakeLists.txt +++ b/test/fuzzing/CMakeLists.txt @@ -22,9 +22,9 @@ function(add_fuzzer source) if (FMT_FUZZ_LDFLAGS) target_link_libraries(${name} PRIVATE ${FMT_FUZZ_LDFLAGS}) endif () - target_compile_features(${name} PRIVATE cxx_generic_lambdas) + target_compile_features(${name} PRIVATE cxx_std_14) endfunction() -foreach (source chrono-duration.cc float.cc named-arg.cc one-arg.cc two-args.cc) +foreach (source chrono-duration.cc chrono-timepoint.cc float.cc named-arg.cc one-arg.cc two-args.cc) add_fuzzer(${source}) endforeach () diff --git a/test/fuzzing/build.sh b/test/fuzzing/build.sh index 28c50633..4497b62c 100755 --- a/test/fuzzing/build.sh +++ b/test/fuzzing/build.sh @@ -22,6 +22,8 @@ here=$(pwd) CXXFLAGSALL="-DFUZZING_BUILD_MODE_UNSAFE_FOR_PRODUCTION= -g" CMAKEFLAGSALL="$root -GNinja -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug -DFMT_DOC=Off -DFMT_TEST=Off -DFMT_FUZZ=On -DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=17" +CLANG=clang++-11 + # For performance analysis of the fuzzers. builddir=$here/build-fuzzers-perfanalysis mkdir -p $builddir @@ -37,7 +39,7 @@ cmake --build $builddir builddir=$here/build-fuzzers-ossfuzz mkdir -p $builddir cd $builddir -CXX="clang++" \ +CXX=$CLANG \ CXXFLAGS="$CXXFLAGSALL -fsanitize=fuzzer-no-link" cmake \ cmake $CMAKEFLAGSALL \ -DFMT_FUZZ_LINKMAIN=Off \ @@ -50,7 +52,7 @@ cmake --build $builddir builddir=$here/build-fuzzers-libfuzzer mkdir -p $builddir cd $builddir -CXX="clang++" \ +CXX=$CLANG \ CXXFLAGS="$CXXFLAGSALL -fsanitize=fuzzer-no-link,address,undefined" cmake \ cmake $CMAKEFLAGSALL \ -DFMT_FUZZ_LINKMAIN=Off \ @@ -62,7 +64,7 @@ cmake --build $builddir builddir=$here/build-fuzzers-fast mkdir -p $builddir cd $builddir -CXX="clang++" \ +CXX=$CLANG \ CXXFLAGS="$CXXFLAGSALL -fsanitize=fuzzer-no-link -O3" cmake \ cmake $CMAKEFLAGSALL \ -DFMT_FUZZ_LINKMAIN=Off \ diff --git a/test/fuzzing/chrono-duration.cc b/test/fuzzing/chrono-duration.cc index fdad9894..d66068d9 100644 --- a/test/fuzzing/chrono-duration.cc +++ b/test/fuzzing/chrono-duration.cc @@ -1,9 +1,10 @@ // Copyright (c) 2019, Paul Dreik // For the license information refer to format.h. -#include <cstdint> #include <fmt/chrono.h> +#include <cstdint> + #include "fuzzer-common.h" template <typename Period, typename Rep> @@ -13,8 +14,8 @@ void invoke_inner(fmt::string_view format_str, Rep rep) { #if FMT_FUZZ_FORMAT_TO_STRING std::string message = fmt::format(format_str, value); #else - fmt::memory_buffer buf; - fmt::format_to(buf, format_str, value); + auto buf = fmt::memory_buffer(); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), format_str, value); #endif } catch (std::exception&) { } @@ -31,7 +32,7 @@ void invoke_outer(const uint8_t* data, size_t size, int period) { data += fixed_size; size -= fixed_size; - // data is already allocated separately in libFuzzer so reading past the end + // data is already allocated separately in libFuzzer so reading past the end // will most likely be detected anyway. const auto format_str = fmt::string_view(as_chars(data), size); @@ -86,7 +87,7 @@ void invoke_outer(const uint8_t* data, size_t size, int period) { } extern "C" int LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(const uint8_t* data, size_t size) { - if (size <= 4) return 0; + if (size <= 4) return 0; const auto representation = data[0]; const auto period = data[1]; diff --git a/test/fuzzing/chrono-timepoint.cc b/test/fuzzing/chrono-timepoint.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..8a1b24d2 --- /dev/null +++ b/test/fuzzing/chrono-timepoint.cc @@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ +// Copyright (c) 2021, Paul Dreik +// For license information refer to format.h. +#include <fmt/chrono.h> + +#include "fuzzer-common.h" + +/* + * a fuzzer for the chrono timepoints formatters + * C is a clock (std::chrono::system_clock etc) + */ +template <typename C> void doit(const uint8_t* data, size_t size) { + using Rep = typename C::time_point::rep; + constexpr auto N = sizeof(Rep); + if (size < N) return; + + const auto x = assign_from_buf<Rep>(data); + typename C::duration dur{x}; + typename C::time_point timepoint{dur}; + data += N; + size -= N; + data_to_string format_str(data, size); + + std::string message = fmt::format(format_str.get(), timepoint); +} + +extern "C" int LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(const uint8_t* data, size_t size) { + try { + doit<std::chrono::system_clock>(data, size); + } catch (...) { + } + return 0; +} diff --git a/test/fuzzing/float.cc b/test/fuzzing/float.cc index a9a347ef..d4c9e4f5 100644 --- a/test/fuzzing/float.cc +++ b/test/fuzzing/float.cc @@ -1,34 +1,39 @@ // A fuzzer for floating-point formatter. // For the license information refer to format.h. +#include <fmt/format.h> + #include <cstdint> #include <cstdlib> -#include <stdexcept> #include <limits> -#include <fmt/format.h> +#include <stdexcept> #include "fuzzer-common.h" -extern "C" int LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(const uint8_t* data, size_t size) { - if (size <= sizeof(double) || !std::numeric_limits<double>::is_iec559) - return 0; - - auto value = assign_from_buf<double>(data); +void check_round_trip(fmt::string_view format_str, double value) { auto buffer = fmt::memory_buffer(); - fmt::format_to(buffer, "{}", value); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buffer), format_str, value); - // Check a round trip. if (std::isnan(value)) { auto nan = std::signbit(value) ? "-nan" : "nan"; if (fmt::string_view(buffer.data(), buffer.size()) != nan) throw std::runtime_error("round trip failure"); - return 0; + return; } + buffer.push_back('\0'); char* ptr = nullptr; if (std::strtod(buffer.data(), &ptr) != value) throw std::runtime_error("round trip failure"); - if (ptr + 1 != buffer.end()) - throw std::runtime_error("unparsed output"); + if (ptr + 1 != buffer.end()) throw std::runtime_error("unparsed output"); +} + +extern "C" int LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(const uint8_t* data, size_t size) { + if (size <= sizeof(double) || !std::numeric_limits<double>::is_iec559) + return 0; + check_round_trip("{}", assign_from_buf<double>(data)); + // A larger than necessary precision is used to trigger the fallback + // formatter. + check_round_trip("{:.50g}", assign_from_buf<double>(data)); return 0; } diff --git a/test/fuzzing/fuzzer-common.h b/test/fuzzing/fuzzer-common.h index 635a5d99..c0a24672 100644 --- a/test/fuzzing/fuzzer-common.h +++ b/test/fuzzing/fuzzer-common.h @@ -4,12 +4,12 @@ #ifndef FUZZER_COMMON_H #define FUZZER_COMMON_H -#include <cstdint> // std::uint8_t -#include <cstring> // memcpy -#include <vector> - #include <fmt/core.h> +#include <cstdint> // std::uint8_t +#include <cstring> // memcpy +#include <vector> + // One can format to either a string, or a buffer. The latter is faster, but // one may be interested in formatting to a string instead to verify it works // as intended. To avoid a combinatoric explosion, select this at compile time @@ -56,7 +56,9 @@ struct data_to_string { data_to_string(const uint8_t* data, size_t size, bool add_terminator = false) : buffer(size + (add_terminator ? 1 : 0)) { - std::memcpy(buffer.data(), data, size); + if (size) { + std::memcpy(buffer.data(), data, size); + } } fmt::string_view get() const { return {buffer.data(), buffer.size()}; } diff --git a/test/fuzzing/named-arg.cc b/test/fuzzing/named-arg.cc index ffd8e903..3bee1ae3 100644 --- a/test/fuzzing/named-arg.cc +++ b/test/fuzzing/named-arg.cc @@ -1,10 +1,11 @@ // Copyright (c) 2019, Paul Dreik // For the license information refer to format.h. +#include <fmt/chrono.h> + #include <cstdint> #include <type_traits> #include <vector> -#include <fmt/chrono.h> #include "fuzzer-common.h" @@ -25,10 +26,11 @@ void invoke_fmt(const uint8_t* data, size_t size, unsigned arg_name_size) { try { #if FMT_FUZZ_FORMAT_TO_STRING std::string message = - fmt::format(format_str.get(), fmt::arg(arg_name.data(), value)); + fmt::format(format_str.get(), fmt::arg(arg_name.data(), value)); #else fmt::memory_buffer out; - fmt::format_to(out, format_str.get(), fmt::arg(arg_name.data(), value)); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), format_str.get(), + fmt::arg(arg_name.data(), value)); #endif } catch (std::exception&) { } diff --git a/test/fuzzing/one-arg.cc b/test/fuzzing/one-arg.cc index df173432..af9787f8 100644 --- a/test/fuzzing/one-arg.cc +++ b/test/fuzzing/one-arg.cc @@ -1,17 +1,18 @@ // Copyright (c) 2019, Paul Dreik // For the license information refer to format.h. +#include <fmt/chrono.h> + #include <cstdint> #include <exception> -#include <fmt/chrono.h> #include "fuzzer-common.h" -template <typename T, typename Repr> -const T* from_repr(const Repr& r) { return &r; } +template <typename T, typename Repr> const T* from_repr(const Repr& r) { + return &r; +} -template <> -const std::tm* from_repr<std::tm>(const std::time_t& t) { +template <> const std::tm* from_repr<std::tm>(const std::time_t& t) { return std::localtime(&t); } @@ -29,8 +30,8 @@ void invoke_fmt(const uint8_t* data, size_t size) { #if FMT_FUZZ_FORMAT_TO_STRING std::string message = fmt::format(format_str.get(), *value); #else - fmt::memory_buffer message; - fmt::format_to(message, format_str.get(), *value); + auto buf = fmt::memory_buffer(); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), format_str.get(), *value); #endif } catch (std::exception&) { } diff --git a/test/fuzzing/two-args.cc b/test/fuzzing/two-args.cc index 4d7d3453..931c6465 100644 --- a/test/fuzzing/two-args.cc +++ b/test/fuzzing/two-args.cc @@ -1,10 +1,11 @@ // Copyright (c) 2019, Paul Dreik // For the license information refer to format.h. +#include <fmt/format.h> + #include <cstdint> #include <exception> #include <string> -#include <fmt/format.h> #include "fuzzer-common.h" @@ -26,8 +27,8 @@ void invoke_fmt(const uint8_t* data, size_t size) { #if FMT_FUZZ_FORMAT_TO_STRING std::string message = fmt::format(format_str, item1, item2); #else - fmt::memory_buffer message; - fmt::format_to(message, format_str, item1, item2); + auto buf = fmt::memory_buffer(); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), format_str, item1, item2); #endif } diff --git a/test/gmock/gmock.h b/test/gmock/gmock.h deleted file mode 100644 index 2a9cbd53..00000000 --- a/test/gmock/gmock.h +++ /dev/null @@ -1,14204 +0,0 @@ -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This is the main header file a user should include. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_H_ - -#ifdef __clang__ -# pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wc99-extensions" -#endif - -// This file implements the following syntax: -// -// ON_CALL(mock_object.Method(...)) -// .With(...) ? -// .WillByDefault(...); -// -// where With() is optional and WillByDefault() must appear exactly -// once. -// -// EXPECT_CALL(mock_object.Method(...)) -// .With(...) ? -// .Times(...) ? -// .InSequence(...) * -// .WillOnce(...) * -// .WillRepeatedly(...) ? -// .RetiresOnSaturation() ? ; -// -// where all clauses are optional and WillOnce() can be repeated. - -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file implements some commonly used actions. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_ACTIONS_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_ACTIONS_H_ - -#ifndef _WIN32_WCE -# include <errno.h> -#endif - -#include <algorithm> -#include <string> - -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file defines some utilities useful for implementing Google -// Mock. They are subject to change without notice, so please DO NOT -// USE THEM IN USER CODE. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_INTERNAL_UTILS_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_INTERNAL_UTILS_H_ - -#include <stdio.h> -#include <ostream> // NOLINT -#include <string> - -// This file was GENERATED by command: -// pump.py gmock-generated-internal-utils.h.pump -// DO NOT EDIT BY HAND!!! - -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file contains template meta-programming utility classes needed -// for implementing Google Mock. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_GENERATED_INTERNAL_UTILS_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_GENERATED_INTERNAL_UTILS_H_ - -// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: vadimb@google.com (Vadim Berman) -// -// Low-level types and utilities for porting Google Mock to various -// platforms. They are subject to change without notice. DO NOT USE -// THEM IN USER CODE. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_PORT_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_PORT_H_ - -#include <assert.h> -#include <stdlib.h> -#include <iostream> - -// Most of the types needed for porting Google Mock are also required -// for Google Test and are defined in gtest-port.h. -#include "gtest.h" - -// To avoid conditional compilation everywhere, we make it -// gmock-port.h's responsibility to #include the header implementing -// tr1/tuple. gmock-port.h does this via gtest-port.h, which is -// guaranteed to pull in the tuple header. - -// For MS Visual C++, check the compiler version. At least VS 2003 is -// required to compile Google Mock. -#if defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER < 1310 -# error "At least Visual C++ 2003 (7.1) is required to compile Google Mock." -#endif - -// Macro for referencing flags. This is public as we want the user to -// use this syntax to reference Google Mock flags. -#define GMOCK_FLAG(name) FLAGS_gmock_##name - -// Macros for declaring flags. -#define GMOCK_DECLARE_bool_(name) extern GTEST_API_ bool GMOCK_FLAG(name) -#define GMOCK_DECLARE_int32_(name) \ - extern GTEST_API_ ::testing::internal::Int32 GMOCK_FLAG(name) -#define GMOCK_DECLARE_string_(name) \ - extern GTEST_API_ ::std::string GMOCK_FLAG(name) - -// Macros for defining flags. -#define GMOCK_DEFINE_bool_(name, default_val, doc) \ - GTEST_API_ bool GMOCK_FLAG(name) = (default_val) -#define GMOCK_DEFINE_int32_(name, default_val, doc) \ - GTEST_API_ ::testing::internal::Int32 GMOCK_FLAG(name) = (default_val) -#define GMOCK_DEFINE_string_(name, default_val, doc) \ - GTEST_API_ ::std::string GMOCK_FLAG(name) = (default_val) - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_PORT_H_ - -namespace testing { - -template <typename T> -class Matcher; - -namespace internal { - -// An IgnoredValue object can be implicitly constructed from ANY value. -// This is used in implementing the IgnoreResult(a) action. -class IgnoredValue { - public: - // This constructor template allows any value to be implicitly - // converted to IgnoredValue. The object has no data member and - // doesn't try to remember anything about the argument. We - // deliberately omit the 'explicit' keyword in order to allow the - // conversion to be implicit. - template <typename T> - IgnoredValue(const T& /* ignored */) {} // NOLINT(runtime/explicit) -}; - -// MatcherTuple<T>::type is a tuple type where each field is a Matcher -// for the corresponding field in tuple type T. -template <typename Tuple> -struct MatcherTuple; - -template <> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple< > type; -}; - -template <typename A1> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1> > type; -}; - -template <typename A1, typename A2> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1>, Matcher<A2> > type; -}; - -template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1>, Matcher<A2>, Matcher<A3> > type; -}; - -template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1>, Matcher<A2>, Matcher<A3>, - Matcher<A4> > type; -}; - -template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1>, Matcher<A2>, Matcher<A3>, Matcher<A4>, - Matcher<A5> > type; -}; - -template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1>, Matcher<A2>, Matcher<A3>, Matcher<A4>, - Matcher<A5>, Matcher<A6> > type; -}; - -template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1>, Matcher<A2>, Matcher<A3>, Matcher<A4>, - Matcher<A5>, Matcher<A6>, Matcher<A7> > type; -}; - -template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1>, Matcher<A2>, Matcher<A3>, Matcher<A4>, - Matcher<A5>, Matcher<A6>, Matcher<A7>, Matcher<A8> > type; -}; - -template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1>, Matcher<A2>, Matcher<A3>, Matcher<A4>, - Matcher<A5>, Matcher<A6>, Matcher<A7>, Matcher<A8>, Matcher<A9> > type; -}; - -template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9, typename A10> -struct MatcherTuple< ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, - A10> > { - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<Matcher<A1>, Matcher<A2>, Matcher<A3>, Matcher<A4>, - Matcher<A5>, Matcher<A6>, Matcher<A7>, Matcher<A8>, Matcher<A9>, - Matcher<A10> > type; -}; - -// Template struct Function<F>, where F must be a function type, contains -// the following typedefs: -// -// Result: the function's return type. -// ArgumentN: the type of the N-th argument, where N starts with 1. -// ArgumentTuple: the tuple type consisting of all parameters of F. -// ArgumentMatcherTuple: the tuple type consisting of Matchers for all -// parameters of F. -// MakeResultVoid: the function type obtained by substituting void -// for the return type of F. -// MakeResultIgnoredValue: -// the function type obtained by substituting Something -// for the return type of F. -template <typename F> -struct Function; - -template <typename R> -struct Function<R()> { - typedef R Result; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1> -struct Function<R(A1)> - : Function<R()> { - typedef A1 Argument1; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2> -struct Function<R(A1, A2)> - : Function<R(A1)> { - typedef A2 Argument2; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1, A2); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1, A2); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> -struct Function<R(A1, A2, A3)> - : Function<R(A1, A2)> { - typedef A3 Argument3; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1, A2, A3); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1, A2, A3); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4> -struct Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4)> - : Function<R(A1, A2, A3)> { - typedef A4 Argument4; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1, A2, A3, A4); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1, A2, A3, A4); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5> -struct Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5)> - : Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4)> { - typedef A5 Argument5; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6> -struct Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6)> - : Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5)> { - typedef A6 Argument6; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7> -struct Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7)> - : Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6)> { - typedef A7 Argument7; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> -struct Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8)> - : Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7)> { - typedef A8 Argument8; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9> -struct Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9)> - : Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8)> { - typedef A9 Argument9; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, - A9); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9, - typename A10> -struct Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10)> - : Function<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9)> { - typedef A10 Argument10; - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, - A10> ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename MatcherTuple<ArgumentTuple>::type ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef void MakeResultVoid(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10); - typedef IgnoredValue MakeResultIgnoredValue(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, - A9, A10); -}; - -} // namespace internal - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_GENERATED_INTERNAL_UTILS_H_ - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// Converts an identifier name to a space-separated list of lower-case -// words. Each maximum substring of the form [A-Za-z][a-z]*|\d+ is -// treated as one word. For example, both "FooBar123" and -// "foo_bar_123" are converted to "foo bar 123". -GTEST_API_ string ConvertIdentifierNameToWords(const char* id_name); - -// PointeeOf<Pointer>::type is the type of a value pointed to by a -// Pointer, which can be either a smart pointer or a raw pointer. The -// following default implementation is for the case where Pointer is a -// smart pointer. -template <typename Pointer> -struct PointeeOf { - // Smart pointer classes define type element_type as the type of - // their pointees. - typedef typename Pointer::element_type type; -}; -// This specialization is for the raw pointer case. -template <typename T> -struct PointeeOf<T*> { typedef T type; }; // NOLINT - -// GetRawPointer(p) returns the raw pointer underlying p when p is a -// smart pointer, or returns p itself when p is already a raw pointer. -// The following default implementation is for the smart pointer case. -template <typename Pointer> -inline const typename Pointer::element_type* GetRawPointer(const Pointer& p) { - return p.get(); -} -// This overloaded version is for the raw pointer case. -template <typename Element> -inline Element* GetRawPointer(Element* p) { return p; } - -// This comparator allows linked_ptr to be stored in sets. -template <typename T> -struct LinkedPtrLessThan { - bool operator()(const ::testing::internal::linked_ptr<T>& lhs, - const ::testing::internal::linked_ptr<T>& rhs) const { - return lhs.get() < rhs.get(); - } -}; - -// Symbian compilation can be done with wchar_t being either a native -// type or a typedef. Using Google Mock with OpenC without wchar_t -// should require the definition of _STLP_NO_WCHAR_T. -// -// MSVC treats wchar_t as a native type usually, but treats it as the -// same as unsigned short when the compiler option /Zc:wchar_t- is -// specified. It defines _NATIVE_WCHAR_T_DEFINED symbol when wchar_t -// is a native type. -#if (GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN && defined(_STLP_NO_WCHAR_T)) || \ - (defined(_MSC_VER) && !defined(_NATIVE_WCHAR_T_DEFINED)) -// wchar_t is a typedef. -#else -# define GMOCK_WCHAR_T_IS_NATIVE_ 1 -#endif - -// signed wchar_t and unsigned wchar_t are NOT in the C++ standard. -// Using them is a bad practice and not portable. So DON'T use them. -// -// Still, Google Mock is designed to work even if the user uses signed -// wchar_t or unsigned wchar_t (obviously, assuming the compiler -// supports them). -// -// To gcc, -// wchar_t == signed wchar_t != unsigned wchar_t == unsigned int -#ifdef __GNUC__ -// signed/unsigned wchar_t are valid types. -# define GMOCK_HAS_SIGNED_WCHAR_T_ 1 -#endif - -// In what follows, we use the term "kind" to indicate whether a type -// is bool, an integer type (excluding bool), a floating-point type, -// or none of them. This categorization is useful for determining -// when a matcher argument type can be safely converted to another -// type in the implementation of SafeMatcherCast. -enum TypeKind { - kBool, kInteger, kFloatingPoint, kOther -}; - -// KindOf<T>::value is the kind of type T. -template <typename T> struct KindOf { - enum { value = kOther }; // The default kind. -}; - -// This macro declares that the kind of 'type' is 'kind'. -#define GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(type, kind) \ - template <> struct KindOf<type> { enum { value = kind }; } - -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(bool, kBool); - -// All standard integer types. -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(char, kInteger); -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(signed char, kInteger); -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(unsigned char, kInteger); -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(short, kInteger); // NOLINT -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(unsigned short, kInteger); // NOLINT -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(int, kInteger); -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(unsigned int, kInteger); -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(long, kInteger); // NOLINT -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(unsigned long, kInteger); // NOLINT - -#if GMOCK_WCHAR_T_IS_NATIVE_ -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(wchar_t, kInteger); -#endif - -// Non-standard integer types. -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(Int64, kInteger); -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(UInt64, kInteger); - -// All standard floating-point types. -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(float, kFloatingPoint); -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(double, kFloatingPoint); -GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(long double, kFloatingPoint); - -#undef GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_ - -// Evaluates to the kind of 'type'. -#define GMOCK_KIND_OF_(type) \ - static_cast< ::testing::internal::TypeKind>( \ - ::testing::internal::KindOf<type>::value) - -// Evaluates to true iff integer type T is signed. -#define GMOCK_IS_SIGNED_(T) (static_cast<T>(-1) < 0) - -// LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kFromKind, From, kToKind, To>::value -// is true iff arithmetic type From can be losslessly converted to -// arithmetic type To. -// -// It's the user's responsibility to ensure that both From and To are -// raw (i.e. has no CV modifier, is not a pointer, and is not a -// reference) built-in arithmetic types, kFromKind is the kind of -// From, and kToKind is the kind of To; the value is -// implementation-defined when the above pre-condition is violated. -template <TypeKind kFromKind, typename From, TypeKind kToKind, typename To> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl : public false_type {}; - -// Converting bool to bool is lossless. -template <> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kBool, bool, kBool, bool> - : public true_type {}; // NOLINT - -// Converting bool to any integer type is lossless. -template <typename To> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kBool, bool, kInteger, To> - : public true_type {}; // NOLINT - -// Converting bool to any floating-point type is lossless. -template <typename To> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kBool, bool, kFloatingPoint, To> - : public true_type {}; // NOLINT - -// Converting an integer to bool is lossy. -template <typename From> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kInteger, From, kBool, bool> - : public false_type {}; // NOLINT - -// Converting an integer to another non-bool integer is lossless iff -// the target type's range encloses the source type's range. -template <typename From, typename To> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kInteger, From, kInteger, To> - : public bool_constant< - // When converting from a smaller size to a larger size, we are - // fine as long as we are not converting from signed to unsigned. - ((sizeof(From) < sizeof(To)) && - (!GMOCK_IS_SIGNED_(From) || GMOCK_IS_SIGNED_(To))) || - // When converting between the same size, the signedness must match. - ((sizeof(From) == sizeof(To)) && - (GMOCK_IS_SIGNED_(From) == GMOCK_IS_SIGNED_(To)))> {}; // NOLINT - -#undef GMOCK_IS_SIGNED_ - -// Converting an integer to a floating-point type may be lossy, since -// the format of a floating-point number is implementation-defined. -template <typename From, typename To> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kInteger, From, kFloatingPoint, To> - : public false_type {}; // NOLINT - -// Converting a floating-point to bool is lossy. -template <typename From> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kFloatingPoint, From, kBool, bool> - : public false_type {}; // NOLINT - -// Converting a floating-point to an integer is lossy. -template <typename From, typename To> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kFloatingPoint, From, kInteger, To> - : public false_type {}; // NOLINT - -// Converting a floating-point to another floating-point is lossless -// iff the target type is at least as big as the source type. -template <typename From, typename To> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl< - kFloatingPoint, From, kFloatingPoint, To> - : public bool_constant<sizeof(From) <= sizeof(To)> {}; // NOLINT - -// LosslessArithmeticConvertible<From, To>::value is true iff arithmetic -// type From can be losslessly converted to arithmetic type To. -// -// It's the user's responsibility to ensure that both From and To are -// raw (i.e. has no CV modifier, is not a pointer, and is not a -// reference) built-in arithmetic types; the value is -// implementation-defined when the above pre-condition is violated. -template <typename From, typename To> -struct LosslessArithmeticConvertible - : public LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl< - GMOCK_KIND_OF_(From), From, GMOCK_KIND_OF_(To), To> {}; // NOLINT - -// This interface knows how to report a Google Mock failure (either -// non-fatal or fatal). -class FailureReporterInterface { - public: - // The type of a failure (either non-fatal or fatal). - enum FailureType { - kNonfatal, kFatal - }; - - virtual ~FailureReporterInterface() {} - - // Reports a failure that occurred at the given source file location. - virtual void ReportFailure(FailureType type, const char* file, int line, - const string& message) = 0; -}; - -// Returns the failure reporter used by Google Mock. -GTEST_API_ FailureReporterInterface* GetFailureReporter(); - -// Asserts that condition is true; aborts the process with the given -// message if condition is false. We cannot use LOG(FATAL) or CHECK() -// as Google Mock might be used to mock the log sink itself. We -// inline this function to prevent it from showing up in the stack -// trace. -inline void Assert(bool condition, const char* file, int line, - const string& msg) { - if (!condition) { - GetFailureReporter()->ReportFailure(FailureReporterInterface::kFatal, - file, line, msg); - } -} -inline void Assert(bool condition, const char* file, int line) { - Assert(condition, file, line, "Assertion failed."); -} - -// Verifies that condition is true; generates a non-fatal failure if -// condition is false. -inline void Expect(bool condition, const char* file, int line, - const string& msg) { - if (!condition) { - GetFailureReporter()->ReportFailure(FailureReporterInterface::kNonfatal, - file, line, msg); - } -} -inline void Expect(bool condition, const char* file, int line) { - Expect(condition, file, line, "Expectation failed."); -} - -// Severity level of a log. -enum LogSeverity { - kInfo = 0, - kWarning = 1 -}; - -// Valid values for the --gmock_verbose flag. - -// All logs (informational and warnings) are printed. -const char kInfoVerbosity[] = "info"; -// Only warnings are printed. -const char kWarningVerbosity[] = "warning"; -// No logs are printed. -const char kErrorVerbosity[] = "error"; - -// Returns true iff a log with the given severity is visible according -// to the --gmock_verbose flag. -GTEST_API_ bool LogIsVisible(LogSeverity severity); - -// Prints the given message to stdout iff 'severity' >= the level -// specified by the --gmock_verbose flag. If stack_frames_to_skip >= -// 0, also prints the stack trace excluding the top -// stack_frames_to_skip frames. In opt mode, any positive -// stack_frames_to_skip is treated as 0, since we don't know which -// function calls will be inlined by the compiler and need to be -// conservative. -GTEST_API_ void Log(LogSeverity severity, - const string& message, - int stack_frames_to_skip); - -// TODO(wan@google.com): group all type utilities together. - -// Type traits. - -// is_reference<T>::value is non-zero iff T is a reference type. -template <typename T> struct is_reference : public false_type {}; -template <typename T> struct is_reference<T&> : public true_type {}; - -// type_equals<T1, T2>::value is non-zero iff T1 and T2 are the same type. -template <typename T1, typename T2> struct type_equals : public false_type {}; -template <typename T> struct type_equals<T, T> : public true_type {}; - -// remove_reference<T>::type removes the reference from type T, if any. -template <typename T> struct remove_reference { typedef T type; }; // NOLINT -template <typename T> struct remove_reference<T&> { typedef T type; }; // NOLINT - -// DecayArray<T>::type turns an array type U[N] to const U* and preserves -// other types. Useful for saving a copy of a function argument. -template <typename T> struct DecayArray { typedef T type; }; // NOLINT -template <typename T, size_t N> struct DecayArray<T[N]> { - typedef const T* type; -}; -// Sometimes people use arrays whose size is not available at the use site -// (e.g. extern const char kNamePrefix[]). This specialization covers that -// case. -template <typename T> struct DecayArray<T[]> { - typedef const T* type; -}; - -// Invalid<T>() returns an invalid value of type T. This is useful -// when a value of type T is needed for compilation, but the statement -// will not really be executed (or we don't care if the statement -// crashes). -template <typename T> -inline T Invalid() { - void *p = NULL; - return const_cast<typename remove_reference<T>::type&>( - *static_cast<volatile typename remove_reference<T>::type*>(p)); -} -template <> -inline void Invalid<void>() {} - -// Given a raw type (i.e. having no top-level reference or const -// modifier) RawContainer that's either an STL-style container or a -// native array, class StlContainerView<RawContainer> has the -// following members: -// -// - type is a type that provides an STL-style container view to -// (i.e. implements the STL container concept for) RawContainer; -// - const_reference is a type that provides a reference to a const -// RawContainer; -// - ConstReference(raw_container) returns a const reference to an STL-style -// container view to raw_container, which is a RawContainer. -// - Copy(raw_container) returns an STL-style container view of a -// copy of raw_container, which is a RawContainer. -// -// This generic version is used when RawContainer itself is already an -// STL-style container. -template <class RawContainer> -class StlContainerView { - public: - typedef RawContainer type; - typedef const type& const_reference; - - static const_reference ConstReference(const RawContainer& container) { - // Ensures that RawContainer is not a const type. - testing::StaticAssertTypeEq<RawContainer, - GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(RawContainer)>(); - return container; - } - static type Copy(const RawContainer& container) { return container; } -}; - -// This specialization is used when RawContainer is a native array type. -template <typename Element, size_t N> -class StlContainerView<Element[N]> { - public: - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(Element) RawElement; - typedef internal::NativeArray<RawElement> type; - // NativeArray<T> can represent a native array either by value or by - // reference (selected by a constructor argument), so 'const type' - // can be used to reference a const native array. We cannot - // 'typedef const type& const_reference' here, as that would mean - // ConstReference() has to return a reference to a local variable. - typedef const type const_reference; - - static const_reference ConstReference(const Element (&array)[N]) { - // Ensures that Element is not a const type. - testing::StaticAssertTypeEq<Element, RawElement>(); -#if GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - // The Nokia Symbian compiler confuses itself in template instantiation - // for this call without the cast to Element*: - // function call '[testing::internal::NativeArray<char *>].NativeArray( - // {lval} const char *[4], long, testing::internal::RelationToSource)' - // does not match - // 'testing::internal::NativeArray<char *>::NativeArray( - // char *const *, unsigned int, testing::internal::RelationToSource)' - // (instantiating: 'testing::internal::ContainsMatcherImpl - // <const char * (&)[4]>::Matches(const char * (&)[4]) const') - // (instantiating: 'testing::internal::StlContainerView<char *[4]>:: - // ConstReference(const char * (&)[4])') - // (and though the N parameter type is mismatched in the above explicit - // conversion of it doesn't help - only the conversion of the array). - return type(const_cast<Element*>(&array[0]), N, kReference); -#else - return type(array, N, kReference); -#endif // GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - } - static type Copy(const Element (&array)[N]) { -#if GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - return type(const_cast<Element*>(&array[0]), N, kCopy); -#else - return type(array, N, kCopy); -#endif // GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - } -}; - -// This specialization is used when RawContainer is a native array -// represented as a (pointer, size) tuple. -template <typename ElementPointer, typename Size> -class StlContainerView< ::std::tr1::tuple<ElementPointer, Size> > { - public: - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_( - typename internal::PointeeOf<ElementPointer>::type) RawElement; - typedef internal::NativeArray<RawElement> type; - typedef const type const_reference; - - static const_reference ConstReference( - const ::std::tr1::tuple<ElementPointer, Size>& array) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<0>(array), get<1>(array), kReference); - } - static type Copy(const ::std::tr1::tuple<ElementPointer, Size>& array) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<0>(array), get<1>(array), kCopy); - } -}; - -// The following specialization prevents the user from instantiating -// StlContainer with a reference type. -template <typename T> class StlContainerView<T&>; - -// A type transform to remove constness from the first part of a pair. -// Pairs like that are used as the value_type of associative containers, -// and this transform produces a similar but assignable pair. -template <typename T> -struct RemoveConstFromKey { - typedef T type; -}; - -// Partially specialized to remove constness from std::pair<const K, V>. -template <typename K, typename V> -struct RemoveConstFromKey<std::pair<const K, V> > { - typedef std::pair<K, V> type; -}; - -// Mapping from booleans to types. Similar to boost::bool_<kValue> and -// std::integral_constant<bool, kValue>. -template <bool kValue> -struct BooleanConstant {}; - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_INTERNAL_UTILS_H_ - -namespace testing { - -// To implement an action Foo, define: -// 1. a class FooAction that implements the ActionInterface interface, and -// 2. a factory function that creates an Action object from a -// const FooAction*. -// -// The two-level delegation design follows that of Matcher, providing -// consistency for extension developers. It also eases ownership -// management as Action objects can now be copied like plain values. - -namespace internal { - -template <typename F1, typename F2> -class ActionAdaptor; - -// BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Get() returns the "built-in" default -// value for type T, which is NULL when T is a pointer type, 0 when T -// is a numeric type, false when T is bool, or "" when T is string or -// std::string. For any other type T, this value is undefined and the -// function will abort the process. -template <typename T> -class BuiltInDefaultValue { - public: - // This function returns true iff type T has a built-in default value. - static bool Exists() { return false; } - static T Get() { - Assert(false, __FILE__, __LINE__, - "Default action undefined for the function return type."); - return internal::Invalid<T>(); - // The above statement will never be reached, but is required in - // order for this function to compile. - } -}; - -// This partial specialization says that we use the same built-in -// default value for T and const T. -template <typename T> -class BuiltInDefaultValue<const T> { - public: - static bool Exists() { return BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Exists(); } - static T Get() { return BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Get(); } -}; - -// This partial specialization defines the default values for pointer -// types. -template <typename T> -class BuiltInDefaultValue<T*> { - public: - static bool Exists() { return true; } - static T* Get() { return NULL; } -}; - -// The following specializations define the default values for -// specific types we care about. -#define GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(type, value) \ - template <> \ - class BuiltInDefaultValue<type> { \ - public: \ - static bool Exists() { return true; } \ - static type Get() { return value; } \ - } - -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(void, ); // NOLINT -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(::string, ""); -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(::std::string, ""); -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(bool, false); -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(unsigned char, '\0'); -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(signed char, '\0'); -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(char, '\0'); - -// There's no need for a default action for signed wchar_t, as that -// type is the same as wchar_t for gcc, and invalid for MSVC. -// -// There's also no need for a default action for unsigned wchar_t, as -// that type is the same as unsigned int for gcc, and invalid for -// MSVC. -#if GMOCK_WCHAR_T_IS_NATIVE_ -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(wchar_t, 0U); // NOLINT -#endif - -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(unsigned short, 0U); // NOLINT -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(signed short, 0); // NOLINT -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(unsigned int, 0U); -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(signed int, 0); -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(unsigned long, 0UL); // NOLINT -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(signed long, 0L); // NOLINT -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(UInt64, 0); -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(Int64, 0); -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(float, 0); -GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(double, 0); - -#undef GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_ - -} // namespace internal - -// When an unexpected function call is encountered, Google Mock will -// let it return a default value if the user has specified one for its -// return type, or if the return type has a built-in default value; -// otherwise Google Mock won't know what value to return and will have -// to abort the process. -// -// The DefaultValue<T> class allows a user to specify the -// default value for a type T that is both copyable and publicly -// destructible (i.e. anything that can be used as a function return -// type). The usage is: -// -// // Sets the default value for type T to be foo. -// DefaultValue<T>::Set(foo); -template <typename T> -class DefaultValue { - public: - // Sets the default value for type T; requires T to be - // copy-constructable and have a public destructor. - static void Set(T x) { - delete value_; - value_ = new T(x); - } - - // Unsets the default value for type T. - static void Clear() { - delete value_; - value_ = NULL; - } - - // Returns true iff the user has set the default value for type T. - static bool IsSet() { return value_ != NULL; } - - // Returns true if T has a default return value set by the user or there - // exists a built-in default value. - static bool Exists() { - return IsSet() || internal::BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Exists(); - } - - // Returns the default value for type T if the user has set one; - // otherwise returns the built-in default value if there is one; - // otherwise aborts the process. - static T Get() { - return value_ == NULL ? - internal::BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Get() : *value_; - } - - private: - static const T* value_; -}; - -// This partial specialization allows a user to set default values for -// reference types. -template <typename T> -class DefaultValue<T&> { - public: - // Sets the default value for type T&. - static void Set(T& x) { // NOLINT - address_ = &x; - } - - // Unsets the default value for type T&. - static void Clear() { - address_ = NULL; - } - - // Returns true iff the user has set the default value for type T&. - static bool IsSet() { return address_ != NULL; } - - // Returns true if T has a default return value set by the user or there - // exists a built-in default value. - static bool Exists() { - return IsSet() || internal::BuiltInDefaultValue<T&>::Exists(); - } - - // Returns the default value for type T& if the user has set one; - // otherwise returns the built-in default value if there is one; - // otherwise aborts the process. - static T& Get() { - return address_ == NULL ? - internal::BuiltInDefaultValue<T&>::Get() : *address_; - } - - private: - static T* address_; -}; - -// This specialization allows DefaultValue<void>::Get() to -// compile. -template <> -class DefaultValue<void> { - public: - static bool Exists() { return true; } - static void Get() {} -}; - -// Points to the user-set default value for type T. -template <typename T> -const T* DefaultValue<T>::value_ = NULL; - -// Points to the user-set default value for type T&. -template <typename T> -T* DefaultValue<T&>::address_ = NULL; - -// Implement this interface to define an action for function type F. -template <typename F> -class ActionInterface { - public: - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - ActionInterface() {} - virtual ~ActionInterface() {} - - // Performs the action. This method is not const, as in general an - // action can have side effects and be stateful. For example, a - // get-the-next-element-from-the-collection action will need to - // remember the current element. - virtual Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) = 0; - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ActionInterface); -}; - -// An Action<F> is a copyable and IMMUTABLE (except by assignment) -// object that represents an action to be taken when a mock function -// of type F is called. The implementation of Action<T> is just a -// linked_ptr to const ActionInterface<T>, so copying is fairly cheap. -// Don't inherit from Action! -// -// You can view an object implementing ActionInterface<F> as a -// concrete action (including its current state), and an Action<F> -// object as a handle to it. -template <typename F> -class Action { - public: - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - // Constructs a null Action. Needed for storing Action objects in - // STL containers. - Action() : impl_(NULL) {} - - // Constructs an Action from its implementation. A NULL impl is - // used to represent the "do-default" action. - explicit Action(ActionInterface<F>* impl) : impl_(impl) {} - - // Copy constructor. - Action(const Action& action) : impl_(action.impl_) {} - - // This constructor allows us to turn an Action<Func> object into an - // Action<F>, as long as F's arguments can be implicitly converted - // to Func's and Func's return type can be implicitly converted to - // F's. - template <typename Func> - explicit Action(const Action<Func>& action); - - // Returns true iff this is the DoDefault() action. - bool IsDoDefault() const { return impl_.get() == NULL; } - - // Performs the action. Note that this method is const even though - // the corresponding method in ActionInterface is not. The reason - // is that a const Action<F> means that it cannot be re-bound to - // another concrete action, not that the concrete action it binds to - // cannot change state. (Think of the difference between a const - // pointer and a pointer to const.) - Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) const { - internal::Assert( - !IsDoDefault(), __FILE__, __LINE__, - "You are using DoDefault() inside a composite action like " - "DoAll() or WithArgs(). This is not supported for technical " - "reasons. Please instead spell out the default action, or " - "assign the default action to an Action variable and use " - "the variable in various places."); - return impl_->Perform(args); - } - - private: - template <typename F1, typename F2> - friend class internal::ActionAdaptor; - - internal::linked_ptr<ActionInterface<F> > impl_; -}; - -// The PolymorphicAction class template makes it easy to implement a -// polymorphic action (i.e. an action that can be used in mock -// functions of than one type, e.g. Return()). -// -// To define a polymorphic action, a user first provides a COPYABLE -// implementation class that has a Perform() method template: -// -// class FooAction { -// public: -// template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> -// Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) const { -// // Processes the arguments and returns a result, using -// // tr1::get<N>(args) to get the N-th (0-based) argument in the tuple. -// } -// ... -// }; -// -// Then the user creates the polymorphic action using -// MakePolymorphicAction(object) where object has type FooAction. See -// the definition of Return(void) and SetArgumentPointee<N>(value) for -// complete examples. -template <typename Impl> -class PolymorphicAction { - public: - explicit PolymorphicAction(const Impl& impl) : impl_(impl) {} - - template <typename F> - operator Action<F>() const { - return Action<F>(new MonomorphicImpl<F>(impl_)); - } - - private: - template <typename F> - class MonomorphicImpl : public ActionInterface<F> { - public: - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - explicit MonomorphicImpl(const Impl& impl) : impl_(impl) {} - - virtual Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - return impl_.template Perform<Result>(args); - } - - private: - Impl impl_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(MonomorphicImpl); - }; - - Impl impl_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(PolymorphicAction); -}; - -// Creates an Action from its implementation and returns it. The -// created Action object owns the implementation. -template <typename F> -Action<F> MakeAction(ActionInterface<F>* impl) { - return Action<F>(impl); -} - -// Creates a polymorphic action from its implementation. This is -// easier to use than the PolymorphicAction<Impl> constructor as it -// doesn't require you to explicitly write the template argument, e.g. -// -// MakePolymorphicAction(foo); -// vs -// PolymorphicAction<TypeOfFoo>(foo); -template <typename Impl> -inline PolymorphicAction<Impl> MakePolymorphicAction(const Impl& impl) { - return PolymorphicAction<Impl>(impl); -} - -namespace internal { - -// Allows an Action<F2> object to pose as an Action<F1>, as long as F2 -// and F1 are compatible. -template <typename F1, typename F2> -class ActionAdaptor : public ActionInterface<F1> { - public: - typedef typename internal::Function<F1>::Result Result; - typedef typename internal::Function<F1>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - explicit ActionAdaptor(const Action<F2>& from) : impl_(from.impl_) {} - - virtual Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - return impl_->Perform(args); - } - - private: - const internal::linked_ptr<ActionInterface<F2> > impl_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ActionAdaptor); -}; - -// Implements the polymorphic Return(x) action, which can be used in -// any function that returns the type of x, regardless of the argument -// types. -// -// Note: The value passed into Return must be converted into -// Function<F>::Result when this action is cast to Action<F> rather than -// when that action is performed. This is important in scenarios like -// -// MOCK_METHOD1(Method, T(U)); -// ... -// { -// Foo foo; -// X x(&foo); -// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Method(_)).WillOnce(Return(x)); -// } -// -// In the example above the variable x holds reference to foo which leaves -// scope and gets destroyed. If copying X just copies a reference to foo, -// that copy will be left with a hanging reference. If conversion to T -// makes a copy of foo, the above code is safe. To support that scenario, we -// need to make sure that the type conversion happens inside the EXPECT_CALL -// statement, and conversion of the result of Return to Action<T(U)> is a -// good place for that. -// -template <typename R> -class ReturnAction { - public: - // Constructs a ReturnAction object from the value to be returned. - // 'value' is passed by value instead of by const reference in order - // to allow Return("string literal") to compile. - explicit ReturnAction(R value) : value_(value) {} - - // This template type conversion operator allows Return(x) to be - // used in ANY function that returns x's type. - template <typename F> - operator Action<F>() const { - // Assert statement belongs here because this is the best place to verify - // conditions on F. It produces the clearest error messages - // in most compilers. - // Impl really belongs in this scope as a local class but can't - // because MSVC produces duplicate symbols in different translation units - // in this case. Until MS fixes that bug we put Impl into the class scope - // and put the typedef both here (for use in assert statement) and - // in the Impl class. But both definitions must be the same. - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( - !internal::is_reference<Result>::value, - use_ReturnRef_instead_of_Return_to_return_a_reference); - return Action<F>(new Impl<F>(value_)); - } - - private: - // Implements the Return(x) action for a particular function type F. - template <typename F> - class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { - public: - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - // The implicit cast is necessary when Result has more than one - // single-argument constructor (e.g. Result is std::vector<int>) and R - // has a type conversion operator template. In that case, value_(value) - // won't compile as the compiler doesn't known which constructor of - // Result to call. ImplicitCast_ forces the compiler to convert R to - // Result without considering explicit constructors, thus resolving the - // ambiguity. value_ is then initialized using its copy constructor. - explicit Impl(R value) - : value_(::testing::internal::ImplicitCast_<Result>(value)) {} - - virtual Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) { return value_; } - - private: - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(!internal::is_reference<Result>::value, - Result_cannot_be_a_reference_type); - Result value_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - R value_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ReturnAction); -}; - -// Implements the ReturnNull() action. -class ReturnNullAction { - public: - // Allows ReturnNull() to be used in any pointer-returning function. - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - static Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) { - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(internal::is_pointer<Result>::value, - ReturnNull_can_be_used_to_return_a_pointer_only); - return NULL; - } -}; - -// Implements the Return() action. -class ReturnVoidAction { - public: - // Allows Return() to be used in any void-returning function. - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - static void Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) { - CompileAssertTypesEqual<void, Result>(); - } -}; - -// Implements the polymorphic ReturnRef(x) action, which can be used -// in any function that returns a reference to the type of x, -// regardless of the argument types. -template <typename T> -class ReturnRefAction { - public: - // Constructs a ReturnRefAction object from the reference to be returned. - explicit ReturnRefAction(T& ref) : ref_(ref) {} // NOLINT - - // This template type conversion operator allows ReturnRef(x) to be - // used in ANY function that returns a reference to x's type. - template <typename F> - operator Action<F>() const { - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - // Asserts that the function return type is a reference. This - // catches the user error of using ReturnRef(x) when Return(x) - // should be used, and generates some helpful error message. - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(internal::is_reference<Result>::value, - use_Return_instead_of_ReturnRef_to_return_a_value); - return Action<F>(new Impl<F>(ref_)); - } - - private: - // Implements the ReturnRef(x) action for a particular function type F. - template <typename F> - class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { - public: - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - explicit Impl(T& ref) : ref_(ref) {} // NOLINT - - virtual Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) { - return ref_; - } - - private: - T& ref_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - T& ref_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ReturnRefAction); -}; - -// Implements the polymorphic ReturnRefOfCopy(x) action, which can be -// used in any function that returns a reference to the type of x, -// regardless of the argument types. -template <typename T> -class ReturnRefOfCopyAction { - public: - // Constructs a ReturnRefOfCopyAction object from the reference to - // be returned. - explicit ReturnRefOfCopyAction(const T& value) : value_(value) {} // NOLINT - - // This template type conversion operator allows ReturnRefOfCopy(x) to be - // used in ANY function that returns a reference to x's type. - template <typename F> - operator Action<F>() const { - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - // Asserts that the function return type is a reference. This - // catches the user error of using ReturnRefOfCopy(x) when Return(x) - // should be used, and generates some helpful error message. - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( - internal::is_reference<Result>::value, - use_Return_instead_of_ReturnRefOfCopy_to_return_a_value); - return Action<F>(new Impl<F>(value_)); - } - - private: - // Implements the ReturnRefOfCopy(x) action for a particular function type F. - template <typename F> - class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { - public: - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - explicit Impl(const T& value) : value_(value) {} // NOLINT - - virtual Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) { - return value_; - } - - private: - T value_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - const T value_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ReturnRefOfCopyAction); -}; - -// Implements the polymorphic DoDefault() action. -class DoDefaultAction { - public: - // This template type conversion operator allows DoDefault() to be - // used in any function. - template <typename F> - operator Action<F>() const { return Action<F>(NULL); } -}; - -// Implements the Assign action to set a given pointer referent to a -// particular value. -template <typename T1, typename T2> -class AssignAction { - public: - AssignAction(T1* ptr, T2 value) : ptr_(ptr), value_(value) {} - - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - void Perform(const ArgumentTuple& /* args */) const { - *ptr_ = value_; - } - - private: - T1* const ptr_; - const T2 value_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(AssignAction); -}; - -#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - -// Implements the SetErrnoAndReturn action to simulate return from -// various system calls and libc functions. -template <typename T> -class SetErrnoAndReturnAction { - public: - SetErrnoAndReturnAction(int errno_value, T result) - : errno_(errno_value), - result_(result) {} - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& /* args */) const { - errno = errno_; - return result_; - } - - private: - const int errno_; - const T result_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(SetErrnoAndReturnAction); -}; - -#endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - -// Implements the SetArgumentPointee<N>(x) action for any function -// whose N-th argument (0-based) is a pointer to x's type. The -// template parameter kIsProto is true iff type A is ProtocolMessage, -// proto2::Message, or a sub-class of those. -template <size_t N, typename A, bool kIsProto> -class SetArgumentPointeeAction { - public: - // Constructs an action that sets the variable pointed to by the - // N-th function argument to 'value'. - explicit SetArgumentPointeeAction(const A& value) : value_(value) {} - - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - void Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) const { - CompileAssertTypesEqual<void, Result>(); - *::std::tr1::get<N>(args) = value_; - } - - private: - const A value_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(SetArgumentPointeeAction); -}; - -template <size_t N, typename Proto> -class SetArgumentPointeeAction<N, Proto, true> { - public: - // Constructs an action that sets the variable pointed to by the - // N-th function argument to 'proto'. Both ProtocolMessage and - // proto2::Message have the CopyFrom() method, so the same - // implementation works for both. - explicit SetArgumentPointeeAction(const Proto& proto) : proto_(new Proto) { - proto_->CopyFrom(proto); - } - - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - void Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) const { - CompileAssertTypesEqual<void, Result>(); - ::std::tr1::get<N>(args)->CopyFrom(*proto_); - } - - private: - const internal::linked_ptr<Proto> proto_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(SetArgumentPointeeAction); -}; - -// Implements the InvokeWithoutArgs(f) action. The template argument -// FunctionImpl is the implementation type of f, which can be either a -// function pointer or a functor. InvokeWithoutArgs(f) can be used as an -// Action<F> as long as f's type is compatible with F (i.e. f can be -// assigned to a tr1::function<F>). -template <typename FunctionImpl> -class InvokeWithoutArgsAction { - public: - // The c'tor makes a copy of function_impl (either a function - // pointer or a functor). - explicit InvokeWithoutArgsAction(FunctionImpl function_impl) - : function_impl_(function_impl) {} - - // Allows InvokeWithoutArgs(f) to be used as any action whose type is - // compatible with f. - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) { return function_impl_(); } - - private: - FunctionImpl function_impl_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(InvokeWithoutArgsAction); -}; - -// Implements the InvokeWithoutArgs(object_ptr, &Class::Method) action. -template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> -class InvokeMethodWithoutArgsAction { - public: - InvokeMethodWithoutArgsAction(Class* obj_ptr, MethodPtr method_ptr) - : obj_ptr_(obj_ptr), method_ptr_(method_ptr) {} - - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) const { - return (obj_ptr_->*method_ptr_)(); - } - - private: - Class* const obj_ptr_; - const MethodPtr method_ptr_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(InvokeMethodWithoutArgsAction); -}; - -// Implements the IgnoreResult(action) action. -template <typename A> -class IgnoreResultAction { - public: - explicit IgnoreResultAction(const A& action) : action_(action) {} - - template <typename F> - operator Action<F>() const { - // Assert statement belongs here because this is the best place to verify - // conditions on F. It produces the clearest error messages - // in most compilers. - // Impl really belongs in this scope as a local class but can't - // because MSVC produces duplicate symbols in different translation units - // in this case. Until MS fixes that bug we put Impl into the class scope - // and put the typedef both here (for use in assert statement) and - // in the Impl class. But both definitions must be the same. - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; - - // Asserts at compile time that F returns void. - CompileAssertTypesEqual<void, Result>(); - - return Action<F>(new Impl<F>(action_)); - } - - private: - template <typename F> - class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { - public: - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - explicit Impl(const A& action) : action_(action) {} - - virtual void Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - // Performs the action and ignores its result. - action_.Perform(args); - } - - private: - // Type OriginalFunction is the same as F except that its return - // type is IgnoredValue. - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::MakeResultIgnoredValue - OriginalFunction; - - const Action<OriginalFunction> action_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - const A action_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(IgnoreResultAction); -}; - -// A ReferenceWrapper<T> object represents a reference to type T, -// which can be either const or not. It can be explicitly converted -// from, and implicitly converted to, a T&. Unlike a reference, -// ReferenceWrapper<T> can be copied and can survive template type -// inference. This is used to support by-reference arguments in the -// InvokeArgument<N>(...) action. The idea was from "reference -// wrappers" in tr1, which we don't have in our source tree yet. -template <typename T> -class ReferenceWrapper { - public: - // Constructs a ReferenceWrapper<T> object from a T&. - explicit ReferenceWrapper(T& l_value) : pointer_(&l_value) {} // NOLINT - - // Allows a ReferenceWrapper<T> object to be implicitly converted to - // a T&. - operator T&() const { return *pointer_; } - private: - T* pointer_; -}; - -// Allows the expression ByRef(x) to be printed as a reference to x. -template <typename T> -void PrintTo(const ReferenceWrapper<T>& ref, ::std::ostream* os) { - T& value = ref; - UniversalPrinter<T&>::Print(value, os); -} - -// Does two actions sequentially. Used for implementing the DoAll(a1, -// a2, ...) action. -template <typename Action1, typename Action2> -class DoBothAction { - public: - DoBothAction(Action1 action1, Action2 action2) - : action1_(action1), action2_(action2) {} - - // This template type conversion operator allows DoAll(a1, ..., a_n) - // to be used in ANY function of compatible type. - template <typename F> - operator Action<F>() const { - return Action<F>(new Impl<F>(action1_, action2_)); - } - - private: - // Implements the DoAll(...) action for a particular function type F. - template <typename F> - class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { - public: - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename Function<F>::MakeResultVoid VoidResult; - - Impl(const Action<VoidResult>& action1, const Action<F>& action2) - : action1_(action1), action2_(action2) {} - - virtual Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - action1_.Perform(args); - return action2_.Perform(args); - } - - private: - const Action<VoidResult> action1_; - const Action<F> action2_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - Action1 action1_; - Action2 action2_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(DoBothAction); -}; - -} // namespace internal - -// An Unused object can be implicitly constructed from ANY value. -// This is handy when defining actions that ignore some or all of the -// mock function arguments. For example, given -// -// MOCK_METHOD3(Foo, double(const string& label, double x, double y)); -// MOCK_METHOD3(Bar, double(int index, double x, double y)); -// -// instead of -// -// double DistanceToOriginWithLabel(const string& label, double x, double y) { -// return sqrt(x*x + y*y); -// } -// double DistanceToOriginWithIndex(int index, double x, double y) { -// return sqrt(x*x + y*y); -// } -// ... -// EXEPCT_CALL(mock, Foo("abc", _, _)) -// .WillOnce(Invoke(DistanceToOriginWithLabel)); -// EXEPCT_CALL(mock, Bar(5, _, _)) -// .WillOnce(Invoke(DistanceToOriginWithIndex)); -// -// you could write -// -// // We can declare any uninteresting argument as Unused. -// double DistanceToOrigin(Unused, double x, double y) { -// return sqrt(x*x + y*y); -// } -// ... -// EXEPCT_CALL(mock, Foo("abc", _, _)).WillOnce(Invoke(DistanceToOrigin)); -// EXEPCT_CALL(mock, Bar(5, _, _)).WillOnce(Invoke(DistanceToOrigin)); -typedef internal::IgnoredValue Unused; - -// This constructor allows us to turn an Action<From> object into an -// Action<To>, as long as To's arguments can be implicitly converted -// to From's and From's return type cann be implicitly converted to -// To's. -template <typename To> -template <typename From> -Action<To>::Action(const Action<From>& from) - : impl_(new internal::ActionAdaptor<To, From>(from)) {} - -// Creates an action that returns 'value'. 'value' is passed by value -// instead of const reference - otherwise Return("string literal") -// will trigger a compiler error about using array as initializer. -template <typename R> -internal::ReturnAction<R> Return(R value) { - return internal::ReturnAction<R>(value); -} - -// Creates an action that returns NULL. -inline PolymorphicAction<internal::ReturnNullAction> ReturnNull() { - return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::ReturnNullAction()); -} - -// Creates an action that returns from a void function. -inline PolymorphicAction<internal::ReturnVoidAction> Return() { - return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::ReturnVoidAction()); -} - -// Creates an action that returns the reference to a variable. -template <typename R> -inline internal::ReturnRefAction<R> ReturnRef(R& x) { // NOLINT - return internal::ReturnRefAction<R>(x); -} - -// Creates an action that returns the reference to a copy of the -// argument. The copy is created when the action is constructed and -// lives as long as the action. -template <typename R> -inline internal::ReturnRefOfCopyAction<R> ReturnRefOfCopy(const R& x) { - return internal::ReturnRefOfCopyAction<R>(x); -} - -// Creates an action that does the default action for the give mock function. -inline internal::DoDefaultAction DoDefault() { - return internal::DoDefaultAction(); -} - -// Creates an action that sets the variable pointed by the N-th -// (0-based) function argument to 'value'. -template <size_t N, typename T> -PolymorphicAction< - internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction< - N, T, internal::IsAProtocolMessage<T>::value> > -SetArgPointee(const T& x) { - return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction< - N, T, internal::IsAProtocolMessage<T>::value>(x)); -} - -#if !((GTEST_GCC_VER_ && GTEST_GCC_VER_ < 40000) || GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN) -// This overload allows SetArgPointee() to accept a string literal. -// GCC prior to the version 4.0 and Symbian C++ compiler cannot distinguish -// this overload from the templated version and emit a compile error. -template <size_t N> -PolymorphicAction< - internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction<N, const char*, false> > -SetArgPointee(const char* p) { - return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction< - N, const char*, false>(p)); -} - -template <size_t N> -PolymorphicAction< - internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction<N, const wchar_t*, false> > -SetArgPointee(const wchar_t* p) { - return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction< - N, const wchar_t*, false>(p)); -} -#endif - -// The following version is DEPRECATED. -template <size_t N, typename T> -PolymorphicAction< - internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction< - N, T, internal::IsAProtocolMessage<T>::value> > -SetArgumentPointee(const T& x) { - return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction< - N, T, internal::IsAProtocolMessage<T>::value>(x)); -} - -// Creates an action that sets a pointer referent to a given value. -template <typename T1, typename T2> -PolymorphicAction<internal::AssignAction<T1, T2> > Assign(T1* ptr, T2 val) { - return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::AssignAction<T1, T2>(ptr, val)); -} - -#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - -// Creates an action that sets errno and returns the appropriate error. -template <typename T> -PolymorphicAction<internal::SetErrnoAndReturnAction<T> > -SetErrnoAndReturn(int errval, T result) { - return MakePolymorphicAction( - internal::SetErrnoAndReturnAction<T>(errval, result)); -} - -#endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - -// Various overloads for InvokeWithoutArgs(). - -// Creates an action that invokes 'function_impl' with no argument. -template <typename FunctionImpl> -PolymorphicAction<internal::InvokeWithoutArgsAction<FunctionImpl> > -InvokeWithoutArgs(FunctionImpl function_impl) { - return MakePolymorphicAction( - internal::InvokeWithoutArgsAction<FunctionImpl>(function_impl)); -} - -// Creates an action that invokes the given method on the given object -// with no argument. -template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> -PolymorphicAction<internal::InvokeMethodWithoutArgsAction<Class, MethodPtr> > -InvokeWithoutArgs(Class* obj_ptr, MethodPtr method_ptr) { - return MakePolymorphicAction( - internal::InvokeMethodWithoutArgsAction<Class, MethodPtr>( - obj_ptr, method_ptr)); -} - -// Creates an action that performs an_action and throws away its -// result. In other words, it changes the return type of an_action to -// void. an_action MUST NOT return void, or the code won't compile. -template <typename A> -inline internal::IgnoreResultAction<A> IgnoreResult(const A& an_action) { - return internal::IgnoreResultAction<A>(an_action); -} - -// Creates a reference wrapper for the given L-value. If necessary, -// you can explicitly specify the type of the reference. For example, -// suppose 'derived' is an object of type Derived, ByRef(derived) -// would wrap a Derived&. If you want to wrap a const Base& instead, -// where Base is a base class of Derived, just write: -// -// ByRef<const Base>(derived) -template <typename T> -inline internal::ReferenceWrapper<T> ByRef(T& l_value) { // NOLINT - return internal::ReferenceWrapper<T>(l_value); -} - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_ACTIONS_H_ -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file implements some commonly used cardinalities. More -// cardinalities can be defined by the user implementing the -// CardinalityInterface interface if necessary. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_CARDINALITIES_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_CARDINALITIES_H_ - -#include <limits.h> -#include <ostream> // NOLINT - -namespace testing { - -// To implement a cardinality Foo, define: -// 1. a class FooCardinality that implements the -// CardinalityInterface interface, and -// 2. a factory function that creates a Cardinality object from a -// const FooCardinality*. -// -// The two-level delegation design follows that of Matcher, providing -// consistency for extension developers. It also eases ownership -// management as Cardinality objects can now be copied like plain values. - -// The implementation of a cardinality. -class CardinalityInterface { - public: - virtual ~CardinalityInterface() {} - - // Conservative estimate on the lower/upper bound of the number of - // calls allowed. - virtual int ConservativeLowerBound() const { return 0; } - virtual int ConservativeUpperBound() const { return INT_MAX; } - - // Returns true iff call_count calls will satisfy this cardinality. - virtual bool IsSatisfiedByCallCount(int call_count) const = 0; - - // Returns true iff call_count calls will saturate this cardinality. - virtual bool IsSaturatedByCallCount(int call_count) const = 0; - - // Describes self to an ostream. - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const = 0; -}; - -// A Cardinality is a copyable and IMMUTABLE (except by assignment) -// object that specifies how many times a mock function is expected to -// be called. The implementation of Cardinality is just a linked_ptr -// to const CardinalityInterface, so copying is fairly cheap. -// Don't inherit from Cardinality! -class GTEST_API_ Cardinality { - public: - // Constructs a null cardinality. Needed for storing Cardinality - // objects in STL containers. - Cardinality() {} - - // Constructs a Cardinality from its implementation. - explicit Cardinality(const CardinalityInterface* impl) : impl_(impl) {} - - // Conservative estimate on the lower/upper bound of the number of - // calls allowed. - int ConservativeLowerBound() const { return impl_->ConservativeLowerBound(); } - int ConservativeUpperBound() const { return impl_->ConservativeUpperBound(); } - - // Returns true iff call_count calls will satisfy this cardinality. - bool IsSatisfiedByCallCount(int call_count) const { - return impl_->IsSatisfiedByCallCount(call_count); - } - - // Returns true iff call_count calls will saturate this cardinality. - bool IsSaturatedByCallCount(int call_count) const { - return impl_->IsSaturatedByCallCount(call_count); - } - - // Returns true iff call_count calls will over-saturate this - // cardinality, i.e. exceed the maximum number of allowed calls. - bool IsOverSaturatedByCallCount(int call_count) const { - return impl_->IsSaturatedByCallCount(call_count) && - !impl_->IsSatisfiedByCallCount(call_count); - } - - // Describes self to an ostream - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { impl_->DescribeTo(os); } - - // Describes the given actual call count to an ostream. - static void DescribeActualCallCountTo(int actual_call_count, - ::std::ostream* os); - - private: - internal::linked_ptr<const CardinalityInterface> impl_; -}; - -// Creates a cardinality that allows at least n calls. -GTEST_API_ Cardinality AtLeast(int n); - -// Creates a cardinality that allows at most n calls. -GTEST_API_ Cardinality AtMost(int n); - -// Creates a cardinality that allows any number of calls. -GTEST_API_ Cardinality AnyNumber(); - -// Creates a cardinality that allows between min and max calls. -GTEST_API_ Cardinality Between(int min, int max); - -// Creates a cardinality that allows exactly n calls. -GTEST_API_ Cardinality Exactly(int n); - -// Creates a cardinality from its implementation. -inline Cardinality MakeCardinality(const CardinalityInterface* c) { - return Cardinality(c); -} - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_CARDINALITIES_H_ -// This file was GENERATED by a script. DO NOT EDIT BY HAND!!! - -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file implements some commonly used variadic actions. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_ACTIONS_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_ACTIONS_H_ - - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// InvokeHelper<F> knows how to unpack an N-tuple and invoke an N-ary -// function or method with the unpacked values, where F is a function -// type that takes N arguments. -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> -class InvokeHelper; - -template <typename R> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<>&) { - return function(); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<>&) { - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args), get<1>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args), get<1>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, - A3>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, - A4>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), - get<3>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), - get<4>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), - get<3>(args), get<4>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5, A6>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), - get<4>(args), get<5>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), - get<3>(args), get<4>(args), get<5>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5, A6, A7>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), - get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, - A7>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), - get<3>(args), get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5, A6, A7, A8>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), - get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args), get<7>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, - A8>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), - get<3>(args), get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args), get<7>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5, A6, A7, A8, A9>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), - get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args), get<7>(args), get<8>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, - A9>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), - get<3>(args), get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args), get<7>(args), - get<8>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9, - typename A10> -class InvokeHelper<R, ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, - A10> > { - public: - template <typename Function> - static R Invoke(Function function, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return function(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), - get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args), get<7>(args), get<8>(args), - get<9>(args)); - } - - template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> - static R InvokeMethod(Class* obj_ptr, - MethodPtr method_ptr, - const ::std::tr1::tuple<A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, - A9, A10>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), - get<3>(args), get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args), get<7>(args), - get<8>(args), get<9>(args)); - } -}; - -// CallableHelper has static methods for invoking "callables", -// i.e. function pointers and functors. It uses overloading to -// provide a uniform interface for invoking different kinds of -// callables. In particular, you can use: -// -// CallableHelper<R>::Call(callable, a1, a2, ..., an) -// -// to invoke an n-ary callable, where R is its return type. If an -// argument, say a2, needs to be passed by reference, you should write -// ByRef(a2) instead of a2 in the above expression. -template <typename R> -class CallableHelper { - public: - // Calls a nullary callable. - template <typename Function> - static R Call(Function function) { return function(); } - - // Calls a unary callable. - - // We deliberately pass a1 by value instead of const reference here - // in case it is a C-string literal. If we had declared the - // parameter as 'const A1& a1' and write Call(function, "Hi"), the - // compiler would've thought A1 is 'char[3]', which causes trouble - // when you need to copy a value of type A1. By declaring the - // parameter as 'A1 a1', the compiler will correctly infer that A1 - // is 'const char*' when it sees Call(function, "Hi"). - // - // Since this function is defined inline, the compiler can get rid - // of the copying of the arguments. Therefore the performance won't - // be hurt. - template <typename Function, typename A1> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1) { return function(a1); } - - // Calls a binary callable. - template <typename Function, typename A1, typename A2> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1, A2 a2) { - return function(a1, a2); - } - - // Calls a ternary callable. - template <typename Function, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3) { - return function(a1, a2, a3); - } - - // Calls a 4-ary callable. - template <typename Function, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4) { - return function(a1, a2, a3, a4); - } - - // Calls a 5-ary callable. - template <typename Function, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5) { - return function(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5); - } - - // Calls a 6-ary callable. - template <typename Function, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5, typename A6> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6) { - return function(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6); - } - - // Calls a 7-ary callable. - template <typename Function, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5, typename A6, typename A7> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6, - A7 a7) { - return function(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7); - } - - // Calls a 8-ary callable. - template <typename Function, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6, - A7 a7, A8 a8) { - return function(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8); - } - - // Calls a 9-ary callable. - template <typename Function, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, - typename A9> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6, - A7 a7, A8 a8, A9 a9) { - return function(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9); - } - - // Calls a 10-ary callable. - template <typename Function, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, - typename A9, typename A10> - static R Call(Function function, A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6, - A7 a7, A8 a8, A9 a9, A10 a10) { - return function(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9, a10); - } -}; // class CallableHelper - -// An INTERNAL macro for extracting the type of a tuple field. It's -// subject to change without notice - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE! -#define GMOCK_FIELD_(Tuple, N) \ - typename ::std::tr1::tuple_element<N, Tuple>::type - -// SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, k1, k2, ..., k_n>::type is the -// type of an n-ary function whose i-th (1-based) argument type is the -// k{i}-th (0-based) field of ArgumentTuple, which must be a tuple -// type, and whose return type is Result. For example, -// SelectArgs<int, ::std::tr1::tuple<bool, char, double, long>, 0, 3>::type -// is int(bool, long). -// -// SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, k1, k2, ..., k_n>::Select(args) -// returns the selected fields (k1, k2, ..., k_n) of args as a tuple. -// For example, -// SelectArgs<int, ::std::tr1::tuple<bool, char, double>, 2, 0>::Select( -// ::std::tr1::make_tuple(true, 'a', 2.5)) -// returns ::std::tr1::tuple (2.5, true). -// -// The numbers in list k1, k2, ..., k_n must be >= 0, where n can be -// in the range [0, 10]. Duplicates are allowed and they don't have -// to be in an ascending or descending order. - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1, int k2, int k3, - int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, int k8, int k9, int k10> -class SelectArgs { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k2), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k3), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k4), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k5), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k6), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k7), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k8), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k9), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k10)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args), get<k2>(args), get<k3>(args), - get<k4>(args), get<k5>(args), get<k6>(args), get<k7>(args), - get<k8>(args), get<k9>(args), get<k10>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& /* args */) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1, int k2> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, k2, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k2)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args), get<k2>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1, int k2, int k3> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, k2, k3, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k2), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k3)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args), get<k2>(args), get<k3>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1, int k2, int k3, - int k4> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, k2, k3, k4, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k2), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k3), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k4)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args), get<k2>(args), get<k3>(args), - get<k4>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1, int k2, int k3, - int k4, int k5> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k2), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k3), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k4), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k5)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args), get<k2>(args), get<k3>(args), - get<k4>(args), get<k5>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1, int k2, int k3, - int k4, int k5, int k6> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k2), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k3), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k4), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k5), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k6)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args), get<k2>(args), get<k3>(args), - get<k4>(args), get<k5>(args), get<k6>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1, int k2, int k3, - int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k2), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k3), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k4), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k5), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k6), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k7)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args), get<k2>(args), get<k3>(args), - get<k4>(args), get<k5>(args), get<k6>(args), get<k7>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1, int k2, int k3, - int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, int k8> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k2), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k3), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k4), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k5), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k6), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k7), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k8)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args), get<k2>(args), get<k3>(args), - get<k4>(args), get<k5>(args), get<k6>(args), get<k7>(args), - get<k8>(args)); - } -}; - -template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple, int k1, int k2, int k3, - int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, int k8, int k9> -class SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, k9, -1> { - public: - typedef Result type(GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k1), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k2), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k3), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k4), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k5), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k6), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k7), - GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k8), GMOCK_FIELD_(ArgumentTuple, k9)); - typedef typename Function<type>::ArgumentTuple SelectedArgs; - static SelectedArgs Select(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return SelectedArgs(get<k1>(args), get<k2>(args), get<k3>(args), - get<k4>(args), get<k5>(args), get<k6>(args), get<k7>(args), - get<k8>(args), get<k9>(args)); - } -}; - -#undef GMOCK_FIELD_ - -// Implements the WithArgs action. -template <typename InnerAction, int k1 = -1, int k2 = -1, int k3 = -1, - int k4 = -1, int k5 = -1, int k6 = -1, int k7 = -1, int k8 = -1, - int k9 = -1, int k10 = -1> -class WithArgsAction { - public: - explicit WithArgsAction(const InnerAction& action) : action_(action) {} - - template <typename F> - operator Action<F>() const { return MakeAction(new Impl<F>(action_)); } - - private: - template <typename F> - class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { - public: - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - explicit Impl(const InnerAction& action) : action_(action) {} - - virtual Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - return action_.Perform(SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, k1, k2, k3, k4, - k5, k6, k7, k8, k9, k10>::Select(args)); - } - - private: - typedef typename SelectArgs<Result, ArgumentTuple, - k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, k9, k10>::type InnerFunctionType; - - Action<InnerFunctionType> action_; - }; - - const InnerAction action_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(WithArgsAction); -}; - -// A macro from the ACTION* family (defined later in this file) -// defines an action that can be used in a mock function. Typically, -// these actions only care about a subset of the arguments of the mock -// function. For example, if such an action only uses the second -// argument, it can be used in any mock function that takes >= 2 -// arguments where the type of the second argument is compatible. -// -// Therefore, the action implementation must be prepared to take more -// arguments than it needs. The ExcessiveArg type is used to -// represent those excessive arguments. In order to keep the compiler -// error messages tractable, we define it in the testing namespace -// instead of testing::internal. However, this is an INTERNAL TYPE -// and subject to change without notice, so a user MUST NOT USE THIS -// TYPE DIRECTLY. -struct ExcessiveArg {}; - -// A helper class needed for implementing the ACTION* macros. -template <typename Result, class Impl> -class ActionHelper { - public: - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<>(args, ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0>(args, get<0>(args), - ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0, typename A1> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0, A1>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0, A1>(args, get<0>(args), - get<1>(args), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0, typename A1, typename A2> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0, A1, A2>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0, A1, A2>(args, get<0>(args), - get<1>(args), get<2>(args), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0, A1, A2, - A3>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0, A1, A2, A3>(args, get<0>(args), - get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0, A1, A2, A3, - A4>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4>(args, - get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), get<4>(args), - ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5>(args, - get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), get<4>(args), - get<5>(args), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5, A6>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6>(args, - get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), get<4>(args), - get<5>(args), get<6>(args), ExcessiveArg(), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5, A6, A7>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, - A7>(args, get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), - get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args), get<7>(args), ExcessiveArg(), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5, A6, A7, A8>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, - A8>(args, get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), - get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args), get<7>(args), get<8>(args), - ExcessiveArg()); - } - - template <typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9> - static Result Perform(Impl* impl, const ::std::tr1::tuple<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, - A5, A6, A7, A8, A9>& args) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return impl->template gmock_PerformImpl<A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, - A9>(args, get<0>(args), get<1>(args), get<2>(args), get<3>(args), - get<4>(args), get<5>(args), get<6>(args), get<7>(args), get<8>(args), - get<9>(args)); - } -}; - -} // namespace internal - -// Various overloads for Invoke(). - -// WithArgs<N1, N2, ..., Nk>(an_action) creates an action that passes -// the selected arguments of the mock function to an_action and -// performs it. It serves as an adaptor between actions with -// different argument lists. C++ doesn't support default arguments for -// function templates, so we have to overload it. -template <int k1, typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1>(action); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2>(action); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3>(action); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4>(action); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5>(action); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6>(action); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, - typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, - k7>(action); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, int k8, - typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, - k8>(action); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, int k8, - int k9, typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, k9> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, - k9>(action); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, int k8, - int k9, int k10, typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, - k9, k10> -WithArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, - k9, k10>(action); -} - -// Creates an action that does actions a1, a2, ..., sequentially in -// each invocation. -template <typename Action1, typename Action2> -inline internal::DoBothAction<Action1, Action2> -DoAll(Action1 a1, Action2 a2) { - return internal::DoBothAction<Action1, Action2>(a1, a2); -} - -template <typename Action1, typename Action2, typename Action3> -inline internal::DoBothAction<Action1, internal::DoBothAction<Action2, - Action3> > -DoAll(Action1 a1, Action2 a2, Action3 a3) { - return DoAll(a1, DoAll(a2, a3)); -} - -template <typename Action1, typename Action2, typename Action3, - typename Action4> -inline internal::DoBothAction<Action1, internal::DoBothAction<Action2, - internal::DoBothAction<Action3, Action4> > > -DoAll(Action1 a1, Action2 a2, Action3 a3, Action4 a4) { - return DoAll(a1, DoAll(a2, a3, a4)); -} - -template <typename Action1, typename Action2, typename Action3, - typename Action4, typename Action5> -inline internal::DoBothAction<Action1, internal::DoBothAction<Action2, - internal::DoBothAction<Action3, internal::DoBothAction<Action4, - Action5> > > > -DoAll(Action1 a1, Action2 a2, Action3 a3, Action4 a4, Action5 a5) { - return DoAll(a1, DoAll(a2, a3, a4, a5)); -} - -template <typename Action1, typename Action2, typename Action3, - typename Action4, typename Action5, typename Action6> -inline internal::DoBothAction<Action1, internal::DoBothAction<Action2, - internal::DoBothAction<Action3, internal::DoBothAction<Action4, - internal::DoBothAction<Action5, Action6> > > > > -DoAll(Action1 a1, Action2 a2, Action3 a3, Action4 a4, Action5 a5, Action6 a6) { - return DoAll(a1, DoAll(a2, a3, a4, a5, a6)); -} - -template <typename Action1, typename Action2, typename Action3, - typename Action4, typename Action5, typename Action6, typename Action7> -inline internal::DoBothAction<Action1, internal::DoBothAction<Action2, - internal::DoBothAction<Action3, internal::DoBothAction<Action4, - internal::DoBothAction<Action5, internal::DoBothAction<Action6, - Action7> > > > > > -DoAll(Action1 a1, Action2 a2, Action3 a3, Action4 a4, Action5 a5, Action6 a6, - Action7 a7) { - return DoAll(a1, DoAll(a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7)); -} - -template <typename Action1, typename Action2, typename Action3, - typename Action4, typename Action5, typename Action6, typename Action7, - typename Action8> -inline internal::DoBothAction<Action1, internal::DoBothAction<Action2, - internal::DoBothAction<Action3, internal::DoBothAction<Action4, - internal::DoBothAction<Action5, internal::DoBothAction<Action6, - internal::DoBothAction<Action7, Action8> > > > > > > -DoAll(Action1 a1, Action2 a2, Action3 a3, Action4 a4, Action5 a5, Action6 a6, - Action7 a7, Action8 a8) { - return DoAll(a1, DoAll(a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8)); -} - -template <typename Action1, typename Action2, typename Action3, - typename Action4, typename Action5, typename Action6, typename Action7, - typename Action8, typename Action9> -inline internal::DoBothAction<Action1, internal::DoBothAction<Action2, - internal::DoBothAction<Action3, internal::DoBothAction<Action4, - internal::DoBothAction<Action5, internal::DoBothAction<Action6, - internal::DoBothAction<Action7, internal::DoBothAction<Action8, - Action9> > > > > > > > -DoAll(Action1 a1, Action2 a2, Action3 a3, Action4 a4, Action5 a5, Action6 a6, - Action7 a7, Action8 a8, Action9 a9) { - return DoAll(a1, DoAll(a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9)); -} - -template <typename Action1, typename Action2, typename Action3, - typename Action4, typename Action5, typename Action6, typename Action7, - typename Action8, typename Action9, typename Action10> -inline internal::DoBothAction<Action1, internal::DoBothAction<Action2, - internal::DoBothAction<Action3, internal::DoBothAction<Action4, - internal::DoBothAction<Action5, internal::DoBothAction<Action6, - internal::DoBothAction<Action7, internal::DoBothAction<Action8, - internal::DoBothAction<Action9, Action10> > > > > > > > > -DoAll(Action1 a1, Action2 a2, Action3 a3, Action4 a4, Action5 a5, Action6 a6, - Action7 a7, Action8 a8, Action9 a9, Action10 a10) { - return DoAll(a1, DoAll(a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9, a10)); -} - -} // namespace testing - -// The ACTION* family of macros can be used in a namespace scope to -// define custom actions easily. The syntax: -// -// ACTION(name) { statements; } -// -// will define an action with the given name that executes the -// statements. The value returned by the statements will be used as -// the return value of the action. Inside the statements, you can -// refer to the K-th (0-based) argument of the mock function by -// 'argK', and refer to its type by 'argK_type'. For example: -// -// ACTION(IncrementArg1) { -// arg1_type temp = arg1; -// return ++(*temp); -// } -// -// allows you to write -// -// ...WillOnce(IncrementArg1()); -// -// You can also refer to the entire argument tuple and its type by -// 'args' and 'args_type', and refer to the mock function type and its -// return type by 'function_type' and 'return_type'. -// -// Note that you don't need to specify the types of the mock function -// arguments. However rest assured that your code is still type-safe: -// you'll get a compiler error if *arg1 doesn't support the ++ -// operator, or if the type of ++(*arg1) isn't compatible with the -// mock function's return type, for example. -// -// Sometimes you'll want to parameterize the action. For that you can use -// another macro: -// -// ACTION_P(name, param_name) { statements; } -// -// For example: -// -// ACTION_P(Add, n) { return arg0 + n; } -// -// will allow you to write: -// -// ...WillOnce(Add(5)); -// -// Note that you don't need to provide the type of the parameter -// either. If you need to reference the type of a parameter named -// 'foo', you can write 'foo_type'. For example, in the body of -// ACTION_P(Add, n) above, you can write 'n_type' to refer to the type -// of 'n'. -// -// We also provide ACTION_P2, ACTION_P3, ..., up to ACTION_P10 to support -// multi-parameter actions. -// -// For the purpose of typing, you can view -// -// ACTION_Pk(Foo, p1, ..., pk) { ... } -// -// as shorthand for -// -// template <typename p1_type, ..., typename pk_type> -// FooActionPk<p1_type, ..., pk_type> Foo(p1_type p1, ..., pk_type pk) { ... } -// -// In particular, you can provide the template type arguments -// explicitly when invoking Foo(), as in Foo<long, bool>(5, false); -// although usually you can rely on the compiler to infer the types -// for you automatically. You can assign the result of expression -// Foo(p1, ..., pk) to a variable of type FooActionPk<p1_type, ..., -// pk_type>. This can be useful when composing actions. -// -// You can also overload actions with different numbers of parameters: -// -// ACTION_P(Plus, a) { ... } -// ACTION_P2(Plus, a, b) { ... } -// -// While it's tempting to always use the ACTION* macros when defining -// a new action, you should also consider implementing ActionInterface -// or using MakePolymorphicAction() instead, especially if you need to -// use the action a lot. While these approaches require more work, -// they give you more control on the types of the mock function -// arguments and the action parameters, which in general leads to -// better compiler error messages that pay off in the long run. They -// also allow overloading actions based on parameter types (as opposed -// to just based on the number of parameters). -// -// CAVEAT: -// -// ACTION*() can only be used in a namespace scope. The reason is -// that C++ doesn't yet allow function-local types to be used to -// instantiate templates. The up-coming C++0x standard will fix this. -// Once that's done, we'll consider supporting using ACTION*() inside -// a function. -// -// MORE INFORMATION: -// -// To learn more about using these macros, please search for 'ACTION' -// on http://code.google.com/p/googlemock/wiki/CookBook. - -// An internal macro needed for implementing ACTION*(). -#define GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_\ - const args_type& args GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg0_type arg0 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg1_type arg1 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg2_type arg2 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg3_type arg3 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg4_type arg4 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg5_type arg5 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg6_type arg6 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg7_type arg7 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg8_type arg8 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_, \ - arg9_type arg9 GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ - -// Sometimes you want to give an action explicit template parameters -// that cannot be inferred from its value parameters. ACTION() and -// ACTION_P*() don't support that. ACTION_TEMPLATE() remedies that -// and can be viewed as an extension to ACTION() and ACTION_P*(). -// -// The syntax: -// -// ACTION_TEMPLATE(ActionName, -// HAS_m_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind1, name1, ..., kind_m, name_m), -// AND_n_VALUE_PARAMS(p1, ..., p_n)) { statements; } -// -// defines an action template that takes m explicit template -// parameters and n value parameters. name_i is the name of the i-th -// template parameter, and kind_i specifies whether it's a typename, -// an integral constant, or a template. p_i is the name of the i-th -// value parameter. -// -// Example: -// -// // DuplicateArg<k, T>(output) converts the k-th argument of the mock -// // function to type T and copies it to *output. -// ACTION_TEMPLATE(DuplicateArg, -// HAS_2_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k, typename, T), -// AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(output)) { -// *output = T(std::tr1::get<k>(args)); -// } -// ... -// int n; -// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Foo(_, _)) -// .WillOnce(DuplicateArg<1, unsigned char>(&n)); -// -// To create an instance of an action template, write: -// -// ActionName<t1, ..., t_m>(v1, ..., v_n) -// -// where the ts are the template arguments and the vs are the value -// arguments. The value argument types are inferred by the compiler. -// If you want to explicitly specify the value argument types, you can -// provide additional template arguments: -// -// ActionName<t1, ..., t_m, u1, ..., u_k>(v1, ..., v_n) -// -// where u_i is the desired type of v_i. -// -// ACTION_TEMPLATE and ACTION/ACTION_P* can be overloaded on the -// number of value parameters, but not on the number of template -// parameters. Without the restriction, the meaning of the following -// is unclear: -// -// OverloadedAction<int, bool>(x); -// -// Are we using a single-template-parameter action where 'bool' refers -// to the type of x, or are we using a two-template-parameter action -// where the compiler is asked to infer the type of x? -// -// Implementation notes: -// -// GMOCK_INTERNAL_*_HAS_m_TEMPLATE_PARAMS and -// GMOCK_INTERNAL_*_AND_n_VALUE_PARAMS are internal macros for -// implementing ACTION_TEMPLATE. The main trick we use is to create -// new macro invocations when expanding a macro. For example, we have -// -// #define ACTION_TEMPLATE(name, template_params, value_params) -// ... GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##template_params ... -// -// which causes ACTION_TEMPLATE(..., HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), ...) -// to expand to -// -// ... GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T) ... -// -// Since GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS is a macro, the -// preprocessor will continue to expand it to -// -// ... typename T ... -// -// This technique conforms to the C++ standard and is portable. It -// allows us to implement action templates using O(N) code, where N is -// the maximum number of template/value parameters supported. Without -// using it, we'd have to devote O(N^2) amount of code to implement all -// combinations of m and n. - -// Declares the template parameters. -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0) kind0 name0 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_2_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, \ - name1) kind0 name0, kind1 name1 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_3_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_4_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2, \ - kind3 name3 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_5_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, \ - kind2 name2, kind3 name3, kind4 name4 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_6_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5) kind0 name0, \ - kind1 name1, kind2 name2, kind3 name3, kind4 name4, kind5 name5 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_7_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, \ - name6) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2, kind3 name3, kind4 name4, \ - kind5 name5, kind6 name6 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_8_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, name6, \ - kind7, name7) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2, kind3 name3, \ - kind4 name4, kind5 name5, kind6 name6, kind7 name7 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_9_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, name6, \ - kind7, name7, kind8, name8) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2, \ - kind3 name3, kind4 name4, kind5 name5, kind6 name6, kind7 name7, \ - kind8 name8 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_10_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, \ - name1, kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, \ - name6, kind7, name7, kind8, name8, kind9, name9) kind0 name0, \ - kind1 name1, kind2 name2, kind3 name3, kind4 name4, kind5 name5, \ - kind6 name6, kind7 name7, kind8 name8, kind9 name9 - -// Lists the template parameters. -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0) name0 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_2_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, \ - name1) name0, name1 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_3_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2) name0, name1, name2 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_4_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3) name0, name1, name2, name3 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_5_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4) name0, name1, name2, name3, \ - name4 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_6_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5) name0, name1, \ - name2, name3, name4, name5 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_7_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, \ - name6) name0, name1, name2, name3, name4, name5, name6 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_8_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, name6, \ - kind7, name7) name0, name1, name2, name3, name4, name5, name6, name7 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_9_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ - kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, name6, \ - kind7, name7, kind8, name8) name0, name1, name2, name3, name4, name5, \ - name6, name7, name8 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_10_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, \ - name1, kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, \ - name6, kind7, name7, kind8, name8, kind9, name9) name0, name1, name2, \ - name3, name4, name5, name6, name7, name8, name9 - -// Declares the types of value parameters. -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) , typename p0##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) , \ - typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) , \ - typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) , \ - typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4) , \ - typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5) , \ - typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6) , typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7) , typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7, p8) , typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7, p8, p9) , typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, \ - typename p2##_type, typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, \ - typename p5##_type, typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, \ - typename p8##_type, typename p9##_type - -// Initializes the value parameters. -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS()\ - () -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0) : p0(gmock_p0) -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1) -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2) -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3) -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), \ - p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4) -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5) -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6) -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), \ - p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), \ - p7(gmock_p7) -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, \ - p8##_type gmock_p8) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), p7(gmock_p7), \ - p8(gmock_p8) -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8, p9)\ - (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, p8##_type gmock_p8, \ - p9##_type gmock_p9) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), p7(gmock_p7), \ - p8(gmock_p8), p9(gmock_p9) - -// Declares the fields for storing the value parameters. -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) p0##_type p0; -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) p0##_type p0; \ - p1##_type p1; -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) p0##_type p0; \ - p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) p0##_type p0; \ - p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, \ - p4) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; p4##_type p4; -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, \ - p5) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; p4##_type p4; \ - p5##_type p5; -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; p4##_type p4; \ - p5##_type p5; p6##_type p6; -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; p4##_type p4; \ - p5##_type p5; p6##_type p6; p7##_type p7; -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; \ - p4##_type p4; p5##_type p5; p6##_type p6; p7##_type p7; p8##_type p8; -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8, p9) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; \ - p4##_type p4; p5##_type p5; p6##_type p6; p7##_type p7; p8##_type p8; \ - p9##_type p9; - -// Lists the value parameters. -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) p0 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) p0, p1 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) p0, p1, p2 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) p0, p1, p2, p3 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4) p0, p1, \ - p2, p3, p4 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5) p0, \ - p1, p2, p3, p4, p5 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6) p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7) p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8) p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8, p9) p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9 - -// Lists the value parameter types. -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) , p0##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) , p0##_type, \ - p1##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) , p0##_type, \ - p1##_type, p2##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) , \ - p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4) , \ - p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5) , \ - p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, p5##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6) , p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, p5##_type, \ - p6##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7) , p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7, p8) , p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7, p8, p9) , p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type, p9##_type - -// Declares the value parameters. -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) p0##_type p0 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) p0##_type p0, \ - p1##_type p1 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) p0##_type p0, \ - p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) p0##_type p0, \ - p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, \ - p4) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, \ - p5) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, \ - p5##_type p5 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, \ - p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, \ - p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ - p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7, p8##_type p8 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8, p9) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ - p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7, p8##_type p8, \ - p9##_type p9 - -// The suffix of the class template implementing the action template. -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) P -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) P2 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) P3 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) P4 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4) P5 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5) P6 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6) P7 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7) P8 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8) P9 -#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ - p7, p8, p9) P10 - -// The name of the class template implementing the action template. -#define GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)\ - GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(name##Action, GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_##value_params) - -#define ACTION_TEMPLATE(name, template_params, value_params)\ - template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##template_params\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_##value_params>\ - class GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params) {\ - public:\ - GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_##value_params {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - explicit gmock_Impl GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_##value_params {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_##value_params\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(\ - new gmock_Impl<F>(GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##value_params));\ - }\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_##value_params\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params));\ - };\ - template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##template_params\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_##value_params>\ - inline GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)<\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##template_params\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_##value_params> name(\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##value_params) {\ - return GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)<\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##template_params\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_##value_params>(\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##value_params);\ - }\ - template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##template_params\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_##value_params>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)<\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##template_params\ - GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_##value_params>::gmock_Impl<F>::\ - gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION(name)\ - class name##Action {\ - public:\ - name##Action() {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl() {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>());\ - }\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##Action);\ - };\ - inline name##Action name() {\ - return name##Action();\ - }\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##Action::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P(name, p0)\ - template <typename p0##_type>\ - class name##ActionP {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP(p0##_type gmock_p0) : p0(gmock_p0) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - explicit gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0) : p0(gmock_p0) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP<p0##_type> name(p0##_type p0) {\ - return name##ActionP<p0##_type>(p0);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP<p0##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P2(name, p0, p1)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type>\ - class name##ActionP2 {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP2(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1) : p0(gmock_p0), \ - p1(gmock_p1) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1) : p0(gmock_p0), \ - p1(gmock_p1) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0, p1));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP2);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP2<p0##_type, p1##_type> name(p0##_type p0, \ - p1##_type p1) {\ - return name##ActionP2<p0##_type, p1##_type>(p0, p1);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP2<p0##_type, p1##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P3(name, p0, p1, p2)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type>\ - class name##ActionP3 {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP3(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0, p1, p2));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP3);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP3<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type> name(p0##_type p0, \ - p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2) {\ - return name##ActionP3<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type>(p0, p1, p2);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP3<p0##_type, p1##_type, \ - p2##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P4(name, p0, p1, p2, p3)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type>\ - class name##ActionP4 {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP4(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), \ - p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0, p1, p2, p3));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP4);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP4<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, \ - p3##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, \ - p3##_type p3) {\ - return name##ActionP4<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type>(p0, p1, \ - p2, p3);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP4<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, \ - p3##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P5(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type>\ - class name##ActionP5 {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP5(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, \ - p4##_type gmock_p4) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4) : p0(gmock_p0), \ - p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP5);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP5<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ - p4##_type p4) {\ - return name##ActionP5<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP5<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P6(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type>\ - class name##ActionP6 {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP6(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP6);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP6<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, \ - p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5) {\ - return name##ActionP6<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP6<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P7(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type>\ - class name##ActionP7 {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP7(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5, p6##_type gmock_p6) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), \ - p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), \ - p6(gmock_p6) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP7);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP7<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, \ - p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, \ - p6##_type p6) {\ - return name##ActionP7<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP7<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P8(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type>\ - class name##ActionP8 {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP8(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5, p6##_type gmock_p6, \ - p7##_type gmock_p7) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), \ - p7(gmock_p7) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7) : p0(gmock_p0), \ - p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), \ - p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), p7(gmock_p7) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP8);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP8<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type> name(p0##_type p0, \ - p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, \ - p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7) {\ - return name##ActionP8<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP8<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type, \ - p7##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P9(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type>\ - class name##ActionP9 {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP9(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5, p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, \ - p8##_type gmock_p8) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), p7(gmock_p7), \ - p8(gmock_p8) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, \ - p8##_type gmock_p8) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), \ - p7(gmock_p7), p8(gmock_p8) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - p8##_type p8;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7, p8));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - p8##_type p8;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP9);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP9<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, \ - p8##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ - p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7, \ - p8##_type p8) {\ - return name##ActionP9<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type>(p0, p1, p2, \ - p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP9<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, \ - p8##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -#define ACTION_P10(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type, \ - typename p9##_type>\ - class name##ActionP10 {\ - public:\ - name##ActionP10(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5, p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, \ - p8##_type gmock_p8, p9##_type gmock_p9) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), \ - p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), \ - p7(gmock_p7), p8(gmock_p8), p9(gmock_p9) {}\ - template <typename F>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::ActionInterface<F> {\ - public:\ - typedef F function_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result return_type;\ - typedef typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple\ - args_type;\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, p8##_type gmock_p8, \ - p9##_type gmock_p9) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), \ - p7(gmock_p7), p8(gmock_p8), p9(gmock_p9) {}\ - virtual return_type Perform(const args_type& args) {\ - return ::testing::internal::ActionHelper<return_type, gmock_Impl>::\ - Perform(this, args);\ - }\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - return_type gmock_PerformImpl(const args_type& args, arg0_type arg0, \ - arg1_type arg1, arg2_type arg2, arg3_type arg3, arg4_type arg4, \ - arg5_type arg5, arg6_type arg6, arg7_type arg7, arg8_type arg8, \ - arg9_type arg9) const;\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - p8##_type p8;\ - p9##_type p9;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename F> operator ::testing::Action<F>() const {\ - return ::testing::Action<F>(new gmock_Impl<F>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7, p8, p9));\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - p8##_type p8;\ - p9##_type p9;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##ActionP10);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type, \ - typename p9##_type>\ - inline name##ActionP10<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type, \ - p9##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ - p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7, p8##_type p8, \ - p9##_type p9) {\ - return name##ActionP10<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type, p9##_type>(p0, \ - p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type, \ - typename p9##_type>\ - template <typename F>\ - template <typename arg0_type, typename arg1_type, typename arg2_type, \ - typename arg3_type, typename arg4_type, typename arg5_type, \ - typename arg6_type, typename arg7_type, typename arg8_type, \ - typename arg9_type>\ - typename ::testing::internal::Function<F>::Result\ - name##ActionP10<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type, \ - p9##_type>::gmock_Impl<F>::gmock_PerformImpl(\ - GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const - -namespace testing { - -// The ACTION*() macros trigger warning C4100 (unreferenced formal -// parameter) in MSVC with -W4. Unfortunately they cannot be fixed in -// the macro definition, as the warnings are generated when the macro -// is expanded and macro expansion cannot contain #pragma. Therefore -// we suppress them here. -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) -# pragma warning(disable:4100) -#endif - -// Various overloads for InvokeArgument<N>(). -// -// The InvokeArgument<N>(a1, a2, ..., a_k) action invokes the N-th -// (0-based) argument, which must be a k-ary callable, of the mock -// function, with arguments a1, a2, ..., a_k. -// -// Notes: -// -// 1. The arguments are passed by value by default. If you need to -// pass an argument by reference, wrap it inside ByRef(). For -// example, -// -// InvokeArgument<1>(5, string("Hello"), ByRef(foo)) -// -// passes 5 and string("Hello") by value, and passes foo by -// reference. -// -// 2. If the callable takes an argument by reference but ByRef() is -// not used, it will receive the reference to a copy of the value, -// instead of the original value. For example, when the 0-th -// argument of the mock function takes a const string&, the action -// -// InvokeArgument<0>(string("Hello")) -// -// makes a copy of the temporary string("Hello") object and passes a -// reference of the copy, instead of the original temporary object, -// to the callable. This makes it easy for a user to define an -// InvokeArgument action from temporary values and have it performed -// later. - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS()) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args)); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0, p1); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0, p1, p2); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0, p1, p2, p3); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0, p1, p2, p3, p4); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(InvokeArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9)) { - return internal::CallableHelper<return_type>::Call( - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args), p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9); -} - -// Various overloads for ReturnNew<T>(). -// -// The ReturnNew<T>(a1, a2, ..., a_k) action returns a pointer to a new -// instance of type T, constructed on the heap with constructor arguments -// a1, a2, ..., and a_k. The caller assumes ownership of the returned value. -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS()) { - return new T(); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0)) { - return new T(p0); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1)) { - return new T(p0, p1); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2)) { - return new T(p0, p1, p2); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3)) { - return new T(p0, p1, p2, p3); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4)) { - return new T(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5)) { - return new T(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6)) { - return new T(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7)) { - return new T(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8)) { - return new T(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8); -} - -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnNew, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), - AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9)) { - return new T(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9); -} - -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) -#endif - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_ACTIONS_H_ -// This file was GENERATED by command: -// pump.py gmock-generated-function-mockers.h.pump -// DO NOT EDIT BY HAND!!! - -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file implements function mockers of various arities. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_FUNCTION_MOCKERS_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_FUNCTION_MOCKERS_H_ - -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file implements the ON_CALL() and EXPECT_CALL() macros. -// -// A user can use the ON_CALL() macro to specify the default action of -// a mock method. The syntax is: -// -// ON_CALL(mock_object, Method(argument-matchers)) -// .With(multi-argument-matcher) -// .WillByDefault(action); -// -// where the .With() clause is optional. -// -// A user can use the EXPECT_CALL() macro to specify an expectation on -// a mock method. The syntax is: -// -// EXPECT_CALL(mock_object, Method(argument-matchers)) -// .With(multi-argument-matchers) -// .Times(cardinality) -// .InSequence(sequences) -// .After(expectations) -// .WillOnce(action) -// .WillRepeatedly(action) -// .RetiresOnSaturation(); -// -// where all clauses are optional, and .InSequence()/.After()/ -// .WillOnce() can appear any number of times. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_SPEC_BUILDERS_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_SPEC_BUILDERS_H_ - -#include <map> -#include <set> -#include <sstream> -#include <string> -#include <vector> - -#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS -# include <stdexcept> // NOLINT -#endif - -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file implements some commonly used argument matchers. More -// matchers can be defined by the user implementing the -// MatcherInterface<T> interface if necessary. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MATCHERS_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MATCHERS_H_ - -#include <math.h> -#include <algorithm> -#include <iterator> -#include <limits> -#include <ostream> // NOLINT -#include <sstream> -#include <string> -#include <utility> -#include <vector> - - -#if GTEST_LANG_CXX11 -#include <initializer_list> // NOLINT -- must be after gtest.h -#endif - -namespace testing { - -// To implement a matcher Foo for type T, define: -// 1. a class FooMatcherImpl that implements the -// MatcherInterface<T> interface, and -// 2. a factory function that creates a Matcher<T> object from a -// FooMatcherImpl*. -// -// The two-level delegation design makes it possible to allow a user -// to write "v" instead of "Eq(v)" where a Matcher is expected, which -// is impossible if we pass matchers by pointers. It also eases -// ownership management as Matcher objects can now be copied like -// plain values. - -// MatchResultListener is an abstract class. Its << operator can be -// used by a matcher to explain why a value matches or doesn't match. -// -// TODO(wan@google.com): add method -// bool InterestedInWhy(bool result) const; -// to indicate whether the listener is interested in why the match -// result is 'result'. -class MatchResultListener { - public: - // Creates a listener object with the given underlying ostream. The - // listener does not own the ostream, and does not dereference it - // in the constructor or destructor. - explicit MatchResultListener(::std::ostream* os) : stream_(os) {} - virtual ~MatchResultListener() = 0; // Makes this class abstract. - - // Streams x to the underlying ostream; does nothing if the ostream - // is NULL. - template <typename T> - MatchResultListener& operator<<(const T& x) { - if (stream_ != NULL) - *stream_ << x; - return *this; - } - - // Returns the underlying ostream. - ::std::ostream* stream() { return stream_; } - - // Returns true iff the listener is interested in an explanation of - // the match result. A matcher's MatchAndExplain() method can use - // this information to avoid generating the explanation when no one - // intends to hear it. - bool IsInterested() const { return stream_ != NULL; } - - private: - ::std::ostream* const stream_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MatchResultListener); -}; - -inline MatchResultListener::~MatchResultListener() { -} - -// An instance of a subclass of this knows how to describe itself as a -// matcher. -class MatcherDescriberInterface { - public: - virtual ~MatcherDescriberInterface() {} - - // Describes this matcher to an ostream. The function should print - // a verb phrase that describes the property a value matching this - // matcher should have. The subject of the verb phrase is the value - // being matched. For example, the DescribeTo() method of the Gt(7) - // matcher prints "is greater than 7". - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const = 0; - - // Describes the negation of this matcher to an ostream. For - // example, if the description of this matcher is "is greater than - // 7", the negated description could be "is not greater than 7". - // You are not required to override this when implementing - // MatcherInterface, but it is highly advised so that your matcher - // can produce good error messages. - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "not ("; - DescribeTo(os); - *os << ")"; - } -}; - -// The implementation of a matcher. -template <typename T> -class MatcherInterface : public MatcherDescriberInterface { - public: - // Returns true iff the matcher matches x; also explains the match - // result to 'listener' if necessary (see the next paragraph), in - // the form of a non-restrictive relative clause ("which ...", - // "whose ...", etc) that describes x. For example, the - // MatchAndExplain() method of the Pointee(...) matcher should - // generate an explanation like "which points to ...". - // - // Implementations of MatchAndExplain() should add an explanation of - // the match result *if and only if* they can provide additional - // information that's not already present (or not obvious) in the - // print-out of x and the matcher's description. Whether the match - // succeeds is not a factor in deciding whether an explanation is - // needed, as sometimes the caller needs to print a failure message - // when the match succeeds (e.g. when the matcher is used inside - // Not()). - // - // For example, a "has at least 10 elements" matcher should explain - // what the actual element count is, regardless of the match result, - // as it is useful information to the reader; on the other hand, an - // "is empty" matcher probably only needs to explain what the actual - // size is when the match fails, as it's redundant to say that the - // size is 0 when the value is already known to be empty. - // - // You should override this method when defining a new matcher. - // - // It's the responsibility of the caller (Google Mock) to guarantee - // that 'listener' is not NULL. This helps to simplify a matcher's - // implementation when it doesn't care about the performance, as it - // can talk to 'listener' without checking its validity first. - // However, in order to implement dummy listeners efficiently, - // listener->stream() may be NULL. - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const = 0; - - // Inherits these methods from MatcherDescriberInterface: - // virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const = 0; - // virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const; -}; - -// A match result listener that stores the explanation in a string. -class StringMatchResultListener : public MatchResultListener { - public: - StringMatchResultListener() : MatchResultListener(&ss_) {} - - // Returns the explanation accumulated so far. - internal::string str() const { return ss_.str(); } - - // Clears the explanation accumulated so far. - void Clear() { ss_.str(""); } - - private: - ::std::stringstream ss_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(StringMatchResultListener); -}; - -namespace internal { - -// A match result listener that ignores the explanation. -class DummyMatchResultListener : public MatchResultListener { - public: - DummyMatchResultListener() : MatchResultListener(NULL) {} - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(DummyMatchResultListener); -}; - -// A match result listener that forwards the explanation to a given -// ostream. The difference between this and MatchResultListener is -// that the former is concrete. -class StreamMatchResultListener : public MatchResultListener { - public: - explicit StreamMatchResultListener(::std::ostream* os) - : MatchResultListener(os) {} - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(StreamMatchResultListener); -}; - -// An internal class for implementing Matcher<T>, which will derive -// from it. We put functionalities common to all Matcher<T> -// specializations here to avoid code duplication. -template <typename T> -class MatcherBase { - public: - // Returns true iff the matcher matches x; also explains the match - // result to 'listener'. - bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return impl_->MatchAndExplain(x, listener); - } - - // Returns true iff this matcher matches x. - bool Matches(T x) const { - DummyMatchResultListener dummy; - return MatchAndExplain(x, &dummy); - } - - // Describes this matcher to an ostream. - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { impl_->DescribeTo(os); } - - // Describes the negation of this matcher to an ostream. - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - impl_->DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - // Explains why x matches, or doesn't match, the matcher. - void ExplainMatchResultTo(T x, ::std::ostream* os) const { - StreamMatchResultListener listener(os); - MatchAndExplain(x, &listener); - } - - // Returns the describer for this matcher object; retains ownership - // of the describer, which is only guaranteed to be alive when - // this matcher object is alive. - const MatcherDescriberInterface* GetDescriber() const { - return impl_.get(); - } - - protected: - MatcherBase() {} - - // Constructs a matcher from its implementation. - explicit MatcherBase(const MatcherInterface<T>* impl) - : impl_(impl) {} - - virtual ~MatcherBase() {} - - private: - // shared_ptr (util/gtl/shared_ptr.h) and linked_ptr have similar - // interfaces. The former dynamically allocates a chunk of memory - // to hold the reference count, while the latter tracks all - // references using a circular linked list without allocating - // memory. It has been observed that linked_ptr performs better in - // typical scenarios. However, shared_ptr can out-perform - // linked_ptr when there are many more uses of the copy constructor - // than the default constructor. - // - // If performance becomes a problem, we should see if using - // shared_ptr helps. - ::testing::internal::linked_ptr<const MatcherInterface<T> > impl_; -}; - -} // namespace internal - -// A Matcher<T> is a copyable and IMMUTABLE (except by assignment) -// object that can check whether a value of type T matches. The -// implementation of Matcher<T> is just a linked_ptr to const -// MatcherInterface<T>, so copying is fairly cheap. Don't inherit -// from Matcher! -template <typename T> -class Matcher : public internal::MatcherBase<T> { - public: - // Constructs a null matcher. Needed for storing Matcher objects in STL - // containers. A default-constructed matcher is not yet initialized. You - // cannot use it until a valid value has been assigned to it. - Matcher() {} - - // Constructs a matcher from its implementation. - explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<T>* impl) - : internal::MatcherBase<T>(impl) {} - - // Implicit constructor here allows people to write - // EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar(5)) instead of EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar(Eq(5))) sometimes - Matcher(T value); // NOLINT -}; - -// The following two specializations allow the user to write str -// instead of Eq(str) and "foo" instead of Eq("foo") when a string -// matcher is expected. -template <> -class GTEST_API_ Matcher<const internal::string&> - : public internal::MatcherBase<const internal::string&> { - public: - Matcher() {} - - explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<const internal::string&>* impl) - : internal::MatcherBase<const internal::string&>(impl) {} - - // Allows the user to write str instead of Eq(str) sometimes, where - // str is a string object. - Matcher(const internal::string& s); // NOLINT - - // Allows the user to write "foo" instead of Eq("foo") sometimes. - Matcher(const char* s); // NOLINT -}; - -template <> -class GTEST_API_ Matcher<internal::string> - : public internal::MatcherBase<internal::string> { - public: - Matcher() {} - - explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<internal::string>* impl) - : internal::MatcherBase<internal::string>(impl) {} - - // Allows the user to write str instead of Eq(str) sometimes, where - // str is a string object. - Matcher(const internal::string& s); // NOLINT - - // Allows the user to write "foo" instead of Eq("foo") sometimes. - Matcher(const char* s); // NOLINT -}; - -#if GTEST_HAS_STRING_PIECE_ -// The following two specializations allow the user to write str -// instead of Eq(str) and "foo" instead of Eq("foo") when a StringPiece -// matcher is expected. -template <> -class GTEST_API_ Matcher<const StringPiece&> - : public internal::MatcherBase<const StringPiece&> { - public: - Matcher() {} - - explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<const StringPiece&>* impl) - : internal::MatcherBase<const StringPiece&>(impl) {} - - // Allows the user to write str instead of Eq(str) sometimes, where - // str is a string object. - Matcher(const internal::string& s); // NOLINT - - // Allows the user to write "foo" instead of Eq("foo") sometimes. - Matcher(const char* s); // NOLINT - - // Allows the user to pass StringPieces directly. - Matcher(StringPiece s); // NOLINT -}; - -template <> -class GTEST_API_ Matcher<StringPiece> - : public internal::MatcherBase<StringPiece> { - public: - Matcher() {} - - explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<StringPiece>* impl) - : internal::MatcherBase<StringPiece>(impl) {} - - // Allows the user to write str instead of Eq(str) sometimes, where - // str is a string object. - Matcher(const internal::string& s); // NOLINT - - // Allows the user to write "foo" instead of Eq("foo") sometimes. - Matcher(const char* s); // NOLINT - - // Allows the user to pass StringPieces directly. - Matcher(StringPiece s); // NOLINT -}; -#endif // GTEST_HAS_STRING_PIECE_ - -// The PolymorphicMatcher class template makes it easy to implement a -// polymorphic matcher (i.e. a matcher that can match values of more -// than one type, e.g. Eq(n) and NotNull()). -// -// To define a polymorphic matcher, a user should provide an Impl -// class that has a DescribeTo() method and a DescribeNegationTo() -// method, and define a member function (or member function template) -// -// bool MatchAndExplain(const Value& value, -// MatchResultListener* listener) const; -// -// See the definition of NotNull() for a complete example. -template <class Impl> -class PolymorphicMatcher { - public: - explicit PolymorphicMatcher(const Impl& an_impl) : impl_(an_impl) {} - - // Returns a mutable reference to the underlying matcher - // implementation object. - Impl& mutable_impl() { return impl_; } - - // Returns an immutable reference to the underlying matcher - // implementation object. - const Impl& impl() const { return impl_; } - - template <typename T> - operator Matcher<T>() const { - return Matcher<T>(new MonomorphicImpl<T>(impl_)); - } - - private: - template <typename T> - class MonomorphicImpl : public MatcherInterface<T> { - public: - explicit MonomorphicImpl(const Impl& impl) : impl_(impl) {} - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - impl_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - impl_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return impl_.MatchAndExplain(x, listener); - } - - private: - const Impl impl_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(MonomorphicImpl); - }; - - Impl impl_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(PolymorphicMatcher); -}; - -// Creates a matcher from its implementation. This is easier to use -// than the Matcher<T> constructor as it doesn't require you to -// explicitly write the template argument, e.g. -// -// MakeMatcher(foo); -// vs -// Matcher<const string&>(foo); -template <typename T> -inline Matcher<T> MakeMatcher(const MatcherInterface<T>* impl) { - return Matcher<T>(impl); -} - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher from its implementation. This is -// easier to use than the PolymorphicMatcher<Impl> constructor as it -// doesn't require you to explicitly write the template argument, e.g. -// -// MakePolymorphicMatcher(foo); -// vs -// PolymorphicMatcher<TypeOfFoo>(foo); -template <class Impl> -inline PolymorphicMatcher<Impl> MakePolymorphicMatcher(const Impl& impl) { - return PolymorphicMatcher<Impl>(impl); -} - -// Anything inside the 'internal' namespace IS INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION -// and MUST NOT BE USED IN USER CODE!!! -namespace internal { - -// The MatcherCastImpl class template is a helper for implementing -// MatcherCast(). We need this helper in order to partially -// specialize the implementation of MatcherCast() (C++ allows -// class/struct templates to be partially specialized, but not -// function templates.). - -// This general version is used when MatcherCast()'s argument is a -// polymorphic matcher (i.e. something that can be converted to a -// Matcher but is not one yet; for example, Eq(value)) or a value (for -// example, "hello"). -template <typename T, typename M> -class MatcherCastImpl { - public: - static Matcher<T> Cast(M polymorphic_matcher_or_value) { - // M can be a polymorhic matcher, in which case we want to use - // its conversion operator to create Matcher<T>. Or it can be a value - // that should be passed to the Matcher<T>'s constructor. - // - // We can't call Matcher<T>(polymorphic_matcher_or_value) when M is a - // polymorphic matcher because it'll be ambiguous if T has an implicit - // constructor from M (this usually happens when T has an implicit - // constructor from any type). - // - // It won't work to unconditionally implict_cast - // polymorphic_matcher_or_value to Matcher<T> because it won't trigger - // a user-defined conversion from M to T if one exists (assuming M is - // a value). - return CastImpl( - polymorphic_matcher_or_value, - BooleanConstant< - internal::ImplicitlyConvertible<M, Matcher<T> >::value>()); - } - - private: - static Matcher<T> CastImpl(M value, BooleanConstant<false>) { - // M can't be implicitly converted to Matcher<T>, so M isn't a polymorphic - // matcher. It must be a value then. Use direct initialization to create - // a matcher. - return Matcher<T>(ImplicitCast_<T>(value)); - } - - static Matcher<T> CastImpl(M polymorphic_matcher_or_value, - BooleanConstant<true>) { - // M is implicitly convertible to Matcher<T>, which means that either - // M is a polymorhpic matcher or Matcher<T> has an implicit constructor - // from M. In both cases using the implicit conversion will produce a - // matcher. - // - // Even if T has an implicit constructor from M, it won't be called because - // creating Matcher<T> would require a chain of two user-defined conversions - // (first to create T from M and then to create Matcher<T> from T). - return polymorphic_matcher_or_value; - } -}; - -// This more specialized version is used when MatcherCast()'s argument -// is already a Matcher. This only compiles when type T can be -// statically converted to type U. -template <typename T, typename U> -class MatcherCastImpl<T, Matcher<U> > { - public: - static Matcher<T> Cast(const Matcher<U>& source_matcher) { - return Matcher<T>(new Impl(source_matcher)); - } - - private: - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<T> { - public: - explicit Impl(const Matcher<U>& source_matcher) - : source_matcher_(source_matcher) {} - - // We delegate the matching logic to the source matcher. - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return source_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(static_cast<U>(x), listener); - } - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - source_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - source_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - private: - const Matcher<U> source_matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; -}; - -// This even more specialized version is used for efficiently casting -// a matcher to its own type. -template <typename T> -class MatcherCastImpl<T, Matcher<T> > { - public: - static Matcher<T> Cast(const Matcher<T>& matcher) { return matcher; } -}; - -} // namespace internal - -// In order to be safe and clear, casting between different matcher -// types is done explicitly via MatcherCast<T>(m), which takes a -// matcher m and returns a Matcher<T>. It compiles only when T can be -// statically converted to the argument type of m. -template <typename T, typename M> -inline Matcher<T> MatcherCast(M matcher) { - return internal::MatcherCastImpl<T, M>::Cast(matcher); -} - -// Implements SafeMatcherCast(). -// -// We use an intermediate class to do the actual safe casting as Nokia's -// Symbian compiler cannot decide between -// template <T, M> ... (M) and -// template <T, U> ... (const Matcher<U>&) -// for function templates but can for member function templates. -template <typename T> -class SafeMatcherCastImpl { - public: - // This overload handles polymorphic matchers and values only since - // monomorphic matchers are handled by the next one. - template <typename M> - static inline Matcher<T> Cast(M polymorphic_matcher_or_value) { - return internal::MatcherCastImpl<T, M>::Cast(polymorphic_matcher_or_value); - } - - // This overload handles monomorphic matchers. - // - // In general, if type T can be implicitly converted to type U, we can - // safely convert a Matcher<U> to a Matcher<T> (i.e. Matcher is - // contravariant): just keep a copy of the original Matcher<U>, convert the - // argument from type T to U, and then pass it to the underlying Matcher<U>. - // The only exception is when U is a reference and T is not, as the - // underlying Matcher<U> may be interested in the argument's address, which - // is not preserved in the conversion from T to U. - template <typename U> - static inline Matcher<T> Cast(const Matcher<U>& matcher) { - // Enforce that T can be implicitly converted to U. - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((internal::ImplicitlyConvertible<T, U>::value), - T_must_be_implicitly_convertible_to_U); - // Enforce that we are not converting a non-reference type T to a reference - // type U. - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( - internal::is_reference<T>::value || !internal::is_reference<U>::value, - cannot_convert_non_referentce_arg_to_reference); - // In case both T and U are arithmetic types, enforce that the - // conversion is not lossy. - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(T) RawT; - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(U) RawU; - const bool kTIsOther = GMOCK_KIND_OF_(RawT) == internal::kOther; - const bool kUIsOther = GMOCK_KIND_OF_(RawU) == internal::kOther; - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( - kTIsOther || kUIsOther || - (internal::LosslessArithmeticConvertible<RawT, RawU>::value), - conversion_of_arithmetic_types_must_be_lossless); - return MatcherCast<T>(matcher); - } -}; - -template <typename T, typename M> -inline Matcher<T> SafeMatcherCast(const M& polymorphic_matcher) { - return SafeMatcherCastImpl<T>::Cast(polymorphic_matcher); -} - -// A<T>() returns a matcher that matches any value of type T. -template <typename T> -Matcher<T> A(); - -// Anything inside the 'internal' namespace IS INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION -// and MUST NOT BE USED IN USER CODE!!! -namespace internal { - -// If the explanation is not empty, prints it to the ostream. -inline void PrintIfNotEmpty(const internal::string& explanation, - ::std::ostream* os) { - if (explanation != "" && os != NULL) { - *os << ", " << explanation; - } -} - -// Returns true if the given type name is easy to read by a human. -// This is used to decide whether printing the type of a value might -// be helpful. -inline bool IsReadableTypeName(const string& type_name) { - // We consider a type name readable if it's short or doesn't contain - // a template or function type. - return (type_name.length() <= 20 || - type_name.find_first_of("<(") == string::npos); -} - -// Matches the value against the given matcher, prints the value and explains -// the match result to the listener. Returns the match result. -// 'listener' must not be NULL. -// Value cannot be passed by const reference, because some matchers take a -// non-const argument. -template <typename Value, typename T> -bool MatchPrintAndExplain(Value& value, const Matcher<T>& matcher, - MatchResultListener* listener) { - if (!listener->IsInterested()) { - // If the listener is not interested, we do not need to construct the - // inner explanation. - return matcher.Matches(value); - } - - StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; - const bool match = matcher.MatchAndExplain(value, &inner_listener); - - UniversalPrint(value, listener->stream()); -#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI - const string& type_name = GetTypeName<Value>(); - if (IsReadableTypeName(type_name)) - *listener->stream() << " (of type " << type_name << ")"; -#endif - PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); - - return match; -} - -// An internal helper class for doing compile-time loop on a tuple's -// fields. -template <size_t N> -class TuplePrefix { - public: - // TuplePrefix<N>::Matches(matcher_tuple, value_tuple) returns true - // iff the first N fields of matcher_tuple matches the first N - // fields of value_tuple, respectively. - template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> - static bool Matches(const MatcherTuple& matcher_tuple, - const ValueTuple& value_tuple) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return TuplePrefix<N - 1>::Matches(matcher_tuple, value_tuple) - && get<N - 1>(matcher_tuple).Matches(get<N - 1>(value_tuple)); - } - - // TuplePrefix<N>::ExplainMatchFailuresTo(matchers, values, os) - // describes failures in matching the first N fields of matchers - // against the first N fields of values. If there is no failure, - // nothing will be streamed to os. - template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> - static void ExplainMatchFailuresTo(const MatcherTuple& matchers, - const ValueTuple& values, - ::std::ostream* os) { - using ::std::tr1::tuple_element; - using ::std::tr1::get; - - // First, describes failures in the first N - 1 fields. - TuplePrefix<N - 1>::ExplainMatchFailuresTo(matchers, values, os); - - // Then describes the failure (if any) in the (N - 1)-th (0-based) - // field. - typename tuple_element<N - 1, MatcherTuple>::type matcher = - get<N - 1>(matchers); - typedef typename tuple_element<N - 1, ValueTuple>::type Value; - Value value = get<N - 1>(values); - StringMatchResultListener listener; - if (!matcher.MatchAndExplain(value, &listener)) { - // TODO(wan): include in the message the name of the parameter - // as used in MOCK_METHOD*() when possible. - *os << " Expected arg #" << N - 1 << ": "; - get<N - 1>(matchers).DescribeTo(os); - *os << "\n Actual: "; - // We remove the reference in type Value to prevent the - // universal printer from printing the address of value, which - // isn't interesting to the user most of the time. The - // matcher's MatchAndExplain() method handles the case when - // the address is interesting. - internal::UniversalPrint(value, os); - PrintIfNotEmpty(listener.str(), os); - *os << "\n"; - } - } -}; - -// The base case. -template <> -class TuplePrefix<0> { - public: - template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> - static bool Matches(const MatcherTuple& /* matcher_tuple */, - const ValueTuple& /* value_tuple */) { - return true; - } - - template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> - static void ExplainMatchFailuresTo(const MatcherTuple& /* matchers */, - const ValueTuple& /* values */, - ::std::ostream* /* os */) {} -}; - -// TupleMatches(matcher_tuple, value_tuple) returns true iff all -// matchers in matcher_tuple match the corresponding fields in -// value_tuple. It is a compiler error if matcher_tuple and -// value_tuple have different number of fields or incompatible field -// types. -template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> -bool TupleMatches(const MatcherTuple& matcher_tuple, - const ValueTuple& value_tuple) { - using ::std::tr1::tuple_size; - // Makes sure that matcher_tuple and value_tuple have the same - // number of fields. - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(tuple_size<MatcherTuple>::value == - tuple_size<ValueTuple>::value, - matcher_and_value_have_different_numbers_of_fields); - return TuplePrefix<tuple_size<ValueTuple>::value>:: - Matches(matcher_tuple, value_tuple); -} - -// Describes failures in matching matchers against values. If there -// is no failure, nothing will be streamed to os. -template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> -void ExplainMatchFailureTupleTo(const MatcherTuple& matchers, - const ValueTuple& values, - ::std::ostream* os) { - using ::std::tr1::tuple_size; - TuplePrefix<tuple_size<MatcherTuple>::value>::ExplainMatchFailuresTo( - matchers, values, os); -} - -// TransformTupleValues and its helper. -// -// TransformTupleValuesHelper hides the internal machinery that -// TransformTupleValues uses to implement a tuple traversal. -template <typename Tuple, typename Func, typename OutIter> -class TransformTupleValuesHelper { - private: - typedef typename ::std::tr1::tuple_size<Tuple> TupleSize; - - public: - // For each member of tuple 't', taken in order, evaluates '*out++ = f(t)'. - // Returns the final value of 'out' in case the caller needs it. - static OutIter Run(Func f, const Tuple& t, OutIter out) { - return IterateOverTuple<Tuple, TupleSize::value>()(f, t, out); - } - - private: - template <typename Tup, size_t kRemainingSize> - struct IterateOverTuple { - OutIter operator() (Func f, const Tup& t, OutIter out) const { - *out++ = f(::std::tr1::get<TupleSize::value - kRemainingSize>(t)); - return IterateOverTuple<Tup, kRemainingSize - 1>()(f, t, out); - } - }; - template <typename Tup> - struct IterateOverTuple<Tup, 0> { - OutIter operator() (Func /* f */, const Tup& /* t */, OutIter out) const { - return out; - } - }; -}; - -// Successively invokes 'f(element)' on each element of the tuple 't', -// appending each result to the 'out' iterator. Returns the final value -// of 'out'. -template <typename Tuple, typename Func, typename OutIter> -OutIter TransformTupleValues(Func f, const Tuple& t, OutIter out) { - return TransformTupleValuesHelper<Tuple, Func, OutIter>::Run(f, t, out); -} - -// Implements A<T>(). -template <typename T> -class AnyMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<T> { - public: - virtual bool MatchAndExplain( - T /* x */, MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { return true; } - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { *os << "is anything"; } - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - // This is mostly for completeness' safe, as it's not very useful - // to write Not(A<bool>()). However we cannot completely rule out - // such a possibility, and it doesn't hurt to be prepared. - *os << "never matches"; - } -}; - -// Implements _, a matcher that matches any value of any -// type. This is a polymorphic matcher, so we need a template type -// conversion operator to make it appearing as a Matcher<T> for any -// type T. -class AnythingMatcher { - public: - template <typename T> - operator Matcher<T>() const { return A<T>(); } -}; - -// Implements a matcher that compares a given value with a -// pre-supplied value using one of the ==, <=, <, etc, operators. The -// two values being compared don't have to have the same type. -// -// The matcher defined here is polymorphic (for example, Eq(5) can be -// used to match an int, a short, a double, etc). Therefore we use -// a template type conversion operator in the implementation. -// -// We define this as a macro in order to eliminate duplicated source -// code. -// -// The following template definition assumes that the Rhs parameter is -// a "bare" type (i.e. neither 'const T' nor 'T&'). -#define GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON_MATCHER_( \ - name, op, relation, negated_relation) \ - template <typename Rhs> class name##Matcher { \ - public: \ - explicit name##Matcher(const Rhs& rhs) : rhs_(rhs) {} \ - template <typename Lhs> \ - operator Matcher<Lhs>() const { \ - return MakeMatcher(new Impl<Lhs>(rhs_)); \ - } \ - private: \ - template <typename Lhs> \ - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Lhs> { \ - public: \ - explicit Impl(const Rhs& rhs) : rhs_(rhs) {} \ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - Lhs lhs, MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { \ - return lhs op rhs_; \ - } \ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { \ - *os << relation " "; \ - UniversalPrint(rhs_, os); \ - } \ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { \ - *os << negated_relation " "; \ - UniversalPrint(rhs_, os); \ - } \ - private: \ - Rhs rhs_; \ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); \ - }; \ - Rhs rhs_; \ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##Matcher); \ - } - -// Implements Eq(v), Ge(v), Gt(v), Le(v), Lt(v), and Ne(v) -// respectively. -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON_MATCHER_(Eq, ==, "is equal to", "isn't equal to"); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON_MATCHER_(Ge, >=, "is >=", "isn't >="); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON_MATCHER_(Gt, >, "is >", "isn't >"); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON_MATCHER_(Le, <=, "is <=", "isn't <="); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON_MATCHER_(Lt, <, "is <", "isn't <"); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON_MATCHER_(Ne, !=, "isn't equal to", "is equal to"); - -#undef GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON_MATCHER_ - -// Implements the polymorphic IsNull() matcher, which matches any raw or smart -// pointer that is NULL. -class IsNullMatcher { - public: - template <typename Pointer> - bool MatchAndExplain(const Pointer& p, - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { - return GetRawPointer(p) == NULL; - } - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { *os << "is NULL"; } - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "isn't NULL"; - } -}; - -// Implements the polymorphic NotNull() matcher, which matches any raw or smart -// pointer that is not NULL. -class NotNullMatcher { - public: - template <typename Pointer> - bool MatchAndExplain(const Pointer& p, - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { - return GetRawPointer(p) != NULL; - } - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { *os << "isn't NULL"; } - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "is NULL"; - } -}; - -// Ref(variable) matches any argument that is a reference to -// 'variable'. This matcher is polymorphic as it can match any -// super type of the type of 'variable'. -// -// The RefMatcher template class implements Ref(variable). It can -// only be instantiated with a reference type. This prevents a user -// from mistakenly using Ref(x) to match a non-reference function -// argument. For example, the following will righteously cause a -// compiler error: -// -// int n; -// Matcher<int> m1 = Ref(n); // This won't compile. -// Matcher<int&> m2 = Ref(n); // This will compile. -template <typename T> -class RefMatcher; - -template <typename T> -class RefMatcher<T&> { - // Google Mock is a generic framework and thus needs to support - // mocking any function types, including those that take non-const - // reference arguments. Therefore the template parameter T (and - // Super below) can be instantiated to either a const type or a - // non-const type. - public: - // RefMatcher() takes a T& instead of const T&, as we want the - // compiler to catch using Ref(const_value) as a matcher for a - // non-const reference. - explicit RefMatcher(T& x) : object_(x) {} // NOLINT - - template <typename Super> - operator Matcher<Super&>() const { - // By passing object_ (type T&) to Impl(), which expects a Super&, - // we make sure that Super is a super type of T. In particular, - // this catches using Ref(const_value) as a matcher for a - // non-const reference, as you cannot implicitly convert a const - // reference to a non-const reference. - return MakeMatcher(new Impl<Super>(object_)); - } - - private: - template <typename Super> - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Super&> { - public: - explicit Impl(Super& x) : object_(x) {} // NOLINT - - // MatchAndExplain() takes a Super& (as opposed to const Super&) - // in order to match the interface MatcherInterface<Super&>. - virtual bool MatchAndExplain( - Super& x, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - *listener << "which is located @" << static_cast<const void*>(&x); - return &x == &object_; - } - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "references the variable "; - UniversalPrinter<Super&>::Print(object_, os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "does not reference the variable "; - UniversalPrinter<Super&>::Print(object_, os); - } - - private: - const Super& object_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - T& object_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(RefMatcher); -}; - -// Polymorphic helper functions for narrow and wide string matchers. -inline bool CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(const char* lhs, const char* rhs) { - return String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(lhs, rhs); -} - -inline bool CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(const wchar_t* lhs, - const wchar_t* rhs) { - return String::CaseInsensitiveWideCStringEquals(lhs, rhs); -} - -// String comparison for narrow or wide strings that can have embedded NUL -// characters. -template <typename StringType> -bool CaseInsensitiveStringEquals(const StringType& s1, - const StringType& s2) { - // Are the heads equal? - if (!CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str())) { - return false; - } - - // Skip the equal heads. - const typename StringType::value_type nul = 0; - const size_t i1 = s1.find(nul), i2 = s2.find(nul); - - // Are we at the end of either s1 or s2? - if (i1 == StringType::npos || i2 == StringType::npos) { - return i1 == i2; - } - - // Are the tails equal? - return CaseInsensitiveStringEquals(s1.substr(i1 + 1), s2.substr(i2 + 1)); -} - -// String matchers. - -// Implements equality-based string matchers like StrEq, StrCaseNe, and etc. -template <typename StringType> -class StrEqualityMatcher { - public: - StrEqualityMatcher(const StringType& str, bool expect_eq, - bool case_sensitive) - : string_(str), expect_eq_(expect_eq), case_sensitive_(case_sensitive) {} - - // Accepts pointer types, particularly: - // const char* - // char* - // const wchar_t* - // wchar_t* - template <typename CharType> - bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - if (s == NULL) { - return !expect_eq_; - } - return MatchAndExplain(StringType(s), listener); - } - - // Matches anything that can convert to StringType. - // - // This is a template, not just a plain function with const StringType&, - // because StringPiece has some interfering non-explicit constructors. - template <typename MatcheeStringType> - bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { - const StringType& s2(s); - const bool eq = case_sensitive_ ? s2 == string_ : - CaseInsensitiveStringEquals(s2, string_); - return expect_eq_ == eq; - } - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - DescribeToHelper(expect_eq_, os); - } - - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - DescribeToHelper(!expect_eq_, os); - } - - private: - void DescribeToHelper(bool expect_eq, ::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << (expect_eq ? "is " : "isn't "); - *os << "equal to "; - if (!case_sensitive_) { - *os << "(ignoring case) "; - } - UniversalPrint(string_, os); - } - - const StringType string_; - const bool expect_eq_; - const bool case_sensitive_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(StrEqualityMatcher); -}; - -// Implements the polymorphic HasSubstr(substring) matcher, which -// can be used as a Matcher<T> as long as T can be converted to a -// string. -template <typename StringType> -class HasSubstrMatcher { - public: - explicit HasSubstrMatcher(const StringType& substring) - : substring_(substring) {} - - // Accepts pointer types, particularly: - // const char* - // char* - // const wchar_t* - // wchar_t* - template <typename CharType> - bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return s != NULL && MatchAndExplain(StringType(s), listener); - } - - // Matches anything that can convert to StringType. - // - // This is a template, not just a plain function with const StringType&, - // because StringPiece has some interfering non-explicit constructors. - template <typename MatcheeStringType> - bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { - const StringType& s2(s); - return s2.find(substring_) != StringType::npos; - } - - // Describes what this matcher matches. - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "has substring "; - UniversalPrint(substring_, os); - } - - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "has no substring "; - UniversalPrint(substring_, os); - } - - private: - const StringType substring_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(HasSubstrMatcher); -}; - -// Implements the polymorphic StartsWith(substring) matcher, which -// can be used as a Matcher<T> as long as T can be converted to a -// string. -template <typename StringType> -class StartsWithMatcher { - public: - explicit StartsWithMatcher(const StringType& prefix) : prefix_(prefix) { - } - - // Accepts pointer types, particularly: - // const char* - // char* - // const wchar_t* - // wchar_t* - template <typename CharType> - bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return s != NULL && MatchAndExplain(StringType(s), listener); - } - - // Matches anything that can convert to StringType. - // - // This is a template, not just a plain function with const StringType&, - // because StringPiece has some interfering non-explicit constructors. - template <typename MatcheeStringType> - bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { - const StringType& s2(s); - return s2.length() >= prefix_.length() && - s2.substr(0, prefix_.length()) == prefix_; - } - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "starts with "; - UniversalPrint(prefix_, os); - } - - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "doesn't start with "; - UniversalPrint(prefix_, os); - } - - private: - const StringType prefix_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(StartsWithMatcher); -}; - -// Implements the polymorphic EndsWith(substring) matcher, which -// can be used as a Matcher<T> as long as T can be converted to a -// string. -template <typename StringType> -class EndsWithMatcher { - public: - explicit EndsWithMatcher(const StringType& suffix) : suffix_(suffix) {} - - // Accepts pointer types, particularly: - // const char* - // char* - // const wchar_t* - // wchar_t* - template <typename CharType> - bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return s != NULL && MatchAndExplain(StringType(s), listener); - } - - // Matches anything that can convert to StringType. - // - // This is a template, not just a plain function with const StringType&, - // because StringPiece has some interfering non-explicit constructors. - template <typename MatcheeStringType> - bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { - const StringType& s2(s); - return s2.length() >= suffix_.length() && - s2.substr(s2.length() - suffix_.length()) == suffix_; - } - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "ends with "; - UniversalPrint(suffix_, os); - } - - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "doesn't end with "; - UniversalPrint(suffix_, os); - } - - private: - const StringType suffix_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(EndsWithMatcher); -}; - -// Implements polymorphic matchers MatchesRegex(regex) and -// ContainsRegex(regex), which can be used as a Matcher<T> as long as -// T can be converted to a string. -class MatchesRegexMatcher { - public: - MatchesRegexMatcher(const RE* regex, bool full_match) - : regex_(regex), full_match_(full_match) {} - - // Accepts pointer types, particularly: - // const char* - // char* - // const wchar_t* - // wchar_t* - template <typename CharType> - bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return s != NULL && MatchAndExplain(internal::string(s), listener); - } - - // Matches anything that can convert to internal::string. - // - // This is a template, not just a plain function with const internal::string&, - // because StringPiece has some interfering non-explicit constructors. - template <class MatcheeStringType> - bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { - const internal::string& s2(s); - return full_match_ ? RE::FullMatch(s2, *regex_) : - RE::PartialMatch(s2, *regex_); - } - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << (full_match_ ? "matches" : "contains") - << " regular expression "; - UniversalPrinter<internal::string>::Print(regex_->pattern(), os); - } - - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "doesn't " << (full_match_ ? "match" : "contain") - << " regular expression "; - UniversalPrinter<internal::string>::Print(regex_->pattern(), os); - } - - private: - const internal::linked_ptr<const RE> regex_; - const bool full_match_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(MatchesRegexMatcher); -}; - -// Implements a matcher that compares the two fields of a 2-tuple -// using one of the ==, <=, <, etc, operators. The two fields being -// compared don't have to have the same type. -// -// The matcher defined here is polymorphic (for example, Eq() can be -// used to match a tuple<int, short>, a tuple<const long&, double>, -// etc). Therefore we use a template type conversion operator in the -// implementation. -// -// We define this as a macro in order to eliminate duplicated source -// code. -#define GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON2_MATCHER_(name, op, relation) \ - class name##2Matcher { \ - public: \ - template <typename T1, typename T2> \ - operator Matcher< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2> >() const { \ - return MakeMatcher(new Impl< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2> >); \ - } \ - template <typename T1, typename T2> \ - operator Matcher<const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2>&>() const { \ - return MakeMatcher(new Impl<const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2>&>); \ - } \ - private: \ - template <typename Tuple> \ - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Tuple> { \ - public: \ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain( \ - Tuple args, \ - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { \ - return ::std::tr1::get<0>(args) op ::std::tr1::get<1>(args); \ - } \ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { \ - *os << "are " relation; \ - } \ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { \ - *os << "aren't " relation; \ - } \ - }; \ - } - -// Implements Eq(), Ge(), Gt(), Le(), Lt(), and Ne() respectively. -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON2_MATCHER_(Eq, ==, "an equal pair"); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON2_MATCHER_( - Ge, >=, "a pair where the first >= the second"); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON2_MATCHER_( - Gt, >, "a pair where the first > the second"); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON2_MATCHER_( - Le, <=, "a pair where the first <= the second"); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON2_MATCHER_( - Lt, <, "a pair where the first < the second"); -GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON2_MATCHER_(Ne, !=, "an unequal pair"); - -#undef GMOCK_IMPLEMENT_COMPARISON2_MATCHER_ - -// Implements the Not(...) matcher for a particular argument type T. -// We do not nest it inside the NotMatcher class template, as that -// will prevent different instantiations of NotMatcher from sharing -// the same NotMatcherImpl<T> class. -template <typename T> -class NotMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<T> { - public: - explicit NotMatcherImpl(const Matcher<T>& matcher) - : matcher_(matcher) {} - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return !matcher_.MatchAndExplain(x, listener); - } - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - private: - const Matcher<T> matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(NotMatcherImpl); -}; - -// Implements the Not(m) matcher, which matches a value that doesn't -// match matcher m. -template <typename InnerMatcher> -class NotMatcher { - public: - explicit NotMatcher(InnerMatcher matcher) : matcher_(matcher) {} - - // This template type conversion operator allows Not(m) to be used - // to match any type m can match. - template <typename T> - operator Matcher<T>() const { - return Matcher<T>(new NotMatcherImpl<T>(SafeMatcherCast<T>(matcher_))); - } - - private: - InnerMatcher matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(NotMatcher); -}; - -// Implements the AllOf(m1, m2) matcher for a particular argument type -// T. We do not nest it inside the BothOfMatcher class template, as -// that will prevent different instantiations of BothOfMatcher from -// sharing the same BothOfMatcherImpl<T> class. -template <typename T> -class BothOfMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<T> { - public: - BothOfMatcherImpl(const Matcher<T>& matcher1, const Matcher<T>& matcher2) - : matcher1_(matcher1), matcher2_(matcher2) {} - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "("; - matcher1_.DescribeTo(os); - *os << ") and ("; - matcher2_.DescribeTo(os); - *os << ")"; - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "("; - matcher1_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - *os << ") or ("; - matcher2_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - *os << ")"; - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - // If either matcher1_ or matcher2_ doesn't match x, we only need - // to explain why one of them fails. - StringMatchResultListener listener1; - if (!matcher1_.MatchAndExplain(x, &listener1)) { - *listener << listener1.str(); - return false; - } - - StringMatchResultListener listener2; - if (!matcher2_.MatchAndExplain(x, &listener2)) { - *listener << listener2.str(); - return false; - } - - // Otherwise we need to explain why *both* of them match. - const internal::string s1 = listener1.str(); - const internal::string s2 = listener2.str(); - - if (s1 == "") { - *listener << s2; - } else { - *listener << s1; - if (s2 != "") { - *listener << ", and " << s2; - } - } - return true; - } - - private: - const Matcher<T> matcher1_; - const Matcher<T> matcher2_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(BothOfMatcherImpl); -}; - -#if GTEST_LANG_CXX11 -// MatcherList provides mechanisms for storing a variable number of matchers in -// a list structure (ListType) and creating a combining matcher from such a -// list. -// The template is defined recursively using the following template paramters: -// * kSize is the length of the MatcherList. -// * Head is the type of the first matcher of the list. -// * Tail denotes the types of the remaining matchers of the list. -template <int kSize, typename Head, typename... Tail> -struct MatcherList { - typedef MatcherList<kSize - 1, Tail...> MatcherListTail; - typedef ::std::pair<Head, typename MatcherListTail::ListType> ListType; - - // BuildList stores variadic type values in a nested pair structure. - // Example: - // MatcherList<3, int, string, float>::BuildList(5, "foo", 2.0) will return - // the corresponding result of type pair<int, pair<string, float>>. - static ListType BuildList(const Head& matcher, const Tail&... tail) { - return ListType(matcher, MatcherListTail::BuildList(tail...)); - } - - // CreateMatcher<T> creates a Matcher<T> from a given list of matchers (built - // by BuildList()). CombiningMatcher<T> is used to combine the matchers of the - // list. CombiningMatcher<T> must implement MatcherInterface<T> and have a - // constructor taking two Matcher<T>s as input. - template <typename T, template <typename /* T */> class CombiningMatcher> - static Matcher<T> CreateMatcher(const ListType& matchers) { - return Matcher<T>(new CombiningMatcher<T>( - SafeMatcherCast<T>(matchers.first), - MatcherListTail::template CreateMatcher<T, CombiningMatcher>( - matchers.second))); - } -}; - -// The following defines the base case for the recursive definition of -// MatcherList. -template <typename Matcher1, typename Matcher2> -struct MatcherList<2, Matcher1, Matcher2> { - typedef ::std::pair<Matcher1, Matcher2> ListType; - - static ListType BuildList(const Matcher1& matcher1, - const Matcher2& matcher2) { - return ::std::pair<Matcher1, Matcher2>(matcher1, matcher2); - } - - template <typename T, template <typename /* T */> class CombiningMatcher> - static Matcher<T> CreateMatcher(const ListType& matchers) { - return Matcher<T>(new CombiningMatcher<T>( - SafeMatcherCast<T>(matchers.first), - SafeMatcherCast<T>(matchers.second))); - } -}; - -// VariadicMatcher is used for the variadic implementation of -// AllOf(m_1, m_2, ...) and AnyOf(m_1, m_2, ...). -// CombiningMatcher<T> is used to recursively combine the provided matchers -// (of type Args...). -template <template <typename T> class CombiningMatcher, typename... Args> -class VariadicMatcher { - public: - VariadicMatcher(const Args&... matchers) // NOLINT - : matchers_(MatcherListType::BuildList(matchers...)) {} - - // This template type conversion operator allows an - // VariadicMatcher<Matcher1, Matcher2...> object to match any type that - // all of the provided matchers (Matcher1, Matcher2, ...) can match. - template <typename T> - operator Matcher<T>() const { - return MatcherListType::template CreateMatcher<T, CombiningMatcher>( - matchers_); - } - - private: - typedef MatcherList<sizeof...(Args), Args...> MatcherListType; - - const typename MatcherListType::ListType matchers_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(VariadicMatcher); -}; - -template <typename... Args> -using AllOfMatcher = VariadicMatcher<BothOfMatcherImpl, Args...>; - -#endif // GTEST_LANG_CXX11 - -// Used for implementing the AllOf(m_1, ..., m_n) matcher, which -// matches a value that matches all of the matchers m_1, ..., and m_n. -template <typename Matcher1, typename Matcher2> -class BothOfMatcher { - public: - BothOfMatcher(Matcher1 matcher1, Matcher2 matcher2) - : matcher1_(matcher1), matcher2_(matcher2) {} - - // This template type conversion operator allows a - // BothOfMatcher<Matcher1, Matcher2> object to match any type that - // both Matcher1 and Matcher2 can match. - template <typename T> - operator Matcher<T>() const { - return Matcher<T>(new BothOfMatcherImpl<T>(SafeMatcherCast<T>(matcher1_), - SafeMatcherCast<T>(matcher2_))); - } - - private: - Matcher1 matcher1_; - Matcher2 matcher2_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(BothOfMatcher); -}; - -// Implements the AnyOf(m1, m2) matcher for a particular argument type -// T. We do not nest it inside the AnyOfMatcher class template, as -// that will prevent different instantiations of AnyOfMatcher from -// sharing the same EitherOfMatcherImpl<T> class. -template <typename T> -class EitherOfMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<T> { - public: - EitherOfMatcherImpl(const Matcher<T>& matcher1, const Matcher<T>& matcher2) - : matcher1_(matcher1), matcher2_(matcher2) {} - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "("; - matcher1_.DescribeTo(os); - *os << ") or ("; - matcher2_.DescribeTo(os); - *os << ")"; - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "("; - matcher1_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - *os << ") and ("; - matcher2_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - *os << ")"; - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - // If either matcher1_ or matcher2_ matches x, we just need to - // explain why *one* of them matches. - StringMatchResultListener listener1; - if (matcher1_.MatchAndExplain(x, &listener1)) { - *listener << listener1.str(); - return true; - } - - StringMatchResultListener listener2; - if (matcher2_.MatchAndExplain(x, &listener2)) { - *listener << listener2.str(); - return true; - } - - // Otherwise we need to explain why *both* of them fail. - const internal::string s1 = listener1.str(); - const internal::string s2 = listener2.str(); - - if (s1 == "") { - *listener << s2; - } else { - *listener << s1; - if (s2 != "") { - *listener << ", and " << s2; - } - } - return false; - } - - private: - const Matcher<T> matcher1_; - const Matcher<T> matcher2_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(EitherOfMatcherImpl); -}; - -#if GTEST_LANG_CXX11 -// AnyOfMatcher is used for the variadic implementation of AnyOf(m_1, m_2, ...). -template <typename... Args> -using AnyOfMatcher = VariadicMatcher<EitherOfMatcherImpl, Args...>; - -#endif // GTEST_LANG_CXX11 - -// Used for implementing the AnyOf(m_1, ..., m_n) matcher, which -// matches a value that matches at least one of the matchers m_1, ..., -// and m_n. -template <typename Matcher1, typename Matcher2> -class EitherOfMatcher { - public: - EitherOfMatcher(Matcher1 matcher1, Matcher2 matcher2) - : matcher1_(matcher1), matcher2_(matcher2) {} - - // This template type conversion operator allows a - // EitherOfMatcher<Matcher1, Matcher2> object to match any type that - // both Matcher1 and Matcher2 can match. - template <typename T> - operator Matcher<T>() const { - return Matcher<T>(new EitherOfMatcherImpl<T>( - SafeMatcherCast<T>(matcher1_), SafeMatcherCast<T>(matcher2_))); - } - - private: - Matcher1 matcher1_; - Matcher2 matcher2_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(EitherOfMatcher); -}; - -// Used for implementing Truly(pred), which turns a predicate into a -// matcher. -template <typename Predicate> -class TrulyMatcher { - public: - explicit TrulyMatcher(Predicate pred) : predicate_(pred) {} - - // This method template allows Truly(pred) to be used as a matcher - // for type T where T is the argument type of predicate 'pred'. The - // argument is passed by reference as the predicate may be - // interested in the address of the argument. - template <typename T> - bool MatchAndExplain(T& x, // NOLINT - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { - // Without the if-statement, MSVC sometimes warns about converting - // a value to bool (warning 4800). - // - // We cannot write 'return !!predicate_(x);' as that doesn't work - // when predicate_(x) returns a class convertible to bool but - // having no operator!(). - if (predicate_(x)) - return true; - return false; - } - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "satisfies the given predicate"; - } - - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "doesn't satisfy the given predicate"; - } - - private: - Predicate predicate_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(TrulyMatcher); -}; - -// Used for implementing Matches(matcher), which turns a matcher into -// a predicate. -template <typename M> -class MatcherAsPredicate { - public: - explicit MatcherAsPredicate(M matcher) : matcher_(matcher) {} - - // This template operator() allows Matches(m) to be used as a - // predicate on type T where m is a matcher on type T. - // - // The argument x is passed by reference instead of by value, as - // some matcher may be interested in its address (e.g. as in - // Matches(Ref(n))(x)). - template <typename T> - bool operator()(const T& x) const { - // We let matcher_ commit to a particular type here instead of - // when the MatcherAsPredicate object was constructed. This - // allows us to write Matches(m) where m is a polymorphic matcher - // (e.g. Eq(5)). - // - // If we write Matcher<T>(matcher_).Matches(x) here, it won't - // compile when matcher_ has type Matcher<const T&>; if we write - // Matcher<const T&>(matcher_).Matches(x) here, it won't compile - // when matcher_ has type Matcher<T>; if we just write - // matcher_.Matches(x), it won't compile when matcher_ is - // polymorphic, e.g. Eq(5). - // - // MatcherCast<const T&>() is necessary for making the code work - // in all of the above situations. - return MatcherCast<const T&>(matcher_).Matches(x); - } - - private: - M matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(MatcherAsPredicate); -}; - -// For implementing ASSERT_THAT() and EXPECT_THAT(). The template -// argument M must be a type that can be converted to a matcher. -template <typename M> -class PredicateFormatterFromMatcher { - public: - explicit PredicateFormatterFromMatcher(const M& m) : matcher_(m) {} - - // This template () operator allows a PredicateFormatterFromMatcher - // object to act as a predicate-formatter suitable for using with - // Google Test's EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1() macro. - template <typename T> - AssertionResult operator()(const char* value_text, const T& x) const { - // We convert matcher_ to a Matcher<const T&> *now* instead of - // when the PredicateFormatterFromMatcher object was constructed, - // as matcher_ may be polymorphic (e.g. NotNull()) and we won't - // know which type to instantiate it to until we actually see the - // type of x here. - // - // We write SafeMatcherCast<const T&>(matcher_) instead of - // Matcher<const T&>(matcher_), as the latter won't compile when - // matcher_ has type Matcher<T> (e.g. An<int>()). - // We don't write MatcherCast<const T&> either, as that allows - // potentially unsafe downcasting of the matcher argument. - const Matcher<const T&> matcher = SafeMatcherCast<const T&>(matcher_); - StringMatchResultListener listener; - if (MatchPrintAndExplain(x, matcher, &listener)) - return AssertionSuccess(); - - ::std::stringstream ss; - ss << "Value of: " << value_text << "\n" - << "Expected: "; - matcher.DescribeTo(&ss); - ss << "\n Actual: " << listener.str(); - return AssertionFailure() << ss.str(); - } - - private: - const M matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(PredicateFormatterFromMatcher); -}; - -// A helper function for converting a matcher to a predicate-formatter -// without the user needing to explicitly write the type. This is -// used for implementing ASSERT_THAT() and EXPECT_THAT(). -template <typename M> -inline PredicateFormatterFromMatcher<M> -MakePredicateFormatterFromMatcher(const M& matcher) { - return PredicateFormatterFromMatcher<M>(matcher); -} - -// Implements the polymorphic floating point equality matcher, which matches -// two float values using ULP-based approximation or, optionally, a -// user-specified epsilon. The template is meant to be instantiated with -// FloatType being either float or double. -template <typename FloatType> -class FloatingEqMatcher { - public: - // Constructor for FloatingEqMatcher. - // The matcher's input will be compared with rhs. The matcher treats two - // NANs as equal if nan_eq_nan is true. Otherwise, under IEEE standards, - // equality comparisons between NANs will always return false. We specify a - // negative max_abs_error_ term to indicate that ULP-based approximation will - // be used for comparison. - FloatingEqMatcher(FloatType rhs, bool nan_eq_nan) : - rhs_(rhs), nan_eq_nan_(nan_eq_nan), max_abs_error_(-1) { - } - - // Constructor that supports a user-specified max_abs_error that will be used - // for comparison instead of ULP-based approximation. The max absolute - // should be non-negative. - FloatingEqMatcher(FloatType rhs, bool nan_eq_nan, FloatType max_abs_error) : - rhs_(rhs), nan_eq_nan_(nan_eq_nan), max_abs_error_(max_abs_error) { - GTEST_CHECK_(max_abs_error >= 0) - << ", where max_abs_error is" << max_abs_error; - } - - // Implements floating point equality matcher as a Matcher<T>. - template <typename T> - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<T> { - public: - Impl(FloatType rhs, bool nan_eq_nan, FloatType max_abs_error) : - rhs_(rhs), nan_eq_nan_(nan_eq_nan), max_abs_error_(max_abs_error) {} - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(T value, - MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { - const FloatingPoint<FloatType> lhs(value), rhs(rhs_); - - // Compares NaNs first, if nan_eq_nan_ is true. - if (lhs.is_nan() || rhs.is_nan()) { - if (lhs.is_nan() && rhs.is_nan()) { - return nan_eq_nan_; - } - // One is nan; the other is not nan. - return false; - } - if (HasMaxAbsError()) { - // We perform an equality check so that inf will match inf, regardless - // of error bounds. If the result of value - rhs_ would result in - // overflow or if either value is inf, the default result is infinity, - // which should only match if max_abs_error_ is also infinity. - return value == rhs_ || fabs(value - rhs_) <= max_abs_error_; - } else { - return lhs.AlmostEquals(rhs); - } - } - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - // os->precision() returns the previously set precision, which we - // store to restore the ostream to its original configuration - // after outputting. - const ::std::streamsize old_precision = os->precision( - ::std::numeric_limits<FloatType>::digits10 + 2); - if (FloatingPoint<FloatType>(rhs_).is_nan()) { - if (nan_eq_nan_) { - *os << "is NaN"; - } else { - *os << "never matches"; - } - } else { - *os << "is approximately " << rhs_; - if (HasMaxAbsError()) { - *os << " (absolute error <= " << max_abs_error_ << ")"; - } - } - os->precision(old_precision); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - // As before, get original precision. - const ::std::streamsize old_precision = os->precision( - ::std::numeric_limits<FloatType>::digits10 + 2); - if (FloatingPoint<FloatType>(rhs_).is_nan()) { - if (nan_eq_nan_) { - *os << "isn't NaN"; - } else { - *os << "is anything"; - } - } else { - *os << "isn't approximately " << rhs_; - if (HasMaxAbsError()) { - *os << " (absolute error > " << max_abs_error_ << ")"; - } - } - // Restore original precision. - os->precision(old_precision); - } - - private: - bool HasMaxAbsError() const { - return max_abs_error_ >= 0; - } - - const FloatType rhs_; - const bool nan_eq_nan_; - // max_abs_error will be used for value comparison when >= 0. - const FloatType max_abs_error_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - // The following 3 type conversion operators allow FloatEq(rhs) and - // NanSensitiveFloatEq(rhs) to be used as a Matcher<float>, a - // Matcher<const float&>, or a Matcher<float&>, but nothing else. - // (While Google's C++ coding style doesn't allow arguments passed - // by non-const reference, we may see them in code not conforming to - // the style. Therefore Google Mock needs to support them.) - operator Matcher<FloatType>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new Impl<FloatType>(rhs_, nan_eq_nan_, max_abs_error_)); - } - - operator Matcher<const FloatType&>() const { - return MakeMatcher( - new Impl<const FloatType&>(rhs_, nan_eq_nan_, max_abs_error_)); - } - - operator Matcher<FloatType&>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new Impl<FloatType&>(rhs_, nan_eq_nan_, max_abs_error_)); - } - - private: - const FloatType rhs_; - const bool nan_eq_nan_; - // max_abs_error will be used for value comparison when >= 0. - const FloatType max_abs_error_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(FloatingEqMatcher); -}; - -// Implements the Pointee(m) matcher for matching a pointer whose -// pointee matches matcher m. The pointer can be either raw or smart. -template <typename InnerMatcher> -class PointeeMatcher { - public: - explicit PointeeMatcher(const InnerMatcher& matcher) : matcher_(matcher) {} - - // This type conversion operator template allows Pointee(m) to be - // used as a matcher for any pointer type whose pointee type is - // compatible with the inner matcher, where type Pointer can be - // either a raw pointer or a smart pointer. - // - // The reason we do this instead of relying on - // MakePolymorphicMatcher() is that the latter is not flexible - // enough for implementing the DescribeTo() method of Pointee(). - template <typename Pointer> - operator Matcher<Pointer>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new Impl<Pointer>(matcher_)); - } - - private: - // The monomorphic implementation that works for a particular pointer type. - template <typename Pointer> - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Pointer> { - public: - typedef typename PointeeOf<GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_( // NOLINT - GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_(Pointer))>::type Pointee; - - explicit Impl(const InnerMatcher& matcher) - : matcher_(MatcherCast<const Pointee&>(matcher)) {} - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "points to a value that "; - matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "does not point to a value that "; - matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(Pointer pointer, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - if (GetRawPointer(pointer) == NULL) - return false; - - *listener << "which points to "; - return MatchPrintAndExplain(*pointer, matcher_, listener); - } - - private: - const Matcher<const Pointee&> matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - const InnerMatcher matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(PointeeMatcher); -}; - -// Implements the Field() matcher for matching a field (i.e. member -// variable) of an object. -template <typename Class, typename FieldType> -class FieldMatcher { - public: - FieldMatcher(FieldType Class::*field, - const Matcher<const FieldType&>& matcher) - : field_(field), matcher_(matcher) {} - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "is an object whose given field "; - matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "is an object whose given field "; - matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - template <typename T> - bool MatchAndExplain(const T& value, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return MatchAndExplainImpl( - typename ::testing::internal:: - is_pointer<GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(T)>::type(), - value, listener); - } - - private: - // The first argument of MatchAndExplainImpl() is needed to help - // Symbian's C++ compiler choose which overload to use. Its type is - // true_type iff the Field() matcher is used to match a pointer. - bool MatchAndExplainImpl(false_type /* is_not_pointer */, const Class& obj, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - *listener << "whose given field is "; - return MatchPrintAndExplain(obj.*field_, matcher_, listener); - } - - bool MatchAndExplainImpl(true_type /* is_pointer */, const Class* p, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - if (p == NULL) - return false; - - *listener << "which points to an object "; - // Since *p has a field, it must be a class/struct/union type and - // thus cannot be a pointer. Therefore we pass false_type() as - // the first argument. - return MatchAndExplainImpl(false_type(), *p, listener); - } - - const FieldType Class::*field_; - const Matcher<const FieldType&> matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(FieldMatcher); -}; - -// Implements the Property() matcher for matching a property -// (i.e. return value of a getter method) of an object. -template <typename Class, typename PropertyType> -class PropertyMatcher { - public: - // The property may have a reference type, so 'const PropertyType&' - // may cause double references and fail to compile. That's why we - // need GTEST_REFERENCE_TO_CONST, which works regardless of - // PropertyType being a reference or not. - typedef GTEST_REFERENCE_TO_CONST_(PropertyType) RefToConstProperty; - - PropertyMatcher(PropertyType (Class::*property)() const, - const Matcher<RefToConstProperty>& matcher) - : property_(property), matcher_(matcher) {} - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "is an object whose given property "; - matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "is an object whose given property "; - matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - template <typename T> - bool MatchAndExplain(const T&value, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return MatchAndExplainImpl( - typename ::testing::internal:: - is_pointer<GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(T)>::type(), - value, listener); - } - - private: - // The first argument of MatchAndExplainImpl() is needed to help - // Symbian's C++ compiler choose which overload to use. Its type is - // true_type iff the Property() matcher is used to match a pointer. - bool MatchAndExplainImpl(false_type /* is_not_pointer */, const Class& obj, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - *listener << "whose given property is "; - // Cannot pass the return value (for example, int) to MatchPrintAndExplain, - // which takes a non-const reference as argument. - RefToConstProperty result = (obj.*property_)(); - return MatchPrintAndExplain(result, matcher_, listener); - } - - bool MatchAndExplainImpl(true_type /* is_pointer */, const Class* p, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - if (p == NULL) - return false; - - *listener << "which points to an object "; - // Since *p has a property method, it must be a class/struct/union - // type and thus cannot be a pointer. Therefore we pass - // false_type() as the first argument. - return MatchAndExplainImpl(false_type(), *p, listener); - } - - PropertyType (Class::*property_)() const; - const Matcher<RefToConstProperty> matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(PropertyMatcher); -}; - -// Type traits specifying various features of different functors for ResultOf. -// The default template specifies features for functor objects. -// Functor classes have to typedef argument_type and result_type -// to be compatible with ResultOf. -template <typename Functor> -struct CallableTraits { - typedef typename Functor::result_type ResultType; - typedef Functor StorageType; - - static void CheckIsValid(Functor /* functor */) {} - template <typename T> - static ResultType Invoke(Functor f, T arg) { return f(arg); } -}; - -// Specialization for function pointers. -template <typename ArgType, typename ResType> -struct CallableTraits<ResType(*)(ArgType)> { - typedef ResType ResultType; - typedef ResType(*StorageType)(ArgType); - - static void CheckIsValid(ResType(*f)(ArgType)) { - GTEST_CHECK_(f != NULL) - << "NULL function pointer is passed into ResultOf()."; - } - template <typename T> - static ResType Invoke(ResType(*f)(ArgType), T arg) { - return (*f)(arg); - } -}; - -// Implements the ResultOf() matcher for matching a return value of a -// unary function of an object. -template <typename Callable> -class ResultOfMatcher { - public: - typedef typename CallableTraits<Callable>::ResultType ResultType; - - ResultOfMatcher(Callable callable, const Matcher<ResultType>& matcher) - : callable_(callable), matcher_(matcher) { - CallableTraits<Callable>::CheckIsValid(callable_); - } - - template <typename T> - operator Matcher<T>() const { - return Matcher<T>(new Impl<T>(callable_, matcher_)); - } - - private: - typedef typename CallableTraits<Callable>::StorageType CallableStorageType; - - template <typename T> - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<T> { - public: - Impl(CallableStorageType callable, const Matcher<ResultType>& matcher) - : callable_(callable), matcher_(matcher) {} - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "is mapped by the given callable to a value that "; - matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "is mapped by the given callable to a value that "; - matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(T obj, MatchResultListener* listener) const { - *listener << "which is mapped by the given callable to "; - // Cannot pass the return value (for example, int) to - // MatchPrintAndExplain, which takes a non-const reference as argument. - ResultType result = - CallableTraits<Callable>::template Invoke<T>(callable_, obj); - return MatchPrintAndExplain(result, matcher_, listener); - } - - private: - // Functors often define operator() as non-const method even though - // they are actualy stateless. But we need to use them even when - // 'this' is a const pointer. It's the user's responsibility not to - // use stateful callables with ResultOf(), which does't guarantee - // how many times the callable will be invoked. - mutable CallableStorageType callable_; - const Matcher<ResultType> matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; // class Impl - - const CallableStorageType callable_; - const Matcher<ResultType> matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ResultOfMatcher); -}; - -// Implements a matcher that checks the size of an STL-style container. -template <typename SizeMatcher> -class SizeIsMatcher { - public: - explicit SizeIsMatcher(const SizeMatcher& size_matcher) - : size_matcher_(size_matcher) { - } - - template <typename Container> - operator Matcher<Container>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new Impl<Container>(size_matcher_)); - } - - template <typename Container> - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Container> { - public: - typedef internal::StlContainerView< - GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container)> ContainerView; - typedef typename ContainerView::type::size_type SizeType; - explicit Impl(const SizeMatcher& size_matcher) - : size_matcher_(MatcherCast<SizeType>(size_matcher)) {} - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "size "; - size_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "size "; - size_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - SizeType size = container.size(); - StringMatchResultListener size_listener; - const bool result = size_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(size, &size_listener); - *listener - << "whose size " << size << (result ? " matches" : " doesn't match"); - PrintIfNotEmpty(size_listener.str(), listener->stream()); - return result; - } - - private: - const Matcher<SizeType> size_matcher_; - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - private: - const SizeMatcher size_matcher_; - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(SizeIsMatcher); -}; - -// Implements an equality matcher for any STL-style container whose elements -// support ==. This matcher is like Eq(), but its failure explanations provide -// more detailed information that is useful when the container is used as a set. -// The failure message reports elements that are in one of the operands but not -// the other. The failure messages do not report duplicate or out-of-order -// elements in the containers (which don't properly matter to sets, but can -// occur if the containers are vectors or lists, for example). -// -// Uses the container's const_iterator, value_type, operator ==, -// begin(), and end(). -template <typename Container> -class ContainerEqMatcher { - public: - typedef internal::StlContainerView<Container> View; - typedef typename View::type StlContainer; - typedef typename View::const_reference StlContainerReference; - - // We make a copy of rhs in case the elements in it are modified - // after this matcher is created. - explicit ContainerEqMatcher(const Container& rhs) : rhs_(View::Copy(rhs)) { - // Makes sure the user doesn't instantiate this class template - // with a const or reference type. - (void)testing::StaticAssertTypeEq<Container, - GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container)>(); - } - - void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "equals "; - UniversalPrint(rhs_, os); - } - void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "does not equal "; - UniversalPrint(rhs_, os); - } - - template <typename LhsContainer> - bool MatchAndExplain(const LhsContainer& lhs, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - // GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_() is needed to work around an MSVC 8.0 bug - // that causes LhsContainer to be a const type sometimes. - typedef internal::StlContainerView<GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(LhsContainer)> - LhsView; - typedef typename LhsView::type LhsStlContainer; - StlContainerReference lhs_stl_container = LhsView::ConstReference(lhs); - if (lhs_stl_container == rhs_) - return true; - - ::std::ostream* const os = listener->stream(); - if (os != NULL) { - // Something is different. Check for extra values first. - bool printed_header = false; - for (typename LhsStlContainer::const_iterator it = - lhs_stl_container.begin(); - it != lhs_stl_container.end(); ++it) { - if (internal::ArrayAwareFind(rhs_.begin(), rhs_.end(), *it) == - rhs_.end()) { - if (printed_header) { - *os << ", "; - } else { - *os << "which has these unexpected elements: "; - printed_header = true; - } - UniversalPrint(*it, os); - } - } - - // Now check for missing values. - bool printed_header2 = false; - for (typename StlContainer::const_iterator it = rhs_.begin(); - it != rhs_.end(); ++it) { - if (internal::ArrayAwareFind( - lhs_stl_container.begin(), lhs_stl_container.end(), *it) == - lhs_stl_container.end()) { - if (printed_header2) { - *os << ", "; - } else { - *os << (printed_header ? ",\nand" : "which") - << " doesn't have these expected elements: "; - printed_header2 = true; - } - UniversalPrint(*it, os); - } - } - } - - return false; - } - - private: - const StlContainer rhs_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ContainerEqMatcher); -}; - -// A comparator functor that uses the < operator to compare two values. -struct LessComparator { - template <typename T, typename U> - bool operator()(const T& lhs, const U& rhs) const { return lhs < rhs; } -}; - -// Implements WhenSortedBy(comparator, container_matcher). -template <typename Comparator, typename ContainerMatcher> -class WhenSortedByMatcher { - public: - WhenSortedByMatcher(const Comparator& comparator, - const ContainerMatcher& matcher) - : comparator_(comparator), matcher_(matcher) {} - - template <typename LhsContainer> - operator Matcher<LhsContainer>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new Impl<LhsContainer>(comparator_, matcher_)); - } - - template <typename LhsContainer> - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<LhsContainer> { - public: - typedef internal::StlContainerView< - GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(LhsContainer)> LhsView; - typedef typename LhsView::type LhsStlContainer; - typedef typename LhsView::const_reference LhsStlContainerReference; - // Transforms std::pair<const Key, Value> into std::pair<Key, Value> - // so that we can match associative containers. - typedef typename RemoveConstFromKey< - typename LhsStlContainer::value_type>::type LhsValue; - - Impl(const Comparator& comparator, const ContainerMatcher& matcher) - : comparator_(comparator), matcher_(matcher) {} - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "(when sorted) "; - matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "(when sorted) "; - matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(LhsContainer lhs, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - LhsStlContainerReference lhs_stl_container = LhsView::ConstReference(lhs); - ::std::vector<LhsValue> sorted_container(lhs_stl_container.begin(), - lhs_stl_container.end()); - ::std::sort( - sorted_container.begin(), sorted_container.end(), comparator_); - - if (!listener->IsInterested()) { - // If the listener is not interested, we do not need to - // construct the inner explanation. - return matcher_.Matches(sorted_container); - } - - *listener << "which is "; - UniversalPrint(sorted_container, listener->stream()); - *listener << " when sorted"; - - StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; - const bool match = matcher_.MatchAndExplain(sorted_container, - &inner_listener); - PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); - return match; - } - - private: - const Comparator comparator_; - const Matcher<const ::std::vector<LhsValue>&> matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - private: - const Comparator comparator_; - const ContainerMatcher matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(WhenSortedByMatcher); -}; - -// Implements Pointwise(tuple_matcher, rhs_container). tuple_matcher -// must be able to be safely cast to Matcher<tuple<const T1&, const -// T2&> >, where T1 and T2 are the types of elements in the LHS -// container and the RHS container respectively. -template <typename TupleMatcher, typename RhsContainer> -class PointwiseMatcher { - public: - typedef internal::StlContainerView<RhsContainer> RhsView; - typedef typename RhsView::type RhsStlContainer; - typedef typename RhsStlContainer::value_type RhsValue; - - // Like ContainerEq, we make a copy of rhs in case the elements in - // it are modified after this matcher is created. - PointwiseMatcher(const TupleMatcher& tuple_matcher, const RhsContainer& rhs) - : tuple_matcher_(tuple_matcher), rhs_(RhsView::Copy(rhs)) { - // Makes sure the user doesn't instantiate this class template - // with a const or reference type. - (void)testing::StaticAssertTypeEq<RhsContainer, - GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(RhsContainer)>(); - } - - template <typename LhsContainer> - operator Matcher<LhsContainer>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new Impl<LhsContainer>(tuple_matcher_, rhs_)); - } - - template <typename LhsContainer> - class Impl : public MatcherInterface<LhsContainer> { - public: - typedef internal::StlContainerView< - GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(LhsContainer)> LhsView; - typedef typename LhsView::type LhsStlContainer; - typedef typename LhsView::const_reference LhsStlContainerReference; - typedef typename LhsStlContainer::value_type LhsValue; - // We pass the LHS value and the RHS value to the inner matcher by - // reference, as they may be expensive to copy. We must use tuple - // instead of pair here, as a pair cannot hold references (C++ 98, - // 20.2.2 [lib.pairs]). - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<const LhsValue&, const RhsValue&> InnerMatcherArg; - - Impl(const TupleMatcher& tuple_matcher, const RhsStlContainer& rhs) - // mono_tuple_matcher_ holds a monomorphic version of the tuple matcher. - : mono_tuple_matcher_(SafeMatcherCast<InnerMatcherArg>(tuple_matcher)), - rhs_(rhs) {} - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "contains " << rhs_.size() - << " values, where each value and its corresponding value in "; - UniversalPrinter<RhsStlContainer>::Print(rhs_, os); - *os << " "; - mono_tuple_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "doesn't contain exactly " << rhs_.size() - << " values, or contains a value x at some index i" - << " where x and the i-th value of "; - UniversalPrint(rhs_, os); - *os << " "; - mono_tuple_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(LhsContainer lhs, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - LhsStlContainerReference lhs_stl_container = LhsView::ConstReference(lhs); - const size_t actual_size = lhs_stl_container.size(); - if (actual_size != rhs_.size()) { - *listener << "which contains " << actual_size << " values"; - return false; - } - - typename LhsStlContainer::const_iterator left = lhs_stl_container.begin(); - typename RhsStlContainer::const_iterator right = rhs_.begin(); - for (size_t i = 0; i != actual_size; ++i, ++left, ++right) { - const InnerMatcherArg value_pair(*left, *right); - - if (listener->IsInterested()) { - StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; - if (!mono_tuple_matcher_.MatchAndExplain( - value_pair, &inner_listener)) { - *listener << "where the value pair ("; - UniversalPrint(*left, listener->stream()); - *listener << ", "; - UniversalPrint(*right, listener->stream()); - *listener << ") at index #" << i << " don't match"; - PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); - return false; - } - } else { - if (!mono_tuple_matcher_.Matches(value_pair)) - return false; - } - } - - return true; - } - - private: - const Matcher<InnerMatcherArg> mono_tuple_matcher_; - const RhsStlContainer rhs_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(Impl); - }; - - private: - const TupleMatcher tuple_matcher_; - const RhsStlContainer rhs_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(PointwiseMatcher); -}; - -// Holds the logic common to ContainsMatcherImpl and EachMatcherImpl. -template <typename Container> -class QuantifierMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<Container> { - public: - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; - typedef StlContainerView<RawContainer> View; - typedef typename View::type StlContainer; - typedef typename View::const_reference StlContainerReference; - typedef typename StlContainer::value_type Element; - - template <typename InnerMatcher> - explicit QuantifierMatcherImpl(InnerMatcher inner_matcher) - : inner_matcher_( - testing::SafeMatcherCast<const Element&>(inner_matcher)) {} - - // Checks whether: - // * All elements in the container match, if all_elements_should_match. - // * Any element in the container matches, if !all_elements_should_match. - bool MatchAndExplainImpl(bool all_elements_should_match, - Container container, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - StlContainerReference stl_container = View::ConstReference(container); - size_t i = 0; - for (typename StlContainer::const_iterator it = stl_container.begin(); - it != stl_container.end(); ++it, ++i) { - StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; - const bool matches = inner_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(*it, &inner_listener); - - if (matches != all_elements_should_match) { - *listener << "whose element #" << i - << (matches ? " matches" : " doesn't match"); - PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); - return !all_elements_should_match; - } - } - return all_elements_should_match; - } - - protected: - const Matcher<const Element&> inner_matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(QuantifierMatcherImpl); -}; - -// Implements Contains(element_matcher) for the given argument type Container. -// Symmetric to EachMatcherImpl. -template <typename Container> -class ContainsMatcherImpl : public QuantifierMatcherImpl<Container> { - public: - template <typename InnerMatcher> - explicit ContainsMatcherImpl(InnerMatcher inner_matcher) - : QuantifierMatcherImpl<Container>(inner_matcher) {} - - // Describes what this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "contains at least one element that "; - this->inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "doesn't contain any element that "; - this->inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return this->MatchAndExplainImpl(false, container, listener); - } - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ContainsMatcherImpl); -}; - -// Implements Each(element_matcher) for the given argument type Container. -// Symmetric to ContainsMatcherImpl. -template <typename Container> -class EachMatcherImpl : public QuantifierMatcherImpl<Container> { - public: - template <typename InnerMatcher> - explicit EachMatcherImpl(InnerMatcher inner_matcher) - : QuantifierMatcherImpl<Container>(inner_matcher) {} - - // Describes what this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "only contains elements that "; - this->inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "contains some element that "; - this->inner_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - return this->MatchAndExplainImpl(true, container, listener); - } - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(EachMatcherImpl); -}; - -// Implements polymorphic Contains(element_matcher). -template <typename M> -class ContainsMatcher { - public: - explicit ContainsMatcher(M m) : inner_matcher_(m) {} - - template <typename Container> - operator Matcher<Container>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new ContainsMatcherImpl<Container>(inner_matcher_)); - } - - private: - const M inner_matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ContainsMatcher); -}; - -// Implements polymorphic Each(element_matcher). -template <typename M> -class EachMatcher { - public: - explicit EachMatcher(M m) : inner_matcher_(m) {} - - template <typename Container> - operator Matcher<Container>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new EachMatcherImpl<Container>(inner_matcher_)); - } - - private: - const M inner_matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(EachMatcher); -}; - -// Implements Key(inner_matcher) for the given argument pair type. -// Key(inner_matcher) matches an std::pair whose 'first' field matches -// inner_matcher. For example, Contains(Key(Ge(5))) can be used to match an -// std::map that contains at least one element whose key is >= 5. -template <typename PairType> -class KeyMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<PairType> { - public: - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(PairType) RawPairType; - typedef typename RawPairType::first_type KeyType; - - template <typename InnerMatcher> - explicit KeyMatcherImpl(InnerMatcher inner_matcher) - : inner_matcher_( - testing::SafeMatcherCast<const KeyType&>(inner_matcher)) { - } - - // Returns true iff 'key_value.first' (the key) matches the inner matcher. - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(PairType key_value, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; - const bool match = inner_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(key_value.first, - &inner_listener); - const internal::string explanation = inner_listener.str(); - if (explanation != "") { - *listener << "whose first field is a value " << explanation; - } - return match; - } - - // Describes what this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "has a key that "; - inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - // Describes what the negation of this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "doesn't have a key that "; - inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - private: - const Matcher<const KeyType&> inner_matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(KeyMatcherImpl); -}; - -// Implements polymorphic Key(matcher_for_key). -template <typename M> -class KeyMatcher { - public: - explicit KeyMatcher(M m) : matcher_for_key_(m) {} - - template <typename PairType> - operator Matcher<PairType>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new KeyMatcherImpl<PairType>(matcher_for_key_)); - } - - private: - const M matcher_for_key_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(KeyMatcher); -}; - -// Implements Pair(first_matcher, second_matcher) for the given argument pair -// type with its two matchers. See Pair() function below. -template <typename PairType> -class PairMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<PairType> { - public: - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(PairType) RawPairType; - typedef typename RawPairType::first_type FirstType; - typedef typename RawPairType::second_type SecondType; - - template <typename FirstMatcher, typename SecondMatcher> - PairMatcherImpl(FirstMatcher first_matcher, SecondMatcher second_matcher) - : first_matcher_( - testing::SafeMatcherCast<const FirstType&>(first_matcher)), - second_matcher_( - testing::SafeMatcherCast<const SecondType&>(second_matcher)) { - } - - // Describes what this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "has a first field that "; - first_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - *os << ", and has a second field that "; - second_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - // Describes what the negation of this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "has a first field that "; - first_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - *os << ", or has a second field that "; - second_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - // Returns true iff 'a_pair.first' matches first_matcher and 'a_pair.second' - // matches second_matcher. - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(PairType a_pair, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - if (!listener->IsInterested()) { - // If the listener is not interested, we don't need to construct the - // explanation. - return first_matcher_.Matches(a_pair.first) && - second_matcher_.Matches(a_pair.second); - } - StringMatchResultListener first_inner_listener; - if (!first_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(a_pair.first, - &first_inner_listener)) { - *listener << "whose first field does not match"; - PrintIfNotEmpty(first_inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); - return false; - } - StringMatchResultListener second_inner_listener; - if (!second_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(a_pair.second, - &second_inner_listener)) { - *listener << "whose second field does not match"; - PrintIfNotEmpty(second_inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); - return false; - } - ExplainSuccess(first_inner_listener.str(), second_inner_listener.str(), - listener); - return true; - } - - private: - void ExplainSuccess(const internal::string& first_explanation, - const internal::string& second_explanation, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - *listener << "whose both fields match"; - if (first_explanation != "") { - *listener << ", where the first field is a value " << first_explanation; - } - if (second_explanation != "") { - *listener << ", "; - if (first_explanation != "") { - *listener << "and "; - } else { - *listener << "where "; - } - *listener << "the second field is a value " << second_explanation; - } - } - - const Matcher<const FirstType&> first_matcher_; - const Matcher<const SecondType&> second_matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(PairMatcherImpl); -}; - -// Implements polymorphic Pair(first_matcher, second_matcher). -template <typename FirstMatcher, typename SecondMatcher> -class PairMatcher { - public: - PairMatcher(FirstMatcher first_matcher, SecondMatcher second_matcher) - : first_matcher_(first_matcher), second_matcher_(second_matcher) {} - - template <typename PairType> - operator Matcher<PairType> () const { - return MakeMatcher( - new PairMatcherImpl<PairType>( - first_matcher_, second_matcher_)); - } - - private: - const FirstMatcher first_matcher_; - const SecondMatcher second_matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(PairMatcher); -}; - -// Implements ElementsAre() and ElementsAreArray(). -template <typename Container> -class ElementsAreMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<Container> { - public: - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; - typedef internal::StlContainerView<RawContainer> View; - typedef typename View::type StlContainer; - typedef typename View::const_reference StlContainerReference; - typedef typename StlContainer::value_type Element; - - // Constructs the matcher from a sequence of element values or - // element matchers. - template <typename InputIter> - ElementsAreMatcherImpl(InputIter first, InputIter last) { - while (first != last) { - matchers_.push_back(MatcherCast<const Element&>(*first++)); - } - } - - // Describes what this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - if (count() == 0) { - *os << "is empty"; - } else if (count() == 1) { - *os << "has 1 element that "; - matchers_[0].DescribeTo(os); - } else { - *os << "has " << Elements(count()) << " where\n"; - for (size_t i = 0; i != count(); ++i) { - *os << "element #" << i << " "; - matchers_[i].DescribeTo(os); - if (i + 1 < count()) { - *os << ",\n"; - } - } - } - } - - // Describes what the negation of this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - if (count() == 0) { - *os << "isn't empty"; - return; - } - - *os << "doesn't have " << Elements(count()) << ", or\n"; - for (size_t i = 0; i != count(); ++i) { - *os << "element #" << i << " "; - matchers_[i].DescribeNegationTo(os); - if (i + 1 < count()) { - *os << ", or\n"; - } - } - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - // To work with stream-like "containers", we must only walk - // through the elements in one pass. - - const bool listener_interested = listener->IsInterested(); - - // explanations[i] is the explanation of the element at index i. - ::std::vector<internal::string> explanations(count()); - StlContainerReference stl_container = View::ConstReference(container); - typename StlContainer::const_iterator it = stl_container.begin(); - size_t exam_pos = 0; - bool mismatch_found = false; // Have we found a mismatched element yet? - - // Go through the elements and matchers in pairs, until we reach - // the end of either the elements or the matchers, or until we find a - // mismatch. - for (; it != stl_container.end() && exam_pos != count(); ++it, ++exam_pos) { - bool match; // Does the current element match the current matcher? - if (listener_interested) { - StringMatchResultListener s; - match = matchers_[exam_pos].MatchAndExplain(*it, &s); - explanations[exam_pos] = s.str(); - } else { - match = matchers_[exam_pos].Matches(*it); - } - - if (!match) { - mismatch_found = true; - break; - } - } - // If mismatch_found is true, 'exam_pos' is the index of the mismatch. - - // Find how many elements the actual container has. We avoid - // calling size() s.t. this code works for stream-like "containers" - // that don't define size(). - size_t actual_count = exam_pos; - for (; it != stl_container.end(); ++it) { - ++actual_count; - } - - if (actual_count != count()) { - // The element count doesn't match. If the container is empty, - // there's no need to explain anything as Google Mock already - // prints the empty container. Otherwise we just need to show - // how many elements there actually are. - if (listener_interested && (actual_count != 0)) { - *listener << "which has " << Elements(actual_count); - } - return false; - } - - if (mismatch_found) { - // The element count matches, but the exam_pos-th element doesn't match. - if (listener_interested) { - *listener << "whose element #" << exam_pos << " doesn't match"; - PrintIfNotEmpty(explanations[exam_pos], listener->stream()); - } - return false; - } - - // Every element matches its expectation. We need to explain why - // (the obvious ones can be skipped). - if (listener_interested) { - bool reason_printed = false; - for (size_t i = 0; i != count(); ++i) { - const internal::string& s = explanations[i]; - if (!s.empty()) { - if (reason_printed) { - *listener << ",\nand "; - } - *listener << "whose element #" << i << " matches, " << s; - reason_printed = true; - } - } - } - return true; - } - - private: - static Message Elements(size_t count) { - return Message() << count << (count == 1 ? " element" : " elements"); - } - - size_t count() const { return matchers_.size(); } - - ::std::vector<Matcher<const Element&> > matchers_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ElementsAreMatcherImpl); -}; - -// Connectivity matrix of (elements X matchers), in element-major order. -// Initially, there are no edges. -// Use NextGraph() to iterate over all possible edge configurations. -// Use Randomize() to generate a random edge configuration. -class GTEST_API_ MatchMatrix { - public: - MatchMatrix(size_t num_elements, size_t num_matchers) - : num_elements_(num_elements), - num_matchers_(num_matchers), - matched_(num_elements_* num_matchers_, 0) { - } - - size_t LhsSize() const { return num_elements_; } - size_t RhsSize() const { return num_matchers_; } - bool HasEdge(size_t ilhs, size_t irhs) const { - return matched_[SpaceIndex(ilhs, irhs)] == 1; - } - void SetEdge(size_t ilhs, size_t irhs, bool b) { - matched_[SpaceIndex(ilhs, irhs)] = b ? 1 : 0; - } - - // Treating the connectivity matrix as a (LhsSize()*RhsSize())-bit number, - // adds 1 to that number; returns false if incrementing the graph left it - // empty. - bool NextGraph(); - - void Randomize(); - - string DebugString() const; - - private: - size_t SpaceIndex(size_t ilhs, size_t irhs) const { - return ilhs * num_matchers_ + irhs; - } - - size_t num_elements_; - size_t num_matchers_; - - // Each element is a char interpreted as bool. They are stored as a - // flattened array in lhs-major order, use 'SpaceIndex()' to translate - // a (ilhs, irhs) matrix coordinate into an offset. - ::std::vector<char> matched_; -}; - -typedef ::std::pair<size_t, size_t> ElementMatcherPair; -typedef ::std::vector<ElementMatcherPair> ElementMatcherPairs; - -// Returns a maximum bipartite matching for the specified graph 'g'. -// The matching is represented as a vector of {element, matcher} pairs. -GTEST_API_ ElementMatcherPairs -FindMaxBipartiteMatching(const MatchMatrix& g); - -GTEST_API_ bool FindPairing(const MatchMatrix& matrix, - MatchResultListener* listener); - -// Untyped base class for implementing UnorderedElementsAre. By -// putting logic that's not specific to the element type here, we -// reduce binary bloat and increase compilation speed. -class GTEST_API_ UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase { - protected: - // A vector of matcher describers, one for each element matcher. - // Does not own the describers (and thus can be used only when the - // element matchers are alive). - typedef ::std::vector<const MatcherDescriberInterface*> MatcherDescriberVec; - - // Describes this UnorderedElementsAre matcher. - void DescribeToImpl(::std::ostream* os) const; - - // Describes the negation of this UnorderedElementsAre matcher. - void DescribeNegationToImpl(::std::ostream* os) const; - - bool VerifyAllElementsAndMatchersAreMatched( - const ::std::vector<string>& element_printouts, - const MatchMatrix& matrix, - MatchResultListener* listener) const; - - MatcherDescriberVec& matcher_describers() { - return matcher_describers_; - } - - static Message Elements(size_t n) { - return Message() << n << " element" << (n == 1 ? "" : "s"); - } - - private: - MatcherDescriberVec matcher_describers_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase); -}; - -// Implements unordered ElementsAre and unordered ElementsAreArray. -template <typename Container> -class UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImpl - : public MatcherInterface<Container>, - public UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase { - public: - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; - typedef internal::StlContainerView<RawContainer> View; - typedef typename View::type StlContainer; - typedef typename View::const_reference StlContainerReference; - typedef typename StlContainer::const_iterator StlContainerConstIterator; - typedef typename StlContainer::value_type Element; - - // Constructs the matcher from a sequence of element values or - // element matchers. - template <typename InputIter> - UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImpl(InputIter first, InputIter last) { - for (; first != last; ++first) { - matchers_.push_back(MatcherCast<const Element&>(*first)); - matcher_describers().push_back(matchers_.back().GetDescriber()); - } - } - - // Describes what this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - return UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase::DescribeToImpl(os); - } - - // Describes what the negation of this matcher does. - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - return UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase::DescribeNegationToImpl(os); - } - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - StlContainerReference stl_container = View::ConstReference(container); - ::std::vector<string> element_printouts; - MatchMatrix matrix = AnalyzeElements(stl_container.begin(), - stl_container.end(), - &element_printouts, - listener); - - const size_t actual_count = matrix.LhsSize(); - if (actual_count == 0 && matchers_.empty()) { - return true; - } - if (actual_count != matchers_.size()) { - // The element count doesn't match. If the container is empty, - // there's no need to explain anything as Google Mock already - // prints the empty container. Otherwise we just need to show - // how many elements there actually are. - if (actual_count != 0 && listener->IsInterested()) { - *listener << "which has " << Elements(actual_count); - } - return false; - } - - return VerifyAllElementsAndMatchersAreMatched(element_printouts, - matrix, listener) && - FindPairing(matrix, listener); - } - - private: - typedef ::std::vector<Matcher<const Element&> > MatcherVec; - - template <typename ElementIter> - MatchMatrix AnalyzeElements(ElementIter elem_first, ElementIter elem_last, - ::std::vector<string>* element_printouts, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - element_printouts->clear(); - ::std::vector<char> did_match; - size_t num_elements = 0; - for (; elem_first != elem_last; ++num_elements, ++elem_first) { - if (listener->IsInterested()) { - element_printouts->push_back(PrintToString(*elem_first)); - } - for (size_t irhs = 0; irhs != matchers_.size(); ++irhs) { - did_match.push_back(Matches(matchers_[irhs])(*elem_first)); - } - } - - MatchMatrix matrix(num_elements, matchers_.size()); - ::std::vector<char>::const_iterator did_match_iter = did_match.begin(); - for (size_t ilhs = 0; ilhs != num_elements; ++ilhs) { - for (size_t irhs = 0; irhs != matchers_.size(); ++irhs) { - matrix.SetEdge(ilhs, irhs, *did_match_iter++ != 0); - } - } - return matrix; - } - - MatcherVec matchers_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImpl); -}; - -// Functor for use in TransformTuple. -// Performs MatcherCast<Target> on an input argument of any type. -template <typename Target> -struct CastAndAppendTransform { - template <typename Arg> - Matcher<Target> operator()(const Arg& a) const { - return MatcherCast<Target>(a); - } -}; - -// Implements UnorderedElementsAre. -template <typename MatcherTuple> -class UnorderedElementsAreMatcher { - public: - explicit UnorderedElementsAreMatcher(const MatcherTuple& args) - : matchers_(args) {} - - template <typename Container> - operator Matcher<Container>() const { - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; - typedef typename internal::StlContainerView<RawContainer>::type View; - typedef typename View::value_type Element; - typedef ::std::vector<Matcher<const Element&> > MatcherVec; - MatcherVec matchers; - matchers.reserve(::std::tr1::tuple_size<MatcherTuple>::value); - TransformTupleValues(CastAndAppendTransform<const Element&>(), matchers_, - ::std::back_inserter(matchers)); - return MakeMatcher(new UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImpl<Container>( - matchers.begin(), matchers.end())); - } - - private: - const MatcherTuple matchers_; - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(UnorderedElementsAreMatcher); -}; - -// Implements ElementsAre. -template <typename MatcherTuple> -class ElementsAreMatcher { - public: - explicit ElementsAreMatcher(const MatcherTuple& args) : matchers_(args) {} - - template <typename Container> - operator Matcher<Container>() const { - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; - typedef typename internal::StlContainerView<RawContainer>::type View; - typedef typename View::value_type Element; - typedef ::std::vector<Matcher<const Element&> > MatcherVec; - MatcherVec matchers; - matchers.reserve(::std::tr1::tuple_size<MatcherTuple>::value); - TransformTupleValues(CastAndAppendTransform<const Element&>(), matchers_, - ::std::back_inserter(matchers)); - return MakeMatcher(new ElementsAreMatcherImpl<Container>( - matchers.begin(), matchers.end())); - } - - private: - const MatcherTuple matchers_; - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ElementsAreMatcher); -}; - -// Implements UnorderedElementsAreArray(). -template <typename T> -class UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher { - public: - UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher() {} - - template <typename Iter> - UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher(Iter first, Iter last) - : matchers_(first, last) {} - - template <typename Container> - operator Matcher<Container>() const { - return MakeMatcher( - new UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImpl<Container>(matchers_.begin(), - matchers_.end())); - } - - private: - ::std::vector<T> matchers_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher); -}; - -// Implements ElementsAreArray(). -template <typename T> -class ElementsAreArrayMatcher { - public: - template <typename Iter> - ElementsAreArrayMatcher(Iter first, Iter last) : matchers_(first, last) {} - - template <typename Container> - operator Matcher<Container>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new ElementsAreMatcherImpl<Container>( - matchers_.begin(), matchers_.end())); - } - - private: - const ::std::vector<T> matchers_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ElementsAreArrayMatcher); -}; - -// Returns the description for a matcher defined using the MATCHER*() -// macro where the user-supplied description string is "", if -// 'negation' is false; otherwise returns the description of the -// negation of the matcher. 'param_values' contains a list of strings -// that are the print-out of the matcher's parameters. -GTEST_API_ string FormatMatcherDescription(bool negation, - const char* matcher_name, - const Strings& param_values); - -} // namespace internal - -// ElementsAreArray(first, last) -// ElementsAreArray(pointer, count) -// ElementsAreArray(array) -// ElementsAreArray(vector) -// ElementsAreArray({ e1, e2, ..., en }) -// -// The ElementsAreArray() functions are like ElementsAre(...), except -// that they are given a homogeneous sequence rather than taking each -// element as a function argument. The sequence can be specified as an -// array, a pointer and count, a vector, an initializer list, or an -// STL iterator range. In each of these cases, the underlying sequence -// can be either a sequence of values or a sequence of matchers. -// -// All forms of ElementsAreArray() make a copy of the input matcher sequence. - -template <typename Iter> -inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher< - typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type> -ElementsAreArray(Iter first, Iter last) { - typedef typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type T; - return internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<T>(first, last); -} - -template <typename T> -inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> ElementsAreArray( - const T* pointer, size_t count) { - return ElementsAreArray(pointer, pointer + count); -} - -template <typename T, size_t N> -inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> ElementsAreArray( - const T (&array)[N]) { - return ElementsAreArray(array, N); -} - -template <typename T, typename A> -inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> ElementsAreArray( - const ::std::vector<T, A>& vec) { - return ElementsAreArray(vec.begin(), vec.end()); -} - -#if GTEST_LANG_CXX11 -template <typename T> -inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> -ElementsAreArray(::std::initializer_list<T> xs) { - return ElementsAreArray(xs.begin(), xs.end()); -} -#endif - -// UnorderedElementsAreArray(first, last) -// UnorderedElementsAreArray(pointer, count) -// UnorderedElementsAreArray(array) -// UnorderedElementsAreArray(vector) -// UnorderedElementsAreArray({ e1, e2, ..., en }) -// -// The UnorderedElementsAreArray() functions are like -// ElementsAreArray(...), but allow matching the elements in any order. -template <typename Iter> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher< - typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type> -UnorderedElementsAreArray(Iter first, Iter last) { - typedef typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type T; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T>(first, last); -} - -template <typename T> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> -UnorderedElementsAreArray(const T* pointer, size_t count) { - return UnorderedElementsAreArray(pointer, pointer + count); -} - -template <typename T, size_t N> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> -UnorderedElementsAreArray(const T (&array)[N]) { - return UnorderedElementsAreArray(array, N); -} - -template <typename T, typename A> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> -UnorderedElementsAreArray(const ::std::vector<T, A>& vec) { - return UnorderedElementsAreArray(vec.begin(), vec.end()); -} - -#if GTEST_LANG_CXX11 -template <typename T> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> -UnorderedElementsAreArray(::std::initializer_list<T> xs) { - return UnorderedElementsAreArray(xs.begin(), xs.end()); -} -#endif - -// _ is a matcher that matches anything of any type. -// -// This definition is fine as: -// -// 1. The C++ standard permits using the name _ in a namespace that -// is not the global namespace or ::std. -// 2. The AnythingMatcher class has no data member or constructor, -// so it's OK to create global variables of this type. -// 3. c-style has approved of using _ in this case. -const internal::AnythingMatcher _ = {}; -// Creates a matcher that matches any value of the given type T. -template <typename T> -inline Matcher<T> A() { return MakeMatcher(new internal::AnyMatcherImpl<T>()); } - -// Creates a matcher that matches any value of the given type T. -template <typename T> -inline Matcher<T> An() { return A<T>(); } - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything equal to x. -// Note: if the parameter of Eq() were declared as const T&, Eq("foo") -// wouldn't compile. -template <typename T> -inline internal::EqMatcher<T> Eq(T x) { return internal::EqMatcher<T>(x); } - -// Constructs a Matcher<T> from a 'value' of type T. The constructed -// matcher matches any value that's equal to 'value'. -template <typename T> -Matcher<T>::Matcher(T value) { *this = Eq(value); } - -// Creates a monomorphic matcher that matches anything with type Lhs -// and equal to rhs. A user may need to use this instead of Eq(...) -// in order to resolve an overloading ambiguity. -// -// TypedEq<T>(x) is just a convenient short-hand for Matcher<T>(Eq(x)) -// or Matcher<T>(x), but more readable than the latter. -// -// We could define similar monomorphic matchers for other comparison -// operations (e.g. TypedLt, TypedGe, and etc), but decided not to do -// it yet as those are used much less than Eq() in practice. A user -// can always write Matcher<T>(Lt(5)) to be explicit about the type, -// for example. -template <typename Lhs, typename Rhs> -inline Matcher<Lhs> TypedEq(const Rhs& rhs) { return Eq(rhs); } - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything >= x. -template <typename Rhs> -inline internal::GeMatcher<Rhs> Ge(Rhs x) { - return internal::GeMatcher<Rhs>(x); -} - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything > x. -template <typename Rhs> -inline internal::GtMatcher<Rhs> Gt(Rhs x) { - return internal::GtMatcher<Rhs>(x); -} - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything <= x. -template <typename Rhs> -inline internal::LeMatcher<Rhs> Le(Rhs x) { - return internal::LeMatcher<Rhs>(x); -} - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything < x. -template <typename Rhs> -inline internal::LtMatcher<Rhs> Lt(Rhs x) { - return internal::LtMatcher<Rhs>(x); -} - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything != x. -template <typename Rhs> -inline internal::NeMatcher<Rhs> Ne(Rhs x) { - return internal::NeMatcher<Rhs>(x); -} - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches any NULL pointer. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::IsNullMatcher > IsNull() { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::IsNullMatcher()); -} - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches any non-NULL pointer. -// This is convenient as Not(NULL) doesn't compile (the compiler -// thinks that that expression is comparing a pointer with an integer). -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::NotNullMatcher > NotNull() { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::NotNullMatcher()); -} - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches any argument that -// references variable x. -template <typename T> -inline internal::RefMatcher<T&> Ref(T& x) { // NOLINT - return internal::RefMatcher<T&>(x); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any double argument approximately -// equal to rhs, where two NANs are considered unequal. -inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double> DoubleEq(double rhs) { - return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double>(rhs, false); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any double argument approximately -// equal to rhs, including NaN values when rhs is NaN. -inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double> NanSensitiveDoubleEq(double rhs) { - return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double>(rhs, true); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any double argument approximately equal to -// rhs, up to the specified max absolute error bound, where two NANs are -// considered unequal. The max absolute error bound must be non-negative. -inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double> DoubleNear( - double rhs, double max_abs_error) { - return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double>(rhs, false, max_abs_error); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any double argument approximately equal to -// rhs, up to the specified max absolute error bound, including NaN values when -// rhs is NaN. The max absolute error bound must be non-negative. -inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double> NanSensitiveDoubleNear( - double rhs, double max_abs_error) { - return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double>(rhs, true, max_abs_error); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any float argument approximately -// equal to rhs, where two NANs are considered unequal. -inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float> FloatEq(float rhs) { - return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float>(rhs, false); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any float argument approximately -// equal to rhs, including NaN values when rhs is NaN. -inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float> NanSensitiveFloatEq(float rhs) { - return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float>(rhs, true); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any float argument approximately equal to -// rhs, up to the specified max absolute error bound, where two NANs are -// considered unequal. The max absolute error bound must be non-negative. -inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float> FloatNear( - float rhs, float max_abs_error) { - return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float>(rhs, false, max_abs_error); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any float argument approximately equal to -// rhs, up to the specified max absolute error bound, including NaN values when -// rhs is NaN. The max absolute error bound must be non-negative. -inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float> NanSensitiveFloatNear( - float rhs, float max_abs_error) { - return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float>(rhs, true, max_abs_error); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches a pointer (raw or smart) that points -// to a value that matches inner_matcher. -template <typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::PointeeMatcher<InnerMatcher> Pointee( - const InnerMatcher& inner_matcher) { - return internal::PointeeMatcher<InnerMatcher>(inner_matcher); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches an object whose given field matches -// 'matcher'. For example, -// Field(&Foo::number, Ge(5)) -// matches a Foo object x iff x.number >= 5. -template <typename Class, typename FieldType, typename FieldMatcher> -inline PolymorphicMatcher< - internal::FieldMatcher<Class, FieldType> > Field( - FieldType Class::*field, const FieldMatcher& matcher) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher( - internal::FieldMatcher<Class, FieldType>( - field, MatcherCast<const FieldType&>(matcher))); - // The call to MatcherCast() is required for supporting inner - // matchers of compatible types. For example, it allows - // Field(&Foo::bar, m) - // to compile where bar is an int32 and m is a matcher for int64. -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches an object whose given property -// matches 'matcher'. For example, -// Property(&Foo::str, StartsWith("hi")) -// matches a Foo object x iff x.str() starts with "hi". -template <typename Class, typename PropertyType, typename PropertyMatcher> -inline PolymorphicMatcher< - internal::PropertyMatcher<Class, PropertyType> > Property( - PropertyType (Class::*property)() const, const PropertyMatcher& matcher) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher( - internal::PropertyMatcher<Class, PropertyType>( - property, - MatcherCast<GTEST_REFERENCE_TO_CONST_(PropertyType)>(matcher))); - // The call to MatcherCast() is required for supporting inner - // matchers of compatible types. For example, it allows - // Property(&Foo::bar, m) - // to compile where bar() returns an int32 and m is a matcher for int64. -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches an object iff the result of applying -// a callable to x matches 'matcher'. -// For example, -// ResultOf(f, StartsWith("hi")) -// matches a Foo object x iff f(x) starts with "hi". -// callable parameter can be a function, function pointer, or a functor. -// Callable has to satisfy the following conditions: -// * It is required to keep no state affecting the results of -// the calls on it and make no assumptions about how many calls -// will be made. Any state it keeps must be protected from the -// concurrent access. -// * If it is a function object, it has to define type result_type. -// We recommend deriving your functor classes from std::unary_function. -template <typename Callable, typename ResultOfMatcher> -internal::ResultOfMatcher<Callable> ResultOf( - Callable callable, const ResultOfMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ResultOfMatcher<Callable>( - callable, - MatcherCast<typename internal::CallableTraits<Callable>::ResultType>( - matcher)); - // The call to MatcherCast() is required for supporting inner - // matchers of compatible types. For example, it allows - // ResultOf(Function, m) - // to compile where Function() returns an int32 and m is a matcher for int64. -} - -// String matchers. - -// Matches a string equal to str. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::string> > - StrEq(const internal::string& str) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::string>( - str, true, true)); -} - -// Matches a string not equal to str. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::string> > - StrNe(const internal::string& str) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::string>( - str, false, true)); -} - -// Matches a string equal to str, ignoring case. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::string> > - StrCaseEq(const internal::string& str) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::string>( - str, true, false)); -} - -// Matches a string not equal to str, ignoring case. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::string> > - StrCaseNe(const internal::string& str) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::string>( - str, false, false)); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any string, std::string, or C string -// that contains the given substring. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::HasSubstrMatcher<internal::string> > - HasSubstr(const internal::string& substring) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::HasSubstrMatcher<internal::string>( - substring)); -} - -// Matches a string that starts with 'prefix' (case-sensitive). -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StartsWithMatcher<internal::string> > - StartsWith(const internal::string& prefix) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StartsWithMatcher<internal::string>( - prefix)); -} - -// Matches a string that ends with 'suffix' (case-sensitive). -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::EndsWithMatcher<internal::string> > - EndsWith(const internal::string& suffix) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::EndsWithMatcher<internal::string>( - suffix)); -} - -// Matches a string that fully matches regular expression 'regex'. -// The matcher takes ownership of 'regex'. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::MatchesRegexMatcher> MatchesRegex( - const internal::RE* regex) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::MatchesRegexMatcher(regex, true)); -} -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::MatchesRegexMatcher> MatchesRegex( - const internal::string& regex) { - return MatchesRegex(new internal::RE(regex)); -} - -// Matches a string that contains regular expression 'regex'. -// The matcher takes ownership of 'regex'. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::MatchesRegexMatcher> ContainsRegex( - const internal::RE* regex) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::MatchesRegexMatcher(regex, false)); -} -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::MatchesRegexMatcher> ContainsRegex( - const internal::string& regex) { - return ContainsRegex(new internal::RE(regex)); -} - -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING || GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING -// Wide string matchers. - -// Matches a string equal to str. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::wstring> > - StrEq(const internal::wstring& str) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::wstring>( - str, true, true)); -} - -// Matches a string not equal to str. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::wstring> > - StrNe(const internal::wstring& str) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::wstring>( - str, false, true)); -} - -// Matches a string equal to str, ignoring case. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::wstring> > - StrCaseEq(const internal::wstring& str) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::wstring>( - str, true, false)); -} - -// Matches a string not equal to str, ignoring case. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::wstring> > - StrCaseNe(const internal::wstring& str) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StrEqualityMatcher<internal::wstring>( - str, false, false)); -} - -// Creates a matcher that matches any wstring, std::wstring, or C wide string -// that contains the given substring. -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::HasSubstrMatcher<internal::wstring> > - HasSubstr(const internal::wstring& substring) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::HasSubstrMatcher<internal::wstring>( - substring)); -} - -// Matches a string that starts with 'prefix' (case-sensitive). -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StartsWithMatcher<internal::wstring> > - StartsWith(const internal::wstring& prefix) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StartsWithMatcher<internal::wstring>( - prefix)); -} - -// Matches a string that ends with 'suffix' (case-sensitive). -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::EndsWithMatcher<internal::wstring> > - EndsWith(const internal::wstring& suffix) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::EndsWithMatcher<internal::wstring>( - suffix)); -} - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING || GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the -// first field == the second field. -inline internal::Eq2Matcher Eq() { return internal::Eq2Matcher(); } - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the -// first field >= the second field. -inline internal::Ge2Matcher Ge() { return internal::Ge2Matcher(); } - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the -// first field > the second field. -inline internal::Gt2Matcher Gt() { return internal::Gt2Matcher(); } - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the -// first field <= the second field. -inline internal::Le2Matcher Le() { return internal::Le2Matcher(); } - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the -// first field < the second field. -inline internal::Lt2Matcher Lt() { return internal::Lt2Matcher(); } - -// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the -// first field != the second field. -inline internal::Ne2Matcher Ne() { return internal::Ne2Matcher(); } - -// Creates a matcher that matches any value of type T that m doesn't -// match. -template <typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::NotMatcher<InnerMatcher> Not(InnerMatcher m) { - return internal::NotMatcher<InnerMatcher>(m); -} - -// Returns a matcher that matches anything that satisfies the given -// predicate. The predicate can be any unary function or functor -// whose return type can be implicitly converted to bool. -template <typename Predicate> -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::TrulyMatcher<Predicate> > -Truly(Predicate pred) { - return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::TrulyMatcher<Predicate>(pred)); -} - -// Returns a matcher that matches the container size. The container must -// support both size() and size_type which all STL-like containers provide. -// Note that the parameter 'size' can be a value of type size_type as well as -// matcher. For instance: -// EXPECT_THAT(container, SizeIs(2)); // Checks container has 2 elements. -// EXPECT_THAT(container, SizeIs(Le(2)); // Checks container has at most 2. -template <typename SizeMatcher> -inline internal::SizeIsMatcher<SizeMatcher> -SizeIs(const SizeMatcher& size_matcher) { - return internal::SizeIsMatcher<SizeMatcher>(size_matcher); -} - -// Returns a matcher that matches an equal container. -// This matcher behaves like Eq(), but in the event of mismatch lists the -// values that are included in one container but not the other. (Duplicate -// values and order differences are not explained.) -template <typename Container> -inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::ContainerEqMatcher< // NOLINT - GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(Container)> > - ContainerEq(const Container& rhs) { - // This following line is for working around a bug in MSVC 8.0, - // which causes Container to be a const type sometimes. - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; - return MakePolymorphicMatcher( - internal::ContainerEqMatcher<RawContainer>(rhs)); -} - -// Returns a matcher that matches a container that, when sorted using -// the given comparator, matches container_matcher. -template <typename Comparator, typename ContainerMatcher> -inline internal::WhenSortedByMatcher<Comparator, ContainerMatcher> -WhenSortedBy(const Comparator& comparator, - const ContainerMatcher& container_matcher) { - return internal::WhenSortedByMatcher<Comparator, ContainerMatcher>( - comparator, container_matcher); -} - -// Returns a matcher that matches a container that, when sorted using -// the < operator, matches container_matcher. -template <typename ContainerMatcher> -inline internal::WhenSortedByMatcher<internal::LessComparator, ContainerMatcher> -WhenSorted(const ContainerMatcher& container_matcher) { - return - internal::WhenSortedByMatcher<internal::LessComparator, ContainerMatcher>( - internal::LessComparator(), container_matcher); -} - -// Matches an STL-style container or a native array that contains the -// same number of elements as in rhs, where its i-th element and rhs's -// i-th element (as a pair) satisfy the given pair matcher, for all i. -// TupleMatcher must be able to be safely cast to Matcher<tuple<const -// T1&, const T2&> >, where T1 and T2 are the types of elements in the -// LHS container and the RHS container respectively. -template <typename TupleMatcher, typename Container> -inline internal::PointwiseMatcher<TupleMatcher, - GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(Container)> -Pointwise(const TupleMatcher& tuple_matcher, const Container& rhs) { - // This following line is for working around a bug in MSVC 8.0, - // which causes Container to be a const type sometimes. - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; - return internal::PointwiseMatcher<TupleMatcher, RawContainer>( - tuple_matcher, rhs); -} - -// Matches an STL-style container or a native array that contains at -// least one element matching the given value or matcher. -// -// Examples: -// ::std::set<int> page_ids; -// page_ids.insert(3); -// page_ids.insert(1); -// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Contains(1)); -// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Contains(Gt(2))); -// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Not(Contains(4))); -// -// ::std::map<int, size_t> page_lengths; -// page_lengths[1] = 100; -// EXPECT_THAT(page_lengths, -// Contains(::std::pair<const int, size_t>(1, 100))); -// -// const char* user_ids[] = { "joe", "mike", "tom" }; -// EXPECT_THAT(user_ids, Contains(Eq(::std::string("tom")))); -template <typename M> -inline internal::ContainsMatcher<M> Contains(M matcher) { - return internal::ContainsMatcher<M>(matcher); -} - -// Matches an STL-style container or a native array that contains only -// elements matching the given value or matcher. -// -// Each(m) is semantically equivalent to Not(Contains(Not(m))). Only -// the messages are different. -// -// Examples: -// ::std::set<int> page_ids; -// // Each(m) matches an empty container, regardless of what m is. -// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Each(Eq(1))); -// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Each(Eq(77))); -// -// page_ids.insert(3); -// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Each(Gt(0))); -// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Not(Each(Gt(4)))); -// page_ids.insert(1); -// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Not(Each(Lt(2)))); -// -// ::std::map<int, size_t> page_lengths; -// page_lengths[1] = 100; -// page_lengths[2] = 200; -// page_lengths[3] = 300; -// EXPECT_THAT(page_lengths, Not(Each(Pair(1, 100)))); -// EXPECT_THAT(page_lengths, Each(Key(Le(3)))); -// -// const char* user_ids[] = { "joe", "mike", "tom" }; -// EXPECT_THAT(user_ids, Not(Each(Eq(::std::string("tom"))))); -template <typename M> -inline internal::EachMatcher<M> Each(M matcher) { - return internal::EachMatcher<M>(matcher); -} - -// Key(inner_matcher) matches an std::pair whose 'first' field matches -// inner_matcher. For example, Contains(Key(Ge(5))) can be used to match an -// std::map that contains at least one element whose key is >= 5. -template <typename M> -inline internal::KeyMatcher<M> Key(M inner_matcher) { - return internal::KeyMatcher<M>(inner_matcher); -} - -// Pair(first_matcher, second_matcher) matches a std::pair whose 'first' field -// matches first_matcher and whose 'second' field matches second_matcher. For -// example, EXPECT_THAT(map_type, ElementsAre(Pair(Ge(5), "foo"))) can be used -// to match a std::map<int, string> that contains exactly one element whose key -// is >= 5 and whose value equals "foo". -template <typename FirstMatcher, typename SecondMatcher> -inline internal::PairMatcher<FirstMatcher, SecondMatcher> -Pair(FirstMatcher first_matcher, SecondMatcher second_matcher) { - return internal::PairMatcher<FirstMatcher, SecondMatcher>( - first_matcher, second_matcher); -} - -// Returns a predicate that is satisfied by anything that matches the -// given matcher. -template <typename M> -inline internal::MatcherAsPredicate<M> Matches(M matcher) { - return internal::MatcherAsPredicate<M>(matcher); -} - -// Returns true iff the value matches the matcher. -template <typename T, typename M> -inline bool Value(const T& value, M matcher) { - return testing::Matches(matcher)(value); -} - -// Matches the value against the given matcher and explains the match -// result to listener. -template <typename T, typename M> -inline bool ExplainMatchResult( - M matcher, const T& value, MatchResultListener* listener) { - return SafeMatcherCast<const T&>(matcher).MatchAndExplain(value, listener); -} - -#if GTEST_LANG_CXX11 -// Define variadic matcher versions. They are overloaded in -// gmock-generated-matchers.h for the cases supported by pre C++11 compilers. -template <typename... Args> -inline internal::AllOfMatcher<Args...> AllOf(const Args&... matchers) { - return internal::AllOfMatcher<Args...>(matchers...); -} - -template <typename... Args> -inline internal::AnyOfMatcher<Args...> AnyOf(const Args&... matchers) { - return internal::AnyOfMatcher<Args...>(matchers...); -} - -#endif // GTEST_LANG_CXX11 - -// AllArgs(m) is a synonym of m. This is useful in -// -// EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar(_, _)).With(AllArgs(Eq())); -// -// which is easier to read than -// -// EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar(_, _)).With(Eq()); -template <typename InnerMatcher> -inline InnerMatcher AllArgs(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { return matcher; } - -// These macros allow using matchers to check values in Google Test -// tests. ASSERT_THAT(value, matcher) and EXPECT_THAT(value, matcher) -// succeed iff the value matches the matcher. If the assertion fails, -// the value and the description of the matcher will be printed. -#define ASSERT_THAT(value, matcher) ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(\ - ::testing::internal::MakePredicateFormatterFromMatcher(matcher), value) -#define EXPECT_THAT(value, matcher) EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(\ - ::testing::internal::MakePredicateFormatterFromMatcher(matcher), value) - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MATCHERS_H_ - -namespace testing { - -// An abstract handle of an expectation. -class Expectation; - -// A set of expectation handles. -class ExpectationSet; - -// Anything inside the 'internal' namespace IS INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION -// and MUST NOT BE USED IN USER CODE!!! -namespace internal { - -// Implements a mock function. -template <typename F> class FunctionMocker; - -// Base class for expectations. -class ExpectationBase; - -// Implements an expectation. -template <typename F> class TypedExpectation; - -// Helper class for testing the Expectation class template. -class ExpectationTester; - -// Base class for function mockers. -template <typename F> class FunctionMockerBase; - -// Protects the mock object registry (in class Mock), all function -// mockers, and all expectations. -// -// The reason we don't use more fine-grained protection is: when a -// mock function Foo() is called, it needs to consult its expectations -// to see which one should be picked. If another thread is allowed to -// call a mock function (either Foo() or a different one) at the same -// time, it could affect the "retired" attributes of Foo()'s -// expectations when InSequence() is used, and thus affect which -// expectation gets picked. Therefore, we sequence all mock function -// calls to ensure the integrity of the mock objects' states. -GTEST_API_ GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_gmock_mutex); - -// Untyped base class for ActionResultHolder<R>. -class UntypedActionResultHolderBase; - -// Abstract base class of FunctionMockerBase. This is the -// type-agnostic part of the function mocker interface. Its pure -// virtual methods are implemented by FunctionMockerBase. -class GTEST_API_ UntypedFunctionMockerBase { - public: - UntypedFunctionMockerBase(); - virtual ~UntypedFunctionMockerBase(); - - // Verifies that all expectations on this mock function have been - // satisfied. Reports one or more Google Test non-fatal failures - // and returns false if not. - bool VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked() - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - // Clears the ON_CALL()s set on this mock function. - virtual void ClearDefaultActionsLocked() - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) = 0; - - // In all of the following Untyped* functions, it's the caller's - // responsibility to guarantee the correctness of the arguments' - // types. - - // Performs the default action with the given arguments and returns - // the action's result. The call description string will be used in - // the error message to describe the call in the case the default - // action fails. - // L = * - virtual UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedPerformDefaultAction( - const void* untyped_args, - const string& call_description) const = 0; - - // Performs the given action with the given arguments and returns - // the action's result. - // L = * - virtual UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedPerformAction( - const void* untyped_action, - const void* untyped_args) const = 0; - - // Writes a message that the call is uninteresting (i.e. neither - // explicitly expected nor explicitly unexpected) to the given - // ostream. - virtual void UntypedDescribeUninterestingCall( - const void* untyped_args, - ::std::ostream* os) const - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) = 0; - - // Returns the expectation that matches the given function arguments - // (or NULL is there's no match); when a match is found, - // untyped_action is set to point to the action that should be - // performed (or NULL if the action is "do default"), and - // is_excessive is modified to indicate whether the call exceeds the - // expected number. - virtual const ExpectationBase* UntypedFindMatchingExpectation( - const void* untyped_args, - const void** untyped_action, bool* is_excessive, - ::std::ostream* what, ::std::ostream* why) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) = 0; - - // Prints the given function arguments to the ostream. - virtual void UntypedPrintArgs(const void* untyped_args, - ::std::ostream* os) const = 0; - - // Sets the mock object this mock method belongs to, and registers - // this information in the global mock registry. Will be called - // whenever an EXPECT_CALL() or ON_CALL() is executed on this mock - // method. - // TODO(wan@google.com): rename to SetAndRegisterOwner(). - void RegisterOwner(const void* mock_obj) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - // Sets the mock object this mock method belongs to, and sets the - // name of the mock function. Will be called upon each invocation - // of this mock function. - void SetOwnerAndName(const void* mock_obj, const char* name) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - // Returns the mock object this mock method belongs to. Must be - // called after RegisterOwner() or SetOwnerAndName() has been - // called. - const void* MockObject() const - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - // Returns the name of this mock method. Must be called after - // SetOwnerAndName() has been called. - const char* Name() const - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - // Returns the result of invoking this mock function with the given - // arguments. This function can be safely called from multiple - // threads concurrently. The caller is responsible for deleting the - // result. - const UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedInvokeWith( - const void* untyped_args) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - protected: - typedef std::vector<const void*> UntypedOnCallSpecs; - - typedef std::vector<internal::linked_ptr<ExpectationBase> > - UntypedExpectations; - - // Returns an Expectation object that references and co-owns exp, - // which must be an expectation on this mock function. - Expectation GetHandleOf(ExpectationBase* exp); - - // Address of the mock object this mock method belongs to. Only - // valid after this mock method has been called or - // ON_CALL/EXPECT_CALL has been invoked on it. - const void* mock_obj_; // Protected by g_gmock_mutex. - - // Name of the function being mocked. Only valid after this mock - // method has been called. - const char* name_; // Protected by g_gmock_mutex. - - // All default action specs for this function mocker. - UntypedOnCallSpecs untyped_on_call_specs_; - - // All expectations for this function mocker. - UntypedExpectations untyped_expectations_; -}; // class UntypedFunctionMockerBase - -// Untyped base class for OnCallSpec<F>. -class UntypedOnCallSpecBase { - public: - // The arguments are the location of the ON_CALL() statement. - UntypedOnCallSpecBase(const char* a_file, int a_line) - : file_(a_file), line_(a_line), last_clause_(kNone) {} - - // Where in the source file was the default action spec defined? - const char* file() const { return file_; } - int line() const { return line_; } - - protected: - // Gives each clause in the ON_CALL() statement a name. - enum Clause { - // Do not change the order of the enum members! The run-time - // syntax checking relies on it. - kNone, - kWith, - kWillByDefault - }; - - // Asserts that the ON_CALL() statement has a certain property. - void AssertSpecProperty(bool property, const string& failure_message) const { - Assert(property, file_, line_, failure_message); - } - - // Expects that the ON_CALL() statement has a certain property. - void ExpectSpecProperty(bool property, const string& failure_message) const { - Expect(property, file_, line_, failure_message); - } - - const char* file_; - int line_; - - // The last clause in the ON_CALL() statement as seen so far. - // Initially kNone and changes as the statement is parsed. - Clause last_clause_; -}; // class UntypedOnCallSpecBase - -// This template class implements an ON_CALL spec. -template <typename F> -class OnCallSpec : public UntypedOnCallSpecBase { - public: - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentMatcherTuple ArgumentMatcherTuple; - - // Constructs an OnCallSpec object from the information inside - // the parenthesis of an ON_CALL() statement. - OnCallSpec(const char* a_file, int a_line, - const ArgumentMatcherTuple& matchers) - : UntypedOnCallSpecBase(a_file, a_line), - matchers_(matchers), - // By default, extra_matcher_ should match anything. However, - // we cannot initialize it with _ as that triggers a compiler - // bug in Symbian's C++ compiler (cannot decide between two - // overloaded constructors of Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&>). - extra_matcher_(A<const ArgumentTuple&>()) { - } - - // Implements the .With() clause. - OnCallSpec& With(const Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&>& m) { - // Makes sure this is called at most once. - ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kWith, - ".With() cannot appear " - "more than once in an ON_CALL()."); - last_clause_ = kWith; - - extra_matcher_ = m; - return *this; - } - - // Implements the .WillByDefault() clause. - OnCallSpec& WillByDefault(const Action<F>& action) { - ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kWillByDefault, - ".WillByDefault() must appear " - "exactly once in an ON_CALL()."); - last_clause_ = kWillByDefault; - - ExpectSpecProperty(!action.IsDoDefault(), - "DoDefault() cannot be used in ON_CALL()."); - action_ = action; - return *this; - } - - // Returns true iff the given arguments match the matchers. - bool Matches(const ArgumentTuple& args) const { - return TupleMatches(matchers_, args) && extra_matcher_.Matches(args); - } - - // Returns the action specified by the user. - const Action<F>& GetAction() const { - AssertSpecProperty(last_clause_ == kWillByDefault, - ".WillByDefault() must appear exactly " - "once in an ON_CALL()."); - return action_; - } - - private: - // The information in statement - // - // ON_CALL(mock_object, Method(matchers)) - // .With(multi-argument-matcher) - // .WillByDefault(action); - // - // is recorded in the data members like this: - // - // source file that contains the statement => file_ - // line number of the statement => line_ - // matchers => matchers_ - // multi-argument-matcher => extra_matcher_ - // action => action_ - ArgumentMatcherTuple matchers_; - Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&> extra_matcher_; - Action<F> action_; -}; // class OnCallSpec - -// Possible reactions on uninteresting calls. -enum CallReaction { - kAllow, - kWarn, - kFail, - kDefault = kWarn // By default, warn about uninteresting calls. -}; - -} // namespace internal - -// Utilities for manipulating mock objects. -class GTEST_API_ Mock { - public: - // The following public methods can be called concurrently. - - // Tells Google Mock to ignore mock_obj when checking for leaked - // mock objects. - static void AllowLeak(const void* mock_obj) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Verifies and clears all expectations on the given mock object. - // If the expectations aren't satisfied, generates one or more - // Google Test non-fatal failures and returns false. - static bool VerifyAndClearExpectations(void* mock_obj) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Verifies all expectations on the given mock object and clears its - // default actions and expectations. Returns true iff the - // verification was successful. - static bool VerifyAndClear(void* mock_obj) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - private: - friend class internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase; - - // Needed for a function mocker to register itself (so that we know - // how to clear a mock object). - template <typename F> - friend class internal::FunctionMockerBase; - - template <typename M> - friend class NiceMock; - - template <typename M> - friend class NaggyMock; - - template <typename M> - friend class StrictMock; - - // Tells Google Mock to allow uninteresting calls on the given mock - // object. - static void AllowUninterestingCalls(const void* mock_obj) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Tells Google Mock to warn the user about uninteresting calls on - // the given mock object. - static void WarnUninterestingCalls(const void* mock_obj) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Tells Google Mock to fail uninteresting calls on the given mock - // object. - static void FailUninterestingCalls(const void* mock_obj) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Tells Google Mock the given mock object is being destroyed and - // its entry in the call-reaction table should be removed. - static void UnregisterCallReaction(const void* mock_obj) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Returns the reaction Google Mock will have on uninteresting calls - // made on the given mock object. - static internal::CallReaction GetReactionOnUninterestingCalls( - const void* mock_obj) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Verifies that all expectations on the given mock object have been - // satisfied. Reports one or more Google Test non-fatal failures - // and returns false if not. - static bool VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked(void* mock_obj) - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Clears all ON_CALL()s set on the given mock object. - static void ClearDefaultActionsLocked(void* mock_obj) - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Registers a mock object and a mock method it owns. - static void Register( - const void* mock_obj, - internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase* mocker) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Tells Google Mock where in the source code mock_obj is used in an - // ON_CALL or EXPECT_CALL. In case mock_obj is leaked, this - // information helps the user identify which object it is. - static void RegisterUseByOnCallOrExpectCall( - const void* mock_obj, const char* file, int line) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); - - // Unregisters a mock method; removes the owning mock object from - // the registry when the last mock method associated with it has - // been unregistered. This is called only in the destructor of - // FunctionMockerBase. - static void UnregisterLocked(internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase* mocker) - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); -}; // class Mock - -// An abstract handle of an expectation. Useful in the .After() -// clause of EXPECT_CALL() for setting the (partial) order of -// expectations. The syntax: -// -// Expectation e1 = EXPECT_CALL(...)...; -// EXPECT_CALL(...).After(e1)...; -// -// sets two expectations where the latter can only be matched after -// the former has been satisfied. -// -// Notes: -// - This class is copyable and has value semantics. -// - Constness is shallow: a const Expectation object itself cannot -// be modified, but the mutable methods of the ExpectationBase -// object it references can be called via expectation_base(). -// - The constructors and destructor are defined out-of-line because -// the Symbian WINSCW compiler wants to otherwise instantiate them -// when it sees this class definition, at which point it doesn't have -// ExpectationBase available yet, leading to incorrect destruction -// in the linked_ptr (or compilation errors if using a checking -// linked_ptr). -class GTEST_API_ Expectation { - public: - // Constructs a null object that doesn't reference any expectation. - Expectation(); - - ~Expectation(); - - // This single-argument ctor must not be explicit, in order to support the - // Expectation e = EXPECT_CALL(...); - // syntax. - // - // A TypedExpectation object stores its pre-requisites as - // Expectation objects, and needs to call the non-const Retire() - // method on the ExpectationBase objects they reference. Therefore - // Expectation must receive a *non-const* reference to the - // ExpectationBase object. - Expectation(internal::ExpectationBase& exp); // NOLINT - - // The compiler-generated copy ctor and operator= work exactly as - // intended, so we don't need to define our own. - - // Returns true iff rhs references the same expectation as this object does. - bool operator==(const Expectation& rhs) const { - return expectation_base_ == rhs.expectation_base_; - } - - bool operator!=(const Expectation& rhs) const { return !(*this == rhs); } - - private: - friend class ExpectationSet; - friend class Sequence; - friend class ::testing::internal::ExpectationBase; - friend class ::testing::internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase; - - template <typename F> - friend class ::testing::internal::FunctionMockerBase; - - template <typename F> - friend class ::testing::internal::TypedExpectation; - - // This comparator is needed for putting Expectation objects into a set. - class Less { - public: - bool operator()(const Expectation& lhs, const Expectation& rhs) const { - return lhs.expectation_base_.get() < rhs.expectation_base_.get(); - } - }; - - typedef ::std::set<Expectation, Less> Set; - - Expectation( - const internal::linked_ptr<internal::ExpectationBase>& expectation_base); - - // Returns the expectation this object references. - const internal::linked_ptr<internal::ExpectationBase>& - expectation_base() const { - return expectation_base_; - } - - // A linked_ptr that co-owns the expectation this handle references. - internal::linked_ptr<internal::ExpectationBase> expectation_base_; -}; - -// A set of expectation handles. Useful in the .After() clause of -// EXPECT_CALL() for setting the (partial) order of expectations. The -// syntax: -// -// ExpectationSet es; -// es += EXPECT_CALL(...)...; -// es += EXPECT_CALL(...)...; -// EXPECT_CALL(...).After(es)...; -// -// sets three expectations where the last one can only be matched -// after the first two have both been satisfied. -// -// This class is copyable and has value semantics. -class ExpectationSet { - public: - // A bidirectional iterator that can read a const element in the set. - typedef Expectation::Set::const_iterator const_iterator; - - // An object stored in the set. This is an alias of Expectation. - typedef Expectation::Set::value_type value_type; - - // Constructs an empty set. - ExpectationSet() {} - - // This single-argument ctor must not be explicit, in order to support the - // ExpectationSet es = EXPECT_CALL(...); - // syntax. - ExpectationSet(internal::ExpectationBase& exp) { // NOLINT - *this += Expectation(exp); - } - - // This single-argument ctor implements implicit conversion from - // Expectation and thus must not be explicit. This allows either an - // Expectation or an ExpectationSet to be used in .After(). - ExpectationSet(const Expectation& e) { // NOLINT - *this += e; - } - - // The compiler-generator ctor and operator= works exactly as - // intended, so we don't need to define our own. - - // Returns true iff rhs contains the same set of Expectation objects - // as this does. - bool operator==(const ExpectationSet& rhs) const { - return expectations_ == rhs.expectations_; - } - - bool operator!=(const ExpectationSet& rhs) const { return !(*this == rhs); } - - // Implements the syntax - // expectation_set += EXPECT_CALL(...); - ExpectationSet& operator+=(const Expectation& e) { - expectations_.insert(e); - return *this; - } - - int size() const { return static_cast<int>(expectations_.size()); } - - const_iterator begin() const { return expectations_.begin(); } - const_iterator end() const { return expectations_.end(); } - - private: - Expectation::Set expectations_; -}; - - -// Sequence objects are used by a user to specify the relative order -// in which the expectations should match. They are copyable (we rely -// on the compiler-defined copy constructor and assignment operator). -class GTEST_API_ Sequence { - public: - // Constructs an empty sequence. - Sequence() : last_expectation_(new Expectation) {} - - // Adds an expectation to this sequence. The caller must ensure - // that no other thread is accessing this Sequence object. - void AddExpectation(const Expectation& expectation) const; - - private: - // The last expectation in this sequence. We use a linked_ptr here - // because Sequence objects are copyable and we want the copies to - // be aliases. The linked_ptr allows the copies to co-own and share - // the same Expectation object. - internal::linked_ptr<Expectation> last_expectation_; -}; // class Sequence - -// An object of this type causes all EXPECT_CALL() statements -// encountered in its scope to be put in an anonymous sequence. The -// work is done in the constructor and destructor. You should only -// create an InSequence object on the stack. -// -// The sole purpose for this class is to support easy definition of -// sequential expectations, e.g. -// -// { -// InSequence dummy; // The name of the object doesn't matter. -// -// // The following expectations must match in the order they appear. -// EXPECT_CALL(a, Bar())...; -// EXPECT_CALL(a, Baz())...; -// ... -// EXPECT_CALL(b, Xyz())...; -// } -// -// You can create InSequence objects in multiple threads, as long as -// they are used to affect different mock objects. The idea is that -// each thread can create and set up its own mocks as if it's the only -// thread. However, for clarity of your tests we recommend you to set -// up mocks in the main thread unless you have a good reason not to do -// so. -class GTEST_API_ InSequence { - public: - InSequence(); - ~InSequence(); - private: - bool sequence_created_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(InSequence); // NOLINT -} GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; - -namespace internal { - -// Points to the implicit sequence introduced by a living InSequence -// object (if any) in the current thread or NULL. -GTEST_API_ extern ThreadLocal<Sequence*> g_gmock_implicit_sequence; - -// Base class for implementing expectations. -// -// There are two reasons for having a type-agnostic base class for -// Expectation: -// -// 1. We need to store collections of expectations of different -// types (e.g. all pre-requisites of a particular expectation, all -// expectations in a sequence). Therefore these expectation objects -// must share a common base class. -// -// 2. We can avoid binary code bloat by moving methods not depending -// on the template argument of Expectation to the base class. -// -// This class is internal and mustn't be used by user code directly. -class GTEST_API_ ExpectationBase { - public: - // source_text is the EXPECT_CALL(...) source that created this Expectation. - ExpectationBase(const char* file, int line, const string& source_text); - - virtual ~ExpectationBase(); - - // Where in the source file was the expectation spec defined? - const char* file() const { return file_; } - int line() const { return line_; } - const char* source_text() const { return source_text_.c_str(); } - // Returns the cardinality specified in the expectation spec. - const Cardinality& cardinality() const { return cardinality_; } - - // Describes the source file location of this expectation. - void DescribeLocationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << FormatFileLocation(file(), line()) << " "; - } - - // Describes how many times a function call matching this - // expectation has occurred. - void DescribeCallCountTo(::std::ostream* os) const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - // If this mock method has an extra matcher (i.e. .With(matcher)), - // describes it to the ostream. - virtual void MaybeDescribeExtraMatcherTo(::std::ostream* os) = 0; - - protected: - friend class ::testing::Expectation; - friend class UntypedFunctionMockerBase; - - enum Clause { - // Don't change the order of the enum members! - kNone, - kWith, - kTimes, - kInSequence, - kAfter, - kWillOnce, - kWillRepeatedly, - kRetiresOnSaturation - }; - - typedef std::vector<const void*> UntypedActions; - - // Returns an Expectation object that references and co-owns this - // expectation. - virtual Expectation GetHandle() = 0; - - // Asserts that the EXPECT_CALL() statement has the given property. - void AssertSpecProperty(bool property, const string& failure_message) const { - Assert(property, file_, line_, failure_message); - } - - // Expects that the EXPECT_CALL() statement has the given property. - void ExpectSpecProperty(bool property, const string& failure_message) const { - Expect(property, file_, line_, failure_message); - } - - // Explicitly specifies the cardinality of this expectation. Used - // by the subclasses to implement the .Times() clause. - void SpecifyCardinality(const Cardinality& cardinality); - - // Returns true iff the user specified the cardinality explicitly - // using a .Times(). - bool cardinality_specified() const { return cardinality_specified_; } - - // Sets the cardinality of this expectation spec. - void set_cardinality(const Cardinality& a_cardinality) { - cardinality_ = a_cardinality; - } - - // The following group of methods should only be called after the - // EXPECT_CALL() statement, and only when g_gmock_mutex is held by - // the current thread. - - // Retires all pre-requisites of this expectation. - void RetireAllPreRequisites() - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - // Returns true iff this expectation is retired. - bool is_retired() const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - return retired_; - } - - // Retires this expectation. - void Retire() - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - retired_ = true; - } - - // Returns true iff this expectation is satisfied. - bool IsSatisfied() const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - return cardinality().IsSatisfiedByCallCount(call_count_); - } - - // Returns true iff this expectation is saturated. - bool IsSaturated() const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - return cardinality().IsSaturatedByCallCount(call_count_); - } - - // Returns true iff this expectation is over-saturated. - bool IsOverSaturated() const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - return cardinality().IsOverSaturatedByCallCount(call_count_); - } - - // Returns true iff all pre-requisites of this expectation are satisfied. - bool AllPrerequisitesAreSatisfied() const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - // Adds unsatisfied pre-requisites of this expectation to 'result'. - void FindUnsatisfiedPrerequisites(ExpectationSet* result) const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); - - // Returns the number this expectation has been invoked. - int call_count() const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - return call_count_; - } - - // Increments the number this expectation has been invoked. - void IncrementCallCount() - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - call_count_++; - } - - // Checks the action count (i.e. the number of WillOnce() and - // WillRepeatedly() clauses) against the cardinality if this hasn't - // been done before. Prints a warning if there are too many or too - // few actions. - void CheckActionCountIfNotDone() const - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); - - friend class ::testing::Sequence; - friend class ::testing::internal::ExpectationTester; - - template <typename Function> - friend class TypedExpectation; - - // Implements the .Times() clause. - void UntypedTimes(const Cardinality& a_cardinality); - - // This group of fields are part of the spec and won't change after - // an EXPECT_CALL() statement finishes. - const char* file_; // The file that contains the expectation. - int line_; // The line number of the expectation. - const string source_text_; // The EXPECT_CALL(...) source text. - // True iff the cardinality is specified explicitly. - bool cardinality_specified_; - Cardinality cardinality_; // The cardinality of the expectation. - // The immediate pre-requisites (i.e. expectations that must be - // satisfied before this expectation can be matched) of this - // expectation. We use linked_ptr in the set because we want an - // Expectation object to be co-owned by its FunctionMocker and its - // successors. This allows multiple mock objects to be deleted at - // different times. - ExpectationSet immediate_prerequisites_; - - // This group of fields are the current state of the expectation, - // and can change as the mock function is called. - int call_count_; // How many times this expectation has been invoked. - bool retired_; // True iff this expectation has retired. - UntypedActions untyped_actions_; - bool extra_matcher_specified_; - bool repeated_action_specified_; // True if a WillRepeatedly() was specified. - bool retires_on_saturation_; - Clause last_clause_; - mutable bool action_count_checked_; // Under mutex_. - mutable Mutex mutex_; // Protects action_count_checked_. - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ExpectationBase); -}; // class ExpectationBase - -// Impements an expectation for the given function type. -template <typename F> -class TypedExpectation : public ExpectationBase { - public: - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentMatcherTuple ArgumentMatcherTuple; - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - - TypedExpectation(FunctionMockerBase<F>* owner, - const char* a_file, int a_line, const string& a_source_text, - const ArgumentMatcherTuple& m) - : ExpectationBase(a_file, a_line, a_source_text), - owner_(owner), - matchers_(m), - // By default, extra_matcher_ should match anything. However, - // we cannot initialize it with _ as that triggers a compiler - // bug in Symbian's C++ compiler (cannot decide between two - // overloaded constructors of Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&>). - extra_matcher_(A<const ArgumentTuple&>()), - repeated_action_(DoDefault()) {} - - virtual ~TypedExpectation() { - // Check the validity of the action count if it hasn't been done - // yet (for example, if the expectation was never used). - CheckActionCountIfNotDone(); - for (UntypedActions::const_iterator it = untyped_actions_.begin(); - it != untyped_actions_.end(); ++it) { - delete static_cast<const Action<F>*>(*it); - } - } - - // Implements the .With() clause. - TypedExpectation& With(const Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&>& m) { - if (last_clause_ == kWith) { - ExpectSpecProperty(false, - ".With() cannot appear " - "more than once in an EXPECT_CALL()."); - } else { - ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kWith, - ".With() must be the first " - "clause in an EXPECT_CALL()."); - } - last_clause_ = kWith; - - extra_matcher_ = m; - extra_matcher_specified_ = true; - return *this; - } - - // Implements the .Times() clause. - TypedExpectation& Times(const Cardinality& a_cardinality) { - ExpectationBase::UntypedTimes(a_cardinality); - return *this; - } - - // Implements the .Times() clause. - TypedExpectation& Times(int n) { - return Times(Exactly(n)); - } - - // Implements the .InSequence() clause. - TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s) { - ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ <= kInSequence, - ".InSequence() cannot appear after .After()," - " .WillOnce(), .WillRepeatedly(), or " - ".RetiresOnSaturation()."); - last_clause_ = kInSequence; - - s.AddExpectation(GetHandle()); - return *this; - } - TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s1, const Sequence& s2) { - return InSequence(s1).InSequence(s2); - } - TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s1, const Sequence& s2, - const Sequence& s3) { - return InSequence(s1, s2).InSequence(s3); - } - TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s1, const Sequence& s2, - const Sequence& s3, const Sequence& s4) { - return InSequence(s1, s2, s3).InSequence(s4); - } - TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s1, const Sequence& s2, - const Sequence& s3, const Sequence& s4, - const Sequence& s5) { - return InSequence(s1, s2, s3, s4).InSequence(s5); - } - - // Implements that .After() clause. - TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s) { - ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ <= kAfter, - ".After() cannot appear after .WillOnce()," - " .WillRepeatedly(), or " - ".RetiresOnSaturation()."); - last_clause_ = kAfter; - - for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it) { - immediate_prerequisites_ += *it; - } - return *this; - } - TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s1, const ExpectationSet& s2) { - return After(s1).After(s2); - } - TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s1, const ExpectationSet& s2, - const ExpectationSet& s3) { - return After(s1, s2).After(s3); - } - TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s1, const ExpectationSet& s2, - const ExpectationSet& s3, const ExpectationSet& s4) { - return After(s1, s2, s3).After(s4); - } - TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s1, const ExpectationSet& s2, - const ExpectationSet& s3, const ExpectationSet& s4, - const ExpectationSet& s5) { - return After(s1, s2, s3, s4).After(s5); - } - - // Implements the .WillOnce() clause. - TypedExpectation& WillOnce(const Action<F>& action) { - ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ <= kWillOnce, - ".WillOnce() cannot appear after " - ".WillRepeatedly() or .RetiresOnSaturation()."); - last_clause_ = kWillOnce; - - untyped_actions_.push_back(new Action<F>(action)); - if (!cardinality_specified()) { - set_cardinality(Exactly(static_cast<int>(untyped_actions_.size()))); - } - return *this; - } - - // Implements the .WillRepeatedly() clause. - TypedExpectation& WillRepeatedly(const Action<F>& action) { - if (last_clause_ == kWillRepeatedly) { - ExpectSpecProperty(false, - ".WillRepeatedly() cannot appear " - "more than once in an EXPECT_CALL()."); - } else { - ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kWillRepeatedly, - ".WillRepeatedly() cannot appear " - "after .RetiresOnSaturation()."); - } - last_clause_ = kWillRepeatedly; - repeated_action_specified_ = true; - - repeated_action_ = action; - if (!cardinality_specified()) { - set_cardinality(AtLeast(static_cast<int>(untyped_actions_.size()))); - } - - // Now that no more action clauses can be specified, we check - // whether their count makes sense. - CheckActionCountIfNotDone(); - return *this; - } - - // Implements the .RetiresOnSaturation() clause. - TypedExpectation& RetiresOnSaturation() { - ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kRetiresOnSaturation, - ".RetiresOnSaturation() cannot appear " - "more than once."); - last_clause_ = kRetiresOnSaturation; - retires_on_saturation_ = true; - - // Now that no more action clauses can be specified, we check - // whether their count makes sense. - CheckActionCountIfNotDone(); - return *this; - } - - // Returns the matchers for the arguments as specified inside the - // EXPECT_CALL() macro. - const ArgumentMatcherTuple& matchers() const { - return matchers_; - } - - // Returns the matcher specified by the .With() clause. - const Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&>& extra_matcher() const { - return extra_matcher_; - } - - // Returns the action specified by the .WillRepeatedly() clause. - const Action<F>& repeated_action() const { return repeated_action_; } - - // If this mock method has an extra matcher (i.e. .With(matcher)), - // describes it to the ostream. - virtual void MaybeDescribeExtraMatcherTo(::std::ostream* os) { - if (extra_matcher_specified_) { - *os << " Expected args: "; - extra_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - *os << "\n"; - } - } - - private: - template <typename Function> - friend class FunctionMockerBase; - - // Returns an Expectation object that references and co-owns this - // expectation. - virtual Expectation GetHandle() { - return owner_->GetHandleOf(this); - } - - // The following methods will be called only after the EXPECT_CALL() - // statement finishes and when the current thread holds - // g_gmock_mutex. - - // Returns true iff this expectation matches the given arguments. - bool Matches(const ArgumentTuple& args) const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - return TupleMatches(matchers_, args) && extra_matcher_.Matches(args); - } - - // Returns true iff this expectation should handle the given arguments. - bool ShouldHandleArguments(const ArgumentTuple& args) const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - - // In case the action count wasn't checked when the expectation - // was defined (e.g. if this expectation has no WillRepeatedly() - // or RetiresOnSaturation() clause), we check it when the - // expectation is used for the first time. - CheckActionCountIfNotDone(); - return !is_retired() && AllPrerequisitesAreSatisfied() && Matches(args); - } - - // Describes the result of matching the arguments against this - // expectation to the given ostream. - void ExplainMatchResultTo( - const ArgumentTuple& args, - ::std::ostream* os) const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - - if (is_retired()) { - *os << " Expected: the expectation is active\n" - << " Actual: it is retired\n"; - } else if (!Matches(args)) { - if (!TupleMatches(matchers_, args)) { - ExplainMatchFailureTupleTo(matchers_, args, os); - } - StringMatchResultListener listener; - if (!extra_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(args, &listener)) { - *os << " Expected args: "; - extra_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - *os << "\n Actual: don't match"; - - internal::PrintIfNotEmpty(listener.str(), os); - *os << "\n"; - } - } else if (!AllPrerequisitesAreSatisfied()) { - *os << " Expected: all pre-requisites are satisfied\n" - << " Actual: the following immediate pre-requisites " - << "are not satisfied:\n"; - ExpectationSet unsatisfied_prereqs; - FindUnsatisfiedPrerequisites(&unsatisfied_prereqs); - int i = 0; - for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = unsatisfied_prereqs.begin(); - it != unsatisfied_prereqs.end(); ++it) { - it->expectation_base()->DescribeLocationTo(os); - *os << "pre-requisite #" << i++ << "\n"; - } - *os << " (end of pre-requisites)\n"; - } else { - // This line is here just for completeness' sake. It will never - // be executed as currently the ExplainMatchResultTo() function - // is called only when the mock function call does NOT match the - // expectation. - *os << "The call matches the expectation.\n"; - } - } - - // Returns the action that should be taken for the current invocation. - const Action<F>& GetCurrentAction( - const FunctionMockerBase<F>* mocker, - const ArgumentTuple& args) const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - const int count = call_count(); - Assert(count >= 1, __FILE__, __LINE__, - "call_count() is <= 0 when GetCurrentAction() is " - "called - this should never happen."); - - const int action_count = static_cast<int>(untyped_actions_.size()); - if (action_count > 0 && !repeated_action_specified_ && - count > action_count) { - // If there is at least one WillOnce() and no WillRepeatedly(), - // we warn the user when the WillOnce() clauses ran out. - ::std::stringstream ss; - DescribeLocationTo(&ss); - ss << "Actions ran out in " << source_text() << "...\n" - << "Called " << count << " times, but only " - << action_count << " WillOnce()" - << (action_count == 1 ? " is" : "s are") << " specified - "; - mocker->DescribeDefaultActionTo(args, &ss); - Log(kWarning, ss.str(), 1); - } - - return count <= action_count ? - *static_cast<const Action<F>*>(untyped_actions_[count - 1]) : - repeated_action(); - } - - // Given the arguments of a mock function call, if the call will - // over-saturate this expectation, returns the default action; - // otherwise, returns the next action in this expectation. Also - // describes *what* happened to 'what', and explains *why* Google - // Mock does it to 'why'. This method is not const as it calls - // IncrementCallCount(). A return value of NULL means the default - // action. - const Action<F>* GetActionForArguments( - const FunctionMockerBase<F>* mocker, - const ArgumentTuple& args, - ::std::ostream* what, - ::std::ostream* why) - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - if (IsSaturated()) { - // We have an excessive call. - IncrementCallCount(); - *what << "Mock function called more times than expected - "; - mocker->DescribeDefaultActionTo(args, what); - DescribeCallCountTo(why); - - // TODO(wan@google.com): allow the user to control whether - // unexpected calls should fail immediately or continue using a - // flag --gmock_unexpected_calls_are_fatal. - return NULL; - } - - IncrementCallCount(); - RetireAllPreRequisites(); - - if (retires_on_saturation_ && IsSaturated()) { - Retire(); - } - - // Must be done after IncrementCount()! - *what << "Mock function call matches " << source_text() <<"...\n"; - return &(GetCurrentAction(mocker, args)); - } - - // All the fields below won't change once the EXPECT_CALL() - // statement finishes. - FunctionMockerBase<F>* const owner_; - ArgumentMatcherTuple matchers_; - Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&> extra_matcher_; - Action<F> repeated_action_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TypedExpectation); -}; // class TypedExpectation - -// A MockSpec object is used by ON_CALL() or EXPECT_CALL() for -// specifying the default behavior of, or expectation on, a mock -// function. - -// Note: class MockSpec really belongs to the ::testing namespace. -// However if we define it in ::testing, MSVC will complain when -// classes in ::testing::internal declare it as a friend class -// template. To workaround this compiler bug, we define MockSpec in -// ::testing::internal and import it into ::testing. - -// Logs a message including file and line number information. -GTEST_API_ void LogWithLocation(testing::internal::LogSeverity severity, - const char* file, int line, - const string& message); - -template <typename F> -class MockSpec { - public: - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentMatcherTuple - ArgumentMatcherTuple; - - // Constructs a MockSpec object, given the function mocker object - // that the spec is associated with. - explicit MockSpec(internal::FunctionMockerBase<F>* function_mocker) - : function_mocker_(function_mocker) {} - - // Adds a new default action spec to the function mocker and returns - // the newly created spec. - internal::OnCallSpec<F>& InternalDefaultActionSetAt( - const char* file, int line, const char* obj, const char* call) { - LogWithLocation(internal::kInfo, file, line, - string("ON_CALL(") + obj + ", " + call + ") invoked"); - return function_mocker_->AddNewOnCallSpec(file, line, matchers_); - } - - // Adds a new expectation spec to the function mocker and returns - // the newly created spec. - internal::TypedExpectation<F>& InternalExpectedAt( - const char* file, int line, const char* obj, const char* call) { - const string source_text(string("EXPECT_CALL(") + obj + ", " + call + ")"); - LogWithLocation(internal::kInfo, file, line, source_text + " invoked"); - return function_mocker_->AddNewExpectation( - file, line, source_text, matchers_); - } - - private: - template <typename Function> - friend class internal::FunctionMocker; - - void SetMatchers(const ArgumentMatcherTuple& matchers) { - matchers_ = matchers; - } - - // The function mocker that owns this spec. - internal::FunctionMockerBase<F>* const function_mocker_; - // The argument matchers specified in the spec. - ArgumentMatcherTuple matchers_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(MockSpec); -}; // class MockSpec - -// MSVC warns about using 'this' in base member initializer list, so -// we need to temporarily disable the warning. We have to do it for -// the entire class to suppress the warning, even though it's about -// the constructor only. - -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable:4355) // Temporarily disables warning 4355. -#endif // _MSV_VER - -// C++ treats the void type specially. For example, you cannot define -// a void-typed variable or pass a void value to a function. -// ActionResultHolder<T> holds a value of type T, where T must be a -// copyable type or void (T doesn't need to be default-constructable). -// It hides the syntactic difference between void and other types, and -// is used to unify the code for invoking both void-returning and -// non-void-returning mock functions. - -// Untyped base class for ActionResultHolder<T>. -class UntypedActionResultHolderBase { - public: - virtual ~UntypedActionResultHolderBase() {} - - // Prints the held value as an action's result to os. - virtual void PrintAsActionResult(::std::ostream* os) const = 0; -}; - -// This generic definition is used when T is not void. -template <typename T> -class ActionResultHolder : public UntypedActionResultHolderBase { - public: - explicit ActionResultHolder(T a_value) : value_(a_value) {} - - // The compiler-generated copy constructor and assignment operator - // are exactly what we need, so we don't need to define them. - - // Returns the held value and deletes this object. - T GetValueAndDelete() const { - T retval(value_); - delete this; - return retval; - } - - // Prints the held value as an action's result to os. - virtual void PrintAsActionResult(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "\n Returns: "; - // T may be a reference type, so we don't use UniversalPrint(). - UniversalPrinter<T>::Print(value_, os); - } - - // Performs the given mock function's default action and returns the - // result in a new-ed ActionResultHolder. - template <typename F> - static ActionResultHolder* PerformDefaultAction( - const FunctionMockerBase<F>* func_mocker, - const typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple& args, - const string& call_description) { - return new ActionResultHolder( - func_mocker->PerformDefaultAction(args, call_description)); - } - - // Performs the given action and returns the result in a new-ed - // ActionResultHolder. - template <typename F> - static ActionResultHolder* - PerformAction(const Action<F>& action, - const typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple& args) { - return new ActionResultHolder(action.Perform(args)); - } - - private: - T value_; - - // T could be a reference type, so = isn't supported. - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ActionResultHolder); -}; - -// Specialization for T = void. -template <> -class ActionResultHolder<void> : public UntypedActionResultHolderBase { - public: - void GetValueAndDelete() const { delete this; } - - virtual void PrintAsActionResult(::std::ostream* /* os */) const {} - - // Performs the given mock function's default action and returns NULL; - template <typename F> - static ActionResultHolder* PerformDefaultAction( - const FunctionMockerBase<F>* func_mocker, - const typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple& args, - const string& call_description) { - func_mocker->PerformDefaultAction(args, call_description); - return NULL; - } - - // Performs the given action and returns NULL. - template <typename F> - static ActionResultHolder* PerformAction( - const Action<F>& action, - const typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple& args) { - action.Perform(args); - return NULL; - } -}; - -// The base of the function mocker class for the given function type. -// We put the methods in this class instead of its child to avoid code -// bloat. -template <typename F> -class FunctionMockerBase : public UntypedFunctionMockerBase { - public: - typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentMatcherTuple ArgumentMatcherTuple; - - FunctionMockerBase() : current_spec_(this) {} - - // The destructor verifies that all expectations on this mock - // function have been satisfied. If not, it will report Google Test - // non-fatal failures for the violations. - virtual ~FunctionMockerBase() - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - MutexLock l(&g_gmock_mutex); - VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked(); - Mock::UnregisterLocked(this); - ClearDefaultActionsLocked(); - } - - // Returns the ON_CALL spec that matches this mock function with the - // given arguments; returns NULL if no matching ON_CALL is found. - // L = * - const OnCallSpec<F>* FindOnCallSpec( - const ArgumentTuple& args) const { - for (UntypedOnCallSpecs::const_reverse_iterator it - = untyped_on_call_specs_.rbegin(); - it != untyped_on_call_specs_.rend(); ++it) { - const OnCallSpec<F>* spec = static_cast<const OnCallSpec<F>*>(*it); - if (spec->Matches(args)) - return spec; - } - - return NULL; - } - - // Performs the default action of this mock function on the given - // arguments and returns the result. Asserts (or throws if - // exceptions are enabled) with a helpful call descrption if there - // is no valid return value. This method doesn't depend on the - // mutable state of this object, and thus can be called concurrently - // without locking. - // L = * - Result PerformDefaultAction(const ArgumentTuple& args, - const string& call_description) const { - const OnCallSpec<F>* const spec = - this->FindOnCallSpec(args); - if (spec != NULL) { - return spec->GetAction().Perform(args); - } - const string message = call_description + - "\n The mock function has no default action " - "set, and its return type has no default value set."; -#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS - if (!DefaultValue<Result>::Exists()) { - throw std::runtime_error(message); - } -#else - Assert(DefaultValue<Result>::Exists(), "", -1, message); -#endif - return DefaultValue<Result>::Get(); - } - - // Performs the default action with the given arguments and returns - // the action's result. The call description string will be used in - // the error message to describe the call in the case the default - // action fails. The caller is responsible for deleting the result. - // L = * - virtual UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedPerformDefaultAction( - const void* untyped_args, // must point to an ArgumentTuple - const string& call_description) const { - const ArgumentTuple& args = - *static_cast<const ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); - return ResultHolder::PerformDefaultAction(this, args, call_description); - } - - // Performs the given action with the given arguments and returns - // the action's result. The caller is responsible for deleting the - // result. - // L = * - virtual UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedPerformAction( - const void* untyped_action, const void* untyped_args) const { - // Make a copy of the action before performing it, in case the - // action deletes the mock object (and thus deletes itself). - const Action<F> action = *static_cast<const Action<F>*>(untyped_action); - const ArgumentTuple& args = - *static_cast<const ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); - return ResultHolder::PerformAction(action, args); - } - - // Implements UntypedFunctionMockerBase::ClearDefaultActionsLocked(): - // clears the ON_CALL()s set on this mock function. - virtual void ClearDefaultActionsLocked() - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - - // Deleting our default actions may trigger other mock objects to be - // deleted, for example if an action contains a reference counted smart - // pointer to that mock object, and that is the last reference. So if we - // delete our actions within the context of the global mutex we may deadlock - // when this method is called again. Instead, make a copy of the set of - // actions to delete, clear our set within the mutex, and then delete the - // actions outside of the mutex. - UntypedOnCallSpecs specs_to_delete; - untyped_on_call_specs_.swap(specs_to_delete); - - g_gmock_mutex.Unlock(); - for (UntypedOnCallSpecs::const_iterator it = - specs_to_delete.begin(); - it != specs_to_delete.end(); ++it) { - delete static_cast<const OnCallSpec<F>*>(*it); - } - - // Lock the mutex again, since the caller expects it to be locked when we - // return. - g_gmock_mutex.Lock(); - } - - protected: - template <typename Function> - friend class MockSpec; - - typedef ActionResultHolder<Result> ResultHolder; - - // Returns the result of invoking this mock function with the given - // arguments. This function can be safely called from multiple - // threads concurrently. - Result InvokeWith(const ArgumentTuple& args) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - const ResultHolder *rh = static_cast<const ResultHolder*>( - this->UntypedInvokeWith(&args)); - return rh ? rh->GetValueAndDelete() : Result(); - } - - // Adds and returns a default action spec for this mock function. - OnCallSpec<F>& AddNewOnCallSpec( - const char* file, int line, - const ArgumentMatcherTuple& m) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - Mock::RegisterUseByOnCallOrExpectCall(MockObject(), file, line); - OnCallSpec<F>* const on_call_spec = new OnCallSpec<F>(file, line, m); - untyped_on_call_specs_.push_back(on_call_spec); - return *on_call_spec; - } - - // Adds and returns an expectation spec for this mock function. - TypedExpectation<F>& AddNewExpectation( - const char* file, - int line, - const string& source_text, - const ArgumentMatcherTuple& m) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - Mock::RegisterUseByOnCallOrExpectCall(MockObject(), file, line); - TypedExpectation<F>* const expectation = - new TypedExpectation<F>(this, file, line, source_text, m); - const linked_ptr<ExpectationBase> untyped_expectation(expectation); - untyped_expectations_.push_back(untyped_expectation); - - // Adds this expectation into the implicit sequence if there is one. - Sequence* const implicit_sequence = g_gmock_implicit_sequence.get(); - if (implicit_sequence != NULL) { - implicit_sequence->AddExpectation(Expectation(untyped_expectation)); - } - - return *expectation; - } - - // The current spec (either default action spec or expectation spec) - // being described on this function mocker. - MockSpec<F>& current_spec() { return current_spec_; } - - private: - template <typename Func> friend class TypedExpectation; - - // Some utilities needed for implementing UntypedInvokeWith(). - - // Describes what default action will be performed for the given - // arguments. - // L = * - void DescribeDefaultActionTo(const ArgumentTuple& args, - ::std::ostream* os) const { - const OnCallSpec<F>* const spec = FindOnCallSpec(args); - - if (spec == NULL) { - *os << (internal::type_equals<Result, void>::value ? - "returning directly.\n" : - "returning default value.\n"); - } else { - *os << "taking default action specified at:\n" - << FormatFileLocation(spec->file(), spec->line()) << "\n"; - } - } - - // Writes a message that the call is uninteresting (i.e. neither - // explicitly expected nor explicitly unexpected) to the given - // ostream. - virtual void UntypedDescribeUninterestingCall( - const void* untyped_args, - ::std::ostream* os) const - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - const ArgumentTuple& args = - *static_cast<const ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); - *os << "Uninteresting mock function call - "; - DescribeDefaultActionTo(args, os); - *os << " Function call: " << Name(); - UniversalPrint(args, os); - } - - // Returns the expectation that matches the given function arguments - // (or NULL is there's no match); when a match is found, - // untyped_action is set to point to the action that should be - // performed (or NULL if the action is "do default"), and - // is_excessive is modified to indicate whether the call exceeds the - // expected number. - // - // Critical section: We must find the matching expectation and the - // corresponding action that needs to be taken in an ATOMIC - // transaction. Otherwise another thread may call this mock - // method in the middle and mess up the state. - // - // However, performing the action has to be left out of the critical - // section. The reason is that we have no control on what the - // action does (it can invoke an arbitrary user function or even a - // mock function) and excessive locking could cause a dead lock. - virtual const ExpectationBase* UntypedFindMatchingExpectation( - const void* untyped_args, - const void** untyped_action, bool* is_excessive, - ::std::ostream* what, ::std::ostream* why) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - const ArgumentTuple& args = - *static_cast<const ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); - MutexLock l(&g_gmock_mutex); - TypedExpectation<F>* exp = this->FindMatchingExpectationLocked(args); - if (exp == NULL) { // A match wasn't found. - this->FormatUnexpectedCallMessageLocked(args, what, why); - return NULL; - } - - // This line must be done before calling GetActionForArguments(), - // which will increment the call count for *exp and thus affect - // its saturation status. - *is_excessive = exp->IsSaturated(); - const Action<F>* action = exp->GetActionForArguments(this, args, what, why); - if (action != NULL && action->IsDoDefault()) - action = NULL; // Normalize "do default" to NULL. - *untyped_action = action; - return exp; - } - - // Prints the given function arguments to the ostream. - virtual void UntypedPrintArgs(const void* untyped_args, - ::std::ostream* os) const { - const ArgumentTuple& args = - *static_cast<const ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); - UniversalPrint(args, os); - } - - // Returns the expectation that matches the arguments, or NULL if no - // expectation matches them. - TypedExpectation<F>* FindMatchingExpectationLocked( - const ArgumentTuple& args) const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - for (typename UntypedExpectations::const_reverse_iterator it = - untyped_expectations_.rbegin(); - it != untyped_expectations_.rend(); ++it) { - TypedExpectation<F>* const exp = - static_cast<TypedExpectation<F>*>(it->get()); - if (exp->ShouldHandleArguments(args)) { - return exp; - } - } - return NULL; - } - - // Returns a message that the arguments don't match any expectation. - void FormatUnexpectedCallMessageLocked( - const ArgumentTuple& args, - ::std::ostream* os, - ::std::ostream* why) const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - *os << "\nUnexpected mock function call - "; - DescribeDefaultActionTo(args, os); - PrintTriedExpectationsLocked(args, why); - } - - // Prints a list of expectations that have been tried against the - // current mock function call. - void PrintTriedExpectationsLocked( - const ArgumentTuple& args, - ::std::ostream* why) const - GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { - g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - const int count = static_cast<int>(untyped_expectations_.size()); - *why << "Google Mock tried the following " << count << " " - << (count == 1 ? "expectation, but it didn't match" : - "expectations, but none matched") - << ":\n"; - for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { - TypedExpectation<F>* const expectation = - static_cast<TypedExpectation<F>*>(untyped_expectations_[i].get()); - *why << "\n"; - expectation->DescribeLocationTo(why); - if (count > 1) { - *why << "tried expectation #" << i << ": "; - } - *why << expectation->source_text() << "...\n"; - expectation->ExplainMatchResultTo(args, why); - expectation->DescribeCallCountTo(why); - } - } - - // The current spec (either default action spec or expectation spec) - // being described on this function mocker. - MockSpec<F> current_spec_; - - // There is no generally useful and implementable semantics of - // copying a mock object, so copying a mock is usually a user error. - // Thus we disallow copying function mockers. If the user really - // wants to copy a mock object, he should implement his own copy - // operation, for example: - // - // class MockFoo : public Foo { - // public: - // // Defines a copy constructor explicitly. - // MockFoo(const MockFoo& src) {} - // ... - // }; - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(FunctionMockerBase); -}; // class FunctionMockerBase - -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state. -#endif // _MSV_VER - -// Implements methods of FunctionMockerBase. - -// Verifies that all expectations on this mock function have been -// satisfied. Reports one or more Google Test non-fatal failures and -// returns false if not. - -// Reports an uninteresting call (whose description is in msg) in the -// manner specified by 'reaction'. -void ReportUninterestingCall(CallReaction reaction, const string& msg); - -} // namespace internal - -// The style guide prohibits "using" statements in a namespace scope -// inside a header file. However, the MockSpec class template is -// meant to be defined in the ::testing namespace. The following line -// is just a trick for working around a bug in MSVC 8.0, which cannot -// handle it if we define MockSpec in ::testing. -using internal::MockSpec; - -// Const(x) is a convenient function for obtaining a const reference -// to x. This is useful for setting expectations on an overloaded -// const mock method, e.g. -// -// class MockFoo : public FooInterface { -// public: -// MOCK_METHOD0(Bar, int()); -// MOCK_CONST_METHOD0(Bar, int&()); -// }; -// -// MockFoo foo; -// // Expects a call to non-const MockFoo::Bar(). -// EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar()); -// // Expects a call to const MockFoo::Bar(). -// EXPECT_CALL(Const(foo), Bar()); -template <typename T> -inline const T& Const(const T& x) { return x; } - -// Constructs an Expectation object that references and co-owns exp. -inline Expectation::Expectation(internal::ExpectationBase& exp) // NOLINT - : expectation_base_(exp.GetHandle().expectation_base()) {} - -} // namespace testing - -// A separate macro is required to avoid compile errors when the name -// of the method used in call is a result of macro expansion. -// See CompilesWithMethodNameExpandedFromMacro tests in -// internal/gmock-spec-builders_test.cc for more details. -#define GMOCK_ON_CALL_IMPL_(obj, call) \ - ((obj).gmock_##call).InternalDefaultActionSetAt(__FILE__, __LINE__, \ - #obj, #call) -#define ON_CALL(obj, call) GMOCK_ON_CALL_IMPL_(obj, call) - -#define GMOCK_EXPECT_CALL_IMPL_(obj, call) \ - ((obj).gmock_##call).InternalExpectedAt(__FILE__, __LINE__, #obj, #call) -#define EXPECT_CALL(obj, call) GMOCK_EXPECT_CALL_IMPL_(obj, call) - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_SPEC_BUILDERS_H_ - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -template <typename F> -class FunctionMockerBase; - -// Note: class FunctionMocker really belongs to the ::testing -// namespace. However if we define it in ::testing, MSVC will -// complain when classes in ::testing::internal declare it as a -// friend class template. To workaround this compiler bug, we define -// FunctionMocker in ::testing::internal and import it into ::testing. -template <typename F> -class FunctionMocker; - -template <typename R> -class FunctionMocker<R()> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R()> { - public: - typedef R F(); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With() { - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke() { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple()); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1, A2)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1, A2)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1, A2); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1, const Matcher<A2>& m2) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1, m2)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1, A2 a2) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1, a2)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1, A2, A3)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1, A2, A3)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1, A2, A3); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1, const Matcher<A2>& m2, - const Matcher<A3>& m3) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1, m2, m3)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1, a2, a3)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1, A2, A3, A4)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1, A2, A3, A4)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1, A2, A3, A4); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1, const Matcher<A2>& m2, - const Matcher<A3>& m3, const Matcher<A4>& m4) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1, m2, m3, m4)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1, a2, a3, a4)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1, const Matcher<A2>& m2, - const Matcher<A3>& m3, const Matcher<A4>& m4, const Matcher<A5>& m5) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1, m2, m3, m4, - m5)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1, const Matcher<A2>& m2, - const Matcher<A3>& m3, const Matcher<A4>& m4, const Matcher<A5>& m5, - const Matcher<A6>& m6) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, - m6)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1, const Matcher<A2>& m2, - const Matcher<A3>& m3, const Matcher<A4>& m4, const Matcher<A5>& m5, - const Matcher<A6>& m6, const Matcher<A7>& m7) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, - m6, m7)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6, A7 a7) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1, const Matcher<A2>& m2, - const Matcher<A3>& m3, const Matcher<A4>& m4, const Matcher<A5>& m5, - const Matcher<A6>& m6, const Matcher<A7>& m7, const Matcher<A8>& m8) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, - m6, m7, m8)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6, A7 a7, A8 a8) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1, const Matcher<A2>& m2, - const Matcher<A3>& m3, const Matcher<A4>& m4, const Matcher<A5>& m5, - const Matcher<A6>& m6, const Matcher<A7>& m7, const Matcher<A8>& m8, - const Matcher<A9>& m9) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, - m6, m7, m8, m9)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6, A7 a7, A8 a8, A9 a9) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9)); - } -}; - -template <typename R, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, - typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9, - typename A10> -class FunctionMocker<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10)> : public - internal::FunctionMockerBase<R(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10)> { - public: - typedef R F(A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10); - typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; - - MockSpec<F>& With(const Matcher<A1>& m1, const Matcher<A2>& m2, - const Matcher<A3>& m3, const Matcher<A4>& m4, const Matcher<A5>& m5, - const Matcher<A6>& m6, const Matcher<A7>& m7, const Matcher<A8>& m8, - const Matcher<A9>& m9, const Matcher<A10>& m10) { - this->current_spec().SetMatchers(::std::tr1::make_tuple(m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, - m6, m7, m8, m9, m10)); - return this->current_spec(); - } - - R Invoke(A1 a1, A2 a2, A3 a3, A4 a4, A5 a5, A6 a6, A7 a7, A8 a8, A9 a9, - A10 a10) { - // Even though gcc and MSVC don't enforce it, 'this->' is required - // by the C++ standard [14.6.4] here, as the base class type is - // dependent on the template argument (and thus shouldn't be - // looked into when resolving InvokeWith). - return this->InvokeWith(ArgumentTuple(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9, - a10)); - } -}; - -} // namespace internal - -// The style guide prohibits "using" statements in a namespace scope -// inside a header file. However, the FunctionMocker class template -// is meant to be defined in the ::testing namespace. The following -// line is just a trick for working around a bug in MSVC 8.0, which -// cannot handle it if we define FunctionMocker in ::testing. -using internal::FunctionMocker; - -// GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, F) expands to the result type of function type F. -// We define this as a variadic macro in case F contains unprotected -// commas (the same reason that we use variadic macros in other places -// in this file). -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, ...) \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::Result - -// The type of argument N of the given function type. -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_ARG_(tn, N, ...) \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::Argument##N - -// The matcher type for argument N of the given function type. -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, N, ...) \ - const ::testing::Matcher<GMOCK_ARG_(tn, N, __VA_ARGS__)>& - -// The variable for mocking the given method. -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_MOCKER_(arity, constness, Method) \ - GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gmock##constness##arity##_##Method##_, __LINE__) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD0_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - ) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 0), \ - this_method_does_not_take_0_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(0, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(0, constness, Method).Invoke(); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method() constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(0, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(0, constness, Method).With(); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(0, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD1_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 1), \ - this_method_does_not_take_1_argument); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(1, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(1, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(1, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(1, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(1, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD2_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 2), \ - this_method_does_not_take_2_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(2, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(2, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1, gmock_a2); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(2, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(2, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1, gmock_a2); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(2, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD3_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 3), \ - this_method_does_not_take_3_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(3, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(3, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(3, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(3, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(3, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD4_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 4), \ - this_method_does_not_take_4_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(4, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(4, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(4, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(4, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(4, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD5_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 5), \ - this_method_does_not_take_5_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(5, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(5, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(5, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(5, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(5, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD6_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 6), \ - this_method_does_not_take_6_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(6, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(6, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(6, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(6, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(6, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD7_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 7, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a7) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 7), \ - this_method_does_not_take_7_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(7, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(7, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6, gmock_a7); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 7, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a7) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(7, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(7, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6, gmock_a7); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(7, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD8_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 7, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a7, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 8, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a8) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 8), \ - this_method_does_not_take_8_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(8, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(8, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6, gmock_a7, gmock_a8); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 7, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a7, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 8, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a8) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(8, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(8, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6, gmock_a7, gmock_a8); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(8, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD9_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 7, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a7, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 8, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a8, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 9, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a9) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 9), \ - this_method_does_not_take_9_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(9, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(9, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6, gmock_a7, gmock_a8, \ - gmock_a9); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 7, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a7, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 8, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a8, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 9, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a9) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(9, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(9, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6, gmock_a7, gmock_a8, \ - gmock_a9); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(9, constness, \ - Method) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DON'T USE IN USER CODE!!! -#define GMOCK_METHOD10_(tn, constness, ct, Method, ...) \ - GMOCK_RESULT_(tn, __VA_ARGS__) ct Method( \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 7, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a7, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 8, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a8, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 9, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a9, \ - GMOCK_ARG_(tn, 10, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a10) constness { \ - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_((::std::tr1::tuple_size< \ - tn ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value \ - == 10), \ - this_method_does_not_take_10_arguments); \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(10, constness, Method).SetOwnerAndName(this, #Method); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(10, constness, Method).Invoke(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6, gmock_a7, gmock_a8, gmock_a9, \ - gmock_a10); \ - } \ - ::testing::MockSpec<__VA_ARGS__>& \ - gmock_##Method(GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 1, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a1, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 2, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a2, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 3, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a3, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 4, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a4, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 5, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a5, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 6, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a6, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 7, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a7, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 8, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a8, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 9, __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a9, \ - GMOCK_MATCHER_(tn, 10, \ - __VA_ARGS__) gmock_a10) constness { \ - GMOCK_MOCKER_(10, constness, Method).RegisterOwner(this); \ - return GMOCK_MOCKER_(10, constness, Method).With(gmock_a1, gmock_a2, \ - gmock_a3, gmock_a4, gmock_a5, gmock_a6, gmock_a7, gmock_a8, gmock_a9, \ - gmock_a10); \ - } \ - mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<__VA_ARGS__> GMOCK_MOCKER_(10, constness, \ - Method) - -#define MOCK_METHOD0(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD0_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD1(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD1_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD2(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD2_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD3(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD3_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD4(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD4_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD5(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD5_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD6(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD6_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD7(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD7_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD8(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD8_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD9(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD9_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD10(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD10_(, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) - -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD0(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD0_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD1(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD1_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD2(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD2_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD3(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD3_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD4(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD4_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD5(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD5_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD6(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD6_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD7(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD7_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD8(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD8_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD9(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD9_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD10(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD10_(, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) - -#define MOCK_METHOD0_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD0_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD1_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD1_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD2_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD2_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD3_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD3_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD4_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD4_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD5_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD5_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD6_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD6_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD7_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD7_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD8_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD8_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD9_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD9_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD10_T(m, ...) GMOCK_METHOD10_(typename, , , m, __VA_ARGS__) - -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD0_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD0_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD1_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD1_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD2_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD2_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD3_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD3_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD4_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD4_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD5_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD5_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD6_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD6_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD7_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD7_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD8_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD8_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD9_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD9_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD10_T(m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD10_(typename, const, , m, __VA_ARGS__) - -#define MOCK_METHOD0_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD0_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD1_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD1_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD2_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD2_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD3_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD3_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD4_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD4_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD5_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD5_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD6_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD6_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD7_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD7_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD8_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD8_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD9_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD9_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD10_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD10_(, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) - -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD0_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD0_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD1_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD1_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD2_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD2_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD3_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD3_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD4_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD4_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD5_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD5_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD6_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD6_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD7_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD7_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD8_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD8_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD9_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD9_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD10_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD10_(, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) - -#define MOCK_METHOD0_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD0_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD1_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD1_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD2_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD2_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD3_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD3_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD4_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD4_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD5_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD5_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD6_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD6_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD7_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD7_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD8_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD8_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD9_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD9_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_METHOD10_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD10_(typename, , ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) - -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD0_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD0_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD1_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD1_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD2_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD2_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD3_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD3_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD4_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD4_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD5_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD5_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD6_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD6_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD7_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD7_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD8_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD8_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD9_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD9_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) -#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD10_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ - GMOCK_METHOD10_(typename, const, ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) - -// A MockFunction<F> class has one mock method whose type is F. It is -// useful when you just want your test code to emit some messages and -// have Google Mock verify the right messages are sent (and perhaps at -// the right times). For example, if you are exercising code: -// -// Foo(1); -// Foo(2); -// Foo(3); -// -// and want to verify that Foo(1) and Foo(3) both invoke -// mock.Bar("a"), but Foo(2) doesn't invoke anything, you can write: -// -// TEST(FooTest, InvokesBarCorrectly) { -// MyMock mock; -// MockFunction<void(string check_point_name)> check; -// { -// InSequence s; -// -// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Bar("a")); -// EXPECT_CALL(check, Call("1")); -// EXPECT_CALL(check, Call("2")); -// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Bar("a")); -// } -// Foo(1); -// check.Call("1"); -// Foo(2); -// check.Call("2"); -// Foo(3); -// } -// -// The expectation spec says that the first Bar("a") must happen -// before check point "1", the second Bar("a") must happen after check -// point "2", and nothing should happen between the two check -// points. The explicit check points make it easy to tell which -// Bar("a") is called by which call to Foo(). -template <typename F> -class MockFunction; - -template <typename R> -class MockFunction<R()> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD0_T(Call, R()); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0> -class MockFunction<R(A0)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD1_T(Call, R(A0)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0, typename A1> -class MockFunction<R(A0, A1)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD2_T(Call, R(A0, A1)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0, typename A1, typename A2> -class MockFunction<R(A0, A1, A2)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD3_T(Call, R(A0, A1, A2)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> -class MockFunction<R(A0, A1, A2, A3)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD4_T(Call, R(A0, A1, A2, A3)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4> -class MockFunction<R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD5_T(Call, R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5> -class MockFunction<R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD6_T(Call, R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5, typename A6> -class MockFunction<R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD7_T(Call, R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5, typename A6, typename A7> -class MockFunction<R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD8_T(Call, R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> -class MockFunction<R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD9_T(Call, R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -template <typename R, typename A0, typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, - typename A4, typename A5, typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, - typename A9> -class MockFunction<R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9)> { - public: - MockFunction() {} - - MOCK_METHOD10_T(Call, R(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9)); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MockFunction); -}; - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_FUNCTION_MOCKERS_H_ -// This file was GENERATED by command: -// pump.py gmock-generated-nice-strict.h.pump -// DO NOT EDIT BY HAND!!! - -// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Implements class templates NiceMock, NaggyMock, and StrictMock. -// -// Given a mock class MockFoo that is created using Google Mock, -// NiceMock<MockFoo> is a subclass of MockFoo that allows -// uninteresting calls (i.e. calls to mock methods that have no -// EXPECT_CALL specs), NaggyMock<MockFoo> is a subclass of MockFoo -// that prints a warning when an uninteresting call occurs, and -// StrictMock<MockFoo> is a subclass of MockFoo that treats all -// uninteresting calls as errors. -// -// Currently a mock is naggy by default, so MockFoo and -// NaggyMock<MockFoo> behave like the same. However, we will soon -// switch the default behavior of mocks to be nice, as that in general -// leads to more maintainable tests. When that happens, MockFoo will -// stop behaving like NaggyMock<MockFoo> and start behaving like -// NiceMock<MockFoo>. -// -// NiceMock, NaggyMock, and StrictMock "inherit" the constructors of -// their respective base class, with up-to 10 arguments. Therefore -// you can write NiceMock<MockFoo>(5, "a") to construct a nice mock -// where MockFoo has a constructor that accepts (int, const char*), -// for example. -// -// A known limitation is that NiceMock<MockFoo>, NaggyMock<MockFoo>, -// and StrictMock<MockFoo> only works for mock methods defined using -// the MOCK_METHOD* family of macros DIRECTLY in the MockFoo class. -// If a mock method is defined in a base class of MockFoo, the "nice" -// or "strict" modifier may not affect it, depending on the compiler. -// In particular, nesting NiceMock, NaggyMock, and StrictMock is NOT -// supported. -// -// Another known limitation is that the constructors of the base mock -// cannot have arguments passed by non-const reference, which are -// banned by the Google C++ style guide anyway. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_NICE_STRICT_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_NICE_STRICT_H_ - - -namespace testing { - -template <class MockClass> -class NiceMock : public MockClass { - public: - // We don't factor out the constructor body to a common method, as - // we have to avoid a possible clash with members of MockClass. - NiceMock() { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - // C++ doesn't (yet) allow inheritance of constructors, so we have - // to define it for each arity. - template <typename A1> - explicit NiceMock(const A1& a1) : MockClass(a1) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - template <typename A1, typename A2> - NiceMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2) : MockClass(a1, a2) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> - NiceMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4> - NiceMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, - const A4& a4) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5> - NiceMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6> - NiceMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7> - NiceMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, - a6, a7) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> - NiceMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7, const A8& a8) : MockClass(a1, - a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9> - NiceMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7, const A8& a8, - const A9& a9) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9, typename A10> - NiceMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7, const A8& a8, const A9& a9, - const A10& a10) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9, a10) { - ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - virtual ~NiceMock() { - ::testing::Mock::UnregisterCallReaction( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(NiceMock); -}; - -template <class MockClass> -class NaggyMock : public MockClass { - public: - // We don't factor out the constructor body to a common method, as - // we have to avoid a possible clash with members of MockClass. - NaggyMock() { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - // C++ doesn't (yet) allow inheritance of constructors, so we have - // to define it for each arity. - template <typename A1> - explicit NaggyMock(const A1& a1) : MockClass(a1) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - template <typename A1, typename A2> - NaggyMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2) : MockClass(a1, a2) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> - NaggyMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4> - NaggyMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, - const A4& a4) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5> - NaggyMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6> - NaggyMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7> - NaggyMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, - a6, a7) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> - NaggyMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7, const A8& a8) : MockClass(a1, - a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9> - NaggyMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7, const A8& a8, - const A9& a9) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9, typename A10> - NaggyMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7, const A8& a8, const A9& a9, - const A10& a10) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9, a10) { - ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - virtual ~NaggyMock() { - ::testing::Mock::UnregisterCallReaction( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(NaggyMock); -}; - -template <class MockClass> -class StrictMock : public MockClass { - public: - // We don't factor out the constructor body to a common method, as - // we have to avoid a possible clash with members of MockClass. - StrictMock() { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - // C++ doesn't (yet) allow inheritance of constructors, so we have - // to define it for each arity. - template <typename A1> - explicit StrictMock(const A1& a1) : MockClass(a1) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - template <typename A1, typename A2> - StrictMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2) : MockClass(a1, a2) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3> - StrictMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4> - StrictMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, - const A4& a4) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5> - StrictMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6> - StrictMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7> - StrictMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, - a6, a7) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8> - StrictMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7, const A8& a8) : MockClass(a1, - a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9> - StrictMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7, const A8& a8, - const A9& a9) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - template <typename A1, typename A2, typename A3, typename A4, typename A5, - typename A6, typename A7, typename A8, typename A9, typename A10> - StrictMock(const A1& a1, const A2& a2, const A3& a3, const A4& a4, - const A5& a5, const A6& a6, const A7& a7, const A8& a8, const A9& a9, - const A10& a10) : MockClass(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9, a10) { - ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - virtual ~StrictMock() { - ::testing::Mock::UnregisterCallReaction( - internal::ImplicitCast_<MockClass*>(this)); - } - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(StrictMock); -}; - -// The following specializations catch some (relatively more common) -// user errors of nesting nice and strict mocks. They do NOT catch -// all possible errors. - -// These specializations are declared but not defined, as NiceMock, -// NaggyMock, and StrictMock cannot be nested. - -template <typename MockClass> -class NiceMock<NiceMock<MockClass> >; -template <typename MockClass> -class NiceMock<NaggyMock<MockClass> >; -template <typename MockClass> -class NiceMock<StrictMock<MockClass> >; - -template <typename MockClass> -class NaggyMock<NiceMock<MockClass> >; -template <typename MockClass> -class NaggyMock<NaggyMock<MockClass> >; -template <typename MockClass> -class NaggyMock<StrictMock<MockClass> >; - -template <typename MockClass> -class StrictMock<NiceMock<MockClass> >; -template <typename MockClass> -class StrictMock<NaggyMock<MockClass> >; -template <typename MockClass> -class StrictMock<StrictMock<MockClass> >; - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_NICE_STRICT_H_ -// This file was GENERATED by command: -// pump.py gmock-generated-matchers.h.pump -// DO NOT EDIT BY HAND!!! - -// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file implements some commonly used variadic matchers. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_MATCHERS_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_MATCHERS_H_ - -#include <iterator> -#include <sstream> -#include <string> -#include <vector> - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// The type of the i-th (0-based) field of Tuple. -#define GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, i) \ - typename ::std::tr1::tuple_element<i, Tuple>::type - -// TupleFields<Tuple, k0, ..., kn> is for selecting fields from a -// tuple of type Tuple. It has two members: -// -// type: a tuple type whose i-th field is the ki-th field of Tuple. -// GetSelectedFields(t): returns fields k0, ..., and kn of t as a tuple. -// -// For example, in class TupleFields<tuple<bool, char, int>, 2, 0>, we have: -// -// type is tuple<int, bool>, and -// GetSelectedFields(make_tuple(true, 'a', 42)) is (42, true). - -template <class Tuple, int k0 = -1, int k1 = -1, int k2 = -1, int k3 = -1, - int k4 = -1, int k5 = -1, int k6 = -1, int k7 = -1, int k8 = -1, - int k9 = -1> -class TupleFields; - -// This generic version is used when there are 10 selectors. -template <class Tuple, int k0, int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, - int k7, int k8, int k9> -class TupleFields { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k1), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k2), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k3), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k4), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k5), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k6), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k7), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k8), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k9)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t), get<k1>(t), get<k2>(t), get<k3>(t), get<k4>(t), - get<k5>(t), get<k6>(t), get<k7>(t), get<k8>(t), get<k9>(t)); - } -}; - -// The following specialization is used for 0 ~ 9 selectors. - -template <class Tuple> -class TupleFields<Tuple, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& /* t */) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(); - } -}; - -template <class Tuple, int k0> -class TupleFields<Tuple, k0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t)); - } -}; - -template <class Tuple, int k0, int k1> -class TupleFields<Tuple, k0, k1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k1)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t), get<k1>(t)); - } -}; - -template <class Tuple, int k0, int k1, int k2> -class TupleFields<Tuple, k0, k1, k2, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k1), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k2)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t), get<k1>(t), get<k2>(t)); - } -}; - -template <class Tuple, int k0, int k1, int k2, int k3> -class TupleFields<Tuple, k0, k1, k2, k3, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k1), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k2), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k3)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t), get<k1>(t), get<k2>(t), get<k3>(t)); - } -}; - -template <class Tuple, int k0, int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4> -class TupleFields<Tuple, k0, k1, k2, k3, k4, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k1), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k2), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k3), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k4)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t), get<k1>(t), get<k2>(t), get<k3>(t), get<k4>(t)); - } -}; - -template <class Tuple, int k0, int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5> -class TupleFields<Tuple, k0, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, -1, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k1), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k2), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k3), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k4), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k5)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t), get<k1>(t), get<k2>(t), get<k3>(t), get<k4>(t), - get<k5>(t)); - } -}; - -template <class Tuple, int k0, int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6> -class TupleFields<Tuple, k0, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, -1, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k1), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k2), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k3), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k4), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k5), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k6)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t), get<k1>(t), get<k2>(t), get<k3>(t), get<k4>(t), - get<k5>(t), get<k6>(t)); - } -}; - -template <class Tuple, int k0, int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, - int k7> -class TupleFields<Tuple, k0, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, -1, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k1), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k2), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k3), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k4), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k5), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k6), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k7)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t), get<k1>(t), get<k2>(t), get<k3>(t), get<k4>(t), - get<k5>(t), get<k6>(t), get<k7>(t)); - } -}; - -template <class Tuple, int k0, int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, - int k7, int k8> -class TupleFields<Tuple, k0, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, -1> { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k0), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k1), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k2), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k3), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k4), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k5), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k6), - GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k7), GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_(Tuple, k8)> type; - static type GetSelectedFields(const Tuple& t) { - using ::std::tr1::get; - return type(get<k0>(t), get<k1>(t), get<k2>(t), get<k3>(t), get<k4>(t), - get<k5>(t), get<k6>(t), get<k7>(t), get<k8>(t)); - } -}; - -#undef GMOCK_FIELD_TYPE_ - -// Implements the Args() matcher. -template <class ArgsTuple, int k0 = -1, int k1 = -1, int k2 = -1, int k3 = -1, - int k4 = -1, int k5 = -1, int k6 = -1, int k7 = -1, int k8 = -1, - int k9 = -1> -class ArgsMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<ArgsTuple> { - public: - // ArgsTuple may have top-level const or reference modifiers. - typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(ArgsTuple) RawArgsTuple; - typedef typename internal::TupleFields<RawArgsTuple, k0, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, - k6, k7, k8, k9>::type SelectedArgs; - typedef Matcher<const SelectedArgs&> MonomorphicInnerMatcher; - - template <typename InnerMatcher> - explicit ArgsMatcherImpl(const InnerMatcher& inner_matcher) - : inner_matcher_(SafeMatcherCast<const SelectedArgs&>(inner_matcher)) {} - - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(ArgsTuple args, - MatchResultListener* listener) const { - const SelectedArgs& selected_args = GetSelectedArgs(args); - if (!listener->IsInterested()) - return inner_matcher_.Matches(selected_args); - - PrintIndices(listener->stream()); - *listener << "are " << PrintToString(selected_args); - - StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; - const bool match = inner_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(selected_args, - &inner_listener); - PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); - return match; - } - - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "are a tuple "; - PrintIndices(os); - inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); - } - - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { - *os << "are a tuple "; - PrintIndices(os); - inner_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); - } - - private: - static SelectedArgs GetSelectedArgs(ArgsTuple args) { - return TupleFields<RawArgsTuple, k0, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, - k9>::GetSelectedFields(args); - } - - // Prints the indices of the selected fields. - static void PrintIndices(::std::ostream* os) { - *os << "whose fields ("; - const int indices[10] = { k0, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, k9 }; - for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { - if (indices[i] < 0) - break; - - if (i >= 1) - *os << ", "; - - *os << "#" << indices[i]; - } - *os << ") "; - } - - const MonomorphicInnerMatcher inner_matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ArgsMatcherImpl); -}; - -template <class InnerMatcher, int k0 = -1, int k1 = -1, int k2 = -1, - int k3 = -1, int k4 = -1, int k5 = -1, int k6 = -1, int k7 = -1, - int k8 = -1, int k9 = -1> -class ArgsMatcher { - public: - explicit ArgsMatcher(const InnerMatcher& inner_matcher) - : inner_matcher_(inner_matcher) {} - - template <typename ArgsTuple> - operator Matcher<ArgsTuple>() const { - return MakeMatcher(new ArgsMatcherImpl<ArgsTuple, k0, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, - k6, k7, k8, k9>(inner_matcher_)); - } - - private: - const InnerMatcher inner_matcher_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(ArgsMatcher); -}; - -// A set of metafunctions for computing the result type of AllOf. -// AllOf(m1, ..., mN) returns -// AllOfResultN<decltype(m1), ..., decltype(mN)>::type. - -// Although AllOf isn't defined for one argument, AllOfResult1 is defined -// to simplify the implementation. -template <typename M1> -struct AllOfResult1 { - typedef M1 type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2> -struct AllOfResult2 { - typedef BothOfMatcher< - typename AllOfResult1<M1>::type, - typename AllOfResult1<M2>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3> -struct AllOfResult3 { - typedef BothOfMatcher< - typename AllOfResult1<M1>::type, - typename AllOfResult2<M2, M3>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4> -struct AllOfResult4 { - typedef BothOfMatcher< - typename AllOfResult2<M1, M2>::type, - typename AllOfResult2<M3, M4>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5> -struct AllOfResult5 { - typedef BothOfMatcher< - typename AllOfResult2<M1, M2>::type, - typename AllOfResult3<M3, M4, M5>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6> -struct AllOfResult6 { - typedef BothOfMatcher< - typename AllOfResult3<M1, M2, M3>::type, - typename AllOfResult3<M4, M5, M6>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7> -struct AllOfResult7 { - typedef BothOfMatcher< - typename AllOfResult3<M1, M2, M3>::type, - typename AllOfResult4<M4, M5, M6, M7>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8> -struct AllOfResult8 { - typedef BothOfMatcher< - typename AllOfResult4<M1, M2, M3, M4>::type, - typename AllOfResult4<M5, M6, M7, M8>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8, typename M9> -struct AllOfResult9 { - typedef BothOfMatcher< - typename AllOfResult4<M1, M2, M3, M4>::type, - typename AllOfResult5<M5, M6, M7, M8, M9>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8, typename M9, typename M10> -struct AllOfResult10 { - typedef BothOfMatcher< - typename AllOfResult5<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5>::type, - typename AllOfResult5<M6, M7, M8, M9, M10>::type - > type; -}; - -// A set of metafunctions for computing the result type of AnyOf. -// AnyOf(m1, ..., mN) returns -// AnyOfResultN<decltype(m1), ..., decltype(mN)>::type. - -// Although AnyOf isn't defined for one argument, AnyOfResult1 is defined -// to simplify the implementation. -template <typename M1> -struct AnyOfResult1 { - typedef M1 type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2> -struct AnyOfResult2 { - typedef EitherOfMatcher< - typename AnyOfResult1<M1>::type, - typename AnyOfResult1<M2>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3> -struct AnyOfResult3 { - typedef EitherOfMatcher< - typename AnyOfResult1<M1>::type, - typename AnyOfResult2<M2, M3>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4> -struct AnyOfResult4 { - typedef EitherOfMatcher< - typename AnyOfResult2<M1, M2>::type, - typename AnyOfResult2<M3, M4>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5> -struct AnyOfResult5 { - typedef EitherOfMatcher< - typename AnyOfResult2<M1, M2>::type, - typename AnyOfResult3<M3, M4, M5>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6> -struct AnyOfResult6 { - typedef EitherOfMatcher< - typename AnyOfResult3<M1, M2, M3>::type, - typename AnyOfResult3<M4, M5, M6>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7> -struct AnyOfResult7 { - typedef EitherOfMatcher< - typename AnyOfResult3<M1, M2, M3>::type, - typename AnyOfResult4<M4, M5, M6, M7>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8> -struct AnyOfResult8 { - typedef EitherOfMatcher< - typename AnyOfResult4<M1, M2, M3, M4>::type, - typename AnyOfResult4<M5, M6, M7, M8>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8, typename M9> -struct AnyOfResult9 { - typedef EitherOfMatcher< - typename AnyOfResult4<M1, M2, M3, M4>::type, - typename AnyOfResult5<M5, M6, M7, M8, M9>::type - > type; -}; - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8, typename M9, typename M10> -struct AnyOfResult10 { - typedef EitherOfMatcher< - typename AnyOfResult5<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5>::type, - typename AnyOfResult5<M6, M7, M8, M9, M10>::type - > type; -}; - -} // namespace internal - -// Args<N1, N2, ..., Nk>(a_matcher) matches a tuple if the selected -// fields of it matches a_matcher. C++ doesn't support default -// arguments for function templates, so we have to overload it. -template <typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, - typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, - k7>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, int k8, - typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, - k8>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, int k8, - int k9, typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, k9> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, - k9>(matcher); -} - -template <int k1, int k2, int k3, int k4, int k5, int k6, int k7, int k8, - int k9, int k10, typename InnerMatcher> -inline internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, k9, - k10> -Args(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { - return internal::ArgsMatcher<InnerMatcher, k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, - k9, k10>(matcher); -} - -// ElementsAre(e_1, e_2, ... e_n) matches an STL-style container with -// n elements, where the i-th element in the container must -// match the i-th argument in the list. Each argument of -// ElementsAre() can be either a value or a matcher. We support up to -// 10 arguments. -// -// The use of DecayArray in the implementation allows ElementsAre() -// to accept string literals, whose type is const char[N], but we -// want to treat them as const char*. -// -// NOTE: Since ElementsAre() cares about the order of the elements, it -// must not be used with containers whose elements's order is -// undefined (e.g. hash_map). - -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple<> > -ElementsAre() { - typedef std::tr1::tuple<> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args()); -} - -template <typename T1> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, e6)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6, const T7& e7) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, e6, e7)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6, const T7& e7, const T8& e8) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, e6, e7, - e8)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T9>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6, const T7& e7, const T8& e8, const T9& e9) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T9>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, e6, e7, - e8, e9)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10> -inline internal::ElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T9>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T10>::type> > -ElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6, const T7& e7, const T8& e8, const T9& e9, - const T10& e10) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T9>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T10>::type> Args; - return internal::ElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, e6, e7, - e8, e9, e10)); -} - -// UnorderedElementsAre(e_1, e_2, ..., e_n) is an ElementsAre extension -// that matches n elements in any order. We support up to n=10 arguments. - -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple<> > -UnorderedElementsAre() { - typedef std::tr1::tuple<> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args()); -} - -template <typename T1> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, - e6)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6, const T7& e7) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, - e6, e7)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6, const T7& e7, const T8& e8) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, - e6, e7, e8)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T9>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6, const T7& e7, const T8& e8, const T9& e9) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T9>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, - e6, e7, e8, e9)); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10> -inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< - std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T9>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T10>::type> > -UnorderedElementsAre(const T1& e1, const T2& e2, const T3& e3, const T4& e4, - const T5& e5, const T6& e6, const T7& e7, const T8& e8, const T9& e9, - const T10& e10) { - typedef std::tr1::tuple< - typename internal::DecayArray<T1>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T2>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T3>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T4>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T5>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T6>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T7>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T8>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T9>::type, - typename internal::DecayArray<T10>::type> Args; - return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher<Args>(Args(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, - e6, e7, e8, e9, e10)); -} - -// AllOf(m1, m2, ..., mk) matches any value that matches all of the given -// sub-matchers. AllOf is called fully qualified to prevent ADL from firing. - -template <typename M1, typename M2> -inline typename internal::AllOfResult2<M1, M2>::type -AllOf(M1 m1, M2 m2) { - return typename internal::AllOfResult2<M1, M2>::type( - m1, - m2); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3> -inline typename internal::AllOfResult3<M1, M2, M3>::type -AllOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3) { - return typename internal::AllOfResult3<M1, M2, M3>::type( - m1, - ::testing::AllOf(m2, m3)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4> -inline typename internal::AllOfResult4<M1, M2, M3, M4>::type -AllOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4) { - return typename internal::AllOfResult4<M1, M2, M3, M4>::type( - ::testing::AllOf(m1, m2), - ::testing::AllOf(m3, m4)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5> -inline typename internal::AllOfResult5<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5>::type -AllOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5) { - return typename internal::AllOfResult5<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5>::type( - ::testing::AllOf(m1, m2), - ::testing::AllOf(m3, m4, m5)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6> -inline typename internal::AllOfResult6<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6>::type -AllOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6) { - return typename internal::AllOfResult6<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6>::type( - ::testing::AllOf(m1, m2, m3), - ::testing::AllOf(m4, m5, m6)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7> -inline typename internal::AllOfResult7<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7>::type -AllOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6, M7 m7) { - return typename internal::AllOfResult7<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7>::type( - ::testing::AllOf(m1, m2, m3), - ::testing::AllOf(m4, m5, m6, m7)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8> -inline typename internal::AllOfResult8<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8>::type -AllOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6, M7 m7, M8 m8) { - return typename internal::AllOfResult8<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8>::type( - ::testing::AllOf(m1, m2, m3, m4), - ::testing::AllOf(m5, m6, m7, m8)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8, typename M9> -inline typename internal::AllOfResult9<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9>::type -AllOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6, M7 m7, M8 m8, M9 m9) { - return typename internal::AllOfResult9<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, - M9>::type( - ::testing::AllOf(m1, m2, m3, m4), - ::testing::AllOf(m5, m6, m7, m8, m9)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8, typename M9, typename M10> -inline typename internal::AllOfResult10<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, - M10>::type -AllOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6, M7 m7, M8 m8, M9 m9, M10 m10) { - return typename internal::AllOfResult10<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, - M10>::type( - ::testing::AllOf(m1, m2, m3, m4, m5), - ::testing::AllOf(m6, m7, m8, m9, m10)); -} - -// AnyOf(m1, m2, ..., mk) matches any value that matches any of the given -// sub-matchers. AnyOf is called fully qualified to prevent ADL from firing. - -template <typename M1, typename M2> -inline typename internal::AnyOfResult2<M1, M2>::type -AnyOf(M1 m1, M2 m2) { - return typename internal::AnyOfResult2<M1, M2>::type( - m1, - m2); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3> -inline typename internal::AnyOfResult3<M1, M2, M3>::type -AnyOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3) { - return typename internal::AnyOfResult3<M1, M2, M3>::type( - m1, - ::testing::AnyOf(m2, m3)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4> -inline typename internal::AnyOfResult4<M1, M2, M3, M4>::type -AnyOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4) { - return typename internal::AnyOfResult4<M1, M2, M3, M4>::type( - ::testing::AnyOf(m1, m2), - ::testing::AnyOf(m3, m4)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5> -inline typename internal::AnyOfResult5<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5>::type -AnyOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5) { - return typename internal::AnyOfResult5<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5>::type( - ::testing::AnyOf(m1, m2), - ::testing::AnyOf(m3, m4, m5)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6> -inline typename internal::AnyOfResult6<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6>::type -AnyOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6) { - return typename internal::AnyOfResult6<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6>::type( - ::testing::AnyOf(m1, m2, m3), - ::testing::AnyOf(m4, m5, m6)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7> -inline typename internal::AnyOfResult7<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7>::type -AnyOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6, M7 m7) { - return typename internal::AnyOfResult7<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7>::type( - ::testing::AnyOf(m1, m2, m3), - ::testing::AnyOf(m4, m5, m6, m7)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8> -inline typename internal::AnyOfResult8<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8>::type -AnyOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6, M7 m7, M8 m8) { - return typename internal::AnyOfResult8<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8>::type( - ::testing::AnyOf(m1, m2, m3, m4), - ::testing::AnyOf(m5, m6, m7, m8)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8, typename M9> -inline typename internal::AnyOfResult9<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9>::type -AnyOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6, M7 m7, M8 m8, M9 m9) { - return typename internal::AnyOfResult9<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, - M9>::type( - ::testing::AnyOf(m1, m2, m3, m4), - ::testing::AnyOf(m5, m6, m7, m8, m9)); -} - -template <typename M1, typename M2, typename M3, typename M4, typename M5, - typename M6, typename M7, typename M8, typename M9, typename M10> -inline typename internal::AnyOfResult10<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, - M10>::type -AnyOf(M1 m1, M2 m2, M3 m3, M4 m4, M5 m5, M6 m6, M7 m7, M8 m8, M9 m9, M10 m10) { - return typename internal::AnyOfResult10<M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, - M10>::type( - ::testing::AnyOf(m1, m2, m3, m4, m5), - ::testing::AnyOf(m6, m7, m8, m9, m10)); -} - -} // namespace testing - - -// The MATCHER* family of macros can be used in a namespace scope to -// define custom matchers easily. -// -// Basic Usage -// =========== -// -// The syntax -// -// MATCHER(name, description_string) { statements; } -// -// defines a matcher with the given name that executes the statements, -// which must return a bool to indicate if the match succeeds. Inside -// the statements, you can refer to the value being matched by 'arg', -// and refer to its type by 'arg_type'. -// -// The description string documents what the matcher does, and is used -// to generate the failure message when the match fails. Since a -// MATCHER() is usually defined in a header file shared by multiple -// C++ source files, we require the description to be a C-string -// literal to avoid possible side effects. It can be empty, in which -// case we'll use the sequence of words in the matcher name as the -// description. -// -// For example: -// -// MATCHER(IsEven, "") { return (arg % 2) == 0; } -// -// allows you to write -// -// // Expects mock_foo.Bar(n) to be called where n is even. -// EXPECT_CALL(mock_foo, Bar(IsEven())); -// -// or, -// -// // Verifies that the value of some_expression is even. -// EXPECT_THAT(some_expression, IsEven()); -// -// If the above assertion fails, it will print something like: -// -// Value of: some_expression -// Expected: is even -// Actual: 7 -// -// where the description "is even" is automatically calculated from the -// matcher name IsEven. -// -// Argument Type -// ============= -// -// Note that the type of the value being matched (arg_type) is -// determined by the context in which you use the matcher and is -// supplied to you by the compiler, so you don't need to worry about -// declaring it (nor can you). This allows the matcher to be -// polymorphic. For example, IsEven() can be used to match any type -// where the value of "(arg % 2) == 0" can be implicitly converted to -// a bool. In the "Bar(IsEven())" example above, if method Bar() -// takes an int, 'arg_type' will be int; if it takes an unsigned long, -// 'arg_type' will be unsigned long; and so on. -// -// Parameterizing Matchers -// ======================= -// -// Sometimes you'll want to parameterize the matcher. For that you -// can use another macro: -// -// MATCHER_P(name, param_name, description_string) { statements; } -// -// For example: -// -// MATCHER_P(HasAbsoluteValue, value, "") { return abs(arg) == value; } -// -// will allow you to write: -// -// EXPECT_THAT(Blah("a"), HasAbsoluteValue(n)); -// -// which may lead to this message (assuming n is 10): -// -// Value of: Blah("a") -// Expected: has absolute value 10 -// Actual: -9 -// -// Note that both the matcher description and its parameter are -// printed, making the message human-friendly. -// -// In the matcher definition body, you can write 'foo_type' to -// reference the type of a parameter named 'foo'. For example, in the -// body of MATCHER_P(HasAbsoluteValue, value) above, you can write -// 'value_type' to refer to the type of 'value'. -// -// We also provide MATCHER_P2, MATCHER_P3, ..., up to MATCHER_P10 to -// support multi-parameter matchers. -// -// Describing Parameterized Matchers -// ================================= -// -// The last argument to MATCHER*() is a string-typed expression. The -// expression can reference all of the matcher's parameters and a -// special bool-typed variable named 'negation'. When 'negation' is -// false, the expression should evaluate to the matcher's description; -// otherwise it should evaluate to the description of the negation of -// the matcher. For example, -// -// using testing::PrintToString; -// -// MATCHER_P2(InClosedRange, low, hi, -// string(negation ? "is not" : "is") + " in range [" + -// PrintToString(low) + ", " + PrintToString(hi) + "]") { -// return low <= arg && arg <= hi; -// } -// ... -// EXPECT_THAT(3, InClosedRange(4, 6)); -// EXPECT_THAT(3, Not(InClosedRange(2, 4))); -// -// would generate two failures that contain the text: -// -// Expected: is in range [4, 6] -// ... -// Expected: is not in range [2, 4] -// -// If you specify "" as the description, the failure message will -// contain the sequence of words in the matcher name followed by the -// parameter values printed as a tuple. For example, -// -// MATCHER_P2(InClosedRange, low, hi, "") { ... } -// ... -// EXPECT_THAT(3, InClosedRange(4, 6)); -// EXPECT_THAT(3, Not(InClosedRange(2, 4))); -// -// would generate two failures that contain the text: -// -// Expected: in closed range (4, 6) -// ... -// Expected: not (in closed range (2, 4)) -// -// Types of Matcher Parameters -// =========================== -// -// For the purpose of typing, you can view -// -// MATCHER_Pk(Foo, p1, ..., pk, description_string) { ... } -// -// as shorthand for -// -// template <typename p1_type, ..., typename pk_type> -// FooMatcherPk<p1_type, ..., pk_type> -// Foo(p1_type p1, ..., pk_type pk) { ... } -// -// When you write Foo(v1, ..., vk), the compiler infers the types of -// the parameters v1, ..., and vk for you. If you are not happy with -// the result of the type inference, you can specify the types by -// explicitly instantiating the template, as in Foo<long, bool>(5, -// false). As said earlier, you don't get to (or need to) specify -// 'arg_type' as that's determined by the context in which the matcher -// is used. You can assign the result of expression Foo(p1, ..., pk) -// to a variable of type FooMatcherPk<p1_type, ..., pk_type>. This -// can be useful when composing matchers. -// -// While you can instantiate a matcher template with reference types, -// passing the parameters by pointer usually makes your code more -// readable. If, however, you still want to pass a parameter by -// reference, be aware that in the failure message generated by the -// matcher you will see the value of the referenced object but not its -// address. -// -// Explaining Match Results -// ======================== -// -// Sometimes the matcher description alone isn't enough to explain why -// the match has failed or succeeded. For example, when expecting a -// long string, it can be very helpful to also print the diff between -// the expected string and the actual one. To achieve that, you can -// optionally stream additional information to a special variable -// named result_listener, whose type is a pointer to class -// MatchResultListener: -// -// MATCHER_P(EqualsLongString, str, "") { -// if (arg == str) return true; -// -// *result_listener << "the difference: " -/// << DiffStrings(str, arg); -// return false; -// } -// -// Overloading Matchers -// ==================== -// -// You can overload matchers with different numbers of parameters: -// -// MATCHER_P(Blah, a, description_string1) { ... } -// MATCHER_P2(Blah, a, b, description_string2) { ... } -// -// Caveats -// ======= -// -// When defining a new matcher, you should also consider implementing -// MatcherInterface or using MakePolymorphicMatcher(). These -// approaches require more work than the MATCHER* macros, but also -// give you more control on the types of the value being matched and -// the matcher parameters, which may leads to better compiler error -// messages when the matcher is used wrong. They also allow -// overloading matchers based on parameter types (as opposed to just -// based on the number of parameters). -// -// MATCHER*() can only be used in a namespace scope. The reason is -// that C++ doesn't yet allow function-local types to be used to -// instantiate templates. The up-coming C++0x standard will fix this. -// Once that's done, we'll consider supporting using MATCHER*() inside -// a function. -// -// More Information -// ================ -// -// To learn more about using these macros, please search for 'MATCHER' -// on http://code.google.com/p/googlemock/wiki/CookBook. - -#define MATCHER(name, description)\ - class name##Matcher {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl()\ - {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<>()));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>());\ - }\ - name##Matcher() {\ - }\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##Matcher);\ - };\ - inline name##Matcher name() {\ - return name##Matcher();\ - }\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##Matcher::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P(name, p0, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - explicit gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0)\ - : p0(gmock_p0) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type>(p0)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP(p0##_type gmock_p0) : p0(gmock_p0) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP<p0##_type> name(p0##_type p0) {\ - return name##MatcherP<p0##_type>(p0);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP<p0##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P2(name, p0, p1, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP2 {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1)\ - : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type, p1##_type>(p0, p1)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0, p1));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP2(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1) : p0(gmock_p0), \ - p1(gmock_p1) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP2);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP2<p0##_type, p1##_type> name(p0##_type p0, \ - p1##_type p1) {\ - return name##MatcherP2<p0##_type, p1##_type>(p0, p1);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP2<p0##_type, \ - p1##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P3(name, p0, p1, p2, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP3 {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2)\ - : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type>(p0, p1, \ - p2)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0, p1, p2));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP3(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP3);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP3<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type> name(p0##_type p0, \ - p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2) {\ - return name##MatcherP3<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type>(p0, p1, p2);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP3<p0##_type, p1##_type, \ - p2##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P4(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP4 {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3)\ - : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, \ - p3##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP4(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), \ - p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP4);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP4<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, \ - p3##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, \ - p3##_type p3) {\ - return name##MatcherP4<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type>(p0, \ - p1, p2, p3);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP4<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, \ - p3##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P5(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP5 {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4)\ - : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), \ - p4(gmock_p4) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP5(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, \ - p4##_type gmock_p4) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP5);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP5<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ - p4##_type p4) {\ - return name##MatcherP5<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP5<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P6(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP6 {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5)\ - : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), \ - p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP6(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP6);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP6<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, \ - p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5) {\ - return name##MatcherP6<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP6<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P7(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP7 {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6)\ - : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), \ - p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP7(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5, p6##_type gmock_p6) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), \ - p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), \ - p6(gmock_p6) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP7);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP7<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, \ - p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, \ - p6##_type p6) {\ - return name##MatcherP7<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP7<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P8(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP8 {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7)\ - : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), \ - p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), p7(gmock_p7) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type>(p0, p1, p2, \ - p3, p4, p5, p6, p7)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP8(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5, p6##_type gmock_p6, \ - p7##_type gmock_p7) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), \ - p7(gmock_p7) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP8);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP8<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type> name(p0##_type p0, \ - p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, \ - p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7) {\ - return name##MatcherP8<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ - p6, p7);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP8<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type, \ - p7##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P9(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP9 {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, p8##_type gmock_p8)\ - : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), \ - p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), p7(gmock_p7), \ - p8(gmock_p8) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - p8##_type p8;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, \ - p8##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP9(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5, p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, \ - p8##_type gmock_p8) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), \ - p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), p7(gmock_p7), \ - p8(gmock_p8) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - p8##_type p8;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP9);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP9<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, \ - p8##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ - p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7, \ - p8##_type p8) {\ - return name##MatcherP9<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type>(p0, p1, p2, \ - p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP9<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ - p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, \ - p8##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#define MATCHER_P10(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9, description)\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type, \ - typename p9##_type>\ - class name##MatcherP10 {\ - public:\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<arg_type> {\ - public:\ - gmock_Impl(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ - p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ - p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, p8##_type gmock_p8, \ - p9##_type gmock_p9)\ - : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), \ - p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), p7(gmock_p7), \ - p8(gmock_p8), p9(gmock_p9) {}\ - virtual bool MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const;\ - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false);\ - }\ - virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const {\ - *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true);\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - p8##_type p8;\ - p9##_type p9;\ - private:\ - ::testing::internal::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const {\ - const ::testing::internal::string gmock_description = (description);\ - if (!gmock_description.empty())\ - return gmock_description;\ - return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(\ - negation, #name, \ - ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(\ - ::std::tr1::tuple<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type, \ - p9##_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9)));\ - }\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(gmock_Impl);\ - };\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - operator ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>() const {\ - return ::testing::Matcher<arg_type>(\ - new gmock_Impl<arg_type>(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9));\ - }\ - name##MatcherP10(p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ - p2##_type gmock_p2, p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ - p5##_type gmock_p5, p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, \ - p8##_type gmock_p8, p9##_type gmock_p9) : p0(gmock_p0), p1(gmock_p1), \ - p2(gmock_p2), p3(gmock_p3), p4(gmock_p4), p5(gmock_p5), p6(gmock_p6), \ - p7(gmock_p7), p8(gmock_p8), p9(gmock_p9) {\ - }\ - p0##_type p0;\ - p1##_type p1;\ - p2##_type p2;\ - p3##_type p3;\ - p4##_type p4;\ - p5##_type p5;\ - p6##_type p6;\ - p7##_type p7;\ - p8##_type p8;\ - p9##_type p9;\ - private:\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(name##MatcherP10);\ - };\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type, \ - typename p9##_type>\ - inline name##MatcherP10<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type, \ - p9##_type> name(p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ - p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7, p8##_type p8, \ - p9##_type p9) {\ - return name##MatcherP10<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type, p9##_type>(p0, \ - p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9);\ - }\ - template <typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ - typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ - typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type, \ - typename p9##_type>\ - template <typename arg_type>\ - bool name##MatcherP10<p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, \ - p4##_type, p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type, \ - p9##_type>::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(\ - arg_type arg, \ - ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_)\ - const - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_GENERATED_MATCHERS_H_ -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file implements some actions that depend on gmock-generated-actions.h. - -#ifndef GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_ACTIONS_H_ -#define GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_ACTIONS_H_ - -#include <algorithm> - - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// Implements the Invoke(f) action. The template argument -// FunctionImpl is the implementation type of f, which can be either a -// function pointer or a functor. Invoke(f) can be used as an -// Action<F> as long as f's type is compatible with F (i.e. f can be -// assigned to a tr1::function<F>). -template <typename FunctionImpl> -class InvokeAction { - public: - // The c'tor makes a copy of function_impl (either a function - // pointer or a functor). - explicit InvokeAction(FunctionImpl function_impl) - : function_impl_(function_impl) {} - - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) { - return InvokeHelper<Result, ArgumentTuple>::Invoke(function_impl_, args); - } - - private: - FunctionImpl function_impl_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(InvokeAction); -}; - -// Implements the Invoke(object_ptr, &Class::Method) action. -template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> -class InvokeMethodAction { - public: - InvokeMethodAction(Class* obj_ptr, MethodPtr method_ptr) - : obj_ptr_(obj_ptr), method_ptr_(method_ptr) {} - - template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> - Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) const { - return InvokeHelper<Result, ArgumentTuple>::InvokeMethod( - obj_ptr_, method_ptr_, args); - } - - private: - Class* const obj_ptr_; - const MethodPtr method_ptr_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(InvokeMethodAction); -}; - -} // namespace internal - -// Various overloads for Invoke(). - -// Creates an action that invokes 'function_impl' with the mock -// function's arguments. -template <typename FunctionImpl> -PolymorphicAction<internal::InvokeAction<FunctionImpl> > Invoke( - FunctionImpl function_impl) { - return MakePolymorphicAction( - internal::InvokeAction<FunctionImpl>(function_impl)); -} - -// Creates an action that invokes the given method on the given object -// with the mock function's arguments. -template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> -PolymorphicAction<internal::InvokeMethodAction<Class, MethodPtr> > Invoke( - Class* obj_ptr, MethodPtr method_ptr) { - return MakePolymorphicAction( - internal::InvokeMethodAction<Class, MethodPtr>(obj_ptr, method_ptr)); -} - -// WithoutArgs(inner_action) can be used in a mock function with a -// non-empty argument list to perform inner_action, which takes no -// argument. In other words, it adapts an action accepting no -// argument to one that accepts (and ignores) arguments. -template <typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction> -WithoutArgs(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction>(action); -} - -// WithArg<k>(an_action) creates an action that passes the k-th -// (0-based) argument of the mock function to an_action and performs -// it. It adapts an action accepting one argument to one that accepts -// multiple arguments. For convenience, we also provide -// WithArgs<k>(an_action) (defined below) as a synonym. -template <int k, typename InnerAction> -inline internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k> -WithArg(const InnerAction& action) { - return internal::WithArgsAction<InnerAction, k>(action); -} - -// The ACTION*() macros trigger warning C4100 (unreferenced formal -// parameter) in MSVC with -W4. Unfortunately they cannot be fixed in -// the macro definition, as the warnings are generated when the macro -// is expanded and macro expansion cannot contain #pragma. Therefore -// we suppress them here. -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) -# pragma warning(disable:4100) -#endif - -// Action ReturnArg<k>() returns the k-th argument of the mock function. -ACTION_TEMPLATE(ReturnArg, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS()) { - return std::tr1::get<k>(args); -} - -// Action SaveArg<k>(pointer) saves the k-th (0-based) argument of the -// mock function to *pointer. -ACTION_TEMPLATE(SaveArg, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(pointer)) { - *pointer = ::std::tr1::get<k>(args); -} - -// Action SaveArgPointee<k>(pointer) saves the value pointed to -// by the k-th (0-based) argument of the mock function to *pointer. -ACTION_TEMPLATE(SaveArgPointee, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(pointer)) { - *pointer = *::std::tr1::get<k>(args); -} - -// Action SetArgReferee<k>(value) assigns 'value' to the variable -// referenced by the k-th (0-based) argument of the mock function. -ACTION_TEMPLATE(SetArgReferee, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(value)) { - typedef typename ::std::tr1::tuple_element<k, args_type>::type argk_type; - // Ensures that argument #k is a reference. If you get a compiler - // error on the next line, you are using SetArgReferee<k>(value) in - // a mock function whose k-th (0-based) argument is not a reference. - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(internal::is_reference<argk_type>::value, - SetArgReferee_must_be_used_with_a_reference_argument); - ::std::tr1::get<k>(args) = value; -} - -// Action SetArrayArgument<k>(first, last) copies the elements in -// source range [first, last) to the array pointed to by the k-th -// (0-based) argument, which can be either a pointer or an -// iterator. The action does not take ownership of the elements in the -// source range. -ACTION_TEMPLATE(SetArrayArgument, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(first, last)) { - // Microsoft compiler deprecates ::std::copy, so we want to suppress warning - // 4996 (Function call with parameters that may be unsafe) there. -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable:4996) // Temporarily disables warning 4996. -#endif - ::std::copy(first, last, ::std::tr1::get<k>(args)); -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state. -#endif -} - -// Action DeleteArg<k>() deletes the k-th (0-based) argument of the mock -// function. -ACTION_TEMPLATE(DeleteArg, - HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k), - AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS()) { - delete ::std::tr1::get<k>(args); -} - -// This action returns the value pointed to by 'pointer'. -ACTION_P(ReturnPointee, pointer) { return *pointer; } - -// Action Throw(exception) can be used in a mock function of any type -// to throw the given exception. Any copyable value can be thrown. -#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS - -// Suppresses the 'unreachable code' warning that VC generates in opt modes. -# ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable:4702) // Temporarily disables warning 4702. -# endif -ACTION_P(Throw, exception) { throw exception; } -# ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state. -# endif - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS - -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) -#endif - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_ACTIONS_H_ -// Copyright 2013, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: marcus.boerger@google.com (Marcus Boerger) - -// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. -// -// This file implements some matchers that depend on gmock-generated-matchers.h. -// -// Note that tests are implemented in gmock-matchers_test.cc rather than -// gmock-more-matchers-test.cc. - -#ifndef GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_MATCHERS_H_ -#define GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_MATCHERS_H_ - - -namespace testing { - -// Defines a matcher that matches an empty container. The container must -// support both size() and empty(), which all STL-like containers provide. -MATCHER(IsEmpty, negation ? "isn't empty" : "is empty") { - if (arg.empty()) { - return true; - } - *result_listener << "whose size is " << arg.size(); - return false; -} - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_MATCHERS_H_ - -namespace testing { - -// Declares Google Mock flags that we want a user to use programmatically. -GMOCK_DECLARE_bool_(catch_leaked_mocks); -GMOCK_DECLARE_string_(verbose); - -// Initializes Google Mock. This must be called before running the -// tests. In particular, it parses the command line for the flags -// that Google Mock recognizes. Whenever a Google Mock flag is seen, -// it is removed from argv, and *argc is decremented. -// -// No value is returned. Instead, the Google Mock flag variables are -// updated. -// -// Since Google Test is needed for Google Mock to work, this function -// also initializes Google Test and parses its flags, if that hasn't -// been done. -GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleMock(int* argc, char** argv); - -// This overloaded version can be used in Windows programs compiled in -// UNICODE mode. -GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleMock(int* argc, wchar_t** argv); - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_H_ diff --git a/test/gtest-extra-test.cc b/test/gtest-extra-test.cc index ea728607..42340a2d 100644 --- a/test/gtest-extra-test.cc +++ b/test/gtest-extra-test.cc @@ -9,31 +9,18 @@ #include <gtest/gtest-spi.h> -#include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <memory> #include <stdexcept> -#if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__) -# include <crtdbg.h> // for _CrtSetReportMode -#endif // _WIN32 - +#include "fmt/os.h" #include "util.h" -namespace { - -// This is used to suppress coverity warnings about untrusted values. -std::string sanitize(const std::string& s) { - std::string result; - for (std::string::const_iterator i = s.begin(), end = s.end(); i != end; ++i) - result.push_back(static_cast<char>(*i & 0xff)); - return result; -} - // Tests that assertion macros evaluate their arguments exactly once. -class SingleEvaluationTest : public ::testing::Test { +namespace { +class single_evaluation_test : public ::testing::Test { protected: - SingleEvaluationTest() { + single_evaluation_test() { p_ = s_; a_ = 0; b_ = 0; @@ -45,11 +32,12 @@ class SingleEvaluationTest : public ::testing::Test { static int a_; static int b_; }; +} // namespace -const char* const SingleEvaluationTest::s_ = "01234"; -const char* SingleEvaluationTest::p_; -int SingleEvaluationTest::a_; -int SingleEvaluationTest::b_; +const char* const single_evaluation_test::s_ = "01234"; +const char* single_evaluation_test::p_; +int single_evaluation_test::a_; +int single_evaluation_test::b_; void do_nothing() {} @@ -61,7 +49,7 @@ FMT_NORETURN void throw_system_error() { // Tests that when EXPECT_THROW_MSG fails, it evaluates its message argument // exactly once. -TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, FailedEXPECT_THROW_MSG) { +TEST_F(single_evaluation_test, failed_expect_throw_msg) { EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE( EXPECT_THROW_MSG(throw_exception(), std::exception, p_++), "01234"); EXPECT_EQ(s_ + 1, p_); @@ -69,14 +57,14 @@ TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, FailedEXPECT_THROW_MSG) { // Tests that when EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR fails, it evaluates its message argument // exactly once. -TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, FailedEXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR) { +TEST_F(single_evaluation_test, failed_expect_system_error) { EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE(EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(throw_system_error(), EDOM, p_++), "01234"); EXPECT_EQ(s_ + 1, p_); } // Tests that assertion arguments are evaluated exactly once. -TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, ExceptionTests) { +TEST_F(single_evaluation_test, exception_tests) { // successful EXPECT_THROW_MSG EXPECT_THROW_MSG( { // NOLINT @@ -116,7 +104,7 @@ TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, ExceptionTests) { EXPECT_EQ(4, b_); } -TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, SystemErrorTests) { +TEST_F(single_evaluation_test, system_error_tests) { // successful EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR( { // NOLINT @@ -159,14 +147,14 @@ TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, SystemErrorTests) { #if FMT_USE_FCNTL // Tests that when EXPECT_WRITE fails, it evaluates its message argument // exactly once. -TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, FailedEXPECT_WRITE) { +TEST_F(single_evaluation_test, failed_expect_write) { EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE(EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, std::printf("test"), p_++), "01234"); EXPECT_EQ(s_ + 1, p_); } // Tests that assertion arguments are evaluated exactly once. -TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, WriteTests) { +TEST_F(single_evaluation_test, write_tests) { // successful EXPECT_WRITE EXPECT_WRITE( stdout, @@ -192,7 +180,7 @@ TEST_F(SingleEvaluationTest, WriteTests) { } // Tests EXPECT_WRITE. -TEST(ExpectTest, EXPECT_WRITE) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_write) { EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, do_nothing(), ""); EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, std::printf("test"), "test"); EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, std::fprintf(stderr, "test"), "test"); @@ -201,7 +189,7 @@ TEST(ExpectTest, EXPECT_WRITE) { " Actual: that"); } -TEST(StreamingAssertionsTest, EXPECT_WRITE) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_write_streaming) { EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, std::printf("test"), "test") << "unexpected failure"; EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE(EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, std::printf("test"), "other") << "expected failure", @@ -211,8 +199,9 @@ TEST(StreamingAssertionsTest, EXPECT_WRITE) { // Tests that the compiler will not complain about unreachable code in the // EXPECT_THROW_MSG macro. -TEST(ExpectThrowTest, DoesNotGenerateUnreachableCodeWarning) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_throw_no_unreachable_code_warning) { int n = 0; + (void)n; using std::runtime_error; EXPECT_THROW_MSG(throw runtime_error(""), runtime_error, ""); EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE(EXPECT_THROW_MSG(n++, runtime_error, ""), ""); @@ -223,8 +212,9 @@ TEST(ExpectThrowTest, DoesNotGenerateUnreachableCodeWarning) { // Tests that the compiler will not complain about unreachable code in the // EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR macro. -TEST(ExpectSystemErrorTest, DoesNotGenerateUnreachableCodeWarning) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_system_error_no_unreachable_code_warning) { int n = 0; + (void)n; EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(throw fmt::system_error(EDOM, "test"), EDOM, "test"); EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE(EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(n++, EDOM, ""), ""); EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE(EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(throw 1, EDOM, ""), ""); @@ -233,7 +223,7 @@ TEST(ExpectSystemErrorTest, DoesNotGenerateUnreachableCodeWarning) { ""); } -TEST(AssertionSyntaxTest, ExceptionAssertionBehavesLikeSingleStatement) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_throw_behaves_like_single_statement) { if (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) EXPECT_THROW_MSG(do_nothing(), std::exception, ""); @@ -243,7 +233,7 @@ TEST(AssertionSyntaxTest, ExceptionAssertionBehavesLikeSingleStatement) { do_nothing(); } -TEST(AssertionSyntaxTest, SystemErrorAssertionBehavesLikeSingleStatement) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_system_error_behaves_like_single_statement) { if (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(do_nothing(), EDOM, ""); @@ -253,7 +243,7 @@ TEST(AssertionSyntaxTest, SystemErrorAssertionBehavesLikeSingleStatement) { do_nothing(); } -TEST(AssertionSyntaxTest, WriteAssertionBehavesLikeSingleStatement) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_write_behaves_like_single_statement) { if (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, std::printf("x"), "x"); @@ -264,7 +254,7 @@ TEST(AssertionSyntaxTest, WriteAssertionBehavesLikeSingleStatement) { } // Tests EXPECT_THROW_MSG. -TEST(ExpectTest, EXPECT_THROW_MSG) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_throw_msg) { EXPECT_THROW_MSG(throw_exception(), std::exception, "test"); EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE( EXPECT_THROW_MSG(throw_exception(), std::logic_error, "test"), @@ -282,15 +272,15 @@ TEST(ExpectTest, EXPECT_THROW_MSG) { } // Tests EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR. -TEST(ExpectTest, EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_system_error) { EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(throw_system_error(), EDOM, "test"); EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE( EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(throw_exception(), EDOM, "test"), "Expected: throw_exception() throws an exception of " - "type fmt::system_error.\n Actual: it throws a different type."); + "type std::system_error.\n Actual: it throws a different type."); EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE( EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(do_nothing(), EDOM, "test"), - "Expected: do_nothing() throws an exception of type fmt::system_error.\n" + "Expected: do_nothing() throws an exception of type std::system_error.\n" " Actual: it throws nothing."); EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE( EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(throw_system_error(), EDOM, "other"), @@ -298,11 +288,11 @@ TEST(ExpectTest, EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR) { "throw_system_error() throws an exception with a different message.\n" "Expected: {}\n" " Actual: {}", - format_system_error(EDOM, "other"), - format_system_error(EDOM, "test"))); + system_error_message(EDOM, "other"), + system_error_message(EDOM, "test"))); } -TEST(StreamingAssertionsTest, EXPECT_THROW_MSG) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_throw_msg_streaming) { EXPECT_THROW_MSG(throw_exception(), std::exception, "test") << "unexpected failure"; EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE( @@ -311,7 +301,7 @@ TEST(StreamingAssertionsTest, EXPECT_THROW_MSG) { "expected failure"); } -TEST(StreamingAssertionsTest, EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR) { +TEST(gtest_extra_test, expect_system_error_streaming) { EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(throw_system_error(), EDOM, "test") << "unexpected failure"; EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE( @@ -320,31 +310,19 @@ TEST(StreamingAssertionsTest, EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR) { "expected failure"); } -TEST(UtilTest, FormatSystemError) { - fmt::memory_buffer out; - fmt::format_system_error(out, EDOM, "test message"); - EXPECT_EQ(to_string(out), format_system_error(EDOM, "test message")); -} - #if FMT_USE_FCNTL using fmt::buffered_file; -using fmt::error_code; using fmt::file; -TEST(ErrorCodeTest, Ctor) { - EXPECT_EQ(error_code().get(), 0); - EXPECT_EQ(error_code(42).get(), 42); -} - -TEST(OutputRedirectTest, ScopedRedirect) { +TEST(output_redirect_test, scoped_redirect) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); { buffered_file file(write_end.fdopen("w")); std::fprintf(file.get(), "[[["); { - OutputRedirect redir(file.get()); + output_redirect redir(file.get()); std::fprintf(file.get(), "censored"); } std::fprintf(file.get(), "]]]"); @@ -352,8 +330,8 @@ TEST(OutputRedirectTest, ScopedRedirect) { EXPECT_READ(read_end, "[[[]]]"); } -// Test that OutputRedirect handles errors in flush correctly. -TEST(OutputRedirectTest, FlushErrorInCtor) { +// Test that output_redirect handles errors in flush correctly. +TEST(output_redirect_test, flush_error_in_ctor) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); int write_fd = write_end.descriptor(); @@ -362,47 +340,47 @@ TEST(OutputRedirectTest, FlushErrorInCtor) { // Put a character in a file buffer. EXPECT_EQ('x', fputc('x', f.get())); FMT_POSIX(close(write_fd)); - std::unique_ptr<OutputRedirect> redir{nullptr}; - EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR_NOASSERT(redir.reset(new OutputRedirect(f.get())), EBADF, + std::unique_ptr<output_redirect> redir{nullptr}; + EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR_NOASSERT(redir.reset(new output_redirect(f.get())), EBADF, "cannot flush stream"); redir.reset(nullptr); write_copy.dup2(write_fd); // "undo" close or dtor will fail } -TEST(OutputRedirectTest, DupErrorInCtor) { +TEST(output_redirect_test, dup_error_in_ctor) { buffered_file f = open_buffered_file(); - int fd = (f.fileno)(); + int fd = (f.descriptor)(); file copy = file::dup(fd); FMT_POSIX(close(fd)); - std::unique_ptr<OutputRedirect> redir{nullptr}; + std::unique_ptr<output_redirect> redir{nullptr}; EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR_NOASSERT( - redir.reset(new OutputRedirect(f.get())), EBADF, + redir.reset(new output_redirect(f.get())), EBADF, fmt::format("cannot duplicate file descriptor {}", fd)); copy.dup2(fd); // "undo" close or dtor will fail } -TEST(OutputRedirectTest, RestoreAndRead) { +TEST(output_redirect_test, restore_and_read) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); buffered_file file(write_end.fdopen("w")); std::fprintf(file.get(), "[[["); - OutputRedirect redir(file.get()); + output_redirect redir(file.get()); std::fprintf(file.get(), "censored"); - EXPECT_EQ("censored", sanitize(redir.restore_and_read())); - EXPECT_EQ("", sanitize(redir.restore_and_read())); + EXPECT_EQ("censored", redir.restore_and_read()); + EXPECT_EQ("", redir.restore_and_read()); std::fprintf(file.get(), "]]]"); file = buffered_file(); EXPECT_READ(read_end, "[[[]]]"); } // Test that OutputRedirect handles errors in flush correctly. -TEST(OutputRedirectTest, FlushErrorInRestoreAndRead) { +TEST(output_redirect_test, flush_error_in_restore_and_read) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); int write_fd = write_end.descriptor(); file write_copy = write_end.dup(write_fd); buffered_file f = write_end.fdopen("w"); - OutputRedirect redir(f.get()); + output_redirect redir(f.get()); // Put a character in a file buffer. EXPECT_EQ('x', fputc('x', f.get())); FMT_POSIX(close(write_fd)); @@ -411,13 +389,13 @@ TEST(OutputRedirectTest, FlushErrorInRestoreAndRead) { write_copy.dup2(write_fd); // "undo" close or dtor will fail } -TEST(OutputRedirectTest, ErrorInDtor) { +TEST(output_redirect_test, error_in_dtor) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); int write_fd = write_end.descriptor(); file write_copy = write_end.dup(write_fd); buffered_file f = write_end.fdopen("w"); - std::unique_ptr<OutputRedirect> redir(new OutputRedirect(f.get())); + std::unique_ptr<output_redirect> redir(new output_redirect(f.get())); // Put a character in a file buffer. EXPECT_EQ('x', fputc('x', f.get())); EXPECT_WRITE( @@ -430,10 +408,8 @@ TEST(OutputRedirectTest, ErrorInDtor) { FMT_POSIX(close(write_fd)); SUPPRESS_ASSERT(redir.reset(nullptr)); }, - format_system_error(EBADF, "cannot flush stream")); + system_error_message(EBADF, "cannot flush stream")); write_copy.dup2(write_fd); // "undo" close or dtor of buffered_file will fail } -#endif // FMT_USE_FILE_DESCRIPTORS - -} // namespace +#endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL diff --git a/test/gtest-extra.cc b/test/gtest-extra.cc index 58628a8a..542e4b5e 100644 --- a/test/gtest-extra.cc +++ b/test/gtest-extra.cc @@ -11,24 +11,7 @@ using fmt::file; -void OutputRedirect::flush() { -# if EOF != -1 -# error "FMT_RETRY assumes return value of -1 indicating failure" -# endif - int result = 0; - FMT_RETRY(result, fflush(file_)); - if (result != 0) throw fmt::system_error(errno, "cannot flush stream"); -} - -void OutputRedirect::restore() { - if (original_.descriptor() == -1) return; // Already restored. - flush(); - // Restore the original file. - original_.dup2(FMT_POSIX(fileno(file_))); - original_.close(); -} - -OutputRedirect::OutputRedirect(FILE* f) : file_(f) { +output_redirect::output_redirect(FILE* f) : file_(f) { flush(); int fd = FMT_POSIX(fileno(f)); // Create a file object referring to the original file. @@ -40,7 +23,7 @@ OutputRedirect::OutputRedirect(FILE* f) : file_(f) { write_end.dup2(fd); } -OutputRedirect::~OutputRedirect() FMT_NOEXCEPT { +output_redirect::~output_redirect() noexcept { try { restore(); } catch (const std::exception& e) { @@ -48,7 +31,23 @@ OutputRedirect::~OutputRedirect() FMT_NOEXCEPT { } } -std::string OutputRedirect::restore_and_read() { +void output_redirect::flush() { + int result = 0; + do { + result = fflush(file_); + } while (result == EOF && errno == EINTR); + if (result != 0) throw fmt::system_error(errno, "cannot flush stream"); +} + +void output_redirect::restore() { + if (original_.descriptor() == -1) return; // Already restored. + flush(); + // Restore the original file. + original_.dup2(FMT_POSIX(fileno(file_))); + original_.close(); +} + +std::string output_redirect::restore_and_read() { // Restore output. restore(); @@ -79,9 +78,3 @@ std::string read(file& f, size_t count) { } #endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL - -std::string format_system_error(int error_code, fmt::string_view message) { - fmt::memory_buffer out; - format_system_error(out, error_code, message); - return to_string(out); -} diff --git a/test/gtest-extra.h b/test/gtest-extra.h index 949ff50e..03a07a2a 100644 --- a/test/gtest-extra.h +++ b/test/gtest-extra.h @@ -8,10 +8,12 @@ #ifndef FMT_GTEST_EXTRA_H_ #define FMT_GTEST_EXTRA_H_ +#include <stdlib.h> // _invalid_parameter_handler + #include <string> #include "fmt/os.h" -#include "gmock.h" +#include "gmock/gmock.h" #define FMT_TEST_THROW_(statement, expected_exception, expected_message, fail) \ GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ @@ -51,17 +53,21 @@ FMT_TEST_THROW_(statement, expected_exception, expected_message, \ GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -std::string format_system_error(int error_code, fmt::string_view message); +inline std::string system_error_message(int error_code, + const std::string& message) { + auto ec = std::error_code(error_code, std::generic_category()); + return std::system_error(ec, message).what(); +} #define EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(statement, error_code, message) \ - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(statement, fmt::system_error, \ - format_system_error(error_code, message)) + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(statement, std::system_error, \ + system_error_message(error_code, message)) #if FMT_USE_FCNTL // Captures file output by redirecting it to a pipe. // The output it can handle is limited by the pipe capacity. -class OutputRedirect { +class output_redirect { private: FILE* file_; fmt::file original_; // Original file passed to redirector. @@ -71,11 +77,11 @@ class OutputRedirect { void restore(); public: - explicit OutputRedirect(FILE* file); - ~OutputRedirect() FMT_NOEXCEPT; + explicit output_redirect(FILE* file); + ~output_redirect() noexcept; - OutputRedirect(const OutputRedirect&) = delete; - OutputRedirect& operator=(const OutputRedirect&) = delete; + output_redirect(const output_redirect&) = delete; + void operator=(const output_redirect&) = delete; // Restores the original file, reads output from the pipe into a string // and returns it. @@ -86,7 +92,7 @@ class OutputRedirect { GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ if (::testing::AssertionResult gtest_ar = ::testing::AssertionSuccess()) { \ std::string gtest_expected_output = expected_output; \ - OutputRedirect gtest_redir(file); \ + output_redirect gtest_redir(file); \ GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ std::string gtest_output = gtest_redir.restore_and_read(); \ if (gtest_output != gtest_expected_output) { \ @@ -107,7 +113,7 @@ class OutputRedirect { // Suppresses Windows assertions on invalid file descriptors, making // POSIX functions return proper error codes instead of crashing on Windows. -class SuppressAssert { +class suppress_assert { private: _invalid_parameter_handler original_handler_; int original_report_mode_; @@ -116,19 +122,20 @@ class SuppressAssert { const wchar_t*, unsigned, uintptr_t) {} public: - SuppressAssert() + suppress_assert() : original_handler_( _set_invalid_parameter_handler(handle_invalid_parameter)), original_report_mode_(_CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_ASSERT, 0)) {} - ~SuppressAssert() { + ~suppress_assert() { _set_invalid_parameter_handler(original_handler_); _CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_ASSERT, original_report_mode_); + (void)original_report_mode_; } }; # define SUPPRESS_ASSERT(statement) \ { \ - SuppressAssert sa; \ + suppress_assert sa; \ statement; \ } # else @@ -142,7 +149,7 @@ class SuppressAssert { std::string read(fmt::file& f, size_t count); # define EXPECT_READ(file, expected_content) \ - EXPECT_EQ(expected_content, \ + EXPECT_EQ(expected_content, \ read(file, fmt::string_view(expected_content).size())) #else @@ -155,9 +162,4 @@ std::string read(fmt::file& f, size_t count); } while (false) #endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL -template <typename Mock> struct ScopedMock : testing::StrictMock<Mock> { - ScopedMock() { Mock::instance = this; } - ~ScopedMock() { Mock::instance = nullptr; } -}; - #endif // FMT_GTEST_EXTRA_H_ diff --git a/test/gtest/.clang-format b/test/gtest/.clang-format new file mode 100644 index 00000000..ec09b9b6 --- /dev/null +++ b/test/gtest/.clang-format @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ +# Disable clang-format here +DisableFormat: true +SortIncludes: Never diff --git a/test/gtest/CMakeLists.txt b/test/gtest/CMakeLists.txt new file mode 100644 index 00000000..0cccc61f --- /dev/null +++ b/test/gtest/CMakeLists.txt @@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ +#------------------------------------------------------------------------------ +# Build the google test library + +# We compile Google Test ourselves instead of using pre-compiled libraries. +# See the Google Test FAQ "Why is it not recommended to install a +# pre-compiled copy of Google Test (for example, into /usr/local)?" +# at http://code.google.com/p/googletest/wiki/FAQ for more details. +add_library(gtest STATIC + gmock-gtest-all.cc gmock/gmock.h gtest/gtest.h gtest/gtest-spi.h) +target_compile_definitions(gtest PUBLIC GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING=1) +target_include_directories(gtest SYSTEM PUBLIC .) +target_compile_features(gtest PUBLIC cxx_std_11) + +find_package(Threads) +if (Threads_FOUND) + target_link_libraries(gtest ${CMAKE_THREAD_LIBS_INIT}) +else () + target_compile_definitions(gtest PUBLIC GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD=0) +endif () + +if (MSVC) + # Disable MSVC warnings of _CRT_INSECURE_DEPRECATE functions. + target_compile_definitions(gtest PRIVATE _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS) + if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang") + # Disable MSVC warnings of POSIX functions. + target_compile_options(gtest PUBLIC -Wno-deprecated-declarations) + endif () +endif () + +# Silence MSVC tr1 deprecation warning in gmock. +target_compile_definitions(gtest + PUBLIC _SILENCE_TR1_NAMESPACE_DEPRECATION_WARNING=1) diff --git a/test/gmock-gtest-all.cc b/test/gtest/gmock-gtest-all.cc index bc43f930..7b33134f 100644 --- a/test/gmock-gtest-all.cc +++ b/test/gtest/gmock-gtest-all.cc @@ -26,17 +26,16 @@ // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + // -// Author: mheule@google.com (Markus Heule) -// -// Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) +// Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) // // Sometimes it's desirable to build Google Test by compiling a single file. // This file serves this purpose. // This line ensures that gtest.h can be compiled on its own, even // when it's fused. -#include "gtest.h" +#include "gtest/gtest.h" // The following lines pull in the real gtest *.cc files. // Copyright 2005, Google Inc. @@ -67,10 +66,9 @@ // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + // -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) -// -// The Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) // Copyright 2007, Google Inc. // All rights reserved. @@ -100,14 +98,19 @@ // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) + // // Utilities for testing Google Test itself and code that uses Google Test // (e.g. frameworks built on top of Google Test). -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ -# define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ +// GOOGLETEST_CM0004 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ + + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) namespace testing { @@ -140,14 +143,14 @@ class GTEST_API_ ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter TestPartResultArray* result); // The d'tor restores the previous test part result reporter. - virtual ~ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter(); + ~ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter() override; // Appends the TestPartResult object to the TestPartResultArray // received in the constructor. // // This method is from the TestPartResultReporterInterface // interface. - virtual void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result); + void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) override; private: void Init(); @@ -170,13 +173,12 @@ class GTEST_API_ SingleFailureChecker { public: // The constructor remembers the arguments. SingleFailureChecker(const TestPartResultArray* results, - TestPartResult::Type type, const string& substr); + TestPartResult::Type type, const std::string& substr); ~SingleFailureChecker(); - private: const TestPartResultArray* const results_; const TestPartResult::Type type_; - const string substr_; + const std::string substr_; GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(SingleFailureChecker); }; @@ -185,6 +187,8 @@ class GTEST_API_ SingleFailureChecker { } // namespace testing +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + // A set of macros for testing Google Test assertions or code that's expected // to generate Google Test fatal failures. It verifies that the given // statement will cause exactly one fatal Google Test failure with 'substr' @@ -208,43 +212,39 @@ class GTEST_API_ SingleFailureChecker { // helper macro, due to some peculiarity in how the preprocessor // works. The AcceptsMacroThatExpandsToUnprotectedComma test in // gtest_unittest.cc will fail to compile if we do that. -# define EXPECT_FATAL_FAILURE(statement, substr) \ - do { \ - class GTestExpectFatalFailureHelper { \ - public: \ - static void Execute() { statement; } \ - }; \ - ::testing::TestPartResultArray gtest_failures; \ - ::testing::internal::SingleFailureChecker gtest_checker( \ - >est_failures, ::testing::TestPartResult::kFatalFailure, \ - (substr)); \ - { \ - ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter gtest_reporter( \ - ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter:: \ - INTERCEPT_ONLY_CURRENT_THREAD, \ - >est_failures); \ - GTestExpectFatalFailureHelper::Execute(); \ - } \ - } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) - -# define EXPECT_FATAL_FAILURE_ON_ALL_THREADS(statement, substr) \ - do { \ - class GTestExpectFatalFailureHelper { \ - public: \ - static void Execute() { statement; } \ - }; \ - ::testing::TestPartResultArray gtest_failures; \ - ::testing::internal::SingleFailureChecker gtest_checker( \ - >est_failures, ::testing::TestPartResult::kFatalFailure, \ - (substr)); \ - { \ - ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter gtest_reporter( \ - ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter:: \ - INTERCEPT_ALL_THREADS, \ - >est_failures); \ - GTestExpectFatalFailureHelper::Execute(); \ - } \ - } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) +#define EXPECT_FATAL_FAILURE(statement, substr) \ + do { \ + class GTestExpectFatalFailureHelper {\ + public:\ + static void Execute() { statement; }\ + };\ + ::testing::TestPartResultArray gtest_failures;\ + ::testing::internal::SingleFailureChecker gtest_checker(\ + >est_failures, ::testing::TestPartResult::kFatalFailure, (substr));\ + {\ + ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter gtest_reporter(\ + ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter:: \ + INTERCEPT_ONLY_CURRENT_THREAD, >est_failures);\ + GTestExpectFatalFailureHelper::Execute();\ + }\ + } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) + +#define EXPECT_FATAL_FAILURE_ON_ALL_THREADS(statement, substr) \ + do { \ + class GTestExpectFatalFailureHelper {\ + public:\ + static void Execute() { statement; }\ + };\ + ::testing::TestPartResultArray gtest_failures;\ + ::testing::internal::SingleFailureChecker gtest_checker(\ + >est_failures, ::testing::TestPartResult::kFatalFailure, (substr));\ + {\ + ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter gtest_reporter(\ + ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter:: \ + INTERCEPT_ALL_THREADS, >est_failures);\ + GTestExpectFatalFailureHelper::Execute();\ + }\ + } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) // A macro for testing Google Test assertions or code that's expected to // generate Google Test non-fatal failures. It asserts that the given @@ -278,44 +278,37 @@ class GTEST_API_ SingleFailureChecker { // instead of // GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement) // to avoid an MSVC warning on unreachable code. -# define EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE(statement, substr) \ - do { \ - ::testing::TestPartResultArray gtest_failures; \ - ::testing::internal::SingleFailureChecker gtest_checker( \ - >est_failures, ::testing::TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure, \ - (substr)); \ - { \ - ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter gtest_reporter( \ - ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter:: \ - INTERCEPT_ONLY_CURRENT_THREAD, \ - >est_failures); \ - if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ - statement; \ - } \ - } \ - } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) - -# define EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE_ON_ALL_THREADS(statement, substr) \ - do { \ - ::testing::TestPartResultArray gtest_failures; \ - ::testing::internal::SingleFailureChecker gtest_checker( \ - >est_failures, ::testing::TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure, \ - (substr)); \ - { \ - ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter gtest_reporter( \ - ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter:: \ - INTERCEPT_ALL_THREADS, \ - >est_failures); \ - if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ - statement; \ - } \ - } \ - } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ +#define EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE(statement, substr) \ + do {\ + ::testing::TestPartResultArray gtest_failures;\ + ::testing::internal::SingleFailureChecker gtest_checker(\ + >est_failures, ::testing::TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure, \ + (substr));\ + {\ + ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter gtest_reporter(\ + ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter:: \ + INTERCEPT_ONLY_CURRENT_THREAD, >est_failures);\ + if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { statement; }\ + }\ + } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) + +#define EXPECT_NONFATAL_FAILURE_ON_ALL_THREADS(statement, substr) \ + do {\ + ::testing::TestPartResultArray gtest_failures;\ + ::testing::internal::SingleFailureChecker gtest_checker(\ + >est_failures, ::testing::TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure, \ + (substr));\ + {\ + ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter gtest_reporter(\ + ::testing::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter::INTERCEPT_ALL_THREADS, \ + >est_failures);\ + if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { statement; }\ + }\ + } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ #include <ctype.h> -#include <math.h> #include <stdarg.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> @@ -324,95 +317,78 @@ class GTEST_API_ SingleFailureChecker { #include <wctype.h> #include <algorithm> +#include <chrono> // NOLINT +#include <cmath> +#include <cstdint> #include <iomanip> #include <limits> +#include <list> +#include <map> #include <ostream> // NOLINT #include <sstream> #include <vector> #if GTEST_OS_LINUX -// TODO(kenton@google.com): Use autoconf to detect availability of -// gettimeofday(). -# define GTEST_HAS_GETTIMEOFDAY_ 1 - -# include <fcntl.h> // NOLINT -# include <limits.h> // NOLINT -# include <sched.h> // NOLINT +# include <fcntl.h> // NOLINT +# include <limits.h> // NOLINT +# include <sched.h> // NOLINT // Declares vsnprintf(). This header is not available on Windows. -# include <strings.h> // NOLINT -# include <sys/mman.h> // NOLINT -# include <sys/time.h> // NOLINT -# include <unistd.h> // NOLINT - -# include <string> - -#elif GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN -# define GTEST_HAS_GETTIMEOFDAY_ 1 -# include <sys/time.h> // NOLINT +# include <strings.h> // NOLINT +# include <sys/mman.h> // NOLINT +# include <sys/time.h> // NOLINT +# include <unistd.h> // NOLINT +# include <string> #elif GTEST_OS_ZOS -# define GTEST_HAS_GETTIMEOFDAY_ 1 -# include <sys/time.h> // NOLINT +# include <sys/time.h> // NOLINT // On z/OS we additionally need strings.h for strcasecmp. -# include <strings.h> // NOLINT +# include <strings.h> // NOLINT #elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE // We are on Windows CE. -# include <windows.h> // NOLINT +# include <windows.h> // NOLINT +# undef min #elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS // We are on Windows proper. -# include <io.h> // NOLINT -# include <sys/stat.h> // NOLINT -# include <sys/timeb.h> // NOLINT -# include <sys/types.h> // NOLINT - -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW -// MinGW has gettimeofday() but not _ftime64(). -// TODO(kenton@google.com): Use autoconf to detect availability of -// gettimeofday(). -// TODO(kenton@google.com): There are other ways to get the time on -// Windows, like GetTickCount() or GetSystemTimeAsFileTime(). MinGW -// supports these. consider using them instead. -# define GTEST_HAS_GETTIMEOFDAY_ 1 -# include <sys/time.h> // NOLINT -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW +# include <windows.h> // NOLINT +# undef min -// cpplint thinks that the header is already included, so we want to -// silence it. -# include <windows.h> // NOLINT +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# include <crtdbg.h> // NOLINT +#endif -#else +# include <io.h> // NOLINT +# include <sys/timeb.h> // NOLINT +# include <sys/types.h> // NOLINT +# include <sys/stat.h> // NOLINT + +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW +# include <sys/time.h> // NOLINT +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW -// Assume other platforms have gettimeofday(). -// TODO(kenton@google.com): Use autoconf to detect availability of -// gettimeofday(). -# define GTEST_HAS_GETTIMEOFDAY_ 1 +#else // cpplint thinks that the header is already included, so we want to // silence it. -# include <sys/time.h> // NOLINT -# include <unistd.h> // NOLINT +# include <sys/time.h> // NOLINT +# include <unistd.h> // NOLINT #endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX #if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS -# include <stdexcept> +# include <stdexcept> #endif #if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ -# include <arpa/inet.h> // NOLINT -# include <netdb.h> // NOLINT +# include <arpa/inet.h> // NOLINT +# include <netdb.h> // NOLINT +# include <sys/socket.h> // NOLINT +# include <sys/types.h> // NOLINT #endif -// Indicates that this translation unit is part of Google Test's -// implementation. It must come before gtest-internal-inl.h is -// included, or there will be a compiler error. This trick is to -// prevent a user from accidentally including gtest-internal-inl.h in -// his code. -#define GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ 1 // Copyright 2005, Google Inc. // All rights reserved. // @@ -442,44 +418,39 @@ class GTEST_API_ SingleFailureChecker { // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// Utility functions and classes used by the Google C++ testing framework. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) -// +// Utility functions and classes used by the Google C++ testing framework.// // This file contains purely Google Test's internal implementation. Please // DO NOT #INCLUDE IT IN A USER PROGRAM. -#ifndef GTEST_SRC_GTEST_INTERNAL_INL_H_ -# define GTEST_SRC_GTEST_INTERNAL_INL_H_ - -// GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ is defined to 1 iff the current translation unit is -// part of Google Test's implementation; otherwise it's undefined. -# if !GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ -// A user is trying to include this from his code - just say no. -# error \ - "gtest-internal-inl.h is part of Google Test's internal implementation." -# error "It must not be included except by Google Test itself." -# endif // GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ - -# ifndef _WIN32_WCE -# include <errno.h> -# endif // !_WIN32_WCE -# include <stddef.h> -# include <stdlib.h> // For strtoll/_strtoul64/malloc/free. -# include <string.h> // For memmove. - -# include <algorithm> -# include <string> -# include <vector> - -# if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ -# include <arpa/inet.h> // NOLINT -# include <netdb.h> // NOLINT -# endif +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_SRC_GTEST_INTERNAL_INL_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_SRC_GTEST_INTERNAL_INL_H_ + +#ifndef _WIN32_WCE +# include <errno.h> +#endif // !_WIN32_WCE +#include <stddef.h> +#include <stdlib.h> // For strtoll/_strtoul64/malloc/free. +#include <string.h> // For memmove. + +#include <algorithm> +#include <cstdint> +#include <memory> +#include <string> +#include <vector> + + +#if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ +# include <arpa/inet.h> // NOLINT +# include <netdb.h> // NOLINT +#endif + +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# include <windows.h> // NOLINT +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -# include <windows.h> // NOLINT -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) namespace testing { @@ -501,28 +472,32 @@ const char kAlsoRunDisabledTestsFlag[] = "also_run_disabled_tests"; const char kBreakOnFailureFlag[] = "break_on_failure"; const char kCatchExceptionsFlag[] = "catch_exceptions"; const char kColorFlag[] = "color"; +const char kFailFast[] = "fail_fast"; const char kFilterFlag[] = "filter"; const char kListTestsFlag[] = "list_tests"; const char kOutputFlag[] = "output"; +const char kBriefFlag[] = "brief"; const char kPrintTimeFlag[] = "print_time"; +const char kPrintUTF8Flag[] = "print_utf8"; const char kRandomSeedFlag[] = "random_seed"; const char kRepeatFlag[] = "repeat"; const char kShuffleFlag[] = "shuffle"; const char kStackTraceDepthFlag[] = "stack_trace_depth"; const char kStreamResultToFlag[] = "stream_result_to"; const char kThrowOnFailureFlag[] = "throw_on_failure"; +const char kFlagfileFlag[] = "flagfile"; // A valid random seed must be in [1, kMaxRandomSeed]. const int kMaxRandomSeed = 99999; -// g_help_flag is true iff the --help flag or an equivalent form is -// specified on the command line. +// g_help_flag is true if and only if the --help flag or an equivalent form +// is specified on the command line. GTEST_API_ extern bool g_help_flag; // Returns the current time in milliseconds. GTEST_API_ TimeInMillis GetTimeInMillis(); -// Returns true iff Google Test should use colors in the output. +// Returns true if and only if Google Test should use colors in the output. GTEST_API_ bool ShouldUseColor(bool stdout_is_tty); // Formats the given time in milliseconds as seconds. @@ -538,21 +513,21 @@ GTEST_API_ std::string FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsIso8601(TimeInMillis ms); // // On success, stores the value of the flag in *value, and returns // true. On failure, returns false without changing *value. -GTEST_API_ bool ParseInt32Flag(const char* str, const char* flag, Int32* value); +GTEST_API_ bool ParseInt32Flag( + const char* str, const char* flag, int32_t* value); // Returns a random seed in range [1, kMaxRandomSeed] based on the // given --gtest_random_seed flag value. -inline int GetRandomSeedFromFlag(Int32 random_seed_flag) { - const unsigned int raw_seed = - (random_seed_flag == 0) ? static_cast<unsigned int>(GetTimeInMillis()) - : static_cast<unsigned int>(random_seed_flag); +inline int GetRandomSeedFromFlag(int32_t random_seed_flag) { + const unsigned int raw_seed = (random_seed_flag == 0) ? + static_cast<unsigned int>(GetTimeInMillis()) : + static_cast<unsigned int>(random_seed_flag); // Normalizes the actual seed to range [1, kMaxRandomSeed] such that // it's easy to type. const int normalized_seed = static_cast<int>((raw_seed - 1U) % - static_cast<unsigned int>(kMaxRandomSeed)) + - 1; + static_cast<unsigned int>(kMaxRandomSeed)) + 1; return normalized_seed; } @@ -579,11 +554,14 @@ class GTestFlagSaver { color_ = GTEST_FLAG(color); death_test_style_ = GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style); death_test_use_fork_ = GTEST_FLAG(death_test_use_fork); + fail_fast_ = GTEST_FLAG(fail_fast); filter_ = GTEST_FLAG(filter); internal_run_death_test_ = GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test); list_tests_ = GTEST_FLAG(list_tests); output_ = GTEST_FLAG(output); + brief_ = GTEST_FLAG(brief); print_time_ = GTEST_FLAG(print_time); + print_utf8_ = GTEST_FLAG(print_utf8); random_seed_ = GTEST_FLAG(random_seed); repeat_ = GTEST_FLAG(repeat); shuffle_ = GTEST_FLAG(shuffle); @@ -601,10 +579,13 @@ class GTestFlagSaver { GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) = death_test_style_; GTEST_FLAG(death_test_use_fork) = death_test_use_fork_; GTEST_FLAG(filter) = filter_; + GTEST_FLAG(fail_fast) = fail_fast_; GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test) = internal_run_death_test_; GTEST_FLAG(list_tests) = list_tests_; GTEST_FLAG(output) = output_; + GTEST_FLAG(brief) = brief_; GTEST_FLAG(print_time) = print_time_; + GTEST_FLAG(print_utf8) = print_utf8_; GTEST_FLAG(random_seed) = random_seed_; GTEST_FLAG(repeat) = repeat_; GTEST_FLAG(shuffle) = shuffle_; @@ -621,15 +602,18 @@ class GTestFlagSaver { std::string color_; std::string death_test_style_; bool death_test_use_fork_; + bool fail_fast_; std::string filter_; std::string internal_run_death_test_; bool list_tests_; std::string output_; + bool brief_; bool print_time_; - internal::Int32 random_seed_; - internal::Int32 repeat_; + bool print_utf8_; + int32_t random_seed_; + int32_t repeat_; bool shuffle_; - internal::Int32 stack_trace_depth_; + int32_t stack_trace_depth_; std::string stream_result_to_; bool throw_on_failure_; } GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; @@ -640,11 +624,11 @@ class GTestFlagSaver { // If the code_point is not a valid Unicode code point // (i.e. outside of Unicode range U+0 to U+10FFFF) it will be converted // to "(Invalid Unicode 0xXXXXXXXX)". -GTEST_API_ std::string CodePointToUtf8(UInt32 code_point); +GTEST_API_ std::string CodePointToUtf8(uint32_t code_point); // Converts a wide string to a narrow string in UTF-8 encoding. // The wide string is assumed to have the following encoding: -// UTF-16 if sizeof(wchar_t) == 2 (on Windows, Cygwin, Symbian OS) +// UTF-16 if sizeof(wchar_t) == 2 (on Windows, Cygwin) // UTF-32 if sizeof(wchar_t) == 4 (on Linux) // Parameter str points to a null-terminated wide string. // Parameter num_chars may additionally limit the number @@ -673,17 +657,17 @@ GTEST_API_ bool ShouldShard(const char* total_shards_str, const char* shard_index_str, bool in_subprocess_for_death_test); -// Parses the environment variable var as an Int32. If it is unset, -// returns default_val. If it is not an Int32, prints an error and +// Parses the environment variable var as a 32-bit integer. If it is unset, +// returns default_val. If it is not a 32-bit integer, prints an error and // and aborts. -GTEST_API_ Int32 Int32FromEnvOrDie(const char* env_var, Int32 default_val); +GTEST_API_ int32_t Int32FromEnvOrDie(const char* env_var, int32_t default_val); // Given the total number of shards, the shard index, and the test id, -// returns true iff the test should be run on this shard. The test id is -// some arbitrary but unique non-negative integer assigned to each test +// returns true if and only if the test should be run on this shard. The test id +// is some arbitrary but unique non-negative integer assigned to each test // method. Assumes that 0 <= shard_index < total_shards. -GTEST_API_ bool ShouldRunTestOnShard(int total_shards, int shard_index, - int test_id); +GTEST_API_ bool ShouldRunTestOnShard( + int total_shards, int shard_index, int test_id); // STL container utilities. @@ -695,7 +679,8 @@ inline int CountIf(const Container& c, Predicate predicate) { // Solaris has a non-standard signature. int count = 0; for (typename Container::const_iterator it = c.begin(); it != c.end(); ++it) { - if (predicate(*it)) ++count; + if (predicate(*it)) + ++count; } return count; } @@ -710,7 +695,8 @@ void ForEach(const Container& c, Functor functor) { // in range [0, v.size()). template <typename E> inline E GetElementOr(const std::vector<E>& v, int i, E default_value) { - return (i < 0 || i >= static_cast<int>(v.size())) ? default_value : v[i]; + return (i < 0 || i >= static_cast<int>(v.size())) ? default_value + : v[static_cast<size_t>(i)]; } // Performs an in-place shuffle of a range of the vector's elements. @@ -732,8 +718,11 @@ void ShuffleRange(internal::Random* random, int begin, int end, // http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fisher-Yates_shuffle for (int range_width = end - begin; range_width >= 2; range_width--) { const int last_in_range = begin + range_width - 1; - const int selected = begin + random->Generate(range_width); - std::swap((*v)[selected], (*v)[last_in_range]); + const int selected = + begin + + static_cast<int>(random->Generate(static_cast<uint32_t>(range_width))); + std::swap((*v)[static_cast<size_t>(selected)], + (*v)[static_cast<size_t>(last_in_range)]); } } @@ -745,7 +734,10 @@ inline void Shuffle(internal::Random* random, std::vector<E>* v) { // A function for deleting an object. Handy for being used as a // functor. -template <typename T> static void Delete(T* x) { delete x; } +template <typename T> +static void Delete(T* x) { + delete x; +} // A predicate that checks the key of a TestProperty against a known key. // @@ -757,7 +749,7 @@ class TestPropertyKeyIs { // TestPropertyKeyIs has NO default constructor. explicit TestPropertyKeyIs(const std::string& key) : key_(key) {} - // Returns true iff the test name of test property matches on key_. + // Returns true if and only if the test name of test property matches on key_. bool operator()(const TestProperty& test_property) const { return test_property.key() == key_; } @@ -790,26 +782,19 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestOptions { // Functions for processing the gtest_filter flag. - // Returns true iff the wildcard pattern matches the string. The - // first ':' or '\0' character in pattern marks the end of it. - // - // This recursive algorithm isn't very efficient, but is clear and - // works well enough for matching test names, which are short. - static bool PatternMatchesString(const char* pattern, const char* str); - - // Returns true iff the user-specified filter matches the test case - // name and the test name. - static bool FilterMatchesTest(const std::string& test_case_name, + // Returns true if and only if the user-specified filter matches the test + // suite name and the test name. + static bool FilterMatchesTest(const std::string& test_suite_name, const std::string& test_name); -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS // Function for supporting the gtest_catch_exception flag. // Returns EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_HANDLER if Google Test should handle the // given SEH exception, or EXCEPTION_CONTINUE_SEARCH otherwise. // This function is useful as an __except condition. static int GTestShouldProcessSEH(DWORD exception_code); -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS // Returns true if "name" matches the ':' separated list of glob-style // filters in "filter". @@ -832,13 +817,17 @@ class OsStackTraceGetterInterface { // in the trace. // skip_count - the number of top frames to be skipped; doesn't count // against max_depth. - virtual string CurrentStackTrace(int max_depth, int skip_count) = 0; + virtual std::string CurrentStackTrace(int max_depth, int skip_count) = 0; // UponLeavingGTest() should be called immediately before Google Test calls // user code. It saves some information about the current stack that // CurrentStackTrace() will use to find and hide Google Test stack frames. virtual void UponLeavingGTest() = 0; + // This string is inserted in place of stack frames that are part of + // Google Test's implementation. + static const char* const kElidedFramesMarker; + private: GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(OsStackTraceGetterInterface); }; @@ -846,25 +835,21 @@ class OsStackTraceGetterInterface { // A working implementation of the OsStackTraceGetterInterface interface. class OsStackTraceGetter : public OsStackTraceGetterInterface { public: - OsStackTraceGetter() : caller_frame_(NULL) {} - - virtual string CurrentStackTrace(int max_depth, int skip_count) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); + OsStackTraceGetter() {} - virtual void UponLeavingGTest() GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); - - // This string is inserted in place of stack frames that are part of - // Google Test's implementation. - static const char* const kElidedFramesMarker; + std::string CurrentStackTrace(int max_depth, int skip_count) override; + void UponLeavingGTest() override; private: - Mutex mutex_; // protects all internal state +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL + Mutex mutex_; // Protects all internal state. // We save the stack frame below the frame that calls user code. // We do this because the address of the frame immediately below // the user code changes between the call to UponLeavingGTest() - // and any calls to CurrentStackTrace() from within the user code. - void* caller_frame_; + // and any calls to the stack trace code from within the user code. + void* caller_frame_ = nullptr; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(OsStackTraceGetter); }; @@ -879,12 +864,12 @@ struct TraceInfo { // This is the default global test part result reporter used in UnitTestImpl. // This class should only be used by UnitTestImpl. class DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter - : public TestPartResultReporterInterface { + : public TestPartResultReporterInterface { public: explicit DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter(UnitTestImpl* unit_test); // Implements the TestPartResultReporterInterface. Reports the test part // result in the current test. - virtual void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result); + void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) override; private: UnitTestImpl* const unit_test_; @@ -900,7 +885,7 @@ class DefaultPerThreadTestPartResultReporter explicit DefaultPerThreadTestPartResultReporter(UnitTestImpl* unit_test); // Implements the TestPartResultReporterInterface. The implementation just // delegates to the current global test part result reporter of *unit_test_. - virtual void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result); + void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) override; private: UnitTestImpl* const unit_test_; @@ -938,22 +923,25 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { void SetTestPartResultReporterForCurrentThread( TestPartResultReporterInterface* reporter); - // Gets the number of successful test cases. - int successful_test_case_count() const; + // Gets the number of successful test suites. + int successful_test_suite_count() const; - // Gets the number of failed test cases. - int failed_test_case_count() const; + // Gets the number of failed test suites. + int failed_test_suite_count() const; - // Gets the number of all test cases. - int total_test_case_count() const; + // Gets the number of all test suites. + int total_test_suite_count() const; - // Gets the number of all test cases that contain at least one test + // Gets the number of all test suites that contain at least one test // that should run. - int test_case_to_run_count() const; + int test_suite_to_run_count() const; // Gets the number of successful tests. int successful_test_count() const; + // Gets the number of skipped tests. + int skipped_test_count() const; + // Gets the number of failed tests. int failed_test_count() const; @@ -979,27 +967,33 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { // Gets the elapsed time, in milliseconds. TimeInMillis elapsed_time() const { return elapsed_time_; } - // Returns true iff the unit test passed (i.e. all test cases passed). + // Returns true if and only if the unit test passed (i.e. all test suites + // passed). bool Passed() const { return !Failed(); } - // Returns true iff the unit test failed (i.e. some test case failed - // or something outside of all tests failed). + // Returns true if and only if the unit test failed (i.e. some test suite + // failed or something outside of all tests failed). bool Failed() const { - return failed_test_case_count() > 0 || ad_hoc_test_result()->Failed(); + return failed_test_suite_count() > 0 || ad_hoc_test_result()->Failed(); } - // Gets the i-th test case among all the test cases. i can range from 0 to - // total_test_case_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. - const TestCase* GetTestCase(int i) const { - const int index = GetElementOr(test_case_indices_, i, -1); - return index < 0 ? NULL : test_cases_[i]; + // Gets the i-th test suite among all the test suites. i can range from 0 to + // total_test_suite_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. + const TestSuite* GetTestSuite(int i) const { + const int index = GetElementOr(test_suite_indices_, i, -1); + return index < 0 ? nullptr : test_suites_[static_cast<size_t>(i)]; } - // Gets the i-th test case among all the test cases. i can range from 0 to - // total_test_case_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. - TestCase* GetMutableTestCase(int i) { - const int index = GetElementOr(test_case_indices_, i, -1); - return index < 0 ? NULL : test_cases_[index]; + // Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + const TestCase* GetTestCase(int i) const { return GetTestSuite(i); } +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + // Gets the i-th test suite among all the test suites. i can range from 0 to + // total_test_suite_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. + TestSuite* GetMutableSuiteCase(int i) { + const int index = GetElementOr(test_suite_indices_, i, -1); + return index < 0 ? nullptr : test_suites_[static_cast<size_t>(index)]; } // Provides access to the event listener list. @@ -1036,30 +1030,40 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { // trace but Bar() and CurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop() won't. std::string CurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop(int skip_count) GTEST_NO_INLINE_; - // Finds and returns a TestCase with the given name. If one doesn't + // Finds and returns a TestSuite with the given name. If one doesn't // exist, creates one and returns it. // // Arguments: // - // test_case_name: name of the test case - // type_param: the name of the test's type parameter, or NULL if - // this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test. - // set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test case - // tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test case + // test_suite_name: name of the test suite + // type_param: the name of the test's type parameter, or NULL if + // this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test. + // set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test suite + // tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test suite + TestSuite* GetTestSuite(const char* test_suite_name, const char* type_param, + internal::SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc, + internal::TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc); + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ TestCase* GetTestCase(const char* test_case_name, const char* type_param, - Test::SetUpTestCaseFunc set_up_tc, - Test::TearDownTestCaseFunc tear_down_tc); + internal::SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc, + internal::TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc) { + return GetTestSuite(test_case_name, type_param, set_up_tc, tear_down_tc); + } +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ // Adds a TestInfo to the unit test. // // Arguments: // - // set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test case - // tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test case + // set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test suite + // tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test suite // test_info: the TestInfo object - void AddTestInfo(Test::SetUpTestCaseFunc set_up_tc, - Test::TearDownTestCaseFunc tear_down_tc, + void AddTestInfo(internal::SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc, + internal::TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc, TestInfo* test_info) { +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST // In order to support thread-safe death tests, we need to // remember the original working directory when the test program // was first invoked. We cannot do this in RUN_ALL_TESTS(), as @@ -1072,23 +1076,33 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { GTEST_CHECK_(!original_working_dir_.IsEmpty()) << "Failed to get the current working directory."; } +#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - GetTestCase(test_info->test_case_name(), test_info->type_param(), set_up_tc, - tear_down_tc) + GetTestSuite(test_info->test_suite_name(), test_info->type_param(), + set_up_tc, tear_down_tc) ->AddTestInfo(test_info); } -# if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - // Returns ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry object used to keep track of + // Returns ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry object used to keep track of // value-parameterized tests and instantiate and register them. - internal::ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry& parameterized_test_registry() { + internal::ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry& parameterized_test_registry() { return parameterized_test_registry_; } -# endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - // Sets the TestCase object for the test that's currently running. - void set_current_test_case(TestCase* a_current_test_case) { - current_test_case_ = a_current_test_case; + std::set<std::string>* ignored_parameterized_test_suites() { + return &ignored_parameterized_test_suites_; + } + + // Returns TypeParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry object used to keep track of + // type-parameterized tests and instantiations of them. + internal::TypeParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry& + type_parameterized_test_registry() { + return type_parameterized_test_registry_; + } + + // Sets the TestSuite object for the test that's currently running. + void set_current_test_suite(TestSuite* a_current_test_suite) { + current_test_suite_ = a_current_test_suite; } // Sets the TestInfo object for the test that's currently running. If @@ -1099,7 +1113,7 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { } // Registers all parameterized tests defined using TEST_P and - // INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P, creating regular tests for each test/parameter + // INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P, creating regular tests for each test/parameter // combination. This method can be called more then once; it has guards // protecting from registering the tests more then once. If // value-parameterized tests are disabled, RegisterParameterizedTests is @@ -1114,23 +1128,28 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { // Clears the results of all tests, except the ad hoc tests. void ClearNonAdHocTestResult() { - ForEach(test_cases_, TestCase::ClearTestCaseResult); + ForEach(test_suites_, TestSuite::ClearTestSuiteResult); } // Clears the results of ad-hoc test assertions. - void ClearAdHocTestResult() { ad_hoc_test_result_.Clear(); } + void ClearAdHocTestResult() { + ad_hoc_test_result_.Clear(); + } // Adds a TestProperty to the current TestResult object when invoked in a - // context of a test or a test case, or to the global property set. If the + // context of a test or a test suite, or to the global property set. If the // result already contains a property with the same key, the value will be // updated. void RecordProperty(const TestProperty& test_property); - enum ReactionToSharding { HONOR_SHARDING_PROTOCOL, IGNORE_SHARDING_PROTOCOL }; + enum ReactionToSharding { + HONOR_SHARDING_PROTOCOL, + IGNORE_SHARDING_PROTOCOL + }; // Matches the full name of each test against the user-specified // filter to decide whether the test should run, then records the - // result in each TestCase and TestInfo object. + // result in each TestSuite and TestInfo object. // If shard_tests == HONOR_SHARDING_PROTOCOL, further filters tests // based on sharding variables in the environment. // Returns the number of tests that should run. @@ -1139,7 +1158,7 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { // Prints the names of the tests matching the user-specified filter flag. void ListTestsMatchingFilter(); - const TestCase* current_test_case() const { return current_test_case_; } + const TestSuite* current_test_suite() const { return current_test_suite_; } TestInfo* current_test_info() { return current_test_info_; } const TestInfo* current_test_info() const { return current_test_info_; } @@ -1155,7 +1174,7 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { return gtest_trace_stack_.get(); } -# if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST void InitDeathTestSubprocessControlInfo() { internal_run_death_test_flag_.reset(ParseInternalRunDeathTestFlag()); } @@ -1175,17 +1194,17 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { void SuppressTestEventsIfInSubprocess(); friend class ReplaceDeathTestFactory; -# endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST // Initializes the event listener performing XML output as specified by // UnitTestOptions. Must not be called before InitGoogleTest. void ConfigureXmlOutput(); -# if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ +#if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ // Initializes the event listener for streaming test results to a socket. // Must not be called before InitGoogleTest. void ConfigureStreamingOutput(); -# endif +#endif // Performs initialization dependent upon flag values obtained in // ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnly. Is called from InitGoogleTest after the call to @@ -1200,11 +1219,11 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { // Gets the random number generator. internal::Random* random() { return &random_; } - // Shuffles all test cases, and the tests within each test case, + // Shuffles all test suites, and the tests within each test suite, // making sure that death tests are still run first. void ShuffleTests(); - // Restores the test cases and tests to their order before the first shuffle. + // Restores the test suites and tests to their order before the first shuffle. void UnshuffleTests(); // Returns the value of GTEST_FLAG(catch_exceptions) at the moment @@ -1244,33 +1263,37 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { // before/after the tests are run. std::vector<Environment*> environments_; - // The vector of TestCases in their original order. It owns the + // The vector of TestSuites in their original order. It owns the // elements in the vector. - std::vector<TestCase*> test_cases_; + std::vector<TestSuite*> test_suites_; - // Provides a level of indirection for the test case list to allow - // easy shuffling and restoring the test case order. The i-th - // element of this vector is the index of the i-th test case in the + // Provides a level of indirection for the test suite list to allow + // easy shuffling and restoring the test suite order. The i-th + // element of this vector is the index of the i-th test suite in the // shuffled order. - std::vector<int> test_case_indices_; + std::vector<int> test_suite_indices_; -# if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST // ParameterizedTestRegistry object used to register value-parameterized // tests. - internal::ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry parameterized_test_registry_; + internal::ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry parameterized_test_registry_; + internal::TypeParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry + type_parameterized_test_registry_; + + // The set holding the name of parameterized + // test suites that may go uninstantiated. + std::set<std::string> ignored_parameterized_test_suites_; // Indicates whether RegisterParameterizedTests() has been called already. bool parameterized_tests_registered_; -# endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - // Index of the last death test case registered. Initially -1. - int last_death_test_case_; + // Index of the last death test suite registered. Initially -1. + int last_death_test_suite_; - // This points to the TestCase for the currently running test. It - // changes as Google Test goes through one test case after another. + // This points to the TestSuite for the currently running test. It + // changes as Google Test goes through one test suite after another. // When no test is running, this is set to NULL and Google Test // stores assertion results in ad_hoc_test_result_. Initially NULL. - TestCase* current_test_case_; + TestSuite* current_test_suite_; // This points to the TestInfo for the currently running test. It // changes as Google Test goes through one test after another. When @@ -1298,7 +1321,7 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { // desired. OsStackTraceGetterInterface* os_stack_trace_getter_; - // True iff PostFlagParsingInit() has been called. + // True if and only if PostFlagParsingInit() has been called. bool post_flag_parse_init_performed_; // The random number seed used at the beginning of the test run. @@ -1314,12 +1337,12 @@ class GTEST_API_ UnitTestImpl { // How long the test took to run, in milliseconds. TimeInMillis elapsed_time_; -# if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST // The decomposed components of the gtest_internal_run_death_test flag, // parsed when RUN_ALL_TESTS is called. - internal::scoped_ptr<InternalRunDeathTestFlag> internal_run_death_test_flag_; - internal::scoped_ptr<internal::DeathTestFactory> death_test_factory_; -# endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST + std::unique_ptr<InternalRunDeathTestFlag> internal_run_death_test_flag_; + std::unique_ptr<internal::DeathTestFactory> death_test_factory_; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST // A per-thread stack of traces created by the SCOPED_TRACE() macro. internal::ThreadLocal<std::vector<TraceInfo> > gtest_trace_stack_; @@ -1337,7 +1360,7 @@ inline UnitTestImpl* GetUnitTestImpl() { return UnitTest::GetInstance()->impl(); } -# if GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE +#if GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE // Internal helper functions for implementing the simple regular // expression matcher. @@ -1351,49 +1374,23 @@ GTEST_API_ bool IsValidEscape(char ch); GTEST_API_ bool AtomMatchesChar(bool escaped, char pattern, char ch); GTEST_API_ bool ValidateRegex(const char* regex); GTEST_API_ bool MatchRegexAtHead(const char* regex, const char* str); -GTEST_API_ bool MatchRepetitionAndRegexAtHead(bool escaped, char ch, - char repeat, const char* regex, - const char* str); +GTEST_API_ bool MatchRepetitionAndRegexAtHead( + bool escaped, char ch, char repeat, const char* regex, const char* str); GTEST_API_ bool MatchRegexAnywhere(const char* regex, const char* str); -# endif // GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE +#endif // GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE // Parses the command line for Google Test flags, without initializing // other parts of Google Test. GTEST_API_ void ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnly(int* argc, char** argv); GTEST_API_ void ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnly(int* argc, wchar_t** argv); -# if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST // Returns the message describing the last system error, regardless of the // platform. GTEST_API_ std::string GetLastErrnoDescription(); -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -// Provides leak-safe Windows kernel handle ownership. -class AutoHandle { - public: - AutoHandle() : handle_(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) {} - explicit AutoHandle(HANDLE handle) : handle_(handle) {} - - ~AutoHandle() { Reset(); } - - HANDLE Get() const { return handle_; } - void Reset() { Reset(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE); } - void Reset(HANDLE handle) { - if (handle != handle_) { - if (handle_ != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) ::CloseHandle(handle_); - handle_ = handle; - } - } - - private: - HANDLE handle_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(AutoHandle); -}; -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - // Attempts to parse a string into a positive integer pointed to by the // number parameter. Returns true if that is possible. // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST implies that we have ::std::string, so we can use @@ -1411,24 +1408,11 @@ bool ParseNaturalNumber(const ::std::string& str, Integer* number) { char* end; // BiggestConvertible is the largest integer type that system-provided // string-to-number conversion routines can return. + using BiggestConvertible = unsigned long long; // NOLINT -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !defined(__GNUC__) - - // MSVC and C++ Builder define __int64 instead of the standard long long. - typedef unsigned __int64 BiggestConvertible; - const BiggestConvertible parsed = _strtoui64(str.c_str(), &end, 10); - -# else - - typedef unsigned long long BiggestConvertible; // NOLINT - const BiggestConvertible parsed = strtoull(str.c_str(), &end, 10); - -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !defined(__GNUC__) - + const BiggestConvertible parsed = strtoull(str.c_str(), &end, 10); // NOLINT const bool parse_success = *end == '\0' && errno == 0; - // TODO(vladl@google.com): Convert this to compile time assertion when it is - // available. GTEST_CHECK_(sizeof(Integer) <= sizeof(parsed)); const Integer result = static_cast<Integer>(parsed); @@ -1438,7 +1422,7 @@ bool ParseNaturalNumber(const ::std::string& str, Integer* number) { } return false; } -# endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST // TestResult contains some private methods that should be hidden from // Google Test user but are required for testing. This class allow our tests @@ -1464,7 +1448,7 @@ class TestResultAccessor { } }; -# if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ +#if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ // Streams test results to the given port on the given host machine. class StreamingListener : public EmptyTestEventListener { @@ -1475,36 +1459,38 @@ class StreamingListener : public EmptyTestEventListener { virtual ~AbstractSocketWriter() {} // Sends a string to the socket. - virtual void Send(const string& message) = 0; + virtual void Send(const std::string& message) = 0; // Closes the socket. virtual void CloseConnection() {} // Sends a string and a newline to the socket. - void SendLn(const string& message) { Send(message + "\n"); } + void SendLn(const std::string& message) { Send(message + "\n"); } }; // Concrete class for actually writing strings to a socket. class SocketWriter : public AbstractSocketWriter { public: - SocketWriter(const string& host, const string& port) + SocketWriter(const std::string& host, const std::string& port) : sockfd_(-1), host_name_(host), port_num_(port) { MakeConnection(); } - virtual ~SocketWriter() { - if (sockfd_ != -1) CloseConnection(); + ~SocketWriter() override { + if (sockfd_ != -1) + CloseConnection(); } // Sends a string to the socket. - virtual void Send(const string& message) { + void Send(const std::string& message) override { GTEST_CHECK_(sockfd_ != -1) << "Send() can be called only when there is a connection."; - const int len = static_cast<int>(message.length()); - if (write(sockfd_, message.c_str(), len) != len) { - GTEST_LOG_(WARNING) << "stream_result_to: failed to stream to " - << host_name_ << ":" << port_num_; + const auto len = static_cast<size_t>(message.length()); + if (write(sockfd_, message.c_str(), len) != static_cast<ssize_t>(len)) { + GTEST_LOG_(WARNING) + << "stream_result_to: failed to stream to " + << host_name_ << ":" << port_num_; } } @@ -1513,7 +1499,7 @@ class StreamingListener : public EmptyTestEventListener { void MakeConnection(); // Closes the socket. - void CloseConnection() { + void CloseConnection() override { GTEST_CHECK_(sockfd_ != -1) << "CloseConnection() can be called only when there is a connection."; @@ -1522,30 +1508,28 @@ class StreamingListener : public EmptyTestEventListener { } int sockfd_; // socket file descriptor - const string host_name_; - const string port_num_; + const std::string host_name_; + const std::string port_num_; GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(SocketWriter); }; // class SocketWriter // Escapes '=', '&', '%', and '\n' characters in str as "%xx". - static string UrlEncode(const char* str); + static std::string UrlEncode(const char* str); - StreamingListener(const string& host, const string& port) + StreamingListener(const std::string& host, const std::string& port) : socket_writer_(new SocketWriter(host, port)) { Start(); } explicit StreamingListener(AbstractSocketWriter* socket_writer) - : socket_writer_(socket_writer) { - Start(); - } + : socket_writer_(socket_writer) { Start(); } - void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& /* unit_test */) { + void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& /* unit_test */) override { SendLn("event=TestProgramStart"); } - void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) { + void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) override { // Note that Google Test current only report elapsed time for each // test iteration, not for the entire test program. SendLn("event=TestProgramEnd&passed=" + FormatBool(unit_test.Passed())); @@ -1554,40 +1538,47 @@ class StreamingListener : public EmptyTestEventListener { socket_writer_->CloseConnection(); } - void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& /* unit_test */, int iteration) { + void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& /* unit_test */, + int iteration) override { SendLn("event=TestIterationStart&iteration=" + StreamableToString(iteration)); } - void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int /* iteration */) { - SendLn("event=TestIterationEnd&passed=" + FormatBool(unit_test.Passed()) + - "&elapsed_time=" + StreamableToString(unit_test.elapsed_time()) + - "ms"); + void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, + int /* iteration */) override { + SendLn("event=TestIterationEnd&passed=" + + FormatBool(unit_test.Passed()) + "&elapsed_time=" + + StreamableToString(unit_test.elapsed_time()) + "ms"); } - void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& test_case) { + // Note that "event=TestCaseStart" is a wire format and has to remain + // "case" for compatibility + void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& test_case) override { SendLn(std::string("event=TestCaseStart&name=") + test_case.name()); } - void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& test_case) { + // Note that "event=TestCaseEnd" is a wire format and has to remain + // "case" for compatibility + void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& test_case) override { SendLn("event=TestCaseEnd&passed=" + FormatBool(test_case.Passed()) + "&elapsed_time=" + StreamableToString(test_case.elapsed_time()) + "ms"); } - void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info) { + void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info) override { SendLn(std::string("event=TestStart&name=") + test_info.name()); } - void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info) { + void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info) override { SendLn("event=TestEnd&passed=" + - FormatBool((test_info.result())->Passed()) + "&elapsed_time=" + + FormatBool((test_info.result())->Passed()) + + "&elapsed_time=" + StreamableToString((test_info.result())->elapsed_time()) + "ms"); } - void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& test_part_result) { + void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& test_part_result) override { const char* file_name = test_part_result.file_name(); - if (file_name == NULL) file_name = ""; + if (file_name == nullptr) file_name = ""; SendLn("event=TestPartResult&file=" + UrlEncode(file_name) + "&line=" + StreamableToString(test_part_result.line_number()) + "&message=" + UrlEncode(test_part_result.message())); @@ -1595,31 +1586,45 @@ class StreamingListener : public EmptyTestEventListener { private: // Sends the given message and a newline to the socket. - void SendLn(const string& message) { socket_writer_->SendLn(message); } + void SendLn(const std::string& message) { socket_writer_->SendLn(message); } // Called at the start of streaming to notify the receiver what // protocol we are using. void Start() { SendLn("gtest_streaming_protocol_version=1.0"); } - string FormatBool(bool value) { return value ? "1" : "0"; } + std::string FormatBool(bool value) { return value ? "1" : "0"; } - const scoped_ptr<AbstractSocketWriter> socket_writer_; + const std::unique_ptr<AbstractSocketWriter> socket_writer_; GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(StreamingListener); }; // class StreamingListener -# endif // GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ +#endif // GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ } // namespace internal } // namespace testing -#endif // GTEST_SRC_GTEST_INTERNAL_INL_H_ -#undef GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_SRC_GTEST_INTERNAL_INL_H_ #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -# define vsnprintf _vsnprintf +# define vsnprintf _vsnprintf #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +#if GTEST_OS_MAC +#ifndef GTEST_OS_IOS +#include <crt_externs.h> +#endif +#endif + +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL +#include "absl/debugging/failure_signal_handler.h" +#include "absl/debugging/stacktrace.h" +#include "absl/debugging/symbolize.h" +#include "absl/strings/str_cat.h" +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL + namespace testing { using internal::CountIf; @@ -1629,20 +1634,22 @@ using internal::Shuffle; // Constants. -// A test whose test case name or test name matches this filter is +// A test whose test suite name or test name matches this filter is // disabled and not run. static const char kDisableTestFilter[] = "DISABLED_*:*/DISABLED_*"; -// A test case whose name matches this filter is considered a death -// test case and will be run before test cases whose name doesn't +// A test suite whose name matches this filter is considered a death +// test suite and will be run before test suites whose name doesn't // match this filter. -static const char kDeathTestCaseFilter[] = "*DeathTest:*DeathTest/*"; +static const char kDeathTestSuiteFilter[] = "*DeathTest:*DeathTest/*"; // A test filter that matches everything. static const char kUniversalFilter[] = "*"; -// The default output file for XML output. -static const char kDefaultOutputFile[] = "test_detail.xml"; +// The default output format. +static const char kDefaultOutputFormat[] = "xml"; +// The default output file. +static const char kDefaultOutputFile[] = "test_detail"; // The environment variable name for the test shard index. static const char kTestShardIndex[] = "GTEST_SHARD_INDEX"; @@ -1657,13 +1664,52 @@ namespace internal { // stack trace. const char kStackTraceMarker[] = "\nStack trace:\n"; -// g_help_flag is true iff the --help flag or an equivalent form is -// specified on the command line. +// g_help_flag is true if and only if the --help flag or an equivalent form +// is specified on the command line. bool g_help_flag = false; +// Utilty function to Open File for Writing +static FILE* OpenFileForWriting(const std::string& output_file) { + FILE* fileout = nullptr; + FilePath output_file_path(output_file); + FilePath output_dir(output_file_path.RemoveFileName()); + + if (output_dir.CreateDirectoriesRecursively()) { + fileout = posix::FOpen(output_file.c_str(), "w"); + } + if (fileout == nullptr) { + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "Unable to open file \"" << output_file << "\""; + } + return fileout; +} + } // namespace internal -static const char* GetDefaultFilter() { return kUniversalFilter; } +// Bazel passes in the argument to '--test_filter' via the TESTBRIDGE_TEST_ONLY +// environment variable. +static const char* GetDefaultFilter() { + const char* const testbridge_test_only = + internal::posix::GetEnv("TESTBRIDGE_TEST_ONLY"); + if (testbridge_test_only != nullptr) { + return testbridge_test_only; + } + return kUniversalFilter; +} + +// Bazel passes in the argument to '--test_runner_fail_fast' via the +// TESTBRIDGE_TEST_RUNNER_FAIL_FAST environment variable. +static bool GetDefaultFailFast() { + const char* const testbridge_test_runner_fail_fast = + internal::posix::GetEnv("TESTBRIDGE_TEST_RUNNER_FAIL_FAST"); + if (testbridge_test_runner_fail_fast != nullptr) { + return strcmp(testbridge_test_runner_fail_fast, "1") == 0; + } + return false; +} + +GTEST_DEFINE_bool_( + fail_fast, internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("fail_fast", GetDefaultFailFast()), + "True if and only if a test failure should stop further test execution."); GTEST_DEFINE_bool_( also_run_disabled_tests, @@ -1672,62 +1718,90 @@ GTEST_DEFINE_bool_( GTEST_DEFINE_bool_( break_on_failure, internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("break_on_failure", false), - "True iff a failed assertion should be a debugger break-point."); + "True if and only if a failed assertion should be a debugger " + "break-point."); GTEST_DEFINE_bool_(catch_exceptions, internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("catch_exceptions", true), - "True iff " GTEST_NAME_ + "True if and only if " GTEST_NAME_ " should catch exceptions and treat them as test failures."); GTEST_DEFINE_string_( - color, internal::StringFromGTestEnv("color", "auto"), + color, + internal::StringFromGTestEnv("color", "auto"), "Whether to use colors in the output. Valid values: yes, no, " "and auto. 'auto' means to use colors if the output is " "being sent to a terminal and the TERM environment variable " "is set to a terminal type that supports colors."); GTEST_DEFINE_string_( - filter, internal::StringFromGTestEnv("filter", GetDefaultFilter()), + filter, + internal::StringFromGTestEnv("filter", GetDefaultFilter()), "A colon-separated list of glob (not regex) patterns " "for filtering the tests to run, optionally followed by a " "'-' and a : separated list of negative patterns (tests to " "exclude). A test is run if it matches one of the positive " "patterns and does not match any of the negative patterns."); -GTEST_DEFINE_bool_(list_tests, false, "List all tests without running them."); - +GTEST_DEFINE_bool_( + install_failure_signal_handler, + internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("install_failure_signal_handler", false), + "If true and supported on the current platform, " GTEST_NAME_ " should " + "install a signal handler that dumps debugging information when fatal " + "signals are raised."); + +GTEST_DEFINE_bool_(list_tests, false, + "List all tests without running them."); + +// The net priority order after flag processing is thus: +// --gtest_output command line flag +// GTEST_OUTPUT environment variable +// XML_OUTPUT_FILE environment variable +// '' GTEST_DEFINE_string_( - output, internal::StringFromGTestEnv("output", ""), - "A format (currently must be \"xml\"), optionally followed " - "by a colon and an output file name or directory. A directory " - "is indicated by a trailing pathname separator. " + output, + internal::StringFromGTestEnv("output", + internal::OutputFlagAlsoCheckEnvVar().c_str()), + "A format (defaults to \"xml\" but can be specified to be \"json\"), " + "optionally followed by a colon and an output file name or directory. " + "A directory is indicated by a trailing pathname separator. " "Examples: \"xml:filename.xml\", \"xml::directoryname/\". " "If a directory is specified, output files will be created " "within that directory, with file-names based on the test " "executable's name and, if necessary, made unique by adding " "digits."); +GTEST_DEFINE_bool_( + brief, internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("brief", false), + "True if only test failures should be displayed in text output."); + GTEST_DEFINE_bool_(print_time, internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("print_time", true), - "True iff " GTEST_NAME_ + "True if and only if " GTEST_NAME_ " should display elapsed time in text output."); +GTEST_DEFINE_bool_(print_utf8, internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("print_utf8", true), + "True if and only if " GTEST_NAME_ + " prints UTF8 characters as text."); + GTEST_DEFINE_int32_( - random_seed, internal::Int32FromGTestEnv("random_seed", 0), + random_seed, + internal::Int32FromGTestEnv("random_seed", 0), "Random number seed to use when shuffling test orders. Must be in range " "[1, 99999], or 0 to use a seed based on the current time."); GTEST_DEFINE_int32_( - repeat, internal::Int32FromGTestEnv("repeat", 1), + repeat, + internal::Int32FromGTestEnv("repeat", 1), "How many times to repeat each test. Specify a negative number " "for repeating forever. Useful for shaking out flaky tests."); GTEST_DEFINE_bool_(show_internal_stack_frames, false, - "True iff " GTEST_NAME_ + "True if and only if " GTEST_NAME_ " should include internal stack frames when " "printing test failure stack traces."); GTEST_DEFINE_bool_(shuffle, internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("shuffle", false), - "True iff " GTEST_NAME_ + "True if and only if " GTEST_NAME_ " should randomize tests' order on every run."); GTEST_DEFINE_int32_( @@ -1737,27 +1811,38 @@ GTEST_DEFINE_int32_( "assertion fails. The valid range is 0 through 100, inclusive."); GTEST_DEFINE_string_( - stream_result_to, internal::StringFromGTestEnv("stream_result_to", ""), + stream_result_to, + internal::StringFromGTestEnv("stream_result_to", ""), "This flag specifies the host name and the port number on which to stream " "test results. Example: \"localhost:555\". The flag is effective only on " "Linux."); GTEST_DEFINE_bool_( - throw_on_failure, internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("throw_on_failure", false), + throw_on_failure, + internal::BoolFromGTestEnv("throw_on_failure", false), "When this flag is specified, a failed assertion will throw an exception " "if exceptions are enabled or exit the program with a non-zero code " - "otherwise."); + "otherwise. For use with an external test framework."); + +#if GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_ +GTEST_DEFINE_string_( + flagfile, + internal::StringFromGTestEnv("flagfile", ""), + "This flag specifies the flagfile to read command-line flags from."); +#endif // GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_ namespace internal { // Generates a random number from [0, range), using a Linear // Congruential Generator (LCG). Crashes if 'range' is 0 or greater // than kMaxRange. -UInt32 Random::Generate(UInt32 range) { +uint32_t Random::Generate(uint32_t range) { // These constants are the same as are used in glibc's rand(3). - state_ = (1103515245U * state_ + 12345U) % kMaxRange; + // Use wider types than necessary to prevent unsigned overflow diagnostics. + state_ = static_cast<uint32_t>(1103515245ULL*state_ + 12345U) % kMaxRange; - GTEST_CHECK_(range > 0) << "Cannot generate a number in the range [0, 0)."; + GTEST_CHECK_(range > 0) + << "Cannot generate a number in the range [0, 0)."; GTEST_CHECK_(range <= kMaxRange) << "Generation of a number in [0, " << range << ") was requested, " << "but this can only generate numbers in [0, " << kMaxRange << ")."; @@ -1768,22 +1853,16 @@ UInt32 Random::Generate(UInt32 range) { return state_ % range; } -// GTestIsInitialized() returns true iff the user has initialized +// GTestIsInitialized() returns true if and only if the user has initialized // Google Test. Useful for catching the user mistake of not initializing // Google Test before calling RUN_ALL_TESTS(). -// -// A user must call testing::InitGoogleTest() to initialize Google -// Test. g_init_gtest_count is set to the number of times -// InitGoogleTest() has been called. We don't protect this variable -// under a mutex as it is only accessed in the main thread. -GTEST_API_ int g_init_gtest_count = 0; -static bool GTestIsInitialized() { return g_init_gtest_count != 0; } +static bool GTestIsInitialized() { return GetArgvs().size() > 0; } -// Iterates over a vector of TestCases, keeping a running sum of the +// Iterates over a vector of TestSuites, keeping a running sum of the // results of calling a given int-returning method on each. // Returns the sum. -static int SumOverTestCaseList(const std::vector<TestCase*>& case_list, - int (TestCase::*method)() const) { +static int SumOverTestSuiteList(const std::vector<TestSuite*>& case_list, + int (TestSuite::*method)() const) { int sum = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < case_list.size(); i++) { sum += (case_list[i]->*method)(); @@ -1791,54 +1870,224 @@ static int SumOverTestCaseList(const std::vector<TestCase*>& case_list, return sum; } -// Returns true iff the test case passed. -static bool TestCasePassed(const TestCase* test_case) { - return test_case->should_run() && test_case->Passed(); +// Returns true if and only if the test suite passed. +static bool TestSuitePassed(const TestSuite* test_suite) { + return test_suite->should_run() && test_suite->Passed(); } -// Returns true iff the test case failed. -static bool TestCaseFailed(const TestCase* test_case) { - return test_case->should_run() && test_case->Failed(); +// Returns true if and only if the test suite failed. +static bool TestSuiteFailed(const TestSuite* test_suite) { + return test_suite->should_run() && test_suite->Failed(); } -// Returns true iff test_case contains at least one test that should -// run. -static bool ShouldRunTestCase(const TestCase* test_case) { - return test_case->should_run(); +// Returns true if and only if test_suite contains at least one test that +// should run. +static bool ShouldRunTestSuite(const TestSuite* test_suite) { + return test_suite->should_run(); } // AssertHelper constructor. -AssertHelper::AssertHelper(TestPartResult::Type type, const char* file, - int line, const char* message) - : data_(new AssertHelperData(type, file, line, message)) {} +AssertHelper::AssertHelper(TestPartResult::Type type, + const char* file, + int line, + const char* message) + : data_(new AssertHelperData(type, file, line, message)) { +} -AssertHelper::~AssertHelper() { delete data_; } +AssertHelper::~AssertHelper() { + delete data_; +} // Message assignment, for assertion streaming support. void AssertHelper::operator=(const Message& message) const { - UnitTest::GetInstance()->AddTestPartResult( - data_->type, data_->file, data_->line, - AppendUserMessage(data_->message, message), - UnitTest::GetInstance()->impl()->CurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop(1) - // Skips the stack frame for this function itself. - ); // NOLINT + UnitTest::GetInstance()-> + AddTestPartResult(data_->type, data_->file, data_->line, + AppendUserMessage(data_->message, message), + UnitTest::GetInstance()->impl() + ->CurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop(1) + // Skips the stack frame for this function itself. + ); // NOLINT } -// Mutex for linked pointers. -GTEST_API_ GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_linked_ptr_mutex); +namespace { + +// When TEST_P is found without a matching INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P +// to creates test cases for it, a syntetic test case is +// inserted to report ether an error or a log message. +// +// This configuration bit will likely be removed at some point. +constexpr bool kErrorOnUninstantiatedParameterizedTest = true; +constexpr bool kErrorOnUninstantiatedTypeParameterizedTest = true; + +// A test that fails at a given file/line location with a given message. +class FailureTest : public Test { + public: + explicit FailureTest(const CodeLocation& loc, std::string error_message, + bool as_error) + : loc_(loc), + error_message_(std::move(error_message)), + as_error_(as_error) {} + + void TestBody() override { + if (as_error_) { + AssertHelper(TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure, loc_.file.c_str(), + loc_.line, "") = Message() << error_message_; + } else { + std::cout << error_message_ << std::endl; + } + } + + private: + const CodeLocation loc_; + const std::string error_message_; + const bool as_error_; +}; -// Application pathname gotten in InitGoogleTest. -std::string g_executable_path; + +} // namespace + +std::set<std::string>* GetIgnoredParameterizedTestSuites() { + return UnitTest::GetInstance()->impl()->ignored_parameterized_test_suites(); +} + +// Add a given test_suit to the list of them allow to go un-instantiated. +MarkAsIgnored::MarkAsIgnored(const char* test_suite) { + GetIgnoredParameterizedTestSuites()->insert(test_suite); +} + +// If this parameterized test suite has no instantiations (and that +// has not been marked as okay), emit a test case reporting that. +void InsertSyntheticTestCase(const std::string& name, CodeLocation location, + bool has_test_p) { + const auto& ignored = *GetIgnoredParameterizedTestSuites(); + if (ignored.find(name) != ignored.end()) return; + + const char kMissingInstantiation[] = // + " is defined via TEST_P, but never instantiated. None of the test cases " + "will run. Either no INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P is provided or the only " + "ones provided expand to nothing." + "\n\n" + "Ideally, TEST_P definitions should only ever be included as part of " + "binaries that intend to use them. (As opposed to, for example, being " + "placed in a library that may be linked in to get other utilities.)"; + + const char kMissingTestCase[] = // + " is instantiated via INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P, but no tests are " + "defined via TEST_P . No test cases will run." + "\n\n" + "Ideally, INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P should only ever be invoked from " + "code that always depend on code that provides TEST_P. Failing to do " + "so is often an indication of dead code, e.g. the last TEST_P was " + "removed but the rest got left behind."; + + std::string message = + "Parameterized test suite " + name + + (has_test_p ? kMissingInstantiation : kMissingTestCase) + + "\n\n" + "To suppress this error for this test suite, insert the following line " + "(in a non-header) in the namespace it is defined in:" + "\n\n" + "GTEST_ALLOW_UNINSTANTIATED_PARAMETERIZED_TEST(" + name + ");"; + + std::string full_name = "UninstantiatedParameterizedTestSuite<" + name + ">"; + RegisterTest( // + "GoogleTestVerification", full_name.c_str(), + nullptr, // No type parameter. + nullptr, // No value parameter. + location.file.c_str(), location.line, [message, location] { + return new FailureTest(location, message, + kErrorOnUninstantiatedParameterizedTest); + }); +} + +void RegisterTypeParameterizedTestSuite(const char* test_suite_name, + CodeLocation code_location) { + GetUnitTestImpl()->type_parameterized_test_registry().RegisterTestSuite( + test_suite_name, code_location); +} + +void RegisterTypeParameterizedTestSuiteInstantiation(const char* case_name) { + GetUnitTestImpl() + ->type_parameterized_test_registry() + .RegisterInstantiation(case_name); +} + +void TypeParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry::RegisterTestSuite( + const char* test_suite_name, CodeLocation code_location) { + suites_.emplace(std::string(test_suite_name), + TypeParameterizedTestSuiteInfo(code_location)); +} + +void TypeParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry::RegisterInstantiation( + const char* test_suite_name) { + auto it = suites_.find(std::string(test_suite_name)); + if (it != suites_.end()) { + it->second.instantiated = true; + } else { + GTEST_LOG_(ERROR) << "Unknown type parameterized test suit '" + << test_suite_name << "'"; + } +} + +void TypeParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry::CheckForInstantiations() { + const auto& ignored = *GetIgnoredParameterizedTestSuites(); + for (const auto& testcase : suites_) { + if (testcase.second.instantiated) continue; + if (ignored.find(testcase.first) != ignored.end()) continue; + + std::string message = + "Type parameterized test suite " + testcase.first + + " is defined via REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P, but never instantiated " + "via INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P. None of the test cases will run." + "\n\n" + "Ideally, TYPED_TEST_P definitions should only ever be included as " + "part of binaries that intend to use them. (As opposed to, for " + "example, being placed in a library that may be linked in to get other " + "utilities.)" + "\n\n" + "To suppress this error for this test suite, insert the following line " + "(in a non-header) in the namespace it is defined in:" + "\n\n" + "GTEST_ALLOW_UNINSTANTIATED_PARAMETERIZED_TEST(" + + testcase.first + ");"; + + std::string full_name = + "UninstantiatedTypeParameterizedTestSuite<" + testcase.first + ">"; + RegisterTest( // + "GoogleTestVerification", full_name.c_str(), + nullptr, // No type parameter. + nullptr, // No value parameter. + testcase.second.code_location.file.c_str(), + testcase.second.code_location.line, [message, testcase] { + return new FailureTest(testcase.second.code_location, message, + kErrorOnUninstantiatedTypeParameterizedTest); + }); + } +} + +// A copy of all command line arguments. Set by InitGoogleTest(). +static ::std::vector<std::string> g_argvs; + +::std::vector<std::string> GetArgvs() { +#if defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_GET_ARGVS_) + // GTEST_CUSTOM_GET_ARGVS_() may return a container of std::string or + // ::string. This code converts it to the appropriate type. + const auto& custom = GTEST_CUSTOM_GET_ARGVS_(); + return ::std::vector<std::string>(custom.begin(), custom.end()); +#else // defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_GET_ARGVS_) + return g_argvs; +#endif // defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_GET_ARGVS_) +} // Returns the current application's name, removing directory path if that // is present. FilePath GetCurrentExecutableName() { FilePath result; -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - result.Set(FilePath(g_executable_path).RemoveExtension("exe")); +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS || GTEST_OS_OS2 + result.Set(FilePath(GetArgvs()[0]).RemoveExtension("exe")); #else - result.Set(FilePath(g_executable_path)); + result.Set(FilePath(GetArgvs()[0])); #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS return result.RemoveDirectoryName(); @@ -1849,39 +2098,38 @@ FilePath GetCurrentExecutableName() { // Returns the output format, or "" for normal printed output. std::string UnitTestOptions::GetOutputFormat() { const char* const gtest_output_flag = GTEST_FLAG(output).c_str(); - if (gtest_output_flag == NULL) return std::string(""); - const char* const colon = strchr(gtest_output_flag, ':'); - return (colon == NULL) + return (colon == nullptr) ? std::string(gtest_output_flag) - : std::string(gtest_output_flag, colon - gtest_output_flag); + : std::string(gtest_output_flag, + static_cast<size_t>(colon - gtest_output_flag)); } // Returns the name of the requested output file, or the default if none // was explicitly specified. std::string UnitTestOptions::GetAbsolutePathToOutputFile() { const char* const gtest_output_flag = GTEST_FLAG(output).c_str(); - if (gtest_output_flag == NULL) return ""; + + std::string format = GetOutputFormat(); + if (format.empty()) + format = std::string(kDefaultOutputFormat); const char* const colon = strchr(gtest_output_flag, ':'); - if (colon == NULL) - return internal::FilePath::ConcatPaths( - internal::FilePath( - UnitTest::GetInstance()->original_working_dir()), - internal::FilePath(kDefaultOutputFile)) - .string(); + if (colon == nullptr) + return internal::FilePath::MakeFileName( + internal::FilePath( + UnitTest::GetInstance()->original_working_dir()), + internal::FilePath(kDefaultOutputFile), 0, + format.c_str()).string(); internal::FilePath output_name(colon + 1); if (!output_name.IsAbsolutePath()) - // TODO(wan@google.com): on Windows \some\path is not an absolute - // path (as its meaning depends on the current drive), yet the - // following logic for turning it into an absolute path is wrong. - // Fix it. output_name = internal::FilePath::ConcatPaths( internal::FilePath(UnitTest::GetInstance()->original_working_dir()), internal::FilePath(colon + 1)); - if (!output_name.IsDirectory()) return output_name.string(); + if (!output_name.IsDirectory()) + return output_name.string(); internal::FilePath result(internal::FilePath::GenerateUniqueFileName( output_name, internal::GetCurrentExecutableName(), @@ -1889,53 +2137,89 @@ std::string UnitTestOptions::GetAbsolutePathToOutputFile() { return result.string(); } -// Returns true iff the wildcard pattern matches the string. The -// first ':' or '\0' character in pattern marks the end of it. -// -// This recursive algorithm isn't very efficient, but is clear and -// works well enough for matching test names, which are short. -bool UnitTestOptions::PatternMatchesString(const char* pattern, - const char* str) { - switch (*pattern) { - case '\0': - case ':': // Either ':' or '\0' marks the end of the pattern. - return *str == '\0'; - case '?': // Matches any single character. - return *str != '\0' && PatternMatchesString(pattern + 1, str + 1); - case '*': // Matches any string (possibly empty) of characters. - return (*str != '\0' && PatternMatchesString(pattern, str + 1)) || - PatternMatchesString(pattern + 1, str); - default: // Non-special character. Matches itself. - return *pattern == *str && PatternMatchesString(pattern + 1, str + 1); +// Returns true if and only if the wildcard pattern matches the string. Each +// pattern consists of regular characters, single-character wildcards (?), and +// multi-character wildcards (*). +// +// This function implements a linear-time string globbing algorithm based on +// https://research.swtch.com/glob. +static bool PatternMatchesString(const std::string& name_str, + const char* pattern, const char* pattern_end) { + const char* name = name_str.c_str(); + const char* const name_begin = name; + const char* const name_end = name + name_str.size(); + + const char* pattern_next = pattern; + const char* name_next = name; + + while (pattern < pattern_end || name < name_end) { + if (pattern < pattern_end) { + switch (*pattern) { + default: // Match an ordinary character. + if (name < name_end && *name == *pattern) { + ++pattern; + ++name; + continue; + } + break; + case '?': // Match any single character. + if (name < name_end) { + ++pattern; + ++name; + continue; + } + break; + case '*': + // Match zero or more characters. Start by skipping over the wildcard + // and matching zero characters from name. If that fails, restart and + // match one more character than the last attempt. + pattern_next = pattern; + name_next = name + 1; + ++pattern; + continue; + } + } + // Failed to match a character. Restart if possible. + if (name_begin < name_next && name_next <= name_end) { + pattern = pattern_next; + name = name_next; + continue; + } + return false; } + return true; } -bool UnitTestOptions::MatchesFilter(const std::string& name, +bool UnitTestOptions::MatchesFilter(const std::string& name_str, const char* filter) { - const char* cur_pattern = filter; - for (;;) { - if (PatternMatchesString(cur_pattern, name.c_str())) { - return true; + // The filter is a list of patterns separated by colons (:). + const char* pattern = filter; + while (true) { + // Find the bounds of this pattern. + const char* const next_sep = strchr(pattern, ':'); + const char* const pattern_end = + next_sep != nullptr ? next_sep : pattern + strlen(pattern); + + // Check if this pattern matches name_str. + if (PatternMatchesString(name_str, pattern, pattern_end)) { + break; } - // Finds the next pattern in the filter. - cur_pattern = strchr(cur_pattern, ':'); - - // Returns if no more pattern can be found. - if (cur_pattern == NULL) { + // Give up on this pattern. However, if we found a pattern separator (:), + // advance to the next pattern (skipping over the separator) and restart. + if (next_sep == nullptr) { return false; } - - // Skips the pattern separater (the ':' character). - cur_pattern++; + pattern = next_sep + 1; } + return true; } -// Returns true iff the user-specified filter matches the test case -// name and the test name. -bool UnitTestOptions::FilterMatchesTest(const std::string& test_case_name, +// Returns true if and only if the user-specified filter matches the test +// suite name and the test name. +bool UnitTestOptions::FilterMatchesTest(const std::string& test_suite_name, const std::string& test_name) { - const std::string& full_name = test_case_name + "." + test_name.c_str(); + const std::string& full_name = test_suite_name + "." + test_name.c_str(); // Split --gtest_filter at '-', if there is one, to separate into // positive filter and negative filter portions @@ -1943,7 +2227,7 @@ bool UnitTestOptions::FilterMatchesTest(const std::string& test_case_name, const char* const dash = strchr(p, '-'); std::string positive; std::string negative; - if (dash == NULL) { + if (dash == nullptr) { positive = GTEST_FLAG(filter).c_str(); // Whole string is a positive filter negative = ""; } else { @@ -1996,7 +2280,8 @@ int UnitTestOptions::GTestShouldProcessSEH(DWORD exception_code) { // results. Intercepts only failures from the current thread. ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter( TestPartResultArray* result) - : intercept_mode_(INTERCEPT_ONLY_CURRENT_THREAD), result_(result) { + : intercept_mode_(INTERCEPT_ONLY_CURRENT_THREAD), + result_(result) { Init(); } @@ -2005,7 +2290,8 @@ ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter( // results. ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter::ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter( InterceptMode intercept_mode, TestPartResultArray* result) - : intercept_mode_(intercept_mode), result_(result) { + : intercept_mode_(intercept_mode), + result_(result) { Init(); } @@ -2049,7 +2335,9 @@ namespace internal { // from user test code. GetTestTypeId() is guaranteed to always // return the same value, as it always calls GetTypeId<>() from the // gtest.cc, which is within the Google Test framework. -TypeId GetTestTypeId() { return GetTypeId<Test>(); } +TypeId GetTestTypeId() { + return GetTypeId<Test>(); +} // The value of GetTestTypeId() as seen from within the Google Test // library. This is solely for testing GetTestTypeId(). @@ -2058,14 +2346,15 @@ extern const TypeId kTestTypeIdInGoogleTest = GetTestTypeId(); // This predicate-formatter checks that 'results' contains a test part // failure of the given type and that the failure message contains the // given substring. -AssertionResult HasOneFailure(const char* /* results_expr */, - const char* /* type_expr */, - const char* /* substr_expr */, - const TestPartResultArray& results, - TestPartResult::Type type, const string& substr) { - const std::string expected(type == TestPartResult::kFatalFailure - ? "1 fatal failure" - : "1 non-fatal failure"); +static AssertionResult HasOneFailure(const char* /* results_expr */, + const char* /* type_expr */, + const char* /* substr_expr */, + const TestPartResultArray& results, + TestPartResult::Type type, + const std::string& substr) { + const std::string expected(type == TestPartResult::kFatalFailure ? + "1 fatal failure" : + "1 non-fatal failure"); Message msg; if (results.size() != 1) { msg << "Expected: " << expected << "\n" @@ -2083,11 +2372,11 @@ AssertionResult HasOneFailure(const char* /* results_expr */, << r; } - if (strstr(r.message(), substr.c_str()) == NULL) { - return AssertionFailure() - << "Expected: " << expected << " containing \"" << substr << "\"\n" - << " Actual:\n" - << r; + if (strstr(r.message(), substr.c_str()) == nullptr) { + return AssertionFailure() << "Expected: " << expected << " containing \"" + << substr << "\"\n" + << " Actual:\n" + << r; } return AssertionSuccess(); @@ -2098,7 +2387,7 @@ AssertionResult HasOneFailure(const char* /* results_expr */, // substring the failure message should contain. SingleFailureChecker::SingleFailureChecker(const TestPartResultArray* results, TestPartResult::Type type, - const string& substr) + const std::string& substr) : results_(results), type_(type), substr_(substr) {} // The destructor of SingleFailureChecker verifies that the given @@ -2110,8 +2399,7 @@ SingleFailureChecker::~SingleFailureChecker() { } DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter::DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter( - UnitTestImpl* unit_test) - : unit_test_(unit_test) {} + UnitTestImpl* unit_test) : unit_test_(unit_test) {} void DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter::ReportTestPartResult( const TestPartResult& result) { @@ -2120,8 +2408,7 @@ void DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter::ReportTestPartResult( } DefaultPerThreadTestPartResultReporter::DefaultPerThreadTestPartResultReporter( - UnitTestImpl* unit_test) - : unit_test_(unit_test) {} + UnitTestImpl* unit_test) : unit_test_(unit_test) {} void DefaultPerThreadTestPartResultReporter::ReportTestPartResult( const TestPartResult& result) { @@ -2154,61 +2441,66 @@ void UnitTestImpl::SetTestPartResultReporterForCurrentThread( per_thread_test_part_result_reporter_.set(reporter); } -// Gets the number of successful test cases. -int UnitTestImpl::successful_test_case_count() const { - return CountIf(test_cases_, TestCasePassed); +// Gets the number of successful test suites. +int UnitTestImpl::successful_test_suite_count() const { + return CountIf(test_suites_, TestSuitePassed); } -// Gets the number of failed test cases. -int UnitTestImpl::failed_test_case_count() const { - return CountIf(test_cases_, TestCaseFailed); +// Gets the number of failed test suites. +int UnitTestImpl::failed_test_suite_count() const { + return CountIf(test_suites_, TestSuiteFailed); } -// Gets the number of all test cases. -int UnitTestImpl::total_test_case_count() const { - return static_cast<int>(test_cases_.size()); +// Gets the number of all test suites. +int UnitTestImpl::total_test_suite_count() const { + return static_cast<int>(test_suites_.size()); } -// Gets the number of all test cases that contain at least one test +// Gets the number of all test suites that contain at least one test // that should run. -int UnitTestImpl::test_case_to_run_count() const { - return CountIf(test_cases_, ShouldRunTestCase); +int UnitTestImpl::test_suite_to_run_count() const { + return CountIf(test_suites_, ShouldRunTestSuite); } // Gets the number of successful tests. int UnitTestImpl::successful_test_count() const { - return SumOverTestCaseList(test_cases_, &TestCase::successful_test_count); + return SumOverTestSuiteList(test_suites_, &TestSuite::successful_test_count); +} + +// Gets the number of skipped tests. +int UnitTestImpl::skipped_test_count() const { + return SumOverTestSuiteList(test_suites_, &TestSuite::skipped_test_count); } // Gets the number of failed tests. int UnitTestImpl::failed_test_count() const { - return SumOverTestCaseList(test_cases_, &TestCase::failed_test_count); + return SumOverTestSuiteList(test_suites_, &TestSuite::failed_test_count); } // Gets the number of disabled tests that will be reported in the XML report. int UnitTestImpl::reportable_disabled_test_count() const { - return SumOverTestCaseList(test_cases_, - &TestCase::reportable_disabled_test_count); + return SumOverTestSuiteList(test_suites_, + &TestSuite::reportable_disabled_test_count); } // Gets the number of disabled tests. int UnitTestImpl::disabled_test_count() const { - return SumOverTestCaseList(test_cases_, &TestCase::disabled_test_count); + return SumOverTestSuiteList(test_suites_, &TestSuite::disabled_test_count); } // Gets the number of tests to be printed in the XML report. int UnitTestImpl::reportable_test_count() const { - return SumOverTestCaseList(test_cases_, &TestCase::reportable_test_count); + return SumOverTestSuiteList(test_suites_, &TestSuite::reportable_test_count); } // Gets the number of all tests. int UnitTestImpl::total_test_count() const { - return SumOverTestCaseList(test_cases_, &TestCase::total_test_count); + return SumOverTestSuiteList(test_suites_, &TestSuite::total_test_count); } // Gets the number of tests that should run. int UnitTestImpl::test_to_run_count() const { - return SumOverTestCaseList(test_cases_, &TestCase::test_to_run_count); + return SumOverTestSuiteList(test_suites_, &TestSuite::test_to_run_count); } // Returns the current OS stack trace as an std::string. @@ -2222,60 +2514,38 @@ int UnitTestImpl::test_to_run_count() const { // CurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop(1), Foo() will be included in the // trace but Bar() and CurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop() won't. std::string UnitTestImpl::CurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop(int skip_count) { - (void)skip_count; - return ""; + return os_stack_trace_getter()->CurrentStackTrace( + static_cast<int>(GTEST_FLAG(stack_trace_depth)), + skip_count + 1 + // Skips the user-specified number of frames plus this function + // itself. + ); // NOLINT } -// Returns the current time in milliseconds. -TimeInMillis GetTimeInMillis() { -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || defined(__BORLANDC__) - // Difference between 1970-01-01 and 1601-01-01 in milliseconds. - // http://analogous.blogspot.com/2005/04/epoch.html - const TimeInMillis kJavaEpochToWinFileTimeDelta = - static_cast<TimeInMillis>(116444736UL) * 100000UL; - const DWORD kTenthMicrosInMilliSecond = 10000; - - SYSTEMTIME now_systime; - FILETIME now_filetime; - ULARGE_INTEGER now_int64; - // TODO(kenton@google.com): Shouldn't this just use - // GetSystemTimeAsFileTime()? - GetSystemTime(&now_systime); - if (SystemTimeToFileTime(&now_systime, &now_filetime)) { - now_int64.LowPart = now_filetime.dwLowDateTime; - now_int64.HighPart = now_filetime.dwHighDateTime; - now_int64.QuadPart = (now_int64.QuadPart / kTenthMicrosInMilliSecond) - - kJavaEpochToWinFileTimeDelta; - return now_int64.QuadPart; - } - return 0; -#elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_HAS_GETTIMEOFDAY_ - __timeb64 now; - -# ifdef _MSC_VER - - // MSVC 8 deprecates _ftime64(), so we want to suppress warning 4996 - // (deprecated function) there. - // TODO(kenton@google.com): Use GetTickCount()? Or use - // SystemTimeToFileTime() -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable : 4996) // Temporarily disables warning 4996. - _ftime64(&now); -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state. -# else +// A helper class for measuring elapsed times. +class Timer { + public: + Timer() : start_(std::chrono::steady_clock::now()) {} - _ftime64(&now); + // Return time elapsed in milliseconds since the timer was created. + TimeInMillis Elapsed() { + return std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>( + std::chrono::steady_clock::now() - start_) + .count(); + } -# endif // _MSC_VER + private: + std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point start_; +}; - return static_cast<TimeInMillis>(now.time) * 1000 + now.millitm; -#elif GTEST_HAS_GETTIMEOFDAY_ - struct timeval now; - gettimeofday(&now, NULL); - return static_cast<TimeInMillis>(now.tv_sec) * 1000 + now.tv_usec / 1000; -#else -# error "Don't know how to get the current time on your system." -#endif +// Returns a timestamp as milliseconds since the epoch. Note this time may jump +// around subject to adjustments by the system, to measure elapsed time use +// Timer instead. +TimeInMillis GetTimeInMillis() { + return std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>( + std::chrono::system_clock::now() - + std::chrono::system_clock::from_time_t(0)) + .count(); } // Utilities @@ -2288,12 +2558,13 @@ TimeInMillis GetTimeInMillis() { // value using delete[]. Returns the wide string, or NULL if the // input is NULL. LPCWSTR String::AnsiToUtf16(const char* ansi) { - if (!ansi) return NULL; + if (!ansi) return nullptr; const int length = strlen(ansi); const int unicode_length = - MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP, 0, ansi, length, NULL, 0); + MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP, 0, ansi, length, nullptr, 0); WCHAR* unicode = new WCHAR[unicode_length + 1]; - MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP, 0, ansi, length, unicode, unicode_length); + MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP, 0, ansi, length, + unicode, unicode_length); unicode[unicode_length] = 0; return unicode; } @@ -2302,41 +2573,44 @@ LPCWSTR String::AnsiToUtf16(const char* ansi) { // memory using new. The caller is responsible for deleting the return // value using delete[]. Returns the ANSI string, or NULL if the // input is NULL. -const char* String::Utf16ToAnsi(LPCWSTR utf16_str) { - if (!utf16_str) return NULL; - const int ansi_length = - WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, utf16_str, -1, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL); +const char* String::Utf16ToAnsi(LPCWSTR utf16_str) { + if (!utf16_str) return nullptr; + const int ansi_length = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, utf16_str, -1, nullptr, + 0, nullptr, nullptr); char* ansi = new char[ansi_length + 1]; - WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, utf16_str, -1, ansi, ansi_length, NULL, NULL); + WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, utf16_str, -1, ansi, ansi_length, nullptr, + nullptr); ansi[ansi_length] = 0; return ansi; } #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -// Compares two C strings. Returns true iff they have the same content. +// Compares two C strings. Returns true if and only if they have the same +// content. // // Unlike strcmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). A NULL // C string is considered different to any non-NULL C string, // including the empty string. -bool String::CStringEquals(const char* lhs, const char* rhs) { - if (lhs == NULL) return rhs == NULL; +bool String::CStringEquals(const char * lhs, const char * rhs) { + if (lhs == nullptr) return rhs == nullptr; - if (rhs == NULL) return false; + if (rhs == nullptr) return false; return strcmp(lhs, rhs) == 0; } -#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING || GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING +#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING // Converts an array of wide chars to a narrow string using the UTF-8 // encoding, and streams the result to the given Message object. static void StreamWideCharsToMessage(const wchar_t* wstr, size_t length, Message* msg) { - for (size_t i = 0; i != length;) { // NOLINT + for (size_t i = 0; i != length; ) { // NOLINT if (wstr[i] != L'\0') { *msg << WideStringToUtf8(wstr + i, static_cast<int>(length - i)); - while (i != length && wstr[i] != L'\0') i++; + while (i != length && wstr[i] != L'\0') + i++; } else { *msg << '\0'; i++; @@ -2344,7 +2618,24 @@ static void StreamWideCharsToMessage(const wchar_t* wstr, size_t length, } } -#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING || GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING +#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING + +void SplitString(const ::std::string& str, char delimiter, + ::std::vector< ::std::string>* dest) { + ::std::vector< ::std::string> parsed; + ::std::string::size_type pos = 0; + while (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { + const ::std::string::size_type colon = str.find(delimiter, pos); + if (colon == ::std::string::npos) { + parsed.push_back(str.substr(pos)); + break; + } else { + parsed.push_back(str.substr(pos, colon - pos)); + pos = colon + 1; + } + } + dest->swap(parsed); +} } // namespace internal @@ -2361,31 +2652,22 @@ Message::Message() : ss_(new ::std::stringstream) { // These two overloads allow streaming a wide C string to a Message // using the UTF-8 encoding. -Message& Message::operator<<(const wchar_t* wide_c_str) { +Message& Message::operator <<(const wchar_t* wide_c_str) { return *this << internal::String::ShowWideCString(wide_c_str); } -Message& Message::operator<<(wchar_t* wide_c_str) { +Message& Message::operator <<(wchar_t* wide_c_str) { return *this << internal::String::ShowWideCString(wide_c_str); } #if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING // Converts the given wide string to a narrow string using the UTF-8 // encoding, and streams the result to this Message object. -Message& Message::operator<<(const ::std::wstring& wstr) { +Message& Message::operator <<(const ::std::wstring& wstr) { internal::StreamWideCharsToMessage(wstr.c_str(), wstr.length(), this); return *this; } #endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING -// Converts the given wide string to a narrow string using the UTF-8 -// encoding, and streams the result to this Message object. -Message& Message::operator<<(const ::wstring& wstr) { - internal::StreamWideCharsToMessage(wstr.c_str(), wstr.length(), this); - return *this; -} -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING - // Gets the text streamed to this object so far as an std::string. // Each '\0' character in the buffer is replaced with "\\0". std::string Message::GetString() const { @@ -2396,22 +2678,33 @@ std::string Message::GetString() const { // Used in EXPECT_TRUE/FALSE(assertion_result). AssertionResult::AssertionResult(const AssertionResult& other) : success_(other.success_), - message_(other.message_.get() != NULL + message_(other.message_.get() != nullptr ? new ::std::string(*other.message_) - : static_cast< ::std::string*>(NULL)) {} + : static_cast< ::std::string*>(nullptr)) {} + +// Swaps two AssertionResults. +void AssertionResult::swap(AssertionResult& other) { + using std::swap; + swap(success_, other.success_); + swap(message_, other.message_); +} // Returns the assertion's negation. Used with EXPECT/ASSERT_FALSE. AssertionResult AssertionResult::operator!() const { AssertionResult negation(!success_); - if (message_.get() != NULL) negation << *message_; + if (message_.get() != nullptr) negation << *message_; return negation; } // Makes a successful assertion result. -AssertionResult AssertionSuccess() { return AssertionResult(true); } +AssertionResult AssertionSuccess() { + return AssertionResult(true); +} // Makes a failed assertion result. -AssertionResult AssertionFailure() { return AssertionResult(false); } +AssertionResult AssertionFailure() { + return AssertionResult(false); +} // Makes a failed assertion result with the given failure message. // Deprecated; use AssertionFailure() << message. @@ -2421,6 +2714,277 @@ AssertionResult AssertionFailure(const Message& message) { namespace internal { +namespace edit_distance { +std::vector<EditType> CalculateOptimalEdits(const std::vector<size_t>& left, + const std::vector<size_t>& right) { + std::vector<std::vector<double> > costs( + left.size() + 1, std::vector<double>(right.size() + 1)); + std::vector<std::vector<EditType> > best_move( + left.size() + 1, std::vector<EditType>(right.size() + 1)); + + // Populate for empty right. + for (size_t l_i = 0; l_i < costs.size(); ++l_i) { + costs[l_i][0] = static_cast<double>(l_i); + best_move[l_i][0] = kRemove; + } + // Populate for empty left. + for (size_t r_i = 1; r_i < costs[0].size(); ++r_i) { + costs[0][r_i] = static_cast<double>(r_i); + best_move[0][r_i] = kAdd; + } + + for (size_t l_i = 0; l_i < left.size(); ++l_i) { + for (size_t r_i = 0; r_i < right.size(); ++r_i) { + if (left[l_i] == right[r_i]) { + // Found a match. Consume it. + costs[l_i + 1][r_i + 1] = costs[l_i][r_i]; + best_move[l_i + 1][r_i + 1] = kMatch; + continue; + } + + const double add = costs[l_i + 1][r_i]; + const double remove = costs[l_i][r_i + 1]; + const double replace = costs[l_i][r_i]; + if (add < remove && add < replace) { + costs[l_i + 1][r_i + 1] = add + 1; + best_move[l_i + 1][r_i + 1] = kAdd; + } else if (remove < add && remove < replace) { + costs[l_i + 1][r_i + 1] = remove + 1; + best_move[l_i + 1][r_i + 1] = kRemove; + } else { + // We make replace a little more expensive than add/remove to lower + // their priority. + costs[l_i + 1][r_i + 1] = replace + 1.00001; + best_move[l_i + 1][r_i + 1] = kReplace; + } + } + } + + // Reconstruct the best path. We do it in reverse order. + std::vector<EditType> best_path; + for (size_t l_i = left.size(), r_i = right.size(); l_i > 0 || r_i > 0;) { + EditType move = best_move[l_i][r_i]; + best_path.push_back(move); + l_i -= move != kAdd; + r_i -= move != kRemove; + } + std::reverse(best_path.begin(), best_path.end()); + return best_path; +} + +namespace { + +// Helper class to convert string into ids with deduplication. +class InternalStrings { + public: + size_t GetId(const std::string& str) { + IdMap::iterator it = ids_.find(str); + if (it != ids_.end()) return it->second; + size_t id = ids_.size(); + return ids_[str] = id; + } + + private: + typedef std::map<std::string, size_t> IdMap; + IdMap ids_; +}; + +} // namespace + +std::vector<EditType> CalculateOptimalEdits( + const std::vector<std::string>& left, + const std::vector<std::string>& right) { + std::vector<size_t> left_ids, right_ids; + { + InternalStrings intern_table; + for (size_t i = 0; i < left.size(); ++i) { + left_ids.push_back(intern_table.GetId(left[i])); + } + for (size_t i = 0; i < right.size(); ++i) { + right_ids.push_back(intern_table.GetId(right[i])); + } + } + return CalculateOptimalEdits(left_ids, right_ids); +} + +namespace { + +// Helper class that holds the state for one hunk and prints it out to the +// stream. +// It reorders adds/removes when possible to group all removes before all +// adds. It also adds the hunk header before printint into the stream. +class Hunk { + public: + Hunk(size_t left_start, size_t right_start) + : left_start_(left_start), + right_start_(right_start), + adds_(), + removes_(), + common_() {} + + void PushLine(char edit, const char* line) { + switch (edit) { + case ' ': + ++common_; + FlushEdits(); + hunk_.push_back(std::make_pair(' ', line)); + break; + case '-': + ++removes_; + hunk_removes_.push_back(std::make_pair('-', line)); + break; + case '+': + ++adds_; + hunk_adds_.push_back(std::make_pair('+', line)); + break; + } + } + + void PrintTo(std::ostream* os) { + PrintHeader(os); + FlushEdits(); + for (std::list<std::pair<char, const char*> >::const_iterator it = + hunk_.begin(); + it != hunk_.end(); ++it) { + *os << it->first << it->second << "\n"; + } + } + + bool has_edits() const { return adds_ || removes_; } + + private: + void FlushEdits() { + hunk_.splice(hunk_.end(), hunk_removes_); + hunk_.splice(hunk_.end(), hunk_adds_); + } + + // Print a unified diff header for one hunk. + // The format is + // "@@ -<left_start>,<left_length> +<right_start>,<right_length> @@" + // where the left/right parts are omitted if unnecessary. + void PrintHeader(std::ostream* ss) const { + *ss << "@@ "; + if (removes_) { + *ss << "-" << left_start_ << "," << (removes_ + common_); + } + if (removes_ && adds_) { + *ss << " "; + } + if (adds_) { + *ss << "+" << right_start_ << "," << (adds_ + common_); + } + *ss << " @@\n"; + } + + size_t left_start_, right_start_; + size_t adds_, removes_, common_; + std::list<std::pair<char, const char*> > hunk_, hunk_adds_, hunk_removes_; +}; + +} // namespace + +// Create a list of diff hunks in Unified diff format. +// Each hunk has a header generated by PrintHeader above plus a body with +// lines prefixed with ' ' for no change, '-' for deletion and '+' for +// addition. +// 'context' represents the desired unchanged prefix/suffix around the diff. +// If two hunks are close enough that their contexts overlap, then they are +// joined into one hunk. +std::string CreateUnifiedDiff(const std::vector<std::string>& left, + const std::vector<std::string>& right, + size_t context) { + const std::vector<EditType> edits = CalculateOptimalEdits(left, right); + + size_t l_i = 0, r_i = 0, edit_i = 0; + std::stringstream ss; + while (edit_i < edits.size()) { + // Find first edit. + while (edit_i < edits.size() && edits[edit_i] == kMatch) { + ++l_i; + ++r_i; + ++edit_i; + } + + // Find the first line to include in the hunk. + const size_t prefix_context = std::min(l_i, context); + Hunk hunk(l_i - prefix_context + 1, r_i - prefix_context + 1); + for (size_t i = prefix_context; i > 0; --i) { + hunk.PushLine(' ', left[l_i - i].c_str()); + } + + // Iterate the edits until we found enough suffix for the hunk or the input + // is over. + size_t n_suffix = 0; + for (; edit_i < edits.size(); ++edit_i) { + if (n_suffix >= context) { + // Continue only if the next hunk is very close. + auto it = edits.begin() + static_cast<int>(edit_i); + while (it != edits.end() && *it == kMatch) ++it; + if (it == edits.end() || + static_cast<size_t>(it - edits.begin()) - edit_i >= context) { + // There is no next edit or it is too far away. + break; + } + } + + EditType edit = edits[edit_i]; + // Reset count when a non match is found. + n_suffix = edit == kMatch ? n_suffix + 1 : 0; + + if (edit == kMatch || edit == kRemove || edit == kReplace) { + hunk.PushLine(edit == kMatch ? ' ' : '-', left[l_i].c_str()); + } + if (edit == kAdd || edit == kReplace) { + hunk.PushLine('+', right[r_i].c_str()); + } + + // Advance indices, depending on edit type. + l_i += edit != kAdd; + r_i += edit != kRemove; + } + + if (!hunk.has_edits()) { + // We are done. We don't want this hunk. + break; + } + + hunk.PrintTo(&ss); + } + return ss.str(); +} + +} // namespace edit_distance + +namespace { + +// The string representation of the values received in EqFailure() are already +// escaped. Split them on escaped '\n' boundaries. Leave all other escaped +// characters the same. +std::vector<std::string> SplitEscapedString(const std::string& str) { + std::vector<std::string> lines; + size_t start = 0, end = str.size(); + if (end > 2 && str[0] == '"' && str[end - 1] == '"') { + ++start; + --end; + } + bool escaped = false; + for (size_t i = start; i + 1 < end; ++i) { + if (escaped) { + escaped = false; + if (str[i] == 'n') { + lines.push_back(str.substr(start, i - start - 1)); + start = i + 1; + } + } else { + escaped = str[i] == '\\'; + } + } + lines.push_back(str.substr(start, end - start)); + return lines; +} + +} // namespace + // Constructs and returns the message for an equality assertion // (e.g. ASSERT_EQ, EXPECT_STREQ, etc) failure. // @@ -2428,30 +2992,43 @@ namespace internal { // and their values, as strings. For example, for ASSERT_EQ(foo, bar) // where foo is 5 and bar is 6, we have: // -// expected_expression: "foo" -// actual_expression: "bar" -// expected_value: "5" -// actual_value: "6" +// lhs_expression: "foo" +// rhs_expression: "bar" +// lhs_value: "5" +// rhs_value: "6" // -// The ignoring_case parameter is true iff the assertion is a -// *_STRCASEEQ*. When it's true, the string " (ignoring case)" will +// The ignoring_case parameter is true if and only if the assertion is a +// *_STRCASEEQ*. When it's true, the string "Ignoring case" will // be inserted into the message. -AssertionResult EqFailure(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const std::string& expected_value, - const std::string& actual_value, bool ignoring_case) { +AssertionResult EqFailure(const char* lhs_expression, + const char* rhs_expression, + const std::string& lhs_value, + const std::string& rhs_value, + bool ignoring_case) { Message msg; - msg << "Value of: " << actual_expression; - if (actual_value != actual_expression) { - msg << "\n Actual: " << actual_value; + msg << "Expected equality of these values:"; + msg << "\n " << lhs_expression; + if (lhs_value != lhs_expression) { + msg << "\n Which is: " << lhs_value; + } + msg << "\n " << rhs_expression; + if (rhs_value != rhs_expression) { + msg << "\n Which is: " << rhs_value; } - msg << "\nExpected: " << expected_expression; if (ignoring_case) { - msg << " (ignoring case)"; + msg << "\nIgnoring case"; } - if (expected_value != expected_expression) { - msg << "\nWhich is: " << expected_value; + + if (!lhs_value.empty() && !rhs_value.empty()) { + const std::vector<std::string> lhs_lines = + SplitEscapedString(lhs_value); + const std::vector<std::string> rhs_lines = + SplitEscapedString(rhs_value); + if (lhs_lines.size() > 1 || rhs_lines.size() > 1) { + msg << "\nWith diff:\n" + << edit_distance::CreateUnifiedDiff(lhs_lines, rhs_lines); + } } return AssertionFailure() << msg; @@ -2459,38 +3036,70 @@ AssertionResult EqFailure(const char* expected_expression, // Constructs a failure message for Boolean assertions such as EXPECT_TRUE. std::string GetBoolAssertionFailureMessage( - const AssertionResult& assertion_result, const char* expression_text, - const char* actual_predicate_value, const char* expected_predicate_value) { + const AssertionResult& assertion_result, + const char* expression_text, + const char* actual_predicate_value, + const char* expected_predicate_value) { const char* actual_message = assertion_result.message(); Message msg; msg << "Value of: " << expression_text << "\n Actual: " << actual_predicate_value; - if (actual_message[0] != '\0') msg << " (" << actual_message << ")"; + if (actual_message[0] != '\0') + msg << " (" << actual_message << ")"; msg << "\nExpected: " << expected_predicate_value; return msg.GetString(); } // Helper function for implementing ASSERT_NEAR. -AssertionResult DoubleNearPredFormat(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, - const char* abs_error_expr, double val1, - double val2, double abs_error) { +AssertionResult DoubleNearPredFormat(const char* expr1, + const char* expr2, + const char* abs_error_expr, + double val1, + double val2, + double abs_error) { const double diff = fabs(val1 - val2); if (diff <= abs_error) return AssertionSuccess(); - // TODO(wan): do not print the value of an expression if it's - // already a literal. + // Find the value which is closest to zero. + const double min_abs = std::min(fabs(val1), fabs(val2)); + // Find the distance to the next double from that value. + const double epsilon = + nextafter(min_abs, std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity()) - min_abs; + // Detect the case where abs_error is so small that EXPECT_NEAR is + // effectively the same as EXPECT_EQUAL, and give an informative error + // message so that the situation can be more easily understood without + // requiring exotic floating-point knowledge. + // Don't do an epsilon check if abs_error is zero because that implies + // that an equality check was actually intended. + if (!(std::isnan)(val1) && !(std::isnan)(val2) && abs_error > 0 && + abs_error < epsilon) { + return AssertionFailure() + << "The difference between " << expr1 << " and " << expr2 << " is " + << diff << ", where\n" + << expr1 << " evaluates to " << val1 << ",\n" + << expr2 << " evaluates to " << val2 << ".\nThe abs_error parameter " + << abs_error_expr << " evaluates to " << abs_error + << " which is smaller than the minimum distance between doubles for " + "numbers of this magnitude which is " + << epsilon + << ", thus making this EXPECT_NEAR check equivalent to " + "EXPECT_EQUAL. Consider using EXPECT_DOUBLE_EQ instead."; + } return AssertionFailure() - << "The difference between " << expr1 << " and " << expr2 << " is " - << diff << ", which exceeds " << abs_error_expr << ", where\n" - << expr1 << " evaluates to " << val1 << ",\n" - << expr2 << " evaluates to " << val2 << ", and\n" - << abs_error_expr << " evaluates to " << abs_error << "."; + << "The difference between " << expr1 << " and " << expr2 + << " is " << diff << ", which exceeds " << abs_error_expr << ", where\n" + << expr1 << " evaluates to " << val1 << ",\n" + << expr2 << " evaluates to " << val2 << ", and\n" + << abs_error_expr << " evaluates to " << abs_error << "."; } + // Helper template for implementing FloatLE() and DoubleLE(). template <typename RawType> -AssertionResult FloatingPointLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, - RawType val1, RawType val2) { +AssertionResult FloatingPointLE(const char* expr1, + const char* expr2, + RawType val1, + RawType val2) { // Returns success if val1 is less than val2, if (val1 < val2) { return AssertionSuccess(); @@ -2515,124 +3124,87 @@ AssertionResult FloatingPointLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, << val2; return AssertionFailure() - << "Expected: (" << expr1 << ") <= (" << expr2 << ")\n" - << " Actual: " << StringStreamToString(&val1_ss) << " vs " - << StringStreamToString(&val2_ss); + << "Expected: (" << expr1 << ") <= (" << expr2 << ")\n" + << " Actual: " << StringStreamToString(&val1_ss) << " vs " + << StringStreamToString(&val2_ss); } } // namespace internal // Asserts that val1 is less than, or almost equal to, val2. Fails // otherwise. In particular, it fails if either val1 or val2 is NaN. -AssertionResult FloatLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, float val1, - float val2) { +AssertionResult FloatLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, + float val1, float val2) { return internal::FloatingPointLE<float>(expr1, expr2, val1, val2); } // Asserts that val1 is less than, or almost equal to, val2. Fails // otherwise. In particular, it fails if either val1 or val2 is NaN. -AssertionResult DoubleLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, double val1, - double val2) { +AssertionResult DoubleLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, + double val1, double val2) { return internal::FloatingPointLE<double>(expr1, expr2, val1, val2); } namespace internal { -// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ with int or enum -// arguments. -AssertionResult CmpHelperEQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, BiggestInt expected, - BiggestInt actual) { - if (expected == actual) { - return AssertionSuccess(); - } - - return EqFailure(expected_expression, actual_expression, - FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(expected, actual), - FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(actual, expected), false); -} - -// A macro for implementing the helper functions needed to implement -// ASSERT_?? and EXPECT_?? with integer or enum arguments. It is here -// just to avoid copy-and-paste of similar code. -#define GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(op_name, op) \ - AssertionResult CmpHelper##op_name(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, \ - BiggestInt val1, BiggestInt val2) { \ - if (val1 op val2) { \ - return AssertionSuccess(); \ - } else { \ - return AssertionFailure() \ - << "Expected: (" << expr1 << ") " #op " (" << expr2 \ - << "), actual: " << FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(val1, val2) \ - << " vs " << FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(val2, val1); \ - } \ - } - -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NE with int or -// enum arguments. -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(NE, !=) -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LE with int or -// enum arguments. -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(LE, <=) -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LT with int or -// enum arguments. -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(LT, <) -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GE with int or -// enum arguments. -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(GE, >=) -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GT with int or -// enum arguments. -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(GT, >) - -#undef GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_ - // The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STREQ. -AssertionResult CmpHelperSTREQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const char* expected, const char* actual) { - if (String::CStringEquals(expected, actual)) { +AssertionResult CmpHelperSTREQ(const char* lhs_expression, + const char* rhs_expression, + const char* lhs, + const char* rhs) { + if (String::CStringEquals(lhs, rhs)) { return AssertionSuccess(); } - return EqFailure(expected_expression, actual_expression, - PrintToString(expected), PrintToString(actual), false); + return EqFailure(lhs_expression, + rhs_expression, + PrintToString(lhs), + PrintToString(rhs), + false); } // The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASEEQ. -AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRCASEEQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const char* expected, const char* actual) { - if (String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(expected, actual)) { +AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRCASEEQ(const char* lhs_expression, + const char* rhs_expression, + const char* lhs, + const char* rhs) { + if (String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(lhs, rhs)) { return AssertionSuccess(); } - return EqFailure(expected_expression, actual_expression, - PrintToString(expected), PrintToString(actual), true); + return EqFailure(lhs_expression, + rhs_expression, + PrintToString(lhs), + PrintToString(rhs), + true); } // The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRNE. AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRNE(const char* s1_expression, - const char* s2_expression, const char* s1, + const char* s2_expression, + const char* s1, const char* s2) { if (!String::CStringEquals(s1, s2)) { return AssertionSuccess(); } else { - return AssertionFailure() - << "Expected: (" << s1_expression << ") != (" << s2_expression - << "), actual: \"" << s1 << "\" vs \"" << s2 << "\""; + return AssertionFailure() << "Expected: (" << s1_expression << ") != (" + << s2_expression << "), actual: \"" + << s1 << "\" vs \"" << s2 << "\""; } } // The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASENE. AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRCASENE(const char* s1_expression, - const char* s2_expression, const char* s1, + const char* s2_expression, + const char* s1, const char* s2) { if (!String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(s1, s2)) { return AssertionSuccess(); } else { return AssertionFailure() - << "Expected: (" << s1_expression << ") != (" << s2_expression - << ") (ignoring case), actual: \"" << s1 << "\" vs \"" << s2 << "\""; + << "Expected: (" << s1_expression << ") != (" + << s2_expression << ") (ignoring case), actual: \"" + << s1 << "\" vs \"" << s2 << "\""; } } @@ -2642,25 +3214,26 @@ namespace { // Helper functions for implementing IsSubString() and IsNotSubstring(). -// This group of overloaded functions return true iff needle is a -// substring of haystack. NULL is considered a substring of itself -// only. +// This group of overloaded functions return true if and only if needle +// is a substring of haystack. NULL is considered a substring of +// itself only. bool IsSubstringPred(const char* needle, const char* haystack) { - if (needle == NULL || haystack == NULL) return needle == haystack; + if (needle == nullptr || haystack == nullptr) return needle == haystack; - return strstr(haystack, needle) != NULL; + return strstr(haystack, needle) != nullptr; } bool IsSubstringPred(const wchar_t* needle, const wchar_t* haystack) { - if (needle == NULL || haystack == NULL) return needle == haystack; + if (needle == nullptr || haystack == nullptr) return needle == haystack; - return wcsstr(haystack, needle) != NULL; + return wcsstr(haystack, needle) != nullptr; } // StringType here can be either ::std::string or ::std::wstring. template <typename StringType> -bool IsSubstringPred(const StringType& needle, const StringType& haystack) { +bool IsSubstringPred(const StringType& needle, + const StringType& haystack) { return haystack.find(needle) != StringType::npos; } @@ -2669,22 +3242,21 @@ bool IsSubstringPred(const StringType& needle, const StringType& haystack) { // StringType here can be const char*, const wchar_t*, ::std::string, // or ::std::wstring. template <typename StringType> -AssertionResult IsSubstringImpl(bool expected_to_be_substring, - const char* needle_expr, - const char* haystack_expr, - const StringType& needle, - const StringType& haystack) { +AssertionResult IsSubstringImpl( + bool expected_to_be_substring, + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const StringType& needle, const StringType& haystack) { if (IsSubstringPred(needle, haystack) == expected_to_be_substring) return AssertionSuccess(); const bool is_wide_string = sizeof(needle[0]) > 1; const char* const begin_string_quote = is_wide_string ? "L\"" : "\""; return AssertionFailure() - << "Value of: " << needle_expr << "\n" - << " Actual: " << begin_string_quote << needle << "\"\n" - << "Expected: " << (expected_to_be_substring ? "" : "not ") - << "a substring of " << haystack_expr << "\n" - << "Which is: " << begin_string_quote << haystack << "\""; + << "Value of: " << needle_expr << "\n" + << " Actual: " << begin_string_quote << needle << "\"\n" + << "Expected: " << (expected_to_be_substring ? "" : "not ") + << "a substring of " << haystack_expr << "\n" + << "Which is: " << begin_string_quote << haystack << "\""; } } // namespace @@ -2693,52 +3265,52 @@ AssertionResult IsSubstringImpl(bool expected_to_be_substring, // substring of haystack (NULL is considered a substring of itself // only), and return an appropriate error message when they fail. -AssertionResult IsSubstring(const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const char* needle, const char* haystack) { +AssertionResult IsSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const char* needle, const char* haystack) { return IsSubstringImpl(true, needle_expr, haystack_expr, needle, haystack); } -AssertionResult IsSubstring(const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const wchar_t* needle, const wchar_t* haystack) { +AssertionResult IsSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const wchar_t* needle, const wchar_t* haystack) { return IsSubstringImpl(true, needle_expr, haystack_expr, needle, haystack); } -AssertionResult IsNotSubstring(const char* needle_expr, - const char* haystack_expr, const char* needle, - const char* haystack) { +AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const char* needle, const char* haystack) { return IsSubstringImpl(false, needle_expr, haystack_expr, needle, haystack); } -AssertionResult IsNotSubstring(const char* needle_expr, - const char* haystack_expr, const wchar_t* needle, - const wchar_t* haystack) { +AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const wchar_t* needle, const wchar_t* haystack) { return IsSubstringImpl(false, needle_expr, haystack_expr, needle, haystack); } -AssertionResult IsSubstring(const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const ::std::string& needle, - const ::std::string& haystack) { +AssertionResult IsSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const ::std::string& needle, const ::std::string& haystack) { return IsSubstringImpl(true, needle_expr, haystack_expr, needle, haystack); } -AssertionResult IsNotSubstring(const char* needle_expr, - const char* haystack_expr, - const ::std::string& needle, - const ::std::string& haystack) { +AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const ::std::string& needle, const ::std::string& haystack) { return IsSubstringImpl(false, needle_expr, haystack_expr, needle, haystack); } #if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING -AssertionResult IsSubstring(const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const ::std::wstring& needle, - const ::std::wstring& haystack) { +AssertionResult IsSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const ::std::wstring& needle, const ::std::wstring& haystack) { return IsSubstringImpl(true, needle_expr, haystack_expr, needle, haystack); } -AssertionResult IsNotSubstring(const char* needle_expr, - const char* haystack_expr, - const ::std::wstring& needle, - const ::std::wstring& haystack) { +AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const ::std::wstring& needle, const ::std::wstring& haystack) { return IsSubstringImpl(false, needle_expr, haystack_expr, needle, haystack); } #endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING @@ -2750,42 +3322,43 @@ namespace internal { namespace { // Helper function for IsHRESULT{SuccessFailure} predicates -AssertionResult HRESULTFailureHelper(const char* expr, const char* expected, +AssertionResult HRESULTFailureHelper(const char* expr, + const char* expected, long hr) { // NOLINT -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_TV_TITLE // Windows CE doesn't support FormatMessage. const char error_text[] = ""; -# else +# else // Looks up the human-readable system message for the HRESULT code // and since we're not passing any params to FormatMessage, we don't // want inserts expanded. - const DWORD kFlags = - FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS; + const DWORD kFlags = FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | + FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS; const DWORD kBufSize = 4096; // Gets the system's human readable message string for this HRESULT. - char error_text[kBufSize] = {'\0'}; + char error_text[kBufSize] = { '\0' }; DWORD message_length = ::FormatMessageA(kFlags, 0, // no source, we're asking system - hr, // the error + static_cast<DWORD>(hr), // the error 0, // no line width restrictions error_text, // output buffer kBufSize, // buf size - NULL); // no arguments for inserts + nullptr); // no arguments for inserts // Trims tailing white space (FormatMessage leaves a trailing CR-LF) for (; message_length && IsSpace(error_text[message_length - 1]); - --message_length) { + --message_length) { error_text[message_length - 1] = '\0'; } -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE const std::string error_hex("0x" + String::FormatHexInt(hr)); return ::testing::AssertionFailure() - << "Expected: " << expr << " " << expected << ".\n" - << " Actual: " << error_hex << " " << error_text << "\n"; + << "Expected: " << expr << " " << expected << ".\n" + << " Actual: " << error_hex << " " << error_text << "\n"; } } // namespace @@ -2809,7 +3382,7 @@ AssertionResult IsHRESULTFailure(const char* expr, long hr) { // NOLINT // Utility functions for encoding Unicode text (wide strings) in // UTF-8. -// A Unicode code-point can have upto 21 bits, and is encoded in UTF-8 +// A Unicode code-point can have up to 21 bits, and is encoded in UTF-8 // like this: // // Code-point length Encoding @@ -2819,41 +3392,41 @@ AssertionResult IsHRESULTFailure(const char* expr, long hr) { // NOLINT // 17 - 21 bits 11110xxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx // The maximum code-point a one-byte UTF-8 sequence can represent. -const UInt32 kMaxCodePoint1 = (static_cast<UInt32>(1) << 7) - 1; +constexpr uint32_t kMaxCodePoint1 = (static_cast<uint32_t>(1) << 7) - 1; // The maximum code-point a two-byte UTF-8 sequence can represent. -const UInt32 kMaxCodePoint2 = (static_cast<UInt32>(1) << (5 + 6)) - 1; +constexpr uint32_t kMaxCodePoint2 = (static_cast<uint32_t>(1) << (5 + 6)) - 1; // The maximum code-point a three-byte UTF-8 sequence can represent. -const UInt32 kMaxCodePoint3 = (static_cast<UInt32>(1) << (4 + 2 * 6)) - 1; +constexpr uint32_t kMaxCodePoint3 = (static_cast<uint32_t>(1) << (4 + 2*6)) - 1; // The maximum code-point a four-byte UTF-8 sequence can represent. -const UInt32 kMaxCodePoint4 = (static_cast<UInt32>(1) << (3 + 3 * 6)) - 1; +constexpr uint32_t kMaxCodePoint4 = (static_cast<uint32_t>(1) << (3 + 3*6)) - 1; // Chops off the n lowest bits from a bit pattern. Returns the n // lowest bits. As a side effect, the original bit pattern will be // shifted to the right by n bits. -inline UInt32 ChopLowBits(UInt32* bits, int n) { - const UInt32 low_bits = *bits & ((static_cast<UInt32>(1) << n) - 1); +inline uint32_t ChopLowBits(uint32_t* bits, int n) { + const uint32_t low_bits = *bits & ((static_cast<uint32_t>(1) << n) - 1); *bits >>= n; return low_bits; } // Converts a Unicode code point to a narrow string in UTF-8 encoding. -// code_point parameter is of type UInt32 because wchar_t may not be +// code_point parameter is of type uint32_t because wchar_t may not be // wide enough to contain a code point. // If the code_point is not a valid Unicode code point // (i.e. outside of Unicode range U+0 to U+10FFFF) it will be converted // to "(Invalid Unicode 0xXXXXXXXX)". -std::string CodePointToUtf8(UInt32 code_point) { +std::string CodePointToUtf8(uint32_t code_point) { if (code_point > kMaxCodePoint4) { - return "(Invalid Unicode 0x" + String::FormatHexInt(code_point) + ")"; + return "(Invalid Unicode 0x" + String::FormatHexUInt32(code_point) + ")"; } char str[5]; // Big enough for the largest valid code point. if (code_point <= kMaxCodePoint1) { str[1] = '\0'; - str[0] = static_cast<char>(code_point); // 0xxxxxxx + str[0] = static_cast<char>(code_point); // 0xxxxxxx } else if (code_point <= kMaxCodePoint2) { str[2] = '\0'; str[1] = static_cast<char>(0x80 | ChopLowBits(&code_point, 6)); // 10xxxxxx @@ -2873,33 +3446,35 @@ std::string CodePointToUtf8(UInt32 code_point) { return str; } -// The following two functions only make sense if the the system +// The following two functions only make sense if the system // uses UTF-16 for wide string encoding. All supported systems -// with 16 bit wchar_t (Windows, Cygwin, Symbian OS) do use UTF-16. +// with 16 bit wchar_t (Windows, Cygwin) do use UTF-16. // Determines if the arguments constitute UTF-16 surrogate pair // and thus should be combined into a single Unicode code point // using CreateCodePointFromUtf16SurrogatePair. inline bool IsUtf16SurrogatePair(wchar_t first, wchar_t second) { - return sizeof(wchar_t) == 2 && (first & 0xFC00) == 0xD800 && - (second & 0xFC00) == 0xDC00; + return sizeof(wchar_t) == 2 && + (first & 0xFC00) == 0xD800 && (second & 0xFC00) == 0xDC00; } // Creates a Unicode code point from UTF16 surrogate pair. -inline UInt32 CreateCodePointFromUtf16SurrogatePair(wchar_t first, - wchar_t second) { - const UInt32 mask = (1 << 10) - 1; +inline uint32_t CreateCodePointFromUtf16SurrogatePair(wchar_t first, + wchar_t second) { + const auto first_u = static_cast<uint32_t>(first); + const auto second_u = static_cast<uint32_t>(second); + const uint32_t mask = (1 << 10) - 1; return (sizeof(wchar_t) == 2) - ? (((first & mask) << 10) | (second & mask)) + 0x10000 + ? (((first_u & mask) << 10) | (second_u & mask)) + 0x10000 : // This function should not be called when the condition is // false, but we provide a sensible default in case it is. - static_cast<UInt32>(first); + first_u; } // Converts a wide string to a narrow string in UTF-8 encoding. // The wide string is assumed to have the following encoding: -// UTF-16 if sizeof(wchar_t) == 2 (on Windows, Cygwin, Symbian OS) +// UTF-16 if sizeof(wchar_t) == 2 (on Windows, Cygwin) // UTF-32 if sizeof(wchar_t) == 4 (on Linux) // Parameter str points to a null-terminated wide string. // Parameter num_chars may additionally limit the number @@ -2911,20 +3486,21 @@ inline UInt32 CreateCodePointFromUtf16SurrogatePair(wchar_t first, // and contains invalid UTF-16 surrogate pairs, values in those pairs // will be encoded as individual Unicode characters from Basic Normal Plane. std::string WideStringToUtf8(const wchar_t* str, int num_chars) { - if (num_chars == -1) num_chars = static_cast<int>(wcslen(str)); + if (num_chars == -1) + num_chars = static_cast<int>(wcslen(str)); ::std::stringstream stream; for (int i = 0; i < num_chars; ++i) { - UInt32 unicode_code_point; + uint32_t unicode_code_point; if (str[i] == L'\0') { break; } else if (i + 1 < num_chars && IsUtf16SurrogatePair(str[i], str[i + 1])) { - unicode_code_point = - CreateCodePointFromUtf16SurrogatePair(str[i], str[i + 1]); + unicode_code_point = CreateCodePointFromUtf16SurrogatePair(str[i], + str[i + 1]); i++; } else { - unicode_code_point = static_cast<UInt32>(str[i]); + unicode_code_point = static_cast<uint32_t>(str[i]); } stream << CodePointToUtf8(unicode_code_point); @@ -2934,64 +3510,70 @@ std::string WideStringToUtf8(const wchar_t* str, int num_chars) { // Converts a wide C string to an std::string using the UTF-8 encoding. // NULL will be converted to "(null)". -std::string String::ShowWideCString(const wchar_t* wide_c_str) { - if (wide_c_str == NULL) return "(null)"; +std::string String::ShowWideCString(const wchar_t * wide_c_str) { + if (wide_c_str == nullptr) return "(null)"; return internal::WideStringToUtf8(wide_c_str, -1); } -// Compares two wide C strings. Returns true iff they have the same -// content. +// Compares two wide C strings. Returns true if and only if they have the +// same content. // // Unlike wcscmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). A NULL // C string is considered different to any non-NULL C string, // including the empty string. -bool String::WideCStringEquals(const wchar_t* lhs, const wchar_t* rhs) { - if (lhs == NULL) return rhs == NULL; +bool String::WideCStringEquals(const wchar_t * lhs, const wchar_t * rhs) { + if (lhs == nullptr) return rhs == nullptr; - if (rhs == NULL) return false; + if (rhs == nullptr) return false; return wcscmp(lhs, rhs) == 0; } // Helper function for *_STREQ on wide strings. -AssertionResult CmpHelperSTREQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const wchar_t* expected, const wchar_t* actual) { - if (String::WideCStringEquals(expected, actual)) { +AssertionResult CmpHelperSTREQ(const char* lhs_expression, + const char* rhs_expression, + const wchar_t* lhs, + const wchar_t* rhs) { + if (String::WideCStringEquals(lhs, rhs)) { return AssertionSuccess(); } - return EqFailure(expected_expression, actual_expression, - PrintToString(expected), PrintToString(actual), false); + return EqFailure(lhs_expression, + rhs_expression, + PrintToString(lhs), + PrintToString(rhs), + false); } // Helper function for *_STRNE on wide strings. AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRNE(const char* s1_expression, - const char* s2_expression, const wchar_t* s1, + const char* s2_expression, + const wchar_t* s1, const wchar_t* s2) { if (!String::WideCStringEquals(s1, s2)) { return AssertionSuccess(); } - return AssertionFailure() - << "Expected: (" << s1_expression << ") != (" << s2_expression - << "), actual: " << PrintToString(s1) << " vs " << PrintToString(s2); + return AssertionFailure() << "Expected: (" << s1_expression << ") != (" + << s2_expression << "), actual: " + << PrintToString(s1) + << " vs " << PrintToString(s2); } -// Compares two C strings, ignoring case. Returns true iff they have +// Compares two C strings, ignoring case. Returns true if and only if they have // the same content. // // Unlike strcasecmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). A // NULL C string is considered different to any non-NULL C string, // including the empty string. -bool String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(const char* lhs, const char* rhs) { - if (lhs == NULL) return rhs == NULL; - if (rhs == NULL) return false; +bool String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(const char * lhs, const char * rhs) { + if (lhs == nullptr) return rhs == nullptr; + if (rhs == nullptr) return false; return posix::StrCaseCmp(lhs, rhs) == 0; } -// Compares two wide C strings, ignoring case. Returns true iff they +// Compares two wide C strings, ignoring case. Returns true if and only if they // have the same content. // // Unlike wcscasecmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). @@ -3005,9 +3587,9 @@ bool String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(const char* lhs, const char* rhs) { // current locale. bool String::CaseInsensitiveWideCStringEquals(const wchar_t* lhs, const wchar_t* rhs) { - if (lhs == NULL) return rhs == NULL; + if (lhs == nullptr) return rhs == nullptr; - if (rhs == NULL) return false; + if (rhs == nullptr) return false; #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS return _wcsicmp(lhs, rhs) == 0; @@ -3018,17 +3600,17 @@ bool String::CaseInsensitiveWideCStringEquals(const wchar_t* lhs, // Other unknown OSes may not define it either. wint_t left, right; do { - left = towlower(*lhs++); - right = towlower(*rhs++); + left = towlower(static_cast<wint_t>(*lhs++)); + right = towlower(static_cast<wint_t>(*rhs++)); } while (left && left == right); return left == right; #endif // OS selector } -// Returns true iff str ends with the given suffix, ignoring case. +// Returns true if and only if str ends with the given suffix, ignoring case. // Any string is considered to end with an empty suffix. -bool String::EndsWithCaseInsensitive(const std::string& str, - const std::string& suffix) { +bool String::EndsWithCaseInsensitive( + const std::string& str, const std::string& suffix) { const size_t str_len = str.length(); const size_t suffix_len = suffix.length(); return (str_len >= suffix_len) && @@ -3038,18 +3620,28 @@ bool String::EndsWithCaseInsensitive(const std::string& str, // Formats an int value as "%02d". std::string String::FormatIntWidth2(int value) { + return FormatIntWidthN(value, 2); +} + +// Formats an int value to given width with leading zeros. +std::string String::FormatIntWidthN(int value, int width) { std::stringstream ss; - ss << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(2) << value; + ss << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(width) << value; return ss.str(); } // Formats an int value as "%X". -std::string String::FormatHexInt(int value) { +std::string String::FormatHexUInt32(uint32_t value) { std::stringstream ss; ss << std::hex << std::uppercase << value; return ss.str(); } +// Formats an int value as "%X". +std::string String::FormatHexInt(int value) { + return FormatHexUInt32(static_cast<uint32_t>(value)); +} + // Formats a byte as "%02X". std::string String::FormatByte(unsigned char value) { std::stringstream ss; @@ -3066,7 +3658,7 @@ std::string StringStreamToString(::std::stringstream* ss) { const char* const end = start + str.length(); std::string result; - result.reserve(2 * (end - start)); + result.reserve(static_cast<size_t>(2 * (end - start))); for (const char* ch = start; ch != end; ++ch) { if (*ch == '\0') { result += "\\0"; // Replaces NUL with "\\0"; @@ -3086,7 +3678,9 @@ std::string AppendUserMessage(const std::string& gtest_msg, if (user_msg_string.empty()) { return gtest_msg; } - + if (gtest_msg.empty()) { + return user_msg_string; + } return gtest_msg + "\n" + user_msg_string; } @@ -3095,29 +3689,35 @@ std::string AppendUserMessage(const std::string& gtest_msg, // class TestResult // Creates an empty TestResult. -TestResult::TestResult() : death_test_count_(0), elapsed_time_(0) {} +TestResult::TestResult() + : death_test_count_(0), start_timestamp_(0), elapsed_time_(0) {} // D'tor. -TestResult::~TestResult() {} +TestResult::~TestResult() { +} // Returns the i-th test part result among all the results. i can // range from 0 to total_part_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, // aborts the program. const TestPartResult& TestResult::GetTestPartResult(int i) const { - if (i < 0 || i >= total_part_count()) internal::posix::Abort(); - return test_part_results_.at(i); + if (i < 0 || i >= total_part_count()) + internal::posix::Abort(); + return test_part_results_.at(static_cast<size_t>(i)); } // Returns the i-th test property. i can range from 0 to // test_property_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, aborts the // program. const TestProperty& TestResult::GetTestProperty(int i) const { - if (i < 0 || i >= test_property_count()) internal::posix::Abort(); - return test_properties_.at(i); + if (i < 0 || i >= test_property_count()) + internal::posix::Abort(); + return test_properties_.at(static_cast<size_t>(i)); } // Clears the test part results. -void TestResult::ClearTestPartResults() { test_part_results_.clear(); } +void TestResult::ClearTestPartResults() { + test_part_results_.clear(); +} // Adds a test part result to the list. void TestResult::AddTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& test_part_result) { @@ -3132,7 +3732,7 @@ void TestResult::RecordProperty(const std::string& xml_element, if (!ValidateTestProperty(xml_element, test_property)) { return; } - internal::MutexLock lock(&test_properites_mutex_); + internal::MutexLock lock(&test_properties_mutex_); const std::vector<TestProperty>::iterator property_with_matching_key = std::find_if(test_properties_.begin(), test_properties_.end(), internal::TestPropertyKeyIs(test_property.key())); @@ -3146,19 +3746,34 @@ void TestResult::RecordProperty(const std::string& xml_element, // The list of reserved attributes used in the <testsuites> element of XML // output. static const char* const kReservedTestSuitesAttributes[] = { - "disabled", "errors", "failures", "name", - "random_seed", "tests", "time", "timestamp"}; + "disabled", + "errors", + "failures", + "name", + "random_seed", + "tests", + "time", + "timestamp" +}; // The list of reserved attributes used in the <testsuite> element of XML // output. static const char* const kReservedTestSuiteAttributes[] = { - "disabled", "errors", "failures", "name", "tests", "time"}; + "disabled", "errors", "failures", "name", + "tests", "time", "timestamp", "skipped"}; // The list of reserved attributes used in the <testcase> element of XML output. static const char* const kReservedTestCaseAttributes[] = { - "classname", "name", "status", "time", "type_param", "value_param"}; + "classname", "name", "status", "time", "type_param", + "value_param", "file", "line"}; -template <int kSize> +// Use a slightly different set for allowed output to ensure existing tests can +// still RecordProperty("result") or "RecordProperty(timestamp") +static const char* const kReservedOutputTestCaseAttributes[] = { + "classname", "name", "status", "time", "type_param", + "value_param", "file", "line", "result", "timestamp"}; + +template <size_t kSize> std::vector<std::string> ArrayAsVector(const char* const (&array)[kSize]) { return std::vector<std::string>(array, array + kSize); } @@ -3178,6 +3793,22 @@ static std::vector<std::string> GetReservedAttributesForElement( return std::vector<std::string>(); } +// TODO(jdesprez): Merge the two getReserved attributes once skip is improved +static std::vector<std::string> GetReservedOutputAttributesForElement( + const std::string& xml_element) { + if (xml_element == "testsuites") { + return ArrayAsVector(kReservedTestSuitesAttributes); + } else if (xml_element == "testsuite") { + return ArrayAsVector(kReservedTestSuiteAttributes); + } else if (xml_element == "testcase") { + return ArrayAsVector(kReservedOutputTestCaseAttributes); + } else { + GTEST_CHECK_(false) << "Unrecognized xml_element provided: " << xml_element; + } + // This code is unreachable but some compilers may not realizes that. + return std::vector<std::string>(); +} + static std::string FormatWordList(const std::vector<std::string>& words) { Message word_list; for (size_t i = 0; i < words.size(); ++i) { @@ -3192,10 +3823,11 @@ static std::string FormatWordList(const std::vector<std::string>& words) { return word_list.GetString(); } -bool ValidateTestPropertyName(const std::string& property_name, - const std::vector<std::string>& reserved_names) { +static bool ValidateTestPropertyName( + const std::string& property_name, + const std::vector<std::string>& reserved_names) { if (std::find(reserved_names.begin(), reserved_names.end(), property_name) != - reserved_names.end()) { + reserved_names.end()) { ADD_FAILURE() << "Reserved key used in RecordProperty(): " << property_name << " (" << FormatWordList(reserved_names) << " are reserved by " << GTEST_NAME_ << ")"; @@ -3220,30 +3852,41 @@ void TestResult::Clear() { elapsed_time_ = 0; } -// Returns true iff the test failed. +// Returns true off the test part was skipped. +static bool TestPartSkipped(const TestPartResult& result) { + return result.skipped(); +} + +// Returns true if and only if the test was skipped. +bool TestResult::Skipped() const { + return !Failed() && CountIf(test_part_results_, TestPartSkipped) > 0; +} + +// Returns true if and only if the test failed. bool TestResult::Failed() const { for (int i = 0; i < total_part_count(); ++i) { - if (GetTestPartResult(i).failed()) return true; + if (GetTestPartResult(i).failed()) + return true; } return false; } -// Returns true iff the test part fatally failed. +// Returns true if and only if the test part fatally failed. static bool TestPartFatallyFailed(const TestPartResult& result) { return result.fatally_failed(); } -// Returns true iff the test fatally failed. +// Returns true if and only if the test fatally failed. bool TestResult::HasFatalFailure() const { return CountIf(test_part_results_, TestPartFatallyFailed) > 0; } -// Returns true iff the test part non-fatally failed. +// Returns true if and only if the test part non-fatally failed. static bool TestPartNonfatallyFailed(const TestPartResult& result) { return result.nonfatally_failed(); } -// Returns true iff the test has a non-fatal failure. +// Returns true if and only if the test has a non-fatal failure. bool TestResult::HasNonfatalFailure() const { return CountIf(test_part_results_, TestPartNonfatallyFailed) > 0; } @@ -3263,21 +3906,28 @@ int TestResult::test_property_count() const { // Creates a Test object. -// The c'tor saves the values of all Google Test flags. -Test::Test() : gtest_flag_saver_(new internal::GTestFlagSaver) {} +// The c'tor saves the states of all flags. +Test::Test() + : gtest_flag_saver_(new GTEST_FLAG_SAVER_) { +} -// The d'tor restores the values of all Google Test flags. -Test::~Test() { delete gtest_flag_saver_; } +// The d'tor restores the states of all flags. The actual work is +// done by the d'tor of the gtest_flag_saver_ field, and thus not +// visible here. +Test::~Test() { +} // Sets up the test fixture. // // A sub-class may override this. -void Test::SetUp() {} +void Test::SetUp() { +} // Tears down the test fixture. // // A sub-class may override this. -void Test::TearDown() {} +void Test::TearDown() { +} // Allows user supplied key value pairs to be recorded for later output. void Test::RecordProperty(const std::string& key, const std::string& value) { @@ -3299,25 +3949,25 @@ void ReportFailureInUnknownLocation(TestPartResult::Type result_type, // AddTestPartResult. UnitTest::GetInstance()->AddTestPartResult( result_type, - NULL, // No info about the source file where the exception occurred. - -1, // We have no info on which line caused the exception. + nullptr, // No info about the source file where the exception occurred. + -1, // We have no info on which line caused the exception. message, ""); // No stack trace, either. } } // namespace internal -// Google Test requires all tests in the same test case to use the same test +// Google Test requires all tests in the same test suite to use the same test // fixture class. This function checks if the current test has the -// same fixture class as the first test in the current test case. If +// same fixture class as the first test in the current test suite. If // yes, it returns true; otherwise it generates a Google Test failure and // returns false. bool Test::HasSameFixtureClass() { internal::UnitTestImpl* const impl = internal::GetUnitTestImpl(); - const TestCase* const test_case = impl->current_test_case(); + const TestSuite* const test_suite = impl->current_test_suite(); - // Info about the first test in the current test case. - const TestInfo* const first_test_info = test_case->test_info_list()[0]; + // Info about the first test in the current test suite. + const TestInfo* const first_test_info = test_suite->test_info_list()[0]; const internal::TypeId first_fixture_id = first_test_info->fixture_class_id_; const char* const first_test_name = first_test_info->name(); @@ -3333,8 +3983,8 @@ bool Test::HasSameFixtureClass() { const bool this_is_TEST = this_fixture_id == internal::GetTestTypeId(); if (first_is_TEST || this_is_TEST) { - // The user mixed TEST and TEST_F in this test case - we'll tell - // him/her how to fix it. + // Both TEST and TEST_F appear in same test suite, which is incorrect. + // Tell the user how to fix this. // Gets the name of the TEST and the name of the TEST_F. Note // that first_is_TEST and this_is_TEST cannot both be true, as @@ -3345,27 +3995,27 @@ bool Test::HasSameFixtureClass() { first_is_TEST ? this_test_name : first_test_name; ADD_FAILURE() - << "All tests in the same test case must use the same test fixture\n" - << "class, so mixing TEST_F and TEST in the same test case is\n" - << "illegal. In test case " << this_test_info->test_case_name() + << "All tests in the same test suite must use the same test fixture\n" + << "class, so mixing TEST_F and TEST in the same test suite is\n" + << "illegal. In test suite " << this_test_info->test_suite_name() << ",\n" << "test " << TEST_F_name << " is defined using TEST_F but\n" << "test " << TEST_name << " is defined using TEST. You probably\n" << "want to change the TEST to TEST_F or move it to another test\n" << "case."; } else { - // The user defined two fixture classes with the same name in - // two namespaces - we'll tell him/her how to fix it. + // Two fixture classes with the same name appear in two different + // namespaces, which is not allowed. Tell the user how to fix this. ADD_FAILURE() - << "All tests in the same test case must use the same test fixture\n" - << "class. However, in test case " - << this_test_info->test_case_name() << ",\n" + << "All tests in the same test suite must use the same test fixture\n" + << "class. However, in test suite " + << this_test_info->test_suite_name() << ",\n" << "you defined test " << first_test_name << " and test " << this_test_name << "\n" << "using two different test fixture classes. This can happen if\n" << "the two classes are from different namespaces or translation\n" << "units and have the same name. You should probably rename one\n" - << "of the classes to put the tests into different test cases."; + << "of the classes to put the tests into different test suites."; } return false; } @@ -3382,8 +4032,8 @@ bool Test::HasSameFixtureClass() { static std::string* FormatSehExceptionMessage(DWORD exception_code, const char* location) { Message message; - message << "SEH exception with code 0x" << std::setbase(16) << exception_code - << std::setbase(10) << " thrown in " << location << "."; + message << "SEH exception with code 0x" << std::setbase(16) << + exception_code << std::setbase(10) << " thrown in " << location << "."; return new std::string(message.GetString()); } @@ -3398,7 +4048,7 @@ namespace internal { static std::string FormatCxxExceptionMessage(const char* description, const char* location) { Message message; - if (description != NULL) { + if (description != nullptr) { message << "C++ exception with description \"" << description << "\""; } else { message << "Unknown C++ exception"; @@ -3426,8 +4076,8 @@ GoogleTestFailureException::GoogleTestFailureException( // exceptions in the same function. Therefore, we provide a separate // wrapper function for handling SEH exceptions.) template <class T, typename Result> -Result HandleSehExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(T* object, Result (T::*method)(), - const char* location) { +Result HandleSehExceptionsInMethodIfSupported( + T* object, Result (T::*method)(), const char* location) { #if GTEST_HAS_SEH __try { return (object->*method)(); @@ -3436,8 +4086,8 @@ Result HandleSehExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(T* object, Result (T::*method)(), // We create the exception message on the heap because VC++ prohibits // creation of objects with destructors on stack in functions using __try // (see error C2712). - std::string* exception_message = - FormatSehExceptionMessage(GetExceptionCode(), location); + std::string* exception_message = FormatSehExceptionMessage( + GetExceptionCode(), location); internal::ReportFailureInUnknownLocation(TestPartResult::kFatalFailure, *exception_message); delete exception_message; @@ -3453,8 +4103,8 @@ Result HandleSehExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(T* object, Result (T::*method)(), // exceptions, if they are supported; returns the 0-value for type // Result in case of an SEH exception. template <class T, typename Result> -Result HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(T* object, Result (T::*method)(), - const char* location) { +Result HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported( + T* object, Result (T::*method)(), const char* location) { // NOTE: The user code can affect the way in which Google Test handles // exceptions by setting GTEST_FLAG(catch_exceptions), but only before // RUN_ALL_TESTS() starts. It is technically possible to check the flag @@ -3482,6 +4132,8 @@ Result HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(T* object, Result (T::*method)(), #if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS try { return HandleSehExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(object, method, location); + } catch (const AssertionException&) { // NOLINT + // This failure was reported already. } catch (const internal::GoogleTestFailureException&) { // NOLINT // This exception type can only be thrown by a failed Google // Test assertion with the intention of letting another testing @@ -3494,7 +4146,7 @@ Result HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(T* object, Result (T::*method)(), } catch (...) { // NOLINT internal::ReportFailureInUnknownLocation( TestPartResult::kFatalFailure, - FormatCxxExceptionMessage(NULL, location)); + FormatCxxExceptionMessage(nullptr, location)); } return static_cast<Result>(0); #else @@ -3514,49 +4166,58 @@ void Test::Run() { internal::UnitTestImpl* const impl = internal::GetUnitTestImpl(); impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest(); internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(this, &Test::SetUp, "SetUp()"); - // We will run the test only if SetUp() was successful. - if (!HasFatalFailure()) { + // We will run the test only if SetUp() was successful and didn't call + // GTEST_SKIP(). + if (!HasFatalFailure() && !IsSkipped()) { impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest(); - internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(this, &Test::TestBody, - "the test body"); + internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported( + this, &Test::TestBody, "the test body"); } // However, we want to clean up as much as possible. Hence we will // always call TearDown(), even if SetUp() or the test body has // failed. impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest(); - internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(this, &Test::TearDown, - "TearDown()"); + internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported( + this, &Test::TearDown, "TearDown()"); } -// Returns true iff the current test has a fatal failure. +// Returns true if and only if the current test has a fatal failure. bool Test::HasFatalFailure() { return internal::GetUnitTestImpl()->current_test_result()->HasFatalFailure(); } -// Returns true iff the current test has a non-fatal failure. +// Returns true if and only if the current test has a non-fatal failure. bool Test::HasNonfatalFailure() { - return internal::GetUnitTestImpl() - ->current_test_result() - ->HasNonfatalFailure(); + return internal::GetUnitTestImpl()->current_test_result()-> + HasNonfatalFailure(); +} + +// Returns true if and only if the current test was skipped. +bool Test::IsSkipped() { + return internal::GetUnitTestImpl()->current_test_result()->Skipped(); } // class TestInfo // Constructs a TestInfo object. It assumes ownership of the test factory // object. -TestInfo::TestInfo(const std::string& a_test_case_name, +TestInfo::TestInfo(const std::string& a_test_suite_name, const std::string& a_name, const char* a_type_param, - const char* a_value_param, internal::TypeId fixture_class_id, + const char* a_value_param, + internal::CodeLocation a_code_location, + internal::TypeId fixture_class_id, internal::TestFactoryBase* factory) - : test_case_name_(a_test_case_name), + : test_suite_name_(a_test_suite_name), name_(a_name), - type_param_(a_type_param ? new std::string(a_type_param) : NULL), - value_param_(a_value_param ? new std::string(a_value_param) : NULL), + type_param_(a_type_param ? new std::string(a_type_param) : nullptr), + value_param_(a_value_param ? new std::string(a_value_param) : nullptr), + location_(a_code_location), fixture_class_id_(fixture_class_id), should_run_(false), is_disabled_(false), matches_filter_(false), + is_in_another_shard_(false), factory_(factory), result_() {} @@ -3570,50 +4231,48 @@ namespace internal { // // Arguments: // -// test_case_name: name of the test case +// test_suite_name: name of the test suite // name: name of the test // type_param: the name of the test's type parameter, or NULL if // this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test. // value_param: text representation of the test's value parameter, // or NULL if this is not a value-parameterized test. +// code_location: code location where the test is defined // fixture_class_id: ID of the test fixture class -// set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test case -// tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test case +// set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test suite +// tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test suite // factory: pointer to the factory that creates a test object. // The newly created TestInfo instance will assume // ownership of the factory object. -TestInfo* MakeAndRegisterTestInfo(const char* test_case_name, const char* name, - const char* type_param, - const char* value_param, - TypeId fixture_class_id, - SetUpTestCaseFunc set_up_tc, - TearDownTestCaseFunc tear_down_tc, - TestFactoryBase* factory) { - TestInfo* const test_info = new TestInfo( - test_case_name, name, type_param, value_param, fixture_class_id, factory); +TestInfo* MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( + const char* test_suite_name, const char* name, const char* type_param, + const char* value_param, CodeLocation code_location, + TypeId fixture_class_id, SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc, + TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc, TestFactoryBase* factory) { + TestInfo* const test_info = + new TestInfo(test_suite_name, name, type_param, value_param, + code_location, fixture_class_id, factory); GetUnitTestImpl()->AddTestInfo(set_up_tc, tear_down_tc, test_info); return test_info; } -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST -void ReportInvalidTestCaseType(const char* test_case_name, const char* file, - int line) { +void ReportInvalidTestSuiteType(const char* test_suite_name, + CodeLocation code_location) { Message errors; errors - << "Attempted redefinition of test case " << test_case_name << ".\n" - << "All tests in the same test case must use the same test fixture\n" - << "class. However, in test case " << test_case_name << ", you tried\n" + << "Attempted redefinition of test suite " << test_suite_name << ".\n" + << "All tests in the same test suite must use the same test fixture\n" + << "class. However, in test suite " << test_suite_name << ", you tried\n" << "to define a test using a fixture class different from the one\n" << "used earlier. This can happen if the two fixture classes are\n" << "from different namespaces and have the same name. You should\n" << "probably rename one of the classes to put the tests into different\n" - << "test cases."; + << "test suites."; - fprintf(stderr, "%s %s", FormatFileLocation(file, line).c_str(), - errors.GetString().c_str()); + GTEST_LOG_(ERROR) << FormatFileLocation(code_location.file.c_str(), + code_location.line) + << " " << errors.GetString(); } -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - } // namespace internal namespace { @@ -3621,7 +4280,7 @@ namespace { // A predicate that checks the test name of a TestInfo against a known // value. // -// This is used for implementation of the TestCase class only. We put +// This is used for implementation of the TestSuite class only. We put // it in the anonymous namespace to prevent polluting the outer // namespace. // @@ -3631,10 +4290,11 @@ class TestNameIs { // Constructor. // // TestNameIs has NO default constructor. - explicit TestNameIs(const char* name) : name_(name) {} + explicit TestNameIs(const char* name) + : name_(name) {} - // Returns true iff the test name of test_info matches name_. - bool operator()(const TestInfo* test_info) const { + // Returns true if and only if the test name of test_info matches name_. + bool operator()(const TestInfo * test_info) const { return test_info && test_info->name() == name_; } @@ -3647,15 +4307,14 @@ class TestNameIs { namespace internal { // This method expands all parameterized tests registered with macros TEST_P -// and INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P into regular tests and registers those. +// and INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P into regular tests and registers those. // This will be done just once during the program runtime. void UnitTestImpl::RegisterParameterizedTests() { -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST if (!parameterized_tests_registered_) { parameterized_test_registry_.RegisterTests(); + type_parameterized_test_registry_.CheckForInstantiations(); parameterized_tests_registered_ = true; } -#endif } } // namespace internal @@ -3674,7 +4333,8 @@ void TestInfo::Run() { // Notifies the unit test event listeners that a test is about to start. repeater->OnTestStart(*this); - const TimeInMillis start = internal::GetTimeInMillis(); + result_.set_start_timestamp(internal::GetTimeInMillis()); + internal::Timer timer; impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest(); @@ -3683,153 +4343,233 @@ void TestInfo::Run() { factory_, &internal::TestFactoryBase::CreateTest, "the test fixture's constructor"); - // Runs the test only if the test object was created and its - // constructor didn't generate a fatal failure. - if ((test != NULL) && !Test::HasFatalFailure()) { + // Runs the test if the constructor didn't generate a fatal failure or invoke + // GTEST_SKIP(). + // Note that the object will not be null + if (!Test::HasFatalFailure() && !Test::IsSkipped()) { // This doesn't throw as all user code that can throw are wrapped into // exception handling code. test->Run(); } - // Deletes the test object. - impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest(); - internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported( - test, &Test::DeleteSelf_, "the test fixture's destructor"); + if (test != nullptr) { + // Deletes the test object. + impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest(); + internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported( + test, &Test::DeleteSelf_, "the test fixture's destructor"); + } - result_.set_elapsed_time(internal::GetTimeInMillis() - start); + result_.set_elapsed_time(timer.Elapsed()); // Notifies the unit test event listener that a test has just finished. repeater->OnTestEnd(*this); // Tells UnitTest to stop associating assertion results to this // test. - impl->set_current_test_info(NULL); + impl->set_current_test_info(nullptr); } -// class TestCase +// Skip and records a skipped test result for this object. +void TestInfo::Skip() { + if (!should_run_) return; + + internal::UnitTestImpl* const impl = internal::GetUnitTestImpl(); + impl->set_current_test_info(this); -// Gets the number of successful tests in this test case. -int TestCase::successful_test_count() const { + TestEventListener* repeater = UnitTest::GetInstance()->listeners().repeater(); + + // Notifies the unit test event listeners that a test is about to start. + repeater->OnTestStart(*this); + + const TestPartResult test_part_result = + TestPartResult(TestPartResult::kSkip, this->file(), this->line(), ""); + impl->GetTestPartResultReporterForCurrentThread()->ReportTestPartResult( + test_part_result); + + // Notifies the unit test event listener that a test has just finished. + repeater->OnTestEnd(*this); + impl->set_current_test_info(nullptr); +} + +// class TestSuite + +// Gets the number of successful tests in this test suite. +int TestSuite::successful_test_count() const { return CountIf(test_info_list_, TestPassed); } -// Gets the number of failed tests in this test case. -int TestCase::failed_test_count() const { +// Gets the number of successful tests in this test suite. +int TestSuite::skipped_test_count() const { + return CountIf(test_info_list_, TestSkipped); +} + +// Gets the number of failed tests in this test suite. +int TestSuite::failed_test_count() const { return CountIf(test_info_list_, TestFailed); } // Gets the number of disabled tests that will be reported in the XML report. -int TestCase::reportable_disabled_test_count() const { +int TestSuite::reportable_disabled_test_count() const { return CountIf(test_info_list_, TestReportableDisabled); } -// Gets the number of disabled tests in this test case. -int TestCase::disabled_test_count() const { +// Gets the number of disabled tests in this test suite. +int TestSuite::disabled_test_count() const { return CountIf(test_info_list_, TestDisabled); } // Gets the number of tests to be printed in the XML report. -int TestCase::reportable_test_count() const { +int TestSuite::reportable_test_count() const { return CountIf(test_info_list_, TestReportable); } -// Get the number of tests in this test case that should run. -int TestCase::test_to_run_count() const { +// Get the number of tests in this test suite that should run. +int TestSuite::test_to_run_count() const { return CountIf(test_info_list_, ShouldRunTest); } // Gets the number of all tests. -int TestCase::total_test_count() const { +int TestSuite::total_test_count() const { return static_cast<int>(test_info_list_.size()); } -// Creates a TestCase with the given name. +// Creates a TestSuite with the given name. // // Arguments: // -// name: name of the test case -// a_type_param: the name of the test case's type parameter, or NULL if -// this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test case. -// set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test case -// tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test case -TestCase::TestCase(const char* a_name, const char* a_type_param, - Test::SetUpTestCaseFunc set_up_tc, - Test::TearDownTestCaseFunc tear_down_tc) +// a_name: name of the test suite +// a_type_param: the name of the test suite's type parameter, or NULL if +// this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test suite. +// set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test suite +// tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test suite +TestSuite::TestSuite(const char* a_name, const char* a_type_param, + internal::SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc, + internal::TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc) : name_(a_name), - type_param_(a_type_param ? new std::string(a_type_param) : NULL), + type_param_(a_type_param ? new std::string(a_type_param) : nullptr), set_up_tc_(set_up_tc), tear_down_tc_(tear_down_tc), should_run_(false), + start_timestamp_(0), elapsed_time_(0) {} -// Destructor of TestCase. -TestCase::~TestCase() { +// Destructor of TestSuite. +TestSuite::~TestSuite() { // Deletes every Test in the collection. ForEach(test_info_list_, internal::Delete<TestInfo>); } // Returns the i-th test among all the tests. i can range from 0 to // total_test_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. -const TestInfo* TestCase::GetTestInfo(int i) const { +const TestInfo* TestSuite::GetTestInfo(int i) const { const int index = GetElementOr(test_indices_, i, -1); - return index < 0 ? NULL : test_info_list_[index]; + return index < 0 ? nullptr : test_info_list_[static_cast<size_t>(index)]; } // Returns the i-th test among all the tests. i can range from 0 to // total_test_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. -TestInfo* TestCase::GetMutableTestInfo(int i) { +TestInfo* TestSuite::GetMutableTestInfo(int i) { const int index = GetElementOr(test_indices_, i, -1); - return index < 0 ? NULL : test_info_list_[index]; + return index < 0 ? nullptr : test_info_list_[static_cast<size_t>(index)]; } -// Adds a test to this test case. Will delete the test upon -// destruction of the TestCase object. -void TestCase::AddTestInfo(TestInfo* test_info) { +// Adds a test to this test suite. Will delete the test upon +// destruction of the TestSuite object. +void TestSuite::AddTestInfo(TestInfo* test_info) { test_info_list_.push_back(test_info); test_indices_.push_back(static_cast<int>(test_indices_.size())); } -// Runs every test in this TestCase. -void TestCase::Run() { +// Runs every test in this TestSuite. +void TestSuite::Run() { if (!should_run_) return; internal::UnitTestImpl* const impl = internal::GetUnitTestImpl(); - impl->set_current_test_case(this); + impl->set_current_test_suite(this); TestEventListener* repeater = UnitTest::GetInstance()->listeners().repeater(); + // Call both legacy and the new API + repeater->OnTestSuiteStart(*this); +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ repeater->OnTestCaseStart(*this); +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest(); internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported( - this, &TestCase::RunSetUpTestCase, "SetUpTestCase()"); + this, &TestSuite::RunSetUpTestSuite, "SetUpTestSuite()"); - const internal::TimeInMillis start = internal::GetTimeInMillis(); + start_timestamp_ = internal::GetTimeInMillis(); + internal::Timer timer; for (int i = 0; i < total_test_count(); i++) { GetMutableTestInfo(i)->Run(); + if (GTEST_FLAG(fail_fast) && GetMutableTestInfo(i)->result()->Failed()) { + for (int j = i + 1; j < total_test_count(); j++) { + GetMutableTestInfo(j)->Skip(); + } + break; + } } - elapsed_time_ = internal::GetTimeInMillis() - start; + elapsed_time_ = timer.Elapsed(); impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest(); internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported( - this, &TestCase::RunTearDownTestCase, "TearDownTestCase()"); + this, &TestSuite::RunTearDownTestSuite, "TearDownTestSuite()"); + // Call both legacy and the new API + repeater->OnTestSuiteEnd(*this); +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ repeater->OnTestCaseEnd(*this); - impl->set_current_test_case(NULL); +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + impl->set_current_test_suite(nullptr); } -// Clears the results of all tests in this test case. -void TestCase::ClearResult() { +// Skips all tests under this TestSuite. +void TestSuite::Skip() { + if (!should_run_) return; + + internal::UnitTestImpl* const impl = internal::GetUnitTestImpl(); + impl->set_current_test_suite(this); + + TestEventListener* repeater = UnitTest::GetInstance()->listeners().repeater(); + + // Call both legacy and the new API + repeater->OnTestSuiteStart(*this); +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + repeater->OnTestCaseStart(*this); +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + for (int i = 0; i < total_test_count(); i++) { + GetMutableTestInfo(i)->Skip(); + } + + // Call both legacy and the new API + repeater->OnTestSuiteEnd(*this); + // Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + repeater->OnTestCaseEnd(*this); +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + impl->set_current_test_suite(nullptr); +} + +// Clears the results of all tests in this test suite. +void TestSuite::ClearResult() { ad_hoc_test_result_.Clear(); ForEach(test_info_list_, TestInfo::ClearTestResult); } -// Shuffles the tests in this test case. -void TestCase::ShuffleTests(internal::Random* random) { +// Shuffles the tests in this test suite. +void TestSuite::ShuffleTests(internal::Random* random) { Shuffle(random, &test_indices_); } // Restores the test order to before the first shuffle. -void TestCase::UnshuffleTests() { +void TestSuite::UnshuffleTests() { for (size_t i = 0; i < test_indices_.size(); i++) { test_indices_[i] = static_cast<int>(i); } @@ -3840,10 +4580,11 @@ void TestCase::UnshuffleTests() { // // FormatCountableNoun(1, "formula", "formuli") returns "1 formula". // FormatCountableNoun(5, "book", "books") returns "5 books". -static std::string FormatCountableNoun(int count, const char* singular_form, - const char* plural_form) { +static std::string FormatCountableNoun(int count, + const char * singular_form, + const char * plural_form) { return internal::StreamableToString(count) + " " + - (count == 1 ? singular_form : plural_form); + (count == 1 ? singular_form : plural_form); } // Formats the count of tests. @@ -3851,49 +4592,53 @@ static std::string FormatTestCount(int test_count) { return FormatCountableNoun(test_count, "test", "tests"); } -// Formats the count of test cases. -static std::string FormatTestCaseCount(int test_case_count) { - return FormatCountableNoun(test_case_count, "test case", "test cases"); +// Formats the count of test suites. +static std::string FormatTestSuiteCount(int test_suite_count) { + return FormatCountableNoun(test_suite_count, "test suite", "test suites"); } // Converts a TestPartResult::Type enum to human-friendly string // representation. Both kNonFatalFailure and kFatalFailure are translated // to "Failure", as the user usually doesn't care about the difference // between the two when viewing the test result. -static const char* TestPartResultTypeToString(TestPartResult::Type type) { +static const char * TestPartResultTypeToString(TestPartResult::Type type) { switch (type) { - case TestPartResult::kSuccess: - return "Success"; + case TestPartResult::kSkip: + return "Skipped\n"; + case TestPartResult::kSuccess: + return "Success"; - case TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure: - case TestPartResult::kFatalFailure: + case TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure: + case TestPartResult::kFatalFailure: #ifdef _MSC_VER - return "error: "; + return "error: "; #else - return "Failure\n"; + return "Failure\n"; #endif - default: - return "Unknown result type"; + default: + return "Unknown result type"; } } namespace internal { +namespace { +enum class GTestColor { kDefault, kRed, kGreen, kYellow }; +} // namespace // Prints a TestPartResult to an std::string. static std::string PrintTestPartResultToString( const TestPartResult& test_part_result) { - return (Message() << internal::FormatFileLocation( - test_part_result.file_name(), - test_part_result.line_number()) - << " " - << TestPartResultTypeToString(test_part_result.type()) - << test_part_result.message()) - .GetString(); + return (Message() + << internal::FormatFileLocation(test_part_result.file_name(), + test_part_result.line_number()) + << " " << TestPartResultTypeToString(test_part_result.type()) + << test_part_result.message()).GetString(); } // Prints a TestPartResult. static void PrintTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& test_part_result) { - const std::string& result = PrintTestPartResultToString(test_part_result); + const std::string& result = + PrintTestPartResultToString(test_part_result); printf("%s\n", result.c_str()); fflush(stdout); // If the test program runs in Visual Studio or a debugger, the @@ -3910,50 +4655,78 @@ static void PrintTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& test_part_result) { } // class PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter - -enum GTestColor { COLOR_DEFAULT, COLOR_RED, COLOR_GREEN, COLOR_YELLOW }; - -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE && \ + !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW // Returns the character attribute for the given color. -WORD GetColorAttribute(GTestColor color) { +static WORD GetColorAttribute(GTestColor color) { switch (color) { - case COLOR_RED: - return FOREGROUND_RED; - case COLOR_GREEN: - return FOREGROUND_GREEN; - case COLOR_YELLOW: - return FOREGROUND_RED | FOREGROUND_GREEN; - default: - return 0; + case GTestColor::kRed: + return FOREGROUND_RED; + case GTestColor::kGreen: + return FOREGROUND_GREEN; + case GTestColor::kYellow: + return FOREGROUND_RED | FOREGROUND_GREEN; + default: return 0; + } +} + +static int GetBitOffset(WORD color_mask) { + if (color_mask == 0) return 0; + + int bitOffset = 0; + while ((color_mask & 1) == 0) { + color_mask >>= 1; + ++bitOffset; + } + return bitOffset; +} + +static WORD GetNewColor(GTestColor color, WORD old_color_attrs) { + // Let's reuse the BG + static const WORD background_mask = BACKGROUND_BLUE | BACKGROUND_GREEN | + BACKGROUND_RED | BACKGROUND_INTENSITY; + static const WORD foreground_mask = FOREGROUND_BLUE | FOREGROUND_GREEN | + FOREGROUND_RED | FOREGROUND_INTENSITY; + const WORD existing_bg = old_color_attrs & background_mask; + + WORD new_color = + GetColorAttribute(color) | existing_bg | FOREGROUND_INTENSITY; + static const int bg_bitOffset = GetBitOffset(background_mask); + static const int fg_bitOffset = GetBitOffset(foreground_mask); + + if (((new_color & background_mask) >> bg_bitOffset) == + ((new_color & foreground_mask) >> fg_bitOffset)) { + new_color ^= FOREGROUND_INTENSITY; // invert intensity } + return new_color; } #else -// Returns the ANSI color code for the given color. COLOR_DEFAULT is +// Returns the ANSI color code for the given color. GTestColor::kDefault is // an invalid input. -const char* GetAnsiColorCode(GTestColor color) { +static const char* GetAnsiColorCode(GTestColor color) { switch (color) { - case COLOR_RED: - return "1"; - case COLOR_GREEN: - return "2"; - case COLOR_YELLOW: - return "3"; - default: - return NULL; - }; + case GTestColor::kRed: + return "1"; + case GTestColor::kGreen: + return "2"; + case GTestColor::kYellow: + return "3"; + default: + return nullptr; + } } #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -// Returns true iff Google Test should use colors in the output. +// Returns true if and only if Google Test should use colors in the output. bool ShouldUseColor(bool stdout_is_tty) { const char* const gtest_color = GTEST_FLAG(color).c_str(); if (String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(gtest_color, "auto")) { -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW // On Windows the TERM variable is usually not set, but the // console there does support colors. return stdout_is_tty; @@ -3966,6 +4739,10 @@ bool ShouldUseColor(bool stdout_is_tty) { String::CStringEquals(term, "xterm-256color") || String::CStringEquals(term, "screen") || String::CStringEquals(term, "screen-256color") || + String::CStringEquals(term, "tmux") || + String::CStringEquals(term, "tmux-256color") || + String::CStringEquals(term, "rxvt-unicode") || + String::CStringEquals(term, "rxvt-unicode-256color") || String::CStringEquals(term, "linux") || String::CStringEquals(term, "cygwin"); return stdout_is_tty && term_supports_color; @@ -3973,9 +4750,9 @@ bool ShouldUseColor(bool stdout_is_tty) { } return String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(gtest_color, "yes") || - String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(gtest_color, "true") || - String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(gtest_color, "t") || - String::CStringEquals(gtest_color, "1"); + String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(gtest_color, "true") || + String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(gtest_color, "t") || + String::CStringEquals(gtest_color, "1"); // We take "yes", "true", "t", and "1" as meaning "yes". If the // value is neither one of these nor "auto", we treat it as "no" to // be conservative. @@ -3985,18 +4762,20 @@ bool ShouldUseColor(bool stdout_is_tty) { // cannot simply emit special characters and have the terminal change colors. // This routine must actually emit the characters rather than return a string // that would be colored when printed, as can be done on Linux. -void ColoredPrintf(GTestColor color, const char* fmt, ...) { + +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_PRINTF_(2, 3) +static void ColoredPrintf(GTestColor color, const char *fmt, ...) { va_list args; va_start(args, fmt); -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN || GTEST_OS_ZOS || GTEST_OS_IOS - const bool use_color = false; +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || GTEST_OS_ZOS || GTEST_OS_IOS || \ + GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE || GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT || defined(ESP_PLATFORM) + const bool use_color = AlwaysFalse(); #else static const bool in_color_mode = ShouldUseColor(posix::IsATTY(posix::FileNo(stdout)) != 0); - const bool use_color = in_color_mode && (color != COLOR_DEFAULT); -#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN || GTEST_OS_ZOS - // The '!= 0' comparison is necessary to satisfy MSVC 7.1. + const bool use_color = in_color_mode && (color != GTestColor::kDefault); +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || GTEST_OS_ZOS if (!use_color) { vprintf(fmt, args); @@ -4004,20 +4783,22 @@ void ColoredPrintf(GTestColor color, const char* fmt, ...) { return; } -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE && \ + !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW const HANDLE stdout_handle = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE); // Gets the current text color. CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO buffer_info; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(stdout_handle, &buffer_info); const WORD old_color_attrs = buffer_info.wAttributes; + const WORD new_color = GetNewColor(color, old_color_attrs); // We need to flush the stream buffers into the console before each // SetConsoleTextAttribute call lest it affect the text that is already // printed but has not yet reached the console. fflush(stdout); - SetConsoleTextAttribute(stdout_handle, - GetColorAttribute(color) | FOREGROUND_INTENSITY); + SetConsoleTextAttribute(stdout_handle, new_color); + vprintf(fmt, args); fflush(stdout); @@ -4031,22 +4812,22 @@ void ColoredPrintf(GTestColor color, const char* fmt, ...) { va_end(args); } -// Text printed in Google Test's text output and --gunit_list_tests +// Text printed in Google Test's text output and --gtest_list_tests // output to label the type parameter and value parameter for a test. static const char kTypeParamLabel[] = "TypeParam"; static const char kValueParamLabel[] = "GetParam()"; -void PrintFullTestCommentIfPresent(const TestInfo& test_info) { +static void PrintFullTestCommentIfPresent(const TestInfo& test_info) { const char* const type_param = test_info.type_param(); const char* const value_param = test_info.value_param(); - if (type_param != NULL || value_param != NULL) { + if (type_param != nullptr || value_param != nullptr) { printf(", where "); - if (type_param != NULL) { + if (type_param != nullptr) { printf("%s = %s", kTypeParamLabel, type_param); - if (value_param != NULL) printf(" and "); + if (value_param != nullptr) printf(" and "); } - if (value_param != NULL) { + if (value_param != nullptr) { printf("%s = %s", kValueParamLabel, value_param); } } @@ -4058,30 +4839,43 @@ void PrintFullTestCommentIfPresent(const TestInfo& test_info) { class PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter : public TestEventListener { public: PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter() {} - static void PrintTestName(const char* test_case, const char* test) { - printf("%s.%s", test_case, test); + static void PrintTestName(const char* test_suite, const char* test) { + printf("%s.%s", test_suite, test); } // The following methods override what's in the TestEventListener class. - virtual void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} - virtual void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration); - virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(const UnitTest& unit_test); - virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} - virtual void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& test_case); - virtual void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info); - virtual void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result); - virtual void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info); - virtual void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& test_case); - virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(const UnitTest& unit_test); - virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} - virtual void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration); - virtual void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} + void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration) override; + void OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) override; + void OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& test_case) override; +#else + void OnTestSuiteStart(const TestSuite& test_suite) override; +#endif // OnTestCaseStart + + void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info) override; + + void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) override; + void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info) override; +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& test_case) override; +#else + void OnTestSuiteEnd(const TestSuite& test_suite) override; +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + void OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) override; + void OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration) override; + void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} private: static void PrintFailedTests(const UnitTest& unit_test); + static void PrintFailedTestSuites(const UnitTest& unit_test); + static void PrintSkippedTests(const UnitTest& unit_test); }; -// Fired before each iteration of tests starts. + // Fired before each iteration of tests starts. void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestIterationStart( const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration) { if (GTEST_FLAG(repeat) != 1) @@ -4092,52 +4886,69 @@ void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestIterationStart( // Prints the filter if it's not *. This reminds the user that some // tests may be skipped. if (!String::CStringEquals(filter, kUniversalFilter)) { - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_YELLOW, "Note: %s filter = %s\n", GTEST_NAME_, filter); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kYellow, "Note: %s filter = %s\n", GTEST_NAME_, + filter); } if (internal::ShouldShard(kTestTotalShards, kTestShardIndex, false)) { - const Int32 shard_index = Int32FromEnvOrDie(kTestShardIndex, -1); - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_YELLOW, "Note: This is test shard %d of %s.\n", + const int32_t shard_index = Int32FromEnvOrDie(kTestShardIndex, -1); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kYellow, "Note: This is test shard %d of %s.\n", static_cast<int>(shard_index) + 1, internal::posix::GetEnv(kTestTotalShards)); } if (GTEST_FLAG(shuffle)) { - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_YELLOW, + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kYellow, "Note: Randomizing tests' orders with a seed of %d .\n", unit_test.random_seed()); } - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_GREEN, "[==========] "); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[==========] "); printf("Running %s from %s.\n", FormatTestCount(unit_test.test_to_run_count()).c_str(), - FormatTestCaseCount(unit_test.test_case_to_run_count()).c_str()); + FormatTestSuiteCount(unit_test.test_suite_to_run_count()).c_str()); fflush(stdout); } void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart( const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) { - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_GREEN, "[----------] "); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[----------] "); printf("Global test environment set-up.\n"); fflush(stdout); } +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& test_case) { const std::string counts = FormatCountableNoun(test_case.test_to_run_count(), "test", "tests"); - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_GREEN, "[----------] "); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[----------] "); printf("%s from %s", counts.c_str(), test_case.name()); - if (test_case.type_param() == NULL) { + if (test_case.type_param() == nullptr) { printf("\n"); } else { printf(", where %s = %s\n", kTypeParamLabel, test_case.type_param()); } fflush(stdout); } +#else +void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestSuiteStart( + const TestSuite& test_suite) { + const std::string counts = + FormatCountableNoun(test_suite.test_to_run_count(), "test", "tests"); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[----------] "); + printf("%s from %s", counts.c_str(), test_suite.name()); + if (test_suite.type_param() == nullptr) { + printf("\n"); + } else { + printf(", where %s = %s\n", kTypeParamLabel, test_suite.type_param()); + } + fflush(stdout); +} +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info) { - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_GREEN, "[ RUN ] "); - PrintTestName(test_info.test_case_name(), test_info.name()); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[ RUN ] "); + PrintTestName(test_info.test_suite_name(), test_info.name()); printf("\n"); fflush(stdout); } @@ -4145,47 +4956,66 @@ void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info) { // Called after an assertion failure. void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestPartResult( const TestPartResult& result) { - // If the test part succeeded, we don't need to do anything. - if (result.type() == TestPartResult::kSuccess) return; - - // Print failure message from the assertion (e.g. expected this and got that). - PrintTestPartResult(result); - fflush(stdout); + switch (result.type()) { + // If the test part succeeded, we don't need to do anything. + case TestPartResult::kSuccess: + return; + default: + // Print failure message from the assertion + // (e.g. expected this and got that). + PrintTestPartResult(result); + fflush(stdout); + } } void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info) { if (test_info.result()->Passed()) { - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_GREEN, "[ OK ] "); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[ OK ] "); + } else if (test_info.result()->Skipped()) { + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[ SKIPPED ] "); } else { - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_RED, "[ FAILED ] "); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, "[ FAILED ] "); } - PrintTestName(test_info.test_case_name(), test_info.name()); - if (test_info.result()->Failed()) PrintFullTestCommentIfPresent(test_info); + PrintTestName(test_info.test_suite_name(), test_info.name()); + if (test_info.result()->Failed()) + PrintFullTestCommentIfPresent(test_info); if (GTEST_FLAG(print_time)) { - printf(" (%s ms)\n", - internal::StreamableToString(test_info.result()->elapsed_time()) - .c_str()); + printf(" (%s ms)\n", internal::StreamableToString( + test_info.result()->elapsed_time()).c_str()); } else { printf("\n"); } fflush(stdout); } +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& test_case) { if (!GTEST_FLAG(print_time)) return; const std::string counts = FormatCountableNoun(test_case.test_to_run_count(), "test", "tests"); - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_GREEN, "[----------] "); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[----------] "); printf("%s from %s (%s ms total)\n\n", counts.c_str(), test_case.name(), internal::StreamableToString(test_case.elapsed_time()).c_str()); fflush(stdout); } +#else +void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestSuiteEnd(const TestSuite& test_suite) { + if (!GTEST_FLAG(print_time)) return; + + const std::string counts = + FormatCountableNoun(test_suite.test_to_run_count(), "test", "tests"); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[----------] "); + printf("%s from %s (%s ms total)\n\n", counts.c_str(), test_suite.name(), + internal::StreamableToString(test_suite.elapsed_time()).c_str()); + fflush(stdout); +} +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart( const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) { - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_GREEN, "[----------] "); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[----------] "); printf("Global test environment tear-down\n"); fflush(stdout); } @@ -4193,23 +5023,70 @@ void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart( // Internal helper for printing the list of failed tests. void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintFailedTests(const UnitTest& unit_test) { const int failed_test_count = unit_test.failed_test_count(); - if (failed_test_count == 0) { + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, "[ FAILED ] "); + printf("%s, listed below:\n", FormatTestCount(failed_test_count).c_str()); + + for (int i = 0; i < unit_test.total_test_suite_count(); ++i) { + const TestSuite& test_suite = *unit_test.GetTestSuite(i); + if (!test_suite.should_run() || (test_suite.failed_test_count() == 0)) { + continue; + } + for (int j = 0; j < test_suite.total_test_count(); ++j) { + const TestInfo& test_info = *test_suite.GetTestInfo(j); + if (!test_info.should_run() || !test_info.result()->Failed()) { + continue; + } + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, "[ FAILED ] "); + printf("%s.%s", test_suite.name(), test_info.name()); + PrintFullTestCommentIfPresent(test_info); + printf("\n"); + } + } + printf("\n%2d FAILED %s\n", failed_test_count, + failed_test_count == 1 ? "TEST" : "TESTS"); +} + +// Internal helper for printing the list of test suite failures not covered by +// PrintFailedTests. +void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintFailedTestSuites( + const UnitTest& unit_test) { + int suite_failure_count = 0; + for (int i = 0; i < unit_test.total_test_suite_count(); ++i) { + const TestSuite& test_suite = *unit_test.GetTestSuite(i); + if (!test_suite.should_run()) { + continue; + } + if (test_suite.ad_hoc_test_result().Failed()) { + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, "[ FAILED ] "); + printf("%s: SetUpTestSuite or TearDownTestSuite\n", test_suite.name()); + ++suite_failure_count; + } + } + if (suite_failure_count > 0) { + printf("\n%2d FAILED TEST %s\n", suite_failure_count, + suite_failure_count == 1 ? "SUITE" : "SUITES"); + } +} + +// Internal helper for printing the list of skipped tests. +void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintSkippedTests(const UnitTest& unit_test) { + const int skipped_test_count = unit_test.skipped_test_count(); + if (skipped_test_count == 0) { return; } - for (int i = 0; i < unit_test.total_test_case_count(); ++i) { - const TestCase& test_case = *unit_test.GetTestCase(i); - if (!test_case.should_run() || (test_case.failed_test_count() == 0)) { + for (int i = 0; i < unit_test.total_test_suite_count(); ++i) { + const TestSuite& test_suite = *unit_test.GetTestSuite(i); + if (!test_suite.should_run() || (test_suite.skipped_test_count() == 0)) { continue; } - for (int j = 0; j < test_case.total_test_count(); ++j) { - const TestInfo& test_info = *test_case.GetTestInfo(j); - if (!test_info.should_run() || test_info.result()->Passed()) { + for (int j = 0; j < test_suite.total_test_count(); ++j) { + const TestInfo& test_info = *test_suite.GetTestInfo(j); + if (!test_info.should_run() || !test_info.result()->Skipped()) { continue; } - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_RED, "[ FAILED ] "); - printf("%s.%s", test_case.name(), test_info.name()); - PrintFullTestCommentIfPresent(test_info); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[ SKIPPED ] "); + printf("%s.%s", test_suite.name(), test_info.name()); printf("\n"); } } @@ -4217,35 +5094,37 @@ void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintFailedTests(const UnitTest& unit_test) { void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int /*iteration*/) { - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_GREEN, "[==========] "); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[==========] "); printf("%s from %s ran.", FormatTestCount(unit_test.test_to_run_count()).c_str(), - FormatTestCaseCount(unit_test.test_case_to_run_count()).c_str()); + FormatTestSuiteCount(unit_test.test_suite_to_run_count()).c_str()); if (GTEST_FLAG(print_time)) { printf(" (%s ms total)", internal::StreamableToString(unit_test.elapsed_time()).c_str()); } printf("\n"); - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_GREEN, "[ PASSED ] "); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[ PASSED ] "); printf("%s.\n", FormatTestCount(unit_test.successful_test_count()).c_str()); - int num_failures = unit_test.failed_test_count(); + const int skipped_test_count = unit_test.skipped_test_count(); + if (skipped_test_count > 0) { + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[ SKIPPED ] "); + printf("%s, listed below:\n", FormatTestCount(skipped_test_count).c_str()); + PrintSkippedTests(unit_test); + } + if (!unit_test.Passed()) { - const int failed_test_count = unit_test.failed_test_count(); - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_RED, "[ FAILED ] "); - printf("%s, listed below:\n", FormatTestCount(failed_test_count).c_str()); PrintFailedTests(unit_test); - printf("\n%2d FAILED %s\n", num_failures, - num_failures == 1 ? "TEST" : "TESTS"); + PrintFailedTestSuites(unit_test); } int num_disabled = unit_test.reportable_disabled_test_count(); if (num_disabled && !GTEST_FLAG(also_run_disabled_tests)) { - if (!num_failures) { + if (unit_test.Passed()) { printf("\n"); // Add a spacer if no FAILURE banner is displayed. } - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_YELLOW, " YOU HAVE %d DISABLED %s\n\n", num_disabled, - num_disabled == 1 ? "TEST" : "TESTS"); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kYellow, " YOU HAVE %d DISABLED %s\n\n", + num_disabled, num_disabled == 1 ? "TEST" : "TESTS"); } // Ensure that Google Test output is printed before, e.g., heapchecker output. fflush(stdout); @@ -4253,14 +5132,118 @@ void PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, // End PrettyUnitTestResultPrinter +// This class implements the TestEventListener interface. +// +// Class BriefUnitTestResultPrinter is copyable. +class BriefUnitTestResultPrinter : public TestEventListener { + public: + BriefUnitTestResultPrinter() {} + static void PrintTestName(const char* test_suite, const char* test) { + printf("%s.%s", test_suite, test); + } + + // The following methods override what's in the TestEventListener class. + void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/, + int /*iteration*/) override {} + void OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& /*test_case*/) override {} +#else + void OnTestSuiteStart(const TestSuite& /*test_suite*/) override {} +#endif // OnTestCaseStart + + void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& /*test_info*/) override {} + + void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) override; + void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info) override; +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& /*test_case*/) override {} +#else + void OnTestSuiteEnd(const TestSuite& /*test_suite*/) override {} +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + void OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration) override; + void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} +}; + +// Called after an assertion failure. +void BriefUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestPartResult( + const TestPartResult& result) { + switch (result.type()) { + // If the test part succeeded, we don't need to do anything. + case TestPartResult::kSuccess: + return; + default: + // Print failure message from the assertion + // (e.g. expected this and got that). + PrintTestPartResult(result); + fflush(stdout); + } +} + +void BriefUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info) { + if (test_info.result()->Failed()) { + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, "[ FAILED ] "); + PrintTestName(test_info.test_suite_name(), test_info.name()); + PrintFullTestCommentIfPresent(test_info); + + if (GTEST_FLAG(print_time)) { + printf(" (%s ms)\n", + internal::StreamableToString(test_info.result()->elapsed_time()) + .c_str()); + } else { + printf("\n"); + } + fflush(stdout); + } +} + +void BriefUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, + int /*iteration*/) { + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[==========] "); + printf("%s from %s ran.", + FormatTestCount(unit_test.test_to_run_count()).c_str(), + FormatTestSuiteCount(unit_test.test_suite_to_run_count()).c_str()); + if (GTEST_FLAG(print_time)) { + printf(" (%s ms total)", + internal::StreamableToString(unit_test.elapsed_time()).c_str()); + } + printf("\n"); + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[ PASSED ] "); + printf("%s.\n", FormatTestCount(unit_test.successful_test_count()).c_str()); + + const int skipped_test_count = unit_test.skipped_test_count(); + if (skipped_test_count > 0) { + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kGreen, "[ SKIPPED ] "); + printf("%s.\n", FormatTestCount(skipped_test_count).c_str()); + } + + int num_disabled = unit_test.reportable_disabled_test_count(); + if (num_disabled && !GTEST_FLAG(also_run_disabled_tests)) { + if (unit_test.Passed()) { + printf("\n"); // Add a spacer if no FAILURE banner is displayed. + } + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kYellow, " YOU HAVE %d DISABLED %s\n\n", + num_disabled, num_disabled == 1 ? "TEST" : "TESTS"); + } + // Ensure that Google Test output is printed before, e.g., heapchecker output. + fflush(stdout); +} + +// End BriefUnitTestResultPrinter + // class TestEventRepeater // // This class forwards events to other event listeners. class TestEventRepeater : public TestEventListener { public: TestEventRepeater() : forwarding_enabled_(true) {} - virtual ~TestEventRepeater(); - void Append(TestEventListener* listener); + ~TestEventRepeater() override; + void Append(TestEventListener *listener); TestEventListener* Release(TestEventListener* listener); // Controls whether events will be forwarded to listeners_. Set to false @@ -4268,19 +5251,27 @@ class TestEventRepeater : public TestEventListener { bool forwarding_enabled() const { return forwarding_enabled_; } void set_forwarding_enabled(bool enable) { forwarding_enabled_ = enable; } - virtual void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& unit_test); - virtual void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration); - virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(const UnitTest& unit_test); - virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test); - virtual void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& test_case); - virtual void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info); - virtual void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result); - virtual void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info); - virtual void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& test_case); - virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(const UnitTest& unit_test); - virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test); - virtual void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration); - virtual void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test); + void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) override; + void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration) override; + void OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) override; + void OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) override; +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestCaseStart(const TestSuite& parameter) override; +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestSuiteStart(const TestSuite& parameter) override; + void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info) override; + void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) override; + void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info) override; +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& parameter) override; +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestSuiteEnd(const TestSuite& parameter) override; + void OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) override; + void OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) override; + void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration) override; + void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) override; private: // Controls whether events will be forwarded to listeners_. Set to false @@ -4296,53 +5287,60 @@ TestEventRepeater::~TestEventRepeater() { ForEach(listeners_, Delete<TestEventListener>); } -void TestEventRepeater::Append(TestEventListener* listener) { +void TestEventRepeater::Append(TestEventListener *listener) { listeners_.push_back(listener); } -// TODO(vladl@google.com): Factor the search functionality into Vector::Find. -TestEventListener* TestEventRepeater::Release(TestEventListener* listener) { +TestEventListener* TestEventRepeater::Release(TestEventListener *listener) { for (size_t i = 0; i < listeners_.size(); ++i) { if (listeners_[i] == listener) { - listeners_.erase(listeners_.begin() + i); + listeners_.erase(listeners_.begin() + static_cast<int>(i)); return listener; } } - return NULL; + return nullptr; } // Since most methods are very similar, use macros to reduce boilerplate. // This defines a member that forwards the call to all listeners. -#define GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(Name, Type) \ +#define GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(Name, Type) \ +void TestEventRepeater::Name(const Type& parameter) { \ + if (forwarding_enabled_) { \ + for (size_t i = 0; i < listeners_.size(); i++) { \ + listeners_[i]->Name(parameter); \ + } \ + } \ +} +// This defines a member that forwards the call to all listeners in reverse +// order. +#define GTEST_REVERSE_REPEATER_METHOD_(Name, Type) \ void TestEventRepeater::Name(const Type& parameter) { \ if (forwarding_enabled_) { \ - for (size_t i = 0; i < listeners_.size(); i++) { \ - listeners_[i]->Name(parameter); \ + for (size_t i = listeners_.size(); i != 0; i--) { \ + listeners_[i - 1]->Name(parameter); \ } \ } \ } -// This defines a member that forwards the call to all listeners in reverse -// order. -#define GTEST_REVERSE_REPEATER_METHOD_(Name, Type) \ - void TestEventRepeater::Name(const Type& parameter) { \ - if (forwarding_enabled_) { \ - for (int i = static_cast<int>(listeners_.size()) - 1; i >= 0; i--) { \ - listeners_[i]->Name(parameter); \ - } \ - } \ - } GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestProgramStart, UnitTest) GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart, UnitTest) -GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestCaseStart, TestCase) +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestCaseStart, TestSuite) +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestSuiteStart, TestSuite) GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestStart, TestInfo) GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestPartResult, TestPartResult) GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart, UnitTest) GTEST_REVERSE_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd, UnitTest) GTEST_REVERSE_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd, UnitTest) GTEST_REVERSE_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestEnd, TestInfo) -GTEST_REVERSE_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestCaseEnd, TestCase) +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +GTEST_REVERSE_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestCaseEnd, TestSuite) +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +GTEST_REVERSE_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestSuiteEnd, TestSuite) GTEST_REVERSE_REPEATER_METHOD_(OnTestProgramEnd, UnitTest) #undef GTEST_REPEATER_METHOD_ @@ -4360,8 +5358,8 @@ void TestEventRepeater::OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& unit_test, void TestEventRepeater::OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration) { if (forwarding_enabled_) { - for (int i = static_cast<int>(listeners_.size()) - 1; i >= 0; i--) { - listeners_[i]->OnTestIterationEnd(unit_test, iteration); + for (size_t i = listeners_.size(); i > 0; i--) { + listeners_[i - 1]->OnTestIterationEnd(unit_test, iteration); } } } @@ -4373,7 +5371,12 @@ class XmlUnitTestResultPrinter : public EmptyTestEventListener { public: explicit XmlUnitTestResultPrinter(const char* output_file); - virtual void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration); + void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration) override; + void ListTestsMatchingFilter(const std::vector<TestSuite*>& test_suites); + + // Prints an XML summary of all unit tests. + static void PrintXmlTestsList(std::ostream* stream, + const std::vector<TestSuite*>& test_suites); private: // Is c a whitespace character that is normalized to a space character @@ -4416,14 +5419,24 @@ class XmlUnitTestResultPrinter : public EmptyTestEventListener { // Streams an XML CDATA section, escaping invalid CDATA sequences as needed. static void OutputXmlCDataSection(::std::ostream* stream, const char* data); + // Streams a test suite XML stanza containing the given test result. + // + // Requires: result.Failed() + static void OutputXmlTestSuiteForTestResult(::std::ostream* stream, + const TestResult& result); + + // Streams an XML representation of a TestResult object. + static void OutputXmlTestResult(::std::ostream* stream, + const TestResult& result); + // Streams an XML representation of a TestInfo object. static void OutputXmlTestInfo(::std::ostream* stream, - const char* test_case_name, + const char* test_suite_name, const TestInfo& test_info); - // Prints an XML representation of a TestCase object - static void PrintXmlTestCase(::std::ostream* stream, - const TestCase& test_case); + // Prints an XML representation of a TestSuite object + static void PrintXmlTestSuite(::std::ostream* stream, + const TestSuite& test_suite); // Prints an XML summary of unit_test to output stream out. static void PrintXmlUnitTest(::std::ostream* stream, @@ -4435,6 +5448,11 @@ class XmlUnitTestResultPrinter : public EmptyTestEventListener { // to delimit this attribute from prior attributes. static std::string TestPropertiesAsXmlAttributes(const TestResult& result); + // Streams an XML representation of the test properties of a TestResult + // object. + static void OutputXmlTestProperties(std::ostream* stream, + const TestResult& result); + // The output file. const std::string output_file_; @@ -4444,44 +5462,30 @@ class XmlUnitTestResultPrinter : public EmptyTestEventListener { // Creates a new XmlUnitTestResultPrinter. XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::XmlUnitTestResultPrinter(const char* output_file) : output_file_(output_file) { - if (output_file_.c_str() == NULL || output_file_.empty()) { - fprintf(stderr, "XML output file may not be null\n"); - fflush(stderr); - exit(EXIT_FAILURE); + if (output_file_.empty()) { + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "XML output file may not be null"; } } // Called after the unit test ends. void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int /*iteration*/) { - FILE* xmlout = NULL; - FilePath output_file(output_file_); - FilePath output_dir(output_file.RemoveFileName()); - - if (output_dir.CreateDirectoriesRecursively()) { - xmlout = posix::FOpen(output_file_.c_str(), "w"); - } - if (xmlout == NULL) { - // TODO(wan): report the reason of the failure. - // - // We don't do it for now as: - // - // 1. There is no urgent need for it. - // 2. It's a bit involved to make the errno variable thread-safe on - // all three operating systems (Linux, Windows, and Mac OS). - // 3. To interpret the meaning of errno in a thread-safe way, - // we need the strerror_r() function, which is not available on - // Windows. - fprintf(stderr, "Unable to open file \"%s\"\n", output_file_.c_str()); - fflush(stderr); - exit(EXIT_FAILURE); - } + FILE* xmlout = OpenFileForWriting(output_file_); std::stringstream stream; PrintXmlUnitTest(&stream, unit_test); fprintf(xmlout, "%s", StringStreamToString(&stream).c_str()); fclose(xmlout); } +void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::ListTestsMatchingFilter( + const std::vector<TestSuite*>& test_suites) { + FILE* xmlout = OpenFileForWriting(output_file_); + std::stringstream stream; + PrintXmlTestsList(&stream, test_suites); + fprintf(xmlout, "%s", StringStreamToString(&stream).c_str()); + fclose(xmlout); +} + // Returns an XML-escaped copy of the input string str. If is_attribute // is true, the text is meant to appear as an attribute value, and // normalizable whitespace is preserved by replacing it with character @@ -4492,45 +5496,43 @@ void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, // module will consist of ordinary English text. // If this module is ever modified to produce version 1.1 XML output, // most invalid characters can be retained using character references. -// TODO(wan): It might be nice to have a minimally invasive, human-readable -// escaping scheme for invalid characters, rather than dropping them. -std::string XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::EscapeXml(const std::string& str, - bool is_attribute) { +std::string XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::EscapeXml( + const std::string& str, bool is_attribute) { Message m; for (size_t i = 0; i < str.size(); ++i) { const char ch = str[i]; switch (ch) { - case '<': - m << "<"; - break; - case '>': - m << ">"; - break; - case '&': - m << "&"; - break; - case '\'': - if (is_attribute) - m << "'"; - else - m << '\''; - break; - case '"': - if (is_attribute) - m << """; - else - m << '"'; - break; - default: - if (IsValidXmlCharacter(ch)) { - if (is_attribute && IsNormalizableWhitespace(ch)) - m << "&#x" << String::FormatByte(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) - << ";"; + case '<': + m << "<"; + break; + case '>': + m << ">"; + break; + case '&': + m << "&"; + break; + case '\'': + if (is_attribute) + m << "'"; else - m << ch; - } - break; + m << '\''; + break; + case '"': + if (is_attribute) + m << """; + else + m << '"'; + break; + default: + if (IsValidXmlCharacter(ch)) { + if (is_attribute && IsNormalizableWhitespace(ch)) + m << "&#x" << String::FormatByte(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) + << ";"; + else + m << ch; + } + break; } } @@ -4545,18 +5547,20 @@ std::string XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::RemoveInvalidXmlCharacters( std::string output; output.reserve(str.size()); for (std::string::const_iterator it = str.begin(); it != str.end(); ++it) - if (IsValidXmlCharacter(*it)) output.push_back(*it); + if (IsValidXmlCharacter(*it)) + output.push_back(*it); return output; } // The following routines generate an XML representation of a UnitTest // object. +// GOOGLETEST_CM0009 DO NOT DELETE // // This is how Google Test concepts map to the DTD: // // <testsuites name="AllTests"> <-- corresponds to a UnitTest object -// <testsuite name="testcase-name"> <-- corresponds to a TestCase object +// <testsuite name="testcase-name"> <-- corresponds to a TestSuite object // <testcase name="test-name"> <-- corresponds to a TestInfo object // <failure message="...">...</failure> // <failure message="...">...</failure> @@ -4569,33 +5573,43 @@ std::string XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::RemoveInvalidXmlCharacters( // Formats the given time in milliseconds as seconds. std::string FormatTimeInMillisAsSeconds(TimeInMillis ms) { ::std::stringstream ss; - ss << ms / 1000.0; + ss << (static_cast<double>(ms) * 1e-3); return ss.str(); } -// Converts the given epoch time in milliseconds to a date string in the ISO -// 8601 format, without the timezone information. -std::string FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsIso8601(TimeInMillis ms) { - // Using non-reentrant version as localtime_r is not portable. - time_t seconds = static_cast<time_t>(ms / 1000); -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable : 4996) // Temporarily disables warning 4996 - // (function or variable may be unsafe). - const struct tm* const time_struct = localtime(&seconds); // NOLINT -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state again. +static bool PortableLocaltime(time_t seconds, struct tm* out) { +#if defined(_MSC_VER) + return localtime_s(out, &seconds) == 0; +#elif defined(__MINGW32__) || defined(__MINGW64__) + // MINGW <time.h> provides neither localtime_r nor localtime_s, but uses + // Windows' localtime(), which has a thread-local tm buffer. + struct tm* tm_ptr = localtime(&seconds); // NOLINT + if (tm_ptr == nullptr) return false; + *out = *tm_ptr; + return true; +#elif defined(__STDC_LIB_EXT1__) + // Uses localtime_s when available as localtime_r is only available from + // C23 standard. + return localtime_s(&seconds, out) != nullptr; #else - const struct tm* const time_struct = localtime(&seconds); // NOLINT + return localtime_r(&seconds, out) != nullptr; #endif - if (time_struct == NULL) return ""; // Invalid ms value +} - // YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss - return StreamableToString(time_struct->tm_year + 1900) + "-" + - String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct->tm_mon + 1) + "-" + - String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct->tm_mday) + "T" + - String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct->tm_hour) + ":" + - String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct->tm_min) + ":" + - String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct->tm_sec); +// Converts the given epoch time in milliseconds to a date string in the ISO +// 8601 format, without the timezone information. +std::string FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsIso8601(TimeInMillis ms) { + struct tm time_struct; + if (!PortableLocaltime(static_cast<time_t>(ms / 1000), &time_struct)) + return ""; + // YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss.sss + return StreamableToString(time_struct.tm_year + 1900) + "-" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_mon + 1) + "-" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_mday) + "T" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_hour) + ":" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_min) + ":" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_sec) + "." + + String::FormatIntWidthN(static_cast<int>(ms % 1000), 3); } // Streams an XML CDATA section, escaping invalid CDATA sequences as needed. @@ -4605,9 +5619,9 @@ void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputXmlCDataSection(::std::ostream* stream, *stream << "<![CDATA["; for (;;) { const char* const next_segment = strstr(segment, "]]>"); - if (next_segment != NULL) { - stream->write(segment, - static_cast<std::streamsize>(next_segment - segment)); + if (next_segment != nullptr) { + stream->write( + segment, static_cast<std::streamsize>(next_segment - segment)); *stream << "]]>]]><![CDATA["; segment = next_segment + strlen("]]>"); } else { @@ -4619,91 +5633,181 @@ void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputXmlCDataSection(::std::ostream* stream, } void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputXmlAttribute( - std::ostream* stream, const std::string& element_name, - const std::string& name, const std::string& value) { + std::ostream* stream, + const std::string& element_name, + const std::string& name, + const std::string& value) { const std::vector<std::string>& allowed_names = - GetReservedAttributesForElement(element_name); + GetReservedOutputAttributesForElement(element_name); GTEST_CHECK_(std::find(allowed_names.begin(), allowed_names.end(), name) != - allowed_names.end()) + allowed_names.end()) << "Attribute " << name << " is not allowed for element <" << element_name << ">."; *stream << " " << name << "=\"" << EscapeXmlAttribute(value) << "\""; } +// Streams a test suite XML stanza containing the given test result. +void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputXmlTestSuiteForTestResult( + ::std::ostream* stream, const TestResult& result) { + // Output the boilerplate for a minimal test suite with one test. + *stream << " <testsuite"; + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testsuite", "name", "NonTestSuiteFailure"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testsuite", "tests", "1"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testsuite", "failures", "1"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testsuite", "disabled", "0"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testsuite", "skipped", "0"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testsuite", "errors", "0"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testsuite", "time", + FormatTimeInMillisAsSeconds(result.elapsed_time())); + OutputXmlAttribute( + stream, "testsuite", "timestamp", + FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsIso8601(result.start_timestamp())); + *stream << ">"; + + // Output the boilerplate for a minimal test case with a single test. + *stream << " <testcase"; + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testcase", "name", ""); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testcase", "status", "run"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testcase", "result", "completed"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testcase", "classname", ""); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, "testcase", "time", + FormatTimeInMillisAsSeconds(result.elapsed_time())); + OutputXmlAttribute( + stream, "testcase", "timestamp", + FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsIso8601(result.start_timestamp())); + + // Output the actual test result. + OutputXmlTestResult(stream, result); + + // Complete the test suite. + *stream << " </testsuite>\n"; +} + // Prints an XML representation of a TestInfo object. -// TODO(wan): There is also value in printing properties with the plain printer. void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputXmlTestInfo(::std::ostream* stream, - const char* test_case_name, + const char* test_suite_name, const TestInfo& test_info) { const TestResult& result = *test_info.result(); - const std::string kTestcase = "testcase"; + const std::string kTestsuite = "testcase"; + + if (test_info.is_in_another_shard()) { + return; + } *stream << " <testcase"; - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestcase, "name", test_info.name()); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "name", test_info.name()); - if (test_info.value_param() != NULL) { - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestcase, "value_param", + if (test_info.value_param() != nullptr) { + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "value_param", test_info.value_param()); } - if (test_info.type_param() != NULL) { - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestcase, "type_param", test_info.type_param()); + if (test_info.type_param() != nullptr) { + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "type_param", + test_info.type_param()); + } + if (GTEST_FLAG(list_tests)) { + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "file", test_info.file()); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "line", + StreamableToString(test_info.line())); + *stream << " />\n"; + return; } - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestcase, "status", + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "status", test_info.should_run() ? "run" : "notrun"); - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestcase, "time", + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "result", + test_info.should_run() + ? (result.Skipped() ? "skipped" : "completed") + : "suppressed"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "time", FormatTimeInMillisAsSeconds(result.elapsed_time())); - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestcase, "classname", test_case_name); - *stream << TestPropertiesAsXmlAttributes(result); + OutputXmlAttribute( + stream, kTestsuite, "timestamp", + FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsIso8601(result.start_timestamp())); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "classname", test_suite_name); + OutputXmlTestResult(stream, result); +} + +void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputXmlTestResult(::std::ostream* stream, + const TestResult& result) { int failures = 0; + int skips = 0; for (int i = 0; i < result.total_part_count(); ++i) { const TestPartResult& part = result.GetTestPartResult(i); if (part.failed()) { - if (++failures == 1) { + if (++failures == 1 && skips == 0) { *stream << ">\n"; } - const string location = internal::FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation( - part.file_name(), part.line_number()); - const string summary = location + "\n" + part.summary(); + const std::string location = + internal::FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation(part.file_name(), + part.line_number()); + const std::string summary = location + "\n" + part.summary(); *stream << " <failure message=\"" - << EscapeXmlAttribute(summary.c_str()) << "\" type=\"\">"; - const string detail = location + "\n" + part.message(); + << EscapeXmlAttribute(summary) + << "\" type=\"\">"; + const std::string detail = location + "\n" + part.message(); OutputXmlCDataSection(stream, RemoveInvalidXmlCharacters(detail).c_str()); *stream << "</failure>\n"; + } else if (part.skipped()) { + if (++skips == 1 && failures == 0) { + *stream << ">\n"; + } + const std::string location = + internal::FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation(part.file_name(), + part.line_number()); + const std::string summary = location + "\n" + part.summary(); + *stream << " <skipped message=\"" + << EscapeXmlAttribute(summary.c_str()) << "\">"; + const std::string detail = location + "\n" + part.message(); + OutputXmlCDataSection(stream, RemoveInvalidXmlCharacters(detail).c_str()); + *stream << "</skipped>\n"; } } - if (failures == 0) + if (failures == 0 && skips == 0 && result.test_property_count() == 0) { *stream << " />\n"; - else + } else { + if (failures == 0 && skips == 0) { + *stream << ">\n"; + } + OutputXmlTestProperties(stream, result); *stream << " </testcase>\n"; + } } -// Prints an XML representation of a TestCase object -void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintXmlTestCase(std::ostream* stream, - const TestCase& test_case) { +// Prints an XML representation of a TestSuite object +void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintXmlTestSuite(std::ostream* stream, + const TestSuite& test_suite) { const std::string kTestsuite = "testsuite"; *stream << " <" << kTestsuite; - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "name", test_case.name()); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "name", test_suite.name()); OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "tests", - StreamableToString(test_case.reportable_test_count())); - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "failures", - StreamableToString(test_case.failed_test_count())); - OutputXmlAttribute( - stream, kTestsuite, "disabled", - StreamableToString(test_case.reportable_disabled_test_count())); - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "errors", "0"); - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "time", - FormatTimeInMillisAsSeconds(test_case.elapsed_time())); - *stream << TestPropertiesAsXmlAttributes(test_case.ad_hoc_test_result()) - << ">\n"; - - for (int i = 0; i < test_case.total_test_count(); ++i) { - if (test_case.GetTestInfo(i)->is_reportable()) - OutputXmlTestInfo(stream, test_case.name(), *test_case.GetTestInfo(i)); + StreamableToString(test_suite.reportable_test_count())); + if (!GTEST_FLAG(list_tests)) { + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "failures", + StreamableToString(test_suite.failed_test_count())); + OutputXmlAttribute( + stream, kTestsuite, "disabled", + StreamableToString(test_suite.reportable_disabled_test_count())); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "skipped", + StreamableToString(test_suite.skipped_test_count())); + + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "errors", "0"); + + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuite, "time", + FormatTimeInMillisAsSeconds(test_suite.elapsed_time())); + OutputXmlAttribute( + stream, kTestsuite, "timestamp", + FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsIso8601(test_suite.start_timestamp())); + *stream << TestPropertiesAsXmlAttributes(test_suite.ad_hoc_test_result()); + } + *stream << ">\n"; + for (int i = 0; i < test_suite.total_test_count(); ++i) { + if (test_suite.GetTestInfo(i)->is_reportable()) + OutputXmlTestInfo(stream, test_suite.name(), *test_suite.GetTestInfo(i)); } *stream << " </" << kTestsuite << ">\n"; } @@ -4724,25 +5828,53 @@ void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintXmlUnitTest(std::ostream* stream, stream, kTestsuites, "disabled", StreamableToString(unit_test.reportable_disabled_test_count())); OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuites, "errors", "0"); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuites, "time", + FormatTimeInMillisAsSeconds(unit_test.elapsed_time())); OutputXmlAttribute( stream, kTestsuites, "timestamp", FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsIso8601(unit_test.start_timestamp())); - OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuites, "time", - FormatTimeInMillisAsSeconds(unit_test.elapsed_time())); if (GTEST_FLAG(shuffle)) { OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuites, "random_seed", StreamableToString(unit_test.random_seed())); } - *stream << TestPropertiesAsXmlAttributes(unit_test.ad_hoc_test_result()); OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuites, "name", "AllTests"); *stream << ">\n"; - for (int i = 0; i < unit_test.total_test_case_count(); ++i) { - if (unit_test.GetTestCase(i)->reportable_test_count() > 0) - PrintXmlTestCase(stream, *unit_test.GetTestCase(i)); + for (int i = 0; i < unit_test.total_test_suite_count(); ++i) { + if (unit_test.GetTestSuite(i)->reportable_test_count() > 0) + PrintXmlTestSuite(stream, *unit_test.GetTestSuite(i)); + } + + // If there was a test failure outside of one of the test suites (like in a + // test environment) include that in the output. + if (unit_test.ad_hoc_test_result().Failed()) { + OutputXmlTestSuiteForTestResult(stream, unit_test.ad_hoc_test_result()); + } + + *stream << "</" << kTestsuites << ">\n"; +} + +void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintXmlTestsList( + std::ostream* stream, const std::vector<TestSuite*>& test_suites) { + const std::string kTestsuites = "testsuites"; + + *stream << "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>\n"; + *stream << "<" << kTestsuites; + + int total_tests = 0; + for (auto test_suite : test_suites) { + total_tests += test_suite->total_test_count(); + } + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuites, "tests", + StreamableToString(total_tests)); + OutputXmlAttribute(stream, kTestsuites, "name", "AllTests"); + *stream << ">\n"; + + for (auto test_suite : test_suites) { + PrintXmlTestSuite(stream, *test_suite); } *stream << "</" << kTestsuites << ">\n"; } @@ -4755,13 +5887,473 @@ std::string XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::TestPropertiesAsXmlAttributes( for (int i = 0; i < result.test_property_count(); ++i) { const TestProperty& property = result.GetTestProperty(i); attributes << " " << property.key() << "=" - << "\"" << EscapeXmlAttribute(property.value()) << "\""; + << "\"" << EscapeXmlAttribute(property.value()) << "\""; } return attributes.GetString(); } +void XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputXmlTestProperties( + std::ostream* stream, const TestResult& result) { + const std::string kProperties = "properties"; + const std::string kProperty = "property"; + + if (result.test_property_count() <= 0) { + return; + } + + *stream << "<" << kProperties << ">\n"; + for (int i = 0; i < result.test_property_count(); ++i) { + const TestProperty& property = result.GetTestProperty(i); + *stream << "<" << kProperty; + *stream << " name=\"" << EscapeXmlAttribute(property.key()) << "\""; + *stream << " value=\"" << EscapeXmlAttribute(property.value()) << "\""; + *stream << "/>\n"; + } + *stream << "</" << kProperties << ">\n"; +} + // End XmlUnitTestResultPrinter +// This class generates an JSON output file. +class JsonUnitTestResultPrinter : public EmptyTestEventListener { + public: + explicit JsonUnitTestResultPrinter(const char* output_file); + + void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, int iteration) override; + + // Prints an JSON summary of all unit tests. + static void PrintJsonTestList(::std::ostream* stream, + const std::vector<TestSuite*>& test_suites); + + private: + // Returns an JSON-escaped copy of the input string str. + static std::string EscapeJson(const std::string& str); + + //// Verifies that the given attribute belongs to the given element and + //// streams the attribute as JSON. + static void OutputJsonKey(std::ostream* stream, + const std::string& element_name, + const std::string& name, + const std::string& value, + const std::string& indent, + bool comma = true); + static void OutputJsonKey(std::ostream* stream, + const std::string& element_name, + const std::string& name, + int value, + const std::string& indent, + bool comma = true); + + // Streams a test suite JSON stanza containing the given test result. + // + // Requires: result.Failed() + static void OutputJsonTestSuiteForTestResult(::std::ostream* stream, + const TestResult& result); + + // Streams a JSON representation of a TestResult object. + static void OutputJsonTestResult(::std::ostream* stream, + const TestResult& result); + + // Streams a JSON representation of a TestInfo object. + static void OutputJsonTestInfo(::std::ostream* stream, + const char* test_suite_name, + const TestInfo& test_info); + + // Prints a JSON representation of a TestSuite object + static void PrintJsonTestSuite(::std::ostream* stream, + const TestSuite& test_suite); + + // Prints a JSON summary of unit_test to output stream out. + static void PrintJsonUnitTest(::std::ostream* stream, + const UnitTest& unit_test); + + // Produces a string representing the test properties in a result as + // a JSON dictionary. + static std::string TestPropertiesAsJson(const TestResult& result, + const std::string& indent); + + // The output file. + const std::string output_file_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(JsonUnitTestResultPrinter); +}; + +// Creates a new JsonUnitTestResultPrinter. +JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::JsonUnitTestResultPrinter(const char* output_file) + : output_file_(output_file) { + if (output_file_.empty()) { + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "JSON output file may not be null"; + } +} + +void JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, + int /*iteration*/) { + FILE* jsonout = OpenFileForWriting(output_file_); + std::stringstream stream; + PrintJsonUnitTest(&stream, unit_test); + fprintf(jsonout, "%s", StringStreamToString(&stream).c_str()); + fclose(jsonout); +} + +// Returns an JSON-escaped copy of the input string str. +std::string JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::EscapeJson(const std::string& str) { + Message m; + + for (size_t i = 0; i < str.size(); ++i) { + const char ch = str[i]; + switch (ch) { + case '\\': + case '"': + case '/': + m << '\\' << ch; + break; + case '\b': + m << "\\b"; + break; + case '\t': + m << "\\t"; + break; + case '\n': + m << "\\n"; + break; + case '\f': + m << "\\f"; + break; + case '\r': + m << "\\r"; + break; + default: + if (ch < ' ') { + m << "\\u00" << String::FormatByte(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)); + } else { + m << ch; + } + break; + } + } + + return m.GetString(); +} + +// The following routines generate an JSON representation of a UnitTest +// object. + +// Formats the given time in milliseconds as seconds. +static std::string FormatTimeInMillisAsDuration(TimeInMillis ms) { + ::std::stringstream ss; + ss << (static_cast<double>(ms) * 1e-3) << "s"; + return ss.str(); +} + +// Converts the given epoch time in milliseconds to a date string in the +// RFC3339 format, without the timezone information. +static std::string FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsRFC3339(TimeInMillis ms) { + struct tm time_struct; + if (!PortableLocaltime(static_cast<time_t>(ms / 1000), &time_struct)) + return ""; + // YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss + return StreamableToString(time_struct.tm_year + 1900) + "-" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_mon + 1) + "-" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_mday) + "T" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_hour) + ":" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_min) + ":" + + String::FormatIntWidth2(time_struct.tm_sec) + "Z"; +} + +static inline std::string Indent(size_t width) { + return std::string(width, ' '); +} + +void JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputJsonKey( + std::ostream* stream, + const std::string& element_name, + const std::string& name, + const std::string& value, + const std::string& indent, + bool comma) { + const std::vector<std::string>& allowed_names = + GetReservedOutputAttributesForElement(element_name); + + GTEST_CHECK_(std::find(allowed_names.begin(), allowed_names.end(), name) != + allowed_names.end()) + << "Key \"" << name << "\" is not allowed for value \"" << element_name + << "\"."; + + *stream << indent << "\"" << name << "\": \"" << EscapeJson(value) << "\""; + if (comma) + *stream << ",\n"; +} + +void JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputJsonKey( + std::ostream* stream, + const std::string& element_name, + const std::string& name, + int value, + const std::string& indent, + bool comma) { + const std::vector<std::string>& allowed_names = + GetReservedOutputAttributesForElement(element_name); + + GTEST_CHECK_(std::find(allowed_names.begin(), allowed_names.end(), name) != + allowed_names.end()) + << "Key \"" << name << "\" is not allowed for value \"" << element_name + << "\"."; + + *stream << indent << "\"" << name << "\": " << StreamableToString(value); + if (comma) + *stream << ",\n"; +} + +// Streams a test suite JSON stanza containing the given test result. +void JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputJsonTestSuiteForTestResult( + ::std::ostream* stream, const TestResult& result) { + // Output the boilerplate for a new test suite. + *stream << Indent(4) << "{\n"; + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testsuite", "name", "NonTestSuiteFailure", Indent(6)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testsuite", "tests", 1, Indent(6)); + if (!GTEST_FLAG(list_tests)) { + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testsuite", "failures", 1, Indent(6)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testsuite", "disabled", 0, Indent(6)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testsuite", "skipped", 0, Indent(6)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testsuite", "errors", 0, Indent(6)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testsuite", "time", + FormatTimeInMillisAsDuration(result.elapsed_time()), + Indent(6)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testsuite", "timestamp", + FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsRFC3339(result.start_timestamp()), + Indent(6)); + } + *stream << Indent(6) << "\"testsuite\": [\n"; + + // Output the boilerplate for a new test case. + *stream << Indent(8) << "{\n"; + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testcase", "name", "", Indent(10)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testcase", "status", "RUN", Indent(10)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testcase", "result", "COMPLETED", Indent(10)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testcase", "timestamp", + FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsRFC3339(result.start_timestamp()), + Indent(10)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testcase", "time", + FormatTimeInMillisAsDuration(result.elapsed_time()), + Indent(10)); + OutputJsonKey(stream, "testcase", "classname", "", Indent(10), false); + *stream << TestPropertiesAsJson(result, Indent(10)); + + // Output the actual test result. + OutputJsonTestResult(stream, result); + + // Finish the test suite. + *stream << "\n" << Indent(6) << "]\n" << Indent(4) << "}"; +} + +// Prints a JSON representation of a TestInfo object. +void JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputJsonTestInfo(::std::ostream* stream, + const char* test_suite_name, + const TestInfo& test_info) { + const TestResult& result = *test_info.result(); + const std::string kTestsuite = "testcase"; + const std::string kIndent = Indent(10); + + *stream << Indent(8) << "{\n"; + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "name", test_info.name(), kIndent); + + if (test_info.value_param() != nullptr) { + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "value_param", test_info.value_param(), + kIndent); + } + if (test_info.type_param() != nullptr) { + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "type_param", test_info.type_param(), + kIndent); + } + if (GTEST_FLAG(list_tests)) { + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "file", test_info.file(), kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "line", test_info.line(), kIndent, false); + *stream << "\n" << Indent(8) << "}"; + return; + } + + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "status", + test_info.should_run() ? "RUN" : "NOTRUN", kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "result", + test_info.should_run() + ? (result.Skipped() ? "SKIPPED" : "COMPLETED") + : "SUPPRESSED", + kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "timestamp", + FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsRFC3339(result.start_timestamp()), + kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "time", + FormatTimeInMillisAsDuration(result.elapsed_time()), kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "classname", test_suite_name, kIndent, + false); + *stream << TestPropertiesAsJson(result, kIndent); + + OutputJsonTestResult(stream, result); +} + +void JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::OutputJsonTestResult(::std::ostream* stream, + const TestResult& result) { + const std::string kIndent = Indent(10); + + int failures = 0; + for (int i = 0; i < result.total_part_count(); ++i) { + const TestPartResult& part = result.GetTestPartResult(i); + if (part.failed()) { + *stream << ",\n"; + if (++failures == 1) { + *stream << kIndent << "\"" << "failures" << "\": [\n"; + } + const std::string location = + internal::FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation(part.file_name(), + part.line_number()); + const std::string message = EscapeJson(location + "\n" + part.message()); + *stream << kIndent << " {\n" + << kIndent << " \"failure\": \"" << message << "\",\n" + << kIndent << " \"type\": \"\"\n" + << kIndent << " }"; + } + } + + if (failures > 0) + *stream << "\n" << kIndent << "]"; + *stream << "\n" << Indent(8) << "}"; +} + +// Prints an JSON representation of a TestSuite object +void JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintJsonTestSuite( + std::ostream* stream, const TestSuite& test_suite) { + const std::string kTestsuite = "testsuite"; + const std::string kIndent = Indent(6); + + *stream << Indent(4) << "{\n"; + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "name", test_suite.name(), kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "tests", test_suite.reportable_test_count(), + kIndent); + if (!GTEST_FLAG(list_tests)) { + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "failures", + test_suite.failed_test_count(), kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "disabled", + test_suite.reportable_disabled_test_count(), kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "errors", 0, kIndent); + OutputJsonKey( + stream, kTestsuite, "timestamp", + FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsRFC3339(test_suite.start_timestamp()), + kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuite, "time", + FormatTimeInMillisAsDuration(test_suite.elapsed_time()), + kIndent, false); + *stream << TestPropertiesAsJson(test_suite.ad_hoc_test_result(), kIndent) + << ",\n"; + } + + *stream << kIndent << "\"" << kTestsuite << "\": [\n"; + + bool comma = false; + for (int i = 0; i < test_suite.total_test_count(); ++i) { + if (test_suite.GetTestInfo(i)->is_reportable()) { + if (comma) { + *stream << ",\n"; + } else { + comma = true; + } + OutputJsonTestInfo(stream, test_suite.name(), *test_suite.GetTestInfo(i)); + } + } + *stream << "\n" << kIndent << "]\n" << Indent(4) << "}"; +} + +// Prints a JSON summary of unit_test to output stream out. +void JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintJsonUnitTest(std::ostream* stream, + const UnitTest& unit_test) { + const std::string kTestsuites = "testsuites"; + const std::string kIndent = Indent(2); + *stream << "{\n"; + + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "tests", unit_test.reportable_test_count(), + kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "failures", unit_test.failed_test_count(), + kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "disabled", + unit_test.reportable_disabled_test_count(), kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "errors", 0, kIndent); + if (GTEST_FLAG(shuffle)) { + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "random_seed", unit_test.random_seed(), + kIndent); + } + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "timestamp", + FormatEpochTimeInMillisAsRFC3339(unit_test.start_timestamp()), + kIndent); + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "time", + FormatTimeInMillisAsDuration(unit_test.elapsed_time()), kIndent, + false); + + *stream << TestPropertiesAsJson(unit_test.ad_hoc_test_result(), kIndent) + << ",\n"; + + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "name", "AllTests", kIndent); + *stream << kIndent << "\"" << kTestsuites << "\": [\n"; + + bool comma = false; + for (int i = 0; i < unit_test.total_test_suite_count(); ++i) { + if (unit_test.GetTestSuite(i)->reportable_test_count() > 0) { + if (comma) { + *stream << ",\n"; + } else { + comma = true; + } + PrintJsonTestSuite(stream, *unit_test.GetTestSuite(i)); + } + } + + // If there was a test failure outside of one of the test suites (like in a + // test environment) include that in the output. + if (unit_test.ad_hoc_test_result().Failed()) { + OutputJsonTestSuiteForTestResult(stream, unit_test.ad_hoc_test_result()); + } + + *stream << "\n" << kIndent << "]\n" << "}\n"; +} + +void JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::PrintJsonTestList( + std::ostream* stream, const std::vector<TestSuite*>& test_suites) { + const std::string kTestsuites = "testsuites"; + const std::string kIndent = Indent(2); + *stream << "{\n"; + int total_tests = 0; + for (auto test_suite : test_suites) { + total_tests += test_suite->total_test_count(); + } + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "tests", total_tests, kIndent); + + OutputJsonKey(stream, kTestsuites, "name", "AllTests", kIndent); + *stream << kIndent << "\"" << kTestsuites << "\": [\n"; + + for (size_t i = 0; i < test_suites.size(); ++i) { + if (i != 0) { + *stream << ",\n"; + } + PrintJsonTestSuite(stream, *test_suites[i]); + } + + *stream << "\n" + << kIndent << "]\n" + << "}\n"; +} +// Produces a string representing the test properties in a result as +// a JSON dictionary. +std::string JsonUnitTestResultPrinter::TestPropertiesAsJson( + const TestResult& result, const std::string& indent) { + Message attributes; + for (int i = 0; i < result.test_property_count(); ++i) { + const TestProperty& property = result.GetTestProperty(i); + attributes << ",\n" << indent << "\"" << property.key() << "\": " + << "\"" << EscapeJson(property.value()) << "\""; + } + return attributes.GetString(); +} + +// End JsonUnitTestResultPrinter + #if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ // Checks if str contains '=', '&', '%' or '\n' characters. If yes, @@ -4769,20 +6361,20 @@ std::string XmlUnitTestResultPrinter::TestPropertiesAsXmlAttributes( // example, replaces "=" with "%3D". This algorithm is O(strlen(str)) // in both time and space -- important as the input str may contain an // arbitrarily long test failure message and stack trace. -string StreamingListener::UrlEncode(const char* str) { - string result; +std::string StreamingListener::UrlEncode(const char* str) { + std::string result; result.reserve(strlen(str) + 1); for (char ch = *str; ch != '\0'; ch = *++str) { switch (ch) { - case '%': - case '=': - case '&': - case '\n': - result.append("%" + String::FormatByte(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch))); - break; - default: - result.push_back(ch); - break; + case '%': + case '=': + case '&': + case '\n': + result.append("%" + String::FormatByte(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch))); + break; + default: + result.push_back(ch); + break; } } return result; @@ -4794,24 +6386,24 @@ void StreamingListener::SocketWriter::MakeConnection() { addrinfo hints; memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(hints)); - hints.ai_family = AF_UNSPEC; // To allow both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. + hints.ai_family = AF_UNSPEC; // To allow both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; - addrinfo* servinfo = NULL; + addrinfo* servinfo = nullptr; // Use the getaddrinfo() to get a linked list of IP addresses for // the given host name. - const int error_num = - getaddrinfo(host_name_.c_str(), port_num_.c_str(), &hints, &servinfo); + const int error_num = getaddrinfo( + host_name_.c_str(), port_num_.c_str(), &hints, &servinfo); if (error_num != 0) { GTEST_LOG_(WARNING) << "stream_result_to: getaddrinfo() failed: " << gai_strerror(error_num); } // Loop through all the results and connect to the first we can. - for (addrinfo* cur_addr = servinfo; sockfd_ == -1 && cur_addr != NULL; + for (addrinfo* cur_addr = servinfo; sockfd_ == -1 && cur_addr != nullptr; cur_addr = cur_addr->ai_next) { - sockfd_ = socket(cur_addr->ai_family, cur_addr->ai_socktype, - cur_addr->ai_protocol); + sockfd_ = socket( + cur_addr->ai_family, cur_addr->ai_socktype, cur_addr->ai_protocol); if (sockfd_ != -1) { // Connect the client socket to the server socket. if (connect(sockfd_, cur_addr->ai_addr, cur_addr->ai_addrlen) == -1) { @@ -4832,53 +6424,82 @@ void StreamingListener::SocketWriter::MakeConnection() { // End of class Streaming Listener #endif // GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS__ -// Class ScopedTrace +// class OsStackTraceGetter -// Pushes the given source file location and message onto a per-thread -// trace stack maintained by Google Test. -ScopedTrace::ScopedTrace(const char* file, int line, const Message& message) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(&UnitTest::mutex_) { - TraceInfo trace; - trace.file = file; - trace.line = line; - trace.message = message.GetString(); +const char* const OsStackTraceGetterInterface::kElidedFramesMarker = + "... " GTEST_NAME_ " internal frames ..."; - UnitTest::GetInstance()->PushGTestTrace(trace); -} +std::string OsStackTraceGetter::CurrentStackTrace(int max_depth, int skip_count) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL + std::string result; -// Pops the info pushed by the c'tor. -ScopedTrace::~ScopedTrace() GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(&UnitTest::mutex_) { - UnitTest::GetInstance()->PopGTestTrace(); -} + if (max_depth <= 0) { + return result; + } -// class OsStackTraceGetter + max_depth = std::min(max_depth, kMaxStackTraceDepth); -// Returns the current OS stack trace as an std::string. Parameters: -// -// max_depth - the maximum number of stack frames to be included -// in the trace. -// skip_count - the number of top frames to be skipped; doesn't count -// against max_depth. -// -string OsStackTraceGetter::CurrentStackTrace(int /* max_depth */, - int /* skip_count */) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { + std::vector<void*> raw_stack(max_depth); + // Skips the frames requested by the caller, plus this function. + const int raw_stack_size = + absl::GetStackTrace(&raw_stack[0], max_depth, skip_count + 1); + + void* caller_frame = nullptr; + { + MutexLock lock(&mutex_); + caller_frame = caller_frame_; + } + + for (int i = 0; i < raw_stack_size; ++i) { + if (raw_stack[i] == caller_frame && + !GTEST_FLAG(show_internal_stack_frames)) { + // Add a marker to the trace and stop adding frames. + absl::StrAppend(&result, kElidedFramesMarker, "\n"); + break; + } + + char tmp[1024]; + const char* symbol = "(unknown)"; + if (absl::Symbolize(raw_stack[i], tmp, sizeof(tmp))) { + symbol = tmp; + } + + char line[1024]; + snprintf(line, sizeof(line), " %p: %s\n", raw_stack[i], symbol); + result += line; + } + + return result; + +#else // !GTEST_HAS_ABSL + static_cast<void>(max_depth); + static_cast<void>(skip_count); return ""; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL } -void OsStackTraceGetter::UponLeavingGTest() GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) {} +void OsStackTraceGetter::UponLeavingGTest() GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL + void* caller_frame = nullptr; + if (absl::GetStackTrace(&caller_frame, 1, 3) <= 0) { + caller_frame = nullptr; + } -const char* const OsStackTraceGetter::kElidedFramesMarker = - "... " GTEST_NAME_ " internal frames ..."; + MutexLock lock(&mutex_); + caller_frame_ = caller_frame; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL +} // A helper class that creates the premature-exit file in its // constructor and deletes the file in its destructor. class ScopedPrematureExitFile { public: explicit ScopedPrematureExitFile(const char* premature_exit_filepath) - : premature_exit_filepath_(premature_exit_filepath) { + : premature_exit_filepath_(premature_exit_filepath ? + premature_exit_filepath : "") { // If a path to the premature-exit file is specified... - if (premature_exit_filepath != NULL && *premature_exit_filepath != '\0') { + if (!premature_exit_filepath_.empty()) { // create the file with a single "0" character in it. I/O // errors are ignored as there's nothing better we can do and we // don't want to fail the test because of this. @@ -4889,13 +6510,20 @@ class ScopedPrematureExitFile { } ~ScopedPrematureExitFile() { - if (premature_exit_filepath_ != NULL && *premature_exit_filepath_ != '\0') { - remove(premature_exit_filepath_); +#if !defined GTEST_OS_ESP8266 + if (!premature_exit_filepath_.empty()) { + int retval = remove(premature_exit_filepath_.c_str()); + if (retval) { + GTEST_LOG_(ERROR) << "Failed to remove premature exit filepath \"" + << premature_exit_filepath_ << "\" with error " + << retval; + } } +#endif } private: - const char* const premature_exit_filepath_; + const std::string premature_exit_filepath_; GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ScopedPrematureExitFile); }; @@ -4906,8 +6534,8 @@ class ScopedPrematureExitFile { TestEventListeners::TestEventListeners() : repeater_(new internal::TestEventRepeater()), - default_result_printer_(NULL), - default_xml_generator_(NULL) {} + default_result_printer_(nullptr), + default_xml_generator_(nullptr) {} TestEventListeners::~TestEventListeners() { delete repeater_; } @@ -4924,9 +6552,9 @@ void TestEventListeners::Append(TestEventListener* listener) { // NULL if the listener is not found in the list. TestEventListener* TestEventListeners::Release(TestEventListener* listener) { if (listener == default_result_printer_) - default_result_printer_ = NULL; + default_result_printer_ = nullptr; else if (listener == default_xml_generator_) - default_xml_generator_ = NULL; + default_xml_generator_ = nullptr; return repeater_->Release(listener); } @@ -4945,7 +6573,7 @@ void TestEventListeners::SetDefaultResultPrinter(TestEventListener* listener) { // list. delete Release(default_result_printer_); default_result_printer_ = listener; - if (listener != NULL) Append(listener); + if (listener != nullptr) Append(listener); } } @@ -4960,7 +6588,7 @@ void TestEventListeners::SetDefaultXmlGenerator(TestEventListener* listener) { // list. delete Release(default_xml_generator_); default_xml_generator_ = listener; - if (listener != NULL) Append(listener); + if (listener != nullptr) Append(listener); } } @@ -4984,52 +6612,66 @@ void TestEventListeners::SuppressEventForwarding() { // call this before main() starts, from which point on the return // value will never change. UnitTest* UnitTest::GetInstance() { - // When compiled with MSVC 7.1 in optimized mode, destroying the - // UnitTest object upon exiting the program messes up the exit code, - // causing successful tests to appear failed. We have to use a - // different implementation in this case to bypass the compiler bug. - // This implementation makes the compiler happy, at the cost of - // leaking the UnitTest object. - // CodeGear C++Builder insists on a public destructor for the // default implementation. Use this implementation to keep good OO // design with private destructor. -#if (_MSC_VER == 1310 && !defined(_DEBUG)) || defined(__BORLANDC__) +#if defined(__BORLANDC__) static UnitTest* const instance = new UnitTest; return instance; #else static UnitTest instance; return &instance; -#endif // (_MSC_VER == 1310 && !defined(_DEBUG)) || defined(__BORLANDC__) +#endif // defined(__BORLANDC__) } -// Gets the number of successful test cases. -int UnitTest::successful_test_case_count() const { - return impl()->successful_test_case_count(); +// Gets the number of successful test suites. +int UnitTest::successful_test_suite_count() const { + return impl()->successful_test_suite_count(); } -// Gets the number of failed test cases. -int UnitTest::failed_test_case_count() const { - return impl()->failed_test_case_count(); +// Gets the number of failed test suites. +int UnitTest::failed_test_suite_count() const { + return impl()->failed_test_suite_count(); } -// Gets the number of all test cases. -int UnitTest::total_test_case_count() const { - return impl()->total_test_case_count(); +// Gets the number of all test suites. +int UnitTest::total_test_suite_count() const { + return impl()->total_test_suite_count(); } -// Gets the number of all test cases that contain at least one test +// Gets the number of all test suites that contain at least one test // that should run. +int UnitTest::test_suite_to_run_count() const { + return impl()->test_suite_to_run_count(); +} + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +int UnitTest::successful_test_case_count() const { + return impl()->successful_test_suite_count(); +} +int UnitTest::failed_test_case_count() const { + return impl()->failed_test_suite_count(); +} +int UnitTest::total_test_case_count() const { + return impl()->total_test_suite_count(); +} int UnitTest::test_case_to_run_count() const { - return impl()->test_case_to_run_count(); + return impl()->test_suite_to_run_count(); } +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ // Gets the number of successful tests. int UnitTest::successful_test_count() const { return impl()->successful_test_count(); } +// Gets the number of skipped tests. +int UnitTest::skipped_test_count() const { + return impl()->skipped_test_count(); +} + // Gets the number of failed tests. int UnitTest::failed_test_count() const { return impl()->failed_test_count(); } @@ -5057,7 +6699,7 @@ int UnitTest::test_to_run_count() const { return impl()->test_to_run_count(); } // Gets the time of the test program start, in ms from the start of the // UNIX epoch. internal::TimeInMillis UnitTest::start_timestamp() const { - return impl()->start_timestamp(); + return impl()->start_timestamp(); } // Gets the elapsed time, in milliseconds. @@ -5065,34 +6707,44 @@ internal::TimeInMillis UnitTest::elapsed_time() const { return impl()->elapsed_time(); } -// Returns true iff the unit test passed (i.e. all test cases passed). +// Returns true if and only if the unit test passed (i.e. all test suites +// passed). bool UnitTest::Passed() const { return impl()->Passed(); } -// Returns true iff the unit test failed (i.e. some test case failed -// or something outside of all tests failed). +// Returns true if and only if the unit test failed (i.e. some test suite +// failed or something outside of all tests failed). bool UnitTest::Failed() const { return impl()->Failed(); } -// Gets the i-th test case among all the test cases. i can range from 0 to -// total_test_case_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. +// Gets the i-th test suite among all the test suites. i can range from 0 to +// total_test_suite_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. +const TestSuite* UnitTest::GetTestSuite(int i) const { + return impl()->GetTestSuite(i); +} + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ const TestCase* UnitTest::GetTestCase(int i) const { return impl()->GetTestCase(i); } +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ // Returns the TestResult containing information on test failures and -// properties logged outside of individual test cases. +// properties logged outside of individual test suites. const TestResult& UnitTest::ad_hoc_test_result() const { return *impl()->ad_hoc_test_result(); } -// Gets the i-th test case among all the test cases. i can range from 0 to -// total_test_case_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. -TestCase* UnitTest::GetMutableTestCase(int i) { - return impl()->GetMutableTestCase(i); +// Gets the i-th test suite among all the test suites. i can range from 0 to +// total_test_suite_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. +TestSuite* UnitTest::GetMutableTestSuite(int i) { + return impl()->GetMutableSuiteCase(i); } // Returns the list of event listeners that can be used to track events // inside Google Test. -TestEventListeners& UnitTest::listeners() { return *impl()->listeners(); } +TestEventListeners& UnitTest::listeners() { + return *impl()->listeners(); +} // Registers and returns a global test environment. When a test // program is run, all global test environments will be set-up in the @@ -5105,8 +6757,8 @@ TestEventListeners& UnitTest::listeners() { return *impl()->listeners(); } // We don't protect this under mutex_, as we only support calling it // from the main thread. Environment* UnitTest::AddEnvironment(Environment* env) { - if (env == NULL) { - return NULL; + if (env == nullptr) { + return nullptr; } impl_->environments().push_back(env); @@ -5117,11 +6769,12 @@ Environment* UnitTest::AddEnvironment(Environment* env) { // assertion macros (e.g. ASSERT_TRUE, EXPECT_EQ, etc) eventually call // this to report their results. The user code should use the // assertion macros instead of calling this directly. -void UnitTest::AddTestPartResult(TestPartResult::Type result_type, - const char* file_name, int line_number, - const std::string& message, - const std::string& os_stack_trace) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { +void UnitTest::AddTestPartResult( + TestPartResult::Type result_type, + const char* file_name, + int line_number, + const std::string& message, + const std::string& os_stack_trace) GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { Message msg; msg << message; @@ -5129,42 +6782,45 @@ void UnitTest::AddTestPartResult(TestPartResult::Type result_type, if (impl_->gtest_trace_stack().size() > 0) { msg << "\n" << GTEST_NAME_ << " trace:"; - for (int i = static_cast<int>(impl_->gtest_trace_stack().size()); i > 0; - --i) { + for (size_t i = impl_->gtest_trace_stack().size(); i > 0; --i) { const internal::TraceInfo& trace = impl_->gtest_trace_stack()[i - 1]; - msg << "\n" - << internal::FormatFileLocation(trace.file, trace.line) << " " - << trace.message; + msg << "\n" << internal::FormatFileLocation(trace.file, trace.line) + << " " << trace.message; } } - if (os_stack_trace.c_str() != NULL && !os_stack_trace.empty()) { + if (os_stack_trace.c_str() != nullptr && !os_stack_trace.empty()) { msg << internal::kStackTraceMarker << os_stack_trace; } const TestPartResult result = TestPartResult( result_type, file_name, line_number, msg.GetString().c_str()); - impl_->GetTestPartResultReporterForCurrentThread()->ReportTestPartResult( - result); + impl_->GetTestPartResultReporterForCurrentThread()-> + ReportTestPartResult(result); - if (result_type != TestPartResult::kSuccess) { + if (result_type != TestPartResult::kSuccess && + result_type != TestPartResult::kSkip) { // gtest_break_on_failure takes precedence over // gtest_throw_on_failure. This allows a user to set the latter // in the code (perhaps in order to use Google Test assertions // with another testing framework) and specify the former on the // command line for debugging. if (GTEST_FLAG(break_on_failure)) { -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT // Using DebugBreak on Windows allows gtest to still break into a debugger // when a failure happens and both the --gtest_break_on_failure and // the --gtest_catch_exceptions flags are specified. DebugBreak(); +#elif (!defined(__native_client__)) && \ + ((defined(__clang__) || defined(__GNUC__)) && \ + (defined(__x86_64__) || defined(__i386__))) + // with clang/gcc we can achieve the same effect on x86 by invoking int3 + asm("int3"); #else - // Dereference NULL through a volatile pointer to prevent the compiler + // Dereference nullptr through a volatile pointer to prevent the compiler // from removing. We use this rather than abort() or __builtin_trap() for - // portability: Symbian doesn't implement abort() well, and some debuggers - // don't correctly trap abort(). - *static_cast<volatile int*>(NULL) = 1; + // portability: some debuggers don't correctly trap abort(). + *static_cast<volatile int*>(nullptr) = 1; #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS } else if (GTEST_FLAG(throw_on_failure)) { #if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS @@ -5179,8 +6835,8 @@ void UnitTest::AddTestPartResult(TestPartResult::Type result_type, } // Adds a TestProperty to the current TestResult object when invoked from -// inside a test, to current TestCase's ad_hoc_test_result_ when invoked -// from SetUpTestCase or TearDownTestCase, or to the global property set +// inside a test, to current TestSuite's ad_hoc_test_result_ when invoked +// from SetUpTestSuite or TearDownTestSuite, or to the global property set // when invoked elsewhere. If the result already contains a property with // the same key, the value will be updated. void UnitTest::RecordProperty(const std::string& key, @@ -5220,57 +6876,60 @@ int UnitTest::Run() { // test as having failed. const internal::ScopedPrematureExitFile premature_exit_file( in_death_test_child_process - ? NULL + ? nullptr : internal::posix::GetEnv("TEST_PREMATURE_EXIT_FILE")); // Captures the value of GTEST_FLAG(catch_exceptions). This value will be // used for the duration of the program. impl()->set_catch_exceptions(GTEST_FLAG(catch_exceptions)); -#if GTEST_HAS_SEH +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS // Either the user wants Google Test to catch exceptions thrown by the // tests or this is executing in the context of death test child // process. In either case the user does not want to see pop-up dialogs // about crashes - they are expected. if (impl()->catch_exceptions() || in_death_test_child_process) { -# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT // SetErrorMode doesn't exist on CE. SetErrorMode(SEM_FAILCRITICALERRORS | SEM_NOALIGNMENTFAULTEXCEPT | SEM_NOGPFAULTERRORBOX | SEM_NOOPENFILEERRORBOX); -# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -# if (defined(_MSC_VER) || GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW) && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# if (defined(_MSC_VER) || GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW) && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE // Death test children can be terminated with _abort(). On Windows, // _abort() can show a dialog with a warning message. This forces the // abort message to go to stderr instead. _set_error_mode(_OUT_TO_STDERR); -# endif +# endif -# if _MSC_VER >= 1400 && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# if defined(_MSC_VER) && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE // In the debug version, Visual Studio pops up a separate dialog // offering a choice to debug the aborted program. We need to suppress // this dialog or it will pop up for every EXPECT/ASSERT_DEATH statement // executed. Google Test will notify the user of any unexpected // failure via stderr. - // - // VC++ doesn't define _set_abort_behavior() prior to the version 8.0. - // Users of prior VC versions shall suffer the agony and pain of - // clicking through the countless debug dialogs. - // TODO(vladl@google.com): find a way to suppress the abort dialog() in the - // debug mode when compiled with VC 7.1 or lower. if (!GTEST_FLAG(break_on_failure)) _set_abort_behavior( 0x0, // Clear the following flags: _WRITE_ABORT_MSG | _CALL_REPORTFAULT); // pop-up window, core dump. -# endif + + // In debug mode, the Windows CRT can crash with an assertion over invalid + // input (e.g. passing an invalid file descriptor). The default handling + // for these assertions is to pop up a dialog and wait for user input. + // Instead ask the CRT to dump such assertions to stderr non-interactively. + if (!IsDebuggerPresent()) { + (void)_CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_ASSERT, + _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE | _CRTDBG_MODE_DEBUG); + (void)_CrtSetReportFile(_CRT_ASSERT, _CRTDBG_FILE_STDERR); + } +# endif } -#endif // GTEST_HAS_SEH +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS return internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported( - impl(), &internal::UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests, - "auxiliary test code (environments or event listeners)") - ? 0 - : 1; + impl(), + &internal::UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests, + "auxiliary test code (environments or event listeners)") ? 0 : 1; } // Returns the working directory when the first TEST() or TEST_F() was @@ -5279,13 +6938,22 @@ const char* UnitTest::original_working_dir() const { return impl_->original_working_dir_.c_str(); } -// Returns the TestCase object for the test that's currently running, +// Returns the TestSuite object for the test that's currently running, // or NULL if no test is running. +const TestSuite* UnitTest::current_test_suite() const + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { + internal::MutexLock lock(&mutex_); + return impl_->current_test_suite(); +} + +// Legacy API is still available but deprecated +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ const TestCase* UnitTest::current_test_case() const GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { internal::MutexLock lock(&mutex_); - return impl_->current_test_case(); + return impl_->current_test_suite(); } +#endif // Returns the TestInfo object for the test that's currently running, // or NULL if no test is running. @@ -5298,20 +6966,22 @@ const TestInfo* UnitTest::current_test_info() const // Returns the random seed used at the start of the current test run. int UnitTest::random_seed() const { return impl_->random_seed(); } -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST -// Returns ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry object used to keep track of +// Returns ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry object used to keep track of // value-parameterized tests and instantiate and register them. -internal::ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry& UnitTest::parameterized_test_registry() - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { +internal::ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry& +UnitTest::parameterized_test_registry() GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { return impl_->parameterized_test_registry(); } -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST // Creates an empty UnitTest. -UnitTest::UnitTest() { impl_ = new internal::UnitTestImpl(this); } +UnitTest::UnitTest() { + impl_ = new internal::UnitTestImpl(this); +} // Destructor of UnitTest. -UnitTest::~UnitTest() { delete impl_; } +UnitTest::~UnitTest() { + delete impl_; +} // Pushes a trace defined by SCOPED_TRACE() on to the per-thread // Google Test trace stack. @@ -5322,7 +6992,8 @@ void UnitTest::PushGTestTrace(const internal::TraceInfo& trace) } // Pops a trace from the per-thread Google Test trace stack. -void UnitTest::PopGTestTrace() GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { +void UnitTest::PopGTestTrace() + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_) { internal::MutexLock lock(&mutex_); impl_->gtest_trace_stack().pop_back(); } @@ -5331,30 +7002,20 @@ namespace internal { UnitTestImpl::UnitTestImpl(UnitTest* parent) : parent_(parent), -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable : 4355) // Temporarily disables warning 4355 - // (using this in initializer). - default_global_test_part_result_reporter_(this), + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4355 /* using this in initializer */) + default_global_test_part_result_reporter_(this), default_per_thread_test_part_result_reporter_(this), -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state again. -#else - default_global_test_part_result_reporter_(this), - default_per_thread_test_part_result_reporter_(this), -#endif // _MSC_VER - global_test_part_result_repoter_( + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() global_test_part_result_repoter_( &default_global_test_part_result_reporter_), per_thread_test_part_result_reporter_( &default_per_thread_test_part_result_reporter_), -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST parameterized_test_registry_(), parameterized_tests_registered_(false), -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - last_death_test_case_(-1), - current_test_case_(NULL), - current_test_info_(NULL), + last_death_test_suite_(-1), + current_test_suite_(nullptr), + current_test_info_(nullptr), ad_hoc_test_result_(), - os_stack_trace_getter_(NULL), + os_stack_trace_getter_(nullptr), post_flag_parse_init_performed_(false), random_seed_(0), // Will be overridden by the flag before first use. random_(0), // Will be reseeded before first use. @@ -5369,8 +7030,8 @@ UnitTestImpl::UnitTestImpl(UnitTest* parent) } UnitTestImpl::~UnitTestImpl() { - // Deletes every TestCase. - ForEach(test_cases_, internal::Delete<TestCase>); + // Deletes every TestSuite. + ForEach(test_suites_, internal::Delete<TestSuite>); // Deletes every Environment. ForEach(environments_, internal::Delete<Environment>); @@ -5379,20 +7040,20 @@ UnitTestImpl::~UnitTestImpl() { } // Adds a TestProperty to the current TestResult object when invoked in a -// context of a test, to current test case's ad_hoc_test_result when invoke -// from SetUpTestCase/TearDownTestCase, or to the global property set +// context of a test, to current test suite's ad_hoc_test_result when invoke +// from SetUpTestSuite/TearDownTestSuite, or to the global property set // otherwise. If the result already contains a property with the same key, // the value will be updated. void UnitTestImpl::RecordProperty(const TestProperty& test_property) { std::string xml_element; TestResult* test_result; // TestResult appropriate for property recording. - if (current_test_info_ != NULL) { + if (current_test_info_ != nullptr) { xml_element = "testcase"; test_result = &(current_test_info_->result_); - } else if (current_test_case_ != NULL) { + } else if (current_test_suite_ != nullptr) { xml_element = "testsuite"; - test_result = &(current_test_case_->ad_hoc_test_result_); + test_result = &(current_test_suite_->ad_hoc_test_result_); } else { xml_element = "testsuites"; test_result = &ad_hoc_test_result_; @@ -5404,7 +7065,7 @@ void UnitTestImpl::RecordProperty(const TestProperty& test_property) { // Disables event forwarding if the control is currently in a death test // subprocess. Must not be called before InitGoogleTest. void UnitTestImpl::SuppressTestEventsIfInSubprocess() { - if (internal_run_death_test_flag_.get() != NULL) + if (internal_run_death_test_flag_.get() != nullptr) listeners()->SuppressEventForwarding(); } #endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST @@ -5416,10 +7077,12 @@ void UnitTestImpl::ConfigureXmlOutput() { if (output_format == "xml") { listeners()->SetDefaultXmlGenerator(new XmlUnitTestResultPrinter( UnitTestOptions::GetAbsolutePathToOutputFile().c_str())); + } else if (output_format == "json") { + listeners()->SetDefaultXmlGenerator(new JsonUnitTestResultPrinter( + UnitTestOptions::GetAbsolutePathToOutputFile().c_str())); } else if (output_format != "") { - printf("WARNING: unrecognized output format \"%s\" ignored.\n", - output_format.c_str()); - fflush(stdout); + GTEST_LOG_(WARNING) << "WARNING: unrecognized output format \"" + << output_format << "\" ignored."; } } @@ -5431,12 +7094,11 @@ void UnitTestImpl::ConfigureStreamingOutput() { if (!target.empty()) { const size_t pos = target.find(':'); if (pos != std::string::npos) { - listeners()->Append( - new StreamingListener(target.substr(0, pos), target.substr(pos + 1))); + listeners()->Append(new StreamingListener(target.substr(0, pos), + target.substr(pos+1))); } else { - printf("WARNING: unrecognized streaming target \"%s\" ignored.\n", - target.c_str()); - fflush(stdout); + GTEST_LOG_(WARNING) << "unrecognized streaming target \"" << target + << "\" ignored."; } } } @@ -5452,6 +7114,11 @@ void UnitTestImpl::PostFlagParsingInit() { if (!post_flag_parse_init_performed_) { post_flag_parse_init_performed_ = true; +#if defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_TEST_EVENT_LISTENER_) + // Register to send notifications about key process state changes. + listeners()->Append(new GTEST_CUSTOM_TEST_EVENT_LISTENER_()); +#endif // defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_TEST_EVENT_LISTENER_) + #if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST InitDeathTestSubprocessControlInfo(); SuppressTestEventsIfInSubprocess(); @@ -5466,78 +7133,91 @@ void UnitTestImpl::PostFlagParsingInit() { // to shut down the default XML output before invoking RUN_ALL_TESTS. ConfigureXmlOutput(); + if (GTEST_FLAG(brief)) { + listeners()->SetDefaultResultPrinter(new BriefUnitTestResultPrinter); + } + #if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ // Configures listeners for streaming test results to the specified server. ConfigureStreamingOutput(); #endif // GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ + +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL + if (GTEST_FLAG(install_failure_signal_handler)) { + absl::FailureSignalHandlerOptions options; + absl::InstallFailureSignalHandler(options); + } +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL } } -// A predicate that checks the name of a TestCase against a known +// A predicate that checks the name of a TestSuite against a known // value. // // This is used for implementation of the UnitTest class only. We put // it in the anonymous namespace to prevent polluting the outer // namespace. // -// TestCaseNameIs is copyable. -class TestCaseNameIs { +// TestSuiteNameIs is copyable. +class TestSuiteNameIs { public: // Constructor. - explicit TestCaseNameIs(const std::string& name) : name_(name) {} + explicit TestSuiteNameIs(const std::string& name) : name_(name) {} - // Returns true iff the name of test_case matches name_. - bool operator()(const TestCase* test_case) const { - return test_case != NULL && strcmp(test_case->name(), name_.c_str()) == 0; + // Returns true if and only if the name of test_suite matches name_. + bool operator()(const TestSuite* test_suite) const { + return test_suite != nullptr && + strcmp(test_suite->name(), name_.c_str()) == 0; } private: std::string name_; }; -// Finds and returns a TestCase with the given name. If one doesn't +// Finds and returns a TestSuite with the given name. If one doesn't // exist, creates one and returns it. It's the CALLER'S // RESPONSIBILITY to ensure that this function is only called WHEN THE // TESTS ARE NOT SHUFFLED. // // Arguments: // -// test_case_name: name of the test case -// type_param: the name of the test case's type parameter, or NULL if -// this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test case. -// set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test case -// tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test case -TestCase* UnitTestImpl::GetTestCase(const char* test_case_name, - const char* type_param, - Test::SetUpTestCaseFunc set_up_tc, - Test::TearDownTestCaseFunc tear_down_tc) { - // Can we find a TestCase with the given name? - const std::vector<TestCase*>::const_iterator test_case = std::find_if( - test_cases_.begin(), test_cases_.end(), TestCaseNameIs(test_case_name)); - - if (test_case != test_cases_.end()) return *test_case; +// test_suite_name: name of the test suite +// type_param: the name of the test suite's type parameter, or NULL if +// this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test suite. +// set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test suite +// tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test suite +TestSuite* UnitTestImpl::GetTestSuite( + const char* test_suite_name, const char* type_param, + internal::SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc, + internal::TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc) { + // Can we find a TestSuite with the given name? + const auto test_suite = + std::find_if(test_suites_.rbegin(), test_suites_.rend(), + TestSuiteNameIs(test_suite_name)); + + if (test_suite != test_suites_.rend()) return *test_suite; // No. Let's create one. - TestCase* const new_test_case = - new TestCase(test_case_name, type_param, set_up_tc, tear_down_tc); - - // Is this a death test case? - if (internal::UnitTestOptions::MatchesFilter(test_case_name, - kDeathTestCaseFilter)) { - // Yes. Inserts the test case after the last death test case - // defined so far. This only works when the test cases haven't + auto* const new_test_suite = + new TestSuite(test_suite_name, type_param, set_up_tc, tear_down_tc); + + // Is this a death test suite? + if (internal::UnitTestOptions::MatchesFilter(test_suite_name, + kDeathTestSuiteFilter)) { + // Yes. Inserts the test suite after the last death test suite + // defined so far. This only works when the test suites haven't // been shuffled. Otherwise we may end up running a death test // after a non-death test. - ++last_death_test_case_; - test_cases_.insert(test_cases_.begin() + last_death_test_case_, - new_test_case); + ++last_death_test_suite_; + test_suites_.insert(test_suites_.begin() + last_death_test_suite_, + new_test_suite); } else { // No. Appends to the end of the list. - test_cases_.push_back(new_test_case); + test_suites_.push_back(new_test_suite); } - test_case_indices_.push_back(static_cast<int>(test_case_indices_.size())); - return new_test_case; + test_suite_indices_.push_back(static_cast<int>(test_suite_indices_.size())); + return new_test_suite; } // Helpers for setting up / tearing down the given environment. They @@ -5555,16 +7235,13 @@ static void TearDownEnvironment(Environment* env) { env->TearDown(); } // All other functions called from RunAllTests() may safely assume that // parameterized tests are ready to be counted and run. bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() { - // Makes sure InitGoogleTest() was called. - if (!GTestIsInitialized()) { - printf("%s", - "\nThis test program did NOT call ::testing::InitGoogleTest " - "before calling RUN_ALL_TESTS(). Please fix it.\n"); - return false; - } + // True if and only if Google Test is initialized before RUN_ALL_TESTS() is + // called. + const bool gtest_is_initialized_before_run_all_tests = GTestIsInitialized(); // Do not run any test if the --help flag was specified. - if (g_help_flag) return true; + if (g_help_flag) + return true; // Repeats the call to the post-flag parsing initialization in case the // user didn't call InitGoogleTest. @@ -5575,12 +7252,18 @@ bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() { // protocol. internal::WriteToShardStatusFileIfNeeded(); - // True iff we are in a subprocess for running a thread-safe-style + // True if and only if we are in a subprocess for running a thread-safe-style // death test. bool in_subprocess_for_death_test = false; #if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - in_subprocess_for_death_test = (internal_run_death_test_flag_.get() != NULL); + in_subprocess_for_death_test = + (internal_run_death_test_flag_.get() != nullptr); +# if defined(GTEST_EXTRA_DEATH_TEST_CHILD_SETUP_) + if (in_subprocess_for_death_test) { + GTEST_EXTRA_DEATH_TEST_CHILD_SETUP_(); + } +# endif // defined(GTEST_EXTRA_DEATH_TEST_CHILD_SETUP_) #endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST const bool should_shard = ShouldShard(kTestTotalShards, kTestShardIndex, @@ -5588,9 +7271,9 @@ bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() { // Compares the full test names with the filter to decide which // tests to run. - const bool has_tests_to_run = - FilterTests(should_shard ? HONOR_SHARDING_PROTOCOL - : IGNORE_SHARDING_PROTOCOL) > 0; + const bool has_tests_to_run = FilterTests(should_shard + ? HONOR_SHARDING_PROTOCOL + : IGNORE_SHARDING_PROTOCOL) > 0; // Lists the tests and exits if the --gtest_list_tests flag was specified. if (GTEST_FLAG(list_tests)) { @@ -5599,10 +7282,10 @@ bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() { return true; } - random_seed_ = - GTEST_FLAG(shuffle) ? GetRandomSeedFromFlag(GTEST_FLAG(random_seed)) : 0; + random_seed_ = GTEST_FLAG(shuffle) ? + GetRandomSeedFromFlag(GTEST_FLAG(random_seed)) : 0; - // True iff at least one test has failed. + // True if and only if at least one test has failed. bool failed = false; TestEventListener* repeater = listeners()->repeater(); @@ -5614,17 +7297,17 @@ bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() { // when we are inside the subprocess of a death test. const int repeat = in_subprocess_for_death_test ? 1 : GTEST_FLAG(repeat); // Repeats forever if the repeat count is negative. - const bool forever = repeat < 0; - for (int i = 0; forever || i != repeat; i++) { + const bool gtest_repeat_forever = repeat < 0; + for (int i = 0; gtest_repeat_forever || i != repeat; i++) { // We want to preserve failures generated by ad-hoc test // assertions executed before RUN_ALL_TESTS(). ClearNonAdHocTestResult(); - const TimeInMillis start = GetTimeInMillis(); + Timer timer; - // Shuffles test cases and tests if requested. + // Shuffles test suites and tests if requested. if (has_tests_to_run && GTEST_FLAG(shuffle)) { - random()->Reseed(random_seed_); + random()->Reseed(static_cast<uint32_t>(random_seed_)); // This should be done before calling OnTestIterationStart(), // such that a test event listener can see the actual test order // in the event. @@ -5634,19 +7317,48 @@ bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() { // Tells the unit test event listeners that the tests are about to start. repeater->OnTestIterationStart(*parent_, i); - // Runs each test case if there is at least one test to run. + // Runs each test suite if there is at least one test to run. if (has_tests_to_run) { // Sets up all environments beforehand. repeater->OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(*parent_); ForEach(environments_, SetUpEnvironment); repeater->OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(*parent_); - // Runs the tests only if there was no fatal failure during global - // set-up. - if (!Test::HasFatalFailure()) { - for (int test_index = 0; test_index < total_test_case_count(); + // Runs the tests only if there was no fatal failure or skip triggered + // during global set-up. + if (Test::IsSkipped()) { + // Emit diagnostics when global set-up calls skip, as it will not be + // emitted by default. + TestResult& test_result = + *internal::GetUnitTestImpl()->current_test_result(); + for (int j = 0; j < test_result.total_part_count(); ++j) { + const TestPartResult& test_part_result = + test_result.GetTestPartResult(j); + if (test_part_result.type() == TestPartResult::kSkip) { + const std::string& result = test_part_result.message(); + printf("%s\n", result.c_str()); + } + } + fflush(stdout); + } else if (!Test::HasFatalFailure()) { + for (int test_index = 0; test_index < total_test_suite_count(); + test_index++) { + GetMutableSuiteCase(test_index)->Run(); + if (GTEST_FLAG(fail_fast) && + GetMutableSuiteCase(test_index)->Failed()) { + for (int j = test_index + 1; j < total_test_suite_count(); j++) { + GetMutableSuiteCase(j)->Skip(); + } + break; + } + } + } else if (Test::HasFatalFailure()) { + // If there was a fatal failure during the global setup then we know we + // aren't going to run any tests. Explicitly mark all of the tests as + // skipped to make this obvious in the output. + for (int test_index = 0; test_index < total_test_suite_count(); test_index++) { - GetMutableTestCase(test_index)->Run(); + GetMutableSuiteCase(test_index)->Skip(); } } @@ -5657,7 +7369,7 @@ bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() { repeater->OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(*parent_); } - elapsed_time_ = GetTimeInMillis() - start; + elapsed_time_ = timer.Elapsed(); // Tells the unit test event listener that the tests have just finished. repeater->OnTestIterationEnd(*parent_, i); @@ -5683,6 +7395,20 @@ bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() { repeater->OnTestProgramEnd(*parent_); + if (!gtest_is_initialized_before_run_all_tests) { + ColoredPrintf( + GTestColor::kRed, + "\nIMPORTANT NOTICE - DO NOT IGNORE:\n" + "This test program did NOT call " GTEST_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_NAME_ + "() before calling RUN_ALL_TESTS(). This is INVALID. Soon " GTEST_NAME_ + " will start to enforce the valid usage. " + "Please fix it ASAP, or IT WILL START TO FAIL.\n"); // NOLINT +#if GTEST_FOR_GOOGLE_ + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, + "For more details, see http://wiki/Main/ValidGUnitMain.\n"); +#endif // GTEST_FOR_GOOGLE_ + } + return !failed; } @@ -5692,10 +7418,10 @@ bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() { // be created, prints an error and exits. void WriteToShardStatusFileIfNeeded() { const char* const test_shard_file = posix::GetEnv(kTestShardStatusFile); - if (test_shard_file != NULL) { + if (test_shard_file != nullptr) { FILE* const file = posix::FOpen(test_shard_file, "w"); - if (file == NULL) { - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_RED, + if (file == nullptr) { + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, "Could not write to the test shard status file \"%s\" " "specified by the %s environment variable.\n", test_shard_file, kTestShardStatusFile); @@ -5712,40 +7438,41 @@ void WriteToShardStatusFileIfNeeded() { // an error and exits. If in_subprocess_for_death_test, sharding is // disabled because it must only be applied to the original test // process. Otherwise, we could filter out death tests we intended to execute. -bool ShouldShard(const char* total_shards_env, const char* shard_index_env, +bool ShouldShard(const char* total_shards_env, + const char* shard_index_env, bool in_subprocess_for_death_test) { if (in_subprocess_for_death_test) { return false; } - const Int32 total_shards = Int32FromEnvOrDie(total_shards_env, -1); - const Int32 shard_index = Int32FromEnvOrDie(shard_index_env, -1); + const int32_t total_shards = Int32FromEnvOrDie(total_shards_env, -1); + const int32_t shard_index = Int32FromEnvOrDie(shard_index_env, -1); if (total_shards == -1 && shard_index == -1) { return false; } else if (total_shards == -1 && shard_index != -1) { - const Message msg = Message() << "Invalid environment variables: you have " - << kTestShardIndex << " = " << shard_index - << ", but have left " << kTestTotalShards - << " unset.\n"; - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_RED, msg.GetString().c_str()); + const Message msg = Message() + << "Invalid environment variables: you have " + << kTestShardIndex << " = " << shard_index + << ", but have left " << kTestTotalShards << " unset.\n"; + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, "%s", msg.GetString().c_str()); fflush(stdout); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } else if (total_shards != -1 && shard_index == -1) { const Message msg = Message() - << "Invalid environment variables: you have " - << kTestTotalShards << " = " << total_shards - << ", but have left " << kTestShardIndex << " unset.\n"; - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_RED, msg.GetString().c_str()); + << "Invalid environment variables: you have " + << kTestTotalShards << " = " << total_shards + << ", but have left " << kTestShardIndex << " unset.\n"; + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, "%s", msg.GetString().c_str()); fflush(stdout); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } else if (shard_index < 0 || shard_index >= total_shards) { - const Message msg = - Message() << "Invalid environment variables: we require 0 <= " - << kTestShardIndex << " < " << kTestTotalShards - << ", but you have " << kTestShardIndex << "=" << shard_index - << ", " << kTestTotalShards << "=" << total_shards << ".\n"; - ColoredPrintf(COLOR_RED, msg.GetString().c_str()); + const Message msg = Message() + << "Invalid environment variables: we require 0 <= " + << kTestShardIndex << " < " << kTestTotalShards + << ", but you have " << kTestShardIndex << "=" << shard_index + << ", " << kTestTotalShards << "=" << total_shards << ".\n"; + ColoredPrintf(GTestColor::kRed, "%s", msg.GetString().c_str()); fflush(stdout); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } @@ -5756,13 +7483,13 @@ bool ShouldShard(const char* total_shards_env, const char* shard_index_env, // Parses the environment variable var as an Int32. If it is unset, // returns default_val. If it is not an Int32, prints an error // and aborts. -Int32 Int32FromEnvOrDie(const char* var, Int32 default_val) { +int32_t Int32FromEnvOrDie(const char* var, int32_t default_val) { const char* str_val = posix::GetEnv(var); - if (str_val == NULL) { + if (str_val == nullptr) { return default_val; } - Int32 result; + int32_t result; if (!ParseInt32(Message() << "The value of environment variable " << var, str_val, &result)) { exit(EXIT_FAILURE); @@ -5771,8 +7498,8 @@ Int32 Int32FromEnvOrDie(const char* var, Int32 default_val) { } // Given the total number of shards, the shard index, and the test id, -// returns true iff the test should be run on this shard. The test id is -// some arbitrary but unique non-negative integer assigned to each test +// returns true if and only if the test should be run on this shard. The test id +// is some arbitrary but unique non-negative integer assigned to each test // method. Assumes that 0 <= shard_index < total_shards. bool ShouldRunTestOnShard(int total_shards, int shard_index, int test_id) { return (test_id % total_shards) == shard_index; @@ -5780,18 +7507,16 @@ bool ShouldRunTestOnShard(int total_shards, int shard_index, int test_id) { // Compares the name of each test with the user-specified filter to // decide whether the test should be run, then records the result in -// each TestCase and TestInfo object. +// each TestSuite and TestInfo object. // If shard_tests == true, further filters tests based on sharding // variables in the environment - see -// http://code.google.com/p/googletest/wiki/GoogleTestAdvancedGuide. -// Returns the number of tests that should run. +// https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/googletest/docs/advanced.md +// . Returns the number of tests that should run. int UnitTestImpl::FilterTests(ReactionToSharding shard_tests) { - const Int32 total_shards = shard_tests == HONOR_SHARDING_PROTOCOL - ? Int32FromEnvOrDie(kTestTotalShards, -1) - : -1; - const Int32 shard_index = shard_tests == HONOR_SHARDING_PROTOCOL - ? Int32FromEnvOrDie(kTestShardIndex, -1) - : -1; + const int32_t total_shards = shard_tests == HONOR_SHARDING_PROTOCOL ? + Int32FromEnvOrDie(kTestTotalShards, -1) : -1; + const int32_t shard_index = shard_tests == HONOR_SHARDING_PROTOCOL ? + Int32FromEnvOrDie(kTestShardIndex, -1) : -1; // num_runnable_tests are the number of tests that will // run across all shards (i.e., match filter and are not disabled). @@ -5799,40 +7524,40 @@ int UnitTestImpl::FilterTests(ReactionToSharding shard_tests) { // this shard. int num_runnable_tests = 0; int num_selected_tests = 0; - for (size_t i = 0; i < test_cases_.size(); i++) { - TestCase* const test_case = test_cases_[i]; - const std::string& test_case_name = test_case->name(); - test_case->set_should_run(false); + for (auto* test_suite : test_suites_) { + const std::string& test_suite_name = test_suite->name(); + test_suite->set_should_run(false); - for (size_t j = 0; j < test_case->test_info_list().size(); j++) { - TestInfo* const test_info = test_case->test_info_list()[j]; + for (size_t j = 0; j < test_suite->test_info_list().size(); j++) { + TestInfo* const test_info = test_suite->test_info_list()[j]; const std::string test_name(test_info->name()); - // A test is disabled if test case name or test name matches + // A test is disabled if test suite name or test name matches // kDisableTestFilter. const bool is_disabled = internal::UnitTestOptions::MatchesFilter( - test_case_name, kDisableTestFilter) || + test_suite_name, kDisableTestFilter) || internal::UnitTestOptions::MatchesFilter( test_name, kDisableTestFilter); test_info->is_disabled_ = is_disabled; const bool matches_filter = internal::UnitTestOptions::FilterMatchesTest( - test_case_name, test_name); + test_suite_name, test_name); test_info->matches_filter_ = matches_filter; const bool is_runnable = (GTEST_FLAG(also_run_disabled_tests) || !is_disabled) && matches_filter; - const bool is_selected = - is_runnable && - (shard_tests == IGNORE_SHARDING_PROTOCOL || - ShouldRunTestOnShard(total_shards, shard_index, num_runnable_tests)); + const bool is_in_another_shard = + shard_tests != IGNORE_SHARDING_PROTOCOL && + !ShouldRunTestOnShard(total_shards, shard_index, num_runnable_tests); + test_info->is_in_another_shard_ = is_in_another_shard; + const bool is_selected = is_runnable && !is_in_another_shard; num_runnable_tests += is_runnable; num_selected_tests += is_selected; test_info->should_run_ = is_selected; - test_case->set_should_run(test_case->should_run() || is_selected); + test_suite->set_should_run(test_suite->should_run() || is_selected); } } return num_selected_tests; @@ -5843,7 +7568,7 @@ int UnitTestImpl::FilterTests(ReactionToSharding shard_tests) { // max_length characters, only prints the first max_length characters // and "...". static void PrintOnOneLine(const char* str, int max_length) { - if (str != NULL) { + if (str != nullptr) { for (int i = 0; *str != '\0'; ++str) { if (i >= max_length) { printf("..."); @@ -5865,26 +7590,25 @@ void UnitTestImpl::ListTestsMatchingFilter() { // Print at most this many characters for each type/value parameter. const int kMaxParamLength = 250; - for (size_t i = 0; i < test_cases_.size(); i++) { - const TestCase* const test_case = test_cases_[i]; - bool printed_test_case_name = false; + for (auto* test_suite : test_suites_) { + bool printed_test_suite_name = false; - for (size_t j = 0; j < test_case->test_info_list().size(); j++) { - const TestInfo* const test_info = test_case->test_info_list()[j]; + for (size_t j = 0; j < test_suite->test_info_list().size(); j++) { + const TestInfo* const test_info = test_suite->test_info_list()[j]; if (test_info->matches_filter_) { - if (!printed_test_case_name) { - printed_test_case_name = true; - printf("%s.", test_case->name()); - if (test_case->type_param() != NULL) { + if (!printed_test_suite_name) { + printed_test_suite_name = true; + printf("%s.", test_suite->name()); + if (test_suite->type_param() != nullptr) { printf(" # %s = ", kTypeParamLabel); // We print the type parameter on a single line to make // the output easy to parse by a program. - PrintOnOneLine(test_case->type_param(), kMaxParamLength); + PrintOnOneLine(test_suite->type_param(), kMaxParamLength); } printf("\n"); } printf(" %s", test_info->name()); - if (test_info->value_param() != NULL) { + if (test_info->value_param() != nullptr) { printf(" # %s = ", kValueParamLabel); // We print the value parameter on a single line to make the // output easy to parse by a program. @@ -5895,6 +7619,23 @@ void UnitTestImpl::ListTestsMatchingFilter() { } } fflush(stdout); + const std::string& output_format = UnitTestOptions::GetOutputFormat(); + if (output_format == "xml" || output_format == "json") { + FILE* fileout = OpenFileForWriting( + UnitTestOptions::GetAbsolutePathToOutputFile().c_str()); + std::stringstream stream; + if (output_format == "xml") { + XmlUnitTestResultPrinter( + UnitTestOptions::GetAbsolutePathToOutputFile().c_str()) + .PrintXmlTestsList(&stream, test_suites_); + } else if (output_format == "json") { + JsonUnitTestResultPrinter( + UnitTestOptions::GetAbsolutePathToOutputFile().c_str()) + .PrintJsonTestList(&stream, test_suites_); + } + fprintf(fileout, "%s", StringStreamToString(&stream).c_str()); + fclose(fileout); + } } // Sets the OS stack trace getter. @@ -5914,43 +7655,51 @@ void UnitTestImpl::set_os_stack_trace_getter( // otherwise, creates an OsStackTraceGetter, makes it the current // getter, and returns it. OsStackTraceGetterInterface* UnitTestImpl::os_stack_trace_getter() { - if (os_stack_trace_getter_ == NULL) { + if (os_stack_trace_getter_ == nullptr) { +#ifdef GTEST_OS_STACK_TRACE_GETTER_ + os_stack_trace_getter_ = new GTEST_OS_STACK_TRACE_GETTER_; +#else os_stack_trace_getter_ = new OsStackTraceGetter; +#endif // GTEST_OS_STACK_TRACE_GETTER_ } return os_stack_trace_getter_; } -// Returns the TestResult for the test that's currently running, or -// the TestResult for the ad hoc test if no test is running. +// Returns the most specific TestResult currently running. TestResult* UnitTestImpl::current_test_result() { - return current_test_info_ ? &(current_test_info_->result_) - : &ad_hoc_test_result_; + if (current_test_info_ != nullptr) { + return ¤t_test_info_->result_; + } + if (current_test_suite_ != nullptr) { + return ¤t_test_suite_->ad_hoc_test_result_; + } + return &ad_hoc_test_result_; } -// Shuffles all test cases, and the tests within each test case, +// Shuffles all test suites, and the tests within each test suite, // making sure that death tests are still run first. void UnitTestImpl::ShuffleTests() { - // Shuffles the death test cases. - ShuffleRange(random(), 0, last_death_test_case_ + 1, &test_case_indices_); + // Shuffles the death test suites. + ShuffleRange(random(), 0, last_death_test_suite_ + 1, &test_suite_indices_); - // Shuffles the non-death test cases. - ShuffleRange(random(), last_death_test_case_ + 1, - static_cast<int>(test_cases_.size()), &test_case_indices_); + // Shuffles the non-death test suites. + ShuffleRange(random(), last_death_test_suite_ + 1, + static_cast<int>(test_suites_.size()), &test_suite_indices_); - // Shuffles the tests inside each test case. - for (size_t i = 0; i < test_cases_.size(); i++) { - test_cases_[i]->ShuffleTests(random()); + // Shuffles the tests inside each test suite. + for (auto& test_suite : test_suites_) { + test_suite->ShuffleTests(random()); } } -// Restores the test cases and tests to their order before the first shuffle. +// Restores the test suites and tests to their order before the first shuffle. void UnitTestImpl::UnshuffleTests() { - for (size_t i = 0; i < test_cases_.size(); i++) { - // Unshuffles the tests in each test case. - test_cases_[i]->UnshuffleTests(); - // Resets the index of each test case. - test_case_indices_[i] = static_cast<int>(i); + for (size_t i = 0; i < test_suites_.size(); i++) { + // Unshuffles the tests in each test suite. + test_suites_[i]->UnshuffleTests(); + // Resets the index of each test suite. + test_suite_indices_[i] = static_cast<int>(i); } } @@ -5975,7 +7724,7 @@ std::string GetCurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop(UnitTest* /*unit_test*/, // suppress unreachable code warnings. namespace { class ClassUniqueToAlwaysTrue {}; -} // namespace +} bool IsTrue(bool condition) { return condition; } @@ -5983,7 +7732,8 @@ bool AlwaysTrue() { #if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS // This condition is always false so AlwaysTrue() never actually throws, // but it makes the compiler think that it may throw. - if (IsTrue(false)) throw ClassUniqueToAlwaysTrue(); + if (IsTrue(false)) + throw ClassUniqueToAlwaysTrue(); #endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS return true; } @@ -6005,15 +7755,15 @@ bool SkipPrefix(const char* prefix, const char** pstr) { // part can be omitted. // // Returns the value of the flag, or NULL if the parsing failed. -const char* ParseFlagValue(const char* str, const char* flag, - bool def_optional) { +static const char* ParseFlagValue(const char* str, const char* flag, + bool def_optional) { // str and flag must not be NULL. - if (str == NULL || flag == NULL) return NULL; + if (str == nullptr || flag == nullptr) return nullptr; // The flag must start with "--" followed by GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_. const std::string flag_str = std::string("--") + GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + flag; const size_t flag_len = flag_str.length(); - if (strncmp(str, flag_str.c_str(), flag_len) != 0) return NULL; + if (strncmp(str, flag_str.c_str(), flag_len) != 0) return nullptr; // Skips the flag name. const char* flag_end = str + flag_len; @@ -6026,7 +7776,7 @@ const char* ParseFlagValue(const char* str, const char* flag, // If def_optional is true and there are more characters after the // flag name, or if def_optional is false, there must be a '=' after // the flag name. - if (flag_end[0] != '=') return NULL; + if (flag_end[0] != '=') return nullptr; // Returns the string after "=". return flag_end + 1; @@ -6042,46 +7792,45 @@ const char* ParseFlagValue(const char* str, const char* flag, // // On success, stores the value of the flag in *value, and returns // true. On failure, returns false without changing *value. -bool ParseBoolFlag(const char* str, const char* flag, bool* value) { +static bool ParseBoolFlag(const char* str, const char* flag, bool* value) { // Gets the value of the flag as a string. const char* const value_str = ParseFlagValue(str, flag, true); // Aborts if the parsing failed. - if (value_str == NULL) return false; + if (value_str == nullptr) return false; // Converts the string value to a bool. *value = !(*value_str == '0' || *value_str == 'f' || *value_str == 'F'); return true; } -// Parses a string for an Int32 flag, in the form of -// "--flag=value". +// Parses a string for an int32_t flag, in the form of "--flag=value". // // On success, stores the value of the flag in *value, and returns // true. On failure, returns false without changing *value. -bool ParseInt32Flag(const char* str, const char* flag, Int32* value) { +bool ParseInt32Flag(const char* str, const char* flag, int32_t* value) { // Gets the value of the flag as a string. const char* const value_str = ParseFlagValue(str, flag, false); // Aborts if the parsing failed. - if (value_str == NULL) return false; + if (value_str == nullptr) return false; // Sets *value to the value of the flag. - return ParseInt32(Message() << "The value of flag --" << flag, value_str, - value); + return ParseInt32(Message() << "The value of flag --" << flag, + value_str, value); } -// Parses a string for a string flag, in the form of -// "--flag=value". +// Parses a string for a string flag, in the form of "--flag=value". // // On success, stores the value of the flag in *value, and returns // true. On failure, returns false without changing *value. -bool ParseStringFlag(const char* str, const char* flag, std::string* value) { +template <typename String> +static bool ParseStringFlag(const char* str, const char* flag, String* value) { // Gets the value of the flag as a string. const char* const value_str = ParseFlagValue(str, flag, false); // Aborts if the parsing failed. - if (value_str == NULL) return false; + if (value_str == nullptr) return false; // Sets *value to the value of the flag. *value = value_str; @@ -6095,7 +7844,8 @@ bool ParseStringFlag(const char* str, const char* flag, std::string* value) { // GTEST_INTERNAL_PREFIX_ followed by "internal_" are considered Google Test // internal flags and do not trigger the help message. static bool HasGoogleTestFlagPrefix(const char* str) { - return (SkipPrefix("--", &str) || SkipPrefix("-", &str) || + return (SkipPrefix("--", &str) || + SkipPrefix("-", &str) || SkipPrefix("/", &str)) && !SkipPrefix(GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "internal_", &str) && (SkipPrefix(GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_, &str) || @@ -6111,10 +7861,8 @@ static bool HasGoogleTestFlagPrefix(const char* str) { // @Y changes the color to yellow. // @D changes to the default terminal text color. // -// TODO(wan@google.com): Write tests for this once we add stdout -// capturing to Google Test. static void PrintColorEncoded(const char* str) { - GTestColor color = COLOR_DEFAULT; // The current color. + GTestColor color = GTestColor::kDefault; // The current color. // Conceptually, we split the string into segments divided by escape // sequences. Then we print one segment at a time. At the end of @@ -6122,7 +7870,7 @@ static void PrintColorEncoded(const char* str) { // next segment. for (;;) { const char* p = strchr(str, '@'); - if (p == NULL) { + if (p == nullptr) { ColoredPrintf(color, "%s", str); return; } @@ -6134,13 +7882,13 @@ static void PrintColorEncoded(const char* str) { if (ch == '@') { ColoredPrintf(color, "@"); } else if (ch == 'D') { - color = COLOR_DEFAULT; + color = GTestColor::kDefault; } else if (ch == 'R') { - color = COLOR_RED; + color = GTestColor::kRed; } else if (ch == 'G') { - color = COLOR_GREEN; + color = GTestColor::kGreen; } else if (ch == 'Y') { - color = COLOR_YELLOW; + color = GTestColor::kYellow; } else { --str; } @@ -6158,7 +7906,7 @@ static const char kColorEncodedHelpMessage[] = " List the names of all tests instead of running them. The name of\n" " TEST(Foo, Bar) is \"Foo.Bar\".\n" " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ - "filter=@YPOSTIVE_PATTERNS" + "filter=@YPOSITIVE_PATTERNS" "[@G-@YNEGATIVE_PATTERNS]@D\n" " Run only the tests whose name matches one of the positive patterns " "but\n" @@ -6185,33 +7933,37 @@ static const char kColorEncodedHelpMessage[] = " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "color=@Y(@Gyes@Y|@Gno@Y|@Gauto@Y)@D\n" " Enable/disable colored output. The default is @Gauto@D.\n" - " -@G-" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + "brief=1@D\n" + " Only print test failures.\n" + " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "print_time=0@D\n" " Don't print the elapsed time of each test.\n" " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ - "output=xml@Y[@G:@YDIRECTORY_PATH@G" GTEST_PATH_SEP_ + "output=@Y(@Gjson@Y|@Gxml@Y)[@G:@YDIRECTORY_PATH@G" GTEST_PATH_SEP_ "@Y|@G:@YFILE_PATH]@D\n" - " Generate an XML report in the given directory or with the given " - "file\n" - " name. @YFILE_PATH@D defaults to @Gtest_details.xml@D.\n" -#if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ + " Generate a JSON or XML report in the given directory or with the " + "given\n" + " file name. @YFILE_PATH@D defaults to @Gtest_detail.xml@D.\n" +# if GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "stream_result_to=@YHOST@G:@YPORT@D\n" " Stream test results to the given server.\n" -#endif // GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ +# endif // GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ "\n" "Assertion Behavior:\n" -#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "death_test_style=@Y(@Gfast@Y|@Gthreadsafe@Y)@D\n" " Set the default death test style.\n" -#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "break_on_failure@D\n" " Turn assertion failures into debugger break-points.\n" " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "throw_on_failure@D\n" - " Turn assertion failures into C++ exceptions.\n" + " Turn assertion failures into C++ exceptions for use by an external\n" + " test framework.\n" " @G--" GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "catch_exceptions=0@D\n" " Do not report exceptions as test failures. Instead, allow them\n" @@ -6235,6 +7987,57 @@ static const char kColorEncodedHelpMessage[] = "(not one in your own code or tests), please report it to\n" "@G<" GTEST_DEV_EMAIL_ ">@D.\n"; +static bool ParseGoogleTestFlag(const char* const arg) { + return ParseBoolFlag(arg, kAlsoRunDisabledTestsFlag, + >EST_FLAG(also_run_disabled_tests)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kBreakOnFailureFlag, + >EST_FLAG(break_on_failure)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kCatchExceptionsFlag, + >EST_FLAG(catch_exceptions)) || + ParseStringFlag(arg, kColorFlag, >EST_FLAG(color)) || + ParseStringFlag(arg, kDeathTestStyleFlag, + >EST_FLAG(death_test_style)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kDeathTestUseFork, + >EST_FLAG(death_test_use_fork)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kFailFast, >EST_FLAG(fail_fast)) || + ParseStringFlag(arg, kFilterFlag, >EST_FLAG(filter)) || + ParseStringFlag(arg, kInternalRunDeathTestFlag, + >EST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kListTestsFlag, >EST_FLAG(list_tests)) || + ParseStringFlag(arg, kOutputFlag, >EST_FLAG(output)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kBriefFlag, >EST_FLAG(brief)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kPrintTimeFlag, >EST_FLAG(print_time)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kPrintUTF8Flag, >EST_FLAG(print_utf8)) || + ParseInt32Flag(arg, kRandomSeedFlag, >EST_FLAG(random_seed)) || + ParseInt32Flag(arg, kRepeatFlag, >EST_FLAG(repeat)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kShuffleFlag, >EST_FLAG(shuffle)) || + ParseInt32Flag(arg, kStackTraceDepthFlag, + >EST_FLAG(stack_trace_depth)) || + ParseStringFlag(arg, kStreamResultToFlag, + >EST_FLAG(stream_result_to)) || + ParseBoolFlag(arg, kThrowOnFailureFlag, >EST_FLAG(throw_on_failure)); +} + +#if GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_ +static void LoadFlagsFromFile(const std::string& path) { + FILE* flagfile = posix::FOpen(path.c_str(), "r"); + if (!flagfile) { + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "Unable to open file \"" << GTEST_FLAG(flagfile) + << "\""; + } + std::string contents(ReadEntireFile(flagfile)); + posix::FClose(flagfile); + std::vector<std::string> lines; + SplitString(contents, '\n', &lines); + for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); ++i) { + if (lines[i].empty()) + continue; + if (!ParseGoogleTestFlag(lines[i].c_str())) + g_help_flag = true; + } +} +#endif // GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_ + // Parses the command line for Google Test flags, without initializing // other parts of Google Test. The type parameter CharType can be // instantiated to either char or wchar_t. @@ -6248,34 +8051,24 @@ void ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnlyImpl(int* argc, CharType** argv) { using internal::ParseInt32Flag; using internal::ParseStringFlag; - // Do we see a Google Test flag? - if (ParseBoolFlag(arg, kAlsoRunDisabledTestsFlag, - >EST_FLAG(also_run_disabled_tests)) || - ParseBoolFlag(arg, kBreakOnFailureFlag, - >EST_FLAG(break_on_failure)) || - ParseBoolFlag(arg, kCatchExceptionsFlag, - >EST_FLAG(catch_exceptions)) || - ParseStringFlag(arg, kColorFlag, >EST_FLAG(color)) || - ParseStringFlag(arg, kDeathTestStyleFlag, - >EST_FLAG(death_test_style)) || - ParseBoolFlag(arg, kDeathTestUseFork, - >EST_FLAG(death_test_use_fork)) || - ParseStringFlag(arg, kFilterFlag, >EST_FLAG(filter)) || - ParseStringFlag(arg, kInternalRunDeathTestFlag, - >EST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test)) || - ParseBoolFlag(arg, kListTestsFlag, >EST_FLAG(list_tests)) || - ParseStringFlag(arg, kOutputFlag, >EST_FLAG(output)) || - ParseBoolFlag(arg, kPrintTimeFlag, >EST_FLAG(print_time)) || - ParseInt32Flag(arg, kRandomSeedFlag, >EST_FLAG(random_seed)) || - ParseInt32Flag(arg, kRepeatFlag, >EST_FLAG(repeat)) || - ParseBoolFlag(arg, kShuffleFlag, >EST_FLAG(shuffle)) || - ParseInt32Flag(arg, kStackTraceDepthFlag, - >EST_FLAG(stack_trace_depth)) || - ParseStringFlag(arg, kStreamResultToFlag, - >EST_FLAG(stream_result_to)) || - ParseBoolFlag(arg, kThrowOnFailureFlag, - >EST_FLAG(throw_on_failure))) { - // Yes. Shift the remainder of the argv list left by one. Note + bool remove_flag = false; + if (ParseGoogleTestFlag(arg)) { + remove_flag = true; +#if GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_ + } else if (ParseStringFlag(arg, kFlagfileFlag, >EST_FLAG(flagfile))) { + LoadFlagsFromFile(GTEST_FLAG(flagfile)); + remove_flag = true; +#endif // GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_ + } else if (arg_string == "--help" || arg_string == "-h" || + arg_string == "-?" || arg_string == "/?" || + HasGoogleTestFlagPrefix(arg)) { + // Both help flag and unrecognized Google Test flags (excluding + // internal ones) trigger help display. + g_help_flag = true; + } + + if (remove_flag) { + // Shift the remainder of the argv list left by one. Note // that argv has (*argc + 1) elements, the last one always being // NULL. The following loop moves the trailing NULL element as // well. @@ -6289,12 +8082,6 @@ void ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnlyImpl(int* argc, CharType** argv) { // We also need to decrement the iterator as we just removed // an element. i--; - } else if (arg_string == "--help" || arg_string == "-h" || - arg_string == "-?" || arg_string == "/?" || - HasGoogleTestFlagPrefix(arg)) { - // Both help flag and unrecognized Google Test flags (excluding - // internal ones) trigger help display. - g_help_flag = true; } } @@ -6310,6 +8097,17 @@ void ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnlyImpl(int* argc, CharType** argv) { // other parts of Google Test. void ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnly(int* argc, char** argv) { ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnlyImpl(argc, argv); + + // Fix the value of *_NSGetArgc() on macOS, but if and only if + // *_NSGetArgv() == argv + // Only applicable to char** version of argv +#if GTEST_OS_MAC +#ifndef GTEST_OS_IOS + if (*_NSGetArgv() == argv) { + *_NSGetArgc() = *argc; + } +#endif +#endif } void ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnly(int* argc, wchar_t** argv) { ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnlyImpl(argc, argv); @@ -6321,23 +8119,19 @@ void ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnly(int* argc, wchar_t** argv) { // wchar_t. template <typename CharType> void InitGoogleTestImpl(int* argc, CharType** argv) { - g_init_gtest_count++; - // We don't want to run the initialization code twice. - if (g_init_gtest_count != 1) return; + if (GTestIsInitialized()) return; if (*argc <= 0) return; - internal::g_executable_path = internal::StreamableToString(argv[0]); - -#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - g_argvs.clear(); for (int i = 0; i != *argc; i++) { g_argvs.push_back(StreamableToString(argv[i])); } -#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL + absl::InitializeSymbolizer(g_argvs[0].c_str()); +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL ParseGoogleTestFlagsOnly(argc, argv); GetUnitTestImpl()->PostFlagParsingInit(); @@ -6355,13 +8149,89 @@ void InitGoogleTestImpl(int* argc, CharType** argv) { // // Calling the function for the second time has no user-visible effect. void InitGoogleTest(int* argc, char** argv) { +#if defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_) + GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_(argc, argv); +#else // defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_) internal::InitGoogleTestImpl(argc, argv); +#endif // defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_) } // This overloaded version can be used in Windows programs compiled in // UNICODE mode. void InitGoogleTest(int* argc, wchar_t** argv) { +#if defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_) + GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_(argc, argv); +#else // defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_) internal::InitGoogleTestImpl(argc, argv); +#endif // defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_) +} + +// This overloaded version can be used on Arduino/embedded platforms where +// there is no argc/argv. +void InitGoogleTest() { + // Since Arduino doesn't have a command line, fake out the argc/argv arguments + int argc = 1; + const auto arg0 = "dummy"; + char* argv0 = const_cast<char*>(arg0); + char** argv = &argv0; + +#if defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_) + GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_(&argc, argv); +#else // defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_) + internal::InitGoogleTestImpl(&argc, argv); +#endif // defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_FUNCTION_) +} + +std::string TempDir() { +#if defined(GTEST_CUSTOM_TEMPDIR_FUNCTION_) + return GTEST_CUSTOM_TEMPDIR_FUNCTION_(); +#elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE + return "\\temp\\"; +#elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + const char* temp_dir = internal::posix::GetEnv("TEMP"); + if (temp_dir == nullptr || temp_dir[0] == '\0') { + return "\\temp\\"; + } else if (temp_dir[strlen(temp_dir) - 1] == '\\') { + return temp_dir; + } else { + return std::string(temp_dir) + "\\"; + } +#elif GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID + const char* temp_dir = internal::posix::GetEnv("TEST_TMPDIR"); + if (temp_dir == nullptr || temp_dir[0] == '\0') { + return "/data/local/tmp/"; + } else { + return temp_dir; + } +#elif GTEST_OS_LINUX + const char* temp_dir = internal::posix::GetEnv("TEST_TMPDIR"); + if (temp_dir == nullptr || temp_dir[0] == '\0') { + return "/tmp/"; + } else { + return temp_dir; + } +#else + return "/tmp/"; +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +} + +// Class ScopedTrace + +// Pushes the given source file location and message onto a per-thread +// trace stack maintained by Google Test. +void ScopedTrace::PushTrace(const char* file, int line, std::string message) { + internal::TraceInfo trace; + trace.file = file; + trace.line = line; + trace.message.swap(message); + + UnitTest::GetInstance()->PushGTestTrace(trace); +} + +// Pops the info pushed by the c'tor. +ScopedTrace::~ScopedTrace() + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(&UnitTest::mutex_) { + UnitTest::GetInstance()->PopGTestTrace(); } } // namespace testing @@ -6393,54 +8263,69 @@ void InitGoogleTest(int* argc, wchar_t** argv) { // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan), vladl@google.com (Vlad Losev) + // // This file implements death tests. -#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST -# if GTEST_OS_MAC -# include <crt_externs.h> -# endif // GTEST_OS_MAC +#include <functional> +#include <utility> -# include <errno.h> -# include <fcntl.h> -# include <limits.h> -# if GTEST_OS_LINUX -# include <signal.h> -# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST -# include <stdarg.h> +# if GTEST_OS_MAC +# include <crt_externs.h> +# endif // GTEST_OS_MAC -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -# include <windows.h> -# else -# include <sys/mman.h> -# include <sys/wait.h> -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# include <errno.h> +# include <fcntl.h> +# include <limits.h> -# if GTEST_OS_QNX -# include <spawn.h> -# endif // GTEST_OS_QNX +# if GTEST_OS_LINUX +# include <signal.h> +# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX + +# include <stdarg.h> + +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# include <windows.h> +# else +# include <sys/mman.h> +# include <sys/wait.h> +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +# if GTEST_OS_QNX +# include <spawn.h> +# endif // GTEST_OS_QNX + +# if GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA +# include <lib/fdio/fd.h> +# include <lib/fdio/io.h> +# include <lib/fdio/spawn.h> +# include <lib/zx/channel.h> +# include <lib/zx/port.h> +# include <lib/zx/process.h> +# include <lib/zx/socket.h> +# include <zircon/processargs.h> +# include <zircon/syscalls.h> +# include <zircon/syscalls/policy.h> +# include <zircon/syscalls/port.h> +# endif // GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA #endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST -// Indicates that this translation unit is part of Google Test's -// implementation. It must come before gtest-internal-inl.h is -// included, or there will be a compiler error. This trick is to -// prevent a user from accidentally including gtest-internal-inl.h in -// his code. -#define GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ 1 -#undef GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ namespace testing { // Constants. // The default death test style. -static const char kDefaultDeathTestStyle[] = "fast"; +// +// This is defined in internal/gtest-port.h as "fast", but can be overridden by +// a definition in internal/custom/gtest-port.h. The recommended value, which is +// used internally at Google, is "threadsafe". +static const char kDefaultDeathTestStyle[] = GTEST_DEFAULT_DEATH_TEST_STYLE; GTEST_DEFINE_string_( death_test_style, @@ -6469,8 +8354,8 @@ GTEST_DEFINE_string_( "Indicates the file, line number, temporal index of " "the single death test to run, and a file descriptor to " "which a success code may be sent, all separated by " - "the '|' characters. This flag is specified if and only if the current " - "process is a sub-process launched for running a thread-safe " + "the '|' characters. This flag is specified if and only if the " + "current process is a sub-process launched for running a thread-safe " "death test. FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY."); } // namespace internal @@ -6480,7 +8365,9 @@ namespace internal { // Valid only for fast death tests. Indicates the code is running in the // child process of a fast style death test. +# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA static bool g_in_fast_death_test_child = false; +# endif // Returns a Boolean value indicating whether the caller is currently // executing in the context of the death test child process. Tools such as @@ -6488,48 +8375,58 @@ static bool g_in_fast_death_test_child = false; // tests. IMPORTANT: This is an internal utility. Using it may break the // implementation of death tests. User code MUST NOT use it. bool InDeathTestChild() { -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS || GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA - // On Windows, death tests are thread-safe regardless of the value of the - // death_test_style flag. + // On Windows and Fuchsia, death tests are thread-safe regardless of the value + // of the death_test_style flag. return !GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test).empty(); -# else +# else if (GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) == "threadsafe") return !GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test).empty(); else return g_in_fast_death_test_child; -# endif +#endif } } // namespace internal // ExitedWithCode constructor. -ExitedWithCode::ExitedWithCode(int exit_code) : exit_code_(exit_code) {} +ExitedWithCode::ExitedWithCode(int exit_code) : exit_code_(exit_code) { +} // ExitedWithCode function-call operator. bool ExitedWithCode::operator()(int exit_status) const { -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS || GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA return exit_status == exit_code_; -# else +# else return WIFEXITED(exit_status) && WEXITSTATUS(exit_status) == exit_code_; -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS || GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA } -# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA // KilledBySignal constructor. -KilledBySignal::KilledBySignal(int signum) : signum_(signum) {} +KilledBySignal::KilledBySignal(int signum) : signum_(signum) { +} // KilledBySignal function-call operator. bool KilledBySignal::operator()(int exit_status) const { +# if defined(GTEST_KILLED_BY_SIGNAL_OVERRIDE_) + { + bool result; + if (GTEST_KILLED_BY_SIGNAL_OVERRIDE_(signum_, exit_status, &result)) { + return result; + } + } +# endif // defined(GTEST_KILLED_BY_SIGNAL_OVERRIDE_) return WIFSIGNALED(exit_status) && WTERMSIG(exit_status) == signum_; } -# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA namespace internal { @@ -6540,23 +8437,23 @@ namespace internal { static std::string ExitSummary(int exit_code) { Message m; -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS || GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA m << "Exited with exit status " << exit_code; -# else +# else if (WIFEXITED(exit_code)) { m << "Exited with exit status " << WEXITSTATUS(exit_code); } else if (WIFSIGNALED(exit_code)) { m << "Terminated by signal " << WTERMSIG(exit_code); } -# ifdef WCOREDUMP +# ifdef WCOREDUMP if (WCOREDUMP(exit_code)) { m << " (core dumped)"; } -# endif -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# endif +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS || GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA return m.GetString(); } @@ -6567,7 +8464,7 @@ bool ExitedUnsuccessfully(int exit_status) { return !ExitedWithCode(0)(exit_status); } -# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA // Generates a textual failure message when a death test finds more than // one thread running, or cannot determine the number of threads, prior // to executing the given statement. It is the responsibility of the @@ -6576,13 +8473,19 @@ static std::string DeathTestThreadWarning(size_t thread_count) { Message msg; msg << "Death tests use fork(), which is unsafe particularly" << " in a threaded context. For this test, " << GTEST_NAME_ << " "; - if (thread_count == 0) + if (thread_count == 0) { msg << "couldn't detect the number of threads."; - else + } else { msg << "detected " << thread_count << " threads."; + } + msg << " See " + "https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/docs/" + "advanced.md#death-tests-and-threads" + << " for more explanation and suggested solutions, especially if" + << " this is the last message you see before your test times out."; return msg.GetString(); } -# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA // Flag characters for reporting a death test that did not die. static const char kDeathTestLived = 'L'; @@ -6590,6 +8493,13 @@ static const char kDeathTestReturned = 'R'; static const char kDeathTestThrew = 'T'; static const char kDeathTestInternalError = 'I'; +#if GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA + +// File descriptor used for the pipe in the child process. +static const int kFuchsiaReadPipeFd = 3; + +#endif + // An enumeration describing all of the possible ways that a death test can // conclude. DIED means that the process died while executing the test // code; LIVED means that process lived beyond the end of the test code; @@ -6597,8 +8507,6 @@ static const char kDeathTestInternalError = 'I'; // statement, which is not allowed; THREW means that the test statement // returned control by throwing an exception. IN_PROGRESS means the test // has not yet concluded. -// TODO(vladl@google.com): Unify names and possibly values for -// AbortReason, DeathTestOutcome, and flag characters above. enum DeathTestOutcome { IN_PROGRESS, DIED, LIVED, RETURNED, THREW }; // Routine for aborting the program which is safe to call from an @@ -6606,13 +8514,13 @@ enum DeathTestOutcome { IN_PROGRESS, DIED, LIVED, RETURNED, THREW }; // message is propagated back to the parent process. Otherwise, the // message is simply printed to stderr. In either case, the program // then exits with status 1. -void DeathTestAbort(const std::string& message) { +static void DeathTestAbort(const std::string& message) { // On a POSIX system, this function may be called from a threadsafe-style // death test child process, which operates on a very small stack. Use // the heap for any additional non-minuscule memory requirements. const InternalRunDeathTestFlag* const flag = GetUnitTestImpl()->internal_run_death_test_flag(); - if (flag != NULL) { + if (flag != nullptr) { FILE* parent = posix::FDOpen(flag->write_fd(), "w"); fputc(kDeathTestInternalError, parent); fprintf(parent, "%s", message.c_str()); @@ -6627,15 +8535,15 @@ void DeathTestAbort(const std::string& message) { // A replacement for CHECK that calls DeathTestAbort if the assertion // fails. -# define GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(expression) \ - do { \ - if (!::testing::internal::IsTrue(expression)) { \ - DeathTestAbort(::std::string("CHECK failed: File ") + __FILE__ + \ - ", line " + \ - ::testing::internal::StreamableToString(__LINE__) + \ - ": " + #expression); \ - } \ - } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) +# define GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(expression) \ + do { \ + if (!::testing::internal::IsTrue(expression)) { \ + DeathTestAbort( \ + ::std::string("CHECK failed: File ") + __FILE__ + ", line " \ + + ::testing::internal::StreamableToString(__LINE__) + ": " \ + + #expression); \ + } \ + } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) // This macro is similar to GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_, but it is meant for // evaluating any system call that fulfills two conditions: it must return @@ -6644,23 +8552,23 @@ void DeathTestAbort(const std::string& message) { // evaluates the expression as long as it evaluates to -1 and sets // errno to EINTR. If the expression evaluates to -1 but errno is // something other than EINTR, DeathTestAbort is called. -# define GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_(expression) \ - do { \ - int gtest_retval; \ - do { \ - gtest_retval = (expression); \ - } while (gtest_retval == -1 && errno == EINTR); \ - if (gtest_retval == -1) { \ - DeathTestAbort(::std::string("CHECK failed: File ") + __FILE__ + \ - ", line " + \ - ::testing::internal::StreamableToString(__LINE__) + \ - ": " + #expression + " != -1"); \ - } \ - } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) +# define GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_(expression) \ + do { \ + int gtest_retval; \ + do { \ + gtest_retval = (expression); \ + } while (gtest_retval == -1 && errno == EINTR); \ + if (gtest_retval == -1) { \ + DeathTestAbort( \ + ::std::string("CHECK failed: File ") + __FILE__ + ", line " \ + + ::testing::internal::StreamableToString(__LINE__) + ": " \ + + #expression + " != -1"); \ + } \ + } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) // Returns the message describing the last system error in errno. std::string GetLastErrnoDescription() { - return errno == 0 ? "" : posix::StrError(errno); + return errno == 0 ? "" : posix::StrError(errno); } // This is called from a death test parent process to read a failure @@ -6692,19 +8600,19 @@ static void FailFromInternalError(int fd) { // for the current test. DeathTest::DeathTest() { TestInfo* const info = GetUnitTestImpl()->current_test_info(); - if (info == NULL) { - DeathTestAbort( - "Cannot run a death test outside of a TEST or " - "TEST_F construct"); + if (info == nullptr) { + DeathTestAbort("Cannot run a death test outside of a TEST or " + "TEST_F construct"); } } // Creates and returns a death test by dispatching to the current // death test factory. -bool DeathTest::Create(const char* statement, const RE* regex, const char* file, +bool DeathTest::Create(const char* statement, + Matcher<const std::string&> matcher, const char* file, int line, DeathTest** test) { - return GetUnitTestImpl()->death_test_factory()->Create(statement, regex, file, - line, test); + return GetUnitTestImpl()->death_test_factory()->Create( + statement, std::move(matcher), file, line, test); } const char* DeathTest::LastMessage() { @@ -6720,9 +8628,9 @@ std::string DeathTest::last_death_test_message_; // Provides cross platform implementation for some death functionality. class DeathTestImpl : public DeathTest { protected: - DeathTestImpl(const char* a_statement, const RE* a_regex) + DeathTestImpl(const char* a_statement, Matcher<const std::string&> matcher) : statement_(a_statement), - regex_(a_regex), + matcher_(std::move(matcher)), spawned_(false), status_(-1), outcome_(IN_PROGRESS), @@ -6730,13 +8638,12 @@ class DeathTestImpl : public DeathTest { write_fd_(-1) {} // read_fd_ is expected to be closed and cleared by a derived class. - ~DeathTestImpl() { GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(read_fd_ == -1); } + ~DeathTestImpl() override { GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(read_fd_ == -1); } - void Abort(AbortReason reason); - virtual bool Passed(bool status_ok); + void Abort(AbortReason reason) override; + bool Passed(bool status_ok) override; const char* statement() const { return statement_; } - const RE* regex() const { return regex_; } bool spawned() const { return spawned_; } void set_spawned(bool is_spawned) { spawned_ = is_spawned; } int status() const { return status_; } @@ -6754,13 +8661,15 @@ class DeathTestImpl : public DeathTest { // case of unexpected codes. void ReadAndInterpretStatusByte(); + // Returns stderr output from the child process. + virtual std::string GetErrorLogs(); + private: // The textual content of the code this object is testing. This class // doesn't own this string and should not attempt to delete it. const char* const statement_; - // The regular expression which test output must match. DeathTestImpl - // doesn't own this object and should not attempt to delete it. - const RE* const regex_; + // A matcher that's expected to match the stderr output by the child process. + Matcher<const std::string&> matcher_; // True if the death test child process has been successfully spawned. bool spawned_; // The exit status of the child process. @@ -6797,22 +8706,22 @@ void DeathTestImpl::ReadAndInterpretStatusByte() { set_outcome(DIED); } else if (bytes_read == 1) { switch (flag) { - case kDeathTestReturned: - set_outcome(RETURNED); - break; - case kDeathTestThrew: - set_outcome(THREW); - break; - case kDeathTestLived: - set_outcome(LIVED); - break; - case kDeathTestInternalError: - FailFromInternalError(read_fd()); // Does not return. - break; - default: - GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "Death test child process reported " - << "unexpected status byte (" - << static_cast<unsigned int>(flag) << ")"; + case kDeathTestReturned: + set_outcome(RETURNED); + break; + case kDeathTestThrew: + set_outcome(THREW); + break; + case kDeathTestLived: + set_outcome(LIVED); + break; + case kDeathTestInternalError: + FailFromInternalError(read_fd()); // Does not return. + break; + default: + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "Death test child process reported " + << "unexpected status byte (" + << static_cast<unsigned int>(flag) << ")"; } } else { GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "Read from death test child process failed: " @@ -6822,6 +8731,10 @@ void DeathTestImpl::ReadAndInterpretStatusByte() { set_read_fd(-1); } +std::string DeathTestImpl::GetErrorLogs() { + return GetCapturedStderr(); +} + // Signals that the death test code which should have exited, didn't. // Should be called only in a death test child process. // Writes a status byte to the child's status file descriptor, then @@ -6830,11 +8743,9 @@ void DeathTestImpl::Abort(AbortReason reason) { // The parent process considers the death test to be a failure if // it finds any data in our pipe. So, here we write a single flag byte // to the pipe, then exit. - const char status_ch = reason == TEST_DID_NOT_DIE - ? kDeathTestLived - : reason == TEST_THREW_EXCEPTION - ? kDeathTestThrew - : kDeathTestReturned; + const char status_ch = + reason == TEST_DID_NOT_DIE ? kDeathTestLived : + reason == TEST_THREW_EXCEPTION ? kDeathTestThrew : kDeathTestReturned; GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_(posix::Write(write_fd(), &status_ch, 1)); // We are leaking the descriptor here because on some platforms (i.e., @@ -6853,7 +8764,7 @@ void DeathTestImpl::Abort(AbortReason reason) { // much easier. static ::std::string FormatDeathTestOutput(const ::std::string& output) { ::std::string ret; - for (size_t at = 0;;) { + for (size_t at = 0; ; ) { const size_t line_end = output.find('\n', at); ret += "[ DEATH ] "; if (line_end == ::std::string::npos) { @@ -6877,71 +8788,68 @@ static ::std::string FormatDeathTestOutput(const ::std::string& output) { // in the format specified by wait(2). On Windows, this is the // value supplied to the ExitProcess() API or a numeric code // of the exception that terminated the program. -// regex: A regular expression object to be applied to -// the test's captured standard error output; the death test -// fails if it does not match. +// matcher_: A matcher that's expected to match the stderr output by the child +// process. // // Argument: // status_ok: true if exit_status is acceptable in the context of // this particular death test, which fails if it is false // -// Returns true iff all of the above conditions are met. Otherwise, the -// first failing condition, in the order given above, is the one that is +// Returns true if and only if all of the above conditions are met. Otherwise, +// the first failing condition, in the order given above, is the one that is // reported. Also sets the last death test message string. bool DeathTestImpl::Passed(bool status_ok) { - if (!spawned()) return false; + if (!spawned()) + return false; - const std::string error_message = GetCapturedStderr(); + const std::string error_message = GetErrorLogs(); bool success = false; Message buffer; buffer << "Death test: " << statement() << "\n"; switch (outcome()) { - case LIVED: - buffer << " Result: failed to die.\n" - << " Error msg:\n" - << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); - break; - case THREW: - buffer << " Result: threw an exception.\n" - << " Error msg:\n" - << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); - break; - case RETURNED: - buffer << " Result: illegal return in test statement.\n" - << " Error msg:\n" - << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); - break; - case DIED: - if (status_ok) { - const bool matched = RE::PartialMatch(error_message.c_str(), *regex()); - if (matched) { - success = true; + case LIVED: + buffer << " Result: failed to die.\n" + << " Error msg:\n" << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); + break; + case THREW: + buffer << " Result: threw an exception.\n" + << " Error msg:\n" << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); + break; + case RETURNED: + buffer << " Result: illegal return in test statement.\n" + << " Error msg:\n" << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); + break; + case DIED: + if (status_ok) { + if (matcher_.Matches(error_message)) { + success = true; + } else { + std::ostringstream stream; + matcher_.DescribeTo(&stream); + buffer << " Result: died but not with expected error.\n" + << " Expected: " << stream.str() << "\n" + << "Actual msg:\n" + << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); + } } else { - buffer << " Result: died but not with expected error.\n" - << " Expected: " << regex()->pattern() << "\n" - << "Actual msg:\n" - << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); + buffer << " Result: died but not with expected exit code:\n" + << " " << ExitSummary(status()) << "\n" + << "Actual msg:\n" << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); } - } else { - buffer << " Result: died but not with expected exit code:\n" - << " " << ExitSummary(status()) << "\n" - << "Actual msg:\n" - << FormatDeathTestOutput(error_message); - } - break; - case IN_PROGRESS: - default: - GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) - << "DeathTest::Passed somehow called before conclusion of test"; + break; + case IN_PROGRESS: + default: + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) + << "DeathTest::Passed somehow called before conclusion of test"; } DeathTest::set_last_death_test_message(buffer.GetString()); return success; } -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS // WindowsDeathTest implements death tests on Windows. Due to the // specifics of starting new processes on Windows, death tests there are // always threadsafe, and Google Test considers the @@ -6972,9 +8880,11 @@ bool DeathTestImpl::Passed(bool status_ok) { // class WindowsDeathTest : public DeathTestImpl { public: - WindowsDeathTest(const char* a_statement, const RE* a_regex, const char* file, - int line) - : DeathTestImpl(a_statement, a_regex), file_(file), line_(line) {} + WindowsDeathTest(const char* a_statement, Matcher<const std::string&> matcher, + const char* file, int line) + : DeathTestImpl(a_statement, std::move(matcher)), + file_(file), + line_(line) {} // All of these virtual functions are inherited from DeathTest. virtual int Wait(); @@ -7000,19 +8910,21 @@ class WindowsDeathTest : public DeathTestImpl { // status, or 0 if no child process exists. As a side effect, sets the // outcome data member. int WindowsDeathTest::Wait() { - if (!spawned()) return 0; + if (!spawned()) + return 0; // Wait until the child either signals that it has acquired the write end // of the pipe or it dies. - const HANDLE wait_handles[2] = {child_handle_.Get(), event_handle_.Get()}; - switch (::WaitForMultipleObjects(2, wait_handles, + const HANDLE wait_handles[2] = { child_handle_.Get(), event_handle_.Get() }; + switch (::WaitForMultipleObjects(2, + wait_handles, FALSE, // Waits for any of the handles. INFINITE)) { - case WAIT_OBJECT_0: - case WAIT_OBJECT_0 + 1: - break; - default: - GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(false); // Should not get here. + case WAIT_OBJECT_0: + case WAIT_OBJECT_0 + 1: + break; + default: + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(false); // Should not get here. } // The child has acquired the write end of the pipe or exited. @@ -7026,8 +8938,9 @@ int WindowsDeathTest::Wait() { // returns immediately if the child has already exited, regardless of // whether previous calls to WaitForMultipleObjects synchronized on this // handle or not. - GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(WAIT_OBJECT_0 == - ::WaitForSingleObject(child_handle_.Get(), INFINITE)); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_( + WAIT_OBJECT_0 == ::WaitForSingleObject(child_handle_.Get(), + INFINITE)); DWORD status_code; GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_( ::GetExitCodeProcess(child_handle_.Get(), &status_code) != FALSE); @@ -7048,7 +8961,7 @@ DeathTest::TestRole WindowsDeathTest::AssumeRole() { const TestInfo* const info = impl->current_test_info(); const int death_test_index = info->result()->death_test_count(); - if (flag != NULL) { + if (flag != nullptr) { // ParseInternalRunDeathTestFlag() has performed all the necessary // processing. set_write_fd(flag->write_fd()); @@ -7058,41 +8971,43 @@ DeathTest::TestRole WindowsDeathTest::AssumeRole() { // WindowsDeathTest uses an anonymous pipe to communicate results of // a death test. SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES handles_are_inheritable = {sizeof(SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES), - NULL, TRUE}; + nullptr, TRUE}; HANDLE read_handle, write_handle; - GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(::CreatePipe(&read_handle, &write_handle, - &handles_are_inheritable, - 0) // Default buffer size. - != FALSE); - set_read_fd( - ::_open_osfhandle(reinterpret_cast<intptr_t>(read_handle), O_RDONLY)); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_( + ::CreatePipe(&read_handle, &write_handle, &handles_are_inheritable, + 0) // Default buffer size. + != FALSE); + set_read_fd(::_open_osfhandle(reinterpret_cast<intptr_t>(read_handle), + O_RDONLY)); write_handle_.Reset(write_handle); event_handle_.Reset(::CreateEvent( &handles_are_inheritable, - TRUE, // The event will automatically reset to non-signaled state. - FALSE, // The initial state is non-signalled. - NULL)); // The even is unnamed. - GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(event_handle_.Get() != NULL); + TRUE, // The event will automatically reset to non-signaled state. + FALSE, // The initial state is non-signalled. + nullptr)); // The even is unnamed. + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(event_handle_.Get() != nullptr); const std::string filter_flag = std::string("--") + GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + - kFilterFlag + "=" + info->test_case_name() + + kFilterFlag + "=" + info->test_suite_name() + "." + info->name(); const std::string internal_flag = - std::string("--") + GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + kInternalRunDeathTestFlag + "=" + - file_ + "|" + StreamableToString(line_) + "|" + + std::string("--") + GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + kInternalRunDeathTestFlag + + "=" + file_ + "|" + StreamableToString(line_) + "|" + StreamableToString(death_test_index) + "|" + StreamableToString(static_cast<unsigned int>(::GetCurrentProcessId())) + // size_t has the same width as pointers on both 32-bit and 64-bit // Windows platforms. // See http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/tcxf1dw6.aspx. - "|" + StreamableToString(reinterpret_cast<size_t>(write_handle)) + "|" + - StreamableToString(reinterpret_cast<size_t>(event_handle_.Get())); + "|" + StreamableToString(reinterpret_cast<size_t>(write_handle)) + + "|" + StreamableToString(reinterpret_cast<size_t>(event_handle_.Get())); char executable_path[_MAX_PATH + 1]; // NOLINT - GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_( - _MAX_PATH + 1 != ::GetModuleFileNameA(NULL, executable_path, _MAX_PATH)); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(_MAX_PATH + 1 != ::GetModuleFileNameA(nullptr, + executable_path, + _MAX_PATH)); - std::string command_line = std::string(::GetCommandLineA()) + " " + - filter_flag + " \"" + internal_flag + "\""; + std::string command_line = + std::string(::GetCommandLineA()) + " " + filter_flag + " \"" + + internal_flag + "\""; DeathTest::set_last_death_test_message(""); @@ -7112,11 +9027,11 @@ DeathTest::TestRole WindowsDeathTest::AssumeRole() { GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_( ::CreateProcessA( executable_path, const_cast<char*>(command_line.c_str()), - NULL, // Retuned process handle is not inheritable. - NULL, // Retuned thread handle is not inheritable. + nullptr, // Retuned process handle is not inheritable. + nullptr, // Retuned thread handle is not inheritable. TRUE, // Child inherits all inheritable handles (for write_handle_). 0x0, // Default creation flags. - NULL, // Inherit the parent's environment. + nullptr, // Inherit the parent's environment. UnitTest::GetInstance()->original_working_dir(), &startup_info, &process_info) != FALSE); child_handle_.Reset(process_info.hProcess); @@ -7124,17 +9039,273 @@ DeathTest::TestRole WindowsDeathTest::AssumeRole() { set_spawned(true); return OVERSEE_TEST; } -# else // We are not on Windows. + +# elif GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA + +class FuchsiaDeathTest : public DeathTestImpl { + public: + FuchsiaDeathTest(const char* a_statement, Matcher<const std::string&> matcher, + const char* file, int line) + : DeathTestImpl(a_statement, std::move(matcher)), + file_(file), + line_(line) {} + + // All of these virtual functions are inherited from DeathTest. + int Wait() override; + TestRole AssumeRole() override; + std::string GetErrorLogs() override; + + private: + // The name of the file in which the death test is located. + const char* const file_; + // The line number on which the death test is located. + const int line_; + // The stderr data captured by the child process. + std::string captured_stderr_; + + zx::process child_process_; + zx::channel exception_channel_; + zx::socket stderr_socket_; +}; + +// Utility class for accumulating command-line arguments. +class Arguments { + public: + Arguments() { args_.push_back(nullptr); } + + ~Arguments() { + for (std::vector<char*>::iterator i = args_.begin(); i != args_.end(); + ++i) { + free(*i); + } + } + void AddArgument(const char* argument) { + args_.insert(args_.end() - 1, posix::StrDup(argument)); + } + + template <typename Str> + void AddArguments(const ::std::vector<Str>& arguments) { + for (typename ::std::vector<Str>::const_iterator i = arguments.begin(); + i != arguments.end(); + ++i) { + args_.insert(args_.end() - 1, posix::StrDup(i->c_str())); + } + } + char* const* Argv() { + return &args_[0]; + } + + int size() { + return static_cast<int>(args_.size()) - 1; + } + + private: + std::vector<char*> args_; +}; + +// Waits for the child in a death test to exit, returning its exit +// status, or 0 if no child process exists. As a side effect, sets the +// outcome data member. +int FuchsiaDeathTest::Wait() { + const int kProcessKey = 0; + const int kSocketKey = 1; + const int kExceptionKey = 2; + + if (!spawned()) + return 0; + + // Create a port to wait for socket/task/exception events. + zx_status_t status_zx; + zx::port port; + status_zx = zx::port::create(0, &port); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status_zx == ZX_OK); + + // Register to wait for the child process to terminate. + status_zx = child_process_.wait_async( + port, kProcessKey, ZX_PROCESS_TERMINATED, 0); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status_zx == ZX_OK); + + // Register to wait for the socket to be readable or closed. + status_zx = stderr_socket_.wait_async( + port, kSocketKey, ZX_SOCKET_READABLE | ZX_SOCKET_PEER_CLOSED, 0); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status_zx == ZX_OK); + + // Register to wait for an exception. + status_zx = exception_channel_.wait_async( + port, kExceptionKey, ZX_CHANNEL_READABLE, 0); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status_zx == ZX_OK); + + bool process_terminated = false; + bool socket_closed = false; + do { + zx_port_packet_t packet = {}; + status_zx = port.wait(zx::time::infinite(), &packet); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status_zx == ZX_OK); + + if (packet.key == kExceptionKey) { + // Process encountered an exception. Kill it directly rather than + // letting other handlers process the event. We will get a kProcessKey + // event when the process actually terminates. + status_zx = child_process_.kill(); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status_zx == ZX_OK); + } else if (packet.key == kProcessKey) { + // Process terminated. + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(ZX_PKT_IS_SIGNAL_ONE(packet.type)); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(packet.signal.observed & ZX_PROCESS_TERMINATED); + process_terminated = true; + } else if (packet.key == kSocketKey) { + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(ZX_PKT_IS_SIGNAL_ONE(packet.type)); + if (packet.signal.observed & ZX_SOCKET_READABLE) { + // Read data from the socket. + constexpr size_t kBufferSize = 1024; + do { + size_t old_length = captured_stderr_.length(); + size_t bytes_read = 0; + captured_stderr_.resize(old_length + kBufferSize); + status_zx = stderr_socket_.read( + 0, &captured_stderr_.front() + old_length, kBufferSize, + &bytes_read); + captured_stderr_.resize(old_length + bytes_read); + } while (status_zx == ZX_OK); + if (status_zx == ZX_ERR_PEER_CLOSED) { + socket_closed = true; + } else { + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status_zx == ZX_ERR_SHOULD_WAIT); + status_zx = stderr_socket_.wait_async( + port, kSocketKey, ZX_SOCKET_READABLE | ZX_SOCKET_PEER_CLOSED, 0); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status_zx == ZX_OK); + } + } else { + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(packet.signal.observed & ZX_SOCKET_PEER_CLOSED); + socket_closed = true; + } + } + } while (!process_terminated && !socket_closed); + + ReadAndInterpretStatusByte(); + + zx_info_process_v2_t buffer; + status_zx = child_process_.get_info( + ZX_INFO_PROCESS_V2, &buffer, sizeof(buffer), nullptr, nullptr); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status_zx == ZX_OK); + + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(buffer.flags & ZX_INFO_PROCESS_FLAG_EXITED); + set_status(static_cast<int>(buffer.return_code)); + return status(); +} + +// The AssumeRole process for a Fuchsia death test. It creates a child +// process with the same executable as the current process to run the +// death test. The child process is given the --gtest_filter and +// --gtest_internal_run_death_test flags such that it knows to run the +// current death test only. +DeathTest::TestRole FuchsiaDeathTest::AssumeRole() { + const UnitTestImpl* const impl = GetUnitTestImpl(); + const InternalRunDeathTestFlag* const flag = + impl->internal_run_death_test_flag(); + const TestInfo* const info = impl->current_test_info(); + const int death_test_index = info->result()->death_test_count(); + + if (flag != nullptr) { + // ParseInternalRunDeathTestFlag() has performed all the necessary + // processing. + set_write_fd(kFuchsiaReadPipeFd); + return EXECUTE_TEST; + } + + // Flush the log buffers since the log streams are shared with the child. + FlushInfoLog(); + + // Build the child process command line. + const std::string filter_flag = std::string("--") + GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + + kFilterFlag + "=" + info->test_suite_name() + + "." + info->name(); + const std::string internal_flag = + std::string("--") + GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + kInternalRunDeathTestFlag + "=" + + file_ + "|" + + StreamableToString(line_) + "|" + + StreamableToString(death_test_index); + Arguments args; + args.AddArguments(GetInjectableArgvs()); + args.AddArgument(filter_flag.c_str()); + args.AddArgument(internal_flag.c_str()); + + // Build the pipe for communication with the child. + zx_status_t status; + zx_handle_t child_pipe_handle; + int child_pipe_fd; + status = fdio_pipe_half(&child_pipe_fd, &child_pipe_handle); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status == ZX_OK); + set_read_fd(child_pipe_fd); + + // Set the pipe handle for the child. + fdio_spawn_action_t spawn_actions[2] = {}; + fdio_spawn_action_t* add_handle_action = &spawn_actions[0]; + add_handle_action->action = FDIO_SPAWN_ACTION_ADD_HANDLE; + add_handle_action->h.id = PA_HND(PA_FD, kFuchsiaReadPipeFd); + add_handle_action->h.handle = child_pipe_handle; + + // Create a socket pair will be used to receive the child process' stderr. + zx::socket stderr_producer_socket; + status = + zx::socket::create(0, &stderr_producer_socket, &stderr_socket_); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status >= 0); + int stderr_producer_fd = -1; + status = + fdio_fd_create(stderr_producer_socket.release(), &stderr_producer_fd); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status >= 0); + + // Make the stderr socket nonblocking. + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(fcntl(stderr_producer_fd, F_SETFL, 0) == 0); + + fdio_spawn_action_t* add_stderr_action = &spawn_actions[1]; + add_stderr_action->action = FDIO_SPAWN_ACTION_CLONE_FD; + add_stderr_action->fd.local_fd = stderr_producer_fd; + add_stderr_action->fd.target_fd = STDERR_FILENO; + + // Create a child job. + zx_handle_t child_job = ZX_HANDLE_INVALID; + status = zx_job_create(zx_job_default(), 0, & child_job); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status == ZX_OK); + zx_policy_basic_t policy; + policy.condition = ZX_POL_NEW_ANY; + policy.policy = ZX_POL_ACTION_ALLOW; + status = zx_job_set_policy( + child_job, ZX_JOB_POL_RELATIVE, ZX_JOB_POL_BASIC, &policy, 1); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status == ZX_OK); + + // Create an exception channel attached to the |child_job|, to allow + // us to suppress the system default exception handler from firing. + status = + zx_task_create_exception_channel( + child_job, 0, exception_channel_.reset_and_get_address()); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status == ZX_OK); + + // Spawn the child process. + status = fdio_spawn_etc( + child_job, FDIO_SPAWN_CLONE_ALL, args.Argv()[0], args.Argv(), nullptr, + 2, spawn_actions, child_process_.reset_and_get_address(), nullptr); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(status == ZX_OK); + + set_spawned(true); + return OVERSEE_TEST; +} + +std::string FuchsiaDeathTest::GetErrorLogs() { + return captured_stderr_; +} + +#else // We are neither on Windows, nor on Fuchsia. // ForkingDeathTest provides implementations for most of the abstract // methods of the DeathTest interface. Only the AssumeRole method is // left undefined. class ForkingDeathTest : public DeathTestImpl { public: - ForkingDeathTest(const char* statement, const RE* regex); + ForkingDeathTest(const char* statement, Matcher<const std::string&> matcher); // All of these virtual functions are inherited from DeathTest. - virtual int Wait(); + int Wait() override; protected: void set_child_pid(pid_t child_pid) { child_pid_ = child_pid; } @@ -7145,14 +9316,16 @@ class ForkingDeathTest : public DeathTestImpl { }; // Constructs a ForkingDeathTest. -ForkingDeathTest::ForkingDeathTest(const char* a_statement, const RE* a_regex) - : DeathTestImpl(a_statement, a_regex), child_pid_(-1) {} +ForkingDeathTest::ForkingDeathTest(const char* a_statement, + Matcher<const std::string&> matcher) + : DeathTestImpl(a_statement, std::move(matcher)), child_pid_(-1) {} // Waits for the child in a death test to exit, returning its exit // status, or 0 if no child process exists. As a side effect, sets the // outcome data member. int ForkingDeathTest::Wait() { - if (!spawned()) return 0; + if (!spawned()) + return 0; ReadAndInterpretStatusByte(); @@ -7166,9 +9339,9 @@ int ForkingDeathTest::Wait() { // in the child process. class NoExecDeathTest : public ForkingDeathTest { public: - NoExecDeathTest(const char* a_statement, const RE* a_regex) - : ForkingDeathTest(a_statement, a_regex) {} - virtual TestRole AssumeRole(); + NoExecDeathTest(const char* a_statement, Matcher<const std::string&> matcher) + : ForkingDeathTest(a_statement, std::move(matcher)) {} + TestRole AssumeRole() override; }; // The AssumeRole process for a fork-and-run death test. It implements a @@ -7221,15 +9394,21 @@ DeathTest::TestRole NoExecDeathTest::AssumeRole() { // only this specific death test to be run. class ExecDeathTest : public ForkingDeathTest { public: - ExecDeathTest(const char* a_statement, const RE* a_regex, const char* file, - int line) - : ForkingDeathTest(a_statement, a_regex), file_(file), line_(line) {} - virtual TestRole AssumeRole(); + ExecDeathTest(const char* a_statement, Matcher<const std::string&> matcher, + const char* file, int line) + : ForkingDeathTest(a_statement, std::move(matcher)), + file_(file), + line_(line) {} + TestRole AssumeRole() override; private: - static ::std::vector<testing::internal::string> - GetArgvsForDeathTestChildProcess() { - ::std::vector<testing::internal::string> args = GetInjectableArgvs(); + static ::std::vector<std::string> GetArgvsForDeathTestChildProcess() { + ::std::vector<std::string> args = GetInjectableArgvs(); +# if defined(GTEST_EXTRA_DEATH_TEST_COMMAND_LINE_ARGS_) + ::std::vector<std::string> extra_args = + GTEST_EXTRA_DEATH_TEST_COMMAND_LINE_ARGS_(); + args.insert(args.end(), extra_args.begin(), extra_args.end()); +# endif // defined(GTEST_EXTRA_DEATH_TEST_COMMAND_LINE_ARGS_) return args; } // The name of the file in which the death test is located. @@ -7241,7 +9420,7 @@ class ExecDeathTest : public ForkingDeathTest { // Utility class for accumulating command-line arguments. class Arguments { public: - Arguments() { args_.push_back(NULL); } + Arguments() { args_.push_back(nullptr); } ~Arguments() { for (std::vector<char*>::iterator i = args_.begin(); i != args_.end(); @@ -7256,11 +9435,14 @@ class Arguments { template <typename Str> void AddArguments(const ::std::vector<Str>& arguments) { for (typename ::std::vector<Str>::const_iterator i = arguments.begin(); - i != arguments.end(); ++i) { + i != arguments.end(); + ++i) { args_.insert(args_.end() - 1, posix::StrDup(i->c_str())); } } - char* const* Argv() { return &args_[0]; } + char* const* Argv() { + return &args_[0]; + } private: std::vector<char*> args_; @@ -7273,21 +9455,9 @@ struct ExecDeathTestArgs { int close_fd; // File descriptor to close; the read end of a pipe }; -# if GTEST_OS_MAC -inline char** GetEnviron() { - // When Google Test is built as a framework on MacOS X, the environ variable - // is unavailable. Apple's documentation (man environ) recommends using - // _NSGetEnviron() instead. - return *_NSGetEnviron(); -} -# else -// Some POSIX platforms expect you to declare environ. extern "C" makes -// it reside in the global namespace. +# if GTEST_OS_QNX extern "C" char** environ; -inline char** GetEnviron() { return environ; } -# endif // GTEST_OS_MAC - -# if !GTEST_OS_QNX +# else // GTEST_OS_QNX // The main function for a threadsafe-style death test child process. // This function is called in a clone()-ed process and thus must avoid // any potentially unsafe operations like malloc or libc functions. @@ -7302,23 +9472,25 @@ static int ExecDeathTestChildMain(void* child_arg) { UnitTest::GetInstance()->original_working_dir(); // We can safely call chdir() as it's a direct system call. if (chdir(original_dir) != 0) { - DeathTestAbort(std::string("chdir(\"") + original_dir + - "\") failed: " + GetLastErrnoDescription()); + DeathTestAbort(std::string("chdir(\"") + original_dir + "\") failed: " + + GetLastErrnoDescription()); return EXIT_FAILURE; } - // We can safely call execve() as it's a direct system call. We + // We can safely call execv() as it's almost a direct system call. We // cannot use execvp() as it's a libc function and thus potentially - // unsafe. Since execve() doesn't search the PATH, the user must + // unsafe. Since execv() doesn't search the PATH, the user must // invoke the test program via a valid path that contains at least // one path separator. - execve(args->argv[0], args->argv, GetEnviron()); - DeathTestAbort(std::string("execve(") + args->argv[0] + ", ...) in " + - original_dir + " failed: " + GetLastErrnoDescription()); + execv(args->argv[0], args->argv); + DeathTestAbort(std::string("execv(") + args->argv[0] + ", ...) in " + + original_dir + " failed: " + + GetLastErrnoDescription()); return EXIT_FAILURE; } -# endif // !GTEST_OS_QNX +# endif // GTEST_OS_QNX +# if GTEST_HAS_CLONE // Two utility routines that together determine the direction the stack // grows. // This could be accomplished more elegantly by a single recursive @@ -7328,18 +9500,31 @@ static int ExecDeathTestChildMain(void* child_arg) { // GTEST_NO_INLINE_ is required to prevent GCC 4.6 from inlining // StackLowerThanAddress into StackGrowsDown, which then doesn't give // correct answer. -void StackLowerThanAddress(const void* ptr, bool* result) GTEST_NO_INLINE_; -void StackLowerThanAddress(const void* ptr, bool* result) { - int dummy; - *result = (&dummy < ptr); -} - -bool StackGrowsDown() { - int dummy; +static void StackLowerThanAddress(const void* ptr, + bool* result) GTEST_NO_INLINE_; +// Make sure sanitizers do not tamper with the stack here. +// Ideally, we want to use `__builtin_frame_address` instead of a local variable +// address with sanitizer disabled, but it does not work when the +// compiler optimizes the stack frame out, which happens on PowerPC targets. +// HWAddressSanitizer add a random tag to the MSB of the local variable address, +// making comparison result unpredictable. +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_ADDRESS_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_HWADDRESS_ +static void StackLowerThanAddress(const void* ptr, bool* result) { + int dummy = 0; + *result = std::less<const void*>()(&dummy, ptr); +} + +// Make sure AddressSanitizer does not tamper with the stack here. +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_ADDRESS_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_HWADDRESS_ +static bool StackGrowsDown() { + int dummy = 0; bool result; StackLowerThanAddress(&dummy, &result); return result; } +# endif // GTEST_HAS_CLONE // Spawns a child process with the same executable as the current process in // a thread-safe manner and instructs it to run the death test. The @@ -7349,10 +9534,10 @@ bool StackGrowsDown() { // spawn(2) there instead. The function dies with an error message if // anything goes wrong. static pid_t ExecDeathTestSpawnChild(char* const* argv, int close_fd) { - ExecDeathTestArgs args = {argv, close_fd}; + ExecDeathTestArgs args = { argv, close_fd }; pid_t child_pid = -1; -# if GTEST_OS_QNX +# if GTEST_OS_QNX // Obtains the current directory and sets it to be closed in the child // process. const int cwd_fd = open(".", O_RDONLY); @@ -7365,25 +9550,25 @@ static pid_t ExecDeathTestSpawnChild(char* const* argv, int close_fd) { UnitTest::GetInstance()->original_working_dir(); // We can safely call chdir() as it's a direct system call. if (chdir(original_dir) != 0) { - DeathTestAbort(std::string("chdir(\"") + original_dir + - "\") failed: " + GetLastErrnoDescription()); + DeathTestAbort(std::string("chdir(\"") + original_dir + "\") failed: " + + GetLastErrnoDescription()); return EXIT_FAILURE; } int fd_flags; // Set close_fd to be closed after spawn. GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_(fd_flags = fcntl(close_fd, F_GETFD)); - GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_( - fcntl(close_fd, F_SETFD, fd_flags | FD_CLOEXEC)); + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_(fcntl(close_fd, F_SETFD, + fd_flags | FD_CLOEXEC)); struct inheritance inherit = {0}; // spawn is a system call. - child_pid = spawn(args.argv[0], 0, NULL, &inherit, args.argv, GetEnviron()); + child_pid = spawn(args.argv[0], 0, nullptr, &inherit, args.argv, environ); // Restores the current working directory. GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(fchdir(cwd_fd) != -1); GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_(close(cwd_fd)); -# else // GTEST_OS_QNX -# if GTEST_OS_LINUX +# else // GTEST_OS_QNX +# if GTEST_OS_LINUX // When a SIGPROF signal is received while fork() or clone() are executing, // the process may hang. To avoid this, we ignore SIGPROF here and re-enable // it after the call to fork()/clone() is complete. @@ -7392,18 +9577,18 @@ static pid_t ExecDeathTestSpawnChild(char* const* argv, int close_fd) { memset(&ignore_sigprof_action, 0, sizeof(ignore_sigprof_action)); sigemptyset(&ignore_sigprof_action.sa_mask); ignore_sigprof_action.sa_handler = SIG_IGN; - GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_( - sigaction(SIGPROF, &ignore_sigprof_action, &saved_sigprof_action)); -# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_(sigaction( + SIGPROF, &ignore_sigprof_action, &saved_sigprof_action)); +# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX -# if GTEST_HAS_CLONE +# if GTEST_HAS_CLONE const bool use_fork = GTEST_FLAG(death_test_use_fork); if (!use_fork) { static const bool stack_grows_down = StackGrowsDown(); - const size_t stack_size = getpagesize(); + const auto stack_size = static_cast<size_t>(getpagesize() * 2); // MMAP_ANONYMOUS is not defined on Mac, so we use MAP_ANON instead. - void* const stack = mmap(NULL, stack_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, + void* const stack = mmap(nullptr, stack_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_ANON | MAP_PRIVATE, -1, 0); GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(stack != MAP_FAILED); @@ -7416,28 +9601,28 @@ static pid_t ExecDeathTestSpawnChild(char* const* argv, int close_fd) { const size_t kMaxStackAlignment = 64; void* const stack_top = static_cast<char*>(stack) + - (stack_grows_down ? stack_size - kMaxStackAlignment : 0); + (stack_grows_down ? stack_size - kMaxStackAlignment : 0); GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_( - stack_size > kMaxStackAlignment && - reinterpret_cast<intptr_t>(stack_top) % kMaxStackAlignment == 0); + static_cast<size_t>(stack_size) > kMaxStackAlignment && + reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(stack_top) % kMaxStackAlignment == 0); child_pid = clone(&ExecDeathTestChildMain, stack_top, SIGCHLD, &args); GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(munmap(stack, stack_size) != -1); } -# else +# else const bool use_fork = true; -# endif // GTEST_HAS_CLONE +# endif // GTEST_HAS_CLONE if (use_fork && (child_pid = fork()) == 0) { - ExecDeathTestChildMain(&args); - _exit(0); + ExecDeathTestChildMain(&args); + _exit(0); } -# endif // GTEST_OS_QNX -# if GTEST_OS_LINUX +# endif // GTEST_OS_QNX +# if GTEST_OS_LINUX GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_SYSCALL_( - sigaction(SIGPROF, &saved_sigprof_action, NULL)); -# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX + sigaction(SIGPROF, &saved_sigprof_action, nullptr)); +# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(child_pid != -1); return child_pid; @@ -7454,7 +9639,7 @@ DeathTest::TestRole ExecDeathTest::AssumeRole() { const TestInfo* const info = impl->current_test_info(); const int death_test_index = info->result()->death_test_count(); - if (flag != NULL) { + if (flag != nullptr) { set_write_fd(flag->write_fd()); return EXECUTE_TEST; } @@ -7466,13 +9651,13 @@ DeathTest::TestRole ExecDeathTest::AssumeRole() { GTEST_DEATH_TEST_CHECK_(fcntl(pipe_fd[1], F_SETFD, 0) != -1); const std::string filter_flag = std::string("--") + GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + - kFilterFlag + "=" + info->test_case_name() + + kFilterFlag + "=" + info->test_suite_name() + "." + info->name(); - const std::string internal_flag = std::string("--") + GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + - kInternalRunDeathTestFlag + "=" + file_ + - "|" + StreamableToString(line_) + "|" + - StreamableToString(death_test_index) + "|" + - StreamableToString(pipe_fd[1]); + const std::string internal_flag = + std::string("--") + GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ + kInternalRunDeathTestFlag + "=" + + file_ + "|" + StreamableToString(line_) + "|" + + StreamableToString(death_test_index) + "|" + + StreamableToString(pipe_fd[1]); Arguments args; args.AddArguments(GetArgvsForDeathTestChildProcess()); args.AddArgument(filter_flag.c_str()); @@ -7493,108 +9678,95 @@ DeathTest::TestRole ExecDeathTest::AssumeRole() { return OVERSEE_TEST; } -# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS // Creates a concrete DeathTest-derived class that depends on the // --gtest_death_test_style flag, and sets the pointer pointed to // by the "test" argument to its address. If the test should be // skipped, sets that pointer to NULL. Returns true, unless the // flag is set to an invalid value. -bool DefaultDeathTestFactory::Create(const char* statement, const RE* regex, +bool DefaultDeathTestFactory::Create(const char* statement, + Matcher<const std::string&> matcher, const char* file, int line, DeathTest** test) { UnitTestImpl* const impl = GetUnitTestImpl(); const InternalRunDeathTestFlag* const flag = impl->internal_run_death_test_flag(); - const int death_test_index = - impl->current_test_info()->increment_death_test_count(); + const int death_test_index = impl->current_test_info() + ->increment_death_test_count(); - if (flag != NULL) { + if (flag != nullptr) { if (death_test_index > flag->index()) { DeathTest::set_last_death_test_message( - "Death test count (" + StreamableToString(death_test_index) + - ") somehow exceeded expected maximum (" + - StreamableToString(flag->index()) + ")"); + "Death test count (" + StreamableToString(death_test_index) + + ") somehow exceeded expected maximum (" + + StreamableToString(flag->index()) + ")"); return false; } if (!(flag->file() == file && flag->line() == line && flag->index() == death_test_index)) { - *test = NULL; + *test = nullptr; return true; } } -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS if (GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) == "threadsafe" || GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) == "fast") { - *test = new WindowsDeathTest(statement, regex, file, line); + *test = new WindowsDeathTest(statement, std::move(matcher), file, line); } -# else +# elif GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA + + if (GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) == "threadsafe" || + GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) == "fast") { + *test = new FuchsiaDeathTest(statement, std::move(matcher), file, line); + } + +# else if (GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) == "threadsafe") { - *test = new ExecDeathTest(statement, regex, file, line); + *test = new ExecDeathTest(statement, std::move(matcher), file, line); } else if (GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) == "fast") { - *test = new NoExecDeathTest(statement, regex); + *test = new NoExecDeathTest(statement, std::move(matcher)); } -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS else { // NOLINT - this is more readable than unbalanced brackets inside #if. - DeathTest::set_last_death_test_message("Unknown death test style \"" + - GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) + - "\" encountered"); + DeathTest::set_last_death_test_message( + "Unknown death test style \"" + GTEST_FLAG(death_test_style) + + "\" encountered"); return false; } return true; } -// Splits a given string on a given delimiter, populating a given -// vector with the fields. GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST implies that we have -// ::std::string, so we can use it here. -static void SplitString(const ::std::string& str, char delimiter, - ::std::vector< ::std::string>* dest) { - ::std::vector< ::std::string> parsed; - ::std::string::size_type pos = 0; - while (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { - const ::std::string::size_type colon = str.find(delimiter, pos); - if (colon == ::std::string::npos) { - parsed.push_back(str.substr(pos)); - break; - } else { - parsed.push_back(str.substr(pos, colon - pos)); - pos = colon + 1; - } - } - dest->swap(parsed); -} - -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS // Recreates the pipe and event handles from the provided parameters, // signals the event, and returns a file descriptor wrapped around the pipe // handle. This function is called in the child process only. -int GetStatusFileDescriptor(unsigned int parent_process_id, +static int GetStatusFileDescriptor(unsigned int parent_process_id, size_t write_handle_as_size_t, size_t event_handle_as_size_t) { AutoHandle parent_process_handle(::OpenProcess(PROCESS_DUP_HANDLE, - FALSE, // Non-inheritable. - parent_process_id)); + FALSE, // Non-inheritable. + parent_process_id)); if (parent_process_handle.Get() == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) { DeathTestAbort("Unable to open parent process " + StreamableToString(parent_process_id)); } - // TODO(vladl@google.com): Replace the following check with a - // compile-time assertion when available. GTEST_CHECK_(sizeof(HANDLE) <= sizeof(size_t)); - const HANDLE write_handle = reinterpret_cast<HANDLE>(write_handle_as_size_t); + const HANDLE write_handle = + reinterpret_cast<HANDLE>(write_handle_as_size_t); HANDLE dup_write_handle; - // The newly initialized handle is accessible only in in the parent + // The newly initialized handle is accessible only in the parent // process. To obtain one accessible within the child, we need to use // DuplicateHandle. if (!::DuplicateHandle(parent_process_handle.Get(), write_handle, @@ -7613,7 +9785,9 @@ int GetStatusFileDescriptor(unsigned int parent_process_id, HANDLE dup_event_handle; if (!::DuplicateHandle(parent_process_handle.Get(), event_handle, - ::GetCurrentProcess(), &dup_event_handle, 0x0, FALSE, + ::GetCurrentProcess(), &dup_event_handle, + 0x0, + FALSE, DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS)) { DeathTestAbort("Unable to duplicate the event handle " + StreamableToString(event_handle_as_size_t) + @@ -7635,13 +9809,13 @@ int GetStatusFileDescriptor(unsigned int parent_process_id, return write_fd; } -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS // Returns a newly created InternalRunDeathTestFlag object with fields // initialized from the GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test) flag if // the flag is specified; otherwise returns NULL. InternalRunDeathTestFlag* ParseInternalRunDeathTestFlag() { - if (GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test) == "") return NULL; + if (GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test) == "") return nullptr; // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST implies that we have ::std::string, so we // can use it here. @@ -7651,32 +9825,45 @@ InternalRunDeathTestFlag* ParseInternalRunDeathTestFlag() { SplitString(GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test).c_str(), '|', &fields); int write_fd = -1; -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS unsigned int parent_process_id = 0; size_t write_handle_as_size_t = 0; size_t event_handle_as_size_t = 0; - if (fields.size() != 6 || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[1], &line) || - !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[2], &index) || - !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[3], &parent_process_id) || - !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[4], &write_handle_as_size_t) || - !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[5], &event_handle_as_size_t)) { + if (fields.size() != 6 + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[1], &line) + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[2], &index) + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[3], &parent_process_id) + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[4], &write_handle_as_size_t) + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[5], &event_handle_as_size_t)) { DeathTestAbort("Bad --gtest_internal_run_death_test flag: " + GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test)); } - write_fd = GetStatusFileDescriptor(parent_process_id, write_handle_as_size_t, + write_fd = GetStatusFileDescriptor(parent_process_id, + write_handle_as_size_t, event_handle_as_size_t); -# else - if (fields.size() != 4 || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[1], &line) || - !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[2], &index) || - !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[3], &write_fd)) { - DeathTestAbort("Bad --gtest_internal_run_death_test flag: " + - GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test)); +# elif GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA + + if (fields.size() != 3 + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[1], &line) + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[2], &index)) { + DeathTestAbort("Bad --gtest_internal_run_death_test flag: " + + GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test)); } -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# else + + if (fields.size() != 4 + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[1], &line) + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[2], &index) + || !ParseNaturalNumber(fields[3], &write_fd)) { + DeathTestAbort("Bad --gtest_internal_run_death_test flag: " + + GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test)); + } + +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS return new InternalRunDeathTestFlag(fields[0], line, index, write_fd); } @@ -7714,33 +9901,29 @@ InternalRunDeathTestFlag* ParseInternalRunDeathTestFlag() { // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Authors: keith.ray@gmail.com (Keith Ray) + #include <stdlib.h> #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -# include <windows.h> +# include <windows.h> #elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -# include <direct.h> -# include <io.h> -#elif GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN -// Symbian OpenC has PATH_MAX in sys/syslimits.h -# include <sys/syslimits.h> +# include <direct.h> +# include <io.h> #else -# include <limits.h> +# include <limits.h> +# include <climits> // Some Linux distributions define PATH_MAX here. +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -# include <climits> // Some Linux distributions define PATH_MAX here. -#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -# define GTEST_PATH_MAX_ _MAX_PATH +# define GTEST_PATH_MAX_ _MAX_PATH #elif defined(PATH_MAX) -# define GTEST_PATH_MAX_ PATH_MAX +# define GTEST_PATH_MAX_ PATH_MAX #elif defined(_XOPEN_PATH_MAX) -# define GTEST_PATH_MAX_ _XOPEN_PATH_MAX +# define GTEST_PATH_MAX_ _XOPEN_PATH_MAX #else -# define GTEST_PATH_MAX_ _POSIX_PATH_MAX +# define GTEST_PATH_MAX_ _POSIX_PATH_MAX #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS namespace testing { @@ -7753,21 +9936,19 @@ namespace internal { // of them. const char kPathSeparator = '\\'; const char kAlternatePathSeparator = '/'; -const char kPathSeparatorString[] = "\\"; const char kAlternatePathSeparatorString[] = "/"; -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE // Windows CE doesn't have a current directory. You should not use // the current directory in tests on Windows CE, but this at least // provides a reasonable fallback. const char kCurrentDirectoryString[] = "\\"; // Windows CE doesn't define INVALID_FILE_ATTRIBUTES const DWORD kInvalidFileAttributes = 0xffffffff; -# else +# else const char kCurrentDirectoryString[] = ".\\"; -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE #else const char kPathSeparator = '/'; -const char kPathSeparatorString[] = "/"; const char kCurrentDirectoryString[] = "./"; #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS @@ -7782,16 +9963,25 @@ static bool IsPathSeparator(char c) { // Returns the current working directory, or "" if unsuccessful. FilePath FilePath::GetCurrentDir() { -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - // Windows CE doesn't have a current directory, so we just return +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE || \ + GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT || GTEST_OS_ESP8266 || GTEST_OS_ESP32 || \ + GTEST_OS_XTENSA + // These platforms do not have a current directory, so we just return // something reasonable. return FilePath(kCurrentDirectoryString); #elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - char cwd[GTEST_PATH_MAX_ + 1] = {'\0'}; - return FilePath(_getcwd(cwd, sizeof(cwd)) == NULL ? "" : cwd); + char cwd[GTEST_PATH_MAX_ + 1] = { '\0' }; + return FilePath(_getcwd(cwd, sizeof(cwd)) == nullptr ? "" : cwd); #else - char cwd[GTEST_PATH_MAX_ + 1] = {'\0'}; - return FilePath(getcwd(cwd, sizeof(cwd)) == NULL ? "" : cwd); + char cwd[GTEST_PATH_MAX_ + 1] = { '\0' }; + char* result = getcwd(cwd, sizeof(cwd)); +# if GTEST_OS_NACL + // getcwd will likely fail in NaCl due to the sandbox, so return something + // reasonable. The user may have provided a shim implementation for getcwd, + // however, so fallback only when failure is detected. + return FilePath(result == nullptr ? kCurrentDirectoryString : cwd); +# endif // GTEST_OS_NACL + return FilePath(result == nullptr ? "" : cwd); #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE } @@ -7802,13 +9992,13 @@ FilePath FilePath::GetCurrentDir() { FilePath FilePath::RemoveExtension(const char* extension) const { const std::string dot_extension = std::string(".") + extension; if (String::EndsWithCaseInsensitive(pathname_, dot_extension)) { - return FilePath( - pathname_.substr(0, pathname_.length() - dot_extension.length())); + return FilePath(pathname_.substr( + 0, pathname_.length() - dot_extension.length())); } return *this; } -// Returns a pointer to the last occurence of a valid path separator in +// Returns a pointer to the last occurrence of a valid path separator in // the FilePath. On Windows, for example, both '/' and '\' are valid path // separators. Returns NULL if no path separator was found. const char* FilePath::FindLastPathSeparator() const { @@ -7816,7 +10006,8 @@ const char* FilePath::FindLastPathSeparator() const { #if GTEST_HAS_ALT_PATH_SEP_ const char* const last_alt_sep = strrchr(c_str(), kAlternatePathSeparator); // Comparing two pointers of which only one is NULL is undefined. - if (last_alt_sep != NULL && (last_sep == NULL || last_alt_sep > last_sep)) { + if (last_alt_sep != nullptr && + (last_sep == nullptr || last_alt_sep > last_sep)) { return last_alt_sep; } #endif @@ -7844,7 +10035,7 @@ FilePath FilePath::RemoveFileName() const { const char* const last_sep = FindLastPathSeparator(); std::string dir; if (last_sep) { - dir = std::string(c_str(), last_sep + 1 - c_str()); + dir = std::string(c_str(), static_cast<size_t>(last_sep + 1 - c_str())); } else { dir = kCurrentDirectoryString; } @@ -7858,14 +10049,15 @@ FilePath FilePath::RemoveFileName() const { // than zero (e.g., 12), returns "dir/test_12.xml". // On Windows platform, uses \ as the separator rather than /. FilePath FilePath::MakeFileName(const FilePath& directory, - const FilePath& base_name, int number, + const FilePath& base_name, + int number, const char* extension) { std::string file; if (number == 0) { file = base_name.string() + "." + extension; } else { - file = - base_name.string() + "_" + StreamableToString(number) + "." + extension; + file = base_name.string() + "_" + StreamableToString(number) + + "." + extension; } return ConcatPaths(directory, FilePath(file)); } @@ -7874,7 +10066,8 @@ FilePath FilePath::MakeFileName(const FilePath& directory, // On Windows, uses \ as the separator rather than /. FilePath FilePath::ConcatPaths(const FilePath& directory, const FilePath& relative_path) { - if (directory.IsEmpty()) return relative_path; + if (directory.IsEmpty()) + return relative_path; const FilePath dir(directory.RemoveTrailingPathSeparator()); return FilePath(dir.string() + kPathSeparator + relative_path.string()); } @@ -7885,7 +10078,7 @@ bool FilePath::FileOrDirectoryExists() const { #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE LPCWSTR unicode = String::AnsiToUtf16(pathname_.c_str()); const DWORD attributes = GetFileAttributes(unicode); - delete[] unicode; + delete [] unicode; return attributes != kInvalidFileAttributes; #else posix::StatStruct file_stat; @@ -7900,8 +10093,8 @@ bool FilePath::DirectoryExists() const { #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS // Don't strip off trailing separator if path is a root directory on // Windows (like "C:\\"). - const FilePath& path(IsRootDirectory() ? *this - : RemoveTrailingPathSeparator()); + const FilePath& path(IsRootDirectory() ? *this : + RemoveTrailingPathSeparator()); #else const FilePath& path(*this); #endif @@ -7909,15 +10102,15 @@ bool FilePath::DirectoryExists() const { #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE LPCWSTR unicode = String::AnsiToUtf16(path.c_str()); const DWORD attributes = GetFileAttributes(unicode); - delete[] unicode; + delete [] unicode; if ((attributes != kInvalidFileAttributes) && (attributes & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY)) { result = true; } #else posix::StatStruct file_stat; - result = - posix::Stat(path.c_str(), &file_stat) == 0 && posix::IsDir(file_stat); + result = posix::Stat(path.c_str(), &file_stat) == 0 && + posix::IsDir(file_stat); #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE return result; @@ -7927,9 +10120,6 @@ bool FilePath::DirectoryExists() const { // root directory per disk drive.) bool FilePath::IsRootDirectory() const { #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - // TODO(wan@google.com): on Windows a network share like - // \\server\share can be a root directory, although it cannot be the - // current directory. Handle this properly. return pathname_.length() == 3 && IsAbsolutePath(); #else return pathname_.length() == 1 && IsPathSeparator(pathname_.c_str()[0]); @@ -7941,9 +10131,10 @@ bool FilePath::IsAbsolutePath() const { const char* const name = pathname_.c_str(); #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS return pathname_.length() >= 3 && - ((name[0] >= 'a' && name[0] <= 'z') || - (name[0] >= 'A' && name[0] <= 'Z')) && - name[1] == ':' && IsPathSeparator(name[2]); + ((name[0] >= 'a' && name[0] <= 'z') || + (name[0] >= 'A' && name[0] <= 'Z')) && + name[1] == ':' && + IsPathSeparator(name[2]); #else return IsPathSeparator(name[0]); #endif @@ -8000,10 +10191,13 @@ bool FilePath::CreateFolder() const { #if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE FilePath removed_sep(this->RemoveTrailingPathSeparator()); LPCWSTR unicode = String::AnsiToUtf16(removed_sep.c_str()); - int result = CreateDirectory(unicode, NULL) ? 0 : -1; - delete[] unicode; + int result = CreateDirectory(unicode, nullptr) ? 0 : -1; + delete [] unicode; #elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS int result = _mkdir(pathname_.c_str()); +#elif GTEST_OS_ESP8266 || GTEST_OS_XTENSA + // do nothing + int result = 0; #else int result = mkdir(pathname_.c_str(), 0777); #endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE @@ -8018,46 +10212,33 @@ bool FilePath::CreateFolder() const { // name, otherwise return the name string unmodified. // On Windows platform, uses \ as the separator, other platforms use /. FilePath FilePath::RemoveTrailingPathSeparator() const { - return IsDirectory() ? FilePath(pathname_.substr(0, pathname_.length() - 1)) - : *this; + return IsDirectory() + ? FilePath(pathname_.substr(0, pathname_.length() - 1)) + : *this; } // Removes any redundant separators that might be in the pathname. // For example, "bar///foo" becomes "bar/foo". Does not eliminate other // redundancies that might be in a pathname involving "." or "..". -// TODO(wan@google.com): handle Windows network shares (e.g. \\server\share). void FilePath::Normalize() { - if (pathname_.c_str() == NULL) { - pathname_ = ""; - return; - } - const char* src = pathname_.c_str(); - char* const dest = new char[pathname_.length() + 1]; - char* dest_ptr = dest; - memset(dest_ptr, 0, pathname_.length() + 1); + auto out = pathname_.begin(); - while (*src != '\0') { - *dest_ptr = *src; - if (!IsPathSeparator(*src)) { - src++; + for (const char character : pathname_) { + if (!IsPathSeparator(character)) { + *(out++) = character; + } else if (out == pathname_.begin() || *std::prev(out) != kPathSeparator) { + *(out++) = kPathSeparator; } else { -#if GTEST_HAS_ALT_PATH_SEP_ - if (*dest_ptr == kAlternatePathSeparator) { - *dest_ptr = kPathSeparator; - } -#endif - while (IsPathSeparator(*src)) src++; + continue; } - dest_ptr++; } - *dest_ptr = '\0'; - pathname_ = dest; - delete[] dest; + + pathname_.erase(out, pathname_.end()); } } // namespace internal } // namespace testing -// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. // All rights reserved. // // Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without @@ -8085,41 +10266,153 @@ void FilePath::Normalize() { // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// This file implements just enough of the matcher interface to allow +// EXPECT_DEATH and friends to accept a matcher argument. + + +#include <string> + +namespace testing { + +// Constructs a matcher that matches a const std::string& whose value is +// equal to s. +Matcher<const std::string&>::Matcher(const std::string& s) { *this = Eq(s); } + +// Constructs a matcher that matches a const std::string& whose value is +// equal to s. +Matcher<const std::string&>::Matcher(const char* s) { + *this = Eq(std::string(s)); +} + +// Constructs a matcher that matches a std::string whose value is equal to +// s. +Matcher<std::string>::Matcher(const std::string& s) { *this = Eq(s); } + +// Constructs a matcher that matches a std::string whose value is equal to +// s. +Matcher<std::string>::Matcher(const char* s) { *this = Eq(std::string(s)); } + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW +// Constructs a matcher that matches a const StringView& whose value is +// equal to s. +Matcher<const internal::StringView&>::Matcher(const std::string& s) { + *this = Eq(s); +} + +// Constructs a matcher that matches a const StringView& whose value is +// equal to s. +Matcher<const internal::StringView&>::Matcher(const char* s) { + *this = Eq(std::string(s)); +} + +// Constructs a matcher that matches a const StringView& whose value is +// equal to s. +Matcher<const internal::StringView&>::Matcher(internal::StringView s) { + *this = Eq(std::string(s)); +} + +// Constructs a matcher that matches a StringView whose value is equal to +// s. +Matcher<internal::StringView>::Matcher(const std::string& s) { *this = Eq(s); } + +// Constructs a matcher that matches a StringView whose value is equal to +// s. +Matcher<internal::StringView>::Matcher(const char* s) { + *this = Eq(std::string(s)); +} + +// Constructs a matcher that matches a StringView whose value is equal to +// s. +Matcher<internal::StringView>::Matcher(internal::StringView s) { + *this = Eq(std::string(s)); +} +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + +} // namespace testing +// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. // -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + #include <limits.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> +#include <cstdint> +#include <fstream> +#include <memory> -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -# include <windows.h> // For TerminateProcess() -#elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -# include <io.h> -# include <sys/stat.h> +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# include <windows.h> +# include <io.h> +# include <sys/stat.h> +# include <map> // Used in ThreadLocal. +# ifdef _MSC_VER +# include <crtdbg.h> +# endif // _MSC_VER #else -# include <unistd.h> -#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# include <unistd.h> +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS #if GTEST_OS_MAC -# include <mach/mach_init.h> -# include <mach/task.h> -# include <mach/vm_map.h> +# include <mach/mach_init.h> +# include <mach/task.h> +# include <mach/vm_map.h> #endif // GTEST_OS_MAC +#if GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY || GTEST_OS_FREEBSD || GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD || \ + GTEST_OS_NETBSD || GTEST_OS_OPENBSD +# include <sys/sysctl.h> +# if GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY || GTEST_OS_FREEBSD || GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD +# include <sys/user.h> +# endif +#endif + #if GTEST_OS_QNX -# include <devctl.h> -# include <sys/procfs.h> +# include <devctl.h> +# include <fcntl.h> +# include <sys/procfs.h> #endif // GTEST_OS_QNX -// Indicates that this translation unit is part of Google Test's -// implementation. It must come before gtest-internal-inl.h is -// included, or there will be a compiler error. This trick is to -// prevent a user from accidentally including gtest-internal-inl.h in -// his code. -#define GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ 1 -#undef GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ +#if GTEST_OS_AIX +# include <procinfo.h> +# include <sys/types.h> +#endif // GTEST_OS_AIX + +#if GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA +# include <zircon/process.h> +# include <zircon/syscalls.h> +#endif // GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA + namespace testing { namespace internal { @@ -8133,10 +10426,31 @@ const int kStdOutFileno = STDOUT_FILENO; const int kStdErrFileno = STDERR_FILENO; #endif // _MSC_VER -#if GTEST_OS_MAC +#if GTEST_OS_LINUX + +namespace { +template <typename T> +T ReadProcFileField(const std::string& filename, int field) { + std::string dummy; + std::ifstream file(filename.c_str()); + while (field-- > 0) { + file >> dummy; + } + T output = 0; + file >> output; + return output; +} +} // namespace + +// Returns the number of active threads, or 0 when there is an error. +size_t GetThreadCount() { + const std::string filename = + (Message() << "/proc/" << getpid() << "/stat").GetString(); + return ReadProcFileField<size_t>(filename, 19); +} + +#elif GTEST_OS_MAC -// Returns the number of threads running in the process, or 0 to indicate that -// we cannot detect it. size_t GetThreadCount() { const task_t task = mach_task_self(); mach_msg_type_number_t thread_count; @@ -8145,7 +10459,8 @@ size_t GetThreadCount() { if (status == KERN_SUCCESS) { // task_threads allocates resources in thread_list and we need to free them // to avoid leaks. - vm_deallocate(task, reinterpret_cast<vm_address_t>(thread_list), + vm_deallocate(task, + reinterpret_cast<vm_address_t>(thread_list), sizeof(thread_t) * thread_count); return static_cast<size_t>(thread_count); } else { @@ -8153,6 +10468,82 @@ size_t GetThreadCount() { } } +#elif GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY || GTEST_OS_FREEBSD || GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD || \ + GTEST_OS_NETBSD + +#if GTEST_OS_NETBSD +#undef KERN_PROC +#define KERN_PROC KERN_PROC2 +#define kinfo_proc kinfo_proc2 +#endif + +#if GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY +#define KP_NLWP(kp) (kp.kp_nthreads) +#elif GTEST_OS_FREEBSD || GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD +#define KP_NLWP(kp) (kp.ki_numthreads) +#elif GTEST_OS_NETBSD +#define KP_NLWP(kp) (kp.p_nlwps) +#endif + +// Returns the number of threads running in the process, or 0 to indicate that +// we cannot detect it. +size_t GetThreadCount() { + int mib[] = { + CTL_KERN, + KERN_PROC, + KERN_PROC_PID, + getpid(), +#if GTEST_OS_NETBSD + sizeof(struct kinfo_proc), + 1, +#endif + }; + u_int miblen = sizeof(mib) / sizeof(mib[0]); + struct kinfo_proc info; + size_t size = sizeof(info); + if (sysctl(mib, miblen, &info, &size, NULL, 0)) { + return 0; + } + return static_cast<size_t>(KP_NLWP(info)); +} +#elif GTEST_OS_OPENBSD + +// Returns the number of threads running in the process, or 0 to indicate that +// we cannot detect it. +size_t GetThreadCount() { + int mib[] = { + CTL_KERN, + KERN_PROC, + KERN_PROC_PID | KERN_PROC_SHOW_THREADS, + getpid(), + sizeof(struct kinfo_proc), + 0, + }; + u_int miblen = sizeof(mib) / sizeof(mib[0]); + + // get number of structs + size_t size; + if (sysctl(mib, miblen, NULL, &size, NULL, 0)) { + return 0; + } + + mib[5] = static_cast<int>(size / static_cast<size_t>(mib[4])); + + // populate array of structs + struct kinfo_proc info[mib[5]]; + if (sysctl(mib, miblen, &info, &size, NULL, 0)) { + return 0; + } + + // exclude empty members + size_t nthreads = 0; + for (size_t i = 0; i < size / static_cast<size_t>(mib[4]); i++) { + if (info[i].p_tid != -1) + nthreads++; + } + return nthreads; +} + #elif GTEST_OS_QNX // Returns the number of threads running in the process, or 0 to indicate that @@ -8164,7 +10555,7 @@ size_t GetThreadCount() { } procfs_info process_info; const int status = - devctl(fd, DCMD_PROC_INFO, &process_info, sizeof(process_info), NULL); + devctl(fd, DCMD_PROC_INFO, &process_info, sizeof(process_info), nullptr); close(fd); if (status == EOK) { return static_cast<size_t>(process_info.num_threads); @@ -8173,6 +10564,38 @@ size_t GetThreadCount() { } } +#elif GTEST_OS_AIX + +size_t GetThreadCount() { + struct procentry64 entry; + pid_t pid = getpid(); + int status = getprocs64(&entry, sizeof(entry), nullptr, 0, &pid, 1); + if (status == 1) { + return entry.pi_thcount; + } else { + return 0; + } +} + +#elif GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA + +size_t GetThreadCount() { + int dummy_buffer; + size_t avail; + zx_status_t status = zx_object_get_info( + zx_process_self(), + ZX_INFO_PROCESS_THREADS, + &dummy_buffer, + 0, + nullptr, + &avail); + if (status == ZX_OK) { + return avail; + } else { + return 0; + } +} + #else size_t GetThreadCount() { @@ -8181,7 +10604,433 @@ size_t GetThreadCount() { return 0; } -#endif // GTEST_OS_MAC +#endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX + +#if GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE && GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +void SleepMilliseconds(int n) { + ::Sleep(static_cast<DWORD>(n)); +} + +AutoHandle::AutoHandle() + : handle_(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) {} + +AutoHandle::AutoHandle(Handle handle) + : handle_(handle) {} + +AutoHandle::~AutoHandle() { + Reset(); +} + +AutoHandle::Handle AutoHandle::Get() const { + return handle_; +} + +void AutoHandle::Reset() { + Reset(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE); +} + +void AutoHandle::Reset(HANDLE handle) { + // Resetting with the same handle we already own is invalid. + if (handle_ != handle) { + if (IsCloseable()) { + ::CloseHandle(handle_); + } + handle_ = handle; + } else { + GTEST_CHECK_(!IsCloseable()) + << "Resetting a valid handle to itself is likely a programmer error " + "and thus not allowed."; + } +} + +bool AutoHandle::IsCloseable() const { + // Different Windows APIs may use either of these values to represent an + // invalid handle. + return handle_ != nullptr && handle_ != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE; +} + +Notification::Notification() + : event_(::CreateEvent(nullptr, // Default security attributes. + TRUE, // Do not reset automatically. + FALSE, // Initially unset. + nullptr)) { // Anonymous event. + GTEST_CHECK_(event_.Get() != nullptr); +} + +void Notification::Notify() { + GTEST_CHECK_(::SetEvent(event_.Get()) != FALSE); +} + +void Notification::WaitForNotification() { + GTEST_CHECK_( + ::WaitForSingleObject(event_.Get(), INFINITE) == WAIT_OBJECT_0); +} + +Mutex::Mutex() + : owner_thread_id_(0), + type_(kDynamic), + critical_section_init_phase_(0), + critical_section_(new CRITICAL_SECTION) { + ::InitializeCriticalSection(critical_section_); +} + +Mutex::~Mutex() { + // Static mutexes are leaked intentionally. It is not thread-safe to try + // to clean them up. + if (type_ == kDynamic) { + ::DeleteCriticalSection(critical_section_); + delete critical_section_; + critical_section_ = nullptr; + } +} + +void Mutex::Lock() { + ThreadSafeLazyInit(); + ::EnterCriticalSection(critical_section_); + owner_thread_id_ = ::GetCurrentThreadId(); +} + +void Mutex::Unlock() { + ThreadSafeLazyInit(); + // We don't protect writing to owner_thread_id_ here, as it's the + // caller's responsibility to ensure that the current thread holds the + // mutex when this is called. + owner_thread_id_ = 0; + ::LeaveCriticalSection(critical_section_); +} + +// Does nothing if the current thread holds the mutex. Otherwise, crashes +// with high probability. +void Mutex::AssertHeld() { + ThreadSafeLazyInit(); + GTEST_CHECK_(owner_thread_id_ == ::GetCurrentThreadId()) + << "The current thread is not holding the mutex @" << this; +} + +namespace { + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +// Use the RAII idiom to flag mem allocs that are intentionally never +// deallocated. The motivation is to silence the false positive mem leaks +// that are reported by the debug version of MS's CRT which can only detect +// if an alloc is missing a matching deallocation. +// Example: +// MemoryIsNotDeallocated memory_is_not_deallocated; +// critical_section_ = new CRITICAL_SECTION; +// +class MemoryIsNotDeallocated +{ + public: + MemoryIsNotDeallocated() : old_crtdbg_flag_(0) { + old_crtdbg_flag_ = _CrtSetDbgFlag(_CRTDBG_REPORT_FLAG); + // Set heap allocation block type to _IGNORE_BLOCK so that MS debug CRT + // doesn't report mem leak if there's no matching deallocation. + _CrtSetDbgFlag(old_crtdbg_flag_ & ~_CRTDBG_ALLOC_MEM_DF); + } + + ~MemoryIsNotDeallocated() { + // Restore the original _CRTDBG_ALLOC_MEM_DF flag + _CrtSetDbgFlag(old_crtdbg_flag_); + } + + private: + int old_crtdbg_flag_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MemoryIsNotDeallocated); +}; +#endif // _MSC_VER + +} // namespace + +// Initializes owner_thread_id_ and critical_section_ in static mutexes. +void Mutex::ThreadSafeLazyInit() { + // Dynamic mutexes are initialized in the constructor. + if (type_ == kStatic) { + switch ( + ::InterlockedCompareExchange(&critical_section_init_phase_, 1L, 0L)) { + case 0: + // If critical_section_init_phase_ was 0 before the exchange, we + // are the first to test it and need to perform the initialization. + owner_thread_id_ = 0; + { + // Use RAII to flag that following mem alloc is never deallocated. +#ifdef _MSC_VER + MemoryIsNotDeallocated memory_is_not_deallocated; +#endif // _MSC_VER + critical_section_ = new CRITICAL_SECTION; + } + ::InitializeCriticalSection(critical_section_); + // Updates the critical_section_init_phase_ to 2 to signal + // initialization complete. + GTEST_CHECK_(::InterlockedCompareExchange( + &critical_section_init_phase_, 2L, 1L) == + 1L); + break; + case 1: + // Somebody else is already initializing the mutex; spin until they + // are done. + while (::InterlockedCompareExchange(&critical_section_init_phase_, + 2L, + 2L) != 2L) { + // Possibly yields the rest of the thread's time slice to other + // threads. + ::Sleep(0); + } + break; + + case 2: + break; // The mutex is already initialized and ready for use. + + default: + GTEST_CHECK_(false) + << "Unexpected value of critical_section_init_phase_ " + << "while initializing a static mutex."; + } + } +} + +namespace { + +class ThreadWithParamSupport : public ThreadWithParamBase { + public: + static HANDLE CreateThread(Runnable* runnable, + Notification* thread_can_start) { + ThreadMainParam* param = new ThreadMainParam(runnable, thread_can_start); + DWORD thread_id; + HANDLE thread_handle = ::CreateThread( + nullptr, // Default security. + 0, // Default stack size. + &ThreadWithParamSupport::ThreadMain, + param, // Parameter to ThreadMainStatic + 0x0, // Default creation flags. + &thread_id); // Need a valid pointer for the call to work under Win98. + GTEST_CHECK_(thread_handle != nullptr) + << "CreateThread failed with error " << ::GetLastError() << "."; + if (thread_handle == nullptr) { + delete param; + } + return thread_handle; + } + + private: + struct ThreadMainParam { + ThreadMainParam(Runnable* runnable, Notification* thread_can_start) + : runnable_(runnable), + thread_can_start_(thread_can_start) { + } + std::unique_ptr<Runnable> runnable_; + // Does not own. + Notification* thread_can_start_; + }; + + static DWORD WINAPI ThreadMain(void* ptr) { + // Transfers ownership. + std::unique_ptr<ThreadMainParam> param(static_cast<ThreadMainParam*>(ptr)); + if (param->thread_can_start_ != nullptr) + param->thread_can_start_->WaitForNotification(); + param->runnable_->Run(); + return 0; + } + + // Prohibit instantiation. + ThreadWithParamSupport(); + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ThreadWithParamSupport); +}; + +} // namespace + +ThreadWithParamBase::ThreadWithParamBase(Runnable *runnable, + Notification* thread_can_start) + : thread_(ThreadWithParamSupport::CreateThread(runnable, + thread_can_start)) { +} + +ThreadWithParamBase::~ThreadWithParamBase() { + Join(); +} + +void ThreadWithParamBase::Join() { + GTEST_CHECK_(::WaitForSingleObject(thread_.Get(), INFINITE) == WAIT_OBJECT_0) + << "Failed to join the thread with error " << ::GetLastError() << "."; +} + +// Maps a thread to a set of ThreadIdToThreadLocals that have values +// instantiated on that thread and notifies them when the thread exits. A +// ThreadLocal instance is expected to persist until all threads it has +// values on have terminated. +class ThreadLocalRegistryImpl { + public: + // Registers thread_local_instance as having value on the current thread. + // Returns a value that can be used to identify the thread from other threads. + static ThreadLocalValueHolderBase* GetValueOnCurrentThread( + const ThreadLocalBase* thread_local_instance) { +#ifdef _MSC_VER + MemoryIsNotDeallocated memory_is_not_deallocated; +#endif // _MSC_VER + DWORD current_thread = ::GetCurrentThreadId(); + MutexLock lock(&mutex_); + ThreadIdToThreadLocals* const thread_to_thread_locals = + GetThreadLocalsMapLocked(); + ThreadIdToThreadLocals::iterator thread_local_pos = + thread_to_thread_locals->find(current_thread); + if (thread_local_pos == thread_to_thread_locals->end()) { + thread_local_pos = thread_to_thread_locals->insert( + std::make_pair(current_thread, ThreadLocalValues())).first; + StartWatcherThreadFor(current_thread); + } + ThreadLocalValues& thread_local_values = thread_local_pos->second; + ThreadLocalValues::iterator value_pos = + thread_local_values.find(thread_local_instance); + if (value_pos == thread_local_values.end()) { + value_pos = + thread_local_values + .insert(std::make_pair( + thread_local_instance, + std::shared_ptr<ThreadLocalValueHolderBase>( + thread_local_instance->NewValueForCurrentThread()))) + .first; + } + return value_pos->second.get(); + } + + static void OnThreadLocalDestroyed( + const ThreadLocalBase* thread_local_instance) { + std::vector<std::shared_ptr<ThreadLocalValueHolderBase> > value_holders; + // Clean up the ThreadLocalValues data structure while holding the lock, but + // defer the destruction of the ThreadLocalValueHolderBases. + { + MutexLock lock(&mutex_); + ThreadIdToThreadLocals* const thread_to_thread_locals = + GetThreadLocalsMapLocked(); + for (ThreadIdToThreadLocals::iterator it = + thread_to_thread_locals->begin(); + it != thread_to_thread_locals->end(); + ++it) { + ThreadLocalValues& thread_local_values = it->second; + ThreadLocalValues::iterator value_pos = + thread_local_values.find(thread_local_instance); + if (value_pos != thread_local_values.end()) { + value_holders.push_back(value_pos->second); + thread_local_values.erase(value_pos); + // This 'if' can only be successful at most once, so theoretically we + // could break out of the loop here, but we don't bother doing so. + } + } + } + // Outside the lock, let the destructor for 'value_holders' deallocate the + // ThreadLocalValueHolderBases. + } + + static void OnThreadExit(DWORD thread_id) { + GTEST_CHECK_(thread_id != 0) << ::GetLastError(); + std::vector<std::shared_ptr<ThreadLocalValueHolderBase> > value_holders; + // Clean up the ThreadIdToThreadLocals data structure while holding the + // lock, but defer the destruction of the ThreadLocalValueHolderBases. + { + MutexLock lock(&mutex_); + ThreadIdToThreadLocals* const thread_to_thread_locals = + GetThreadLocalsMapLocked(); + ThreadIdToThreadLocals::iterator thread_local_pos = + thread_to_thread_locals->find(thread_id); + if (thread_local_pos != thread_to_thread_locals->end()) { + ThreadLocalValues& thread_local_values = thread_local_pos->second; + for (ThreadLocalValues::iterator value_pos = + thread_local_values.begin(); + value_pos != thread_local_values.end(); + ++value_pos) { + value_holders.push_back(value_pos->second); + } + thread_to_thread_locals->erase(thread_local_pos); + } + } + // Outside the lock, let the destructor for 'value_holders' deallocate the + // ThreadLocalValueHolderBases. + } + + private: + // In a particular thread, maps a ThreadLocal object to its value. + typedef std::map<const ThreadLocalBase*, + std::shared_ptr<ThreadLocalValueHolderBase> > + ThreadLocalValues; + // Stores all ThreadIdToThreadLocals having values in a thread, indexed by + // thread's ID. + typedef std::map<DWORD, ThreadLocalValues> ThreadIdToThreadLocals; + + // Holds the thread id and thread handle that we pass from + // StartWatcherThreadFor to WatcherThreadFunc. + typedef std::pair<DWORD, HANDLE> ThreadIdAndHandle; + + static void StartWatcherThreadFor(DWORD thread_id) { + // The returned handle will be kept in thread_map and closed by + // watcher_thread in WatcherThreadFunc. + HANDLE thread = ::OpenThread(SYNCHRONIZE | THREAD_QUERY_INFORMATION, + FALSE, + thread_id); + GTEST_CHECK_(thread != nullptr); + // We need to pass a valid thread ID pointer into CreateThread for it + // to work correctly under Win98. + DWORD watcher_thread_id; + HANDLE watcher_thread = ::CreateThread( + nullptr, // Default security. + 0, // Default stack size + &ThreadLocalRegistryImpl::WatcherThreadFunc, + reinterpret_cast<LPVOID>(new ThreadIdAndHandle(thread_id, thread)), + CREATE_SUSPENDED, &watcher_thread_id); + GTEST_CHECK_(watcher_thread != nullptr); + // Give the watcher thread the same priority as ours to avoid being + // blocked by it. + ::SetThreadPriority(watcher_thread, + ::GetThreadPriority(::GetCurrentThread())); + ::ResumeThread(watcher_thread); + ::CloseHandle(watcher_thread); + } + + // Monitors exit from a given thread and notifies those + // ThreadIdToThreadLocals about thread termination. + static DWORD WINAPI WatcherThreadFunc(LPVOID param) { + const ThreadIdAndHandle* tah = + reinterpret_cast<const ThreadIdAndHandle*>(param); + GTEST_CHECK_( + ::WaitForSingleObject(tah->second, INFINITE) == WAIT_OBJECT_0); + OnThreadExit(tah->first); + ::CloseHandle(tah->second); + delete tah; + return 0; + } + + // Returns map of thread local instances. + static ThreadIdToThreadLocals* GetThreadLocalsMapLocked() { + mutex_.AssertHeld(); +#ifdef _MSC_VER + MemoryIsNotDeallocated memory_is_not_deallocated; +#endif // _MSC_VER + static ThreadIdToThreadLocals* map = new ThreadIdToThreadLocals(); + return map; + } + + // Protects access to GetThreadLocalsMapLocked() and its return value. + static Mutex mutex_; + // Protects access to GetThreadMapLocked() and its return value. + static Mutex thread_map_mutex_; +}; + +Mutex ThreadLocalRegistryImpl::mutex_(Mutex::kStaticMutex); +Mutex ThreadLocalRegistryImpl::thread_map_mutex_(Mutex::kStaticMutex); + +ThreadLocalValueHolderBase* ThreadLocalRegistry::GetValueOnCurrentThread( + const ThreadLocalBase* thread_local_instance) { + return ThreadLocalRegistryImpl::GetValueOnCurrentThread( + thread_local_instance); +} + +void ThreadLocalRegistry::OnThreadLocalDestroyed( + const ThreadLocalBase* thread_local_instance) { + ThreadLocalRegistryImpl::OnThreadLocalDestroyed(thread_local_instance); +} + +#endif // GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE && GTEST_OS_WINDOWS #if GTEST_USES_POSIX_RE @@ -8199,7 +11048,7 @@ RE::~RE() { free(const_cast<char*>(pattern_)); } -// Returns true iff regular expression re matches the entire str. +// Returns true if and only if regular expression re matches the entire str. bool RE::FullMatch(const char* str, const RE& re) { if (!re.is_valid_) return false; @@ -8207,8 +11056,8 @@ bool RE::FullMatch(const char* str, const RE& re) { return regexec(&re.full_regex_, str, 1, &match, 0) == 0; } -// Returns true iff regular expression re matches a substring of str -// (including str itself). +// Returns true if and only if regular expression re matches a substring of +// str (including str itself). bool RE::PartialMatch(const char* str, const RE& re) { if (!re.is_valid_) return false; @@ -8248,14 +11097,14 @@ void RE::Init(const char* regex) { #elif GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE -// Returns true iff ch appears anywhere in str (excluding the +// Returns true if and only if ch appears anywhere in str (excluding the // terminating '\0' character). bool IsInSet(char ch, const char* str) { - return ch != '\0' && strchr(str, ch) != NULL; + return ch != '\0' && strchr(str, ch) != nullptr; } -// Returns true iff ch belongs to the given classification. Unlike -// similar functions in <ctype.h>, these aren't affected by the +// Returns true if and only if ch belongs to the given classification. +// Unlike similar functions in <ctype.h>, these aren't affected by the // current locale. bool IsAsciiDigit(char ch) { return '0' <= ch && ch <= '9'; } bool IsAsciiPunct(char ch) { @@ -8265,41 +11114,30 @@ bool IsRepeat(char ch) { return IsInSet(ch, "?*+"); } bool IsAsciiWhiteSpace(char ch) { return IsInSet(ch, " \f\n\r\t\v"); } bool IsAsciiWordChar(char ch) { return ('a' <= ch && ch <= 'z') || ('A' <= ch && ch <= 'Z') || - ('0' <= ch && ch <= '9') || ch == '_'; + ('0' <= ch && ch <= '9') || ch == '_'; } -// Returns true iff "\\c" is a supported escape sequence. +// Returns true if and only if "\\c" is a supported escape sequence. bool IsValidEscape(char c) { return (IsAsciiPunct(c) || IsInSet(c, "dDfnrsStvwW")); } -// Returns true iff the given atom (specified by escaped and pattern) -// matches ch. The result is undefined if the atom is invalid. +// Returns true if and only if the given atom (specified by escaped and +// pattern) matches ch. The result is undefined if the atom is invalid. bool AtomMatchesChar(bool escaped, char pattern_char, char ch) { if (escaped) { // "\\p" where p is pattern_char. switch (pattern_char) { - case 'd': - return IsAsciiDigit(ch); - case 'D': - return !IsAsciiDigit(ch); - case 'f': - return ch == '\f'; - case 'n': - return ch == '\n'; - case 'r': - return ch == '\r'; - case 's': - return IsAsciiWhiteSpace(ch); - case 'S': - return !IsAsciiWhiteSpace(ch); - case 't': - return ch == '\t'; - case 'v': - return ch == '\v'; - case 'w': - return IsAsciiWordChar(ch); - case 'W': - return !IsAsciiWordChar(ch); + case 'd': return IsAsciiDigit(ch); + case 'D': return !IsAsciiDigit(ch); + case 'f': return ch == '\f'; + case 'n': return ch == '\n'; + case 'r': return ch == '\r'; + case 's': return IsAsciiWhiteSpace(ch); + case 'S': return !IsAsciiWhiteSpace(ch); + case 't': return ch == '\t'; + case 'v': return ch == '\v'; + case 'w': return IsAsciiWordChar(ch); + case 'W': return !IsAsciiWordChar(ch); } return IsAsciiPunct(pattern_char) && pattern_char == ch; } @@ -8308,26 +11146,22 @@ bool AtomMatchesChar(bool escaped, char pattern_char, char ch) { } // Helper function used by ValidateRegex() to format error messages. -std::string FormatRegexSyntaxError(const char* regex, int index) { +static std::string FormatRegexSyntaxError(const char* regex, int index) { return (Message() << "Syntax error at index " << index - << " in simple regular expression \"" << regex << "\": ") - .GetString(); + << " in simple regular expression \"" << regex << "\": ").GetString(); } // Generates non-fatal failures and returns false if regex is invalid; // otherwise returns true. bool ValidateRegex(const char* regex) { - if (regex == NULL) { - // TODO(wan@google.com): fix the source file location in the - // assertion failures to match where the regex is used in user - // code. + if (regex == nullptr) { ADD_FAILURE() << "NULL is not a valid simple regular expression."; return false; } bool is_valid = true; - // True iff ?, *, or + can follow the previous atom. + // True if and only if ?, *, or + can follow the previous atom. bool prev_repeatable = false; for (int i = 0; regex[i]; i++) { if (regex[i] == '\\') { // An escape sequence @@ -8356,12 +11190,12 @@ bool ValidateRegex(const char* regex) { << "'$' can only appear at the end."; is_valid = false; } else if (IsInSet(ch, "()[]{}|")) { - ADD_FAILURE() << FormatRegexSyntaxError(regex, i) << "'" << ch - << "' is unsupported."; + ADD_FAILURE() << FormatRegexSyntaxError(regex, i) + << "'" << ch << "' is unsupported."; is_valid = false; } else if (IsRepeat(ch) && !prev_repeatable) { - ADD_FAILURE() << FormatRegexSyntaxError(regex, i) << "'" << ch - << "' can only follow a repeatable token."; + ADD_FAILURE() << FormatRegexSyntaxError(regex, i) + << "'" << ch << "' can only follow a repeatable token."; is_valid = false; } @@ -8379,10 +11213,12 @@ bool ValidateRegex(const char* regex) { // characters to be indexable by size_t, in which case the test will // probably time out anyway. We are fine with this limitation as // std::string has it too. -bool MatchRepetitionAndRegexAtHead(bool escaped, char c, char repeat, - const char* regex, const char* str) { +bool MatchRepetitionAndRegexAtHead( + bool escaped, char c, char repeat, const char* regex, + const char* str) { const size_t min_count = (repeat == '+') ? 1 : 0; - const size_t max_count = (repeat == '?') ? 1 : static_cast<size_t>(-1) - 1; + const size_t max_count = (repeat == '?') ? 1 : + static_cast<size_t>(-1) - 1; // We cannot call numeric_limits::max() as it conflicts with the // max() macro on Windows. @@ -8395,13 +11231,14 @@ bool MatchRepetitionAndRegexAtHead(bool escaped, char c, char repeat, // greedy match. return true; } - if (str[i] == '\0' || !AtomMatchesChar(escaped, c, str[i])) return false; + if (str[i] == '\0' || !AtomMatchesChar(escaped, c, str[i])) + return false; } return false; } -// Returns true iff regex matches a prefix of str. regex must be a -// valid simple regular expression and not start with "^", or the +// Returns true if and only if regex matches a prefix of str. regex must +// be a valid simple regular expression and not start with "^", or the // result is undefined. bool MatchRegexAtHead(const char* regex, const char* str) { if (*regex == '\0') // An empty regex matches a prefix of anything. @@ -8409,28 +11246,30 @@ bool MatchRegexAtHead(const char* regex, const char* str) { // "$" only matches the end of a string. Note that regex being // valid guarantees that there's nothing after "$" in it. - if (*regex == '$') return *str == '\0'; + if (*regex == '$') + return *str == '\0'; // Is the first thing in regex an escape sequence? const bool escaped = *regex == '\\'; - if (escaped) ++regex; + if (escaped) + ++regex; if (IsRepeat(regex[1])) { // MatchRepetitionAndRegexAtHead() calls MatchRegexAtHead(), so // here's an indirect recursion. It terminates as the regex gets // shorter in each recursion. - return MatchRepetitionAndRegexAtHead(escaped, regex[0], regex[1], regex + 2, - str); + return MatchRepetitionAndRegexAtHead( + escaped, regex[0], regex[1], regex + 2, str); } else { // regex isn't empty, isn't "$", and doesn't start with a // repetition. We match the first atom of regex with the first // character of str and recurse. return (*str != '\0') && AtomMatchesChar(escaped, *regex, *str) && - MatchRegexAtHead(regex + 1, str + 1); + MatchRegexAtHead(regex + 1, str + 1); } } -// Returns true iff regex matches any substring of str. regex must be -// a valid simple regular expression, or the result is undefined. +// Returns true if and only if regex matches any substring of str. regex must +// be a valid simple regular expression, or the result is undefined. // // The algorithm is recursive, but the recursion depth doesn't exceed // the regex length, so we won't need to worry about running out of @@ -8438,13 +11277,15 @@ bool MatchRegexAtHead(const char* regex, const char* str) { // exponential with respect to the regex length + the string length, // but usually it's must faster (often close to linear). bool MatchRegexAnywhere(const char* regex, const char* str) { - if (regex == NULL || str == NULL) return false; + if (regex == nullptr || str == nullptr) return false; - if (*regex == '^') return MatchRegexAtHead(regex + 1, str); + if (*regex == '^') + return MatchRegexAtHead(regex + 1, str); // A successful match can be anywhere in str. do { - if (MatchRegexAtHead(regex, str)) return true; + if (MatchRegexAtHead(regex, str)) + return true; } while (*str++ != '\0'); return false; } @@ -8456,21 +11297,21 @@ RE::~RE() { free(const_cast<char*>(full_pattern_)); } -// Returns true iff regular expression re matches the entire str. +// Returns true if and only if regular expression re matches the entire str. bool RE::FullMatch(const char* str, const RE& re) { return re.is_valid_ && MatchRegexAnywhere(re.full_pattern_, str); } -// Returns true iff regular expression re matches a substring of str -// (including str itself). +// Returns true if and only if regular expression re matches a substring of +// str (including str itself). bool RE::PartialMatch(const char* str, const RE& re) { return re.is_valid_ && MatchRegexAnywhere(re.pattern_, str); } // Initializes an RE from its string representation. void RE::Init(const char* regex) { - pattern_ = full_pattern_ = NULL; - if (regex != NULL) { + pattern_ = full_pattern_ = nullptr; + if (regex != nullptr) { pattern_ = posix::StrDup(regex); } @@ -8508,7 +11349,7 @@ const char kUnknownFile[] = "unknown file"; // Formats a source file path and a line number as they would appear // in an error message from the compiler used to compile this code. GTEST_API_ ::std::string FormatFileLocation(const char* file, int line) { - const std::string file_name(file == NULL ? kUnknownFile : file); + const std::string file_name(file == nullptr ? kUnknownFile : file); if (line < 0) { return file_name + ":"; @@ -8525,9 +11366,9 @@ GTEST_API_ ::std::string FormatFileLocation(const char* file, int line) { // FormatFileLocation in order to contrast the two functions. // Note that FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation() does NOT append colon // to the file location it produces, unlike FormatFileLocation(). -GTEST_API_ ::std::string FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation(const char* file, - int line) { - const std::string file_name(file == NULL ? kUnknownFile : file); +GTEST_API_ ::std::string FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation( + const char* file, int line) { + const std::string file_name(file == nullptr ? kUnknownFile : file); if (line < 0) return file_name; @@ -8538,14 +11379,11 @@ GTEST_API_ ::std::string FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation(const char* file, GTestLog::GTestLog(GTestLogSeverity severity, const char* file, int line) : severity_(severity) { const char* const marker = - severity == GTEST_INFO - ? "[ INFO ]" - : severity == GTEST_WARNING - ? "[WARNING]" - : severity == GTEST_ERROR ? "[ ERROR ]" : "[ FATAL ]"; - GetStream() << ::std::endl - << marker << " " << FormatFileLocation(file, line).c_str() - << ": "; + severity == GTEST_INFO ? "[ INFO ]" : + severity == GTEST_WARNING ? "[WARNING]" : + severity == GTEST_ERROR ? "[ ERROR ]" : "[ FATAL ]"; + GetStream() << ::std::endl << marker << " " + << FormatFileLocation(file, line).c_str() << ": "; } // Flushes the buffers and, if severity is GTEST_FATAL, aborts the program. @@ -8556,12 +11394,10 @@ GTestLog::~GTestLog() { posix::Abort(); } } + // Disable Microsoft deprecation warnings for POSIX functions called from // this class (creat, dup, dup2, and close) -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) -# pragma warning(disable : 4996) -#endif // _MSC_VER +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_DEPRECATED_PUSH_() #if GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION @@ -8570,26 +11406,27 @@ class CapturedStream { public: // The ctor redirects the stream to a temporary file. explicit CapturedStream(int fd) : fd_(fd), uncaptured_fd_(dup(fd)) { -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - char temp_dir_path[MAX_PATH + 1] = {'\0'}; // NOLINT - char temp_file_path[MAX_PATH + 1] = {'\0'}; // NOLINT +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + char temp_dir_path[MAX_PATH + 1] = { '\0' }; // NOLINT + char temp_file_path[MAX_PATH + 1] = { '\0' }; // NOLINT ::GetTempPathA(sizeof(temp_dir_path), temp_dir_path); - const UINT success = ::GetTempFileNameA(temp_dir_path, "gtest_redir", + const UINT success = ::GetTempFileNameA(temp_dir_path, + "gtest_redir", 0, // Generate unique file name. temp_file_path); GTEST_CHECK_(success != 0) << "Unable to create a temporary file in " << temp_dir_path; const int captured_fd = creat(temp_file_path, _S_IREAD | _S_IWRITE); - GTEST_CHECK_(captured_fd != -1) - << "Unable to open temporary file " << temp_file_path; + GTEST_CHECK_(captured_fd != -1) << "Unable to open temporary file " + << temp_file_path; filename_ = temp_file_path; -# else +# else // There's no guarantee that a test has write access to the current // directory, so we create the temporary file in the /tmp directory // instead. We use /tmp on most systems, and /sdcard on Android. // That's because Android doesn't have /tmp. -# if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID +# if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID // Note: Android applications are expected to call the framework's // Context.getExternalStorageDirectory() method through JNI to get // the location of the world-writable SD Card directory. However, @@ -8598,48 +11435,50 @@ class CapturedStream { // code as part of a regular standalone executable, which doesn't // run in a Dalvik process (e.g. when running it through 'adb shell'). // - // The location /sdcard is directly accessible from native code - // and is the only location (unofficially) supported by the Android - // team. It's generally a symlink to the real SD Card mount point - // which can be /mnt/sdcard, /mnt/sdcard0, /system/media/sdcard, or - // other OEM-customized locations. Never rely on these, and always - // use /sdcard. - char name_template[] = "/sdcard/gtest_captured_stream.XXXXXX"; -# else + // The location /data/local/tmp is directly accessible from native code. + // '/sdcard' and other variants cannot be relied on, as they are not + // guaranteed to be mounted, or may have a delay in mounting. + char name_template[] = "/data/local/tmp/gtest_captured_stream.XXXXXX"; +# else char name_template[] = "/tmp/captured_stream.XXXXXX"; -# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID +# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID const int captured_fd = mkstemp(name_template); + if (captured_fd == -1) { + GTEST_LOG_(WARNING) + << "Failed to create tmp file " << name_template + << " for test; does the test have access to the /tmp directory?"; + } filename_ = name_template; -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - fflush(NULL); +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + fflush(nullptr); dup2(captured_fd, fd_); close(captured_fd); } - ~CapturedStream() { remove(filename_.c_str()); } + ~CapturedStream() { + remove(filename_.c_str()); + } std::string GetCapturedString() { if (uncaptured_fd_ != -1) { // Restores the original stream. - fflush(NULL); + fflush(nullptr); dup2(uncaptured_fd_, fd_); close(uncaptured_fd_); uncaptured_fd_ = -1; } FILE* const file = posix::FOpen(filename_.c_str(), "r"); + if (file == nullptr) { + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "Failed to open tmp file " << filename_ + << " for capturing stream."; + } const std::string content = ReadEntireFile(file); posix::FClose(file); return content; } private: - // Reads the entire content of a file as an std::string. - static std::string ReadEntireFile(FILE* file); - - // Returns the size (in bytes) of a file. - static size_t GetFileSize(FILE* file); - const int fd_; // A stream to capture. int uncaptured_fd_; // Name of the temporary file holding the stderr output. @@ -8648,46 +11487,15 @@ class CapturedStream { GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(CapturedStream); }; -// Returns the size (in bytes) of a file. -size_t CapturedStream::GetFileSize(FILE* file) { - fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END); - return static_cast<size_t>(ftell(file)); -} - -// Reads the entire content of a file as a string. -std::string CapturedStream::ReadEntireFile(FILE* file) { - const size_t file_size = GetFileSize(file); - char* const buffer = new char[file_size]; - - size_t bytes_last_read = 0; // # of bytes read in the last fread() - size_t bytes_read = 0; // # of bytes read so far - - fseek(file, 0, SEEK_SET); - - // Keeps reading the file until we cannot read further or the - // pre-determined file size is reached. - do { - bytes_last_read = - fread(buffer + bytes_read, 1, file_size - bytes_read, file); - bytes_read += bytes_last_read; - } while (bytes_last_read > 0 && bytes_read < file_size); - - const std::string content(buffer, bytes_read); - delete[] buffer; +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_DEPRECATED_POP_() - return content; -} - -# ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) -# endif // _MSC_VER - -static CapturedStream* g_captured_stderr = NULL; -static CapturedStream* g_captured_stdout = NULL; +static CapturedStream* g_captured_stderr = nullptr; +static CapturedStream* g_captured_stdout = nullptr; // Starts capturing an output stream (stdout/stderr). -void CaptureStream(int fd, const char* stream_name, CapturedStream** stream) { - if (*stream != NULL) { +static void CaptureStream(int fd, const char* stream_name, + CapturedStream** stream) { + if (*stream != nullptr) { GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "Only one " << stream_name << " capturer can exist at a time."; } @@ -8695,11 +11503,11 @@ void CaptureStream(int fd, const char* stream_name, CapturedStream** stream) { } // Stops capturing the output stream and returns the captured string. -std::string GetCapturedStream(CapturedStream** captured_stream) { +static std::string GetCapturedStream(CapturedStream** captured_stream) { const std::string content = (*captured_stream)->GetCapturedString(); delete *captured_stream; - *captured_stream = NULL; + *captured_stream = nullptr; return content; } @@ -8726,24 +11534,61 @@ std::string GetCapturedStderr() { #endif // GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION -#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST -// A copy of all command line arguments. Set by InitGoogleTest(). -::std::vector<testing::internal::string> g_argvs; -static const ::std::vector<testing::internal::string>* g_injected_test_argvs = - NULL; // Owned. -void SetInjectableArgvs(const ::std::vector<testing::internal::string>* argvs) { - if (g_injected_test_argvs != argvs) delete g_injected_test_argvs; - g_injected_test_argvs = argvs; + +size_t GetFileSize(FILE* file) { + fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END); + return static_cast<size_t>(ftell(file)); } -const ::std::vector<testing::internal::string>& GetInjectableArgvs() { - if (g_injected_test_argvs != NULL) { +std::string ReadEntireFile(FILE* file) { + const size_t file_size = GetFileSize(file); + char* const buffer = new char[file_size]; + + size_t bytes_last_read = 0; // # of bytes read in the last fread() + size_t bytes_read = 0; // # of bytes read so far + + fseek(file, 0, SEEK_SET); + + // Keeps reading the file until we cannot read further or the + // pre-determined file size is reached. + do { + bytes_last_read = fread(buffer+bytes_read, 1, file_size-bytes_read, file); + bytes_read += bytes_last_read; + } while (bytes_last_read > 0 && bytes_read < file_size); + + const std::string content(buffer, bytes_read); + delete[] buffer; + + return content; +} + +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +static const std::vector<std::string>* g_injected_test_argvs = + nullptr; // Owned. + +std::vector<std::string> GetInjectableArgvs() { + if (g_injected_test_argvs != nullptr) { return *g_injected_test_argvs; } - return g_argvs; + return GetArgvs(); +} + +void SetInjectableArgvs(const std::vector<std::string>* new_argvs) { + if (g_injected_test_argvs != new_argvs) delete g_injected_test_argvs; + g_injected_test_argvs = new_argvs; +} + +void SetInjectableArgvs(const std::vector<std::string>& new_argvs) { + SetInjectableArgvs( + new std::vector<std::string>(new_argvs.begin(), new_argvs.end())); +} + +void ClearInjectableArgvs() { + delete g_injected_test_argvs; + g_injected_test_argvs = nullptr; } #endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST @@ -8774,9 +11619,9 @@ static std::string FlagToEnvVar(const char* flag) { // Parses 'str' for a 32-bit signed integer. If successful, writes // the result to *value and returns true; otherwise leaves *value // unchanged and returns false. -bool ParseInt32(const Message& src_text, const char* str, Int32* value) { +bool ParseInt32(const Message& src_text, const char* str, int32_t* value) { // Parses the environment variable as a decimal integer. - char* end = NULL; + char* end = nullptr; const long long_value = strtol(str, &end, 10); // NOLINT // Has strtol() consumed all characters in the string? @@ -8791,14 +11636,14 @@ bool ParseInt32(const Message& src_text, const char* str, Int32* value) { return false; } - // Is the parsed value in the range of an Int32? - const Int32 result = static_cast<Int32>(long_value); + // Is the parsed value in the range of an int32_t? + const auto result = static_cast<int32_t>(long_value); if (long_value == LONG_MAX || long_value == LONG_MIN || // The parsed value overflows as a long. (strtol() returns // LONG_MAX or LONG_MIN when the input overflows.) result != long_value - // The parsed value overflows as an Int32. - ) { + // The parsed value overflows as an int32_t. + ) { Message msg; msg << "WARNING: " << src_text << " is expected to be a 32-bit integer, but actually" @@ -8815,27 +11660,35 @@ bool ParseInt32(const Message& src_text, const char* str, Int32* value) { // Reads and returns the Boolean environment variable corresponding to // the given flag; if it's not set, returns default_value. // -// The value is considered true iff it's not "0". +// The value is considered true if and only if it's not "0". bool BoolFromGTestEnv(const char* flag, bool default_value) { +#if defined(GTEST_GET_BOOL_FROM_ENV_) + return GTEST_GET_BOOL_FROM_ENV_(flag, default_value); +#else const std::string env_var = FlagToEnvVar(flag); const char* const string_value = posix::GetEnv(env_var.c_str()); - return string_value == NULL ? default_value : strcmp(string_value, "0") != 0; + return string_value == nullptr ? default_value + : strcmp(string_value, "0") != 0; +#endif // defined(GTEST_GET_BOOL_FROM_ENV_) } // Reads and returns a 32-bit integer stored in the environment // variable corresponding to the given flag; if it isn't set or // doesn't represent a valid 32-bit integer, returns default_value. -Int32 Int32FromGTestEnv(const char* flag, Int32 default_value) { +int32_t Int32FromGTestEnv(const char* flag, int32_t default_value) { +#if defined(GTEST_GET_INT32_FROM_ENV_) + return GTEST_GET_INT32_FROM_ENV_(flag, default_value); +#else const std::string env_var = FlagToEnvVar(flag); const char* const string_value = posix::GetEnv(env_var.c_str()); - if (string_value == NULL) { + if (string_value == nullptr) { // The environment variable is not set. return default_value; } - Int32 result = default_value; - if (!ParseInt32(Message() << "Environment variable " << env_var, string_value, - &result)) { + int32_t result = default_value; + if (!ParseInt32(Message() << "Environment variable " << env_var, + string_value, &result)) { printf("The default value %s is used.\n", (Message() << default_value).GetString().c_str()); fflush(stdout); @@ -8843,14 +11696,36 @@ Int32 Int32FromGTestEnv(const char* flag, Int32 default_value) { } return result; +#endif // defined(GTEST_GET_INT32_FROM_ENV_) +} + +// As a special case for the 'output' flag, if GTEST_OUTPUT is not +// set, we look for XML_OUTPUT_FILE, which is set by the Bazel build +// system. The value of XML_OUTPUT_FILE is a filename without the +// "xml:" prefix of GTEST_OUTPUT. +// Note that this is meant to be called at the call site so it does +// not check that the flag is 'output' +// In essence this checks an env variable called XML_OUTPUT_FILE +// and if it is set we prepend "xml:" to its value, if it not set we return "" +std::string OutputFlagAlsoCheckEnvVar(){ + std::string default_value_for_output_flag = ""; + const char* xml_output_file_env = posix::GetEnv("XML_OUTPUT_FILE"); + if (nullptr != xml_output_file_env) { + default_value_for_output_flag = std::string("xml:") + xml_output_file_env; + } + return default_value_for_output_flag; } // Reads and returns the string environment variable corresponding to // the given flag; if it's not set, returns default_value. const char* StringFromGTestEnv(const char* flag, const char* default_value) { +#if defined(GTEST_GET_STRING_FROM_ENV_) + return GTEST_GET_STRING_FROM_ENV_(flag, default_value); +#else const std::string env_var = FlagToEnvVar(flag); const char* const value = posix::GetEnv(env_var.c_str()); - return value == NULL ? default_value : value; + return value == nullptr ? default_value : value; +#endif // defined(GTEST_GET_STRING_FROM_ENV_) } } // namespace internal @@ -8883,10 +11758,9 @@ const char* StringFromGTestEnv(const char* flag, const char* default_value) { // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) -// Google Test - The Google C++ Testing Framework + +// Google Test - The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework // // This file implements a universal value printer that can print a // value of any type T: @@ -8899,11 +11773,16 @@ const char* StringFromGTestEnv(const char* flag, const char* default_value) { // or void PrintTo(const Foo&, ::std::ostream*) in the namespace that // defines Foo. -#include <ctype.h> + #include <stdio.h> +#include <cctype> +#include <cstdint> +#include <cwchar> #include <ostream> // NOLINT #include <string> +#include <type_traits> + namespace testing { @@ -8912,6 +11791,10 @@ namespace { using ::std::ostream; // Prints a segment of bytes in the given object. +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_MEMORY_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_ADDRESS_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_HWADDRESS_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_THREAD_ void PrintByteSegmentInObjectTo(const unsigned char* obj_bytes, size_t start, size_t count, ostream* os) { char text[5] = ""; @@ -8941,22 +11824,31 @@ void PrintBytesInObjectToImpl(const unsigned char* obj_bytes, size_t count, // If the object size is bigger than kThreshold, we'll have to omit // some details by printing only the first and the last kChunkSize // bytes. - // TODO(wan): let the user control the threshold using a flag. if (count < kThreshold) { PrintByteSegmentInObjectTo(obj_bytes, 0, count, os); } else { PrintByteSegmentInObjectTo(obj_bytes, 0, kChunkSize, os); *os << " ... "; // Rounds up to 2-byte boundary. - const size_t resume_pos = (count - kChunkSize + 1) / 2 * 2; + const size_t resume_pos = (count - kChunkSize + 1)/2*2; PrintByteSegmentInObjectTo(obj_bytes, resume_pos, count - resume_pos, os); } *os << ">"; } +// Helpers for widening a character to char32_t. Since the standard does not +// specify if char / wchar_t is signed or unsigned, it is important to first +// convert it to the unsigned type of the same width before widening it to +// char32_t. +template <typename CharType> +char32_t ToChar32(CharType in) { + return static_cast<char32_t>( + static_cast<typename std::make_unsigned<CharType>::type>(in)); +} + } // namespace -namespace internal2 { +namespace internal { // Delegates to PrintBytesInObjectToImpl() to print the bytes in the // given object. The delegation simplifies the implementation, which @@ -8968,160 +11860,221 @@ void PrintBytesInObjectTo(const unsigned char* obj_bytes, size_t count, PrintBytesInObjectToImpl(obj_bytes, count, os); } -} // namespace internal2 - -namespace internal { - // Depending on the value of a char (or wchar_t), we print it in one // of three formats: // - as is if it's a printable ASCII (e.g. 'a', '2', ' '), -// - as a hexidecimal escape sequence (e.g. '\x7F'), or +// - as a hexadecimal escape sequence (e.g. '\x7F'), or // - as a special escape sequence (e.g. '\r', '\n'). -enum CharFormat { kAsIs, kHexEscape, kSpecialEscape }; +enum CharFormat { + kAsIs, + kHexEscape, + kSpecialEscape +}; // Returns true if c is a printable ASCII character. We test the // value of c directly instead of calling isprint(), which is buggy on // Windows Mobile. -inline bool IsPrintableAscii(wchar_t c) { return 0x20 <= c && c <= 0x7E; } +inline bool IsPrintableAscii(char32_t c) { return 0x20 <= c && c <= 0x7E; } -// Prints a wide or narrow char c as a character literal without the -// quotes, escaping it when necessary; returns how c was formatted. -// The template argument UnsignedChar is the unsigned version of Char, -// which is the type of c. -template <typename UnsignedChar, typename Char> +// Prints c (of type char, char8_t, char16_t, char32_t, or wchar_t) as a +// character literal without the quotes, escaping it when necessary; returns how +// c was formatted. +template <typename Char> static CharFormat PrintAsCharLiteralTo(Char c, ostream* os) { - switch (static_cast<wchar_t>(c)) { - case L'\0': - *os << "\\0"; - break; - case L'\'': - *os << "\\'"; - break; - case L'\\': - *os << "\\\\"; - break; - case L'\a': - *os << "\\a"; - break; - case L'\b': - *os << "\\b"; - break; - case L'\f': - *os << "\\f"; - break; - case L'\n': - *os << "\\n"; - break; - case L'\r': - *os << "\\r"; - break; - case L'\t': - *os << "\\t"; - break; - case L'\v': - *os << "\\v"; - break; - default: - if (IsPrintableAscii(c)) { - *os << static_cast<char>(c); - return kAsIs; - } else { - *os << "\\x" + String::FormatHexInt(static_cast<UnsignedChar>(c)); - return kHexEscape; - } + const char32_t u_c = ToChar32(c); + switch (u_c) { + case L'\0': + *os << "\\0"; + break; + case L'\'': + *os << "\\'"; + break; + case L'\\': + *os << "\\\\"; + break; + case L'\a': + *os << "\\a"; + break; + case L'\b': + *os << "\\b"; + break; + case L'\f': + *os << "\\f"; + break; + case L'\n': + *os << "\\n"; + break; + case L'\r': + *os << "\\r"; + break; + case L'\t': + *os << "\\t"; + break; + case L'\v': + *os << "\\v"; + break; + default: + if (IsPrintableAscii(u_c)) { + *os << static_cast<char>(c); + return kAsIs; + } else { + ostream::fmtflags flags = os->flags(); + *os << "\\x" << std::hex << std::uppercase << static_cast<int>(u_c); + os->flags(flags); + return kHexEscape; + } } return kSpecialEscape; } -// Prints a wchar_t c as if it's part of a string literal, escaping it when +// Prints a char32_t c as if it's part of a string literal, escaping it when // necessary; returns how c was formatted. -static CharFormat PrintAsStringLiteralTo(wchar_t c, ostream* os) { +static CharFormat PrintAsStringLiteralTo(char32_t c, ostream* os) { switch (c) { - case L'\'': - *os << "'"; - return kAsIs; - case L'"': - *os << "\\\""; - return kSpecialEscape; - default: - return PrintAsCharLiteralTo<wchar_t>(c, os); + case L'\'': + *os << "'"; + return kAsIs; + case L'"': + *os << "\\\""; + return kSpecialEscape; + default: + return PrintAsCharLiteralTo(c, os); } } +static const char* GetCharWidthPrefix(char) { + return ""; +} + +static const char* GetCharWidthPrefix(signed char) { + return ""; +} + +static const char* GetCharWidthPrefix(unsigned char) { + return ""; +} + +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +static const char* GetCharWidthPrefix(char8_t) { + return "u8"; +} +#endif + +static const char* GetCharWidthPrefix(char16_t) { + return "u"; +} + +static const char* GetCharWidthPrefix(char32_t) { + return "U"; +} + +static const char* GetCharWidthPrefix(wchar_t) { + return "L"; +} + // Prints a char c as if it's part of a string literal, escaping it when // necessary; returns how c was formatted. static CharFormat PrintAsStringLiteralTo(char c, ostream* os) { - return PrintAsStringLiteralTo( - static_cast<wchar_t>(static_cast<unsigned char>(c)), os); + return PrintAsStringLiteralTo(ToChar32(c), os); +} + +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +static CharFormat PrintAsStringLiteralTo(char8_t c, ostream* os) { + return PrintAsStringLiteralTo(ToChar32(c), os); +} +#endif + +static CharFormat PrintAsStringLiteralTo(char16_t c, ostream* os) { + return PrintAsStringLiteralTo(ToChar32(c), os); +} + +static CharFormat PrintAsStringLiteralTo(wchar_t c, ostream* os) { + return PrintAsStringLiteralTo(ToChar32(c), os); } -// Prints a wide or narrow character c and its code. '\0' is printed -// as "'\\0'", other unprintable characters are also properly escaped -// using the standard C++ escape sequence. The template argument -// UnsignedChar is the unsigned version of Char, which is the type of c. -template <typename UnsignedChar, typename Char> +// Prints a character c (of type char, char8_t, char16_t, char32_t, or wchar_t) +// and its code. '\0' is printed as "'\\0'", other unprintable characters are +// also properly escaped using the standard C++ escape sequence. +template <typename Char> void PrintCharAndCodeTo(Char c, ostream* os) { // First, print c as a literal in the most readable form we can find. - *os << ((sizeof(c) > 1) ? "L'" : "'"); - const CharFormat format = PrintAsCharLiteralTo<UnsignedChar>(c, os); + *os << GetCharWidthPrefix(c) << "'"; + const CharFormat format = PrintAsCharLiteralTo(c, os); *os << "'"; // To aid user debugging, we also print c's code in decimal, unless // it's 0 (in which case c was printed as '\\0', making the code // obvious). - if (c == 0) return; + if (c == 0) + return; *os << " (" << static_cast<int>(c); - // For more convenience, we print c's code again in hexidecimal, + // For more convenience, we print c's code again in hexadecimal, // unless c was already printed in the form '\x##' or the code is in // [1, 9]. if (format == kHexEscape || (1 <= c && c <= 9)) { // Do nothing. } else { - *os << ", 0x" << String::FormatHexInt(static_cast<UnsignedChar>(c)); + *os << ", 0x" << String::FormatHexInt(static_cast<int>(c)); } *os << ")"; } -void PrintTo(unsigned char c, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintCharAndCodeTo<unsigned char>(c, os); -} -void PrintTo(signed char c, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintCharAndCodeTo<unsigned char>(c, os); -} +void PrintTo(unsigned char c, ::std::ostream* os) { PrintCharAndCodeTo(c, os); } +void PrintTo(signed char c, ::std::ostream* os) { PrintCharAndCodeTo(c, os); } // Prints a wchar_t as a symbol if it is printable or as its internal // code otherwise and also as its code. L'\0' is printed as "L'\\0'". -void PrintTo(wchar_t wc, ostream* os) { PrintCharAndCodeTo<wchar_t>(wc, os); } +void PrintTo(wchar_t wc, ostream* os) { PrintCharAndCodeTo(wc, os); } + +// TODO(dcheng): Consider making this delegate to PrintCharAndCodeTo() as well. +void PrintTo(char32_t c, ::std::ostream* os) { + *os << std::hex << "U+" << std::uppercase << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(4) + << static_cast<uint32_t>(c); +} // Prints the given array of characters to the ostream. CharType must be either -// char or wchar_t. +// char, char8_t, char16_t, char32_t, or wchar_t. // The array starts at begin, the length is len, it may include '\0' characters // and may not be NUL-terminated. template <typename CharType> -static void PrintCharsAsStringTo(const CharType* begin, size_t len, - ostream* os) { - const char* const kQuoteBegin = sizeof(CharType) == 1 ? "\"" : "L\""; - *os << kQuoteBegin; +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_MEMORY_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_ADDRESS_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_HWADDRESS_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_THREAD_ +static CharFormat PrintCharsAsStringTo( + const CharType* begin, size_t len, ostream* os) { + const char* const quote_prefix = GetCharWidthPrefix(*begin); + *os << quote_prefix << "\""; bool is_previous_hex = false; + CharFormat print_format = kAsIs; for (size_t index = 0; index < len; ++index) { const CharType cur = begin[index]; if (is_previous_hex && IsXDigit(cur)) { // Previous character is of '\x..' form and this character can be // interpreted as another hexadecimal digit in its number. Break string to // disambiguate. - *os << "\" " << kQuoteBegin; + *os << "\" " << quote_prefix << "\""; } is_previous_hex = PrintAsStringLiteralTo(cur, os) == kHexEscape; + // Remember if any characters required hex escaping. + if (is_previous_hex) { + print_format = kHexEscape; + } } *os << "\""; + return print_format; } // Prints a (const) char/wchar_t array of 'len' elements, starting at address // 'begin'. CharType must be either char or wchar_t. template <typename CharType> -static void UniversalPrintCharArray(const CharType* begin, size_t len, - ostream* os) { +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_MEMORY_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_ADDRESS_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_HWADDRESS_ +GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_THREAD_ +static void UniversalPrintCharArray( + const CharType* begin, size_t len, ostream* os) { // The code // const char kFoo[] = "foo"; // generates an array of 4, not 3, elements, with the last one being '\0'. @@ -9147,22 +12100,57 @@ void UniversalPrintArray(const char* begin, size_t len, ostream* os) { UniversalPrintCharArray(begin, len, os); } +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +// Prints a (const) char8_t array of 'len' elements, starting at address +// 'begin'. +void UniversalPrintArray(const char8_t* begin, size_t len, ostream* os) { + UniversalPrintCharArray(begin, len, os); +} +#endif + +// Prints a (const) char16_t array of 'len' elements, starting at address +// 'begin'. +void UniversalPrintArray(const char16_t* begin, size_t len, ostream* os) { + UniversalPrintCharArray(begin, len, os); +} + +// Prints a (const) char32_t array of 'len' elements, starting at address +// 'begin'. +void UniversalPrintArray(const char32_t* begin, size_t len, ostream* os) { + UniversalPrintCharArray(begin, len, os); +} + // Prints a (const) wchar_t array of 'len' elements, starting at address // 'begin'. void UniversalPrintArray(const wchar_t* begin, size_t len, ostream* os) { UniversalPrintCharArray(begin, len, os); } -// Prints the given C string to the ostream. -void PrintTo(const char* s, ostream* os) { - if (s == NULL) { +namespace { + +// Prints a null-terminated C-style string to the ostream. +template <typename Char> +void PrintCStringTo(const Char* s, ostream* os) { + if (s == nullptr) { *os << "NULL"; } else { *os << ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s) << " pointing to "; - PrintCharsAsStringTo(s, strlen(s), os); + PrintCharsAsStringTo(s, std::char_traits<Char>::length(s), os); } } +} // anonymous namespace + +void PrintTo(const char* s, ostream* os) { PrintCStringTo(s, os); } + +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +void PrintTo(const char8_t* s, ostream* os) { PrintCStringTo(s, os); } +#endif + +void PrintTo(const char16_t* s, ostream* os) { PrintCStringTo(s, os); } + +void PrintTo(const char32_t* s, ostream* os) { PrintCStringTo(s, os); } + // MSVC compiler can be configured to define whar_t as a typedef // of unsigned short. Defining an overload for const wchar_t* in that case // would cause pointers to unsigned shorts be printed as wide strings, @@ -9171,33 +12159,97 @@ void PrintTo(const char* s, ostream* os) { // wchar_t is implemented as a native type. #if !defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(_NATIVE_WCHAR_T_DEFINED) // Prints the given wide C string to the ostream. -void PrintTo(const wchar_t* s, ostream* os) { - if (s == NULL) { - *os << "NULL"; - } else { - *os << ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s) << " pointing to "; - PrintCharsAsStringTo(s, wcslen(s), os); +void PrintTo(const wchar_t* s, ostream* os) { PrintCStringTo(s, os); } +#endif // wchar_t is native + +namespace { + +bool ContainsUnprintableControlCodes(const char* str, size_t length) { + const unsigned char *s = reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char *>(str); + + for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++) { + unsigned char ch = *s++; + if (std::iscntrl(ch)) { + switch (ch) { + case '\t': + case '\n': + case '\r': + break; + default: + return true; + } + } } + return false; } -#endif // wchar_t is native -// Prints a ::string object. -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING -void PrintStringTo(const ::string& s, ostream* os) { - PrintCharsAsStringTo(s.data(), s.size(), os); +bool IsUTF8TrailByte(unsigned char t) { return 0x80 <= t && t<= 0xbf; } + +bool IsValidUTF8(const char* str, size_t length) { + const unsigned char *s = reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char *>(str); + + for (size_t i = 0; i < length;) { + unsigned char lead = s[i++]; + + if (lead <= 0x7f) { + continue; // single-byte character (ASCII) 0..7F + } + if (lead < 0xc2) { + return false; // trail byte or non-shortest form + } else if (lead <= 0xdf && (i + 1) <= length && IsUTF8TrailByte(s[i])) { + ++i; // 2-byte character + } else if (0xe0 <= lead && lead <= 0xef && (i + 2) <= length && + IsUTF8TrailByte(s[i]) && + IsUTF8TrailByte(s[i + 1]) && + // check for non-shortest form and surrogate + (lead != 0xe0 || s[i] >= 0xa0) && + (lead != 0xed || s[i] < 0xa0)) { + i += 2; // 3-byte character + } else if (0xf0 <= lead && lead <= 0xf4 && (i + 3) <= length && + IsUTF8TrailByte(s[i]) && + IsUTF8TrailByte(s[i + 1]) && + IsUTF8TrailByte(s[i + 2]) && + // check for non-shortest form + (lead != 0xf0 || s[i] >= 0x90) && + (lead != 0xf4 || s[i] < 0x90)) { + i += 3; // 4-byte character + } else { + return false; + } + } + return true; +} + +void ConditionalPrintAsText(const char* str, size_t length, ostream* os) { + if (!ContainsUnprintableControlCodes(str, length) && + IsValidUTF8(str, length)) { + *os << "\n As Text: \"" << str << "\""; + } } -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING + +} // anonymous namespace void PrintStringTo(const ::std::string& s, ostream* os) { + if (PrintCharsAsStringTo(s.data(), s.size(), os) == kHexEscape) { + if (GTEST_FLAG(print_utf8)) { + ConditionalPrintAsText(s.data(), s.size(), os); + } + } +} + +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +void PrintU8StringTo(const ::std::u8string& s, ostream* os) { PrintCharsAsStringTo(s.data(), s.size(), os); } +#endif -// Prints a ::wstring object. -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING -void PrintWideStringTo(const ::wstring& s, ostream* os) { +void PrintU16StringTo(const ::std::u16string& s, ostream* os) { + PrintCharsAsStringTo(s.data(), s.size(), os); +} + +void PrintU32StringTo(const ::std::u32string& s, ostream* os) { PrintCharsAsStringTo(s.data(), s.size(), os); } -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING #if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING void PrintWideStringTo(const ::std::wstring& s, ostream* os) { @@ -9236,18 +12288,11 @@ void PrintWideStringTo(const ::std::wstring& s, ostream* os) { // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + // -// Author: mheule@google.com (Markus Heule) -// -// The Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) + -// Indicates that this translation unit is part of Google Test's -// implementation. It must come before gtest-internal-inl.h is -// included, or there will be a compiler error. This trick is to -// prevent a user from accidentally including gtest-internal-inl.h in -// his code. -#define GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ 1 -#undef GTEST_IMPLEMENTATION_ namespace testing { @@ -9257,17 +12302,21 @@ using internal::GetUnitTestImpl; // in it. std::string TestPartResult::ExtractSummary(const char* message) { const char* const stack_trace = strstr(message, internal::kStackTraceMarker); - return stack_trace == NULL ? message : std::string(message, stack_trace); + return stack_trace == nullptr ? message : std::string(message, stack_trace); } // Prints a TestPartResult object. std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const TestPartResult& result) { - return os << result.file_name() << ":" << result.line_number() << ": " + return os << internal::FormatFileLocation(result.file_name(), + result.line_number()) + << " " << (result.type() == TestPartResult::kSuccess ? "Success" - : result.type() == TestPartResult::kFatalFailure - ? "Fatal failure" - : "Non-fatal failure") + : result.type() == TestPartResult::kSkip + ? "Skipped" + : result.type() == TestPartResult::kFatalFailure + ? "Fatal failure" + : "Non-fatal failure") << ":\n" << result.message() << std::endl; } @@ -9284,7 +12333,7 @@ const TestPartResult& TestPartResultArray::GetTestPartResult(int index) const { internal::posix::Abort(); } - return array_[index]; + return array_[static_cast<size_t>(index)]; } // Returns the number of TestPartResult objects in the array. @@ -9296,8 +12345,8 @@ namespace internal { HasNewFatalFailureHelper::HasNewFatalFailureHelper() : has_new_fatal_failure_(false), - original_reporter_( - GetUnitTestImpl()->GetTestPartResultReporterForCurrentThread()) { + original_reporter_(GetUnitTestImpl()-> + GetTestPartResultReporterForCurrentThread()) { GetUnitTestImpl()->SetTestPartResultReporterForCurrentThread(this); } @@ -9308,7 +12357,8 @@ HasNewFatalFailureHelper::~HasNewFatalFailureHelper() { void HasNewFatalFailureHelper::ReportTestPartResult( const TestPartResult& result) { - if (result.fatally_failed()) has_new_fatal_failure_ = true; + if (result.fatally_failed()) + has_new_fatal_failure_ = true; original_reporter_->ReportTestPartResult(result); } @@ -9343,64 +12393,67 @@ void HasNewFatalFailureHelper::ReportTestPartResult( // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) + + + namespace testing { namespace internal { -#if GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - // Skips to the first non-space char in str. Returns an empty string if str // contains only whitespace characters. static const char* SkipSpaces(const char* str) { - while (IsSpace(*str)) str++; + while (IsSpace(*str)) + str++; return str; } +static std::vector<std::string> SplitIntoTestNames(const char* src) { + std::vector<std::string> name_vec; + src = SkipSpaces(src); + for (; src != nullptr; src = SkipComma(src)) { + name_vec.push_back(StripTrailingSpaces(GetPrefixUntilComma(src))); + } + return name_vec; +} + // Verifies that registered_tests match the test names in -// defined_test_names_; returns registered_tests if successful, or +// registered_tests_; returns registered_tests if successful, or // aborts the program otherwise. -const char* TypedTestCasePState::VerifyRegisteredTestNames( - const char* file, int line, const char* registered_tests) { - typedef ::std::set<const char*>::const_iterator DefinedTestIter; +const char* TypedTestSuitePState::VerifyRegisteredTestNames( + const char* test_suite_name, const char* file, int line, + const char* registered_tests) { + RegisterTypeParameterizedTestSuite(test_suite_name, CodeLocation(file, line)); + + typedef RegisteredTestsMap::const_iterator RegisteredTestIter; registered_ = true; - // Skip initial whitespace in registered_tests since some - // preprocessors prefix stringizied literals with whitespace. - registered_tests = SkipSpaces(registered_tests); + std::vector<std::string> name_vec = SplitIntoTestNames(registered_tests); Message errors; - ::std::set<std::string> tests; - for (const char* names = registered_tests; names != NULL; - names = SkipComma(names)) { - const std::string name = GetPrefixUntilComma(names); + + std::set<std::string> tests; + for (std::vector<std::string>::const_iterator name_it = name_vec.begin(); + name_it != name_vec.end(); ++name_it) { + const std::string& name = *name_it; if (tests.count(name) != 0) { errors << "Test " << name << " is listed more than once.\n"; continue; } - bool found = false; - for (DefinedTestIter it = defined_test_names_.begin(); - it != defined_test_names_.end(); ++it) { - if (name == *it) { - found = true; - break; - } - } - - if (found) { + if (registered_tests_.count(name) != 0) { tests.insert(name); } else { errors << "No test named " << name - << " can be found in this test case.\n"; + << " can be found in this test suite.\n"; } } - for (DefinedTestIter it = defined_test_names_.begin(); - it != defined_test_names_.end(); ++it) { - if (tests.count(*it) == 0) { - errors << "You forgot to list test " << *it << ".\n"; + for (RegisteredTestIter it = registered_tests_.begin(); + it != registered_tests_.end(); + ++it) { + if (tests.count(it->first) == 0) { + errors << "You forgot to list test " << it->first << ".\n"; } } @@ -9415,8 +12468,6 @@ const char* TypedTestCasePState::VerifyRegisteredTestNames( return registered_tests; } -#endif // GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - } // namespace internal } // namespace testing // Copyright 2008, Google Inc. @@ -9447,8 +12498,7 @@ const char* TypedTestCasePState::VerifyRegisteredTestNames( // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) + // // Google C++ Mocking Framework (Google Mock) // @@ -9489,15 +12539,14 @@ const char* TypedTestCasePState::VerifyRegisteredTestNames( // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) + // Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. // // This file implements cardinalities. -#include <limits.h> +#include <limits.h> #include <ostream> // NOLINT #include <sstream> #include <string> @@ -9510,7 +12559,8 @@ namespace { class BetweenCardinalityImpl : public CardinalityInterface { public: BetweenCardinalityImpl(int min, int max) - : min_(min >= 0 ? min : 0), max_(max >= min_ ? max : min_) { + : min_(min >= 0 ? min : 0), + max_(max >= min_ ? max : min_) { std::stringstream ss; if (min < 0) { ss << "The invocation lower bound must be >= 0, " @@ -9522,25 +12572,26 @@ class BetweenCardinalityImpl : public CardinalityInterface { internal::Expect(false, __FILE__, __LINE__, ss.str()); } else if (min > max) { ss << "The invocation upper bound (" << max - << ") must be >= the invocation lower bound (" << min << ")."; + << ") must be >= the invocation lower bound (" << min + << ")."; internal::Expect(false, __FILE__, __LINE__, ss.str()); } } // Conservative estimate on the lower/upper bound of the number of // calls allowed. - virtual int ConservativeLowerBound() const { return min_; } - virtual int ConservativeUpperBound() const { return max_; } + int ConservativeLowerBound() const override { return min_; } + int ConservativeUpperBound() const override { return max_; } - virtual bool IsSatisfiedByCallCount(int call_count) const { + bool IsSatisfiedByCallCount(int call_count) const override { return min_ <= call_count && call_count <= max_; } - virtual bool IsSaturatedByCallCount(int call_count) const { + bool IsSaturatedByCallCount(int call_count) const override { return call_count >= max_; } - virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const; + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override; private: const int min_; @@ -9550,7 +12601,7 @@ class BetweenCardinalityImpl : public CardinalityInterface { }; // Formats "n times" in a human-friendly way. -inline internal::string FormatTimes(int n) { +inline std::string FormatTimes(int n) { if (n == 1) { return "once"; } else if (n == 2) { @@ -9640,8 +12691,7 @@ GTEST_API_ Cardinality Exactly(int n) { return Between(n, n); } // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) + // Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. // @@ -9649,30 +12699,50 @@ GTEST_API_ Cardinality Exactly(int n) { return Between(n, n); } // Mock. They are subject to change without notice, so please DO NOT // USE THEM IN USER CODE. -#include <ctype.h> +#include <ctype.h> #include <ostream> // NOLINT #include <string> namespace testing { namespace internal { +// Joins a vector of strings as if they are fields of a tuple; returns +// the joined string. +GTEST_API_ std::string JoinAsTuple(const Strings& fields) { + switch (fields.size()) { + case 0: + return ""; + case 1: + return fields[0]; + default: + std::string result = "(" + fields[0]; + for (size_t i = 1; i < fields.size(); i++) { + result += ", "; + result += fields[i]; + } + result += ")"; + return result; + } +} + // Converts an identifier name to a space-separated list of lower-case // words. Each maximum substring of the form [A-Za-z][a-z]*|\d+ is // treated as one word. For example, both "FooBar123" and // "foo_bar_123" are converted to "foo bar 123". -GTEST_API_ string ConvertIdentifierNameToWords(const char* id_name) { - string result; +GTEST_API_ std::string ConvertIdentifierNameToWords(const char* id_name) { + std::string result; char prev_char = '\0'; for (const char* p = id_name; *p != '\0'; prev_char = *(p++)) { // We don't care about the current locale as the input is // guaranteed to be a valid C++ identifier name. const bool starts_new_word = IsUpper(*p) || - (!IsAlpha(prev_char) && IsLower(*p)) || - (!IsDigit(prev_char) && IsDigit(*p)); + (!IsAlpha(prev_char) && IsLower(*p)) || + (!IsDigit(prev_char) && IsDigit(*p)); if (IsAlNum(*p)) { - if (starts_new_word && result != "") result += ' '; + if (starts_new_word && result != "") + result += ' '; result += ToLower(*p); } } @@ -9680,15 +12750,18 @@ GTEST_API_ string ConvertIdentifierNameToWords(const char* id_name) { } // This class reports Google Mock failures as Google Test failures. A -// user can define another class in a similar fashion if he intends to +// user can define another class in a similar fashion if they intend to // use Google Mock with a testing framework other than Google Test. class GoogleTestFailureReporter : public FailureReporterInterface { public: - virtual void ReportFailure(FailureType type, const char* file, int line, - const string& message) { - AssertHelper(type == kFatal ? TestPartResult::kFatalFailure - : TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure, - file, line, message.c_str()) = Message(); + void ReportFailure(FailureType type, const char* file, int line, + const std::string& message) override { + AssertHelper(type == kFatal ? + TestPartResult::kFatalFailure : + TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure, + file, + line, + message.c_str()) = Message(); if (type == kFatal) { posix::Abort(); } @@ -9711,8 +12784,8 @@ GTEST_API_ FailureReporterInterface* GetFailureReporter() { // Protects global resources (stdout in particular) used by Log(). static GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_log_mutex); -// Returns true iff a log with the given severity is visible according -// to the --gmock_verbose flag. +// Returns true if and only if a log with the given severity is visible +// according to the --gmock_verbose flag. GTEST_API_ bool LogIsVisible(LogSeverity severity) { if (GMOCK_FLAG(verbose) == kInfoVerbosity) { // Always show the log if --gmock_verbose=info. @@ -9727,23 +12800,21 @@ GTEST_API_ bool LogIsVisible(LogSeverity severity) { } } -// Prints the given message to stdout iff 'severity' >= the level +// Prints the given message to stdout if and only if 'severity' >= the level // specified by the --gmock_verbose flag. If stack_frames_to_skip >= // 0, also prints the stack trace excluding the top // stack_frames_to_skip frames. In opt mode, any positive // stack_frames_to_skip is treated as 0, since we don't know which // function calls will be inlined by the compiler and need to be // conservative. -GTEST_API_ void Log(LogSeverity severity, const string& message, +GTEST_API_ void Log(LogSeverity severity, const std::string& message, int stack_frames_to_skip) { - if (!LogIsVisible(severity)) return; + if (!LogIsVisible(severity)) + return; // Ensures that logs from different threads don't interleave. MutexLock l(&g_log_mutex); - // "using ::std::cout;" doesn't work with Symbian's STLport, where cout is a - // macro. - if (severity == kWarning) { // Prints a GMOCK WARNING marker to make the warnings easily searchable. std::cout << "\nGMOCK WARNING:"; @@ -9768,12 +12839,24 @@ GTEST_API_ void Log(LogSeverity severity, const string& message, std::cout << "\n"; } std::cout << "Stack trace:\n" - << ::testing::internal::GetCurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop( - ::testing::UnitTest::GetInstance(), actual_to_skip); + << ::testing::internal::GetCurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop( + ::testing::UnitTest::GetInstance(), actual_to_skip); } std::cout << ::std::flush; } +GTEST_API_ WithoutMatchers GetWithoutMatchers() { return WithoutMatchers(); } + +GTEST_API_ void IllegalDoDefault(const char* file, int line) { + internal::Assert( + false, file, line, + "You are using DoDefault() inside a composite action like " + "DoAll() or WithArgs(). This is not supported for technical " + "reasons. Please instead spell out the default action, or " + "assign the default action to an Action variable and use " + "the variable in various places."); +} + } // namespace internal } // namespace testing // Copyright 2007, Google Inc. @@ -9804,102 +12887,31 @@ GTEST_API_ void Log(LogSeverity severity, const string& message, // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) + // Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. // // This file implements Matcher<const string&>, Matcher<string>, and // utilities for defining matchers. -#include <string.h> +#include <string.h> +#include <iostream> #include <sstream> #include <string> namespace testing { - -// Constructs a matcher that matches a const string& whose value is -// equal to s. -Matcher<const internal::string&>::Matcher(const internal::string& s) { - *this = Eq(s); -} - -// Constructs a matcher that matches a const string& whose value is -// equal to s. -Matcher<const internal::string&>::Matcher(const char* s) { - *this = Eq(internal::string(s)); -} - -// Constructs a matcher that matches a string whose value is equal to s. -Matcher<internal::string>::Matcher(const internal::string& s) { *this = Eq(s); } - -// Constructs a matcher that matches a string whose value is equal to s. -Matcher<internal::string>::Matcher(const char* s) { - *this = Eq(internal::string(s)); -} - -#if GTEST_HAS_STRING_PIECE_ -// Constructs a matcher that matches a const StringPiece& whose value is -// equal to s. -Matcher<const StringPiece&>::Matcher(const internal::string& s) { - *this = Eq(s); -} - -// Constructs a matcher that matches a const StringPiece& whose value is -// equal to s. -Matcher<const StringPiece&>::Matcher(const char* s) { - *this = Eq(internal::string(s)); -} - -// Constructs a matcher that matches a const StringPiece& whose value is -// equal to s. -Matcher<const StringPiece&>::Matcher(StringPiece s) { - *this = Eq(s.ToString()); -} - -// Constructs a matcher that matches a StringPiece whose value is equal to s. -Matcher<StringPiece>::Matcher(const internal::string& s) { *this = Eq(s); } - -// Constructs a matcher that matches a StringPiece whose value is equal to s. -Matcher<StringPiece>::Matcher(const char* s) { - *this = Eq(internal::string(s)); -} - -// Constructs a matcher that matches a StringPiece whose value is equal to s. -Matcher<StringPiece>::Matcher(StringPiece s) { *this = Eq(s.ToString()); } -#endif // GTEST_HAS_STRING_PIECE_ - namespace internal { -// Joins a vector of strings as if they are fields of a tuple; returns -// the joined string. -GTEST_API_ string JoinAsTuple(const Strings& fields) { - switch (fields.size()) { - case 0: - return ""; - case 1: - return fields[0]; - default: - string result = "(" + fields[0]; - for (size_t i = 1; i < fields.size(); i++) { - result += ", "; - result += fields[i]; - } - result += ")"; - return result; - } -} - // Returns the description for a matcher defined using the MATCHER*() // macro where the user-supplied description string is "", if // 'negation' is false; otherwise returns the description of the // negation of the matcher. 'param_values' contains a list of strings // that are the print-out of the matcher's parameters. -GTEST_API_ string FormatMatcherDescription(bool negation, - const char* matcher_name, - const Strings& param_values) { - string result = ConvertIdentifierNameToWords(matcher_name); +GTEST_API_ std::string FormatMatcherDescription(bool negation, + const char* matcher_name, + const Strings& param_values) { + std::string result = ConvertIdentifierNameToWords(matcher_name); if (param_values.size() >= 1) result += " " + JoinAsTuple(param_values); return negation ? "not (" + result + ")" : result; } @@ -9962,9 +12974,9 @@ GTEST_API_ string FormatMatcherDescription(bool negation, // . [ sink ] . // // See Also: -// [1] Cormen, et al (2001). "Section 26.2: The Ford–Fulkerson method". -// "Introduction to Algorithms (Second ed.)", pp. 651–664. -// [2] "Ford–Fulkerson algorithm", Wikipedia, +// [1] Cormen, et al (2001). "Section 26.2: The Ford-Fulkerson method". +// "Introduction to Algorithms (Second ed.)", pp. 651-664. +// [2] "Ford-Fulkerson algorithm", Wikipedia, // 'http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ford%E2%80%93Fulkerson_algorithm' class MaxBipartiteMatchState { public: @@ -10056,7 +13068,7 @@ class MaxBipartiteMatchState { // Each element of the left_ vector represents a left hand side node // (i.e. an element) and each element of right_ is a right hand side // node (i.e. a matcher). The values in the left_ vector indicate - // outflow from that node to a node on the the right_ side. The values + // outflow from that node to a node on the right_ side. The values // in the right_ indicate inflow, and specify which left_ node is // feeding that right_ node, if any. For example, left_[3] == 1 means // there's a flow from element #3 to matcher #1. Such a flow would also @@ -10066,8 +13078,6 @@ class MaxBipartiteMatchState { // right_[left_[i]] = i. ::std::vector<size_t> left_; ::std::vector<size_t> right_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(MaxBipartiteMatchState); }; const size_t MaxBipartiteMatchState::kUnused; @@ -10091,38 +13101,6 @@ static void LogElementMatcherPairVec(const ElementMatcherPairs& pairs, os << "\n}"; } -// Tries to find a pairing, and explains the result. -GTEST_API_ bool FindPairing(const MatchMatrix& matrix, - MatchResultListener* listener) { - ElementMatcherPairs matches = FindMaxBipartiteMatching(matrix); - - size_t max_flow = matches.size(); - bool result = (max_flow == matrix.RhsSize()); - - if (!result) { - if (listener->IsInterested()) { - *listener << "where no permutation of the elements can " - "satisfy all matchers, and the closest match is " - << max_flow << " of " << matrix.RhsSize() - << " matchers with the pairings:\n"; - LogElementMatcherPairVec(matches, listener->stream()); - } - return false; - } - - if (matches.size() > 1) { - if (listener->IsInterested()) { - const char* sep = "where:\n"; - for (size_t mi = 0; mi < matches.size(); ++mi) { - *listener << sep << " - element #" << matches[mi].first - << " is matched by matcher #" << matches[mi].second; - sep = ",\n"; - } - } - } - return true; -} - bool MatchMatrix::NextGraph() { for (size_t ilhs = 0; ilhs < LhsSize(); ++ilhs) { for (size_t irhs = 0; irhs < RhsSize(); ++irhs) { @@ -10146,7 +13124,7 @@ void MatchMatrix::Randomize() { } } -string MatchMatrix::DebugString() const { +std::string MatchMatrix::DebugString() const { ::std::stringstream ss; const char* sep = ""; for (size_t i = 0; i < LhsSize(); ++i) { @@ -10161,44 +13139,83 @@ string MatchMatrix::DebugString() const { void UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase::DescribeToImpl( ::std::ostream* os) const { - if (matcher_describers_.empty()) { - *os << "is empty"; - return; - } - if (matcher_describers_.size() == 1) { - *os << "has " << Elements(1) << " and that element "; - matcher_describers_[0]->DescribeTo(os); - return; + switch (match_flags()) { + case UnorderedMatcherRequire::ExactMatch: + if (matcher_describers_.empty()) { + *os << "is empty"; + return; + } + if (matcher_describers_.size() == 1) { + *os << "has " << Elements(1) << " and that element "; + matcher_describers_[0]->DescribeTo(os); + return; + } + *os << "has " << Elements(matcher_describers_.size()) + << " and there exists some permutation of elements such that:\n"; + break; + case UnorderedMatcherRequire::Superset: + *os << "a surjection from elements to requirements exists such that:\n"; + break; + case UnorderedMatcherRequire::Subset: + *os << "an injection from elements to requirements exists such that:\n"; + break; } - *os << "has " << Elements(matcher_describers_.size()) - << " and there exists some permutation of elements such that:\n"; + const char* sep = ""; for (size_t i = 0; i != matcher_describers_.size(); ++i) { - *os << sep << " - element #" << i << " "; + *os << sep; + if (match_flags() == UnorderedMatcherRequire::ExactMatch) { + *os << " - element #" << i << " "; + } else { + *os << " - an element "; + } matcher_describers_[i]->DescribeTo(os); - sep = ", and\n"; + if (match_flags() == UnorderedMatcherRequire::ExactMatch) { + sep = ", and\n"; + } else { + sep = "\n"; + } } } void UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase::DescribeNegationToImpl( ::std::ostream* os) const { - if (matcher_describers_.empty()) { - *os << "isn't empty"; - return; - } - if (matcher_describers_.size() == 1) { - *os << "doesn't have " << Elements(1) << ", or has " << Elements(1) - << " that "; - matcher_describers_[0]->DescribeNegationTo(os); - return; + switch (match_flags()) { + case UnorderedMatcherRequire::ExactMatch: + if (matcher_describers_.empty()) { + *os << "isn't empty"; + return; + } + if (matcher_describers_.size() == 1) { + *os << "doesn't have " << Elements(1) << ", or has " << Elements(1) + << " that "; + matcher_describers_[0]->DescribeNegationTo(os); + return; + } + *os << "doesn't have " << Elements(matcher_describers_.size()) + << ", or there exists no permutation of elements such that:\n"; + break; + case UnorderedMatcherRequire::Superset: + *os << "no surjection from elements to requirements exists such that:\n"; + break; + case UnorderedMatcherRequire::Subset: + *os << "no injection from elements to requirements exists such that:\n"; + break; } - *os << "doesn't have " << Elements(matcher_describers_.size()) - << ", or there exists no permutation of elements such that:\n"; const char* sep = ""; for (size_t i = 0; i != matcher_describers_.size(); ++i) { - *os << sep << " - element #" << i << " "; + *os << sep; + if (match_flags() == UnorderedMatcherRequire::ExactMatch) { + *os << " - element #" << i << " "; + } else { + *os << " - an element "; + } matcher_describers_[i]->DescribeTo(os); - sep = ", and\n"; + if (match_flags() == UnorderedMatcherRequire::ExactMatch) { + sep = ", and\n"; + } else { + sep = "\n"; + } } } @@ -10207,10 +13224,9 @@ void UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase::DescribeNegationToImpl( // and better error reporting. // Returns false, writing an explanation to 'listener', if and only // if the success criteria are not met. -bool UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase:: - VerifyAllElementsAndMatchersAreMatched( - const ::std::vector<string>& element_printouts, - const MatchMatrix& matrix, MatchResultListener* listener) const { +bool UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase::VerifyMatchMatrix( + const ::std::vector<std::string>& element_printouts, + const MatchMatrix& matrix, MatchResultListener* listener) const { bool result = true; ::std::vector<char> element_matched(matrix.LhsSize(), 0); ::std::vector<char> matcher_matched(matrix.RhsSize(), 0); @@ -10223,7 +13239,7 @@ bool UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase:: } } - { + if (match_flags() & UnorderedMatcherRequire::Superset) { const char* sep = "where the following matchers don't match any elements:\n"; for (size_t mi = 0; mi < matcher_matched.size(); ++mi) { @@ -10237,7 +13253,7 @@ bool UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase:: } } - { + if (match_flags() & UnorderedMatcherRequire::Subset) { const char* sep = "where the following elements don't match any matchers:\n"; const char* outer_sep = ""; @@ -10258,6 +13274,47 @@ bool UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase:: return result; } +bool UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase::FindPairing( + const MatchMatrix& matrix, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + ElementMatcherPairs matches = FindMaxBipartiteMatching(matrix); + + size_t max_flow = matches.size(); + if ((match_flags() & UnorderedMatcherRequire::Superset) && + max_flow < matrix.RhsSize()) { + if (listener->IsInterested()) { + *listener << "where no permutation of the elements can satisfy all " + "matchers, and the closest match is " + << max_flow << " of " << matrix.RhsSize() + << " matchers with the pairings:\n"; + LogElementMatcherPairVec(matches, listener->stream()); + } + return false; + } + if ((match_flags() & UnorderedMatcherRequire::Subset) && + max_flow < matrix.LhsSize()) { + if (listener->IsInterested()) { + *listener + << "where not all elements can be matched, and the closest match is " + << max_flow << " of " << matrix.RhsSize() + << " matchers with the pairings:\n"; + LogElementMatcherPairVec(matches, listener->stream()); + } + return false; + } + + if (matches.size() > 1) { + if (listener->IsInterested()) { + const char* sep = "where:\n"; + for (size_t mi = 0; mi < matches.size(); ++mi) { + *listener << sep << " - element #" << matches[mi].first + << " is matched by matcher #" << matches[mi].second; + sep = ",\n"; + } + } + } + return true; +} + } // namespace internal } // namespace testing // Copyright 2007, Google Inc. @@ -10288,23 +13345,35 @@ bool UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase:: // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) + // Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. // // This file implements the spec builder syntax (ON_CALL and // EXPECT_CALL). + #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> // NOLINT #include <map> +#include <memory> #include <set> #include <string> +#include <vector> + #if GTEST_OS_CYGWIN || GTEST_OS_LINUX || GTEST_OS_MAC -# include <unistd.h> // NOLINT +# include <unistd.h> // NOLINT +#endif + +// Silence C4800 (C4800: 'int *const ': forcing value +// to bool 'true' or 'false') for MSVC 15 +#ifdef _MSC_VER +#if _MSC_VER == 1900 +# pragma warning(push) +# pragma warning(disable:4800) +#endif #endif namespace testing { @@ -10317,15 +13386,16 @@ GTEST_API_ GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_gmock_mutex); // Logs a message including file and line number information. GTEST_API_ void LogWithLocation(testing::internal::LogSeverity severity, const char* file, int line, - const string& message) { + const std::string& message) { ::std::ostringstream s; - s << file << ":" << line << ": " << message << ::std::endl; + s << internal::FormatFileLocation(file, line) << " " << message + << ::std::endl; Log(severity, s.str(), 0); } // Constructs an ExpectationBase object. ExpectationBase::ExpectationBase(const char* a_file, int a_line, - const string& a_source_text) + const std::string& a_source_text) : file_(a_file), line_(a_line), source_text_(a_source_text), @@ -10358,26 +13428,40 @@ void ExpectationBase::RetireAllPreRequisites() return; } - for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = immediate_prerequisites_.begin(); - it != immediate_prerequisites_.end(); ++it) { - ExpectationBase* const prerequisite = it->expectation_base().get(); - if (!prerequisite->is_retired()) { - prerequisite->RetireAllPreRequisites(); - prerequisite->Retire(); + ::std::vector<ExpectationBase*> expectations(1, this); + while (!expectations.empty()) { + ExpectationBase* exp = expectations.back(); + expectations.pop_back(); + + for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = + exp->immediate_prerequisites_.begin(); + it != exp->immediate_prerequisites_.end(); ++it) { + ExpectationBase* next = it->expectation_base().get(); + if (!next->is_retired()) { + next->Retire(); + expectations.push_back(next); + } } } } -// Returns true iff all pre-requisites of this expectation have been -// satisfied. +// Returns true if and only if all pre-requisites of this expectation +// have been satisfied. bool ExpectationBase::AllPrerequisitesAreSatisfied() const GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = immediate_prerequisites_.begin(); - it != immediate_prerequisites_.end(); ++it) { - if (!(it->expectation_base()->IsSatisfied()) || - !(it->expectation_base()->AllPrerequisitesAreSatisfied())) - return false; + ::std::vector<const ExpectationBase*> expectations(1, this); + while (!expectations.empty()) { + const ExpectationBase* exp = expectations.back(); + expectations.pop_back(); + + for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = + exp->immediate_prerequisites_.begin(); + it != exp->immediate_prerequisites_.end(); ++it) { + const ExpectationBase* next = it->expectation_base().get(); + if (!next->IsSatisfied()) return false; + expectations.push_back(next); + } } return true; } @@ -10386,19 +13470,28 @@ bool ExpectationBase::AllPrerequisitesAreSatisfied() const void ExpectationBase::FindUnsatisfiedPrerequisites(ExpectationSet* result) const GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); - for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = immediate_prerequisites_.begin(); - it != immediate_prerequisites_.end(); ++it) { - if (it->expectation_base()->IsSatisfied()) { - // If *it is satisfied and has a call count of 0, some of its - // pre-requisites may not be satisfied yet. - if (it->expectation_base()->call_count_ == 0) { - it->expectation_base()->FindUnsatisfiedPrerequisites(result); + ::std::vector<const ExpectationBase*> expectations(1, this); + while (!expectations.empty()) { + const ExpectationBase* exp = expectations.back(); + expectations.pop_back(); + + for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = + exp->immediate_prerequisites_.begin(); + it != exp->immediate_prerequisites_.end(); ++it) { + const ExpectationBase* next = it->expectation_base().get(); + + if (next->IsSatisfied()) { + // If *it is satisfied and has a call count of 0, some of its + // pre-requisites may not be satisfied yet. + if (next->call_count_ == 0) { + expectations.push_back(next); + } + } else { + // Now that we know next is unsatisfied, we are not so interested + // in whether its pre-requisites are satisfied. Therefore we + // don't iterate into it here. + *result += *it; } - } else { - // Now that we know *it is unsatisfied, we are not so interested - // in whether its pre-requisites are satisfied. Therefore we - // don't recursively call FindUnsatisfiedPrerequisites() here. - *result += *it; } } } @@ -10417,12 +13510,11 @@ void ExpectationBase::DescribeCallCountTo(::std::ostream* os) const // Describes the state of the expectation (e.g. is it satisfied? // is it active?). - *os << " - " - << (IsOverSaturated() - ? "over-saturated" - : IsSaturated() ? "saturated" - : IsSatisfied() ? "satisfied" : "unsatisfied") - << " and " << (is_retired() ? "retired" : "active"); + *os << " - " << (IsOverSaturated() ? "over-saturated" : + IsSaturated() ? "saturated" : + IsSatisfied() ? "satisfied" : "unsatisfied") + << " and " + << (is_retired() ? "retired" : "active"); } // Checks the action count (i.e. the number of WillOnce() and @@ -10465,12 +13557,13 @@ void ExpectationBase::CheckActionCountIfNotDone() const ::std::stringstream ss; DescribeLocationTo(&ss); - ss << "Too " << (too_many ? "many" : "few") << " actions specified in " - << source_text() << "...\n" + ss << "Too " << (too_many ? "many" : "few") + << " actions specified in " << source_text() << "...\n" << "Expected to be "; cardinality().DescribeTo(&ss); - ss << ", but has " << (too_many ? "" : "only ") << action_count - << " WillOnce()" << (action_count == 1 ? "" : "s"); + ss << ", but has " << (too_many ? "" : "only ") + << action_count << " WillOnce()" + << (action_count == 1 ? "" : "s"); if (repeated_action_specified_) { ss << " and a WillRepeatedly()"; } @@ -10502,21 +13595,33 @@ GTEST_API_ ThreadLocal<Sequence*> g_gmock_implicit_sequence; // Reports an uninteresting call (whose description is in msg) in the // manner specified by 'reaction'. -void ReportUninterestingCall(CallReaction reaction, const string& msg) { +void ReportUninterestingCall(CallReaction reaction, const std::string& msg) { + // Include a stack trace only if --gmock_verbose=info is specified. + const int stack_frames_to_skip = + GMOCK_FLAG(verbose) == kInfoVerbosity ? 3 : -1; switch (reaction) { - case kAllow: - Log(kInfo, msg, 3); - break; - case kWarn: - Log(kWarning, msg, 3); - break; - default: // FAIL - Expect(false, NULL, -1, msg); + case kAllow: + Log(kInfo, msg, stack_frames_to_skip); + break; + case kWarn: + Log(kWarning, + msg + + "\nNOTE: You can safely ignore the above warning unless this " + "call should not happen. Do not suppress it by blindly adding " + "an EXPECT_CALL() if you don't mean to enforce the call. " + "See " + "https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/docs/" + "gmock_cook_book.md#" + "knowing-when-to-expect for details.\n", + stack_frames_to_skip); + break; + default: // FAIL + Expect(false, nullptr, -1, msg); } } UntypedFunctionMockerBase::UntypedFunctionMockerBase() - : mock_obj_(NULL), name_("") {} + : mock_obj_(nullptr), name_("") {} UntypedFunctionMockerBase::~UntypedFunctionMockerBase() {} @@ -10555,7 +13660,7 @@ const void* UntypedFunctionMockerBase::MockObject() const // We protect mock_obj_ under g_gmock_mutex in case this mock // function is called from two threads concurrently. MutexLock l(&g_gmock_mutex); - Assert(mock_obj_ != NULL, __FILE__, __LINE__, + Assert(mock_obj_ != nullptr, __FILE__, __LINE__, "MockObject() must not be called before RegisterOwner() or " "SetOwnerAndName() has been called."); mock_obj = mock_obj_; @@ -10572,7 +13677,7 @@ const char* UntypedFunctionMockerBase::Name() const // We protect name_ under g_gmock_mutex in case this mock // function is called from two threads concurrently. MutexLock l(&g_gmock_mutex); - Assert(name_ != NULL, __FILE__, __LINE__, + Assert(name_ != nullptr, __FILE__, __LINE__, "Name() must not be called before SetOwnerAndName() has " "been called."); name = name_; @@ -10583,9 +13688,10 @@ const char* UntypedFunctionMockerBase::Name() const // Calculates the result of invoking this mock function with the given // arguments, prints it, and returns it. The caller is responsible // for deleting the result. -const UntypedActionResultHolderBase* -UntypedFunctionMockerBase::UntypedInvokeWith(const void* const untyped_args) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { +UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedFunctionMockerBase::UntypedInvokeWith( + void* const untyped_args) GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + // See the definition of untyped_expectations_ for why access to it + // is unprotected here. if (untyped_expectations_.size() == 0) { // No expectation is set on this mock method - we have an // uninteresting call. @@ -10597,15 +13703,15 @@ UntypedFunctionMockerBase::UntypedInvokeWith(const void* const untyped_args) const CallReaction reaction = Mock::GetReactionOnUninterestingCalls(MockObject()); - // True iff we need to print this call's arguments and return + // True if and only if we need to print this call's arguments and return // value. This definition must be kept in sync with // the behavior of ReportUninterestingCall(). const bool need_to_report_uninteresting_call = // If the user allows this uninteresting call, we print it - // only when he wants informational messages. + // only when they want informational messages. reaction == kAllow ? LogIsVisible(kInfo) : // If the user wants this to be a warning, we print - // it only when he wants to see warnings. + // it only when they want to see warnings. reaction == kWarn ? LogIsVisible(kWarning) : @@ -10615,7 +13721,8 @@ UntypedFunctionMockerBase::UntypedInvokeWith(const void* const untyped_args) if (!need_to_report_uninteresting_call) { // Perform the action without printing the call information. - return this->UntypedPerformDefaultAction(untyped_args, ""); + return this->UntypedPerformDefaultAction( + untyped_args, "Function call: " + std::string(Name())); } // Warns about the uninteresting call. @@ -10623,11 +13730,11 @@ UntypedFunctionMockerBase::UntypedInvokeWith(const void* const untyped_args) this->UntypedDescribeUninterestingCall(untyped_args, &ss); // Calculates the function result. - const UntypedActionResultHolderBase* const result = + UntypedActionResultHolderBase* const result = this->UntypedPerformDefaultAction(untyped_args, ss.str()); // Prints the function result. - if (result != NULL) result->PrintAsActionResult(&ss); + if (result != nullptr) result->PrintAsActionResult(&ss); ReportUninterestingCall(reaction, ss.str()); return result; @@ -10637,23 +13744,25 @@ UntypedFunctionMockerBase::UntypedInvokeWith(const void* const untyped_args) ::std::stringstream ss; ::std::stringstream why; ::std::stringstream loc; - const void* untyped_action = NULL; + const void* untyped_action = nullptr; // The UntypedFindMatchingExpectation() function acquires and // releases g_gmock_mutex. + const ExpectationBase* const untyped_expectation = this->UntypedFindMatchingExpectation(untyped_args, &untyped_action, &is_excessive, &ss, &why); - const bool found = untyped_expectation != NULL; + const bool found = untyped_expectation != nullptr; - // True iff we need to print the call's arguments and return value. + // True if and only if we need to print the call's arguments + // and return value. // This definition must be kept in sync with the uses of Expect() // and Log() in this function. const bool need_to_report_call = !found || is_excessive || LogIsVisible(kInfo); if (!need_to_report_call) { // Perform the action without printing the call information. - return untyped_action == NULL + return untyped_action == nullptr ? this->UntypedPerformDefaultAction(untyped_args, "") : this->UntypedPerformAction(untyped_action, untyped_args); } @@ -10667,33 +13776,52 @@ UntypedFunctionMockerBase::UntypedInvokeWith(const void* const untyped_args) untyped_expectation->DescribeLocationTo(&loc); } - const UntypedActionResultHolderBase* const result = - untyped_action == NULL - ? this->UntypedPerformDefaultAction(untyped_args, ss.str()) - : this->UntypedPerformAction(untyped_action, untyped_args); - if (result != NULL) result->PrintAsActionResult(&ss); - ss << "\n" << why.str(); - - if (!found) { - // No expectation matches this call - reports a failure. - Expect(false, NULL, -1, ss.str()); - } else if (is_excessive) { - // We had an upper-bound violation and the failure message is in ss. - Expect(false, untyped_expectation->file(), untyped_expectation->line(), - ss.str()); - } else { - // We had an expected call and the matching expectation is - // described in ss. - Log(kInfo, loc.str() + ss.str(), 2); + UntypedActionResultHolderBase* result = nullptr; + + auto perform_action = [&, this] { + return untyped_action == nullptr + ? this->UntypedPerformDefaultAction(untyped_args, ss.str()) + : this->UntypedPerformAction(untyped_action, untyped_args); + }; + auto handle_failures = [&] { + ss << "\n" << why.str(); + + if (!found) { + // No expectation matches this call - reports a failure. + Expect(false, nullptr, -1, ss.str()); + } else if (is_excessive) { + // We had an upper-bound violation and the failure message is in ss. + Expect(false, untyped_expectation->file(), untyped_expectation->line(), + ss.str()); + } else { + // We had an expected call and the matching expectation is + // described in ss. + Log(kInfo, loc.str() + ss.str(), 2); + } + }; +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + try { + result = perform_action(); + } catch (...) { + handle_failures(); + throw; } +#else + result = perform_action(); +#endif + if (result != nullptr) result->PrintAsActionResult(&ss); + handle_failures(); return result; } // Returns an Expectation object that references and co-owns exp, // which must be an expectation on this mock function. Expectation UntypedFunctionMockerBase::GetHandleOf(ExpectationBase* exp) { - for (UntypedExpectations::const_iterator it = untyped_expectations_.begin(); + // See the definition of untyped_expectations_ for why access to it + // is unprotected here. + for (UntypedExpectations::const_iterator it = + untyped_expectations_.begin(); it != untyped_expectations_.end(); ++it) { if (it->get() == exp) { return Expectation(*it); @@ -10713,7 +13841,8 @@ bool UntypedFunctionMockerBase::VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked() GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); bool expectations_met = true; - for (UntypedExpectations::const_iterator it = untyped_expectations_.begin(); + for (UntypedExpectations::const_iterator it = + untyped_expectations_.begin(); it != untyped_expectations_.end(); ++it) { ExpectationBase* const untyped_expectation = it->get(); if (untyped_expectation->IsOverSaturated()) { @@ -10724,15 +13853,15 @@ bool UntypedFunctionMockerBase::VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked() } else if (!untyped_expectation->IsSatisfied()) { expectations_met = false; ::std::stringstream ss; - ss << "Actual function call count doesn't match " - << untyped_expectation->source_text() << "...\n"; + ss << "Actual function call count doesn't match " + << untyped_expectation->source_text() << "...\n"; // No need to show the source file location of the expectation // in the description, as the Expect() call that follows already // takes care of it. untyped_expectation->MaybeDescribeExtraMatcherTo(&ss); untyped_expectation->DescribeCallCountTo(&ss); - Expect(false, untyped_expectation->file(), untyped_expectation->line(), - ss.str()); + Expect(false, untyped_expectation->file(), + untyped_expectation->line(), ss.str()); } } @@ -10753,6 +13882,13 @@ bool UntypedFunctionMockerBase::VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked() return expectations_met; } +CallReaction intToCallReaction(int mock_behavior) { + if (mock_behavior >= kAllow && mock_behavior <= kFail) { + return static_cast<internal::CallReaction>(mock_behavior); + } + return kWarn; +} + } // namespace internal // Class Mock. @@ -10766,15 +13902,15 @@ typedef std::set<internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase*> FunctionMockers; // expectations. struct MockObjectState { MockObjectState() - : first_used_file(NULL), first_used_line(-1), leakable(false) {} + : first_used_file(nullptr), first_used_line(-1), leakable(false) {} // Where in the source file an ON_CALL or EXPECT_CALL is first // invoked on this mock object. const char* first_used_file; int first_used_line; - ::std::string first_used_test_case; + ::std::string first_used_test_suite; ::std::string first_used_test; - bool leakable; // true iff it's OK to leak the object. + bool leakable; // true if and only if it's OK to leak the object. FunctionMockers function_mockers; // All registered methods of the object. }; @@ -10792,10 +13928,8 @@ class MockObjectRegistry { // object alive. Therefore we report any living object as test // failure, unless the user explicitly asked us to ignore it. ~MockObjectRegistry() { - // "using ::std::cout;" doesn't work with Symbian's STLport, where cout is - // a macro. - - if (!GMOCK_FLAG(catch_leaked_mocks)) return; + if (!GMOCK_FLAG(catch_leaked_mocks)) + return; int leaked_count = 0; for (StateMap::const_iterator it = states_.begin(); it != states_.end(); @@ -10803,7 +13937,7 @@ class MockObjectRegistry { if (it->second.leakable) // The user said it's fine to leak this object. continue; - // TODO(wan@google.com): Print the type of the leaked object. + // FIXME: Print the type of the leaked object. // This can help the user identify the leaked object. std::cout << "\n"; const MockObjectState& state = it->second; @@ -10811,17 +13945,23 @@ class MockObjectRegistry { state.first_used_line); std::cout << " ERROR: this mock object"; if (state.first_used_test != "") { - std::cout << " (used in test " << state.first_used_test_case << "." + std::cout << " (used in test " << state.first_used_test_suite << "." << state.first_used_test << ")"; } std::cout << " should be deleted but never is. Its address is @" - << it->first << "."; + << it->first << "."; leaked_count++; } if (leaked_count > 0) { std::cout << "\nERROR: " << leaked_count << " leaked mock " << (leaked_count == 1 ? "object" : "objects") - << " found at program exit.\n"; + << " found at program exit. Expectations on a mock object are " + "verified when the object is destructed. Leaking a mock " + "means that its expectations aren't verified, which is " + "usually a test bug. If you really intend to leak a mock, " + "you can suppress this error using " + "testing::Mock::AllowLeak(mock_object), or you may use a " + "fake or stub instead of a mock.\n"; std::cout.flush(); ::std::cerr.flush(); // RUN_ALL_TESTS() has already returned when this destructor is @@ -10888,11 +14028,12 @@ void Mock::UnregisterCallReaction(const void* mock_obj) // Returns the reaction Google Mock will have on uninteresting calls // made on the given mock object. internal::CallReaction Mock::GetReactionOnUninterestingCalls( - const void* mock_obj) GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex) { + const void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex) { internal::MutexLock l(&internal::g_gmock_mutex); - return (g_uninteresting_call_reaction.count(mock_obj) == 0) - ? internal::kDefault - : g_uninteresting_call_reaction[mock_obj]; + return (g_uninteresting_call_reaction.count(mock_obj) == 0) ? + internal::intToCallReaction(GMOCK_FLAG(default_mock_behavior)) : + g_uninteresting_call_reaction[mock_obj]; } // Tells Google Mock to ignore mock_obj when checking for leaked mock @@ -10913,7 +14054,7 @@ bool Mock::VerifyAndClearExpectations(void* mock_obj) } // Verifies all expectations on the given mock object and clears its -// default actions and expectations. Returns true iff the +// default actions and expectations. Returns true if and only if the // verification was successful. bool Mock::VerifyAndClear(void* mock_obj) GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex) { @@ -10950,6 +14091,19 @@ bool Mock::VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked(void* mock_obj) return expectations_met; } +bool Mock::IsNaggy(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex) { + return Mock::GetReactionOnUninterestingCalls(mock_obj) == internal::kWarn; +} +bool Mock::IsNice(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex) { + return Mock::GetReactionOnUninterestingCalls(mock_obj) == internal::kAllow; +} +bool Mock::IsStrict(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex) { + return Mock::GetReactionOnUninterestingCalls(mock_obj) == internal::kFail; +} + // Registers a mock object and a mock method it owns. void Mock::Register(const void* mock_obj, internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase* mocker) @@ -10966,16 +14120,13 @@ void Mock::RegisterUseByOnCallOrExpectCall(const void* mock_obj, GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex) { internal::MutexLock l(&internal::g_gmock_mutex); MockObjectState& state = g_mock_object_registry.states()[mock_obj]; - if (state.first_used_file == NULL) { + if (state.first_used_file == nullptr) { state.first_used_file = file; state.first_used_line = line; const TestInfo* const test_info = UnitTest::GetInstance()->current_test_info(); - if (test_info != NULL) { - // TODO(wan@google.com): record the test case name when the - // ON_CALL or EXPECT_CALL is invoked from SetUpTestCase() or - // TearDownTestCase(). - state.first_used_test_case = test_info->test_case_name(); + if (test_info != nullptr) { + state.first_used_test_suite = test_info->test_suite_name(); state.first_used_test = test_info->name(); } } @@ -11028,7 +14179,7 @@ void Mock::ClearDefaultActionsLocked(void* mock_obj) Expectation::Expectation() {} Expectation::Expectation( - const internal::linked_ptr<internal::ExpectationBase>& an_expectation_base) + const std::shared_ptr<internal::ExpectationBase>& an_expectation_base) : expectation_base_(an_expectation_base) {} Expectation::~Expectation() {} @@ -11036,9 +14187,9 @@ Expectation::~Expectation() {} // Adds an expectation to a sequence. void Sequence::AddExpectation(const Expectation& expectation) const { if (*last_expectation_ != expectation) { - if (last_expectation_->expectation_base() != NULL) { - expectation.expectation_base()->immediate_prerequisites_ += - *last_expectation_; + if (last_expectation_->expectation_base() != nullptr) { + expectation.expectation_base()->immediate_prerequisites_ + += *last_expectation_; } *last_expectation_ = expectation; } @@ -11046,7 +14197,7 @@ void Sequence::AddExpectation(const Expectation& expectation) const { // Creates the implicit sequence if there isn't one. InSequence::InSequence() { - if (internal::g_gmock_implicit_sequence.get() == NULL) { + if (internal::g_gmock_implicit_sequence.get() == nullptr) { internal::g_gmock_implicit_sequence.set(new Sequence); sequence_created_ = true; } else { @@ -11059,11 +14210,17 @@ InSequence::InSequence() { InSequence::~InSequence() { if (sequence_created_) { delete internal::g_gmock_implicit_sequence.get(); - internal::g_gmock_implicit_sequence.set(NULL); + internal::g_gmock_implicit_sequence.set(nullptr); } } } // namespace testing + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +#if _MSC_VER == 1900 +# pragma warning(pop) +#endif +#endif // Copyright 2008, Google Inc. // All rights reserved. // @@ -11092,17 +14249,14 @@ InSequence::~InSequence() { // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) -namespace testing { -// TODO(wan@google.com): support using environment variables to -// control the flag values, like what Google Test does. + +namespace testing { GMOCK_DEFINE_bool_(catch_leaked_mocks, true, - "true iff Google Mock should report leaked mock objects " - "as failures."); + "true if and only if Google Mock should report leaked " + "mock objects as failures."); GMOCK_DEFINE_string_(verbose, internal::kWarningVerbosity, "Controls how verbose Google Mock's output is." @@ -11111,6 +14265,13 @@ GMOCK_DEFINE_string_(verbose, internal::kWarningVerbosity, " warning - prints warnings and errors.\n" " error - prints errors only."); +GMOCK_DEFINE_int32_(default_mock_behavior, 1, + "Controls the default behavior of mocks." + " Valid values:\n" + " 0 - by default, mocks act as NiceMocks.\n" + " 1 - by default, mocks act as NaggyMocks.\n" + " 2 - by default, mocks act as StrictMocks."); + namespace internal { // Parses a string as a command line flag. The string should have the @@ -11118,15 +14279,16 @@ namespace internal { // "=value" part can be omitted. // // Returns the value of the flag, or NULL if the parsing failed. -static const char* ParseGoogleMockFlagValue(const char* str, const char* flag, +static const char* ParseGoogleMockFlagValue(const char* str, + const char* flag, bool def_optional) { // str and flag must not be NULL. - if (str == NULL || flag == NULL) return NULL; + if (str == nullptr || flag == nullptr) return nullptr; // The flag must start with "--gmock_". const std::string flag_str = std::string("--gmock_") + flag; const size_t flag_len = flag_str.length(); - if (strncmp(str, flag_str.c_str(), flag_len) != 0) return NULL; + if (strncmp(str, flag_str.c_str(), flag_len) != 0) return nullptr; // Skips the flag name. const char* flag_end = str + flag_len; @@ -11139,7 +14301,7 @@ static const char* ParseGoogleMockFlagValue(const char* str, const char* flag, // If def_optional is true and there are more characters after the // flag name, or if def_optional is false, there must be a '=' after // the flag name. - if (flag_end[0] != '=') return NULL; + if (flag_end[0] != '=') return nullptr; // Returns the string after "=". return flag_end + 1; @@ -11156,7 +14318,7 @@ static bool ParseGoogleMockBoolFlag(const char* str, const char* flag, const char* const value_str = ParseGoogleMockFlagValue(str, flag, true); // Aborts if the parsing failed. - if (value_str == NULL) return false; + if (value_str == nullptr) return false; // Converts the string value to a bool. *value = !(*value_str == '0' || *value_str == 'f' || *value_str == 'F'); @@ -11168,19 +14330,33 @@ static bool ParseGoogleMockBoolFlag(const char* str, const char* flag, // // On success, stores the value of the flag in *value, and returns // true. On failure, returns false without changing *value. +template <typename String> static bool ParseGoogleMockStringFlag(const char* str, const char* flag, - std::string* value) { + String* value) { // Gets the value of the flag as a string. const char* const value_str = ParseGoogleMockFlagValue(str, flag, false); // Aborts if the parsing failed. - if (value_str == NULL) return false; + if (value_str == nullptr) return false; // Sets *value to the value of the flag. *value = value_str; return true; } +static bool ParseGoogleMockIntFlag(const char* str, const char* flag, + int32_t* value) { + // Gets the value of the flag as a string. + const char* const value_str = ParseGoogleMockFlagValue(str, flag, true); + + // Aborts if the parsing failed. + if (value_str == nullptr) return false; + + // Sets *value to the value of the flag. + return ParseInt32(Message() << "The value of flag --" << flag, + value_str, value); +} + // The internal implementation of InitGoogleMock(). // // The type parameter CharType can be instantiated to either char or @@ -11199,7 +14375,9 @@ void InitGoogleMockImpl(int* argc, CharType** argv) { // Do we see a Google Mock flag? if (ParseGoogleMockBoolFlag(arg, "catch_leaked_mocks", &GMOCK_FLAG(catch_leaked_mocks)) || - ParseGoogleMockStringFlag(arg, "verbose", &GMOCK_FLAG(verbose))) { + ParseGoogleMockStringFlag(arg, "verbose", &GMOCK_FLAG(verbose)) || + ParseGoogleMockIntFlag(arg, "default_mock_behavior", + &GMOCK_FLAG(default_mock_behavior))) { // Yes. Shift the remainder of the argv list left by one. Note // that argv has (*argc + 1) elements, the last one always being // NULL. The following loop moves the trailing NULL element as @@ -11241,4 +14419,16 @@ GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleMock(int* argc, wchar_t** argv) { internal::InitGoogleMockImpl(argc, argv); } +// This overloaded version can be used on Arduino/embedded platforms where +// there is no argc/argv. +GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleMock() { + // Since Arduino doesn't have a command line, fake out the argc/argv arguments + int argc = 1; + const auto arg0 = "dummy"; + char* argv0 = const_cast<char*>(arg0); + char** argv = &argv0; + + internal::InitGoogleMockImpl(&argc, argv); +} + } // namespace testing diff --git a/test/gtest/gmock/gmock.h b/test/gtest/gmock/gmock.h new file mode 100644 index 00000000..d121f7df --- /dev/null +++ b/test/gtest/gmock/gmock.h @@ -0,0 +1,11645 @@ +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. +// +// This is the main header file a user should include. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_H_ + +// This file implements the following syntax: +// +// ON_CALL(mock_object, Method(...)) +// .With(...) ? +// .WillByDefault(...); +// +// where With() is optional and WillByDefault() must appear exactly +// once. +// +// EXPECT_CALL(mock_object, Method(...)) +// .With(...) ? +// .Times(...) ? +// .InSequence(...) * +// .WillOnce(...) * +// .WillRepeatedly(...) ? +// .RetiresOnSaturation() ? ; +// +// where all clauses are optional and WillOnce() can be repeated. + +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. +// +// The ACTION* family of macros can be used in a namespace scope to +// define custom actions easily. The syntax: +// +// ACTION(name) { statements; } +// +// will define an action with the given name that executes the +// statements. The value returned by the statements will be used as +// the return value of the action. Inside the statements, you can +// refer to the K-th (0-based) argument of the mock function by +// 'argK', and refer to its type by 'argK_type'. For example: +// +// ACTION(IncrementArg1) { +// arg1_type temp = arg1; +// return ++(*temp); +// } +// +// allows you to write +// +// ...WillOnce(IncrementArg1()); +// +// You can also refer to the entire argument tuple and its type by +// 'args' and 'args_type', and refer to the mock function type and its +// return type by 'function_type' and 'return_type'. +// +// Note that you don't need to specify the types of the mock function +// arguments. However rest assured that your code is still type-safe: +// you'll get a compiler error if *arg1 doesn't support the ++ +// operator, or if the type of ++(*arg1) isn't compatible with the +// mock function's return type, for example. +// +// Sometimes you'll want to parameterize the action. For that you can use +// another macro: +// +// ACTION_P(name, param_name) { statements; } +// +// For example: +// +// ACTION_P(Add, n) { return arg0 + n; } +// +// will allow you to write: +// +// ...WillOnce(Add(5)); +// +// Note that you don't need to provide the type of the parameter +// either. If you need to reference the type of a parameter named +// 'foo', you can write 'foo_type'. For example, in the body of +// ACTION_P(Add, n) above, you can write 'n_type' to refer to the type +// of 'n'. +// +// We also provide ACTION_P2, ACTION_P3, ..., up to ACTION_P10 to support +// multi-parameter actions. +// +// For the purpose of typing, you can view +// +// ACTION_Pk(Foo, p1, ..., pk) { ... } +// +// as shorthand for +// +// template <typename p1_type, ..., typename pk_type> +// FooActionPk<p1_type, ..., pk_type> Foo(p1_type p1, ..., pk_type pk) { ... } +// +// In particular, you can provide the template type arguments +// explicitly when invoking Foo(), as in Foo<long, bool>(5, false); +// although usually you can rely on the compiler to infer the types +// for you automatically. You can assign the result of expression +// Foo(p1, ..., pk) to a variable of type FooActionPk<p1_type, ..., +// pk_type>. This can be useful when composing actions. +// +// You can also overload actions with different numbers of parameters: +// +// ACTION_P(Plus, a) { ... } +// ACTION_P2(Plus, a, b) { ... } +// +// While it's tempting to always use the ACTION* macros when defining +// a new action, you should also consider implementing ActionInterface +// or using MakePolymorphicAction() instead, especially if you need to +// use the action a lot. While these approaches require more work, +// they give you more control on the types of the mock function +// arguments and the action parameters, which in general leads to +// better compiler error messages that pay off in the long run. They +// also allow overloading actions based on parameter types (as opposed +// to just based on the number of parameters). +// +// CAVEAT: +// +// ACTION*() can only be used in a namespace scope as templates cannot be +// declared inside of a local class. +// Users can, however, define any local functors (e.g. a lambda) that +// can be used as actions. +// +// MORE INFORMATION: +// +// To learn more about using these macros, please search for 'ACTION' on +// https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/docs/gmock_cook_book.md + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_ACTIONS_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_ACTIONS_H_ + +#ifndef _WIN32_WCE +# include <errno.h> +#endif + +#include <algorithm> +#include <functional> +#include <memory> +#include <string> +#include <tuple> +#include <type_traits> +#include <utility> + +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. +// +// This file defines some utilities useful for implementing Google +// Mock. They are subject to change without notice, so please DO NOT +// USE THEM IN USER CODE. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_INTERNAL_UTILS_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_INTERNAL_UTILS_H_ + +#include <stdio.h> +#include <ostream> // NOLINT +#include <string> +#include <type_traits> +// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// +// Low-level types and utilities for porting Google Mock to various +// platforms. All macros ending with _ and symbols defined in an +// internal namespace are subject to change without notice. Code +// outside Google Mock MUST NOT USE THEM DIRECTLY. Macros that don't +// end with _ are part of Google Mock's public API and can be used by +// code outside Google Mock. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_PORT_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_PORT_H_ + +#include <assert.h> +#include <stdlib.h> +#include <cstdint> +#include <iostream> + +// Most of the utilities needed for porting Google Mock are also +// required for Google Test and are defined in gtest-port.h. +// +// Note to maintainers: to reduce code duplication, prefer adding +// portability utilities to Google Test's gtest-port.h instead of +// here, as Google Mock depends on Google Test. Only add a utility +// here if it's truly specific to Google Mock. + +#include "gtest/gtest.h" +// Copyright 2015, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// Injection point for custom user configurations. See README for details +// +// ** Custom implementation starts here ** + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GMOCK_PORT_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GMOCK_PORT_H_ + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GMOCK_PORT_H_ + +// For MS Visual C++, check the compiler version. At least VS 2015 is +// required to compile Google Mock. +#if defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER < 1900 +# error "At least Visual C++ 2015 (14.0) is required to compile Google Mock." +#endif + +// Macro for referencing flags. This is public as we want the user to +// use this syntax to reference Google Mock flags. +#define GMOCK_FLAG(name) FLAGS_gmock_##name + +#if !defined(GMOCK_DECLARE_bool_) + +// Macros for declaring flags. +# define GMOCK_DECLARE_bool_(name) extern GTEST_API_ bool GMOCK_FLAG(name) +# define GMOCK_DECLARE_int32_(name) extern GTEST_API_ int32_t GMOCK_FLAG(name) +# define GMOCK_DECLARE_string_(name) \ + extern GTEST_API_ ::std::string GMOCK_FLAG(name) + +// Macros for defining flags. +# define GMOCK_DEFINE_bool_(name, default_val, doc) \ + GTEST_API_ bool GMOCK_FLAG(name) = (default_val) +# define GMOCK_DEFINE_int32_(name, default_val, doc) \ + GTEST_API_ int32_t GMOCK_FLAG(name) = (default_val) +# define GMOCK_DEFINE_string_(name, default_val, doc) \ + GTEST_API_ ::std::string GMOCK_FLAG(name) = (default_val) + +#endif // !defined(GMOCK_DECLARE_bool_) + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_PORT_H_ + +namespace testing { + +template <typename> +class Matcher; + +namespace internal { + +// Silence MSVC C4100 (unreferenced formal parameter) and +// C4805('==': unsafe mix of type 'const int' and type 'const bool') +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(push) +# pragma warning(disable:4100) +# pragma warning(disable:4805) +#endif + +// Joins a vector of strings as if they are fields of a tuple; returns +// the joined string. +GTEST_API_ std::string JoinAsTuple(const Strings& fields); + +// Converts an identifier name to a space-separated list of lower-case +// words. Each maximum substring of the form [A-Za-z][a-z]*|\d+ is +// treated as one word. For example, both "FooBar123" and +// "foo_bar_123" are converted to "foo bar 123". +GTEST_API_ std::string ConvertIdentifierNameToWords(const char* id_name); + +// GetRawPointer(p) returns the raw pointer underlying p when p is a +// smart pointer, or returns p itself when p is already a raw pointer. +// The following default implementation is for the smart pointer case. +template <typename Pointer> +inline const typename Pointer::element_type* GetRawPointer(const Pointer& p) { + return p.get(); +} +// This overloaded version is for the raw pointer case. +template <typename Element> +inline Element* GetRawPointer(Element* p) { return p; } + +// MSVC treats wchar_t as a native type usually, but treats it as the +// same as unsigned short when the compiler option /Zc:wchar_t- is +// specified. It defines _NATIVE_WCHAR_T_DEFINED symbol when wchar_t +// is a native type. +#if defined(_MSC_VER) && !defined(_NATIVE_WCHAR_T_DEFINED) +// wchar_t is a typedef. +#else +# define GMOCK_WCHAR_T_IS_NATIVE_ 1 +#endif + +// In what follows, we use the term "kind" to indicate whether a type +// is bool, an integer type (excluding bool), a floating-point type, +// or none of them. This categorization is useful for determining +// when a matcher argument type can be safely converted to another +// type in the implementation of SafeMatcherCast. +enum TypeKind { + kBool, kInteger, kFloatingPoint, kOther +}; + +// KindOf<T>::value is the kind of type T. +template <typename T> struct KindOf { + enum { value = kOther }; // The default kind. +}; + +// This macro declares that the kind of 'type' is 'kind'. +#define GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(type, kind) \ + template <> struct KindOf<type> { enum { value = kind }; } + +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(bool, kBool); + +// All standard integer types. +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(char, kInteger); +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(signed char, kInteger); +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(unsigned char, kInteger); +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(short, kInteger); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(unsigned short, kInteger); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(int, kInteger); +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(unsigned int, kInteger); +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(long, kInteger); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(unsigned long, kInteger); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(long long, kInteger); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(unsigned long long, kInteger); // NOLINT + +#if GMOCK_WCHAR_T_IS_NATIVE_ +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(wchar_t, kInteger); +#endif + +// All standard floating-point types. +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(float, kFloatingPoint); +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(double, kFloatingPoint); +GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_(long double, kFloatingPoint); + +#undef GMOCK_DECLARE_KIND_ + +// Evaluates to the kind of 'type'. +#define GMOCK_KIND_OF_(type) \ + static_cast< ::testing::internal::TypeKind>( \ + ::testing::internal::KindOf<type>::value) + +// LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<kFromKind, From, kToKind, To>::value +// is true if and only if arithmetic type From can be losslessly converted to +// arithmetic type To. +// +// It's the user's responsibility to ensure that both From and To are +// raw (i.e. has no CV modifier, is not a pointer, and is not a +// reference) built-in arithmetic types, kFromKind is the kind of +// From, and kToKind is the kind of To; the value is +// implementation-defined when the above pre-condition is violated. +template <TypeKind kFromKind, typename From, TypeKind kToKind, typename To> +using LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl = std::integral_constant< + bool, + // clang-format off + // Converting from bool is always lossless + (kFromKind == kBool) ? true + // Converting between any other type kinds will be lossy if the type + // kinds are not the same. + : (kFromKind != kToKind) ? false + : (kFromKind == kInteger && + // Converting between integers of different widths is allowed so long + // as the conversion does not go from signed to unsigned. + (((sizeof(From) < sizeof(To)) && + !(std::is_signed<From>::value && !std::is_signed<To>::value)) || + // Converting between integers of the same width only requires the + // two types to have the same signedness. + ((sizeof(From) == sizeof(To)) && + (std::is_signed<From>::value == std::is_signed<To>::value))) + ) ? true + // Floating point conversions are lossless if and only if `To` is at least + // as wide as `From`. + : (kFromKind == kFloatingPoint && (sizeof(From) <= sizeof(To))) ? true + : false + // clang-format on + >; + +// LosslessArithmeticConvertible<From, To>::value is true if and only if +// arithmetic type From can be losslessly converted to arithmetic type To. +// +// It's the user's responsibility to ensure that both From and To are +// raw (i.e. has no CV modifier, is not a pointer, and is not a +// reference) built-in arithmetic types; the value is +// implementation-defined when the above pre-condition is violated. +template <typename From, typename To> +using LosslessArithmeticConvertible = + LosslessArithmeticConvertibleImpl<GMOCK_KIND_OF_(From), From, + GMOCK_KIND_OF_(To), To>; + +// This interface knows how to report a Google Mock failure (either +// non-fatal or fatal). +class FailureReporterInterface { + public: + // The type of a failure (either non-fatal or fatal). + enum FailureType { + kNonfatal, kFatal + }; + + virtual ~FailureReporterInterface() {} + + // Reports a failure that occurred at the given source file location. + virtual void ReportFailure(FailureType type, const char* file, int line, + const std::string& message) = 0; +}; + +// Returns the failure reporter used by Google Mock. +GTEST_API_ FailureReporterInterface* GetFailureReporter(); + +// Asserts that condition is true; aborts the process with the given +// message if condition is false. We cannot use LOG(FATAL) or CHECK() +// as Google Mock might be used to mock the log sink itself. We +// inline this function to prevent it from showing up in the stack +// trace. +inline void Assert(bool condition, const char* file, int line, + const std::string& msg) { + if (!condition) { + GetFailureReporter()->ReportFailure(FailureReporterInterface::kFatal, + file, line, msg); + } +} +inline void Assert(bool condition, const char* file, int line) { + Assert(condition, file, line, "Assertion failed."); +} + +// Verifies that condition is true; generates a non-fatal failure if +// condition is false. +inline void Expect(bool condition, const char* file, int line, + const std::string& msg) { + if (!condition) { + GetFailureReporter()->ReportFailure(FailureReporterInterface::kNonfatal, + file, line, msg); + } +} +inline void Expect(bool condition, const char* file, int line) { + Expect(condition, file, line, "Expectation failed."); +} + +// Severity level of a log. +enum LogSeverity { + kInfo = 0, + kWarning = 1 +}; + +// Valid values for the --gmock_verbose flag. + +// All logs (informational and warnings) are printed. +const char kInfoVerbosity[] = "info"; +// Only warnings are printed. +const char kWarningVerbosity[] = "warning"; +// No logs are printed. +const char kErrorVerbosity[] = "error"; + +// Returns true if and only if a log with the given severity is visible +// according to the --gmock_verbose flag. +GTEST_API_ bool LogIsVisible(LogSeverity severity); + +// Prints the given message to stdout if and only if 'severity' >= the level +// specified by the --gmock_verbose flag. If stack_frames_to_skip >= +// 0, also prints the stack trace excluding the top +// stack_frames_to_skip frames. In opt mode, any positive +// stack_frames_to_skip is treated as 0, since we don't know which +// function calls will be inlined by the compiler and need to be +// conservative. +GTEST_API_ void Log(LogSeverity severity, const std::string& message, + int stack_frames_to_skip); + +// A marker class that is used to resolve parameterless expectations to the +// correct overload. This must not be instantiable, to prevent client code from +// accidentally resolving to the overload; for example: +// +// ON_CALL(mock, Method({}, nullptr))... +// +class WithoutMatchers { + private: + WithoutMatchers() {} + friend GTEST_API_ WithoutMatchers GetWithoutMatchers(); +}; + +// Internal use only: access the singleton instance of WithoutMatchers. +GTEST_API_ WithoutMatchers GetWithoutMatchers(); + +// Disable MSVC warnings for infinite recursion, since in this case the +// the recursion is unreachable. +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(push) +# pragma warning(disable:4717) +#endif + +// Invalid<T>() is usable as an expression of type T, but will terminate +// the program with an assertion failure if actually run. This is useful +// when a value of type T is needed for compilation, but the statement +// will not really be executed (or we don't care if the statement +// crashes). +template <typename T> +inline T Invalid() { + Assert(false, "", -1, "Internal error: attempt to return invalid value"); + // This statement is unreachable, and would never terminate even if it + // could be reached. It is provided only to placate compiler warnings + // about missing return statements. + return Invalid<T>(); +} + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(pop) +#endif + +// Given a raw type (i.e. having no top-level reference or const +// modifier) RawContainer that's either an STL-style container or a +// native array, class StlContainerView<RawContainer> has the +// following members: +// +// - type is a type that provides an STL-style container view to +// (i.e. implements the STL container concept for) RawContainer; +// - const_reference is a type that provides a reference to a const +// RawContainer; +// - ConstReference(raw_container) returns a const reference to an STL-style +// container view to raw_container, which is a RawContainer. +// - Copy(raw_container) returns an STL-style container view of a +// copy of raw_container, which is a RawContainer. +// +// This generic version is used when RawContainer itself is already an +// STL-style container. +template <class RawContainer> +class StlContainerView { + public: + typedef RawContainer type; + typedef const type& const_reference; + + static const_reference ConstReference(const RawContainer& container) { + static_assert(!std::is_const<RawContainer>::value, + "RawContainer type must not be const"); + return container; + } + static type Copy(const RawContainer& container) { return container; } +}; + +// This specialization is used when RawContainer is a native array type. +template <typename Element, size_t N> +class StlContainerView<Element[N]> { + public: + typedef typename std::remove_const<Element>::type RawElement; + typedef internal::NativeArray<RawElement> type; + // NativeArray<T> can represent a native array either by value or by + // reference (selected by a constructor argument), so 'const type' + // can be used to reference a const native array. We cannot + // 'typedef const type& const_reference' here, as that would mean + // ConstReference() has to return a reference to a local variable. + typedef const type const_reference; + + static const_reference ConstReference(const Element (&array)[N]) { + static_assert(std::is_same<Element, RawElement>::value, + "Element type must not be const"); + return type(array, N, RelationToSourceReference()); + } + static type Copy(const Element (&array)[N]) { + return type(array, N, RelationToSourceCopy()); + } +}; + +// This specialization is used when RawContainer is a native array +// represented as a (pointer, size) tuple. +template <typename ElementPointer, typename Size> +class StlContainerView< ::std::tuple<ElementPointer, Size> > { + public: + typedef typename std::remove_const< + typename std::pointer_traits<ElementPointer>::element_type>::type + RawElement; + typedef internal::NativeArray<RawElement> type; + typedef const type const_reference; + + static const_reference ConstReference( + const ::std::tuple<ElementPointer, Size>& array) { + return type(std::get<0>(array), std::get<1>(array), + RelationToSourceReference()); + } + static type Copy(const ::std::tuple<ElementPointer, Size>& array) { + return type(std::get<0>(array), std::get<1>(array), RelationToSourceCopy()); + } +}; + +// The following specialization prevents the user from instantiating +// StlContainer with a reference type. +template <typename T> class StlContainerView<T&>; + +// A type transform to remove constness from the first part of a pair. +// Pairs like that are used as the value_type of associative containers, +// and this transform produces a similar but assignable pair. +template <typename T> +struct RemoveConstFromKey { + typedef T type; +}; + +// Partially specialized to remove constness from std::pair<const K, V>. +template <typename K, typename V> +struct RemoveConstFromKey<std::pair<const K, V> > { + typedef std::pair<K, V> type; +}; + +// Emit an assertion failure due to incorrect DoDefault() usage. Out-of-lined to +// reduce code size. +GTEST_API_ void IllegalDoDefault(const char* file, int line); + +template <typename F, typename Tuple, size_t... Idx> +auto ApplyImpl(F&& f, Tuple&& args, IndexSequence<Idx...>) -> decltype( + std::forward<F>(f)(std::get<Idx>(std::forward<Tuple>(args))...)) { + return std::forward<F>(f)(std::get<Idx>(std::forward<Tuple>(args))...); +} + +// Apply the function to a tuple of arguments. +template <typename F, typename Tuple> +auto Apply(F&& f, Tuple&& args) -> decltype( + ApplyImpl(std::forward<F>(f), std::forward<Tuple>(args), + MakeIndexSequence<std::tuple_size< + typename std::remove_reference<Tuple>::type>::value>())) { + return ApplyImpl(std::forward<F>(f), std::forward<Tuple>(args), + MakeIndexSequence<std::tuple_size< + typename std::remove_reference<Tuple>::type>::value>()); +} + +// Template struct Function<F>, where F must be a function type, contains +// the following typedefs: +// +// Result: the function's return type. +// Arg<N>: the type of the N-th argument, where N starts with 0. +// ArgumentTuple: the tuple type consisting of all parameters of F. +// ArgumentMatcherTuple: the tuple type consisting of Matchers for all +// parameters of F. +// MakeResultVoid: the function type obtained by substituting void +// for the return type of F. +// MakeResultIgnoredValue: +// the function type obtained by substituting Something +// for the return type of F. +template <typename T> +struct Function; + +template <typename R, typename... Args> +struct Function<R(Args...)> { + using Result = R; + static constexpr size_t ArgumentCount = sizeof...(Args); + template <size_t I> + using Arg = ElemFromList<I, Args...>; + using ArgumentTuple = std::tuple<Args...>; + using ArgumentMatcherTuple = std::tuple<Matcher<Args>...>; + using MakeResultVoid = void(Args...); + using MakeResultIgnoredValue = IgnoredValue(Args...); +}; + +template <typename R, typename... Args> +constexpr size_t Function<R(Args...)>::ArgumentCount; + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(pop) +#endif + +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_INTERNAL_UTILS_H_ +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_PP_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_PP_H_ + +// Expands and concatenates the arguments. Constructed macros reevaluate. +#define GMOCK_PP_CAT(_1, _2) GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CAT(_1, _2) + +// Expands and stringifies the only argument. +#define GMOCK_PP_STRINGIZE(...) GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_STRINGIZE(__VA_ARGS__) + +// Returns empty. Given a variadic number of arguments. +#define GMOCK_PP_EMPTY(...) + +// Returns a comma. Given a variadic number of arguments. +#define GMOCK_PP_COMMA(...) , + +// Returns the only argument. +#define GMOCK_PP_IDENTITY(_1) _1 + +// Evaluates to the number of arguments after expansion. +// +// #define PAIR x, y +// +// GMOCK_PP_NARG() => 1 +// GMOCK_PP_NARG(x) => 1 +// GMOCK_PP_NARG(x, y) => 2 +// GMOCK_PP_NARG(PAIR) => 2 +// +// Requires: the number of arguments after expansion is at most 15. +#define GMOCK_PP_NARG(...) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_16TH( \ + (__VA_ARGS__, 15, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0)) + +// Returns 1 if the expansion of arguments has an unprotected comma. Otherwise +// returns 0. Requires no more than 15 unprotected commas. +#define GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(...) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_16TH( \ + (__VA_ARGS__, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0)) + +// Returns the first argument. +#define GMOCK_PP_HEAD(...) GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_HEAD((__VA_ARGS__, unusedArg)) + +// Returns the tail. A variadic list of all arguments minus the first. Requires +// at least one argument. +#define GMOCK_PP_TAIL(...) GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_TAIL((__VA_ARGS__)) + +// Calls CAT(_Macro, NARG(__VA_ARGS__))(__VA_ARGS__) +#define GMOCK_PP_VARIADIC_CALL(_Macro, ...) \ + GMOCK_PP_IDENTITY( \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(_Macro, GMOCK_PP_NARG(__VA_ARGS__))(__VA_ARGS__)) + +// If the arguments after expansion have no tokens, evaluates to `1`. Otherwise +// evaluates to `0`. +// +// Requires: * the number of arguments after expansion is at most 15. +// * If the argument is a macro, it must be able to be called with one +// argument. +// +// Implementation details: +// +// There is one case when it generates a compile error: if the argument is macro +// that cannot be called with one argument. +// +// #define M(a, b) // it doesn't matter what it expands to +// +// // Expected: expands to `0`. +// // Actual: compile error. +// GMOCK_PP_IS_EMPTY(M) +// +// There are 4 cases tested: +// +// * __VA_ARGS__ possible expansion has no unparen'd commas. Expected 0. +// * __VA_ARGS__ possible expansion is not enclosed in parenthesis. Expected 0. +// * __VA_ARGS__ possible expansion is not a macro that ()-evaluates to a comma. +// Expected 0 +// * __VA_ARGS__ is empty, or has unparen'd commas, or is enclosed in +// parenthesis, or is a macro that ()-evaluates to comma. Expected 1. +// +// We trigger detection on '0001', i.e. on empty. +#define GMOCK_PP_IS_EMPTY(...) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IS_EMPTY(GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(__VA_ARGS__), \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_PP_COMMA __VA_ARGS__), \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(__VA_ARGS__()), \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_PP_COMMA __VA_ARGS__())) + +// Evaluates to _Then if _Cond is 1 and _Else if _Cond is 0. +#define GMOCK_PP_IF(_Cond, _Then, _Else) \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IF_, _Cond)(_Then, _Else) + +// Similar to GMOCK_PP_IF but takes _Then and _Else in parentheses. +// +// GMOCK_PP_GENERIC_IF(1, (a, b, c), (d, e, f)) => a, b, c +// GMOCK_PP_GENERIC_IF(0, (a, b, c), (d, e, f)) => d, e, f +// +#define GMOCK_PP_GENERIC_IF(_Cond, _Then, _Else) \ + GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(GMOCK_PP_IF(_Cond, _Then, _Else)) + +// Evaluates to the number of arguments after expansion. Identifies 'empty' as +// 0. +// +// #define PAIR x, y +// +// GMOCK_PP_NARG0() => 0 +// GMOCK_PP_NARG0(x) => 1 +// GMOCK_PP_NARG0(x, y) => 2 +// GMOCK_PP_NARG0(PAIR) => 2 +// +// Requires: * the number of arguments after expansion is at most 15. +// * If the argument is a macro, it must be able to be called with one +// argument. +#define GMOCK_PP_NARG0(...) \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(GMOCK_PP_IS_EMPTY(__VA_ARGS__), 0, GMOCK_PP_NARG(__VA_ARGS__)) + +// Expands to 1 if the first argument starts with something in parentheses, +// otherwise to 0. +#define GMOCK_PP_IS_BEGIN_PARENS(...) \ + GMOCK_PP_HEAD(GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IBP_IS_VARIADIC_R_, \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IBP_IS_VARIADIC_C __VA_ARGS__)) + +// Expands to 1 is there is only one argument and it is enclosed in parentheses. +#define GMOCK_PP_IS_ENCLOSED_PARENS(...) \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(GMOCK_PP_IS_BEGIN_PARENS(__VA_ARGS__), \ + GMOCK_PP_IS_EMPTY(GMOCK_PP_EMPTY __VA_ARGS__), 0) + +// Remove the parens, requires GMOCK_PP_IS_ENCLOSED_PARENS(args) => 1. +#define GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(...) GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_REMOVE_PARENS __VA_ARGS__ + +// Expands to _Macro(0, _Data, e1) _Macro(1, _Data, e2) ... _Macro(K -1, _Data, +// eK) as many of GMOCK_INTERNAL_NARG0 _Tuple. +// Requires: * |_Macro| can be called with 3 arguments. +// * |_Tuple| expansion has no more than 15 elements. +#define GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(_Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_, GMOCK_PP_NARG0 _Tuple) \ + (0, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) + +// Expands to _Macro(0, _Data, ) _Macro(1, _Data, ) ... _Macro(K - 1, _Data, ) +// Empty if _K = 0. +// Requires: * |_Macro| can be called with 3 arguments. +// * |_K| literal between 0 and 15 +#define GMOCK_PP_REPEAT(_Macro, _Data, _N) \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_, _N) \ + (0, _Macro, _Data, GMOCK_PP_INTENRAL_EMPTY_TUPLE) + +// Increments the argument, requires the argument to be between 0 and 15. +#define GMOCK_PP_INC(_i) GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_, _i) + +// Returns comma if _i != 0. Requires _i to be between 0 and 15. +#define GMOCK_PP_COMMA_IF(_i) GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_, _i) + +// Internal details follow. Do not use any of these symbols outside of this +// file or we will break your code. +#define GMOCK_PP_INTENRAL_EMPTY_TUPLE (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CAT(_1, _2) _1##_2 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_STRINGIZE(...) #__VA_ARGS__ +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CAT_5(_1, _2, _3, _4, _5) _1##_2##_3##_4##_5 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IS_EMPTY(_1, _2, _3, _4) \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CAT_5(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IS_EMPTY_CASE_, \ + _1, _2, _3, _4)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IS_EMPTY_CASE_0001 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IF_1(_Then, _Else) _Then +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IF_0(_Then, _Else) _Else + +// Because of MSVC treating a token with a comma in it as a single token when +// passed to another macro, we need to force it to evaluate it as multiple +// tokens. We do that by using a "IDENTITY(MACRO PARENTHESIZED_ARGS)" macro. We +// define one per possible macro that relies on this behavior. Note "_Args" must +// be parenthesized. +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INTERNAL_16TH(_1, _2, _3, _4, _5, _6, _7, _8, _9, \ + _10, _11, _12, _13, _14, _15, _16, \ + ...) \ + _16 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_16TH(_Args) \ + GMOCK_PP_IDENTITY(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INTERNAL_16TH _Args) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INTERNAL_HEAD(_1, ...) _1 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_HEAD(_Args) \ + GMOCK_PP_IDENTITY(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INTERNAL_HEAD _Args) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INTERNAL_TAIL(_1, ...) __VA_ARGS__ +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_TAIL(_Args) \ + GMOCK_PP_IDENTITY(GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INTERNAL_TAIL _Args) + +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IBP_IS_VARIADIC_C(...) 1 _ +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IBP_IS_VARIADIC_R_1 1, +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IBP_IS_VARIADIC_R_GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_IBP_IS_VARIADIC_C \ + 0, +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_REMOVE_PARENS(...) __VA_ARGS__ +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_0 1 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_1 2 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_2 3 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_3 4 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_4 5 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_5 6 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_6 7 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_7 8 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_8 9 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_9 10 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_10 11 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_11 12 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_12 13 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_13 14 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_14 15 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_INC_15 16 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_0 +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_1 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_2 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_3 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_4 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_5 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_6 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_7 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_8 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_9 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_10 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_11 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_12 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_13 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_14 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_COMMA_IF_15 , +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, _element) \ + _Macro(_i, _Data, _element) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_0(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_1(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_2(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_1(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_3(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_2(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_4(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_3(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_5(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_4(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_6(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_5(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_7(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_6(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_8(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_7(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_9(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_8(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_10(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_9(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_11(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_10(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_12(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_11(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_13(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_12(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_14(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_13(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) +#define GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_15(_i, _Macro, _Data, _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_CALL_MACRO(_Macro, _i, _Data, GMOCK_PP_HEAD _Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_INTERNAL_FOR_EACH_IMPL_14(GMOCK_PP_INC(_i), _Macro, _Data, \ + (GMOCK_PP_TAIL _Tuple)) + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_PP_H_ + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(push) +# pragma warning(disable:4100) +#endif + +namespace testing { + +// To implement an action Foo, define: +// 1. a class FooAction that implements the ActionInterface interface, and +// 2. a factory function that creates an Action object from a +// const FooAction*. +// +// The two-level delegation design follows that of Matcher, providing +// consistency for extension developers. It also eases ownership +// management as Action objects can now be copied like plain values. + +namespace internal { + +// BuiltInDefaultValueGetter<T, true>::Get() returns a +// default-constructed T value. BuiltInDefaultValueGetter<T, +// false>::Get() crashes with an error. +// +// This primary template is used when kDefaultConstructible is true. +template <typename T, bool kDefaultConstructible> +struct BuiltInDefaultValueGetter { + static T Get() { return T(); } +}; +template <typename T> +struct BuiltInDefaultValueGetter<T, false> { + static T Get() { + Assert(false, __FILE__, __LINE__, + "Default action undefined for the function return type."); + return internal::Invalid<T>(); + // The above statement will never be reached, but is required in + // order for this function to compile. + } +}; + +// BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Get() returns the "built-in" default value +// for type T, which is NULL when T is a raw pointer type, 0 when T is +// a numeric type, false when T is bool, or "" when T is string or +// std::string. In addition, in C++11 and above, it turns a +// default-constructed T value if T is default constructible. For any +// other type T, the built-in default T value is undefined, and the +// function will abort the process. +template <typename T> +class BuiltInDefaultValue { + public: + // This function returns true if and only if type T has a built-in default + // value. + static bool Exists() { + return ::std::is_default_constructible<T>::value; + } + + static T Get() { + return BuiltInDefaultValueGetter< + T, ::std::is_default_constructible<T>::value>::Get(); + } +}; + +// This partial specialization says that we use the same built-in +// default value for T and const T. +template <typename T> +class BuiltInDefaultValue<const T> { + public: + static bool Exists() { return BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Exists(); } + static T Get() { return BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Get(); } +}; + +// This partial specialization defines the default values for pointer +// types. +template <typename T> +class BuiltInDefaultValue<T*> { + public: + static bool Exists() { return true; } + static T* Get() { return nullptr; } +}; + +// The following specializations define the default values for +// specific types we care about. +#define GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(type, value) \ + template <> \ + class BuiltInDefaultValue<type> { \ + public: \ + static bool Exists() { return true; } \ + static type Get() { return value; } \ + } + +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(void, ); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(::std::string, ""); +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(bool, false); +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(unsigned char, '\0'); +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(signed char, '\0'); +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(char, '\0'); + +// There's no need for a default action for signed wchar_t, as that +// type is the same as wchar_t for gcc, and invalid for MSVC. +// +// There's also no need for a default action for unsigned wchar_t, as +// that type is the same as unsigned int for gcc, and invalid for +// MSVC. +#if GMOCK_WCHAR_T_IS_NATIVE_ +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(wchar_t, 0U); // NOLINT +#endif + +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(unsigned short, 0U); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(signed short, 0); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(unsigned int, 0U); +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(signed int, 0); +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(unsigned long, 0UL); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(signed long, 0L); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(unsigned long long, 0); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(signed long long, 0); // NOLINT +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(float, 0); +GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_(double, 0); + +#undef GMOCK_DEFINE_DEFAULT_ACTION_FOR_RETURN_TYPE_ + +// Simple two-arg form of std::disjunction. +template <typename P, typename Q> +using disjunction = typename ::std::conditional<P::value, P, Q>::type; + +} // namespace internal + +// When an unexpected function call is encountered, Google Mock will +// let it return a default value if the user has specified one for its +// return type, or if the return type has a built-in default value; +// otherwise Google Mock won't know what value to return and will have +// to abort the process. +// +// The DefaultValue<T> class allows a user to specify the +// default value for a type T that is both copyable and publicly +// destructible (i.e. anything that can be used as a function return +// type). The usage is: +// +// // Sets the default value for type T to be foo. +// DefaultValue<T>::Set(foo); +template <typename T> +class DefaultValue { + public: + // Sets the default value for type T; requires T to be + // copy-constructable and have a public destructor. + static void Set(T x) { + delete producer_; + producer_ = new FixedValueProducer(x); + } + + // Provides a factory function to be called to generate the default value. + // This method can be used even if T is only move-constructible, but it is not + // limited to that case. + typedef T (*FactoryFunction)(); + static void SetFactory(FactoryFunction factory) { + delete producer_; + producer_ = new FactoryValueProducer(factory); + } + + // Unsets the default value for type T. + static void Clear() { + delete producer_; + producer_ = nullptr; + } + + // Returns true if and only if the user has set the default value for type T. + static bool IsSet() { return producer_ != nullptr; } + + // Returns true if T has a default return value set by the user or there + // exists a built-in default value. + static bool Exists() { + return IsSet() || internal::BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Exists(); + } + + // Returns the default value for type T if the user has set one; + // otherwise returns the built-in default value. Requires that Exists() + // is true, which ensures that the return value is well-defined. + static T Get() { + return producer_ == nullptr ? internal::BuiltInDefaultValue<T>::Get() + : producer_->Produce(); + } + + private: + class ValueProducer { + public: + virtual ~ValueProducer() {} + virtual T Produce() = 0; + }; + + class FixedValueProducer : public ValueProducer { + public: + explicit FixedValueProducer(T value) : value_(value) {} + T Produce() override { return value_; } + + private: + const T value_; + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(FixedValueProducer); + }; + + class FactoryValueProducer : public ValueProducer { + public: + explicit FactoryValueProducer(FactoryFunction factory) + : factory_(factory) {} + T Produce() override { return factory_(); } + + private: + const FactoryFunction factory_; + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(FactoryValueProducer); + }; + + static ValueProducer* producer_; +}; + +// This partial specialization allows a user to set default values for +// reference types. +template <typename T> +class DefaultValue<T&> { + public: + // Sets the default value for type T&. + static void Set(T& x) { // NOLINT + address_ = &x; + } + + // Unsets the default value for type T&. + static void Clear() { address_ = nullptr; } + + // Returns true if and only if the user has set the default value for type T&. + static bool IsSet() { return address_ != nullptr; } + + // Returns true if T has a default return value set by the user or there + // exists a built-in default value. + static bool Exists() { + return IsSet() || internal::BuiltInDefaultValue<T&>::Exists(); + } + + // Returns the default value for type T& if the user has set one; + // otherwise returns the built-in default value if there is one; + // otherwise aborts the process. + static T& Get() { + return address_ == nullptr ? internal::BuiltInDefaultValue<T&>::Get() + : *address_; + } + + private: + static T* address_; +}; + +// This specialization allows DefaultValue<void>::Get() to +// compile. +template <> +class DefaultValue<void> { + public: + static bool Exists() { return true; } + static void Get() {} +}; + +// Points to the user-set default value for type T. +template <typename T> +typename DefaultValue<T>::ValueProducer* DefaultValue<T>::producer_ = nullptr; + +// Points to the user-set default value for type T&. +template <typename T> +T* DefaultValue<T&>::address_ = nullptr; + +// Implement this interface to define an action for function type F. +template <typename F> +class ActionInterface { + public: + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + + ActionInterface() {} + virtual ~ActionInterface() {} + + // Performs the action. This method is not const, as in general an + // action can have side effects and be stateful. For example, a + // get-the-next-element-from-the-collection action will need to + // remember the current element. + virtual Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) = 0; + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ActionInterface); +}; + +// An Action<F> is a copyable and IMMUTABLE (except by assignment) +// object that represents an action to be taken when a mock function +// of type F is called. The implementation of Action<T> is just a +// std::shared_ptr to const ActionInterface<T>. Don't inherit from Action! +// You can view an object implementing ActionInterface<F> as a +// concrete action (including its current state), and an Action<F> +// object as a handle to it. +template <typename F> +class Action { + // Adapter class to allow constructing Action from a legacy ActionInterface. + // New code should create Actions from functors instead. + struct ActionAdapter { + // Adapter must be copyable to satisfy std::function requirements. + ::std::shared_ptr<ActionInterface<F>> impl_; + + template <typename... Args> + typename internal::Function<F>::Result operator()(Args&&... args) { + return impl_->Perform( + ::std::forward_as_tuple(::std::forward<Args>(args)...)); + } + }; + + template <typename G> + using IsCompatibleFunctor = std::is_constructible<std::function<F>, G>; + + public: + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + + // Constructs a null Action. Needed for storing Action objects in + // STL containers. + Action() {} + + // Construct an Action from a specified callable. + // This cannot take std::function directly, because then Action would not be + // directly constructible from lambda (it would require two conversions). + template < + typename G, + typename = typename std::enable_if<internal::disjunction< + IsCompatibleFunctor<G>, std::is_constructible<std::function<Result()>, + G>>::value>::type> + Action(G&& fun) { // NOLINT + Init(::std::forward<G>(fun), IsCompatibleFunctor<G>()); + } + + // Constructs an Action from its implementation. + explicit Action(ActionInterface<F>* impl) + : fun_(ActionAdapter{::std::shared_ptr<ActionInterface<F>>(impl)}) {} + + // This constructor allows us to turn an Action<Func> object into an + // Action<F>, as long as F's arguments can be implicitly converted + // to Func's and Func's return type can be implicitly converted to F's. + template <typename Func> + explicit Action(const Action<Func>& action) : fun_(action.fun_) {} + + // Returns true if and only if this is the DoDefault() action. + bool IsDoDefault() const { return fun_ == nullptr; } + + // Performs the action. Note that this method is const even though + // the corresponding method in ActionInterface is not. The reason + // is that a const Action<F> means that it cannot be re-bound to + // another concrete action, not that the concrete action it binds to + // cannot change state. (Think of the difference between a const + // pointer and a pointer to const.) + Result Perform(ArgumentTuple args) const { + if (IsDoDefault()) { + internal::IllegalDoDefault(__FILE__, __LINE__); + } + return internal::Apply(fun_, ::std::move(args)); + } + + private: + template <typename G> + friend class Action; + + template <typename G> + void Init(G&& g, ::std::true_type) { + fun_ = ::std::forward<G>(g); + } + + template <typename G> + void Init(G&& g, ::std::false_type) { + fun_ = IgnoreArgs<typename ::std::decay<G>::type>{::std::forward<G>(g)}; + } + + template <typename FunctionImpl> + struct IgnoreArgs { + template <typename... Args> + Result operator()(const Args&...) const { + return function_impl(); + } + + FunctionImpl function_impl; + }; + + // fun_ is an empty function if and only if this is the DoDefault() action. + ::std::function<F> fun_; +}; + +// The PolymorphicAction class template makes it easy to implement a +// polymorphic action (i.e. an action that can be used in mock +// functions of than one type, e.g. Return()). +// +// To define a polymorphic action, a user first provides a COPYABLE +// implementation class that has a Perform() method template: +// +// class FooAction { +// public: +// template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> +// Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) const { +// // Processes the arguments and returns a result, using +// // std::get<N>(args) to get the N-th (0-based) argument in the tuple. +// } +// ... +// }; +// +// Then the user creates the polymorphic action using +// MakePolymorphicAction(object) where object has type FooAction. See +// the definition of Return(void) and SetArgumentPointee<N>(value) for +// complete examples. +template <typename Impl> +class PolymorphicAction { + public: + explicit PolymorphicAction(const Impl& impl) : impl_(impl) {} + + template <typename F> + operator Action<F>() const { + return Action<F>(new MonomorphicImpl<F>(impl_)); + } + + private: + template <typename F> + class MonomorphicImpl : public ActionInterface<F> { + public: + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + + explicit MonomorphicImpl(const Impl& impl) : impl_(impl) {} + + Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) override { + return impl_.template Perform<Result>(args); + } + + private: + Impl impl_; + }; + + Impl impl_; +}; + +// Creates an Action from its implementation and returns it. The +// created Action object owns the implementation. +template <typename F> +Action<F> MakeAction(ActionInterface<F>* impl) { + return Action<F>(impl); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic action from its implementation. This is +// easier to use than the PolymorphicAction<Impl> constructor as it +// doesn't require you to explicitly write the template argument, e.g. +// +// MakePolymorphicAction(foo); +// vs +// PolymorphicAction<TypeOfFoo>(foo); +template <typename Impl> +inline PolymorphicAction<Impl> MakePolymorphicAction(const Impl& impl) { + return PolymorphicAction<Impl>(impl); +} + +namespace internal { + +// Helper struct to specialize ReturnAction to execute a move instead of a copy +// on return. Useful for move-only types, but could be used on any type. +template <typename T> +struct ByMoveWrapper { + explicit ByMoveWrapper(T value) : payload(std::move(value)) {} + T payload; +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic Return(x) action, which can be used in +// any function that returns the type of x, regardless of the argument +// types. +// +// Note: The value passed into Return must be converted into +// Function<F>::Result when this action is cast to Action<F> rather than +// when that action is performed. This is important in scenarios like +// +// MOCK_METHOD1(Method, T(U)); +// ... +// { +// Foo foo; +// X x(&foo); +// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Method(_)).WillOnce(Return(x)); +// } +// +// In the example above the variable x holds reference to foo which leaves +// scope and gets destroyed. If copying X just copies a reference to foo, +// that copy will be left with a hanging reference. If conversion to T +// makes a copy of foo, the above code is safe. To support that scenario, we +// need to make sure that the type conversion happens inside the EXPECT_CALL +// statement, and conversion of the result of Return to Action<T(U)> is a +// good place for that. +// +// The real life example of the above scenario happens when an invocation +// of gtl::Container() is passed into Return. +// +template <typename R> +class ReturnAction { + public: + // Constructs a ReturnAction object from the value to be returned. + // 'value' is passed by value instead of by const reference in order + // to allow Return("string literal") to compile. + explicit ReturnAction(R value) : value_(new R(std::move(value))) {} + + // This template type conversion operator allows Return(x) to be + // used in ANY function that returns x's type. + template <typename F> + operator Action<F>() const { // NOLINT + // Assert statement belongs here because this is the best place to verify + // conditions on F. It produces the clearest error messages + // in most compilers. + // Impl really belongs in this scope as a local class but can't + // because MSVC produces duplicate symbols in different translation units + // in this case. Until MS fixes that bug we put Impl into the class scope + // and put the typedef both here (for use in assert statement) and + // in the Impl class. But both definitions must be the same. + typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( + !std::is_reference<Result>::value, + use_ReturnRef_instead_of_Return_to_return_a_reference); + static_assert(!std::is_void<Result>::value, + "Can't use Return() on an action expected to return `void`."); + return Action<F>(new Impl<R, F>(value_)); + } + + private: + // Implements the Return(x) action for a particular function type F. + template <typename R_, typename F> + class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { + public: + typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; + typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + + // The implicit cast is necessary when Result has more than one + // single-argument constructor (e.g. Result is std::vector<int>) and R + // has a type conversion operator template. In that case, value_(value) + // won't compile as the compiler doesn't known which constructor of + // Result to call. ImplicitCast_ forces the compiler to convert R to + // Result without considering explicit constructors, thus resolving the + // ambiguity. value_ is then initialized using its copy constructor. + explicit Impl(const std::shared_ptr<R>& value) + : value_before_cast_(*value), + value_(ImplicitCast_<Result>(value_before_cast_)) {} + + Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) override { return value_; } + + private: + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(!std::is_reference<Result>::value, + Result_cannot_be_a_reference_type); + // We save the value before casting just in case it is being cast to a + // wrapper type. + R value_before_cast_; + Result value_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Impl); + }; + + // Partially specialize for ByMoveWrapper. This version of ReturnAction will + // move its contents instead. + template <typename R_, typename F> + class Impl<ByMoveWrapper<R_>, F> : public ActionInterface<F> { + public: + typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; + typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + + explicit Impl(const std::shared_ptr<R>& wrapper) + : performed_(false), wrapper_(wrapper) {} + + Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) override { + GTEST_CHECK_(!performed_) + << "A ByMove() action should only be performed once."; + performed_ = true; + return std::move(wrapper_->payload); + } + + private: + bool performed_; + const std::shared_ptr<R> wrapper_; + }; + + const std::shared_ptr<R> value_; +}; + +// Implements the ReturnNull() action. +class ReturnNullAction { + public: + // Allows ReturnNull() to be used in any pointer-returning function. In C++11 + // this is enforced by returning nullptr, and in non-C++11 by asserting a + // pointer type on compile time. + template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> + static Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) { + return nullptr; + } +}; + +// Implements the Return() action. +class ReturnVoidAction { + public: + // Allows Return() to be used in any void-returning function. + template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> + static void Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) { + static_assert(std::is_void<Result>::value, "Result should be void."); + } +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic ReturnRef(x) action, which can be used +// in any function that returns a reference to the type of x, +// regardless of the argument types. +template <typename T> +class ReturnRefAction { + public: + // Constructs a ReturnRefAction object from the reference to be returned. + explicit ReturnRefAction(T& ref) : ref_(ref) {} // NOLINT + + // This template type conversion operator allows ReturnRef(x) to be + // used in ANY function that returns a reference to x's type. + template <typename F> + operator Action<F>() const { + typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; + // Asserts that the function return type is a reference. This + // catches the user error of using ReturnRef(x) when Return(x) + // should be used, and generates some helpful error message. + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(std::is_reference<Result>::value, + use_Return_instead_of_ReturnRef_to_return_a_value); + return Action<F>(new Impl<F>(ref_)); + } + + private: + // Implements the ReturnRef(x) action for a particular function type F. + template <typename F> + class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { + public: + typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; + typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + + explicit Impl(T& ref) : ref_(ref) {} // NOLINT + + Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) override { return ref_; } + + private: + T& ref_; + }; + + T& ref_; +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic ReturnRefOfCopy(x) action, which can be +// used in any function that returns a reference to the type of x, +// regardless of the argument types. +template <typename T> +class ReturnRefOfCopyAction { + public: + // Constructs a ReturnRefOfCopyAction object from the reference to + // be returned. + explicit ReturnRefOfCopyAction(const T& value) : value_(value) {} // NOLINT + + // This template type conversion operator allows ReturnRefOfCopy(x) to be + // used in ANY function that returns a reference to x's type. + template <typename F> + operator Action<F>() const { + typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; + // Asserts that the function return type is a reference. This + // catches the user error of using ReturnRefOfCopy(x) when Return(x) + // should be used, and generates some helpful error message. + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( + std::is_reference<Result>::value, + use_Return_instead_of_ReturnRefOfCopy_to_return_a_value); + return Action<F>(new Impl<F>(value_)); + } + + private: + // Implements the ReturnRefOfCopy(x) action for a particular function type F. + template <typename F> + class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { + public: + typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; + typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + + explicit Impl(const T& value) : value_(value) {} // NOLINT + + Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple&) override { return value_; } + + private: + T value_; + }; + + const T value_; +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic ReturnRoundRobin(v) action, which can be +// used in any function that returns the element_type of v. +template <typename T> +class ReturnRoundRobinAction { + public: + explicit ReturnRoundRobinAction(std::vector<T> values) { + GTEST_CHECK_(!values.empty()) + << "ReturnRoundRobin requires at least one element."; + state_->values = std::move(values); + } + + template <typename... Args> + T operator()(Args&&...) const { + return state_->Next(); + } + + private: + struct State { + T Next() { + T ret_val = values[i++]; + if (i == values.size()) i = 0; + return ret_val; + } + + std::vector<T> values; + size_t i = 0; + }; + std::shared_ptr<State> state_ = std::make_shared<State>(); +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic DoDefault() action. +class DoDefaultAction { + public: + // This template type conversion operator allows DoDefault() to be + // used in any function. + template <typename F> + operator Action<F>() const { return Action<F>(); } // NOLINT +}; + +// Implements the Assign action to set a given pointer referent to a +// particular value. +template <typename T1, typename T2> +class AssignAction { + public: + AssignAction(T1* ptr, T2 value) : ptr_(ptr), value_(value) {} + + template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> + void Perform(const ArgumentTuple& /* args */) const { + *ptr_ = value_; + } + + private: + T1* const ptr_; + const T2 value_; +}; + +#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE + +// Implements the SetErrnoAndReturn action to simulate return from +// various system calls and libc functions. +template <typename T> +class SetErrnoAndReturnAction { + public: + SetErrnoAndReturnAction(int errno_value, T result) + : errno_(errno_value), + result_(result) {} + template <typename Result, typename ArgumentTuple> + Result Perform(const ArgumentTuple& /* args */) const { + errno = errno_; + return result_; + } + + private: + const int errno_; + const T result_; +}; + +#endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE + +// Implements the SetArgumentPointee<N>(x) action for any function +// whose N-th argument (0-based) is a pointer to x's type. +template <size_t N, typename A, typename = void> +struct SetArgumentPointeeAction { + A value; + + template <typename... Args> + void operator()(const Args&... args) const { + *::std::get<N>(std::tie(args...)) = value; + } +}; + +// Implements the Invoke(object_ptr, &Class::Method) action. +template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> +struct InvokeMethodAction { + Class* const obj_ptr; + const MethodPtr method_ptr; + + template <typename... Args> + auto operator()(Args&&... args) const + -> decltype((obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(std::forward<Args>(args)...)) { + return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(std::forward<Args>(args)...); + } +}; + +// Implements the InvokeWithoutArgs(f) action. The template argument +// FunctionImpl is the implementation type of f, which can be either a +// function pointer or a functor. InvokeWithoutArgs(f) can be used as an +// Action<F> as long as f's type is compatible with F. +template <typename FunctionImpl> +struct InvokeWithoutArgsAction { + FunctionImpl function_impl; + + // Allows InvokeWithoutArgs(f) to be used as any action whose type is + // compatible with f. + template <typename... Args> + auto operator()(const Args&...) -> decltype(function_impl()) { + return function_impl(); + } +}; + +// Implements the InvokeWithoutArgs(object_ptr, &Class::Method) action. +template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> +struct InvokeMethodWithoutArgsAction { + Class* const obj_ptr; + const MethodPtr method_ptr; + + using ReturnType = + decltype((std::declval<Class*>()->*std::declval<MethodPtr>())()); + + template <typename... Args> + ReturnType operator()(const Args&...) const { + return (obj_ptr->*method_ptr)(); + } +}; + +// Implements the IgnoreResult(action) action. +template <typename A> +class IgnoreResultAction { + public: + explicit IgnoreResultAction(const A& action) : action_(action) {} + + template <typename F> + operator Action<F>() const { + // Assert statement belongs here because this is the best place to verify + // conditions on F. It produces the clearest error messages + // in most compilers. + // Impl really belongs in this scope as a local class but can't + // because MSVC produces duplicate symbols in different translation units + // in this case. Until MS fixes that bug we put Impl into the class scope + // and put the typedef both here (for use in assert statement) and + // in the Impl class. But both definitions must be the same. + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; + + // Asserts at compile time that F returns void. + static_assert(std::is_void<Result>::value, "Result type should be void."); + + return Action<F>(new Impl<F>(action_)); + } + + private: + template <typename F> + class Impl : public ActionInterface<F> { + public: + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::Result Result; + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + + explicit Impl(const A& action) : action_(action) {} + + void Perform(const ArgumentTuple& args) override { + // Performs the action and ignores its result. + action_.Perform(args); + } + + private: + // Type OriginalFunction is the same as F except that its return + // type is IgnoredValue. + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::MakeResultIgnoredValue + OriginalFunction; + + const Action<OriginalFunction> action_; + }; + + const A action_; +}; + +template <typename InnerAction, size_t... I> +struct WithArgsAction { + InnerAction action; + + // The inner action could be anything convertible to Action<X>. + // We use the conversion operator to detect the signature of the inner Action. + template <typename R, typename... Args> + operator Action<R(Args...)>() const { // NOLINT + using TupleType = std::tuple<Args...>; + Action<R(typename std::tuple_element<I, TupleType>::type...)> + converted(action); + + return [converted](Args... args) -> R { + return converted.Perform(std::forward_as_tuple( + std::get<I>(std::forward_as_tuple(std::forward<Args>(args)...))...)); + }; + } +}; + +template <typename... Actions> +struct DoAllAction { + private: + template <typename T> + using NonFinalType = + typename std::conditional<std::is_scalar<T>::value, T, const T&>::type; + + template <typename ActionT, size_t... I> + std::vector<ActionT> Convert(IndexSequence<I...>) const { + return {ActionT(std::get<I>(actions))...}; + } + + public: + std::tuple<Actions...> actions; + + template <typename R, typename... Args> + operator Action<R(Args...)>() const { // NOLINT + struct Op { + std::vector<Action<void(NonFinalType<Args>...)>> converted; + Action<R(Args...)> last; + R operator()(Args... args) const { + auto tuple_args = std::forward_as_tuple(std::forward<Args>(args)...); + for (auto& a : converted) { + a.Perform(tuple_args); + } + return last.Perform(std::move(tuple_args)); + } + }; + return Op{Convert<Action<void(NonFinalType<Args>...)>>( + MakeIndexSequence<sizeof...(Actions) - 1>()), + std::get<sizeof...(Actions) - 1>(actions)}; + } +}; + +template <typename T, typename... Params> +struct ReturnNewAction { + T* operator()() const { + return internal::Apply( + [](const Params&... unpacked_params) { + return new T(unpacked_params...); + }, + params); + } + std::tuple<Params...> params; +}; + +template <size_t k> +struct ReturnArgAction { + template <typename... Args> + auto operator()(const Args&... args) const -> + typename std::tuple_element<k, std::tuple<Args...>>::type { + return std::get<k>(std::tie(args...)); + } +}; + +template <size_t k, typename Ptr> +struct SaveArgAction { + Ptr pointer; + + template <typename... Args> + void operator()(const Args&... args) const { + *pointer = std::get<k>(std::tie(args...)); + } +}; + +template <size_t k, typename Ptr> +struct SaveArgPointeeAction { + Ptr pointer; + + template <typename... Args> + void operator()(const Args&... args) const { + *pointer = *std::get<k>(std::tie(args...)); + } +}; + +template <size_t k, typename T> +struct SetArgRefereeAction { + T value; + + template <typename... Args> + void operator()(Args&&... args) const { + using argk_type = + typename ::std::tuple_element<k, std::tuple<Args...>>::type; + static_assert(std::is_lvalue_reference<argk_type>::value, + "Argument must be a reference type."); + std::get<k>(std::tie(args...)) = value; + } +}; + +template <size_t k, typename I1, typename I2> +struct SetArrayArgumentAction { + I1 first; + I2 last; + + template <typename... Args> + void operator()(const Args&... args) const { + auto value = std::get<k>(std::tie(args...)); + for (auto it = first; it != last; ++it, (void)++value) { + *value = *it; + } + } +}; + +template <size_t k> +struct DeleteArgAction { + template <typename... Args> + void operator()(const Args&... args) const { + delete std::get<k>(std::tie(args...)); + } +}; + +template <typename Ptr> +struct ReturnPointeeAction { + Ptr pointer; + template <typename... Args> + auto operator()(const Args&...) const -> decltype(*pointer) { + return *pointer; + } +}; + +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS +template <typename T> +struct ThrowAction { + T exception; + // We use a conversion operator to adapt to any return type. + template <typename R, typename... Args> + operator Action<R(Args...)>() const { // NOLINT + T copy = exception; + return [copy](Args...) -> R { throw copy; }; + } +}; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +} // namespace internal + +// An Unused object can be implicitly constructed from ANY value. +// This is handy when defining actions that ignore some or all of the +// mock function arguments. For example, given +// +// MOCK_METHOD3(Foo, double(const string& label, double x, double y)); +// MOCK_METHOD3(Bar, double(int index, double x, double y)); +// +// instead of +// +// double DistanceToOriginWithLabel(const string& label, double x, double y) { +// return sqrt(x*x + y*y); +// } +// double DistanceToOriginWithIndex(int index, double x, double y) { +// return sqrt(x*x + y*y); +// } +// ... +// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Foo("abc", _, _)) +// .WillOnce(Invoke(DistanceToOriginWithLabel)); +// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Bar(5, _, _)) +// .WillOnce(Invoke(DistanceToOriginWithIndex)); +// +// you could write +// +// // We can declare any uninteresting argument as Unused. +// double DistanceToOrigin(Unused, double x, double y) { +// return sqrt(x*x + y*y); +// } +// ... +// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Foo("abc", _, _)).WillOnce(Invoke(DistanceToOrigin)); +// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Bar(5, _, _)).WillOnce(Invoke(DistanceToOrigin)); +typedef internal::IgnoredValue Unused; + +// Creates an action that does actions a1, a2, ..., sequentially in +// each invocation. All but the last action will have a readonly view of the +// arguments. +template <typename... Action> +internal::DoAllAction<typename std::decay<Action>::type...> DoAll( + Action&&... action) { + return {std::forward_as_tuple(std::forward<Action>(action)...)}; +} + +// WithArg<k>(an_action) creates an action that passes the k-th +// (0-based) argument of the mock function to an_action and performs +// it. It adapts an action accepting one argument to one that accepts +// multiple arguments. For convenience, we also provide +// WithArgs<k>(an_action) (defined below) as a synonym. +template <size_t k, typename InnerAction> +internal::WithArgsAction<typename std::decay<InnerAction>::type, k> +WithArg(InnerAction&& action) { + return {std::forward<InnerAction>(action)}; +} + +// WithArgs<N1, N2, ..., Nk>(an_action) creates an action that passes +// the selected arguments of the mock function to an_action and +// performs it. It serves as an adaptor between actions with +// different argument lists. +template <size_t k, size_t... ks, typename InnerAction> +internal::WithArgsAction<typename std::decay<InnerAction>::type, k, ks...> +WithArgs(InnerAction&& action) { + return {std::forward<InnerAction>(action)}; +} + +// WithoutArgs(inner_action) can be used in a mock function with a +// non-empty argument list to perform inner_action, which takes no +// argument. In other words, it adapts an action accepting no +// argument to one that accepts (and ignores) arguments. +template <typename InnerAction> +internal::WithArgsAction<typename std::decay<InnerAction>::type> +WithoutArgs(InnerAction&& action) { + return {std::forward<InnerAction>(action)}; +} + +// Creates an action that returns 'value'. 'value' is passed by value +// instead of const reference - otherwise Return("string literal") +// will trigger a compiler error about using array as initializer. +template <typename R> +internal::ReturnAction<R> Return(R value) { + return internal::ReturnAction<R>(std::move(value)); +} + +// Creates an action that returns NULL. +inline PolymorphicAction<internal::ReturnNullAction> ReturnNull() { + return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::ReturnNullAction()); +} + +// Creates an action that returns from a void function. +inline PolymorphicAction<internal::ReturnVoidAction> Return() { + return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::ReturnVoidAction()); +} + +// Creates an action that returns the reference to a variable. +template <typename R> +inline internal::ReturnRefAction<R> ReturnRef(R& x) { // NOLINT + return internal::ReturnRefAction<R>(x); +} + +// Prevent using ReturnRef on reference to temporary. +template <typename R, R* = nullptr> +internal::ReturnRefAction<R> ReturnRef(R&&) = delete; + +// Creates an action that returns the reference to a copy of the +// argument. The copy is created when the action is constructed and +// lives as long as the action. +template <typename R> +inline internal::ReturnRefOfCopyAction<R> ReturnRefOfCopy(const R& x) { + return internal::ReturnRefOfCopyAction<R>(x); +} + +// Modifies the parent action (a Return() action) to perform a move of the +// argument instead of a copy. +// Return(ByMove()) actions can only be executed once and will assert this +// invariant. +template <typename R> +internal::ByMoveWrapper<R> ByMove(R x) { + return internal::ByMoveWrapper<R>(std::move(x)); +} + +// Creates an action that returns an element of `vals`. Calling this action will +// repeatedly return the next value from `vals` until it reaches the end and +// will restart from the beginning. +template <typename T> +internal::ReturnRoundRobinAction<T> ReturnRoundRobin(std::vector<T> vals) { + return internal::ReturnRoundRobinAction<T>(std::move(vals)); +} + +// Creates an action that returns an element of `vals`. Calling this action will +// repeatedly return the next value from `vals` until it reaches the end and +// will restart from the beginning. +template <typename T> +internal::ReturnRoundRobinAction<T> ReturnRoundRobin( + std::initializer_list<T> vals) { + return internal::ReturnRoundRobinAction<T>(std::vector<T>(vals)); +} + +// Creates an action that does the default action for the give mock function. +inline internal::DoDefaultAction DoDefault() { + return internal::DoDefaultAction(); +} + +// Creates an action that sets the variable pointed by the N-th +// (0-based) function argument to 'value'. +template <size_t N, typename T> +internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction<N, T> SetArgPointee(T value) { + return {std::move(value)}; +} + +// The following version is DEPRECATED. +template <size_t N, typename T> +internal::SetArgumentPointeeAction<N, T> SetArgumentPointee(T value) { + return {std::move(value)}; +} + +// Creates an action that sets a pointer referent to a given value. +template <typename T1, typename T2> +PolymorphicAction<internal::AssignAction<T1, T2> > Assign(T1* ptr, T2 val) { + return MakePolymorphicAction(internal::AssignAction<T1, T2>(ptr, val)); +} + +#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE + +// Creates an action that sets errno and returns the appropriate error. +template <typename T> +PolymorphicAction<internal::SetErrnoAndReturnAction<T> > +SetErrnoAndReturn(int errval, T result) { + return MakePolymorphicAction( + internal::SetErrnoAndReturnAction<T>(errval, result)); +} + +#endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE + +// Various overloads for Invoke(). + +// Legacy function. +// Actions can now be implicitly constructed from callables. No need to create +// wrapper objects. +// This function exists for backwards compatibility. +template <typename FunctionImpl> +typename std::decay<FunctionImpl>::type Invoke(FunctionImpl&& function_impl) { + return std::forward<FunctionImpl>(function_impl); +} + +// Creates an action that invokes the given method on the given object +// with the mock function's arguments. +template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> +internal::InvokeMethodAction<Class, MethodPtr> Invoke(Class* obj_ptr, + MethodPtr method_ptr) { + return {obj_ptr, method_ptr}; +} + +// Creates an action that invokes 'function_impl' with no argument. +template <typename FunctionImpl> +internal::InvokeWithoutArgsAction<typename std::decay<FunctionImpl>::type> +InvokeWithoutArgs(FunctionImpl function_impl) { + return {std::move(function_impl)}; +} + +// Creates an action that invokes the given method on the given object +// with no argument. +template <class Class, typename MethodPtr> +internal::InvokeMethodWithoutArgsAction<Class, MethodPtr> InvokeWithoutArgs( + Class* obj_ptr, MethodPtr method_ptr) { + return {obj_ptr, method_ptr}; +} + +// Creates an action that performs an_action and throws away its +// result. In other words, it changes the return type of an_action to +// void. an_action MUST NOT return void, or the code won't compile. +template <typename A> +inline internal::IgnoreResultAction<A> IgnoreResult(const A& an_action) { + return internal::IgnoreResultAction<A>(an_action); +} + +// Creates a reference wrapper for the given L-value. If necessary, +// you can explicitly specify the type of the reference. For example, +// suppose 'derived' is an object of type Derived, ByRef(derived) +// would wrap a Derived&. If you want to wrap a const Base& instead, +// where Base is a base class of Derived, just write: +// +// ByRef<const Base>(derived) +// +// N.B. ByRef is redundant with std::ref, std::cref and std::reference_wrapper. +// However, it may still be used for consistency with ByMove(). +template <typename T> +inline ::std::reference_wrapper<T> ByRef(T& l_value) { // NOLINT + return ::std::reference_wrapper<T>(l_value); +} + +// The ReturnNew<T>(a1, a2, ..., a_k) action returns a pointer to a new +// instance of type T, constructed on the heap with constructor arguments +// a1, a2, ..., and a_k. The caller assumes ownership of the returned value. +template <typename T, typename... Params> +internal::ReturnNewAction<T, typename std::decay<Params>::type...> ReturnNew( + Params&&... params) { + return {std::forward_as_tuple(std::forward<Params>(params)...)}; +} + +// Action ReturnArg<k>() returns the k-th argument of the mock function. +template <size_t k> +internal::ReturnArgAction<k> ReturnArg() { + return {}; +} + +// Action SaveArg<k>(pointer) saves the k-th (0-based) argument of the +// mock function to *pointer. +template <size_t k, typename Ptr> +internal::SaveArgAction<k, Ptr> SaveArg(Ptr pointer) { + return {pointer}; +} + +// Action SaveArgPointee<k>(pointer) saves the value pointed to +// by the k-th (0-based) argument of the mock function to *pointer. +template <size_t k, typename Ptr> +internal::SaveArgPointeeAction<k, Ptr> SaveArgPointee(Ptr pointer) { + return {pointer}; +} + +// Action SetArgReferee<k>(value) assigns 'value' to the variable +// referenced by the k-th (0-based) argument of the mock function. +template <size_t k, typename T> +internal::SetArgRefereeAction<k, typename std::decay<T>::type> SetArgReferee( + T&& value) { + return {std::forward<T>(value)}; +} + +// Action SetArrayArgument<k>(first, last) copies the elements in +// source range [first, last) to the array pointed to by the k-th +// (0-based) argument, which can be either a pointer or an +// iterator. The action does not take ownership of the elements in the +// source range. +template <size_t k, typename I1, typename I2> +internal::SetArrayArgumentAction<k, I1, I2> SetArrayArgument(I1 first, + I2 last) { + return {first, last}; +} + +// Action DeleteArg<k>() deletes the k-th (0-based) argument of the mock +// function. +template <size_t k> +internal::DeleteArgAction<k> DeleteArg() { + return {}; +} + +// This action returns the value pointed to by 'pointer'. +template <typename Ptr> +internal::ReturnPointeeAction<Ptr> ReturnPointee(Ptr pointer) { + return {pointer}; +} + +// Action Throw(exception) can be used in a mock function of any type +// to throw the given exception. Any copyable value can be thrown. +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS +template <typename T> +internal::ThrowAction<typename std::decay<T>::type> Throw(T&& exception) { + return {std::forward<T>(exception)}; +} +#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +namespace internal { + +// A macro from the ACTION* family (defined later in gmock-generated-actions.h) +// defines an action that can be used in a mock function. Typically, +// these actions only care about a subset of the arguments of the mock +// function. For example, if such an action only uses the second +// argument, it can be used in any mock function that takes >= 2 +// arguments where the type of the second argument is compatible. +// +// Therefore, the action implementation must be prepared to take more +// arguments than it needs. The ExcessiveArg type is used to +// represent those excessive arguments. In order to keep the compiler +// error messages tractable, we define it in the testing namespace +// instead of testing::internal. However, this is an INTERNAL TYPE +// and subject to change without notice, so a user MUST NOT USE THIS +// TYPE DIRECTLY. +struct ExcessiveArg {}; + +// Builds an implementation of an Action<> for some particular signature, using +// a class defined by an ACTION* macro. +template <typename F, typename Impl> struct ActionImpl; + +template <typename Impl> +struct ImplBase { + struct Holder { + // Allows each copy of the Action<> to get to the Impl. + explicit operator const Impl&() const { return *ptr; } + std::shared_ptr<Impl> ptr; + }; + using type = typename std::conditional<std::is_constructible<Impl>::value, + Impl, Holder>::type; +}; + +template <typename R, typename... Args, typename Impl> +struct ActionImpl<R(Args...), Impl> : ImplBase<Impl>::type { + using Base = typename ImplBase<Impl>::type; + using function_type = R(Args...); + using args_type = std::tuple<Args...>; + + ActionImpl() = default; // Only defined if appropriate for Base. + explicit ActionImpl(std::shared_ptr<Impl> impl) : Base{std::move(impl)} { } + + R operator()(Args&&... arg) const { + static constexpr size_t kMaxArgs = + sizeof...(Args) <= 10 ? sizeof...(Args) : 10; + return Apply(MakeIndexSequence<kMaxArgs>{}, + MakeIndexSequence<10 - kMaxArgs>{}, + args_type{std::forward<Args>(arg)...}); + } + + template <std::size_t... arg_id, std::size_t... excess_id> + R Apply(IndexSequence<arg_id...>, IndexSequence<excess_id...>, + const args_type& args) const { + // Impl need not be specific to the signature of action being implemented; + // only the implementing function body needs to have all of the specific + // types instantiated. Up to 10 of the args that are provided by the + // args_type get passed, followed by a dummy of unspecified type for the + // remainder up to 10 explicit args. + static constexpr ExcessiveArg kExcessArg{}; + return static_cast<const Impl&>(*this).template gmock_PerformImpl< + /*function_type=*/function_type, /*return_type=*/R, + /*args_type=*/args_type, + /*argN_type=*/typename std::tuple_element<arg_id, args_type>::type...>( + /*args=*/args, std::get<arg_id>(args)..., + ((void)excess_id, kExcessArg)...); + } +}; + +// Stores a default-constructed Impl as part of the Action<>'s +// std::function<>. The Impl should be trivial to copy. +template <typename F, typename Impl> +::testing::Action<F> MakeAction() { + return ::testing::Action<F>(ActionImpl<F, Impl>()); +} + +// Stores just the one given instance of Impl. +template <typename F, typename Impl> +::testing::Action<F> MakeAction(std::shared_ptr<Impl> impl) { + return ::testing::Action<F>(ActionImpl<F, Impl>(std::move(impl))); +} + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_ARG_UNUSED(i, data, el) \ + , const arg##i##_type& arg##i GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ +#define GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_ \ + const args_type& args GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ GMOCK_PP_REPEAT( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ARG_UNUSED, , 10) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_ARG(i, data, el) , const arg##i##_type& arg##i +#define GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_ \ + const args_type& args GMOCK_PP_REPEAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_ARG, , 10) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_TEMPLATE_ARG(i, data, el) , typename arg##i##_type +#define GMOCK_ACTION_TEMPLATE_ARGS_NAMES_ \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_REPEAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_TEMPLATE_ARG, , 10)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_TYPENAME_PARAM(i, data, param) , typename param##_type +#define GMOCK_ACTION_TYPENAME_PARAMS_(params) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_TYPENAME_PARAM, , params)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_TYPE_PARAM(i, data, param) , param##_type +#define GMOCK_ACTION_TYPE_PARAMS_(params) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_TYPE_PARAM, , params)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_TYPE_GVALUE_PARAM(i, data, param) \ + , param##_type gmock_p##i +#define GMOCK_ACTION_TYPE_GVALUE_PARAMS_(params) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_TYPE_GVALUE_PARAM, , params)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_GVALUE_PARAM(i, data, param) \ + , std::forward<param##_type>(gmock_p##i) +#define GMOCK_ACTION_GVALUE_PARAMS_(params) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_GVALUE_PARAM, , params)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_PARAM(i, data, param) \ + , param(::std::forward<param##_type>(gmock_p##i)) +#define GMOCK_ACTION_INIT_PARAMS_(params) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_PARAM, , params)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_FIELD_PARAM(i, data, param) param##_type param; +#define GMOCK_ACTION_FIELD_PARAMS_(params) \ + GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_FIELD_PARAM, , params) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, full_name, params) \ + template <GMOCK_ACTION_TYPENAME_PARAMS_(params)> \ + class full_name { \ + public: \ + explicit full_name(GMOCK_ACTION_TYPE_GVALUE_PARAMS_(params)) \ + : impl_(std::make_shared<gmock_Impl>( \ + GMOCK_ACTION_GVALUE_PARAMS_(params))) { } \ + full_name(const full_name&) = default; \ + full_name(full_name&&) noexcept = default; \ + template <typename F> \ + operator ::testing::Action<F>() const { \ + return ::testing::internal::MakeAction<F>(impl_); \ + } \ + private: \ + class gmock_Impl { \ + public: \ + explicit gmock_Impl(GMOCK_ACTION_TYPE_GVALUE_PARAMS_(params)) \ + : GMOCK_ACTION_INIT_PARAMS_(params) {} \ + template <typename function_type, typename return_type, \ + typename args_type, GMOCK_ACTION_TEMPLATE_ARGS_NAMES_> \ + return_type gmock_PerformImpl(GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_) const; \ + GMOCK_ACTION_FIELD_PARAMS_(params) \ + }; \ + std::shared_ptr<const gmock_Impl> impl_; \ + }; \ + template <GMOCK_ACTION_TYPENAME_PARAMS_(params)> \ + inline full_name<GMOCK_ACTION_TYPE_PARAMS_(params)> name( \ + GMOCK_ACTION_TYPE_GVALUE_PARAMS_(params)) { \ + return full_name<GMOCK_ACTION_TYPE_PARAMS_(params)>( \ + GMOCK_ACTION_GVALUE_PARAMS_(params)); \ + } \ + template <GMOCK_ACTION_TYPENAME_PARAMS_(params)> \ + template <typename function_type, typename return_type, typename args_type, \ + GMOCK_ACTION_TEMPLATE_ARGS_NAMES_> \ + return_type full_name<GMOCK_ACTION_TYPE_PARAMS_(params)>::gmock_Impl:: \ + gmock_PerformImpl(GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const + +} // namespace internal + +// Similar to GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION, but no bound parameters are stored. +#define ACTION(name) \ + class name##Action { \ + public: \ + explicit name##Action() noexcept {} \ + name##Action(const name##Action&) noexcept {} \ + template <typename F> \ + operator ::testing::Action<F>() const { \ + return ::testing::internal::MakeAction<F, gmock_Impl>(); \ + } \ + private: \ + class gmock_Impl { \ + public: \ + template <typename function_type, typename return_type, \ + typename args_type, GMOCK_ACTION_TEMPLATE_ARGS_NAMES_> \ + return_type gmock_PerformImpl(GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_) const; \ + }; \ + }; \ + inline name##Action name() GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_; \ + inline name##Action name() { return name##Action(); } \ + template <typename function_type, typename return_type, typename args_type, \ + GMOCK_ACTION_TEMPLATE_ARGS_NAMES_> \ + return_type name##Action::gmock_Impl::gmock_PerformImpl( \ + GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const + +#define ACTION_P(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +#define ACTION_P2(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP2, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +#define ACTION_P3(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP3, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +#define ACTION_P4(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP4, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +#define ACTION_P5(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP5, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +#define ACTION_P6(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP6, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +#define ACTION_P7(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP7, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +#define ACTION_P8(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP8, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +#define ACTION_P9(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP9, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +#define ACTION_P10(name, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ACTION(name, name##ActionP10, (__VA_ARGS__)) + +} // namespace testing + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(pop) +#endif + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_ACTIONS_H_ +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. +// +// This file implements some commonly used cardinalities. More +// cardinalities can be defined by the user implementing the +// CardinalityInterface interface if necessary. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_CARDINALITIES_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_CARDINALITIES_H_ + +#include <limits.h> +#include <memory> +#include <ostream> // NOLINT + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) + +namespace testing { + +// To implement a cardinality Foo, define: +// 1. a class FooCardinality that implements the +// CardinalityInterface interface, and +// 2. a factory function that creates a Cardinality object from a +// const FooCardinality*. +// +// The two-level delegation design follows that of Matcher, providing +// consistency for extension developers. It also eases ownership +// management as Cardinality objects can now be copied like plain values. + +// The implementation of a cardinality. +class CardinalityInterface { + public: + virtual ~CardinalityInterface() {} + + // Conservative estimate on the lower/upper bound of the number of + // calls allowed. + virtual int ConservativeLowerBound() const { return 0; } + virtual int ConservativeUpperBound() const { return INT_MAX; } + + // Returns true if and only if call_count calls will satisfy this + // cardinality. + virtual bool IsSatisfiedByCallCount(int call_count) const = 0; + + // Returns true if and only if call_count calls will saturate this + // cardinality. + virtual bool IsSaturatedByCallCount(int call_count) const = 0; + + // Describes self to an ostream. + virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const = 0; +}; + +// A Cardinality is a copyable and IMMUTABLE (except by assignment) +// object that specifies how many times a mock function is expected to +// be called. The implementation of Cardinality is just a std::shared_ptr +// to const CardinalityInterface. Don't inherit from Cardinality! +class GTEST_API_ Cardinality { + public: + // Constructs a null cardinality. Needed for storing Cardinality + // objects in STL containers. + Cardinality() {} + + // Constructs a Cardinality from its implementation. + explicit Cardinality(const CardinalityInterface* impl) : impl_(impl) {} + + // Conservative estimate on the lower/upper bound of the number of + // calls allowed. + int ConservativeLowerBound() const { return impl_->ConservativeLowerBound(); } + int ConservativeUpperBound() const { return impl_->ConservativeUpperBound(); } + + // Returns true if and only if call_count calls will satisfy this + // cardinality. + bool IsSatisfiedByCallCount(int call_count) const { + return impl_->IsSatisfiedByCallCount(call_count); + } + + // Returns true if and only if call_count calls will saturate this + // cardinality. + bool IsSaturatedByCallCount(int call_count) const { + return impl_->IsSaturatedByCallCount(call_count); + } + + // Returns true if and only if call_count calls will over-saturate this + // cardinality, i.e. exceed the maximum number of allowed calls. + bool IsOverSaturatedByCallCount(int call_count) const { + return impl_->IsSaturatedByCallCount(call_count) && + !impl_->IsSatisfiedByCallCount(call_count); + } + + // Describes self to an ostream + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { impl_->DescribeTo(os); } + + // Describes the given actual call count to an ostream. + static void DescribeActualCallCountTo(int actual_call_count, + ::std::ostream* os); + + private: + std::shared_ptr<const CardinalityInterface> impl_; +}; + +// Creates a cardinality that allows at least n calls. +GTEST_API_ Cardinality AtLeast(int n); + +// Creates a cardinality that allows at most n calls. +GTEST_API_ Cardinality AtMost(int n); + +// Creates a cardinality that allows any number of calls. +GTEST_API_ Cardinality AnyNumber(); + +// Creates a cardinality that allows between min and max calls. +GTEST_API_ Cardinality Between(int min, int max); + +// Creates a cardinality that allows exactly n calls. +GTEST_API_ Cardinality Exactly(int n); + +// Creates a cardinality from its implementation. +inline Cardinality MakeCardinality(const CardinalityInterface* c) { + return Cardinality(c); +} + +} // namespace testing + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_CARDINALITIES_H_ +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. +// +// This file implements MOCK_METHOD. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_FUNCTION_MOCKER_H_ // NOLINT +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_FUNCTION_MOCKER_H_ // NOLINT + +#include <type_traits> // IWYU pragma: keep +#include <utility> // IWYU pragma: keep + +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. +// +// This file implements the ON_CALL() and EXPECT_CALL() macros. +// +// A user can use the ON_CALL() macro to specify the default action of +// a mock method. The syntax is: +// +// ON_CALL(mock_object, Method(argument-matchers)) +// .With(multi-argument-matcher) +// .WillByDefault(action); +// +// where the .With() clause is optional. +// +// A user can use the EXPECT_CALL() macro to specify an expectation on +// a mock method. The syntax is: +// +// EXPECT_CALL(mock_object, Method(argument-matchers)) +// .With(multi-argument-matchers) +// .Times(cardinality) +// .InSequence(sequences) +// .After(expectations) +// .WillOnce(action) +// .WillRepeatedly(action) +// .RetiresOnSaturation(); +// +// where all clauses are optional, and .InSequence()/.After()/ +// .WillOnce() can appear any number of times. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_SPEC_BUILDERS_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_SPEC_BUILDERS_H_ + +#include <functional> +#include <map> +#include <memory> +#include <set> +#include <sstream> +#include <string> +#include <type_traits> +#include <utility> +#include <vector> +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. +// +// The MATCHER* family of macros can be used in a namespace scope to +// define custom matchers easily. +// +// Basic Usage +// =========== +// +// The syntax +// +// MATCHER(name, description_string) { statements; } +// +// defines a matcher with the given name that executes the statements, +// which must return a bool to indicate if the match succeeds. Inside +// the statements, you can refer to the value being matched by 'arg', +// and refer to its type by 'arg_type'. +// +// The description string documents what the matcher does, and is used +// to generate the failure message when the match fails. Since a +// MATCHER() is usually defined in a header file shared by multiple +// C++ source files, we require the description to be a C-string +// literal to avoid possible side effects. It can be empty, in which +// case we'll use the sequence of words in the matcher name as the +// description. +// +// For example: +// +// MATCHER(IsEven, "") { return (arg % 2) == 0; } +// +// allows you to write +// +// // Expects mock_foo.Bar(n) to be called where n is even. +// EXPECT_CALL(mock_foo, Bar(IsEven())); +// +// or, +// +// // Verifies that the value of some_expression is even. +// EXPECT_THAT(some_expression, IsEven()); +// +// If the above assertion fails, it will print something like: +// +// Value of: some_expression +// Expected: is even +// Actual: 7 +// +// where the description "is even" is automatically calculated from the +// matcher name IsEven. +// +// Argument Type +// ============= +// +// Note that the type of the value being matched (arg_type) is +// determined by the context in which you use the matcher and is +// supplied to you by the compiler, so you don't need to worry about +// declaring it (nor can you). This allows the matcher to be +// polymorphic. For example, IsEven() can be used to match any type +// where the value of "(arg % 2) == 0" can be implicitly converted to +// a bool. In the "Bar(IsEven())" example above, if method Bar() +// takes an int, 'arg_type' will be int; if it takes an unsigned long, +// 'arg_type' will be unsigned long; and so on. +// +// Parameterizing Matchers +// ======================= +// +// Sometimes you'll want to parameterize the matcher. For that you +// can use another macro: +// +// MATCHER_P(name, param_name, description_string) { statements; } +// +// For example: +// +// MATCHER_P(HasAbsoluteValue, value, "") { return abs(arg) == value; } +// +// will allow you to write: +// +// EXPECT_THAT(Blah("a"), HasAbsoluteValue(n)); +// +// which may lead to this message (assuming n is 10): +// +// Value of: Blah("a") +// Expected: has absolute value 10 +// Actual: -9 +// +// Note that both the matcher description and its parameter are +// printed, making the message human-friendly. +// +// In the matcher definition body, you can write 'foo_type' to +// reference the type of a parameter named 'foo'. For example, in the +// body of MATCHER_P(HasAbsoluteValue, value) above, you can write +// 'value_type' to refer to the type of 'value'. +// +// We also provide MATCHER_P2, MATCHER_P3, ..., up to MATCHER_P$n to +// support multi-parameter matchers. +// +// Describing Parameterized Matchers +// ================================= +// +// The last argument to MATCHER*() is a string-typed expression. The +// expression can reference all of the matcher's parameters and a +// special bool-typed variable named 'negation'. When 'negation' is +// false, the expression should evaluate to the matcher's description; +// otherwise it should evaluate to the description of the negation of +// the matcher. For example, +// +// using testing::PrintToString; +// +// MATCHER_P2(InClosedRange, low, hi, +// std::string(negation ? "is not" : "is") + " in range [" + +// PrintToString(low) + ", " + PrintToString(hi) + "]") { +// return low <= arg && arg <= hi; +// } +// ... +// EXPECT_THAT(3, InClosedRange(4, 6)); +// EXPECT_THAT(3, Not(InClosedRange(2, 4))); +// +// would generate two failures that contain the text: +// +// Expected: is in range [4, 6] +// ... +// Expected: is not in range [2, 4] +// +// If you specify "" as the description, the failure message will +// contain the sequence of words in the matcher name followed by the +// parameter values printed as a tuple. For example, +// +// MATCHER_P2(InClosedRange, low, hi, "") { ... } +// ... +// EXPECT_THAT(3, InClosedRange(4, 6)); +// EXPECT_THAT(3, Not(InClosedRange(2, 4))); +// +// would generate two failures that contain the text: +// +// Expected: in closed range (4, 6) +// ... +// Expected: not (in closed range (2, 4)) +// +// Types of Matcher Parameters +// =========================== +// +// For the purpose of typing, you can view +// +// MATCHER_Pk(Foo, p1, ..., pk, description_string) { ... } +// +// as shorthand for +// +// template <typename p1_type, ..., typename pk_type> +// FooMatcherPk<p1_type, ..., pk_type> +// Foo(p1_type p1, ..., pk_type pk) { ... } +// +// When you write Foo(v1, ..., vk), the compiler infers the types of +// the parameters v1, ..., and vk for you. If you are not happy with +// the result of the type inference, you can specify the types by +// explicitly instantiating the template, as in Foo<long, bool>(5, +// false). As said earlier, you don't get to (or need to) specify +// 'arg_type' as that's determined by the context in which the matcher +// is used. You can assign the result of expression Foo(p1, ..., pk) +// to a variable of type FooMatcherPk<p1_type, ..., pk_type>. This +// can be useful when composing matchers. +// +// While you can instantiate a matcher template with reference types, +// passing the parameters by pointer usually makes your code more +// readable. If, however, you still want to pass a parameter by +// reference, be aware that in the failure message generated by the +// matcher you will see the value of the referenced object but not its +// address. +// +// Explaining Match Results +// ======================== +// +// Sometimes the matcher description alone isn't enough to explain why +// the match has failed or succeeded. For example, when expecting a +// long string, it can be very helpful to also print the diff between +// the expected string and the actual one. To achieve that, you can +// optionally stream additional information to a special variable +// named result_listener, whose type is a pointer to class +// MatchResultListener: +// +// MATCHER_P(EqualsLongString, str, "") { +// if (arg == str) return true; +// +// *result_listener << "the difference: " +/// << DiffStrings(str, arg); +// return false; +// } +// +// Overloading Matchers +// ==================== +// +// You can overload matchers with different numbers of parameters: +// +// MATCHER_P(Blah, a, description_string1) { ... } +// MATCHER_P2(Blah, a, b, description_string2) { ... } +// +// Caveats +// ======= +// +// When defining a new matcher, you should also consider implementing +// MatcherInterface or using MakePolymorphicMatcher(). These +// approaches require more work than the MATCHER* macros, but also +// give you more control on the types of the value being matched and +// the matcher parameters, which may leads to better compiler error +// messages when the matcher is used wrong. They also allow +// overloading matchers based on parameter types (as opposed to just +// based on the number of parameters). +// +// MATCHER*() can only be used in a namespace scope as templates cannot be +// declared inside of a local class. +// +// More Information +// ================ +// +// To learn more about using these macros, please search for 'MATCHER' +// on +// https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/docs/gmock_cook_book.md +// +// This file also implements some commonly used argument matchers. More +// matchers can be defined by the user implementing the +// MatcherInterface<T> interface if necessary. +// +// See googletest/include/gtest/gtest-matchers.h for the definition of class +// Matcher, class MatcherInterface, and others. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MATCHERS_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MATCHERS_H_ + +#include <algorithm> +#include <cmath> +#include <initializer_list> +#include <iterator> +#include <limits> +#include <memory> +#include <ostream> // NOLINT +#include <sstream> +#include <string> +#include <type_traits> +#include <utility> +#include <vector> + + +// MSVC warning C5046 is new as of VS2017 version 15.8. +#if defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER >= 1915 +#define GMOCK_MAYBE_5046_ 5046 +#else +#define GMOCK_MAYBE_5046_ +#endif + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_( + 4251 GMOCK_MAYBE_5046_ /* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by + clients of class B */ + /* Symbol involving type with internal linkage not defined */) + +namespace testing { + +// To implement a matcher Foo for type T, define: +// 1. a class FooMatcherImpl that implements the +// MatcherInterface<T> interface, and +// 2. a factory function that creates a Matcher<T> object from a +// FooMatcherImpl*. +// +// The two-level delegation design makes it possible to allow a user +// to write "v" instead of "Eq(v)" where a Matcher is expected, which +// is impossible if we pass matchers by pointers. It also eases +// ownership management as Matcher objects can now be copied like +// plain values. + +// A match result listener that stores the explanation in a string. +class StringMatchResultListener : public MatchResultListener { + public: + StringMatchResultListener() : MatchResultListener(&ss_) {} + + // Returns the explanation accumulated so far. + std::string str() const { return ss_.str(); } + + // Clears the explanation accumulated so far. + void Clear() { ss_.str(""); } + + private: + ::std::stringstream ss_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(StringMatchResultListener); +}; + +// Anything inside the 'internal' namespace IS INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION +// and MUST NOT BE USED IN USER CODE!!! +namespace internal { + +// The MatcherCastImpl class template is a helper for implementing +// MatcherCast(). We need this helper in order to partially +// specialize the implementation of MatcherCast() (C++ allows +// class/struct templates to be partially specialized, but not +// function templates.). + +// This general version is used when MatcherCast()'s argument is a +// polymorphic matcher (i.e. something that can be converted to a +// Matcher but is not one yet; for example, Eq(value)) or a value (for +// example, "hello"). +template <typename T, typename M> +class MatcherCastImpl { + public: + static Matcher<T> Cast(const M& polymorphic_matcher_or_value) { + // M can be a polymorphic matcher, in which case we want to use + // its conversion operator to create Matcher<T>. Or it can be a value + // that should be passed to the Matcher<T>'s constructor. + // + // We can't call Matcher<T>(polymorphic_matcher_or_value) when M is a + // polymorphic matcher because it'll be ambiguous if T has an implicit + // constructor from M (this usually happens when T has an implicit + // constructor from any type). + // + // It won't work to unconditionally implicit_cast + // polymorphic_matcher_or_value to Matcher<T> because it won't trigger + // a user-defined conversion from M to T if one exists (assuming M is + // a value). + return CastImpl(polymorphic_matcher_or_value, + std::is_convertible<M, Matcher<T>>{}, + std::is_convertible<M, T>{}); + } + + private: + template <bool Ignore> + static Matcher<T> CastImpl(const M& polymorphic_matcher_or_value, + std::true_type /* convertible_to_matcher */, + std::integral_constant<bool, Ignore>) { + // M is implicitly convertible to Matcher<T>, which means that either + // M is a polymorphic matcher or Matcher<T> has an implicit constructor + // from M. In both cases using the implicit conversion will produce a + // matcher. + // + // Even if T has an implicit constructor from M, it won't be called because + // creating Matcher<T> would require a chain of two user-defined conversions + // (first to create T from M and then to create Matcher<T> from T). + return polymorphic_matcher_or_value; + } + + // M can't be implicitly converted to Matcher<T>, so M isn't a polymorphic + // matcher. It's a value of a type implicitly convertible to T. Use direct + // initialization to create a matcher. + static Matcher<T> CastImpl(const M& value, + std::false_type /* convertible_to_matcher */, + std::true_type /* convertible_to_T */) { + return Matcher<T>(ImplicitCast_<T>(value)); + } + + // M can't be implicitly converted to either Matcher<T> or T. Attempt to use + // polymorphic matcher Eq(value) in this case. + // + // Note that we first attempt to perform an implicit cast on the value and + // only fall back to the polymorphic Eq() matcher afterwards because the + // latter calls bool operator==(const Lhs& lhs, const Rhs& rhs) in the end + // which might be undefined even when Rhs is implicitly convertible to Lhs + // (e.g. std::pair<const int, int> vs. std::pair<int, int>). + // + // We don't define this method inline as we need the declaration of Eq(). + static Matcher<T> CastImpl(const M& value, + std::false_type /* convertible_to_matcher */, + std::false_type /* convertible_to_T */); +}; + +// This more specialized version is used when MatcherCast()'s argument +// is already a Matcher. This only compiles when type T can be +// statically converted to type U. +template <typename T, typename U> +class MatcherCastImpl<T, Matcher<U> > { + public: + static Matcher<T> Cast(const Matcher<U>& source_matcher) { + return Matcher<T>(new Impl(source_matcher)); + } + + private: + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<T> { + public: + explicit Impl(const Matcher<U>& source_matcher) + : source_matcher_(source_matcher) {} + + // We delegate the matching logic to the source matcher. + bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + using FromType = typename std::remove_cv<typename std::remove_pointer< + typename std::remove_reference<T>::type>::type>::type; + using ToType = typename std::remove_cv<typename std::remove_pointer< + typename std::remove_reference<U>::type>::type>::type; + // Do not allow implicitly converting base*/& to derived*/&. + static_assert( + // Do not trigger if only one of them is a pointer. That implies a + // regular conversion and not a down_cast. + (std::is_pointer<typename std::remove_reference<T>::type>::value != + std::is_pointer<typename std::remove_reference<U>::type>::value) || + std::is_same<FromType, ToType>::value || + !std::is_base_of<FromType, ToType>::value, + "Can't implicitly convert from <base> to <derived>"); + + // Do the cast to `U` explicitly if necessary. + // Otherwise, let implicit conversions do the trick. + using CastType = + typename std::conditional<std::is_convertible<T&, const U&>::value, + T&, U>::type; + + return source_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(static_cast<CastType>(x), + listener); + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + source_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + source_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + private: + const Matcher<U> source_matcher_; + }; +}; + +// This even more specialized version is used for efficiently casting +// a matcher to its own type. +template <typename T> +class MatcherCastImpl<T, Matcher<T> > { + public: + static Matcher<T> Cast(const Matcher<T>& matcher) { return matcher; } +}; + +// Template specialization for parameterless Matcher. +template <typename Derived> +class MatcherBaseImpl { + public: + MatcherBaseImpl() = default; + + template <typename T> + operator ::testing::Matcher<T>() const { // NOLINT(runtime/explicit) + return ::testing::Matcher<T>(new + typename Derived::template gmock_Impl<T>()); + } +}; + +// Template specialization for Matcher with parameters. +template <template <typename...> class Derived, typename... Ts> +class MatcherBaseImpl<Derived<Ts...>> { + public: + // Mark the constructor explicit for single argument T to avoid implicit + // conversions. + template <typename E = std::enable_if<sizeof...(Ts) == 1>, + typename E::type* = nullptr> + explicit MatcherBaseImpl(Ts... params) + : params_(std::forward<Ts>(params)...) {} + template <typename E = std::enable_if<sizeof...(Ts) != 1>, + typename = typename E::type> + MatcherBaseImpl(Ts... params) // NOLINT + : params_(std::forward<Ts>(params)...) {} + + template <typename F> + operator ::testing::Matcher<F>() const { // NOLINT(runtime/explicit) + return Apply<F>(MakeIndexSequence<sizeof...(Ts)>{}); + } + + private: + template <typename F, std::size_t... tuple_ids> + ::testing::Matcher<F> Apply(IndexSequence<tuple_ids...>) const { + return ::testing::Matcher<F>( + new typename Derived<Ts...>::template gmock_Impl<F>( + std::get<tuple_ids>(params_)...)); + } + + const std::tuple<Ts...> params_; +}; + +} // namespace internal + +// In order to be safe and clear, casting between different matcher +// types is done explicitly via MatcherCast<T>(m), which takes a +// matcher m and returns a Matcher<T>. It compiles only when T can be +// statically converted to the argument type of m. +template <typename T, typename M> +inline Matcher<T> MatcherCast(const M& matcher) { + return internal::MatcherCastImpl<T, M>::Cast(matcher); +} + +// This overload handles polymorphic matchers and values only since +// monomorphic matchers are handled by the next one. +template <typename T, typename M> +inline Matcher<T> SafeMatcherCast(const M& polymorphic_matcher_or_value) { + return MatcherCast<T>(polymorphic_matcher_or_value); +} + +// This overload handles monomorphic matchers. +// +// In general, if type T can be implicitly converted to type U, we can +// safely convert a Matcher<U> to a Matcher<T> (i.e. Matcher is +// contravariant): just keep a copy of the original Matcher<U>, convert the +// argument from type T to U, and then pass it to the underlying Matcher<U>. +// The only exception is when U is a reference and T is not, as the +// underlying Matcher<U> may be interested in the argument's address, which +// is not preserved in the conversion from T to U. +template <typename T, typename U> +inline Matcher<T> SafeMatcherCast(const Matcher<U>& matcher) { + // Enforce that T can be implicitly converted to U. + static_assert(std::is_convertible<const T&, const U&>::value, + "T must be implicitly convertible to U"); + // Enforce that we are not converting a non-reference type T to a reference + // type U. + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( + std::is_reference<T>::value || !std::is_reference<U>::value, + cannot_convert_non_reference_arg_to_reference); + // In case both T and U are arithmetic types, enforce that the + // conversion is not lossy. + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(T) RawT; + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(U) RawU; + constexpr bool kTIsOther = GMOCK_KIND_OF_(RawT) == internal::kOther; + constexpr bool kUIsOther = GMOCK_KIND_OF_(RawU) == internal::kOther; + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( + kTIsOther || kUIsOther || + (internal::LosslessArithmeticConvertible<RawT, RawU>::value), + conversion_of_arithmetic_types_must_be_lossless); + return MatcherCast<T>(matcher); +} + +// A<T>() returns a matcher that matches any value of type T. +template <typename T> +Matcher<T> A(); + +// Anything inside the 'internal' namespace IS INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION +// and MUST NOT BE USED IN USER CODE!!! +namespace internal { + +// If the explanation is not empty, prints it to the ostream. +inline void PrintIfNotEmpty(const std::string& explanation, + ::std::ostream* os) { + if (explanation != "" && os != nullptr) { + *os << ", " << explanation; + } +} + +// Returns true if the given type name is easy to read by a human. +// This is used to decide whether printing the type of a value might +// be helpful. +inline bool IsReadableTypeName(const std::string& type_name) { + // We consider a type name readable if it's short or doesn't contain + // a template or function type. + return (type_name.length() <= 20 || + type_name.find_first_of("<(") == std::string::npos); +} + +// Matches the value against the given matcher, prints the value and explains +// the match result to the listener. Returns the match result. +// 'listener' must not be NULL. +// Value cannot be passed by const reference, because some matchers take a +// non-const argument. +template <typename Value, typename T> +bool MatchPrintAndExplain(Value& value, const Matcher<T>& matcher, + MatchResultListener* listener) { + if (!listener->IsInterested()) { + // If the listener is not interested, we do not need to construct the + // inner explanation. + return matcher.Matches(value); + } + + StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; + const bool match = matcher.MatchAndExplain(value, &inner_listener); + + UniversalPrint(value, listener->stream()); +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI + const std::string& type_name = GetTypeName<Value>(); + if (IsReadableTypeName(type_name)) + *listener->stream() << " (of type " << type_name << ")"; +#endif + PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + + return match; +} + +// An internal helper class for doing compile-time loop on a tuple's +// fields. +template <size_t N> +class TuplePrefix { + public: + // TuplePrefix<N>::Matches(matcher_tuple, value_tuple) returns true + // if and only if the first N fields of matcher_tuple matches + // the first N fields of value_tuple, respectively. + template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> + static bool Matches(const MatcherTuple& matcher_tuple, + const ValueTuple& value_tuple) { + return TuplePrefix<N - 1>::Matches(matcher_tuple, value_tuple) && + std::get<N - 1>(matcher_tuple).Matches(std::get<N - 1>(value_tuple)); + } + + // TuplePrefix<N>::ExplainMatchFailuresTo(matchers, values, os) + // describes failures in matching the first N fields of matchers + // against the first N fields of values. If there is no failure, + // nothing will be streamed to os. + template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> + static void ExplainMatchFailuresTo(const MatcherTuple& matchers, + const ValueTuple& values, + ::std::ostream* os) { + // First, describes failures in the first N - 1 fields. + TuplePrefix<N - 1>::ExplainMatchFailuresTo(matchers, values, os); + + // Then describes the failure (if any) in the (N - 1)-th (0-based) + // field. + typename std::tuple_element<N - 1, MatcherTuple>::type matcher = + std::get<N - 1>(matchers); + typedef typename std::tuple_element<N - 1, ValueTuple>::type Value; + const Value& value = std::get<N - 1>(values); + StringMatchResultListener listener; + if (!matcher.MatchAndExplain(value, &listener)) { + *os << " Expected arg #" << N - 1 << ": "; + std::get<N - 1>(matchers).DescribeTo(os); + *os << "\n Actual: "; + // We remove the reference in type Value to prevent the + // universal printer from printing the address of value, which + // isn't interesting to the user most of the time. The + // matcher's MatchAndExplain() method handles the case when + // the address is interesting. + internal::UniversalPrint(value, os); + PrintIfNotEmpty(listener.str(), os); + *os << "\n"; + } + } +}; + +// The base case. +template <> +class TuplePrefix<0> { + public: + template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> + static bool Matches(const MatcherTuple& /* matcher_tuple */, + const ValueTuple& /* value_tuple */) { + return true; + } + + template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> + static void ExplainMatchFailuresTo(const MatcherTuple& /* matchers */, + const ValueTuple& /* values */, + ::std::ostream* /* os */) {} +}; + +// TupleMatches(matcher_tuple, value_tuple) returns true if and only if +// all matchers in matcher_tuple match the corresponding fields in +// value_tuple. It is a compiler error if matcher_tuple and +// value_tuple have different number of fields or incompatible field +// types. +template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> +bool TupleMatches(const MatcherTuple& matcher_tuple, + const ValueTuple& value_tuple) { + // Makes sure that matcher_tuple and value_tuple have the same + // number of fields. + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(std::tuple_size<MatcherTuple>::value == + std::tuple_size<ValueTuple>::value, + matcher_and_value_have_different_numbers_of_fields); + return TuplePrefix<std::tuple_size<ValueTuple>::value>::Matches(matcher_tuple, + value_tuple); +} + +// Describes failures in matching matchers against values. If there +// is no failure, nothing will be streamed to os. +template <typename MatcherTuple, typename ValueTuple> +void ExplainMatchFailureTupleTo(const MatcherTuple& matchers, + const ValueTuple& values, + ::std::ostream* os) { + TuplePrefix<std::tuple_size<MatcherTuple>::value>::ExplainMatchFailuresTo( + matchers, values, os); +} + +// TransformTupleValues and its helper. +// +// TransformTupleValuesHelper hides the internal machinery that +// TransformTupleValues uses to implement a tuple traversal. +template <typename Tuple, typename Func, typename OutIter> +class TransformTupleValuesHelper { + private: + typedef ::std::tuple_size<Tuple> TupleSize; + + public: + // For each member of tuple 't', taken in order, evaluates '*out++ = f(t)'. + // Returns the final value of 'out' in case the caller needs it. + static OutIter Run(Func f, const Tuple& t, OutIter out) { + return IterateOverTuple<Tuple, TupleSize::value>()(f, t, out); + } + + private: + template <typename Tup, size_t kRemainingSize> + struct IterateOverTuple { + OutIter operator() (Func f, const Tup& t, OutIter out) const { + *out++ = f(::std::get<TupleSize::value - kRemainingSize>(t)); + return IterateOverTuple<Tup, kRemainingSize - 1>()(f, t, out); + } + }; + template <typename Tup> + struct IterateOverTuple<Tup, 0> { + OutIter operator() (Func /* f */, const Tup& /* t */, OutIter out) const { + return out; + } + }; +}; + +// Successively invokes 'f(element)' on each element of the tuple 't', +// appending each result to the 'out' iterator. Returns the final value +// of 'out'. +template <typename Tuple, typename Func, typename OutIter> +OutIter TransformTupleValues(Func f, const Tuple& t, OutIter out) { + return TransformTupleValuesHelper<Tuple, Func, OutIter>::Run(f, t, out); +} + +// Implements _, a matcher that matches any value of any +// type. This is a polymorphic matcher, so we need a template type +// conversion operator to make it appearing as a Matcher<T> for any +// type T. +class AnythingMatcher { + public: + using is_gtest_matcher = void; + + template <typename T> + bool MatchAndExplain(const T& /* x */, std::ostream* /* listener */) const { + return true; + } + void DescribeTo(std::ostream* os) const { *os << "is anything"; } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + // This is mostly for completeness' sake, as it's not very useful + // to write Not(A<bool>()). However we cannot completely rule out + // such a possibility, and it doesn't hurt to be prepared. + *os << "never matches"; + } +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic IsNull() matcher, which matches any raw or smart +// pointer that is NULL. +class IsNullMatcher { + public: + template <typename Pointer> + bool MatchAndExplain(const Pointer& p, + MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { + return p == nullptr; + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { *os << "is NULL"; } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "isn't NULL"; + } +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic NotNull() matcher, which matches any raw or smart +// pointer that is not NULL. +class NotNullMatcher { + public: + template <typename Pointer> + bool MatchAndExplain(const Pointer& p, + MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { + return p != nullptr; + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { *os << "isn't NULL"; } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "is NULL"; + } +}; + +// Ref(variable) matches any argument that is a reference to +// 'variable'. This matcher is polymorphic as it can match any +// super type of the type of 'variable'. +// +// The RefMatcher template class implements Ref(variable). It can +// only be instantiated with a reference type. This prevents a user +// from mistakenly using Ref(x) to match a non-reference function +// argument. For example, the following will righteously cause a +// compiler error: +// +// int n; +// Matcher<int> m1 = Ref(n); // This won't compile. +// Matcher<int&> m2 = Ref(n); // This will compile. +template <typename T> +class RefMatcher; + +template <typename T> +class RefMatcher<T&> { + // Google Mock is a generic framework and thus needs to support + // mocking any function types, including those that take non-const + // reference arguments. Therefore the template parameter T (and + // Super below) can be instantiated to either a const type or a + // non-const type. + public: + // RefMatcher() takes a T& instead of const T&, as we want the + // compiler to catch using Ref(const_value) as a matcher for a + // non-const reference. + explicit RefMatcher(T& x) : object_(x) {} // NOLINT + + template <typename Super> + operator Matcher<Super&>() const { + // By passing object_ (type T&) to Impl(), which expects a Super&, + // we make sure that Super is a super type of T. In particular, + // this catches using Ref(const_value) as a matcher for a + // non-const reference, as you cannot implicitly convert a const + // reference to a non-const reference. + return MakeMatcher(new Impl<Super>(object_)); + } + + private: + template <typename Super> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Super&> { + public: + explicit Impl(Super& x) : object_(x) {} // NOLINT + + // MatchAndExplain() takes a Super& (as opposed to const Super&) + // in order to match the interface MatcherInterface<Super&>. + bool MatchAndExplain(Super& x, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + *listener << "which is located @" << static_cast<const void*>(&x); + return &x == &object_; + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "references the variable "; + UniversalPrinter<Super&>::Print(object_, os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "does not reference the variable "; + UniversalPrinter<Super&>::Print(object_, os); + } + + private: + const Super& object_; + }; + + T& object_; +}; + +// Polymorphic helper functions for narrow and wide string matchers. +inline bool CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(const char* lhs, const char* rhs) { + return String::CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(lhs, rhs); +} + +inline bool CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(const wchar_t* lhs, + const wchar_t* rhs) { + return String::CaseInsensitiveWideCStringEquals(lhs, rhs); +} + +// String comparison for narrow or wide strings that can have embedded NUL +// characters. +template <typename StringType> +bool CaseInsensitiveStringEquals(const StringType& s1, + const StringType& s2) { + // Are the heads equal? + if (!CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str())) { + return false; + } + + // Skip the equal heads. + const typename StringType::value_type nul = 0; + const size_t i1 = s1.find(nul), i2 = s2.find(nul); + + // Are we at the end of either s1 or s2? + if (i1 == StringType::npos || i2 == StringType::npos) { + return i1 == i2; + } + + // Are the tails equal? + return CaseInsensitiveStringEquals(s1.substr(i1 + 1), s2.substr(i2 + 1)); +} + +// String matchers. + +// Implements equality-based string matchers like StrEq, StrCaseNe, and etc. +template <typename StringType> +class StrEqualityMatcher { + public: + StrEqualityMatcher(StringType str, bool expect_eq, bool case_sensitive) + : string_(std::move(str)), + expect_eq_(expect_eq), + case_sensitive_(case_sensitive) {} + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + bool MatchAndExplain(const internal::StringView& s, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + // This should fail to compile if StringView is used with wide + // strings. + const StringType& str = std::string(s); + return MatchAndExplain(str, listener); + } +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + + // Accepts pointer types, particularly: + // const char* + // char* + // const wchar_t* + // wchar_t* + template <typename CharType> + bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + if (s == nullptr) { + return !expect_eq_; + } + return MatchAndExplain(StringType(s), listener); + } + + // Matches anything that can convert to StringType. + // + // This is a template, not just a plain function with const StringType&, + // because StringView has some interfering non-explicit constructors. + template <typename MatcheeStringType> + bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, + MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { + const StringType s2(s); + const bool eq = case_sensitive_ ? s2 == string_ : + CaseInsensitiveStringEquals(s2, string_); + return expect_eq_ == eq; + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + DescribeToHelper(expect_eq_, os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + DescribeToHelper(!expect_eq_, os); + } + + private: + void DescribeToHelper(bool expect_eq, ::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << (expect_eq ? "is " : "isn't "); + *os << "equal to "; + if (!case_sensitive_) { + *os << "(ignoring case) "; + } + UniversalPrint(string_, os); + } + + const StringType string_; + const bool expect_eq_; + const bool case_sensitive_; +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic HasSubstr(substring) matcher, which +// can be used as a Matcher<T> as long as T can be converted to a +// string. +template <typename StringType> +class HasSubstrMatcher { + public: + explicit HasSubstrMatcher(const StringType& substring) + : substring_(substring) {} + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + bool MatchAndExplain(const internal::StringView& s, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + // This should fail to compile if StringView is used with wide + // strings. + const StringType& str = std::string(s); + return MatchAndExplain(str, listener); + } +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + + // Accepts pointer types, particularly: + // const char* + // char* + // const wchar_t* + // wchar_t* + template <typename CharType> + bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + return s != nullptr && MatchAndExplain(StringType(s), listener); + } + + // Matches anything that can convert to StringType. + // + // This is a template, not just a plain function with const StringType&, + // because StringView has some interfering non-explicit constructors. + template <typename MatcheeStringType> + bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, + MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { + return StringType(s).find(substring_) != StringType::npos; + } + + // Describes what this matcher matches. + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "has substring "; + UniversalPrint(substring_, os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "has no substring "; + UniversalPrint(substring_, os); + } + + private: + const StringType substring_; +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic StartsWith(substring) matcher, which +// can be used as a Matcher<T> as long as T can be converted to a +// string. +template <typename StringType> +class StartsWithMatcher { + public: + explicit StartsWithMatcher(const StringType& prefix) : prefix_(prefix) { + } + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + bool MatchAndExplain(const internal::StringView& s, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + // This should fail to compile if StringView is used with wide + // strings. + const StringType& str = std::string(s); + return MatchAndExplain(str, listener); + } +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + + // Accepts pointer types, particularly: + // const char* + // char* + // const wchar_t* + // wchar_t* + template <typename CharType> + bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + return s != nullptr && MatchAndExplain(StringType(s), listener); + } + + // Matches anything that can convert to StringType. + // + // This is a template, not just a plain function with const StringType&, + // because StringView has some interfering non-explicit constructors. + template <typename MatcheeStringType> + bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, + MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { + const StringType& s2(s); + return s2.length() >= prefix_.length() && + s2.substr(0, prefix_.length()) == prefix_; + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "starts with "; + UniversalPrint(prefix_, os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "doesn't start with "; + UniversalPrint(prefix_, os); + } + + private: + const StringType prefix_; +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic EndsWith(substring) matcher, which +// can be used as a Matcher<T> as long as T can be converted to a +// string. +template <typename StringType> +class EndsWithMatcher { + public: + explicit EndsWithMatcher(const StringType& suffix) : suffix_(suffix) {} + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + bool MatchAndExplain(const internal::StringView& s, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + // This should fail to compile if StringView is used with wide + // strings. + const StringType& str = std::string(s); + return MatchAndExplain(str, listener); + } +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + + // Accepts pointer types, particularly: + // const char* + // char* + // const wchar_t* + // wchar_t* + template <typename CharType> + bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + return s != nullptr && MatchAndExplain(StringType(s), listener); + } + + // Matches anything that can convert to StringType. + // + // This is a template, not just a plain function with const StringType&, + // because StringView has some interfering non-explicit constructors. + template <typename MatcheeStringType> + bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, + MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { + const StringType& s2(s); + return s2.length() >= suffix_.length() && + s2.substr(s2.length() - suffix_.length()) == suffix_; + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "ends with "; + UniversalPrint(suffix_, os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "doesn't end with "; + UniversalPrint(suffix_, os); + } + + private: + const StringType suffix_; +}; + +// Implements a matcher that compares the two fields of a 2-tuple +// using one of the ==, <=, <, etc, operators. The two fields being +// compared don't have to have the same type. +// +// The matcher defined here is polymorphic (for example, Eq() can be +// used to match a std::tuple<int, short>, a std::tuple<const long&, double>, +// etc). Therefore we use a template type conversion operator in the +// implementation. +template <typename D, typename Op> +class PairMatchBase { + public: + template <typename T1, typename T2> + operator Matcher<::std::tuple<T1, T2>>() const { + return Matcher<::std::tuple<T1, T2>>(new Impl<const ::std::tuple<T1, T2>&>); + } + template <typename T1, typename T2> + operator Matcher<const ::std::tuple<T1, T2>&>() const { + return MakeMatcher(new Impl<const ::std::tuple<T1, T2>&>); + } + + private: + static ::std::ostream& GetDesc(::std::ostream& os) { // NOLINT + return os << D::Desc(); + } + + template <typename Tuple> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Tuple> { + public: + bool MatchAndExplain(Tuple args, + MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const override { + return Op()(::std::get<0>(args), ::std::get<1>(args)); + } + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "are " << GetDesc; + } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "aren't " << GetDesc; + } + }; +}; + +class Eq2Matcher : public PairMatchBase<Eq2Matcher, AnyEq> { + public: + static const char* Desc() { return "an equal pair"; } +}; +class Ne2Matcher : public PairMatchBase<Ne2Matcher, AnyNe> { + public: + static const char* Desc() { return "an unequal pair"; } +}; +class Lt2Matcher : public PairMatchBase<Lt2Matcher, AnyLt> { + public: + static const char* Desc() { return "a pair where the first < the second"; } +}; +class Gt2Matcher : public PairMatchBase<Gt2Matcher, AnyGt> { + public: + static const char* Desc() { return "a pair where the first > the second"; } +}; +class Le2Matcher : public PairMatchBase<Le2Matcher, AnyLe> { + public: + static const char* Desc() { return "a pair where the first <= the second"; } +}; +class Ge2Matcher : public PairMatchBase<Ge2Matcher, AnyGe> { + public: + static const char* Desc() { return "a pair where the first >= the second"; } +}; + +// Implements the Not(...) matcher for a particular argument type T. +// We do not nest it inside the NotMatcher class template, as that +// will prevent different instantiations of NotMatcher from sharing +// the same NotMatcherImpl<T> class. +template <typename T> +class NotMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<const T&> { + public: + explicit NotMatcherImpl(const Matcher<T>& matcher) + : matcher_(matcher) {} + + bool MatchAndExplain(const T& x, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + return !matcher_.MatchAndExplain(x, listener); + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + private: + const Matcher<T> matcher_; +}; + +// Implements the Not(m) matcher, which matches a value that doesn't +// match matcher m. +template <typename InnerMatcher> +class NotMatcher { + public: + explicit NotMatcher(InnerMatcher matcher) : matcher_(matcher) {} + + // This template type conversion operator allows Not(m) to be used + // to match any type m can match. + template <typename T> + operator Matcher<T>() const { + return Matcher<T>(new NotMatcherImpl<T>(SafeMatcherCast<T>(matcher_))); + } + + private: + InnerMatcher matcher_; +}; + +// Implements the AllOf(m1, m2) matcher for a particular argument type +// T. We do not nest it inside the BothOfMatcher class template, as +// that will prevent different instantiations of BothOfMatcher from +// sharing the same BothOfMatcherImpl<T> class. +template <typename T> +class AllOfMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<const T&> { + public: + explicit AllOfMatcherImpl(std::vector<Matcher<T> > matchers) + : matchers_(std::move(matchers)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "("; + for (size_t i = 0; i < matchers_.size(); ++i) { + if (i != 0) *os << ") and ("; + matchers_[i].DescribeTo(os); + } + *os << ")"; + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "("; + for (size_t i = 0; i < matchers_.size(); ++i) { + if (i != 0) *os << ") or ("; + matchers_[i].DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + *os << ")"; + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(const T& x, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + // If either matcher1_ or matcher2_ doesn't match x, we only need + // to explain why one of them fails. + std::string all_match_result; + + for (size_t i = 0; i < matchers_.size(); ++i) { + StringMatchResultListener slistener; + if (matchers_[i].MatchAndExplain(x, &slistener)) { + if (all_match_result.empty()) { + all_match_result = slistener.str(); + } else { + std::string result = slistener.str(); + if (!result.empty()) { + all_match_result += ", and "; + all_match_result += result; + } + } + } else { + *listener << slistener.str(); + return false; + } + } + + // Otherwise we need to explain why *both* of them match. + *listener << all_match_result; + return true; + } + + private: + const std::vector<Matcher<T> > matchers_; +}; + +// VariadicMatcher is used for the variadic implementation of +// AllOf(m_1, m_2, ...) and AnyOf(m_1, m_2, ...). +// CombiningMatcher<T> is used to recursively combine the provided matchers +// (of type Args...). +template <template <typename T> class CombiningMatcher, typename... Args> +class VariadicMatcher { + public: + VariadicMatcher(const Args&... matchers) // NOLINT + : matchers_(matchers...) { + static_assert(sizeof...(Args) > 0, "Must have at least one matcher."); + } + + VariadicMatcher(const VariadicMatcher&) = default; + VariadicMatcher& operator=(const VariadicMatcher&) = delete; + + // This template type conversion operator allows an + // VariadicMatcher<Matcher1, Matcher2...> object to match any type that + // all of the provided matchers (Matcher1, Matcher2, ...) can match. + template <typename T> + operator Matcher<T>() const { + std::vector<Matcher<T> > values; + CreateVariadicMatcher<T>(&values, std::integral_constant<size_t, 0>()); + return Matcher<T>(new CombiningMatcher<T>(std::move(values))); + } + + private: + template <typename T, size_t I> + void CreateVariadicMatcher(std::vector<Matcher<T> >* values, + std::integral_constant<size_t, I>) const { + values->push_back(SafeMatcherCast<T>(std::get<I>(matchers_))); + CreateVariadicMatcher<T>(values, std::integral_constant<size_t, I + 1>()); + } + + template <typename T> + void CreateVariadicMatcher( + std::vector<Matcher<T> >*, + std::integral_constant<size_t, sizeof...(Args)>) const {} + + std::tuple<Args...> matchers_; +}; + +template <typename... Args> +using AllOfMatcher = VariadicMatcher<AllOfMatcherImpl, Args...>; + +// Implements the AnyOf(m1, m2) matcher for a particular argument type +// T. We do not nest it inside the AnyOfMatcher class template, as +// that will prevent different instantiations of AnyOfMatcher from +// sharing the same EitherOfMatcherImpl<T> class. +template <typename T> +class AnyOfMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<const T&> { + public: + explicit AnyOfMatcherImpl(std::vector<Matcher<T> > matchers) + : matchers_(std::move(matchers)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "("; + for (size_t i = 0; i < matchers_.size(); ++i) { + if (i != 0) *os << ") or ("; + matchers_[i].DescribeTo(os); + } + *os << ")"; + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "("; + for (size_t i = 0; i < matchers_.size(); ++i) { + if (i != 0) *os << ") and ("; + matchers_[i].DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + *os << ")"; + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(const T& x, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + std::string no_match_result; + + // If either matcher1_ or matcher2_ matches x, we just need to + // explain why *one* of them matches. + for (size_t i = 0; i < matchers_.size(); ++i) { + StringMatchResultListener slistener; + if (matchers_[i].MatchAndExplain(x, &slistener)) { + *listener << slistener.str(); + return true; + } else { + if (no_match_result.empty()) { + no_match_result = slistener.str(); + } else { + std::string result = slistener.str(); + if (!result.empty()) { + no_match_result += ", and "; + no_match_result += result; + } + } + } + } + + // Otherwise we need to explain why *both* of them fail. + *listener << no_match_result; + return false; + } + + private: + const std::vector<Matcher<T> > matchers_; +}; + +// AnyOfMatcher is used for the variadic implementation of AnyOf(m_1, m_2, ...). +template <typename... Args> +using AnyOfMatcher = VariadicMatcher<AnyOfMatcherImpl, Args...>; + +// Wrapper for implementation of Any/AllOfArray(). +template <template <class> class MatcherImpl, typename T> +class SomeOfArrayMatcher { + public: + // Constructs the matcher from a sequence of element values or + // element matchers. + template <typename Iter> + SomeOfArrayMatcher(Iter first, Iter last) : matchers_(first, last) {} + + template <typename U> + operator Matcher<U>() const { // NOLINT + using RawU = typename std::decay<U>::type; + std::vector<Matcher<RawU>> matchers; + for (const auto& matcher : matchers_) { + matchers.push_back(MatcherCast<RawU>(matcher)); + } + return Matcher<U>(new MatcherImpl<RawU>(std::move(matchers))); + } + + private: + const ::std::vector<T> matchers_; +}; + +template <typename T> +using AllOfArrayMatcher = SomeOfArrayMatcher<AllOfMatcherImpl, T>; + +template <typename T> +using AnyOfArrayMatcher = SomeOfArrayMatcher<AnyOfMatcherImpl, T>; + +// Used for implementing Truly(pred), which turns a predicate into a +// matcher. +template <typename Predicate> +class TrulyMatcher { + public: + explicit TrulyMatcher(Predicate pred) : predicate_(pred) {} + + // This method template allows Truly(pred) to be used as a matcher + // for type T where T is the argument type of predicate 'pred'. The + // argument is passed by reference as the predicate may be + // interested in the address of the argument. + template <typename T> + bool MatchAndExplain(T& x, // NOLINT + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + // Without the if-statement, MSVC sometimes warns about converting + // a value to bool (warning 4800). + // + // We cannot write 'return !!predicate_(x);' as that doesn't work + // when predicate_(x) returns a class convertible to bool but + // having no operator!(). + if (predicate_(x)) + return true; + *listener << "didn't satisfy the given predicate"; + return false; + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "satisfies the given predicate"; + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "doesn't satisfy the given predicate"; + } + + private: + Predicate predicate_; +}; + +// Used for implementing Matches(matcher), which turns a matcher into +// a predicate. +template <typename M> +class MatcherAsPredicate { + public: + explicit MatcherAsPredicate(M matcher) : matcher_(matcher) {} + + // This template operator() allows Matches(m) to be used as a + // predicate on type T where m is a matcher on type T. + // + // The argument x is passed by reference instead of by value, as + // some matcher may be interested in its address (e.g. as in + // Matches(Ref(n))(x)). + template <typename T> + bool operator()(const T& x) const { + // We let matcher_ commit to a particular type here instead of + // when the MatcherAsPredicate object was constructed. This + // allows us to write Matches(m) where m is a polymorphic matcher + // (e.g. Eq(5)). + // + // If we write Matcher<T>(matcher_).Matches(x) here, it won't + // compile when matcher_ has type Matcher<const T&>; if we write + // Matcher<const T&>(matcher_).Matches(x) here, it won't compile + // when matcher_ has type Matcher<T>; if we just write + // matcher_.Matches(x), it won't compile when matcher_ is + // polymorphic, e.g. Eq(5). + // + // MatcherCast<const T&>() is necessary for making the code work + // in all of the above situations. + return MatcherCast<const T&>(matcher_).Matches(x); + } + + private: + M matcher_; +}; + +// For implementing ASSERT_THAT() and EXPECT_THAT(). The template +// argument M must be a type that can be converted to a matcher. +template <typename M> +class PredicateFormatterFromMatcher { + public: + explicit PredicateFormatterFromMatcher(M m) : matcher_(std::move(m)) {} + + // This template () operator allows a PredicateFormatterFromMatcher + // object to act as a predicate-formatter suitable for using with + // Google Test's EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1() macro. + template <typename T> + AssertionResult operator()(const char* value_text, const T& x) const { + // We convert matcher_ to a Matcher<const T&> *now* instead of + // when the PredicateFormatterFromMatcher object was constructed, + // as matcher_ may be polymorphic (e.g. NotNull()) and we won't + // know which type to instantiate it to until we actually see the + // type of x here. + // + // We write SafeMatcherCast<const T&>(matcher_) instead of + // Matcher<const T&>(matcher_), as the latter won't compile when + // matcher_ has type Matcher<T> (e.g. An<int>()). + // We don't write MatcherCast<const T&> either, as that allows + // potentially unsafe downcasting of the matcher argument. + const Matcher<const T&> matcher = SafeMatcherCast<const T&>(matcher_); + + // The expected path here is that the matcher should match (i.e. that most + // tests pass) so optimize for this case. + if (matcher.Matches(x)) { + return AssertionSuccess(); + } + + ::std::stringstream ss; + ss << "Value of: " << value_text << "\n" + << "Expected: "; + matcher.DescribeTo(&ss); + + // Rerun the matcher to "PrintAndExplain" the failure. + StringMatchResultListener listener; + if (MatchPrintAndExplain(x, matcher, &listener)) { + ss << "\n The matcher failed on the initial attempt; but passed when " + "rerun to generate the explanation."; + } + ss << "\n Actual: " << listener.str(); + return AssertionFailure() << ss.str(); + } + + private: + const M matcher_; +}; + +// A helper function for converting a matcher to a predicate-formatter +// without the user needing to explicitly write the type. This is +// used for implementing ASSERT_THAT() and EXPECT_THAT(). +// Implementation detail: 'matcher' is received by-value to force decaying. +template <typename M> +inline PredicateFormatterFromMatcher<M> +MakePredicateFormatterFromMatcher(M matcher) { + return PredicateFormatterFromMatcher<M>(std::move(matcher)); +} + +// Implements the polymorphic IsNan() matcher, which matches any floating type +// value that is Nan. +class IsNanMatcher { + public: + template <typename FloatType> + bool MatchAndExplain(const FloatType& f, + MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { + return (::std::isnan)(f); + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { *os << "is NaN"; } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "isn't NaN"; + } +}; + +// Implements the polymorphic floating point equality matcher, which matches +// two float values using ULP-based approximation or, optionally, a +// user-specified epsilon. The template is meant to be instantiated with +// FloatType being either float or double. +template <typename FloatType> +class FloatingEqMatcher { + public: + // Constructor for FloatingEqMatcher. + // The matcher's input will be compared with expected. The matcher treats two + // NANs as equal if nan_eq_nan is true. Otherwise, under IEEE standards, + // equality comparisons between NANs will always return false. We specify a + // negative max_abs_error_ term to indicate that ULP-based approximation will + // be used for comparison. + FloatingEqMatcher(FloatType expected, bool nan_eq_nan) : + expected_(expected), nan_eq_nan_(nan_eq_nan), max_abs_error_(-1) { + } + + // Constructor that supports a user-specified max_abs_error that will be used + // for comparison instead of ULP-based approximation. The max absolute + // should be non-negative. + FloatingEqMatcher(FloatType expected, bool nan_eq_nan, + FloatType max_abs_error) + : expected_(expected), + nan_eq_nan_(nan_eq_nan), + max_abs_error_(max_abs_error) { + GTEST_CHECK_(max_abs_error >= 0) + << ", where max_abs_error is" << max_abs_error; + } + + // Implements floating point equality matcher as a Matcher<T>. + template <typename T> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<T> { + public: + Impl(FloatType expected, bool nan_eq_nan, FloatType max_abs_error) + : expected_(expected), + nan_eq_nan_(nan_eq_nan), + max_abs_error_(max_abs_error) {} + + bool MatchAndExplain(T value, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + const FloatingPoint<FloatType> actual(value), expected(expected_); + + // Compares NaNs first, if nan_eq_nan_ is true. + if (actual.is_nan() || expected.is_nan()) { + if (actual.is_nan() && expected.is_nan()) { + return nan_eq_nan_; + } + // One is nan; the other is not nan. + return false; + } + if (HasMaxAbsError()) { + // We perform an equality check so that inf will match inf, regardless + // of error bounds. If the result of value - expected_ would result in + // overflow or if either value is inf, the default result is infinity, + // which should only match if max_abs_error_ is also infinity. + if (value == expected_) { + return true; + } + + const FloatType diff = value - expected_; + if (::std::fabs(diff) <= max_abs_error_) { + return true; + } + + if (listener->IsInterested()) { + *listener << "which is " << diff << " from " << expected_; + } + return false; + } else { + return actual.AlmostEquals(expected); + } + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + // os->precision() returns the previously set precision, which we + // store to restore the ostream to its original configuration + // after outputting. + const ::std::streamsize old_precision = os->precision( + ::std::numeric_limits<FloatType>::digits10 + 2); + if (FloatingPoint<FloatType>(expected_).is_nan()) { + if (nan_eq_nan_) { + *os << "is NaN"; + } else { + *os << "never matches"; + } + } else { + *os << "is approximately " << expected_; + if (HasMaxAbsError()) { + *os << " (absolute error <= " << max_abs_error_ << ")"; + } + } + os->precision(old_precision); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + // As before, get original precision. + const ::std::streamsize old_precision = os->precision( + ::std::numeric_limits<FloatType>::digits10 + 2); + if (FloatingPoint<FloatType>(expected_).is_nan()) { + if (nan_eq_nan_) { + *os << "isn't NaN"; + } else { + *os << "is anything"; + } + } else { + *os << "isn't approximately " << expected_; + if (HasMaxAbsError()) { + *os << " (absolute error > " << max_abs_error_ << ")"; + } + } + // Restore original precision. + os->precision(old_precision); + } + + private: + bool HasMaxAbsError() const { + return max_abs_error_ >= 0; + } + + const FloatType expected_; + const bool nan_eq_nan_; + // max_abs_error will be used for value comparison when >= 0. + const FloatType max_abs_error_; + }; + + // The following 3 type conversion operators allow FloatEq(expected) and + // NanSensitiveFloatEq(expected) to be used as a Matcher<float>, a + // Matcher<const float&>, or a Matcher<float&>, but nothing else. + operator Matcher<FloatType>() const { + return MakeMatcher( + new Impl<FloatType>(expected_, nan_eq_nan_, max_abs_error_)); + } + + operator Matcher<const FloatType&>() const { + return MakeMatcher( + new Impl<const FloatType&>(expected_, nan_eq_nan_, max_abs_error_)); + } + + operator Matcher<FloatType&>() const { + return MakeMatcher( + new Impl<FloatType&>(expected_, nan_eq_nan_, max_abs_error_)); + } + + private: + const FloatType expected_; + const bool nan_eq_nan_; + // max_abs_error will be used for value comparison when >= 0. + const FloatType max_abs_error_; +}; + +// A 2-tuple ("binary") wrapper around FloatingEqMatcher: +// FloatingEq2Matcher() matches (x, y) by matching FloatingEqMatcher(x, false) +// against y, and FloatingEq2Matcher(e) matches FloatingEqMatcher(x, false, e) +// against y. The former implements "Eq", the latter "Near". At present, there +// is no version that compares NaNs as equal. +template <typename FloatType> +class FloatingEq2Matcher { + public: + FloatingEq2Matcher() { Init(-1, false); } + + explicit FloatingEq2Matcher(bool nan_eq_nan) { Init(-1, nan_eq_nan); } + + explicit FloatingEq2Matcher(FloatType max_abs_error) { + Init(max_abs_error, false); + } + + FloatingEq2Matcher(FloatType max_abs_error, bool nan_eq_nan) { + Init(max_abs_error, nan_eq_nan); + } + + template <typename T1, typename T2> + operator Matcher<::std::tuple<T1, T2>>() const { + return MakeMatcher( + new Impl<::std::tuple<T1, T2>>(max_abs_error_, nan_eq_nan_)); + } + template <typename T1, typename T2> + operator Matcher<const ::std::tuple<T1, T2>&>() const { + return MakeMatcher( + new Impl<const ::std::tuple<T1, T2>&>(max_abs_error_, nan_eq_nan_)); + } + + private: + static ::std::ostream& GetDesc(::std::ostream& os) { // NOLINT + return os << "an almost-equal pair"; + } + + template <typename Tuple> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Tuple> { + public: + Impl(FloatType max_abs_error, bool nan_eq_nan) : + max_abs_error_(max_abs_error), + nan_eq_nan_(nan_eq_nan) {} + + bool MatchAndExplain(Tuple args, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + if (max_abs_error_ == -1) { + FloatingEqMatcher<FloatType> fm(::std::get<0>(args), nan_eq_nan_); + return static_cast<Matcher<FloatType>>(fm).MatchAndExplain( + ::std::get<1>(args), listener); + } else { + FloatingEqMatcher<FloatType> fm(::std::get<0>(args), nan_eq_nan_, + max_abs_error_); + return static_cast<Matcher<FloatType>>(fm).MatchAndExplain( + ::std::get<1>(args), listener); + } + } + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "are " << GetDesc; + } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "aren't " << GetDesc; + } + + private: + FloatType max_abs_error_; + const bool nan_eq_nan_; + }; + + void Init(FloatType max_abs_error_val, bool nan_eq_nan_val) { + max_abs_error_ = max_abs_error_val; + nan_eq_nan_ = nan_eq_nan_val; + } + FloatType max_abs_error_; + bool nan_eq_nan_; +}; + +// Implements the Pointee(m) matcher for matching a pointer whose +// pointee matches matcher m. The pointer can be either raw or smart. +template <typename InnerMatcher> +class PointeeMatcher { + public: + explicit PointeeMatcher(const InnerMatcher& matcher) : matcher_(matcher) {} + + // This type conversion operator template allows Pointee(m) to be + // used as a matcher for any pointer type whose pointee type is + // compatible with the inner matcher, where type Pointer can be + // either a raw pointer or a smart pointer. + // + // The reason we do this instead of relying on + // MakePolymorphicMatcher() is that the latter is not flexible + // enough for implementing the DescribeTo() method of Pointee(). + template <typename Pointer> + operator Matcher<Pointer>() const { + return Matcher<Pointer>(new Impl<const Pointer&>(matcher_)); + } + + private: + // The monomorphic implementation that works for a particular pointer type. + template <typename Pointer> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Pointer> { + public: + using Pointee = + typename std::pointer_traits<GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_( + Pointer)>::element_type; + + explicit Impl(const InnerMatcher& matcher) + : matcher_(MatcherCast<const Pointee&>(matcher)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "points to a value that "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "does not point to a value that "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Pointer pointer, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + if (GetRawPointer(pointer) == nullptr) return false; + + *listener << "which points to "; + return MatchPrintAndExplain(*pointer, matcher_, listener); + } + + private: + const Matcher<const Pointee&> matcher_; + }; + + const InnerMatcher matcher_; +}; + +// Implements the Pointer(m) matcher +// Implements the Pointer(m) matcher for matching a pointer that matches matcher +// m. The pointer can be either raw or smart, and will match `m` against the +// raw pointer. +template <typename InnerMatcher> +class PointerMatcher { + public: + explicit PointerMatcher(const InnerMatcher& matcher) : matcher_(matcher) {} + + // This type conversion operator template allows Pointer(m) to be + // used as a matcher for any pointer type whose pointer type is + // compatible with the inner matcher, where type PointerType can be + // either a raw pointer or a smart pointer. + // + // The reason we do this instead of relying on + // MakePolymorphicMatcher() is that the latter is not flexible + // enough for implementing the DescribeTo() method of Pointer(). + template <typename PointerType> + operator Matcher<PointerType>() const { // NOLINT + return Matcher<PointerType>(new Impl<const PointerType&>(matcher_)); + } + + private: + // The monomorphic implementation that works for a particular pointer type. + template <typename PointerType> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<PointerType> { + public: + using Pointer = + const typename std::pointer_traits<GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_( + PointerType)>::element_type*; + + explicit Impl(const InnerMatcher& matcher) + : matcher_(MatcherCast<Pointer>(matcher)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "is a pointer that "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "is not a pointer that "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(PointerType pointer, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + *listener << "which is a pointer that "; + Pointer p = GetRawPointer(pointer); + return MatchPrintAndExplain(p, matcher_, listener); + } + + private: + Matcher<Pointer> matcher_; + }; + + const InnerMatcher matcher_; +}; + +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI +// Implements the WhenDynamicCastTo<T>(m) matcher that matches a pointer or +// reference that matches inner_matcher when dynamic_cast<T> is applied. +// The result of dynamic_cast<To> is forwarded to the inner matcher. +// If To is a pointer and the cast fails, the inner matcher will receive NULL. +// If To is a reference and the cast fails, this matcher returns false +// immediately. +template <typename To> +class WhenDynamicCastToMatcherBase { + public: + explicit WhenDynamicCastToMatcherBase(const Matcher<To>& matcher) + : matcher_(matcher) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + GetCastTypeDescription(os); + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + GetCastTypeDescription(os); + matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + protected: + const Matcher<To> matcher_; + + static std::string GetToName() { + return GetTypeName<To>(); + } + + private: + static void GetCastTypeDescription(::std::ostream* os) { + *os << "when dynamic_cast to " << GetToName() << ", "; + } +}; + +// Primary template. +// To is a pointer. Cast and forward the result. +template <typename To> +class WhenDynamicCastToMatcher : public WhenDynamicCastToMatcherBase<To> { + public: + explicit WhenDynamicCastToMatcher(const Matcher<To>& matcher) + : WhenDynamicCastToMatcherBase<To>(matcher) {} + + template <typename From> + bool MatchAndExplain(From from, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + To to = dynamic_cast<To>(from); + return MatchPrintAndExplain(to, this->matcher_, listener); + } +}; + +// Specialize for references. +// In this case we return false if the dynamic_cast fails. +template <typename To> +class WhenDynamicCastToMatcher<To&> : public WhenDynamicCastToMatcherBase<To&> { + public: + explicit WhenDynamicCastToMatcher(const Matcher<To&>& matcher) + : WhenDynamicCastToMatcherBase<To&>(matcher) {} + + template <typename From> + bool MatchAndExplain(From& from, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + // We don't want an std::bad_cast here, so do the cast with pointers. + To* to = dynamic_cast<To*>(&from); + if (to == nullptr) { + *listener << "which cannot be dynamic_cast to " << this->GetToName(); + return false; + } + return MatchPrintAndExplain(*to, this->matcher_, listener); + } +}; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI + +// Implements the Field() matcher for matching a field (i.e. member +// variable) of an object. +template <typename Class, typename FieldType> +class FieldMatcher { + public: + FieldMatcher(FieldType Class::*field, + const Matcher<const FieldType&>& matcher) + : field_(field), matcher_(matcher), whose_field_("whose given field ") {} + + FieldMatcher(const std::string& field_name, FieldType Class::*field, + const Matcher<const FieldType&>& matcher) + : field_(field), + matcher_(matcher), + whose_field_("whose field `" + field_name + "` ") {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "is an object " << whose_field_; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "is an object " << whose_field_; + matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + template <typename T> + bool MatchAndExplain(const T& value, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + // FIXME: The dispatch on std::is_pointer was introduced as a workaround for + // a compiler bug, and can now be removed. + return MatchAndExplainImpl( + typename std::is_pointer<typename std::remove_const<T>::type>::type(), + value, listener); + } + + private: + bool MatchAndExplainImpl(std::false_type /* is_not_pointer */, + const Class& obj, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + *listener << whose_field_ << "is "; + return MatchPrintAndExplain(obj.*field_, matcher_, listener); + } + + bool MatchAndExplainImpl(std::true_type /* is_pointer */, const Class* p, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + if (p == nullptr) return false; + + *listener << "which points to an object "; + // Since *p has a field, it must be a class/struct/union type and + // thus cannot be a pointer. Therefore we pass false_type() as + // the first argument. + return MatchAndExplainImpl(std::false_type(), *p, listener); + } + + const FieldType Class::*field_; + const Matcher<const FieldType&> matcher_; + + // Contains either "whose given field " if the name of the field is unknown + // or "whose field `name_of_field` " if the name is known. + const std::string whose_field_; +}; + +// Implements the Property() matcher for matching a property +// (i.e. return value of a getter method) of an object. +// +// Property is a const-qualified member function of Class returning +// PropertyType. +template <typename Class, typename PropertyType, typename Property> +class PropertyMatcher { + public: + typedef const PropertyType& RefToConstProperty; + + PropertyMatcher(Property property, const Matcher<RefToConstProperty>& matcher) + : property_(property), + matcher_(matcher), + whose_property_("whose given property ") {} + + PropertyMatcher(const std::string& property_name, Property property, + const Matcher<RefToConstProperty>& matcher) + : property_(property), + matcher_(matcher), + whose_property_("whose property `" + property_name + "` ") {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "is an object " << whose_property_; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "is an object " << whose_property_; + matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + template <typename T> + bool MatchAndExplain(const T&value, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + return MatchAndExplainImpl( + typename std::is_pointer<typename std::remove_const<T>::type>::type(), + value, listener); + } + + private: + bool MatchAndExplainImpl(std::false_type /* is_not_pointer */, + const Class& obj, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + *listener << whose_property_ << "is "; + // Cannot pass the return value (for example, int) to MatchPrintAndExplain, + // which takes a non-const reference as argument. + RefToConstProperty result = (obj.*property_)(); + return MatchPrintAndExplain(result, matcher_, listener); + } + + bool MatchAndExplainImpl(std::true_type /* is_pointer */, const Class* p, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + if (p == nullptr) return false; + + *listener << "which points to an object "; + // Since *p has a property method, it must be a class/struct/union + // type and thus cannot be a pointer. Therefore we pass + // false_type() as the first argument. + return MatchAndExplainImpl(std::false_type(), *p, listener); + } + + Property property_; + const Matcher<RefToConstProperty> matcher_; + + // Contains either "whose given property " if the name of the property is + // unknown or "whose property `name_of_property` " if the name is known. + const std::string whose_property_; +}; + +// Type traits specifying various features of different functors for ResultOf. +// The default template specifies features for functor objects. +template <typename Functor> +struct CallableTraits { + typedef Functor StorageType; + + static void CheckIsValid(Functor /* functor */) {} + + template <typename T> + static auto Invoke(Functor f, const T& arg) -> decltype(f(arg)) { + return f(arg); + } +}; + +// Specialization for function pointers. +template <typename ArgType, typename ResType> +struct CallableTraits<ResType(*)(ArgType)> { + typedef ResType ResultType; + typedef ResType(*StorageType)(ArgType); + + static void CheckIsValid(ResType(*f)(ArgType)) { + GTEST_CHECK_(f != nullptr) + << "NULL function pointer is passed into ResultOf()."; + } + template <typename T> + static ResType Invoke(ResType(*f)(ArgType), T arg) { + return (*f)(arg); + } +}; + +// Implements the ResultOf() matcher for matching a return value of a +// unary function of an object. +template <typename Callable, typename InnerMatcher> +class ResultOfMatcher { + public: + ResultOfMatcher(Callable callable, InnerMatcher matcher) + : callable_(std::move(callable)), matcher_(std::move(matcher)) { + CallableTraits<Callable>::CheckIsValid(callable_); + } + + template <typename T> + operator Matcher<T>() const { + return Matcher<T>(new Impl<const T&>(callable_, matcher_)); + } + + private: + typedef typename CallableTraits<Callable>::StorageType CallableStorageType; + + template <typename T> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<T> { + using ResultType = decltype(CallableTraits<Callable>::template Invoke<T>( + std::declval<CallableStorageType>(), std::declval<T>())); + + public: + template <typename M> + Impl(const CallableStorageType& callable, const M& matcher) + : callable_(callable), matcher_(MatcherCast<ResultType>(matcher)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "is mapped by the given callable to a value that "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "is mapped by the given callable to a value that "; + matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(T obj, MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + *listener << "which is mapped by the given callable to "; + // Cannot pass the return value directly to MatchPrintAndExplain, which + // takes a non-const reference as argument. + // Also, specifying template argument explicitly is needed because T could + // be a non-const reference (e.g. Matcher<Uncopyable&>). + ResultType result = + CallableTraits<Callable>::template Invoke<T>(callable_, obj); + return MatchPrintAndExplain(result, matcher_, listener); + } + + private: + // Functors often define operator() as non-const method even though + // they are actually stateless. But we need to use them even when + // 'this' is a const pointer. It's the user's responsibility not to + // use stateful callables with ResultOf(), which doesn't guarantee + // how many times the callable will be invoked. + mutable CallableStorageType callable_; + const Matcher<ResultType> matcher_; + }; // class Impl + + const CallableStorageType callable_; + const InnerMatcher matcher_; +}; + +// Implements a matcher that checks the size of an STL-style container. +template <typename SizeMatcher> +class SizeIsMatcher { + public: + explicit SizeIsMatcher(const SizeMatcher& size_matcher) + : size_matcher_(size_matcher) { + } + + template <typename Container> + operator Matcher<Container>() const { + return Matcher<Container>(new Impl<const Container&>(size_matcher_)); + } + + template <typename Container> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Container> { + public: + using SizeType = decltype(std::declval<Container>().size()); + explicit Impl(const SizeMatcher& size_matcher) + : size_matcher_(MatcherCast<SizeType>(size_matcher)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "size "; + size_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "size "; + size_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + SizeType size = container.size(); + StringMatchResultListener size_listener; + const bool result = size_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(size, &size_listener); + *listener + << "whose size " << size << (result ? " matches" : " doesn't match"); + PrintIfNotEmpty(size_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return result; + } + + private: + const Matcher<SizeType> size_matcher_; + }; + + private: + const SizeMatcher size_matcher_; +}; + +// Implements a matcher that checks the begin()..end() distance of an STL-style +// container. +template <typename DistanceMatcher> +class BeginEndDistanceIsMatcher { + public: + explicit BeginEndDistanceIsMatcher(const DistanceMatcher& distance_matcher) + : distance_matcher_(distance_matcher) {} + + template <typename Container> + operator Matcher<Container>() const { + return Matcher<Container>(new Impl<const Container&>(distance_matcher_)); + } + + template <typename Container> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Container> { + public: + typedef internal::StlContainerView< + GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container)> ContainerView; + typedef typename std::iterator_traits< + typename ContainerView::type::const_iterator>::difference_type + DistanceType; + explicit Impl(const DistanceMatcher& distance_matcher) + : distance_matcher_(MatcherCast<DistanceType>(distance_matcher)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "distance between begin() and end() "; + distance_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "distance between begin() and end() "; + distance_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + using std::begin; + using std::end; + DistanceType distance = std::distance(begin(container), end(container)); + StringMatchResultListener distance_listener; + const bool result = + distance_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(distance, &distance_listener); + *listener << "whose distance between begin() and end() " << distance + << (result ? " matches" : " doesn't match"); + PrintIfNotEmpty(distance_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return result; + } + + private: + const Matcher<DistanceType> distance_matcher_; + }; + + private: + const DistanceMatcher distance_matcher_; +}; + +// Implements an equality matcher for any STL-style container whose elements +// support ==. This matcher is like Eq(), but its failure explanations provide +// more detailed information that is useful when the container is used as a set. +// The failure message reports elements that are in one of the operands but not +// the other. The failure messages do not report duplicate or out-of-order +// elements in the containers (which don't properly matter to sets, but can +// occur if the containers are vectors or lists, for example). +// +// Uses the container's const_iterator, value_type, operator ==, +// begin(), and end(). +template <typename Container> +class ContainerEqMatcher { + public: + typedef internal::StlContainerView<Container> View; + typedef typename View::type StlContainer; + typedef typename View::const_reference StlContainerReference; + + static_assert(!std::is_const<Container>::value, + "Container type must not be const"); + static_assert(!std::is_reference<Container>::value, + "Container type must not be a reference"); + + // We make a copy of expected in case the elements in it are modified + // after this matcher is created. + explicit ContainerEqMatcher(const Container& expected) + : expected_(View::Copy(expected)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "equals "; + UniversalPrint(expected_, os); + } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "does not equal "; + UniversalPrint(expected_, os); + } + + template <typename LhsContainer> + bool MatchAndExplain(const LhsContainer& lhs, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + typedef internal::StlContainerView< + typename std::remove_const<LhsContainer>::type> + LhsView; + typedef typename LhsView::type LhsStlContainer; + StlContainerReference lhs_stl_container = LhsView::ConstReference(lhs); + if (lhs_stl_container == expected_) + return true; + + ::std::ostream* const os = listener->stream(); + if (os != nullptr) { + // Something is different. Check for extra values first. + bool printed_header = false; + for (typename LhsStlContainer::const_iterator it = + lhs_stl_container.begin(); + it != lhs_stl_container.end(); ++it) { + if (internal::ArrayAwareFind(expected_.begin(), expected_.end(), *it) == + expected_.end()) { + if (printed_header) { + *os << ", "; + } else { + *os << "which has these unexpected elements: "; + printed_header = true; + } + UniversalPrint(*it, os); + } + } + + // Now check for missing values. + bool printed_header2 = false; + for (typename StlContainer::const_iterator it = expected_.begin(); + it != expected_.end(); ++it) { + if (internal::ArrayAwareFind( + lhs_stl_container.begin(), lhs_stl_container.end(), *it) == + lhs_stl_container.end()) { + if (printed_header2) { + *os << ", "; + } else { + *os << (printed_header ? ",\nand" : "which") + << " doesn't have these expected elements: "; + printed_header2 = true; + } + UniversalPrint(*it, os); + } + } + } + + return false; + } + + private: + const StlContainer expected_; +}; + +// A comparator functor that uses the < operator to compare two values. +struct LessComparator { + template <typename T, typename U> + bool operator()(const T& lhs, const U& rhs) const { return lhs < rhs; } +}; + +// Implements WhenSortedBy(comparator, container_matcher). +template <typename Comparator, typename ContainerMatcher> +class WhenSortedByMatcher { + public: + WhenSortedByMatcher(const Comparator& comparator, + const ContainerMatcher& matcher) + : comparator_(comparator), matcher_(matcher) {} + + template <typename LhsContainer> + operator Matcher<LhsContainer>() const { + return MakeMatcher(new Impl<LhsContainer>(comparator_, matcher_)); + } + + template <typename LhsContainer> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<LhsContainer> { + public: + typedef internal::StlContainerView< + GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(LhsContainer)> LhsView; + typedef typename LhsView::type LhsStlContainer; + typedef typename LhsView::const_reference LhsStlContainerReference; + // Transforms std::pair<const Key, Value> into std::pair<Key, Value> + // so that we can match associative containers. + typedef typename RemoveConstFromKey< + typename LhsStlContainer::value_type>::type LhsValue; + + Impl(const Comparator& comparator, const ContainerMatcher& matcher) + : comparator_(comparator), matcher_(matcher) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "(when sorted) "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "(when sorted) "; + matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(LhsContainer lhs, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + LhsStlContainerReference lhs_stl_container = LhsView::ConstReference(lhs); + ::std::vector<LhsValue> sorted_container(lhs_stl_container.begin(), + lhs_stl_container.end()); + ::std::sort( + sorted_container.begin(), sorted_container.end(), comparator_); + + if (!listener->IsInterested()) { + // If the listener is not interested, we do not need to + // construct the inner explanation. + return matcher_.Matches(sorted_container); + } + + *listener << "which is "; + UniversalPrint(sorted_container, listener->stream()); + *listener << " when sorted"; + + StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; + const bool match = matcher_.MatchAndExplain(sorted_container, + &inner_listener); + PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return match; + } + + private: + const Comparator comparator_; + const Matcher<const ::std::vector<LhsValue>&> matcher_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Impl); + }; + + private: + const Comparator comparator_; + const ContainerMatcher matcher_; +}; + +// Implements Pointwise(tuple_matcher, rhs_container). tuple_matcher +// must be able to be safely cast to Matcher<std::tuple<const T1&, const +// T2&> >, where T1 and T2 are the types of elements in the LHS +// container and the RHS container respectively. +template <typename TupleMatcher, typename RhsContainer> +class PointwiseMatcher { + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( + !IsHashTable<GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(RhsContainer)>::value, + use_UnorderedPointwise_with_hash_tables); + + public: + typedef internal::StlContainerView<RhsContainer> RhsView; + typedef typename RhsView::type RhsStlContainer; + typedef typename RhsStlContainer::value_type RhsValue; + + static_assert(!std::is_const<RhsContainer>::value, + "RhsContainer type must not be const"); + static_assert(!std::is_reference<RhsContainer>::value, + "RhsContainer type must not be a reference"); + + // Like ContainerEq, we make a copy of rhs in case the elements in + // it are modified after this matcher is created. + PointwiseMatcher(const TupleMatcher& tuple_matcher, const RhsContainer& rhs) + : tuple_matcher_(tuple_matcher), rhs_(RhsView::Copy(rhs)) {} + + template <typename LhsContainer> + operator Matcher<LhsContainer>() const { + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( + !IsHashTable<GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(LhsContainer)>::value, + use_UnorderedPointwise_with_hash_tables); + + return Matcher<LhsContainer>( + new Impl<const LhsContainer&>(tuple_matcher_, rhs_)); + } + + template <typename LhsContainer> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<LhsContainer> { + public: + typedef internal::StlContainerView< + GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(LhsContainer)> LhsView; + typedef typename LhsView::type LhsStlContainer; + typedef typename LhsView::const_reference LhsStlContainerReference; + typedef typename LhsStlContainer::value_type LhsValue; + // We pass the LHS value and the RHS value to the inner matcher by + // reference, as they may be expensive to copy. We must use tuple + // instead of pair here, as a pair cannot hold references (C++ 98, + // 20.2.2 [lib.pairs]). + typedef ::std::tuple<const LhsValue&, const RhsValue&> InnerMatcherArg; + + Impl(const TupleMatcher& tuple_matcher, const RhsStlContainer& rhs) + // mono_tuple_matcher_ holds a monomorphic version of the tuple matcher. + : mono_tuple_matcher_(SafeMatcherCast<InnerMatcherArg>(tuple_matcher)), + rhs_(rhs) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "contains " << rhs_.size() + << " values, where each value and its corresponding value in "; + UniversalPrinter<RhsStlContainer>::Print(rhs_, os); + *os << " "; + mono_tuple_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "doesn't contain exactly " << rhs_.size() + << " values, or contains a value x at some index i" + << " where x and the i-th value of "; + UniversalPrint(rhs_, os); + *os << " "; + mono_tuple_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(LhsContainer lhs, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + LhsStlContainerReference lhs_stl_container = LhsView::ConstReference(lhs); + const size_t actual_size = lhs_stl_container.size(); + if (actual_size != rhs_.size()) { + *listener << "which contains " << actual_size << " values"; + return false; + } + + typename LhsStlContainer::const_iterator left = lhs_stl_container.begin(); + typename RhsStlContainer::const_iterator right = rhs_.begin(); + for (size_t i = 0; i != actual_size; ++i, ++left, ++right) { + if (listener->IsInterested()) { + StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; + // Create InnerMatcherArg as a temporarily object to avoid it outlives + // *left and *right. Dereference or the conversion to `const T&` may + // return temp objects, e.g for vector<bool>. + if (!mono_tuple_matcher_.MatchAndExplain( + InnerMatcherArg(ImplicitCast_<const LhsValue&>(*left), + ImplicitCast_<const RhsValue&>(*right)), + &inner_listener)) { + *listener << "where the value pair ("; + UniversalPrint(*left, listener->stream()); + *listener << ", "; + UniversalPrint(*right, listener->stream()); + *listener << ") at index #" << i << " don't match"; + PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return false; + } + } else { + if (!mono_tuple_matcher_.Matches( + InnerMatcherArg(ImplicitCast_<const LhsValue&>(*left), + ImplicitCast_<const RhsValue&>(*right)))) + return false; + } + } + + return true; + } + + private: + const Matcher<InnerMatcherArg> mono_tuple_matcher_; + const RhsStlContainer rhs_; + }; + + private: + const TupleMatcher tuple_matcher_; + const RhsStlContainer rhs_; +}; + +// Holds the logic common to ContainsMatcherImpl and EachMatcherImpl. +template <typename Container> +class QuantifierMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<Container> { + public: + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; + typedef StlContainerView<RawContainer> View; + typedef typename View::type StlContainer; + typedef typename View::const_reference StlContainerReference; + typedef typename StlContainer::value_type Element; + + template <typename InnerMatcher> + explicit QuantifierMatcherImpl(InnerMatcher inner_matcher) + : inner_matcher_( + testing::SafeMatcherCast<const Element&>(inner_matcher)) {} + + // Checks whether: + // * All elements in the container match, if all_elements_should_match. + // * Any element in the container matches, if !all_elements_should_match. + bool MatchAndExplainImpl(bool all_elements_should_match, + Container container, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + StlContainerReference stl_container = View::ConstReference(container); + size_t i = 0; + for (typename StlContainer::const_iterator it = stl_container.begin(); + it != stl_container.end(); ++it, ++i) { + StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; + const bool matches = inner_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(*it, &inner_listener); + + if (matches != all_elements_should_match) { + *listener << "whose element #" << i + << (matches ? " matches" : " doesn't match"); + PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return !all_elements_should_match; + } + } + return all_elements_should_match; + } + + protected: + const Matcher<const Element&> inner_matcher_; +}; + +// Implements Contains(element_matcher) for the given argument type Container. +// Symmetric to EachMatcherImpl. +template <typename Container> +class ContainsMatcherImpl : public QuantifierMatcherImpl<Container> { + public: + template <typename InnerMatcher> + explicit ContainsMatcherImpl(InnerMatcher inner_matcher) + : QuantifierMatcherImpl<Container>(inner_matcher) {} + + // Describes what this matcher does. + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "contains at least one element that "; + this->inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "doesn't contain any element that "; + this->inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + return this->MatchAndExplainImpl(false, container, listener); + } +}; + +// Implements Each(element_matcher) for the given argument type Container. +// Symmetric to ContainsMatcherImpl. +template <typename Container> +class EachMatcherImpl : public QuantifierMatcherImpl<Container> { + public: + template <typename InnerMatcher> + explicit EachMatcherImpl(InnerMatcher inner_matcher) + : QuantifierMatcherImpl<Container>(inner_matcher) {} + + // Describes what this matcher does. + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "only contains elements that "; + this->inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "contains some element that "; + this->inner_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + return this->MatchAndExplainImpl(true, container, listener); + } +}; + +// Implements polymorphic Contains(element_matcher). +template <typename M> +class ContainsMatcher { + public: + explicit ContainsMatcher(M m) : inner_matcher_(m) {} + + template <typename Container> + operator Matcher<Container>() const { + return Matcher<Container>( + new ContainsMatcherImpl<const Container&>(inner_matcher_)); + } + + private: + const M inner_matcher_; +}; + +// Implements polymorphic Each(element_matcher). +template <typename M> +class EachMatcher { + public: + explicit EachMatcher(M m) : inner_matcher_(m) {} + + template <typename Container> + operator Matcher<Container>() const { + return Matcher<Container>( + new EachMatcherImpl<const Container&>(inner_matcher_)); + } + + private: + const M inner_matcher_; +}; + +struct Rank1 {}; +struct Rank0 : Rank1 {}; + +namespace pair_getters { +using std::get; +template <typename T> +auto First(T& x, Rank1) -> decltype(get<0>(x)) { // NOLINT + return get<0>(x); +} +template <typename T> +auto First(T& x, Rank0) -> decltype((x.first)) { // NOLINT + return x.first; +} + +template <typename T> +auto Second(T& x, Rank1) -> decltype(get<1>(x)) { // NOLINT + return get<1>(x); +} +template <typename T> +auto Second(T& x, Rank0) -> decltype((x.second)) { // NOLINT + return x.second; +} +} // namespace pair_getters + +// Implements Key(inner_matcher) for the given argument pair type. +// Key(inner_matcher) matches an std::pair whose 'first' field matches +// inner_matcher. For example, Contains(Key(Ge(5))) can be used to match an +// std::map that contains at least one element whose key is >= 5. +template <typename PairType> +class KeyMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<PairType> { + public: + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(PairType) RawPairType; + typedef typename RawPairType::first_type KeyType; + + template <typename InnerMatcher> + explicit KeyMatcherImpl(InnerMatcher inner_matcher) + : inner_matcher_( + testing::SafeMatcherCast<const KeyType&>(inner_matcher)) { + } + + // Returns true if and only if 'key_value.first' (the key) matches the inner + // matcher. + bool MatchAndExplain(PairType key_value, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; + const bool match = inner_matcher_.MatchAndExplain( + pair_getters::First(key_value, Rank0()), &inner_listener); + const std::string explanation = inner_listener.str(); + if (explanation != "") { + *listener << "whose first field is a value " << explanation; + } + return match; + } + + // Describes what this matcher does. + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "has a key that "; + inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + // Describes what the negation of this matcher does. + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "doesn't have a key that "; + inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + private: + const Matcher<const KeyType&> inner_matcher_; +}; + +// Implements polymorphic Key(matcher_for_key). +template <typename M> +class KeyMatcher { + public: + explicit KeyMatcher(M m) : matcher_for_key_(m) {} + + template <typename PairType> + operator Matcher<PairType>() const { + return Matcher<PairType>( + new KeyMatcherImpl<const PairType&>(matcher_for_key_)); + } + + private: + const M matcher_for_key_; +}; + +// Implements polymorphic Address(matcher_for_address). +template <typename InnerMatcher> +class AddressMatcher { + public: + explicit AddressMatcher(InnerMatcher m) : matcher_(m) {} + + template <typename Type> + operator Matcher<Type>() const { // NOLINT + return Matcher<Type>(new Impl<const Type&>(matcher_)); + } + + private: + // The monomorphic implementation that works for a particular object type. + template <typename Type> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Type> { + public: + using Address = const GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Type) *; + explicit Impl(const InnerMatcher& matcher) + : matcher_(MatcherCast<Address>(matcher)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "has address that "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "does not have address that "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Type object, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + *listener << "which has address "; + Address address = std::addressof(object); + return MatchPrintAndExplain(address, matcher_, listener); + } + + private: + const Matcher<Address> matcher_; + }; + const InnerMatcher matcher_; +}; + +// Implements Pair(first_matcher, second_matcher) for the given argument pair +// type with its two matchers. See Pair() function below. +template <typename PairType> +class PairMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<PairType> { + public: + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(PairType) RawPairType; + typedef typename RawPairType::first_type FirstType; + typedef typename RawPairType::second_type SecondType; + + template <typename FirstMatcher, typename SecondMatcher> + PairMatcherImpl(FirstMatcher first_matcher, SecondMatcher second_matcher) + : first_matcher_( + testing::SafeMatcherCast<const FirstType&>(first_matcher)), + second_matcher_( + testing::SafeMatcherCast<const SecondType&>(second_matcher)) { + } + + // Describes what this matcher does. + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "has a first field that "; + first_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + *os << ", and has a second field that "; + second_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + // Describes what the negation of this matcher does. + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "has a first field that "; + first_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + *os << ", or has a second field that "; + second_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + // Returns true if and only if 'a_pair.first' matches first_matcher and + // 'a_pair.second' matches second_matcher. + bool MatchAndExplain(PairType a_pair, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + if (!listener->IsInterested()) { + // If the listener is not interested, we don't need to construct the + // explanation. + return first_matcher_.Matches(pair_getters::First(a_pair, Rank0())) && + second_matcher_.Matches(pair_getters::Second(a_pair, Rank0())); + } + StringMatchResultListener first_inner_listener; + if (!first_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(pair_getters::First(a_pair, Rank0()), + &first_inner_listener)) { + *listener << "whose first field does not match"; + PrintIfNotEmpty(first_inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return false; + } + StringMatchResultListener second_inner_listener; + if (!second_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(pair_getters::Second(a_pair, Rank0()), + &second_inner_listener)) { + *listener << "whose second field does not match"; + PrintIfNotEmpty(second_inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return false; + } + ExplainSuccess(first_inner_listener.str(), second_inner_listener.str(), + listener); + return true; + } + + private: + void ExplainSuccess(const std::string& first_explanation, + const std::string& second_explanation, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + *listener << "whose both fields match"; + if (first_explanation != "") { + *listener << ", where the first field is a value " << first_explanation; + } + if (second_explanation != "") { + *listener << ", "; + if (first_explanation != "") { + *listener << "and "; + } else { + *listener << "where "; + } + *listener << "the second field is a value " << second_explanation; + } + } + + const Matcher<const FirstType&> first_matcher_; + const Matcher<const SecondType&> second_matcher_; +}; + +// Implements polymorphic Pair(first_matcher, second_matcher). +template <typename FirstMatcher, typename SecondMatcher> +class PairMatcher { + public: + PairMatcher(FirstMatcher first_matcher, SecondMatcher second_matcher) + : first_matcher_(first_matcher), second_matcher_(second_matcher) {} + + template <typename PairType> + operator Matcher<PairType> () const { + return Matcher<PairType>( + new PairMatcherImpl<const PairType&>(first_matcher_, second_matcher_)); + } + + private: + const FirstMatcher first_matcher_; + const SecondMatcher second_matcher_; +}; + +template <typename T, size_t... I> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, IndexSequence<I...>, int) + -> decltype(std::tie(get<I>(t)...)) { + static_assert(std::tuple_size<T>::value == sizeof...(I), + "Number of arguments doesn't match the number of fields."); + return std::tie(get<I>(t)...); +} + +#if defined(__cpp_structured_bindings) && __cpp_structured_bindings >= 201606 +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<1>, char) { + const auto& [a] = t; + return std::tie(a); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<2>, char) { + const auto& [a, b] = t; + return std::tie(a, b); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<3>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<4>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<5>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<6>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<7>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<8>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<9>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<10>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<11>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<12>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<13>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<14>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<15>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n, o] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n, o); +} +template <typename T> +auto UnpackStructImpl(const T& t, MakeIndexSequence<16>, char) { + const auto& [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n, o, p] = t; + return std::tie(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n, o, p); +} +#endif // defined(__cpp_structured_bindings) + +template <size_t I, typename T> +auto UnpackStruct(const T& t) + -> decltype((UnpackStructImpl)(t, MakeIndexSequence<I>{}, 0)) { + return (UnpackStructImpl)(t, MakeIndexSequence<I>{}, 0); +} + +// Helper function to do comma folding in C++11. +// The array ensures left-to-right order of evaluation. +// Usage: VariadicExpand({expr...}); +template <typename T, size_t N> +void VariadicExpand(const T (&)[N]) {} + +template <typename Struct, typename StructSize> +class FieldsAreMatcherImpl; + +template <typename Struct, size_t... I> +class FieldsAreMatcherImpl<Struct, IndexSequence<I...>> + : public MatcherInterface<Struct> { + using UnpackedType = + decltype(UnpackStruct<sizeof...(I)>(std::declval<const Struct&>())); + using MatchersType = std::tuple< + Matcher<const typename std::tuple_element<I, UnpackedType>::type&>...>; + + public: + template <typename Inner> + explicit FieldsAreMatcherImpl(const Inner& matchers) + : matchers_(testing::SafeMatcherCast< + const typename std::tuple_element<I, UnpackedType>::type&>( + std::get<I>(matchers))...) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + const char* separator = ""; + VariadicExpand( + {(*os << separator << "has field #" << I << " that ", + std::get<I>(matchers_).DescribeTo(os), separator = ", and ")...}); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + const char* separator = ""; + VariadicExpand({(*os << separator << "has field #" << I << " that ", + std::get<I>(matchers_).DescribeNegationTo(os), + separator = ", or ")...}); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Struct t, MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + return MatchInternal((UnpackStruct<sizeof...(I)>)(t), listener); + } + + private: + bool MatchInternal(UnpackedType tuple, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + if (!listener->IsInterested()) { + // If the listener is not interested, we don't need to construct the + // explanation. + bool good = true; + VariadicExpand({good = good && std::get<I>(matchers_).Matches( + std::get<I>(tuple))...}); + return good; + } + + size_t failed_pos = ~size_t{}; + + std::vector<StringMatchResultListener> inner_listener(sizeof...(I)); + + VariadicExpand( + {failed_pos == ~size_t{} && !std::get<I>(matchers_).MatchAndExplain( + std::get<I>(tuple), &inner_listener[I]) + ? failed_pos = I + : 0 ...}); + if (failed_pos != ~size_t{}) { + *listener << "whose field #" << failed_pos << " does not match"; + PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener[failed_pos].str(), listener->stream()); + return false; + } + + *listener << "whose all elements match"; + const char* separator = ", where"; + for (size_t index = 0; index < sizeof...(I); ++index) { + const std::string str = inner_listener[index].str(); + if (!str.empty()) { + *listener << separator << " field #" << index << " is a value " << str; + separator = ", and"; + } + } + + return true; + } + + MatchersType matchers_; +}; + +template <typename... Inner> +class FieldsAreMatcher { + public: + explicit FieldsAreMatcher(Inner... inner) : matchers_(std::move(inner)...) {} + + template <typename Struct> + operator Matcher<Struct>() const { // NOLINT + return Matcher<Struct>( + new FieldsAreMatcherImpl<const Struct&, IndexSequenceFor<Inner...>>( + matchers_)); + } + + private: + std::tuple<Inner...> matchers_; +}; + +// Implements ElementsAre() and ElementsAreArray(). +template <typename Container> +class ElementsAreMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<Container> { + public: + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; + typedef internal::StlContainerView<RawContainer> View; + typedef typename View::type StlContainer; + typedef typename View::const_reference StlContainerReference; + typedef typename StlContainer::value_type Element; + + // Constructs the matcher from a sequence of element values or + // element matchers. + template <typename InputIter> + ElementsAreMatcherImpl(InputIter first, InputIter last) { + while (first != last) { + matchers_.push_back(MatcherCast<const Element&>(*first++)); + } + } + + // Describes what this matcher does. + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + if (count() == 0) { + *os << "is empty"; + } else if (count() == 1) { + *os << "has 1 element that "; + matchers_[0].DescribeTo(os); + } else { + *os << "has " << Elements(count()) << " where\n"; + for (size_t i = 0; i != count(); ++i) { + *os << "element #" << i << " "; + matchers_[i].DescribeTo(os); + if (i + 1 < count()) { + *os << ",\n"; + } + } + } + } + + // Describes what the negation of this matcher does. + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + if (count() == 0) { + *os << "isn't empty"; + return; + } + + *os << "doesn't have " << Elements(count()) << ", or\n"; + for (size_t i = 0; i != count(); ++i) { + *os << "element #" << i << " "; + matchers_[i].DescribeNegationTo(os); + if (i + 1 < count()) { + *os << ", or\n"; + } + } + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + // To work with stream-like "containers", we must only walk + // through the elements in one pass. + + const bool listener_interested = listener->IsInterested(); + + // explanations[i] is the explanation of the element at index i. + ::std::vector<std::string> explanations(count()); + StlContainerReference stl_container = View::ConstReference(container); + typename StlContainer::const_iterator it = stl_container.begin(); + size_t exam_pos = 0; + bool mismatch_found = false; // Have we found a mismatched element yet? + + // Go through the elements and matchers in pairs, until we reach + // the end of either the elements or the matchers, or until we find a + // mismatch. + for (; it != stl_container.end() && exam_pos != count(); ++it, ++exam_pos) { + bool match; // Does the current element match the current matcher? + if (listener_interested) { + StringMatchResultListener s; + match = matchers_[exam_pos].MatchAndExplain(*it, &s); + explanations[exam_pos] = s.str(); + } else { + match = matchers_[exam_pos].Matches(*it); + } + + if (!match) { + mismatch_found = true; + break; + } + } + // If mismatch_found is true, 'exam_pos' is the index of the mismatch. + + // Find how many elements the actual container has. We avoid + // calling size() s.t. this code works for stream-like "containers" + // that don't define size(). + size_t actual_count = exam_pos; + for (; it != stl_container.end(); ++it) { + ++actual_count; + } + + if (actual_count != count()) { + // The element count doesn't match. If the container is empty, + // there's no need to explain anything as Google Mock already + // prints the empty container. Otherwise we just need to show + // how many elements there actually are. + if (listener_interested && (actual_count != 0)) { + *listener << "which has " << Elements(actual_count); + } + return false; + } + + if (mismatch_found) { + // The element count matches, but the exam_pos-th element doesn't match. + if (listener_interested) { + *listener << "whose element #" << exam_pos << " doesn't match"; + PrintIfNotEmpty(explanations[exam_pos], listener->stream()); + } + return false; + } + + // Every element matches its expectation. We need to explain why + // (the obvious ones can be skipped). + if (listener_interested) { + bool reason_printed = false; + for (size_t i = 0; i != count(); ++i) { + const std::string& s = explanations[i]; + if (!s.empty()) { + if (reason_printed) { + *listener << ",\nand "; + } + *listener << "whose element #" << i << " matches, " << s; + reason_printed = true; + } + } + } + return true; + } + + private: + static Message Elements(size_t count) { + return Message() << count << (count == 1 ? " element" : " elements"); + } + + size_t count() const { return matchers_.size(); } + + ::std::vector<Matcher<const Element&> > matchers_; +}; + +// Connectivity matrix of (elements X matchers), in element-major order. +// Initially, there are no edges. +// Use NextGraph() to iterate over all possible edge configurations. +// Use Randomize() to generate a random edge configuration. +class GTEST_API_ MatchMatrix { + public: + MatchMatrix(size_t num_elements, size_t num_matchers) + : num_elements_(num_elements), + num_matchers_(num_matchers), + matched_(num_elements_* num_matchers_, 0) { + } + + size_t LhsSize() const { return num_elements_; } + size_t RhsSize() const { return num_matchers_; } + bool HasEdge(size_t ilhs, size_t irhs) const { + return matched_[SpaceIndex(ilhs, irhs)] == 1; + } + void SetEdge(size_t ilhs, size_t irhs, bool b) { + matched_[SpaceIndex(ilhs, irhs)] = b ? 1 : 0; + } + + // Treating the connectivity matrix as a (LhsSize()*RhsSize())-bit number, + // adds 1 to that number; returns false if incrementing the graph left it + // empty. + bool NextGraph(); + + void Randomize(); + + std::string DebugString() const; + + private: + size_t SpaceIndex(size_t ilhs, size_t irhs) const { + return ilhs * num_matchers_ + irhs; + } + + size_t num_elements_; + size_t num_matchers_; + + // Each element is a char interpreted as bool. They are stored as a + // flattened array in lhs-major order, use 'SpaceIndex()' to translate + // a (ilhs, irhs) matrix coordinate into an offset. + ::std::vector<char> matched_; +}; + +typedef ::std::pair<size_t, size_t> ElementMatcherPair; +typedef ::std::vector<ElementMatcherPair> ElementMatcherPairs; + +// Returns a maximum bipartite matching for the specified graph 'g'. +// The matching is represented as a vector of {element, matcher} pairs. +GTEST_API_ ElementMatcherPairs +FindMaxBipartiteMatching(const MatchMatrix& g); + +struct UnorderedMatcherRequire { + enum Flags { + Superset = 1 << 0, + Subset = 1 << 1, + ExactMatch = Superset | Subset, + }; +}; + +// Untyped base class for implementing UnorderedElementsAre. By +// putting logic that's not specific to the element type here, we +// reduce binary bloat and increase compilation speed. +class GTEST_API_ UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase { + protected: + explicit UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase( + UnorderedMatcherRequire::Flags matcher_flags) + : match_flags_(matcher_flags) {} + + // A vector of matcher describers, one for each element matcher. + // Does not own the describers (and thus can be used only when the + // element matchers are alive). + typedef ::std::vector<const MatcherDescriberInterface*> MatcherDescriberVec; + + // Describes this UnorderedElementsAre matcher. + void DescribeToImpl(::std::ostream* os) const; + + // Describes the negation of this UnorderedElementsAre matcher. + void DescribeNegationToImpl(::std::ostream* os) const; + + bool VerifyMatchMatrix(const ::std::vector<std::string>& element_printouts, + const MatchMatrix& matrix, + MatchResultListener* listener) const; + + bool FindPairing(const MatchMatrix& matrix, + MatchResultListener* listener) const; + + MatcherDescriberVec& matcher_describers() { + return matcher_describers_; + } + + static Message Elements(size_t n) { + return Message() << n << " element" << (n == 1 ? "" : "s"); + } + + UnorderedMatcherRequire::Flags match_flags() const { return match_flags_; } + + private: + UnorderedMatcherRequire::Flags match_flags_; + MatcherDescriberVec matcher_describers_; +}; + +// Implements UnorderedElementsAre, UnorderedElementsAreArray, IsSubsetOf, and +// IsSupersetOf. +template <typename Container> +class UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImpl + : public MatcherInterface<Container>, + public UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase { + public: + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; + typedef internal::StlContainerView<RawContainer> View; + typedef typename View::type StlContainer; + typedef typename View::const_reference StlContainerReference; + typedef typename StlContainer::const_iterator StlContainerConstIterator; + typedef typename StlContainer::value_type Element; + + template <typename InputIter> + UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImpl(UnorderedMatcherRequire::Flags matcher_flags, + InputIter first, InputIter last) + : UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase(matcher_flags) { + for (; first != last; ++first) { + matchers_.push_back(MatcherCast<const Element&>(*first)); + } + for (const auto& m : matchers_) { + matcher_describers().push_back(m.GetDescriber()); + } + } + + // Describes what this matcher does. + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + return UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase::DescribeToImpl(os); + } + + // Describes what the negation of this matcher does. + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + return UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImplBase::DescribeNegationToImpl(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Container container, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + StlContainerReference stl_container = View::ConstReference(container); + ::std::vector<std::string> element_printouts; + MatchMatrix matrix = + AnalyzeElements(stl_container.begin(), stl_container.end(), + &element_printouts, listener); + + if (matrix.LhsSize() == 0 && matrix.RhsSize() == 0) { + return true; + } + + if (match_flags() == UnorderedMatcherRequire::ExactMatch) { + if (matrix.LhsSize() != matrix.RhsSize()) { + // The element count doesn't match. If the container is empty, + // there's no need to explain anything as Google Mock already + // prints the empty container. Otherwise we just need to show + // how many elements there actually are. + if (matrix.LhsSize() != 0 && listener->IsInterested()) { + *listener << "which has " << Elements(matrix.LhsSize()); + } + return false; + } + } + + return VerifyMatchMatrix(element_printouts, matrix, listener) && + FindPairing(matrix, listener); + } + + private: + template <typename ElementIter> + MatchMatrix AnalyzeElements(ElementIter elem_first, ElementIter elem_last, + ::std::vector<std::string>* element_printouts, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + element_printouts->clear(); + ::std::vector<char> did_match; + size_t num_elements = 0; + DummyMatchResultListener dummy; + for (; elem_first != elem_last; ++num_elements, ++elem_first) { + if (listener->IsInterested()) { + element_printouts->push_back(PrintToString(*elem_first)); + } + for (size_t irhs = 0; irhs != matchers_.size(); ++irhs) { + did_match.push_back( + matchers_[irhs].MatchAndExplain(*elem_first, &dummy)); + } + } + + MatchMatrix matrix(num_elements, matchers_.size()); + ::std::vector<char>::const_iterator did_match_iter = did_match.begin(); + for (size_t ilhs = 0; ilhs != num_elements; ++ilhs) { + for (size_t irhs = 0; irhs != matchers_.size(); ++irhs) { + matrix.SetEdge(ilhs, irhs, *did_match_iter++ != 0); + } + } + return matrix; + } + + ::std::vector<Matcher<const Element&> > matchers_; +}; + +// Functor for use in TransformTuple. +// Performs MatcherCast<Target> on an input argument of any type. +template <typename Target> +struct CastAndAppendTransform { + template <typename Arg> + Matcher<Target> operator()(const Arg& a) const { + return MatcherCast<Target>(a); + } +}; + +// Implements UnorderedElementsAre. +template <typename MatcherTuple> +class UnorderedElementsAreMatcher { + public: + explicit UnorderedElementsAreMatcher(const MatcherTuple& args) + : matchers_(args) {} + + template <typename Container> + operator Matcher<Container>() const { + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; + typedef typename internal::StlContainerView<RawContainer>::type View; + typedef typename View::value_type Element; + typedef ::std::vector<Matcher<const Element&> > MatcherVec; + MatcherVec matchers; + matchers.reserve(::std::tuple_size<MatcherTuple>::value); + TransformTupleValues(CastAndAppendTransform<const Element&>(), matchers_, + ::std::back_inserter(matchers)); + return Matcher<Container>( + new UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImpl<const Container&>( + UnorderedMatcherRequire::ExactMatch, matchers.begin(), + matchers.end())); + } + + private: + const MatcherTuple matchers_; +}; + +// Implements ElementsAre. +template <typename MatcherTuple> +class ElementsAreMatcher { + public: + explicit ElementsAreMatcher(const MatcherTuple& args) : matchers_(args) {} + + template <typename Container> + operator Matcher<Container>() const { + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( + !IsHashTable<GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container)>::value || + ::std::tuple_size<MatcherTuple>::value < 2, + use_UnorderedElementsAre_with_hash_tables); + + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container) RawContainer; + typedef typename internal::StlContainerView<RawContainer>::type View; + typedef typename View::value_type Element; + typedef ::std::vector<Matcher<const Element&> > MatcherVec; + MatcherVec matchers; + matchers.reserve(::std::tuple_size<MatcherTuple>::value); + TransformTupleValues(CastAndAppendTransform<const Element&>(), matchers_, + ::std::back_inserter(matchers)); + return Matcher<Container>(new ElementsAreMatcherImpl<const Container&>( + matchers.begin(), matchers.end())); + } + + private: + const MatcherTuple matchers_; +}; + +// Implements UnorderedElementsAreArray(), IsSubsetOf(), and IsSupersetOf(). +template <typename T> +class UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher { + public: + template <typename Iter> + UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher(UnorderedMatcherRequire::Flags match_flags, + Iter first, Iter last) + : match_flags_(match_flags), matchers_(first, last) {} + + template <typename Container> + operator Matcher<Container>() const { + return Matcher<Container>( + new UnorderedElementsAreMatcherImpl<const Container&>( + match_flags_, matchers_.begin(), matchers_.end())); + } + + private: + UnorderedMatcherRequire::Flags match_flags_; + ::std::vector<T> matchers_; +}; + +// Implements ElementsAreArray(). +template <typename T> +class ElementsAreArrayMatcher { + public: + template <typename Iter> + ElementsAreArrayMatcher(Iter first, Iter last) : matchers_(first, last) {} + + template <typename Container> + operator Matcher<Container>() const { + GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_( + !IsHashTable<GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Container)>::value, + use_UnorderedElementsAreArray_with_hash_tables); + + return Matcher<Container>(new ElementsAreMatcherImpl<const Container&>( + matchers_.begin(), matchers_.end())); + } + + private: + const ::std::vector<T> matchers_; +}; + +// Given a 2-tuple matcher tm of type Tuple2Matcher and a value second +// of type Second, BoundSecondMatcher<Tuple2Matcher, Second>(tm, +// second) is a polymorphic matcher that matches a value x if and only if +// tm matches tuple (x, second). Useful for implementing +// UnorderedPointwise() in terms of UnorderedElementsAreArray(). +// +// BoundSecondMatcher is copyable and assignable, as we need to put +// instances of this class in a vector when implementing +// UnorderedPointwise(). +template <typename Tuple2Matcher, typename Second> +class BoundSecondMatcher { + public: + BoundSecondMatcher(const Tuple2Matcher& tm, const Second& second) + : tuple2_matcher_(tm), second_value_(second) {} + + BoundSecondMatcher(const BoundSecondMatcher& other) = default; + + template <typename T> + operator Matcher<T>() const { + return MakeMatcher(new Impl<T>(tuple2_matcher_, second_value_)); + } + + // We have to define this for UnorderedPointwise() to compile in + // C++98 mode, as it puts BoundSecondMatcher instances in a vector, + // which requires the elements to be assignable in C++98. The + // compiler cannot generate the operator= for us, as Tuple2Matcher + // and Second may not be assignable. + // + // However, this should never be called, so the implementation just + // need to assert. + void operator=(const BoundSecondMatcher& /*rhs*/) { + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "BoundSecondMatcher should never be assigned."; + } + + private: + template <typename T> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<T> { + public: + typedef ::std::tuple<T, Second> ArgTuple; + + Impl(const Tuple2Matcher& tm, const Second& second) + : mono_tuple2_matcher_(SafeMatcherCast<const ArgTuple&>(tm)), + second_value_(second) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "and "; + UniversalPrint(second_value_, os); + *os << " "; + mono_tuple2_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + return mono_tuple2_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(ArgTuple(x, second_value_), + listener); + } + + private: + const Matcher<const ArgTuple&> mono_tuple2_matcher_; + const Second second_value_; + }; + + const Tuple2Matcher tuple2_matcher_; + const Second second_value_; +}; + +// Given a 2-tuple matcher tm and a value second, +// MatcherBindSecond(tm, second) returns a matcher that matches a +// value x if and only if tm matches tuple (x, second). Useful for +// implementing UnorderedPointwise() in terms of UnorderedElementsAreArray(). +template <typename Tuple2Matcher, typename Second> +BoundSecondMatcher<Tuple2Matcher, Second> MatcherBindSecond( + const Tuple2Matcher& tm, const Second& second) { + return BoundSecondMatcher<Tuple2Matcher, Second>(tm, second); +} + +// Returns the description for a matcher defined using the MATCHER*() +// macro where the user-supplied description string is "", if +// 'negation' is false; otherwise returns the description of the +// negation of the matcher. 'param_values' contains a list of strings +// that are the print-out of the matcher's parameters. +GTEST_API_ std::string FormatMatcherDescription(bool negation, + const char* matcher_name, + const Strings& param_values); + +// Implements a matcher that checks the value of a optional<> type variable. +template <typename ValueMatcher> +class OptionalMatcher { + public: + explicit OptionalMatcher(const ValueMatcher& value_matcher) + : value_matcher_(value_matcher) {} + + template <typename Optional> + operator Matcher<Optional>() const { + return Matcher<Optional>(new Impl<const Optional&>(value_matcher_)); + } + + template <typename Optional> + class Impl : public MatcherInterface<Optional> { + public: + typedef GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Optional) OptionalView; + typedef typename OptionalView::value_type ValueType; + explicit Impl(const ValueMatcher& value_matcher) + : value_matcher_(MatcherCast<ValueType>(value_matcher)) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "value "; + value_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "value "; + value_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(Optional optional, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + if (!optional) { + *listener << "which is not engaged"; + return false; + } + const ValueType& value = *optional; + StringMatchResultListener value_listener; + const bool match = value_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(value, &value_listener); + *listener << "whose value " << PrintToString(value) + << (match ? " matches" : " doesn't match"); + PrintIfNotEmpty(value_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return match; + } + + private: + const Matcher<ValueType> value_matcher_; + }; + + private: + const ValueMatcher value_matcher_; +}; + +namespace variant_matcher { +// Overloads to allow VariantMatcher to do proper ADL lookup. +template <typename T> +void holds_alternative() {} +template <typename T> +void get() {} + +// Implements a matcher that checks the value of a variant<> type variable. +template <typename T> +class VariantMatcher { + public: + explicit VariantMatcher(::testing::Matcher<const T&> matcher) + : matcher_(std::move(matcher)) {} + + template <typename Variant> + bool MatchAndExplain(const Variant& value, + ::testing::MatchResultListener* listener) const { + using std::get; + if (!listener->IsInterested()) { + return holds_alternative<T>(value) && matcher_.Matches(get<T>(value)); + } + + if (!holds_alternative<T>(value)) { + *listener << "whose value is not of type '" << GetTypeName() << "'"; + return false; + } + + const T& elem = get<T>(value); + StringMatchResultListener elem_listener; + const bool match = matcher_.MatchAndExplain(elem, &elem_listener); + *listener << "whose value " << PrintToString(elem) + << (match ? " matches" : " doesn't match"); + PrintIfNotEmpty(elem_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return match; + } + + void DescribeTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "is a variant<> with value of type '" << GetTypeName() + << "' and the value "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "is a variant<> with value of type other than '" << GetTypeName() + << "' or the value "; + matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + private: + static std::string GetTypeName() { +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_( + return internal::GetTypeName<T>()); +#endif + return "the element type"; + } + + const ::testing::Matcher<const T&> matcher_; +}; + +} // namespace variant_matcher + +namespace any_cast_matcher { + +// Overloads to allow AnyCastMatcher to do proper ADL lookup. +template <typename T> +void any_cast() {} + +// Implements a matcher that any_casts the value. +template <typename T> +class AnyCastMatcher { + public: + explicit AnyCastMatcher(const ::testing::Matcher<const T&>& matcher) + : matcher_(matcher) {} + + template <typename AnyType> + bool MatchAndExplain(const AnyType& value, + ::testing::MatchResultListener* listener) const { + if (!listener->IsInterested()) { + const T* ptr = any_cast<T>(&value); + return ptr != nullptr && matcher_.Matches(*ptr); + } + + const T* elem = any_cast<T>(&value); + if (elem == nullptr) { + *listener << "whose value is not of type '" << GetTypeName() << "'"; + return false; + } + + StringMatchResultListener elem_listener; + const bool match = matcher_.MatchAndExplain(*elem, &elem_listener); + *listener << "whose value " << PrintToString(*elem) + << (match ? " matches" : " doesn't match"); + PrintIfNotEmpty(elem_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return match; + } + + void DescribeTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "is an 'any' type with value of type '" << GetTypeName() + << "' and the value "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "is an 'any' type with value of type other than '" << GetTypeName() + << "' or the value "; + matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + private: + static std::string GetTypeName() { +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_( + return internal::GetTypeName<T>()); +#endif + return "the element type"; + } + + const ::testing::Matcher<const T&> matcher_; +}; + +} // namespace any_cast_matcher + +// Implements the Args() matcher. +template <class ArgsTuple, size_t... k> +class ArgsMatcherImpl : public MatcherInterface<ArgsTuple> { + public: + using RawArgsTuple = typename std::decay<ArgsTuple>::type; + using SelectedArgs = + std::tuple<typename std::tuple_element<k, RawArgsTuple>::type...>; + using MonomorphicInnerMatcher = Matcher<const SelectedArgs&>; + + template <typename InnerMatcher> + explicit ArgsMatcherImpl(const InnerMatcher& inner_matcher) + : inner_matcher_(SafeMatcherCast<const SelectedArgs&>(inner_matcher)) {} + + bool MatchAndExplain(ArgsTuple args, + MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + // Workaround spurious C4100 on MSVC<=15.7 when k is empty. + (void)args; + const SelectedArgs& selected_args = + std::forward_as_tuple(std::get<k>(args)...); + if (!listener->IsInterested()) return inner_matcher_.Matches(selected_args); + + PrintIndices(listener->stream()); + *listener << "are " << PrintToString(selected_args); + + StringMatchResultListener inner_listener; + const bool match = + inner_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(selected_args, &inner_listener); + PrintIfNotEmpty(inner_listener.str(), listener->stream()); + return match; + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "are a tuple "; + PrintIndices(os); + inner_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "are a tuple "; + PrintIndices(os); + inner_matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + private: + // Prints the indices of the selected fields. + static void PrintIndices(::std::ostream* os) { + *os << "whose fields ("; + const char* sep = ""; + // Workaround spurious C4189 on MSVC<=15.7 when k is empty. + (void)sep; + const char* dummy[] = {"", (*os << sep << "#" << k, sep = ", ")...}; + (void)dummy; + *os << ") "; + } + + MonomorphicInnerMatcher inner_matcher_; +}; + +template <class InnerMatcher, size_t... k> +class ArgsMatcher { + public: + explicit ArgsMatcher(InnerMatcher inner_matcher) + : inner_matcher_(std::move(inner_matcher)) {} + + template <typename ArgsTuple> + operator Matcher<ArgsTuple>() const { // NOLINT + return MakeMatcher(new ArgsMatcherImpl<ArgsTuple, k...>(inner_matcher_)); + } + + private: + InnerMatcher inner_matcher_; +}; + +} // namespace internal + +// ElementsAreArray(iterator_first, iterator_last) +// ElementsAreArray(pointer, count) +// ElementsAreArray(array) +// ElementsAreArray(container) +// ElementsAreArray({ e1, e2, ..., en }) +// +// The ElementsAreArray() functions are like ElementsAre(...), except +// that they are given a homogeneous sequence rather than taking each +// element as a function argument. The sequence can be specified as an +// array, a pointer and count, a vector, an initializer list, or an +// STL iterator range. In each of these cases, the underlying sequence +// can be either a sequence of values or a sequence of matchers. +// +// All forms of ElementsAreArray() make a copy of the input matcher sequence. + +template <typename Iter> +inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher< + typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type> +ElementsAreArray(Iter first, Iter last) { + typedef typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type T; + return internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<T>(first, last); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> ElementsAreArray( + const T* pointer, size_t count) { + return ElementsAreArray(pointer, pointer + count); +} + +template <typename T, size_t N> +inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> ElementsAreArray( + const T (&array)[N]) { + return ElementsAreArray(array, N); +} + +template <typename Container> +inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<typename Container::value_type> +ElementsAreArray(const Container& container) { + return ElementsAreArray(container.begin(), container.end()); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::ElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> +ElementsAreArray(::std::initializer_list<T> xs) { + return ElementsAreArray(xs.begin(), xs.end()); +} + +// UnorderedElementsAreArray(iterator_first, iterator_last) +// UnorderedElementsAreArray(pointer, count) +// UnorderedElementsAreArray(array) +// UnorderedElementsAreArray(container) +// UnorderedElementsAreArray({ e1, e2, ..., en }) +// +// UnorderedElementsAreArray() verifies that a bijective mapping onto a +// collection of matchers exists. +// +// The matchers can be specified as an array, a pointer and count, a container, +// an initializer list, or an STL iterator range. In each of these cases, the +// underlying matchers can be either values or matchers. + +template <typename Iter> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher< + typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type> +UnorderedElementsAreArray(Iter first, Iter last) { + typedef typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type T; + return internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T>( + internal::UnorderedMatcherRequire::ExactMatch, first, last); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> +UnorderedElementsAreArray(const T* pointer, size_t count) { + return UnorderedElementsAreArray(pointer, pointer + count); +} + +template <typename T, size_t N> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> +UnorderedElementsAreArray(const T (&array)[N]) { + return UnorderedElementsAreArray(array, N); +} + +template <typename Container> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher< + typename Container::value_type> +UnorderedElementsAreArray(const Container& container) { + return UnorderedElementsAreArray(container.begin(), container.end()); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> +UnorderedElementsAreArray(::std::initializer_list<T> xs) { + return UnorderedElementsAreArray(xs.begin(), xs.end()); +} + +// _ is a matcher that matches anything of any type. +// +// This definition is fine as: +// +// 1. The C++ standard permits using the name _ in a namespace that +// is not the global namespace or ::std. +// 2. The AnythingMatcher class has no data member or constructor, +// so it's OK to create global variables of this type. +// 3. c-style has approved of using _ in this case. +const internal::AnythingMatcher _ = {}; +// Creates a matcher that matches any value of the given type T. +template <typename T> +inline Matcher<T> A() { + return _; +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any value of the given type T. +template <typename T> +inline Matcher<T> An() { + return _; +} + +template <typename T, typename M> +Matcher<T> internal::MatcherCastImpl<T, M>::CastImpl( + const M& value, std::false_type /* convertible_to_matcher */, + std::false_type /* convertible_to_T */) { + return Eq(value); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches any NULL pointer. +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::IsNullMatcher > IsNull() { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::IsNullMatcher()); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches any non-NULL pointer. +// This is convenient as Not(NULL) doesn't compile (the compiler +// thinks that that expression is comparing a pointer with an integer). +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::NotNullMatcher > NotNull() { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::NotNullMatcher()); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches any argument that +// references variable x. +template <typename T> +inline internal::RefMatcher<T&> Ref(T& x) { // NOLINT + return internal::RefMatcher<T&>(x); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches any NaN floating point. +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::IsNanMatcher> IsNan() { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::IsNanMatcher()); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any double argument approximately +// equal to rhs, where two NANs are considered unequal. +inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double> DoubleEq(double rhs) { + return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double>(rhs, false); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any double argument approximately +// equal to rhs, including NaN values when rhs is NaN. +inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double> NanSensitiveDoubleEq(double rhs) { + return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double>(rhs, true); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any double argument approximately equal to +// rhs, up to the specified max absolute error bound, where two NANs are +// considered unequal. The max absolute error bound must be non-negative. +inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double> DoubleNear( + double rhs, double max_abs_error) { + return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double>(rhs, false, max_abs_error); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any double argument approximately equal to +// rhs, up to the specified max absolute error bound, including NaN values when +// rhs is NaN. The max absolute error bound must be non-negative. +inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double> NanSensitiveDoubleNear( + double rhs, double max_abs_error) { + return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<double>(rhs, true, max_abs_error); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any float argument approximately +// equal to rhs, where two NANs are considered unequal. +inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float> FloatEq(float rhs) { + return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float>(rhs, false); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any float argument approximately +// equal to rhs, including NaN values when rhs is NaN. +inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float> NanSensitiveFloatEq(float rhs) { + return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float>(rhs, true); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any float argument approximately equal to +// rhs, up to the specified max absolute error bound, where two NANs are +// considered unequal. The max absolute error bound must be non-negative. +inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float> FloatNear( + float rhs, float max_abs_error) { + return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float>(rhs, false, max_abs_error); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any float argument approximately equal to +// rhs, up to the specified max absolute error bound, including NaN values when +// rhs is NaN. The max absolute error bound must be non-negative. +inline internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float> NanSensitiveFloatNear( + float rhs, float max_abs_error) { + return internal::FloatingEqMatcher<float>(rhs, true, max_abs_error); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches a pointer (raw or smart) that points +// to a value that matches inner_matcher. +template <typename InnerMatcher> +inline internal::PointeeMatcher<InnerMatcher> Pointee( + const InnerMatcher& inner_matcher) { + return internal::PointeeMatcher<InnerMatcher>(inner_matcher); +} + +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI +// Creates a matcher that matches a pointer or reference that matches +// inner_matcher when dynamic_cast<To> is applied. +// The result of dynamic_cast<To> is forwarded to the inner matcher. +// If To is a pointer and the cast fails, the inner matcher will receive NULL. +// If To is a reference and the cast fails, this matcher returns false +// immediately. +template <typename To> +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::WhenDynamicCastToMatcher<To> > +WhenDynamicCastTo(const Matcher<To>& inner_matcher) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::WhenDynamicCastToMatcher<To>(inner_matcher)); +} +#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI + +// Creates a matcher that matches an object whose given field matches +// 'matcher'. For example, +// Field(&Foo::number, Ge(5)) +// matches a Foo object x if and only if x.number >= 5. +template <typename Class, typename FieldType, typename FieldMatcher> +inline PolymorphicMatcher< + internal::FieldMatcher<Class, FieldType> > Field( + FieldType Class::*field, const FieldMatcher& matcher) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::FieldMatcher<Class, FieldType>( + field, MatcherCast<const FieldType&>(matcher))); + // The call to MatcherCast() is required for supporting inner + // matchers of compatible types. For example, it allows + // Field(&Foo::bar, m) + // to compile where bar is an int32 and m is a matcher for int64. +} + +// Same as Field() but also takes the name of the field to provide better error +// messages. +template <typename Class, typename FieldType, typename FieldMatcher> +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::FieldMatcher<Class, FieldType> > Field( + const std::string& field_name, FieldType Class::*field, + const FieldMatcher& matcher) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::FieldMatcher<Class, FieldType>( + field_name, field, MatcherCast<const FieldType&>(matcher))); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches an object whose given property +// matches 'matcher'. For example, +// Property(&Foo::str, StartsWith("hi")) +// matches a Foo object x if and only if x.str() starts with "hi". +template <typename Class, typename PropertyType, typename PropertyMatcher> +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::PropertyMatcher< + Class, PropertyType, PropertyType (Class::*)() const> > +Property(PropertyType (Class::*property)() const, + const PropertyMatcher& matcher) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::PropertyMatcher<Class, PropertyType, + PropertyType (Class::*)() const>( + property, MatcherCast<const PropertyType&>(matcher))); + // The call to MatcherCast() is required for supporting inner + // matchers of compatible types. For example, it allows + // Property(&Foo::bar, m) + // to compile where bar() returns an int32 and m is a matcher for int64. +} + +// Same as Property() above, but also takes the name of the property to provide +// better error messages. +template <typename Class, typename PropertyType, typename PropertyMatcher> +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::PropertyMatcher< + Class, PropertyType, PropertyType (Class::*)() const> > +Property(const std::string& property_name, + PropertyType (Class::*property)() const, + const PropertyMatcher& matcher) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::PropertyMatcher<Class, PropertyType, + PropertyType (Class::*)() const>( + property_name, property, MatcherCast<const PropertyType&>(matcher))); +} + +// The same as above but for reference-qualified member functions. +template <typename Class, typename PropertyType, typename PropertyMatcher> +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::PropertyMatcher< + Class, PropertyType, PropertyType (Class::*)() const &> > +Property(PropertyType (Class::*property)() const &, + const PropertyMatcher& matcher) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::PropertyMatcher<Class, PropertyType, + PropertyType (Class::*)() const&>( + property, MatcherCast<const PropertyType&>(matcher))); +} + +// Three-argument form for reference-qualified member functions. +template <typename Class, typename PropertyType, typename PropertyMatcher> +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::PropertyMatcher< + Class, PropertyType, PropertyType (Class::*)() const &> > +Property(const std::string& property_name, + PropertyType (Class::*property)() const &, + const PropertyMatcher& matcher) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::PropertyMatcher<Class, PropertyType, + PropertyType (Class::*)() const&>( + property_name, property, MatcherCast<const PropertyType&>(matcher))); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches an object if and only if the result of +// applying a callable to x matches 'matcher'. For example, +// ResultOf(f, StartsWith("hi")) +// matches a Foo object x if and only if f(x) starts with "hi". +// `callable` parameter can be a function, function pointer, or a functor. It is +// required to keep no state affecting the results of the calls on it and make +// no assumptions about how many calls will be made. Any state it keeps must be +// protected from the concurrent access. +template <typename Callable, typename InnerMatcher> +internal::ResultOfMatcher<Callable, InnerMatcher> ResultOf( + Callable callable, InnerMatcher matcher) { + return internal::ResultOfMatcher<Callable, InnerMatcher>( + std::move(callable), std::move(matcher)); +} + +// String matchers. + +// Matches a string equal to str. +template <typename T = std::string> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::string> > StrEq( + const internal::StringLike<T>& str) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::string>(std::string(str), true, true)); +} + +// Matches a string not equal to str. +template <typename T = std::string> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::string> > StrNe( + const internal::StringLike<T>& str) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::string>(std::string(str), false, true)); +} + +// Matches a string equal to str, ignoring case. +template <typename T = std::string> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::string> > StrCaseEq( + const internal::StringLike<T>& str) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::string>(std::string(str), true, false)); +} + +// Matches a string not equal to str, ignoring case. +template <typename T = std::string> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::string> > StrCaseNe( + const internal::StringLike<T>& str) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::string>( + std::string(str), false, false)); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any string, std::string, or C string +// that contains the given substring. +template <typename T = std::string> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::HasSubstrMatcher<std::string> > HasSubstr( + const internal::StringLike<T>& substring) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::HasSubstrMatcher<std::string>(std::string(substring))); +} + +// Matches a string that starts with 'prefix' (case-sensitive). +template <typename T = std::string> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StartsWithMatcher<std::string> > StartsWith( + const internal::StringLike<T>& prefix) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::StartsWithMatcher<std::string>(std::string(prefix))); +} + +// Matches a string that ends with 'suffix' (case-sensitive). +template <typename T = std::string> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::EndsWithMatcher<std::string> > EndsWith( + const internal::StringLike<T>& suffix) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::EndsWithMatcher<std::string>(std::string(suffix))); +} + +#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING +// Wide string matchers. + +// Matches a string equal to str. +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::wstring> > StrEq( + const std::wstring& str) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::wstring>(str, true, true)); +} + +// Matches a string not equal to str. +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::wstring> > StrNe( + const std::wstring& str) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::wstring>(str, false, true)); +} + +// Matches a string equal to str, ignoring case. +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::wstring> > +StrCaseEq(const std::wstring& str) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::wstring>(str, true, false)); +} + +// Matches a string not equal to str, ignoring case. +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::wstring> > +StrCaseNe(const std::wstring& str) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::StrEqualityMatcher<std::wstring>(str, false, false)); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any ::wstring, std::wstring, or C wide string +// that contains the given substring. +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::HasSubstrMatcher<std::wstring> > HasSubstr( + const std::wstring& substring) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::HasSubstrMatcher<std::wstring>(substring)); +} + +// Matches a string that starts with 'prefix' (case-sensitive). +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::StartsWithMatcher<std::wstring> > +StartsWith(const std::wstring& prefix) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::StartsWithMatcher<std::wstring>(prefix)); +} + +// Matches a string that ends with 'suffix' (case-sensitive). +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::EndsWithMatcher<std::wstring> > EndsWith( + const std::wstring& suffix) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::EndsWithMatcher<std::wstring>(suffix)); +} + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the +// first field == the second field. +inline internal::Eq2Matcher Eq() { return internal::Eq2Matcher(); } + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the +// first field >= the second field. +inline internal::Ge2Matcher Ge() { return internal::Ge2Matcher(); } + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the +// first field > the second field. +inline internal::Gt2Matcher Gt() { return internal::Gt2Matcher(); } + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the +// first field <= the second field. +inline internal::Le2Matcher Le() { return internal::Le2Matcher(); } + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the +// first field < the second field. +inline internal::Lt2Matcher Lt() { return internal::Lt2Matcher(); } + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where the +// first field != the second field. +inline internal::Ne2Matcher Ne() { return internal::Ne2Matcher(); } + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where +// FloatEq(first field) matches the second field. +inline internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<float> FloatEq() { + return internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<float>(); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where +// DoubleEq(first field) matches the second field. +inline internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<double> DoubleEq() { + return internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<double>(); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where +// FloatEq(first field) matches the second field with NaN equality. +inline internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<float> NanSensitiveFloatEq() { + return internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<float>(true); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where +// DoubleEq(first field) matches the second field with NaN equality. +inline internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<double> NanSensitiveDoubleEq() { + return internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<double>(true); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where +// FloatNear(first field, max_abs_error) matches the second field. +inline internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<float> FloatNear(float max_abs_error) { + return internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<float>(max_abs_error); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where +// DoubleNear(first field, max_abs_error) matches the second field. +inline internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<double> DoubleNear(double max_abs_error) { + return internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<double>(max_abs_error); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where +// FloatNear(first field, max_abs_error) matches the second field with NaN +// equality. +inline internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<float> NanSensitiveFloatNear( + float max_abs_error) { + return internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<float>(max_abs_error, true); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches a 2-tuple where +// DoubleNear(first field, max_abs_error) matches the second field with NaN +// equality. +inline internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<double> NanSensitiveDoubleNear( + double max_abs_error) { + return internal::FloatingEq2Matcher<double>(max_abs_error, true); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches any value of type T that m doesn't +// match. +template <typename InnerMatcher> +inline internal::NotMatcher<InnerMatcher> Not(InnerMatcher m) { + return internal::NotMatcher<InnerMatcher>(m); +} + +// Returns a matcher that matches anything that satisfies the given +// predicate. The predicate can be any unary function or functor +// whose return type can be implicitly converted to bool. +template <typename Predicate> +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::TrulyMatcher<Predicate> > +Truly(Predicate pred) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::TrulyMatcher<Predicate>(pred)); +} + +// Returns a matcher that matches the container size. The container must +// support both size() and size_type which all STL-like containers provide. +// Note that the parameter 'size' can be a value of type size_type as well as +// matcher. For instance: +// EXPECT_THAT(container, SizeIs(2)); // Checks container has 2 elements. +// EXPECT_THAT(container, SizeIs(Le(2)); // Checks container has at most 2. +template <typename SizeMatcher> +inline internal::SizeIsMatcher<SizeMatcher> +SizeIs(const SizeMatcher& size_matcher) { + return internal::SizeIsMatcher<SizeMatcher>(size_matcher); +} + +// Returns a matcher that matches the distance between the container's begin() +// iterator and its end() iterator, i.e. the size of the container. This matcher +// can be used instead of SizeIs with containers such as std::forward_list which +// do not implement size(). The container must provide const_iterator (with +// valid iterator_traits), begin() and end(). +template <typename DistanceMatcher> +inline internal::BeginEndDistanceIsMatcher<DistanceMatcher> +BeginEndDistanceIs(const DistanceMatcher& distance_matcher) { + return internal::BeginEndDistanceIsMatcher<DistanceMatcher>(distance_matcher); +} + +// Returns a matcher that matches an equal container. +// This matcher behaves like Eq(), but in the event of mismatch lists the +// values that are included in one container but not the other. (Duplicate +// values and order differences are not explained.) +template <typename Container> +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::ContainerEqMatcher< + typename std::remove_const<Container>::type>> +ContainerEq(const Container& rhs) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::ContainerEqMatcher<Container>(rhs)); +} + +// Returns a matcher that matches a container that, when sorted using +// the given comparator, matches container_matcher. +template <typename Comparator, typename ContainerMatcher> +inline internal::WhenSortedByMatcher<Comparator, ContainerMatcher> +WhenSortedBy(const Comparator& comparator, + const ContainerMatcher& container_matcher) { + return internal::WhenSortedByMatcher<Comparator, ContainerMatcher>( + comparator, container_matcher); +} + +// Returns a matcher that matches a container that, when sorted using +// the < operator, matches container_matcher. +template <typename ContainerMatcher> +inline internal::WhenSortedByMatcher<internal::LessComparator, ContainerMatcher> +WhenSorted(const ContainerMatcher& container_matcher) { + return + internal::WhenSortedByMatcher<internal::LessComparator, ContainerMatcher>( + internal::LessComparator(), container_matcher); +} + +// Matches an STL-style container or a native array that contains the +// same number of elements as in rhs, where its i-th element and rhs's +// i-th element (as a pair) satisfy the given pair matcher, for all i. +// TupleMatcher must be able to be safely cast to Matcher<std::tuple<const +// T1&, const T2&> >, where T1 and T2 are the types of elements in the +// LHS container and the RHS container respectively. +template <typename TupleMatcher, typename Container> +inline internal::PointwiseMatcher<TupleMatcher, + typename std::remove_const<Container>::type> +Pointwise(const TupleMatcher& tuple_matcher, const Container& rhs) { + return internal::PointwiseMatcher<TupleMatcher, Container>(tuple_matcher, + rhs); +} + + +// Supports the Pointwise(m, {a, b, c}) syntax. +template <typename TupleMatcher, typename T> +inline internal::PointwiseMatcher<TupleMatcher, std::vector<T> > Pointwise( + const TupleMatcher& tuple_matcher, std::initializer_list<T> rhs) { + return Pointwise(tuple_matcher, std::vector<T>(rhs)); +} + + +// UnorderedPointwise(pair_matcher, rhs) matches an STL-style +// container or a native array that contains the same number of +// elements as in rhs, where in some permutation of the container, its +// i-th element and rhs's i-th element (as a pair) satisfy the given +// pair matcher, for all i. Tuple2Matcher must be able to be safely +// cast to Matcher<std::tuple<const T1&, const T2&> >, where T1 and T2 are +// the types of elements in the LHS container and the RHS container +// respectively. +// +// This is like Pointwise(pair_matcher, rhs), except that the element +// order doesn't matter. +template <typename Tuple2Matcher, typename RhsContainer> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher< + typename internal::BoundSecondMatcher< + Tuple2Matcher, + typename internal::StlContainerView< + typename std::remove_const<RhsContainer>::type>::type::value_type>> +UnorderedPointwise(const Tuple2Matcher& tuple2_matcher, + const RhsContainer& rhs_container) { + // RhsView allows the same code to handle RhsContainer being a + // STL-style container and it being a native C-style array. + typedef typename internal::StlContainerView<RhsContainer> RhsView; + typedef typename RhsView::type RhsStlContainer; + typedef typename RhsStlContainer::value_type Second; + const RhsStlContainer& rhs_stl_container = + RhsView::ConstReference(rhs_container); + + // Create a matcher for each element in rhs_container. + ::std::vector<internal::BoundSecondMatcher<Tuple2Matcher, Second> > matchers; + for (typename RhsStlContainer::const_iterator it = rhs_stl_container.begin(); + it != rhs_stl_container.end(); ++it) { + matchers.push_back( + internal::MatcherBindSecond(tuple2_matcher, *it)); + } + + // Delegate the work to UnorderedElementsAreArray(). + return UnorderedElementsAreArray(matchers); +} + + +// Supports the UnorderedPointwise(m, {a, b, c}) syntax. +template <typename Tuple2Matcher, typename T> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher< + typename internal::BoundSecondMatcher<Tuple2Matcher, T> > +UnorderedPointwise(const Tuple2Matcher& tuple2_matcher, + std::initializer_list<T> rhs) { + return UnorderedPointwise(tuple2_matcher, std::vector<T>(rhs)); +} + + +// Matches an STL-style container or a native array that contains at +// least one element matching the given value or matcher. +// +// Examples: +// ::std::set<int> page_ids; +// page_ids.insert(3); +// page_ids.insert(1); +// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Contains(1)); +// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Contains(Gt(2))); +// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Not(Contains(4))); +// +// ::std::map<int, size_t> page_lengths; +// page_lengths[1] = 100; +// EXPECT_THAT(page_lengths, +// Contains(::std::pair<const int, size_t>(1, 100))); +// +// const char* user_ids[] = { "joe", "mike", "tom" }; +// EXPECT_THAT(user_ids, Contains(Eq(::std::string("tom")))); +template <typename M> +inline internal::ContainsMatcher<M> Contains(M matcher) { + return internal::ContainsMatcher<M>(matcher); +} + +// IsSupersetOf(iterator_first, iterator_last) +// IsSupersetOf(pointer, count) +// IsSupersetOf(array) +// IsSupersetOf(container) +// IsSupersetOf({e1, e2, ..., en}) +// +// IsSupersetOf() verifies that a surjective partial mapping onto a collection +// of matchers exists. In other words, a container matches +// IsSupersetOf({e1, ..., en}) if and only if there is a permutation +// {y1, ..., yn} of some of the container's elements where y1 matches e1, +// ..., and yn matches en. Obviously, the size of the container must be >= n +// in order to have a match. Examples: +// +// - {1, 2, 3} matches IsSupersetOf({Ge(3), Ne(0)}), as 3 matches Ge(3) and +// 1 matches Ne(0). +// - {1, 2} doesn't match IsSupersetOf({Eq(1), Lt(2)}), even though 1 matches +// both Eq(1) and Lt(2). The reason is that different matchers must be used +// for elements in different slots of the container. +// - {1, 1, 2} matches IsSupersetOf({Eq(1), Lt(2)}), as (the first) 1 matches +// Eq(1) and (the second) 1 matches Lt(2). +// - {1, 2, 3} matches IsSupersetOf(Gt(1), Gt(1)), as 2 matches (the first) +// Gt(1) and 3 matches (the second) Gt(1). +// +// The matchers can be specified as an array, a pointer and count, a container, +// an initializer list, or an STL iterator range. In each of these cases, the +// underlying matchers can be either values or matchers. + +template <typename Iter> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher< + typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type> +IsSupersetOf(Iter first, Iter last) { + typedef typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type T; + return internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T>( + internal::UnorderedMatcherRequire::Superset, first, last); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> IsSupersetOf( + const T* pointer, size_t count) { + return IsSupersetOf(pointer, pointer + count); +} + +template <typename T, size_t N> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> IsSupersetOf( + const T (&array)[N]) { + return IsSupersetOf(array, N); +} + +template <typename Container> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher< + typename Container::value_type> +IsSupersetOf(const Container& container) { + return IsSupersetOf(container.begin(), container.end()); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> IsSupersetOf( + ::std::initializer_list<T> xs) { + return IsSupersetOf(xs.begin(), xs.end()); +} + +// IsSubsetOf(iterator_first, iterator_last) +// IsSubsetOf(pointer, count) +// IsSubsetOf(array) +// IsSubsetOf(container) +// IsSubsetOf({e1, e2, ..., en}) +// +// IsSubsetOf() verifies that an injective mapping onto a collection of matchers +// exists. In other words, a container matches IsSubsetOf({e1, ..., en}) if and +// only if there is a subset of matchers {m1, ..., mk} which would match the +// container using UnorderedElementsAre. Obviously, the size of the container +// must be <= n in order to have a match. Examples: +// +// - {1} matches IsSubsetOf({Gt(0), Lt(0)}), as 1 matches Gt(0). +// - {1, -1} matches IsSubsetOf({Lt(0), Gt(0)}), as 1 matches Gt(0) and -1 +// matches Lt(0). +// - {1, 2} doesn't matches IsSubsetOf({Gt(0), Lt(0)}), even though 1 and 2 both +// match Gt(0). The reason is that different matchers must be used for +// elements in different slots of the container. +// +// The matchers can be specified as an array, a pointer and count, a container, +// an initializer list, or an STL iterator range. In each of these cases, the +// underlying matchers can be either values or matchers. + +template <typename Iter> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher< + typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type> +IsSubsetOf(Iter first, Iter last) { + typedef typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type T; + return internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T>( + internal::UnorderedMatcherRequire::Subset, first, last); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> IsSubsetOf( + const T* pointer, size_t count) { + return IsSubsetOf(pointer, pointer + count); +} + +template <typename T, size_t N> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> IsSubsetOf( + const T (&array)[N]) { + return IsSubsetOf(array, N); +} + +template <typename Container> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher< + typename Container::value_type> +IsSubsetOf(const Container& container) { + return IsSubsetOf(container.begin(), container.end()); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::UnorderedElementsAreArrayMatcher<T> IsSubsetOf( + ::std::initializer_list<T> xs) { + return IsSubsetOf(xs.begin(), xs.end()); +} + +// Matches an STL-style container or a native array that contains only +// elements matching the given value or matcher. +// +// Each(m) is semantically equivalent to Not(Contains(Not(m))). Only +// the messages are different. +// +// Examples: +// ::std::set<int> page_ids; +// // Each(m) matches an empty container, regardless of what m is. +// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Each(Eq(1))); +// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Each(Eq(77))); +// +// page_ids.insert(3); +// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Each(Gt(0))); +// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Not(Each(Gt(4)))); +// page_ids.insert(1); +// EXPECT_THAT(page_ids, Not(Each(Lt(2)))); +// +// ::std::map<int, size_t> page_lengths; +// page_lengths[1] = 100; +// page_lengths[2] = 200; +// page_lengths[3] = 300; +// EXPECT_THAT(page_lengths, Not(Each(Pair(1, 100)))); +// EXPECT_THAT(page_lengths, Each(Key(Le(3)))); +// +// const char* user_ids[] = { "joe", "mike", "tom" }; +// EXPECT_THAT(user_ids, Not(Each(Eq(::std::string("tom"))))); +template <typename M> +inline internal::EachMatcher<M> Each(M matcher) { + return internal::EachMatcher<M>(matcher); +} + +// Key(inner_matcher) matches an std::pair whose 'first' field matches +// inner_matcher. For example, Contains(Key(Ge(5))) can be used to match an +// std::map that contains at least one element whose key is >= 5. +template <typename M> +inline internal::KeyMatcher<M> Key(M inner_matcher) { + return internal::KeyMatcher<M>(inner_matcher); +} + +// Pair(first_matcher, second_matcher) matches a std::pair whose 'first' field +// matches first_matcher and whose 'second' field matches second_matcher. For +// example, EXPECT_THAT(map_type, ElementsAre(Pair(Ge(5), "foo"))) can be used +// to match a std::map<int, string> that contains exactly one element whose key +// is >= 5 and whose value equals "foo". +template <typename FirstMatcher, typename SecondMatcher> +inline internal::PairMatcher<FirstMatcher, SecondMatcher> +Pair(FirstMatcher first_matcher, SecondMatcher second_matcher) { + return internal::PairMatcher<FirstMatcher, SecondMatcher>( + first_matcher, second_matcher); +} + +namespace no_adl { +// FieldsAre(matchers...) matches piecewise the fields of compatible structs. +// These include those that support `get<I>(obj)`, and when structured bindings +// are enabled any class that supports them. +// In particular, `std::tuple`, `std::pair`, `std::array` and aggregate types. +template <typename... M> +internal::FieldsAreMatcher<typename std::decay<M>::type...> FieldsAre( + M&&... matchers) { + return internal::FieldsAreMatcher<typename std::decay<M>::type...>( + std::forward<M>(matchers)...); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches a pointer (raw or smart) that matches +// inner_matcher. +template <typename InnerMatcher> +inline internal::PointerMatcher<InnerMatcher> Pointer( + const InnerMatcher& inner_matcher) { + return internal::PointerMatcher<InnerMatcher>(inner_matcher); +} + +// Creates a matcher that matches an object that has an address that matches +// inner_matcher. +template <typename InnerMatcher> +inline internal::AddressMatcher<InnerMatcher> Address( + const InnerMatcher& inner_matcher) { + return internal::AddressMatcher<InnerMatcher>(inner_matcher); +} +} // namespace no_adl + +// Returns a predicate that is satisfied by anything that matches the +// given matcher. +template <typename M> +inline internal::MatcherAsPredicate<M> Matches(M matcher) { + return internal::MatcherAsPredicate<M>(matcher); +} + +// Returns true if and only if the value matches the matcher. +template <typename T, typename M> +inline bool Value(const T& value, M matcher) { + return testing::Matches(matcher)(value); +} + +// Matches the value against the given matcher and explains the match +// result to listener. +template <typename T, typename M> +inline bool ExplainMatchResult( + M matcher, const T& value, MatchResultListener* listener) { + return SafeMatcherCast<const T&>(matcher).MatchAndExplain(value, listener); +} + +// Returns a string representation of the given matcher. Useful for description +// strings of matchers defined using MATCHER_P* macros that accept matchers as +// their arguments. For example: +// +// MATCHER_P(XAndYThat, matcher, +// "X that " + DescribeMatcher<int>(matcher, negation) + +// " and Y that " + DescribeMatcher<double>(matcher, negation)) { +// return ExplainMatchResult(matcher, arg.x(), result_listener) && +// ExplainMatchResult(matcher, arg.y(), result_listener); +// } +template <typename T, typename M> +std::string DescribeMatcher(const M& matcher, bool negation = false) { + ::std::stringstream ss; + Matcher<T> monomorphic_matcher = SafeMatcherCast<T>(matcher); + if (negation) { + monomorphic_matcher.DescribeNegationTo(&ss); + } else { + monomorphic_matcher.DescribeTo(&ss); + } + return ss.str(); +} + +template <typename... Args> +internal::ElementsAreMatcher< + std::tuple<typename std::decay<const Args&>::type...>> +ElementsAre(const Args&... matchers) { + return internal::ElementsAreMatcher< + std::tuple<typename std::decay<const Args&>::type...>>( + std::make_tuple(matchers...)); +} + +template <typename... Args> +internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< + std::tuple<typename std::decay<const Args&>::type...>> +UnorderedElementsAre(const Args&... matchers) { + return internal::UnorderedElementsAreMatcher< + std::tuple<typename std::decay<const Args&>::type...>>( + std::make_tuple(matchers...)); +} + +// Define variadic matcher versions. +template <typename... Args> +internal::AllOfMatcher<typename std::decay<const Args&>::type...> AllOf( + const Args&... matchers) { + return internal::AllOfMatcher<typename std::decay<const Args&>::type...>( + matchers...); +} + +template <typename... Args> +internal::AnyOfMatcher<typename std::decay<const Args&>::type...> AnyOf( + const Args&... matchers) { + return internal::AnyOfMatcher<typename std::decay<const Args&>::type...>( + matchers...); +} + +// AnyOfArray(array) +// AnyOfArray(pointer, count) +// AnyOfArray(container) +// AnyOfArray({ e1, e2, ..., en }) +// AnyOfArray(iterator_first, iterator_last) +// +// AnyOfArray() verifies whether a given value matches any member of a +// collection of matchers. +// +// AllOfArray(array) +// AllOfArray(pointer, count) +// AllOfArray(container) +// AllOfArray({ e1, e2, ..., en }) +// AllOfArray(iterator_first, iterator_last) +// +// AllOfArray() verifies whether a given value matches all members of a +// collection of matchers. +// +// The matchers can be specified as an array, a pointer and count, a container, +// an initializer list, or an STL iterator range. In each of these cases, the +// underlying matchers can be either values or matchers. + +template <typename Iter> +inline internal::AnyOfArrayMatcher< + typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type> +AnyOfArray(Iter first, Iter last) { + return internal::AnyOfArrayMatcher< + typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type>(first, last); +} + +template <typename Iter> +inline internal::AllOfArrayMatcher< + typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type> +AllOfArray(Iter first, Iter last) { + return internal::AllOfArrayMatcher< + typename ::std::iterator_traits<Iter>::value_type>(first, last); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::AnyOfArrayMatcher<T> AnyOfArray(const T* ptr, size_t count) { + return AnyOfArray(ptr, ptr + count); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::AllOfArrayMatcher<T> AllOfArray(const T* ptr, size_t count) { + return AllOfArray(ptr, ptr + count); +} + +template <typename T, size_t N> +inline internal::AnyOfArrayMatcher<T> AnyOfArray(const T (&array)[N]) { + return AnyOfArray(array, N); +} + +template <typename T, size_t N> +inline internal::AllOfArrayMatcher<T> AllOfArray(const T (&array)[N]) { + return AllOfArray(array, N); +} + +template <typename Container> +inline internal::AnyOfArrayMatcher<typename Container::value_type> AnyOfArray( + const Container& container) { + return AnyOfArray(container.begin(), container.end()); +} + +template <typename Container> +inline internal::AllOfArrayMatcher<typename Container::value_type> AllOfArray( + const Container& container) { + return AllOfArray(container.begin(), container.end()); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::AnyOfArrayMatcher<T> AnyOfArray( + ::std::initializer_list<T> xs) { + return AnyOfArray(xs.begin(), xs.end()); +} + +template <typename T> +inline internal::AllOfArrayMatcher<T> AllOfArray( + ::std::initializer_list<T> xs) { + return AllOfArray(xs.begin(), xs.end()); +} + +// Args<N1, N2, ..., Nk>(a_matcher) matches a tuple if the selected +// fields of it matches a_matcher. C++ doesn't support default +// arguments for function templates, so we have to overload it. +template <size_t... k, typename InnerMatcher> +internal::ArgsMatcher<typename std::decay<InnerMatcher>::type, k...> Args( + InnerMatcher&& matcher) { + return internal::ArgsMatcher<typename std::decay<InnerMatcher>::type, k...>( + std::forward<InnerMatcher>(matcher)); +} + +// AllArgs(m) is a synonym of m. This is useful in +// +// EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar(_, _)).With(AllArgs(Eq())); +// +// which is easier to read than +// +// EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar(_, _)).With(Eq()); +template <typename InnerMatcher> +inline InnerMatcher AllArgs(const InnerMatcher& matcher) { return matcher; } + +// Returns a matcher that matches the value of an optional<> type variable. +// The matcher implementation only uses '!arg' and requires that the optional<> +// type has a 'value_type' member type and that '*arg' is of type 'value_type' +// and is printable using 'PrintToString'. It is compatible with +// std::optional/std::experimental::optional. +// Note that to compare an optional type variable against nullopt you should +// use Eq(nullopt) and not Eq(Optional(nullopt)). The latter implies that the +// optional value contains an optional itself. +template <typename ValueMatcher> +inline internal::OptionalMatcher<ValueMatcher> Optional( + const ValueMatcher& value_matcher) { + return internal::OptionalMatcher<ValueMatcher>(value_matcher); +} + +// Returns a matcher that matches the value of a absl::any type variable. +template <typename T> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::any_cast_matcher::AnyCastMatcher<T> > AnyWith( + const Matcher<const T&>& matcher) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::any_cast_matcher::AnyCastMatcher<T>(matcher)); +} + +// Returns a matcher that matches the value of a variant<> type variable. +// The matcher implementation uses ADL to find the holds_alternative and get +// functions. +// It is compatible with std::variant. +template <typename T> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::variant_matcher::VariantMatcher<T> > VariantWith( + const Matcher<const T&>& matcher) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::variant_matcher::VariantMatcher<T>(matcher)); +} + +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +// Anything inside the `internal` namespace is internal to the implementation +// and must not be used in user code! +namespace internal { + +class WithWhatMatcherImpl { + public: + WithWhatMatcherImpl(Matcher<std::string> matcher) + : matcher_(std::move(matcher)) {} + + void DescribeTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "contains .what() that "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "contains .what() that does not "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + template <typename Err> + bool MatchAndExplain(const Err& err, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + *listener << "which contains .what() that "; + return matcher_.MatchAndExplain(err.what(), listener); + } + + private: + const Matcher<std::string> matcher_; +}; + +inline PolymorphicMatcher<WithWhatMatcherImpl> WithWhat( + Matcher<std::string> m) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(WithWhatMatcherImpl(std::move(m))); +} + +template <typename Err> +class ExceptionMatcherImpl { + class NeverThrown { + public: + const char* what() const noexcept { + return "this exception should never be thrown"; + } + }; + + // If the matchee raises an exception of a wrong type, we'd like to + // catch it and print its message and type. To do that, we add an additional + // catch clause: + // + // try { ... } + // catch (const Err&) { /* an expected exception */ } + // catch (const std::exception&) { /* exception of a wrong type */ } + // + // However, if the `Err` itself is `std::exception`, we'd end up with two + // identical `catch` clauses: + // + // try { ... } + // catch (const std::exception&) { /* an expected exception */ } + // catch (const std::exception&) { /* exception of a wrong type */ } + // + // This can cause a warning or an error in some compilers. To resolve + // the issue, we use a fake error type whenever `Err` is `std::exception`: + // + // try { ... } + // catch (const std::exception&) { /* an expected exception */ } + // catch (const NeverThrown&) { /* exception of a wrong type */ } + using DefaultExceptionType = typename std::conditional< + std::is_same<typename std::remove_cv< + typename std::remove_reference<Err>::type>::type, + std::exception>::value, + const NeverThrown&, const std::exception&>::type; + + public: + ExceptionMatcherImpl(Matcher<const Err&> matcher) + : matcher_(std::move(matcher)) {} + + void DescribeTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "throws an exception which is a " << GetTypeName<Err>(); + *os << " which "; + matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "throws an exception which is not a " << GetTypeName<Err>(); + *os << " which "; + matcher_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + template <typename T> + bool MatchAndExplain(T&& x, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + try { + (void)(std::forward<T>(x)()); + } catch (const Err& err) { + *listener << "throws an exception which is a " << GetTypeName<Err>(); + *listener << " "; + return matcher_.MatchAndExplain(err, listener); + } catch (DefaultExceptionType err) { +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI + *listener << "throws an exception of type " << GetTypeName(typeid(err)); + *listener << " "; +#else + *listener << "throws an std::exception-derived type "; +#endif + *listener << "with description \"" << err.what() << "\""; + return false; + } catch (...) { + *listener << "throws an exception of an unknown type"; + return false; + } + + *listener << "does not throw any exception"; + return false; + } + + private: + const Matcher<const Err&> matcher_; +}; + +} // namespace internal + +// Throws() +// Throws(exceptionMatcher) +// ThrowsMessage(messageMatcher) +// +// This matcher accepts a callable and verifies that when invoked, it throws +// an exception with the given type and properties. +// +// Examples: +// +// EXPECT_THAT( +// []() { throw std::runtime_error("message"); }, +// Throws<std::runtime_error>()); +// +// EXPECT_THAT( +// []() { throw std::runtime_error("message"); }, +// ThrowsMessage<std::runtime_error>(HasSubstr("message"))); +// +// EXPECT_THAT( +// []() { throw std::runtime_error("message"); }, +// Throws<std::runtime_error>( +// Property(&std::runtime_error::what, HasSubstr("message")))); + +template <typename Err> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::ExceptionMatcherImpl<Err>> Throws() { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher( + internal::ExceptionMatcherImpl<Err>(A<const Err&>())); +} + +template <typename Err, typename ExceptionMatcher> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::ExceptionMatcherImpl<Err>> Throws( + const ExceptionMatcher& exception_matcher) { + // Using matcher cast allows users to pass a matcher of a more broad type. + // For example user may want to pass Matcher<std::exception> + // to Throws<std::runtime_error>, or Matcher<int64> to Throws<int32>. + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::ExceptionMatcherImpl<Err>( + SafeMatcherCast<const Err&>(exception_matcher))); +} + +template <typename Err, typename MessageMatcher> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::ExceptionMatcherImpl<Err>> ThrowsMessage( + MessageMatcher&& message_matcher) { + static_assert(std::is_base_of<std::exception, Err>::value, + "expected an std::exception-derived type"); + return Throws<Err>(internal::WithWhat( + MatcherCast<std::string>(std::forward<MessageMatcher>(message_matcher)))); +} + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +// These macros allow using matchers to check values in Google Test +// tests. ASSERT_THAT(value, matcher) and EXPECT_THAT(value, matcher) +// succeed if and only if the value matches the matcher. If the assertion +// fails, the value and the description of the matcher will be printed. +#define ASSERT_THAT(value, matcher) ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(\ + ::testing::internal::MakePredicateFormatterFromMatcher(matcher), value) +#define EXPECT_THAT(value, matcher) EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(\ + ::testing::internal::MakePredicateFormatterFromMatcher(matcher), value) + +// MATCHER* macroses itself are listed below. +#define MATCHER(name, description) \ + class name##Matcher \ + : public ::testing::internal::MatcherBaseImpl<name##Matcher> { \ + public: \ + template <typename arg_type> \ + class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<const arg_type&> { \ + public: \ + gmock_Impl() {} \ + bool MatchAndExplain( \ + const arg_type& arg, \ + ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const override; \ + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const override { \ + *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false); \ + } \ + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const override { \ + *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true); \ + } \ + \ + private: \ + ::std::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const { \ + ::std::string gmock_description = (description); \ + if (!gmock_description.empty()) { \ + return gmock_description; \ + } \ + return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription(negation, #name, \ + {}); \ + } \ + }; \ + }; \ + GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ inline name##Matcher name() { return {}; } \ + template <typename arg_type> \ + bool name##Matcher::gmock_Impl<arg_type>::MatchAndExplain( \ + const arg_type& arg, \ + ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_) \ + const + +#define MATCHER_P(name, p0, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP, description, (p0)) +#define MATCHER_P2(name, p0, p1, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP2, description, (p0, p1)) +#define MATCHER_P3(name, p0, p1, p2, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP3, description, (p0, p1, p2)) +#define MATCHER_P4(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP4, description, (p0, p1, p2, p3)) +#define MATCHER_P5(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP5, description, \ + (p0, p1, p2, p3, p4)) +#define MATCHER_P6(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP6, description, \ + (p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5)) +#define MATCHER_P7(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP7, description, \ + (p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6)) +#define MATCHER_P8(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP8, description, \ + (p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7)) +#define MATCHER_P9(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP9, description, \ + (p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8)) +#define MATCHER_P10(name, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9, description) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, name##MatcherP10, description, \ + (p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER(name, full_name, description, args) \ + template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(args)> \ + class full_name : public ::testing::internal::MatcherBaseImpl< \ + full_name<GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TYPE_PARAMS(args)>> { \ + public: \ + using full_name::MatcherBaseImpl::MatcherBaseImpl; \ + template <typename arg_type> \ + class gmock_Impl : public ::testing::MatcherInterface<const arg_type&> { \ + public: \ + explicit gmock_Impl(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_FUNCTION_ARGS(args)) \ + : GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_FORWARD_ARGS(args) {} \ + bool MatchAndExplain( \ + const arg_type& arg, \ + ::testing::MatchResultListener* result_listener) const override; \ + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const override { \ + *gmock_os << FormatDescription(false); \ + } \ + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* gmock_os) const override { \ + *gmock_os << FormatDescription(true); \ + } \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_MEMBERS(args) \ + \ + private: \ + ::std::string FormatDescription(bool negation) const { \ + ::std::string gmock_description = (description); \ + if (!gmock_description.empty()) { \ + return gmock_description; \ + } \ + return ::testing::internal::FormatMatcherDescription( \ + negation, #name, \ + ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings( \ + ::std::tuple<GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TYPE_PARAMS(args)>( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_MEMBERS_USAGE(args)))); \ + } \ + }; \ + }; \ + template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(args)> \ + inline full_name<GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TYPE_PARAMS(args)> name( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_FUNCTION_ARGS(args)) { \ + return full_name<GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TYPE_PARAMS(args)>( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_ARGS_USAGE(args)); \ + } \ + template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(args)> \ + template <typename arg_type> \ + bool full_name<GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TYPE_PARAMS(args)>::gmock_Impl< \ + arg_type>::MatchAndExplain(const arg_type& arg, \ + ::testing::MatchResultListener* \ + result_listener GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_) \ + const + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(args) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL( \ + GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TEMPLATE_PARAM, , args)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TEMPLATE_PARAM(i_unused, data_unused, arg) \ + , typename arg##_type + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TYPE_PARAMS(args) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TYPE_PARAM, , args)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_TYPE_PARAM(i_unused, data_unused, arg) \ + , arg##_type + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_FUNCTION_ARGS(args) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(dummy_first GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_FUNCTION_ARG, , args)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_FUNCTION_ARG(i, data_unused, arg) \ + , arg##_type gmock_p##i + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_FORWARD_ARGS(args) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_FORWARD_ARG, , args)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_FORWARD_ARG(i, data_unused, arg) \ + , arg(::std::forward<arg##_type>(gmock_p##i)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_MEMBERS(args) \ + GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_MEMBER, , args) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_MEMBER(i_unused, data_unused, arg) \ + const arg##_type arg; + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_MEMBERS_USAGE(args) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_MEMBER_USAGE, , args)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_MEMBER_USAGE(i_unused, data_unused, arg) , arg + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_ARGS_USAGE(args) \ + GMOCK_PP_TAIL(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_ARG_USAGE, , args)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_ARG_USAGE(i, data_unused, arg_unused) \ + , gmock_p##i + +// To prevent ADL on certain functions we put them on a separate namespace. +using namespace no_adl; // NOLINT + +} // namespace testing + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 5046 + +// Include any custom callback matchers added by the local installation. +// We must include this header at the end to make sure it can use the +// declarations from this file. +// Copyright 2015, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// Injection point for custom user configurations. See README for details +// +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GMOCK_MATCHERS_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GMOCK_MATCHERS_H_ +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GMOCK_MATCHERS_H_ + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MATCHERS_H_ + +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS +# include <stdexcept> // NOLINT +#endif + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) + +namespace testing { + +// An abstract handle of an expectation. +class Expectation; + +// A set of expectation handles. +class ExpectationSet; + +// Anything inside the 'internal' namespace IS INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION +// and MUST NOT BE USED IN USER CODE!!! +namespace internal { + +// Implements a mock function. +template <typename F> class FunctionMocker; + +// Base class for expectations. +class ExpectationBase; + +// Implements an expectation. +template <typename F> class TypedExpectation; + +// Helper class for testing the Expectation class template. +class ExpectationTester; + +// Helper classes for implementing NiceMock, StrictMock, and NaggyMock. +template <typename MockClass> +class NiceMockImpl; +template <typename MockClass> +class StrictMockImpl; +template <typename MockClass> +class NaggyMockImpl; + +// Protects the mock object registry (in class Mock), all function +// mockers, and all expectations. +// +// The reason we don't use more fine-grained protection is: when a +// mock function Foo() is called, it needs to consult its expectations +// to see which one should be picked. If another thread is allowed to +// call a mock function (either Foo() or a different one) at the same +// time, it could affect the "retired" attributes of Foo()'s +// expectations when InSequence() is used, and thus affect which +// expectation gets picked. Therefore, we sequence all mock function +// calls to ensure the integrity of the mock objects' states. +GTEST_API_ GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_gmock_mutex); + +// Untyped base class for ActionResultHolder<R>. +class UntypedActionResultHolderBase; + +// Abstract base class of FunctionMocker. This is the +// type-agnostic part of the function mocker interface. Its pure +// virtual methods are implemented by FunctionMocker. +class GTEST_API_ UntypedFunctionMockerBase { + public: + UntypedFunctionMockerBase(); + virtual ~UntypedFunctionMockerBase(); + + // Verifies that all expectations on this mock function have been + // satisfied. Reports one or more Google Test non-fatal failures + // and returns false if not. + bool VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked() + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + // Clears the ON_CALL()s set on this mock function. + virtual void ClearDefaultActionsLocked() + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) = 0; + + // In all of the following Untyped* functions, it's the caller's + // responsibility to guarantee the correctness of the arguments' + // types. + + // Performs the default action with the given arguments and returns + // the action's result. The call description string will be used in + // the error message to describe the call in the case the default + // action fails. + // L = * + virtual UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedPerformDefaultAction( + void* untyped_args, const std::string& call_description) const = 0; + + // Performs the given action with the given arguments and returns + // the action's result. + // L = * + virtual UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedPerformAction( + const void* untyped_action, void* untyped_args) const = 0; + + // Writes a message that the call is uninteresting (i.e. neither + // explicitly expected nor explicitly unexpected) to the given + // ostream. + virtual void UntypedDescribeUninterestingCall( + const void* untyped_args, + ::std::ostream* os) const + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) = 0; + + // Returns the expectation that matches the given function arguments + // (or NULL is there's no match); when a match is found, + // untyped_action is set to point to the action that should be + // performed (or NULL if the action is "do default"), and + // is_excessive is modified to indicate whether the call exceeds the + // expected number. + virtual const ExpectationBase* UntypedFindMatchingExpectation( + const void* untyped_args, + const void** untyped_action, bool* is_excessive, + ::std::ostream* what, ::std::ostream* why) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) = 0; + + // Prints the given function arguments to the ostream. + virtual void UntypedPrintArgs(const void* untyped_args, + ::std::ostream* os) const = 0; + + // Sets the mock object this mock method belongs to, and registers + // this information in the global mock registry. Will be called + // whenever an EXPECT_CALL() or ON_CALL() is executed on this mock + // method. + void RegisterOwner(const void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + // Sets the mock object this mock method belongs to, and sets the + // name of the mock function. Will be called upon each invocation + // of this mock function. + void SetOwnerAndName(const void* mock_obj, const char* name) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + // Returns the mock object this mock method belongs to. Must be + // called after RegisterOwner() or SetOwnerAndName() has been + // called. + const void* MockObject() const + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + // Returns the name of this mock method. Must be called after + // SetOwnerAndName() has been called. + const char* Name() const + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + // Returns the result of invoking this mock function with the given + // arguments. This function can be safely called from multiple + // threads concurrently. The caller is responsible for deleting the + // result. + UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedInvokeWith(void* untyped_args) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + protected: + typedef std::vector<const void*> UntypedOnCallSpecs; + + using UntypedExpectations = std::vector<std::shared_ptr<ExpectationBase>>; + + // Returns an Expectation object that references and co-owns exp, + // which must be an expectation on this mock function. + Expectation GetHandleOf(ExpectationBase* exp); + + // Address of the mock object this mock method belongs to. Only + // valid after this mock method has been called or + // ON_CALL/EXPECT_CALL has been invoked on it. + const void* mock_obj_; // Protected by g_gmock_mutex. + + // Name of the function being mocked. Only valid after this mock + // method has been called. + const char* name_; // Protected by g_gmock_mutex. + + // All default action specs for this function mocker. + UntypedOnCallSpecs untyped_on_call_specs_; + + // All expectations for this function mocker. + // + // It's undefined behavior to interleave expectations (EXPECT_CALLs + // or ON_CALLs) and mock function calls. Also, the order of + // expectations is important. Therefore it's a logic race condition + // to read/write untyped_expectations_ concurrently. In order for + // tools like tsan to catch concurrent read/write accesses to + // untyped_expectations, we deliberately leave accesses to it + // unprotected. + UntypedExpectations untyped_expectations_; +}; // class UntypedFunctionMockerBase + +// Untyped base class for OnCallSpec<F>. +class UntypedOnCallSpecBase { + public: + // The arguments are the location of the ON_CALL() statement. + UntypedOnCallSpecBase(const char* a_file, int a_line) + : file_(a_file), line_(a_line), last_clause_(kNone) {} + + // Where in the source file was the default action spec defined? + const char* file() const { return file_; } + int line() const { return line_; } + + protected: + // Gives each clause in the ON_CALL() statement a name. + enum Clause { + // Do not change the order of the enum members! The run-time + // syntax checking relies on it. + kNone, + kWith, + kWillByDefault + }; + + // Asserts that the ON_CALL() statement has a certain property. + void AssertSpecProperty(bool property, + const std::string& failure_message) const { + Assert(property, file_, line_, failure_message); + } + + // Expects that the ON_CALL() statement has a certain property. + void ExpectSpecProperty(bool property, + const std::string& failure_message) const { + Expect(property, file_, line_, failure_message); + } + + const char* file_; + int line_; + + // The last clause in the ON_CALL() statement as seen so far. + // Initially kNone and changes as the statement is parsed. + Clause last_clause_; +}; // class UntypedOnCallSpecBase + +// This template class implements an ON_CALL spec. +template <typename F> +class OnCallSpec : public UntypedOnCallSpecBase { + public: + typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentMatcherTuple ArgumentMatcherTuple; + + // Constructs an OnCallSpec object from the information inside + // the parenthesis of an ON_CALL() statement. + OnCallSpec(const char* a_file, int a_line, + const ArgumentMatcherTuple& matchers) + : UntypedOnCallSpecBase(a_file, a_line), + matchers_(matchers), + // By default, extra_matcher_ should match anything. However, + // we cannot initialize it with _ as that causes ambiguity between + // Matcher's copy and move constructor for some argument types. + extra_matcher_(A<const ArgumentTuple&>()) {} + + // Implements the .With() clause. + OnCallSpec& With(const Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&>& m) { + // Makes sure this is called at most once. + ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kWith, + ".With() cannot appear " + "more than once in an ON_CALL()."); + last_clause_ = kWith; + + extra_matcher_ = m; + return *this; + } + + // Implements the .WillByDefault() clause. + OnCallSpec& WillByDefault(const Action<F>& action) { + ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kWillByDefault, + ".WillByDefault() must appear " + "exactly once in an ON_CALL()."); + last_clause_ = kWillByDefault; + + ExpectSpecProperty(!action.IsDoDefault(), + "DoDefault() cannot be used in ON_CALL()."); + action_ = action; + return *this; + } + + // Returns true if and only if the given arguments match the matchers. + bool Matches(const ArgumentTuple& args) const { + return TupleMatches(matchers_, args) && extra_matcher_.Matches(args); + } + + // Returns the action specified by the user. + const Action<F>& GetAction() const { + AssertSpecProperty(last_clause_ == kWillByDefault, + ".WillByDefault() must appear exactly " + "once in an ON_CALL()."); + return action_; + } + + private: + // The information in statement + // + // ON_CALL(mock_object, Method(matchers)) + // .With(multi-argument-matcher) + // .WillByDefault(action); + // + // is recorded in the data members like this: + // + // source file that contains the statement => file_ + // line number of the statement => line_ + // matchers => matchers_ + // multi-argument-matcher => extra_matcher_ + // action => action_ + ArgumentMatcherTuple matchers_; + Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&> extra_matcher_; + Action<F> action_; +}; // class OnCallSpec + +// Possible reactions on uninteresting calls. +enum CallReaction { + kAllow, + kWarn, + kFail, +}; + +} // namespace internal + +// Utilities for manipulating mock objects. +class GTEST_API_ Mock { + public: + // The following public methods can be called concurrently. + + // Tells Google Mock to ignore mock_obj when checking for leaked + // mock objects. + static void AllowLeak(const void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Verifies and clears all expectations on the given mock object. + // If the expectations aren't satisfied, generates one or more + // Google Test non-fatal failures and returns false. + static bool VerifyAndClearExpectations(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Verifies all expectations on the given mock object and clears its + // default actions and expectations. Returns true if and only if the + // verification was successful. + static bool VerifyAndClear(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Returns whether the mock was created as a naggy mock (default) + static bool IsNaggy(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + // Returns whether the mock was created as a nice mock + static bool IsNice(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + // Returns whether the mock was created as a strict mock + static bool IsStrict(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + private: + friend class internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase; + + // Needed for a function mocker to register itself (so that we know + // how to clear a mock object). + template <typename F> + friend class internal::FunctionMocker; + + template <typename MockClass> + friend class internal::NiceMockImpl; + template <typename MockClass> + friend class internal::NaggyMockImpl; + template <typename MockClass> + friend class internal::StrictMockImpl; + + // Tells Google Mock to allow uninteresting calls on the given mock + // object. + static void AllowUninterestingCalls(const void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Tells Google Mock to warn the user about uninteresting calls on + // the given mock object. + static void WarnUninterestingCalls(const void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Tells Google Mock to fail uninteresting calls on the given mock + // object. + static void FailUninterestingCalls(const void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Tells Google Mock the given mock object is being destroyed and + // its entry in the call-reaction table should be removed. + static void UnregisterCallReaction(const void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Returns the reaction Google Mock will have on uninteresting calls + // made on the given mock object. + static internal::CallReaction GetReactionOnUninterestingCalls( + const void* mock_obj) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Verifies that all expectations on the given mock object have been + // satisfied. Reports one or more Google Test non-fatal failures + // and returns false if not. + static bool VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Clears all ON_CALL()s set on the given mock object. + static void ClearDefaultActionsLocked(void* mock_obj) + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Registers a mock object and a mock method it owns. + static void Register( + const void* mock_obj, + internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase* mocker) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Tells Google Mock where in the source code mock_obj is used in an + // ON_CALL or EXPECT_CALL. In case mock_obj is leaked, this + // information helps the user identify which object it is. + static void RegisterUseByOnCallOrExpectCall( + const void* mock_obj, const char* file, int line) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); + + // Unregisters a mock method; removes the owning mock object from + // the registry when the last mock method associated with it has + // been unregistered. This is called only in the destructor of + // FunctionMocker. + static void UnregisterLocked(internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase* mocker) + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(internal::g_gmock_mutex); +}; // class Mock + +// An abstract handle of an expectation. Useful in the .After() +// clause of EXPECT_CALL() for setting the (partial) order of +// expectations. The syntax: +// +// Expectation e1 = EXPECT_CALL(...)...; +// EXPECT_CALL(...).After(e1)...; +// +// sets two expectations where the latter can only be matched after +// the former has been satisfied. +// +// Notes: +// - This class is copyable and has value semantics. +// - Constness is shallow: a const Expectation object itself cannot +// be modified, but the mutable methods of the ExpectationBase +// object it references can be called via expectation_base(). + +class GTEST_API_ Expectation { + public: + // Constructs a null object that doesn't reference any expectation. + Expectation(); + Expectation(Expectation&&) = default; + Expectation(const Expectation&) = default; + Expectation& operator=(Expectation&&) = default; + Expectation& operator=(const Expectation&) = default; + ~Expectation(); + + // This single-argument ctor must not be explicit, in order to support the + // Expectation e = EXPECT_CALL(...); + // syntax. + // + // A TypedExpectation object stores its pre-requisites as + // Expectation objects, and needs to call the non-const Retire() + // method on the ExpectationBase objects they reference. Therefore + // Expectation must receive a *non-const* reference to the + // ExpectationBase object. + Expectation(internal::ExpectationBase& exp); // NOLINT + + // The compiler-generated copy ctor and operator= work exactly as + // intended, so we don't need to define our own. + + // Returns true if and only if rhs references the same expectation as this + // object does. + bool operator==(const Expectation& rhs) const { + return expectation_base_ == rhs.expectation_base_; + } + + bool operator!=(const Expectation& rhs) const { return !(*this == rhs); } + + private: + friend class ExpectationSet; + friend class Sequence; + friend class ::testing::internal::ExpectationBase; + friend class ::testing::internal::UntypedFunctionMockerBase; + + template <typename F> + friend class ::testing::internal::FunctionMocker; + + template <typename F> + friend class ::testing::internal::TypedExpectation; + + // This comparator is needed for putting Expectation objects into a set. + class Less { + public: + bool operator()(const Expectation& lhs, const Expectation& rhs) const { + return lhs.expectation_base_.get() < rhs.expectation_base_.get(); + } + }; + + typedef ::std::set<Expectation, Less> Set; + + Expectation( + const std::shared_ptr<internal::ExpectationBase>& expectation_base); + + // Returns the expectation this object references. + const std::shared_ptr<internal::ExpectationBase>& expectation_base() const { + return expectation_base_; + } + + // A shared_ptr that co-owns the expectation this handle references. + std::shared_ptr<internal::ExpectationBase> expectation_base_; +}; + +// A set of expectation handles. Useful in the .After() clause of +// EXPECT_CALL() for setting the (partial) order of expectations. The +// syntax: +// +// ExpectationSet es; +// es += EXPECT_CALL(...)...; +// es += EXPECT_CALL(...)...; +// EXPECT_CALL(...).After(es)...; +// +// sets three expectations where the last one can only be matched +// after the first two have both been satisfied. +// +// This class is copyable and has value semantics. +class ExpectationSet { + public: + // A bidirectional iterator that can read a const element in the set. + typedef Expectation::Set::const_iterator const_iterator; + + // An object stored in the set. This is an alias of Expectation. + typedef Expectation::Set::value_type value_type; + + // Constructs an empty set. + ExpectationSet() {} + + // This single-argument ctor must not be explicit, in order to support the + // ExpectationSet es = EXPECT_CALL(...); + // syntax. + ExpectationSet(internal::ExpectationBase& exp) { // NOLINT + *this += Expectation(exp); + } + + // This single-argument ctor implements implicit conversion from + // Expectation and thus must not be explicit. This allows either an + // Expectation or an ExpectationSet to be used in .After(). + ExpectationSet(const Expectation& e) { // NOLINT + *this += e; + } + + // The compiler-generator ctor and operator= works exactly as + // intended, so we don't need to define our own. + + // Returns true if and only if rhs contains the same set of Expectation + // objects as this does. + bool operator==(const ExpectationSet& rhs) const { + return expectations_ == rhs.expectations_; + } + + bool operator!=(const ExpectationSet& rhs) const { return !(*this == rhs); } + + // Implements the syntax + // expectation_set += EXPECT_CALL(...); + ExpectationSet& operator+=(const Expectation& e) { + expectations_.insert(e); + return *this; + } + + int size() const { return static_cast<int>(expectations_.size()); } + + const_iterator begin() const { return expectations_.begin(); } + const_iterator end() const { return expectations_.end(); } + + private: + Expectation::Set expectations_; +}; + + +// Sequence objects are used by a user to specify the relative order +// in which the expectations should match. They are copyable (we rely +// on the compiler-defined copy constructor and assignment operator). +class GTEST_API_ Sequence { + public: + // Constructs an empty sequence. + Sequence() : last_expectation_(new Expectation) {} + + // Adds an expectation to this sequence. The caller must ensure + // that no other thread is accessing this Sequence object. + void AddExpectation(const Expectation& expectation) const; + + private: + // The last expectation in this sequence. + std::shared_ptr<Expectation> last_expectation_; +}; // class Sequence + +// An object of this type causes all EXPECT_CALL() statements +// encountered in its scope to be put in an anonymous sequence. The +// work is done in the constructor and destructor. You should only +// create an InSequence object on the stack. +// +// The sole purpose for this class is to support easy definition of +// sequential expectations, e.g. +// +// { +// InSequence dummy; // The name of the object doesn't matter. +// +// // The following expectations must match in the order they appear. +// EXPECT_CALL(a, Bar())...; +// EXPECT_CALL(a, Baz())...; +// ... +// EXPECT_CALL(b, Xyz())...; +// } +// +// You can create InSequence objects in multiple threads, as long as +// they are used to affect different mock objects. The idea is that +// each thread can create and set up its own mocks as if it's the only +// thread. However, for clarity of your tests we recommend you to set +// up mocks in the main thread unless you have a good reason not to do +// so. +class GTEST_API_ InSequence { + public: + InSequence(); + ~InSequence(); + private: + bool sequence_created_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(InSequence); // NOLINT +} GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; + +namespace internal { + +// Points to the implicit sequence introduced by a living InSequence +// object (if any) in the current thread or NULL. +GTEST_API_ extern ThreadLocal<Sequence*> g_gmock_implicit_sequence; + +// Base class for implementing expectations. +// +// There are two reasons for having a type-agnostic base class for +// Expectation: +// +// 1. We need to store collections of expectations of different +// types (e.g. all pre-requisites of a particular expectation, all +// expectations in a sequence). Therefore these expectation objects +// must share a common base class. +// +// 2. We can avoid binary code bloat by moving methods not depending +// on the template argument of Expectation to the base class. +// +// This class is internal and mustn't be used by user code directly. +class GTEST_API_ ExpectationBase { + public: + // source_text is the EXPECT_CALL(...) source that created this Expectation. + ExpectationBase(const char* file, int line, const std::string& source_text); + + virtual ~ExpectationBase(); + + // Where in the source file was the expectation spec defined? + const char* file() const { return file_; } + int line() const { return line_; } + const char* source_text() const { return source_text_.c_str(); } + // Returns the cardinality specified in the expectation spec. + const Cardinality& cardinality() const { return cardinality_; } + + // Describes the source file location of this expectation. + void DescribeLocationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << FormatFileLocation(file(), line()) << " "; + } + + // Describes how many times a function call matching this + // expectation has occurred. + void DescribeCallCountTo(::std::ostream* os) const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + // If this mock method has an extra matcher (i.e. .With(matcher)), + // describes it to the ostream. + virtual void MaybeDescribeExtraMatcherTo(::std::ostream* os) = 0; + + protected: + friend class ::testing::Expectation; + friend class UntypedFunctionMockerBase; + + enum Clause { + // Don't change the order of the enum members! + kNone, + kWith, + kTimes, + kInSequence, + kAfter, + kWillOnce, + kWillRepeatedly, + kRetiresOnSaturation + }; + + typedef std::vector<const void*> UntypedActions; + + // Returns an Expectation object that references and co-owns this + // expectation. + virtual Expectation GetHandle() = 0; + + // Asserts that the EXPECT_CALL() statement has the given property. + void AssertSpecProperty(bool property, + const std::string& failure_message) const { + Assert(property, file_, line_, failure_message); + } + + // Expects that the EXPECT_CALL() statement has the given property. + void ExpectSpecProperty(bool property, + const std::string& failure_message) const { + Expect(property, file_, line_, failure_message); + } + + // Explicitly specifies the cardinality of this expectation. Used + // by the subclasses to implement the .Times() clause. + void SpecifyCardinality(const Cardinality& cardinality); + + // Returns true if and only if the user specified the cardinality + // explicitly using a .Times(). + bool cardinality_specified() const { return cardinality_specified_; } + + // Sets the cardinality of this expectation spec. + void set_cardinality(const Cardinality& a_cardinality) { + cardinality_ = a_cardinality; + } + + // The following group of methods should only be called after the + // EXPECT_CALL() statement, and only when g_gmock_mutex is held by + // the current thread. + + // Retires all pre-requisites of this expectation. + void RetireAllPreRequisites() + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + // Returns true if and only if this expectation is retired. + bool is_retired() const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + return retired_; + } + + // Retires this expectation. + void Retire() + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + retired_ = true; + } + + // Returns true if and only if this expectation is satisfied. + bool IsSatisfied() const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + return cardinality().IsSatisfiedByCallCount(call_count_); + } + + // Returns true if and only if this expectation is saturated. + bool IsSaturated() const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + return cardinality().IsSaturatedByCallCount(call_count_); + } + + // Returns true if and only if this expectation is over-saturated. + bool IsOverSaturated() const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + return cardinality().IsOverSaturatedByCallCount(call_count_); + } + + // Returns true if and only if all pre-requisites of this expectation are + // satisfied. + bool AllPrerequisitesAreSatisfied() const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + // Adds unsatisfied pre-requisites of this expectation to 'result'. + void FindUnsatisfiedPrerequisites(ExpectationSet* result) const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex); + + // Returns the number this expectation has been invoked. + int call_count() const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + return call_count_; + } + + // Increments the number this expectation has been invoked. + void IncrementCallCount() + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + call_count_++; + } + + // Checks the action count (i.e. the number of WillOnce() and + // WillRepeatedly() clauses) against the cardinality if this hasn't + // been done before. Prints a warning if there are too many or too + // few actions. + void CheckActionCountIfNotDone() const + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); + + friend class ::testing::Sequence; + friend class ::testing::internal::ExpectationTester; + + template <typename Function> + friend class TypedExpectation; + + // Implements the .Times() clause. + void UntypedTimes(const Cardinality& a_cardinality); + + // This group of fields are part of the spec and won't change after + // an EXPECT_CALL() statement finishes. + const char* file_; // The file that contains the expectation. + int line_; // The line number of the expectation. + const std::string source_text_; // The EXPECT_CALL(...) source text. + // True if and only if the cardinality is specified explicitly. + bool cardinality_specified_; + Cardinality cardinality_; // The cardinality of the expectation. + // The immediate pre-requisites (i.e. expectations that must be + // satisfied before this expectation can be matched) of this + // expectation. We use std::shared_ptr in the set because we want an + // Expectation object to be co-owned by its FunctionMocker and its + // successors. This allows multiple mock objects to be deleted at + // different times. + ExpectationSet immediate_prerequisites_; + + // This group of fields are the current state of the expectation, + // and can change as the mock function is called. + int call_count_; // How many times this expectation has been invoked. + bool retired_; // True if and only if this expectation has retired. + UntypedActions untyped_actions_; + bool extra_matcher_specified_; + bool repeated_action_specified_; // True if a WillRepeatedly() was specified. + bool retires_on_saturation_; + Clause last_clause_; + mutable bool action_count_checked_; // Under mutex_. + mutable Mutex mutex_; // Protects action_count_checked_. +}; // class ExpectationBase + +// Impements an expectation for the given function type. +template <typename F> +class TypedExpectation : public ExpectationBase { + public: + typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + typedef typename Function<F>::ArgumentMatcherTuple ArgumentMatcherTuple; + typedef typename Function<F>::Result Result; + + TypedExpectation(FunctionMocker<F>* owner, const char* a_file, int a_line, + const std::string& a_source_text, + const ArgumentMatcherTuple& m) + : ExpectationBase(a_file, a_line, a_source_text), + owner_(owner), + matchers_(m), + // By default, extra_matcher_ should match anything. However, + // we cannot initialize it with _ as that causes ambiguity between + // Matcher's copy and move constructor for some argument types. + extra_matcher_(A<const ArgumentTuple&>()), + repeated_action_(DoDefault()) {} + + ~TypedExpectation() override { + // Check the validity of the action count if it hasn't been done + // yet (for example, if the expectation was never used). + CheckActionCountIfNotDone(); + for (UntypedActions::const_iterator it = untyped_actions_.begin(); + it != untyped_actions_.end(); ++it) { + delete static_cast<const Action<F>*>(*it); + } + } + + // Implements the .With() clause. + TypedExpectation& With(const Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&>& m) { + if (last_clause_ == kWith) { + ExpectSpecProperty(false, + ".With() cannot appear " + "more than once in an EXPECT_CALL()."); + } else { + ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kWith, + ".With() must be the first " + "clause in an EXPECT_CALL()."); + } + last_clause_ = kWith; + + extra_matcher_ = m; + extra_matcher_specified_ = true; + return *this; + } + + // Implements the .Times() clause. + TypedExpectation& Times(const Cardinality& a_cardinality) { + ExpectationBase::UntypedTimes(a_cardinality); + return *this; + } + + // Implements the .Times() clause. + TypedExpectation& Times(int n) { + return Times(Exactly(n)); + } + + // Implements the .InSequence() clause. + TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s) { + ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ <= kInSequence, + ".InSequence() cannot appear after .After()," + " .WillOnce(), .WillRepeatedly(), or " + ".RetiresOnSaturation()."); + last_clause_ = kInSequence; + + s.AddExpectation(GetHandle()); + return *this; + } + TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s1, const Sequence& s2) { + return InSequence(s1).InSequence(s2); + } + TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s1, const Sequence& s2, + const Sequence& s3) { + return InSequence(s1, s2).InSequence(s3); + } + TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s1, const Sequence& s2, + const Sequence& s3, const Sequence& s4) { + return InSequence(s1, s2, s3).InSequence(s4); + } + TypedExpectation& InSequence(const Sequence& s1, const Sequence& s2, + const Sequence& s3, const Sequence& s4, + const Sequence& s5) { + return InSequence(s1, s2, s3, s4).InSequence(s5); + } + + // Implements that .After() clause. + TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s) { + ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ <= kAfter, + ".After() cannot appear after .WillOnce()," + " .WillRepeatedly(), or " + ".RetiresOnSaturation()."); + last_clause_ = kAfter; + + for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it) { + immediate_prerequisites_ += *it; + } + return *this; + } + TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s1, const ExpectationSet& s2) { + return After(s1).After(s2); + } + TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s1, const ExpectationSet& s2, + const ExpectationSet& s3) { + return After(s1, s2).After(s3); + } + TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s1, const ExpectationSet& s2, + const ExpectationSet& s3, const ExpectationSet& s4) { + return After(s1, s2, s3).After(s4); + } + TypedExpectation& After(const ExpectationSet& s1, const ExpectationSet& s2, + const ExpectationSet& s3, const ExpectationSet& s4, + const ExpectationSet& s5) { + return After(s1, s2, s3, s4).After(s5); + } + + // Implements the .WillOnce() clause. + TypedExpectation& WillOnce(const Action<F>& action) { + ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ <= kWillOnce, + ".WillOnce() cannot appear after " + ".WillRepeatedly() or .RetiresOnSaturation()."); + last_clause_ = kWillOnce; + + untyped_actions_.push_back(new Action<F>(action)); + if (!cardinality_specified()) { + set_cardinality(Exactly(static_cast<int>(untyped_actions_.size()))); + } + return *this; + } + + // Implements the .WillRepeatedly() clause. + TypedExpectation& WillRepeatedly(const Action<F>& action) { + if (last_clause_ == kWillRepeatedly) { + ExpectSpecProperty(false, + ".WillRepeatedly() cannot appear " + "more than once in an EXPECT_CALL()."); + } else { + ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kWillRepeatedly, + ".WillRepeatedly() cannot appear " + "after .RetiresOnSaturation()."); + } + last_clause_ = kWillRepeatedly; + repeated_action_specified_ = true; + + repeated_action_ = action; + if (!cardinality_specified()) { + set_cardinality(AtLeast(static_cast<int>(untyped_actions_.size()))); + } + + // Now that no more action clauses can be specified, we check + // whether their count makes sense. + CheckActionCountIfNotDone(); + return *this; + } + + // Implements the .RetiresOnSaturation() clause. + TypedExpectation& RetiresOnSaturation() { + ExpectSpecProperty(last_clause_ < kRetiresOnSaturation, + ".RetiresOnSaturation() cannot appear " + "more than once."); + last_clause_ = kRetiresOnSaturation; + retires_on_saturation_ = true; + + // Now that no more action clauses can be specified, we check + // whether their count makes sense. + CheckActionCountIfNotDone(); + return *this; + } + + // Returns the matchers for the arguments as specified inside the + // EXPECT_CALL() macro. + const ArgumentMatcherTuple& matchers() const { + return matchers_; + } + + // Returns the matcher specified by the .With() clause. + const Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&>& extra_matcher() const { + return extra_matcher_; + } + + // Returns the action specified by the .WillRepeatedly() clause. + const Action<F>& repeated_action() const { return repeated_action_; } + + // If this mock method has an extra matcher (i.e. .With(matcher)), + // describes it to the ostream. + void MaybeDescribeExtraMatcherTo(::std::ostream* os) override { + if (extra_matcher_specified_) { + *os << " Expected args: "; + extra_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + *os << "\n"; + } + } + + private: + template <typename Function> + friend class FunctionMocker; + + // Returns an Expectation object that references and co-owns this + // expectation. + Expectation GetHandle() override { return owner_->GetHandleOf(this); } + + // The following methods will be called only after the EXPECT_CALL() + // statement finishes and when the current thread holds + // g_gmock_mutex. + + // Returns true if and only if this expectation matches the given arguments. + bool Matches(const ArgumentTuple& args) const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + return TupleMatches(matchers_, args) && extra_matcher_.Matches(args); + } + + // Returns true if and only if this expectation should handle the given + // arguments. + bool ShouldHandleArguments(const ArgumentTuple& args) const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + + // In case the action count wasn't checked when the expectation + // was defined (e.g. if this expectation has no WillRepeatedly() + // or RetiresOnSaturation() clause), we check it when the + // expectation is used for the first time. + CheckActionCountIfNotDone(); + return !is_retired() && AllPrerequisitesAreSatisfied() && Matches(args); + } + + // Describes the result of matching the arguments against this + // expectation to the given ostream. + void ExplainMatchResultTo( + const ArgumentTuple& args, + ::std::ostream* os) const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + + if (is_retired()) { + *os << " Expected: the expectation is active\n" + << " Actual: it is retired\n"; + } else if (!Matches(args)) { + if (!TupleMatches(matchers_, args)) { + ExplainMatchFailureTupleTo(matchers_, args, os); + } + StringMatchResultListener listener; + if (!extra_matcher_.MatchAndExplain(args, &listener)) { + *os << " Expected args: "; + extra_matcher_.DescribeTo(os); + *os << "\n Actual: don't match"; + + internal::PrintIfNotEmpty(listener.str(), os); + *os << "\n"; + } + } else if (!AllPrerequisitesAreSatisfied()) { + *os << " Expected: all pre-requisites are satisfied\n" + << " Actual: the following immediate pre-requisites " + << "are not satisfied:\n"; + ExpectationSet unsatisfied_prereqs; + FindUnsatisfiedPrerequisites(&unsatisfied_prereqs); + int i = 0; + for (ExpectationSet::const_iterator it = unsatisfied_prereqs.begin(); + it != unsatisfied_prereqs.end(); ++it) { + it->expectation_base()->DescribeLocationTo(os); + *os << "pre-requisite #" << i++ << "\n"; + } + *os << " (end of pre-requisites)\n"; + } else { + // This line is here just for completeness' sake. It will never + // be executed as currently the ExplainMatchResultTo() function + // is called only when the mock function call does NOT match the + // expectation. + *os << "The call matches the expectation.\n"; + } + } + + // Returns the action that should be taken for the current invocation. + const Action<F>& GetCurrentAction(const FunctionMocker<F>* mocker, + const ArgumentTuple& args) const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + const int count = call_count(); + Assert(count >= 1, __FILE__, __LINE__, + "call_count() is <= 0 when GetCurrentAction() is " + "called - this should never happen."); + + const int action_count = static_cast<int>(untyped_actions_.size()); + if (action_count > 0 && !repeated_action_specified_ && + count > action_count) { + // If there is at least one WillOnce() and no WillRepeatedly(), + // we warn the user when the WillOnce() clauses ran out. + ::std::stringstream ss; + DescribeLocationTo(&ss); + ss << "Actions ran out in " << source_text() << "...\n" + << "Called " << count << " times, but only " + << action_count << " WillOnce()" + << (action_count == 1 ? " is" : "s are") << " specified - "; + mocker->DescribeDefaultActionTo(args, &ss); + Log(kWarning, ss.str(), 1); + } + + return count <= action_count + ? *static_cast<const Action<F>*>( + untyped_actions_[static_cast<size_t>(count - 1)]) + : repeated_action(); + } + + // Given the arguments of a mock function call, if the call will + // over-saturate this expectation, returns the default action; + // otherwise, returns the next action in this expectation. Also + // describes *what* happened to 'what', and explains *why* Google + // Mock does it to 'why'. This method is not const as it calls + // IncrementCallCount(). A return value of NULL means the default + // action. + const Action<F>* GetActionForArguments(const FunctionMocker<F>* mocker, + const ArgumentTuple& args, + ::std::ostream* what, + ::std::ostream* why) + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + if (IsSaturated()) { + // We have an excessive call. + IncrementCallCount(); + *what << "Mock function called more times than expected - "; + mocker->DescribeDefaultActionTo(args, what); + DescribeCallCountTo(why); + + return nullptr; + } + + IncrementCallCount(); + RetireAllPreRequisites(); + + if (retires_on_saturation_ && IsSaturated()) { + Retire(); + } + + // Must be done after IncrementCount()! + *what << "Mock function call matches " << source_text() <<"...\n"; + return &(GetCurrentAction(mocker, args)); + } + + // All the fields below won't change once the EXPECT_CALL() + // statement finishes. + FunctionMocker<F>* const owner_; + ArgumentMatcherTuple matchers_; + Matcher<const ArgumentTuple&> extra_matcher_; + Action<F> repeated_action_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TypedExpectation); +}; // class TypedExpectation + +// A MockSpec object is used by ON_CALL() or EXPECT_CALL() for +// specifying the default behavior of, or expectation on, a mock +// function. + +// Note: class MockSpec really belongs to the ::testing namespace. +// However if we define it in ::testing, MSVC will complain when +// classes in ::testing::internal declare it as a friend class +// template. To workaround this compiler bug, we define MockSpec in +// ::testing::internal and import it into ::testing. + +// Logs a message including file and line number information. +GTEST_API_ void LogWithLocation(testing::internal::LogSeverity severity, + const char* file, int line, + const std::string& message); + +template <typename F> +class MockSpec { + public: + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentTuple ArgumentTuple; + typedef typename internal::Function<F>::ArgumentMatcherTuple + ArgumentMatcherTuple; + + // Constructs a MockSpec object, given the function mocker object + // that the spec is associated with. + MockSpec(internal::FunctionMocker<F>* function_mocker, + const ArgumentMatcherTuple& matchers) + : function_mocker_(function_mocker), matchers_(matchers) {} + + // Adds a new default action spec to the function mocker and returns + // the newly created spec. + internal::OnCallSpec<F>& InternalDefaultActionSetAt( + const char* file, int line, const char* obj, const char* call) { + LogWithLocation(internal::kInfo, file, line, + std::string("ON_CALL(") + obj + ", " + call + ") invoked"); + return function_mocker_->AddNewOnCallSpec(file, line, matchers_); + } + + // Adds a new expectation spec to the function mocker and returns + // the newly created spec. + internal::TypedExpectation<F>& InternalExpectedAt( + const char* file, int line, const char* obj, const char* call) { + const std::string source_text(std::string("EXPECT_CALL(") + obj + ", " + + call + ")"); + LogWithLocation(internal::kInfo, file, line, source_text + " invoked"); + return function_mocker_->AddNewExpectation( + file, line, source_text, matchers_); + } + + // This operator overload is used to swallow the superfluous parameter list + // introduced by the ON/EXPECT_CALL macros. See the macro comments for more + // explanation. + MockSpec<F>& operator()(const internal::WithoutMatchers&, void* const) { + return *this; + } + + private: + template <typename Function> + friend class internal::FunctionMocker; + + // The function mocker that owns this spec. + internal::FunctionMocker<F>* const function_mocker_; + // The argument matchers specified in the spec. + ArgumentMatcherTuple matchers_; +}; // class MockSpec + +// Wrapper type for generically holding an ordinary value or lvalue reference. +// If T is not a reference type, it must be copyable or movable. +// ReferenceOrValueWrapper<T> is movable, and will also be copyable unless +// T is a move-only value type (which means that it will always be copyable +// if the current platform does not support move semantics). +// +// The primary template defines handling for values, but function header +// comments describe the contract for the whole template (including +// specializations). +template <typename T> +class ReferenceOrValueWrapper { + public: + // Constructs a wrapper from the given value/reference. + explicit ReferenceOrValueWrapper(T value) + : value_(std::move(value)) { + } + + // Unwraps and returns the underlying value/reference, exactly as + // originally passed. The behavior of calling this more than once on + // the same object is unspecified. + T Unwrap() { return std::move(value_); } + + // Provides nondestructive access to the underlying value/reference. + // Always returns a const reference (more precisely, + // const std::add_lvalue_reference<T>::type). The behavior of calling this + // after calling Unwrap on the same object is unspecified. + const T& Peek() const { + return value_; + } + + private: + T value_; +}; + +// Specialization for lvalue reference types. See primary template +// for documentation. +template <typename T> +class ReferenceOrValueWrapper<T&> { + public: + // Workaround for debatable pass-by-reference lint warning (c-library-team + // policy precludes NOLINT in this context) + typedef T& reference; + explicit ReferenceOrValueWrapper(reference ref) + : value_ptr_(&ref) {} + T& Unwrap() { return *value_ptr_; } + const T& Peek() const { return *value_ptr_; } + + private: + T* value_ptr_; +}; + +// C++ treats the void type specially. For example, you cannot define +// a void-typed variable or pass a void value to a function. +// ActionResultHolder<T> holds a value of type T, where T must be a +// copyable type or void (T doesn't need to be default-constructable). +// It hides the syntactic difference between void and other types, and +// is used to unify the code for invoking both void-returning and +// non-void-returning mock functions. + +// Untyped base class for ActionResultHolder<T>. +class UntypedActionResultHolderBase { + public: + virtual ~UntypedActionResultHolderBase() {} + + // Prints the held value as an action's result to os. + virtual void PrintAsActionResult(::std::ostream* os) const = 0; +}; + +// This generic definition is used when T is not void. +template <typename T> +class ActionResultHolder : public UntypedActionResultHolderBase { + public: + // Returns the held value. Must not be called more than once. + T Unwrap() { + return result_.Unwrap(); + } + + // Prints the held value as an action's result to os. + void PrintAsActionResult(::std::ostream* os) const override { + *os << "\n Returns: "; + // T may be a reference type, so we don't use UniversalPrint(). + UniversalPrinter<T>::Print(result_.Peek(), os); + } + + // Performs the given mock function's default action and returns the + // result in a new-ed ActionResultHolder. + template <typename F> + static ActionResultHolder* PerformDefaultAction( + const FunctionMocker<F>* func_mocker, + typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple&& args, + const std::string& call_description) { + return new ActionResultHolder(Wrapper(func_mocker->PerformDefaultAction( + std::move(args), call_description))); + } + + // Performs the given action and returns the result in a new-ed + // ActionResultHolder. + template <typename F> + static ActionResultHolder* PerformAction( + const Action<F>& action, typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple&& args) { + return new ActionResultHolder( + Wrapper(action.Perform(std::move(args)))); + } + + private: + typedef ReferenceOrValueWrapper<T> Wrapper; + + explicit ActionResultHolder(Wrapper result) + : result_(std::move(result)) { + } + + Wrapper result_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ActionResultHolder); +}; + +// Specialization for T = void. +template <> +class ActionResultHolder<void> : public UntypedActionResultHolderBase { + public: + void Unwrap() { } + + void PrintAsActionResult(::std::ostream* /* os */) const override {} + + // Performs the given mock function's default action and returns ownership + // of an empty ActionResultHolder*. + template <typename F> + static ActionResultHolder* PerformDefaultAction( + const FunctionMocker<F>* func_mocker, + typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple&& args, + const std::string& call_description) { + func_mocker->PerformDefaultAction(std::move(args), call_description); + return new ActionResultHolder; + } + + // Performs the given action and returns ownership of an empty + // ActionResultHolder*. + template <typename F> + static ActionResultHolder* PerformAction( + const Action<F>& action, typename Function<F>::ArgumentTuple&& args) { + action.Perform(std::move(args)); + return new ActionResultHolder; + } + + private: + ActionResultHolder() {} + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ActionResultHolder); +}; + +template <typename F> +class FunctionMocker; + +template <typename R, typename... Args> +class FunctionMocker<R(Args...)> final : public UntypedFunctionMockerBase { + using F = R(Args...); + + public: + using Result = R; + using ArgumentTuple = std::tuple<Args...>; + using ArgumentMatcherTuple = std::tuple<Matcher<Args>...>; + + FunctionMocker() {} + + // There is no generally useful and implementable semantics of + // copying a mock object, so copying a mock is usually a user error. + // Thus we disallow copying function mockers. If the user really + // wants to copy a mock object, they should implement their own copy + // operation, for example: + // + // class MockFoo : public Foo { + // public: + // // Defines a copy constructor explicitly. + // MockFoo(const MockFoo& src) {} + // ... + // }; + FunctionMocker(const FunctionMocker&) = delete; + FunctionMocker& operator=(const FunctionMocker&) = delete; + + // The destructor verifies that all expectations on this mock + // function have been satisfied. If not, it will report Google Test + // non-fatal failures for the violations. + ~FunctionMocker() override GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + MutexLock l(&g_gmock_mutex); + VerifyAndClearExpectationsLocked(); + Mock::UnregisterLocked(this); + ClearDefaultActionsLocked(); + } + + // Returns the ON_CALL spec that matches this mock function with the + // given arguments; returns NULL if no matching ON_CALL is found. + // L = * + const OnCallSpec<F>* FindOnCallSpec( + const ArgumentTuple& args) const { + for (UntypedOnCallSpecs::const_reverse_iterator it + = untyped_on_call_specs_.rbegin(); + it != untyped_on_call_specs_.rend(); ++it) { + const OnCallSpec<F>* spec = static_cast<const OnCallSpec<F>*>(*it); + if (spec->Matches(args)) + return spec; + } + + return nullptr; + } + + // Performs the default action of this mock function on the given + // arguments and returns the result. Asserts (or throws if + // exceptions are enabled) with a helpful call descrption if there + // is no valid return value. This method doesn't depend on the + // mutable state of this object, and thus can be called concurrently + // without locking. + // L = * + Result PerformDefaultAction(ArgumentTuple&& args, + const std::string& call_description) const { + const OnCallSpec<F>* const spec = + this->FindOnCallSpec(args); + if (spec != nullptr) { + return spec->GetAction().Perform(std::move(args)); + } + const std::string message = + call_description + + "\n The mock function has no default action " + "set, and its return type has no default value set."; +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + if (!DefaultValue<Result>::Exists()) { + throw std::runtime_error(message); + } +#else + Assert(DefaultValue<Result>::Exists(), "", -1, message); +#endif + return DefaultValue<Result>::Get(); + } + + // Performs the default action with the given arguments and returns + // the action's result. The call description string will be used in + // the error message to describe the call in the case the default + // action fails. The caller is responsible for deleting the result. + // L = * + UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedPerformDefaultAction( + void* untyped_args, // must point to an ArgumentTuple + const std::string& call_description) const override { + ArgumentTuple* args = static_cast<ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); + return ResultHolder::PerformDefaultAction(this, std::move(*args), + call_description); + } + + // Performs the given action with the given arguments and returns + // the action's result. The caller is responsible for deleting the + // result. + // L = * + UntypedActionResultHolderBase* UntypedPerformAction( + const void* untyped_action, void* untyped_args) const override { + // Make a copy of the action before performing it, in case the + // action deletes the mock object (and thus deletes itself). + const Action<F> action = *static_cast<const Action<F>*>(untyped_action); + ArgumentTuple* args = static_cast<ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); + return ResultHolder::PerformAction(action, std::move(*args)); + } + + // Implements UntypedFunctionMockerBase::ClearDefaultActionsLocked(): + // clears the ON_CALL()s set on this mock function. + void ClearDefaultActionsLocked() override + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + + // Deleting our default actions may trigger other mock objects to be + // deleted, for example if an action contains a reference counted smart + // pointer to that mock object, and that is the last reference. So if we + // delete our actions within the context of the global mutex we may deadlock + // when this method is called again. Instead, make a copy of the set of + // actions to delete, clear our set within the mutex, and then delete the + // actions outside of the mutex. + UntypedOnCallSpecs specs_to_delete; + untyped_on_call_specs_.swap(specs_to_delete); + + g_gmock_mutex.Unlock(); + for (UntypedOnCallSpecs::const_iterator it = + specs_to_delete.begin(); + it != specs_to_delete.end(); ++it) { + delete static_cast<const OnCallSpec<F>*>(*it); + } + + // Lock the mutex again, since the caller expects it to be locked when we + // return. + g_gmock_mutex.Lock(); + } + + // Returns the result of invoking this mock function with the given + // arguments. This function can be safely called from multiple + // threads concurrently. + Result Invoke(Args... args) GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + ArgumentTuple tuple(std::forward<Args>(args)...); + std::unique_ptr<ResultHolder> holder(DownCast_<ResultHolder*>( + this->UntypedInvokeWith(static_cast<void*>(&tuple)))); + return holder->Unwrap(); + } + + MockSpec<F> With(Matcher<Args>... m) { + return MockSpec<F>(this, ::std::make_tuple(std::move(m)...)); + } + + protected: + template <typename Function> + friend class MockSpec; + + typedef ActionResultHolder<Result> ResultHolder; + + // Adds and returns a default action spec for this mock function. + OnCallSpec<F>& AddNewOnCallSpec( + const char* file, int line, + const ArgumentMatcherTuple& m) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + Mock::RegisterUseByOnCallOrExpectCall(MockObject(), file, line); + OnCallSpec<F>* const on_call_spec = new OnCallSpec<F>(file, line, m); + untyped_on_call_specs_.push_back(on_call_spec); + return *on_call_spec; + } + + // Adds and returns an expectation spec for this mock function. + TypedExpectation<F>& AddNewExpectation(const char* file, int line, + const std::string& source_text, + const ArgumentMatcherTuple& m) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + Mock::RegisterUseByOnCallOrExpectCall(MockObject(), file, line); + TypedExpectation<F>* const expectation = + new TypedExpectation<F>(this, file, line, source_text, m); + const std::shared_ptr<ExpectationBase> untyped_expectation(expectation); + // See the definition of untyped_expectations_ for why access to + // it is unprotected here. + untyped_expectations_.push_back(untyped_expectation); + + // Adds this expectation into the implicit sequence if there is one. + Sequence* const implicit_sequence = g_gmock_implicit_sequence.get(); + if (implicit_sequence != nullptr) { + implicit_sequence->AddExpectation(Expectation(untyped_expectation)); + } + + return *expectation; + } + + private: + template <typename Func> friend class TypedExpectation; + + // Some utilities needed for implementing UntypedInvokeWith(). + + // Describes what default action will be performed for the given + // arguments. + // L = * + void DescribeDefaultActionTo(const ArgumentTuple& args, + ::std::ostream* os) const { + const OnCallSpec<F>* const spec = FindOnCallSpec(args); + + if (spec == nullptr) { + *os << (std::is_void<Result>::value ? "returning directly.\n" + : "returning default value.\n"); + } else { + *os << "taking default action specified at:\n" + << FormatFileLocation(spec->file(), spec->line()) << "\n"; + } + } + + // Writes a message that the call is uninteresting (i.e. neither + // explicitly expected nor explicitly unexpected) to the given + // ostream. + void UntypedDescribeUninterestingCall(const void* untyped_args, + ::std::ostream* os) const override + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + const ArgumentTuple& args = + *static_cast<const ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); + *os << "Uninteresting mock function call - "; + DescribeDefaultActionTo(args, os); + *os << " Function call: " << Name(); + UniversalPrint(args, os); + } + + // Returns the expectation that matches the given function arguments + // (or NULL is there's no match); when a match is found, + // untyped_action is set to point to the action that should be + // performed (or NULL if the action is "do default"), and + // is_excessive is modified to indicate whether the call exceeds the + // expected number. + // + // Critical section: We must find the matching expectation and the + // corresponding action that needs to be taken in an ATOMIC + // transaction. Otherwise another thread may call this mock + // method in the middle and mess up the state. + // + // However, performing the action has to be left out of the critical + // section. The reason is that we have no control on what the + // action does (it can invoke an arbitrary user function or even a + // mock function) and excessive locking could cause a dead lock. + const ExpectationBase* UntypedFindMatchingExpectation( + const void* untyped_args, const void** untyped_action, bool* is_excessive, + ::std::ostream* what, ::std::ostream* why) override + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + const ArgumentTuple& args = + *static_cast<const ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); + MutexLock l(&g_gmock_mutex); + TypedExpectation<F>* exp = this->FindMatchingExpectationLocked(args); + if (exp == nullptr) { // A match wasn't found. + this->FormatUnexpectedCallMessageLocked(args, what, why); + return nullptr; + } + + // This line must be done before calling GetActionForArguments(), + // which will increment the call count for *exp and thus affect + // its saturation status. + *is_excessive = exp->IsSaturated(); + const Action<F>* action = exp->GetActionForArguments(this, args, what, why); + if (action != nullptr && action->IsDoDefault()) + action = nullptr; // Normalize "do default" to NULL. + *untyped_action = action; + return exp; + } + + // Prints the given function arguments to the ostream. + void UntypedPrintArgs(const void* untyped_args, + ::std::ostream* os) const override { + const ArgumentTuple& args = + *static_cast<const ArgumentTuple*>(untyped_args); + UniversalPrint(args, os); + } + + // Returns the expectation that matches the arguments, or NULL if no + // expectation matches them. + TypedExpectation<F>* FindMatchingExpectationLocked( + const ArgumentTuple& args) const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + // See the definition of untyped_expectations_ for why access to + // it is unprotected here. + for (typename UntypedExpectations::const_reverse_iterator it = + untyped_expectations_.rbegin(); + it != untyped_expectations_.rend(); ++it) { + TypedExpectation<F>* const exp = + static_cast<TypedExpectation<F>*>(it->get()); + if (exp->ShouldHandleArguments(args)) { + return exp; + } + } + return nullptr; + } + + // Returns a message that the arguments don't match any expectation. + void FormatUnexpectedCallMessageLocked( + const ArgumentTuple& args, + ::std::ostream* os, + ::std::ostream* why) const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + *os << "\nUnexpected mock function call - "; + DescribeDefaultActionTo(args, os); + PrintTriedExpectationsLocked(args, why); + } + + // Prints a list of expectations that have been tried against the + // current mock function call. + void PrintTriedExpectationsLocked( + const ArgumentTuple& args, + ::std::ostream* why) const + GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(g_gmock_mutex) { + g_gmock_mutex.AssertHeld(); + const size_t count = untyped_expectations_.size(); + *why << "Google Mock tried the following " << count << " " + << (count == 1 ? "expectation, but it didn't match" : + "expectations, but none matched") + << ":\n"; + for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) { + TypedExpectation<F>* const expectation = + static_cast<TypedExpectation<F>*>(untyped_expectations_[i].get()); + *why << "\n"; + expectation->DescribeLocationTo(why); + if (count > 1) { + *why << "tried expectation #" << i << ": "; + } + *why << expectation->source_text() << "...\n"; + expectation->ExplainMatchResultTo(args, why); + expectation->DescribeCallCountTo(why); + } + } +}; // class FunctionMocker + +// Reports an uninteresting call (whose description is in msg) in the +// manner specified by 'reaction'. +void ReportUninterestingCall(CallReaction reaction, const std::string& msg); + +} // namespace internal + +namespace internal { + +template <typename F> +class MockFunction; + +template <typename R, typename... Args> +class MockFunction<R(Args...)> { + public: + MockFunction(const MockFunction&) = delete; + MockFunction& operator=(const MockFunction&) = delete; + + std::function<R(Args...)> AsStdFunction() { + return [this](Args... args) -> R { + return this->Call(std::forward<Args>(args)...); + }; + } + + // Implementation detail: the expansion of the MOCK_METHOD macro. + R Call(Args... args) { + mock_.SetOwnerAndName(this, "Call"); + return mock_.Invoke(std::forward<Args>(args)...); + } + + MockSpec<R(Args...)> gmock_Call(Matcher<Args>... m) { + mock_.RegisterOwner(this); + return mock_.With(std::move(m)...); + } + + MockSpec<R(Args...)> gmock_Call(const WithoutMatchers&, R (*)(Args...)) { + return this->gmock_Call(::testing::A<Args>()...); + } + + protected: + MockFunction() = default; + ~MockFunction() = default; + + private: + FunctionMocker<R(Args...)> mock_; +}; + +/* +The SignatureOf<F> struct is a meta-function returning function signature +corresponding to the provided F argument. + +It makes use of MockFunction easier by allowing it to accept more F arguments +than just function signatures. + +Specializations provided here cover only a signature type itself and +std::function. However, if need be it can be easily extended to cover also other +types (like for example boost::function). +*/ + +template <typename F> +struct SignatureOf; + +template <typename R, typename... Args> +struct SignatureOf<R(Args...)> { + using type = R(Args...); +}; + +template <typename F> +struct SignatureOf<std::function<F>> : SignatureOf<F> {}; + +template <typename F> +using SignatureOfT = typename SignatureOf<F>::type; + +} // namespace internal + +// A MockFunction<F> type has one mock method whose type is +// internal::SignatureOfT<F>. It is useful when you just want your +// test code to emit some messages and have Google Mock verify the +// right messages are sent (and perhaps at the right times). For +// example, if you are exercising code: +// +// Foo(1); +// Foo(2); +// Foo(3); +// +// and want to verify that Foo(1) and Foo(3) both invoke +// mock.Bar("a"), but Foo(2) doesn't invoke anything, you can write: +// +// TEST(FooTest, InvokesBarCorrectly) { +// MyMock mock; +// MockFunction<void(string check_point_name)> check; +// { +// InSequence s; +// +// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Bar("a")); +// EXPECT_CALL(check, Call("1")); +// EXPECT_CALL(check, Call("2")); +// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Bar("a")); +// } +// Foo(1); +// check.Call("1"); +// Foo(2); +// check.Call("2"); +// Foo(3); +// } +// +// The expectation spec says that the first Bar("a") must happen +// before check point "1", the second Bar("a") must happen after check +// point "2", and nothing should happen between the two check +// points. The explicit check points make it easy to tell which +// Bar("a") is called by which call to Foo(). +// +// MockFunction<F> can also be used to exercise code that accepts +// std::function<internal::SignatureOfT<F>> callbacks. To do so, use +// AsStdFunction() method to create std::function proxy forwarding to +// original object's Call. Example: +// +// TEST(FooTest, RunsCallbackWithBarArgument) { +// MockFunction<int(string)> callback; +// EXPECT_CALL(callback, Call("bar")).WillOnce(Return(1)); +// Foo(callback.AsStdFunction()); +// } +// +// The internal::SignatureOfT<F> indirection allows to use other types +// than just function signature type. This is typically useful when +// providing a mock for a predefined std::function type. Example: +// +// using FilterPredicate = std::function<bool(string)>; +// void MyFilterAlgorithm(FilterPredicate predicate); +// +// TEST(FooTest, FilterPredicateAlwaysAccepts) { +// MockFunction<FilterPredicate> predicateMock; +// EXPECT_CALL(predicateMock, Call(_)).WillRepeatedly(Return(true)); +// MyFilterAlgorithm(predicateMock.AsStdFunction()); +// } +template <typename F> +class MockFunction : public internal::MockFunction<internal::SignatureOfT<F>> { + using Base = internal::MockFunction<internal::SignatureOfT<F>>; + + public: + using Base::Base; +}; + +// The style guide prohibits "using" statements in a namespace scope +// inside a header file. However, the MockSpec class template is +// meant to be defined in the ::testing namespace. The following line +// is just a trick for working around a bug in MSVC 8.0, which cannot +// handle it if we define MockSpec in ::testing. +using internal::MockSpec; + +// Const(x) is a convenient function for obtaining a const reference +// to x. This is useful for setting expectations on an overloaded +// const mock method, e.g. +// +// class MockFoo : public FooInterface { +// public: +// MOCK_METHOD0(Bar, int()); +// MOCK_CONST_METHOD0(Bar, int&()); +// }; +// +// MockFoo foo; +// // Expects a call to non-const MockFoo::Bar(). +// EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar()); +// // Expects a call to const MockFoo::Bar(). +// EXPECT_CALL(Const(foo), Bar()); +template <typename T> +inline const T& Const(const T& x) { return x; } + +// Constructs an Expectation object that references and co-owns exp. +inline Expectation::Expectation(internal::ExpectationBase& exp) // NOLINT + : expectation_base_(exp.GetHandle().expectation_base()) {} + +} // namespace testing + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + +// Implementation for ON_CALL and EXPECT_CALL macros. A separate macro is +// required to avoid compile errors when the name of the method used in call is +// a result of macro expansion. See CompilesWithMethodNameExpandedFromMacro +// tests in internal/gmock-spec-builders_test.cc for more details. +// +// This macro supports statements both with and without parameter matchers. If +// the parameter list is omitted, gMock will accept any parameters, which allows +// tests to be written that don't need to encode the number of method +// parameter. This technique may only be used for non-overloaded methods. +// +// // These are the same: +// ON_CALL(mock, NoArgsMethod()).WillByDefault(...); +// ON_CALL(mock, NoArgsMethod).WillByDefault(...); +// +// // As are these: +// ON_CALL(mock, TwoArgsMethod(_, _)).WillByDefault(...); +// ON_CALL(mock, TwoArgsMethod).WillByDefault(...); +// +// // Can also specify args if you want, of course: +// ON_CALL(mock, TwoArgsMethod(_, 45)).WillByDefault(...); +// +// // Overloads work as long as you specify parameters: +// ON_CALL(mock, OverloadedMethod(_)).WillByDefault(...); +// ON_CALL(mock, OverloadedMethod(_, _)).WillByDefault(...); +// +// // Oops! Which overload did you want? +// ON_CALL(mock, OverloadedMethod).WillByDefault(...); +// => ERROR: call to member function 'gmock_OverloadedMethod' is ambiguous +// +// How this works: The mock class uses two overloads of the gmock_Method +// expectation setter method plus an operator() overload on the MockSpec object. +// In the matcher list form, the macro expands to: +// +// // This statement: +// ON_CALL(mock, TwoArgsMethod(_, 45))... +// +// // ...expands to: +// mock.gmock_TwoArgsMethod(_, 45)(WithoutMatchers(), nullptr)... +// |-------------v---------------||------------v-------------| +// invokes first overload swallowed by operator() +// +// // ...which is essentially: +// mock.gmock_TwoArgsMethod(_, 45)... +// +// Whereas the form without a matcher list: +// +// // This statement: +// ON_CALL(mock, TwoArgsMethod)... +// +// // ...expands to: +// mock.gmock_TwoArgsMethod(WithoutMatchers(), nullptr)... +// |-----------------------v--------------------------| +// invokes second overload +// +// // ...which is essentially: +// mock.gmock_TwoArgsMethod(_, _)... +// +// The WithoutMatchers() argument is used to disambiguate overloads and to +// block the caller from accidentally invoking the second overload directly. The +// second argument is an internal type derived from the method signature. The +// failure to disambiguate two overloads of this method in the ON_CALL statement +// is how we block callers from setting expectations on overloaded methods. +#define GMOCK_ON_CALL_IMPL_(mock_expr, Setter, call) \ + ((mock_expr).gmock_##call)(::testing::internal::GetWithoutMatchers(), \ + nullptr) \ + .Setter(__FILE__, __LINE__, #mock_expr, #call) + +#define ON_CALL(obj, call) \ + GMOCK_ON_CALL_IMPL_(obj, InternalDefaultActionSetAt, call) + +#define EXPECT_CALL(obj, call) \ + GMOCK_ON_CALL_IMPL_(obj, InternalExpectedAt, call) + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_SPEC_BUILDERS_H_ + +namespace testing { +namespace internal { +template <typename T> +using identity_t = T; + +template <typename Pattern> +struct ThisRefAdjuster { + template <typename T> + using AdjustT = typename std::conditional< + std::is_const<typename std::remove_reference<Pattern>::type>::value, + typename std::conditional<std::is_lvalue_reference<Pattern>::value, + const T&, const T&&>::type, + typename std::conditional<std::is_lvalue_reference<Pattern>::value, T&, + T&&>::type>::type; + + template <typename MockType> + static AdjustT<MockType> Adjust(const MockType& mock) { + return static_cast<AdjustT<MockType>>(const_cast<MockType&>(mock)); + } +}; + +} // namespace internal + +// The style guide prohibits "using" statements in a namespace scope +// inside a header file. However, the FunctionMocker class template +// is meant to be defined in the ::testing namespace. The following +// line is just a trick for working around a bug in MSVC 8.0, which +// cannot handle it if we define FunctionMocker in ::testing. +using internal::FunctionMocker; +} // namespace testing + +#define MOCK_METHOD(...) \ + GMOCK_PP_VARIADIC_CALL(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_ARG_, __VA_ARGS__) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_ARG_1(...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_WRONG_ARITY(__VA_ARGS__) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_ARG_2(...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_WRONG_ARITY(__VA_ARGS__) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_ARG_3(_Ret, _MethodName, _Args) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_ARG_4(_Ret, _MethodName, _Args, ()) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_ARG_4(_Ret, _MethodName, _Args, _Spec) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_PARENTHESIS(_Args); \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_PARENTHESIS(_Spec); \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_VALID_SIGNATURE( \ + GMOCK_PP_NARG0 _Args, GMOCK_INTERNAL_SIGNATURE(_Ret, _Args)); \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_VALID_SPEC(_Spec) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_IMPL( \ + GMOCK_PP_NARG0 _Args, _MethodName, GMOCK_INTERNAL_HAS_CONST(_Spec), \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_HAS_OVERRIDE(_Spec), GMOCK_INTERNAL_HAS_FINAL(_Spec), \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_NOEXCEPT_SPEC(_Spec), \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_CALLTYPE(_Spec), GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_REF_SPEC(_Spec), \ + (GMOCK_INTERNAL_SIGNATURE(_Ret, _Args))) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_ARG_5(...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_WRONG_ARITY(__VA_ARGS__) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_ARG_6(...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_WRONG_ARITY(__VA_ARGS__) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_ARG_7(...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_WRONG_ARITY(__VA_ARGS__) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_WRONG_ARITY(...) \ + static_assert( \ + false, \ + "MOCK_METHOD must be called with 3 or 4 arguments. _Ret, " \ + "_MethodName, _Args and optionally _Spec. _Args and _Spec must be " \ + "enclosed in parentheses. If _Ret is a type with unprotected commas, " \ + "it must also be enclosed in parentheses.") + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_PARENTHESIS(_Tuple) \ + static_assert( \ + GMOCK_PP_IS_ENCLOSED_PARENS(_Tuple), \ + GMOCK_PP_STRINGIZE(_Tuple) " should be enclosed in parentheses.") + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_VALID_SIGNATURE(_N, ...) \ + static_assert( \ + std::is_function<__VA_ARGS__>::value, \ + "Signature must be a function type, maybe return type contains " \ + "unprotected comma."); \ + static_assert( \ + ::testing::tuple_size<typename ::testing::internal::Function< \ + __VA_ARGS__>::ArgumentTuple>::value == _N, \ + "This method does not take " GMOCK_PP_STRINGIZE( \ + _N) " arguments. Parenthesize all types with unprotected commas.") + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_VALID_SPEC(_Spec) \ + GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_VALID_SPEC_ELEMENT, ~, _Spec) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_IMPL(_N, _MethodName, _Constness, \ + _Override, _Final, _NoexceptSpec, \ + _CallType, _RefSpec, _Signature) \ + typename ::testing::internal::Function<GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS( \ + _Signature)>::Result \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_EXPAND(_CallType) \ + _MethodName(GMOCK_PP_REPEAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_PARAMETER, _Signature, _N)) \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(_Constness, const, ) _RefSpec _NoexceptSpec \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(_Override, override, ) GMOCK_PP_IF(_Final, final, ) { \ + GMOCK_MOCKER_(_N, _Constness, _MethodName) \ + .SetOwnerAndName(this, #_MethodName); \ + return GMOCK_MOCKER_(_N, _Constness, _MethodName) \ + .Invoke(GMOCK_PP_REPEAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_FORWARD_ARG, _Signature, _N)); \ + } \ + ::testing::MockSpec<GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(_Signature)> gmock_##_MethodName( \ + GMOCK_PP_REPEAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_PARAMETER, _Signature, _N)) \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(_Constness, const, ) _RefSpec { \ + GMOCK_MOCKER_(_N, _Constness, _MethodName).RegisterOwner(this); \ + return GMOCK_MOCKER_(_N, _Constness, _MethodName) \ + .With(GMOCK_PP_REPEAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_ARGUMENT, , _N)); \ + } \ + ::testing::MockSpec<GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(_Signature)> gmock_##_MethodName( \ + const ::testing::internal::WithoutMatchers&, \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(_Constness, const, )::testing::internal::Function< \ + GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(_Signature)>*) const _RefSpec _NoexceptSpec { \ + return ::testing::internal::ThisRefAdjuster<GMOCK_PP_IF( \ + _Constness, const, ) int _RefSpec>::Adjust(*this) \ + .gmock_##_MethodName(GMOCK_PP_REPEAT( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_A_MATCHER_ARGUMENT, _Signature, _N)); \ + } \ + mutable ::testing::FunctionMocker<GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(_Signature)> \ + GMOCK_MOCKER_(_N, _Constness, _MethodName) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_EXPAND(...) __VA_ARGS__ + +// Five Valid modifiers. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_HAS_CONST(_Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_CONST, ~, _Tuple)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_HAS_OVERRIDE(_Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA( \ + GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_OVERRIDE, ~, _Tuple)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_HAS_FINAL(_Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_FINAL, ~, _Tuple)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_NOEXCEPT_SPEC(_Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_NOEXCEPT_SPEC_IF_NOEXCEPT, ~, _Tuple) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_NOEXCEPT_SPEC_IF_NOEXCEPT(_i, _, _elem) \ + GMOCK_PP_IF( \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_NOEXCEPT(_i, _, _elem)), \ + _elem, ) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_REF_SPEC(_Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_REF_SPEC_IF_REF, ~, _Tuple) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_REF_SPEC_IF_REF(_i, _, _elem) \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_REF(_i, _, _elem)), \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_UNPACK_, _elem), ) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_CALLTYPE(_Tuple) \ + GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_CALLTYPE_IMPL, ~, _Tuple) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_VALID_SPEC_ELEMENT(_i, _, _elem) \ + static_assert( \ + (GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_CONST(_i, _, _elem)) + \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_OVERRIDE(_i, _, _elem)) + \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_FINAL(_i, _, _elem)) + \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_NOEXCEPT(_i, _, _elem)) + \ + GMOCK_PP_HAS_COMMA(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_REF(_i, _, _elem)) + \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_IS_CALLTYPE(_elem)) == 1, \ + GMOCK_PP_STRINGIZE( \ + _elem) " cannot be recognized as a valid specification modifier."); + +// Modifiers implementation. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_CONST(_i, _, _elem) \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_CONST_I_, _elem) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_CONST_I_const , + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_OVERRIDE(_i, _, _elem) \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_OVERRIDE_I_, _elem) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_OVERRIDE_I_override , + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_FINAL(_i, _, _elem) \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_FINAL_I_, _elem) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_FINAL_I_final , + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_NOEXCEPT(_i, _, _elem) \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_NOEXCEPT_I_, _elem) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_NOEXCEPT_I_noexcept , + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_REF(_i, _, _elem) \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_REF_I_, _elem) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DETECT_REF_I_ref , + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_UNPACK_ref(x) x + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_CALLTYPE_IMPL(_i, _, _elem) \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(GMOCK_INTERNAL_IS_CALLTYPE(_elem), \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_VALUE_CALLTYPE, GMOCK_PP_EMPTY) \ + (_elem) + +// TODO(iserna): GMOCK_INTERNAL_IS_CALLTYPE and +// GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_VALUE_CALLTYPE needed more expansions to work on windows +// maybe they can be simplified somehow. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_IS_CALLTYPE(_arg) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_IS_CALLTYPE_I( \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_IS_CALLTYPE_HELPER_, _arg)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_IS_CALLTYPE_I(_arg) GMOCK_PP_IS_ENCLOSED_PARENS(_arg) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_VALUE_CALLTYPE(_arg) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_VALUE_CALLTYPE_I( \ + GMOCK_PP_CAT(GMOCK_INTERNAL_IS_CALLTYPE_HELPER_, _arg)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_VALUE_CALLTYPE_I(_arg) \ + GMOCK_PP_IDENTITY _arg + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_IS_CALLTYPE_HELPER_Calltype + +// Note: The use of `identity_t` here allows _Ret to represent return types that +// would normally need to be specified in a different way. For example, a method +// returning a function pointer must be written as +// +// fn_ptr_return_t (*method(method_args_t...))(fn_ptr_args_t...) +// +// But we only support placing the return type at the beginning. To handle this, +// we wrap all calls in identity_t, so that a declaration will be expanded to +// +// identity_t<fn_ptr_return_t (*)(fn_ptr_args_t...)> method(method_args_t...) +// +// This allows us to work around the syntactic oddities of function/method +// types. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_SIGNATURE(_Ret, _Args) \ + ::testing::internal::identity_t<GMOCK_PP_IF(GMOCK_PP_IS_BEGIN_PARENS(_Ret), \ + GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS, \ + GMOCK_PP_IDENTITY)(_Ret)>( \ + GMOCK_PP_FOR_EACH(GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_TYPE, _, _Args)) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_GET_TYPE(_i, _, _elem) \ + GMOCK_PP_COMMA_IF(_i) \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(GMOCK_PP_IS_BEGIN_PARENS(_elem), GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS, \ + GMOCK_PP_IDENTITY) \ + (_elem) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_PARAMETER(_i, _Signature, _) \ + GMOCK_PP_COMMA_IF(_i) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ARG_O(_i, GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(_Signature)) \ + gmock_a##_i + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_FORWARD_ARG(_i, _Signature, _) \ + GMOCK_PP_COMMA_IF(_i) \ + ::std::forward<GMOCK_INTERNAL_ARG_O( \ + _i, GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(_Signature))>(gmock_a##_i) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_PARAMETER(_i, _Signature, _) \ + GMOCK_PP_COMMA_IF(_i) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_O(_i, GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(_Signature)) \ + gmock_a##_i + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_ARGUMENT(_i, _1, _2) \ + GMOCK_PP_COMMA_IF(_i) \ + gmock_a##_i + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_A_MATCHER_ARGUMENT(_i, _Signature, _) \ + GMOCK_PP_COMMA_IF(_i) \ + ::testing::A<GMOCK_INTERNAL_ARG_O(_i, GMOCK_PP_REMOVE_PARENS(_Signature))>() + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_ARG_O(_i, ...) \ + typename ::testing::internal::Function<__VA_ARGS__>::template Arg<_i>::type + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MATCHER_O(_i, ...) \ + const ::testing::Matcher<typename ::testing::internal::Function< \ + __VA_ARGS__>::template Arg<_i>::type>& + +#define MOCK_METHOD0(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 0, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD1(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 1, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD2(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 2, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD3(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 3, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD4(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 4, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD5(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 5, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD6(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 6, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD7(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 7, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD8(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 8, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD9(m, ...) GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 9, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD10(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, , m, 10, __VA_ARGS__) + +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD0(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 0, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD1(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 1, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD2(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 2, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD3(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 3, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD4(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 4, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD5(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 5, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD6(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 6, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD7(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 7, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD8(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 8, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD9(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 9, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD10(m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, , m, 10, __VA_ARGS__) + +#define MOCK_METHOD0_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD0(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD1_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD1(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD2_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD2(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD3_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD3(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD4_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD4(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD5_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD5(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD6_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD6(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD7_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD7(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD8_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD8(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD9_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD9(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD10_T(m, ...) MOCK_METHOD10(m, __VA_ARGS__) + +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD0_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD0(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD1_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD1(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD2_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD2(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD3_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD3(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD4_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD4(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD5_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD5(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD6_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD6(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD7_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD7(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD8_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD8(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD9_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD9(m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD10_T(m, ...) MOCK_CONST_METHOD10(m, __VA_ARGS__) + +#define MOCK_METHOD0_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 0, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD1_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 1, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD2_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 2, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD3_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 3, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD4_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 4, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD5_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 5, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD6_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 6, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD7_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 7, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD8_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 8, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD9_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 9, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD10_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(, ct, m, 10, __VA_ARGS__) + +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD0_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 0, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD1_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 1, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD2_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 2, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD3_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 3, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD4_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 4, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD5_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 5, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD6_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 6, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD7_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 7, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD8_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 8, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD9_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 9, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD10_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(const, ct, m, 10, __VA_ARGS__) + +#define MOCK_METHOD0_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD0_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD1_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD1_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD2_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD2_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD3_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD3_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD4_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD4_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD5_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD5_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD6_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD6_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD7_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD7_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD8_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD8_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD9_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD9_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_METHOD10_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_METHOD10_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) + +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD0_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD0_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD1_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD1_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD2_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD2_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD3_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD3_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD4_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD4_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD5_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD5_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD6_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD6_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD7_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD7_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD8_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD8_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD9_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD9_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) +#define MOCK_CONST_METHOD10_T_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, ...) \ + MOCK_CONST_METHOD10_WITH_CALLTYPE(ct, m, __VA_ARGS__) + +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHODN(constness, ct, Method, args_num, ...) \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_ASSERT_VALID_SIGNATURE( \ + args_num, ::testing::internal::identity_t<__VA_ARGS__>); \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_MOCK_METHOD_IMPL( \ + args_num, Method, GMOCK_PP_NARG0(constness), 0, 0, , ct, , \ + (::testing::internal::identity_t<__VA_ARGS__>)) + +#define GMOCK_MOCKER_(arity, constness, Method) \ + GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gmock##constness##arity##_##Method##_, __LINE__) + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_GMOCK_FUNCTION_MOCKER_H_ +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. +// +// This file implements some commonly used variadic actions. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_ACTIONS_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_ACTIONS_H_ + +#include <memory> +#include <utility> + + +// Include any custom callback actions added by the local installation. +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GMOCK_GENERATED_ACTIONS_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GMOCK_GENERATED_ACTIONS_H_ + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GMOCK_GENERATED_ACTIONS_H_ + +// Sometimes you want to give an action explicit template parameters +// that cannot be inferred from its value parameters. ACTION() and +// ACTION_P*() don't support that. ACTION_TEMPLATE() remedies that +// and can be viewed as an extension to ACTION() and ACTION_P*(). +// +// The syntax: +// +// ACTION_TEMPLATE(ActionName, +// HAS_m_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind1, name1, ..., kind_m, name_m), +// AND_n_VALUE_PARAMS(p1, ..., p_n)) { statements; } +// +// defines an action template that takes m explicit template +// parameters and n value parameters. name_i is the name of the i-th +// template parameter, and kind_i specifies whether it's a typename, +// an integral constant, or a template. p_i is the name of the i-th +// value parameter. +// +// Example: +// +// // DuplicateArg<k, T>(output) converts the k-th argument of the mock +// // function to type T and copies it to *output. +// ACTION_TEMPLATE(DuplicateArg, +// HAS_2_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(int, k, typename, T), +// AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(output)) { +// *output = T(::std::get<k>(args)); +// } +// ... +// int n; +// EXPECT_CALL(mock, Foo(_, _)) +// .WillOnce(DuplicateArg<1, unsigned char>(&n)); +// +// To create an instance of an action template, write: +// +// ActionName<t1, ..., t_m>(v1, ..., v_n) +// +// where the ts are the template arguments and the vs are the value +// arguments. The value argument types are inferred by the compiler. +// If you want to explicitly specify the value argument types, you can +// provide additional template arguments: +// +// ActionName<t1, ..., t_m, u1, ..., u_k>(v1, ..., v_n) +// +// where u_i is the desired type of v_i. +// +// ACTION_TEMPLATE and ACTION/ACTION_P* can be overloaded on the +// number of value parameters, but not on the number of template +// parameters. Without the restriction, the meaning of the following +// is unclear: +// +// OverloadedAction<int, bool>(x); +// +// Are we using a single-template-parameter action where 'bool' refers +// to the type of x, or are we using a two-template-parameter action +// where the compiler is asked to infer the type of x? +// +// Implementation notes: +// +// GMOCK_INTERNAL_*_HAS_m_TEMPLATE_PARAMS and +// GMOCK_INTERNAL_*_AND_n_VALUE_PARAMS are internal macros for +// implementing ACTION_TEMPLATE. The main trick we use is to create +// new macro invocations when expanding a macro. For example, we have +// +// #define ACTION_TEMPLATE(name, template_params, value_params) +// ... GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##template_params ... +// +// which causes ACTION_TEMPLATE(..., HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T), ...) +// to expand to +// +// ... GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(typename, T) ... +// +// Since GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS is a macro, the +// preprocessor will continue to expand it to +// +// ... typename T ... +// +// This technique conforms to the C++ standard and is portable. It +// allows us to implement action templates using O(N) code, where N is +// the maximum number of template/value parameters supported. Without +// using it, we'd have to devote O(N^2) amount of code to implement all +// combinations of m and n. + +// Declares the template parameters. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0) kind0 name0 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_2_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, \ + name1) kind0 name0, kind1 name1 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_3_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_4_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2, \ + kind3 name3 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_5_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, \ + kind2 name2, kind3 name3, kind4 name4 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_6_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5) kind0 name0, \ + kind1 name1, kind2 name2, kind3 name3, kind4 name4, kind5 name5 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_7_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, \ + name6) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2, kind3 name3, kind4 name4, \ + kind5 name5, kind6 name6 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_8_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, name6, \ + kind7, name7) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2, kind3 name3, \ + kind4 name4, kind5 name5, kind6 name6, kind7 name7 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_9_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, name6, \ + kind7, name7, kind8, name8) kind0 name0, kind1 name1, kind2 name2, \ + kind3 name3, kind4 name4, kind5 name5, kind6 name6, kind7 name7, \ + kind8 name8 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_HAS_10_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, \ + name1, kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, \ + name6, kind7, name7, kind8, name8, kind9, name9) kind0 name0, \ + kind1 name1, kind2 name2, kind3 name3, kind4 name4, kind5 name5, \ + kind6 name6, kind7 name7, kind8 name8, kind9 name9 + +// Lists the template parameters. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_1_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0) name0 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_2_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, \ + name1) name0, name1 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_3_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2) name0, name1, name2 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_4_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3) name0, name1, name2, name3 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_5_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4) name0, name1, name2, name3, \ + name4 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_6_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5) name0, name1, \ + name2, name3, name4, name5 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_7_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, \ + name6) name0, name1, name2, name3, name4, name5, name6 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_8_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, name6, \ + kind7, name7) name0, name1, name2, name3, name4, name5, name6, name7 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_9_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, name1, \ + kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, name6, \ + kind7, name7, kind8, name8) name0, name1, name2, name3, name4, name5, \ + name6, name7, name8 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_HAS_10_TEMPLATE_PARAMS(kind0, name0, kind1, \ + name1, kind2, name2, kind3, name3, kind4, name4, kind5, name5, kind6, \ + name6, kind7, name7, kind8, name8, kind9, name9) name0, name1, name2, \ + name3, name4, name5, name6, name7, name8, name9 + +// Declares the types of value parameters. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) , typename p0##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) , \ + typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) , \ + typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) , \ + typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ + typename p3##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4) , \ + typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ + typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5) , \ + typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ + typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6) , typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ + typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ + typename p6##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6, p7) , typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ + typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ + typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6, p7, p8) , typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, typename p2##_type, \ + typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, typename p5##_type, \ + typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, typename p8##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6, p7, p8, p9) , typename p0##_type, typename p1##_type, \ + typename p2##_type, typename p3##_type, typename p4##_type, \ + typename p5##_type, typename p6##_type, typename p7##_type, \ + typename p8##_type, typename p9##_type + +// Initializes the value parameters. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS()\ + () +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)), \ + p1(::std::move(gmock_p1)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, \ + p2##_type gmock_p2) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)), \ + p1(::std::move(gmock_p1)), p2(::std::move(gmock_p2)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ + p3##_type gmock_p3) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)), \ + p1(::std::move(gmock_p1)), p2(::std::move(gmock_p2)), \ + p3(::std::move(gmock_p3)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ + p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)), \ + p1(::std::move(gmock_p1)), p2(::std::move(gmock_p2)), \ + p3(::std::move(gmock_p3)), p4(::std::move(gmock_p4)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ + p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, \ + p5##_type gmock_p5) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)), \ + p1(::std::move(gmock_p1)), p2(::std::move(gmock_p2)), \ + p3(::std::move(gmock_p3)), p4(::std::move(gmock_p4)), \ + p5(::std::move(gmock_p5)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ + p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ + p6##_type gmock_p6) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)), \ + p1(::std::move(gmock_p1)), p2(::std::move(gmock_p2)), \ + p3(::std::move(gmock_p3)), p4(::std::move(gmock_p4)), \ + p5(::std::move(gmock_p5)), p6(::std::move(gmock_p6)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ + p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ + p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)), \ + p1(::std::move(gmock_p1)), p2(::std::move(gmock_p2)), \ + p3(::std::move(gmock_p3)), p4(::std::move(gmock_p4)), \ + p5(::std::move(gmock_p5)), p6(::std::move(gmock_p6)), \ + p7(::std::move(gmock_p7)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ + p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ + p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, \ + p8##_type gmock_p8) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)), \ + p1(::std::move(gmock_p1)), p2(::std::move(gmock_p2)), \ + p3(::std::move(gmock_p3)), p4(::std::move(gmock_p4)), \ + p5(::std::move(gmock_p5)), p6(::std::move(gmock_p6)), \ + p7(::std::move(gmock_p7)), p8(::std::move(gmock_p8)) +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8, p9)\ + (p0##_type gmock_p0, p1##_type gmock_p1, p2##_type gmock_p2, \ + p3##_type gmock_p3, p4##_type gmock_p4, p5##_type gmock_p5, \ + p6##_type gmock_p6, p7##_type gmock_p7, p8##_type gmock_p8, \ + p9##_type gmock_p9) : p0(::std::move(gmock_p0)), \ + p1(::std::move(gmock_p1)), p2(::std::move(gmock_p2)), \ + p3(::std::move(gmock_p3)), p4(::std::move(gmock_p4)), \ + p5(::std::move(gmock_p5)), p6(::std::move(gmock_p6)), \ + p7(::std::move(gmock_p7)), p8(::std::move(gmock_p8)), \ + p9(::std::move(gmock_p9)) + +// Defines the copy constructor +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() \ + {} // Avoid https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=82134 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(...) = default; + +// Declares the fields for storing the value parameters. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) p0##_type p0; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) p0##_type p0; \ + p1##_type p1; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) p0##_type p0; \ + p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) p0##_type p0; \ + p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, \ + p4) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; p4##_type p4; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, \ + p5) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; p4##_type p4; \ + p5##_type p5; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; p4##_type p4; \ + p5##_type p5; p6##_type p6; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; p4##_type p4; \ + p5##_type p5; p6##_type p6; p7##_type p7; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; \ + p4##_type p4; p5##_type p5; p6##_type p6; p7##_type p7; p8##_type p8; +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8, p9) p0##_type p0; p1##_type p1; p2##_type p2; p3##_type p3; \ + p4##_type p4; p5##_type p5; p6##_type p6; p7##_type p7; p8##_type p8; \ + p9##_type p9; + +// Lists the value parameters. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) p0 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) p0, p1 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) p0, p1, p2 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) p0, p1, p2, p3 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4) p0, p1, \ + p2, p3, p4 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5) p0, \ + p1, p2, p3, p4, p5 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6) p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7) p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8) p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8, p9) p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9 + +// Lists the value parameter types. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) , p0##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) , p0##_type, \ + p1##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) , p0##_type, \ + p1##_type, p2##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) , \ + p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4) , \ + p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5) , \ + p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, p5##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6) , p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, p5##_type, \ + p6##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6, p7) , p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ + p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6, p7, p8) , p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ + p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6, p7, p8, p9) , p0##_type, p1##_type, p2##_type, p3##_type, p4##_type, \ + p5##_type, p6##_type, p7##_type, p8##_type, p9##_type + +// Declares the value parameters. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) p0##_type p0 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) p0##_type p0, \ + p1##_type p1 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) p0##_type p0, \ + p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) p0##_type p0, \ + p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, \ + p4) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, \ + p5) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, \ + p5##_type p5 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, \ + p6) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, \ + p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, p4##_type p4, \ + p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ + p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7, p8##_type p8 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8, p9) p0##_type p0, p1##_type p1, p2##_type p2, p3##_type p3, \ + p4##_type p4, p5##_type p5, p6##_type p6, p7##_type p7, p8##_type p8, \ + p9##_type p9 + +// The suffix of the class template implementing the action template. +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_0_VALUE_PARAMS() +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_1_VALUE_PARAMS(p0) P +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_2_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1) P2 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_3_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2) P3 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_4_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3) P4 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_5_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4) P5 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_6_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5) P6 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_7_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6) P7 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_8_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7) P8 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_9_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8) P9 +#define GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_AND_10_VALUE_PARAMS(p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, \ + p7, p8, p9) P10 + +// The name of the class template implementing the action template. +#define GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)\ + GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(name##Action, GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_##value_params) + +#define ACTION_TEMPLATE(name, template_params, value_params) \ + template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##template_params \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_##value_params> \ + class GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params) { \ + public: \ + explicit GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##value_params) \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(GMOCK_PP_IS_EMPTY(GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_##value_params), \ + = default; , \ + : impl_(std::make_shared<gmock_Impl>( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##value_params)) { }) \ + GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)( \ + const GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)&) noexcept \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_##value_params \ + GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)( \ + GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)&&) noexcept \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_COPY_##value_params \ + template <typename F> \ + operator ::testing::Action<F>() const { \ + return GMOCK_PP_IF( \ + GMOCK_PP_IS_EMPTY(GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_##value_params), \ + (::testing::internal::MakeAction<F, gmock_Impl>()), \ + (::testing::internal::MakeAction<F>(impl_))); \ + } \ + private: \ + class gmock_Impl { \ + public: \ + explicit gmock_Impl GMOCK_INTERNAL_INIT_##value_params {} \ + template <typename function_type, typename return_type, \ + typename args_type, GMOCK_ACTION_TEMPLATE_ARGS_NAMES_> \ + return_type gmock_PerformImpl(GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_) const; \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DEFN_##value_params \ + }; \ + GMOCK_PP_IF(GMOCK_PP_IS_EMPTY(GMOCK_INTERNAL_COUNT_##value_params), \ + , std::shared_ptr<const gmock_Impl> impl_;) \ + }; \ + template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##template_params \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_##value_params> \ + GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)< \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##template_params \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_##value_params> name( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##value_params) GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_; \ + template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##template_params \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_##value_params> \ + inline GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)< \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##template_params \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_##value_params> name( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##value_params) { \ + return GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)< \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##template_params \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_##value_params>( \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##value_params); \ + } \ + template <GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_##template_params \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_DECL_TYPE_##value_params> \ + template <typename function_type, typename return_type, typename args_type, \ + GMOCK_ACTION_TEMPLATE_ARGS_NAMES_> \ + return_type GMOCK_ACTION_CLASS_(name, value_params)< \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_##template_params \ + GMOCK_INTERNAL_LIST_TYPE_##value_params>::gmock_Impl::gmock_PerformImpl( \ + GMOCK_ACTION_ARG_TYPES_AND_NAMES_UNUSED_) const + +namespace testing { + +// The ACTION*() macros trigger warning C4100 (unreferenced formal +// parameter) in MSVC with -W4. Unfortunately they cannot be fixed in +// the macro definition, as the warnings are generated when the macro +// is expanded and macro expansion cannot contain #pragma. Therefore +// we suppress them here. +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(push) +# pragma warning(disable:4100) +#endif + +namespace internal { + +// internal::InvokeArgument - a helper for InvokeArgument action. +// The basic overloads are provided here for generic functors. +// Overloads for other custom-callables are provided in the +// internal/custom/gmock-generated-actions.h header. +template <typename F, typename... Args> +auto InvokeArgument(F f, Args... args) -> decltype(f(args...)) { + return f(args...); +} + +template <std::size_t index, typename... Params> +struct InvokeArgumentAction { + template <typename... Args> + auto operator()(Args&&... args) const -> decltype(internal::InvokeArgument( + std::get<index>(std::forward_as_tuple(std::forward<Args>(args)...)), + std::declval<const Params&>()...)) { + internal::FlatTuple<Args&&...> args_tuple(FlatTupleConstructTag{}, + std::forward<Args>(args)...); + return params.Apply([&](const Params&... unpacked_params) { + auto&& callable = args_tuple.template Get<index>(); + return internal::InvokeArgument( + std::forward<decltype(callable)>(callable), unpacked_params...); + }); + } + + internal::FlatTuple<Params...> params; +}; + +} // namespace internal + +// The InvokeArgument<N>(a1, a2, ..., a_k) action invokes the N-th +// (0-based) argument, which must be a k-ary callable, of the mock +// function, with arguments a1, a2, ..., a_k. +// +// Notes: +// +// 1. The arguments are passed by value by default. If you need to +// pass an argument by reference, wrap it inside std::ref(). For +// example, +// +// InvokeArgument<1>(5, string("Hello"), std::ref(foo)) +// +// passes 5 and string("Hello") by value, and passes foo by +// reference. +// +// 2. If the callable takes an argument by reference but std::ref() is +// not used, it will receive the reference to a copy of the value, +// instead of the original value. For example, when the 0-th +// argument of the mock function takes a const string&, the action +// +// InvokeArgument<0>(string("Hello")) +// +// makes a copy of the temporary string("Hello") object and passes a +// reference of the copy, instead of the original temporary object, +// to the callable. This makes it easy for a user to define an +// InvokeArgument action from temporary values and have it performed +// later. +template <std::size_t index, typename... Params> +internal::InvokeArgumentAction<index, typename std::decay<Params>::type...> +InvokeArgument(Params&&... params) { + return {internal::FlatTuple<typename std::decay<Params>::type...>( + internal::FlatTupleConstructTag{}, std::forward<Params>(params)...)}; +} + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(pop) +#endif + +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_ACTIONS_H_ +// Copyright 2013, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Google Mock - a framework for writing C++ mock classes. +// +// This file implements some matchers that depend on gmock-matchers.h. +// +// Note that tests are implemented in gmock-matchers_test.cc rather than +// gmock-more-matchers-test.cc. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_MATCHERS_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_MATCHERS_H_ + + +namespace testing { + +// Silence C4100 (unreferenced formal +// parameter) for MSVC +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(push) +# pragma warning(disable:4100) +#if (_MSC_VER == 1900) +// and silence C4800 (C4800: 'int *const ': forcing value +// to bool 'true' or 'false') for MSVC 14 +# pragma warning(disable:4800) + #endif +#endif + +// Defines a matcher that matches an empty container. The container must +// support both size() and empty(), which all STL-like containers provide. +MATCHER(IsEmpty, negation ? "isn't empty" : "is empty") { + if (arg.empty()) { + return true; + } + *result_listener << "whose size is " << arg.size(); + return false; +} + +// Define a matcher that matches a value that evaluates in boolean +// context to true. Useful for types that define "explicit operator +// bool" operators and so can't be compared for equality with true +// and false. +MATCHER(IsTrue, negation ? "is false" : "is true") { + return static_cast<bool>(arg); +} + +// Define a matcher that matches a value that evaluates in boolean +// context to false. Useful for types that define "explicit operator +// bool" operators and so can't be compared for equality with true +// and false. +MATCHER(IsFalse, negation ? "is true" : "is false") { + return !static_cast<bool>(arg); +} + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(pop) +#endif + + +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_MORE_MATCHERS_H_ +// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Implements class templates NiceMock, NaggyMock, and StrictMock. +// +// Given a mock class MockFoo that is created using Google Mock, +// NiceMock<MockFoo> is a subclass of MockFoo that allows +// uninteresting calls (i.e. calls to mock methods that have no +// EXPECT_CALL specs), NaggyMock<MockFoo> is a subclass of MockFoo +// that prints a warning when an uninteresting call occurs, and +// StrictMock<MockFoo> is a subclass of MockFoo that treats all +// uninteresting calls as errors. +// +// Currently a mock is naggy by default, so MockFoo and +// NaggyMock<MockFoo> behave like the same. However, we will soon +// switch the default behavior of mocks to be nice, as that in general +// leads to more maintainable tests. When that happens, MockFoo will +// stop behaving like NaggyMock<MockFoo> and start behaving like +// NiceMock<MockFoo>. +// +// NiceMock, NaggyMock, and StrictMock "inherit" the constructors of +// their respective base class. Therefore you can write +// NiceMock<MockFoo>(5, "a") to construct a nice mock where MockFoo +// has a constructor that accepts (int, const char*), for example. +// +// A known limitation is that NiceMock<MockFoo>, NaggyMock<MockFoo>, +// and StrictMock<MockFoo> only works for mock methods defined using +// the MOCK_METHOD* family of macros DIRECTLY in the MockFoo class. +// If a mock method is defined in a base class of MockFoo, the "nice" +// or "strict" modifier may not affect it, depending on the compiler. +// In particular, nesting NiceMock, NaggyMock, and StrictMock is NOT +// supported. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0002 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_NICE_STRICT_H_ +#define GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_NICE_STRICT_H_ + +#include <type_traits> + + +namespace testing { +template <class MockClass> +class NiceMock; +template <class MockClass> +class NaggyMock; +template <class MockClass> +class StrictMock; + +namespace internal { +template <typename T> +std::true_type StrictnessModifierProbe(const NiceMock<T>&); +template <typename T> +std::true_type StrictnessModifierProbe(const NaggyMock<T>&); +template <typename T> +std::true_type StrictnessModifierProbe(const StrictMock<T>&); +std::false_type StrictnessModifierProbe(...); + +template <typename T> +constexpr bool HasStrictnessModifier() { + return decltype(StrictnessModifierProbe(std::declval<const T&>()))::value; +} + +// Base classes that register and deregister with testing::Mock to alter the +// default behavior around uninteresting calls. Inheriting from one of these +// classes first and then MockClass ensures the MockClass constructor is run +// after registration, and that the MockClass destructor runs before +// deregistration. This guarantees that MockClass's constructor and destructor +// run with the same level of strictness as its instance methods. + +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW && \ + (defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(__clang__)) +// We need to mark these classes with this declspec to ensure that +// the empty base class optimization is performed. +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_EMPTY_BASE_CLASS __declspec(empty_bases) +#else +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_EMPTY_BASE_CLASS +#endif + +template <typename Base> +class NiceMockImpl { + public: + NiceMockImpl() { ::testing::Mock::AllowUninterestingCalls(this); } + + ~NiceMockImpl() { ::testing::Mock::UnregisterCallReaction(this); } +}; + +template <typename Base> +class NaggyMockImpl { + public: + NaggyMockImpl() { ::testing::Mock::WarnUninterestingCalls(this); } + + ~NaggyMockImpl() { ::testing::Mock::UnregisterCallReaction(this); } +}; + +template <typename Base> +class StrictMockImpl { + public: + StrictMockImpl() { ::testing::Mock::FailUninterestingCalls(this); } + + ~StrictMockImpl() { ::testing::Mock::UnregisterCallReaction(this); } +}; + +} // namespace internal + +template <class MockClass> +class GTEST_INTERNAL_EMPTY_BASE_CLASS NiceMock + : private internal::NiceMockImpl<MockClass>, + public MockClass { + public: + static_assert(!internal::HasStrictnessModifier<MockClass>(), + "Can't apply NiceMock to a class hierarchy that already has a " + "strictness modifier. See " + "https://google.github.io/googletest/" + "gmock_cook_book.html#NiceStrictNaggy"); + NiceMock() : MockClass() { + static_assert(sizeof(*this) == sizeof(MockClass), + "The impl subclass shouldn't introduce any padding"); + } + + // Ideally, we would inherit base class's constructors through a using + // declaration, which would preserve their visibility. However, many existing + // tests rely on the fact that current implementation reexports protected + // constructors as public. These tests would need to be cleaned up first. + + // Single argument constructor is special-cased so that it can be + // made explicit. + template <typename A> + explicit NiceMock(A&& arg) : MockClass(std::forward<A>(arg)) { + static_assert(sizeof(*this) == sizeof(MockClass), + "The impl subclass shouldn't introduce any padding"); + } + + template <typename TArg1, typename TArg2, typename... An> + NiceMock(TArg1&& arg1, TArg2&& arg2, An&&... args) + : MockClass(std::forward<TArg1>(arg1), std::forward<TArg2>(arg2), + std::forward<An>(args)...) { + static_assert(sizeof(*this) == sizeof(MockClass), + "The impl subclass shouldn't introduce any padding"); + } + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(NiceMock); +}; + +template <class MockClass> +class GTEST_INTERNAL_EMPTY_BASE_CLASS NaggyMock + : private internal::NaggyMockImpl<MockClass>, + public MockClass { + static_assert(!internal::HasStrictnessModifier<MockClass>(), + "Can't apply NaggyMock to a class hierarchy that already has a " + "strictness modifier. See " + "https://google.github.io/googletest/" + "gmock_cook_book.html#NiceStrictNaggy"); + + public: + NaggyMock() : MockClass() { + static_assert(sizeof(*this) == sizeof(MockClass), + "The impl subclass shouldn't introduce any padding"); + } + + // Ideally, we would inherit base class's constructors through a using + // declaration, which would preserve their visibility. However, many existing + // tests rely on the fact that current implementation reexports protected + // constructors as public. These tests would need to be cleaned up first. + + // Single argument constructor is special-cased so that it can be + // made explicit. + template <typename A> + explicit NaggyMock(A&& arg) : MockClass(std::forward<A>(arg)) { + static_assert(sizeof(*this) == sizeof(MockClass), + "The impl subclass shouldn't introduce any padding"); + } + + template <typename TArg1, typename TArg2, typename... An> + NaggyMock(TArg1&& arg1, TArg2&& arg2, An&&... args) + : MockClass(std::forward<TArg1>(arg1), std::forward<TArg2>(arg2), + std::forward<An>(args)...) { + static_assert(sizeof(*this) == sizeof(MockClass), + "The impl subclass shouldn't introduce any padding"); + } + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(NaggyMock); +}; + +template <class MockClass> +class GTEST_INTERNAL_EMPTY_BASE_CLASS StrictMock + : private internal::StrictMockImpl<MockClass>, + public MockClass { + public: + static_assert( + !internal::HasStrictnessModifier<MockClass>(), + "Can't apply StrictMock to a class hierarchy that already has a " + "strictness modifier. See " + "https://google.github.io/googletest/" + "gmock_cook_book.html#NiceStrictNaggy"); + StrictMock() : MockClass() { + static_assert(sizeof(*this) == sizeof(MockClass), + "The impl subclass shouldn't introduce any padding"); + } + + // Ideally, we would inherit base class's constructors through a using + // declaration, which would preserve their visibility. However, many existing + // tests rely on the fact that current implementation reexports protected + // constructors as public. These tests would need to be cleaned up first. + + // Single argument constructor is special-cased so that it can be + // made explicit. + template <typename A> + explicit StrictMock(A&& arg) : MockClass(std::forward<A>(arg)) { + static_assert(sizeof(*this) == sizeof(MockClass), + "The impl subclass shouldn't introduce any padding"); + } + + template <typename TArg1, typename TArg2, typename... An> + StrictMock(TArg1&& arg1, TArg2&& arg2, An&&... args) + : MockClass(std::forward<TArg1>(arg1), std::forward<TArg2>(arg2), + std::forward<An>(args)...) { + static_assert(sizeof(*this) == sizeof(MockClass), + "The impl subclass shouldn't introduce any padding"); + } + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(StrictMock); +}; + +#undef GTEST_INTERNAL_EMPTY_BASE_CLASS + +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_NICE_STRICT_H_ + +namespace testing { + +// Declares Google Mock flags that we want a user to use programmatically. +GMOCK_DECLARE_bool_(catch_leaked_mocks); +GMOCK_DECLARE_string_(verbose); +GMOCK_DECLARE_int32_(default_mock_behavior); + +// Initializes Google Mock. This must be called before running the +// tests. In particular, it parses the command line for the flags +// that Google Mock recognizes. Whenever a Google Mock flag is seen, +// it is removed from argv, and *argc is decremented. +// +// No value is returned. Instead, the Google Mock flag variables are +// updated. +// +// Since Google Test is needed for Google Mock to work, this function +// also initializes Google Test and parses its flags, if that hasn't +// been done. +GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleMock(int* argc, char** argv); + +// This overloaded version can be used in Windows programs compiled in +// UNICODE mode. +GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleMock(int* argc, wchar_t** argv); + +// This overloaded version can be used on Arduino/embedded platforms where +// there is no argc/argv. +GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleMock(); + +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLEMOCK_INCLUDE_GMOCK_GMOCK_H_ diff --git a/test/gtest/gtest.h b/test/gtest/gtest.h deleted file mode 100644 index 52d2ed6d..00000000 --- a/test/gtest/gtest.h +++ /dev/null @@ -1,20065 +0,0 @@ -// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) -// -// The Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) -// -// This header file defines the public API for Google Test. It should be -// included by any test program that uses Google Test. -// -// IMPORTANT NOTE: Due to limitation of the C++ language, we have to -// leave some internal implementation details in this header file. -// They are clearly marked by comments like this: -// -// // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -// -// Such code is NOT meant to be used by a user directly, and is subject -// to CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. Therefore DO NOT DEPEND ON IT in a user -// program! -// -// Acknowledgment: Google Test borrowed the idea of automatic test -// registration from Barthelemy Dagenais' (barthelemy@prologique.com) -// easyUnit framework. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_H_ - -#include <limits> -#include <ostream> -#include <vector> - -// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Authors: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan), eefacm@gmail.com (Sean Mcafee) -// -// The Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) -// -// This header file declares functions and macros used internally by -// Google Test. They are subject to change without notice. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_INTERNAL_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_INTERNAL_H_ - -// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Authors: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) -// -// Low-level types and utilities for porting Google Test to various -// platforms. They are subject to change without notice. DO NOT USE -// THEM IN USER CODE. -// -// This file is fundamental to Google Test. All other Google Test source -// files are expected to #include this. Therefore, it cannot #include -// any other Google Test header. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_H_ - -// The user can define the following macros in the build script to -// control Google Test's behavior. If the user doesn't define a macro -// in this list, Google Test will define it. -// -// GTEST_HAS_CLONE - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that clone(2) -// is/isn't available. -// GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that exceptions -// are enabled. -// GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that ::string -// is/isn't available (some systems define -// ::string, which is different to std::string). -// GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that ::string -// is/isn't available (some systems define -// ::wstring, which is different to std::wstring). -// GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that POSIX regular -// expressions are/aren't available. -// GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that <pthread.h> -// is/isn't available. -// GTEST_HAS_RTTI - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that RTTI is/isn't -// enabled. -// GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that -// std::wstring does/doesn't work (Google Test can -// be used where std::wstring is unavailable). -// GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE - Define it to 1/0 to indicate tr1::tuple -// is/isn't available. -// GTEST_HAS_SEH - Define it to 1/0 to indicate whether the -// compiler supports Microsoft's "Structured -// Exception Handling". -// GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION -// - Define it to 1/0 to indicate whether the -// platform supports I/O stream redirection using -// dup() and dup2(). -// GTEST_USE_OWN_TR1_TUPLE - Define it to 1/0 to indicate whether Google -// Test's own tr1 tuple implementation should be -// used. Unused when the user sets -// GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE to 0. -// GTEST_LANG_CXX11 - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that Google Test -// is building in C++11/C++98 mode. -// GTEST_LINKED_AS_SHARED_LIBRARY -// - Define to 1 when compiling tests that use -// Google Test as a shared library (known as -// DLL on Windows). -// GTEST_CREATE_SHARED_LIBRARY -// - Define to 1 when compiling Google Test itself -// as a shared library. - -// This header defines the following utilities: -// -// Macros indicating the current platform (defined to 1 if compiled on -// the given platform; otherwise undefined): -// GTEST_OS_AIX - IBM AIX -// GTEST_OS_CYGWIN - Cygwin -// GTEST_OS_HPUX - HP-UX -// GTEST_OS_LINUX - Linux -// GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID - Google Android -// GTEST_OS_MAC - Mac OS X -// GTEST_OS_IOS - iOS -// GTEST_OS_IOS_SIMULATOR - iOS simulator -// GTEST_OS_NACL - Google Native Client (NaCl) -// GTEST_OS_OPENBSD - OpenBSD -// GTEST_OS_QNX - QNX -// GTEST_OS_SOLARIS - Sun Solaris -// GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - Symbian -// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - Windows (Desktop, MinGW, or Mobile) -// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP - Windows Desktop -// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW - MinGW -// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - Windows Mobile -// GTEST_OS_ZOS - z/OS -// -// Among the platforms, Cygwin, Linux, Max OS X, and Windows have the -// most stable support. Since core members of the Google Test project -// don't have access to other platforms, support for them may be less -// stable. If you notice any problems on your platform, please notify -// googletestframework@googlegroups.com (patches for fixing them are -// even more welcome!). -// -// Note that it is possible that none of the GTEST_OS_* macros are defined. -// -// Macros indicating available Google Test features (defined to 1 if -// the corresponding feature is supported; otherwise undefined): -// GTEST_HAS_COMBINE - the Combine() function (for value-parameterized -// tests) -// GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - death tests -// GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - value-parameterized tests -// GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST - typed tests -// GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - type-parameterized tests -// GTEST_USES_POSIX_RE - enhanced POSIX regex is used. Do not confuse with -// GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE (see above) which users can -// define themselves. -// GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE - our own simple regex is used; -// the above two are mutually exclusive. -// GTEST_CAN_COMPARE_NULL - accepts untyped NULL in EXPECT_EQ(). -// -// Macros for basic C++ coding: -// GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ - for disabling a gcc warning. -// GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ - declares that a class' instances or a -// variable don't have to be used. -// GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_ - disables operator=. -// GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_ - disables copy ctor and operator=. -// GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_ - declares that a function's result must be used. -// -// Synchronization: -// Mutex, MutexLock, ThreadLocal, GetThreadCount() -// - synchronization primitives. -// GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE - defined to 1 to indicate that the above -// synchronization primitives have real implementations -// and Google Test is thread-safe; or 0 otherwise. -// -// Template meta programming: -// is_pointer - as in TR1; needed on Symbian and IBM XL C/C++ only. -// IteratorTraits - partial implementation of std::iterator_traits, which -// is not available in libCstd when compiled with Sun C++. -// -// Smart pointers: -// scoped_ptr - as in TR2. -// -// Regular expressions: -// RE - a simple regular expression class using the POSIX -// Extended Regular Expression syntax on UNIX-like -// platforms, or a reduced regular exception syntax on -// other platforms, including Windows. -// -// Logging: -// GTEST_LOG_() - logs messages at the specified severity level. -// LogToStderr() - directs all log messages to stderr. -// FlushInfoLog() - flushes informational log messages. -// -// Stdout and stderr capturing: -// CaptureStdout() - starts capturing stdout. -// GetCapturedStdout() - stops capturing stdout and returns the captured -// string. -// CaptureStderr() - starts capturing stderr. -// GetCapturedStderr() - stops capturing stderr and returns the captured -// string. -// -// Integer types: -// TypeWithSize - maps an integer to a int type. -// Int32, UInt32, Int64, UInt64, TimeInMillis -// - integers of known sizes. -// BiggestInt - the biggest signed integer type. -// -// Command-line utilities: -// GTEST_FLAG() - references a flag. -// GTEST_DECLARE_*() - declares a flag. -// GTEST_DEFINE_*() - defines a flag. -// GetInjectableArgvs() - returns the command line as a vector of strings. -// -// Environment variable utilities: -// GetEnv() - gets the value of an environment variable. -// BoolFromGTestEnv() - parses a bool environment variable. -// Int32FromGTestEnv() - parses an Int32 environment variable. -// StringFromGTestEnv() - parses a string environment variable. - -#include <ctype.h> // for isspace, etc -#include <stddef.h> // for ptrdiff_t -#include <stdlib.h> -#include <stdio.h> -#include <string.h> -#ifndef _WIN32_WCE -# include <sys/types.h> -# include <sys/stat.h> -#endif // !_WIN32_WCE - -#if defined __APPLE__ -# include <AvailabilityMacros.h> -# include <TargetConditionals.h> -#endif - -#include <iostream> // NOLINT -#include <sstream> // NOLINT -#include <string> // NOLINT - -#define GTEST_DEV_EMAIL_ "googletestframework@@googlegroups.com" -#define GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "gtest_" -#define GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_DASH_ "gtest-" -#define GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_UPPER_ "GTEST_" -#define GTEST_NAME_ "Google Test" -#define GTEST_PROJECT_URL_ "http://code.google.com/p/googletest/" - -// Determines the version of gcc that is used to compile this. -#ifdef __GNUC__ -// 40302 means version 4.3.2. -# define GTEST_GCC_VER_ \ - (__GNUC__*10000 + __GNUC_MINOR__*100 + __GNUC_PATCHLEVEL__) -#endif // __GNUC__ - -// Determines the platform on which Google Test is compiled. -#ifdef __CYGWIN__ -# define GTEST_OS_CYGWIN 1 -#elif defined __SYMBIAN32__ -# define GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN 1 -#elif defined _WIN32 -# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS 1 -# ifdef _WIN32_WCE -# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE 1 -# elif defined(__MINGW__) || defined(__MINGW32__) -# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW 1 -# else -# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP 1 -# endif // _WIN32_WCE -#elif defined __APPLE__ -# define GTEST_OS_MAC 1 -# if TARGET_OS_IPHONE -# define GTEST_OS_IOS 1 -# if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR -# define GTEST_OS_IOS_SIMULATOR 1 -# endif -# endif -#elif defined __linux__ -# define GTEST_OS_LINUX 1 -# if defined __ANDROID__ -# define GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID 1 -# endif -#elif defined __MVS__ -# define GTEST_OS_ZOS 1 -#elif defined(__sun) && defined(__SVR4) -# define GTEST_OS_SOLARIS 1 -#elif defined(_AIX) -# define GTEST_OS_AIX 1 -#elif defined(__hpux) -# define GTEST_OS_HPUX 1 -#elif defined __native_client__ -# define GTEST_OS_NACL 1 -#elif defined __OpenBSD__ -# define GTEST_OS_OPENBSD 1 -#elif defined __QNX__ -# define GTEST_OS_QNX 1 -#endif // __CYGWIN__ - -#ifndef GTEST_LANG_CXX11 -// gcc and clang define __GXX_EXPERIMENTAL_CXX0X__ when -// -std={c,gnu}++{0x,11} is passed. The C++11 standard specifies a -// value for __cplusplus, and recent versions of clang, gcc, and -// probably other compilers set that too in C++11 mode. -# if __GXX_EXPERIMENTAL_CXX0X__ || __cplusplus >= 201103L -// Compiling in at least C++11 mode. -# define GTEST_LANG_CXX11 1 -# else -# define GTEST_LANG_CXX11 0 -# endif -#endif - -// Brings in definitions for functions used in the testing::internal::posix -// namespace (read, write, close, chdir, isatty, stat). We do not currently -// use them on Windows Mobile. -#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -// This assumes that non-Windows OSes provide unistd.h. For OSes where this -// is not the case, we need to include headers that provide the functions -// mentioned above. -# include <unistd.h> -# include <strings.h> -#elif !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -# include <direct.h> -# include <io.h> -#endif - -#if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID -// Used to define __ANDROID_API__ matching the target NDK API level. -# include <android/api-level.h> // NOLINT -#endif - -// Defines this to true iff Google Test can use POSIX regular expressions. -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE -# if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID -// On Android, <regex.h> is only available starting with Gingerbread. -# define GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE (__ANDROID_API__ >= 9) -# else -# define GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE (!GTEST_OS_WINDOWS) -# endif -#endif - -#if GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE - -// On some platforms, <regex.h> needs someone to define size_t, and -// won't compile otherwise. We can #include it here as we already -// included <stdlib.h>, which is guaranteed to define size_t through -// <stddef.h>. -# include <regex.h> // NOLINT - -# define GTEST_USES_POSIX_RE 1 - -#elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - -// <regex.h> is not available on Windows. Use our own simple regex -// implementation instead. -# define GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE 1 - -#else - -// <regex.h> may not be available on this platform. Use our own -// simple regex implementation instead. -# define GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE 1 - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE - -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS -// The user didn't tell us whether exceptions are enabled, so we need -// to figure it out. -# if defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(__BORLANDC__) -// MSVC's and C++Builder's implementations of the STL use the _HAS_EXCEPTIONS -// macro to enable exceptions, so we'll do the same. -// Assumes that exceptions are enabled by default. -# ifndef _HAS_EXCEPTIONS -# define _HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 -# endif // _HAS_EXCEPTIONS -# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS _HAS_EXCEPTIONS -# elif defined(__GNUC__) && __EXCEPTIONS -// gcc defines __EXCEPTIONS to 1 iff exceptions are enabled. -# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 -# elif defined(__SUNPRO_CC) -// Sun Pro CC supports exceptions. However, there is no compile-time way of -// detecting whether they are enabled or not. Therefore, we assume that -// they are enabled unless the user tells us otherwise. -# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 -# elif defined(__IBMCPP__) && __EXCEPTIONS -// xlC defines __EXCEPTIONS to 1 iff exceptions are enabled. -# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 -# elif defined(__HP_aCC) -// Exception handling is in effect by default in HP aCC compiler. It has to -// be turned of by +noeh compiler option if desired. -# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 -# else -// For other compilers, we assume exceptions are disabled to be -// conservative. -# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 0 -# endif // defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(__BORLANDC__) -#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS - -#if !defined(GTEST_HAS_STD_STRING) -// Even though we don't use this macro any longer, we keep it in case -// some clients still depend on it. -# define GTEST_HAS_STD_STRING 1 -#elif !GTEST_HAS_STD_STRING -// The user told us that ::std::string isn't available. -# error "Google Test cannot be used where ::std::string isn't available." -#endif // !defined(GTEST_HAS_STD_STRING) - -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING -// The user didn't tell us whether ::string is available, so we need -// to figure it out. - -# define GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING 0 - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING - -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING -// The user didn't tell us whether ::std::wstring is available, so we need -// to figure it out. -// TODO(wan@google.com): uses autoconf to detect whether ::std::wstring -// is available. - -// Cygwin 1.7 and below doesn't support ::std::wstring. -// Solaris' libc++ doesn't support it either. Android has -// no support for it at least as recent as Froyo (2.2). -# define GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING \ - (!(GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID || GTEST_OS_CYGWIN || GTEST_OS_SOLARIS)) - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING - -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING -// The user didn't tell us whether ::wstring is available, so we need -// to figure it out. -# define GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING \ - (GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING && GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING) -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING - -// Determines whether RTTI is available. -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_RTTI -// The user didn't tell us whether RTTI is enabled, so we need to -// figure it out. - -# ifdef _MSC_VER - -# ifdef _CPPRTTI // MSVC defines this macro iff RTTI is enabled. -# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 1 -# else -# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 0 -# endif - -// Starting with version 4.3.2, gcc defines __GXX_RTTI iff RTTI is enabled. -# elif defined(__GNUC__) && (GTEST_GCC_VER_ >= 40302) - -# ifdef __GXX_RTTI -// When building against STLport with the Android NDK and with -// -frtti -fno-exceptions, the build fails at link time with undefined -// references to __cxa_bad_typeid. Note sure if STL or toolchain bug, -// so disable RTTI when detected. -# if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID && defined(_STLPORT_MAJOR) && \ - !defined(__EXCEPTIONS) -# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 0 -# else -# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 1 -# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID && __STLPORT_MAJOR && !__EXCEPTIONS -# else -# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 0 -# endif // __GXX_RTTI - -// Clang defines __GXX_RTTI starting with version 3.0, but its manual recommends -// using has_feature instead. has_feature(cxx_rtti) is supported since 2.7, the -// first version with C++ support. -# elif defined(__clang__) - -# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI __has_feature(cxx_rtti) - -// Starting with version 9.0 IBM Visual Age defines __RTTI_ALL__ to 1 if -// both the typeid and dynamic_cast features are present. -# elif defined(__IBMCPP__) && (__IBMCPP__ >= 900) - -# ifdef __RTTI_ALL__ -# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 1 -# else -# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 0 -# endif - -# else - -// For all other compilers, we assume RTTI is enabled. -# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 1 - -# endif // _MSC_VER - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI - -// It's this header's responsibility to #include <typeinfo> when RTTI -// is enabled. -#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI -# include <typeinfo> -#endif - -// Determines whether Google Test can use the pthreads library. -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD -// The user didn't tell us explicitly, so we assume pthreads support is -// available on Linux and Mac. -// -// To disable threading support in Google Test, add -DGTEST_HAS_PTHREAD=0 -// to your compiler flags. -# define GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD (GTEST_OS_LINUX || GTEST_OS_MAC || GTEST_OS_HPUX \ - || GTEST_OS_QNX) -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD - -#if GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD -// gtest-port.h guarantees to #include <pthread.h> when GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD is -// true. -# include <pthread.h> // NOLINT - -// For timespec and nanosleep, used below. -# include <time.h> // NOLINT -#endif - -// Determines whether Google Test can use tr1/tuple. You can define -// this macro to 0 to prevent Google Test from using tuple (any -// feature depending on tuple with be disabled in this mode). -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE -# if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID && defined(_STLPORT_MAJOR) -// STLport, provided with the Android NDK, has neither <tr1/tuple> or <tuple>. -# define GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE 0 -# else -// The user didn't tell us not to do it, so we assume it's OK. -# define GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE 1 -# endif -#endif // GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE - -// Determines whether Google Test's own tr1 tuple implementation -// should be used. -#ifndef GTEST_USE_OWN_TR1_TUPLE -// The user didn't tell us, so we need to figure it out. - -// We use our own TR1 tuple if we aren't sure the user has an -// implementation of it already. At this time, libstdc++ 4.0.0+ and -// MSVC 2010 are the only mainstream standard libraries that come -// with a TR1 tuple implementation. NVIDIA's CUDA NVCC compiler -// pretends to be GCC by defining __GNUC__ and friends, but cannot -// compile GCC's tuple implementation. MSVC 2008 (9.0) provides TR1 -// tuple in a 323 MB Feature Pack download, which we cannot assume the -// user has. QNX's QCC compiler is a modified GCC but it doesn't -// support TR1 tuple. libc++ only provides std::tuple, in C++11 mode, -// and it can be used with some compilers that define __GNUC__. -# if (defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__CUDACC__) && (GTEST_GCC_VER_ >= 40000) \ - && !GTEST_OS_QNX && !defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION)) || _MSC_VER >= 1600 -# define GTEST_ENV_HAS_TR1_TUPLE_ 1 -# endif - -// C++11 specifies that <tuple> provides std::tuple. Use that if gtest is used -// in C++11 mode and libstdc++ isn't very old (binaries targeting OS X 10.6 -// can build with clang but need to use gcc4.2's libstdc++). -# if GTEST_LANG_CXX11 && (!defined(__GLIBCXX__) || __GLIBCXX__ > 20110325) -# define GTEST_ENV_HAS_STD_TUPLE_ 1 -# endif - -# if GTEST_ENV_HAS_TR1_TUPLE_ || GTEST_ENV_HAS_STD_TUPLE_ -# define GTEST_USE_OWN_TR1_TUPLE 0 -# else -# define GTEST_USE_OWN_TR1_TUPLE 1 -# endif - -#endif // GTEST_USE_OWN_TR1_TUPLE - -// To avoid conditional compilation everywhere, we make it -// gtest-port.h's responsibility to #include the header implementing -// tr1/tuple. -#if GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE - -# if GTEST_USE_OWN_TR1_TUPLE -// This file was GENERATED by command: -// pump.py gtest-tuple.h.pump -// DO NOT EDIT BY HAND!!! - -// Copyright 2009 Google Inc. -// All Rights Reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Implements a subset of TR1 tuple needed by Google Test and Google Mock. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_TUPLE_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_TUPLE_H_ - -#include <utility> // For ::std::pair. - -// The compiler used in Symbian has a bug that prevents us from declaring the -// tuple template as a friend (it complains that tuple is redefined). This -// hack bypasses the bug by declaring the members that should otherwise be -// private as public. -// Sun Studio versions < 12 also have the above bug. -#if defined(__SYMBIAN32__) || (defined(__SUNPRO_CC) && __SUNPRO_CC < 0x590) -# define GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ public: -#else -# define GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ \ - template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(U)> friend class tuple; \ - private: -#endif - -// GTEST_n_TUPLE_(T) is the type of an n-tuple. -#define GTEST_0_TUPLE_(T) tuple<> -#define GTEST_1_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, void, void, void, void, void, void, \ - void, void, void> -#define GTEST_2_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, T##1, void, void, void, void, void, \ - void, void, void> -#define GTEST_3_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, T##1, T##2, void, void, void, void, \ - void, void, void> -#define GTEST_4_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, T##1, T##2, T##3, void, void, void, \ - void, void, void> -#define GTEST_5_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, T##1, T##2, T##3, T##4, void, void, \ - void, void, void> -#define GTEST_6_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, T##1, T##2, T##3, T##4, T##5, void, \ - void, void, void> -#define GTEST_7_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, T##1, T##2, T##3, T##4, T##5, T##6, \ - void, void, void> -#define GTEST_8_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, T##1, T##2, T##3, T##4, T##5, T##6, \ - T##7, void, void> -#define GTEST_9_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, T##1, T##2, T##3, T##4, T##5, T##6, \ - T##7, T##8, void> -#define GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) tuple<T##0, T##1, T##2, T##3, T##4, T##5, T##6, \ - T##7, T##8, T##9> - -// GTEST_n_TYPENAMES_(T) declares a list of n typenames. -#define GTEST_0_TYPENAMES_(T) -#define GTEST_1_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0 -#define GTEST_2_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0, typename T##1 -#define GTEST_3_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0, typename T##1, typename T##2 -#define GTEST_4_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0, typename T##1, typename T##2, \ - typename T##3 -#define GTEST_5_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0, typename T##1, typename T##2, \ - typename T##3, typename T##4 -#define GTEST_6_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0, typename T##1, typename T##2, \ - typename T##3, typename T##4, typename T##5 -#define GTEST_7_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0, typename T##1, typename T##2, \ - typename T##3, typename T##4, typename T##5, typename T##6 -#define GTEST_8_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0, typename T##1, typename T##2, \ - typename T##3, typename T##4, typename T##5, typename T##6, typename T##7 -#define GTEST_9_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0, typename T##1, typename T##2, \ - typename T##3, typename T##4, typename T##5, typename T##6, \ - typename T##7, typename T##8 -#define GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T) typename T##0, typename T##1, typename T##2, \ - typename T##3, typename T##4, typename T##5, typename T##6, \ - typename T##7, typename T##8, typename T##9 - -// In theory, defining stuff in the ::std namespace is undefined -// behavior. We can do this as we are playing the role of a standard -// library vendor. -namespace std { -namespace tr1 { - -template <typename T0 = void, typename T1 = void, typename T2 = void, - typename T3 = void, typename T4 = void, typename T5 = void, - typename T6 = void, typename T7 = void, typename T8 = void, - typename T9 = void> -class tuple; - -// Anything in namespace gtest_internal is Google Test's INTERNAL -// IMPLEMENTATION DETAIL and MUST NOT BE USED DIRECTLY in user code. -namespace gtest_internal { - -// ByRef<T>::type is T if T is a reference; otherwise it's const T&. -template <typename T> -struct ByRef { typedef const T& type; }; // NOLINT -template <typename T> -struct ByRef<T&> { typedef T& type; }; // NOLINT - -// A handy wrapper for ByRef. -#define GTEST_BY_REF_(T) typename ::std::tr1::gtest_internal::ByRef<T>::type - -// AddRef<T>::type is T if T is a reference; otherwise it's T&. This -// is the same as tr1::add_reference<T>::type. -template <typename T> -struct AddRef { typedef T& type; }; // NOLINT -template <typename T> -struct AddRef<T&> { typedef T& type; }; // NOLINT - -// A handy wrapper for AddRef. -#define GTEST_ADD_REF_(T) typename ::std::tr1::gtest_internal::AddRef<T>::type - -// A helper for implementing get<k>(). -template <int k> class Get; - -// A helper for implementing tuple_element<k, T>. kIndexValid is true -// iff k < the number of fields in tuple type T. -template <bool kIndexValid, int kIndex, class Tuple> -struct TupleElement; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 0, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T0 type; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 1, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T1 type; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 2, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T2 type; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 3, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T3 type; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 4, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T4 type; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 5, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T5 type; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 6, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T6 type; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 7, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T7 type; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 8, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T8 type; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct TupleElement<true, 9, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - typedef T9 type; -}; - -} // namespace gtest_internal - -template <> -class tuple<> { - public: - tuple() {} - tuple(const tuple& /* t */) {} - tuple& operator=(const tuple& /* t */) { return *this; } -}; - -template <GTEST_1_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class GTEST_1_TUPLE_(T) { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0) : f0_(f0) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_) {} - - template <GTEST_1_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_1_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_1_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_1_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_1_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_1_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; -}; - -template <GTEST_2_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class GTEST_2_TUPLE_(T) { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_(), f1_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0, GTEST_BY_REF_(T1) f1) : f0_(f0), - f1_(f1) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_) {} - - template <GTEST_2_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_2_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_) {} - template <typename U0, typename U1> - tuple(const ::std::pair<U0, U1>& p) : f0_(p.first), f1_(p.second) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_2_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_2_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - template <typename U0, typename U1> - tuple& operator=(const ::std::pair<U0, U1>& p) { - f0_ = p.first; - f1_ = p.second; - return *this; - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_2_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_2_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - f1_ = t.f1_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; - T1 f1_; -}; - -template <GTEST_3_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class GTEST_3_TUPLE_(T) { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_(), f1_(), f2_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0, GTEST_BY_REF_(T1) f1, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T2) f2) : f0_(f0), f1_(f1), f2_(f2) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_) {} - - template <GTEST_3_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_3_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_3_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_3_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_3_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_3_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - f1_ = t.f1_; - f2_ = t.f2_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; - T1 f1_; - T2 f2_; -}; - -template <GTEST_4_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class GTEST_4_TUPLE_(T) { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_(), f1_(), f2_(), f3_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0, GTEST_BY_REF_(T1) f1, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T2) f2, GTEST_BY_REF_(T3) f3) : f0_(f0), f1_(f1), f2_(f2), - f3_(f3) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), f3_(t.f3_) {} - - template <GTEST_4_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_4_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), - f3_(t.f3_) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_4_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_4_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_4_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_4_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - f1_ = t.f1_; - f2_ = t.f2_; - f3_ = t.f3_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; - T1 f1_; - T2 f2_; - T3 f3_; -}; - -template <GTEST_5_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class GTEST_5_TUPLE_(T) { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_(), f1_(), f2_(), f3_(), f4_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0, GTEST_BY_REF_(T1) f1, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T2) f2, GTEST_BY_REF_(T3) f3, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T4) f4) : f0_(f0), f1_(f1), f2_(f2), f3_(f3), f4_(f4) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), f3_(t.f3_), - f4_(t.f4_) {} - - template <GTEST_5_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_5_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), - f3_(t.f3_), f4_(t.f4_) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_5_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_5_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_5_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_5_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - f1_ = t.f1_; - f2_ = t.f2_; - f3_ = t.f3_; - f4_ = t.f4_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; - T1 f1_; - T2 f2_; - T3 f3_; - T4 f4_; -}; - -template <GTEST_6_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class GTEST_6_TUPLE_(T) { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_(), f1_(), f2_(), f3_(), f4_(), f5_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0, GTEST_BY_REF_(T1) f1, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T2) f2, GTEST_BY_REF_(T3) f3, GTEST_BY_REF_(T4) f4, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T5) f5) : f0_(f0), f1_(f1), f2_(f2), f3_(f3), f4_(f4), - f5_(f5) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), f3_(t.f3_), - f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_) {} - - template <GTEST_6_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_6_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), - f3_(t.f3_), f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_6_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_6_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_6_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_6_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - f1_ = t.f1_; - f2_ = t.f2_; - f3_ = t.f3_; - f4_ = t.f4_; - f5_ = t.f5_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; - T1 f1_; - T2 f2_; - T3 f3_; - T4 f4_; - T5 f5_; -}; - -template <GTEST_7_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class GTEST_7_TUPLE_(T) { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_(), f1_(), f2_(), f3_(), f4_(), f5_(), f6_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0, GTEST_BY_REF_(T1) f1, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T2) f2, GTEST_BY_REF_(T3) f3, GTEST_BY_REF_(T4) f4, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T5) f5, GTEST_BY_REF_(T6) f6) : f0_(f0), f1_(f1), f2_(f2), - f3_(f3), f4_(f4), f5_(f5), f6_(f6) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), f3_(t.f3_), - f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_), f6_(t.f6_) {} - - template <GTEST_7_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_7_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), - f3_(t.f3_), f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_), f6_(t.f6_) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_7_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_7_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_7_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_7_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - f1_ = t.f1_; - f2_ = t.f2_; - f3_ = t.f3_; - f4_ = t.f4_; - f5_ = t.f5_; - f6_ = t.f6_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; - T1 f1_; - T2 f2_; - T3 f3_; - T4 f4_; - T5 f5_; - T6 f6_; -}; - -template <GTEST_8_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class GTEST_8_TUPLE_(T) { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_(), f1_(), f2_(), f3_(), f4_(), f5_(), f6_(), f7_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0, GTEST_BY_REF_(T1) f1, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T2) f2, GTEST_BY_REF_(T3) f3, GTEST_BY_REF_(T4) f4, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T5) f5, GTEST_BY_REF_(T6) f6, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T7) f7) : f0_(f0), f1_(f1), f2_(f2), f3_(f3), f4_(f4), - f5_(f5), f6_(f6), f7_(f7) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), f3_(t.f3_), - f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_), f6_(t.f6_), f7_(t.f7_) {} - - template <GTEST_8_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_8_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), - f3_(t.f3_), f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_), f6_(t.f6_), f7_(t.f7_) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_8_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_8_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_8_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_8_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - f1_ = t.f1_; - f2_ = t.f2_; - f3_ = t.f3_; - f4_ = t.f4_; - f5_ = t.f5_; - f6_ = t.f6_; - f7_ = t.f7_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; - T1 f1_; - T2 f2_; - T3 f3_; - T4 f4_; - T5 f5_; - T6 f6_; - T7 f7_; -}; - -template <GTEST_9_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class GTEST_9_TUPLE_(T) { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_(), f1_(), f2_(), f3_(), f4_(), f5_(), f6_(), f7_(), f8_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0, GTEST_BY_REF_(T1) f1, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T2) f2, GTEST_BY_REF_(T3) f3, GTEST_BY_REF_(T4) f4, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T5) f5, GTEST_BY_REF_(T6) f6, GTEST_BY_REF_(T7) f7, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T8) f8) : f0_(f0), f1_(f1), f2_(f2), f3_(f3), f4_(f4), - f5_(f5), f6_(f6), f7_(f7), f8_(f8) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), f3_(t.f3_), - f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_), f6_(t.f6_), f7_(t.f7_), f8_(t.f8_) {} - - template <GTEST_9_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_9_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), - f3_(t.f3_), f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_), f6_(t.f6_), f7_(t.f7_), f8_(t.f8_) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_9_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_9_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_9_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_9_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - f1_ = t.f1_; - f2_ = t.f2_; - f3_ = t.f3_; - f4_ = t.f4_; - f5_ = t.f5_; - f6_ = t.f6_; - f7_ = t.f7_; - f8_ = t.f8_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; - T1 f1_; - T2 f2_; - T3 f3_; - T4 f4_; - T5 f5_; - T6 f6_; - T7 f7_; - T8 f8_; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -class tuple { - public: - template <int k> friend class gtest_internal::Get; - - tuple() : f0_(), f1_(), f2_(), f3_(), f4_(), f5_(), f6_(), f7_(), f8_(), - f9_() {} - - explicit tuple(GTEST_BY_REF_(T0) f0, GTEST_BY_REF_(T1) f1, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T2) f2, GTEST_BY_REF_(T3) f3, GTEST_BY_REF_(T4) f4, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T5) f5, GTEST_BY_REF_(T6) f6, GTEST_BY_REF_(T7) f7, - GTEST_BY_REF_(T8) f8, GTEST_BY_REF_(T9) f9) : f0_(f0), f1_(f1), f2_(f2), - f3_(f3), f4_(f4), f5_(f5), f6_(f6), f7_(f7), f8_(f8), f9_(f9) {} - - tuple(const tuple& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), f3_(t.f3_), - f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_), f6_(t.f6_), f7_(t.f7_), f8_(t.f8_), f9_(t.f9_) {} - - template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple(const GTEST_10_TUPLE_(U)& t) : f0_(t.f0_), f1_(t.f1_), f2_(t.f2_), - f3_(t.f3_), f4_(t.f4_), f5_(t.f5_), f6_(t.f6_), f7_(t.f7_), f8_(t.f8_), - f9_(t.f9_) {} - - tuple& operator=(const tuple& t) { return CopyFrom(t); } - - template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& operator=(const GTEST_10_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - return CopyFrom(t); - } - - GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ - - template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(U)> - tuple& CopyFrom(const GTEST_10_TUPLE_(U)& t) { - f0_ = t.f0_; - f1_ = t.f1_; - f2_ = t.f2_; - f3_ = t.f3_; - f4_ = t.f4_; - f5_ = t.f5_; - f6_ = t.f6_; - f7_ = t.f7_; - f8_ = t.f8_; - f9_ = t.f9_; - return *this; - } - - T0 f0_; - T1 f1_; - T2 f2_; - T3 f3_; - T4 f4_; - T5 f5_; - T6 f6_; - T7 f7_; - T8 f8_; - T9 f9_; -}; - -// 6.1.3.2 Tuple creation functions. - -// Known limitations: we don't support passing an -// std::tr1::reference_wrapper<T> to make_tuple(). And we don't -// implement tie(). - -inline tuple<> make_tuple() { return tuple<>(); } - -template <GTEST_1_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_1_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0) { - return GTEST_1_TUPLE_(T)(f0); -} - -template <GTEST_2_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_2_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0, const T1& f1) { - return GTEST_2_TUPLE_(T)(f0, f1); -} - -template <GTEST_3_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_3_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0, const T1& f1, const T2& f2) { - return GTEST_3_TUPLE_(T)(f0, f1, f2); -} - -template <GTEST_4_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_4_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0, const T1& f1, const T2& f2, - const T3& f3) { - return GTEST_4_TUPLE_(T)(f0, f1, f2, f3); -} - -template <GTEST_5_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_5_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0, const T1& f1, const T2& f2, - const T3& f3, const T4& f4) { - return GTEST_5_TUPLE_(T)(f0, f1, f2, f3, f4); -} - -template <GTEST_6_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_6_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0, const T1& f1, const T2& f2, - const T3& f3, const T4& f4, const T5& f5) { - return GTEST_6_TUPLE_(T)(f0, f1, f2, f3, f4, f5); -} - -template <GTEST_7_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_7_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0, const T1& f1, const T2& f2, - const T3& f3, const T4& f4, const T5& f5, const T6& f6) { - return GTEST_7_TUPLE_(T)(f0, f1, f2, f3, f4, f5, f6); -} - -template <GTEST_8_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_8_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0, const T1& f1, const T2& f2, - const T3& f3, const T4& f4, const T5& f5, const T6& f6, const T7& f7) { - return GTEST_8_TUPLE_(T)(f0, f1, f2, f3, f4, f5, f6, f7); -} - -template <GTEST_9_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_9_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0, const T1& f1, const T2& f2, - const T3& f3, const T4& f4, const T5& f5, const T6& f6, const T7& f7, - const T8& f8) { - return GTEST_9_TUPLE_(T)(f0, f1, f2, f3, f4, f5, f6, f7, f8); -} - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -inline GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) make_tuple(const T0& f0, const T1& f1, const T2& f2, - const T3& f3, const T4& f4, const T5& f5, const T6& f6, const T7& f7, - const T8& f8, const T9& f9) { - return GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T)(f0, f1, f2, f3, f4, f5, f6, f7, f8, f9); -} - -// 6.1.3.3 Tuple helper classes. - -template <typename Tuple> struct tuple_size; - -template <GTEST_0_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_0_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 0; -}; - -template <GTEST_1_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_1_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 1; -}; - -template <GTEST_2_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_2_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 2; -}; - -template <GTEST_3_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_3_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 3; -}; - -template <GTEST_4_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_4_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 4; -}; - -template <GTEST_5_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_5_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 5; -}; - -template <GTEST_6_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_6_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 6; -}; - -template <GTEST_7_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_7_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 7; -}; - -template <GTEST_8_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_8_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 8; -}; - -template <GTEST_9_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_9_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 9; -}; - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -struct tuple_size<GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) > { - static const int value = 10; -}; - -template <int k, class Tuple> -struct tuple_element { - typedef typename gtest_internal::TupleElement< - k < (tuple_size<Tuple>::value), k, Tuple>::type type; -}; - -#define GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(k, Tuple) typename tuple_element<k, Tuple >::type - -// 6.1.3.4 Element access. - -namespace gtest_internal { - -template <> -class Get<0> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(0, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f0_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(0, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f0_; } -}; - -template <> -class Get<1> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(1, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f1_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(1, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f1_; } -}; - -template <> -class Get<2> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(2, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f2_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(2, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f2_; } -}; - -template <> -class Get<3> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(3, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f3_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(3, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f3_; } -}; - -template <> -class Get<4> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(4, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f4_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(4, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f4_; } -}; - -template <> -class Get<5> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(5, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f5_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(5, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f5_; } -}; - -template <> -class Get<6> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(6, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f6_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(6, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f6_; } -}; - -template <> -class Get<7> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(7, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f7_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(7, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f7_; } -}; - -template <> -class Get<8> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(8, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f8_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(8, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f8_; } -}; - -template <> -class Get<9> { - public: - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(9, Tuple)) - Field(Tuple& t) { return t.f9_; } // NOLINT - - template <class Tuple> - static GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(9, Tuple)) - ConstField(const Tuple& t) { return t.f9_; } -}; - -} // namespace gtest_internal - -template <int k, GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -GTEST_ADD_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(k, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T))) -get(GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T)& t) { - return gtest_internal::Get<k>::Field(t); -} - -template <int k, GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T)> -GTEST_BY_REF_(GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_(k, GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T))) -get(const GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T)& t) { - return gtest_internal::Get<k>::ConstField(t); -} - -// 6.1.3.5 Relational operators - -// We only implement == and !=, as we don't have a need for the rest yet. - -namespace gtest_internal { - -// SameSizeTuplePrefixComparator<k, k>::Eq(t1, t2) returns true if the -// first k fields of t1 equals the first k fields of t2. -// SameSizeTuplePrefixComparator(k1, k2) would be a compiler error if -// k1 != k2. -template <int kSize1, int kSize2> -struct SameSizeTuplePrefixComparator; - -template <> -struct SameSizeTuplePrefixComparator<0, 0> { - template <class Tuple1, class Tuple2> - static bool Eq(const Tuple1& /* t1 */, const Tuple2& /* t2 */) { - return true; - } -}; - -template <int k> -struct SameSizeTuplePrefixComparator<k, k> { - template <class Tuple1, class Tuple2> - static bool Eq(const Tuple1& t1, const Tuple2& t2) { - return SameSizeTuplePrefixComparator<k - 1, k - 1>::Eq(t1, t2) && - ::std::tr1::get<k - 1>(t1) == ::std::tr1::get<k - 1>(t2); - } -}; - -} // namespace gtest_internal - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T), GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(U)> -inline bool operator==(const GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T)& t, - const GTEST_10_TUPLE_(U)& u) { - return gtest_internal::SameSizeTuplePrefixComparator< - tuple_size<GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T) >::value, - tuple_size<GTEST_10_TUPLE_(U) >::value>::Eq(t, u); -} - -template <GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(T), GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_(U)> -inline bool operator!=(const GTEST_10_TUPLE_(T)& t, - const GTEST_10_TUPLE_(U)& u) { return !(t == u); } - -// 6.1.4 Pairs. -// Unimplemented. - -} // namespace tr1 -} // namespace std - -#undef GTEST_0_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_1_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_2_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_3_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_4_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_5_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_6_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_7_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_8_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_9_TUPLE_ -#undef GTEST_10_TUPLE_ - -#undef GTEST_0_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_1_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_2_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_3_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_4_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_5_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_6_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_7_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_8_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_9_TYPENAMES_ -#undef GTEST_10_TYPENAMES_ - -#undef GTEST_DECLARE_TUPLE_AS_FRIEND_ -#undef GTEST_BY_REF_ -#undef GTEST_ADD_REF_ -#undef GTEST_TUPLE_ELEMENT_ - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_TUPLE_H_ -# elif GTEST_ENV_HAS_STD_TUPLE_ -# include <tuple> -// C++11 puts its tuple into the ::std namespace rather than -// ::std::tr1. gtest expects tuple to live in ::std::tr1, so put it there. -// This causes undefined behavior, but supported compilers react in -// the way we intend. -namespace std { -namespace tr1 { -using ::std::get; -using ::std::make_tuple; -using ::std::tuple; -using ::std::tuple_element; -using ::std::tuple_size; -} -} - -# elif GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - -// On Symbian, BOOST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE causes Boost's TR1 tuple library to -// use STLport's tuple implementation, which unfortunately doesn't -// work as the copy of STLport distributed with Symbian is incomplete. -// By making sure BOOST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE is undefined, we force Boost to -// use its own tuple implementation. -# ifdef BOOST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE -# undef BOOST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE -# endif // BOOST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE - -// This prevents <boost/tr1/detail/config.hpp>, which defines -// BOOST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE, from being #included by Boost's <tuple>. -# define BOOST_TR1_DETAIL_CONFIG_HPP_INCLUDED -# include <tuple> - -# elif defined(__GNUC__) && (GTEST_GCC_VER_ >= 40000) -// GCC 4.0+ implements tr1/tuple in the <tr1/tuple> header. This does -// not conform to the TR1 spec, which requires the header to be <tuple>. - -# if !GTEST_HAS_RTTI && GTEST_GCC_VER_ < 40302 -// Until version 4.3.2, gcc has a bug that causes <tr1/functional>, -// which is #included by <tr1/tuple>, to not compile when RTTI is -// disabled. _TR1_FUNCTIONAL is the header guard for -// <tr1/functional>. Hence the following #define is a hack to prevent -// <tr1/functional> from being included. -# define _TR1_FUNCTIONAL 1 -# include <tr1/tuple> -# undef _TR1_FUNCTIONAL // Allows the user to #include - // <tr1/functional> if he chooses to. -# else -# include <tr1/tuple> // NOLINT -# endif // !GTEST_HAS_RTTI && GTEST_GCC_VER_ < 40302 - -# else -// If the compiler is not GCC 4.0+, we assume the user is using a -// spec-conforming TR1 implementation. -# include <tuple> // NOLINT -# endif // GTEST_USE_OWN_TR1_TUPLE - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE - -// Determines whether clone(2) is supported. -// Usually it will only be available on Linux, excluding -// Linux on the Itanium architecture. -// Also see http://linux.die.net/man/2/clone. -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_CLONE -// The user didn't tell us, so we need to figure it out. - -# if GTEST_OS_LINUX && !defined(__ia64__) -# if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID -// On Android, clone() is only available on ARM starting with Gingerbread. -# if defined(__arm__) && __ANDROID_API__ >= 9 -# define GTEST_HAS_CLONE 1 -# else -# define GTEST_HAS_CLONE 0 -# endif -# else -# define GTEST_HAS_CLONE 1 -# endif -# else -# define GTEST_HAS_CLONE 0 -# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX && !defined(__ia64__) - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_CLONE - -// Determines whether to support stream redirection. This is used to test -// output correctness and to implement death tests. -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION -// By default, we assume that stream redirection is supported on all -// platforms except known mobile ones. -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN -# define GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION 0 -# else -# define GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION 1 -# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE && !GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN -#endif // GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION - -// Determines whether to support death tests. -// Google Test does not support death tests for VC 7.1 and earlier as -// abort() in a VC 7.1 application compiled as GUI in debug config -// pops up a dialog window that cannot be suppressed programmatically. -#if (GTEST_OS_LINUX || GTEST_OS_CYGWIN || GTEST_OS_SOLARIS || \ - (GTEST_OS_MAC && !GTEST_OS_IOS) || GTEST_OS_IOS_SIMULATOR || \ - (GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP && _MSC_VER >= 1400) || \ - GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW || GTEST_OS_AIX || GTEST_OS_HPUX || \ - GTEST_OS_OPENBSD || GTEST_OS_QNX) -# define GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST 1 -# include <vector> // NOLINT -#endif - -// We don't support MSVC 7.1 with exceptions disabled now. Therefore -// all the compilers we care about are adequate for supporting -// value-parameterized tests. -#define GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST 1 - -// Determines whether to support type-driven tests. - -// Typed tests need <typeinfo> and variadic macros, which GCC, VC++ 8.0, -// Sun Pro CC, IBM Visual Age, and HP aCC support. -#if defined(__GNUC__) || (_MSC_VER >= 1400) || defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || \ - defined(__IBMCPP__) || defined(__HP_aCC) -# define GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST 1 -# define GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P 1 -#endif - -// Determines whether to support Combine(). This only makes sense when -// value-parameterized tests are enabled. The implementation doesn't -// work on Sun Studio since it doesn't understand templated conversion -// operators. -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST && GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE && !defined(__SUNPRO_CC) -# define GTEST_HAS_COMBINE 1 -#endif - -// Determines whether the system compiler uses UTF-16 for encoding wide strings. -#define GTEST_WIDE_STRING_USES_UTF16_ \ - (GTEST_OS_WINDOWS || GTEST_OS_CYGWIN || GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN || GTEST_OS_AIX) - -// Determines whether test results can be streamed to a socket. -#if GTEST_OS_LINUX -# define GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ 1 -#endif - -// Defines some utility macros. - -// The GNU compiler emits a warning if nested "if" statements are followed by -// an "else" statement and braces are not used to explicitly disambiguate the -// "else" binding. This leads to problems with code like: -// -// if (gate) -// ASSERT_*(condition) << "Some message"; -// -// The "switch (0) case 0:" idiom is used to suppress this. -#ifdef __INTEL_COMPILER -# define GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ -#else -# define GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ switch (0) case 0: default: // NOLINT -#endif - -// Use this annotation at the end of a struct/class definition to -// prevent the compiler from optimizing away instances that are never -// used. This is useful when all interesting logic happens inside the -// c'tor and / or d'tor. Example: -// -// struct Foo { -// Foo() { ... } -// } GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; -// -// Also use it after a variable or parameter declaration to tell the -// compiler the variable/parameter does not have to be used. -#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(COMPILER_ICC) -# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ __attribute__ ((unused)) -#else -# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ -#endif - -// A macro to disallow operator= -// This should be used in the private: declarations for a class. -#define GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(type)\ - void operator=(type const &) - -// A macro to disallow copy constructor and operator= -// This should be used in the private: declarations for a class. -#define GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(type)\ - type(type const &);\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(type) - -// Tell the compiler to warn about unused return values for functions declared -// with this macro. The macro should be used on function declarations -// following the argument list: -// -// Sprocket* AllocateSprocket() GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_; -#if defined(__GNUC__) && (GTEST_GCC_VER_ >= 30400) && !defined(COMPILER_ICC) -# define GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_ __attribute__ ((warn_unused_result)) -#else -# define GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_ -#endif // __GNUC__ && (GTEST_GCC_VER_ >= 30400) && !COMPILER_ICC - -// Determine whether the compiler supports Microsoft's Structured Exception -// Handling. This is supported by several Windows compilers but generally -// does not exist on any other system. -#ifndef GTEST_HAS_SEH -// The user didn't tell us, so we need to figure it out. - -# if defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(__BORLANDC__) -// These two compilers are known to support SEH. -# define GTEST_HAS_SEH 1 -# else -// Assume no SEH. -# define GTEST_HAS_SEH 0 -# endif - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_SEH - -#ifdef _MSC_VER - -# if GTEST_LINKED_AS_SHARED_LIBRARY -# define GTEST_API_ __declspec(dllimport) -# elif GTEST_CREATE_SHARED_LIBRARY -# define GTEST_API_ __declspec(dllexport) -# endif - -#endif // _MSC_VER - -#ifndef GTEST_API_ -# define GTEST_API_ -#endif - -#ifdef __GNUC__ -// Ask the compiler to never inline a given function. -# define GTEST_NO_INLINE_ __attribute__((noinline)) -#else -# define GTEST_NO_INLINE_ -#endif - -// _LIBCPP_VERSION is defined by the libc++ library from the LLVM project. -#if defined(__GLIBCXX__) || defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION) -# define GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ 1 -#else -# define GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ 0 -#endif - -namespace testing { - -class Message; - -namespace internal { - -// A secret type that Google Test users don't know about. It has no -// definition on purpose. Therefore it's impossible to create a -// Secret object, which is what we want. -class Secret; - -// The GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_ macro can be used to verify that a compile time -// expression is true. For example, you could use it to verify the -// size of a static array: -// -// GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(ARRAYSIZE(content_type_names) == CONTENT_NUM_TYPES, -// content_type_names_incorrect_size); -// -// or to make sure a struct is smaller than a certain size: -// -// GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(sizeof(foo) < 128, foo_too_large); -// -// The second argument to the macro is the name of the variable. If -// the expression is false, most compilers will issue a warning/error -// containing the name of the variable. - -template <bool> -struct CompileAssert { -}; - -#define GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(expr, msg) \ - typedef ::testing::internal::CompileAssert<(static_cast<bool>(expr))> \ - msg[static_cast<bool>(expr) ? 1 : -1] GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ - -// Implementation details of GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_: -// -// - GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_ works by defining an array type that has -1 -// elements (and thus is invalid) when the expression is false. -// -// - The simpler definition -// -// #define GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(expr, msg) typedef char msg[(expr) ? 1 : -1] -// -// does not work, as gcc supports variable-length arrays whose sizes -// are determined at run-time (this is gcc's extension and not part -// of the C++ standard). As a result, gcc fails to reject the -// following code with the simple definition: -// -// int foo; -// GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(foo, msg); // not supposed to compile as foo is -// // not a compile-time constant. -// -// - By using the type CompileAssert<(bool(expr))>, we ensures that -// expr is a compile-time constant. (Template arguments must be -// determined at compile-time.) -// -// - The outter parentheses in CompileAssert<(bool(expr))> are necessary -// to work around a bug in gcc 3.4.4 and 4.0.1. If we had written -// -// CompileAssert<bool(expr)> -// -// instead, these compilers will refuse to compile -// -// GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(5 > 0, some_message); -// -// (They seem to think the ">" in "5 > 0" marks the end of the -// template argument list.) -// -// - The array size is (bool(expr) ? 1 : -1), instead of simply -// -// ((expr) ? 1 : -1). -// -// This is to avoid running into a bug in MS VC 7.1, which -// causes ((0.0) ? 1 : -1) to incorrectly evaluate to 1. - -// StaticAssertTypeEqHelper is used by StaticAssertTypeEq defined in gtest.h. -// -// This template is declared, but intentionally undefined. -template <typename T1, typename T2> -struct StaticAssertTypeEqHelper; - -template <typename T> -struct StaticAssertTypeEqHelper<T, T> {}; - -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING -typedef ::string string; -#else -typedef ::std::string string; -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING - -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING -typedef ::wstring wstring; -#elif GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING -typedef ::std::wstring wstring; -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING - -// A helper for suppressing warnings on constant condition. It just -// returns 'condition'. -GTEST_API_ bool IsTrue(bool condition); - -// Defines scoped_ptr. - -// This implementation of scoped_ptr is PARTIAL - it only contains -// enough stuff to satisfy Google Test's need. -template <typename T> -class scoped_ptr { - public: - typedef T element_type; - - explicit scoped_ptr(T* p = NULL) : ptr_(p) {} - ~scoped_ptr() { reset(); } - - T& operator*() const { return *ptr_; } - T* operator->() const { return ptr_; } - T* get() const { return ptr_; } - - T* release() { - T* const ptr = ptr_; - ptr_ = NULL; - return ptr; - } - - void reset(T* p = NULL) { - if (p != ptr_) { - if (IsTrue(sizeof(T) > 0)) { // Makes sure T is a complete type. - delete ptr_; - } - ptr_ = p; - } - } - - private: - T* ptr_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(scoped_ptr); -}; - -// Defines RE. - -// A simple C++ wrapper for <regex.h>. It uses the POSIX Extended -// Regular Expression syntax. -class GTEST_API_ RE { - public: - // A copy constructor is required by the Standard to initialize object - // references from r-values. - RE(const RE& other) { Init(other.pattern()); } - - // Constructs an RE from a string. - RE(const ::std::string& regex) { Init(regex.c_str()); } // NOLINT - -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING - - RE(const ::string& regex) { Init(regex.c_str()); } // NOLINT - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING - - RE(const char* regex) { Init(regex); } // NOLINT - ~RE(); - - // Returns the string representation of the regex. - const char* pattern() const { return pattern_; } - - // FullMatch(str, re) returns true iff regular expression re matches - // the entire str. - // PartialMatch(str, re) returns true iff regular expression re - // matches a substring of str (including str itself). - // - // TODO(wan@google.com): make FullMatch() and PartialMatch() work - // when str contains NUL characters. - static bool FullMatch(const ::std::string& str, const RE& re) { - return FullMatch(str.c_str(), re); - } - static bool PartialMatch(const ::std::string& str, const RE& re) { - return PartialMatch(str.c_str(), re); - } - -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING - - static bool FullMatch(const ::string& str, const RE& re) { - return FullMatch(str.c_str(), re); - } - static bool PartialMatch(const ::string& str, const RE& re) { - return PartialMatch(str.c_str(), re); - } - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING - - static bool FullMatch(const char* str, const RE& re); - static bool PartialMatch(const char* str, const RE& re); - - private: - void Init(const char* regex); - - // We use a const char* instead of an std::string, as Google Test used to be - // used where std::string is not available. TODO(wan@google.com): change to - // std::string. - const char* pattern_; - bool is_valid_; - -#if GTEST_USES_POSIX_RE - - regex_t full_regex_; // For FullMatch(). - regex_t partial_regex_; // For PartialMatch(). - -#else // GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE - - const char* full_pattern_; // For FullMatch(); - -#endif - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(RE); -}; - -// Formats a source file path and a line number as they would appear -// in an error message from the compiler used to compile this code. -GTEST_API_ ::std::string FormatFileLocation(const char* file, int line); - -// Formats a file location for compiler-independent XML output. -// Although this function is not platform dependent, we put it next to -// FormatFileLocation in order to contrast the two functions. -GTEST_API_ ::std::string FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation(const char* file, - int line); - -// Defines logging utilities: -// GTEST_LOG_(severity) - logs messages at the specified severity level. The -// message itself is streamed into the macro. -// LogToStderr() - directs all log messages to stderr. -// FlushInfoLog() - flushes informational log messages. - -enum GTestLogSeverity { - GTEST_INFO, - GTEST_WARNING, - GTEST_ERROR, - GTEST_FATAL -}; - -// Formats log entry severity, provides a stream object for streaming the -// log message, and terminates the message with a newline when going out of -// scope. -class GTEST_API_ GTestLog { - public: - GTestLog(GTestLogSeverity severity, const char* file, int line); - - // Flushes the buffers and, if severity is GTEST_FATAL, aborts the program. - ~GTestLog(); - - ::std::ostream& GetStream() { return ::std::cerr; } - - private: - const GTestLogSeverity severity_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(GTestLog); -}; - -#define GTEST_LOG_(severity) \ - ::testing::internal::GTestLog(::testing::internal::GTEST_##severity, \ - __FILE__, __LINE__).GetStream() - -inline void LogToStderr() {} -inline void FlushInfoLog() { fflush(NULL); } - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE. -// -// GTEST_CHECK_ is an all-mode assert. It aborts the program if the condition -// is not satisfied. -// Synopsys: -// GTEST_CHECK_(boolean_condition); -// or -// GTEST_CHECK_(boolean_condition) << "Additional message"; -// -// This checks the condition and if the condition is not satisfied -// it prints message about the condition violation, including the -// condition itself, plus additional message streamed into it, if any, -// and then it aborts the program. It aborts the program irrespective of -// whether it is built in the debug mode or not. -#define GTEST_CHECK_(condition) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (::testing::internal::IsTrue(condition)) \ - ; \ - else \ - GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "Condition " #condition " failed. " - -// An all-mode assert to verify that the given POSIX-style function -// call returns 0 (indicating success). Known limitation: this -// doesn't expand to a balanced 'if' statement, so enclose the macro -// in {} if you need to use it as the only statement in an 'if' -// branch. -#define GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(posix_call) \ - if (const int gtest_error = (posix_call)) \ - GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << #posix_call << "failed with error " \ - << gtest_error - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// Use ImplicitCast_ as a safe version of static_cast for upcasting in -// the type hierarchy (e.g. casting a Foo* to a SuperclassOfFoo* or a -// const Foo*). When you use ImplicitCast_, the compiler checks that -// the cast is safe. Such explicit ImplicitCast_s are necessary in -// surprisingly many situations where C++ demands an exact type match -// instead of an argument type convertable to a target type. -// -// The syntax for using ImplicitCast_ is the same as for static_cast: -// -// ImplicitCast_<ToType>(expr) -// -// ImplicitCast_ would have been part of the C++ standard library, -// but the proposal was submitted too late. It will probably make -// its way into the language in the future. -// -// This relatively ugly name is intentional. It prevents clashes with -// similar functions users may have (e.g., implicit_cast). The internal -// namespace alone is not enough because the function can be found by ADL. -template<typename To> -inline To ImplicitCast_(To x) { return x; } - -// When you upcast (that is, cast a pointer from type Foo to type -// SuperclassOfFoo), it's fine to use ImplicitCast_<>, since upcasts -// always succeed. When you downcast (that is, cast a pointer from -// type Foo to type SubclassOfFoo), static_cast<> isn't safe, because -// how do you know the pointer is really of type SubclassOfFoo? It -// could be a bare Foo, or of type DifferentSubclassOfFoo. Thus, -// when you downcast, you should use this macro. In debug mode, we -// use dynamic_cast<> to double-check the downcast is legal (we die -// if it's not). In normal mode, we do the efficient static_cast<> -// instead. Thus, it's important to test in debug mode to make sure -// the cast is legal! -// This is the only place in the code we should use dynamic_cast<>. -// In particular, you SHOULDN'T be using dynamic_cast<> in order to -// do RTTI (eg code like this: -// if (dynamic_cast<Subclass1>(foo)) HandleASubclass1Object(foo); -// if (dynamic_cast<Subclass2>(foo)) HandleASubclass2Object(foo); -// You should design the code some other way not to need this. -// -// This relatively ugly name is intentional. It prevents clashes with -// similar functions users may have (e.g., down_cast). The internal -// namespace alone is not enough because the function can be found by ADL. -template<typename To, typename From> // use like this: DownCast_<T*>(foo); -inline To DownCast_(From* f) { // so we only accept pointers - // Ensures that To is a sub-type of From *. This test is here only - // for compile-time type checking, and has no overhead in an - // optimized build at run-time, as it will be optimized away - // completely. - if (false) { - const To to = NULL; - ::testing::internal::ImplicitCast_<From*>(to); - } - -#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI - // RTTI: debug mode only! - GTEST_CHECK_(f == NULL || dynamic_cast<To>(f) != NULL); -#endif - return static_cast<To>(f); -} - -// Downcasts the pointer of type Base to Derived. -// Derived must be a subclass of Base. The parameter MUST -// point to a class of type Derived, not any subclass of it. -// When RTTI is available, the function performs a runtime -// check to enforce this. -template <class Derived, class Base> -Derived* CheckedDowncastToActualType(Base* base) { -#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI - GTEST_CHECK_(typeid(*base) == typeid(Derived)); - return dynamic_cast<Derived*>(base); // NOLINT -#else - return static_cast<Derived*>(base); // Poor man's downcast. -#endif -} - -#if GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION - -// Defines the stderr capturer: -// CaptureStdout - starts capturing stdout. -// GetCapturedStdout - stops capturing stdout and returns the captured string. -// CaptureStderr - starts capturing stderr. -// GetCapturedStderr - stops capturing stderr and returns the captured string. -// -GTEST_API_ void CaptureStdout(); -GTEST_API_ std::string GetCapturedStdout(); -GTEST_API_ void CaptureStderr(); -GTEST_API_ std::string GetCapturedStderr(); - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION - - -#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - -const ::std::vector<testing::internal::string>& GetInjectableArgvs(); -void SetInjectableArgvs(const ::std::vector<testing::internal::string>* - new_argvs); - -// A copy of all command line arguments. Set by InitGoogleTest(). -extern ::std::vector<testing::internal::string> g_argvs; - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - -// Defines synchronization primitives. - -#if GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD - -// Sleeps for (roughly) n milli-seconds. This function is only for -// testing Google Test's own constructs. Don't use it in user tests, -// either directly or indirectly. -inline void SleepMilliseconds(int n) { - const timespec time = { - 0, // 0 seconds. - n * 1000L * 1000L, // And n ms. - }; - nanosleep(&time, NULL); -} - -// Allows a controller thread to pause execution of newly created -// threads until notified. Instances of this class must be created -// and destroyed in the controller thread. -// -// This class is only for testing Google Test's own constructs. Do not -// use it in user tests, either directly or indirectly. -class Notification { - public: - Notification() : notified_(false) { - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_, NULL)); - } - ~Notification() { - pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_); - } - - // Notifies all threads created with this notification to start. Must - // be called from the controller thread. - void Notify() { - pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_); - notified_ = true; - pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_); - } - - // Blocks until the controller thread notifies. Must be called from a test - // thread. - void WaitForNotification() { - for (;;) { - pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_); - const bool notified = notified_; - pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_); - if (notified) - break; - SleepMilliseconds(10); - } - } - - private: - pthread_mutex_t mutex_; - bool notified_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Notification); -}; - -// As a C-function, ThreadFuncWithCLinkage cannot be templated itself. -// Consequently, it cannot select a correct instantiation of ThreadWithParam -// in order to call its Run(). Introducing ThreadWithParamBase as a -// non-templated base class for ThreadWithParam allows us to bypass this -// problem. -class ThreadWithParamBase { - public: - virtual ~ThreadWithParamBase() {} - virtual void Run() = 0; -}; - -// pthread_create() accepts a pointer to a function type with the C linkage. -// According to the Standard (7.5/1), function types with different linkages -// are different even if they are otherwise identical. Some compilers (for -// example, SunStudio) treat them as different types. Since class methods -// cannot be defined with C-linkage we need to define a free C-function to -// pass into pthread_create(). -extern "C" inline void* ThreadFuncWithCLinkage(void* thread) { - static_cast<ThreadWithParamBase*>(thread)->Run(); - return NULL; -} - -// Helper class for testing Google Test's multi-threading constructs. -// To use it, write: -// -// void ThreadFunc(int param) { /* Do things with param */ } -// Notification thread_can_start; -// ... -// // The thread_can_start parameter is optional; you can supply NULL. -// ThreadWithParam<int> thread(&ThreadFunc, 5, &thread_can_start); -// thread_can_start.Notify(); -// -// These classes are only for testing Google Test's own constructs. Do -// not use them in user tests, either directly or indirectly. -template <typename T> -class ThreadWithParam : public ThreadWithParamBase { - public: - typedef void (*UserThreadFunc)(T); - - ThreadWithParam( - UserThreadFunc func, T param, Notification* thread_can_start) - : func_(func), - param_(param), - thread_can_start_(thread_can_start), - finished_(false) { - ThreadWithParamBase* const base = this; - // The thread can be created only after all fields except thread_ - // have been initialized. - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_( - pthread_create(&thread_, 0, &ThreadFuncWithCLinkage, base)); - } - ~ThreadWithParam() { Join(); } - - void Join() { - if (!finished_) { - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_join(thread_, 0)); - finished_ = true; - } - } - - virtual void Run() { - if (thread_can_start_ != NULL) - thread_can_start_->WaitForNotification(); - func_(param_); - } - - private: - const UserThreadFunc func_; // User-supplied thread function. - const T param_; // User-supplied parameter to the thread function. - // When non-NULL, used to block execution until the controller thread - // notifies. - Notification* const thread_can_start_; - bool finished_; // true iff we know that the thread function has finished. - pthread_t thread_; // The native thread object. - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ThreadWithParam); -}; - -// MutexBase and Mutex implement mutex on pthreads-based platforms. They -// are used in conjunction with class MutexLock: -// -// Mutex mutex; -// ... -// MutexLock lock(&mutex); // Acquires the mutex and releases it at the end -// // of the current scope. -// -// MutexBase implements behavior for both statically and dynamically -// allocated mutexes. Do not use MutexBase directly. Instead, write -// the following to define a static mutex: -// -// GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_some_mutex); -// -// You can forward declare a static mutex like this: -// -// GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_some_mutex); -// -// To create a dynamic mutex, just define an object of type Mutex. -class MutexBase { - public: - // Acquires this mutex. - void Lock() { - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_)); - owner_ = pthread_self(); - has_owner_ = true; - } - - // Releases this mutex. - void Unlock() { - // Since the lock is being released the owner_ field should no longer be - // considered valid. We don't protect writing to has_owner_ here, as it's - // the caller's responsibility to ensure that the current thread holds the - // mutex when this is called. - has_owner_ = false; - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_)); - } - - // Does nothing if the current thread holds the mutex. Otherwise, crashes - // with high probability. - void AssertHeld() const { - GTEST_CHECK_(has_owner_ && pthread_equal(owner_, pthread_self())) - << "The current thread is not holding the mutex @" << this; - } - - // A static mutex may be used before main() is entered. It may even - // be used before the dynamic initialization stage. Therefore we - // must be able to initialize a static mutex object at link time. - // This means MutexBase has to be a POD and its member variables - // have to be public. - public: - pthread_mutex_t mutex_; // The underlying pthread mutex. - // has_owner_ indicates whether the owner_ field below contains a valid thread - // ID and is therefore safe to inspect (e.g., to use in pthread_equal()). All - // accesses to the owner_ field should be protected by a check of this field. - // An alternative might be to memset() owner_ to all zeros, but there's no - // guarantee that a zero'd pthread_t is necessarily invalid or even different - // from pthread_self(). - bool has_owner_; - pthread_t owner_; // The thread holding the mutex. -}; - -// Forward-declares a static mutex. -# define GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) \ - extern ::testing::internal::MutexBase mutex - -// Defines and statically (i.e. at link time) initializes a static mutex. -// The initialization list here does not explicitly initialize each field, -// instead relying on default initialization for the unspecified fields. In -// particular, the owner_ field (a pthread_t) is not explicitly initialized. -// This allows initialization to work whether pthread_t is a scalar or struct. -// The flag -Wmissing-field-initializers must not be specified for this to work. -# define GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) \ - ::testing::internal::MutexBase mutex = { PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER, false } - -// The Mutex class can only be used for mutexes created at runtime. It -// shares its API with MutexBase otherwise. -class Mutex : public MutexBase { - public: - Mutex() { - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_, NULL)); - has_owner_ = false; - } - ~Mutex() { - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_)); - } - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Mutex); -}; - -// We cannot name this class MutexLock as the ctor declaration would -// conflict with a macro named MutexLock, which is defined on some -// platforms. Hence the typedef trick below. -class GTestMutexLock { - public: - explicit GTestMutexLock(MutexBase* mutex) - : mutex_(mutex) { mutex_->Lock(); } - - ~GTestMutexLock() { mutex_->Unlock(); } - - private: - MutexBase* const mutex_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(GTestMutexLock); -}; - -typedef GTestMutexLock MutexLock; - -// Helpers for ThreadLocal. - -// pthread_key_create() requires DeleteThreadLocalValue() to have -// C-linkage. Therefore it cannot be templatized to access -// ThreadLocal<T>. Hence the need for class -// ThreadLocalValueHolderBase. -class ThreadLocalValueHolderBase { - public: - virtual ~ThreadLocalValueHolderBase() {} -}; - -// Called by pthread to delete thread-local data stored by -// pthread_setspecific(). -extern "C" inline void DeleteThreadLocalValue(void* value_holder) { - delete static_cast<ThreadLocalValueHolderBase*>(value_holder); -} - -// Implements thread-local storage on pthreads-based systems. -// -// // Thread 1 -// ThreadLocal<int> tl(100); // 100 is the default value for each thread. -// -// // Thread 2 -// tl.set(150); // Changes the value for thread 2 only. -// EXPECT_EQ(150, tl.get()); -// -// // Thread 1 -// EXPECT_EQ(100, tl.get()); // In thread 1, tl has the original value. -// tl.set(200); -// EXPECT_EQ(200, tl.get()); -// -// The template type argument T must have a public copy constructor. -// In addition, the default ThreadLocal constructor requires T to have -// a public default constructor. -// -// An object managed for a thread by a ThreadLocal instance is deleted -// when the thread exits. Or, if the ThreadLocal instance dies in -// that thread, when the ThreadLocal dies. It's the user's -// responsibility to ensure that all other threads using a ThreadLocal -// have exited when it dies, or the per-thread objects for those -// threads will not be deleted. -// -// Google Test only uses global ThreadLocal objects. That means they -// will die after main() has returned. Therefore, no per-thread -// object managed by Google Test will be leaked as long as all threads -// using Google Test have exited when main() returns. -template <typename T> -class ThreadLocal { - public: - ThreadLocal() : key_(CreateKey()), - default_() {} - explicit ThreadLocal(const T& value) : key_(CreateKey()), - default_(value) {} - - ~ThreadLocal() { - // Destroys the managed object for the current thread, if any. - DeleteThreadLocalValue(pthread_getspecific(key_)); - - // Releases resources associated with the key. This will *not* - // delete managed objects for other threads. - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_key_delete(key_)); - } - - T* pointer() { return GetOrCreateValue(); } - const T* pointer() const { return GetOrCreateValue(); } - const T& get() const { return *pointer(); } - void set(const T& value) { *pointer() = value; } - - private: - // Holds a value of type T. - class ValueHolder : public ThreadLocalValueHolderBase { - public: - explicit ValueHolder(const T& value) : value_(value) {} - - T* pointer() { return &value_; } - - private: - T value_; - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ValueHolder); - }; - - static pthread_key_t CreateKey() { - pthread_key_t key; - // When a thread exits, DeleteThreadLocalValue() will be called on - // the object managed for that thread. - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_( - pthread_key_create(&key, &DeleteThreadLocalValue)); - return key; - } - - T* GetOrCreateValue() const { - ThreadLocalValueHolderBase* const holder = - static_cast<ThreadLocalValueHolderBase*>(pthread_getspecific(key_)); - if (holder != NULL) { - return CheckedDowncastToActualType<ValueHolder>(holder)->pointer(); - } - - ValueHolder* const new_holder = new ValueHolder(default_); - ThreadLocalValueHolderBase* const holder_base = new_holder; - GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_setspecific(key_, holder_base)); - return new_holder->pointer(); - } - - // A key pthreads uses for looking up per-thread values. - const pthread_key_t key_; - const T default_; // The default value for each thread. - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ThreadLocal); -}; - -# define GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE 1 - -#else // GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD - -// A dummy implementation of synchronization primitives (mutex, lock, -// and thread-local variable). Necessary for compiling Google Test where -// mutex is not supported - using Google Test in multiple threads is not -// supported on such platforms. - -class Mutex { - public: - Mutex() {} - void Lock() {} - void Unlock() {} - void AssertHeld() const {} -}; - -# define GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) \ - extern ::testing::internal::Mutex mutex - -# define GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) ::testing::internal::Mutex mutex - -class GTestMutexLock { - public: - explicit GTestMutexLock(Mutex*) {} // NOLINT -}; - -typedef GTestMutexLock MutexLock; - -template <typename T> -class ThreadLocal { - public: - ThreadLocal() : value_() {} - explicit ThreadLocal(const T& value) : value_(value) {} - T* pointer() { return &value_; } - const T* pointer() const { return &value_; } - const T& get() const { return value_; } - void set(const T& value) { value_ = value; } - private: - T value_; -}; - -// The above synchronization primitives have dummy implementations. -// Therefore Google Test is not thread-safe. -# define GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE 0 - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD - -// Returns the number of threads running in the process, or 0 to indicate that -// we cannot detect it. -GTEST_API_ size_t GetThreadCount(); - -// Passing non-POD classes through ellipsis (...) crashes the ARM -// compiler and generates a warning in Sun Studio. The Nokia Symbian -// and the IBM XL C/C++ compiler try to instantiate a copy constructor -// for objects passed through ellipsis (...), failing for uncopyable -// objects. We define this to ensure that only POD is passed through -// ellipsis on these systems. -#if defined(__SYMBIAN32__) || defined(__IBMCPP__) || defined(__SUNPRO_CC) -// We lose support for NULL detection where the compiler doesn't like -// passing non-POD classes through ellipsis (...). -# define GTEST_ELLIPSIS_NEEDS_POD_ 1 -#else -# define GTEST_CAN_COMPARE_NULL 1 -#endif - -// The Nokia Symbian and IBM XL C/C++ compilers cannot decide between -// const T& and const T* in a function template. These compilers -// _can_ decide between class template specializations for T and T*, -// so a tr1::type_traits-like is_pointer works. -#if defined(__SYMBIAN32__) || defined(__IBMCPP__) -# define GTEST_NEEDS_IS_POINTER_ 1 -#endif - -template <bool bool_value> -struct bool_constant { - typedef bool_constant<bool_value> type; - static const bool value = bool_value; -}; -template <bool bool_value> const bool bool_constant<bool_value>::value; - -typedef bool_constant<false> false_type; -typedef bool_constant<true> true_type; - -template <typename T> -struct is_pointer : public false_type {}; - -template <typename T> -struct is_pointer<T*> : public true_type {}; - -template <typename Iterator> -struct IteratorTraits { - typedef typename Iterator::value_type value_type; -}; - -template <typename T> -struct IteratorTraits<T*> { - typedef T value_type; -}; - -template <typename T> -struct IteratorTraits<const T*> { - typedef T value_type; -}; - -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -# define GTEST_PATH_SEP_ "\\" -# define GTEST_HAS_ALT_PATH_SEP_ 1 -// The biggest signed integer type the compiler supports. -typedef __int64 BiggestInt; -#else -# define GTEST_PATH_SEP_ "/" -# define GTEST_HAS_ALT_PATH_SEP_ 0 -typedef long long BiggestInt; // NOLINT -#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - -// Utilities for char. - -// isspace(int ch) and friends accept an unsigned char or EOF. char -// may be signed, depending on the compiler (or compiler flags). -// Therefore we need to cast a char to unsigned char before calling -// isspace(), etc. - -inline bool IsAlpha(char ch) { - return isalpha(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; -} -inline bool IsAlNum(char ch) { - return isalnum(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; -} -inline bool IsDigit(char ch) { - return isdigit(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; -} -inline bool IsLower(char ch) { - return islower(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; -} -inline bool IsSpace(char ch) { - return isspace(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; -} -inline bool IsUpper(char ch) { - return isupper(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; -} -inline bool IsXDigit(char ch) { - return isxdigit(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; -} -inline bool IsXDigit(wchar_t ch) { - const unsigned char low_byte = static_cast<unsigned char>(ch); - return ch == low_byte && isxdigit(low_byte) != 0; -} - -inline char ToLower(char ch) { - return static_cast<char>(tolower(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch))); -} -inline char ToUpper(char ch) { - return static_cast<char>(toupper(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch))); -} - -// The testing::internal::posix namespace holds wrappers for common -// POSIX functions. These wrappers hide the differences between -// Windows/MSVC and POSIX systems. Since some compilers define these -// standard functions as macros, the wrapper cannot have the same name -// as the wrapped function. - -namespace posix { - -// Functions with a different name on Windows. - -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - -typedef struct _stat StatStruct; - -# ifdef __BORLANDC__ -inline int IsATTY(int fd) { return isatty(fd); } -inline int StrCaseCmp(const char* s1, const char* s2) { - return stricmp(s1, s2); -} -inline char* StrDup(const char* src) { return strdup(src); } -# else // !__BORLANDC__ -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -inline int IsATTY(int /* fd */) { return 0; } -# else -inline int IsATTY(int fd) { return _isatty(fd); } -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -inline int StrCaseCmp(const char* s1, const char* s2) { -# if _EMULATE_GLIBC - return strcasecmp(s1, s2); -# else - return _stricmp(s1, s2); -# endif -} -inline char* StrDup(const char* src) { return _strdup(src); } -# endif // __BORLANDC__ - -# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -inline int FileNo(FILE* file) { return reinterpret_cast<int>(_fileno(file)); } -// Stat(), RmDir(), and IsDir() are not needed on Windows CE at this -// time and thus not defined there. -# else -inline int FileNo(FILE* file) { return _fileno(file); } -inline int Stat(const char* path, StatStruct* buf) { return _stat(path, buf); } -inline int RmDir(const char* dir) { return _rmdir(dir); } -inline bool IsDir(const StatStruct& st) { - return (_S_IFDIR & st.st_mode) != 0; -} -# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - -#else - -typedef struct stat StatStruct; - -inline int FileNo(FILE* file) { return fileno(file); } -inline int IsATTY(int fd) { return isatty(fd); } -inline int Stat(const char* path, StatStruct* buf) { return stat(path, buf); } -inline int StrCaseCmp(const char* s1, const char* s2) { - return strcasecmp(s1, s2); -} -inline char* StrDup(const char* src) { return strdup(src); } -inline int RmDir(const char* dir) { return rmdir(dir); } -inline bool IsDir(const StatStruct& st) { return S_ISDIR(st.st_mode); } - -#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - -// Functions deprecated by MSVC 8.0. - -#ifdef _MSC_VER -// Temporarily disable warning 4996 (deprecated function). -# pragma warning(push) -# pragma warning(disable:4996) -#endif - -inline const char* StrNCpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t n) { - return strncpy(dest, src, n); -} - -// ChDir(), FReopen(), FDOpen(), Read(), Write(), Close(), and -// StrError() aren't needed on Windows CE at this time and thus not -// defined there. - -#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -inline int ChDir(const char* dir) { return chdir(dir); } -#endif -inline FILE* FOpen(const char* path, const char* mode) { - return fopen(path, mode); -} -#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -inline FILE *FReopen(const char* path, const char* mode, FILE* stream) { - return freopen(path, mode, stream); -} -inline FILE* FDOpen(int fd, const char* mode) { return fdopen(fd, mode); } -#endif -inline int FClose(FILE* fp) { return fclose(fp); } -#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -inline int Read(int fd, void* buf, unsigned int count) { - return static_cast<int>(read(fd, buf, count)); -} -inline int Write(int fd, const void* buf, unsigned int count) { - return static_cast<int>(write(fd, buf, count)); -} -inline int Close(int fd) { return close(fd); } -inline const char* StrError(int errnum) { return strerror(errnum); } -#endif -inline const char* GetEnv(const char* name) { -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - // We are on Windows CE, which has no environment variables. - return NULL; -#elif defined(__BORLANDC__) || defined(__SunOS_5_8) || defined(__SunOS_5_9) - // Environment variables which we programmatically clear will be set to the - // empty string rather than unset (NULL). Handle that case. - const char* const env = getenv(name); - return (env != NULL && env[0] != '\0') ? env : NULL; -#else - return getenv(name); -#endif -} - -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state. -#endif - -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -// Windows CE has no C library. The abort() function is used in -// several places in Google Test. This implementation provides a reasonable -// imitation of standard behaviour. -void Abort(); -#else -inline void Abort() { abort(); } -#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - -} // namespace posix - -// MSVC "deprecates" snprintf and issues warnings wherever it is used. In -// order to avoid these warnings, we need to use _snprintf or _snprintf_s on -// MSVC-based platforms. We map the GTEST_SNPRINTF_ macro to the appropriate -// function in order to achieve that. We use macro definition here because -// snprintf is a variadic function. -#if _MSC_VER >= 1400 && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE -// MSVC 2005 and above support variadic macros. -# define GTEST_SNPRINTF_(buffer, size, format, ...) \ - _snprintf_s(buffer, size, size, format, __VA_ARGS__) -#elif defined(_MSC_VER) -// Windows CE does not define _snprintf_s and MSVC prior to 2005 doesn't -// complain about _snprintf. -# define GTEST_SNPRINTF_ _snprintf -#else -# define GTEST_SNPRINTF_ snprintf -#endif - -// The maximum number a BiggestInt can represent. This definition -// works no matter BiggestInt is represented in one's complement or -// two's complement. -// -// We cannot rely on numeric_limits in STL, as __int64 and long long -// are not part of standard C++ and numeric_limits doesn't need to be -// defined for them. -const BiggestInt kMaxBiggestInt = - ~(static_cast<BiggestInt>(1) << (8*sizeof(BiggestInt) - 1)); - -// This template class serves as a compile-time function from size to -// type. It maps a size in bytes to a primitive type with that -// size. e.g. -// -// TypeWithSize<4>::UInt -// -// is typedef-ed to be unsigned int (unsigned integer made up of 4 -// bytes). -// -// Such functionality should belong to STL, but I cannot find it -// there. -// -// Google Test uses this class in the implementation of floating-point -// comparison. -// -// For now it only handles UInt (unsigned int) as that's all Google Test -// needs. Other types can be easily added in the future if need -// arises. -template <size_t size> -class TypeWithSize { - public: - // This prevents the user from using TypeWithSize<N> with incorrect - // values of N. - typedef void UInt; -}; - -// The specialization for size 4. -template <> -class TypeWithSize<4> { - public: - // unsigned int has size 4 in both gcc and MSVC. - // - // As base/basictypes.h doesn't compile on Windows, we cannot use - // uint32, uint64, and etc here. - typedef int Int; - typedef unsigned int UInt; -}; - -// The specialization for size 8. -template <> -class TypeWithSize<8> { - public: -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - typedef __int64 Int; - typedef unsigned __int64 UInt; -#else - typedef long long Int; // NOLINT - typedef unsigned long long UInt; // NOLINT -#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -}; - -// Integer types of known sizes. -typedef TypeWithSize<4>::Int Int32; -typedef TypeWithSize<4>::UInt UInt32; -typedef TypeWithSize<8>::Int Int64; -typedef TypeWithSize<8>::UInt UInt64; -typedef TypeWithSize<8>::Int TimeInMillis; // Represents time in milliseconds. - -// Utilities for command line flags and environment variables. - -// Macro for referencing flags. -#define GTEST_FLAG(name) FLAGS_gtest_##name - -// Macros for declaring flags. -#define GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(name) GTEST_API_ extern bool GTEST_FLAG(name) -#define GTEST_DECLARE_int32_(name) \ - GTEST_API_ extern ::testing::internal::Int32 GTEST_FLAG(name) -#define GTEST_DECLARE_string_(name) \ - GTEST_API_ extern ::std::string GTEST_FLAG(name) - -// Macros for defining flags. -#define GTEST_DEFINE_bool_(name, default_val, doc) \ - GTEST_API_ bool GTEST_FLAG(name) = (default_val) -#define GTEST_DEFINE_int32_(name, default_val, doc) \ - GTEST_API_ ::testing::internal::Int32 GTEST_FLAG(name) = (default_val) -#define GTEST_DEFINE_string_(name, default_val, doc) \ - GTEST_API_ ::std::string GTEST_FLAG(name) = (default_val) - -// Thread annotations -#define GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(locks) -#define GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(locks) - -// Parses 'str' for a 32-bit signed integer. If successful, writes the result -// to *value and returns true; otherwise leaves *value unchanged and returns -// false. -// TODO(chandlerc): Find a better way to refactor flag and environment parsing -// out of both gtest-port.cc and gtest.cc to avoid exporting this utility -// function. -bool ParseInt32(const Message& src_text, const char* str, Int32* value); - -// Parses a bool/Int32/string from the environment variable -// corresponding to the given Google Test flag. -bool BoolFromGTestEnv(const char* flag, bool default_val); -GTEST_API_ Int32 Int32FromGTestEnv(const char* flag, Int32 default_val); -const char* StringFromGTestEnv(const char* flag, const char* default_val); - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_H_ - -#if GTEST_OS_LINUX -# include <stdlib.h> -# include <sys/types.h> -# include <sys/wait.h> -# include <unistd.h> -#endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX - -#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS -# include <stdexcept> -#endif - -#include <ctype.h> -#include <float.h> -#include <string.h> -#include <iomanip> -#include <limits> -#include <set> - -// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) -// -// The Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) -// -// This header file defines the Message class. -// -// IMPORTANT NOTE: Due to limitation of the C++ language, we have to -// leave some internal implementation details in this header file. -// They are clearly marked by comments like this: -// -// // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -// -// Such code is NOT meant to be used by a user directly, and is subject -// to CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. Therefore DO NOT DEPEND ON IT in a user -// program! - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_MESSAGE_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_MESSAGE_H_ - -#include <limits> - - -// Ensures that there is at least one operator<< in the global namespace. -// See Message& operator<<(...) below for why. -void operator<<(const testing::internal::Secret&, int); - -namespace testing { - -// The Message class works like an ostream repeater. -// -// Typical usage: -// -// 1. You stream a bunch of values to a Message object. -// It will remember the text in a stringstream. -// 2. Then you stream the Message object to an ostream. -// This causes the text in the Message to be streamed -// to the ostream. -// -// For example; -// -// testing::Message foo; -// foo << 1 << " != " << 2; -// std::cout << foo; -// -// will print "1 != 2". -// -// Message is not intended to be inherited from. In particular, its -// destructor is not virtual. -// -// Note that stringstream behaves differently in gcc and in MSVC. You -// can stream a NULL char pointer to it in the former, but not in the -// latter (it causes an access violation if you do). The Message -// class hides this difference by treating a NULL char pointer as -// "(null)". -class GTEST_API_ Message { - private: - // The type of basic IO manipulators (endl, ends, and flush) for - // narrow streams. - typedef std::ostream& (*BasicNarrowIoManip)(std::ostream&); - - public: - // Constructs an empty Message. - Message(); - - // Copy constructor. - Message(const Message& msg) : ss_(new ::std::stringstream) { // NOLINT - *ss_ << msg.GetString(); - } - - // Constructs a Message from a C-string. - explicit Message(const char* str) : ss_(new ::std::stringstream) { - *ss_ << str; - } - -#if GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - // Streams a value (either a pointer or not) to this object. - template <typename T> - inline Message& operator <<(const T& value) { - StreamHelper(typename internal::is_pointer<T>::type(), value); - return *this; - } -#else - // Streams a non-pointer value to this object. - template <typename T> - inline Message& operator <<(const T& val) { - // Some libraries overload << for STL containers. These - // overloads are defined in the global namespace instead of ::std. - // - // C++'s symbol lookup rule (i.e. Koenig lookup) says that these - // overloads are visible in either the std namespace or the global - // namespace, but not other namespaces, including the testing - // namespace which Google Test's Message class is in. - // - // To allow STL containers (and other types that has a << operator - // defined in the global namespace) to be used in Google Test - // assertions, testing::Message must access the custom << operator - // from the global namespace. With this using declaration, - // overloads of << defined in the global namespace and those - // visible via Koenig lookup are both exposed in this function. - using ::operator <<; - *ss_ << val; - return *this; - } - - // Streams a pointer value to this object. - // - // This function is an overload of the previous one. When you - // stream a pointer to a Message, this definition will be used as it - // is more specialized. (The C++ Standard, section - // [temp.func.order].) If you stream a non-pointer, then the - // previous definition will be used. - // - // The reason for this overload is that streaming a NULL pointer to - // ostream is undefined behavior. Depending on the compiler, you - // may get "0", "(nil)", "(null)", or an access violation. To - // ensure consistent result across compilers, we always treat NULL - // as "(null)". - template <typename T> - inline Message& operator <<(T* const& pointer) { // NOLINT - if (pointer == NULL) { - *ss_ << "(null)"; - } else { - *ss_ << pointer; - } - return *this; - } -#endif // GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - - // Since the basic IO manipulators are overloaded for both narrow - // and wide streams, we have to provide this specialized definition - // of operator <<, even though its body is the same as the - // templatized version above. Without this definition, streaming - // endl or other basic IO manipulators to Message will confuse the - // compiler. - Message& operator <<(BasicNarrowIoManip val) { - *ss_ << val; - return *this; - } - - // Instead of 1/0, we want to see true/false for bool values. - Message& operator <<(bool b) { - return *this << (b ? "true" : "false"); - } - - // These two overloads allow streaming a wide C string to a Message - // using the UTF-8 encoding. - Message& operator <<(const wchar_t* wide_c_str); - Message& operator <<(wchar_t* wide_c_str); - -#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING - // Converts the given wide string to a narrow string using the UTF-8 - // encoding, and streams the result to this Message object. - Message& operator <<(const ::std::wstring& wstr); -#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING - -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING - // Converts the given wide string to a narrow string using the UTF-8 - // encoding, and streams the result to this Message object. - Message& operator <<(const ::wstring& wstr); -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING - - // Gets the text streamed to this object so far as an std::string. - // Each '\0' character in the buffer is replaced with "\\0". - // - // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. - std::string GetString() const; - - private: - -#if GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - // These are needed as the Nokia Symbian Compiler cannot decide between - // const T& and const T* in a function template. The Nokia compiler _can_ - // decide between class template specializations for T and T*, so a - // tr1::type_traits-like is_pointer works, and we can overload on that. - template <typename T> - inline void StreamHelper(internal::true_type /*is_pointer*/, T* pointer) { - if (pointer == NULL) { - *ss_ << "(null)"; - } else { - *ss_ << pointer; - } - } - template <typename T> - inline void StreamHelper(internal::false_type /*is_pointer*/, - const T& value) { - // See the comments in Message& operator <<(const T&) above for why - // we need this using statement. - using ::operator <<; - *ss_ << value; - } -#endif // GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN - - // We'll hold the text streamed to this object here. - const internal::scoped_ptr< ::std::stringstream> ss_; - - // We declare (but don't implement) this to prevent the compiler - // from implementing the assignment operator. - void operator=(const Message&); -}; - -// Streams a Message to an ostream. -inline std::ostream& operator <<(std::ostream& os, const Message& sb) { - return os << sb.GetString(); -} - -namespace internal { - -// Converts a streamable value to an std::string. A NULL pointer is -// converted to "(null)". When the input value is a ::string, -// ::std::string, ::wstring, or ::std::wstring object, each NUL -// character in it is replaced with "\\0". -template <typename T> -std::string StreamableToString(const T& streamable) { - return (Message() << streamable).GetString(); -} - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_MESSAGE_H_ -// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Authors: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan), eefacm@gmail.com (Sean Mcafee) -// -// The Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) -// -// This header file declares the String class and functions used internally by -// Google Test. They are subject to change without notice. They should not used -// by code external to Google Test. -// -// This header file is #included by <gtest/internal/gtest-internal.h>. -// It should not be #included by other files. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_STRING_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_STRING_H_ - -#ifdef __BORLANDC__ -// string.h is not guaranteed to provide strcpy on C++ Builder. -# include <mem.h> -#endif - -#include <string.h> -#include <string> - - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// String - an abstract class holding static string utilities. -class GTEST_API_ String { - public: - // Static utility methods - - // Clones a 0-terminated C string, allocating memory using new. The - // caller is responsible for deleting the return value using - // delete[]. Returns the cloned string, or NULL if the input is - // NULL. - // - // This is different from strdup() in string.h, which allocates - // memory using malloc(). - static const char* CloneCString(const char* c_str); - -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - // Windows CE does not have the 'ANSI' versions of Win32 APIs. To be - // able to pass strings to Win32 APIs on CE we need to convert them - // to 'Unicode', UTF-16. - - // Creates a UTF-16 wide string from the given ANSI string, allocating - // memory using new. The caller is responsible for deleting the return - // value using delete[]. Returns the wide string, or NULL if the - // input is NULL. - // - // The wide string is created using the ANSI codepage (CP_ACP) to - // match the behaviour of the ANSI versions of Win32 calls and the - // C runtime. - static LPCWSTR AnsiToUtf16(const char* c_str); - - // Creates an ANSI string from the given wide string, allocating - // memory using new. The caller is responsible for deleting the return - // value using delete[]. Returns the ANSI string, or NULL if the - // input is NULL. - // - // The returned string is created using the ANSI codepage (CP_ACP) to - // match the behaviour of the ANSI versions of Win32 calls and the - // C runtime. - static const char* Utf16ToAnsi(LPCWSTR utf16_str); -#endif - - // Compares two C strings. Returns true iff they have the same content. - // - // Unlike strcmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). A - // NULL C string is considered different to any non-NULL C string, - // including the empty string. - static bool CStringEquals(const char* lhs, const char* rhs); - - // Converts a wide C string to a String using the UTF-8 encoding. - // NULL will be converted to "(null)". If an error occurred during - // the conversion, "(failed to convert from wide string)" is - // returned. - static std::string ShowWideCString(const wchar_t* wide_c_str); - - // Compares two wide C strings. Returns true iff they have the same - // content. - // - // Unlike wcscmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). A - // NULL C string is considered different to any non-NULL C string, - // including the empty string. - static bool WideCStringEquals(const wchar_t* lhs, const wchar_t* rhs); - - // Compares two C strings, ignoring case. Returns true iff they - // have the same content. - // - // Unlike strcasecmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). - // A NULL C string is considered different to any non-NULL C string, - // including the empty string. - static bool CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(const char* lhs, - const char* rhs); - - // Compares two wide C strings, ignoring case. Returns true iff they - // have the same content. - // - // Unlike wcscasecmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). - // A NULL C string is considered different to any non-NULL wide C string, - // including the empty string. - // NB: The implementations on different platforms slightly differ. - // On windows, this method uses _wcsicmp which compares according to LC_CTYPE - // environment variable. On GNU platform this method uses wcscasecmp - // which compares according to LC_CTYPE category of the current locale. - // On MacOS X, it uses towlower, which also uses LC_CTYPE category of the - // current locale. - static bool CaseInsensitiveWideCStringEquals(const wchar_t* lhs, - const wchar_t* rhs); - - // Returns true iff the given string ends with the given suffix, ignoring - // case. Any string is considered to end with an empty suffix. - static bool EndsWithCaseInsensitive( - const std::string& str, const std::string& suffix); - - // Formats an int value as "%02d". - static std::string FormatIntWidth2(int value); // "%02d" for width == 2 - - // Formats an int value as "%X". - static std::string FormatHexInt(int value); - - // Formats a byte as "%02X". - static std::string FormatByte(unsigned char value); - - private: - String(); // Not meant to be instantiated. -}; // class String - -// Gets the content of the stringstream's buffer as an std::string. Each '\0' -// character in the buffer is replaced with "\\0". -GTEST_API_ std::string StringStreamToString(::std::stringstream* stream); - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_STRING_H_ -// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: keith.ray@gmail.com (Keith Ray) -// -// Google Test filepath utilities -// -// This header file declares classes and functions used internally by -// Google Test. They are subject to change without notice. -// -// This file is #included in <gtest/internal/gtest-internal.h>. -// Do not include this header file separately! - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_FILEPATH_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_FILEPATH_H_ - - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// FilePath - a class for file and directory pathname manipulation which -// handles platform-specific conventions (like the pathname separator). -// Used for helper functions for naming files in a directory for xml output. -// Except for Set methods, all methods are const or static, which provides an -// "immutable value object" -- useful for peace of mind. -// A FilePath with a value ending in a path separator ("like/this/") represents -// a directory, otherwise it is assumed to represent a file. In either case, -// it may or may not represent an actual file or directory in the file system. -// Names are NOT checked for syntax correctness -- no checking for illegal -// characters, malformed paths, etc. - -class GTEST_API_ FilePath { - public: - FilePath() : pathname_("") { } - FilePath(const FilePath& rhs) : pathname_(rhs.pathname_) { } - - explicit FilePath(const std::string& pathname) : pathname_(pathname) { - Normalize(); - } - - FilePath& operator=(const FilePath& rhs) { - Set(rhs); - return *this; - } - - void Set(const FilePath& rhs) { - pathname_ = rhs.pathname_; - } - - const std::string& string() const { return pathname_; } - const char* c_str() const { return pathname_.c_str(); } - - // Returns the current working directory, or "" if unsuccessful. - static FilePath GetCurrentDir(); - - // Given directory = "dir", base_name = "test", number = 0, - // extension = "xml", returns "dir/test.xml". If number is greater - // than zero (e.g., 12), returns "dir/test_12.xml". - // On Windows platform, uses \ as the separator rather than /. - static FilePath MakeFileName(const FilePath& directory, - const FilePath& base_name, - int number, - const char* extension); - - // Given directory = "dir", relative_path = "test.xml", - // returns "dir/test.xml". - // On Windows, uses \ as the separator rather than /. - static FilePath ConcatPaths(const FilePath& directory, - const FilePath& relative_path); - - // Returns a pathname for a file that does not currently exist. The pathname - // will be directory/base_name.extension or - // directory/base_name_<number>.extension if directory/base_name.extension - // already exists. The number will be incremented until a pathname is found - // that does not already exist. - // Examples: 'dir/foo_test.xml' or 'dir/foo_test_1.xml'. - // There could be a race condition if two or more processes are calling this - // function at the same time -- they could both pick the same filename. - static FilePath GenerateUniqueFileName(const FilePath& directory, - const FilePath& base_name, - const char* extension); - - // Returns true iff the path is "". - bool IsEmpty() const { return pathname_.empty(); } - - // If input name has a trailing separator character, removes it and returns - // the name, otherwise return the name string unmodified. - // On Windows platform, uses \ as the separator, other platforms use /. - FilePath RemoveTrailingPathSeparator() const; - - // Returns a copy of the FilePath with the directory part removed. - // Example: FilePath("path/to/file").RemoveDirectoryName() returns - // FilePath("file"). If there is no directory part ("just_a_file"), it returns - // the FilePath unmodified. If there is no file part ("just_a_dir/") it - // returns an empty FilePath (""). - // On Windows platform, '\' is the path separator, otherwise it is '/'. - FilePath RemoveDirectoryName() const; - - // RemoveFileName returns the directory path with the filename removed. - // Example: FilePath("path/to/file").RemoveFileName() returns "path/to/". - // If the FilePath is "a_file" or "/a_file", RemoveFileName returns - // FilePath("./") or, on Windows, FilePath(".\\"). If the filepath does - // not have a file, like "just/a/dir/", it returns the FilePath unmodified. - // On Windows platform, '\' is the path separator, otherwise it is '/'. - FilePath RemoveFileName() const; - - // Returns a copy of the FilePath with the case-insensitive extension removed. - // Example: FilePath("dir/file.exe").RemoveExtension("EXE") returns - // FilePath("dir/file"). If a case-insensitive extension is not - // found, returns a copy of the original FilePath. - FilePath RemoveExtension(const char* extension) const; - - // Creates directories so that path exists. Returns true if successful or if - // the directories already exist; returns false if unable to create - // directories for any reason. Will also return false if the FilePath does - // not represent a directory (that is, it doesn't end with a path separator). - bool CreateDirectoriesRecursively() const; - - // Create the directory so that path exists. Returns true if successful or - // if the directory already exists; returns false if unable to create the - // directory for any reason, including if the parent directory does not - // exist. Not named "CreateDirectory" because that's a macro on Windows. - bool CreateFolder() const; - - // Returns true if FilePath describes something in the file-system, - // either a file, directory, or whatever, and that something exists. - bool FileOrDirectoryExists() const; - - // Returns true if pathname describes a directory in the file-system - // that exists. - bool DirectoryExists() const; - - // Returns true if FilePath ends with a path separator, which indicates that - // it is intended to represent a directory. Returns false otherwise. - // This does NOT check that a directory (or file) actually exists. - bool IsDirectory() const; - - // Returns true if pathname describes a root directory. (Windows has one - // root directory per disk drive.) - bool IsRootDirectory() const; - - // Returns true if pathname describes an absolute path. - bool IsAbsolutePath() const; - - private: - // Replaces multiple consecutive separators with a single separator. - // For example, "bar///foo" becomes "bar/foo". Does not eliminate other - // redundancies that might be in a pathname involving "." or "..". - // - // A pathname with multiple consecutive separators may occur either through - // user error or as a result of some scripts or APIs that generate a pathname - // with a trailing separator. On other platforms the same API or script - // may NOT generate a pathname with a trailing "/". Then elsewhere that - // pathname may have another "/" and pathname components added to it, - // without checking for the separator already being there. - // The script language and operating system may allow paths like "foo//bar" - // but some of the functions in FilePath will not handle that correctly. In - // particular, RemoveTrailingPathSeparator() only removes one separator, and - // it is called in CreateDirectoriesRecursively() assuming that it will change - // a pathname from directory syntax (trailing separator) to filename syntax. - // - // On Windows this method also replaces the alternate path separator '/' with - // the primary path separator '\\', so that for example "bar\\/\\foo" becomes - // "bar\\foo". - - void Normalize(); - - // Returns a pointer to the last occurence of a valid path separator in - // the FilePath. On Windows, for example, both '/' and '\' are valid path - // separators. Returns NULL if no path separator was found. - const char* FindLastPathSeparator() const; - - std::string pathname_; -}; // class FilePath - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_FILEPATH_H_ -// This file was GENERATED by command: -// pump.py gtest-type-util.h.pump -// DO NOT EDIT BY HAND!!! - -// Copyright 2008 Google Inc. -// All Rights Reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Type utilities needed for implementing typed and type-parameterized -// tests. This file is generated by a SCRIPT. DO NOT EDIT BY HAND! -// -// Currently we support at most 50 types in a list, and at most 50 -// type-parameterized tests in one type-parameterized test case. -// Please contact googletestframework@googlegroups.com if you need -// more. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_TYPE_UTIL_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_TYPE_UTIL_H_ - - -// #ifdef __GNUC__ is too general here. It is possible to use gcc without using -// libstdc++ (which is where cxxabi.h comes from). -# if GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ -# include <cxxabi.h> -# elif defined(__HP_aCC) -# include <acxx_demangle.h> -# endif // GTEST_HASH_CXXABI_H_ - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// GetTypeName<T>() returns a human-readable name of type T. -// NB: This function is also used in Google Mock, so don't move it inside of -// the typed-test-only section below. -template <typename T> -std::string GetTypeName() { -# if GTEST_HAS_RTTI - - const char* const name = typeid(T).name(); -# if GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ || defined(__HP_aCC) - int status = 0; - // gcc's implementation of typeid(T).name() mangles the type name, - // so we have to demangle it. -# if GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ - using abi::__cxa_demangle; -# endif // GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ - char* const readable_name = __cxa_demangle(name, 0, 0, &status); - const std::string name_str(status == 0 ? readable_name : name); - free(readable_name); - return name_str; -# else - return name; -# endif // GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ || __HP_aCC - -# else - - return "<type>"; - -# endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI -} - -#if GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST || GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - -// AssertyTypeEq<T1, T2>::type is defined iff T1 and T2 are the same -// type. This can be used as a compile-time assertion to ensure that -// two types are equal. - -template <typename T1, typename T2> -struct AssertTypeEq; - -template <typename T> -struct AssertTypeEq<T, T> { - typedef bool type; -}; - -// A unique type used as the default value for the arguments of class -// template Types. This allows us to simulate variadic templates -// (e.g. Types<int>, Type<int, double>, and etc), which C++ doesn't -// support directly. -struct None {}; - -// The following family of struct and struct templates are used to -// represent type lists. In particular, TypesN<T1, T2, ..., TN> -// represents a type list with N types (T1, T2, ..., and TN) in it. -// Except for Types0, every struct in the family has two member types: -// Head for the first type in the list, and Tail for the rest of the -// list. - -// The empty type list. -struct Types0 {}; - -// Type lists of length 1, 2, 3, and so on. - -template <typename T1> -struct Types1 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types0 Tail; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2> -struct Types2 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types1<T2> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> -struct Types3 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types2<T2, T3> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4> -struct Types4 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types3<T2, T3, T4> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5> -struct Types5 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types4<T2, T3, T4, T5> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6> -struct Types6 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types5<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7> -struct Types7 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types6<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8> -struct Types8 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types7<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9> -struct Types9 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types8<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10> -struct Types10 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types9<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11> -struct Types11 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types10<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12> -struct Types12 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types11<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13> -struct Types13 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types12<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14> -struct Types14 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types13<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15> -struct Types15 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types14<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16> -struct Types16 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types15<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17> -struct Types17 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types16<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18> -struct Types18 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types17<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19> -struct Types19 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types18<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20> -struct Types20 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types19<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21> -struct Types21 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types20<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22> -struct Types22 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types21<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23> -struct Types23 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types22<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24> -struct Types24 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types23<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25> -struct Types25 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types24<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26> -struct Types26 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types25<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27> -struct Types27 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types26<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28> -struct Types28 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types27<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29> -struct Types29 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types28<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30> -struct Types30 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types29<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31> -struct Types31 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types30<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32> -struct Types32 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types31<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33> -struct Types33 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types32<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34> -struct Types34 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types33<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35> -struct Types35 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types34<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36> -struct Types36 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types35<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37> -struct Types37 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types36<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38> -struct Types38 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types37<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39> -struct Types39 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types38<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40> -struct Types40 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types39<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41> -struct Types41 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types40<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42> -struct Types42 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types41<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43> -struct Types43 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types42<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44> -struct Types44 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types43<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45> -struct Types45 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types44<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46> -struct Types46 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types45<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47> -struct Types47 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types46<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46, T47> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48> -struct Types48 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types47<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46, T47, T48> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48, typename T49> -struct Types49 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types48<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49> Tail; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48, typename T49, typename T50> -struct Types50 { - typedef T1 Head; - typedef Types49<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49, T50> Tail; -}; - - -} // namespace internal - -// We don't want to require the users to write TypesN<...> directly, -// as that would require them to count the length. Types<...> is much -// easier to write, but generates horrible messages when there is a -// compiler error, as gcc insists on printing out each template -// argument, even if it has the default value (this means Types<int> -// will appear as Types<int, None, None, ..., None> in the compiler -// errors). -// -// Our solution is to combine the best part of the two approaches: a -// user would write Types<T1, ..., TN>, and Google Test will translate -// that to TypesN<T1, ..., TN> internally to make error messages -// readable. The translation is done by the 'type' member of the -// Types template. -template <typename T1 = internal::None, typename T2 = internal::None, - typename T3 = internal::None, typename T4 = internal::None, - typename T5 = internal::None, typename T6 = internal::None, - typename T7 = internal::None, typename T8 = internal::None, - typename T9 = internal::None, typename T10 = internal::None, - typename T11 = internal::None, typename T12 = internal::None, - typename T13 = internal::None, typename T14 = internal::None, - typename T15 = internal::None, typename T16 = internal::None, - typename T17 = internal::None, typename T18 = internal::None, - typename T19 = internal::None, typename T20 = internal::None, - typename T21 = internal::None, typename T22 = internal::None, - typename T23 = internal::None, typename T24 = internal::None, - typename T25 = internal::None, typename T26 = internal::None, - typename T27 = internal::None, typename T28 = internal::None, - typename T29 = internal::None, typename T30 = internal::None, - typename T31 = internal::None, typename T32 = internal::None, - typename T33 = internal::None, typename T34 = internal::None, - typename T35 = internal::None, typename T36 = internal::None, - typename T37 = internal::None, typename T38 = internal::None, - typename T39 = internal::None, typename T40 = internal::None, - typename T41 = internal::None, typename T42 = internal::None, - typename T43 = internal::None, typename T44 = internal::None, - typename T45 = internal::None, typename T46 = internal::None, - typename T47 = internal::None, typename T48 = internal::None, - typename T49 = internal::None, typename T50 = internal::None> -struct Types { - typedef internal::Types50<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49, T50> type; -}; - -template <> -struct Types<internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types0 type; -}; -template <typename T1> -struct Types<T1, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types1<T1> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2> -struct Types<T1, T2, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types2<T1, T2> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types3<T1, T2, T3> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types4<T1, T2, T3, T4> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types5<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types6<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types7<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types8<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types9<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types10<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types11<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types12<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types13<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types14<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types15<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types16<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types17<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types18<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types19<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types20<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types21<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types22<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types23<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types24<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types25<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types26<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types27<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types28<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types29<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types30<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types31<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types32<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types33<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types34<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types35<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types36<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types37<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types38<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types39<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types40<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types41<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types42<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types43<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42, T43> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types44<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42, T43, T44> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, - internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, - internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types45<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42, T43, T44, T45> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, - T46, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types46<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, - T46, T47, internal::None, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types47<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, - T46, T47, T48, internal::None, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types48<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48> type; -}; -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48, typename T49> -struct Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, - T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, - T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, - T46, T47, T48, T49, internal::None> { - typedef internal::Types49<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49> type; -}; - -namespace internal { - -# define GTEST_TEMPLATE_ template <typename T> class - -// The template "selector" struct TemplateSel<Tmpl> is used to -// represent Tmpl, which must be a class template with one type -// parameter, as a type. TemplateSel<Tmpl>::Bind<T>::type is defined -// as the type Tmpl<T>. This allows us to actually instantiate the -// template "selected" by TemplateSel<Tmpl>. -// -// This trick is necessary for simulating typedef for class templates, -// which C++ doesn't support directly. -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Tmpl> -struct TemplateSel { - template <typename T> - struct Bind { - typedef Tmpl<T> type; - }; -}; - -# define GTEST_BIND_(TmplSel, T) \ - TmplSel::template Bind<T>::type - -// A unique struct template used as the default value for the -// arguments of class template Templates. This allows us to simulate -// variadic templates (e.g. Templates<int>, Templates<int, double>, -// and etc), which C++ doesn't support directly. -template <typename T> -struct NoneT {}; - -// The following family of struct and struct templates are used to -// represent template lists. In particular, TemplatesN<T1, T2, ..., -// TN> represents a list of N templates (T1, T2, ..., and TN). Except -// for Templates0, every struct in the family has two member types: -// Head for the selector of the first template in the list, and Tail -// for the rest of the list. - -// The empty template list. -struct Templates0 {}; - -// Template lists of length 1, 2, 3, and so on. - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1> -struct Templates1 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates0 Tail; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2> -struct Templates2 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates1<T2> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3> -struct Templates3 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates2<T2, T3> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4> -struct Templates4 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates3<T2, T3, T4> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5> -struct Templates5 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates4<T2, T3, T4, T5> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6> -struct Templates6 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates5<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7> -struct Templates7 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates6<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8> -struct Templates8 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates7<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9> -struct Templates9 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates8<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10> -struct Templates10 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates9<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11> -struct Templates11 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates10<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12> -struct Templates12 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates11<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13> -struct Templates13 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates12<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14> -struct Templates14 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates13<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15> -struct Templates15 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates14<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16> -struct Templates16 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates15<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17> -struct Templates17 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates16<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18> -struct Templates18 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates17<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19> -struct Templates19 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates18<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20> -struct Templates20 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates19<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21> -struct Templates21 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates20<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22> -struct Templates22 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates21<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23> -struct Templates23 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates22<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24> -struct Templates24 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates23<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25> -struct Templates25 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates24<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26> -struct Templates26 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates25<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27> -struct Templates27 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates26<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28> -struct Templates28 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates27<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29> -struct Templates29 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates28<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30> -struct Templates30 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates29<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31> -struct Templates31 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates30<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32> -struct Templates32 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates31<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33> -struct Templates33 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates32<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34> -struct Templates34 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates33<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35> -struct Templates35 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates34<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36> -struct Templates36 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates35<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37> -struct Templates37 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates36<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38> -struct Templates38 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates37<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39> -struct Templates39 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates38<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40> -struct Templates40 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates39<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41> -struct Templates41 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates40<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42> -struct Templates42 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates41<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43> -struct Templates43 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates42<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44> -struct Templates44 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates43<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43, T44> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45> -struct Templates45 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates44<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43, T44, T45> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46> -struct Templates46 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates45<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43, T44, T45, T46> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T47> -struct Templates47 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates46<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43, T44, T45, T46, T47> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T47, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T48> -struct Templates48 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates47<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T47, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T48, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T49> -struct Templates49 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates48<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49> Tail; -}; - -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T47, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T48, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T49, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T50> -struct Templates50 { - typedef TemplateSel<T1> Head; - typedef Templates49<T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49, T50> Tail; -}; - - -// We don't want to require the users to write TemplatesN<...> directly, -// as that would require them to count the length. Templates<...> is much -// easier to write, but generates horrible messages when there is a -// compiler error, as gcc insists on printing out each template -// argument, even if it has the default value (this means Templates<list> -// will appear as Templates<list, NoneT, NoneT, ..., NoneT> in the compiler -// errors). -// -// Our solution is to combine the best part of the two approaches: a -// user would write Templates<T1, ..., TN>, and Google Test will translate -// that to TemplatesN<T1, ..., TN> internally to make error messages -// readable. The translation is done by the 'type' member of the -// Templates template. -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T47 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T48 = NoneT, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T49 = NoneT, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T50 = NoneT> -struct Templates { - typedef Templates50<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49, T50> type; -}; - -template <> -struct Templates<NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT> { - typedef Templates0 type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1> -struct Templates<T1, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT> { - typedef Templates1<T1> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2> -struct Templates<T1, T2, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT> { - typedef Templates2<T1, T2> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates3<T1, T2, T3> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates4<T1, T2, T3, T4> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates5<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates6<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates7<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates8<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates9<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates10<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates11<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates12<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates13<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates14<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates15<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates16<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates17<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates18<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates19<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates20<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates21<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates22<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates23<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates24<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates25<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates26<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates27<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates28<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT> { - typedef Templates29<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates30<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates31<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates32<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates33<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates34<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates35<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates36<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates37<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates38<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates39<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates40<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, NoneT, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates41<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, NoneT, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates42<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates43<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42, T43> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, - NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates44<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42, T43, T44> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, - T45, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates45<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42, T43, T44, T45> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, - T45, T46, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates46<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42, T43, T44, T45, T46> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T47> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, - T45, T46, T47, NoneT, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates47<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T47, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T48> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, - T45, T46, T47, T48, NoneT, NoneT> { - typedef Templates48<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48> type; -}; -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T1, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T2, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T3, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T4, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T5, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T6, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T7, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T8, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T9, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T10, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T11, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T12, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T13, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T14, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T15, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T16, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T17, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T18, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T19, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T20, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T21, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T22, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T23, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T24, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T25, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T26, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T27, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T28, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T29, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T30, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T31, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T32, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T33, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T34, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T35, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T36, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T37, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T38, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T39, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T40, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T41, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T42, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T43, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T44, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T45, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T46, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T47, GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T48, - GTEST_TEMPLATE_ T49> -struct Templates<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, T14, - T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, T29, - T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, - T45, T46, T47, T48, T49, NoneT> { - typedef Templates49<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49> type; -}; - -// The TypeList template makes it possible to use either a single type -// or a Types<...> list in TYPED_TEST_CASE() and -// INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(). - -template <typename T> -struct TypeList { - typedef Types1<T> type; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48, typename T49, typename T50> -struct TypeList<Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49, T50> > { - typedef typename Types<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49, T50>::type type; -}; - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST || GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_TYPE_UTIL_H_ - -// Due to C++ preprocessor weirdness, we need double indirection to -// concatenate two tokens when one of them is __LINE__. Writing -// -// foo ## __LINE__ -// -// will result in the token foo__LINE__, instead of foo followed by -// the current line number. For more details, see -// http://www.parashift.com/c++-faq-lite/misc-technical-issues.html#faq-39.6 -#define GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(foo, bar) GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_IMPL_(foo, bar) -#define GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_IMPL_(foo, bar) foo ## bar - -class ProtocolMessage; -namespace proto2 { class Message; } - -namespace testing { - -// Forward declarations. - -class AssertionResult; // Result of an assertion. -class Message; // Represents a failure message. -class Test; // Represents a test. -class TestInfo; // Information about a test. -class TestPartResult; // Result of a test part. -class UnitTest; // A collection of test cases. - -template <typename T> -::std::string PrintToString(const T& value); - -namespace internal { - -struct TraceInfo; // Information about a trace point. -class ScopedTrace; // Implements scoped trace. -class TestInfoImpl; // Opaque implementation of TestInfo -class UnitTestImpl; // Opaque implementation of UnitTest - -// How many times InitGoogleTest() has been called. -GTEST_API_ extern int g_init_gtest_count; - -// The text used in failure messages to indicate the start of the -// stack trace. -GTEST_API_ extern const char kStackTraceMarker[]; - -// Two overloaded helpers for checking at compile time whether an -// expression is a null pointer literal (i.e. NULL or any 0-valued -// compile-time integral constant). Their return values have -// different sizes, so we can use sizeof() to test which version is -// picked by the compiler. These helpers have no implementations, as -// we only need their signatures. -// -// Given IsNullLiteralHelper(x), the compiler will pick the first -// version if x can be implicitly converted to Secret*, and pick the -// second version otherwise. Since Secret is a secret and incomplete -// type, the only expression a user can write that has type Secret* is -// a null pointer literal. Therefore, we know that x is a null -// pointer literal if and only if the first version is picked by the -// compiler. -char IsNullLiteralHelper(Secret* p); -char (&IsNullLiteralHelper(...))[2]; // NOLINT - -// A compile-time bool constant that is true if and only if x is a -// null pointer literal (i.e. NULL or any 0-valued compile-time -// integral constant). -#ifdef GTEST_ELLIPSIS_NEEDS_POD_ -// We lose support for NULL detection where the compiler doesn't like -// passing non-POD classes through ellipsis (...). -# define GTEST_IS_NULL_LITERAL_(x) false -#else -# define GTEST_IS_NULL_LITERAL_(x) \ - (sizeof(::testing::internal::IsNullLiteralHelper(x)) == 1) -#endif // GTEST_ELLIPSIS_NEEDS_POD_ - -// Appends the user-supplied message to the Google-Test-generated message. -GTEST_API_ std::string AppendUserMessage( - const std::string& gtest_msg, const Message& user_msg); - -#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS - -// This exception is thrown by (and only by) a failed Google Test -// assertion when GTEST_FLAG(throw_on_failure) is true (if exceptions -// are enabled). We derive it from std::runtime_error, which is for -// errors presumably detectable only at run time. Since -// std::runtime_error inherits from std::exception, many testing -// frameworks know how to extract and print the message inside it. -class GTEST_API_ GoogleTestFailureException : public ::std::runtime_error { - public: - explicit GoogleTestFailureException(const TestPartResult& failure); -}; - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS - -// A helper class for creating scoped traces in user programs. -class GTEST_API_ ScopedTrace { - public: - // The c'tor pushes the given source file location and message onto - // a trace stack maintained by Google Test. - ScopedTrace(const char* file, int line, const Message& message); - - // The d'tor pops the info pushed by the c'tor. - // - // Note that the d'tor is not virtual in order to be efficient. - // Don't inherit from ScopedTrace! - ~ScopedTrace(); - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ScopedTrace); -} GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; // A ScopedTrace object does its job in its - // c'tor and d'tor. Therefore it doesn't - // need to be used otherwise. - -// Constructs and returns the message for an equality assertion -// (e.g. ASSERT_EQ, EXPECT_STREQ, etc) failure. -// -// The first four parameters are the expressions used in the assertion -// and their values, as strings. For example, for ASSERT_EQ(foo, bar) -// where foo is 5 and bar is 6, we have: -// -// expected_expression: "foo" -// actual_expression: "bar" -// expected_value: "5" -// actual_value: "6" -// -// The ignoring_case parameter is true iff the assertion is a -// *_STRCASEEQ*. When it's true, the string " (ignoring case)" will -// be inserted into the message. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult EqFailure(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const std::string& expected_value, - const std::string& actual_value, - bool ignoring_case); - -// Constructs a failure message for Boolean assertions such as EXPECT_TRUE. -GTEST_API_ std::string GetBoolAssertionFailureMessage( - const AssertionResult& assertion_result, - const char* expression_text, - const char* actual_predicate_value, - const char* expected_predicate_value); - -// This template class represents an IEEE floating-point number -// (either single-precision or double-precision, depending on the -// template parameters). -// -// The purpose of this class is to do more sophisticated number -// comparison. (Due to round-off error, etc, it's very unlikely that -// two floating-points will be equal exactly. Hence a naive -// comparison by the == operation often doesn't work.) -// -// Format of IEEE floating-point: -// -// The most-significant bit being the leftmost, an IEEE -// floating-point looks like -// -// sign_bit exponent_bits fraction_bits -// -// Here, sign_bit is a single bit that designates the sign of the -// number. -// -// For float, there are 8 exponent bits and 23 fraction bits. -// -// For double, there are 11 exponent bits and 52 fraction bits. -// -// More details can be found at -// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_floating-point_standard. -// -// Template parameter: -// -// RawType: the raw floating-point type (either float or double) -template <typename RawType> -class FloatingPoint { - public: - // Defines the unsigned integer type that has the same size as the - // floating point number. - typedef typename TypeWithSize<sizeof(RawType)>::UInt Bits; - - // Constants. - - // # of bits in a number. - static const size_t kBitCount = 8*sizeof(RawType); - - // # of fraction bits in a number. - static const size_t kFractionBitCount = - std::numeric_limits<RawType>::digits - 1; - - // # of exponent bits in a number. - static const size_t kExponentBitCount = kBitCount - 1 - kFractionBitCount; - - // The mask for the sign bit. - static const Bits kSignBitMask = static_cast<Bits>(1) << (kBitCount - 1); - - // The mask for the fraction bits. - static const Bits kFractionBitMask = - ~static_cast<Bits>(0) >> (kExponentBitCount + 1); - - // The mask for the exponent bits. - static const Bits kExponentBitMask = ~(kSignBitMask | kFractionBitMask); - - // How many ULP's (Units in the Last Place) we want to tolerate when - // comparing two numbers. The larger the value, the more error we - // allow. A 0 value means that two numbers must be exactly the same - // to be considered equal. - // - // The maximum error of a single floating-point operation is 0.5 - // units in the last place. On Intel CPU's, all floating-point - // calculations are done with 80-bit precision, while double has 64 - // bits. Therefore, 4 should be enough for ordinary use. - // - // See the following article for more details on ULP: - // http://randomascii.wordpress.com/2012/02/25/comparing-floating-point-numbers-2012-edition/ - static const size_t kMaxUlps = 4; - - // Constructs a FloatingPoint from a raw floating-point number. - // - // On an Intel CPU, passing a non-normalized NAN (Not a Number) - // around may change its bits, although the new value is guaranteed - // to be also a NAN. Therefore, don't expect this constructor to - // preserve the bits in x when x is a NAN. - explicit FloatingPoint(const RawType& x) { u_.value_ = x; } - - // Static methods - - // Reinterprets a bit pattern as a floating-point number. - // - // This function is needed to test the AlmostEquals() method. - static RawType ReinterpretBits(const Bits bits) { - FloatingPoint fp(0); - fp.u_.bits_ = bits; - return fp.u_.value_; - } - - // Returns the floating-point number that represent positive infinity. - static RawType Infinity() { - return ReinterpretBits(kExponentBitMask); - } - - // Returns the maximum representable finite floating-point number. - static RawType Max(); - - // Non-static methods - - // Returns the bits that represents this number. - const Bits &bits() const { return u_.bits_; } - - // Returns the exponent bits of this number. - Bits exponent_bits() const { return kExponentBitMask & u_.bits_; } - - // Returns the fraction bits of this number. - Bits fraction_bits() const { return kFractionBitMask & u_.bits_; } - - // Returns the sign bit of this number. - Bits sign_bit() const { return kSignBitMask & u_.bits_; } - - // Returns true iff this is NAN (not a number). - bool is_nan() const { - // It's a NAN if the exponent bits are all ones and the fraction - // bits are not entirely zeros. - return (exponent_bits() == kExponentBitMask) && (fraction_bits() != 0); - } - - // Returns true iff this number is at most kMaxUlps ULP's away from - // rhs. In particular, this function: - // - // - returns false if either number is (or both are) NAN. - // - treats really large numbers as almost equal to infinity. - // - thinks +0.0 and -0.0 are 0 DLP's apart. - bool AlmostEquals(const FloatingPoint& rhs) const { - // The IEEE standard says that any comparison operation involving - // a NAN must return false. - if (is_nan() || rhs.is_nan()) return false; - - return DistanceBetweenSignAndMagnitudeNumbers(u_.bits_, rhs.u_.bits_) - <= kMaxUlps; - } - - private: - // The data type used to store the actual floating-point number. - union FloatingPointUnion { - RawType value_; // The raw floating-point number. - Bits bits_; // The bits that represent the number. - }; - - // Converts an integer from the sign-and-magnitude representation to - // the biased representation. More precisely, let N be 2 to the - // power of (kBitCount - 1), an integer x is represented by the - // unsigned number x + N. - // - // For instance, - // - // -N + 1 (the most negative number representable using - // sign-and-magnitude) is represented by 1; - // 0 is represented by N; and - // N - 1 (the biggest number representable using - // sign-and-magnitude) is represented by 2N - 1. - // - // Read http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signed_number_representations - // for more details on signed number representations. - static Bits SignAndMagnitudeToBiased(const Bits &sam) { - if (kSignBitMask & sam) { - // sam represents a negative number. - return ~sam + 1; - } else { - // sam represents a positive number. - return kSignBitMask | sam; - } - } - - // Given two numbers in the sign-and-magnitude representation, - // returns the distance between them as an unsigned number. - static Bits DistanceBetweenSignAndMagnitudeNumbers(const Bits &sam1, - const Bits &sam2) { - const Bits biased1 = SignAndMagnitudeToBiased(sam1); - const Bits biased2 = SignAndMagnitudeToBiased(sam2); - return (biased1 >= biased2) ? (biased1 - biased2) : (biased2 - biased1); - } - - FloatingPointUnion u_; -}; - -// We cannot use std::numeric_limits<T>::max() as it clashes with the max() -// macro defined by <windows.h>. -template <> -inline float FloatingPoint<float>::Max() { return FLT_MAX; } -template <> -inline double FloatingPoint<double>::Max() { return DBL_MAX; } - -// Typedefs the instances of the FloatingPoint template class that we -// care to use. -typedef FloatingPoint<float> Float; -typedef FloatingPoint<double> Double; - -// In order to catch the mistake of putting tests that use different -// test fixture classes in the same test case, we need to assign -// unique IDs to fixture classes and compare them. The TypeId type is -// used to hold such IDs. The user should treat TypeId as an opaque -// type: the only operation allowed on TypeId values is to compare -// them for equality using the == operator. -typedef const void* TypeId; - -template <typename T> -class TypeIdHelper { - public: - // dummy_ must not have a const type. Otherwise an overly eager - // compiler (e.g. MSVC 7.1 & 8.0) may try to merge - // TypeIdHelper<T>::dummy_ for different Ts as an "optimization". - static bool dummy_; -}; - -template <typename T> -bool TypeIdHelper<T>::dummy_ = false; - -// GetTypeId<T>() returns the ID of type T. Different values will be -// returned for different types. Calling the function twice with the -// same type argument is guaranteed to return the same ID. -template <typename T> -TypeId GetTypeId() { - // The compiler is required to allocate a different - // TypeIdHelper<T>::dummy_ variable for each T used to instantiate - // the template. Therefore, the address of dummy_ is guaranteed to - // be unique. - return &(TypeIdHelper<T>::dummy_); -} - -// Returns the type ID of ::testing::Test. Always call this instead -// of GetTypeId< ::testing::Test>() to get the type ID of -// ::testing::Test, as the latter may give the wrong result due to a -// suspected linker bug when compiling Google Test as a Mac OS X -// framework. -GTEST_API_ TypeId GetTestTypeId(); - -// Defines the abstract factory interface that creates instances -// of a Test object. -class TestFactoryBase { - public: - virtual ~TestFactoryBase() {} - - // Creates a test instance to run. The instance is both created and destroyed - // within TestInfoImpl::Run() - virtual Test* CreateTest() = 0; - - protected: - TestFactoryBase() {} - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestFactoryBase); -}; - -// This class provides implementation of TeastFactoryBase interface. -// It is used in TEST and TEST_F macros. -template <class TestClass> -class TestFactoryImpl : public TestFactoryBase { - public: - virtual Test* CreateTest() { return new TestClass; } -}; - -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - -// Predicate-formatters for implementing the HRESULT checking macros -// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_HRESULT_{SUCCEEDED|FAILED} -// We pass a long instead of HRESULT to avoid causing an -// include dependency for the HRESULT type. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsHRESULTSuccess(const char* expr, - long hr); // NOLINT -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsHRESULTFailure(const char* expr, - long hr); // NOLINT - -#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - -// Types of SetUpTestCase() and TearDownTestCase() functions. -typedef void (*SetUpTestCaseFunc)(); -typedef void (*TearDownTestCaseFunc)(); - -// Creates a new TestInfo object and registers it with Google Test; -// returns the created object. -// -// Arguments: -// -// test_case_name: name of the test case -// name: name of the test -// type_param the name of the test's type parameter, or NULL if -// this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test. -// value_param text representation of the test's value parameter, -// or NULL if this is not a type-parameterized test. -// fixture_class_id: ID of the test fixture class -// set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test case -// tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test case -// factory: pointer to the factory that creates a test object. -// The newly created TestInfo instance will assume -// ownership of the factory object. -GTEST_API_ TestInfo* MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( - const char* test_case_name, - const char* name, - const char* type_param, - const char* value_param, - TypeId fixture_class_id, - SetUpTestCaseFunc set_up_tc, - TearDownTestCaseFunc tear_down_tc, - TestFactoryBase* factory); - -// If *pstr starts with the given prefix, modifies *pstr to be right -// past the prefix and returns true; otherwise leaves *pstr unchanged -// and returns false. None of pstr, *pstr, and prefix can be NULL. -GTEST_API_ bool SkipPrefix(const char* prefix, const char** pstr); - -#if GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST || GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - -// State of the definition of a type-parameterized test case. -class GTEST_API_ TypedTestCasePState { - public: - TypedTestCasePState() : registered_(false) {} - - // Adds the given test name to defined_test_names_ and return true - // if the test case hasn't been registered; otherwise aborts the - // program. - bool AddTestName(const char* file, int line, const char* case_name, - const char* test_name) { - if (registered_) { - fprintf(stderr, "%s Test %s must be defined before " - "REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(%s, ...).\n", - FormatFileLocation(file, line).c_str(), test_name, case_name); - fflush(stderr); - posix::Abort(); - } - defined_test_names_.insert(test_name); - return true; - } - - // Verifies that registered_tests match the test names in - // defined_test_names_; returns registered_tests if successful, or - // aborts the program otherwise. - const char* VerifyRegisteredTestNames( - const char* file, int line, const char* registered_tests); - - private: - bool registered_; - ::std::set<const char*> defined_test_names_; -}; - -// Skips to the first non-space char after the first comma in 'str'; -// returns NULL if no comma is found in 'str'. -inline const char* SkipComma(const char* str) { - const char* comma = strchr(str, ','); - if (comma == NULL) { - return NULL; - } - while (IsSpace(*(++comma))) {} - return comma; -} - -// Returns the prefix of 'str' before the first comma in it; returns -// the entire string if it contains no comma. -inline std::string GetPrefixUntilComma(const char* str) { - const char* comma = strchr(str, ','); - return comma == NULL ? str : std::string(str, comma); -} - -// TypeParameterizedTest<Fixture, TestSel, Types>::Register() -// registers a list of type-parameterized tests with Google Test. The -// return value is insignificant - we just need to return something -// such that we can call this function in a namespace scope. -// -// Implementation note: The GTEST_TEMPLATE_ macro declares a template -// template parameter. It's defined in gtest-type-util.h. -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Fixture, class TestSel, typename Types> -class TypeParameterizedTest { - public: - // 'index' is the index of the test in the type list 'Types' - // specified in INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(Prefix, TestCase, - // Types). Valid values for 'index' are [0, N - 1] where N is the - // length of Types. - static bool Register(const char* prefix, const char* case_name, - const char* test_names, int index) { - typedef typename Types::Head Type; - typedef Fixture<Type> FixtureClass; - typedef typename GTEST_BIND_(TestSel, Type) TestClass; - - // First, registers the first type-parameterized test in the type - // list. - MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( - (std::string(prefix) + (prefix[0] == '\0' ? "" : "/") + case_name + "/" - + StreamableToString(index)).c_str(), - GetPrefixUntilComma(test_names).c_str(), - GetTypeName<Type>().c_str(), - NULL, // No value parameter. - GetTypeId<FixtureClass>(), - TestClass::SetUpTestCase, - TestClass::TearDownTestCase, - new TestFactoryImpl<TestClass>); - - // Next, recurses (at compile time) with the tail of the type list. - return TypeParameterizedTest<Fixture, TestSel, typename Types::Tail> - ::Register(prefix, case_name, test_names, index + 1); - } -}; - -// The base case for the compile time recursion. -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Fixture, class TestSel> -class TypeParameterizedTest<Fixture, TestSel, Types0> { - public: - static bool Register(const char* /*prefix*/, const char* /*case_name*/, - const char* /*test_names*/, int /*index*/) { - return true; - } -}; - -// TypeParameterizedTestCase<Fixture, Tests, Types>::Register() -// registers *all combinations* of 'Tests' and 'Types' with Google -// Test. The return value is insignificant - we just need to return -// something such that we can call this function in a namespace scope. -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Fixture, typename Tests, typename Types> -class TypeParameterizedTestCase { - public: - static bool Register(const char* prefix, const char* case_name, - const char* test_names) { - typedef typename Tests::Head Head; - - // First, register the first test in 'Test' for each type in 'Types'. - TypeParameterizedTest<Fixture, Head, Types>::Register( - prefix, case_name, test_names, 0); - - // Next, recurses (at compile time) with the tail of the test list. - return TypeParameterizedTestCase<Fixture, typename Tests::Tail, Types> - ::Register(prefix, case_name, SkipComma(test_names)); - } -}; - -// The base case for the compile time recursion. -template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Fixture, typename Types> -class TypeParameterizedTestCase<Fixture, Templates0, Types> { - public: - static bool Register(const char* /*prefix*/, const char* /*case_name*/, - const char* /*test_names*/) { - return true; - } -}; - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST || GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - -// Returns the current OS stack trace as an std::string. -// -// The maximum number of stack frames to be included is specified by -// the gtest_stack_trace_depth flag. The skip_count parameter -// specifies the number of top frames to be skipped, which doesn't -// count against the number of frames to be included. -// -// For example, if Foo() calls Bar(), which in turn calls -// GetCurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop(..., 1), Foo() will be included in -// the trace but Bar() and GetCurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop() won't. -GTEST_API_ std::string GetCurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop( - UnitTest* unit_test, int skip_count); - -// Helpers for suppressing warnings on unreachable code or constant -// condition. - -// Always returns true. -GTEST_API_ bool AlwaysTrue(); - -// Always returns false. -inline bool AlwaysFalse() { return !AlwaysTrue(); } - -// Helper for suppressing false warning from Clang on a const char* -// variable declared in a conditional expression always being NULL in -// the else branch. -struct GTEST_API_ ConstCharPtr { - ConstCharPtr(const char* str) : value(str) {} - operator bool() const { return true; } - const char* value; -}; - -// A simple Linear Congruential Generator for generating random -// numbers with a uniform distribution. Unlike rand() and srand(), it -// doesn't use global state (and therefore can't interfere with user -// code). Unlike rand_r(), it's portable. An LCG isn't very random, -// but it's good enough for our purposes. -class GTEST_API_ Random { - public: - static const UInt32 kMaxRange = 1u << 31; - - explicit Random(UInt32 seed) : state_(seed) {} - - void Reseed(UInt32 seed) { state_ = seed; } - - // Generates a random number from [0, range). Crashes if 'range' is - // 0 or greater than kMaxRange. - UInt32 Generate(UInt32 range); - - private: - UInt32 state_; - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Random); -}; - -// Defining a variable of type CompileAssertTypesEqual<T1, T2> will cause a -// compiler error iff T1 and T2 are different types. -template <typename T1, typename T2> -struct CompileAssertTypesEqual; - -template <typename T> -struct CompileAssertTypesEqual<T, T> { -}; - -// Removes the reference from a type if it is a reference type, -// otherwise leaves it unchanged. This is the same as -// tr1::remove_reference, which is not widely available yet. -template <typename T> -struct RemoveReference { typedef T type; }; // NOLINT -template <typename T> -struct RemoveReference<T&> { typedef T type; }; // NOLINT - -// A handy wrapper around RemoveReference that works when the argument -// T depends on template parameters. -#define GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_(T) \ - typename ::testing::internal::RemoveReference<T>::type - -// Removes const from a type if it is a const type, otherwise leaves -// it unchanged. This is the same as tr1::remove_const, which is not -// widely available yet. -template <typename T> -struct RemoveConst { typedef T type; }; // NOLINT -template <typename T> -struct RemoveConst<const T> { typedef T type; }; // NOLINT - -// MSVC 8.0, Sun C++, and IBM XL C++ have a bug which causes the above -// definition to fail to remove the const in 'const int[3]' and 'const -// char[3][4]'. The following specialization works around the bug. -template <typename T, size_t N> -struct RemoveConst<const T[N]> { - typedef typename RemoveConst<T>::type type[N]; -}; - -#if defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER < 1400 -// This is the only specialization that allows VC++ 7.1 to remove const in -// 'const int[3] and 'const int[3][4]'. However, it causes trouble with GCC -// and thus needs to be conditionally compiled. -template <typename T, size_t N> -struct RemoveConst<T[N]> { - typedef typename RemoveConst<T>::type type[N]; -}; -#endif - -// A handy wrapper around RemoveConst that works when the argument -// T depends on template parameters. -#define GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(T) \ - typename ::testing::internal::RemoveConst<T>::type - -// Turns const U&, U&, const U, and U all into U. -#define GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(T) \ - GTEST_REMOVE_CONST_(GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_(T)) - -// Adds reference to a type if it is not a reference type, -// otherwise leaves it unchanged. This is the same as -// tr1::add_reference, which is not widely available yet. -template <typename T> -struct AddReference { typedef T& type; }; // NOLINT -template <typename T> -struct AddReference<T&> { typedef T& type; }; // NOLINT - -// A handy wrapper around AddReference that works when the argument T -// depends on template parameters. -#define GTEST_ADD_REFERENCE_(T) \ - typename ::testing::internal::AddReference<T>::type - -// Adds a reference to const on top of T as necessary. For example, -// it transforms -// -// char ==> const char& -// const char ==> const char& -// char& ==> const char& -// const char& ==> const char& -// -// The argument T must depend on some template parameters. -#define GTEST_REFERENCE_TO_CONST_(T) \ - GTEST_ADD_REFERENCE_(const GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_(T)) - -// ImplicitlyConvertible<From, To>::value is a compile-time bool -// constant that's true iff type From can be implicitly converted to -// type To. -template <typename From, typename To> -class ImplicitlyConvertible { - private: - // We need the following helper functions only for their types. - // They have no implementations. - - // MakeFrom() is an expression whose type is From. We cannot simply - // use From(), as the type From may not have a public default - // constructor. - static From MakeFrom(); - - // These two functions are overloaded. Given an expression - // Helper(x), the compiler will pick the first version if x can be - // implicitly converted to type To; otherwise it will pick the - // second version. - // - // The first version returns a value of size 1, and the second - // version returns a value of size 2. Therefore, by checking the - // size of Helper(x), which can be done at compile time, we can tell - // which version of Helper() is used, and hence whether x can be - // implicitly converted to type To. - static char Helper(To); - static char (&Helper(...))[2]; // NOLINT - - // We have to put the 'public' section after the 'private' section, - // or MSVC refuses to compile the code. - public: - // MSVC warns about implicitly converting from double to int for - // possible loss of data, so we need to temporarily disable the - // warning. -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable:4244) // Temporarily disables warning 4244. - - static const bool value = - sizeof(Helper(ImplicitlyConvertible::MakeFrom())) == 1; -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state. -#elif defined(__BORLANDC__) - // C++Builder cannot use member overload resolution during template - // instantiation. The simplest workaround is to use its C++0x type traits - // functions (C++Builder 2009 and above only). - static const bool value = __is_convertible(From, To); -#else - static const bool value = - sizeof(Helper(ImplicitlyConvertible::MakeFrom())) == 1; -#endif // _MSV_VER -}; -template <typename From, typename To> -const bool ImplicitlyConvertible<From, To>::value; - -// IsAProtocolMessage<T>::value is a compile-time bool constant that's -// true iff T is type ProtocolMessage, proto2::Message, or a subclass -// of those. -template <typename T> -struct IsAProtocolMessage - : public bool_constant< - ImplicitlyConvertible<const T*, const ::ProtocolMessage*>::value || - ImplicitlyConvertible<const T*, const ::proto2::Message*>::value> { -}; - -// When the compiler sees expression IsContainerTest<C>(0), if C is an -// STL-style container class, the first overload of IsContainerTest -// will be viable (since both C::iterator* and C::const_iterator* are -// valid types and NULL can be implicitly converted to them). It will -// be picked over the second overload as 'int' is a perfect match for -// the type of argument 0. If C::iterator or C::const_iterator is not -// a valid type, the first overload is not viable, and the second -// overload will be picked. Therefore, we can determine whether C is -// a container class by checking the type of IsContainerTest<C>(0). -// The value of the expression is insignificant. -// -// Note that we look for both C::iterator and C::const_iterator. The -// reason is that C++ injects the name of a class as a member of the -// class itself (e.g. you can refer to class iterator as either -// 'iterator' or 'iterator::iterator'). If we look for C::iterator -// only, for example, we would mistakenly think that a class named -// iterator is an STL container. -// -// Also note that the simpler approach of overloading -// IsContainerTest(typename C::const_iterator*) and -// IsContainerTest(...) doesn't work with Visual Age C++ and Sun C++. -typedef int IsContainer; -template <class C> -IsContainer IsContainerTest(int /* dummy */, - typename C::iterator* /* it */ = NULL, - typename C::const_iterator* /* const_it */ = NULL) { - return 0; -} - -typedef char IsNotContainer; -template <class C> -IsNotContainer IsContainerTest(long /* dummy */) { return '\0'; } - -// EnableIf<condition>::type is void when 'Cond' is true, and -// undefined when 'Cond' is false. To use SFINAE to make a function -// overload only apply when a particular expression is true, add -// "typename EnableIf<expression>::type* = 0" as the last parameter. -template<bool> struct EnableIf; -template<> struct EnableIf<true> { typedef void type; }; // NOLINT - -// Utilities for native arrays. - -// ArrayEq() compares two k-dimensional native arrays using the -// elements' operator==, where k can be any integer >= 0. When k is -// 0, ArrayEq() degenerates into comparing a single pair of values. - -template <typename T, typename U> -bool ArrayEq(const T* lhs, size_t size, const U* rhs); - -// This generic version is used when k is 0. -template <typename T, typename U> -inline bool ArrayEq(const T& lhs, const U& rhs) { return lhs == rhs; } - -// This overload is used when k >= 1. -template <typename T, typename U, size_t N> -inline bool ArrayEq(const T(&lhs)[N], const U(&rhs)[N]) { - return internal::ArrayEq(lhs, N, rhs); -} - -// This helper reduces code bloat. If we instead put its logic inside -// the previous ArrayEq() function, arrays with different sizes would -// lead to different copies of the template code. -template <typename T, typename U> -bool ArrayEq(const T* lhs, size_t size, const U* rhs) { - for (size_t i = 0; i != size; i++) { - if (!internal::ArrayEq(lhs[i], rhs[i])) - return false; - } - return true; -} - -// Finds the first element in the iterator range [begin, end) that -// equals elem. Element may be a native array type itself. -template <typename Iter, typename Element> -Iter ArrayAwareFind(Iter begin, Iter end, const Element& elem) { - for (Iter it = begin; it != end; ++it) { - if (internal::ArrayEq(*it, elem)) - return it; - } - return end; -} - -// CopyArray() copies a k-dimensional native array using the elements' -// operator=, where k can be any integer >= 0. When k is 0, -// CopyArray() degenerates into copying a single value. - -template <typename T, typename U> -void CopyArray(const T* from, size_t size, U* to); - -// This generic version is used when k is 0. -template <typename T, typename U> -inline void CopyArray(const T& from, U* to) { *to = from; } - -// This overload is used when k >= 1. -template <typename T, typename U, size_t N> -inline void CopyArray(const T(&from)[N], U(*to)[N]) { - internal::CopyArray(from, N, *to); -} - -// This helper reduces code bloat. If we instead put its logic inside -// the previous CopyArray() function, arrays with different sizes -// would lead to different copies of the template code. -template <typename T, typename U> -void CopyArray(const T* from, size_t size, U* to) { - for (size_t i = 0; i != size; i++) { - internal::CopyArray(from[i], to + i); - } -} - -// The relation between an NativeArray object (see below) and the -// native array it represents. -enum RelationToSource { - kReference, // The NativeArray references the native array. - kCopy // The NativeArray makes a copy of the native array and - // owns the copy. -}; - -// Adapts a native array to a read-only STL-style container. Instead -// of the complete STL container concept, this adaptor only implements -// members useful for Google Mock's container matchers. New members -// should be added as needed. To simplify the implementation, we only -// support Element being a raw type (i.e. having no top-level const or -// reference modifier). It's the client's responsibility to satisfy -// this requirement. Element can be an array type itself (hence -// multi-dimensional arrays are supported). -template <typename Element> -class NativeArray { - public: - // STL-style container typedefs. - typedef Element value_type; - typedef Element* iterator; - typedef const Element* const_iterator; - - // Constructs from a native array. - NativeArray(const Element* array, size_t count, RelationToSource relation) { - Init(array, count, relation); - } - - // Copy constructor. - NativeArray(const NativeArray& rhs) { - Init(rhs.array_, rhs.size_, rhs.relation_to_source_); - } - - ~NativeArray() { - // Ensures that the user doesn't instantiate NativeArray with a - // const or reference type. - static_cast<void>(StaticAssertTypeEqHelper<Element, - GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(Element)>()); - if (relation_to_source_ == kCopy) - delete[] array_; - } - - // STL-style container methods. - size_t size() const { return size_; } - const_iterator begin() const { return array_; } - const_iterator end() const { return array_ + size_; } - bool operator==(const NativeArray& rhs) const { - return size() == rhs.size() && - ArrayEq(begin(), size(), rhs.begin()); - } - - private: - // Initializes this object; makes a copy of the input array if - // 'relation' is kCopy. - void Init(const Element* array, size_t a_size, RelationToSource relation) { - if (relation == kReference) { - array_ = array; - } else { - Element* const copy = new Element[a_size]; - CopyArray(array, a_size, copy); - array_ = copy; - } - size_ = a_size; - relation_to_source_ = relation; - } - - const Element* array_; - size_t size_; - RelationToSource relation_to_source_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(NativeArray); -}; - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#define GTEST_MESSAGE_AT_(file, line, message, result_type) \ - ::testing::internal::AssertHelper(result_type, file, line, message) \ - = ::testing::Message() - -#define GTEST_MESSAGE_(message, result_type) \ - GTEST_MESSAGE_AT_(__FILE__, __LINE__, message, result_type) - -#define GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_(message) \ - return GTEST_MESSAGE_(message, ::testing::TestPartResult::kFatalFailure) - -#define GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_(message) \ - GTEST_MESSAGE_(message, ::testing::TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure) - -#define GTEST_SUCCESS_(message) \ - GTEST_MESSAGE_(message, ::testing::TestPartResult::kSuccess) - -// Suppresses MSVC warnings 4072 (unreachable code) for the code following -// statement if it returns or throws (or doesn't return or throw in some -// situations). -#define GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement) \ - if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { statement; } - -#define GTEST_TEST_THROW_(statement, expected_exception, fail) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (::testing::internal::ConstCharPtr gtest_msg = "") { \ - bool gtest_caught_expected = false; \ - try { \ - GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ - } \ - catch (expected_exception const&) { \ - gtest_caught_expected = true; \ - } \ - catch (...) { \ - gtest_msg.value = \ - "Expected: " #statement " throws an exception of type " \ - #expected_exception ".\n Actual: it throws a different type."; \ - goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testthrow_, __LINE__); \ - } \ - if (!gtest_caught_expected) { \ - gtest_msg.value = \ - "Expected: " #statement " throws an exception of type " \ - #expected_exception ".\n Actual: it throws nothing."; \ - goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testthrow_, __LINE__); \ - } \ - } else \ - GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testthrow_, __LINE__): \ - fail(gtest_msg.value) - -#define GTEST_TEST_NO_THROW_(statement, fail) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ - try { \ - GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ - } \ - catch (...) { \ - goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testnothrow_, __LINE__); \ - } \ - } else \ - GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testnothrow_, __LINE__): \ - fail("Expected: " #statement " doesn't throw an exception.\n" \ - " Actual: it throws.") - -#define GTEST_TEST_ANY_THROW_(statement, fail) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ - bool gtest_caught_any = false; \ - try { \ - GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ - } \ - catch (...) { \ - gtest_caught_any = true; \ - } \ - if (!gtest_caught_any) { \ - goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testanythrow_, __LINE__); \ - } \ - } else \ - GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testanythrow_, __LINE__): \ - fail("Expected: " #statement " throws an exception.\n" \ - " Actual: it doesn't.") - - -// Implements Boolean test assertions such as EXPECT_TRUE. expression can be -// either a boolean expression or an AssertionResult. text is a textual -// represenation of expression as it was passed into the EXPECT_TRUE. -#define GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(expression, text, actual, expected, fail) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (const ::testing::AssertionResult gtest_ar_ = \ - ::testing::AssertionResult(expression)) \ - ; \ - else \ - fail(::testing::internal::GetBoolAssertionFailureMessage(\ - gtest_ar_, text, #actual, #expected).c_str()) - -#define GTEST_TEST_NO_FATAL_FAILURE_(statement, fail) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ - ::testing::internal::HasNewFatalFailureHelper gtest_fatal_failure_checker; \ - GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ - if (gtest_fatal_failure_checker.has_new_fatal_failure()) { \ - goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testnofatal_, __LINE__); \ - } \ - } else \ - GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testnofatal_, __LINE__): \ - fail("Expected: " #statement " doesn't generate new fatal " \ - "failures in the current thread.\n" \ - " Actual: it does.") - -// Expands to the name of the class that implements the given test. -#define GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name) \ - test_case_name##_##test_name##_Test - -// Helper macro for defining tests. -#define GTEST_TEST_(test_case_name, test_name, parent_class, parent_id)\ -class GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name) : public parent_class {\ - public:\ - GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)() {}\ - private:\ - virtual void TestBody();\ - static ::testing::TestInfo* const test_info_ GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_;\ - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(\ - GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name));\ -};\ -\ -::testing::TestInfo* const GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)\ - ::test_info_ =\ - ::testing::internal::MakeAndRegisterTestInfo(\ - #test_case_name, #test_name, NULL, NULL, \ - (parent_id), \ - parent_class::SetUpTestCase, \ - parent_class::TearDownTestCase, \ - new ::testing::internal::TestFactoryImpl<\ - GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)>);\ -void GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)::TestBody() - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_INTERNAL_H_ -// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) -// -// The Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) -// -// This header file defines the public API for death tests. It is -// #included by gtest.h so a user doesn't need to include this -// directly. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_H_ - -// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Authors: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan), eefacm@gmail.com (Sean Mcafee) -// -// The Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) -// -// This header file defines internal utilities needed for implementing -// death tests. They are subject to change without notice. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_INTERNAL_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_INTERNAL_H_ - - -#include <stdio.h> - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -GTEST_DECLARE_string_(internal_run_death_test); - -// Names of the flags (needed for parsing Google Test flags). -const char kDeathTestStyleFlag[] = "death_test_style"; -const char kDeathTestUseFork[] = "death_test_use_fork"; -const char kInternalRunDeathTestFlag[] = "internal_run_death_test"; - -#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - -// DeathTest is a class that hides much of the complexity of the -// GTEST_DEATH_TEST_ macro. It is abstract; its static Create method -// returns a concrete class that depends on the prevailing death test -// style, as defined by the --gtest_death_test_style and/or -// --gtest_internal_run_death_test flags. - -// In describing the results of death tests, these terms are used with -// the corresponding definitions: -// -// exit status: The integer exit information in the format specified -// by wait(2) -// exit code: The integer code passed to exit(3), _exit(2), or -// returned from main() -class GTEST_API_ DeathTest { - public: - // Create returns false if there was an error determining the - // appropriate action to take for the current death test; for example, - // if the gtest_death_test_style flag is set to an invalid value. - // The LastMessage method will return a more detailed message in that - // case. Otherwise, the DeathTest pointer pointed to by the "test" - // argument is set. If the death test should be skipped, the pointer - // is set to NULL; otherwise, it is set to the address of a new concrete - // DeathTest object that controls the execution of the current test. - static bool Create(const char* statement, const RE* regex, - const char* file, int line, DeathTest** test); - DeathTest(); - virtual ~DeathTest() { } - - // A helper class that aborts a death test when it's deleted. - class ReturnSentinel { - public: - explicit ReturnSentinel(DeathTest* test) : test_(test) { } - ~ReturnSentinel() { test_->Abort(TEST_ENCOUNTERED_RETURN_STATEMENT); } - private: - DeathTest* const test_; - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ReturnSentinel); - } GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; - - // An enumeration of possible roles that may be taken when a death - // test is encountered. EXECUTE means that the death test logic should - // be executed immediately. OVERSEE means that the program should prepare - // the appropriate environment for a child process to execute the death - // test, then wait for it to complete. - enum TestRole { OVERSEE_TEST, EXECUTE_TEST }; - - // An enumeration of the three reasons that a test might be aborted. - enum AbortReason { - TEST_ENCOUNTERED_RETURN_STATEMENT, - TEST_THREW_EXCEPTION, - TEST_DID_NOT_DIE - }; - - // Assumes one of the above roles. - virtual TestRole AssumeRole() = 0; - - // Waits for the death test to finish and returns its status. - virtual int Wait() = 0; - - // Returns true if the death test passed; that is, the test process - // exited during the test, its exit status matches a user-supplied - // predicate, and its stderr output matches a user-supplied regular - // expression. - // The user-supplied predicate may be a macro expression rather - // than a function pointer or functor, or else Wait and Passed could - // be combined. - virtual bool Passed(bool exit_status_ok) = 0; - - // Signals that the death test did not die as expected. - virtual void Abort(AbortReason reason) = 0; - - // Returns a human-readable outcome message regarding the outcome of - // the last death test. - static const char* LastMessage(); - - static void set_last_death_test_message(const std::string& message); - - private: - // A string containing a description of the outcome of the last death test. - static std::string last_death_test_message_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(DeathTest); -}; - -// Factory interface for death tests. May be mocked out for testing. -class DeathTestFactory { - public: - virtual ~DeathTestFactory() { } - virtual bool Create(const char* statement, const RE* regex, - const char* file, int line, DeathTest** test) = 0; -}; - -// A concrete DeathTestFactory implementation for normal use. -class DefaultDeathTestFactory : public DeathTestFactory { - public: - virtual bool Create(const char* statement, const RE* regex, - const char* file, int line, DeathTest** test); -}; - -// Returns true if exit_status describes a process that was terminated -// by a signal, or exited normally with a nonzero exit code. -GTEST_API_ bool ExitedUnsuccessfully(int exit_status); - -// Traps C++ exceptions escaping statement and reports them as test -// failures. Note that trapping SEH exceptions is not implemented here. -# if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS -# define GTEST_EXECUTE_DEATH_TEST_STATEMENT_(statement, death_test) \ - try { \ - GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ - } catch (const ::std::exception& gtest_exception) { \ - fprintf(\ - stderr, \ - "\n%s: Caught std::exception-derived exception escaping the " \ - "death test statement. Exception message: %s\n", \ - ::testing::internal::FormatFileLocation(__FILE__, __LINE__).c_str(), \ - gtest_exception.what()); \ - fflush(stderr); \ - death_test->Abort(::testing::internal::DeathTest::TEST_THREW_EXCEPTION); \ - } catch (...) { \ - death_test->Abort(::testing::internal::DeathTest::TEST_THREW_EXCEPTION); \ - } - -# else -# define GTEST_EXECUTE_DEATH_TEST_STATEMENT_(statement, death_test) \ - GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement) - -# endif - -// This macro is for implementing ASSERT_DEATH*, EXPECT_DEATH*, -// ASSERT_EXIT*, and EXPECT_EXIT*. -# define GTEST_DEATH_TEST_(statement, predicate, regex, fail) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ - const ::testing::internal::RE& gtest_regex = (regex); \ - ::testing::internal::DeathTest* gtest_dt; \ - if (!::testing::internal::DeathTest::Create(#statement, >est_regex, \ - __FILE__, __LINE__, >est_dt)) { \ - goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_, __LINE__); \ - } \ - if (gtest_dt != NULL) { \ - ::testing::internal::scoped_ptr< ::testing::internal::DeathTest> \ - gtest_dt_ptr(gtest_dt); \ - switch (gtest_dt->AssumeRole()) { \ - case ::testing::internal::DeathTest::OVERSEE_TEST: \ - if (!gtest_dt->Passed(predicate(gtest_dt->Wait()))) { \ - goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_, __LINE__); \ - } \ - break; \ - case ::testing::internal::DeathTest::EXECUTE_TEST: { \ - ::testing::internal::DeathTest::ReturnSentinel \ - gtest_sentinel(gtest_dt); \ - GTEST_EXECUTE_DEATH_TEST_STATEMENT_(statement, gtest_dt); \ - gtest_dt->Abort(::testing::internal::DeathTest::TEST_DID_NOT_DIE); \ - break; \ - } \ - default: \ - break; \ - } \ - } \ - } else \ - GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_, __LINE__): \ - fail(::testing::internal::DeathTest::LastMessage()) -// The symbol "fail" here expands to something into which a message -// can be streamed. - -// This macro is for implementing ASSERT/EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH when compiled in -// NDEBUG mode. In this case we need the statements to be executed, the regex is -// ignored, and the macro must accept a streamed message even though the message -// is never printed. -# define GTEST_EXECUTE_STATEMENT_(statement, regex) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ - GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ - } else \ - ::testing::Message() - -// A class representing the parsed contents of the -// --gtest_internal_run_death_test flag, as it existed when -// RUN_ALL_TESTS was called. -class InternalRunDeathTestFlag { - public: - InternalRunDeathTestFlag(const std::string& a_file, - int a_line, - int an_index, - int a_write_fd) - : file_(a_file), line_(a_line), index_(an_index), - write_fd_(a_write_fd) {} - - ~InternalRunDeathTestFlag() { - if (write_fd_ >= 0) - posix::Close(write_fd_); - } - - const std::string& file() const { return file_; } - int line() const { return line_; } - int index() const { return index_; } - int write_fd() const { return write_fd_; } - - private: - std::string file_; - int line_; - int index_; - int write_fd_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(InternalRunDeathTestFlag); -}; - -// Returns a newly created InternalRunDeathTestFlag object with fields -// initialized from the GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test) flag if -// the flag is specified; otherwise returns NULL. -InternalRunDeathTestFlag* ParseInternalRunDeathTestFlag(); - -#else // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - -// This macro is used for implementing macros such as -// EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED and ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED on systems where -// death tests are not supported. Those macros must compile on such systems -// iff EXPECT_DEATH and ASSERT_DEATH compile with the same parameters on -// systems that support death tests. This allows one to write such a macro -// on a system that does not support death tests and be sure that it will -// compile on a death-test supporting system. -// -// Parameters: -// statement - A statement that a macro such as EXPECT_DEATH would test -// for program termination. This macro has to make sure this -// statement is compiled but not executed, to ensure that -// EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED compiles with a certain -// parameter iff EXPECT_DEATH compiles with it. -// regex - A regex that a macro such as EXPECT_DEATH would use to test -// the output of statement. This parameter has to be -// compiled but not evaluated by this macro, to ensure that -// this macro only accepts expressions that a macro such as -// EXPECT_DEATH would accept. -// terminator - Must be an empty statement for EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED -// and a return statement for ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED. -// This ensures that ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED will not -// compile inside functions where ASSERT_DEATH doesn't -// compile. -// -// The branch that has an always false condition is used to ensure that -// statement and regex are compiled (and thus syntactically correct) but -// never executed. The unreachable code macro protects the terminator -// statement from generating an 'unreachable code' warning in case -// statement unconditionally returns or throws. The Message constructor at -// the end allows the syntax of streaming additional messages into the -// macro, for compilational compatibility with EXPECT_DEATH/ASSERT_DEATH. -# define GTEST_UNSUPPORTED_DEATH_TEST_(statement, regex, terminator) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ - GTEST_LOG_(WARNING) \ - << "Death tests are not supported on this platform.\n" \ - << "Statement '" #statement "' cannot be verified."; \ - } else if (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) { \ - ::testing::internal::RE::PartialMatch(".*", (regex)); \ - GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ - terminator; \ - } else \ - ::testing::Message() - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_INTERNAL_H_ - -namespace testing { - -// This flag controls the style of death tests. Valid values are "threadsafe", -// meaning that the death test child process will re-execute the test binary -// from the start, running only a single death test, or "fast", -// meaning that the child process will execute the test logic immediately -// after forking. -GTEST_DECLARE_string_(death_test_style); - -#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - -namespace internal { - -// Returns a Boolean value indicating whether the caller is currently -// executing in the context of the death test child process. Tools such as -// Valgrind heap checkers may need this to modify their behavior in death -// tests. IMPORTANT: This is an internal utility. Using it may break the -// implementation of death tests. User code MUST NOT use it. -GTEST_API_ bool InDeathTestChild(); - -} // namespace internal - -// The following macros are useful for writing death tests. - -// Here's what happens when an ASSERT_DEATH* or EXPECT_DEATH* is -// executed: -// -// 1. It generates a warning if there is more than one active -// thread. This is because it's safe to fork() or clone() only -// when there is a single thread. -// -// 2. The parent process clone()s a sub-process and runs the death -// test in it; the sub-process exits with code 0 at the end of the -// death test, if it hasn't exited already. -// -// 3. The parent process waits for the sub-process to terminate. -// -// 4. The parent process checks the exit code and error message of -// the sub-process. -// -// Examples: -// -// ASSERT_DEATH(server.SendMessage(56, "Hello"), "Invalid port number"); -// for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { -// EXPECT_DEATH(server.ProcessRequest(i), -// "Invalid request .* in ProcessRequest()") -// << "Failed to die on request " << i; -// } -// -// ASSERT_EXIT(server.ExitNow(), ::testing::ExitedWithCode(0), "Exiting"); -// -// bool KilledBySIGHUP(int exit_code) { -// return WIFSIGNALED(exit_code) && WTERMSIG(exit_code) == SIGHUP; -// } -// -// ASSERT_EXIT(client.HangUpServer(), KilledBySIGHUP, "Hanging up!"); -// -// On the regular expressions used in death tests: -// -// On POSIX-compliant systems (*nix), we use the <regex.h> library, -// which uses the POSIX extended regex syntax. -// -// On other platforms (e.g. Windows), we only support a simple regex -// syntax implemented as part of Google Test. This limited -// implementation should be enough most of the time when writing -// death tests; though it lacks many features you can find in PCRE -// or POSIX extended regex syntax. For example, we don't support -// union ("x|y"), grouping ("(xy)"), brackets ("[xy]"), and -// repetition count ("x{5,7}"), among others. -// -// Below is the syntax that we do support. We chose it to be a -// subset of both PCRE and POSIX extended regex, so it's easy to -// learn wherever you come from. In the following: 'A' denotes a -// literal character, period (.), or a single \\ escape sequence; -// 'x' and 'y' denote regular expressions; 'm' and 'n' are for -// natural numbers. -// -// c matches any literal character c -// \\d matches any decimal digit -// \\D matches any character that's not a decimal digit -// \\f matches \f -// \\n matches \n -// \\r matches \r -// \\s matches any ASCII whitespace, including \n -// \\S matches any character that's not a whitespace -// \\t matches \t -// \\v matches \v -// \\w matches any letter, _, or decimal digit -// \\W matches any character that \\w doesn't match -// \\c matches any literal character c, which must be a punctuation -// . matches any single character except \n -// A? matches 0 or 1 occurrences of A -// A* matches 0 or many occurrences of A -// A+ matches 1 or many occurrences of A -// ^ matches the beginning of a string (not that of each line) -// $ matches the end of a string (not that of each line) -// xy matches x followed by y -// -// If you accidentally use PCRE or POSIX extended regex features -// not implemented by us, you will get a run-time failure. In that -// case, please try to rewrite your regular expression within the -// above syntax. -// -// This implementation is *not* meant to be as highly tuned or robust -// as a compiled regex library, but should perform well enough for a -// death test, which already incurs significant overhead by launching -// a child process. -// -// Known caveats: -// -// A "threadsafe" style death test obtains the path to the test -// program from argv[0] and re-executes it in the sub-process. For -// simplicity, the current implementation doesn't search the PATH -// when launching the sub-process. This means that the user must -// invoke the test program via a path that contains at least one -// path separator (e.g. path/to/foo_test and -// /absolute/path/to/bar_test are fine, but foo_test is not). This -// is rarely a problem as people usually don't put the test binary -// directory in PATH. -// -// TODO(wan@google.com): make thread-safe death tests search the PATH. - -// Asserts that a given statement causes the program to exit, with an -// integer exit status that satisfies predicate, and emitting error output -// that matches regex. -# define ASSERT_EXIT(statement, predicate, regex) \ - GTEST_DEATH_TEST_(statement, predicate, regex, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) - -// Like ASSERT_EXIT, but continues on to successive tests in the -// test case, if any: -# define EXPECT_EXIT(statement, predicate, regex) \ - GTEST_DEATH_TEST_(statement, predicate, regex, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) - -// Asserts that a given statement causes the program to exit, either by -// explicitly exiting with a nonzero exit code or being killed by a -// signal, and emitting error output that matches regex. -# define ASSERT_DEATH(statement, regex) \ - ASSERT_EXIT(statement, ::testing::internal::ExitedUnsuccessfully, regex) - -// Like ASSERT_DEATH, but continues on to successive tests in the -// test case, if any: -# define EXPECT_DEATH(statement, regex) \ - EXPECT_EXIT(statement, ::testing::internal::ExitedUnsuccessfully, regex) - -// Two predicate classes that can be used in {ASSERT,EXPECT}_EXIT*: - -// Tests that an exit code describes a normal exit with a given exit code. -class GTEST_API_ ExitedWithCode { - public: - explicit ExitedWithCode(int exit_code); - bool operator()(int exit_status) const; - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ExitedWithCode& other); - - const int exit_code_; -}; - -# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS -// Tests that an exit code describes an exit due to termination by a -// given signal. -class GTEST_API_ KilledBySignal { - public: - explicit KilledBySignal(int signum); - bool operator()(int exit_status) const; - private: - const int signum_; -}; -# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - -// EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH asserts that the given statements die in debug mode. -// The death testing framework causes this to have interesting semantics, -// since the sideeffects of the call are only visible in opt mode, and not -// in debug mode. -// -// In practice, this can be used to test functions that utilize the -// LOG(DFATAL) macro using the following style: -// -// int DieInDebugOr12(int* sideeffect) { -// if (sideeffect) { -// *sideeffect = 12; -// } -// LOG(DFATAL) << "death"; -// return 12; -// } -// -// TEST(TestCase, TestDieOr12WorksInDgbAndOpt) { -// int sideeffect = 0; -// // Only asserts in dbg. -// EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH(DieInDebugOr12(&sideeffect), "death"); -// -// #ifdef NDEBUG -// // opt-mode has sideeffect visible. -// EXPECT_EQ(12, sideeffect); -// #else -// // dbg-mode no visible sideeffect. -// EXPECT_EQ(0, sideeffect); -// #endif -// } -// -// This will assert that DieInDebugReturn12InOpt() crashes in debug -// mode, usually due to a DCHECK or LOG(DFATAL), but returns the -// appropriate fallback value (12 in this case) in opt mode. If you -// need to test that a function has appropriate side-effects in opt -// mode, include assertions against the side-effects. A general -// pattern for this is: -// -// EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH({ -// // Side-effects here will have an effect after this statement in -// // opt mode, but none in debug mode. -// EXPECT_EQ(12, DieInDebugOr12(&sideeffect)); -// }, "death"); -// -# ifdef NDEBUG - -# define EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH(statement, regex) \ - GTEST_EXECUTE_STATEMENT_(statement, regex) - -# define ASSERT_DEBUG_DEATH(statement, regex) \ - GTEST_EXECUTE_STATEMENT_(statement, regex) - -# else - -# define EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH(statement, regex) \ - EXPECT_DEATH(statement, regex) - -# define ASSERT_DEBUG_DEATH(statement, regex) \ - ASSERT_DEATH(statement, regex) - -# endif // NDEBUG for EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH -#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - -// EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) and -// ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) expand to real death tests if -// death tests are supported; otherwise they just issue a warning. This is -// useful when you are combining death test assertions with normal test -// assertions in one test. -#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST -# define EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) \ - EXPECT_DEATH(statement, regex) -# define ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) \ - ASSERT_DEATH(statement, regex) -#else -# define EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) \ - GTEST_UNSUPPORTED_DEATH_TEST_(statement, regex, ) -# define ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) \ - GTEST_UNSUPPORTED_DEATH_TEST_(statement, regex, return) -#endif - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_H_ -// This file was GENERATED by command: -// pump.py gtest-param-test.h.pump -// DO NOT EDIT BY HAND!!! - -// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Authors: vladl@google.com (Vlad Losev) -// -// Macros and functions for implementing parameterized tests -// in Google C++ Testing Framework (Google Test) -// -// This file is generated by a SCRIPT. DO NOT EDIT BY HAND! -// -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PARAM_TEST_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PARAM_TEST_H_ - - -// Value-parameterized tests allow you to test your code with different -// parameters without writing multiple copies of the same test. -// -// Here is how you use value-parameterized tests: - -#if 0 - -// To write value-parameterized tests, first you should define a fixture -// class. It is usually derived from testing::TestWithParam<T> (see below for -// another inheritance scheme that's sometimes useful in more complicated -// class hierarchies), where the type of your parameter values. -// TestWithParam<T> is itself derived from testing::Test. T can be any -// copyable type. If it's a raw pointer, you are responsible for managing the -// lifespan of the pointed values. - -class FooTest : public ::testing::TestWithParam<const char*> { - // You can implement all the usual class fixture members here. -}; - -// Then, use the TEST_P macro to define as many parameterized tests -// for this fixture as you want. The _P suffix is for "parameterized" -// or "pattern", whichever you prefer to think. - -TEST_P(FooTest, DoesBlah) { - // Inside a test, access the test parameter with the GetParam() method - // of the TestWithParam<T> class: - EXPECT_TRUE(foo.Blah(GetParam())); - ... -} - -TEST_P(FooTest, HasBlahBlah) { - ... -} - -// Finally, you can use INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P to instantiate the test -// case with any set of parameters you want. Google Test defines a number -// of functions for generating test parameters. They return what we call -// (surprise!) parameter generators. Here is a summary of them, which -// are all in the testing namespace: -// -// -// Range(begin, end [, step]) - Yields values {begin, begin+step, -// begin+step+step, ...}. The values do not -// include end. step defaults to 1. -// Values(v1, v2, ..., vN) - Yields values {v1, v2, ..., vN}. -// ValuesIn(container) - Yields values from a C-style array, an STL -// ValuesIn(begin,end) container, or an iterator range [begin, end). -// Bool() - Yields sequence {false, true}. -// Combine(g1, g2, ..., gN) - Yields all combinations (the Cartesian product -// for the math savvy) of the values generated -// by the N generators. -// -// For more details, see comments at the definitions of these functions below -// in this file. -// -// The following statement will instantiate tests from the FooTest test case -// each with parameter values "meeny", "miny", and "moe". - -INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(InstantiationName, - FooTest, - Values("meeny", "miny", "moe")); - -// To distinguish different instances of the pattern, (yes, you -// can instantiate it more then once) the first argument to the -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P macro is a prefix that will be added to the -// actual test case name. Remember to pick unique prefixes for different -// instantiations. The tests from the instantiation above will have -// these names: -// -// * InstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/0 for "meeny" -// * InstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/1 for "miny" -// * InstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/2 for "moe" -// * InstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/0 for "meeny" -// * InstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/1 for "miny" -// * InstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/2 for "moe" -// -// You can use these names in --gtest_filter. -// -// This statement will instantiate all tests from FooTest again, each -// with parameter values "cat" and "dog": - -const char* pets[] = {"cat", "dog"}; -INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(AnotherInstantiationName, FooTest, ValuesIn(pets)); - -// The tests from the instantiation above will have these names: -// -// * AnotherInstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/0 for "cat" -// * AnotherInstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/1 for "dog" -// * AnotherInstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/0 for "cat" -// * AnotherInstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/1 for "dog" -// -// Please note that INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P will instantiate all tests -// in the given test case, whether their definitions come before or -// AFTER the INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P statement. -// -// Please also note that generator expressions (including parameters to the -// generators) are evaluated in InitGoogleTest(), after main() has started. -// This allows the user on one hand, to adjust generator parameters in order -// to dynamically determine a set of tests to run and on the other hand, -// give the user a chance to inspect the generated tests with Google Test -// reflection API before RUN_ALL_TESTS() is executed. -// -// You can see samples/sample7_unittest.cc and samples/sample8_unittest.cc -// for more examples. -// -// In the future, we plan to publish the API for defining new parameter -// generators. But for now this interface remains part of the internal -// implementation and is subject to change. -// -// -// A parameterized test fixture must be derived from testing::Test and from -// testing::WithParamInterface<T>, where T is the type of the parameter -// values. Inheriting from TestWithParam<T> satisfies that requirement because -// TestWithParam<T> inherits from both Test and WithParamInterface. In more -// complicated hierarchies, however, it is occasionally useful to inherit -// separately from Test and WithParamInterface. For example: - -class BaseTest : public ::testing::Test { - // You can inherit all the usual members for a non-parameterized test - // fixture here. -}; - -class DerivedTest : public BaseTest, public ::testing::WithParamInterface<int> { - // The usual test fixture members go here too. -}; - -TEST_F(BaseTest, HasFoo) { - // This is an ordinary non-parameterized test. -} - -TEST_P(DerivedTest, DoesBlah) { - // GetParam works just the same here as if you inherit from TestWithParam. - EXPECT_TRUE(foo.Blah(GetParam())); -} - -#endif // 0 - - -#if !GTEST_OS_SYMBIAN -# include <utility> -#endif - -// scripts/fuse_gtest.py depends on gtest's own header being #included -// *unconditionally*. Therefore these #includes cannot be moved -// inside #if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST. -// Copyright 2008 Google Inc. -// All Rights Reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: vladl@google.com (Vlad Losev) - -// Type and function utilities for implementing parameterized tests. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PARAM_UTIL_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PARAM_UTIL_H_ - -#include <iterator> -#include <utility> -#include <vector> - -// scripts/fuse_gtest.py depends on gtest's own header being #included -// *unconditionally*. Therefore these #includes cannot be moved -// inside #if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST. -// Copyright 2003 Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Authors: Dan Egnor (egnor@google.com) -// -// A "smart" pointer type with reference tracking. Every pointer to a -// particular object is kept on a circular linked list. When the last pointer -// to an object is destroyed or reassigned, the object is deleted. -// -// Used properly, this deletes the object when the last reference goes away. -// There are several caveats: -// - Like all reference counting schemes, cycles lead to leaks. -// - Each smart pointer is actually two pointers (8 bytes instead of 4). -// - Every time a pointer is assigned, the entire list of pointers to that -// object is traversed. This class is therefore NOT SUITABLE when there -// will often be more than two or three pointers to a particular object. -// - References are only tracked as long as linked_ptr<> objects are copied. -// If a linked_ptr<> is converted to a raw pointer and back, BAD THINGS -// will happen (double deletion). -// -// A good use of this class is storing object references in STL containers. -// You can safely put linked_ptr<> in a vector<>. -// Other uses may not be as good. -// -// Note: If you use an incomplete type with linked_ptr<>, the class -// *containing* linked_ptr<> must have a constructor and destructor (even -// if they do nothing!). -// -// Bill Gibbons suggested we use something like this. -// -// Thread Safety: -// Unlike other linked_ptr implementations, in this implementation -// a linked_ptr object is thread-safe in the sense that: -// - it's safe to copy linked_ptr objects concurrently, -// - it's safe to copy *from* a linked_ptr and read its underlying -// raw pointer (e.g. via get()) concurrently, and -// - it's safe to write to two linked_ptrs that point to the same -// shared object concurrently. -// TODO(wan@google.com): rename this to safe_linked_ptr to avoid -// confusion with normal linked_ptr. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_LINKED_PTR_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_LINKED_PTR_H_ - -#include <stdlib.h> -#include <assert.h> - - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// Protects copying of all linked_ptr objects. -GTEST_API_ GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_linked_ptr_mutex); - -// This is used internally by all instances of linked_ptr<>. It needs to be -// a non-template class because different types of linked_ptr<> can refer to -// the same object (linked_ptr<Superclass>(obj) vs linked_ptr<Subclass>(obj)). -// So, it needs to be possible for different types of linked_ptr to participate -// in the same circular linked list, so we need a single class type here. -// -// DO NOT USE THIS CLASS DIRECTLY YOURSELF. Use linked_ptr<T>. -class linked_ptr_internal { - public: - // Create a new circle that includes only this instance. - void join_new() { - next_ = this; - } - - // Many linked_ptr operations may change p.link_ for some linked_ptr - // variable p in the same circle as this object. Therefore we need - // to prevent two such operations from occurring concurrently. - // - // Note that different types of linked_ptr objects can coexist in a - // circle (e.g. linked_ptr<Base>, linked_ptr<Derived1>, and - // linked_ptr<Derived2>). Therefore we must use a single mutex to - // protect all linked_ptr objects. This can create serious - // contention in production code, but is acceptable in a testing - // framework. - - // Join an existing circle. - void join(linked_ptr_internal const* ptr) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_linked_ptr_mutex) { - MutexLock lock(&g_linked_ptr_mutex); - - linked_ptr_internal const* p = ptr; - while (p->next_ != ptr) p = p->next_; - p->next_ = this; - next_ = ptr; - } - - // Leave whatever circle we're part of. Returns true if we were the - // last member of the circle. Once this is done, you can join() another. - bool depart() - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(g_linked_ptr_mutex) { - MutexLock lock(&g_linked_ptr_mutex); - - if (next_ == this) return true; - linked_ptr_internal const* p = next_; - while (p->next_ != this) p = p->next_; - p->next_ = next_; - return false; - } - - private: - mutable linked_ptr_internal const* next_; -}; - -template <typename T> -class linked_ptr { - public: - typedef T element_type; - - // Take over ownership of a raw pointer. This should happen as soon as - // possible after the object is created. - explicit linked_ptr(T* ptr = NULL) { capture(ptr); } - ~linked_ptr() { depart(); } - - // Copy an existing linked_ptr<>, adding ourselves to the list of references. - template <typename U> linked_ptr(linked_ptr<U> const& ptr) { copy(&ptr); } - linked_ptr(linked_ptr const& ptr) { // NOLINT - assert(&ptr != this); - copy(&ptr); - } - - // Assignment releases the old value and acquires the new. - template <typename U> linked_ptr& operator=(linked_ptr<U> const& ptr) { - depart(); - copy(&ptr); - return *this; - } - - linked_ptr& operator=(linked_ptr const& ptr) { - if (&ptr != this) { - depart(); - copy(&ptr); - } - return *this; - } - - // Smart pointer members. - void reset(T* ptr = NULL) { - depart(); - capture(ptr); - } - T* get() const { return value_; } - T* operator->() const { return value_; } - T& operator*() const { return *value_; } - - bool operator==(T* p) const { return value_ == p; } - bool operator!=(T* p) const { return value_ != p; } - template <typename U> - bool operator==(linked_ptr<U> const& ptr) const { - return value_ == ptr.get(); - } - template <typename U> - bool operator!=(linked_ptr<U> const& ptr) const { - return value_ != ptr.get(); - } - - private: - template <typename U> - friend class linked_ptr; - - T* value_; - linked_ptr_internal link_; - - void depart() { - if (link_.depart()) delete value_; - } - - void capture(T* ptr) { - value_ = ptr; - link_.join_new(); - } - - template <typename U> void copy(linked_ptr<U> const* ptr) { - value_ = ptr->get(); - if (value_) - link_.join(&ptr->link_); - else - link_.join_new(); - } -}; - -template<typename T> inline -bool operator==(T* ptr, const linked_ptr<T>& x) { - return ptr == x.get(); -} - -template<typename T> inline -bool operator!=(T* ptr, const linked_ptr<T>& x) { - return ptr != x.get(); -} - -// A function to convert T* into linked_ptr<T> -// Doing e.g. make_linked_ptr(new FooBarBaz<type>(arg)) is a shorter notation -// for linked_ptr<FooBarBaz<type> >(new FooBarBaz<type>(arg)) -template <typename T> -linked_ptr<T> make_linked_ptr(T* ptr) { - return linked_ptr<T>(ptr); -} - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_LINKED_PTR_H_ -// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -// Google Test - The Google C++ Testing Framework -// -// This file implements a universal value printer that can print a -// value of any type T: -// -// void ::testing::internal::UniversalPrinter<T>::Print(value, ostream_ptr); -// -// A user can teach this function how to print a class type T by -// defining either operator<<() or PrintTo() in the namespace that -// defines T. More specifically, the FIRST defined function in the -// following list will be used (assuming T is defined in namespace -// foo): -// -// 1. foo::PrintTo(const T&, ostream*) -// 2. operator<<(ostream&, const T&) defined in either foo or the -// global namespace. -// -// If none of the above is defined, it will print the debug string of -// the value if it is a protocol buffer, or print the raw bytes in the -// value otherwise. -// -// To aid debugging: when T is a reference type, the address of the -// value is also printed; when T is a (const) char pointer, both the -// pointer value and the NUL-terminated string it points to are -// printed. -// -// We also provide some convenient wrappers: -// -// // Prints a value to a string. For a (const or not) char -// // pointer, the NUL-terminated string (but not the pointer) is -// // printed. -// std::string ::testing::PrintToString(const T& value); -// -// // Prints a value tersely: for a reference type, the referenced -// // value (but not the address) is printed; for a (const or not) char -// // pointer, the NUL-terminated string (but not the pointer) is -// // printed. -// void ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrint(const T& value, ostream*); -// -// // Prints value using the type inferred by the compiler. The difference -// // from UniversalTersePrint() is that this function prints both the -// // pointer and the NUL-terminated string for a (const or not) char pointer. -// void ::testing::internal::UniversalPrint(const T& value, ostream*); -// -// // Prints the fields of a tuple tersely to a string vector, one -// // element for each field. Tuple support must be enabled in -// // gtest-port.h. -// std::vector<string> UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings( -// const Tuple& value); -// -// Known limitation: -// -// The print primitives print the elements of an STL-style container -// using the compiler-inferred type of *iter where iter is a -// const_iterator of the container. When const_iterator is an input -// iterator but not a forward iterator, this inferred type may not -// match value_type, and the print output may be incorrect. In -// practice, this is rarely a problem as for most containers -// const_iterator is a forward iterator. We'll fix this if there's an -// actual need for it. Note that this fix cannot rely on value_type -// being defined as many user-defined container types don't have -// value_type. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRINTERS_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRINTERS_H_ - -#include <ostream> // NOLINT -#include <sstream> -#include <string> -#include <utility> -#include <vector> - -namespace testing { - -// Definitions in the 'internal' and 'internal2' name spaces are -// subject to change without notice. DO NOT USE THEM IN USER CODE! -namespace internal2 { - -// Prints the given number of bytes in the given object to the given -// ostream. -GTEST_API_ void PrintBytesInObjectTo(const unsigned char* obj_bytes, - size_t count, - ::std::ostream* os); - -// For selecting which printer to use when a given type has neither << -// nor PrintTo(). -enum TypeKind { - kProtobuf, // a protobuf type - kConvertibleToInteger, // a type implicitly convertible to BiggestInt - // (e.g. a named or unnamed enum type) - kOtherType // anything else -}; - -// TypeWithoutFormatter<T, kTypeKind>::PrintValue(value, os) is called -// by the universal printer to print a value of type T when neither -// operator<< nor PrintTo() is defined for T, where kTypeKind is the -// "kind" of T as defined by enum TypeKind. -template <typename T, TypeKind kTypeKind> -class TypeWithoutFormatter { - public: - // This default version is called when kTypeKind is kOtherType. - static void PrintValue(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintBytesInObjectTo(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(&value), - sizeof(value), os); - } -}; - -// We print a protobuf using its ShortDebugString() when the string -// doesn't exceed this many characters; otherwise we print it using -// DebugString() for better readability. -const size_t kProtobufOneLinerMaxLength = 50; - -template <typename T> -class TypeWithoutFormatter<T, kProtobuf> { - public: - static void PrintValue(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - const ::testing::internal::string short_str = value.ShortDebugString(); - const ::testing::internal::string pretty_str = - short_str.length() <= kProtobufOneLinerMaxLength ? - short_str : ("\n" + value.DebugString()); - *os << ("<" + pretty_str + ">"); - } -}; - -template <typename T> -class TypeWithoutFormatter<T, kConvertibleToInteger> { - public: - // Since T has no << operator or PrintTo() but can be implicitly - // converted to BiggestInt, we print it as a BiggestInt. - // - // Most likely T is an enum type (either named or unnamed), in which - // case printing it as an integer is the desired behavior. In case - // T is not an enum, printing it as an integer is the best we can do - // given that it has no user-defined printer. - static void PrintValue(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - const internal::BiggestInt kBigInt = value; - *os << kBigInt; - } -}; - -// Prints the given value to the given ostream. If the value is a -// protocol message, its debug string is printed; if it's an enum or -// of a type implicitly convertible to BiggestInt, it's printed as an -// integer; otherwise the bytes in the value are printed. This is -// what UniversalPrinter<T>::Print() does when it knows nothing about -// type T and T has neither << operator nor PrintTo(). -// -// A user can override this behavior for a class type Foo by defining -// a << operator in the namespace where Foo is defined. -// -// We put this operator in namespace 'internal2' instead of 'internal' -// to simplify the implementation, as much code in 'internal' needs to -// use << in STL, which would conflict with our own << were it defined -// in 'internal'. -// -// Note that this operator<< takes a generic std::basic_ostream<Char, -// CharTraits> type instead of the more restricted std::ostream. If -// we define it to take an std::ostream instead, we'll get an -// "ambiguous overloads" compiler error when trying to print a type -// Foo that supports streaming to std::basic_ostream<Char, -// CharTraits>, as the compiler cannot tell whether -// operator<<(std::ostream&, const T&) or -// operator<<(std::basic_stream<Char, CharTraits>, const Foo&) is more -// specific. -template <typename Char, typename CharTraits, typename T> -::std::basic_ostream<Char, CharTraits>& operator<<( - ::std::basic_ostream<Char, CharTraits>& os, const T& x) { - TypeWithoutFormatter<T, - (internal::IsAProtocolMessage<T>::value ? kProtobuf : - internal::ImplicitlyConvertible<const T&, internal::BiggestInt>::value ? - kConvertibleToInteger : kOtherType)>::PrintValue(x, &os); - return os; -} - -} // namespace internal2 -} // namespace testing - -// This namespace MUST NOT BE NESTED IN ::testing, or the name look-up -// magic needed for implementing UniversalPrinter won't work. -namespace testing_internal { - -// Used to print a value that is not an STL-style container when the -// user doesn't define PrintTo() for it. -template <typename T> -void DefaultPrintNonContainerTo(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - // With the following statement, during unqualified name lookup, - // testing::internal2::operator<< appears as if it was declared in - // the nearest enclosing namespace that contains both - // ::testing_internal and ::testing::internal2, i.e. the global - // namespace. For more details, refer to the C++ Standard section - // 7.3.4-1 [namespace.udir]. This allows us to fall back onto - // testing::internal2::operator<< in case T doesn't come with a << - // operator. - // - // We cannot write 'using ::testing::internal2::operator<<;', which - // gcc 3.3 fails to compile due to a compiler bug. - using namespace ::testing::internal2; // NOLINT - - // Assuming T is defined in namespace foo, in the next statement, - // the compiler will consider all of: - // - // 1. foo::operator<< (thanks to Koenig look-up), - // 2. ::operator<< (as the current namespace is enclosed in ::), - // 3. testing::internal2::operator<< (thanks to the using statement above). - // - // The operator<< whose type matches T best will be picked. - // - // We deliberately allow #2 to be a candidate, as sometimes it's - // impossible to define #1 (e.g. when foo is ::std, defining - // anything in it is undefined behavior unless you are a compiler - // vendor.). - *os << value; -} - -} // namespace testing_internal - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// UniversalPrinter<T>::Print(value, ostream_ptr) prints the given -// value to the given ostream. The caller must ensure that -// 'ostream_ptr' is not NULL, or the behavior is undefined. -// -// We define UniversalPrinter as a class template (as opposed to a -// function template), as we need to partially specialize it for -// reference types, which cannot be done with function templates. -template <typename T> -class UniversalPrinter; - -template <typename T> -void UniversalPrint(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os); - -// Used to print an STL-style container when the user doesn't define -// a PrintTo() for it. -template <typename C> -void DefaultPrintTo(IsContainer /* dummy */, - false_type /* is not a pointer */, - const C& container, ::std::ostream* os) { - const size_t kMaxCount = 32; // The maximum number of elements to print. - *os << '{'; - size_t count = 0; - for (typename C::const_iterator it = container.begin(); - it != container.end(); ++it, ++count) { - if (count > 0) { - *os << ','; - if (count == kMaxCount) { // Enough has been printed. - *os << " ..."; - break; - } - } - *os << ' '; - // We cannot call PrintTo(*it, os) here as PrintTo() doesn't - // handle *it being a native array. - internal::UniversalPrint(*it, os); - } - - if (count > 0) { - *os << ' '; - } - *os << '}'; -} - -// Used to print a pointer that is neither a char pointer nor a member -// pointer, when the user doesn't define PrintTo() for it. (A member -// variable pointer or member function pointer doesn't really point to -// a location in the address space. Their representation is -// implementation-defined. Therefore they will be printed as raw -// bytes.) -template <typename T> -void DefaultPrintTo(IsNotContainer /* dummy */, - true_type /* is a pointer */, - T* p, ::std::ostream* os) { - if (p == NULL) { - *os << "NULL"; - } else { - // C++ doesn't allow casting from a function pointer to any object - // pointer. - // - // IsTrue() silences warnings: "Condition is always true", - // "unreachable code". - if (IsTrue(ImplicitlyConvertible<T*, const void*>::value)) { - // T is not a function type. We just call << to print p, - // relying on ADL to pick up user-defined << for their pointer - // types, if any. - *os << p; - } else { - // T is a function type, so '*os << p' doesn't do what we want - // (it just prints p as bool). We want to print p as a const - // void*. However, we cannot cast it to const void* directly, - // even using reinterpret_cast, as earlier versions of gcc - // (e.g. 3.4.5) cannot compile the cast when p is a function - // pointer. Casting to UInt64 first solves the problem. - *os << reinterpret_cast<const void*>( - reinterpret_cast<internal::UInt64>(p)); - } - } -} - -// Used to print a non-container, non-pointer value when the user -// doesn't define PrintTo() for it. -template <typename T> -void DefaultPrintTo(IsNotContainer /* dummy */, - false_type /* is not a pointer */, - const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - ::testing_internal::DefaultPrintNonContainerTo(value, os); -} - -// Prints the given value using the << operator if it has one; -// otherwise prints the bytes in it. This is what -// UniversalPrinter<T>::Print() does when PrintTo() is not specialized -// or overloaded for type T. -// -// A user can override this behavior for a class type Foo by defining -// an overload of PrintTo() in the namespace where Foo is defined. We -// give the user this option as sometimes defining a << operator for -// Foo is not desirable (e.g. the coding style may prevent doing it, -// or there is already a << operator but it doesn't do what the user -// wants). -template <typename T> -void PrintTo(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - // DefaultPrintTo() is overloaded. The type of its first two - // arguments determine which version will be picked. If T is an - // STL-style container, the version for container will be called; if - // T is a pointer, the pointer version will be called; otherwise the - // generic version will be called. - // - // Note that we check for container types here, prior to we check - // for protocol message types in our operator<<. The rationale is: - // - // For protocol messages, we want to give people a chance to - // override Google Mock's format by defining a PrintTo() or - // operator<<. For STL containers, other formats can be - // incompatible with Google Mock's format for the container - // elements; therefore we check for container types here to ensure - // that our format is used. - // - // The second argument of DefaultPrintTo() is needed to bypass a bug - // in Symbian's C++ compiler that prevents it from picking the right - // overload between: - // - // PrintTo(const T& x, ...); - // PrintTo(T* x, ...); - DefaultPrintTo(IsContainerTest<T>(0), is_pointer<T>(), value, os); -} - -// The following list of PrintTo() overloads tells -// UniversalPrinter<T>::Print() how to print standard types (built-in -// types, strings, plain arrays, and pointers). - -// Overloads for various char types. -GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(unsigned char c, ::std::ostream* os); -GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(signed char c, ::std::ostream* os); -inline void PrintTo(char c, ::std::ostream* os) { - // When printing a plain char, we always treat it as unsigned. This - // way, the output won't be affected by whether the compiler thinks - // char is signed or not. - PrintTo(static_cast<unsigned char>(c), os); -} - -// Overloads for other simple built-in types. -inline void PrintTo(bool x, ::std::ostream* os) { - *os << (x ? "true" : "false"); -} - -// Overload for wchar_t type. -// Prints a wchar_t as a symbol if it is printable or as its internal -// code otherwise and also as its decimal code (except for L'\0'). -// The L'\0' char is printed as "L'\\0'". The decimal code is printed -// as signed integer when wchar_t is implemented by the compiler -// as a signed type and is printed as an unsigned integer when wchar_t -// is implemented as an unsigned type. -GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(wchar_t wc, ::std::ostream* os); - -// Overloads for C strings. -GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(const char* s, ::std::ostream* os); -inline void PrintTo(char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const char*>(s), os); -} - -// signed/unsigned char is often used for representing binary data, so -// we print pointers to it as void* to be safe. -inline void PrintTo(const signed char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s), os); -} -inline void PrintTo(signed char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s), os); -} -inline void PrintTo(const unsigned char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s), os); -} -inline void PrintTo(unsigned char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s), os); -} - -// MSVC can be configured to define wchar_t as a typedef of unsigned -// short. It defines _NATIVE_WCHAR_T_DEFINED when wchar_t is a native -// type. When wchar_t is a typedef, defining an overload for const -// wchar_t* would cause unsigned short* be printed as a wide string, -// possibly causing invalid memory accesses. -#if !defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(_NATIVE_WCHAR_T_DEFINED) -// Overloads for wide C strings -GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(const wchar_t* s, ::std::ostream* os); -inline void PrintTo(wchar_t* s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const wchar_t*>(s), os); -} -#endif - -// Overload for C arrays. Multi-dimensional arrays are printed -// properly. - -// Prints the given number of elements in an array, without printing -// the curly braces. -template <typename T> -void PrintRawArrayTo(const T a[], size_t count, ::std::ostream* os) { - UniversalPrint(a[0], os); - for (size_t i = 1; i != count; i++) { - *os << ", "; - UniversalPrint(a[i], os); - } -} - -// Overloads for ::string and ::std::string. -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING -GTEST_API_ void PrintStringTo(const ::string&s, ::std::ostream* os); -inline void PrintTo(const ::string& s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintStringTo(s, os); -} -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING - -GTEST_API_ void PrintStringTo(const ::std::string&s, ::std::ostream* os); -inline void PrintTo(const ::std::string& s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintStringTo(s, os); -} - -// Overloads for ::wstring and ::std::wstring. -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING -GTEST_API_ void PrintWideStringTo(const ::wstring&s, ::std::ostream* os); -inline void PrintTo(const ::wstring& s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintWideStringTo(s, os); -} -#endif // GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING - -#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING -GTEST_API_ void PrintWideStringTo(const ::std::wstring&s, ::std::ostream* os); -inline void PrintTo(const ::std::wstring& s, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintWideStringTo(s, os); -} -#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING - -#if GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE -// Overload for ::std::tr1::tuple. Needed for printing function arguments, -// which are packed as tuples. - -// Helper function for printing a tuple. T must be instantiated with -// a tuple type. -template <typename T> -void PrintTupleTo(const T& t, ::std::ostream* os); - -// Overloaded PrintTo() for tuples of various arities. We support -// tuples of up-to 10 fields. The following implementation works -// regardless of whether tr1::tuple is implemented using the -// non-standard variadic template feature or not. - -inline void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<>& t, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1> -void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1>& t, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2> -void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2>& t, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> -void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3>& t, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4> -void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4>& t, ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5> -void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5>& t, - ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6> -void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6>& t, - ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7> -void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7>& t, - ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8> -void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8>& t, - ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9> -void PrintTo(const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9>& t, - ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10> -void PrintTo( - const ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10>& t, - ::std::ostream* os) { - PrintTupleTo(t, os); -} -#endif // GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE - -// Overload for std::pair. -template <typename T1, typename T2> -void PrintTo(const ::std::pair<T1, T2>& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - *os << '('; - // We cannot use UniversalPrint(value.first, os) here, as T1 may be - // a reference type. The same for printing value.second. - UniversalPrinter<T1>::Print(value.first, os); - *os << ", "; - UniversalPrinter<T2>::Print(value.second, os); - *os << ')'; -} - -// Implements printing a non-reference type T by letting the compiler -// pick the right overload of PrintTo() for T. -template <typename T> -class UniversalPrinter { - public: - // MSVC warns about adding const to a function type, so we want to - // disable the warning. -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable:4180) // Temporarily disables warning 4180. -#endif // _MSC_VER - - // Note: we deliberately don't call this PrintTo(), as that name - // conflicts with ::testing::internal::PrintTo in the body of the - // function. - static void Print(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - // By default, ::testing::internal::PrintTo() is used for printing - // the value. - // - // Thanks to Koenig look-up, if T is a class and has its own - // PrintTo() function defined in its namespace, that function will - // be visible here. Since it is more specific than the generic ones - // in ::testing::internal, it will be picked by the compiler in the - // following statement - exactly what we want. - PrintTo(value, os); - } - -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state. -#endif // _MSC_VER -}; - -// UniversalPrintArray(begin, len, os) prints an array of 'len' -// elements, starting at address 'begin'. -template <typename T> -void UniversalPrintArray(const T* begin, size_t len, ::std::ostream* os) { - if (len == 0) { - *os << "{}"; - } else { - *os << "{ "; - const size_t kThreshold = 18; - const size_t kChunkSize = 8; - // If the array has more than kThreshold elements, we'll have to - // omit some details by printing only the first and the last - // kChunkSize elements. - // TODO(wan@google.com): let the user control the threshold using a flag. - if (len <= kThreshold) { - PrintRawArrayTo(begin, len, os); - } else { - PrintRawArrayTo(begin, kChunkSize, os); - *os << ", ..., "; - PrintRawArrayTo(begin + len - kChunkSize, kChunkSize, os); - } - *os << " }"; - } -} -// This overload prints a (const) char array compactly. -GTEST_API_ void UniversalPrintArray( - const char* begin, size_t len, ::std::ostream* os); - -// This overload prints a (const) wchar_t array compactly. -GTEST_API_ void UniversalPrintArray( - const wchar_t* begin, size_t len, ::std::ostream* os); - -// Implements printing an array type T[N]. -template <typename T, size_t N> -class UniversalPrinter<T[N]> { - public: - // Prints the given array, omitting some elements when there are too - // many. - static void Print(const T (&a)[N], ::std::ostream* os) { - UniversalPrintArray(a, N, os); - } -}; - -// Implements printing a reference type T&. -template <typename T> -class UniversalPrinter<T&> { - public: - // MSVC warns about adding const to a function type, so we want to - // disable the warning. -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable:4180) // Temporarily disables warning 4180. -#endif // _MSC_VER - - static void Print(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - // Prints the address of the value. We use reinterpret_cast here - // as static_cast doesn't compile when T is a function type. - *os << "@" << reinterpret_cast<const void*>(&value) << " "; - - // Then prints the value itself. - UniversalPrint(value, os); - } - -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state. -#endif // _MSC_VER -}; - -// Prints a value tersely: for a reference type, the referenced value -// (but not the address) is printed; for a (const) char pointer, the -// NUL-terminated string (but not the pointer) is printed. - -template <typename T> -class UniversalTersePrinter { - public: - static void Print(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - UniversalPrint(value, os); - } -}; -template <typename T> -class UniversalTersePrinter<T&> { - public: - static void Print(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - UniversalPrint(value, os); - } -}; -template <typename T, size_t N> -class UniversalTersePrinter<T[N]> { - public: - static void Print(const T (&value)[N], ::std::ostream* os) { - UniversalPrinter<T[N]>::Print(value, os); - } -}; -template <> -class UniversalTersePrinter<const char*> { - public: - static void Print(const char* str, ::std::ostream* os) { - if (str == NULL) { - *os << "NULL"; - } else { - UniversalPrint(string(str), os); - } - } -}; -template <> -class UniversalTersePrinter<char*> { - public: - static void Print(char* str, ::std::ostream* os) { - UniversalTersePrinter<const char*>::Print(str, os); - } -}; - -#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING -template <> -class UniversalTersePrinter<const wchar_t*> { - public: - static void Print(const wchar_t* str, ::std::ostream* os) { - if (str == NULL) { - *os << "NULL"; - } else { - UniversalPrint(::std::wstring(str), os); - } - } -}; -#endif - -template <> -class UniversalTersePrinter<wchar_t*> { - public: - static void Print(wchar_t* str, ::std::ostream* os) { - UniversalTersePrinter<const wchar_t*>::Print(str, os); - } -}; - -template <typename T> -void UniversalTersePrint(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - UniversalTersePrinter<T>::Print(value, os); -} - -// Prints a value using the type inferred by the compiler. The -// difference between this and UniversalTersePrint() is that for a -// (const) char pointer, this prints both the pointer and the -// NUL-terminated string. -template <typename T> -void UniversalPrint(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { - // A workarond for the bug in VC++ 7.1 that prevents us from instantiating - // UniversalPrinter with T directly. - typedef T T1; - UniversalPrinter<T1>::Print(value, os); -} - -#if GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE -typedef ::std::vector<string> Strings; - -// This helper template allows PrintTo() for tuples and -// UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings() to be defined by -// induction on the number of tuple fields. The idea is that -// TuplePrefixPrinter<N>::PrintPrefixTo(t, os) prints the first N -// fields in tuple t, and can be defined in terms of -// TuplePrefixPrinter<N - 1>. - -// The inductive case. -template <size_t N> -struct TuplePrefixPrinter { - // Prints the first N fields of a tuple. - template <typename Tuple> - static void PrintPrefixTo(const Tuple& t, ::std::ostream* os) { - TuplePrefixPrinter<N - 1>::PrintPrefixTo(t, os); - *os << ", "; - UniversalPrinter<typename ::std::tr1::tuple_element<N - 1, Tuple>::type> - ::Print(::std::tr1::get<N - 1>(t), os); - } - - // Tersely prints the first N fields of a tuple to a string vector, - // one element for each field. - template <typename Tuple> - static void TersePrintPrefixToStrings(const Tuple& t, Strings* strings) { - TuplePrefixPrinter<N - 1>::TersePrintPrefixToStrings(t, strings); - ::std::stringstream ss; - UniversalTersePrint(::std::tr1::get<N - 1>(t), &ss); - strings->push_back(ss.str()); - } -}; - -// Base cases. -template <> -struct TuplePrefixPrinter<0> { - template <typename Tuple> - static void PrintPrefixTo(const Tuple&, ::std::ostream*) {} - - template <typename Tuple> - static void TersePrintPrefixToStrings(const Tuple&, Strings*) {} -}; -// We have to specialize the entire TuplePrefixPrinter<> class -// template here, even though the definition of -// TersePrintPrefixToStrings() is the same as the generic version, as -// Embarcadero (formerly CodeGear, formerly Borland) C++ doesn't -// support specializing a method template of a class template. -template <> -struct TuplePrefixPrinter<1> { - template <typename Tuple> - static void PrintPrefixTo(const Tuple& t, ::std::ostream* os) { - UniversalPrinter<typename ::std::tr1::tuple_element<0, Tuple>::type>:: - Print(::std::tr1::get<0>(t), os); - } - - template <typename Tuple> - static void TersePrintPrefixToStrings(const Tuple& t, Strings* strings) { - ::std::stringstream ss; - UniversalTersePrint(::std::tr1::get<0>(t), &ss); - strings->push_back(ss.str()); - } -}; - -// Helper function for printing a tuple. T must be instantiated with -// a tuple type. -template <typename T> -void PrintTupleTo(const T& t, ::std::ostream* os) { - *os << "("; - TuplePrefixPrinter< ::std::tr1::tuple_size<T>::value>:: - PrintPrefixTo(t, os); - *os << ")"; -} - -// Prints the fields of a tuple tersely to a string vector, one -// element for each field. See the comment before -// UniversalTersePrint() for how we define "tersely". -template <typename Tuple> -Strings UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(const Tuple& value) { - Strings result; - TuplePrefixPrinter< ::std::tr1::tuple_size<Tuple>::value>:: - TersePrintPrefixToStrings(value, &result); - return result; -} -#endif // GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE - -} // namespace internal - -template <typename T> -::std::string PrintToString(const T& value) { - ::std::stringstream ss; - internal::UniversalTersePrinter<T>::Print(value, &ss); - return ss.str(); -} - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRINTERS_H_ - -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - -namespace testing { -namespace internal { - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// Outputs a message explaining invalid registration of different -// fixture class for the same test case. This may happen when -// TEST_P macro is used to define two tests with the same name -// but in different namespaces. -GTEST_API_ void ReportInvalidTestCaseType(const char* test_case_name, - const char* file, int line); - -template <typename> class ParamGeneratorInterface; -template <typename> class ParamGenerator; - -// Interface for iterating over elements provided by an implementation -// of ParamGeneratorInterface<T>. -template <typename T> -class ParamIteratorInterface { - public: - virtual ~ParamIteratorInterface() {} - // A pointer to the base generator instance. - // Used only for the purposes of iterator comparison - // to make sure that two iterators belong to the same generator. - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* BaseGenerator() const = 0; - // Advances iterator to point to the next element - // provided by the generator. The caller is responsible - // for not calling Advance() on an iterator equal to - // BaseGenerator()->End(). - virtual void Advance() = 0; - // Clones the iterator object. Used for implementing copy semantics - // of ParamIterator<T>. - virtual ParamIteratorInterface* Clone() const = 0; - // Dereferences the current iterator and provides (read-only) access - // to the pointed value. It is the caller's responsibility not to call - // Current() on an iterator equal to BaseGenerator()->End(). - // Used for implementing ParamGenerator<T>::operator*(). - virtual const T* Current() const = 0; - // Determines whether the given iterator and other point to the same - // element in the sequence generated by the generator. - // Used for implementing ParamGenerator<T>::operator==(). - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface& other) const = 0; -}; - -// Class iterating over elements provided by an implementation of -// ParamGeneratorInterface<T>. It wraps ParamIteratorInterface<T> -// and implements the const forward iterator concept. -template <typename T> -class ParamIterator { - public: - typedef T value_type; - typedef const T& reference; - typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; - - // ParamIterator assumes ownership of the impl_ pointer. - ParamIterator(const ParamIterator& other) : impl_(other.impl_->Clone()) {} - ParamIterator& operator=(const ParamIterator& other) { - if (this != &other) - impl_.reset(other.impl_->Clone()); - return *this; - } - - const T& operator*() const { return *impl_->Current(); } - const T* operator->() const { return impl_->Current(); } - // Prefix version of operator++. - ParamIterator& operator++() { - impl_->Advance(); - return *this; - } - // Postfix version of operator++. - ParamIterator operator++(int /*unused*/) { - ParamIteratorInterface<T>* clone = impl_->Clone(); - impl_->Advance(); - return ParamIterator(clone); - } - bool operator==(const ParamIterator& other) const { - return impl_.get() == other.impl_.get() || impl_->Equals(*other.impl_); - } - bool operator!=(const ParamIterator& other) const { - return !(*this == other); - } - - private: - friend class ParamGenerator<T>; - explicit ParamIterator(ParamIteratorInterface<T>* impl) : impl_(impl) {} - scoped_ptr<ParamIteratorInterface<T> > impl_; -}; - -// ParamGeneratorInterface<T> is the binary interface to access generators -// defined in other translation units. -template <typename T> -class ParamGeneratorInterface { - public: - typedef T ParamType; - - virtual ~ParamGeneratorInterface() {} - - // Generator interface definition - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Begin() const = 0; - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* End() const = 0; -}; - -// Wraps ParamGeneratorInterface<T> and provides general generator syntax -// compatible with the STL Container concept. -// This class implements copy initialization semantics and the contained -// ParamGeneratorInterface<T> instance is shared among all copies -// of the original object. This is possible because that instance is immutable. -template<typename T> -class ParamGenerator { - public: - typedef ParamIterator<T> iterator; - - explicit ParamGenerator(ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* impl) : impl_(impl) {} - ParamGenerator(const ParamGenerator& other) : impl_(other.impl_) {} - - ParamGenerator& operator=(const ParamGenerator& other) { - impl_ = other.impl_; - return *this; - } - - iterator begin() const { return iterator(impl_->Begin()); } - iterator end() const { return iterator(impl_->End()); } - - private: - linked_ptr<const ParamGeneratorInterface<T> > impl_; -}; - -// Generates values from a range of two comparable values. Can be used to -// generate sequences of user-defined types that implement operator+() and -// operator<(). -// This class is used in the Range() function. -template <typename T, typename IncrementT> -class RangeGenerator : public ParamGeneratorInterface<T> { - public: - RangeGenerator(T begin, T end, IncrementT step) - : begin_(begin), end_(end), - step_(step), end_index_(CalculateEndIndex(begin, end, step)) {} - virtual ~RangeGenerator() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, begin_, 0, step_); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, end_, end_index_, step_); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<T> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* base, T value, int index, - IncrementT step) - : base_(base), value_(value), index_(index), step_(step) {} - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - virtual void Advance() { - value_ = value_ + step_; - index_++; - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const T* Current() const { return &value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<T>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const int other_index = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other)->index_; - return index_ == other_index; - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : ParamIteratorInterface<T>(), - base_(other.base_), value_(other.value_), index_(other.index_), - step_(other.step_) {} - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* const base_; - T value_; - int index_; - const IncrementT step_; - }; // class RangeGenerator::Iterator - - static int CalculateEndIndex(const T& begin, - const T& end, - const IncrementT& step) { - int end_index = 0; - for (T i = begin; i < end; i = i + step) - end_index++; - return end_index; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const RangeGenerator& other); - - const T begin_; - const T end_; - const IncrementT step_; - // The index for the end() iterator. All the elements in the generated - // sequence are indexed (0-based) to aid iterator comparison. - const int end_index_; -}; // class RangeGenerator - - -// Generates values from a pair of STL-style iterators. Used in the -// ValuesIn() function. The elements are copied from the source range -// since the source can be located on the stack, and the generator -// is likely to persist beyond that stack frame. -template <typename T> -class ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator : public ParamGeneratorInterface<T> { - public: - template <typename ForwardIterator> - ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator(ForwardIterator begin, ForwardIterator end) - : container_(begin, end) {} - virtual ~ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, container_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, container_.end()); - } - - private: - typedef typename ::std::vector<T> ContainerType; - - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<T> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* base, - typename ContainerType::const_iterator iterator) - : base_(base), iterator_(iterator) {} - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - virtual void Advance() { - ++iterator_; - value_.reset(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - // We need to use cached value referenced by iterator_ because *iterator_ - // can return a temporary object (and of type other then T), so just - // having "return &*iterator_;" doesn't work. - // value_ is updated here and not in Advance() because Advance() - // can advance iterator_ beyond the end of the range, and we cannot - // detect that fact. The client code, on the other hand, is - // responsible for not calling Current() on an out-of-range iterator. - virtual const T* Current() const { - if (value_.get() == NULL) - value_.reset(new T(*iterator_)); - return value_.get(); - } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<T>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - return iterator_ == - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other)->iterator_; - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - // The explicit constructor call suppresses a false warning - // emitted by gcc when supplied with the -Wextra option. - : ParamIteratorInterface<T>(), - base_(other.base_), - iterator_(other.iterator_) {} - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* const base_; - typename ContainerType::const_iterator iterator_; - // A cached value of *iterator_. We keep it here to allow access by - // pointer in the wrapping iterator's operator->(). - // value_ needs to be mutable to be accessed in Current(). - // Use of scoped_ptr helps manage cached value's lifetime, - // which is bound by the lifespan of the iterator itself. - mutable scoped_ptr<const T> value_; - }; // class ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator& other); - - const ContainerType container_; -}; // class ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// Stores a parameter value and later creates tests parameterized with that -// value. -template <class TestClass> -class ParameterizedTestFactory : public TestFactoryBase { - public: - typedef typename TestClass::ParamType ParamType; - explicit ParameterizedTestFactory(ParamType parameter) : - parameter_(parameter) {} - virtual Test* CreateTest() { - TestClass::SetParam(¶meter_); - return new TestClass(); - } - - private: - const ParamType parameter_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ParameterizedTestFactory); -}; - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// TestMetaFactoryBase is a base class for meta-factories that create -// test factories for passing into MakeAndRegisterTestInfo function. -template <class ParamType> -class TestMetaFactoryBase { - public: - virtual ~TestMetaFactoryBase() {} - - virtual TestFactoryBase* CreateTestFactory(ParamType parameter) = 0; -}; - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// TestMetaFactory creates test factories for passing into -// MakeAndRegisterTestInfo function. Since MakeAndRegisterTestInfo receives -// ownership of test factory pointer, same factory object cannot be passed -// into that method twice. But ParameterizedTestCaseInfo is going to call -// it for each Test/Parameter value combination. Thus it needs meta factory -// creator class. -template <class TestCase> -class TestMetaFactory - : public TestMetaFactoryBase<typename TestCase::ParamType> { - public: - typedef typename TestCase::ParamType ParamType; - - TestMetaFactory() {} - - virtual TestFactoryBase* CreateTestFactory(ParamType parameter) { - return new ParameterizedTestFactory<TestCase>(parameter); - } - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestMetaFactory); -}; - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase is a generic interface -// to ParameterizedTestCaseInfo classes. ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase -// accumulates test information provided by TEST_P macro invocations -// and generators provided by INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P macro invocations -// and uses that information to register all resulting test instances -// in RegisterTests method. The ParameterizeTestCaseRegistry class holds -// a collection of pointers to the ParameterizedTestCaseInfo objects -// and calls RegisterTests() on each of them when asked. -class ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase { - public: - virtual ~ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase() {} - - // Base part of test case name for display purposes. - virtual const string& GetTestCaseName() const = 0; - // Test case id to verify identity. - virtual TypeId GetTestCaseTypeId() const = 0; - // UnitTest class invokes this method to register tests in this - // test case right before running them in RUN_ALL_TESTS macro. - // This method should not be called more then once on any single - // instance of a ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase derived class. - virtual void RegisterTests() = 0; - - protected: - ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase() {} - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase); -}; - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// ParameterizedTestCaseInfo accumulates tests obtained from TEST_P -// macro invocations for a particular test case and generators -// obtained from INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P macro invocations for that -// test case. It registers tests with all values generated by all -// generators when asked. -template <class TestCase> -class ParameterizedTestCaseInfo : public ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase { - public: - // ParamType and GeneratorCreationFunc are private types but are required - // for declarations of public methods AddTestPattern() and - // AddTestCaseInstantiation(). - typedef typename TestCase::ParamType ParamType; - // A function that returns an instance of appropriate generator type. - typedef ParamGenerator<ParamType>(GeneratorCreationFunc)(); - - explicit ParameterizedTestCaseInfo(const char* name) - : test_case_name_(name) {} - - // Test case base name for display purposes. - virtual const string& GetTestCaseName() const { return test_case_name_; } - // Test case id to verify identity. - virtual TypeId GetTestCaseTypeId() const { return GetTypeId<TestCase>(); } - // TEST_P macro uses AddTestPattern() to record information - // about a single test in a LocalTestInfo structure. - // test_case_name is the base name of the test case (without invocation - // prefix). test_base_name is the name of an individual test without - // parameter index. For the test SequenceA/FooTest.DoBar/1 FooTest is - // test case base name and DoBar is test base name. - void AddTestPattern(const char* test_case_name, - const char* test_base_name, - TestMetaFactoryBase<ParamType>* meta_factory) { - tests_.push_back(linked_ptr<TestInfo>(new TestInfo(test_case_name, - test_base_name, - meta_factory))); - } - // INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P macro uses AddGenerator() to record information - // about a generator. - int AddTestCaseInstantiation(const string& instantiation_name, - GeneratorCreationFunc* func, - const char* /* file */, - int /* line */) { - instantiations_.push_back(::std::make_pair(instantiation_name, func)); - return 0; // Return value used only to run this method in namespace scope. - } - // UnitTest class invokes this method to register tests in this test case - // test cases right before running tests in RUN_ALL_TESTS macro. - // This method should not be called more then once on any single - // instance of a ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase derived class. - // UnitTest has a guard to prevent from calling this method more then once. - virtual void RegisterTests() { - for (typename TestInfoContainer::iterator test_it = tests_.begin(); - test_it != tests_.end(); ++test_it) { - linked_ptr<TestInfo> test_info = *test_it; - for (typename InstantiationContainer::iterator gen_it = - instantiations_.begin(); gen_it != instantiations_.end(); - ++gen_it) { - const string& instantiation_name = gen_it->first; - ParamGenerator<ParamType> generator((*gen_it->second)()); - - string test_case_name; - if ( !instantiation_name.empty() ) - test_case_name = instantiation_name + "/"; - test_case_name += test_info->test_case_base_name; - - int i = 0; - for (typename ParamGenerator<ParamType>::iterator param_it = - generator.begin(); - param_it != generator.end(); ++param_it, ++i) { - Message test_name_stream; - test_name_stream << test_info->test_base_name << "/" << i; - MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( - test_case_name.c_str(), - test_name_stream.GetString().c_str(), - NULL, // No type parameter. - PrintToString(*param_it).c_str(), - GetTestCaseTypeId(), - TestCase::SetUpTestCase, - TestCase::TearDownTestCase, - test_info->test_meta_factory->CreateTestFactory(*param_it)); - } // for param_it - } // for gen_it - } // for test_it - } // RegisterTests - - private: - // LocalTestInfo structure keeps information about a single test registered - // with TEST_P macro. - struct TestInfo { - TestInfo(const char* a_test_case_base_name, - const char* a_test_base_name, - TestMetaFactoryBase<ParamType>* a_test_meta_factory) : - test_case_base_name(a_test_case_base_name), - test_base_name(a_test_base_name), - test_meta_factory(a_test_meta_factory) {} - - const string test_case_base_name; - const string test_base_name; - const scoped_ptr<TestMetaFactoryBase<ParamType> > test_meta_factory; - }; - typedef ::std::vector<linked_ptr<TestInfo> > TestInfoContainer; - // Keeps pairs of <Instantiation name, Sequence generator creation function> - // received from INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P macros. - typedef ::std::vector<std::pair<string, GeneratorCreationFunc*> > - InstantiationContainer; - - const string test_case_name_; - TestInfoContainer tests_; - InstantiationContainer instantiations_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ParameterizedTestCaseInfo); -}; // class ParameterizedTestCaseInfo - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry contains a map of ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase -// classes accessed by test case names. TEST_P and INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P -// macros use it to locate their corresponding ParameterizedTestCaseInfo -// descriptors. -class ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry { - public: - ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry() {} - ~ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry() { - for (TestCaseInfoContainer::iterator it = test_case_infos_.begin(); - it != test_case_infos_.end(); ++it) { - delete *it; - } - } - - // Looks up or creates and returns a structure containing information about - // tests and instantiations of a particular test case. - template <class TestCase> - ParameterizedTestCaseInfo<TestCase>* GetTestCasePatternHolder( - const char* test_case_name, - const char* file, - int line) { - ParameterizedTestCaseInfo<TestCase>* typed_test_info = NULL; - for (TestCaseInfoContainer::iterator it = test_case_infos_.begin(); - it != test_case_infos_.end(); ++it) { - if ((*it)->GetTestCaseName() == test_case_name) { - if ((*it)->GetTestCaseTypeId() != GetTypeId<TestCase>()) { - // Complain about incorrect usage of Google Test facilities - // and terminate the program since we cannot guaranty correct - // test case setup and tear-down in this case. - ReportInvalidTestCaseType(test_case_name, file, line); - posix::Abort(); - } else { - // At this point we are sure that the object we found is of the same - // type we are looking for, so we downcast it to that type - // without further checks. - typed_test_info = CheckedDowncastToActualType< - ParameterizedTestCaseInfo<TestCase> >(*it); - } - break; - } - } - if (typed_test_info == NULL) { - typed_test_info = new ParameterizedTestCaseInfo<TestCase>(test_case_name); - test_case_infos_.push_back(typed_test_info); - } - return typed_test_info; - } - void RegisterTests() { - for (TestCaseInfoContainer::iterator it = test_case_infos_.begin(); - it != test_case_infos_.end(); ++it) { - (*it)->RegisterTests(); - } - } - - private: - typedef ::std::vector<ParameterizedTestCaseInfoBase*> TestCaseInfoContainer; - - TestCaseInfoContainer test_case_infos_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry); -}; - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PARAM_UTIL_H_ -// This file was GENERATED by command: -// pump.py gtest-param-util-generated.h.pump -// DO NOT EDIT BY HAND!!! - -// Copyright 2008 Google Inc. -// All Rights Reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: vladl@google.com (Vlad Losev) - -// Type and function utilities for implementing parameterized tests. -// This file is generated by a SCRIPT. DO NOT EDIT BY HAND! -// -// Currently Google Test supports at most 50 arguments in Values, -// and at most 10 arguments in Combine. Please contact -// googletestframework@googlegroups.com if you need more. -// Please note that the number of arguments to Combine is limited -// by the maximum arity of the implementation of tr1::tuple which is -// currently set at 10. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PARAM_UTIL_GENERATED_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PARAM_UTIL_GENERATED_H_ - -// scripts/fuse_gtest.py depends on gtest's own header being #included -// *unconditionally*. Therefore these #includes cannot be moved -// inside #if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST. - -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - -namespace testing { - -// Forward declarations of ValuesIn(), which is implemented in -// include/gtest/gtest-param-test.h. -template <typename ForwardIterator> -internal::ParamGenerator< - typename ::testing::internal::IteratorTraits<ForwardIterator>::value_type> -ValuesIn(ForwardIterator begin, ForwardIterator end); - -template <typename T, size_t N> -internal::ParamGenerator<T> ValuesIn(const T (&array)[N]); - -template <class Container> -internal::ParamGenerator<typename Container::value_type> ValuesIn( - const Container& container); - -namespace internal { - -// Used in the Values() function to provide polymorphic capabilities. -template <typename T1> -class ValueArray1 { - public: - explicit ValueArray1(T1 v1) : v1_(v1) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { return ValuesIn(&v1_, &v1_ + 1); } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray1& other); - - const T1 v1_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2> -class ValueArray2 { - public: - ValueArray2(T1 v1, T2 v2) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray2& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> -class ValueArray3 { - public: - ValueArray3(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray3& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4> -class ValueArray4 { - public: - ValueArray4(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), - v4_(v4) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray4& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5> -class ValueArray5 { - public: - ValueArray5(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), - v4_(v4), v5_(v5) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray5& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6> -class ValueArray6 { - public: - ValueArray6(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), - v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray6& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7> -class ValueArray7 { - public: - ValueArray7(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7) : v1_(v1), - v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray7& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8> -class ValueArray8 { - public: - ValueArray8(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, - T8 v8) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray8& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9> -class ValueArray9 { - public: - ValueArray9(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, - T9 v9) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray9& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10> -class ValueArray10 { - public: - ValueArray10(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray10& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11> -class ValueArray11 { - public: - ValueArray11(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), - v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray11& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12> -class ValueArray12 { - public: - ValueArray12(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), - v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray12& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13> -class ValueArray13 { - public: - ValueArray13(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), - v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), - v12_(v12), v13_(v13) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray13& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14> -class ValueArray14 { - public: - ValueArray14(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), - v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray14& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15> -class ValueArray15 { - public: - ValueArray15(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), - v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray15& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16> -class ValueArray16 { - public: - ValueArray16(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16) : v1_(v1), - v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), - v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), - v16_(v16) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray16& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17> -class ValueArray17 { - public: - ValueArray17(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, - T17 v17) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray17& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18> -class ValueArray18 { - public: - ValueArray18(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray18& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19> -class ValueArray19 { - public: - ValueArray19(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), - v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), - v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray19& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20> -class ValueArray20 { - public: - ValueArray20(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), - v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), - v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), - v19_(v19), v20_(v20) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray20& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21> -class ValueArray21 { - public: - ValueArray21(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), - v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), - v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), - v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray21& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22> -class ValueArray22 { - public: - ValueArray22(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), - v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), - v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray22& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23> -class ValueArray23 { - public: - ValueArray23(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), - v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), - v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), - v23_(v23) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray23& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24> -class ValueArray24 { - public: - ValueArray24(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24) : v1_(v1), - v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), - v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), - v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), - v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray24& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25> -class ValueArray25 { - public: - ValueArray25(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, - T25 v25) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), - v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray25& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26> -class ValueArray26 { - public: - ValueArray26(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), - v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray26& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27> -class ValueArray27 { - public: - ValueArray27(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), - v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), - v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), - v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), - v26_(v26), v27_(v27) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray27& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28> -class ValueArray28 { - public: - ValueArray28(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), - v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), - v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), - v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), - v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray28& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29> -class ValueArray29 { - public: - ValueArray29(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), - v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), - v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), - v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), - v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray29& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30> -class ValueArray30 { - public: - ValueArray30(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), - v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), - v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), - v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), - v29_(v29), v30_(v30) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray30& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31> -class ValueArray31 { - public: - ValueArray31(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), - v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), - v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), - v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), - v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray31& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32> -class ValueArray32 { - public: - ValueArray32(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32) : v1_(v1), - v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), - v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), - v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), - v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), - v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray32& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33> -class ValueArray33 { - public: - ValueArray33(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, - T33 v33) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), - v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), - v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), - v33_(v33) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray33& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34> -class ValueArray34 { - public: - ValueArray34(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), - v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), - v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), - v33_(v33), v34_(v34) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray34& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35> -class ValueArray35 { - public: - ValueArray35(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), - v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), - v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), - v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), - v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), - v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray35& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36> -class ValueArray36 { - public: - ValueArray36(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), - v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), - v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), - v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), - v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), - v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35), v36_(v36) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray36& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37> -class ValueArray37 { - public: - ValueArray37(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), - v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), - v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), - v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), - v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), - v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35), - v36_(v36), v37_(v37) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray37& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38> -class ValueArray38 { - public: - ValueArray38(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), - v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), - v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), - v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), - v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), - v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray38& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39> -class ValueArray39 { - public: - ValueArray39(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), - v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), - v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), - v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), - v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), - v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), v39_(v39) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray39& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40> -class ValueArray40 { - public: - ValueArray40(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40) : v1_(v1), - v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), - v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), - v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), - v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), - v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), - v34_(v34), v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), v39_(v39), - v40_(v40) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray40& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41> -class ValueArray41 { - public: - ValueArray41(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, - T41 v41) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), - v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), - v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), - v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), - v39_(v39), v40_(v40), v41_(v41) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray41& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42> -class ValueArray42 { - public: - ValueArray42(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), - v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), - v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), - v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), - v39_(v39), v40_(v40), v41_(v41), v42_(v42) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_), - static_cast<T>(v42_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray42& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; - const T42 v42_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43> -class ValueArray43 { - public: - ValueArray43(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), - v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), - v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), - v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), - v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), - v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), - v38_(v38), v39_(v39), v40_(v40), v41_(v41), v42_(v42), v43_(v43) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_), - static_cast<T>(v42_), static_cast<T>(v43_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray43& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; - const T42 v42_; - const T43 v43_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44> -class ValueArray44 { - public: - ValueArray44(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), - v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), - v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), - v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), - v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), - v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35), v36_(v36), - v37_(v37), v38_(v38), v39_(v39), v40_(v40), v41_(v41), v42_(v42), - v43_(v43), v44_(v44) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_), - static_cast<T>(v42_), static_cast<T>(v43_), static_cast<T>(v44_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray44& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; - const T42 v42_; - const T43 v43_; - const T44 v44_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45> -class ValueArray45 { - public: - ValueArray45(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), - v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), - v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), - v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), - v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), - v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35), - v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), v39_(v39), v40_(v40), v41_(v41), - v42_(v42), v43_(v43), v44_(v44), v45_(v45) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_), - static_cast<T>(v42_), static_cast<T>(v43_), static_cast<T>(v44_), - static_cast<T>(v45_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray45& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; - const T42 v42_; - const T43 v43_; - const T44 v44_; - const T45 v45_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46> -class ValueArray46 { - public: - ValueArray46(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, T46 v46) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), - v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), - v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), - v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), - v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), - v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), v39_(v39), v40_(v40), - v41_(v41), v42_(v42), v43_(v43), v44_(v44), v45_(v45), v46_(v46) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_), - static_cast<T>(v42_), static_cast<T>(v43_), static_cast<T>(v44_), - static_cast<T>(v45_), static_cast<T>(v46_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray46& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; - const T42 v42_; - const T43 v43_; - const T44 v44_; - const T45 v45_; - const T46 v46_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47> -class ValueArray47 { - public: - ValueArray47(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, T46 v46, T47 v47) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), - v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), - v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), v16_(v16), - v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), v22_(v22), - v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), v28_(v28), - v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), v34_(v34), - v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), v39_(v39), v40_(v40), - v41_(v41), v42_(v42), v43_(v43), v44_(v44), v45_(v45), v46_(v46), - v47_(v47) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_), - static_cast<T>(v42_), static_cast<T>(v43_), static_cast<T>(v44_), - static_cast<T>(v45_), static_cast<T>(v46_), static_cast<T>(v47_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray47& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; - const T42 v42_; - const T43 v43_; - const T44 v44_; - const T45 v45_; - const T46 v46_; - const T47 v47_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48> -class ValueArray48 { - public: - ValueArray48(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, T46 v46, T47 v47, T48 v48) : v1_(v1), - v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), v8_(v8), v9_(v9), - v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), v15_(v15), - v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), v21_(v21), - v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), v27_(v27), - v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), v33_(v33), - v34_(v34), v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), v39_(v39), - v40_(v40), v41_(v41), v42_(v42), v43_(v43), v44_(v44), v45_(v45), - v46_(v46), v47_(v47), v48_(v48) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_), - static_cast<T>(v42_), static_cast<T>(v43_), static_cast<T>(v44_), - static_cast<T>(v45_), static_cast<T>(v46_), static_cast<T>(v47_), - static_cast<T>(v48_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray48& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; - const T42 v42_; - const T43 v43_; - const T44 v44_; - const T45 v45_; - const T46 v46_; - const T47 v47_; - const T48 v48_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48, typename T49> -class ValueArray49 { - public: - ValueArray49(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, T46 v46, T47 v47, T48 v48, - T49 v49) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), - v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), - v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), - v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), - v39_(v39), v40_(v40), v41_(v41), v42_(v42), v43_(v43), v44_(v44), - v45_(v45), v46_(v46), v47_(v47), v48_(v48), v49_(v49) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_), - static_cast<T>(v42_), static_cast<T>(v43_), static_cast<T>(v44_), - static_cast<T>(v45_), static_cast<T>(v46_), static_cast<T>(v47_), - static_cast<T>(v48_), static_cast<T>(v49_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray49& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; - const T42 v42_; - const T43 v43_; - const T44 v44_; - const T45 v45_; - const T46 v46_; - const T47 v47_; - const T48 v48_; - const T49 v49_; -}; - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48, typename T49, typename T50> -class ValueArray50 { - public: - ValueArray50(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, T46 v46, T47 v47, T48 v48, T49 v49, - T50 v50) : v1_(v1), v2_(v2), v3_(v3), v4_(v4), v5_(v5), v6_(v6), v7_(v7), - v8_(v8), v9_(v9), v10_(v10), v11_(v11), v12_(v12), v13_(v13), v14_(v14), - v15_(v15), v16_(v16), v17_(v17), v18_(v18), v19_(v19), v20_(v20), - v21_(v21), v22_(v22), v23_(v23), v24_(v24), v25_(v25), v26_(v26), - v27_(v27), v28_(v28), v29_(v29), v30_(v30), v31_(v31), v32_(v32), - v33_(v33), v34_(v34), v35_(v35), v36_(v36), v37_(v37), v38_(v38), - v39_(v39), v40_(v40), v41_(v41), v42_(v42), v43_(v43), v44_(v44), - v45_(v45), v46_(v46), v47_(v47), v48_(v48), v49_(v49), v50_(v50) {} - - template <typename T> - operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { - const T array[] = {static_cast<T>(v1_), static_cast<T>(v2_), - static_cast<T>(v3_), static_cast<T>(v4_), static_cast<T>(v5_), - static_cast<T>(v6_), static_cast<T>(v7_), static_cast<T>(v8_), - static_cast<T>(v9_), static_cast<T>(v10_), static_cast<T>(v11_), - static_cast<T>(v12_), static_cast<T>(v13_), static_cast<T>(v14_), - static_cast<T>(v15_), static_cast<T>(v16_), static_cast<T>(v17_), - static_cast<T>(v18_), static_cast<T>(v19_), static_cast<T>(v20_), - static_cast<T>(v21_), static_cast<T>(v22_), static_cast<T>(v23_), - static_cast<T>(v24_), static_cast<T>(v25_), static_cast<T>(v26_), - static_cast<T>(v27_), static_cast<T>(v28_), static_cast<T>(v29_), - static_cast<T>(v30_), static_cast<T>(v31_), static_cast<T>(v32_), - static_cast<T>(v33_), static_cast<T>(v34_), static_cast<T>(v35_), - static_cast<T>(v36_), static_cast<T>(v37_), static_cast<T>(v38_), - static_cast<T>(v39_), static_cast<T>(v40_), static_cast<T>(v41_), - static_cast<T>(v42_), static_cast<T>(v43_), static_cast<T>(v44_), - static_cast<T>(v45_), static_cast<T>(v46_), static_cast<T>(v47_), - static_cast<T>(v48_), static_cast<T>(v49_), static_cast<T>(v50_)}; - return ValuesIn(array); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const ValueArray50& other); - - const T1 v1_; - const T2 v2_; - const T3 v3_; - const T4 v4_; - const T5 v5_; - const T6 v6_; - const T7 v7_; - const T8 v8_; - const T9 v9_; - const T10 v10_; - const T11 v11_; - const T12 v12_; - const T13 v13_; - const T14 v14_; - const T15 v15_; - const T16 v16_; - const T17 v17_; - const T18 v18_; - const T19 v19_; - const T20 v20_; - const T21 v21_; - const T22 v22_; - const T23 v23_; - const T24 v24_; - const T25 v25_; - const T26 v26_; - const T27 v27_; - const T28 v28_; - const T29 v29_; - const T30 v30_; - const T31 v31_; - const T32 v32_; - const T33 v33_; - const T34 v34_; - const T35 v35_; - const T36 v36_; - const T37 v37_; - const T38 v38_; - const T39 v39_; - const T40 v40_; - const T41 v41_; - const T42 v42_; - const T43 v43_; - const T44 v44_; - const T45 v45_; - const T46 v46_; - const T47 v47_; - const T48 v48_; - const T49 v49_; - const T50 v50_; -}; - -# if GTEST_HAS_COMBINE -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// Generates values from the Cartesian product of values produced -// by the argument generators. -// -template <typename T1, typename T2> -class CartesianProductGenerator2 - : public ParamGeneratorInterface< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2> > { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2> ParamType; - - CartesianProductGenerator2(const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2) {} - virtual ~CartesianProductGenerator2() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.begin(), g2_, g2_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.end(), g2_, g2_.end()); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, - const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator& current1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator& current2) - : base_(base), - begin1_(g1.begin()), end1_(g1.end()), current1_(current1), - begin2_(g2.begin()), end2_(g2.end()), current2_(current2) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators - // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. - virtual void Advance() { - assert(!AtEnd()); - ++current2_; - if (current2_ == end2_) { - current2_ = begin2_; - ++current1_; - } - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const ParamType* Current() const { return ¤t_value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const Iterator* typed_other = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other); - // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their - // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, - // so we have to consult AtEnd(). - return (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) || - ( - current1_ == typed_other->current1_ && - current2_ == typed_other->current2_); - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : base_(other.base_), - begin1_(other.begin1_), - end1_(other.end1_), - current1_(other.current1_), - begin2_(other.begin2_), - end2_(other.end2_), - current2_(other.current2_) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - - void ComputeCurrentValue() { - if (!AtEnd()) - current_value_ = ParamType(*current1_, *current2_); - } - bool AtEnd() const { - // We must report iterator past the end of the range when either of the - // component iterators has reached the end of its range. - return - current1_ == end1_ || - current2_ == end2_; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; - // begin[i]_ and end[i]_ define the i-th range that Iterator traverses. - // current[i]_ is the actual traversing iterator. - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator begin1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator end1_; - typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator current1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator begin2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator end2_; - typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator current2_; - ParamType current_value_; - }; // class CartesianProductGenerator2::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductGenerator2& other); - - const ParamGenerator<T1> g1_; - const ParamGenerator<T2> g2_; -}; // class CartesianProductGenerator2 - - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> -class CartesianProductGenerator3 - : public ParamGeneratorInterface< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3> > { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3> ParamType; - - CartesianProductGenerator3(const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3) {} - virtual ~CartesianProductGenerator3() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.begin(), g2_, g2_.begin(), g3_, - g3_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.end(), g2_, g2_.end(), g3_, g3_.end()); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, - const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator& current1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator& current2, - const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator& current3) - : base_(base), - begin1_(g1.begin()), end1_(g1.end()), current1_(current1), - begin2_(g2.begin()), end2_(g2.end()), current2_(current2), - begin3_(g3.begin()), end3_(g3.end()), current3_(current3) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators - // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. - virtual void Advance() { - assert(!AtEnd()); - ++current3_; - if (current3_ == end3_) { - current3_ = begin3_; - ++current2_; - } - if (current2_ == end2_) { - current2_ = begin2_; - ++current1_; - } - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const ParamType* Current() const { return ¤t_value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const Iterator* typed_other = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other); - // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their - // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, - // so we have to consult AtEnd(). - return (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) || - ( - current1_ == typed_other->current1_ && - current2_ == typed_other->current2_ && - current3_ == typed_other->current3_); - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : base_(other.base_), - begin1_(other.begin1_), - end1_(other.end1_), - current1_(other.current1_), - begin2_(other.begin2_), - end2_(other.end2_), - current2_(other.current2_), - begin3_(other.begin3_), - end3_(other.end3_), - current3_(other.current3_) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - - void ComputeCurrentValue() { - if (!AtEnd()) - current_value_ = ParamType(*current1_, *current2_, *current3_); - } - bool AtEnd() const { - // We must report iterator past the end of the range when either of the - // component iterators has reached the end of its range. - return - current1_ == end1_ || - current2_ == end2_ || - current3_ == end3_; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; - // begin[i]_ and end[i]_ define the i-th range that Iterator traverses. - // current[i]_ is the actual traversing iterator. - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator begin1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator end1_; - typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator current1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator begin2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator end2_; - typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator current2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator begin3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator end3_; - typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator current3_; - ParamType current_value_; - }; // class CartesianProductGenerator3::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductGenerator3& other); - - const ParamGenerator<T1> g1_; - const ParamGenerator<T2> g2_; - const ParamGenerator<T3> g3_; -}; // class CartesianProductGenerator3 - - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4> -class CartesianProductGenerator4 - : public ParamGeneratorInterface< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4> > { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4> ParamType; - - CartesianProductGenerator4(const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4) {} - virtual ~CartesianProductGenerator4() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.begin(), g2_, g2_.begin(), g3_, - g3_.begin(), g4_, g4_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.end(), g2_, g2_.end(), g3_, g3_.end(), - g4_, g4_.end()); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, - const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator& current1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator& current2, - const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator& current3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator& current4) - : base_(base), - begin1_(g1.begin()), end1_(g1.end()), current1_(current1), - begin2_(g2.begin()), end2_(g2.end()), current2_(current2), - begin3_(g3.begin()), end3_(g3.end()), current3_(current3), - begin4_(g4.begin()), end4_(g4.end()), current4_(current4) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators - // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. - virtual void Advance() { - assert(!AtEnd()); - ++current4_; - if (current4_ == end4_) { - current4_ = begin4_; - ++current3_; - } - if (current3_ == end3_) { - current3_ = begin3_; - ++current2_; - } - if (current2_ == end2_) { - current2_ = begin2_; - ++current1_; - } - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const ParamType* Current() const { return ¤t_value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const Iterator* typed_other = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other); - // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their - // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, - // so we have to consult AtEnd(). - return (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) || - ( - current1_ == typed_other->current1_ && - current2_ == typed_other->current2_ && - current3_ == typed_other->current3_ && - current4_ == typed_other->current4_); - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : base_(other.base_), - begin1_(other.begin1_), - end1_(other.end1_), - current1_(other.current1_), - begin2_(other.begin2_), - end2_(other.end2_), - current2_(other.current2_), - begin3_(other.begin3_), - end3_(other.end3_), - current3_(other.current3_), - begin4_(other.begin4_), - end4_(other.end4_), - current4_(other.current4_) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - - void ComputeCurrentValue() { - if (!AtEnd()) - current_value_ = ParamType(*current1_, *current2_, *current3_, - *current4_); - } - bool AtEnd() const { - // We must report iterator past the end of the range when either of the - // component iterators has reached the end of its range. - return - current1_ == end1_ || - current2_ == end2_ || - current3_ == end3_ || - current4_ == end4_; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; - // begin[i]_ and end[i]_ define the i-th range that Iterator traverses. - // current[i]_ is the actual traversing iterator. - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator begin1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator end1_; - typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator current1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator begin2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator end2_; - typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator current2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator begin3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator end3_; - typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator current3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator begin4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator end4_; - typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator current4_; - ParamType current_value_; - }; // class CartesianProductGenerator4::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductGenerator4& other); - - const ParamGenerator<T1> g1_; - const ParamGenerator<T2> g2_; - const ParamGenerator<T3> g3_; - const ParamGenerator<T4> g4_; -}; // class CartesianProductGenerator4 - - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5> -class CartesianProductGenerator5 - : public ParamGeneratorInterface< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5> > { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5> ParamType; - - CartesianProductGenerator5(const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5) {} - virtual ~CartesianProductGenerator5() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.begin(), g2_, g2_.begin(), g3_, - g3_.begin(), g4_, g4_.begin(), g5_, g5_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.end(), g2_, g2_.end(), g3_, g3_.end(), - g4_, g4_.end(), g5_, g5_.end()); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, - const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator& current1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator& current2, - const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator& current3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator& current4, - const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator& current5) - : base_(base), - begin1_(g1.begin()), end1_(g1.end()), current1_(current1), - begin2_(g2.begin()), end2_(g2.end()), current2_(current2), - begin3_(g3.begin()), end3_(g3.end()), current3_(current3), - begin4_(g4.begin()), end4_(g4.end()), current4_(current4), - begin5_(g5.begin()), end5_(g5.end()), current5_(current5) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators - // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. - virtual void Advance() { - assert(!AtEnd()); - ++current5_; - if (current5_ == end5_) { - current5_ = begin5_; - ++current4_; - } - if (current4_ == end4_) { - current4_ = begin4_; - ++current3_; - } - if (current3_ == end3_) { - current3_ = begin3_; - ++current2_; - } - if (current2_ == end2_) { - current2_ = begin2_; - ++current1_; - } - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const ParamType* Current() const { return ¤t_value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const Iterator* typed_other = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other); - // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their - // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, - // so we have to consult AtEnd(). - return (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) || - ( - current1_ == typed_other->current1_ && - current2_ == typed_other->current2_ && - current3_ == typed_other->current3_ && - current4_ == typed_other->current4_ && - current5_ == typed_other->current5_); - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : base_(other.base_), - begin1_(other.begin1_), - end1_(other.end1_), - current1_(other.current1_), - begin2_(other.begin2_), - end2_(other.end2_), - current2_(other.current2_), - begin3_(other.begin3_), - end3_(other.end3_), - current3_(other.current3_), - begin4_(other.begin4_), - end4_(other.end4_), - current4_(other.current4_), - begin5_(other.begin5_), - end5_(other.end5_), - current5_(other.current5_) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - - void ComputeCurrentValue() { - if (!AtEnd()) - current_value_ = ParamType(*current1_, *current2_, *current3_, - *current4_, *current5_); - } - bool AtEnd() const { - // We must report iterator past the end of the range when either of the - // component iterators has reached the end of its range. - return - current1_ == end1_ || - current2_ == end2_ || - current3_ == end3_ || - current4_ == end4_ || - current5_ == end5_; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; - // begin[i]_ and end[i]_ define the i-th range that Iterator traverses. - // current[i]_ is the actual traversing iterator. - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator begin1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator end1_; - typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator current1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator begin2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator end2_; - typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator current2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator begin3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator end3_; - typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator current3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator begin4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator end4_; - typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator current4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator begin5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator end5_; - typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator current5_; - ParamType current_value_; - }; // class CartesianProductGenerator5::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductGenerator5& other); - - const ParamGenerator<T1> g1_; - const ParamGenerator<T2> g2_; - const ParamGenerator<T3> g3_; - const ParamGenerator<T4> g4_; - const ParamGenerator<T5> g5_; -}; // class CartesianProductGenerator5 - - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6> -class CartesianProductGenerator6 - : public ParamGeneratorInterface< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, - T6> > { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6> ParamType; - - CartesianProductGenerator6(const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6) {} - virtual ~CartesianProductGenerator6() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.begin(), g2_, g2_.begin(), g3_, - g3_.begin(), g4_, g4_.begin(), g5_, g5_.begin(), g6_, g6_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.end(), g2_, g2_.end(), g3_, g3_.end(), - g4_, g4_.end(), g5_, g5_.end(), g6_, g6_.end()); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, - const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator& current1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator& current2, - const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator& current3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator& current4, - const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator& current5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6, - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator& current6) - : base_(base), - begin1_(g1.begin()), end1_(g1.end()), current1_(current1), - begin2_(g2.begin()), end2_(g2.end()), current2_(current2), - begin3_(g3.begin()), end3_(g3.end()), current3_(current3), - begin4_(g4.begin()), end4_(g4.end()), current4_(current4), - begin5_(g5.begin()), end5_(g5.end()), current5_(current5), - begin6_(g6.begin()), end6_(g6.end()), current6_(current6) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators - // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. - virtual void Advance() { - assert(!AtEnd()); - ++current6_; - if (current6_ == end6_) { - current6_ = begin6_; - ++current5_; - } - if (current5_ == end5_) { - current5_ = begin5_; - ++current4_; - } - if (current4_ == end4_) { - current4_ = begin4_; - ++current3_; - } - if (current3_ == end3_) { - current3_ = begin3_; - ++current2_; - } - if (current2_ == end2_) { - current2_ = begin2_; - ++current1_; - } - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const ParamType* Current() const { return ¤t_value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const Iterator* typed_other = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other); - // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their - // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, - // so we have to consult AtEnd(). - return (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) || - ( - current1_ == typed_other->current1_ && - current2_ == typed_other->current2_ && - current3_ == typed_other->current3_ && - current4_ == typed_other->current4_ && - current5_ == typed_other->current5_ && - current6_ == typed_other->current6_); - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : base_(other.base_), - begin1_(other.begin1_), - end1_(other.end1_), - current1_(other.current1_), - begin2_(other.begin2_), - end2_(other.end2_), - current2_(other.current2_), - begin3_(other.begin3_), - end3_(other.end3_), - current3_(other.current3_), - begin4_(other.begin4_), - end4_(other.end4_), - current4_(other.current4_), - begin5_(other.begin5_), - end5_(other.end5_), - current5_(other.current5_), - begin6_(other.begin6_), - end6_(other.end6_), - current6_(other.current6_) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - - void ComputeCurrentValue() { - if (!AtEnd()) - current_value_ = ParamType(*current1_, *current2_, *current3_, - *current4_, *current5_, *current6_); - } - bool AtEnd() const { - // We must report iterator past the end of the range when either of the - // component iterators has reached the end of its range. - return - current1_ == end1_ || - current2_ == end2_ || - current3_ == end3_ || - current4_ == end4_ || - current5_ == end5_ || - current6_ == end6_; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; - // begin[i]_ and end[i]_ define the i-th range that Iterator traverses. - // current[i]_ is the actual traversing iterator. - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator begin1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator end1_; - typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator current1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator begin2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator end2_; - typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator current2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator begin3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator end3_; - typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator current3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator begin4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator end4_; - typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator current4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator begin5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator end5_; - typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator current5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator begin6_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator end6_; - typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator current6_; - ParamType current_value_; - }; // class CartesianProductGenerator6::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductGenerator6& other); - - const ParamGenerator<T1> g1_; - const ParamGenerator<T2> g2_; - const ParamGenerator<T3> g3_; - const ParamGenerator<T4> g4_; - const ParamGenerator<T5> g5_; - const ParamGenerator<T6> g6_; -}; // class CartesianProductGenerator6 - - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7> -class CartesianProductGenerator7 - : public ParamGeneratorInterface< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, - T7> > { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7> ParamType; - - CartesianProductGenerator7(const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6, const ParamGenerator<T7>& g7) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6), g7_(g7) {} - virtual ~CartesianProductGenerator7() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.begin(), g2_, g2_.begin(), g3_, - g3_.begin(), g4_, g4_.begin(), g5_, g5_.begin(), g6_, g6_.begin(), g7_, - g7_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.end(), g2_, g2_.end(), g3_, g3_.end(), - g4_, g4_.end(), g5_, g5_.end(), g6_, g6_.end(), g7_, g7_.end()); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, - const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator& current1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator& current2, - const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator& current3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator& current4, - const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator& current5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6, - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator& current6, - const ParamGenerator<T7>& g7, - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator& current7) - : base_(base), - begin1_(g1.begin()), end1_(g1.end()), current1_(current1), - begin2_(g2.begin()), end2_(g2.end()), current2_(current2), - begin3_(g3.begin()), end3_(g3.end()), current3_(current3), - begin4_(g4.begin()), end4_(g4.end()), current4_(current4), - begin5_(g5.begin()), end5_(g5.end()), current5_(current5), - begin6_(g6.begin()), end6_(g6.end()), current6_(current6), - begin7_(g7.begin()), end7_(g7.end()), current7_(current7) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators - // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. - virtual void Advance() { - assert(!AtEnd()); - ++current7_; - if (current7_ == end7_) { - current7_ = begin7_; - ++current6_; - } - if (current6_ == end6_) { - current6_ = begin6_; - ++current5_; - } - if (current5_ == end5_) { - current5_ = begin5_; - ++current4_; - } - if (current4_ == end4_) { - current4_ = begin4_; - ++current3_; - } - if (current3_ == end3_) { - current3_ = begin3_; - ++current2_; - } - if (current2_ == end2_) { - current2_ = begin2_; - ++current1_; - } - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const ParamType* Current() const { return ¤t_value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const Iterator* typed_other = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other); - // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their - // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, - // so we have to consult AtEnd(). - return (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) || - ( - current1_ == typed_other->current1_ && - current2_ == typed_other->current2_ && - current3_ == typed_other->current3_ && - current4_ == typed_other->current4_ && - current5_ == typed_other->current5_ && - current6_ == typed_other->current6_ && - current7_ == typed_other->current7_); - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : base_(other.base_), - begin1_(other.begin1_), - end1_(other.end1_), - current1_(other.current1_), - begin2_(other.begin2_), - end2_(other.end2_), - current2_(other.current2_), - begin3_(other.begin3_), - end3_(other.end3_), - current3_(other.current3_), - begin4_(other.begin4_), - end4_(other.end4_), - current4_(other.current4_), - begin5_(other.begin5_), - end5_(other.end5_), - current5_(other.current5_), - begin6_(other.begin6_), - end6_(other.end6_), - current6_(other.current6_), - begin7_(other.begin7_), - end7_(other.end7_), - current7_(other.current7_) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - - void ComputeCurrentValue() { - if (!AtEnd()) - current_value_ = ParamType(*current1_, *current2_, *current3_, - *current4_, *current5_, *current6_, *current7_); - } - bool AtEnd() const { - // We must report iterator past the end of the range when either of the - // component iterators has reached the end of its range. - return - current1_ == end1_ || - current2_ == end2_ || - current3_ == end3_ || - current4_ == end4_ || - current5_ == end5_ || - current6_ == end6_ || - current7_ == end7_; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; - // begin[i]_ and end[i]_ define the i-th range that Iterator traverses. - // current[i]_ is the actual traversing iterator. - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator begin1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator end1_; - typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator current1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator begin2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator end2_; - typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator current2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator begin3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator end3_; - typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator current3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator begin4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator end4_; - typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator current4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator begin5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator end5_; - typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator current5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator begin6_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator end6_; - typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator current6_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator begin7_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator end7_; - typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator current7_; - ParamType current_value_; - }; // class CartesianProductGenerator7::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductGenerator7& other); - - const ParamGenerator<T1> g1_; - const ParamGenerator<T2> g2_; - const ParamGenerator<T3> g3_; - const ParamGenerator<T4> g4_; - const ParamGenerator<T5> g5_; - const ParamGenerator<T6> g6_; - const ParamGenerator<T7> g7_; -}; // class CartesianProductGenerator7 - - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8> -class CartesianProductGenerator8 - : public ParamGeneratorInterface< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, - T7, T8> > { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8> ParamType; - - CartesianProductGenerator8(const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6, const ParamGenerator<T7>& g7, - const ParamGenerator<T8>& g8) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6), g7_(g7), - g8_(g8) {} - virtual ~CartesianProductGenerator8() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.begin(), g2_, g2_.begin(), g3_, - g3_.begin(), g4_, g4_.begin(), g5_, g5_.begin(), g6_, g6_.begin(), g7_, - g7_.begin(), g8_, g8_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.end(), g2_, g2_.end(), g3_, g3_.end(), - g4_, g4_.end(), g5_, g5_.end(), g6_, g6_.end(), g7_, g7_.end(), g8_, - g8_.end()); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, - const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator& current1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator& current2, - const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator& current3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator& current4, - const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator& current5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6, - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator& current6, - const ParamGenerator<T7>& g7, - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator& current7, - const ParamGenerator<T8>& g8, - const typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator& current8) - : base_(base), - begin1_(g1.begin()), end1_(g1.end()), current1_(current1), - begin2_(g2.begin()), end2_(g2.end()), current2_(current2), - begin3_(g3.begin()), end3_(g3.end()), current3_(current3), - begin4_(g4.begin()), end4_(g4.end()), current4_(current4), - begin5_(g5.begin()), end5_(g5.end()), current5_(current5), - begin6_(g6.begin()), end6_(g6.end()), current6_(current6), - begin7_(g7.begin()), end7_(g7.end()), current7_(current7), - begin8_(g8.begin()), end8_(g8.end()), current8_(current8) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators - // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. - virtual void Advance() { - assert(!AtEnd()); - ++current8_; - if (current8_ == end8_) { - current8_ = begin8_; - ++current7_; - } - if (current7_ == end7_) { - current7_ = begin7_; - ++current6_; - } - if (current6_ == end6_) { - current6_ = begin6_; - ++current5_; - } - if (current5_ == end5_) { - current5_ = begin5_; - ++current4_; - } - if (current4_ == end4_) { - current4_ = begin4_; - ++current3_; - } - if (current3_ == end3_) { - current3_ = begin3_; - ++current2_; - } - if (current2_ == end2_) { - current2_ = begin2_; - ++current1_; - } - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const ParamType* Current() const { return ¤t_value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const Iterator* typed_other = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other); - // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their - // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, - // so we have to consult AtEnd(). - return (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) || - ( - current1_ == typed_other->current1_ && - current2_ == typed_other->current2_ && - current3_ == typed_other->current3_ && - current4_ == typed_other->current4_ && - current5_ == typed_other->current5_ && - current6_ == typed_other->current6_ && - current7_ == typed_other->current7_ && - current8_ == typed_other->current8_); - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : base_(other.base_), - begin1_(other.begin1_), - end1_(other.end1_), - current1_(other.current1_), - begin2_(other.begin2_), - end2_(other.end2_), - current2_(other.current2_), - begin3_(other.begin3_), - end3_(other.end3_), - current3_(other.current3_), - begin4_(other.begin4_), - end4_(other.end4_), - current4_(other.current4_), - begin5_(other.begin5_), - end5_(other.end5_), - current5_(other.current5_), - begin6_(other.begin6_), - end6_(other.end6_), - current6_(other.current6_), - begin7_(other.begin7_), - end7_(other.end7_), - current7_(other.current7_), - begin8_(other.begin8_), - end8_(other.end8_), - current8_(other.current8_) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - - void ComputeCurrentValue() { - if (!AtEnd()) - current_value_ = ParamType(*current1_, *current2_, *current3_, - *current4_, *current5_, *current6_, *current7_, *current8_); - } - bool AtEnd() const { - // We must report iterator past the end of the range when either of the - // component iterators has reached the end of its range. - return - current1_ == end1_ || - current2_ == end2_ || - current3_ == end3_ || - current4_ == end4_ || - current5_ == end5_ || - current6_ == end6_ || - current7_ == end7_ || - current8_ == end8_; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; - // begin[i]_ and end[i]_ define the i-th range that Iterator traverses. - // current[i]_ is the actual traversing iterator. - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator begin1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator end1_; - typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator current1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator begin2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator end2_; - typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator current2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator begin3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator end3_; - typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator current3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator begin4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator end4_; - typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator current4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator begin5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator end5_; - typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator current5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator begin6_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator end6_; - typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator current6_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator begin7_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator end7_; - typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator current7_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator begin8_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator end8_; - typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator current8_; - ParamType current_value_; - }; // class CartesianProductGenerator8::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductGenerator8& other); - - const ParamGenerator<T1> g1_; - const ParamGenerator<T2> g2_; - const ParamGenerator<T3> g3_; - const ParamGenerator<T4> g4_; - const ParamGenerator<T5> g5_; - const ParamGenerator<T6> g6_; - const ParamGenerator<T7> g7_; - const ParamGenerator<T8> g8_; -}; // class CartesianProductGenerator8 - - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9> -class CartesianProductGenerator9 - : public ParamGeneratorInterface< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, - T7, T8, T9> > { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9> ParamType; - - CartesianProductGenerator9(const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6, const ParamGenerator<T7>& g7, - const ParamGenerator<T8>& g8, const ParamGenerator<T9>& g9) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6), g7_(g7), g8_(g8), - g9_(g9) {} - virtual ~CartesianProductGenerator9() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.begin(), g2_, g2_.begin(), g3_, - g3_.begin(), g4_, g4_.begin(), g5_, g5_.begin(), g6_, g6_.begin(), g7_, - g7_.begin(), g8_, g8_.begin(), g9_, g9_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.end(), g2_, g2_.end(), g3_, g3_.end(), - g4_, g4_.end(), g5_, g5_.end(), g6_, g6_.end(), g7_, g7_.end(), g8_, - g8_.end(), g9_, g9_.end()); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, - const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator& current1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator& current2, - const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator& current3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator& current4, - const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator& current5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6, - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator& current6, - const ParamGenerator<T7>& g7, - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator& current7, - const ParamGenerator<T8>& g8, - const typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator& current8, - const ParamGenerator<T9>& g9, - const typename ParamGenerator<T9>::iterator& current9) - : base_(base), - begin1_(g1.begin()), end1_(g1.end()), current1_(current1), - begin2_(g2.begin()), end2_(g2.end()), current2_(current2), - begin3_(g3.begin()), end3_(g3.end()), current3_(current3), - begin4_(g4.begin()), end4_(g4.end()), current4_(current4), - begin5_(g5.begin()), end5_(g5.end()), current5_(current5), - begin6_(g6.begin()), end6_(g6.end()), current6_(current6), - begin7_(g7.begin()), end7_(g7.end()), current7_(current7), - begin8_(g8.begin()), end8_(g8.end()), current8_(current8), - begin9_(g9.begin()), end9_(g9.end()), current9_(current9) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators - // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. - virtual void Advance() { - assert(!AtEnd()); - ++current9_; - if (current9_ == end9_) { - current9_ = begin9_; - ++current8_; - } - if (current8_ == end8_) { - current8_ = begin8_; - ++current7_; - } - if (current7_ == end7_) { - current7_ = begin7_; - ++current6_; - } - if (current6_ == end6_) { - current6_ = begin6_; - ++current5_; - } - if (current5_ == end5_) { - current5_ = begin5_; - ++current4_; - } - if (current4_ == end4_) { - current4_ = begin4_; - ++current3_; - } - if (current3_ == end3_) { - current3_ = begin3_; - ++current2_; - } - if (current2_ == end2_) { - current2_ = begin2_; - ++current1_; - } - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const ParamType* Current() const { return ¤t_value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const Iterator* typed_other = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other); - // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their - // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, - // so we have to consult AtEnd(). - return (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) || - ( - current1_ == typed_other->current1_ && - current2_ == typed_other->current2_ && - current3_ == typed_other->current3_ && - current4_ == typed_other->current4_ && - current5_ == typed_other->current5_ && - current6_ == typed_other->current6_ && - current7_ == typed_other->current7_ && - current8_ == typed_other->current8_ && - current9_ == typed_other->current9_); - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : base_(other.base_), - begin1_(other.begin1_), - end1_(other.end1_), - current1_(other.current1_), - begin2_(other.begin2_), - end2_(other.end2_), - current2_(other.current2_), - begin3_(other.begin3_), - end3_(other.end3_), - current3_(other.current3_), - begin4_(other.begin4_), - end4_(other.end4_), - current4_(other.current4_), - begin5_(other.begin5_), - end5_(other.end5_), - current5_(other.current5_), - begin6_(other.begin6_), - end6_(other.end6_), - current6_(other.current6_), - begin7_(other.begin7_), - end7_(other.end7_), - current7_(other.current7_), - begin8_(other.begin8_), - end8_(other.end8_), - current8_(other.current8_), - begin9_(other.begin9_), - end9_(other.end9_), - current9_(other.current9_) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - - void ComputeCurrentValue() { - if (!AtEnd()) - current_value_ = ParamType(*current1_, *current2_, *current3_, - *current4_, *current5_, *current6_, *current7_, *current8_, - *current9_); - } - bool AtEnd() const { - // We must report iterator past the end of the range when either of the - // component iterators has reached the end of its range. - return - current1_ == end1_ || - current2_ == end2_ || - current3_ == end3_ || - current4_ == end4_ || - current5_ == end5_ || - current6_ == end6_ || - current7_ == end7_ || - current8_ == end8_ || - current9_ == end9_; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; - // begin[i]_ and end[i]_ define the i-th range that Iterator traverses. - // current[i]_ is the actual traversing iterator. - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator begin1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator end1_; - typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator current1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator begin2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator end2_; - typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator current2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator begin3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator end3_; - typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator current3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator begin4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator end4_; - typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator current4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator begin5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator end5_; - typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator current5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator begin6_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator end6_; - typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator current6_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator begin7_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator end7_; - typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator current7_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator begin8_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator end8_; - typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator current8_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T9>::iterator begin9_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T9>::iterator end9_; - typename ParamGenerator<T9>::iterator current9_; - ParamType current_value_; - }; // class CartesianProductGenerator9::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductGenerator9& other); - - const ParamGenerator<T1> g1_; - const ParamGenerator<T2> g2_; - const ParamGenerator<T3> g3_; - const ParamGenerator<T4> g4_; - const ParamGenerator<T5> g5_; - const ParamGenerator<T6> g6_; - const ParamGenerator<T7> g7_; - const ParamGenerator<T8> g8_; - const ParamGenerator<T9> g9_; -}; // class CartesianProductGenerator9 - - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10> -class CartesianProductGenerator10 - : public ParamGeneratorInterface< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, - T7, T8, T9, T10> > { - public: - typedef ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10> ParamType; - - CartesianProductGenerator10(const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6, const ParamGenerator<T7>& g7, - const ParamGenerator<T8>& g8, const ParamGenerator<T9>& g9, - const ParamGenerator<T10>& g10) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6), g7_(g7), g8_(g8), - g9_(g9), g10_(g10) {} - virtual ~CartesianProductGenerator10() {} - - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.begin(), g2_, g2_.begin(), g3_, - g3_.begin(), g4_, g4_.begin(), g5_, g5_.begin(), g6_, g6_.begin(), g7_, - g7_.begin(), g8_, g8_.begin(), g9_, g9_.begin(), g10_, g10_.begin()); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const { - return new Iterator(this, g1_, g1_.end(), g2_, g2_.end(), g3_, g3_.end(), - g4_, g4_.end(), g5_, g5_.end(), g6_, g6_.end(), g7_, g7_.end(), g8_, - g8_.end(), g9_, g9_.end(), g10_, g10_.end()); - } - - private: - class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { - public: - Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, - const ParamGenerator<T1>& g1, - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator& current1, - const ParamGenerator<T2>& g2, - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator& current2, - const ParamGenerator<T3>& g3, - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator& current3, - const ParamGenerator<T4>& g4, - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator& current4, - const ParamGenerator<T5>& g5, - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator& current5, - const ParamGenerator<T6>& g6, - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator& current6, - const ParamGenerator<T7>& g7, - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator& current7, - const ParamGenerator<T8>& g8, - const typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator& current8, - const ParamGenerator<T9>& g9, - const typename ParamGenerator<T9>::iterator& current9, - const ParamGenerator<T10>& g10, - const typename ParamGenerator<T10>::iterator& current10) - : base_(base), - begin1_(g1.begin()), end1_(g1.end()), current1_(current1), - begin2_(g2.begin()), end2_(g2.end()), current2_(current2), - begin3_(g3.begin()), end3_(g3.end()), current3_(current3), - begin4_(g4.begin()), end4_(g4.end()), current4_(current4), - begin5_(g5.begin()), end5_(g5.end()), current5_(current5), - begin6_(g6.begin()), end6_(g6.end()), current6_(current6), - begin7_(g7.begin()), end7_(g7.end()), current7_(current7), - begin8_(g8.begin()), end8_(g8.end()), current8_(current8), - begin9_(g9.begin()), end9_(g9.end()), current9_(current9), - begin10_(g10.begin()), end10_(g10.end()), current10_(current10) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ~Iterator() {} - - virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const { - return base_; - } - // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators - // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. - virtual void Advance() { - assert(!AtEnd()); - ++current10_; - if (current10_ == end10_) { - current10_ = begin10_; - ++current9_; - } - if (current9_ == end9_) { - current9_ = begin9_; - ++current8_; - } - if (current8_ == end8_) { - current8_ = begin8_; - ++current7_; - } - if (current7_ == end7_) { - current7_ = begin7_; - ++current6_; - } - if (current6_ == end6_) { - current6_ = begin6_; - ++current5_; - } - if (current5_ == end5_) { - current5_ = begin5_; - ++current4_; - } - if (current4_ == end4_) { - current4_ = begin4_; - ++current3_; - } - if (current3_ == end3_) { - current3_ = begin3_; - ++current2_; - } - if (current2_ == end2_) { - current2_ = begin2_; - ++current1_; - } - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - virtual ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const { - return new Iterator(*this); - } - virtual const ParamType* Current() const { return ¤t_value_; } - virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const { - // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other - // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. - GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) - << "The program attempted to compare iterators " - << "from different generators." << std::endl; - const Iterator* typed_other = - CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other); - // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their - // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, - // so we have to consult AtEnd(). - return (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) || - ( - current1_ == typed_other->current1_ && - current2_ == typed_other->current2_ && - current3_ == typed_other->current3_ && - current4_ == typed_other->current4_ && - current5_ == typed_other->current5_ && - current6_ == typed_other->current6_ && - current7_ == typed_other->current7_ && - current8_ == typed_other->current8_ && - current9_ == typed_other->current9_ && - current10_ == typed_other->current10_); - } - - private: - Iterator(const Iterator& other) - : base_(other.base_), - begin1_(other.begin1_), - end1_(other.end1_), - current1_(other.current1_), - begin2_(other.begin2_), - end2_(other.end2_), - current2_(other.current2_), - begin3_(other.begin3_), - end3_(other.end3_), - current3_(other.current3_), - begin4_(other.begin4_), - end4_(other.end4_), - current4_(other.current4_), - begin5_(other.begin5_), - end5_(other.end5_), - current5_(other.current5_), - begin6_(other.begin6_), - end6_(other.end6_), - current6_(other.current6_), - begin7_(other.begin7_), - end7_(other.end7_), - current7_(other.current7_), - begin8_(other.begin8_), - end8_(other.end8_), - current8_(other.current8_), - begin9_(other.begin9_), - end9_(other.end9_), - current9_(other.current9_), - begin10_(other.begin10_), - end10_(other.end10_), - current10_(other.current10_) { - ComputeCurrentValue(); - } - - void ComputeCurrentValue() { - if (!AtEnd()) - current_value_ = ParamType(*current1_, *current2_, *current3_, - *current4_, *current5_, *current6_, *current7_, *current8_, - *current9_, *current10_); - } - bool AtEnd() const { - // We must report iterator past the end of the range when either of the - // component iterators has reached the end of its range. - return - current1_ == end1_ || - current2_ == end2_ || - current3_ == end3_ || - current4_ == end4_ || - current5_ == end5_ || - current6_ == end6_ || - current7_ == end7_ || - current8_ == end8_ || - current9_ == end9_ || - current10_ == end10_; - } - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const Iterator& other); - - const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; - // begin[i]_ and end[i]_ define the i-th range that Iterator traverses. - // current[i]_ is the actual traversing iterator. - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator begin1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator end1_; - typename ParamGenerator<T1>::iterator current1_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator begin2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator end2_; - typename ParamGenerator<T2>::iterator current2_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator begin3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator end3_; - typename ParamGenerator<T3>::iterator current3_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator begin4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator end4_; - typename ParamGenerator<T4>::iterator current4_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator begin5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator end5_; - typename ParamGenerator<T5>::iterator current5_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator begin6_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator end6_; - typename ParamGenerator<T6>::iterator current6_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator begin7_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator end7_; - typename ParamGenerator<T7>::iterator current7_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator begin8_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator end8_; - typename ParamGenerator<T8>::iterator current8_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T9>::iterator begin9_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T9>::iterator end9_; - typename ParamGenerator<T9>::iterator current9_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T10>::iterator begin10_; - const typename ParamGenerator<T10>::iterator end10_; - typename ParamGenerator<T10>::iterator current10_; - ParamType current_value_; - }; // class CartesianProductGenerator10::Iterator - - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductGenerator10& other); - - const ParamGenerator<T1> g1_; - const ParamGenerator<T2> g2_; - const ParamGenerator<T3> g3_; - const ParamGenerator<T4> g4_; - const ParamGenerator<T5> g5_; - const ParamGenerator<T6> g6_; - const ParamGenerator<T7> g7_; - const ParamGenerator<T8> g8_; - const ParamGenerator<T9> g9_; - const ParamGenerator<T10> g10_; -}; // class CartesianProductGenerator10 - - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// Helper classes providing Combine() with polymorphic features. They allow -// casting CartesianProductGeneratorN<T> to ParamGenerator<U> if T is -// convertible to U. -// -template <class Generator1, class Generator2> -class CartesianProductHolder2 { - public: -CartesianProductHolder2(const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2) {} - template <typename T1, typename T2> - operator ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2> >() const { - return ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2> >( - new CartesianProductGenerator2<T1, T2>( - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T1> >(g1_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T2> >(g2_))); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductHolder2& other); - - const Generator1 g1_; - const Generator2 g2_; -}; // class CartesianProductHolder2 - -template <class Generator1, class Generator2, class Generator3> -class CartesianProductHolder3 { - public: -CartesianProductHolder3(const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, - const Generator3& g3) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3) {} - template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> - operator ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3> >() const { - return ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3> >( - new CartesianProductGenerator3<T1, T2, T3>( - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T1> >(g1_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T2> >(g2_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T3> >(g3_))); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductHolder3& other); - - const Generator1 g1_; - const Generator2 g2_; - const Generator3 g3_; -}; // class CartesianProductHolder3 - -template <class Generator1, class Generator2, class Generator3, - class Generator4> -class CartesianProductHolder4 { - public: -CartesianProductHolder4(const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, - const Generator3& g3, const Generator4& g4) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4) {} - template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4> - operator ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4> >() const { - return ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4> >( - new CartesianProductGenerator4<T1, T2, T3, T4>( - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T1> >(g1_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T2> >(g2_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T3> >(g3_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T4> >(g4_))); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductHolder4& other); - - const Generator1 g1_; - const Generator2 g2_; - const Generator3 g3_; - const Generator4 g4_; -}; // class CartesianProductHolder4 - -template <class Generator1, class Generator2, class Generator3, - class Generator4, class Generator5> -class CartesianProductHolder5 { - public: -CartesianProductHolder5(const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, - const Generator3& g3, const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5) {} - template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5> - operator ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5> >() const { - return ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5> >( - new CartesianProductGenerator5<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5>( - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T1> >(g1_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T2> >(g2_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T3> >(g3_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T4> >(g4_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T5> >(g5_))); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductHolder5& other); - - const Generator1 g1_; - const Generator2 g2_; - const Generator3 g3_; - const Generator4 g4_; - const Generator5 g5_; -}; // class CartesianProductHolder5 - -template <class Generator1, class Generator2, class Generator3, - class Generator4, class Generator5, class Generator6> -class CartesianProductHolder6 { - public: -CartesianProductHolder6(const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, - const Generator3& g3, const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, - const Generator6& g6) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6) {} - template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6> - operator ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6> >() const { - return ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6> >( - new CartesianProductGenerator6<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6>( - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T1> >(g1_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T2> >(g2_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T3> >(g3_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T4> >(g4_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T5> >(g5_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T6> >(g6_))); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductHolder6& other); - - const Generator1 g1_; - const Generator2 g2_; - const Generator3 g3_; - const Generator4 g4_; - const Generator5 g5_; - const Generator6 g6_; -}; // class CartesianProductHolder6 - -template <class Generator1, class Generator2, class Generator3, - class Generator4, class Generator5, class Generator6, class Generator7> -class CartesianProductHolder7 { - public: -CartesianProductHolder7(const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, - const Generator3& g3, const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, - const Generator6& g6, const Generator7& g7) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6), g7_(g7) {} - template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7> - operator ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, - T7> >() const { - return ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7> >( - new CartesianProductGenerator7<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7>( - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T1> >(g1_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T2> >(g2_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T3> >(g3_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T4> >(g4_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T5> >(g5_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T6> >(g6_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T7> >(g7_))); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductHolder7& other); - - const Generator1 g1_; - const Generator2 g2_; - const Generator3 g3_; - const Generator4 g4_; - const Generator5 g5_; - const Generator6 g6_; - const Generator7 g7_; -}; // class CartesianProductHolder7 - -template <class Generator1, class Generator2, class Generator3, - class Generator4, class Generator5, class Generator6, class Generator7, - class Generator8> -class CartesianProductHolder8 { - public: -CartesianProductHolder8(const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, - const Generator3& g3, const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, - const Generator6& g6, const Generator7& g7, const Generator8& g8) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6), g7_(g7), - g8_(g8) {} - template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8> - operator ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, - T8> >() const { - return ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8> >( - new CartesianProductGenerator8<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8>( - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T1> >(g1_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T2> >(g2_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T3> >(g3_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T4> >(g4_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T5> >(g5_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T6> >(g6_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T7> >(g7_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T8> >(g8_))); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductHolder8& other); - - const Generator1 g1_; - const Generator2 g2_; - const Generator3 g3_; - const Generator4 g4_; - const Generator5 g5_; - const Generator6 g6_; - const Generator7 g7_; - const Generator8 g8_; -}; // class CartesianProductHolder8 - -template <class Generator1, class Generator2, class Generator3, - class Generator4, class Generator5, class Generator6, class Generator7, - class Generator8, class Generator9> -class CartesianProductHolder9 { - public: -CartesianProductHolder9(const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, - const Generator3& g3, const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, - const Generator6& g6, const Generator7& g7, const Generator8& g8, - const Generator9& g9) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6), g7_(g7), g8_(g8), - g9_(g9) {} - template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9> - operator ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, - T9> >() const { - return ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, - T9> >( - new CartesianProductGenerator9<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9>( - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T1> >(g1_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T2> >(g2_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T3> >(g3_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T4> >(g4_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T5> >(g5_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T6> >(g6_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T7> >(g7_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T8> >(g8_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T9> >(g9_))); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductHolder9& other); - - const Generator1 g1_; - const Generator2 g2_; - const Generator3 g3_; - const Generator4 g4_; - const Generator5 g5_; - const Generator6 g6_; - const Generator7 g7_; - const Generator8 g8_; - const Generator9 g9_; -}; // class CartesianProductHolder9 - -template <class Generator1, class Generator2, class Generator3, - class Generator4, class Generator5, class Generator6, class Generator7, - class Generator8, class Generator9, class Generator10> -class CartesianProductHolder10 { - public: -CartesianProductHolder10(const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, - const Generator3& g3, const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, - const Generator6& g6, const Generator7& g7, const Generator8& g8, - const Generator9& g9, const Generator10& g10) - : g1_(g1), g2_(g2), g3_(g3), g4_(g4), g5_(g5), g6_(g6), g7_(g7), g8_(g8), - g9_(g9), g10_(g10) {} - template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10> - operator ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, - T9, T10> >() const { - return ParamGenerator< ::std::tr1::tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, - T9, T10> >( - new CartesianProductGenerator10<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, - T10>( - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T1> >(g1_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T2> >(g2_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T3> >(g3_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T4> >(g4_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T5> >(g5_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T6> >(g6_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T7> >(g7_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T8> >(g8_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T9> >(g9_), - static_cast<ParamGenerator<T10> >(g10_))); - } - - private: - // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. - void operator=(const CartesianProductHolder10& other); - - const Generator1 g1_; - const Generator2 g2_; - const Generator3 g3_; - const Generator4 g4_; - const Generator5 g5_; - const Generator6 g6_; - const Generator7 g7_; - const Generator8 g8_; - const Generator9 g9_; - const Generator10 g10_; -}; // class CartesianProductHolder10 - -# endif // GTEST_HAS_COMBINE - -} // namespace internal -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PARAM_UTIL_GENERATED_H_ - -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - -namespace testing { - -// Functions producing parameter generators. -// -// Google Test uses these generators to produce parameters for value- -// parameterized tests. When a parameterized test case is instantiated -// with a particular generator, Google Test creates and runs tests -// for each element in the sequence produced by the generator. -// -// In the following sample, tests from test case FooTest are instantiated -// each three times with parameter values 3, 5, and 8: -// -// class FooTest : public TestWithParam<int> { ... }; -// -// TEST_P(FooTest, TestThis) { -// } -// TEST_P(FooTest, TestThat) { -// } -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(TestSequence, FooTest, Values(3, 5, 8)); -// - -// Range() returns generators providing sequences of values in a range. -// -// Synopsis: -// Range(start, end) -// - returns a generator producing a sequence of values {start, start+1, -// start+2, ..., }. -// Range(start, end, step) -// - returns a generator producing a sequence of values {start, start+step, -// start+step+step, ..., }. -// Notes: -// * The generated sequences never include end. For example, Range(1, 5) -// returns a generator producing a sequence {1, 2, 3, 4}. Range(1, 9, 2) -// returns a generator producing {1, 3, 5, 7}. -// * start and end must have the same type. That type may be any integral or -// floating-point type or a user defined type satisfying these conditions: -// * It must be assignable (have operator=() defined). -// * It must have operator+() (operator+(int-compatible type) for -// two-operand version). -// * It must have operator<() defined. -// Elements in the resulting sequences will also have that type. -// * Condition start < end must be satisfied in order for resulting sequences -// to contain any elements. -// -template <typename T, typename IncrementT> -internal::ParamGenerator<T> Range(T start, T end, IncrementT step) { - return internal::ParamGenerator<T>( - new internal::RangeGenerator<T, IncrementT>(start, end, step)); -} - -template <typename T> -internal::ParamGenerator<T> Range(T start, T end) { - return Range(start, end, 1); -} - -// ValuesIn() function allows generation of tests with parameters coming from -// a container. -// -// Synopsis: -// ValuesIn(const T (&array)[N]) -// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements from -// a C-style array. -// ValuesIn(const Container& container) -// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements from -// an STL-style container. -// ValuesIn(Iterator begin, Iterator end) -// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements from -// a range [begin, end) defined by a pair of STL-style iterators. These -// iterators can also be plain C pointers. -// -// Please note that ValuesIn copies the values from the containers -// passed in and keeps them to generate tests in RUN_ALL_TESTS(). -// -// Examples: -// -// This instantiates tests from test case StringTest -// each with C-string values of "foo", "bar", and "baz": -// -// const char* strings[] = {"foo", "bar", "baz"}; -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(StringSequence, SrtingTest, ValuesIn(strings)); -// -// This instantiates tests from test case StlStringTest -// each with STL strings with values "a" and "b": -// -// ::std::vector< ::std::string> GetParameterStrings() { -// ::std::vector< ::std::string> v; -// v.push_back("a"); -// v.push_back("b"); -// return v; -// } -// -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(CharSequence, -// StlStringTest, -// ValuesIn(GetParameterStrings())); -// -// -// This will also instantiate tests from CharTest -// each with parameter values 'a' and 'b': -// -// ::std::list<char> GetParameterChars() { -// ::std::list<char> list; -// list.push_back('a'); -// list.push_back('b'); -// return list; -// } -// ::std::list<char> l = GetParameterChars(); -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(CharSequence2, -// CharTest, -// ValuesIn(l.begin(), l.end())); -// -template <typename ForwardIterator> -internal::ParamGenerator< - typename ::testing::internal::IteratorTraits<ForwardIterator>::value_type> -ValuesIn(ForwardIterator begin, ForwardIterator end) { - typedef typename ::testing::internal::IteratorTraits<ForwardIterator> - ::value_type ParamType; - return internal::ParamGenerator<ParamType>( - new internal::ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator<ParamType>(begin, end)); -} - -template <typename T, size_t N> -internal::ParamGenerator<T> ValuesIn(const T (&array)[N]) { - return ValuesIn(array, array + N); -} - -template <class Container> -internal::ParamGenerator<typename Container::value_type> ValuesIn( - const Container& container) { - return ValuesIn(container.begin(), container.end()); -} - -// Values() allows generating tests from explicitly specified list of -// parameters. -// -// Synopsis: -// Values(T v1, T v2, ..., T vN) -// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements v1, v2, ..., vN. -// -// For example, this instantiates tests from test case BarTest each -// with values "one", "two", and "three": -// -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(NumSequence, BarTest, Values("one", "two", "three")); -// -// This instantiates tests from test case BazTest each with values 1, 2, 3.5. -// The exact type of values will depend on the type of parameter in BazTest. -// -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(FloatingNumbers, BazTest, Values(1, 2, 3.5)); -// -// Currently, Values() supports from 1 to 50 parameters. -// -template <typename T1> -internal::ValueArray1<T1> Values(T1 v1) { - return internal::ValueArray1<T1>(v1); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2> -internal::ValueArray2<T1, T2> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2) { - return internal::ValueArray2<T1, T2>(v1, v2); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> -internal::ValueArray3<T1, T2, T3> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3) { - return internal::ValueArray3<T1, T2, T3>(v1, v2, v3); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4> -internal::ValueArray4<T1, T2, T3, T4> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4) { - return internal::ValueArray4<T1, T2, T3, T4>(v1, v2, v3, v4); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5> -internal::ValueArray5<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, - T5 v5) { - return internal::ValueArray5<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6> -internal::ValueArray6<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, - T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6) { - return internal::ValueArray6<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7> -internal::ValueArray7<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, - T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7) { - return internal::ValueArray7<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, - v6, v7); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8> -internal::ValueArray8<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, - T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8) { - return internal::ValueArray8<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8>(v1, v2, v3, v4, - v5, v6, v7, v8); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9> -internal::ValueArray9<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, - T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9) { - return internal::ValueArray9<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9>(v1, v2, v3, - v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10> -internal::ValueArray10<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10> Values(T1 v1, - T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10) { - return internal::ValueArray10<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10>(v1, - v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11> -internal::ValueArray11<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, - T11> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11) { - return internal::ValueArray11<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, - T11>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12> -internal::ValueArray12<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12) { - return internal::ValueArray12<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13> -internal::ValueArray13<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, - T13> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13) { - return internal::ValueArray13<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14> -internal::ValueArray14<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14) { - return internal::ValueArray14<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, - v14); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15> -internal::ValueArray15<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, - T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15) { - return internal::ValueArray15<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, - v13, v14, v15); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16> -internal::ValueArray16<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, - T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, - T16 v16) { - return internal::ValueArray16<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, - v12, v13, v14, v15, v16); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17> -internal::ValueArray17<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, - T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, - T16 v16, T17 v17) { - return internal::ValueArray17<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, - v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18> -internal::ValueArray18<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, - T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, - T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18) { - return internal::ValueArray18<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, - v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19> -internal::ValueArray19<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, - T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, - T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19) { - return internal::ValueArray19<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, - v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20> -internal::ValueArray20<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, - T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, - T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20) { - return internal::ValueArray20<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, - v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21> -internal::ValueArray21<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, - T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, - T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21) { - return internal::ValueArray21<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, - v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22> -internal::ValueArray22<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, - T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, - T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, - T21 v21, T22 v22) { - return internal::ValueArray22<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22>(v1, v2, v3, v4, - v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, - v20, v21, v22); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23> -internal::ValueArray23<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, - T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, - T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, - T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23) { - return internal::ValueArray23<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23>(v1, v2, v3, - v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, - v20, v21, v22, v23); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24> -internal::ValueArray24<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, - T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, - T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, - T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24) { - return internal::ValueArray24<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24>(v1, v2, - v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, - v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25> -internal::ValueArray25<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25> Values(T1 v1, - T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, - T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, - T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25) { - return internal::ValueArray25<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25>(v1, - v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, - v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26> -internal::ValueArray26<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26) { - return internal::ValueArray26<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, - v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27> -internal::ValueArray27<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, - T27> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27) { - return internal::ValueArray27<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, - v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28> -internal::ValueArray28<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, - T28> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28) { - return internal::ValueArray28<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, - v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, - v28); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29> -internal::ValueArray29<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29) { - return internal::ValueArray29<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, - v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, - v27, v28, v29); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30> -internal::ValueArray30<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, - T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, - T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, - T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30) { - return internal::ValueArray30<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, - v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, - v26, v27, v28, v29, v30); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31> -internal::ValueArray31<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, - T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, - T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, - T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31) { - return internal::ValueArray31<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, - v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, - v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32> -internal::ValueArray32<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, - T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, - T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, - T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, - T32 v32) { - return internal::ValueArray32<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, - v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, - v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33> -internal::ValueArray33<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, - T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, - T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, - T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, - T32 v32, T33 v33) { - return internal::ValueArray33<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, - v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, - v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34> -internal::ValueArray34<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, - T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, - T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, - T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, - T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34) { - return internal::ValueArray34<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, - v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, - v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35> -internal::ValueArray35<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, - T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, - T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, - T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, - T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35) { - return internal::ValueArray35<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, - v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, - v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36> -internal::ValueArray36<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, - T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, - T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, - T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, - T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36) { - return internal::ValueArray36<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36>(v1, v2, v3, v4, - v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, - v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, - v34, v35, v36); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37> -internal::ValueArray37<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, - T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, - T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, - T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, - T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, - T37 v37) { - return internal::ValueArray37<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37>(v1, v2, v3, - v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, - v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, - v34, v35, v36, v37); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38> -internal::ValueArray38<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, - T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, - T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, - T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, - T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, - T37 v37, T38 v38) { - return internal::ValueArray38<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38>(v1, v2, - v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, - v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, - v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, v38); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39> -internal::ValueArray39<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, - T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, - T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, - T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, - T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, - T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39) { - return internal::ValueArray39<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39>(v1, - v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, - v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, - v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, v38, v39); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40> -internal::ValueArray40<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40> Values(T1 v1, - T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, - T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, - T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, - T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, - T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40) { - return internal::ValueArray40<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, - v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, - v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, v38, v39, v40); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41> -internal::ValueArray41<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, - T41> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41) { - return internal::ValueArray41<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, - v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, - v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, v38, v39, v40, v41); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42> -internal::ValueArray42<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, - T42> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42) { - return internal::ValueArray42<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41, T42>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, - v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, - v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, v38, v39, v40, v41, - v42); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43> -internal::ValueArray43<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, - T43> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43) { - return internal::ValueArray43<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41, T42, T43>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, - v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, - v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, v38, v39, v40, - v41, v42, v43); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44> -internal::ValueArray44<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, - T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, - T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, - T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, - T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, - T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44) { - return internal::ValueArray44<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41, T42, T43, T44>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, - v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, - v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, v38, v39, - v40, v41, v42, v43, v44); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45> -internal::ValueArray45<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, - T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, - T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, - T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, - T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, - T41 v41, T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45) { - return internal::ValueArray45<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, - v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, - v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, v38, - v39, v40, v41, v42, v43, v44, v45); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46> -internal::ValueArray46<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, - T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, - T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, - T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, - T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, - T40 v40, T41 v41, T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, T46 v46) { - return internal::ValueArray46<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, - v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, - v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, - v38, v39, v40, v41, v42, v43, v44, v45, v46); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47> -internal::ValueArray47<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46, T47> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, - T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, - T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, - T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, - T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, - T40 v40, T41 v41, T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, T46 v46, T47 v47) { - return internal::ValueArray47<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, - v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, v23, - v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, v37, - v38, v39, v40, v41, v42, v43, v44, v45, v46, v47); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48> -internal::ValueArray48<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46, T47, T48> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, T6 v6, - T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, T15 v15, - T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, T23 v23, - T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, T31 v31, - T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, T39 v39, - T40 v40, T41 v41, T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, T46 v46, T47 v47, - T48 v48) { - return internal::ValueArray48<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, - v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22, - v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, v36, - v37, v38, v39, v40, v41, v42, v43, v44, v45, v46, v47, v48); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48, typename T49> -internal::ValueArray49<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, T5 v5, - T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, T14 v14, - T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, T22 v22, - T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, T30 v30, - T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, T38 v38, - T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, T46 v46, - T47 v47, T48 v48, T49 v49) { - return internal::ValueArray49<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49>(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, - v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, v20, v21, - v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, v34, v35, - v36, v37, v38, v39, v40, v41, v42, v43, v44, v45, v46, v47, v48, v49); -} - -template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3, typename T4, typename T5, - typename T6, typename T7, typename T8, typename T9, typename T10, - typename T11, typename T12, typename T13, typename T14, typename T15, - typename T16, typename T17, typename T18, typename T19, typename T20, - typename T21, typename T22, typename T23, typename T24, typename T25, - typename T26, typename T27, typename T28, typename T29, typename T30, - typename T31, typename T32, typename T33, typename T34, typename T35, - typename T36, typename T37, typename T38, typename T39, typename T40, - typename T41, typename T42, typename T43, typename T44, typename T45, - typename T46, typename T47, typename T48, typename T49, typename T50> -internal::ValueArray50<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, - T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, T26, T27, T28, - T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, T40, T41, T42, T43, - T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49, T50> Values(T1 v1, T2 v2, T3 v3, T4 v4, - T5 v5, T6 v6, T7 v7, T8 v8, T9 v9, T10 v10, T11 v11, T12 v12, T13 v13, - T14 v14, T15 v15, T16 v16, T17 v17, T18 v18, T19 v19, T20 v20, T21 v21, - T22 v22, T23 v23, T24 v24, T25 v25, T26 v26, T27 v27, T28 v28, T29 v29, - T30 v30, T31 v31, T32 v32, T33 v33, T34 v34, T35 v35, T36 v36, T37 v37, - T38 v38, T39 v39, T40 v40, T41 v41, T42 v42, T43 v43, T44 v44, T45 v45, - T46 v46, T47 v47, T48 v48, T49 v49, T50 v50) { - return internal::ValueArray50<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, - T12, T13, T14, T15, T16, T17, T18, T19, T20, T21, T22, T23, T24, T25, - T26, T27, T28, T29, T30, T31, T32, T33, T34, T35, T36, T37, T38, T39, - T40, T41, T42, T43, T44, T45, T46, T47, T48, T49, T50>(v1, v2, v3, v4, - v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v10, v11, v12, v13, v14, v15, v16, v17, v18, v19, - v20, v21, v22, v23, v24, v25, v26, v27, v28, v29, v30, v31, v32, v33, - v34, v35, v36, v37, v38, v39, v40, v41, v42, v43, v44, v45, v46, v47, - v48, v49, v50); -} - -// Bool() allows generating tests with parameters in a set of (false, true). -// -// Synopsis: -// Bool() -// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements {false, true}. -// -// It is useful when testing code that depends on Boolean flags. Combinations -// of multiple flags can be tested when several Bool()'s are combined using -// Combine() function. -// -// In the following example all tests in the test case FlagDependentTest -// will be instantiated twice with parameters false and true. -// -// class FlagDependentTest : public testing::TestWithParam<bool> { -// virtual void SetUp() { -// external_flag = GetParam(); -// } -// } -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(BoolSequence, FlagDependentTest, Bool()); -// -inline internal::ParamGenerator<bool> Bool() { - return Values(false, true); -} - -# if GTEST_HAS_COMBINE -// Combine() allows the user to combine two or more sequences to produce -// values of a Cartesian product of those sequences' elements. -// -// Synopsis: -// Combine(gen1, gen2, ..., genN) -// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements coming from -// the Cartesian product of elements from the sequences generated by -// gen1, gen2, ..., genN. The sequence elements will have a type of -// tuple<T1, T2, ..., TN> where T1, T2, ..., TN are the types -// of elements from sequences produces by gen1, gen2, ..., genN. -// -// Combine can have up to 10 arguments. This number is currently limited -// by the maximum number of elements in the tuple implementation used by Google -// Test. -// -// Example: -// -// This will instantiate tests in test case AnimalTest each one with -// the parameter values tuple("cat", BLACK), tuple("cat", WHITE), -// tuple("dog", BLACK), and tuple("dog", WHITE): -// -// enum Color { BLACK, GRAY, WHITE }; -// class AnimalTest -// : public testing::TestWithParam<tuple<const char*, Color> > {...}; -// -// TEST_P(AnimalTest, AnimalLooksNice) {...} -// -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(AnimalVariations, AnimalTest, -// Combine(Values("cat", "dog"), -// Values(BLACK, WHITE))); -// -// This will instantiate tests in FlagDependentTest with all variations of two -// Boolean flags: -// -// class FlagDependentTest -// : public testing::TestWithParam<tuple<bool, bool> > { -// virtual void SetUp() { -// // Assigns external_flag_1 and external_flag_2 values from the tuple. -// tie(external_flag_1, external_flag_2) = GetParam(); -// } -// }; -// -// TEST_P(FlagDependentTest, TestFeature1) { -// // Test your code using external_flag_1 and external_flag_2 here. -// } -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(TwoBoolSequence, FlagDependentTest, -// Combine(Bool(), Bool())); -// -template <typename Generator1, typename Generator2> -internal::CartesianProductHolder2<Generator1, Generator2> Combine( - const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2) { - return internal::CartesianProductHolder2<Generator1, Generator2>( - g1, g2); -} - -template <typename Generator1, typename Generator2, typename Generator3> -internal::CartesianProductHolder3<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3> Combine( - const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, const Generator3& g3) { - return internal::CartesianProductHolder3<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3>( - g1, g2, g3); -} - -template <typename Generator1, typename Generator2, typename Generator3, - typename Generator4> -internal::CartesianProductHolder4<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4> Combine( - const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, const Generator3& g3, - const Generator4& g4) { - return internal::CartesianProductHolder4<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4>( - g1, g2, g3, g4); -} - -template <typename Generator1, typename Generator2, typename Generator3, - typename Generator4, typename Generator5> -internal::CartesianProductHolder5<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5> Combine( - const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, const Generator3& g3, - const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5) { - return internal::CartesianProductHolder5<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5>( - g1, g2, g3, g4, g5); -} - -template <typename Generator1, typename Generator2, typename Generator3, - typename Generator4, typename Generator5, typename Generator6> -internal::CartesianProductHolder6<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6> Combine( - const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, const Generator3& g3, - const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, const Generator6& g6) { - return internal::CartesianProductHolder6<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6>( - g1, g2, g3, g4, g5, g6); -} - -template <typename Generator1, typename Generator2, typename Generator3, - typename Generator4, typename Generator5, typename Generator6, - typename Generator7> -internal::CartesianProductHolder7<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6, Generator7> Combine( - const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, const Generator3& g3, - const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, const Generator6& g6, - const Generator7& g7) { - return internal::CartesianProductHolder7<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6, Generator7>( - g1, g2, g3, g4, g5, g6, g7); -} - -template <typename Generator1, typename Generator2, typename Generator3, - typename Generator4, typename Generator5, typename Generator6, - typename Generator7, typename Generator8> -internal::CartesianProductHolder8<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6, Generator7, Generator8> Combine( - const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, const Generator3& g3, - const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, const Generator6& g6, - const Generator7& g7, const Generator8& g8) { - return internal::CartesianProductHolder8<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6, Generator7, Generator8>( - g1, g2, g3, g4, g5, g6, g7, g8); -} - -template <typename Generator1, typename Generator2, typename Generator3, - typename Generator4, typename Generator5, typename Generator6, - typename Generator7, typename Generator8, typename Generator9> -internal::CartesianProductHolder9<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6, Generator7, Generator8, - Generator9> Combine( - const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, const Generator3& g3, - const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, const Generator6& g6, - const Generator7& g7, const Generator8& g8, const Generator9& g9) { - return internal::CartesianProductHolder9<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6, Generator7, Generator8, Generator9>( - g1, g2, g3, g4, g5, g6, g7, g8, g9); -} - -template <typename Generator1, typename Generator2, typename Generator3, - typename Generator4, typename Generator5, typename Generator6, - typename Generator7, typename Generator8, typename Generator9, - typename Generator10> -internal::CartesianProductHolder10<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6, Generator7, Generator8, Generator9, - Generator10> Combine( - const Generator1& g1, const Generator2& g2, const Generator3& g3, - const Generator4& g4, const Generator5& g5, const Generator6& g6, - const Generator7& g7, const Generator8& g8, const Generator9& g9, - const Generator10& g10) { - return internal::CartesianProductHolder10<Generator1, Generator2, Generator3, - Generator4, Generator5, Generator6, Generator7, Generator8, Generator9, - Generator10>( - g1, g2, g3, g4, g5, g6, g7, g8, g9, g10); -} -# endif // GTEST_HAS_COMBINE - - - -# define TEST_P(test_case_name, test_name) \ - class GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name) \ - : public test_case_name { \ - public: \ - GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)() {} \ - virtual void TestBody(); \ - private: \ - static int AddToRegistry() { \ - ::testing::UnitTest::GetInstance()->parameterized_test_registry(). \ - GetTestCasePatternHolder<test_case_name>(\ - #test_case_name, __FILE__, __LINE__)->AddTestPattern(\ - #test_case_name, \ - #test_name, \ - new ::testing::internal::TestMetaFactory< \ - GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)>()); \ - return 0; \ - } \ - static int gtest_registering_dummy_; \ - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(\ - GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)); \ - }; \ - int GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, \ - test_name)::gtest_registering_dummy_ = \ - GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)::AddToRegistry(); \ - void GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)::TestBody() - -# define INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(prefix, test_case_name, generator) \ - ::testing::internal::ParamGenerator<test_case_name::ParamType> \ - gtest_##prefix##test_case_name##_EvalGenerator_() { return generator; } \ - int gtest_##prefix##test_case_name##_dummy_ = \ - ::testing::UnitTest::GetInstance()->parameterized_test_registry(). \ - GetTestCasePatternHolder<test_case_name>(\ - #test_case_name, __FILE__, __LINE__)->AddTestCaseInstantiation(\ - #prefix, \ - >est_##prefix##test_case_name##_EvalGenerator_, \ - __FILE__, __LINE__) - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PARAM_TEST_H_ -// Copyright 2006, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) -// -// Google C++ Testing Framework definitions useful in production code. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PROD_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PROD_H_ - -// When you need to test the private or protected members of a class, -// use the FRIEND_TEST macro to declare your tests as friends of the -// class. For example: -// -// class MyClass { -// private: -// void MyMethod(); -// FRIEND_TEST(MyClassTest, MyMethod); -// }; -// -// class MyClassTest : public testing::Test { -// // ... -// }; -// -// TEST_F(MyClassTest, MyMethod) { -// // Can call MyClass::MyMethod() here. -// } - -#define FRIEND_TEST(test_case_name, test_name)\ -friend class test_case_name##_##test_name##_Test - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PROD_H_ -// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: mheule@google.com (Markus Heule) -// - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TEST_PART_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TEST_PART_H_ - -#include <iosfwd> -#include <vector> - -namespace testing { - -// A copyable object representing the result of a test part (i.e. an -// assertion or an explicit FAIL(), ADD_FAILURE(), or SUCCESS()). -// -// Don't inherit from TestPartResult as its destructor is not virtual. -class GTEST_API_ TestPartResult { - public: - // The possible outcomes of a test part (i.e. an assertion or an - // explicit SUCCEED(), FAIL(), or ADD_FAILURE()). - enum Type { - kSuccess, // Succeeded. - kNonFatalFailure, // Failed but the test can continue. - kFatalFailure // Failed and the test should be terminated. - }; - - // C'tor. TestPartResult does NOT have a default constructor. - // Always use this constructor (with parameters) to create a - // TestPartResult object. - TestPartResult(Type a_type, - const char* a_file_name, - int a_line_number, - const char* a_message) - : type_(a_type), - file_name_(a_file_name == NULL ? "" : a_file_name), - line_number_(a_line_number), - summary_(ExtractSummary(a_message)), - message_(a_message) { - } - - // Gets the outcome of the test part. - Type type() const { return type_; } - - // Gets the name of the source file where the test part took place, or - // NULL if it's unknown. - const char* file_name() const { - return file_name_.empty() ? NULL : file_name_.c_str(); - } - - // Gets the line in the source file where the test part took place, - // or -1 if it's unknown. - int line_number() const { return line_number_; } - - // Gets the summary of the failure message. - const char* summary() const { return summary_.c_str(); } - - // Gets the message associated with the test part. - const char* message() const { return message_.c_str(); } - - // Returns true iff the test part passed. - bool passed() const { return type_ == kSuccess; } - - // Returns true iff the test part failed. - bool failed() const { return type_ != kSuccess; } - - // Returns true iff the test part non-fatally failed. - bool nonfatally_failed() const { return type_ == kNonFatalFailure; } - - // Returns true iff the test part fatally failed. - bool fatally_failed() const { return type_ == kFatalFailure; } - - private: - Type type_; - - // Gets the summary of the failure message by omitting the stack - // trace in it. - static std::string ExtractSummary(const char* message); - - // The name of the source file where the test part took place, or - // "" if the source file is unknown. - std::string file_name_; - // The line in the source file where the test part took place, or -1 - // if the line number is unknown. - int line_number_; - std::string summary_; // The test failure summary. - std::string message_; // The test failure message. -}; - -// Prints a TestPartResult object. -std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const TestPartResult& result); - -// An array of TestPartResult objects. -// -// Don't inherit from TestPartResultArray as its destructor is not -// virtual. -class GTEST_API_ TestPartResultArray { - public: - TestPartResultArray() {} - - // Appends the given TestPartResult to the array. - void Append(const TestPartResult& result); - - // Returns the TestPartResult at the given index (0-based). - const TestPartResult& GetTestPartResult(int index) const; - - // Returns the number of TestPartResult objects in the array. - int size() const; - - private: - std::vector<TestPartResult> array_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestPartResultArray); -}; - -// This interface knows how to report a test part result. -class TestPartResultReporterInterface { - public: - virtual ~TestPartResultReporterInterface() {} - - virtual void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) = 0; -}; - -namespace internal { - -// This helper class is used by {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NO_FATAL_FAILURE to check if a -// statement generates new fatal failures. To do so it registers itself as the -// current test part result reporter. Besides checking if fatal failures were -// reported, it only delegates the reporting to the former result reporter. -// The original result reporter is restored in the destructor. -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -class GTEST_API_ HasNewFatalFailureHelper - : public TestPartResultReporterInterface { - public: - HasNewFatalFailureHelper(); - virtual ~HasNewFatalFailureHelper(); - virtual void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result); - bool has_new_fatal_failure() const { return has_new_fatal_failure_; } - private: - bool has_new_fatal_failure_; - TestPartResultReporterInterface* original_reporter_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(HasNewFatalFailureHelper); -}; - -} // namespace internal - -} // namespace testing - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TEST_PART_H_ -// Copyright 2008 Google Inc. -// All Rights Reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TYPED_TEST_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TYPED_TEST_H_ - -// This header implements typed tests and type-parameterized tests. - -// Typed (aka type-driven) tests repeat the same test for types in a -// list. You must know which types you want to test with when writing -// typed tests. Here's how you do it: - -#if 0 - -// First, define a fixture class template. It should be parameterized -// by a type. Remember to derive it from testing::Test. -template <typename T> -class FooTest : public testing::Test { - public: - ... - typedef std::list<T> List; - static T shared_; - T value_; -}; - -// Next, associate a list of types with the test case, which will be -// repeated for each type in the list. The typedef is necessary for -// the macro to parse correctly. -typedef testing::Types<char, int, unsigned int> MyTypes; -TYPED_TEST_CASE(FooTest, MyTypes); - -// If the type list contains only one type, you can write that type -// directly without Types<...>: -// TYPED_TEST_CASE(FooTest, int); - -// Then, use TYPED_TEST() instead of TEST_F() to define as many typed -// tests for this test case as you want. -TYPED_TEST(FooTest, DoesBlah) { - // Inside a test, refer to TypeParam to get the type parameter. - // Since we are inside a derived class template, C++ requires use to - // visit the members of FooTest via 'this'. - TypeParam n = this->value_; - - // To visit static members of the fixture, add the TestFixture:: - // prefix. - n += TestFixture::shared_; - - // To refer to typedefs in the fixture, add the "typename - // TestFixture::" prefix. - typename TestFixture::List values; - values.push_back(n); - ... -} - -TYPED_TEST(FooTest, HasPropertyA) { ... } - -#endif // 0 - -// Type-parameterized tests are abstract test patterns parameterized -// by a type. Compared with typed tests, type-parameterized tests -// allow you to define the test pattern without knowing what the type -// parameters are. The defined pattern can be instantiated with -// different types any number of times, in any number of translation -// units. -// -// If you are designing an interface or concept, you can define a -// suite of type-parameterized tests to verify properties that any -// valid implementation of the interface/concept should have. Then, -// each implementation can easily instantiate the test suite to verify -// that it conforms to the requirements, without having to write -// similar tests repeatedly. Here's an example: - -#if 0 - -// First, define a fixture class template. It should be parameterized -// by a type. Remember to derive it from testing::Test. -template <typename T> -class FooTest : public testing::Test { - ... -}; - -// Next, declare that you will define a type-parameterized test case -// (the _P suffix is for "parameterized" or "pattern", whichever you -// prefer): -TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(FooTest); - -// Then, use TYPED_TEST_P() to define as many type-parameterized tests -// for this type-parameterized test case as you want. -TYPED_TEST_P(FooTest, DoesBlah) { - // Inside a test, refer to TypeParam to get the type parameter. - TypeParam n = 0; - ... -} - -TYPED_TEST_P(FooTest, HasPropertyA) { ... } - -// Now the tricky part: you need to register all test patterns before -// you can instantiate them. The first argument of the macro is the -// test case name; the rest are the names of the tests in this test -// case. -REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(FooTest, - DoesBlah, HasPropertyA); - -// Finally, you are free to instantiate the pattern with the types you -// want. If you put the above code in a header file, you can #include -// it in multiple C++ source files and instantiate it multiple times. -// -// To distinguish different instances of the pattern, the first -// argument to the INSTANTIATE_* macro is a prefix that will be added -// to the actual test case name. Remember to pick unique prefixes for -// different instances. -typedef testing::Types<char, int, unsigned int> MyTypes; -INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(My, FooTest, MyTypes); - -// If the type list contains only one type, you can write that type -// directly without Types<...>: -// INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(My, FooTest, int); - -#endif // 0 - - -// Implements typed tests. - -#if GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// Expands to the name of the typedef for the type parameters of the -// given test case. -# define GTEST_TYPE_PARAMS_(TestCaseName) gtest_type_params_##TestCaseName##_ - -// The 'Types' template argument below must have spaces around it -// since some compilers may choke on '>>' when passing a template -// instance (e.g. Types<int>) -# define TYPED_TEST_CASE(CaseName, Types) \ - typedef ::testing::internal::TypeList< Types >::type \ - GTEST_TYPE_PARAMS_(CaseName) - -# define TYPED_TEST(CaseName, TestName) \ - template <typename gtest_TypeParam_> \ - class GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(CaseName, TestName) \ - : public CaseName<gtest_TypeParam_> { \ - private: \ - typedef CaseName<gtest_TypeParam_> TestFixture; \ - typedef gtest_TypeParam_ TypeParam; \ - virtual void TestBody(); \ - }; \ - bool gtest_##CaseName##_##TestName##_registered_ GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ = \ - ::testing::internal::TypeParameterizedTest< \ - CaseName, \ - ::testing::internal::TemplateSel< \ - GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(CaseName, TestName)>, \ - GTEST_TYPE_PARAMS_(CaseName)>::Register(\ - "", #CaseName, #TestName, 0); \ - template <typename gtest_TypeParam_> \ - void GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(CaseName, TestName)<gtest_TypeParam_>::TestBody() - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST - -// Implements type-parameterized tests. - -#if GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// Expands to the namespace name that the type-parameterized tests for -// the given type-parameterized test case are defined in. The exact -// name of the namespace is subject to change without notice. -# define GTEST_CASE_NAMESPACE_(TestCaseName) \ - gtest_case_##TestCaseName##_ - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// -// Expands to the name of the variable used to remember the names of -// the defined tests in the given test case. -# define GTEST_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P_STATE_(TestCaseName) \ - gtest_typed_test_case_p_state_##TestCaseName##_ - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE DIRECTLY. -// -// Expands to the name of the variable used to remember the names of -// the registered tests in the given test case. -# define GTEST_REGISTERED_TEST_NAMES_(TestCaseName) \ - gtest_registered_test_names_##TestCaseName##_ - -// The variables defined in the type-parameterized test macros are -// static as typically these macros are used in a .h file that can be -// #included in multiple translation units linked together. -# define TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(CaseName) \ - static ::testing::internal::TypedTestCasePState \ - GTEST_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P_STATE_(CaseName) - -# define TYPED_TEST_P(CaseName, TestName) \ - namespace GTEST_CASE_NAMESPACE_(CaseName) { \ - template <typename gtest_TypeParam_> \ - class TestName : public CaseName<gtest_TypeParam_> { \ - private: \ - typedef CaseName<gtest_TypeParam_> TestFixture; \ - typedef gtest_TypeParam_ TypeParam; \ - virtual void TestBody(); \ - }; \ - static bool gtest_##TestName##_defined_ GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ = \ - GTEST_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P_STATE_(CaseName).AddTestName(\ - __FILE__, __LINE__, #CaseName, #TestName); \ - } \ - template <typename gtest_TypeParam_> \ - void GTEST_CASE_NAMESPACE_(CaseName)::TestName<gtest_TypeParam_>::TestBody() - -# define REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(CaseName, ...) \ - namespace GTEST_CASE_NAMESPACE_(CaseName) { \ - typedef ::testing::internal::Templates<__VA_ARGS__>::type gtest_AllTests_; \ - } \ - static const char* const GTEST_REGISTERED_TEST_NAMES_(CaseName) = \ - GTEST_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P_STATE_(CaseName).VerifyRegisteredTestNames(\ - __FILE__, __LINE__, #__VA_ARGS__) - -// The 'Types' template argument below must have spaces around it -// since some compilers may choke on '>>' when passing a template -// instance (e.g. Types<int>) -# define INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P(Prefix, CaseName, Types) \ - bool gtest_##Prefix##_##CaseName GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ = \ - ::testing::internal::TypeParameterizedTestCase<CaseName, \ - GTEST_CASE_NAMESPACE_(CaseName)::gtest_AllTests_, \ - ::testing::internal::TypeList< Types >::type>::Register(\ - #Prefix, #CaseName, GTEST_REGISTERED_TEST_NAMES_(CaseName)) - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TYPED_TEST_H_ - -// Depending on the platform, different string classes are available. -// On Linux, in addition to ::std::string, Google also makes use of -// class ::string, which has the same interface as ::std::string, but -// has a different implementation. -// -// The user can define GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING to 1 to indicate that -// ::string is available AND is a distinct type to ::std::string, or -// define it to 0 to indicate otherwise. -// -// If the user's ::std::string and ::string are the same class due to -// aliasing, he should define GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING to 0. -// -// If the user doesn't define GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING, it is defined -// heuristically. - -namespace testing { - -// Declares the flags. - -// This flag temporary enables the disabled tests. -GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(also_run_disabled_tests); - -// This flag brings the debugger on an assertion failure. -GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(break_on_failure); - -// This flag controls whether Google Test catches all test-thrown exceptions -// and logs them as failures. -GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(catch_exceptions); - -// This flag enables using colors in terminal output. Available values are -// "yes" to enable colors, "no" (disable colors), or "auto" (the default) -// to let Google Test decide. -GTEST_DECLARE_string_(color); - -// This flag sets up the filter to select by name using a glob pattern -// the tests to run. If the filter is not given all tests are executed. -GTEST_DECLARE_string_(filter); - -// This flag causes the Google Test to list tests. None of the tests listed -// are actually run if the flag is provided. -GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(list_tests); - -// This flag controls whether Google Test emits a detailed XML report to a file -// in addition to its normal textual output. -GTEST_DECLARE_string_(output); - -// This flags control whether Google Test prints the elapsed time for each -// test. -GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(print_time); - -// This flag specifies the random number seed. -GTEST_DECLARE_int32_(random_seed); - -// This flag sets how many times the tests are repeated. The default value -// is 1. If the value is -1 the tests are repeating forever. -GTEST_DECLARE_int32_(repeat); - -// This flag controls whether Google Test includes Google Test internal -// stack frames in failure stack traces. -GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(show_internal_stack_frames); - -// When this flag is specified, tests' order is randomized on every iteration. -GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(shuffle); - -// This flag specifies the maximum number of stack frames to be -// printed in a failure message. -GTEST_DECLARE_int32_(stack_trace_depth); - -// When this flag is specified, a failed assertion will throw an -// exception if exceptions are enabled, or exit the program with a -// non-zero code otherwise. -GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(throw_on_failure); - -// When this flag is set with a "host:port" string, on supported -// platforms test results are streamed to the specified port on -// the specified host machine. -GTEST_DECLARE_string_(stream_result_to); - -// The upper limit for valid stack trace depths. -const int kMaxStackTraceDepth = 100; - -namespace internal { - -class AssertHelper; -class DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter; -class ExecDeathTest; -class NoExecDeathTest; -class FinalSuccessChecker; -class GTestFlagSaver; -class StreamingListenerTest; -class TestResultAccessor; -class TestEventListenersAccessor; -class TestEventRepeater; -class UnitTestRecordPropertyTestHelper; -class WindowsDeathTest; -class UnitTestImpl* GetUnitTestImpl(); -void ReportFailureInUnknownLocation(TestPartResult::Type result_type, - const std::string& message); - -} // namespace internal - -// The friend relationship of some of these classes is cyclic. -// If we don't forward declare them the compiler might confuse the classes -// in friendship clauses with same named classes on the scope. -class Test; -class TestCase; -class TestInfo; -class UnitTest; - -// A class for indicating whether an assertion was successful. When -// the assertion wasn't successful, the AssertionResult object -// remembers a non-empty message that describes how it failed. -// -// To create an instance of this class, use one of the factory functions -// (AssertionSuccess() and AssertionFailure()). -// -// This class is useful for two purposes: -// 1. Defining predicate functions to be used with Boolean test assertions -// EXPECT_TRUE/EXPECT_FALSE and their ASSERT_ counterparts -// 2. Defining predicate-format functions to be -// used with predicate assertions (ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT*, etc). -// -// For example, if you define IsEven predicate: -// -// testing::AssertionResult IsEven(int n) { -// if ((n % 2) == 0) -// return testing::AssertionSuccess(); -// else -// return testing::AssertionFailure() << n << " is odd"; -// } -// -// Then the failed expectation EXPECT_TRUE(IsEven(Fib(5))) -// will print the message -// -// Value of: IsEven(Fib(5)) -// Actual: false (5 is odd) -// Expected: true -// -// instead of a more opaque -// -// Value of: IsEven(Fib(5)) -// Actual: false -// Expected: true -// -// in case IsEven is a simple Boolean predicate. -// -// If you expect your predicate to be reused and want to support informative -// messages in EXPECT_FALSE and ASSERT_FALSE (negative assertions show up -// about half as often as positive ones in our tests), supply messages for -// both success and failure cases: -// -// testing::AssertionResult IsEven(int n) { -// if ((n % 2) == 0) -// return testing::AssertionSuccess() << n << " is even"; -// else -// return testing::AssertionFailure() << n << " is odd"; -// } -// -// Then a statement EXPECT_FALSE(IsEven(Fib(6))) will print -// -// Value of: IsEven(Fib(6)) -// Actual: true (8 is even) -// Expected: false -// -// NB: Predicates that support negative Boolean assertions have reduced -// performance in positive ones so be careful not to use them in tests -// that have lots (tens of thousands) of positive Boolean assertions. -// -// To use this class with EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT assertions such as: -// -// // Verifies that Foo() returns an even number. -// EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(IsEven, Foo()); -// -// you need to define: -// -// testing::AssertionResult IsEven(const char* expr, int n) { -// if ((n % 2) == 0) -// return testing::AssertionSuccess(); -// else -// return testing::AssertionFailure() -// << "Expected: " << expr << " is even\n Actual: it's " << n; -// } -// -// If Foo() returns 5, you will see the following message: -// -// Expected: Foo() is even -// Actual: it's 5 -// -class GTEST_API_ AssertionResult { - public: - // Copy constructor. - // Used in EXPECT_TRUE/FALSE(assertion_result). - AssertionResult(const AssertionResult& other); - // Used in the EXPECT_TRUE/FALSE(bool_expression). - explicit AssertionResult(bool success) : success_(success) {} - - // Returns true iff the assertion succeeded. - operator bool() const { return success_; } // NOLINT - - // Returns the assertion's negation. Used with EXPECT/ASSERT_FALSE. - AssertionResult operator!() const; - - // Returns the text streamed into this AssertionResult. Test assertions - // use it when they fail (i.e., the predicate's outcome doesn't match the - // assertion's expectation). When nothing has been streamed into the - // object, returns an empty string. - const char* message() const { - return message_.get() != NULL ? message_->c_str() : ""; - } - // TODO(vladl@google.com): Remove this after making sure no clients use it. - // Deprecated; please use message() instead. - const char* failure_message() const { return message(); } - - // Streams a custom failure message into this object. - template <typename T> AssertionResult& operator<<(const T& value) { - AppendMessage(Message() << value); - return *this; - } - - // Allows streaming basic output manipulators such as endl or flush into - // this object. - AssertionResult& operator<<( - ::std::ostream& (*basic_manipulator)(::std::ostream& stream)) { - AppendMessage(Message() << basic_manipulator); - return *this; - } - - private: - // Appends the contents of message to message_. - void AppendMessage(const Message& a_message) { - if (message_.get() == NULL) - message_.reset(new ::std::string); - message_->append(a_message.GetString().c_str()); - } - - // Stores result of the assertion predicate. - bool success_; - // Stores the message describing the condition in case the expectation - // construct is not satisfied with the predicate's outcome. - // Referenced via a pointer to avoid taking too much stack frame space - // with test assertions. - internal::scoped_ptr< ::std::string> message_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(AssertionResult); -}; - -// Makes a successful assertion result. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult AssertionSuccess(); - -// Makes a failed assertion result. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult AssertionFailure(); - -// Makes a failed assertion result with the given failure message. -// Deprecated; use AssertionFailure() << msg. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult AssertionFailure(const Message& msg); - -// The abstract class that all tests inherit from. -// -// In Google Test, a unit test program contains one or many TestCases, and -// each TestCase contains one or many Tests. -// -// When you define a test using the TEST macro, you don't need to -// explicitly derive from Test - the TEST macro automatically does -// this for you. -// -// The only time you derive from Test is when defining a test fixture -// to be used a TEST_F. For example: -// -// class FooTest : public testing::Test { -// protected: -// virtual void SetUp() { ... } -// virtual void TearDown() { ... } -// ... -// }; -// -// TEST_F(FooTest, Bar) { ... } -// TEST_F(FooTest, Baz) { ... } -// -// Test is not copyable. -class GTEST_API_ Test { - public: - friend class TestInfo; - - // Defines types for pointers to functions that set up and tear down - // a test case. - typedef internal::SetUpTestCaseFunc SetUpTestCaseFunc; - typedef internal::TearDownTestCaseFunc TearDownTestCaseFunc; - - // The d'tor is virtual as we intend to inherit from Test. - virtual ~Test(); - - // Sets up the stuff shared by all tests in this test case. - // - // Google Test will call Foo::SetUpTestCase() before running the first - // test in test case Foo. Hence a sub-class can define its own - // SetUpTestCase() method to shadow the one defined in the super - // class. - static void SetUpTestCase() {} - - // Tears down the stuff shared by all tests in this test case. - // - // Google Test will call Foo::TearDownTestCase() after running the last - // test in test case Foo. Hence a sub-class can define its own - // TearDownTestCase() method to shadow the one defined in the super - // class. - static void TearDownTestCase() {} - - // Returns true iff the current test has a fatal failure. - static bool HasFatalFailure(); - - // Returns true iff the current test has a non-fatal failure. - static bool HasNonfatalFailure(); - - // Returns true iff the current test has a (either fatal or - // non-fatal) failure. - static bool HasFailure() { return HasFatalFailure() || HasNonfatalFailure(); } - - // Logs a property for the current test, test case, or for the entire - // invocation of the test program when used outside of the context of a - // test case. Only the last value for a given key is remembered. These - // are public static so they can be called from utility functions that are - // not members of the test fixture. Calls to RecordProperty made during - // lifespan of the test (from the moment its constructor starts to the - // moment its destructor finishes) will be output in XML as attributes of - // the <testcase> element. Properties recorded from fixture's - // SetUpTestCase or TearDownTestCase are logged as attributes of the - // corresponding <testsuite> element. Calls to RecordProperty made in the - // global context (before or after invocation of RUN_ALL_TESTS and from - // SetUp/TearDown method of Environment objects registered with Google - // Test) will be output as attributes of the <testsuites> element. - static void RecordProperty(const std::string& key, const std::string& value); - static void RecordProperty(const std::string& key, int value); - - protected: - // Creates a Test object. - Test(); - - // Sets up the test fixture. - virtual void SetUp(); - - // Tears down the test fixture. - virtual void TearDown(); - - private: - // Returns true iff the current test has the same fixture class as - // the first test in the current test case. - static bool HasSameFixtureClass(); - - // Runs the test after the test fixture has been set up. - // - // A sub-class must implement this to define the test logic. - // - // DO NOT OVERRIDE THIS FUNCTION DIRECTLY IN A USER PROGRAM. - // Instead, use the TEST or TEST_F macro. - virtual void TestBody() = 0; - - // Sets up, executes, and tears down the test. - void Run(); - - // Deletes self. We deliberately pick an unusual name for this - // internal method to avoid clashing with names used in user TESTs. - void DeleteSelf_() { delete this; } - - // Uses a GTestFlagSaver to save and restore all Google Test flags. - const internal::GTestFlagSaver* const gtest_flag_saver_; - - // Often a user mis-spells SetUp() as Setup() and spends a long time - // wondering why it is never called by Google Test. The declaration of - // the following method is solely for catching such an error at - // compile time: - // - // - The return type is deliberately chosen to be not void, so it - // will be a conflict if a user declares void Setup() in his test - // fixture. - // - // - This method is private, so it will be another compiler error - // if a user calls it from his test fixture. - // - // DO NOT OVERRIDE THIS FUNCTION. - // - // If you see an error about overriding the following function or - // about it being private, you have mis-spelled SetUp() as Setup(). - struct Setup_should_be_spelled_SetUp {}; - virtual Setup_should_be_spelled_SetUp* Setup() { return NULL; } - - // We disallow copying Tests. - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Test); -}; - -typedef internal::TimeInMillis TimeInMillis; - -// A copyable object representing a user specified test property which can be -// output as a key/value string pair. -// -// Don't inherit from TestProperty as its destructor is not virtual. -class TestProperty { - public: - // C'tor. TestProperty does NOT have a default constructor. - // Always use this constructor (with parameters) to create a - // TestProperty object. - TestProperty(const std::string& a_key, const std::string& a_value) : - key_(a_key), value_(a_value) { - } - - // Gets the user supplied key. - const char* key() const { - return key_.c_str(); - } - - // Gets the user supplied value. - const char* value() const { - return value_.c_str(); - } - - // Sets a new value, overriding the one supplied in the constructor. - void SetValue(const std::string& new_value) { - value_ = new_value; - } - - private: - // The key supplied by the user. - std::string key_; - // The value supplied by the user. - std::string value_; -}; - -// The result of a single Test. This includes a list of -// TestPartResults, a list of TestProperties, a count of how many -// death tests there are in the Test, and how much time it took to run -// the Test. -// -// TestResult is not copyable. -class GTEST_API_ TestResult { - public: - // Creates an empty TestResult. - TestResult(); - - // D'tor. Do not inherit from TestResult. - ~TestResult(); - - // Gets the number of all test parts. This is the sum of the number - // of successful test parts and the number of failed test parts. - int total_part_count() const; - - // Returns the number of the test properties. - int test_property_count() const; - - // Returns true iff the test passed (i.e. no test part failed). - bool Passed() const { return !Failed(); } - - // Returns true iff the test failed. - bool Failed() const; - - // Returns true iff the test fatally failed. - bool HasFatalFailure() const; - - // Returns true iff the test has a non-fatal failure. - bool HasNonfatalFailure() const; - - // Returns the elapsed time, in milliseconds. - TimeInMillis elapsed_time() const { return elapsed_time_; } - - // Returns the i-th test part result among all the results. i can range - // from 0 to test_property_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, aborts - // the program. - const TestPartResult& GetTestPartResult(int i) const; - - // Returns the i-th test property. i can range from 0 to - // test_property_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, aborts the - // program. - const TestProperty& GetTestProperty(int i) const; - - private: - friend class TestInfo; - friend class TestCase; - friend class UnitTest; - friend class internal::DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter; - friend class internal::ExecDeathTest; - friend class internal::TestResultAccessor; - friend class internal::UnitTestImpl; - friend class internal::WindowsDeathTest; - - // Gets the vector of TestPartResults. - const std::vector<TestPartResult>& test_part_results() const { - return test_part_results_; - } - - // Gets the vector of TestProperties. - const std::vector<TestProperty>& test_properties() const { - return test_properties_; - } - - // Sets the elapsed time. - void set_elapsed_time(TimeInMillis elapsed) { elapsed_time_ = elapsed; } - - // Adds a test property to the list. The property is validated and may add - // a non-fatal failure if invalid (e.g., if it conflicts with reserved - // key names). If a property is already recorded for the same key, the - // value will be updated, rather than storing multiple values for the same - // key. xml_element specifies the element for which the property is being - // recorded and is used for validation. - void RecordProperty(const std::string& xml_element, - const TestProperty& test_property); - - // Adds a failure if the key is a reserved attribute of Google Test - // testcase tags. Returns true if the property is valid. - // TODO(russr): Validate attribute names are legal and human readable. - static bool ValidateTestProperty(const std::string& xml_element, - const TestProperty& test_property); - - // Adds a test part result to the list. - void AddTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& test_part_result); - - // Returns the death test count. - int death_test_count() const { return death_test_count_; } - - // Increments the death test count, returning the new count. - int increment_death_test_count() { return ++death_test_count_; } - - // Clears the test part results. - void ClearTestPartResults(); - - // Clears the object. - void Clear(); - - // Protects mutable state of the property vector and of owned - // properties, whose values may be updated. - internal::Mutex test_properites_mutex_; - - // The vector of TestPartResults - std::vector<TestPartResult> test_part_results_; - // The vector of TestProperties - std::vector<TestProperty> test_properties_; - // Running count of death tests. - int death_test_count_; - // The elapsed time, in milliseconds. - TimeInMillis elapsed_time_; - - // We disallow copying TestResult. - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestResult); -}; // class TestResult - -// A TestInfo object stores the following information about a test: -// -// Test case name -// Test name -// Whether the test should be run -// A function pointer that creates the test object when invoked -// Test result -// -// The constructor of TestInfo registers itself with the UnitTest -// singleton such that the RUN_ALL_TESTS() macro knows which tests to -// run. -class GTEST_API_ TestInfo { - public: - // Destructs a TestInfo object. This function is not virtual, so - // don't inherit from TestInfo. - ~TestInfo(); - - // Returns the test case name. - const char* test_case_name() const { return test_case_name_.c_str(); } - - // Returns the test name. - const char* name() const { return name_.c_str(); } - - // Returns the name of the parameter type, or NULL if this is not a typed - // or a type-parameterized test. - const char* type_param() const { - if (type_param_.get() != NULL) - return type_param_->c_str(); - return NULL; - } - - // Returns the text representation of the value parameter, or NULL if this - // is not a value-parameterized test. - const char* value_param() const { - if (value_param_.get() != NULL) - return value_param_->c_str(); - return NULL; - } - - // Returns true if this test should run, that is if the test is not - // disabled (or it is disabled but the also_run_disabled_tests flag has - // been specified) and its full name matches the user-specified filter. - // - // Google Test allows the user to filter the tests by their full names. - // The full name of a test Bar in test case Foo is defined as - // "Foo.Bar". Only the tests that match the filter will run. - // - // A filter is a colon-separated list of glob (not regex) patterns, - // optionally followed by a '-' and a colon-separated list of - // negative patterns (tests to exclude). A test is run if it - // matches one of the positive patterns and does not match any of - // the negative patterns. - // - // For example, *A*:Foo.* is a filter that matches any string that - // contains the character 'A' or starts with "Foo.". - bool should_run() const { return should_run_; } - - // Returns true iff this test will appear in the XML report. - bool is_reportable() const { - // For now, the XML report includes all tests matching the filter. - // In the future, we may trim tests that are excluded because of - // sharding. - return matches_filter_; - } - - // Returns the result of the test. - const TestResult* result() const { return &result_; } - - private: -#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - friend class internal::DefaultDeathTestFactory; -#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - friend class Test; - friend class TestCase; - friend class internal::UnitTestImpl; - friend class internal::StreamingListenerTest; - friend TestInfo* internal::MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( - const char* test_case_name, - const char* name, - const char* type_param, - const char* value_param, - internal::TypeId fixture_class_id, - Test::SetUpTestCaseFunc set_up_tc, - Test::TearDownTestCaseFunc tear_down_tc, - internal::TestFactoryBase* factory); - - // Constructs a TestInfo object. The newly constructed instance assumes - // ownership of the factory object. - TestInfo(const std::string& test_case_name, - const std::string& name, - const char* a_type_param, // NULL if not a type-parameterized test - const char* a_value_param, // NULL if not a value-parameterized test - internal::TypeId fixture_class_id, - internal::TestFactoryBase* factory); - - // Increments the number of death tests encountered in this test so - // far. - int increment_death_test_count() { - return result_.increment_death_test_count(); - } - - // Creates the test object, runs it, records its result, and then - // deletes it. - void Run(); - - static void ClearTestResult(TestInfo* test_info) { - test_info->result_.Clear(); - } - - // These fields are immutable properties of the test. - const std::string test_case_name_; // Test case name - const std::string name_; // Test name - // Name of the parameter type, or NULL if this is not a typed or a - // type-parameterized test. - const internal::scoped_ptr<const ::std::string> type_param_; - // Text representation of the value parameter, or NULL if this is not a - // value-parameterized test. - const internal::scoped_ptr<const ::std::string> value_param_; - const internal::TypeId fixture_class_id_; // ID of the test fixture class - bool should_run_; // True iff this test should run - bool is_disabled_; // True iff this test is disabled - bool matches_filter_; // True if this test matches the - // user-specified filter. - internal::TestFactoryBase* const factory_; // The factory that creates - // the test object - - // This field is mutable and needs to be reset before running the - // test for the second time. - TestResult result_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestInfo); -}; - -// A test case, which consists of a vector of TestInfos. -// -// TestCase is not copyable. -class GTEST_API_ TestCase { - public: - // Creates a TestCase with the given name. - // - // TestCase does NOT have a default constructor. Always use this - // constructor to create a TestCase object. - // - // Arguments: - // - // name: name of the test case - // a_type_param: the name of the test's type parameter, or NULL if - // this is not a type-parameterized test. - // set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test case - // tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test case - TestCase(const char* name, const char* a_type_param, - Test::SetUpTestCaseFunc set_up_tc, - Test::TearDownTestCaseFunc tear_down_tc); - - // Destructor of TestCase. - virtual ~TestCase(); - - // Gets the name of the TestCase. - const char* name() const { return name_.c_str(); } - - // Returns the name of the parameter type, or NULL if this is not a - // type-parameterized test case. - const char* type_param() const { - if (type_param_.get() != NULL) - return type_param_->c_str(); - return NULL; - } - - // Returns true if any test in this test case should run. - bool should_run() const { return should_run_; } - - // Gets the number of successful tests in this test case. - int successful_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of failed tests in this test case. - int failed_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of disabled tests that will be reported in the XML report. - int reportable_disabled_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of disabled tests in this test case. - int disabled_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of tests to be printed in the XML report. - int reportable_test_count() const; - - // Get the number of tests in this test case that should run. - int test_to_run_count() const; - - // Gets the number of all tests in this test case. - int total_test_count() const; - - // Returns true iff the test case passed. - bool Passed() const { return !Failed(); } - - // Returns true iff the test case failed. - bool Failed() const { return failed_test_count() > 0; } - - // Returns the elapsed time, in milliseconds. - TimeInMillis elapsed_time() const { return elapsed_time_; } - - // Returns the i-th test among all the tests. i can range from 0 to - // total_test_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. - const TestInfo* GetTestInfo(int i) const; - - // Returns the TestResult that holds test properties recorded during - // execution of SetUpTestCase and TearDownTestCase. - const TestResult& ad_hoc_test_result() const { return ad_hoc_test_result_; } - - private: - friend class Test; - friend class internal::UnitTestImpl; - - // Gets the (mutable) vector of TestInfos in this TestCase. - std::vector<TestInfo*>& test_info_list() { return test_info_list_; } - - // Gets the (immutable) vector of TestInfos in this TestCase. - const std::vector<TestInfo*>& test_info_list() const { - return test_info_list_; - } - - // Returns the i-th test among all the tests. i can range from 0 to - // total_test_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. - TestInfo* GetMutableTestInfo(int i); - - // Sets the should_run member. - void set_should_run(bool should) { should_run_ = should; } - - // Adds a TestInfo to this test case. Will delete the TestInfo upon - // destruction of the TestCase object. - void AddTestInfo(TestInfo * test_info); - - // Clears the results of all tests in this test case. - void ClearResult(); - - // Clears the results of all tests in the given test case. - static void ClearTestCaseResult(TestCase* test_case) { - test_case->ClearResult(); - } - - // Runs every test in this TestCase. - void Run(); - - // Runs SetUpTestCase() for this TestCase. This wrapper is needed - // for catching exceptions thrown from SetUpTestCase(). - void RunSetUpTestCase() { (*set_up_tc_)(); } - - // Runs TearDownTestCase() for this TestCase. This wrapper is - // needed for catching exceptions thrown from TearDownTestCase(). - void RunTearDownTestCase() { (*tear_down_tc_)(); } - - // Returns true iff test passed. - static bool TestPassed(const TestInfo* test_info) { - return test_info->should_run() && test_info->result()->Passed(); - } - - // Returns true iff test failed. - static bool TestFailed(const TestInfo* test_info) { - return test_info->should_run() && test_info->result()->Failed(); - } - - // Returns true iff the test is disabled and will be reported in the XML - // report. - static bool TestReportableDisabled(const TestInfo* test_info) { - return test_info->is_reportable() && test_info->is_disabled_; - } - - // Returns true iff test is disabled. - static bool TestDisabled(const TestInfo* test_info) { - return test_info->is_disabled_; - } - - // Returns true iff this test will appear in the XML report. - static bool TestReportable(const TestInfo* test_info) { - return test_info->is_reportable(); - } - - // Returns true if the given test should run. - static bool ShouldRunTest(const TestInfo* test_info) { - return test_info->should_run(); - } - - // Shuffles the tests in this test case. - void ShuffleTests(internal::Random* random); - - // Restores the test order to before the first shuffle. - void UnshuffleTests(); - - // Name of the test case. - std::string name_; - // Name of the parameter type, or NULL if this is not a typed or a - // type-parameterized test. - const internal::scoped_ptr<const ::std::string> type_param_; - // The vector of TestInfos in their original order. It owns the - // elements in the vector. - std::vector<TestInfo*> test_info_list_; - // Provides a level of indirection for the test list to allow easy - // shuffling and restoring the test order. The i-th element in this - // vector is the index of the i-th test in the shuffled test list. - std::vector<int> test_indices_; - // Pointer to the function that sets up the test case. - Test::SetUpTestCaseFunc set_up_tc_; - // Pointer to the function that tears down the test case. - Test::TearDownTestCaseFunc tear_down_tc_; - // True iff any test in this test case should run. - bool should_run_; - // Elapsed time, in milliseconds. - TimeInMillis elapsed_time_; - // Holds test properties recorded during execution of SetUpTestCase and - // TearDownTestCase. - TestResult ad_hoc_test_result_; - - // We disallow copying TestCases. - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestCase); -}; - -// An Environment object is capable of setting up and tearing down an -// environment. The user should subclass this to define his own -// environment(s). -// -// An Environment object does the set-up and tear-down in virtual -// methods SetUp() and TearDown() instead of the constructor and the -// destructor, as: -// -// 1. You cannot safely throw from a destructor. This is a problem -// as in some cases Google Test is used where exceptions are enabled, and -// we may want to implement ASSERT_* using exceptions where they are -// available. -// 2. You cannot use ASSERT_* directly in a constructor or -// destructor. -class Environment { - public: - // The d'tor is virtual as we need to subclass Environment. - virtual ~Environment() {} - - // Override this to define how to set up the environment. - virtual void SetUp() {} - - // Override this to define how to tear down the environment. - virtual void TearDown() {} - private: - // If you see an error about overriding the following function or - // about it being private, you have mis-spelled SetUp() as Setup(). - struct Setup_should_be_spelled_SetUp {}; - virtual Setup_should_be_spelled_SetUp* Setup() { return NULL; } -}; - -// The interface for tracing execution of tests. The methods are organized in -// the order the corresponding events are fired. -class TestEventListener { - public: - virtual ~TestEventListener() {} - - // Fired before any test activity starts. - virtual void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; - - // Fired before each iteration of tests starts. There may be more than - // one iteration if GTEST_FLAG(repeat) is set. iteration is the iteration - // index, starting from 0. - virtual void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& unit_test, - int iteration) = 0; - - // Fired before environment set-up for each iteration of tests starts. - virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; - - // Fired after environment set-up for each iteration of tests ends. - virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; - - // Fired before the test case starts. - virtual void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& test_case) = 0; - - // Fired before the test starts. - virtual void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info) = 0; - - // Fired after a failed assertion or a SUCCEED() invocation. - virtual void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& test_part_result) = 0; - - // Fired after the test ends. - virtual void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info) = 0; - - // Fired after the test case ends. - virtual void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& test_case) = 0; - - // Fired before environment tear-down for each iteration of tests starts. - virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; - - // Fired after environment tear-down for each iteration of tests ends. - virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; - - // Fired after each iteration of tests finishes. - virtual void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, - int iteration) = 0; - - // Fired after all test activities have ended. - virtual void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; -}; - -// The convenience class for users who need to override just one or two -// methods and are not concerned that a possible change to a signature of -// the methods they override will not be caught during the build. For -// comments about each method please see the definition of TestEventListener -// above. -class EmptyTestEventListener : public TestEventListener { - public: - virtual void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} - virtual void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/, - int /*iteration*/) {} - virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} - virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} - virtual void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& /*test_case*/) {} - virtual void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& /*test_info*/) {} - virtual void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& /*test_part_result*/) {} - virtual void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& /*test_info*/) {} - virtual void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& /*test_case*/) {} - virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} - virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} - virtual void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/, - int /*iteration*/) {} - virtual void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) {} -}; - -// TestEventListeners lets users add listeners to track events in Google Test. -class GTEST_API_ TestEventListeners { - public: - TestEventListeners(); - ~TestEventListeners(); - - // Appends an event listener to the end of the list. Google Test assumes - // the ownership of the listener (i.e. it will delete the listener when - // the test program finishes). - void Append(TestEventListener* listener); - - // Removes the given event listener from the list and returns it. It then - // becomes the caller's responsibility to delete the listener. Returns - // NULL if the listener is not found in the list. - TestEventListener* Release(TestEventListener* listener); - - // Returns the standard listener responsible for the default console - // output. Can be removed from the listeners list to shut down default - // console output. Note that removing this object from the listener list - // with Release transfers its ownership to the caller and makes this - // function return NULL the next time. - TestEventListener* default_result_printer() const { - return default_result_printer_; - } - - // Returns the standard listener responsible for the default XML output - // controlled by the --gtest_output=xml flag. Can be removed from the - // listeners list by users who want to shut down the default XML output - // controlled by this flag and substitute it with custom one. Note that - // removing this object from the listener list with Release transfers its - // ownership to the caller and makes this function return NULL the next - // time. - TestEventListener* default_xml_generator() const { - return default_xml_generator_; - } - - private: - friend class TestCase; - friend class TestInfo; - friend class internal::DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter; - friend class internal::NoExecDeathTest; - friend class internal::TestEventListenersAccessor; - friend class internal::UnitTestImpl; - - // Returns repeater that broadcasts the TestEventListener events to all - // subscribers. - TestEventListener* repeater(); - - // Sets the default_result_printer attribute to the provided listener. - // The listener is also added to the listener list and previous - // default_result_printer is removed from it and deleted. The listener can - // also be NULL in which case it will not be added to the list. Does - // nothing if the previous and the current listener objects are the same. - void SetDefaultResultPrinter(TestEventListener* listener); - - // Sets the default_xml_generator attribute to the provided listener. The - // listener is also added to the listener list and previous - // default_xml_generator is removed from it and deleted. The listener can - // also be NULL in which case it will not be added to the list. Does - // nothing if the previous and the current listener objects are the same. - void SetDefaultXmlGenerator(TestEventListener* listener); - - // Controls whether events will be forwarded by the repeater to the - // listeners in the list. - bool EventForwardingEnabled() const; - void SuppressEventForwarding(); - - // The actual list of listeners. - internal::TestEventRepeater* repeater_; - // Listener responsible for the standard result output. - TestEventListener* default_result_printer_; - // Listener responsible for the creation of the XML output file. - TestEventListener* default_xml_generator_; - - // We disallow copying TestEventListeners. - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestEventListeners); -}; - -// A UnitTest consists of a vector of TestCases. -// -// This is a singleton class. The only instance of UnitTest is -// created when UnitTest::GetInstance() is first called. This -// instance is never deleted. -// -// UnitTest is not copyable. -// -// This class is thread-safe as long as the methods are called -// according to their specification. -class GTEST_API_ UnitTest { - public: - // Gets the singleton UnitTest object. The first time this method - // is called, a UnitTest object is constructed and returned. - // Consecutive calls will return the same object. - static UnitTest* GetInstance(); - - // Runs all tests in this UnitTest object and prints the result. - // Returns 0 if successful, or 1 otherwise. - // - // This method can only be called from the main thread. - // - // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. - int Run() GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_; - - // Returns the working directory when the first TEST() or TEST_F() - // was executed. The UnitTest object owns the string. - const char* original_working_dir() const; - - // Returns the TestCase object for the test that's currently running, - // or NULL if no test is running. - const TestCase* current_test_case() const - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); - - // Returns the TestInfo object for the test that's currently running, - // or NULL if no test is running. - const TestInfo* current_test_info() const - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); - - // Returns the random seed used at the start of the current test run. - int random_seed() const; - -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - // Returns the ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry object used to keep track of - // value-parameterized tests and instantiate and register them. - // - // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. - internal::ParameterizedTestCaseRegistry& parameterized_test_registry() - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - - // Gets the number of successful test cases. - int successful_test_case_count() const; - - // Gets the number of failed test cases. - int failed_test_case_count() const; - - // Gets the number of all test cases. - int total_test_case_count() const; - - // Gets the number of all test cases that contain at least one test - // that should run. - int test_case_to_run_count() const; - - // Gets the number of successful tests. - int successful_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of failed tests. - int failed_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of disabled tests that will be reported in the XML report. - int reportable_disabled_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of disabled tests. - int disabled_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of tests to be printed in the XML report. - int reportable_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of all tests. - int total_test_count() const; - - // Gets the number of tests that should run. - int test_to_run_count() const; - - // Gets the time of the test program start, in ms from the start of the - // UNIX epoch. - TimeInMillis start_timestamp() const; - - // Gets the elapsed time, in milliseconds. - TimeInMillis elapsed_time() const; - - // Returns true iff the unit test passed (i.e. all test cases passed). - bool Passed() const; - - // Returns true iff the unit test failed (i.e. some test case failed - // or something outside of all tests failed). - bool Failed() const; - - // Gets the i-th test case among all the test cases. i can range from 0 to - // total_test_case_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. - const TestCase* GetTestCase(int i) const; - - // Returns the TestResult containing information on test failures and - // properties logged outside of individual test cases. - const TestResult& ad_hoc_test_result() const; - - // Returns the list of event listeners that can be used to track events - // inside Google Test. - TestEventListeners& listeners(); - - private: - // Registers and returns a global test environment. When a test - // program is run, all global test environments will be set-up in - // the order they were registered. After all tests in the program - // have finished, all global test environments will be torn-down in - // the *reverse* order they were registered. - // - // The UnitTest object takes ownership of the given environment. - // - // This method can only be called from the main thread. - Environment* AddEnvironment(Environment* env); - - // Adds a TestPartResult to the current TestResult object. All - // Google Test assertion macros (e.g. ASSERT_TRUE, EXPECT_EQ, etc) - // eventually call this to report their results. The user code - // should use the assertion macros instead of calling this directly. - void AddTestPartResult(TestPartResult::Type result_type, - const char* file_name, - int line_number, - const std::string& message, - const std::string& os_stack_trace) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); - - // Adds a TestProperty to the current TestResult object when invoked from - // inside a test, to current TestCase's ad_hoc_test_result_ when invoked - // from SetUpTestCase or TearDownTestCase, or to the global property set - // when invoked elsewhere. If the result already contains a property with - // the same key, the value will be updated. - void RecordProperty(const std::string& key, const std::string& value); - - // Gets the i-th test case among all the test cases. i can range from 0 to - // total_test_case_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. - TestCase* GetMutableTestCase(int i); - - // Accessors for the implementation object. - internal::UnitTestImpl* impl() { return impl_; } - const internal::UnitTestImpl* impl() const { return impl_; } - - // These classes and funcions are friends as they need to access private - // members of UnitTest. - friend class Test; - friend class internal::AssertHelper; - friend class internal::ScopedTrace; - friend class internal::StreamingListenerTest; - friend class internal::UnitTestRecordPropertyTestHelper; - friend Environment* AddGlobalTestEnvironment(Environment* env); - friend internal::UnitTestImpl* internal::GetUnitTestImpl(); - friend void internal::ReportFailureInUnknownLocation( - TestPartResult::Type result_type, - const std::string& message); - - // Creates an empty UnitTest. - UnitTest(); - - // D'tor - virtual ~UnitTest(); - - // Pushes a trace defined by SCOPED_TRACE() on to the per-thread - // Google Test trace stack. - void PushGTestTrace(const internal::TraceInfo& trace) - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); - - // Pops a trace from the per-thread Google Test trace stack. - void PopGTestTrace() - GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); - - // Protects mutable state in *impl_. This is mutable as some const - // methods need to lock it too. - mutable internal::Mutex mutex_; - - // Opaque implementation object. This field is never changed once - // the object is constructed. We don't mark it as const here, as - // doing so will cause a warning in the constructor of UnitTest. - // Mutable state in *impl_ is protected by mutex_. - internal::UnitTestImpl* impl_; - - // We disallow copying UnitTest. - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(UnitTest); -}; - -// A convenient wrapper for adding an environment for the test -// program. -// -// You should call this before RUN_ALL_TESTS() is called, probably in -// main(). If you use gtest_main, you need to call this before main() -// starts for it to take effect. For example, you can define a global -// variable like this: -// -// testing::Environment* const foo_env = -// testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(new FooEnvironment); -// -// However, we strongly recommend you to write your own main() and -// call AddGlobalTestEnvironment() there, as relying on initialization -// of global variables makes the code harder to read and may cause -// problems when you register multiple environments from different -// translation units and the environments have dependencies among them -// (remember that the compiler doesn't guarantee the order in which -// global variables from different translation units are initialized). -inline Environment* AddGlobalTestEnvironment(Environment* env) { - return UnitTest::GetInstance()->AddEnvironment(env); -} - -// Initializes Google Test. This must be called before calling -// RUN_ALL_TESTS(). In particular, it parses a command line for the -// flags that Google Test recognizes. Whenever a Google Test flag is -// seen, it is removed from argv, and *argc is decremented. -// -// No value is returned. Instead, the Google Test flag variables are -// updated. -// -// Calling the function for the second time has no user-visible effect. -GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleTest(int* argc, char** argv); - -// This overloaded version can be used in Windows programs compiled in -// UNICODE mode. -GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleTest(int* argc, wchar_t** argv); - -namespace internal { - -// FormatForComparison<ToPrint, OtherOperand>::Format(value) formats a -// value of type ToPrint that is an operand of a comparison assertion -// (e.g. ASSERT_EQ). OtherOperand is the type of the other operand in -// the comparison, and is used to help determine the best way to -// format the value. In particular, when the value is a C string -// (char pointer) and the other operand is an STL string object, we -// want to format the C string as a string, since we know it is -// compared by value with the string object. If the value is a char -// pointer but the other operand is not an STL string object, we don't -// know whether the pointer is supposed to point to a NUL-terminated -// string, and thus want to print it as a pointer to be safe. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. - -// The default case. -template <typename ToPrint, typename OtherOperand> -class FormatForComparison { - public: - static ::std::string Format(const ToPrint& value) { - return ::testing::PrintToString(value); - } -}; - -// Array. -template <typename ToPrint, size_t N, typename OtherOperand> -class FormatForComparison<ToPrint[N], OtherOperand> { - public: - static ::std::string Format(const ToPrint* value) { - return FormatForComparison<const ToPrint*, OtherOperand>::Format(value); - } -}; - -// By default, print C string as pointers to be safe, as we don't know -// whether they actually point to a NUL-terminated string. - -#define GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(CharType) \ - template <typename OtherOperand> \ - class FormatForComparison<CharType*, OtherOperand> { \ - public: \ - static ::std::string Format(CharType* value) { \ - return ::testing::PrintToString(static_cast<const void*>(value)); \ - } \ - } - -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(char); -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(const char); -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(wchar_t); -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(const wchar_t); - -#undef GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_ - -// If a C string is compared with an STL string object, we know it's meant -// to point to a NUL-terminated string, and thus can print it as a string. - -#define GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(CharType, OtherStringType) \ - template <> \ - class FormatForComparison<CharType*, OtherStringType> { \ - public: \ - static ::std::string Format(CharType* value) { \ - return ::testing::PrintToString(value); \ - } \ - } - -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(char, ::std::string); -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(const char, ::std::string); - -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_STRING -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(char, ::string); -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(const char, ::string); -#endif - -#if GTEST_HAS_GLOBAL_WSTRING -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(wchar_t, ::wstring); -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(const wchar_t, ::wstring); -#endif - -#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(wchar_t, ::std::wstring); -GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(const wchar_t, ::std::wstring); -#endif - -#undef GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_ - -// Formats a comparison assertion (e.g. ASSERT_EQ, EXPECT_LT, and etc) -// operand to be used in a failure message. The type (but not value) -// of the other operand may affect the format. This allows us to -// print a char* as a raw pointer when it is compared against another -// char* or void*, and print it as a C string when it is compared -// against an std::string object, for example. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -template <typename T1, typename T2> -std::string FormatForComparisonFailureMessage( - const T1& value, const T2& /* other_operand */) { - return FormatForComparison<T1, T2>::Format(value); -} - -// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ. -template <typename T1, typename T2> -AssertionResult CmpHelperEQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const T1& expected, - const T2& actual) { -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) // Saves the current warning state. -# pragma warning(disable:4389) // Temporarily disables warning on - // signed/unsigned mismatch. -#endif - - if (expected == actual) { - return AssertionSuccess(); - } - -#ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(pop) // Restores the warning state. -#endif - - return EqFailure(expected_expression, - actual_expression, - FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(expected, actual), - FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(actual, expected), - false); -} - -// With this overloaded version, we allow anonymous enums to be used -// in {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ when compiled with gcc 4, as anonymous enums -// can be implicitly cast to BiggestInt. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperEQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - BiggestInt expected, - BiggestInt actual); - -// The helper class for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ. The template argument -// lhs_is_null_literal is true iff the first argument to ASSERT_EQ() -// is a null pointer literal. The following default implementation is -// for lhs_is_null_literal being false. -template <bool lhs_is_null_literal> -class EqHelper { - public: - // This templatized version is for the general case. - template <typename T1, typename T2> - static AssertionResult Compare(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const T1& expected, - const T2& actual) { - return CmpHelperEQ(expected_expression, actual_expression, expected, - actual); - } - - // With this overloaded version, we allow anonymous enums to be used - // in {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ when compiled with gcc 4, as anonymous - // enums can be implicitly cast to BiggestInt. - // - // Even though its body looks the same as the above version, we - // cannot merge the two, as it will make anonymous enums unhappy. - static AssertionResult Compare(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - BiggestInt expected, - BiggestInt actual) { - return CmpHelperEQ(expected_expression, actual_expression, expected, - actual); - } -}; - -// This specialization is used when the first argument to ASSERT_EQ() -// is a null pointer literal, like NULL, false, or 0. -template <> -class EqHelper<true> { - public: - // We define two overloaded versions of Compare(). The first - // version will be picked when the second argument to ASSERT_EQ() is - // NOT a pointer, e.g. ASSERT_EQ(0, AnIntFunction()) or - // EXPECT_EQ(false, a_bool). - template <typename T1, typename T2> - static AssertionResult Compare( - const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const T1& expected, - const T2& actual, - // The following line prevents this overload from being considered if T2 - // is not a pointer type. We need this because ASSERT_EQ(NULL, my_ptr) - // expands to Compare("", "", NULL, my_ptr), which requires a conversion - // to match the Secret* in the other overload, which would otherwise make - // this template match better. - typename EnableIf<!is_pointer<T2>::value>::type* = 0) { - return CmpHelperEQ(expected_expression, actual_expression, expected, - actual); - } - - // This version will be picked when the second argument to ASSERT_EQ() is a - // pointer, e.g. ASSERT_EQ(NULL, a_pointer). - template <typename T> - static AssertionResult Compare( - const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - // We used to have a second template parameter instead of Secret*. That - // template parameter would deduce to 'long', making this a better match - // than the first overload even without the first overload's EnableIf. - // Unfortunately, gcc with -Wconversion-null warns when "passing NULL to - // non-pointer argument" (even a deduced integral argument), so the old - // implementation caused warnings in user code. - Secret* /* expected (NULL) */, - T* actual) { - // We already know that 'expected' is a null pointer. - return CmpHelperEQ(expected_expression, actual_expression, - static_cast<T*>(NULL), actual); - } -}; - -// A macro for implementing the helper functions needed to implement -// ASSERT_?? and EXPECT_??. It is here just to avoid copy-and-paste -// of similar code. -// -// For each templatized helper function, we also define an overloaded -// version for BiggestInt in order to reduce code bloat and allow -// anonymous enums to be used with {ASSERT|EXPECT}_?? when compiled -// with gcc 4. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -#define GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(op_name, op)\ -template <typename T1, typename T2>\ -AssertionResult CmpHelper##op_name(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, \ - const T1& val1, const T2& val2) {\ - if (val1 op val2) {\ - return AssertionSuccess();\ - } else {\ - return AssertionFailure() \ - << "Expected: (" << expr1 << ") " #op " (" << expr2\ - << "), actual: " << FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(val1, val2)\ - << " vs " << FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(val2, val1);\ - }\ -}\ -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelper##op_name(\ - const char* expr1, const char* expr2, BiggestInt val1, BiggestInt val2) - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. - -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NE -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(NE, !=); -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LE -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(LE, <=); -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LT -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(LT, <); -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GE -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(GE, >=); -// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GT -GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(GT, >); - -#undef GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_ - -// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STREQ. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTREQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const char* expected, - const char* actual); - -// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASEEQ. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRCASEEQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const char* expected, - const char* actual); - -// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRNE. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRNE(const char* s1_expression, - const char* s2_expression, - const char* s1, - const char* s2); - -// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASENE. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRCASENE(const char* s1_expression, - const char* s2_expression, - const char* s1, - const char* s2); - - -// Helper function for *_STREQ on wide strings. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTREQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - const wchar_t* expected, - const wchar_t* actual); - -// Helper function for *_STRNE on wide strings. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRNE(const char* s1_expression, - const char* s2_expression, - const wchar_t* s1, - const wchar_t* s2); - -} // namespace internal - -// IsSubstring() and IsNotSubstring() are intended to be used as the -// first argument to {EXPECT,ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT2(), not by -// themselves. They check whether needle is a substring of haystack -// (NULL is considered a substring of itself only), and return an -// appropriate error message when they fail. -// -// The {needle,haystack}_expr arguments are the stringified -// expressions that generated the two real arguments. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsSubstring( - const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const char* needle, const char* haystack); -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsSubstring( - const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const wchar_t* needle, const wchar_t* haystack); -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( - const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const char* needle, const char* haystack); -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( - const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const wchar_t* needle, const wchar_t* haystack); -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsSubstring( - const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const ::std::string& needle, const ::std::string& haystack); -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( - const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const ::std::string& needle, const ::std::string& haystack); - -#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsSubstring( - const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const ::std::wstring& needle, const ::std::wstring& haystack); -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( - const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, - const ::std::wstring& needle, const ::std::wstring& haystack); -#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING - -namespace internal { - -// Helper template function for comparing floating-points. -// -// Template parameter: -// -// RawType: the raw floating-point type (either float or double) -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -template <typename RawType> -AssertionResult CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ(const char* expected_expression, - const char* actual_expression, - RawType expected, - RawType actual) { - const FloatingPoint<RawType> lhs(expected), rhs(actual); - - if (lhs.AlmostEquals(rhs)) { - return AssertionSuccess(); - } - - ::std::stringstream expected_ss; - expected_ss << std::setprecision(std::numeric_limits<RawType>::digits10 + 2) - << expected; - - ::std::stringstream actual_ss; - actual_ss << std::setprecision(std::numeric_limits<RawType>::digits10 + 2) - << actual; - - return EqFailure(expected_expression, - actual_expression, - StringStreamToString(&expected_ss), - StringStreamToString(&actual_ss), - false); -} - -// Helper function for implementing ASSERT_NEAR. -// -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult DoubleNearPredFormat(const char* expr1, - const char* expr2, - const char* abs_error_expr, - double val1, - double val2, - double abs_error); - -// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. -// A class that enables one to stream messages to assertion macros -class GTEST_API_ AssertHelper { - public: - // Constructor. - AssertHelper(TestPartResult::Type type, - const char* file, - int line, - const char* message); - ~AssertHelper(); - - // Message assignment is a semantic trick to enable assertion - // streaming; see the GTEST_MESSAGE_ macro below. - void operator=(const Message& message) const; - - private: - // We put our data in a struct so that the size of the AssertHelper class can - // be as small as possible. This is important because gcc is incapable of - // re-using stack space even for temporary variables, so every EXPECT_EQ - // reserves stack space for another AssertHelper. - struct AssertHelperData { - AssertHelperData(TestPartResult::Type t, - const char* srcfile, - int line_num, - const char* msg) - : type(t), file(srcfile), line(line_num), message(msg) { } - - TestPartResult::Type const type; - const char* const file; - int const line; - std::string const message; - - private: - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(AssertHelperData); - }; - - AssertHelperData* const data_; - - GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(AssertHelper); -}; - -} // namespace internal - -#if GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST -// The pure interface class that all value-parameterized tests inherit from. -// A value-parameterized class must inherit from both ::testing::Test and -// ::testing::WithParamInterface. In most cases that just means inheriting -// from ::testing::TestWithParam, but more complicated test hierarchies -// may need to inherit from Test and WithParamInterface at different levels. -// -// This interface has support for accessing the test parameter value via -// the GetParam() method. -// -// Use it with one of the parameter generator defining functions, like Range(), -// Values(), ValuesIn(), Bool(), and Combine(). -// -// class FooTest : public ::testing::TestWithParam<int> { -// protected: -// FooTest() { -// // Can use GetParam() here. -// } -// virtual ~FooTest() { -// // Can use GetParam() here. -// } -// virtual void SetUp() { -// // Can use GetParam() here. -// } -// virtual void TearDown { -// // Can use GetParam() here. -// } -// }; -// TEST_P(FooTest, DoesBar) { -// // Can use GetParam() method here. -// Foo foo; -// ASSERT_TRUE(foo.DoesBar(GetParam())); -// } -// INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(OneToTenRange, FooTest, ::testing::Range(1, 10)); - -template <typename T> -class WithParamInterface { - public: - typedef T ParamType; - virtual ~WithParamInterface() {} - - // The current parameter value. Is also available in the test fixture's - // constructor. This member function is non-static, even though it only - // references static data, to reduce the opportunity for incorrect uses - // like writing 'WithParamInterface<bool>::GetParam()' for a test that - // uses a fixture whose parameter type is int. - const ParamType& GetParam() const { - GTEST_CHECK_(parameter_ != NULL) - << "GetParam() can only be called inside a value-parameterized test " - << "-- did you intend to write TEST_P instead of TEST_F?"; - return *parameter_; - } - - private: - // Sets parameter value. The caller is responsible for making sure the value - // remains alive and unchanged throughout the current test. - static void SetParam(const ParamType* parameter) { - parameter_ = parameter; - } - - // Static value used for accessing parameter during a test lifetime. - static const ParamType* parameter_; - - // TestClass must be a subclass of WithParamInterface<T> and Test. - template <class TestClass> friend class internal::ParameterizedTestFactory; -}; - -template <typename T> -const T* WithParamInterface<T>::parameter_ = NULL; - -// Most value-parameterized classes can ignore the existence of -// WithParamInterface, and can just inherit from ::testing::TestWithParam. - -template <typename T> -class TestWithParam : public Test, public WithParamInterface<T> { -}; - -#endif // GTEST_HAS_PARAM_TEST - -// Macros for indicating success/failure in test code. - -// ADD_FAILURE unconditionally adds a failure to the current test. -// SUCCEED generates a success - it doesn't automatically make the -// current test successful, as a test is only successful when it has -// no failure. -// -// EXPECT_* verifies that a certain condition is satisfied. If not, -// it behaves like ADD_FAILURE. In particular: -// -// EXPECT_TRUE verifies that a Boolean condition is true. -// EXPECT_FALSE verifies that a Boolean condition is false. -// -// FAIL and ASSERT_* are similar to ADD_FAILURE and EXPECT_*, except -// that they will also abort the current function on failure. People -// usually want the fail-fast behavior of FAIL and ASSERT_*, but those -// writing data-driven tests often find themselves using ADD_FAILURE -// and EXPECT_* more. - -// Generates a nonfatal failure with a generic message. -#define ADD_FAILURE() GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_("Failed") - -// Generates a nonfatal failure at the given source file location with -// a generic message. -#define ADD_FAILURE_AT(file, line) \ - GTEST_MESSAGE_AT_(file, line, "Failed", \ - ::testing::TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure) - -// Generates a fatal failure with a generic message. -#define GTEST_FAIL() GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_("Failed") - -// Define this macro to 1 to omit the definition of FAIL(), which is a -// generic name and clashes with some other libraries. -#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_FAIL -# define FAIL() GTEST_FAIL() -#endif - -// Generates a success with a generic message. -#define GTEST_SUCCEED() GTEST_SUCCESS_("Succeeded") - -// Define this macro to 1 to omit the definition of SUCCEED(), which -// is a generic name and clashes with some other libraries. -#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_SUCCEED -# define SUCCEED() GTEST_SUCCEED() -#endif - -// Macros for testing exceptions. -// -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_THROW(statement, expected_exception): -// Tests that the statement throws the expected exception. -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NO_THROW(statement): -// Tests that the statement doesn't throw any exception. -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_ANY_THROW(statement): -// Tests that the statement throws an exception. - -#define EXPECT_THROW(statement, expected_exception) \ - GTEST_TEST_THROW_(statement, expected_exception, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define EXPECT_NO_THROW(statement) \ - GTEST_TEST_NO_THROW_(statement, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define EXPECT_ANY_THROW(statement) \ - GTEST_TEST_ANY_THROW_(statement, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_THROW(statement, expected_exception) \ - GTEST_TEST_THROW_(statement, expected_exception, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_NO_THROW(statement) \ - GTEST_TEST_NO_THROW_(statement, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_ANY_THROW(statement) \ - GTEST_TEST_ANY_THROW_(statement, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) - -// Boolean assertions. Condition can be either a Boolean expression or an -// AssertionResult. For more information on how to use AssertionResult with -// these macros see comments on that class. -#define EXPECT_TRUE(condition) \ - GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(condition, #condition, false, true, \ - GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define EXPECT_FALSE(condition) \ - GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(!(condition), #condition, true, false, \ - GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_TRUE(condition) \ - GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(condition, #condition, false, true, \ - GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_FALSE(condition) \ - GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(!(condition), #condition, true, false, \ - GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) - -// Includes the auto-generated header that implements a family of -// generic predicate assertion macros. -// Copyright 2006, Google Inc. -// All rights reserved. -// -// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without -// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are -// met: -// -// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright -// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. -// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above -// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer -// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the -// distribution. -// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its -// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from -// this software without specific prior written permission. -// -// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS -// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR -// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT -// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, -// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT -// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, -// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY -// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT -// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE -// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. - -// This file is AUTOMATICALLY GENERATED on 10/31/2011 by command -// 'gen_gtest_pred_impl.py 5'. DO NOT EDIT BY HAND! -// -// Implements a family of generic predicate assertion macros. - -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRED_IMPL_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRED_IMPL_H_ - -// Makes sure this header is not included before gtest.h. -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_H_ -# error Do not include gtest_pred_impl.h directly. Include gtest.h instead. -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_H_ - -// This header implements a family of generic predicate assertion -// macros: -// -// ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(pred_format, v1) -// ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(pred_format, v1, v2) -// ... -// -// where pred_format is a function or functor that takes n (in the -// case of ASSERT_PRED_FORMATn) values and their source expression -// text, and returns a testing::AssertionResult. See the definition -// of ASSERT_EQ in gtest.h for an example. -// -// If you don't care about formatting, you can use the more -// restrictive version: -// -// ASSERT_PRED1(pred, v1) -// ASSERT_PRED2(pred, v1, v2) -// ... -// -// where pred is an n-ary function or functor that returns bool, -// and the values v1, v2, ..., must support the << operator for -// streaming to std::ostream. -// -// We also define the EXPECT_* variations. -// -// For now we only support predicates whose arity is at most 5. -// Please email googletestframework@googlegroups.com if you need -// support for higher arities. - -// GTEST_ASSERT_ is the basic statement to which all of the assertions -// in this file reduce. Don't use this in your code. - -#define GTEST_ASSERT_(expression, on_failure) \ - GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ - if (const ::testing::AssertionResult gtest_ar = (expression)) \ - ; \ - else \ - on_failure(gtest_ar.failure_message()) - - -// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED1. Don't use -// this in your code. -template <typename Pred, - typename T1> -AssertionResult AssertPred1Helper(const char* pred_text, - const char* e1, - Pred pred, - const T1& v1) { - if (pred(v1)) return AssertionSuccess(); - - return AssertionFailure() << pred_text << "(" - << e1 << ") evaluates to false, where" - << "\n" << e1 << " evaluates to " << v1; -} - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT1. -// Don't use this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT1_(pred_format, v1, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, v1), \ - on_failure) - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED1. Don't use -// this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED1_(pred, v1, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred1Helper(#pred, \ - #v1, \ - pred, \ - v1), on_failure) - -// Unary predicate assertion macros. -#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(pred_format, v1) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT1_(pred_format, v1, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define EXPECT_PRED1(pred, v1) \ - GTEST_PRED1_(pred, v1, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(pred_format, v1) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT1_(pred_format, v1, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED1(pred, v1) \ - GTEST_PRED1_(pred, v1, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) - - - -// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED2. Don't use -// this in your code. -template <typename Pred, - typename T1, - typename T2> -AssertionResult AssertPred2Helper(const char* pred_text, - const char* e1, - const char* e2, - Pred pred, - const T1& v1, - const T2& v2) { - if (pred(v1, v2)) return AssertionSuccess(); - - return AssertionFailure() << pred_text << "(" - << e1 << ", " - << e2 << ") evaluates to false, where" - << "\n" << e1 << " evaluates to " << v1 - << "\n" << e2 << " evaluates to " << v2; -} - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT2. -// Don't use this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT2_(pred_format, v1, v2, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, #v2, v1, v2), \ - on_failure) - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED2. Don't use -// this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED2_(pred, v1, v2, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred2Helper(#pred, \ - #v1, \ - #v2, \ - pred, \ - v1, \ - v2), on_failure) - -// Binary predicate assertion macros. -#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(pred_format, v1, v2) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT2_(pred_format, v1, v2, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define EXPECT_PRED2(pred, v1, v2) \ - GTEST_PRED2_(pred, v1, v2, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(pred_format, v1, v2) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT2_(pred_format, v1, v2, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED2(pred, v1, v2) \ - GTEST_PRED2_(pred, v1, v2, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) - - - -// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED3. Don't use -// this in your code. -template <typename Pred, - typename T1, - typename T2, - typename T3> -AssertionResult AssertPred3Helper(const char* pred_text, - const char* e1, - const char* e2, - const char* e3, - Pred pred, - const T1& v1, - const T2& v2, - const T3& v3) { - if (pred(v1, v2, v3)) return AssertionSuccess(); - - return AssertionFailure() << pred_text << "(" - << e1 << ", " - << e2 << ", " - << e3 << ") evaluates to false, where" - << "\n" << e1 << " evaluates to " << v1 - << "\n" << e2 << " evaluates to " << v2 - << "\n" << e3 << " evaluates to " << v3; -} - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT3. -// Don't use this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT3_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, #v2, #v3, v1, v2, v3), \ - on_failure) - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED3. Don't use -// this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED3_(pred, v1, v2, v3, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred3Helper(#pred, \ - #v1, \ - #v2, \ - #v3, \ - pred, \ - v1, \ - v2, \ - v3), on_failure) - -// Ternary predicate assertion macros. -#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT3(pred_format, v1, v2, v3) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT3_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define EXPECT_PRED3(pred, v1, v2, v3) \ - GTEST_PRED3_(pred, v1, v2, v3, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT3(pred_format, v1, v2, v3) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT3_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED3(pred, v1, v2, v3) \ - GTEST_PRED3_(pred, v1, v2, v3, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) - - - -// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED4. Don't use -// this in your code. -template <typename Pred, - typename T1, - typename T2, - typename T3, - typename T4> -AssertionResult AssertPred4Helper(const char* pred_text, - const char* e1, - const char* e2, - const char* e3, - const char* e4, - Pred pred, - const T1& v1, - const T2& v2, - const T3& v3, - const T4& v4) { - if (pred(v1, v2, v3, v4)) return AssertionSuccess(); - - return AssertionFailure() << pred_text << "(" - << e1 << ", " - << e2 << ", " - << e3 << ", " - << e4 << ") evaluates to false, where" - << "\n" << e1 << " evaluates to " << v1 - << "\n" << e2 << " evaluates to " << v2 - << "\n" << e3 << " evaluates to " << v3 - << "\n" << e4 << " evaluates to " << v4; -} - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT4. -// Don't use this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT4_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, #v2, #v3, #v4, v1, v2, v3, v4), \ - on_failure) - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED4. Don't use -// this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED4_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred4Helper(#pred, \ - #v1, \ - #v2, \ - #v3, \ - #v4, \ - pred, \ - v1, \ - v2, \ - v3, \ - v4), on_failure) - -// 4-ary predicate assertion macros. -#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT4(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT4_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define EXPECT_PRED4(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4) \ - GTEST_PRED4_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT4(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT4_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED4(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4) \ - GTEST_PRED4_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) - - - -// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED5. Don't use -// this in your code. -template <typename Pred, - typename T1, - typename T2, - typename T3, - typename T4, - typename T5> -AssertionResult AssertPred5Helper(const char* pred_text, - const char* e1, - const char* e2, - const char* e3, - const char* e4, - const char* e5, - Pred pred, - const T1& v1, - const T2& v2, - const T3& v3, - const T4& v4, - const T5& v5) { - if (pred(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5)) return AssertionSuccess(); - - return AssertionFailure() << pred_text << "(" - << e1 << ", " - << e2 << ", " - << e3 << ", " - << e4 << ", " - << e5 << ") evaluates to false, where" - << "\n" << e1 << " evaluates to " << v1 - << "\n" << e2 << " evaluates to " << v2 - << "\n" << e3 << " evaluates to " << v3 - << "\n" << e4 << " evaluates to " << v4 - << "\n" << e5 << " evaluates to " << v5; -} - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT5. -// Don't use this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT5_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, #v2, #v3, #v4, #v5, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5), \ - on_failure) - -// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED5. Don't use -// this in your code. -#define GTEST_PRED5_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, on_failure)\ - GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred5Helper(#pred, \ - #v1, \ - #v2, \ - #v3, \ - #v4, \ - #v5, \ - pred, \ - v1, \ - v2, \ - v3, \ - v4, \ - v5), on_failure) - -// 5-ary predicate assertion macros. -#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT5(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT5_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define EXPECT_PRED5(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5) \ - GTEST_PRED5_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT5(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5) \ - GTEST_PRED_FORMAT5_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) -#define ASSERT_PRED5(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5) \ - GTEST_PRED5_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) - - - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRED_IMPL_H_ - -// Macros for testing equalities and inequalities. -// -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ(expected, actual): Tests that expected == actual -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NE(v1, v2): Tests that v1 != v2 -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LT(v1, v2): Tests that v1 < v2 -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LE(v1, v2): Tests that v1 <= v2 -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GT(v1, v2): Tests that v1 > v2 -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GE(v1, v2): Tests that v1 >= v2 -// -// When they are not, Google Test prints both the tested expressions and -// their actual values. The values must be compatible built-in types, -// or you will get a compiler error. By "compatible" we mean that the -// values can be compared by the respective operator. -// -// Note: -// -// 1. It is possible to make a user-defined type work with -// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_??(), but that requires overloading the -// comparison operators and is thus discouraged by the Google C++ -// Usage Guide. Therefore, you are advised to use the -// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_TRUE() macro to assert that two objects are -// equal. -// -// 2. The {ASSERT|EXPECT}_??() macros do pointer comparisons on -// pointers (in particular, C strings). Therefore, if you use it -// with two C strings, you are testing how their locations in memory -// are related, not how their content is related. To compare two C -// strings by content, use {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STR*(). -// -// 3. {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ(expected, actual) is preferred to -// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_TRUE(expected == actual), as the former tells you -// what the actual value is when it fails, and similarly for the -// other comparisons. -// -// 4. Do not depend on the order in which {ASSERT|EXPECT}_??() -// evaluate their arguments, which is undefined. -// -// 5. These macros evaluate their arguments exactly once. -// -// Examples: -// -// EXPECT_NE(5, Foo()); -// EXPECT_EQ(NULL, a_pointer); -// ASSERT_LT(i, array_size); -// ASSERT_GT(records.size(), 0) << "There is no record left."; - -#define EXPECT_EQ(expected, actual) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal:: \ - EqHelper<GTEST_IS_NULL_LITERAL_(expected)>::Compare, \ - expected, actual) -#define EXPECT_NE(expected, actual) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperNE, expected, actual) -#define EXPECT_LE(val1, val2) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperLE, val1, val2) -#define EXPECT_LT(val1, val2) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperLT, val1, val2) -#define EXPECT_GE(val1, val2) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperGE, val1, val2) -#define EXPECT_GT(val1, val2) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperGT, val1, val2) - -#define GTEST_ASSERT_EQ(expected, actual) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal:: \ - EqHelper<GTEST_IS_NULL_LITERAL_(expected)>::Compare, \ - expected, actual) -#define GTEST_ASSERT_NE(val1, val2) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperNE, val1, val2) -#define GTEST_ASSERT_LE(val1, val2) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperLE, val1, val2) -#define GTEST_ASSERT_LT(val1, val2) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperLT, val1, val2) -#define GTEST_ASSERT_GE(val1, val2) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperGE, val1, val2) -#define GTEST_ASSERT_GT(val1, val2) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperGT, val1, val2) - -// Define macro GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_XY to 1 to omit the definition of -// ASSERT_XY(), which clashes with some users' own code. - -#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_EQ -# define ASSERT_EQ(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_EQ(val1, val2) -#endif - -#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_NE -# define ASSERT_NE(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_NE(val1, val2) -#endif - -#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_LE -# define ASSERT_LE(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_LE(val1, val2) -#endif - -#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_LT -# define ASSERT_LT(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_LT(val1, val2) -#endif - -#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_GE -# define ASSERT_GE(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_GE(val1, val2) -#endif - -#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_GT -# define ASSERT_GT(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_GT(val1, val2) -#endif - -// C-string Comparisons. All tests treat NULL and any non-NULL string -// as different. Two NULLs are equal. -// -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STREQ(s1, s2): Tests that s1 == s2 -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRNE(s1, s2): Tests that s1 != s2 -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASEEQ(s1, s2): Tests that s1 == s2, ignoring case -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASENE(s1, s2): Tests that s1 != s2, ignoring case -// -// For wide or narrow string objects, you can use the -// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_??() macros. -// -// Don't depend on the order in which the arguments are evaluated, -// which is undefined. -// -// These macros evaluate their arguments exactly once. - -#define EXPECT_STREQ(expected, actual) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTREQ, expected, actual) -#define EXPECT_STRNE(s1, s2) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRNE, s1, s2) -#define EXPECT_STRCASEEQ(expected, actual) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRCASEEQ, expected, actual) -#define EXPECT_STRCASENE(s1, s2)\ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRCASENE, s1, s2) - -#define ASSERT_STREQ(expected, actual) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTREQ, expected, actual) -#define ASSERT_STRNE(s1, s2) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRNE, s1, s2) -#define ASSERT_STRCASEEQ(expected, actual) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRCASEEQ, expected, actual) -#define ASSERT_STRCASENE(s1, s2)\ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRCASENE, s1, s2) - -// Macros for comparing floating-point numbers. -// -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_FLOAT_EQ(expected, actual): -// Tests that two float values are almost equal. -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_DOUBLE_EQ(expected, actual): -// Tests that two double values are almost equal. -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NEAR(v1, v2, abs_error): -// Tests that v1 and v2 are within the given distance to each other. -// -// Google Test uses ULP-based comparison to automatically pick a default -// error bound that is appropriate for the operands. See the -// FloatingPoint template class in gtest-internal.h if you are -// interested in the implementation details. - -#define EXPECT_FLOAT_EQ(expected, actual)\ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ<float>, \ - expected, actual) - -#define EXPECT_DOUBLE_EQ(expected, actual)\ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ<double>, \ - expected, actual) - -#define ASSERT_FLOAT_EQ(expected, actual)\ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ<float>, \ - expected, actual) - -#define ASSERT_DOUBLE_EQ(expected, actual)\ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ<double>, \ - expected, actual) - -#define EXPECT_NEAR(val1, val2, abs_error)\ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT3(::testing::internal::DoubleNearPredFormat, \ - val1, val2, abs_error) - -#define ASSERT_NEAR(val1, val2, abs_error)\ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT3(::testing::internal::DoubleNearPredFormat, \ - val1, val2, abs_error) - -// These predicate format functions work on floating-point values, and -// can be used in {ASSERT|EXPECT}_PRED_FORMAT2*(), e.g. -// -// EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(testing::DoubleLE, Foo(), 5.0); - -// Asserts that val1 is less than, or almost equal to, val2. Fails -// otherwise. In particular, it fails if either val1 or val2 is NaN. -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult FloatLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, - float val1, float val2); -GTEST_API_ AssertionResult DoubleLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, - double val1, double val2); - - -#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - -// Macros that test for HRESULT failure and success, these are only useful -// on Windows, and rely on Windows SDK macros and APIs to compile. -// -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_HRESULT_{SUCCEEDED|FAILED}(expr) -// -// When expr unexpectedly fails or succeeds, Google Test prints the -// expected result and the actual result with both a human-readable -// string representation of the error, if available, as well as the -// hex result code. -# define EXPECT_HRESULT_SUCCEEDED(expr) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(::testing::internal::IsHRESULTSuccess, (expr)) - -# define ASSERT_HRESULT_SUCCEEDED(expr) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(::testing::internal::IsHRESULTSuccess, (expr)) - -# define EXPECT_HRESULT_FAILED(expr) \ - EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(::testing::internal::IsHRESULTFailure, (expr)) - -# define ASSERT_HRESULT_FAILED(expr) \ - ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(::testing::internal::IsHRESULTFailure, (expr)) - -#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - -// Macros that execute statement and check that it doesn't generate new fatal -// failures in the current thread. -// -// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(statement); -// -// Examples: -// -// EXPECT_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(Process()); -// ASSERT_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(Process()) << "Process() failed"; -// -#define ASSERT_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(statement) \ - GTEST_TEST_NO_FATAL_FAILURE_(statement, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) -#define EXPECT_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(statement) \ - GTEST_TEST_NO_FATAL_FAILURE_(statement, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) - -// Causes a trace (including the source file path, the current line -// number, and the given message) to be included in every test failure -// message generated by code in the current scope. The effect is -// undone when the control leaves the current scope. -// -// The message argument can be anything streamable to std::ostream. -// -// In the implementation, we include the current line number as part -// of the dummy variable name, thus allowing multiple SCOPED_TRACE()s -// to appear in the same block - as long as they are on different -// lines. -#define SCOPED_TRACE(message) \ - ::testing::internal::ScopedTrace GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_trace_, __LINE__)(\ - __FILE__, __LINE__, ::testing::Message() << (message)) - -// Compile-time assertion for type equality. -// StaticAssertTypeEq<type1, type2>() compiles iff type1 and type2 are -// the same type. The value it returns is not interesting. -// -// Instead of making StaticAssertTypeEq a class template, we make it a -// function template that invokes a helper class template. This -// prevents a user from misusing StaticAssertTypeEq<T1, T2> by -// defining objects of that type. -// -// CAVEAT: -// -// When used inside a method of a class template, -// StaticAssertTypeEq<T1, T2>() is effective ONLY IF the method is -// instantiated. For example, given: -// -// template <typename T> class Foo { -// public: -// void Bar() { testing::StaticAssertTypeEq<int, T>(); } -// }; -// -// the code: -// -// void Test1() { Foo<bool> foo; } -// -// will NOT generate a compiler error, as Foo<bool>::Bar() is never -// actually instantiated. Instead, you need: -// -// void Test2() { Foo<bool> foo; foo.Bar(); } -// -// to cause a compiler error. -template <typename T1, typename T2> -bool StaticAssertTypeEq() { - (void)internal::StaticAssertTypeEqHelper<T1, T2>(); - return true; -} - -// Defines a test. -// -// The first parameter is the name of the test case, and the second -// parameter is the name of the test within the test case. -// -// The convention is to end the test case name with "Test". For -// example, a test case for the Foo class can be named FooTest. -// -// The user should put his test code between braces after using this -// macro. Example: -// -// TEST(FooTest, InitializesCorrectly) { -// Foo foo; -// EXPECT_TRUE(foo.StatusIsOK()); -// } - -// Note that we call GetTestTypeId() instead of GetTypeId< -// ::testing::Test>() here to get the type ID of testing::Test. This -// is to work around a suspected linker bug when using Google Test as -// a framework on Mac OS X. The bug causes GetTypeId< -// ::testing::Test>() to return different values depending on whether -// the call is from the Google Test framework itself or from user test -// code. GetTestTypeId() is guaranteed to always return the same -// value, as it always calls GetTypeId<>() from the Google Test -// framework. -#define GTEST_TEST(test_case_name, test_name)\ - GTEST_TEST_(test_case_name, test_name, \ - ::testing::Test, ::testing::internal::GetTestTypeId()) - -// Define this macro to 1 to omit the definition of TEST(), which -// is a generic name and clashes with some other libraries. -#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_TEST -# define TEST(test_case_name, test_name) GTEST_TEST(test_case_name, test_name) -#endif - -// Defines a test that uses a test fixture. -// -// The first parameter is the name of the test fixture class, which -// also doubles as the test case name. The second parameter is the -// name of the test within the test case. -// -// A test fixture class must be declared earlier. The user should put -// his test code between braces after using this macro. Example: -// -// class FooTest : public testing::Test { -// protected: -// virtual void SetUp() { b_.AddElement(3); } -// -// Foo a_; -// Foo b_; -// }; -// -// TEST_F(FooTest, InitializesCorrectly) { -// EXPECT_TRUE(a_.StatusIsOK()); -// } -// -// TEST_F(FooTest, ReturnsElementCountCorrectly) { -// EXPECT_EQ(0, a_.size()); -// EXPECT_EQ(1, b_.size()); -// } - -#define TEST_F(test_fixture, test_name)\ - GTEST_TEST_(test_fixture, test_name, test_fixture, \ - ::testing::internal::GetTypeId<test_fixture>()) - -} // namespace testing - -// Use this function in main() to run all tests. It returns 0 if all -// tests are successful, or 1 otherwise. -// -// RUN_ALL_TESTS() should be invoked after the command line has been -// parsed by InitGoogleTest(). -// -// This function was formerly a macro; thus, it is in the global -// namespace and has an all-caps name. -int RUN_ALL_TESTS() GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_; - -inline int RUN_ALL_TESTS() { - return ::testing::UnitTest::GetInstance()->Run(); -} - -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_H_ diff --git a/test/gtest/gtest-spi.h b/test/gtest/gtest/gtest-spi.h index f63fa9a1..eacef446 100644 --- a/test/gtest/gtest-spi.h +++ b/test/gtest/gtest/gtest-spi.h @@ -26,17 +26,21 @@ // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. -// -// Author: wan@google.com (Zhanyong Wan) + // // Utilities for testing Google Test itself and code that uses Google Test // (e.g. frameworks built on top of Google Test). -#ifndef GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ -#define GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ +// GOOGLETEST_CM0004 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ #include "gtest/gtest.h" +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) + namespace testing { // This helper class can be used to mock out Google Test failure reporting @@ -68,14 +72,15 @@ class GTEST_API_ ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter TestPartResultArray* result); // The d'tor restores the previous test part result reporter. - virtual ~ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter(); + ~ScopedFakeTestPartResultReporter() override; // Appends the TestPartResult object to the TestPartResultArray // received in the constructor. // // This method is from the TestPartResultReporterInterface // interface. - virtual void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result); + void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) override; + private: void Init(); @@ -97,13 +102,12 @@ class GTEST_API_ SingleFailureChecker { public: // The constructor remembers the arguments. SingleFailureChecker(const TestPartResultArray* results, - TestPartResult::Type type, - const string& substr); + TestPartResult::Type type, const std::string& substr); ~SingleFailureChecker(); private: const TestPartResultArray* const results_; const TestPartResult::Type type_; - const string substr_; + const std::string substr_; GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(SingleFailureChecker); }; @@ -112,6 +116,8 @@ class GTEST_API_ SingleFailureChecker { } // namespace testing +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + // A set of macros for testing Google Test assertions or code that's expected // to generate Google Test fatal failures. It verifies that the given // statement will cause exactly one fatal Google Test failure with 'substr' @@ -229,4 +235,4 @@ class GTEST_API_ SingleFailureChecker { }\ } while (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) -#endif // GTEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_SPI_H_ diff --git a/test/gtest/gtest/gtest.h b/test/gtest/gtest/gtest.h new file mode 100644 index 00000000..55a31d0a --- /dev/null +++ b/test/gtest/gtest/gtest.h @@ -0,0 +1,12398 @@ +// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// This header file defines the public API for Google Test. It should be +// included by any test program that uses Google Test. +// +// IMPORTANT NOTE: Due to limitation of the C++ language, we have to +// leave some internal implementation details in this header file. +// They are clearly marked by comments like this: +// +// // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +// +// Such code is NOT meant to be used by a user directly, and is subject +// to CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. Therefore DO NOT DEPEND ON IT in a user +// program! +// +// Acknowledgment: Google Test borrowed the idea of automatic test +// registration from Barthelemy Dagenais' (barthelemy@prologique.com) +// easyUnit framework. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_H_ + +#include <cstddef> +#include <limits> +#include <memory> +#include <ostream> +#include <type_traits> +#include <vector> + +// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// This header file declares functions and macros used internally by +// Google Test. They are subject to change without notice. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_INTERNAL_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_INTERNAL_H_ + +// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// Low-level types and utilities for porting Google Test to various +// platforms. All macros ending with _ and symbols defined in an +// internal namespace are subject to change without notice. Code +// outside Google Test MUST NOT USE THEM DIRECTLY. Macros that don't +// end with _ are part of Google Test's public API and can be used by +// code outside Google Test. +// +// This file is fundamental to Google Test. All other Google Test source +// files are expected to #include this. Therefore, it cannot #include +// any other Google Test header. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_H_ + +// Environment-describing macros +// ----------------------------- +// +// Google Test can be used in many different environments. Macros in +// this section tell Google Test what kind of environment it is being +// used in, such that Google Test can provide environment-specific +// features and implementations. +// +// Google Test tries to automatically detect the properties of its +// environment, so users usually don't need to worry about these +// macros. However, the automatic detection is not perfect. +// Sometimes it's necessary for a user to define some of the following +// macros in the build script to override Google Test's decisions. +// +// If the user doesn't define a macro in the list, Google Test will +// provide a default definition. After this header is #included, all +// macros in this list will be defined to either 1 or 0. +// +// Notes to maintainers: +// - Each macro here is a user-tweakable knob; do not grow the list +// lightly. +// - Use #if to key off these macros. Don't use #ifdef or "#if +// defined(...)", which will not work as these macros are ALWAYS +// defined. +// +// GTEST_HAS_CLONE - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that clone(2) +// is/isn't available. +// GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that exceptions +// are enabled. +// GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that POSIX regular +// expressions are/aren't available. +// GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that <pthread.h> +// is/isn't available. +// GTEST_HAS_RTTI - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that RTTI is/isn't +// enabled. +// GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING - Define it to 1/0 to indicate that +// std::wstring does/doesn't work (Google Test can +// be used where std::wstring is unavailable). +// GTEST_HAS_SEH - Define it to 1/0 to indicate whether the +// compiler supports Microsoft's "Structured +// Exception Handling". +// GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION +// - Define it to 1/0 to indicate whether the +// platform supports I/O stream redirection using +// dup() and dup2(). +// GTEST_LINKED_AS_SHARED_LIBRARY +// - Define to 1 when compiling tests that use +// Google Test as a shared library (known as +// DLL on Windows). +// GTEST_CREATE_SHARED_LIBRARY +// - Define to 1 when compiling Google Test itself +// as a shared library. +// GTEST_DEFAULT_DEATH_TEST_STYLE +// - The default value of --gtest_death_test_style. +// The legacy default has been "fast" in the open +// source version since 2008. The recommended value +// is "threadsafe", and can be set in +// custom/gtest-port.h. + +// Platform-indicating macros +// -------------------------- +// +// Macros indicating the platform on which Google Test is being used +// (a macro is defined to 1 if compiled on the given platform; +// otherwise UNDEFINED -- it's never defined to 0.). Google Test +// defines these macros automatically. Code outside Google Test MUST +// NOT define them. +// +// GTEST_OS_AIX - IBM AIX +// GTEST_OS_CYGWIN - Cygwin +// GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY - DragonFlyBSD +// GTEST_OS_FREEBSD - FreeBSD +// GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA - Fuchsia +// GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD - GNU/kFreeBSD +// GTEST_OS_HAIKU - Haiku +// GTEST_OS_HPUX - HP-UX +// GTEST_OS_LINUX - Linux +// GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID - Google Android +// GTEST_OS_MAC - Mac OS X +// GTEST_OS_IOS - iOS +// GTEST_OS_NACL - Google Native Client (NaCl) +// GTEST_OS_NETBSD - NetBSD +// GTEST_OS_OPENBSD - OpenBSD +// GTEST_OS_OS2 - OS/2 +// GTEST_OS_QNX - QNX +// GTEST_OS_SOLARIS - Sun Solaris +// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS - Windows (Desktop, MinGW, or Mobile) +// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP - Windows Desktop +// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW - MinGW +// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE - Windows Mobile +// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE - Windows Phone +// GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT - Windows Store App/WinRT +// GTEST_OS_ZOS - z/OS +// +// Among the platforms, Cygwin, Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows have the +// most stable support. Since core members of the Google Test project +// don't have access to other platforms, support for them may be less +// stable. If you notice any problems on your platform, please notify +// googletestframework@googlegroups.com (patches for fixing them are +// even more welcome!). +// +// It is possible that none of the GTEST_OS_* macros are defined. + +// Feature-indicating macros +// ------------------------- +// +// Macros indicating which Google Test features are available (a macro +// is defined to 1 if the corresponding feature is supported; +// otherwise UNDEFINED -- it's never defined to 0.). Google Test +// defines these macros automatically. Code outside Google Test MUST +// NOT define them. +// +// These macros are public so that portable tests can be written. +// Such tests typically surround code using a feature with an #if +// which controls that code. For example: +// +// #if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +// EXPECT_DEATH(DoSomethingDeadly()); +// #endif +// +// GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST - death tests +// GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST - typed tests +// GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P - type-parameterized tests +// GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE - Google Test is thread-safe. +// GOOGLETEST_CM0007 DO NOT DELETE +// GTEST_USES_POSIX_RE - enhanced POSIX regex is used. Do not confuse with +// GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE (see above) which users can +// define themselves. +// GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE - our own simple regex is used; +// the above RE\b(s) are mutually exclusive. + +// Misc public macros +// ------------------ +// +// GTEST_FLAG(flag_name) - references the variable corresponding to +// the given Google Test flag. + +// Internal utilities +// ------------------ +// +// The following macros and utilities are for Google Test's INTERNAL +// use only. Code outside Google Test MUST NOT USE THEM DIRECTLY. +// +// Macros for basic C++ coding: +// GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ - for disabling a gcc warning. +// GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ - declares that a class' instances or a +// variable don't have to be used. +// GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_ - disables copy operator=. +// GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_ - disables copy ctor and operator=. +// GTEST_DISALLOW_MOVE_ASSIGN_ - disables move operator=. +// GTEST_DISALLOW_MOVE_AND_ASSIGN_ - disables move ctor and operator=. +// GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_ - declares that a function's result must be used. +// GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_PUSH_ - start code section where MSVC C4127 is +// suppressed (constant conditional). +// GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_POP_ - finish code section where MSVC C4127 +// is suppressed. +// GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_ANY - for enabling UniversalPrinter<std::any> or +// UniversalPrinter<absl::any> specializations. +// GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_OPTIONAL - for enabling UniversalPrinter<std::optional> +// or +// UniversalPrinter<absl::optional> +// specializations. +// GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW - for enabling Matcher<std::string_view> or +// Matcher<absl::string_view> +// specializations. +// GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_VARIANT - for enabling UniversalPrinter<std::variant> or +// UniversalPrinter<absl::variant> +// specializations. +// +// Synchronization: +// Mutex, MutexLock, ThreadLocal, GetThreadCount() +// - synchronization primitives. +// +// Regular expressions: +// RE - a simple regular expression class using the POSIX +// Extended Regular Expression syntax on UNIX-like platforms +// GOOGLETEST_CM0008 DO NOT DELETE +// or a reduced regular exception syntax on other +// platforms, including Windows. +// Logging: +// GTEST_LOG_() - logs messages at the specified severity level. +// LogToStderr() - directs all log messages to stderr. +// FlushInfoLog() - flushes informational log messages. +// +// Stdout and stderr capturing: +// CaptureStdout() - starts capturing stdout. +// GetCapturedStdout() - stops capturing stdout and returns the captured +// string. +// CaptureStderr() - starts capturing stderr. +// GetCapturedStderr() - stops capturing stderr and returns the captured +// string. +// +// Integer types: +// TypeWithSize - maps an integer to a int type. +// TimeInMillis - integers of known sizes. +// BiggestInt - the biggest signed integer type. +// +// Command-line utilities: +// GTEST_DECLARE_*() - declares a flag. +// GTEST_DEFINE_*() - defines a flag. +// GetInjectableArgvs() - returns the command line as a vector of strings. +// +// Environment variable utilities: +// GetEnv() - gets the value of an environment variable. +// BoolFromGTestEnv() - parses a bool environment variable. +// Int32FromGTestEnv() - parses an int32_t environment variable. +// StringFromGTestEnv() - parses a string environment variable. +// +// Deprecation warnings: +// GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED(message) - attribute marking a function as +// deprecated; calling a marked function +// should generate a compiler warning + +#include <ctype.h> // for isspace, etc +#include <stddef.h> // for ptrdiff_t +#include <stdio.h> +#include <stdlib.h> +#include <string.h> + +#include <cerrno> +#include <cstdint> +#include <limits> +#include <type_traits> + +#ifndef _WIN32_WCE +# include <sys/types.h> +# include <sys/stat.h> +#endif // !_WIN32_WCE + +#if defined __APPLE__ +# include <AvailabilityMacros.h> +# include <TargetConditionals.h> +#endif + +#include <iostream> // NOLINT +#include <locale> +#include <memory> +#include <string> // NOLINT +#include <tuple> +#include <vector> // NOLINT + +// Copyright 2015, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// Injection point for custom user configurations. See README for details +// +// ** Custom implementation starts here ** + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GTEST_PORT_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GTEST_PORT_H_ + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GTEST_PORT_H_ +// Copyright 2015, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// This header file defines the GTEST_OS_* macro. +// It is separate from gtest-port.h so that custom/gtest-port.h can include it. + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_ARCH_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_ARCH_H_ + +// Determines the platform on which Google Test is compiled. +#ifdef __CYGWIN__ +# define GTEST_OS_CYGWIN 1 +# elif defined(__MINGW__) || defined(__MINGW32__) || defined(__MINGW64__) +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW 1 +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS 1 +#elif defined _WIN32 +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS 1 +# ifdef _WIN32_WCE +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE 1 +# elif defined(WINAPI_FAMILY) +# include <winapifamily.h> +# if WINAPI_FAMILY_PARTITION(WINAPI_PARTITION_DESKTOP) +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP 1 +# elif WINAPI_FAMILY_PARTITION(WINAPI_PARTITION_PHONE_APP) +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE 1 +# elif WINAPI_FAMILY_PARTITION(WINAPI_PARTITION_APP) +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT 1 +# elif WINAPI_FAMILY_PARTITION(WINAPI_PARTITION_TV_TITLE) +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE 1 +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_TV_TITLE 1 +# else + // WINAPI_FAMILY defined but no known partition matched. + // Default to desktop. +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP 1 +# endif +# else +# define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP 1 +# endif // _WIN32_WCE +#elif defined __OS2__ +# define GTEST_OS_OS2 1 +#elif defined __APPLE__ +# define GTEST_OS_MAC 1 +# include <TargetConditionals.h> +# if TARGET_OS_IPHONE +# define GTEST_OS_IOS 1 +# endif +#elif defined __DragonFly__ +# define GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY 1 +#elif defined __FreeBSD__ +# define GTEST_OS_FREEBSD 1 +#elif defined __Fuchsia__ +# define GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA 1 +#elif defined(__GLIBC__) && defined(__FreeBSD_kernel__) +# define GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD 1 +#elif defined __linux__ +# define GTEST_OS_LINUX 1 +# if defined __ANDROID__ +# define GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID 1 +# endif +#elif defined __MVS__ +# define GTEST_OS_ZOS 1 +#elif defined(__sun) && defined(__SVR4) +# define GTEST_OS_SOLARIS 1 +#elif defined(_AIX) +# define GTEST_OS_AIX 1 +#elif defined(__hpux) +# define GTEST_OS_HPUX 1 +#elif defined __native_client__ +# define GTEST_OS_NACL 1 +#elif defined __NetBSD__ +# define GTEST_OS_NETBSD 1 +#elif defined __OpenBSD__ +# define GTEST_OS_OPENBSD 1 +#elif defined __QNX__ +# define GTEST_OS_QNX 1 +#elif defined(__HAIKU__) +#define GTEST_OS_HAIKU 1 +#elif defined ESP8266 +#define GTEST_OS_ESP8266 1 +#elif defined ESP32 +#define GTEST_OS_ESP32 1 +#elif defined(__XTENSA__) +#define GTEST_OS_XTENSA 1 +#endif // __CYGWIN__ + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_ARCH_H_ + +#if !defined(GTEST_DEV_EMAIL_) +# define GTEST_DEV_EMAIL_ "googletestframework@@googlegroups.com" +# define GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_ "gtest_" +# define GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_DASH_ "gtest-" +# define GTEST_FLAG_PREFIX_UPPER_ "GTEST_" +# define GTEST_NAME_ "Google Test" +# define GTEST_PROJECT_URL_ "https://github.com/google/googletest/" +#endif // !defined(GTEST_DEV_EMAIL_) + +#if !defined(GTEST_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_NAME_) +# define GTEST_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_NAME_ "testing::InitGoogleTest" +#endif // !defined(GTEST_INIT_GOOGLE_TEST_NAME_) + +// Determines the version of gcc that is used to compile this. +#ifdef __GNUC__ +// 40302 means version 4.3.2. +# define GTEST_GCC_VER_ \ + (__GNUC__*10000 + __GNUC_MINOR__*100 + __GNUC_PATCHLEVEL__) +#endif // __GNUC__ + +// Macros for disabling Microsoft Visual C++ warnings. +// +// GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4800 4385) +// /* code that triggers warnings C4800 and C4385 */ +// GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() +#if defined(_MSC_VER) +# define GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(warnings) \ + __pragma(warning(push)) \ + __pragma(warning(disable: warnings)) +# define GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() \ + __pragma(warning(pop)) +#else +// Not all compilers are MSVC +# define GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(warnings) +# define GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() +#endif + +// Clang on Windows does not understand MSVC's pragma warning. +// We need clang-specific way to disable function deprecation warning. +#ifdef __clang__ +# define GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_DEPRECATED_PUSH_() \ + _Pragma("clang diagnostic push") \ + _Pragma("clang diagnostic ignored \"-Wdeprecated-declarations\"") \ + _Pragma("clang diagnostic ignored \"-Wdeprecated-implementations\"") +#define GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_DEPRECATED_POP_() \ + _Pragma("clang diagnostic pop") +#else +# define GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_DEPRECATED_PUSH_() \ + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4996) +# define GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_DEPRECATED_POP_() \ + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() +#endif + +// Brings in definitions for functions used in the testing::internal::posix +// namespace (read, write, close, chdir, isatty, stat). We do not currently +// use them on Windows Mobile. +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +# include <direct.h> +# include <io.h> +# endif +// In order to avoid having to include <windows.h>, use forward declaration +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW && !defined(__MINGW64_VERSION_MAJOR) +// MinGW defined _CRITICAL_SECTION and _RTL_CRITICAL_SECTION as two +// separate (equivalent) structs, instead of using typedef +typedef struct _CRITICAL_SECTION GTEST_CRITICAL_SECTION; +#else +// Assume CRITICAL_SECTION is a typedef of _RTL_CRITICAL_SECTION. +// This assumption is verified by +// WindowsTypesTest.CRITICAL_SECTIONIs_RTL_CRITICAL_SECTION. +typedef struct _RTL_CRITICAL_SECTION GTEST_CRITICAL_SECTION; +#endif +#elif GTEST_OS_XTENSA +#include <unistd.h> +// Xtensa toolchains define strcasecmp in the string.h header instead of +// strings.h. string.h is already included. +#else +// This assumes that non-Windows OSes provide unistd.h. For OSes where this +// is not the case, we need to include headers that provide the functions +// mentioned above. +# include <unistd.h> +# include <strings.h> +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +#if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID +// Used to define __ANDROID_API__ matching the target NDK API level. +# include <android/api-level.h> // NOLINT +#endif + +// Defines this to true if and only if Google Test can use POSIX regular +// expressions. +#ifndef GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE +# if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID +// On Android, <regex.h> is only available starting with Gingerbread. +# define GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE (__ANDROID_API__ >= 9) +# else +#define GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE (!GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_XTENSA) +# endif +#endif + +#if GTEST_USES_PCRE +// The appropriate headers have already been included. + +#elif GTEST_HAS_POSIX_RE + +// On some platforms, <regex.h> needs someone to define size_t, and +// won't compile otherwise. We can #include it here as we already +// included <stdlib.h>, which is guaranteed to define size_t through +// <stddef.h>. +# include <regex.h> // NOLINT + +# define GTEST_USES_POSIX_RE 1 + +#elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +// <regex.h> is not available on Windows. Use our own simple regex +// implementation instead. +# define GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE 1 + +#else + +// <regex.h> may not be available on this platform. Use our own +// simple regex implementation instead. +# define GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE 1 + +#endif // GTEST_USES_PCRE + +#ifndef GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS +// The user didn't tell us whether exceptions are enabled, so we need +// to figure it out. +# if defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_CPPUNWIND) +// MSVC defines _CPPUNWIND to 1 if and only if exceptions are enabled. +# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 +# elif defined(__BORLANDC__) +// C++Builder's implementation of the STL uses the _HAS_EXCEPTIONS +// macro to enable exceptions, so we'll do the same. +// Assumes that exceptions are enabled by default. +# ifndef _HAS_EXCEPTIONS +# define _HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 +# endif // _HAS_EXCEPTIONS +# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS _HAS_EXCEPTIONS +# elif defined(__clang__) +// clang defines __EXCEPTIONS if and only if exceptions are enabled before clang +// 220714, but if and only if cleanups are enabled after that. In Obj-C++ files, +// there can be cleanups for ObjC exceptions which also need cleanups, even if +// C++ exceptions are disabled. clang has __has_feature(cxx_exceptions) which +// checks for C++ exceptions starting at clang r206352, but which checked for +// cleanups prior to that. To reliably check for C++ exception availability with +// clang, check for +// __EXCEPTIONS && __has_feature(cxx_exceptions). +# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS (__EXCEPTIONS && __has_feature(cxx_exceptions)) +# elif defined(__GNUC__) && __EXCEPTIONS +// gcc defines __EXCEPTIONS to 1 if and only if exceptions are enabled. +# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 +# elif defined(__SUNPRO_CC) +// Sun Pro CC supports exceptions. However, there is no compile-time way of +// detecting whether they are enabled or not. Therefore, we assume that +// they are enabled unless the user tells us otherwise. +# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 +# elif defined(__IBMCPP__) && __EXCEPTIONS +// xlC defines __EXCEPTIONS to 1 if and only if exceptions are enabled. +# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 +# elif defined(__HP_aCC) +// Exception handling is in effect by default in HP aCC compiler. It has to +// be turned of by +noeh compiler option if desired. +# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 1 +# else +// For other compilers, we assume exceptions are disabled to be +// conservative. +# define GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS 0 +# endif // defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(__BORLANDC__) +#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +#ifndef GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING +// The user didn't tell us whether ::std::wstring is available, so we need +// to figure it out. +// Cygwin 1.7 and below doesn't support ::std::wstring. +// Solaris' libc++ doesn't support it either. Android has +// no support for it at least as recent as Froyo (2.2). +#define GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING \ + (!(GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID || GTEST_OS_CYGWIN || GTEST_OS_SOLARIS || \ + GTEST_OS_HAIKU || GTEST_OS_ESP32 || GTEST_OS_ESP8266 || GTEST_OS_XTENSA)) + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING + +// Determines whether RTTI is available. +#ifndef GTEST_HAS_RTTI +// The user didn't tell us whether RTTI is enabled, so we need to +// figure it out. + +# ifdef _MSC_VER + +#ifdef _CPPRTTI // MSVC defines this macro if and only if RTTI is enabled. +# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 1 +# else +# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 0 +# endif + +// Starting with version 4.3.2, gcc defines __GXX_RTTI if and only if RTTI is +// enabled. +# elif defined(__GNUC__) + +# ifdef __GXX_RTTI +// When building against STLport with the Android NDK and with +// -frtti -fno-exceptions, the build fails at link time with undefined +// references to __cxa_bad_typeid. Note sure if STL or toolchain bug, +// so disable RTTI when detected. +# if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID && defined(_STLPORT_MAJOR) && \ + !defined(__EXCEPTIONS) +# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 0 +# else +# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 1 +# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID && __STLPORT_MAJOR && !__EXCEPTIONS +# else +# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 0 +# endif // __GXX_RTTI + +// Clang defines __GXX_RTTI starting with version 3.0, but its manual recommends +// using has_feature instead. has_feature(cxx_rtti) is supported since 2.7, the +// first version with C++ support. +# elif defined(__clang__) + +# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI __has_feature(cxx_rtti) + +// Starting with version 9.0 IBM Visual Age defines __RTTI_ALL__ to 1 if +// both the typeid and dynamic_cast features are present. +# elif defined(__IBMCPP__) && (__IBMCPP__ >= 900) + +# ifdef __RTTI_ALL__ +# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 1 +# else +# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 0 +# endif + +# else + +// For all other compilers, we assume RTTI is enabled. +# define GTEST_HAS_RTTI 1 + +# endif // _MSC_VER + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI + +// It's this header's responsibility to #include <typeinfo> when RTTI +// is enabled. +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI +# include <typeinfo> +#endif + +// Determines whether Google Test can use the pthreads library. +#ifndef GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD +// The user didn't tell us explicitly, so we make reasonable assumptions about +// which platforms have pthreads support. +// +// To disable threading support in Google Test, add -DGTEST_HAS_PTHREAD=0 +// to your compiler flags. +#define GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD \ + (GTEST_OS_LINUX || GTEST_OS_MAC || GTEST_OS_HPUX || GTEST_OS_QNX || \ + GTEST_OS_FREEBSD || GTEST_OS_NACL || GTEST_OS_NETBSD || GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA || \ + GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY || GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD || GTEST_OS_OPENBSD || \ + GTEST_OS_HAIKU) +#endif // GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD + +#if GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD +// gtest-port.h guarantees to #include <pthread.h> when GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD is +// true. +# include <pthread.h> // NOLINT + +// For timespec and nanosleep, used below. +# include <time.h> // NOLINT +#endif + +// Determines whether clone(2) is supported. +// Usually it will only be available on Linux, excluding +// Linux on the Itanium architecture. +// Also see http://linux.die.net/man/2/clone. +#ifndef GTEST_HAS_CLONE +// The user didn't tell us, so we need to figure it out. + +# if GTEST_OS_LINUX && !defined(__ia64__) +# if GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID +// On Android, clone() became available at different API levels for each 32-bit +// architecture. +# if defined(__LP64__) || \ + (defined(__arm__) && __ANDROID_API__ >= 9) || \ + (defined(__mips__) && __ANDROID_API__ >= 12) || \ + (defined(__i386__) && __ANDROID_API__ >= 17) +# define GTEST_HAS_CLONE 1 +# else +# define GTEST_HAS_CLONE 0 +# endif +# else +# define GTEST_HAS_CLONE 1 +# endif +# else +# define GTEST_HAS_CLONE 0 +# endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX && !defined(__ia64__) + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_CLONE + +// Determines whether to support stream redirection. This is used to test +// output correctness and to implement death tests. +#ifndef GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION +// By default, we assume that stream redirection is supported on all +// platforms except known mobile ones. +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE || \ + GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT || GTEST_OS_ESP8266 || GTEST_OS_XTENSA +# define GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION 0 +# else +# define GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION 1 +# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +#endif // GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION + +// Determines whether to support death tests. +// pops up a dialog window that cannot be suppressed programmatically. +#if (GTEST_OS_LINUX || GTEST_OS_CYGWIN || GTEST_OS_SOLARIS || \ + (GTEST_OS_MAC && !GTEST_OS_IOS) || \ + (GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP && _MSC_VER) || GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW || \ + GTEST_OS_AIX || GTEST_OS_HPUX || GTEST_OS_OPENBSD || GTEST_OS_QNX || \ + GTEST_OS_FREEBSD || GTEST_OS_NETBSD || GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA || \ + GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY || GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD || GTEST_OS_HAIKU) +# define GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST 1 +#endif + +// Determines whether to support type-driven tests. + +// Typed tests need <typeinfo> and variadic macros, which GCC, VC++ 8.0, +// Sun Pro CC, IBM Visual Age, and HP aCC support. +#if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || \ + defined(__IBMCPP__) || defined(__HP_aCC) +# define GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST 1 +# define GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST_P 1 +#endif + +// Determines whether the system compiler uses UTF-16 for encoding wide strings. +#define GTEST_WIDE_STRING_USES_UTF16_ \ + (GTEST_OS_WINDOWS || GTEST_OS_CYGWIN || GTEST_OS_AIX || GTEST_OS_OS2) + +// Determines whether test results can be streamed to a socket. +#if GTEST_OS_LINUX || GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD || GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY || \ + GTEST_OS_FREEBSD || GTEST_OS_NETBSD || GTEST_OS_OPENBSD +# define GTEST_CAN_STREAM_RESULTS_ 1 +#endif + +// Defines some utility macros. + +// The GNU compiler emits a warning if nested "if" statements are followed by +// an "else" statement and braces are not used to explicitly disambiguate the +// "else" binding. This leads to problems with code like: +// +// if (gate) +// ASSERT_*(condition) << "Some message"; +// +// The "switch (0) case 0:" idiom is used to suppress this. +#ifdef __INTEL_COMPILER +# define GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ +#else +# define GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ switch (0) case 0: default: // NOLINT +#endif + +// Use this annotation at the end of a struct/class definition to +// prevent the compiler from optimizing away instances that are never +// used. This is useful when all interesting logic happens inside the +// c'tor and / or d'tor. Example: +// +// struct Foo { +// Foo() { ... } +// } GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; +// +// Also use it after a variable or parameter declaration to tell the +// compiler the variable/parameter does not have to be used. +#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(COMPILER_ICC) +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ __attribute__ ((unused)) +#elif defined(__clang__) +# if __has_attribute(unused) +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ __attribute__ ((unused)) +# endif +#endif +#ifndef GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ +#endif + +// Use this annotation before a function that takes a printf format string. +#if (defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__)) && !defined(COMPILER_ICC) +# if defined(__MINGW_PRINTF_FORMAT) +// MinGW has two different printf implementations. Ensure the format macro +// matches the selected implementation. See +// https://sourceforge.net/p/mingw-w64/wiki2/gnu%20printf/. +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_PRINTF_(string_index, first_to_check) \ + __attribute__((__format__(__MINGW_PRINTF_FORMAT, string_index, \ + first_to_check))) +# else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_PRINTF_(string_index, first_to_check) \ + __attribute__((__format__(__printf__, string_index, first_to_check))) +# endif +#else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_PRINTF_(string_index, first_to_check) +#endif + + +// A macro to disallow copy operator= +// This should be used in the private: declarations for a class. +#define GTEST_DISALLOW_ASSIGN_(type) \ + type& operator=(type const &) = delete + +// A macro to disallow copy constructor and operator= +// This should be used in the private: declarations for a class. +#define GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(type) \ + type(type const&) = delete; \ + type& operator=(type const&) = delete + +// A macro to disallow move operator= +// This should be used in the private: declarations for a class. +#define GTEST_DISALLOW_MOVE_ASSIGN_(type) \ + type& operator=(type &&) noexcept = delete + +// A macro to disallow move constructor and operator= +// This should be used in the private: declarations for a class. +#define GTEST_DISALLOW_MOVE_AND_ASSIGN_(type) \ + type(type&&) noexcept = delete; \ + type& operator=(type&&) noexcept = delete + +// Tell the compiler to warn about unused return values for functions declared +// with this macro. The macro should be used on function declarations +// following the argument list: +// +// Sprocket* AllocateSprocket() GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_; +#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(COMPILER_ICC) +# define GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_ __attribute__ ((warn_unused_result)) +#else +# define GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_ +#endif // __GNUC__ && !COMPILER_ICC + +// MS C++ compiler emits warning when a conditional expression is compile time +// constant. In some contexts this warning is false positive and needs to be +// suppressed. Use the following two macros in such cases: +// +// GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_PUSH_() +// while (true) { +// GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_POP_() +// } +# define GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_PUSH_() \ + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4127) +# define GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_POP_() \ + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() + +// Determine whether the compiler supports Microsoft's Structured Exception +// Handling. This is supported by several Windows compilers but generally +// does not exist on any other system. +#ifndef GTEST_HAS_SEH +// The user didn't tell us, so we need to figure it out. + +# if defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(__BORLANDC__) +// These two compilers are known to support SEH. +# define GTEST_HAS_SEH 1 +# else +// Assume no SEH. +# define GTEST_HAS_SEH 0 +# endif + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_SEH + +#ifndef GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE + +#define GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE \ + (GTEST_HAS_MUTEX_AND_THREAD_LOCAL_ || \ + (GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT) || \ + GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD) + +#endif // GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE + +// GTEST_API_ qualifies all symbols that must be exported. The definitions below +// are guarded by #ifndef to give embedders a chance to define GTEST_API_ in +// gtest/internal/custom/gtest-port.h +#ifndef GTEST_API_ + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# if GTEST_LINKED_AS_SHARED_LIBRARY +# define GTEST_API_ __declspec(dllimport) +# elif GTEST_CREATE_SHARED_LIBRARY +# define GTEST_API_ __declspec(dllexport) +# endif +#elif __GNUC__ >= 4 || defined(__clang__) +# define GTEST_API_ __attribute__((visibility ("default"))) +#endif // _MSC_VER + +#endif // GTEST_API_ + +#ifndef GTEST_API_ +# define GTEST_API_ +#endif // GTEST_API_ + +#ifndef GTEST_DEFAULT_DEATH_TEST_STYLE +# define GTEST_DEFAULT_DEATH_TEST_STYLE "fast" +#endif // GTEST_DEFAULT_DEATH_TEST_STYLE + +#ifdef __GNUC__ +// Ask the compiler to never inline a given function. +# define GTEST_NO_INLINE_ __attribute__((noinline)) +#else +# define GTEST_NO_INLINE_ +#endif + +// _LIBCPP_VERSION is defined by the libc++ library from the LLVM project. +#if !defined(GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_) +# if defined(__GLIBCXX__) || (defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION) && !defined(_MSC_VER)) +# define GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ 1 +# else +# define GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ 0 +# endif +#endif + +// A function level attribute to disable checking for use of uninitialized +// memory when built with MemorySanitizer. +#if defined(__clang__) +# if __has_feature(memory_sanitizer) +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_MEMORY_ \ + __attribute__((no_sanitize_memory)) +# else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_MEMORY_ +# endif // __has_feature(memory_sanitizer) +#else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_MEMORY_ +#endif // __clang__ + +// A function level attribute to disable AddressSanitizer instrumentation. +#if defined(__clang__) +# if __has_feature(address_sanitizer) +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_ADDRESS_ \ + __attribute__((no_sanitize_address)) +# else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_ADDRESS_ +# endif // __has_feature(address_sanitizer) +#else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_ADDRESS_ +#endif // __clang__ + +// A function level attribute to disable HWAddressSanitizer instrumentation. +#if defined(__clang__) +# if __has_feature(hwaddress_sanitizer) +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_HWADDRESS_ \ + __attribute__((no_sanitize("hwaddress"))) +# else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_HWADDRESS_ +# endif // __has_feature(hwaddress_sanitizer) +#else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_HWADDRESS_ +#endif // __clang__ + +// A function level attribute to disable ThreadSanitizer instrumentation. +#if defined(__clang__) +# if __has_feature(thread_sanitizer) +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_THREAD_ \ + __attribute__((no_sanitize_thread)) +# else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_THREAD_ +# endif // __has_feature(thread_sanitizer) +#else +# define GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_NO_SANITIZE_THREAD_ +#endif // __clang__ + +namespace testing { + +class Message; + +// Legacy imports for backwards compatibility. +// New code should use std:: names directly. +using std::get; +using std::make_tuple; +using std::tuple; +using std::tuple_element; +using std::tuple_size; + +namespace internal { + +// A secret type that Google Test users don't know about. It has no +// definition on purpose. Therefore it's impossible to create a +// Secret object, which is what we want. +class Secret; + +// The GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_ is a legacy macro used to verify that a compile +// time expression is true (in new code, use static_assert instead). For +// example, you could use it to verify the size of a static array: +// +// GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(GTEST_ARRAY_SIZE_(names) == NUM_NAMES, +// names_incorrect_size); +// +// The second argument to the macro must be a valid C++ identifier. If the +// expression is false, compiler will issue an error containing this identifier. +#define GTEST_COMPILE_ASSERT_(expr, msg) static_assert(expr, #msg) + +// A helper for suppressing warnings on constant condition. It just +// returns 'condition'. +GTEST_API_ bool IsTrue(bool condition); + +// Defines RE. + +#if GTEST_USES_PCRE +// if used, PCRE is injected by custom/gtest-port.h +#elif GTEST_USES_POSIX_RE || GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE + +// A simple C++ wrapper for <regex.h>. It uses the POSIX Extended +// Regular Expression syntax. +class GTEST_API_ RE { + public: + // A copy constructor is required by the Standard to initialize object + // references from r-values. + RE(const RE& other) { Init(other.pattern()); } + + // Constructs an RE from a string. + RE(const ::std::string& regex) { Init(regex.c_str()); } // NOLINT + + RE(const char* regex) { Init(regex); } // NOLINT + ~RE(); + + // Returns the string representation of the regex. + const char* pattern() const { return pattern_; } + + // FullMatch(str, re) returns true if and only if regular expression re + // matches the entire str. + // PartialMatch(str, re) returns true if and only if regular expression re + // matches a substring of str (including str itself). + static bool FullMatch(const ::std::string& str, const RE& re) { + return FullMatch(str.c_str(), re); + } + static bool PartialMatch(const ::std::string& str, const RE& re) { + return PartialMatch(str.c_str(), re); + } + + static bool FullMatch(const char* str, const RE& re); + static bool PartialMatch(const char* str, const RE& re); + + private: + void Init(const char* regex); + const char* pattern_; + bool is_valid_; + +# if GTEST_USES_POSIX_RE + + regex_t full_regex_; // For FullMatch(). + regex_t partial_regex_; // For PartialMatch(). + +# else // GTEST_USES_SIMPLE_RE + + const char* full_pattern_; // For FullMatch(); + +# endif +}; + +#endif // GTEST_USES_PCRE + +// Formats a source file path and a line number as they would appear +// in an error message from the compiler used to compile this code. +GTEST_API_ ::std::string FormatFileLocation(const char* file, int line); + +// Formats a file location for compiler-independent XML output. +// Although this function is not platform dependent, we put it next to +// FormatFileLocation in order to contrast the two functions. +GTEST_API_ ::std::string FormatCompilerIndependentFileLocation(const char* file, + int line); + +// Defines logging utilities: +// GTEST_LOG_(severity) - logs messages at the specified severity level. The +// message itself is streamed into the macro. +// LogToStderr() - directs all log messages to stderr. +// FlushInfoLog() - flushes informational log messages. + +enum GTestLogSeverity { + GTEST_INFO, + GTEST_WARNING, + GTEST_ERROR, + GTEST_FATAL +}; + +// Formats log entry severity, provides a stream object for streaming the +// log message, and terminates the message with a newline when going out of +// scope. +class GTEST_API_ GTestLog { + public: + GTestLog(GTestLogSeverity severity, const char* file, int line); + + // Flushes the buffers and, if severity is GTEST_FATAL, aborts the program. + ~GTestLog(); + + ::std::ostream& GetStream() { return ::std::cerr; } + + private: + const GTestLogSeverity severity_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(GTestLog); +}; + +#if !defined(GTEST_LOG_) + +# define GTEST_LOG_(severity) \ + ::testing::internal::GTestLog(::testing::internal::GTEST_##severity, \ + __FILE__, __LINE__).GetStream() + +inline void LogToStderr() {} +inline void FlushInfoLog() { fflush(nullptr); } + +#endif // !defined(GTEST_LOG_) + +#if !defined(GTEST_CHECK_) +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE. +// +// GTEST_CHECK_ is an all-mode assert. It aborts the program if the condition +// is not satisfied. +// Synopsys: +// GTEST_CHECK_(boolean_condition); +// or +// GTEST_CHECK_(boolean_condition) << "Additional message"; +// +// This checks the condition and if the condition is not satisfied +// it prints message about the condition violation, including the +// condition itself, plus additional message streamed into it, if any, +// and then it aborts the program. It aborts the program irrespective of +// whether it is built in the debug mode or not. +# define GTEST_CHECK_(condition) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (::testing::internal::IsTrue(condition)) \ + ; \ + else \ + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << "Condition " #condition " failed. " +#endif // !defined(GTEST_CHECK_) + +// An all-mode assert to verify that the given POSIX-style function +// call returns 0 (indicating success). Known limitation: this +// doesn't expand to a balanced 'if' statement, so enclose the macro +// in {} if you need to use it as the only statement in an 'if' +// branch. +#define GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(posix_call) \ + if (const int gtest_error = (posix_call)) \ + GTEST_LOG_(FATAL) << #posix_call << "failed with error " \ + << gtest_error + +// Transforms "T" into "const T&" according to standard reference collapsing +// rules (this is only needed as a backport for C++98 compilers that do not +// support reference collapsing). Specifically, it transforms: +// +// char ==> const char& +// const char ==> const char& +// char& ==> char& +// const char& ==> const char& +// +// Note that the non-const reference will not have "const" added. This is +// standard, and necessary so that "T" can always bind to "const T&". +template <typename T> +struct ConstRef { typedef const T& type; }; +template <typename T> +struct ConstRef<T&> { typedef T& type; }; + +// The argument T must depend on some template parameters. +#define GTEST_REFERENCE_TO_CONST_(T) \ + typename ::testing::internal::ConstRef<T>::type + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// Use ImplicitCast_ as a safe version of static_cast for upcasting in +// the type hierarchy (e.g. casting a Foo* to a SuperclassOfFoo* or a +// const Foo*). When you use ImplicitCast_, the compiler checks that +// the cast is safe. Such explicit ImplicitCast_s are necessary in +// surprisingly many situations where C++ demands an exact type match +// instead of an argument type convertable to a target type. +// +// The syntax for using ImplicitCast_ is the same as for static_cast: +// +// ImplicitCast_<ToType>(expr) +// +// ImplicitCast_ would have been part of the C++ standard library, +// but the proposal was submitted too late. It will probably make +// its way into the language in the future. +// +// This relatively ugly name is intentional. It prevents clashes with +// similar functions users may have (e.g., implicit_cast). The internal +// namespace alone is not enough because the function can be found by ADL. +template<typename To> +inline To ImplicitCast_(To x) { return x; } + +// When you upcast (that is, cast a pointer from type Foo to type +// SuperclassOfFoo), it's fine to use ImplicitCast_<>, since upcasts +// always succeed. When you downcast (that is, cast a pointer from +// type Foo to type SubclassOfFoo), static_cast<> isn't safe, because +// how do you know the pointer is really of type SubclassOfFoo? It +// could be a bare Foo, or of type DifferentSubclassOfFoo. Thus, +// when you downcast, you should use this macro. In debug mode, we +// use dynamic_cast<> to double-check the downcast is legal (we die +// if it's not). In normal mode, we do the efficient static_cast<> +// instead. Thus, it's important to test in debug mode to make sure +// the cast is legal! +// This is the only place in the code we should use dynamic_cast<>. +// In particular, you SHOULDN'T be using dynamic_cast<> in order to +// do RTTI (eg code like this: +// if (dynamic_cast<Subclass1>(foo)) HandleASubclass1Object(foo); +// if (dynamic_cast<Subclass2>(foo)) HandleASubclass2Object(foo); +// You should design the code some other way not to need this. +// +// This relatively ugly name is intentional. It prevents clashes with +// similar functions users may have (e.g., down_cast). The internal +// namespace alone is not enough because the function can be found by ADL. +template<typename To, typename From> // use like this: DownCast_<T*>(foo); +inline To DownCast_(From* f) { // so we only accept pointers + // Ensures that To is a sub-type of From *. This test is here only + // for compile-time type checking, and has no overhead in an + // optimized build at run-time, as it will be optimized away + // completely. + GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_PUSH_() + if (false) { + GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_POP_() + const To to = nullptr; + ::testing::internal::ImplicitCast_<From*>(to); + } + +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI + // RTTI: debug mode only! + GTEST_CHECK_(f == nullptr || dynamic_cast<To>(f) != nullptr); +#endif + return static_cast<To>(f); +} + +// Downcasts the pointer of type Base to Derived. +// Derived must be a subclass of Base. The parameter MUST +// point to a class of type Derived, not any subclass of it. +// When RTTI is available, the function performs a runtime +// check to enforce this. +template <class Derived, class Base> +Derived* CheckedDowncastToActualType(Base* base) { +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI + GTEST_CHECK_(typeid(*base) == typeid(Derived)); +#endif + +#if GTEST_HAS_DOWNCAST_ + return ::down_cast<Derived*>(base); +#elif GTEST_HAS_RTTI + return dynamic_cast<Derived*>(base); // NOLINT +#else + return static_cast<Derived*>(base); // Poor man's downcast. +#endif +} + +#if GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION + +// Defines the stderr capturer: +// CaptureStdout - starts capturing stdout. +// GetCapturedStdout - stops capturing stdout and returns the captured string. +// CaptureStderr - starts capturing stderr. +// GetCapturedStderr - stops capturing stderr and returns the captured string. +// +GTEST_API_ void CaptureStdout(); +GTEST_API_ std::string GetCapturedStdout(); +GTEST_API_ void CaptureStderr(); +GTEST_API_ std::string GetCapturedStderr(); + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_STREAM_REDIRECTION +// Returns the size (in bytes) of a file. +GTEST_API_ size_t GetFileSize(FILE* file); + +// Reads the entire content of a file as a string. +GTEST_API_ std::string ReadEntireFile(FILE* file); + +// All command line arguments. +GTEST_API_ std::vector<std::string> GetArgvs(); + +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST + +std::vector<std::string> GetInjectableArgvs(); +// Deprecated: pass the args vector by value instead. +void SetInjectableArgvs(const std::vector<std::string>* new_argvs); +void SetInjectableArgvs(const std::vector<std::string>& new_argvs); +void ClearInjectableArgvs(); + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST + +// Defines synchronization primitives. +#if GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE +# if GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD +// Sleeps for (roughly) n milliseconds. This function is only for testing +// Google Test's own constructs. Don't use it in user tests, either +// directly or indirectly. +inline void SleepMilliseconds(int n) { + const timespec time = { + 0, // 0 seconds. + n * 1000L * 1000L, // And n ms. + }; + nanosleep(&time, nullptr); +} +# endif // GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD + +# if GTEST_HAS_NOTIFICATION_ +// Notification has already been imported into the namespace. +// Nothing to do here. + +# elif GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD +// Allows a controller thread to pause execution of newly created +// threads until notified. Instances of this class must be created +// and destroyed in the controller thread. +// +// This class is only for testing Google Test's own constructs. Do not +// use it in user tests, either directly or indirectly. +class Notification { + public: + Notification() : notified_(false) { + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_, nullptr)); + } + ~Notification() { + pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_); + } + + // Notifies all threads created with this notification to start. Must + // be called from the controller thread. + void Notify() { + pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_); + notified_ = true; + pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_); + } + + // Blocks until the controller thread notifies. Must be called from a test + // thread. + void WaitForNotification() { + for (;;) { + pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_); + const bool notified = notified_; + pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_); + if (notified) + break; + SleepMilliseconds(10); + } + } + + private: + pthread_mutex_t mutex_; + bool notified_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Notification); +}; + +# elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT + +GTEST_API_ void SleepMilliseconds(int n); + +// Provides leak-safe Windows kernel handle ownership. +// Used in death tests and in threading support. +class GTEST_API_ AutoHandle { + public: + // Assume that Win32 HANDLE type is equivalent to void*. Doing so allows us to + // avoid including <windows.h> in this header file. Including <windows.h> is + // undesirable because it defines a lot of symbols and macros that tend to + // conflict with client code. This assumption is verified by + // WindowsTypesTest.HANDLEIsVoidStar. + typedef void* Handle; + AutoHandle(); + explicit AutoHandle(Handle handle); + + ~AutoHandle(); + + Handle Get() const; + void Reset(); + void Reset(Handle handle); + + private: + // Returns true if and only if the handle is a valid handle object that can be + // closed. + bool IsCloseable() const; + + Handle handle_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(AutoHandle); +}; + +// Allows a controller thread to pause execution of newly created +// threads until notified. Instances of this class must be created +// and destroyed in the controller thread. +// +// This class is only for testing Google Test's own constructs. Do not +// use it in user tests, either directly or indirectly. +class GTEST_API_ Notification { + public: + Notification(); + void Notify(); + void WaitForNotification(); + + private: + AutoHandle event_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Notification); +}; +# endif // GTEST_HAS_NOTIFICATION_ + +// On MinGW, we can have both GTEST_OS_WINDOWS and GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD +// defined, but we don't want to use MinGW's pthreads implementation, which +// has conformance problems with some versions of the POSIX standard. +# if GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW + +// As a C-function, ThreadFuncWithCLinkage cannot be templated itself. +// Consequently, it cannot select a correct instantiation of ThreadWithParam +// in order to call its Run(). Introducing ThreadWithParamBase as a +// non-templated base class for ThreadWithParam allows us to bypass this +// problem. +class ThreadWithParamBase { + public: + virtual ~ThreadWithParamBase() {} + virtual void Run() = 0; +}; + +// pthread_create() accepts a pointer to a function type with the C linkage. +// According to the Standard (7.5/1), function types with different linkages +// are different even if they are otherwise identical. Some compilers (for +// example, SunStudio) treat them as different types. Since class methods +// cannot be defined with C-linkage we need to define a free C-function to +// pass into pthread_create(). +extern "C" inline void* ThreadFuncWithCLinkage(void* thread) { + static_cast<ThreadWithParamBase*>(thread)->Run(); + return nullptr; +} + +// Helper class for testing Google Test's multi-threading constructs. +// To use it, write: +// +// void ThreadFunc(int param) { /* Do things with param */ } +// Notification thread_can_start; +// ... +// // The thread_can_start parameter is optional; you can supply NULL. +// ThreadWithParam<int> thread(&ThreadFunc, 5, &thread_can_start); +// thread_can_start.Notify(); +// +// These classes are only for testing Google Test's own constructs. Do +// not use them in user tests, either directly or indirectly. +template <typename T> +class ThreadWithParam : public ThreadWithParamBase { + public: + typedef void UserThreadFunc(T); + + ThreadWithParam(UserThreadFunc* func, T param, Notification* thread_can_start) + : func_(func), + param_(param), + thread_can_start_(thread_can_start), + finished_(false) { + ThreadWithParamBase* const base = this; + // The thread can be created only after all fields except thread_ + // have been initialized. + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_( + pthread_create(&thread_, nullptr, &ThreadFuncWithCLinkage, base)); + } + ~ThreadWithParam() override { Join(); } + + void Join() { + if (!finished_) { + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_join(thread_, nullptr)); + finished_ = true; + } + } + + void Run() override { + if (thread_can_start_ != nullptr) thread_can_start_->WaitForNotification(); + func_(param_); + } + + private: + UserThreadFunc* const func_; // User-supplied thread function. + const T param_; // User-supplied parameter to the thread function. + // When non-NULL, used to block execution until the controller thread + // notifies. + Notification* const thread_can_start_; + bool finished_; // true if and only if we know that the thread function has + // finished. + pthread_t thread_; // The native thread object. + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ThreadWithParam); +}; +# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD || + // GTEST_HAS_MUTEX_AND_THREAD_LOCAL_ + +# if GTEST_HAS_MUTEX_AND_THREAD_LOCAL_ +// Mutex and ThreadLocal have already been imported into the namespace. +// Nothing to do here. + +# elif GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT + +// Mutex implements mutex on Windows platforms. It is used in conjunction +// with class MutexLock: +// +// Mutex mutex; +// ... +// MutexLock lock(&mutex); // Acquires the mutex and releases it at the +// // end of the current scope. +// +// A static Mutex *must* be defined or declared using one of the following +// macros: +// GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_some_mutex); +// GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(g_some_mutex); +// +// (A non-static Mutex is defined/declared in the usual way). +class GTEST_API_ Mutex { + public: + enum MutexType { kStatic = 0, kDynamic = 1 }; + // We rely on kStaticMutex being 0 as it is to what the linker initializes + // type_ in static mutexes. critical_section_ will be initialized lazily + // in ThreadSafeLazyInit(). + enum StaticConstructorSelector { kStaticMutex = 0 }; + + // This constructor intentionally does nothing. It relies on type_ being + // statically initialized to 0 (effectively setting it to kStatic) and on + // ThreadSafeLazyInit() to lazily initialize the rest of the members. + explicit Mutex(StaticConstructorSelector /*dummy*/) {} + + Mutex(); + ~Mutex(); + + void Lock(); + + void Unlock(); + + // Does nothing if the current thread holds the mutex. Otherwise, crashes + // with high probability. + void AssertHeld(); + + private: + // Initializes owner_thread_id_ and critical_section_ in static mutexes. + void ThreadSafeLazyInit(); + + // Per https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/oldnewthing/20040223-00/?p=40503, + // we assume that 0 is an invalid value for thread IDs. + unsigned int owner_thread_id_; + + // For static mutexes, we rely on these members being initialized to zeros + // by the linker. + MutexType type_; + long critical_section_init_phase_; // NOLINT + GTEST_CRITICAL_SECTION* critical_section_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Mutex); +}; + +# define GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) \ + extern ::testing::internal::Mutex mutex + +# define GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) \ + ::testing::internal::Mutex mutex(::testing::internal::Mutex::kStaticMutex) + +// We cannot name this class MutexLock because the ctor declaration would +// conflict with a macro named MutexLock, which is defined on some +// platforms. That macro is used as a defensive measure to prevent against +// inadvertent misuses of MutexLock like "MutexLock(&mu)" rather than +// "MutexLock l(&mu)". Hence the typedef trick below. +class GTestMutexLock { + public: + explicit GTestMutexLock(Mutex* mutex) + : mutex_(mutex) { mutex_->Lock(); } + + ~GTestMutexLock() { mutex_->Unlock(); } + + private: + Mutex* const mutex_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(GTestMutexLock); +}; + +typedef GTestMutexLock MutexLock; + +// Base class for ValueHolder<T>. Allows a caller to hold and delete a value +// without knowing its type. +class ThreadLocalValueHolderBase { + public: + virtual ~ThreadLocalValueHolderBase() {} +}; + +// Provides a way for a thread to send notifications to a ThreadLocal +// regardless of its parameter type. +class ThreadLocalBase { + public: + // Creates a new ValueHolder<T> object holding a default value passed to + // this ThreadLocal<T>'s constructor and returns it. It is the caller's + // responsibility not to call this when the ThreadLocal<T> instance already + // has a value on the current thread. + virtual ThreadLocalValueHolderBase* NewValueForCurrentThread() const = 0; + + protected: + ThreadLocalBase() {} + virtual ~ThreadLocalBase() {} + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ThreadLocalBase); +}; + +// Maps a thread to a set of ThreadLocals that have values instantiated on that +// thread and notifies them when the thread exits. A ThreadLocal instance is +// expected to persist until all threads it has values on have terminated. +class GTEST_API_ ThreadLocalRegistry { + public: + // Registers thread_local_instance as having value on the current thread. + // Returns a value that can be used to identify the thread from other threads. + static ThreadLocalValueHolderBase* GetValueOnCurrentThread( + const ThreadLocalBase* thread_local_instance); + + // Invoked when a ThreadLocal instance is destroyed. + static void OnThreadLocalDestroyed( + const ThreadLocalBase* thread_local_instance); +}; + +class GTEST_API_ ThreadWithParamBase { + public: + void Join(); + + protected: + class Runnable { + public: + virtual ~Runnable() {} + virtual void Run() = 0; + }; + + ThreadWithParamBase(Runnable *runnable, Notification* thread_can_start); + virtual ~ThreadWithParamBase(); + + private: + AutoHandle thread_; +}; + +// Helper class for testing Google Test's multi-threading constructs. +template <typename T> +class ThreadWithParam : public ThreadWithParamBase { + public: + typedef void UserThreadFunc(T); + + ThreadWithParam(UserThreadFunc* func, T param, Notification* thread_can_start) + : ThreadWithParamBase(new RunnableImpl(func, param), thread_can_start) { + } + virtual ~ThreadWithParam() {} + + private: + class RunnableImpl : public Runnable { + public: + RunnableImpl(UserThreadFunc* func, T param) + : func_(func), + param_(param) { + } + virtual ~RunnableImpl() {} + virtual void Run() { + func_(param_); + } + + private: + UserThreadFunc* const func_; + const T param_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(RunnableImpl); + }; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ThreadWithParam); +}; + +// Implements thread-local storage on Windows systems. +// +// // Thread 1 +// ThreadLocal<int> tl(100); // 100 is the default value for each thread. +// +// // Thread 2 +// tl.set(150); // Changes the value for thread 2 only. +// EXPECT_EQ(150, tl.get()); +// +// // Thread 1 +// EXPECT_EQ(100, tl.get()); // In thread 1, tl has the original value. +// tl.set(200); +// EXPECT_EQ(200, tl.get()); +// +// The template type argument T must have a public copy constructor. +// In addition, the default ThreadLocal constructor requires T to have +// a public default constructor. +// +// The users of a TheadLocal instance have to make sure that all but one +// threads (including the main one) using that instance have exited before +// destroying it. Otherwise, the per-thread objects managed for them by the +// ThreadLocal instance are not guaranteed to be destroyed on all platforms. +// +// Google Test only uses global ThreadLocal objects. That means they +// will die after main() has returned. Therefore, no per-thread +// object managed by Google Test will be leaked as long as all threads +// using Google Test have exited when main() returns. +template <typename T> +class ThreadLocal : public ThreadLocalBase { + public: + ThreadLocal() : default_factory_(new DefaultValueHolderFactory()) {} + explicit ThreadLocal(const T& value) + : default_factory_(new InstanceValueHolderFactory(value)) {} + + ~ThreadLocal() { ThreadLocalRegistry::OnThreadLocalDestroyed(this); } + + T* pointer() { return GetOrCreateValue(); } + const T* pointer() const { return GetOrCreateValue(); } + const T& get() const { return *pointer(); } + void set(const T& value) { *pointer() = value; } + + private: + // Holds a value of T. Can be deleted via its base class without the caller + // knowing the type of T. + class ValueHolder : public ThreadLocalValueHolderBase { + public: + ValueHolder() : value_() {} + explicit ValueHolder(const T& value) : value_(value) {} + + T* pointer() { return &value_; } + + private: + T value_; + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ValueHolder); + }; + + + T* GetOrCreateValue() const { + return static_cast<ValueHolder*>( + ThreadLocalRegistry::GetValueOnCurrentThread(this))->pointer(); + } + + virtual ThreadLocalValueHolderBase* NewValueForCurrentThread() const { + return default_factory_->MakeNewHolder(); + } + + class ValueHolderFactory { + public: + ValueHolderFactory() {} + virtual ~ValueHolderFactory() {} + virtual ValueHolder* MakeNewHolder() const = 0; + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ValueHolderFactory); + }; + + class DefaultValueHolderFactory : public ValueHolderFactory { + public: + DefaultValueHolderFactory() {} + ValueHolder* MakeNewHolder() const override { return new ValueHolder(); } + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(DefaultValueHolderFactory); + }; + + class InstanceValueHolderFactory : public ValueHolderFactory { + public: + explicit InstanceValueHolderFactory(const T& value) : value_(value) {} + ValueHolder* MakeNewHolder() const override { + return new ValueHolder(value_); + } + + private: + const T value_; // The value for each thread. + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(InstanceValueHolderFactory); + }; + + std::unique_ptr<ValueHolderFactory> default_factory_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ThreadLocal); +}; + +# elif GTEST_HAS_PTHREAD + +// MutexBase and Mutex implement mutex on pthreads-based platforms. +class MutexBase { + public: + // Acquires this mutex. + void Lock() { + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_)); + owner_ = pthread_self(); + has_owner_ = true; + } + + // Releases this mutex. + void Unlock() { + // Since the lock is being released the owner_ field should no longer be + // considered valid. We don't protect writing to has_owner_ here, as it's + // the caller's responsibility to ensure that the current thread holds the + // mutex when this is called. + has_owner_ = false; + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_)); + } + + // Does nothing if the current thread holds the mutex. Otherwise, crashes + // with high probability. + void AssertHeld() const { + GTEST_CHECK_(has_owner_ && pthread_equal(owner_, pthread_self())) + << "The current thread is not holding the mutex @" << this; + } + + // A static mutex may be used before main() is entered. It may even + // be used before the dynamic initialization stage. Therefore we + // must be able to initialize a static mutex object at link time. + // This means MutexBase has to be a POD and its member variables + // have to be public. + public: + pthread_mutex_t mutex_; // The underlying pthread mutex. + // has_owner_ indicates whether the owner_ field below contains a valid thread + // ID and is therefore safe to inspect (e.g., to use in pthread_equal()). All + // accesses to the owner_ field should be protected by a check of this field. + // An alternative might be to memset() owner_ to all zeros, but there's no + // guarantee that a zero'd pthread_t is necessarily invalid or even different + // from pthread_self(). + bool has_owner_; + pthread_t owner_; // The thread holding the mutex. +}; + +// Forward-declares a static mutex. +# define GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) \ + extern ::testing::internal::MutexBase mutex + +// Defines and statically (i.e. at link time) initializes a static mutex. +// The initialization list here does not explicitly initialize each field, +// instead relying on default initialization for the unspecified fields. In +// particular, the owner_ field (a pthread_t) is not explicitly initialized. +// This allows initialization to work whether pthread_t is a scalar or struct. +// The flag -Wmissing-field-initializers must not be specified for this to work. +#define GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) \ + ::testing::internal::MutexBase mutex = {PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER, false, 0} + +// The Mutex class can only be used for mutexes created at runtime. It +// shares its API with MutexBase otherwise. +class Mutex : public MutexBase { + public: + Mutex() { + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_, nullptr)); + has_owner_ = false; + } + ~Mutex() { + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_)); + } + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Mutex); +}; + +// We cannot name this class MutexLock because the ctor declaration would +// conflict with a macro named MutexLock, which is defined on some +// platforms. That macro is used as a defensive measure to prevent against +// inadvertent misuses of MutexLock like "MutexLock(&mu)" rather than +// "MutexLock l(&mu)". Hence the typedef trick below. +class GTestMutexLock { + public: + explicit GTestMutexLock(MutexBase* mutex) + : mutex_(mutex) { mutex_->Lock(); } + + ~GTestMutexLock() { mutex_->Unlock(); } + + private: + MutexBase* const mutex_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(GTestMutexLock); +}; + +typedef GTestMutexLock MutexLock; + +// Helpers for ThreadLocal. + +// pthread_key_create() requires DeleteThreadLocalValue() to have +// C-linkage. Therefore it cannot be templatized to access +// ThreadLocal<T>. Hence the need for class +// ThreadLocalValueHolderBase. +class ThreadLocalValueHolderBase { + public: + virtual ~ThreadLocalValueHolderBase() {} +}; + +// Called by pthread to delete thread-local data stored by +// pthread_setspecific(). +extern "C" inline void DeleteThreadLocalValue(void* value_holder) { + delete static_cast<ThreadLocalValueHolderBase*>(value_holder); +} + +// Implements thread-local storage on pthreads-based systems. +template <typename T> +class GTEST_API_ ThreadLocal { + public: + ThreadLocal() + : key_(CreateKey()), default_factory_(new DefaultValueHolderFactory()) {} + explicit ThreadLocal(const T& value) + : key_(CreateKey()), + default_factory_(new InstanceValueHolderFactory(value)) {} + + ~ThreadLocal() { + // Destroys the managed object for the current thread, if any. + DeleteThreadLocalValue(pthread_getspecific(key_)); + + // Releases resources associated with the key. This will *not* + // delete managed objects for other threads. + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_key_delete(key_)); + } + + T* pointer() { return GetOrCreateValue(); } + const T* pointer() const { return GetOrCreateValue(); } + const T& get() const { return *pointer(); } + void set(const T& value) { *pointer() = value; } + + private: + // Holds a value of type T. + class ValueHolder : public ThreadLocalValueHolderBase { + public: + ValueHolder() : value_() {} + explicit ValueHolder(const T& value) : value_(value) {} + + T* pointer() { return &value_; } + + private: + T value_; + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ValueHolder); + }; + + static pthread_key_t CreateKey() { + pthread_key_t key; + // When a thread exits, DeleteThreadLocalValue() will be called on + // the object managed for that thread. + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_( + pthread_key_create(&key, &DeleteThreadLocalValue)); + return key; + } + + T* GetOrCreateValue() const { + ThreadLocalValueHolderBase* const holder = + static_cast<ThreadLocalValueHolderBase*>(pthread_getspecific(key_)); + if (holder != nullptr) { + return CheckedDowncastToActualType<ValueHolder>(holder)->pointer(); + } + + ValueHolder* const new_holder = default_factory_->MakeNewHolder(); + ThreadLocalValueHolderBase* const holder_base = new_holder; + GTEST_CHECK_POSIX_SUCCESS_(pthread_setspecific(key_, holder_base)); + return new_holder->pointer(); + } + + class ValueHolderFactory { + public: + ValueHolderFactory() {} + virtual ~ValueHolderFactory() {} + virtual ValueHolder* MakeNewHolder() const = 0; + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ValueHolderFactory); + }; + + class DefaultValueHolderFactory : public ValueHolderFactory { + public: + DefaultValueHolderFactory() {} + ValueHolder* MakeNewHolder() const override { return new ValueHolder(); } + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(DefaultValueHolderFactory); + }; + + class InstanceValueHolderFactory : public ValueHolderFactory { + public: + explicit InstanceValueHolderFactory(const T& value) : value_(value) {} + ValueHolder* MakeNewHolder() const override { + return new ValueHolder(value_); + } + + private: + const T value_; // The value for each thread. + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(InstanceValueHolderFactory); + }; + + // A key pthreads uses for looking up per-thread values. + const pthread_key_t key_; + std::unique_ptr<ValueHolderFactory> default_factory_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ThreadLocal); +}; + +# endif // GTEST_HAS_MUTEX_AND_THREAD_LOCAL_ + +#else // GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE + +// A dummy implementation of synchronization primitives (mutex, lock, +// and thread-local variable). Necessary for compiling Google Test where +// mutex is not supported - using Google Test in multiple threads is not +// supported on such platforms. + +class Mutex { + public: + Mutex() {} + void Lock() {} + void Unlock() {} + void AssertHeld() const {} +}; + +# define GTEST_DECLARE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) \ + extern ::testing::internal::Mutex mutex + +# define GTEST_DEFINE_STATIC_MUTEX_(mutex) ::testing::internal::Mutex mutex + +// We cannot name this class MutexLock because the ctor declaration would +// conflict with a macro named MutexLock, which is defined on some +// platforms. That macro is used as a defensive measure to prevent against +// inadvertent misuses of MutexLock like "MutexLock(&mu)" rather than +// "MutexLock l(&mu)". Hence the typedef trick below. +class GTestMutexLock { + public: + explicit GTestMutexLock(Mutex*) {} // NOLINT +}; + +typedef GTestMutexLock MutexLock; + +template <typename T> +class GTEST_API_ ThreadLocal { + public: + ThreadLocal() : value_() {} + explicit ThreadLocal(const T& value) : value_(value) {} + T* pointer() { return &value_; } + const T* pointer() const { return &value_; } + const T& get() const { return value_; } + void set(const T& value) { value_ = value; } + private: + T value_; +}; + +#endif // GTEST_IS_THREADSAFE + +// Returns the number of threads running in the process, or 0 to indicate that +// we cannot detect it. +GTEST_API_ size_t GetThreadCount(); + +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS +# define GTEST_PATH_SEP_ "\\" +# define GTEST_HAS_ALT_PATH_SEP_ 1 +#else +# define GTEST_PATH_SEP_ "/" +# define GTEST_HAS_ALT_PATH_SEP_ 0 +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +// Utilities for char. + +// isspace(int ch) and friends accept an unsigned char or EOF. char +// may be signed, depending on the compiler (or compiler flags). +// Therefore we need to cast a char to unsigned char before calling +// isspace(), etc. + +inline bool IsAlpha(char ch) { + return isalpha(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; +} +inline bool IsAlNum(char ch) { + return isalnum(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; +} +inline bool IsDigit(char ch) { + return isdigit(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; +} +inline bool IsLower(char ch) { + return islower(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; +} +inline bool IsSpace(char ch) { + return isspace(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; +} +inline bool IsUpper(char ch) { + return isupper(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; +} +inline bool IsXDigit(char ch) { + return isxdigit(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; +} +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +inline bool IsXDigit(char8_t ch) { + return isxdigit(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)) != 0; +} +#endif +inline bool IsXDigit(char16_t ch) { + const unsigned char low_byte = static_cast<unsigned char>(ch); + return ch == low_byte && isxdigit(low_byte) != 0; +} +inline bool IsXDigit(char32_t ch) { + const unsigned char low_byte = static_cast<unsigned char>(ch); + return ch == low_byte && isxdigit(low_byte) != 0; +} +inline bool IsXDigit(wchar_t ch) { + const unsigned char low_byte = static_cast<unsigned char>(ch); + return ch == low_byte && isxdigit(low_byte) != 0; +} + +inline char ToLower(char ch) { + return static_cast<char>(tolower(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch))); +} +inline char ToUpper(char ch) { + return static_cast<char>(toupper(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch))); +} + +inline std::string StripTrailingSpaces(std::string str) { + std::string::iterator it = str.end(); + while (it != str.begin() && IsSpace(*--it)) + it = str.erase(it); + return str; +} + +// The testing::internal::posix namespace holds wrappers for common +// POSIX functions. These wrappers hide the differences between +// Windows/MSVC and POSIX systems. Since some compilers define these +// standard functions as macros, the wrapper cannot have the same name +// as the wrapped function. + +namespace posix { + +// Functions with a different name on Windows. + +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +typedef struct _stat StatStruct; + +# ifdef __BORLANDC__ +inline int DoIsATTY(int fd) { return isatty(fd); } +inline int StrCaseCmp(const char* s1, const char* s2) { + return stricmp(s1, s2); +} +inline char* StrDup(const char* src) { return strdup(src); } +# else // !__BORLANDC__ +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +inline int DoIsATTY(int /* fd */) { return 0; } +# else +inline int DoIsATTY(int fd) { return _isatty(fd); } +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +inline int StrCaseCmp(const char* s1, const char* s2) { + return _stricmp(s1, s2); +} +inline char* StrDup(const char* src) { return _strdup(src); } +# endif // __BORLANDC__ + +# if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +inline int FileNo(FILE* file) { return reinterpret_cast<int>(_fileno(file)); } +// Stat(), RmDir(), and IsDir() are not needed on Windows CE at this +// time and thus not defined there. +# else +inline int FileNo(FILE* file) { return _fileno(file); } +inline int Stat(const char* path, StatStruct* buf) { return _stat(path, buf); } +inline int RmDir(const char* dir) { return _rmdir(dir); } +inline bool IsDir(const StatStruct& st) { + return (_S_IFDIR & st.st_mode) != 0; +} +# endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE + +#elif GTEST_OS_ESP8266 +typedef struct stat StatStruct; + +inline int FileNo(FILE* file) { return fileno(file); } +inline int DoIsATTY(int fd) { return isatty(fd); } +inline int Stat(const char* path, StatStruct* buf) { + // stat function not implemented on ESP8266 + return 0; +} +inline int StrCaseCmp(const char* s1, const char* s2) { + return strcasecmp(s1, s2); +} +inline char* StrDup(const char* src) { return strdup(src); } +inline int RmDir(const char* dir) { return rmdir(dir); } +inline bool IsDir(const StatStruct& st) { return S_ISDIR(st.st_mode); } + +#else + +typedef struct stat StatStruct; + +inline int FileNo(FILE* file) { return fileno(file); } +inline int DoIsATTY(int fd) { return isatty(fd); } +inline int Stat(const char* path, StatStruct* buf) { return stat(path, buf); } +inline int StrCaseCmp(const char* s1, const char* s2) { + return strcasecmp(s1, s2); +} +inline char* StrDup(const char* src) { return strdup(src); } +inline int RmDir(const char* dir) { return rmdir(dir); } +inline bool IsDir(const StatStruct& st) { return S_ISDIR(st.st_mode); } + +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +inline int IsATTY(int fd) { + // DoIsATTY might change errno (for example ENOTTY in case you redirect stdout + // to a file on Linux), which is unexpected, so save the previous value, and + // restore it after the call. + int savedErrno = errno; + int isAttyValue = DoIsATTY(fd); + errno = savedErrno; + + return isAttyValue; +} + +// Functions deprecated by MSVC 8.0. + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_DEPRECATED_PUSH_() + +// ChDir(), FReopen(), FDOpen(), Read(), Write(), Close(), and +// StrError() aren't needed on Windows CE at this time and thus not +// defined there. + +#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE && \ + !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT && !GTEST_OS_ESP8266 && !GTEST_OS_XTENSA +inline int ChDir(const char* dir) { return chdir(dir); } +#endif +inline FILE* FOpen(const char* path, const char* mode) { +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW + struct wchar_codecvt : public std::codecvt<wchar_t, char, std::mbstate_t> {}; + std::wstring_convert<wchar_codecvt> converter; + std::wstring wide_path = converter.from_bytes(path); + std::wstring wide_mode = converter.from_bytes(mode); + return _wfopen(wide_path.c_str(), wide_mode.c_str()); +#else // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW + return fopen(path, mode); +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW +} +#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +inline FILE *FReopen(const char* path, const char* mode, FILE* stream) { + return freopen(path, mode, stream); +} +inline FILE* FDOpen(int fd, const char* mode) { return fdopen(fd, mode); } +#endif +inline int FClose(FILE* fp) { return fclose(fp); } +#if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +inline int Read(int fd, void* buf, unsigned int count) { + return static_cast<int>(read(fd, buf, count)); +} +inline int Write(int fd, const void* buf, unsigned int count) { + return static_cast<int>(write(fd, buf, count)); +} +inline int Close(int fd) { return close(fd); } +inline const char* StrError(int errnum) { return strerror(errnum); } +#endif +inline const char* GetEnv(const char* name) { +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE || GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE || \ + GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT || GTEST_OS_ESP8266 || GTEST_OS_XTENSA + // We are on an embedded platform, which has no environment variables. + static_cast<void>(name); // To prevent 'unused argument' warning. + return nullptr; +#elif defined(__BORLANDC__) || defined(__SunOS_5_8) || defined(__SunOS_5_9) + // Environment variables which we programmatically clear will be set to the + // empty string rather than unset (NULL). Handle that case. + const char* const env = getenv(name); + return (env != nullptr && env[0] != '\0') ? env : nullptr; +#else + return getenv(name); +#endif +} + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_DEPRECATED_POP_() + +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +// Windows CE has no C library. The abort() function is used in +// several places in Google Test. This implementation provides a reasonable +// imitation of standard behaviour. +[[noreturn]] void Abort(); +#else +[[noreturn]] inline void Abort() { abort(); } +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE + +} // namespace posix + +// MSVC "deprecates" snprintf and issues warnings wherever it is used. In +// order to avoid these warnings, we need to use _snprintf or _snprintf_s on +// MSVC-based platforms. We map the GTEST_SNPRINTF_ macro to the appropriate +// function in order to achieve that. We use macro definition here because +// snprintf is a variadic function. +#if _MSC_VER && !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE +// MSVC 2005 and above support variadic macros. +# define GTEST_SNPRINTF_(buffer, size, format, ...) \ + _snprintf_s(buffer, size, size, format, __VA_ARGS__) +#elif defined(_MSC_VER) +// Windows CE does not define _snprintf_s +# define GTEST_SNPRINTF_ _snprintf +#else +# define GTEST_SNPRINTF_ snprintf +#endif + +// The biggest signed integer type the compiler supports. +// +// long long is guaranteed to be at least 64-bits in C++11. +using BiggestInt = long long; // NOLINT + +// The maximum number a BiggestInt can represent. +constexpr BiggestInt kMaxBiggestInt = (std::numeric_limits<BiggestInt>::max)(); + +// This template class serves as a compile-time function from size to +// type. It maps a size in bytes to a primitive type with that +// size. e.g. +// +// TypeWithSize<4>::UInt +// +// is typedef-ed to be unsigned int (unsigned integer made up of 4 +// bytes). +// +// Such functionality should belong to STL, but I cannot find it +// there. +// +// Google Test uses this class in the implementation of floating-point +// comparison. +// +// For now it only handles UInt (unsigned int) as that's all Google Test +// needs. Other types can be easily added in the future if need +// arises. +template <size_t size> +class TypeWithSize { + public: + // This prevents the user from using TypeWithSize<N> with incorrect + // values of N. + using UInt = void; +}; + +// The specialization for size 4. +template <> +class TypeWithSize<4> { + public: + using Int = std::int32_t; + using UInt = std::uint32_t; +}; + +// The specialization for size 8. +template <> +class TypeWithSize<8> { + public: + using Int = std::int64_t; + using UInt = std::uint64_t; +}; + +// Integer types of known sizes. +using TimeInMillis = int64_t; // Represents time in milliseconds. + +// Utilities for command line flags and environment variables. + +// Macro for referencing flags. +#if !defined(GTEST_FLAG) +# define GTEST_FLAG(name) FLAGS_gtest_##name +#endif // !defined(GTEST_FLAG) + +#if !defined(GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_) +# define GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_ 1 +#endif // !defined(GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_) + +#if !defined(GTEST_DECLARE_bool_) +# define GTEST_FLAG_SAVER_ ::testing::internal::GTestFlagSaver + +// Macros for declaring flags. +# define GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(name) GTEST_API_ extern bool GTEST_FLAG(name) +# define GTEST_DECLARE_int32_(name) \ + GTEST_API_ extern std::int32_t GTEST_FLAG(name) +# define GTEST_DECLARE_string_(name) \ + GTEST_API_ extern ::std::string GTEST_FLAG(name) + +// Macros for defining flags. +# define GTEST_DEFINE_bool_(name, default_val, doc) \ + GTEST_API_ bool GTEST_FLAG(name) = (default_val) +# define GTEST_DEFINE_int32_(name, default_val, doc) \ + GTEST_API_ std::int32_t GTEST_FLAG(name) = (default_val) +# define GTEST_DEFINE_string_(name, default_val, doc) \ + GTEST_API_ ::std::string GTEST_FLAG(name) = (default_val) + +#endif // !defined(GTEST_DECLARE_bool_) + +// Thread annotations +#if !defined(GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_) +# define GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_(locks) +# define GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(locks) +#endif // !defined(GTEST_EXCLUSIVE_LOCK_REQUIRED_) + +// Parses 'str' for a 32-bit signed integer. If successful, writes the result +// to *value and returns true; otherwise leaves *value unchanged and returns +// false. +GTEST_API_ bool ParseInt32(const Message& src_text, const char* str, + int32_t* value); + +// Parses a bool/int32_t/string from the environment variable +// corresponding to the given Google Test flag. +bool BoolFromGTestEnv(const char* flag, bool default_val); +GTEST_API_ int32_t Int32FromGTestEnv(const char* flag, int32_t default_val); +std::string OutputFlagAlsoCheckEnvVar(); +const char* StringFromGTestEnv(const char* flag, const char* default_val); + +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing + +#if !defined(GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED) + +// Internal Macro to mark an API deprecated, for googletest usage only +// Usage: class GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED(message) MyClass or +// GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED(message) <return_type> myFunction(); Every usage of +// a deprecated entity will trigger a warning when compiled with +// `-Wdeprecated-declarations` option (clang, gcc, any __GNUC__ compiler). +// For msvc /W3 option will need to be used +// Note that for 'other' compilers this macro evaluates to nothing to prevent +// compilations errors. +#if defined(_MSC_VER) +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED(message) __declspec(deprecated(message)) +#elif defined(__GNUC__) +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED(message) __attribute__((deprecated(message))) +#else +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED(message) +#endif + +#endif // !defined(GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED) + +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL +// Always use absl::any for UniversalPrinter<> specializations if googletest +// is built with absl support. +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_ANY 1 +#include "absl/types/any.h" +namespace testing { +namespace internal { +using Any = ::absl::any; +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing +#else +#ifdef __has_include +#if __has_include(<any>) && __cplusplus >= 201703L +// Otherwise for C++17 and higher use std::any for UniversalPrinter<> +// specializations. +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_ANY 1 +#include <any> +namespace testing { +namespace internal { +using Any = ::std::any; +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing +// The case where absl is configured NOT to alias std::any is not +// supported. +#endif // __has_include(<any>) && __cplusplus >= 201703L +#endif // __has_include +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL + +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL +// Always use absl::optional for UniversalPrinter<> specializations if +// googletest is built with absl support. +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_OPTIONAL 1 +#include "absl/types/optional.h" +namespace testing { +namespace internal { +template <typename T> +using Optional = ::absl::optional<T>; +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing +#else +#ifdef __has_include +#if __has_include(<optional>) && __cplusplus >= 201703L +// Otherwise for C++17 and higher use std::optional for UniversalPrinter<> +// specializations. +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_OPTIONAL 1 +#include <optional> +namespace testing { +namespace internal { +template <typename T> +using Optional = ::std::optional<T>; +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing +// The case where absl is configured NOT to alias std::optional is not +// supported. +#endif // __has_include(<optional>) && __cplusplus >= 201703L +#endif // __has_include +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL + +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL +// Always use absl::string_view for Matcher<> specializations if googletest +// is built with absl support. +# define GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW 1 +#include "absl/strings/string_view.h" +namespace testing { +namespace internal { +using StringView = ::absl::string_view; +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing +#else +# ifdef __has_include +# if __has_include(<string_view>) && __cplusplus >= 201703L +// Otherwise for C++17 and higher use std::string_view for Matcher<> +// specializations. +# define GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW 1 +#include <string_view> +namespace testing { +namespace internal { +using StringView = ::std::string_view; +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing +// The case where absl is configured NOT to alias std::string_view is not +// supported. +# endif // __has_include(<string_view>) && __cplusplus >= 201703L +# endif // __has_include +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL + +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL +// Always use absl::variant for UniversalPrinter<> specializations if googletest +// is built with absl support. +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_VARIANT 1 +#include "absl/types/variant.h" +namespace testing { +namespace internal { +template <typename... T> +using Variant = ::absl::variant<T...>; +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing +#else +#ifdef __has_include +#if __has_include(<variant>) && __cplusplus >= 201703L +// Otherwise for C++17 and higher use std::variant for UniversalPrinter<> +// specializations. +#define GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_VARIANT 1 +#include <variant> +namespace testing { +namespace internal { +template <typename... T> +using Variant = ::std::variant<T...>; +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing +// The case where absl is configured NOT to alias std::variant is not supported. +#endif // __has_include(<variant>) && __cplusplus >= 201703L +#endif // __has_include +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_H_ + +#if GTEST_OS_LINUX +# include <stdlib.h> +# include <sys/types.h> +# include <sys/wait.h> +# include <unistd.h> +#endif // GTEST_OS_LINUX + +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS +# include <stdexcept> +#endif + +#include <ctype.h> +#include <float.h> +#include <string.h> +#include <cstdint> +#include <iomanip> +#include <limits> +#include <map> +#include <set> +#include <string> +#include <type_traits> +#include <vector> + +// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// This header file defines the Message class. +// +// IMPORTANT NOTE: Due to limitation of the C++ language, we have to +// leave some internal implementation details in this header file. +// They are clearly marked by comments like this: +// +// // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +// +// Such code is NOT meant to be used by a user directly, and is subject +// to CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. Therefore DO NOT DEPEND ON IT in a user +// program! + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_MESSAGE_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_MESSAGE_H_ + +#include <limits> +#include <memory> +#include <sstream> + + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) + +// Ensures that there is at least one operator<< in the global namespace. +// See Message& operator<<(...) below for why. +void operator<<(const testing::internal::Secret&, int); + +namespace testing { + +// The Message class works like an ostream repeater. +// +// Typical usage: +// +// 1. You stream a bunch of values to a Message object. +// It will remember the text in a stringstream. +// 2. Then you stream the Message object to an ostream. +// This causes the text in the Message to be streamed +// to the ostream. +// +// For example; +// +// testing::Message foo; +// foo << 1 << " != " << 2; +// std::cout << foo; +// +// will print "1 != 2". +// +// Message is not intended to be inherited from. In particular, its +// destructor is not virtual. +// +// Note that stringstream behaves differently in gcc and in MSVC. You +// can stream a NULL char pointer to it in the former, but not in the +// latter (it causes an access violation if you do). The Message +// class hides this difference by treating a NULL char pointer as +// "(null)". +class GTEST_API_ Message { + private: + // The type of basic IO manipulators (endl, ends, and flush) for + // narrow streams. + typedef std::ostream& (*BasicNarrowIoManip)(std::ostream&); + + public: + // Constructs an empty Message. + Message(); + + // Copy constructor. + Message(const Message& msg) : ss_(new ::std::stringstream) { // NOLINT + *ss_ << msg.GetString(); + } + + // Constructs a Message from a C-string. + explicit Message(const char* str) : ss_(new ::std::stringstream) { + *ss_ << str; + } + + // Streams a non-pointer value to this object. + template <typename T> + inline Message& operator <<(const T& val) { + // Some libraries overload << for STL containers. These + // overloads are defined in the global namespace instead of ::std. + // + // C++'s symbol lookup rule (i.e. Koenig lookup) says that these + // overloads are visible in either the std namespace or the global + // namespace, but not other namespaces, including the testing + // namespace which Google Test's Message class is in. + // + // To allow STL containers (and other types that has a << operator + // defined in the global namespace) to be used in Google Test + // assertions, testing::Message must access the custom << operator + // from the global namespace. With this using declaration, + // overloads of << defined in the global namespace and those + // visible via Koenig lookup are both exposed in this function. + using ::operator <<; + *ss_ << val; + return *this; + } + + // Streams a pointer value to this object. + // + // This function is an overload of the previous one. When you + // stream a pointer to a Message, this definition will be used as it + // is more specialized. (The C++ Standard, section + // [temp.func.order].) If you stream a non-pointer, then the + // previous definition will be used. + // + // The reason for this overload is that streaming a NULL pointer to + // ostream is undefined behavior. Depending on the compiler, you + // may get "0", "(nil)", "(null)", or an access violation. To + // ensure consistent result across compilers, we always treat NULL + // as "(null)". + template <typename T> + inline Message& operator <<(T* const& pointer) { // NOLINT + if (pointer == nullptr) { + *ss_ << "(null)"; + } else { + *ss_ << pointer; + } + return *this; + } + + // Since the basic IO manipulators are overloaded for both narrow + // and wide streams, we have to provide this specialized definition + // of operator <<, even though its body is the same as the + // templatized version above. Without this definition, streaming + // endl or other basic IO manipulators to Message will confuse the + // compiler. + Message& operator <<(BasicNarrowIoManip val) { + *ss_ << val; + return *this; + } + + // Instead of 1/0, we want to see true/false for bool values. + Message& operator <<(bool b) { + return *this << (b ? "true" : "false"); + } + + // These two overloads allow streaming a wide C string to a Message + // using the UTF-8 encoding. + Message& operator <<(const wchar_t* wide_c_str); + Message& operator <<(wchar_t* wide_c_str); + +#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING + // Converts the given wide string to a narrow string using the UTF-8 + // encoding, and streams the result to this Message object. + Message& operator <<(const ::std::wstring& wstr); +#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING + + // Gets the text streamed to this object so far as an std::string. + // Each '\0' character in the buffer is replaced with "\\0". + // + // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. + std::string GetString() const; + + private: + // We'll hold the text streamed to this object here. + const std::unique_ptr< ::std::stringstream> ss_; + + // We declare (but don't implement) this to prevent the compiler + // from implementing the assignment operator. + void operator=(const Message&); +}; + +// Streams a Message to an ostream. +inline std::ostream& operator <<(std::ostream& os, const Message& sb) { + return os << sb.GetString(); +} + +namespace internal { + +// Converts a streamable value to an std::string. A NULL pointer is +// converted to "(null)". When the input value is a ::string, +// ::std::string, ::wstring, or ::std::wstring object, each NUL +// character in it is replaced with "\\0". +template <typename T> +std::string StreamableToString(const T& streamable) { + return (Message() << streamable).GetString(); +} + +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_MESSAGE_H_ +// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// Google Test filepath utilities +// +// This header file declares classes and functions used internally by +// Google Test. They are subject to change without notice. +// +// This file is #included in gtest/internal/gtest-internal.h. +// Do not include this header file separately! + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_FILEPATH_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_FILEPATH_H_ + +// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// This header file declares the String class and functions used internally by +// Google Test. They are subject to change without notice. They should not used +// by code external to Google Test. +// +// This header file is #included by gtest-internal.h. +// It should not be #included by other files. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_STRING_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_STRING_H_ + +#ifdef __BORLANDC__ +// string.h is not guaranteed to provide strcpy on C++ Builder. +# include <mem.h> +#endif + +#include <string.h> +#include <cstdint> +#include <string> + + +namespace testing { +namespace internal { + +// String - an abstract class holding static string utilities. +class GTEST_API_ String { + public: + // Static utility methods + + // Clones a 0-terminated C string, allocating memory using new. The + // caller is responsible for deleting the return value using + // delete[]. Returns the cloned string, or NULL if the input is + // NULL. + // + // This is different from strdup() in string.h, which allocates + // memory using malloc(). + static const char* CloneCString(const char* c_str); + +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE + // Windows CE does not have the 'ANSI' versions of Win32 APIs. To be + // able to pass strings to Win32 APIs on CE we need to convert them + // to 'Unicode', UTF-16. + + // Creates a UTF-16 wide string from the given ANSI string, allocating + // memory using new. The caller is responsible for deleting the return + // value using delete[]. Returns the wide string, or NULL if the + // input is NULL. + // + // The wide string is created using the ANSI codepage (CP_ACP) to + // match the behaviour of the ANSI versions of Win32 calls and the + // C runtime. + static LPCWSTR AnsiToUtf16(const char* c_str); + + // Creates an ANSI string from the given wide string, allocating + // memory using new. The caller is responsible for deleting the return + // value using delete[]. Returns the ANSI string, or NULL if the + // input is NULL. + // + // The returned string is created using the ANSI codepage (CP_ACP) to + // match the behaviour of the ANSI versions of Win32 calls and the + // C runtime. + static const char* Utf16ToAnsi(LPCWSTR utf16_str); +#endif + + // Compares two C strings. Returns true if and only if they have the same + // content. + // + // Unlike strcmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). A + // NULL C string is considered different to any non-NULL C string, + // including the empty string. + static bool CStringEquals(const char* lhs, const char* rhs); + + // Converts a wide C string to a String using the UTF-8 encoding. + // NULL will be converted to "(null)". If an error occurred during + // the conversion, "(failed to convert from wide string)" is + // returned. + static std::string ShowWideCString(const wchar_t* wide_c_str); + + // Compares two wide C strings. Returns true if and only if they have the + // same content. + // + // Unlike wcscmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). A + // NULL C string is considered different to any non-NULL C string, + // including the empty string. + static bool WideCStringEquals(const wchar_t* lhs, const wchar_t* rhs); + + // Compares two C strings, ignoring case. Returns true if and only if + // they have the same content. + // + // Unlike strcasecmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). + // A NULL C string is considered different to any non-NULL C string, + // including the empty string. + static bool CaseInsensitiveCStringEquals(const char* lhs, + const char* rhs); + + // Compares two wide C strings, ignoring case. Returns true if and only if + // they have the same content. + // + // Unlike wcscasecmp(), this function can handle NULL argument(s). + // A NULL C string is considered different to any non-NULL wide C string, + // including the empty string. + // NB: The implementations on different platforms slightly differ. + // On windows, this method uses _wcsicmp which compares according to LC_CTYPE + // environment variable. On GNU platform this method uses wcscasecmp + // which compares according to LC_CTYPE category of the current locale. + // On MacOS X, it uses towlower, which also uses LC_CTYPE category of the + // current locale. + static bool CaseInsensitiveWideCStringEquals(const wchar_t* lhs, + const wchar_t* rhs); + + // Returns true if and only if the given string ends with the given suffix, + // ignoring case. Any string is considered to end with an empty suffix. + static bool EndsWithCaseInsensitive( + const std::string& str, const std::string& suffix); + + // Formats an int value as "%02d". + static std::string FormatIntWidth2(int value); // "%02d" for width == 2 + + // Formats an int value to given width with leading zeros. + static std::string FormatIntWidthN(int value, int width); + + // Formats an int value as "%X". + static std::string FormatHexInt(int value); + + // Formats an int value as "%X". + static std::string FormatHexUInt32(uint32_t value); + + // Formats a byte as "%02X". + static std::string FormatByte(unsigned char value); + + private: + String(); // Not meant to be instantiated. +}; // class String + +// Gets the content of the stringstream's buffer as an std::string. Each '\0' +// character in the buffer is replaced with "\\0". +GTEST_API_ std::string StringStreamToString(::std::stringstream* stream); + +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_STRING_H_ + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) + +namespace testing { +namespace internal { + +// FilePath - a class for file and directory pathname manipulation which +// handles platform-specific conventions (like the pathname separator). +// Used for helper functions for naming files in a directory for xml output. +// Except for Set methods, all methods are const or static, which provides an +// "immutable value object" -- useful for peace of mind. +// A FilePath with a value ending in a path separator ("like/this/") represents +// a directory, otherwise it is assumed to represent a file. In either case, +// it may or may not represent an actual file or directory in the file system. +// Names are NOT checked for syntax correctness -- no checking for illegal +// characters, malformed paths, etc. + +class GTEST_API_ FilePath { + public: + FilePath() : pathname_("") { } + FilePath(const FilePath& rhs) : pathname_(rhs.pathname_) { } + + explicit FilePath(const std::string& pathname) : pathname_(pathname) { + Normalize(); + } + + FilePath& operator=(const FilePath& rhs) { + Set(rhs); + return *this; + } + + void Set(const FilePath& rhs) { + pathname_ = rhs.pathname_; + } + + const std::string& string() const { return pathname_; } + const char* c_str() const { return pathname_.c_str(); } + + // Returns the current working directory, or "" if unsuccessful. + static FilePath GetCurrentDir(); + + // Given directory = "dir", base_name = "test", number = 0, + // extension = "xml", returns "dir/test.xml". If number is greater + // than zero (e.g., 12), returns "dir/test_12.xml". + // On Windows platform, uses \ as the separator rather than /. + static FilePath MakeFileName(const FilePath& directory, + const FilePath& base_name, + int number, + const char* extension); + + // Given directory = "dir", relative_path = "test.xml", + // returns "dir/test.xml". + // On Windows, uses \ as the separator rather than /. + static FilePath ConcatPaths(const FilePath& directory, + const FilePath& relative_path); + + // Returns a pathname for a file that does not currently exist. The pathname + // will be directory/base_name.extension or + // directory/base_name_<number>.extension if directory/base_name.extension + // already exists. The number will be incremented until a pathname is found + // that does not already exist. + // Examples: 'dir/foo_test.xml' or 'dir/foo_test_1.xml'. + // There could be a race condition if two or more processes are calling this + // function at the same time -- they could both pick the same filename. + static FilePath GenerateUniqueFileName(const FilePath& directory, + const FilePath& base_name, + const char* extension); + + // Returns true if and only if the path is "". + bool IsEmpty() const { return pathname_.empty(); } + + // If input name has a trailing separator character, removes it and returns + // the name, otherwise return the name string unmodified. + // On Windows platform, uses \ as the separator, other platforms use /. + FilePath RemoveTrailingPathSeparator() const; + + // Returns a copy of the FilePath with the directory part removed. + // Example: FilePath("path/to/file").RemoveDirectoryName() returns + // FilePath("file"). If there is no directory part ("just_a_file"), it returns + // the FilePath unmodified. If there is no file part ("just_a_dir/") it + // returns an empty FilePath (""). + // On Windows platform, '\' is the path separator, otherwise it is '/'. + FilePath RemoveDirectoryName() const; + + // RemoveFileName returns the directory path with the filename removed. + // Example: FilePath("path/to/file").RemoveFileName() returns "path/to/". + // If the FilePath is "a_file" or "/a_file", RemoveFileName returns + // FilePath("./") or, on Windows, FilePath(".\\"). If the filepath does + // not have a file, like "just/a/dir/", it returns the FilePath unmodified. + // On Windows platform, '\' is the path separator, otherwise it is '/'. + FilePath RemoveFileName() const; + + // Returns a copy of the FilePath with the case-insensitive extension removed. + // Example: FilePath("dir/file.exe").RemoveExtension("EXE") returns + // FilePath("dir/file"). If a case-insensitive extension is not + // found, returns a copy of the original FilePath. + FilePath RemoveExtension(const char* extension) const; + + // Creates directories so that path exists. Returns true if successful or if + // the directories already exist; returns false if unable to create + // directories for any reason. Will also return false if the FilePath does + // not represent a directory (that is, it doesn't end with a path separator). + bool CreateDirectoriesRecursively() const; + + // Create the directory so that path exists. Returns true if successful or + // if the directory already exists; returns false if unable to create the + // directory for any reason, including if the parent directory does not + // exist. Not named "CreateDirectory" because that's a macro on Windows. + bool CreateFolder() const; + + // Returns true if FilePath describes something in the file-system, + // either a file, directory, or whatever, and that something exists. + bool FileOrDirectoryExists() const; + + // Returns true if pathname describes a directory in the file-system + // that exists. + bool DirectoryExists() const; + + // Returns true if FilePath ends with a path separator, which indicates that + // it is intended to represent a directory. Returns false otherwise. + // This does NOT check that a directory (or file) actually exists. + bool IsDirectory() const; + + // Returns true if pathname describes a root directory. (Windows has one + // root directory per disk drive.) + bool IsRootDirectory() const; + + // Returns true if pathname describes an absolute path. + bool IsAbsolutePath() const; + + private: + // Replaces multiple consecutive separators with a single separator. + // For example, "bar///foo" becomes "bar/foo". Does not eliminate other + // redundancies that might be in a pathname involving "." or "..". + // + // A pathname with multiple consecutive separators may occur either through + // user error or as a result of some scripts or APIs that generate a pathname + // with a trailing separator. On other platforms the same API or script + // may NOT generate a pathname with a trailing "/". Then elsewhere that + // pathname may have another "/" and pathname components added to it, + // without checking for the separator already being there. + // The script language and operating system may allow paths like "foo//bar" + // but some of the functions in FilePath will not handle that correctly. In + // particular, RemoveTrailingPathSeparator() only removes one separator, and + // it is called in CreateDirectoriesRecursively() assuming that it will change + // a pathname from directory syntax (trailing separator) to filename syntax. + // + // On Windows this method also replaces the alternate path separator '/' with + // the primary path separator '\\', so that for example "bar\\/\\foo" becomes + // "bar\\foo". + + void Normalize(); + + // Returns a pointer to the last occurrence of a valid path separator in + // the FilePath. On Windows, for example, both '/' and '\' are valid path + // separators. Returns NULL if no path separator was found. + const char* FindLastPathSeparator() const; + + std::string pathname_; +}; // class FilePath + +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_FILEPATH_H_ +// Copyright 2008 Google Inc. +// All Rights Reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// Type utilities needed for implementing typed and type-parameterized +// tests. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_TYPE_UTIL_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_TYPE_UTIL_H_ + + +// #ifdef __GNUC__ is too general here. It is possible to use gcc without using +// libstdc++ (which is where cxxabi.h comes from). +# if GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ +# include <cxxabi.h> +# elif defined(__HP_aCC) +# include <acxx_demangle.h> +# endif // GTEST_HASH_CXXABI_H_ + +namespace testing { +namespace internal { + +// Canonicalizes a given name with respect to the Standard C++ Library. +// This handles removing the inline namespace within `std` that is +// used by various standard libraries (e.g., `std::__1`). Names outside +// of namespace std are returned unmodified. +inline std::string CanonicalizeForStdLibVersioning(std::string s) { + static const char prefix[] = "std::__"; + if (s.compare(0, strlen(prefix), prefix) == 0) { + std::string::size_type end = s.find("::", strlen(prefix)); + if (end != s.npos) { + // Erase everything between the initial `std` and the second `::`. + s.erase(strlen("std"), end - strlen("std")); + } + } + return s; +} + +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI +// GetTypeName(const std::type_info&) returns a human-readable name of type T. +inline std::string GetTypeName(const std::type_info& type) { + const char* const name = type.name(); +#if GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ || defined(__HP_aCC) + int status = 0; + // gcc's implementation of typeid(T).name() mangles the type name, + // so we have to demangle it. +#if GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ + using abi::__cxa_demangle; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ + char* const readable_name = __cxa_demangle(name, nullptr, nullptr, &status); + const std::string name_str(status == 0 ? readable_name : name); + free(readable_name); + return CanonicalizeForStdLibVersioning(name_str); +#else + return name; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_CXXABI_H_ || __HP_aCC +} +#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI + +// GetTypeName<T>() returns a human-readable name of type T if and only if +// RTTI is enabled, otherwise it returns a dummy type name. +// NB: This function is also used in Google Mock, so don't move it inside of +// the typed-test-only section below. +template <typename T> +std::string GetTypeName() { +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI + return GetTypeName(typeid(T)); +#else + return "<type>"; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI +} + +// A unique type indicating an empty node +struct None {}; + +# define GTEST_TEMPLATE_ template <typename T> class + +// The template "selector" struct TemplateSel<Tmpl> is used to +// represent Tmpl, which must be a class template with one type +// parameter, as a type. TemplateSel<Tmpl>::Bind<T>::type is defined +// as the type Tmpl<T>. This allows us to actually instantiate the +// template "selected" by TemplateSel<Tmpl>. +// +// This trick is necessary for simulating typedef for class templates, +// which C++ doesn't support directly. +template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Tmpl> +struct TemplateSel { + template <typename T> + struct Bind { + typedef Tmpl<T> type; + }; +}; + +# define GTEST_BIND_(TmplSel, T) \ + TmplSel::template Bind<T>::type + +template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Head_, GTEST_TEMPLATE_... Tail_> +struct Templates { + using Head = TemplateSel<Head_>; + using Tail = Templates<Tail_...>; +}; + +template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Head_> +struct Templates<Head_> { + using Head = TemplateSel<Head_>; + using Tail = None; +}; + +// Tuple-like type lists +template <typename Head_, typename... Tail_> +struct Types { + using Head = Head_; + using Tail = Types<Tail_...>; +}; + +template <typename Head_> +struct Types<Head_> { + using Head = Head_; + using Tail = None; +}; + +// Helper metafunctions to tell apart a single type from types +// generated by ::testing::Types +template <typename... Ts> +struct ProxyTypeList { + using type = Types<Ts...>; +}; + +template <typename> +struct is_proxy_type_list : std::false_type {}; + +template <typename... Ts> +struct is_proxy_type_list<ProxyTypeList<Ts...>> : std::true_type {}; + +// Generator which conditionally creates type lists. +// It recognizes if a requested type list should be created +// and prevents creating a new type list nested within another one. +template <typename T> +struct GenerateTypeList { + private: + using proxy = typename std::conditional<is_proxy_type_list<T>::value, T, + ProxyTypeList<T>>::type; + + public: + using type = typename proxy::type; +}; + +} // namespace internal + +template <typename... Ts> +using Types = internal::ProxyTypeList<Ts...>; + +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_TYPE_UTIL_H_ + +// Due to C++ preprocessor weirdness, we need double indirection to +// concatenate two tokens when one of them is __LINE__. Writing +// +// foo ## __LINE__ +// +// will result in the token foo__LINE__, instead of foo followed by +// the current line number. For more details, see +// http://www.parashift.com/c++-faq-lite/misc-technical-issues.html#faq-39.6 +#define GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(foo, bar) GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_IMPL_(foo, bar) +#define GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_IMPL_(foo, bar) foo ## bar + +// Stringifies its argument. +// Work around a bug in visual studio which doesn't accept code like this: +// +// #define GTEST_STRINGIFY_(name) #name +// #define MACRO(a, b, c) ... GTEST_STRINGIFY_(a) ... +// MACRO(, x, y) +// +// Complaining about the argument to GTEST_STRINGIFY_ being empty. +// This is allowed by the spec. +#define GTEST_STRINGIFY_HELPER_(name, ...) #name +#define GTEST_STRINGIFY_(...) GTEST_STRINGIFY_HELPER_(__VA_ARGS__, ) + +namespace proto2 { +class MessageLite; +} + +namespace testing { + +// Forward declarations. + +class AssertionResult; // Result of an assertion. +class Message; // Represents a failure message. +class Test; // Represents a test. +class TestInfo; // Information about a test. +class TestPartResult; // Result of a test part. +class UnitTest; // A collection of test suites. + +template <typename T> +::std::string PrintToString(const T& value); + +namespace internal { + +struct TraceInfo; // Information about a trace point. +class TestInfoImpl; // Opaque implementation of TestInfo +class UnitTestImpl; // Opaque implementation of UnitTest + +// The text used in failure messages to indicate the start of the +// stack trace. +GTEST_API_ extern const char kStackTraceMarker[]; + +// An IgnoredValue object can be implicitly constructed from ANY value. +class IgnoredValue { + struct Sink {}; + public: + // This constructor template allows any value to be implicitly + // converted to IgnoredValue. The object has no data member and + // doesn't try to remember anything about the argument. We + // deliberately omit the 'explicit' keyword in order to allow the + // conversion to be implicit. + // Disable the conversion if T already has a magical conversion operator. + // Otherwise we get ambiguity. + template <typename T, + typename std::enable_if<!std::is_convertible<T, Sink>::value, + int>::type = 0> + IgnoredValue(const T& /* ignored */) {} // NOLINT(runtime/explicit) +}; + +// Appends the user-supplied message to the Google-Test-generated message. +GTEST_API_ std::string AppendUserMessage( + const std::string& gtest_msg, const Message& user_msg); + +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4275 \ +/* an exported class was derived from a class that was not exported */) + +// This exception is thrown by (and only by) a failed Google Test +// assertion when GTEST_FLAG(throw_on_failure) is true (if exceptions +// are enabled). We derive it from std::runtime_error, which is for +// errors presumably detectable only at run time. Since +// std::runtime_error inherits from std::exception, many testing +// frameworks know how to extract and print the message inside it. +class GTEST_API_ GoogleTestFailureException : public ::std::runtime_error { + public: + explicit GoogleTestFailureException(const TestPartResult& failure); +}; + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4275 + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +namespace edit_distance { +// Returns the optimal edits to go from 'left' to 'right'. +// All edits cost the same, with replace having lower priority than +// add/remove. +// Simple implementation of the Wagner-Fischer algorithm. +// See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wagner-Fischer_algorithm +enum EditType { kMatch, kAdd, kRemove, kReplace }; +GTEST_API_ std::vector<EditType> CalculateOptimalEdits( + const std::vector<size_t>& left, const std::vector<size_t>& right); + +// Same as above, but the input is represented as strings. +GTEST_API_ std::vector<EditType> CalculateOptimalEdits( + const std::vector<std::string>& left, + const std::vector<std::string>& right); + +// Create a diff of the input strings in Unified diff format. +GTEST_API_ std::string CreateUnifiedDiff(const std::vector<std::string>& left, + const std::vector<std::string>& right, + size_t context = 2); + +} // namespace edit_distance + +// Calculate the diff between 'left' and 'right' and return it in unified diff +// format. +// If not null, stores in 'total_line_count' the total number of lines found +// in left + right. +GTEST_API_ std::string DiffStrings(const std::string& left, + const std::string& right, + size_t* total_line_count); + +// Constructs and returns the message for an equality assertion +// (e.g. ASSERT_EQ, EXPECT_STREQ, etc) failure. +// +// The first four parameters are the expressions used in the assertion +// and their values, as strings. For example, for ASSERT_EQ(foo, bar) +// where foo is 5 and bar is 6, we have: +// +// expected_expression: "foo" +// actual_expression: "bar" +// expected_value: "5" +// actual_value: "6" +// +// The ignoring_case parameter is true if and only if the assertion is a +// *_STRCASEEQ*. When it's true, the string " (ignoring case)" will +// be inserted into the message. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult EqFailure(const char* expected_expression, + const char* actual_expression, + const std::string& expected_value, + const std::string& actual_value, + bool ignoring_case); + +// Constructs a failure message for Boolean assertions such as EXPECT_TRUE. +GTEST_API_ std::string GetBoolAssertionFailureMessage( + const AssertionResult& assertion_result, + const char* expression_text, + const char* actual_predicate_value, + const char* expected_predicate_value); + +// This template class represents an IEEE floating-point number +// (either single-precision or double-precision, depending on the +// template parameters). +// +// The purpose of this class is to do more sophisticated number +// comparison. (Due to round-off error, etc, it's very unlikely that +// two floating-points will be equal exactly. Hence a naive +// comparison by the == operation often doesn't work.) +// +// Format of IEEE floating-point: +// +// The most-significant bit being the leftmost, an IEEE +// floating-point looks like +// +// sign_bit exponent_bits fraction_bits +// +// Here, sign_bit is a single bit that designates the sign of the +// number. +// +// For float, there are 8 exponent bits and 23 fraction bits. +// +// For double, there are 11 exponent bits and 52 fraction bits. +// +// More details can be found at +// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_floating-point_standard. +// +// Template parameter: +// +// RawType: the raw floating-point type (either float or double) +template <typename RawType> +class FloatingPoint { + public: + // Defines the unsigned integer type that has the same size as the + // floating point number. + typedef typename TypeWithSize<sizeof(RawType)>::UInt Bits; + + // Constants. + + // # of bits in a number. + static const size_t kBitCount = 8*sizeof(RawType); + + // # of fraction bits in a number. + static const size_t kFractionBitCount = + std::numeric_limits<RawType>::digits - 1; + + // # of exponent bits in a number. + static const size_t kExponentBitCount = kBitCount - 1 - kFractionBitCount; + + // The mask for the sign bit. + static const Bits kSignBitMask = static_cast<Bits>(1) << (kBitCount - 1); + + // The mask for the fraction bits. + static const Bits kFractionBitMask = + ~static_cast<Bits>(0) >> (kExponentBitCount + 1); + + // The mask for the exponent bits. + static const Bits kExponentBitMask = ~(kSignBitMask | kFractionBitMask); + + // How many ULP's (Units in the Last Place) we want to tolerate when + // comparing two numbers. The larger the value, the more error we + // allow. A 0 value means that two numbers must be exactly the same + // to be considered equal. + // + // The maximum error of a single floating-point operation is 0.5 + // units in the last place. On Intel CPU's, all floating-point + // calculations are done with 80-bit precision, while double has 64 + // bits. Therefore, 4 should be enough for ordinary use. + // + // See the following article for more details on ULP: + // http://randomascii.wordpress.com/2012/02/25/comparing-floating-point-numbers-2012-edition/ + static const uint32_t kMaxUlps = 4; + + // Constructs a FloatingPoint from a raw floating-point number. + // + // On an Intel CPU, passing a non-normalized NAN (Not a Number) + // around may change its bits, although the new value is guaranteed + // to be also a NAN. Therefore, don't expect this constructor to + // preserve the bits in x when x is a NAN. + explicit FloatingPoint(const RawType& x) { u_.value_ = x; } + + // Static methods + + // Reinterprets a bit pattern as a floating-point number. + // + // This function is needed to test the AlmostEquals() method. + static RawType ReinterpretBits(const Bits bits) { + FloatingPoint fp(0); + fp.u_.bits_ = bits; + return fp.u_.value_; + } + + // Returns the floating-point number that represent positive infinity. + static RawType Infinity() { + return ReinterpretBits(kExponentBitMask); + } + + // Returns the maximum representable finite floating-point number. + static RawType Max(); + + // Non-static methods + + // Returns the bits that represents this number. + const Bits &bits() const { return u_.bits_; } + + // Returns the exponent bits of this number. + Bits exponent_bits() const { return kExponentBitMask & u_.bits_; } + + // Returns the fraction bits of this number. + Bits fraction_bits() const { return kFractionBitMask & u_.bits_; } + + // Returns the sign bit of this number. + Bits sign_bit() const { return kSignBitMask & u_.bits_; } + + // Returns true if and only if this is NAN (not a number). + bool is_nan() const { + // It's a NAN if the exponent bits are all ones and the fraction + // bits are not entirely zeros. + return (exponent_bits() == kExponentBitMask) && (fraction_bits() != 0); + } + + // Returns true if and only if this number is at most kMaxUlps ULP's away + // from rhs. In particular, this function: + // + // - returns false if either number is (or both are) NAN. + // - treats really large numbers as almost equal to infinity. + // - thinks +0.0 and -0.0 are 0 DLP's apart. + bool AlmostEquals(const FloatingPoint& rhs) const { + // The IEEE standard says that any comparison operation involving + // a NAN must return false. + if (is_nan() || rhs.is_nan()) return false; + + return DistanceBetweenSignAndMagnitudeNumbers(u_.bits_, rhs.u_.bits_) + <= kMaxUlps; + } + + private: + // The data type used to store the actual floating-point number. + union FloatingPointUnion { + RawType value_; // The raw floating-point number. + Bits bits_; // The bits that represent the number. + }; + + // Converts an integer from the sign-and-magnitude representation to + // the biased representation. More precisely, let N be 2 to the + // power of (kBitCount - 1), an integer x is represented by the + // unsigned number x + N. + // + // For instance, + // + // -N + 1 (the most negative number representable using + // sign-and-magnitude) is represented by 1; + // 0 is represented by N; and + // N - 1 (the biggest number representable using + // sign-and-magnitude) is represented by 2N - 1. + // + // Read http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signed_number_representations + // for more details on signed number representations. + static Bits SignAndMagnitudeToBiased(const Bits &sam) { + if (kSignBitMask & sam) { + // sam represents a negative number. + return ~sam + 1; + } else { + // sam represents a positive number. + return kSignBitMask | sam; + } + } + + // Given two numbers in the sign-and-magnitude representation, + // returns the distance between them as an unsigned number. + static Bits DistanceBetweenSignAndMagnitudeNumbers(const Bits &sam1, + const Bits &sam2) { + const Bits biased1 = SignAndMagnitudeToBiased(sam1); + const Bits biased2 = SignAndMagnitudeToBiased(sam2); + return (biased1 >= biased2) ? (biased1 - biased2) : (biased2 - biased1); + } + + FloatingPointUnion u_; +}; + +// We cannot use std::numeric_limits<T>::max() as it clashes with the max() +// macro defined by <windows.h>. +template <> +inline float FloatingPoint<float>::Max() { return FLT_MAX; } +template <> +inline double FloatingPoint<double>::Max() { return DBL_MAX; } + +// Typedefs the instances of the FloatingPoint template class that we +// care to use. +typedef FloatingPoint<float> Float; +typedef FloatingPoint<double> Double; + +// In order to catch the mistake of putting tests that use different +// test fixture classes in the same test suite, we need to assign +// unique IDs to fixture classes and compare them. The TypeId type is +// used to hold such IDs. The user should treat TypeId as an opaque +// type: the only operation allowed on TypeId values is to compare +// them for equality using the == operator. +typedef const void* TypeId; + +template <typename T> +class TypeIdHelper { + public: + // dummy_ must not have a const type. Otherwise an overly eager + // compiler (e.g. MSVC 7.1 & 8.0) may try to merge + // TypeIdHelper<T>::dummy_ for different Ts as an "optimization". + static bool dummy_; +}; + +template <typename T> +bool TypeIdHelper<T>::dummy_ = false; + +// GetTypeId<T>() returns the ID of type T. Different values will be +// returned for different types. Calling the function twice with the +// same type argument is guaranteed to return the same ID. +template <typename T> +TypeId GetTypeId() { + // The compiler is required to allocate a different + // TypeIdHelper<T>::dummy_ variable for each T used to instantiate + // the template. Therefore, the address of dummy_ is guaranteed to + // be unique. + return &(TypeIdHelper<T>::dummy_); +} + +// Returns the type ID of ::testing::Test. Always call this instead +// of GetTypeId< ::testing::Test>() to get the type ID of +// ::testing::Test, as the latter may give the wrong result due to a +// suspected linker bug when compiling Google Test as a Mac OS X +// framework. +GTEST_API_ TypeId GetTestTypeId(); + +// Defines the abstract factory interface that creates instances +// of a Test object. +class TestFactoryBase { + public: + virtual ~TestFactoryBase() {} + + // Creates a test instance to run. The instance is both created and destroyed + // within TestInfoImpl::Run() + virtual Test* CreateTest() = 0; + + protected: + TestFactoryBase() {} + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestFactoryBase); +}; + +// This class provides implementation of TeastFactoryBase interface. +// It is used in TEST and TEST_F macros. +template <class TestClass> +class TestFactoryImpl : public TestFactoryBase { + public: + Test* CreateTest() override { return new TestClass; } +}; + +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +// Predicate-formatters for implementing the HRESULT checking macros +// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_HRESULT_{SUCCEEDED|FAILED} +// We pass a long instead of HRESULT to avoid causing an +// include dependency for the HRESULT type. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsHRESULTSuccess(const char* expr, + long hr); // NOLINT +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsHRESULTFailure(const char* expr, + long hr); // NOLINT + +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +// Types of SetUpTestSuite() and TearDownTestSuite() functions. +using SetUpTestSuiteFunc = void (*)(); +using TearDownTestSuiteFunc = void (*)(); + +struct CodeLocation { + CodeLocation(const std::string& a_file, int a_line) + : file(a_file), line(a_line) {} + + std::string file; + int line; +}; + +// Helper to identify which setup function for TestCase / TestSuite to call. +// Only one function is allowed, either TestCase or TestSute but not both. + +// Utility functions to help SuiteApiResolver +using SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType = void (*)(); + +inline SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType GetNotDefaultOrNull( + SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType a, SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType def) { + return a == def ? nullptr : a; +} + +template <typename T> +// Note that SuiteApiResolver inherits from T because +// SetUpTestSuite()/TearDownTestSuite() could be protected. Ths way +// SuiteApiResolver can access them. +struct SuiteApiResolver : T { + // testing::Test is only forward declared at this point. So we make it a + // dependend class for the compiler to be OK with it. + using Test = + typename std::conditional<sizeof(T) != 0, ::testing::Test, void>::type; + + static SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType GetSetUpCaseOrSuite(const char* filename, + int line_num) { +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType test_case_fp = + GetNotDefaultOrNull(&T::SetUpTestCase, &Test::SetUpTestCase); + SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType test_suite_fp = + GetNotDefaultOrNull(&T::SetUpTestSuite, &Test::SetUpTestSuite); + + GTEST_CHECK_(!test_case_fp || !test_suite_fp) + << "Test can not provide both SetUpTestSuite and SetUpTestCase, please " + "make sure there is only one present at " + << filename << ":" << line_num; + + return test_case_fp != nullptr ? test_case_fp : test_suite_fp; +#else + (void)(filename); + (void)(line_num); + return &T::SetUpTestSuite; +#endif + } + + static SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType GetTearDownCaseOrSuite(const char* filename, + int line_num) { +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType test_case_fp = + GetNotDefaultOrNull(&T::TearDownTestCase, &Test::TearDownTestCase); + SetUpTearDownSuiteFuncType test_suite_fp = + GetNotDefaultOrNull(&T::TearDownTestSuite, &Test::TearDownTestSuite); + + GTEST_CHECK_(!test_case_fp || !test_suite_fp) + << "Test can not provide both TearDownTestSuite and TearDownTestCase," + " please make sure there is only one present at" + << filename << ":" << line_num; + + return test_case_fp != nullptr ? test_case_fp : test_suite_fp; +#else + (void)(filename); + (void)(line_num); + return &T::TearDownTestSuite; +#endif + } +}; + +// Creates a new TestInfo object and registers it with Google Test; +// returns the created object. +// +// Arguments: +// +// test_suite_name: name of the test suite +// name: name of the test +// type_param: the name of the test's type parameter, or NULL if +// this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test. +// value_param: text representation of the test's value parameter, +// or NULL if this is not a type-parameterized test. +// code_location: code location where the test is defined +// fixture_class_id: ID of the test fixture class +// set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test suite +// tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test suite +// factory: pointer to the factory that creates a test object. +// The newly created TestInfo instance will assume +// ownership of the factory object. +GTEST_API_ TestInfo* MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( + const char* test_suite_name, const char* name, const char* type_param, + const char* value_param, CodeLocation code_location, + TypeId fixture_class_id, SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc, + TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc, TestFactoryBase* factory); + +// If *pstr starts with the given prefix, modifies *pstr to be right +// past the prefix and returns true; otherwise leaves *pstr unchanged +// and returns false. None of pstr, *pstr, and prefix can be NULL. +GTEST_API_ bool SkipPrefix(const char* prefix, const char** pstr); + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) + +// State of the definition of a type-parameterized test suite. +class GTEST_API_ TypedTestSuitePState { + public: + TypedTestSuitePState() : registered_(false) {} + + // Adds the given test name to defined_test_names_ and return true + // if the test suite hasn't been registered; otherwise aborts the + // program. + bool AddTestName(const char* file, int line, const char* case_name, + const char* test_name) { + if (registered_) { + fprintf(stderr, + "%s Test %s must be defined before " + "REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(%s, ...).\n", + FormatFileLocation(file, line).c_str(), test_name, case_name); + fflush(stderr); + posix::Abort(); + } + registered_tests_.insert( + ::std::make_pair(test_name, CodeLocation(file, line))); + return true; + } + + bool TestExists(const std::string& test_name) const { + return registered_tests_.count(test_name) > 0; + } + + const CodeLocation& GetCodeLocation(const std::string& test_name) const { + RegisteredTestsMap::const_iterator it = registered_tests_.find(test_name); + GTEST_CHECK_(it != registered_tests_.end()); + return it->second; + } + + // Verifies that registered_tests match the test names in + // defined_test_names_; returns registered_tests if successful, or + // aborts the program otherwise. + const char* VerifyRegisteredTestNames(const char* test_suite_name, + const char* file, int line, + const char* registered_tests); + + private: + typedef ::std::map<std::string, CodeLocation> RegisteredTestsMap; + + bool registered_; + RegisteredTestsMap registered_tests_; +}; + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +using TypedTestCasePState = TypedTestSuitePState; +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + +// Skips to the first non-space char after the first comma in 'str'; +// returns NULL if no comma is found in 'str'. +inline const char* SkipComma(const char* str) { + const char* comma = strchr(str, ','); + if (comma == nullptr) { + return nullptr; + } + while (IsSpace(*(++comma))) {} + return comma; +} + +// Returns the prefix of 'str' before the first comma in it; returns +// the entire string if it contains no comma. +inline std::string GetPrefixUntilComma(const char* str) { + const char* comma = strchr(str, ','); + return comma == nullptr ? str : std::string(str, comma); +} + +// Splits a given string on a given delimiter, populating a given +// vector with the fields. +void SplitString(const ::std::string& str, char delimiter, + ::std::vector< ::std::string>* dest); + +// The default argument to the template below for the case when the user does +// not provide a name generator. +struct DefaultNameGenerator { + template <typename T> + static std::string GetName(int i) { + return StreamableToString(i); + } +}; + +template <typename Provided = DefaultNameGenerator> +struct NameGeneratorSelector { + typedef Provided type; +}; + +template <typename NameGenerator> +void GenerateNamesRecursively(internal::None, std::vector<std::string>*, int) {} + +template <typename NameGenerator, typename Types> +void GenerateNamesRecursively(Types, std::vector<std::string>* result, int i) { + result->push_back(NameGenerator::template GetName<typename Types::Head>(i)); + GenerateNamesRecursively<NameGenerator>(typename Types::Tail(), result, + i + 1); +} + +template <typename NameGenerator, typename Types> +std::vector<std::string> GenerateNames() { + std::vector<std::string> result; + GenerateNamesRecursively<NameGenerator>(Types(), &result, 0); + return result; +} + +// TypeParameterizedTest<Fixture, TestSel, Types>::Register() +// registers a list of type-parameterized tests with Google Test. The +// return value is insignificant - we just need to return something +// such that we can call this function in a namespace scope. +// +// Implementation note: The GTEST_TEMPLATE_ macro declares a template +// template parameter. It's defined in gtest-type-util.h. +template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Fixture, class TestSel, typename Types> +class TypeParameterizedTest { + public: + // 'index' is the index of the test in the type list 'Types' + // specified in INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(Prefix, TestSuite, + // Types). Valid values for 'index' are [0, N - 1] where N is the + // length of Types. + static bool Register(const char* prefix, const CodeLocation& code_location, + const char* case_name, const char* test_names, int index, + const std::vector<std::string>& type_names = + GenerateNames<DefaultNameGenerator, Types>()) { + typedef typename Types::Head Type; + typedef Fixture<Type> FixtureClass; + typedef typename GTEST_BIND_(TestSel, Type) TestClass; + + // First, registers the first type-parameterized test in the type + // list. + MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( + (std::string(prefix) + (prefix[0] == '\0' ? "" : "/") + case_name + + "/" + type_names[static_cast<size_t>(index)]) + .c_str(), + StripTrailingSpaces(GetPrefixUntilComma(test_names)).c_str(), + GetTypeName<Type>().c_str(), + nullptr, // No value parameter. + code_location, GetTypeId<FixtureClass>(), + SuiteApiResolver<TestClass>::GetSetUpCaseOrSuite( + code_location.file.c_str(), code_location.line), + SuiteApiResolver<TestClass>::GetTearDownCaseOrSuite( + code_location.file.c_str(), code_location.line), + new TestFactoryImpl<TestClass>); + + // Next, recurses (at compile time) with the tail of the type list. + return TypeParameterizedTest<Fixture, TestSel, + typename Types::Tail>::Register(prefix, + code_location, + case_name, + test_names, + index + 1, + type_names); + } +}; + +// The base case for the compile time recursion. +template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Fixture, class TestSel> +class TypeParameterizedTest<Fixture, TestSel, internal::None> { + public: + static bool Register(const char* /*prefix*/, const CodeLocation&, + const char* /*case_name*/, const char* /*test_names*/, + int /*index*/, + const std::vector<std::string>& = + std::vector<std::string>() /*type_names*/) { + return true; + } +}; + +GTEST_API_ void RegisterTypeParameterizedTestSuite(const char* test_suite_name, + CodeLocation code_location); +GTEST_API_ void RegisterTypeParameterizedTestSuiteInstantiation( + const char* case_name); + +// TypeParameterizedTestSuite<Fixture, Tests, Types>::Register() +// registers *all combinations* of 'Tests' and 'Types' with Google +// Test. The return value is insignificant - we just need to return +// something such that we can call this function in a namespace scope. +template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Fixture, typename Tests, typename Types> +class TypeParameterizedTestSuite { + public: + static bool Register(const char* prefix, CodeLocation code_location, + const TypedTestSuitePState* state, const char* case_name, + const char* test_names, + const std::vector<std::string>& type_names = + GenerateNames<DefaultNameGenerator, Types>()) { + RegisterTypeParameterizedTestSuiteInstantiation(case_name); + std::string test_name = StripTrailingSpaces( + GetPrefixUntilComma(test_names)); + if (!state->TestExists(test_name)) { + fprintf(stderr, "Failed to get code location for test %s.%s at %s.", + case_name, test_name.c_str(), + FormatFileLocation(code_location.file.c_str(), + code_location.line).c_str()); + fflush(stderr); + posix::Abort(); + } + const CodeLocation& test_location = state->GetCodeLocation(test_name); + + typedef typename Tests::Head Head; + + // First, register the first test in 'Test' for each type in 'Types'. + TypeParameterizedTest<Fixture, Head, Types>::Register( + prefix, test_location, case_name, test_names, 0, type_names); + + // Next, recurses (at compile time) with the tail of the test list. + return TypeParameterizedTestSuite<Fixture, typename Tests::Tail, + Types>::Register(prefix, code_location, + state, case_name, + SkipComma(test_names), + type_names); + } +}; + +// The base case for the compile time recursion. +template <GTEST_TEMPLATE_ Fixture, typename Types> +class TypeParameterizedTestSuite<Fixture, internal::None, Types> { + public: + static bool Register(const char* /*prefix*/, const CodeLocation&, + const TypedTestSuitePState* /*state*/, + const char* /*case_name*/, const char* /*test_names*/, + const std::vector<std::string>& = + std::vector<std::string>() /*type_names*/) { + return true; + } +}; + +// Returns the current OS stack trace as an std::string. +// +// The maximum number of stack frames to be included is specified by +// the gtest_stack_trace_depth flag. The skip_count parameter +// specifies the number of top frames to be skipped, which doesn't +// count against the number of frames to be included. +// +// For example, if Foo() calls Bar(), which in turn calls +// GetCurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop(..., 1), Foo() will be included in +// the trace but Bar() and GetCurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop() won't. +GTEST_API_ std::string GetCurrentOsStackTraceExceptTop( + UnitTest* unit_test, int skip_count); + +// Helpers for suppressing warnings on unreachable code or constant +// condition. + +// Always returns true. +GTEST_API_ bool AlwaysTrue(); + +// Always returns false. +inline bool AlwaysFalse() { return !AlwaysTrue(); } + +// Helper for suppressing false warning from Clang on a const char* +// variable declared in a conditional expression always being NULL in +// the else branch. +struct GTEST_API_ ConstCharPtr { + ConstCharPtr(const char* str) : value(str) {} + operator bool() const { return true; } + const char* value; +}; + +// Helper for declaring std::string within 'if' statement +// in pre C++17 build environment. +struct TrueWithString { + TrueWithString() = default; + explicit TrueWithString(const char* str) : value(str) {} + explicit TrueWithString(const std::string& str) : value(str) {} + explicit operator bool() const { return true; } + std::string value; +}; + +// A simple Linear Congruential Generator for generating random +// numbers with a uniform distribution. Unlike rand() and srand(), it +// doesn't use global state (and therefore can't interfere with user +// code). Unlike rand_r(), it's portable. An LCG isn't very random, +// but it's good enough for our purposes. +class GTEST_API_ Random { + public: + static const uint32_t kMaxRange = 1u << 31; + + explicit Random(uint32_t seed) : state_(seed) {} + + void Reseed(uint32_t seed) { state_ = seed; } + + // Generates a random number from [0, range). Crashes if 'range' is + // 0 or greater than kMaxRange. + uint32_t Generate(uint32_t range); + + private: + uint32_t state_; + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Random); +}; + +// Turns const U&, U&, const U, and U all into U. +#define GTEST_REMOVE_REFERENCE_AND_CONST_(T) \ + typename std::remove_const<typename std::remove_reference<T>::type>::type + +// HasDebugStringAndShortDebugString<T>::value is a compile-time bool constant +// that's true if and only if T has methods DebugString() and ShortDebugString() +// that return std::string. +template <typename T> +class HasDebugStringAndShortDebugString { + private: + template <typename C> + static auto CheckDebugString(C*) -> typename std::is_same< + std::string, decltype(std::declval<const C>().DebugString())>::type; + template <typename> + static std::false_type CheckDebugString(...); + + template <typename C> + static auto CheckShortDebugString(C*) -> typename std::is_same< + std::string, decltype(std::declval<const C>().ShortDebugString())>::type; + template <typename> + static std::false_type CheckShortDebugString(...); + + using HasDebugStringType = decltype(CheckDebugString<T>(nullptr)); + using HasShortDebugStringType = decltype(CheckShortDebugString<T>(nullptr)); + + public: + static constexpr bool value = + HasDebugStringType::value && HasShortDebugStringType::value; +}; + +template <typename T> +constexpr bool HasDebugStringAndShortDebugString<T>::value; + +// When the compiler sees expression IsContainerTest<C>(0), if C is an +// STL-style container class, the first overload of IsContainerTest +// will be viable (since both C::iterator* and C::const_iterator* are +// valid types and NULL can be implicitly converted to them). It will +// be picked over the second overload as 'int' is a perfect match for +// the type of argument 0. If C::iterator or C::const_iterator is not +// a valid type, the first overload is not viable, and the second +// overload will be picked. Therefore, we can determine whether C is +// a container class by checking the type of IsContainerTest<C>(0). +// The value of the expression is insignificant. +// +// In C++11 mode we check the existence of a const_iterator and that an +// iterator is properly implemented for the container. +// +// For pre-C++11 that we look for both C::iterator and C::const_iterator. +// The reason is that C++ injects the name of a class as a member of the +// class itself (e.g. you can refer to class iterator as either +// 'iterator' or 'iterator::iterator'). If we look for C::iterator +// only, for example, we would mistakenly think that a class named +// iterator is an STL container. +// +// Also note that the simpler approach of overloading +// IsContainerTest(typename C::const_iterator*) and +// IsContainerTest(...) doesn't work with Visual Age C++ and Sun C++. +typedef int IsContainer; +template <class C, + class Iterator = decltype(::std::declval<const C&>().begin()), + class = decltype(::std::declval<const C&>().end()), + class = decltype(++::std::declval<Iterator&>()), + class = decltype(*::std::declval<Iterator>()), + class = typename C::const_iterator> +IsContainer IsContainerTest(int /* dummy */) { + return 0; +} + +typedef char IsNotContainer; +template <class C> +IsNotContainer IsContainerTest(long /* dummy */) { return '\0'; } + +// Trait to detect whether a type T is a hash table. +// The heuristic used is that the type contains an inner type `hasher` and does +// not contain an inner type `reverse_iterator`. +// If the container is iterable in reverse, then order might actually matter. +template <typename T> +struct IsHashTable { + private: + template <typename U> + static char test(typename U::hasher*, typename U::reverse_iterator*); + template <typename U> + static int test(typename U::hasher*, ...); + template <typename U> + static char test(...); + + public: + static const bool value = sizeof(test<T>(nullptr, nullptr)) == sizeof(int); +}; + +template <typename T> +const bool IsHashTable<T>::value; + +template <typename C, + bool = sizeof(IsContainerTest<C>(0)) == sizeof(IsContainer)> +struct IsRecursiveContainerImpl; + +template <typename C> +struct IsRecursiveContainerImpl<C, false> : public std::false_type {}; + +// Since the IsRecursiveContainerImpl depends on the IsContainerTest we need to +// obey the same inconsistencies as the IsContainerTest, namely check if +// something is a container is relying on only const_iterator in C++11 and +// is relying on both const_iterator and iterator otherwise +template <typename C> +struct IsRecursiveContainerImpl<C, true> { + using value_type = decltype(*std::declval<typename C::const_iterator>()); + using type = + std::is_same<typename std::remove_const< + typename std::remove_reference<value_type>::type>::type, + C>; +}; + +// IsRecursiveContainer<Type> is a unary compile-time predicate that +// evaluates whether C is a recursive container type. A recursive container +// type is a container type whose value_type is equal to the container type +// itself. An example for a recursive container type is +// boost::filesystem::path, whose iterator has a value_type that is equal to +// boost::filesystem::path. +template <typename C> +struct IsRecursiveContainer : public IsRecursiveContainerImpl<C>::type {}; + +// Utilities for native arrays. + +// ArrayEq() compares two k-dimensional native arrays using the +// elements' operator==, where k can be any integer >= 0. When k is +// 0, ArrayEq() degenerates into comparing a single pair of values. + +template <typename T, typename U> +bool ArrayEq(const T* lhs, size_t size, const U* rhs); + +// This generic version is used when k is 0. +template <typename T, typename U> +inline bool ArrayEq(const T& lhs, const U& rhs) { return lhs == rhs; } + +// This overload is used when k >= 1. +template <typename T, typename U, size_t N> +inline bool ArrayEq(const T(&lhs)[N], const U(&rhs)[N]) { + return internal::ArrayEq(lhs, N, rhs); +} + +// This helper reduces code bloat. If we instead put its logic inside +// the previous ArrayEq() function, arrays with different sizes would +// lead to different copies of the template code. +template <typename T, typename U> +bool ArrayEq(const T* lhs, size_t size, const U* rhs) { + for (size_t i = 0; i != size; i++) { + if (!internal::ArrayEq(lhs[i], rhs[i])) + return false; + } + return true; +} + +// Finds the first element in the iterator range [begin, end) that +// equals elem. Element may be a native array type itself. +template <typename Iter, typename Element> +Iter ArrayAwareFind(Iter begin, Iter end, const Element& elem) { + for (Iter it = begin; it != end; ++it) { + if (internal::ArrayEq(*it, elem)) + return it; + } + return end; +} + +// CopyArray() copies a k-dimensional native array using the elements' +// operator=, where k can be any integer >= 0. When k is 0, +// CopyArray() degenerates into copying a single value. + +template <typename T, typename U> +void CopyArray(const T* from, size_t size, U* to); + +// This generic version is used when k is 0. +template <typename T, typename U> +inline void CopyArray(const T& from, U* to) { *to = from; } + +// This overload is used when k >= 1. +template <typename T, typename U, size_t N> +inline void CopyArray(const T(&from)[N], U(*to)[N]) { + internal::CopyArray(from, N, *to); +} + +// This helper reduces code bloat. If we instead put its logic inside +// the previous CopyArray() function, arrays with different sizes +// would lead to different copies of the template code. +template <typename T, typename U> +void CopyArray(const T* from, size_t size, U* to) { + for (size_t i = 0; i != size; i++) { + internal::CopyArray(from[i], to + i); + } +} + +// The relation between an NativeArray object (see below) and the +// native array it represents. +// We use 2 different structs to allow non-copyable types to be used, as long +// as RelationToSourceReference() is passed. +struct RelationToSourceReference {}; +struct RelationToSourceCopy {}; + +// Adapts a native array to a read-only STL-style container. Instead +// of the complete STL container concept, this adaptor only implements +// members useful for Google Mock's container matchers. New members +// should be added as needed. To simplify the implementation, we only +// support Element being a raw type (i.e. having no top-level const or +// reference modifier). It's the client's responsibility to satisfy +// this requirement. Element can be an array type itself (hence +// multi-dimensional arrays are supported). +template <typename Element> +class NativeArray { + public: + // STL-style container typedefs. + typedef Element value_type; + typedef Element* iterator; + typedef const Element* const_iterator; + + // Constructs from a native array. References the source. + NativeArray(const Element* array, size_t count, RelationToSourceReference) { + InitRef(array, count); + } + + // Constructs from a native array. Copies the source. + NativeArray(const Element* array, size_t count, RelationToSourceCopy) { + InitCopy(array, count); + } + + // Copy constructor. + NativeArray(const NativeArray& rhs) { + (this->*rhs.clone_)(rhs.array_, rhs.size_); + } + + ~NativeArray() { + if (clone_ != &NativeArray::InitRef) + delete[] array_; + } + + // STL-style container methods. + size_t size() const { return size_; } + const_iterator begin() const { return array_; } + const_iterator end() const { return array_ + size_; } + bool operator==(const NativeArray& rhs) const { + return size() == rhs.size() && + ArrayEq(begin(), size(), rhs.begin()); + } + + private: + static_assert(!std::is_const<Element>::value, "Type must not be const"); + static_assert(!std::is_reference<Element>::value, + "Type must not be a reference"); + + // Initializes this object with a copy of the input. + void InitCopy(const Element* array, size_t a_size) { + Element* const copy = new Element[a_size]; + CopyArray(array, a_size, copy); + array_ = copy; + size_ = a_size; + clone_ = &NativeArray::InitCopy; + } + + // Initializes this object with a reference of the input. + void InitRef(const Element* array, size_t a_size) { + array_ = array; + size_ = a_size; + clone_ = &NativeArray::InitRef; + } + + const Element* array_; + size_t size_; + void (NativeArray::*clone_)(const Element*, size_t); +}; + +// Backport of std::index_sequence. +template <size_t... Is> +struct IndexSequence { + using type = IndexSequence; +}; + +// Double the IndexSequence, and one if plus_one is true. +template <bool plus_one, typename T, size_t sizeofT> +struct DoubleSequence; +template <size_t... I, size_t sizeofT> +struct DoubleSequence<true, IndexSequence<I...>, sizeofT> { + using type = IndexSequence<I..., (sizeofT + I)..., 2 * sizeofT>; +}; +template <size_t... I, size_t sizeofT> +struct DoubleSequence<false, IndexSequence<I...>, sizeofT> { + using type = IndexSequence<I..., (sizeofT + I)...>; +}; + +// Backport of std::make_index_sequence. +// It uses O(ln(N)) instantiation depth. +template <size_t N> +struct MakeIndexSequenceImpl + : DoubleSequence<N % 2 == 1, typename MakeIndexSequenceImpl<N / 2>::type, + N / 2>::type {}; + +template <> +struct MakeIndexSequenceImpl<0> : IndexSequence<> {}; + +template <size_t N> +using MakeIndexSequence = typename MakeIndexSequenceImpl<N>::type; + +template <typename... T> +using IndexSequenceFor = typename MakeIndexSequence<sizeof...(T)>::type; + +template <size_t> +struct Ignore { + Ignore(...); // NOLINT +}; + +template <typename> +struct ElemFromListImpl; +template <size_t... I> +struct ElemFromListImpl<IndexSequence<I...>> { + // We make Ignore a template to solve a problem with MSVC. + // A non-template Ignore would work fine with `decltype(Ignore(I))...`, but + // MSVC doesn't understand how to deal with that pack expansion. + // Use `0 * I` to have a single instantiation of Ignore. + template <typename R> + static R Apply(Ignore<0 * I>..., R (*)(), ...); +}; + +template <size_t N, typename... T> +struct ElemFromList { + using type = + decltype(ElemFromListImpl<typename MakeIndexSequence<N>::type>::Apply( + static_cast<T (*)()>(nullptr)...)); +}; + +struct FlatTupleConstructTag {}; + +template <typename... T> +class FlatTuple; + +template <typename Derived, size_t I> +struct FlatTupleElemBase; + +template <typename... T, size_t I> +struct FlatTupleElemBase<FlatTuple<T...>, I> { + using value_type = typename ElemFromList<I, T...>::type; + FlatTupleElemBase() = default; + template <typename Arg> + explicit FlatTupleElemBase(FlatTupleConstructTag, Arg&& t) + : value(std::forward<Arg>(t)) {} + value_type value; +}; + +template <typename Derived, typename Idx> +struct FlatTupleBase; + +template <size_t... Idx, typename... T> +struct FlatTupleBase<FlatTuple<T...>, IndexSequence<Idx...>> + : FlatTupleElemBase<FlatTuple<T...>, Idx>... { + using Indices = IndexSequence<Idx...>; + FlatTupleBase() = default; + template <typename... Args> + explicit FlatTupleBase(FlatTupleConstructTag, Args&&... args) + : FlatTupleElemBase<FlatTuple<T...>, Idx>(FlatTupleConstructTag{}, + std::forward<Args>(args))... {} + + template <size_t I> + const typename ElemFromList<I, T...>::type& Get() const { + return FlatTupleElemBase<FlatTuple<T...>, I>::value; + } + + template <size_t I> + typename ElemFromList<I, T...>::type& Get() { + return FlatTupleElemBase<FlatTuple<T...>, I>::value; + } + + template <typename F> + auto Apply(F&& f) -> decltype(std::forward<F>(f)(this->Get<Idx>()...)) { + return std::forward<F>(f)(Get<Idx>()...); + } + + template <typename F> + auto Apply(F&& f) const -> decltype(std::forward<F>(f)(this->Get<Idx>()...)) { + return std::forward<F>(f)(Get<Idx>()...); + } +}; + +// Analog to std::tuple but with different tradeoffs. +// This class minimizes the template instantiation depth, thus allowing more +// elements than std::tuple would. std::tuple has been seen to require an +// instantiation depth of more than 10x the number of elements in some +// implementations. +// FlatTuple and ElemFromList are not recursive and have a fixed depth +// regardless of T... +// MakeIndexSequence, on the other hand, it is recursive but with an +// instantiation depth of O(ln(N)). +template <typename... T> +class FlatTuple + : private FlatTupleBase<FlatTuple<T...>, + typename MakeIndexSequence<sizeof...(T)>::type> { + using Indices = typename FlatTupleBase< + FlatTuple<T...>, typename MakeIndexSequence<sizeof...(T)>::type>::Indices; + + public: + FlatTuple() = default; + template <typename... Args> + explicit FlatTuple(FlatTupleConstructTag tag, Args&&... args) + : FlatTuple::FlatTupleBase(tag, std::forward<Args>(args)...) {} + + using FlatTuple::FlatTupleBase::Apply; + using FlatTuple::FlatTupleBase::Get; +}; + +// Utility functions to be called with static_assert to induce deprecation +// warnings. +GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED( + "INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P is deprecated, please use " + "INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P") +constexpr bool InstantiateTestCase_P_IsDeprecated() { return true; } + +GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED( + "TYPED_TEST_CASE_P is deprecated, please use " + "TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P") +constexpr bool TypedTestCase_P_IsDeprecated() { return true; } + +GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED( + "TYPED_TEST_CASE is deprecated, please use " + "TYPED_TEST_SUITE") +constexpr bool TypedTestCaseIsDeprecated() { return true; } + +GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED( + "REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P is deprecated, please use " + "REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P") +constexpr bool RegisterTypedTestCase_P_IsDeprecated() { return true; } + +GTEST_INTERNAL_DEPRECATED( + "INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P is deprecated, please use " + "INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P") +constexpr bool InstantiateTypedTestCase_P_IsDeprecated() { return true; } + +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing + +namespace std { +// Some standard library implementations use `struct tuple_size` and some use +// `class tuple_size`. Clang warns about the mismatch. +// https://reviews.llvm.org/D55466 +#ifdef __clang__ +#pragma clang diagnostic push +#pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wmismatched-tags" +#endif +template <typename... Ts> +struct tuple_size<testing::internal::FlatTuple<Ts...>> + : std::integral_constant<size_t, sizeof...(Ts)> {}; +#ifdef __clang__ +#pragma clang diagnostic pop +#endif +} // namespace std + +#define GTEST_MESSAGE_AT_(file, line, message, result_type) \ + ::testing::internal::AssertHelper(result_type, file, line, message) \ + = ::testing::Message() + +#define GTEST_MESSAGE_(message, result_type) \ + GTEST_MESSAGE_AT_(__FILE__, __LINE__, message, result_type) + +#define GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_(message) \ + return GTEST_MESSAGE_(message, ::testing::TestPartResult::kFatalFailure) + +#define GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_(message) \ + GTEST_MESSAGE_(message, ::testing::TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure) + +#define GTEST_SUCCESS_(message) \ + GTEST_MESSAGE_(message, ::testing::TestPartResult::kSuccess) + +#define GTEST_SKIP_(message) \ + return GTEST_MESSAGE_(message, ::testing::TestPartResult::kSkip) + +// Suppress MSVC warning 4072 (unreachable code) for the code following +// statement if it returns or throws (or doesn't return or throw in some +// situations). +// NOTE: The "else" is important to keep this expansion to prevent a top-level +// "else" from attaching to our "if". +#define GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement) \ + if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ + statement; \ + } else /* NOLINT */ \ + static_assert(true, "") // User must have a semicolon after expansion. + +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +namespace testing { +namespace internal { + +class NeverThrown { + public: + const char* what() const noexcept { + return "this exception should never be thrown"; + } +}; + +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing + +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI + +#define GTEST_EXCEPTION_TYPE_(e) ::testing::internal::GetTypeName(typeid(e)) + +#else // GTEST_HAS_RTTI + +#define GTEST_EXCEPTION_TYPE_(e) \ + std::string { "an std::exception-derived error" } + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI + +#define GTEST_TEST_THROW_CATCH_STD_EXCEPTION_(statement, expected_exception) \ + catch (typename std::conditional< \ + std::is_same<typename std::remove_cv<typename std::remove_reference< \ + expected_exception>::type>::type, \ + std::exception>::value, \ + const ::testing::internal::NeverThrown&, const std::exception&>::type \ + e) { \ + gtest_msg.value = "Expected: " #statement \ + " throws an exception of type " #expected_exception \ + ".\n Actual: it throws "; \ + gtest_msg.value += GTEST_EXCEPTION_TYPE_(e); \ + gtest_msg.value += " with description \""; \ + gtest_msg.value += e.what(); \ + gtest_msg.value += "\"."; \ + goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testthrow_, __LINE__); \ + } + +#else // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +#define GTEST_TEST_THROW_CATCH_STD_EXCEPTION_(statement, expected_exception) + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +#define GTEST_TEST_THROW_(statement, expected_exception, fail) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (::testing::internal::TrueWithString gtest_msg{}) { \ + bool gtest_caught_expected = false; \ + try { \ + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ + } catch (expected_exception const&) { \ + gtest_caught_expected = true; \ + } \ + GTEST_TEST_THROW_CATCH_STD_EXCEPTION_(statement, expected_exception) \ + catch (...) { \ + gtest_msg.value = "Expected: " #statement \ + " throws an exception of type " #expected_exception \ + ".\n Actual: it throws a different type."; \ + goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testthrow_, __LINE__); \ + } \ + if (!gtest_caught_expected) { \ + gtest_msg.value = "Expected: " #statement \ + " throws an exception of type " #expected_exception \ + ".\n Actual: it throws nothing."; \ + goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testthrow_, __LINE__); \ + } \ + } else /*NOLINT*/ \ + GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testthrow_, __LINE__) \ + : fail(gtest_msg.value.c_str()) + +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +#define GTEST_TEST_NO_THROW_CATCH_STD_EXCEPTION_() \ + catch (std::exception const& e) { \ + gtest_msg.value = "it throws "; \ + gtest_msg.value += GTEST_EXCEPTION_TYPE_(e); \ + gtest_msg.value += " with description \""; \ + gtest_msg.value += e.what(); \ + gtest_msg.value += "\"."; \ + goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testnothrow_, __LINE__); \ + } + +#else // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +#define GTEST_TEST_NO_THROW_CATCH_STD_EXCEPTION_() + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +#define GTEST_TEST_NO_THROW_(statement, fail) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (::testing::internal::TrueWithString gtest_msg{}) { \ + try { \ + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ + } \ + GTEST_TEST_NO_THROW_CATCH_STD_EXCEPTION_() \ + catch (...) { \ + gtest_msg.value = "it throws."; \ + goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testnothrow_, __LINE__); \ + } \ + } else \ + GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testnothrow_, __LINE__): \ + fail(("Expected: " #statement " doesn't throw an exception.\n" \ + " Actual: " + gtest_msg.value).c_str()) + +#define GTEST_TEST_ANY_THROW_(statement, fail) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ + bool gtest_caught_any = false; \ + try { \ + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ + } \ + catch (...) { \ + gtest_caught_any = true; \ + } \ + if (!gtest_caught_any) { \ + goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testanythrow_, __LINE__); \ + } \ + } else \ + GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testanythrow_, __LINE__): \ + fail("Expected: " #statement " throws an exception.\n" \ + " Actual: it doesn't.") + + +// Implements Boolean test assertions such as EXPECT_TRUE. expression can be +// either a boolean expression or an AssertionResult. text is a textual +// representation of expression as it was passed into the EXPECT_TRUE. +#define GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(expression, text, actual, expected, fail) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (const ::testing::AssertionResult gtest_ar_ = \ + ::testing::AssertionResult(expression)) \ + ; \ + else \ + fail(::testing::internal::GetBoolAssertionFailureMessage(\ + gtest_ar_, text, #actual, #expected).c_str()) + +#define GTEST_TEST_NO_FATAL_FAILURE_(statement, fail) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ + ::testing::internal::HasNewFatalFailureHelper gtest_fatal_failure_checker; \ + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ + if (gtest_fatal_failure_checker.has_new_fatal_failure()) { \ + goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testnofatal_, __LINE__); \ + } \ + } else \ + GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_testnofatal_, __LINE__): \ + fail("Expected: " #statement " doesn't generate new fatal " \ + "failures in the current thread.\n" \ + " Actual: it does.") + +// Expands to the name of the class that implements the given test. +#define GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, test_name) \ + test_suite_name##_##test_name##_Test + +// Helper macro for defining tests. +#define GTEST_TEST_(test_suite_name, test_name, parent_class, parent_id) \ + static_assert(sizeof(GTEST_STRINGIFY_(test_suite_name)) > 1, \ + "test_suite_name must not be empty"); \ + static_assert(sizeof(GTEST_STRINGIFY_(test_name)) > 1, \ + "test_name must not be empty"); \ + class GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, test_name) \ + : public parent_class { \ + public: \ + GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, test_name)() = default; \ + ~GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, test_name)() override = default; \ + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, \ + test_name)); \ + GTEST_DISALLOW_MOVE_AND_ASSIGN_(GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, \ + test_name)); \ + \ + private: \ + void TestBody() override; \ + static ::testing::TestInfo* const test_info_ GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; \ + }; \ + \ + ::testing::TestInfo* const GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, \ + test_name)::test_info_ = \ + ::testing::internal::MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( \ + #test_suite_name, #test_name, nullptr, nullptr, \ + ::testing::internal::CodeLocation(__FILE__, __LINE__), (parent_id), \ + ::testing::internal::SuiteApiResolver< \ + parent_class>::GetSetUpCaseOrSuite(__FILE__, __LINE__), \ + ::testing::internal::SuiteApiResolver< \ + parent_class>::GetTearDownCaseOrSuite(__FILE__, __LINE__), \ + new ::testing::internal::TestFactoryImpl<GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_( \ + test_suite_name, test_name)>); \ + void GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, test_name)::TestBody() + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_INTERNAL_H_ +// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// This header file defines the public API for death tests. It is +// #included by gtest.h so a user doesn't need to include this +// directly. +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_H_ + +// Copyright 2005, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// This header file defines internal utilities needed for implementing +// death tests. They are subject to change without notice. +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_INTERNAL_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_INTERNAL_H_ + +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// This file implements just enough of the matcher interface to allow +// EXPECT_DEATH and friends to accept a matcher argument. + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_MATCHERS_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_MATCHERS_H_ + +#include <atomic> +#include <memory> +#include <ostream> +#include <string> +#include <type_traits> + +// Copyright 2007, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Google Test - The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework +// +// This file implements a universal value printer that can print a +// value of any type T: +// +// void ::testing::internal::UniversalPrinter<T>::Print(value, ostream_ptr); +// +// A user can teach this function how to print a class type T by +// defining either operator<<() or PrintTo() in the namespace that +// defines T. More specifically, the FIRST defined function in the +// following list will be used (assuming T is defined in namespace +// foo): +// +// 1. foo::PrintTo(const T&, ostream*) +// 2. operator<<(ostream&, const T&) defined in either foo or the +// global namespace. +// +// However if T is an STL-style container then it is printed element-wise +// unless foo::PrintTo(const T&, ostream*) is defined. Note that +// operator<<() is ignored for container types. +// +// If none of the above is defined, it will print the debug string of +// the value if it is a protocol buffer, or print the raw bytes in the +// value otherwise. +// +// To aid debugging: when T is a reference type, the address of the +// value is also printed; when T is a (const) char pointer, both the +// pointer value and the NUL-terminated string it points to are +// printed. +// +// We also provide some convenient wrappers: +// +// // Prints a value to a string. For a (const or not) char +// // pointer, the NUL-terminated string (but not the pointer) is +// // printed. +// std::string ::testing::PrintToString(const T& value); +// +// // Prints a value tersely: for a reference type, the referenced +// // value (but not the address) is printed; for a (const or not) char +// // pointer, the NUL-terminated string (but not the pointer) is +// // printed. +// void ::testing::internal::UniversalTersePrint(const T& value, ostream*); +// +// // Prints value using the type inferred by the compiler. The difference +// // from UniversalTersePrint() is that this function prints both the +// // pointer and the NUL-terminated string for a (const or not) char pointer. +// void ::testing::internal::UniversalPrint(const T& value, ostream*); +// +// // Prints the fields of a tuple tersely to a string vector, one +// // element for each field. Tuple support must be enabled in +// // gtest-port.h. +// std::vector<string> UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings( +// const Tuple& value); +// +// Known limitation: +// +// The print primitives print the elements of an STL-style container +// using the compiler-inferred type of *iter where iter is a +// const_iterator of the container. When const_iterator is an input +// iterator but not a forward iterator, this inferred type may not +// match value_type, and the print output may be incorrect. In +// practice, this is rarely a problem as for most containers +// const_iterator is a forward iterator. We'll fix this if there's an +// actual need for it. Note that this fix cannot rely on value_type +// being defined as many user-defined container types don't have +// value_type. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRINTERS_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRINTERS_H_ + +#include <functional> +#include <memory> +#include <ostream> // NOLINT +#include <sstream> +#include <string> +#include <tuple> +#include <type_traits> +#include <utility> +#include <vector> + + +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI +#include <typeindex> +#include <typeinfo> +#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI + +namespace testing { + +// Definitions in the internal* namespaces are subject to change without notice. +// DO NOT USE THEM IN USER CODE! +namespace internal { + +template <typename T> +void UniversalPrint(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os); + +// Used to print an STL-style container when the user doesn't define +// a PrintTo() for it. +struct ContainerPrinter { + template <typename T, + typename = typename std::enable_if< + (sizeof(IsContainerTest<T>(0)) == sizeof(IsContainer)) && + !IsRecursiveContainer<T>::value>::type> + static void PrintValue(const T& container, std::ostream* os) { + const size_t kMaxCount = 32; // The maximum number of elements to print. + *os << '{'; + size_t count = 0; + for (auto&& elem : container) { + if (count > 0) { + *os << ','; + if (count == kMaxCount) { // Enough has been printed. + *os << " ..."; + break; + } + } + *os << ' '; + // We cannot call PrintTo(elem, os) here as PrintTo() doesn't + // handle `elem` being a native array. + internal::UniversalPrint(elem, os); + ++count; + } + + if (count > 0) { + *os << ' '; + } + *os << '}'; + } +}; + +// Used to print a pointer that is neither a char pointer nor a member +// pointer, when the user doesn't define PrintTo() for it. (A member +// variable pointer or member function pointer doesn't really point to +// a location in the address space. Their representation is +// implementation-defined. Therefore they will be printed as raw +// bytes.) +struct FunctionPointerPrinter { + template <typename T, typename = typename std::enable_if< + std::is_function<T>::value>::type> + static void PrintValue(T* p, ::std::ostream* os) { + if (p == nullptr) { + *os << "NULL"; + } else { + // T is a function type, so '*os << p' doesn't do what we want + // (it just prints p as bool). We want to print p as a const + // void*. + *os << reinterpret_cast<const void*>(p); + } + } +}; + +struct PointerPrinter { + template <typename T> + static void PrintValue(T* p, ::std::ostream* os) { + if (p == nullptr) { + *os << "NULL"; + } else { + // T is not a function type. We just call << to print p, + // relying on ADL to pick up user-defined << for their pointer + // types, if any. + *os << p; + } + } +}; + +namespace internal_stream_operator_without_lexical_name_lookup { + +// The presence of an operator<< here will terminate lexical scope lookup +// straight away (even though it cannot be a match because of its argument +// types). Thus, the two operator<< calls in StreamPrinter will find only ADL +// candidates. +struct LookupBlocker {}; +void operator<<(LookupBlocker, LookupBlocker); + +struct StreamPrinter { + template <typename T, + // Don't accept member pointers here. We'd print them via implicit + // conversion to bool, which isn't useful. + typename = typename std::enable_if< + !std::is_member_pointer<T>::value>::type, + // Only accept types for which we can find a streaming operator via + // ADL (possibly involving implicit conversions). + typename = decltype(std::declval<std::ostream&>() + << std::declval<const T&>())> + static void PrintValue(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + // Call streaming operator found by ADL, possibly with implicit conversions + // of the arguments. + *os << value; + } +}; + +} // namespace internal_stream_operator_without_lexical_name_lookup + +struct ProtobufPrinter { + // We print a protobuf using its ShortDebugString() when the string + // doesn't exceed this many characters; otherwise we print it using + // DebugString() for better readability. + static const size_t kProtobufOneLinerMaxLength = 50; + + template <typename T, + typename = typename std::enable_if< + internal::HasDebugStringAndShortDebugString<T>::value>::type> + static void PrintValue(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + std::string pretty_str = value.ShortDebugString(); + if (pretty_str.length() > kProtobufOneLinerMaxLength) { + pretty_str = "\n" + value.DebugString(); + } + *os << ("<" + pretty_str + ">"); + } +}; + +struct ConvertibleToIntegerPrinter { + // Since T has no << operator or PrintTo() but can be implicitly + // converted to BiggestInt, we print it as a BiggestInt. + // + // Most likely T is an enum type (either named or unnamed), in which + // case printing it as an integer is the desired behavior. In case + // T is not an enum, printing it as an integer is the best we can do + // given that it has no user-defined printer. + static void PrintValue(internal::BiggestInt value, ::std::ostream* os) { + *os << value; + } +}; + +struct ConvertibleToStringViewPrinter { +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + static void PrintValue(internal::StringView value, ::std::ostream* os) { + internal::UniversalPrint(value, os); + } +#endif +}; + + +// Prints the given number of bytes in the given object to the given +// ostream. +GTEST_API_ void PrintBytesInObjectTo(const unsigned char* obj_bytes, + size_t count, + ::std::ostream* os); +struct RawBytesPrinter { + // SFINAE on `sizeof` to make sure we have a complete type. + template <typename T, size_t = sizeof(T)> + static void PrintValue(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintBytesInObjectTo( + static_cast<const unsigned char*>( + // Load bearing cast to void* to support iOS + reinterpret_cast<const void*>(std::addressof(value))), + sizeof(value), os); + } +}; + +struct FallbackPrinter { + template <typename T> + static void PrintValue(const T&, ::std::ostream* os) { + *os << "(incomplete type)"; + } +}; + +// Try every printer in order and return the first one that works. +template <typename T, typename E, typename Printer, typename... Printers> +struct FindFirstPrinter : FindFirstPrinter<T, E, Printers...> {}; + +template <typename T, typename Printer, typename... Printers> +struct FindFirstPrinter< + T, decltype(Printer::PrintValue(std::declval<const T&>(), nullptr)), + Printer, Printers...> { + using type = Printer; +}; + +// Select the best printer in the following order: +// - Print containers (they have begin/end/etc). +// - Print function pointers. +// - Print object pointers. +// - Use the stream operator, if available. +// - Print protocol buffers. +// - Print types convertible to BiggestInt. +// - Print types convertible to StringView, if available. +// - Fallback to printing the raw bytes of the object. +template <typename T> +void PrintWithFallback(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + using Printer = typename FindFirstPrinter< + T, void, ContainerPrinter, FunctionPointerPrinter, PointerPrinter, + internal_stream_operator_without_lexical_name_lookup::StreamPrinter, + ProtobufPrinter, ConvertibleToIntegerPrinter, + ConvertibleToStringViewPrinter, RawBytesPrinter, FallbackPrinter>::type; + Printer::PrintValue(value, os); +} + +// FormatForComparison<ToPrint, OtherOperand>::Format(value) formats a +// value of type ToPrint that is an operand of a comparison assertion +// (e.g. ASSERT_EQ). OtherOperand is the type of the other operand in +// the comparison, and is used to help determine the best way to +// format the value. In particular, when the value is a C string +// (char pointer) and the other operand is an STL string object, we +// want to format the C string as a string, since we know it is +// compared by value with the string object. If the value is a char +// pointer but the other operand is not an STL string object, we don't +// know whether the pointer is supposed to point to a NUL-terminated +// string, and thus want to print it as a pointer to be safe. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. + +// The default case. +template <typename ToPrint, typename OtherOperand> +class FormatForComparison { + public: + static ::std::string Format(const ToPrint& value) { + return ::testing::PrintToString(value); + } +}; + +// Array. +template <typename ToPrint, size_t N, typename OtherOperand> +class FormatForComparison<ToPrint[N], OtherOperand> { + public: + static ::std::string Format(const ToPrint* value) { + return FormatForComparison<const ToPrint*, OtherOperand>::Format(value); + } +}; + +// By default, print C string as pointers to be safe, as we don't know +// whether they actually point to a NUL-terminated string. + +#define GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(CharType) \ + template <typename OtherOperand> \ + class FormatForComparison<CharType*, OtherOperand> { \ + public: \ + static ::std::string Format(CharType* value) { \ + return ::testing::PrintToString(static_cast<const void*>(value)); \ + } \ + } + +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(char); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(const char); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(wchar_t); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(const wchar_t); +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(char8_t); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(const char8_t); +#endif +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(char16_t); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(const char16_t); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(char32_t); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_(const char32_t); + +#undef GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_POINTER_ + +// If a C string is compared with an STL string object, we know it's meant +// to point to a NUL-terminated string, and thus can print it as a string. + +#define GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(CharType, OtherStringType) \ + template <> \ + class FormatForComparison<CharType*, OtherStringType> { \ + public: \ + static ::std::string Format(CharType* value) { \ + return ::testing::PrintToString(value); \ + } \ + } + +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(char, ::std::string); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(const char, ::std::string); +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(char8_t, ::std::u8string); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(const char8_t, ::std::u8string); +#endif +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(char16_t, ::std::u16string); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(const char16_t, ::std::u16string); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(char32_t, ::std::u32string); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(const char32_t, ::std::u32string); + +#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(wchar_t, ::std::wstring); +GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_(const wchar_t, ::std::wstring); +#endif + +#undef GTEST_IMPL_FORMAT_C_STRING_AS_STRING_ + +// Formats a comparison assertion (e.g. ASSERT_EQ, EXPECT_LT, and etc) +// operand to be used in a failure message. The type (but not value) +// of the other operand may affect the format. This allows us to +// print a char* as a raw pointer when it is compared against another +// char* or void*, and print it as a C string when it is compared +// against an std::string object, for example. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +template <typename T1, typename T2> +std::string FormatForComparisonFailureMessage( + const T1& value, const T2& /* other_operand */) { + return FormatForComparison<T1, T2>::Format(value); +} + +// UniversalPrinter<T>::Print(value, ostream_ptr) prints the given +// value to the given ostream. The caller must ensure that +// 'ostream_ptr' is not NULL, or the behavior is undefined. +// +// We define UniversalPrinter as a class template (as opposed to a +// function template), as we need to partially specialize it for +// reference types, which cannot be done with function templates. +template <typename T> +class UniversalPrinter; + +// Prints the given value using the << operator if it has one; +// otherwise prints the bytes in it. This is what +// UniversalPrinter<T>::Print() does when PrintTo() is not specialized +// or overloaded for type T. +// +// A user can override this behavior for a class type Foo by defining +// an overload of PrintTo() in the namespace where Foo is defined. We +// give the user this option as sometimes defining a << operator for +// Foo is not desirable (e.g. the coding style may prevent doing it, +// or there is already a << operator but it doesn't do what the user +// wants). +template <typename T> +void PrintTo(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + internal::PrintWithFallback(value, os); +} + +// The following list of PrintTo() overloads tells +// UniversalPrinter<T>::Print() how to print standard types (built-in +// types, strings, plain arrays, and pointers). + +// Overloads for various char types. +GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(unsigned char c, ::std::ostream* os); +GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(signed char c, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(char c, ::std::ostream* os) { + // When printing a plain char, we always treat it as unsigned. This + // way, the output won't be affected by whether the compiler thinks + // char is signed or not. + PrintTo(static_cast<unsigned char>(c), os); +} + +// Overloads for other simple built-in types. +inline void PrintTo(bool x, ::std::ostream* os) { + *os << (x ? "true" : "false"); +} + +// Overload for wchar_t type. +// Prints a wchar_t as a symbol if it is printable or as its internal +// code otherwise and also as its decimal code (except for L'\0'). +// The L'\0' char is printed as "L'\\0'". The decimal code is printed +// as signed integer when wchar_t is implemented by the compiler +// as a signed type and is printed as an unsigned integer when wchar_t +// is implemented as an unsigned type. +GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(wchar_t wc, ::std::ostream* os); + +GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(char32_t c, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(char16_t c, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<char32_t>(c), os); +} +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +inline void PrintTo(char8_t c, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<char32_t>(c), os); +} +#endif + +// Overloads for C strings. +GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(const char* s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const char*>(s), os); +} + +// signed/unsigned char is often used for representing binary data, so +// we print pointers to it as void* to be safe. +inline void PrintTo(const signed char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s), os); +} +inline void PrintTo(signed char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s), os); +} +inline void PrintTo(const unsigned char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s), os); +} +inline void PrintTo(unsigned char* s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const void*>(s), os); +} +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +// Overloads for u8 strings. +void PrintTo(const char8_t* s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(char8_t* s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const char8_t*>(s), os); +} +#endif +// Overloads for u16 strings. +void PrintTo(const char16_t* s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(char16_t* s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const char16_t*>(s), os); +} +// Overloads for u32 strings. +void PrintTo(const char32_t* s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(char32_t* s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const char32_t*>(s), os); +} + +// MSVC can be configured to define wchar_t as a typedef of unsigned +// short. It defines _NATIVE_WCHAR_T_DEFINED when wchar_t is a native +// type. When wchar_t is a typedef, defining an overload for const +// wchar_t* would cause unsigned short* be printed as a wide string, +// possibly causing invalid memory accesses. +#if !defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(_NATIVE_WCHAR_T_DEFINED) +// Overloads for wide C strings +GTEST_API_ void PrintTo(const wchar_t* s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(wchar_t* s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(ImplicitCast_<const wchar_t*>(s), os); +} +#endif + +// Overload for C arrays. Multi-dimensional arrays are printed +// properly. + +// Prints the given number of elements in an array, without printing +// the curly braces. +template <typename T> +void PrintRawArrayTo(const T a[], size_t count, ::std::ostream* os) { + UniversalPrint(a[0], os); + for (size_t i = 1; i != count; i++) { + *os << ", "; + UniversalPrint(a[i], os); + } +} + +// Overloads for ::std::string. +GTEST_API_ void PrintStringTo(const ::std::string&s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(const ::std::string& s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintStringTo(s, os); +} + +// Overloads for ::std::u8string +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +GTEST_API_ void PrintU8StringTo(const ::std::u8string& s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(const ::std::u8string& s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintU8StringTo(s, os); +} +#endif + +// Overloads for ::std::u16string +GTEST_API_ void PrintU16StringTo(const ::std::u16string& s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(const ::std::u16string& s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintU16StringTo(s, os); +} + +// Overloads for ::std::u32string +GTEST_API_ void PrintU32StringTo(const ::std::u32string& s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(const ::std::u32string& s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintU32StringTo(s, os); +} + +// Overloads for ::std::wstring. +#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING +GTEST_API_ void PrintWideStringTo(const ::std::wstring&s, ::std::ostream* os); +inline void PrintTo(const ::std::wstring& s, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintWideStringTo(s, os); +} +#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW +// Overload for internal::StringView. +inline void PrintTo(internal::StringView sp, ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTo(::std::string(sp), os); +} +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + +inline void PrintTo(std::nullptr_t, ::std::ostream* os) { *os << "(nullptr)"; } + +template <typename T> +void PrintTo(std::reference_wrapper<T> ref, ::std::ostream* os) { + UniversalPrinter<T&>::Print(ref.get(), os); +} + +inline const void* VoidifyPointer(const void* p) { return p; } +inline const void* VoidifyPointer(volatile const void* p) { + return const_cast<const void*>(p); +} + +template <typename T, typename Ptr> +void PrintSmartPointer(const Ptr& ptr, std::ostream* os, char) { + if (ptr == nullptr) { + *os << "(nullptr)"; + } else { + // We can't print the value. Just print the pointer.. + *os << "(" << (VoidifyPointer)(ptr.get()) << ")"; + } +} +template <typename T, typename Ptr, + typename = typename std::enable_if<!std::is_void<T>::value && + !std::is_array<T>::value>::type> +void PrintSmartPointer(const Ptr& ptr, std::ostream* os, int) { + if (ptr == nullptr) { + *os << "(nullptr)"; + } else { + *os << "(ptr = " << (VoidifyPointer)(ptr.get()) << ", value = "; + UniversalPrinter<T>::Print(*ptr, os); + *os << ")"; + } +} + +template <typename T, typename D> +void PrintTo(const std::unique_ptr<T, D>& ptr, std::ostream* os) { + (PrintSmartPointer<T>)(ptr, os, 0); +} + +template <typename T> +void PrintTo(const std::shared_ptr<T>& ptr, std::ostream* os) { + (PrintSmartPointer<T>)(ptr, os, 0); +} + +// Helper function for printing a tuple. T must be instantiated with +// a tuple type. +template <typename T> +void PrintTupleTo(const T&, std::integral_constant<size_t, 0>, + ::std::ostream*) {} + +template <typename T, size_t I> +void PrintTupleTo(const T& t, std::integral_constant<size_t, I>, + ::std::ostream* os) { + PrintTupleTo(t, std::integral_constant<size_t, I - 1>(), os); + GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_PUSH_() + if (I > 1) { + GTEST_INTENTIONAL_CONST_COND_POP_() + *os << ", "; + } + UniversalPrinter<typename std::tuple_element<I - 1, T>::type>::Print( + std::get<I - 1>(t), os); +} + +template <typename... Types> +void PrintTo(const ::std::tuple<Types...>& t, ::std::ostream* os) { + *os << "("; + PrintTupleTo(t, std::integral_constant<size_t, sizeof...(Types)>(), os); + *os << ")"; +} + +// Overload for std::pair. +template <typename T1, typename T2> +void PrintTo(const ::std::pair<T1, T2>& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + *os << '('; + // We cannot use UniversalPrint(value.first, os) here, as T1 may be + // a reference type. The same for printing value.second. + UniversalPrinter<T1>::Print(value.first, os); + *os << ", "; + UniversalPrinter<T2>::Print(value.second, os); + *os << ')'; +} + +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI +inline void PrintTo(const ::std::type_info& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + internal::PrintTo<::std::type_info>(value, os); + *os << " (\"" << value.name() << "\")"; +} + +inline void PrintTo(const ::std::type_index& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + internal::PrintTo<::std::type_index>(value, os); + *os << " (\"" << value.name() << "\")"; +} +#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI + +// Implements printing a non-reference type T by letting the compiler +// pick the right overload of PrintTo() for T. +template <typename T> +class UniversalPrinter { + public: + // MSVC warns about adding const to a function type, so we want to + // disable the warning. + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4180) + + // Note: we deliberately don't call this PrintTo(), as that name + // conflicts with ::testing::internal::PrintTo in the body of the + // function. + static void Print(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + // By default, ::testing::internal::PrintTo() is used for printing + // the value. + // + // Thanks to Koenig look-up, if T is a class and has its own + // PrintTo() function defined in its namespace, that function will + // be visible here. Since it is more specific than the generic ones + // in ::testing::internal, it will be picked by the compiler in the + // following statement - exactly what we want. + PrintTo(value, os); + } + + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() +}; + +// Remove any const-qualifiers before passing a type to UniversalPrinter. +template <typename T> +class UniversalPrinter<const T> : public UniversalPrinter<T> {}; + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_ANY + +// Printer for std::any / absl::any + +template <> +class UniversalPrinter<Any> { + public: + static void Print(const Any& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + if (value.has_value()) { + *os << "value of type " << GetTypeName(value); + } else { + *os << "no value"; + } + } + + private: + static std::string GetTypeName(const Any& value) { +#if GTEST_HAS_RTTI + return internal::GetTypeName(value.type()); +#else + static_cast<void>(value); // possibly unused + return "<unknown_type>"; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_RTTI + } +}; + +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_ANY + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_OPTIONAL + +// Printer for std::optional / absl::optional + +template <typename T> +class UniversalPrinter<Optional<T>> { + public: + static void Print(const Optional<T>& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + *os << '('; + if (!value) { + *os << "nullopt"; + } else { + UniversalPrint(*value, os); + } + *os << ')'; + } +}; + +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_OPTIONAL + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_VARIANT + +// Printer for std::variant / absl::variant + +template <typename... T> +class UniversalPrinter<Variant<T...>> { + public: + static void Print(const Variant<T...>& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + *os << '('; +#if GTEST_HAS_ABSL + absl::visit(Visitor{os, value.index()}, value); +#else + std::visit(Visitor{os, value.index()}, value); +#endif // GTEST_HAS_ABSL + *os << ')'; + } + + private: + struct Visitor { + template <typename U> + void operator()(const U& u) const { + *os << "'" << GetTypeName<U>() << "(index = " << index + << ")' with value "; + UniversalPrint(u, os); + } + ::std::ostream* os; + std::size_t index; + }; +}; + +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_VARIANT + +// UniversalPrintArray(begin, len, os) prints an array of 'len' +// elements, starting at address 'begin'. +template <typename T> +void UniversalPrintArray(const T* begin, size_t len, ::std::ostream* os) { + if (len == 0) { + *os << "{}"; + } else { + *os << "{ "; + const size_t kThreshold = 18; + const size_t kChunkSize = 8; + // If the array has more than kThreshold elements, we'll have to + // omit some details by printing only the first and the last + // kChunkSize elements. + if (len <= kThreshold) { + PrintRawArrayTo(begin, len, os); + } else { + PrintRawArrayTo(begin, kChunkSize, os); + *os << ", ..., "; + PrintRawArrayTo(begin + len - kChunkSize, kChunkSize, os); + } + *os << " }"; + } +} +// This overload prints a (const) char array compactly. +GTEST_API_ void UniversalPrintArray( + const char* begin, size_t len, ::std::ostream* os); + +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +// This overload prints a (const) char8_t array compactly. +GTEST_API_ void UniversalPrintArray(const char8_t* begin, size_t len, + ::std::ostream* os); +#endif + +// This overload prints a (const) char16_t array compactly. +GTEST_API_ void UniversalPrintArray(const char16_t* begin, size_t len, + ::std::ostream* os); + +// This overload prints a (const) char32_t array compactly. +GTEST_API_ void UniversalPrintArray(const char32_t* begin, size_t len, + ::std::ostream* os); + +// This overload prints a (const) wchar_t array compactly. +GTEST_API_ void UniversalPrintArray( + const wchar_t* begin, size_t len, ::std::ostream* os); + +// Implements printing an array type T[N]. +template <typename T, size_t N> +class UniversalPrinter<T[N]> { + public: + // Prints the given array, omitting some elements when there are too + // many. + static void Print(const T (&a)[N], ::std::ostream* os) { + UniversalPrintArray(a, N, os); + } +}; + +// Implements printing a reference type T&. +template <typename T> +class UniversalPrinter<T&> { + public: + // MSVC warns about adding const to a function type, so we want to + // disable the warning. + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4180) + + static void Print(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + // Prints the address of the value. We use reinterpret_cast here + // as static_cast doesn't compile when T is a function type. + *os << "@" << reinterpret_cast<const void*>(&value) << " "; + + // Then prints the value itself. + UniversalPrint(value, os); + } + + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() +}; + +// Prints a value tersely: for a reference type, the referenced value +// (but not the address) is printed; for a (const) char pointer, the +// NUL-terminated string (but not the pointer) is printed. + +template <typename T> +class UniversalTersePrinter { + public: + static void Print(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + UniversalPrint(value, os); + } +}; +template <typename T> +class UniversalTersePrinter<T&> { + public: + static void Print(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + UniversalPrint(value, os); + } +}; +template <typename T, size_t N> +class UniversalTersePrinter<T[N]> { + public: + static void Print(const T (&value)[N], ::std::ostream* os) { + UniversalPrinter<T[N]>::Print(value, os); + } +}; +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<const char*> { + public: + static void Print(const char* str, ::std::ostream* os) { + if (str == nullptr) { + *os << "NULL"; + } else { + UniversalPrint(std::string(str), os); + } + } +}; +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<char*> : public UniversalTersePrinter<const char*> { +}; + +#ifdef __cpp_char8_t +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<const char8_t*> { + public: + static void Print(const char8_t* str, ::std::ostream* os) { + if (str == nullptr) { + *os << "NULL"; + } else { + UniversalPrint(::std::u8string(str), os); + } + } +}; +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<char8_t*> + : public UniversalTersePrinter<const char8_t*> {}; +#endif + +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<const char16_t*> { + public: + static void Print(const char16_t* str, ::std::ostream* os) { + if (str == nullptr) { + *os << "NULL"; + } else { + UniversalPrint(::std::u16string(str), os); + } + } +}; +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<char16_t*> + : public UniversalTersePrinter<const char16_t*> {}; + +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<const char32_t*> { + public: + static void Print(const char32_t* str, ::std::ostream* os) { + if (str == nullptr) { + *os << "NULL"; + } else { + UniversalPrint(::std::u32string(str), os); + } + } +}; +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<char32_t*> + : public UniversalTersePrinter<const char32_t*> {}; + +#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<const wchar_t*> { + public: + static void Print(const wchar_t* str, ::std::ostream* os) { + if (str == nullptr) { + *os << "NULL"; + } else { + UniversalPrint(::std::wstring(str), os); + } + } +}; +#endif + +template <> +class UniversalTersePrinter<wchar_t*> { + public: + static void Print(wchar_t* str, ::std::ostream* os) { + UniversalTersePrinter<const wchar_t*>::Print(str, os); + } +}; + +template <typename T> +void UniversalTersePrint(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + UniversalTersePrinter<T>::Print(value, os); +} + +// Prints a value using the type inferred by the compiler. The +// difference between this and UniversalTersePrint() is that for a +// (const) char pointer, this prints both the pointer and the +// NUL-terminated string. +template <typename T> +void UniversalPrint(const T& value, ::std::ostream* os) { + // A workarond for the bug in VC++ 7.1 that prevents us from instantiating + // UniversalPrinter with T directly. + typedef T T1; + UniversalPrinter<T1>::Print(value, os); +} + +typedef ::std::vector< ::std::string> Strings; + + // Tersely prints the first N fields of a tuple to a string vector, + // one element for each field. +template <typename Tuple> +void TersePrintPrefixToStrings(const Tuple&, std::integral_constant<size_t, 0>, + Strings*) {} +template <typename Tuple, size_t I> +void TersePrintPrefixToStrings(const Tuple& t, + std::integral_constant<size_t, I>, + Strings* strings) { + TersePrintPrefixToStrings(t, std::integral_constant<size_t, I - 1>(), + strings); + ::std::stringstream ss; + UniversalTersePrint(std::get<I - 1>(t), &ss); + strings->push_back(ss.str()); +} + +// Prints the fields of a tuple tersely to a string vector, one +// element for each field. See the comment before +// UniversalTersePrint() for how we define "tersely". +template <typename Tuple> +Strings UniversalTersePrintTupleFieldsToStrings(const Tuple& value) { + Strings result; + TersePrintPrefixToStrings( + value, std::integral_constant<size_t, std::tuple_size<Tuple>::value>(), + &result); + return result; +} + +} // namespace internal + +template <typename T> +::std::string PrintToString(const T& value) { + ::std::stringstream ss; + internal::UniversalTersePrinter<T>::Print(value, &ss); + return ss.str(); +} + +} // namespace testing + +// Include any custom printer added by the local installation. +// We must include this header at the end to make sure it can use the +// declarations from this file. +// Copyright 2015, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// This file provides an injection point for custom printers in a local +// installation of gTest. +// It will be included from gtest-printers.h and the overrides in this file +// will be visible to everyone. +// +// Injection point for custom user configurations. See README for details +// +// ** Custom implementation starts here ** + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GTEST_PRINTERS_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GTEST_PRINTERS_H_ + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_CUSTOM_GTEST_PRINTERS_H_ + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRINTERS_H_ + +// MSVC warning C5046 is new as of VS2017 version 15.8. +#if defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER >= 1915 +#define GTEST_MAYBE_5046_ 5046 +#else +#define GTEST_MAYBE_5046_ +#endif + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_( + 4251 GTEST_MAYBE_5046_ /* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by + clients of class B */ + /* Symbol involving type with internal linkage not defined */) + +namespace testing { + +// To implement a matcher Foo for type T, define: +// 1. a class FooMatcherMatcher that implements the matcher interface: +// using is_gtest_matcher = void; +// bool MatchAndExplain(const T&, std::ostream*); +// (MatchResultListener* can also be used instead of std::ostream*) +// void DescribeTo(std::ostream*); +// void DescribeNegationTo(std::ostream*); +// +// 2. a factory function that creates a Matcher<T> object from a +// FooMatcherMatcher. + +class MatchResultListener { + public: + // Creates a listener object with the given underlying ostream. The + // listener does not own the ostream, and does not dereference it + // in the constructor or destructor. + explicit MatchResultListener(::std::ostream* os) : stream_(os) {} + virtual ~MatchResultListener() = 0; // Makes this class abstract. + + // Streams x to the underlying ostream; does nothing if the ostream + // is NULL. + template <typename T> + MatchResultListener& operator<<(const T& x) { + if (stream_ != nullptr) *stream_ << x; + return *this; + } + + // Returns the underlying ostream. + ::std::ostream* stream() { return stream_; } + + // Returns true if and only if the listener is interested in an explanation + // of the match result. A matcher's MatchAndExplain() method can use + // this information to avoid generating the explanation when no one + // intends to hear it. + bool IsInterested() const { return stream_ != nullptr; } + + private: + ::std::ostream* const stream_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(MatchResultListener); +}; + +inline MatchResultListener::~MatchResultListener() { +} + +// An instance of a subclass of this knows how to describe itself as a +// matcher. +class MatcherDescriberInterface { + public: + virtual ~MatcherDescriberInterface() {} + + // Describes this matcher to an ostream. The function should print + // a verb phrase that describes the property a value matching this + // matcher should have. The subject of the verb phrase is the value + // being matched. For example, the DescribeTo() method of the Gt(7) + // matcher prints "is greater than 7". + virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const = 0; + + // Describes the negation of this matcher to an ostream. For + // example, if the description of this matcher is "is greater than + // 7", the negated description could be "is not greater than 7". + // You are not required to override this when implementing + // MatcherInterface, but it is highly advised so that your matcher + // can produce good error messages. + virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "not ("; + DescribeTo(os); + *os << ")"; + } +}; + +// The implementation of a matcher. +template <typename T> +class MatcherInterface : public MatcherDescriberInterface { + public: + // Returns true if and only if the matcher matches x; also explains the + // match result to 'listener' if necessary (see the next paragraph), in + // the form of a non-restrictive relative clause ("which ...", + // "whose ...", etc) that describes x. For example, the + // MatchAndExplain() method of the Pointee(...) matcher should + // generate an explanation like "which points to ...". + // + // Implementations of MatchAndExplain() should add an explanation of + // the match result *if and only if* they can provide additional + // information that's not already present (or not obvious) in the + // print-out of x and the matcher's description. Whether the match + // succeeds is not a factor in deciding whether an explanation is + // needed, as sometimes the caller needs to print a failure message + // when the match succeeds (e.g. when the matcher is used inside + // Not()). + // + // For example, a "has at least 10 elements" matcher should explain + // what the actual element count is, regardless of the match result, + // as it is useful information to the reader; on the other hand, an + // "is empty" matcher probably only needs to explain what the actual + // size is when the match fails, as it's redundant to say that the + // size is 0 when the value is already known to be empty. + // + // You should override this method when defining a new matcher. + // + // It's the responsibility of the caller (Google Test) to guarantee + // that 'listener' is not NULL. This helps to simplify a matcher's + // implementation when it doesn't care about the performance, as it + // can talk to 'listener' without checking its validity first. + // However, in order to implement dummy listeners efficiently, + // listener->stream() may be NULL. + virtual bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const = 0; + + // Inherits these methods from MatcherDescriberInterface: + // virtual void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const = 0; + // virtual void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const; +}; + +namespace internal { + +struct AnyEq { + template <typename A, typename B> + bool operator()(const A& a, const B& b) const { return a == b; } +}; +struct AnyNe { + template <typename A, typename B> + bool operator()(const A& a, const B& b) const { return a != b; } +}; +struct AnyLt { + template <typename A, typename B> + bool operator()(const A& a, const B& b) const { return a < b; } +}; +struct AnyGt { + template <typename A, typename B> + bool operator()(const A& a, const B& b) const { return a > b; } +}; +struct AnyLe { + template <typename A, typename B> + bool operator()(const A& a, const B& b) const { return a <= b; } +}; +struct AnyGe { + template <typename A, typename B> + bool operator()(const A& a, const B& b) const { return a >= b; } +}; + +// A match result listener that ignores the explanation. +class DummyMatchResultListener : public MatchResultListener { + public: + DummyMatchResultListener() : MatchResultListener(nullptr) {} + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(DummyMatchResultListener); +}; + +// A match result listener that forwards the explanation to a given +// ostream. The difference between this and MatchResultListener is +// that the former is concrete. +class StreamMatchResultListener : public MatchResultListener { + public: + explicit StreamMatchResultListener(::std::ostream* os) + : MatchResultListener(os) {} + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(StreamMatchResultListener); +}; + +struct SharedPayloadBase { + std::atomic<int> ref{1}; + void Ref() { ref.fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed); } + bool Unref() { return ref.fetch_sub(1, std::memory_order_acq_rel) == 1; } +}; + +template <typename T> +struct SharedPayload : SharedPayloadBase { + explicit SharedPayload(const T& v) : value(v) {} + explicit SharedPayload(T&& v) : value(std::move(v)) {} + + static void Destroy(SharedPayloadBase* shared) { + delete static_cast<SharedPayload*>(shared); + } + + T value; +}; + +template <typename T> +using is_trivially_copy_constructible = +#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) && __GNUC__ < 5 + std::has_trivial_copy_constructor<T>; +#else + std::is_trivially_copy_constructible<T>; +#endif + +// An internal class for implementing Matcher<T>, which will derive +// from it. We put functionalities common to all Matcher<T> +// specializations here to avoid code duplication. +template <typename T> +class MatcherBase : private MatcherDescriberInterface { + public: + // Returns true if and only if the matcher matches x; also explains the + // match result to 'listener'. + bool MatchAndExplain(const T& x, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + GTEST_CHECK_(vtable_ != nullptr); + return vtable_->match_and_explain(*this, x, listener); + } + + // Returns true if and only if this matcher matches x. + bool Matches(const T& x) const { + DummyMatchResultListener dummy; + return MatchAndExplain(x, &dummy); + } + + // Describes this matcher to an ostream. + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const final { + GTEST_CHECK_(vtable_ != nullptr); + vtable_->describe(*this, os, false); + } + + // Describes the negation of this matcher to an ostream. + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const final { + GTEST_CHECK_(vtable_ != nullptr); + vtable_->describe(*this, os, true); + } + + // Explains why x matches, or doesn't match, the matcher. + void ExplainMatchResultTo(const T& x, ::std::ostream* os) const { + StreamMatchResultListener listener(os); + MatchAndExplain(x, &listener); + } + + // Returns the describer for this matcher object; retains ownership + // of the describer, which is only guaranteed to be alive when + // this matcher object is alive. + const MatcherDescriberInterface* GetDescriber() const { + if (vtable_ == nullptr) return nullptr; + return vtable_->get_describer(*this); + } + + protected: + MatcherBase() : vtable_(nullptr) {} + + // Constructs a matcher from its implementation. + template <typename U> + explicit MatcherBase(const MatcherInterface<U>* impl) { + Init(impl); + } + + template <typename M, typename = typename std::remove_reference< + M>::type::is_gtest_matcher> + MatcherBase(M&& m) { // NOLINT + Init(std::forward<M>(m)); + } + + MatcherBase(const MatcherBase& other) + : vtable_(other.vtable_), buffer_(other.buffer_) { + if (IsShared()) buffer_.shared->Ref(); + } + + MatcherBase& operator=(const MatcherBase& other) { + if (this == &other) return *this; + Destroy(); + vtable_ = other.vtable_; + buffer_ = other.buffer_; + if (IsShared()) buffer_.shared->Ref(); + return *this; + } + + MatcherBase(MatcherBase&& other) + : vtable_(other.vtable_), buffer_(other.buffer_) { + other.vtable_ = nullptr; + } + + MatcherBase& operator=(MatcherBase&& other) { + if (this == &other) return *this; + Destroy(); + vtable_ = other.vtable_; + buffer_ = other.buffer_; + other.vtable_ = nullptr; + return *this; + } + + ~MatcherBase() override { Destroy(); } + + private: + struct VTable { + bool (*match_and_explain)(const MatcherBase&, const T&, + MatchResultListener*); + void (*describe)(const MatcherBase&, std::ostream*, bool negation); + // Returns the captured object if it implements the interface, otherwise + // returns the MatcherBase itself. + const MatcherDescriberInterface* (*get_describer)(const MatcherBase&); + // Called on shared instances when the reference count reaches 0. + void (*shared_destroy)(SharedPayloadBase*); + }; + + bool IsShared() const { + return vtable_ != nullptr && vtable_->shared_destroy != nullptr; + } + + // If the implementation uses a listener, call that. + template <typename P> + static auto MatchAndExplainImpl(const MatcherBase& m, const T& value, + MatchResultListener* listener) + -> decltype(P::Get(m).MatchAndExplain(value, listener->stream())) { + return P::Get(m).MatchAndExplain(value, listener->stream()); + } + + template <typename P> + static auto MatchAndExplainImpl(const MatcherBase& m, const T& value, + MatchResultListener* listener) + -> decltype(P::Get(m).MatchAndExplain(value, listener)) { + return P::Get(m).MatchAndExplain(value, listener); + } + + template <typename P> + static void DescribeImpl(const MatcherBase& m, std::ostream* os, + bool negation) { + if (negation) { + P::Get(m).DescribeNegationTo(os); + } else { + P::Get(m).DescribeTo(os); + } + } + + template <typename P> + static const MatcherDescriberInterface* GetDescriberImpl( + const MatcherBase& m) { + // If the impl is a MatcherDescriberInterface, then return it. + // Otherwise use MatcherBase itself. + // This allows us to implement the GetDescriber() function without support + // from the impl, but some users really want to get their impl back when + // they call GetDescriber(). + // We use std::get on a tuple as a workaround of not having `if constexpr`. + return std::get<( + std::is_convertible<decltype(&P::Get(m)), + const MatcherDescriberInterface*>::value + ? 1 + : 0)>(std::make_tuple(&m, &P::Get(m))); + } + + template <typename P> + const VTable* GetVTable() { + static constexpr VTable kVTable = {&MatchAndExplainImpl<P>, + &DescribeImpl<P>, &GetDescriberImpl<P>, + P::shared_destroy}; + return &kVTable; + } + + union Buffer { + // Add some types to give Buffer some common alignment/size use cases. + void* ptr; + double d; + int64_t i; + // And add one for the out-of-line cases. + SharedPayloadBase* shared; + }; + + void Destroy() { + if (IsShared() && buffer_.shared->Unref()) { + vtable_->shared_destroy(buffer_.shared); + } + } + + template <typename M> + static constexpr bool IsInlined() { + return sizeof(M) <= sizeof(Buffer) && alignof(M) <= alignof(Buffer) && + is_trivially_copy_constructible<M>::value && + std::is_trivially_destructible<M>::value; + } + + template <typename M, bool = MatcherBase::IsInlined<M>()> + struct ValuePolicy { + static const M& Get(const MatcherBase& m) { + // When inlined along with Init, need to be explicit to avoid violating + // strict aliasing rules. + const M *ptr = static_cast<const M*>( + static_cast<const void*>(&m.buffer_)); + return *ptr; + } + static void Init(MatcherBase& m, M impl) { + ::new (static_cast<void*>(&m.buffer_)) M(impl); + } + static constexpr auto shared_destroy = nullptr; + }; + + template <typename M> + struct ValuePolicy<M, false> { + using Shared = SharedPayload<M>; + static const M& Get(const MatcherBase& m) { + return static_cast<Shared*>(m.buffer_.shared)->value; + } + template <typename Arg> + static void Init(MatcherBase& m, Arg&& arg) { + m.buffer_.shared = new Shared(std::forward<Arg>(arg)); + } + static constexpr auto shared_destroy = &Shared::Destroy; + }; + + template <typename U, bool B> + struct ValuePolicy<const MatcherInterface<U>*, B> { + using M = const MatcherInterface<U>; + using Shared = SharedPayload<std::unique_ptr<M>>; + static const M& Get(const MatcherBase& m) { + return *static_cast<Shared*>(m.buffer_.shared)->value; + } + static void Init(MatcherBase& m, M* impl) { + m.buffer_.shared = new Shared(std::unique_ptr<M>(impl)); + } + + static constexpr auto shared_destroy = &Shared::Destroy; + }; + + template <typename M> + void Init(M&& m) { + using MM = typename std::decay<M>::type; + using Policy = ValuePolicy<MM>; + vtable_ = GetVTable<Policy>(); + Policy::Init(*this, std::forward<M>(m)); + } + + const VTable* vtable_; + Buffer buffer_; +}; + +} // namespace internal + +// A Matcher<T> is a copyable and IMMUTABLE (except by assignment) +// object that can check whether a value of type T matches. The +// implementation of Matcher<T> is just a std::shared_ptr to const +// MatcherInterface<T>. Don't inherit from Matcher! +template <typename T> +class Matcher : public internal::MatcherBase<T> { + public: + // Constructs a null matcher. Needed for storing Matcher objects in STL + // containers. A default-constructed matcher is not yet initialized. You + // cannot use it until a valid value has been assigned to it. + explicit Matcher() {} // NOLINT + + // Constructs a matcher from its implementation. + explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<const T&>* impl) + : internal::MatcherBase<T>(impl) {} + + template <typename U> + explicit Matcher( + const MatcherInterface<U>* impl, + typename std::enable_if<!std::is_same<U, const U&>::value>::type* = + nullptr) + : internal::MatcherBase<T>(impl) {} + + template <typename M, typename = typename std::remove_reference< + M>::type::is_gtest_matcher> + Matcher(M&& m) : internal::MatcherBase<T>(std::forward<M>(m)) {} // NOLINT + + // Implicit constructor here allows people to write + // EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar(5)) instead of EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar(Eq(5))) sometimes + Matcher(T value); // NOLINT +}; + +// The following two specializations allow the user to write str +// instead of Eq(str) and "foo" instead of Eq("foo") when a std::string +// matcher is expected. +template <> +class GTEST_API_ Matcher<const std::string&> + : public internal::MatcherBase<const std::string&> { + public: + Matcher() {} + + explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<const std::string&>* impl) + : internal::MatcherBase<const std::string&>(impl) {} + + template <typename M, typename = typename std::remove_reference< + M>::type::is_gtest_matcher> + Matcher(M&& m) // NOLINT + : internal::MatcherBase<const std::string&>(std::forward<M>(m)) {} + + // Allows the user to write str instead of Eq(str) sometimes, where + // str is a std::string object. + Matcher(const std::string& s); // NOLINT + + // Allows the user to write "foo" instead of Eq("foo") sometimes. + Matcher(const char* s); // NOLINT +}; + +template <> +class GTEST_API_ Matcher<std::string> + : public internal::MatcherBase<std::string> { + public: + Matcher() {} + + explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<const std::string&>* impl) + : internal::MatcherBase<std::string>(impl) {} + explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<std::string>* impl) + : internal::MatcherBase<std::string>(impl) {} + + template <typename M, typename = typename std::remove_reference< + M>::type::is_gtest_matcher> + Matcher(M&& m) // NOLINT + : internal::MatcherBase<std::string>(std::forward<M>(m)) {} + + // Allows the user to write str instead of Eq(str) sometimes, where + // str is a string object. + Matcher(const std::string& s); // NOLINT + + // Allows the user to write "foo" instead of Eq("foo") sometimes. + Matcher(const char* s); // NOLINT +}; + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW +// The following two specializations allow the user to write str +// instead of Eq(str) and "foo" instead of Eq("foo") when a absl::string_view +// matcher is expected. +template <> +class GTEST_API_ Matcher<const internal::StringView&> + : public internal::MatcherBase<const internal::StringView&> { + public: + Matcher() {} + + explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<const internal::StringView&>* impl) + : internal::MatcherBase<const internal::StringView&>(impl) {} + + template <typename M, typename = typename std::remove_reference< + M>::type::is_gtest_matcher> + Matcher(M&& m) // NOLINT + : internal::MatcherBase<const internal::StringView&>(std::forward<M>(m)) { + } + + // Allows the user to write str instead of Eq(str) sometimes, where + // str is a std::string object. + Matcher(const std::string& s); // NOLINT + + // Allows the user to write "foo" instead of Eq("foo") sometimes. + Matcher(const char* s); // NOLINT + + // Allows the user to pass absl::string_views or std::string_views directly. + Matcher(internal::StringView s); // NOLINT +}; + +template <> +class GTEST_API_ Matcher<internal::StringView> + : public internal::MatcherBase<internal::StringView> { + public: + Matcher() {} + + explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<const internal::StringView&>* impl) + : internal::MatcherBase<internal::StringView>(impl) {} + explicit Matcher(const MatcherInterface<internal::StringView>* impl) + : internal::MatcherBase<internal::StringView>(impl) {} + + template <typename M, typename = typename std::remove_reference< + M>::type::is_gtest_matcher> + Matcher(M&& m) // NOLINT + : internal::MatcherBase<internal::StringView>(std::forward<M>(m)) {} + + // Allows the user to write str instead of Eq(str) sometimes, where + // str is a std::string object. + Matcher(const std::string& s); // NOLINT + + // Allows the user to write "foo" instead of Eq("foo") sometimes. + Matcher(const char* s); // NOLINT + + // Allows the user to pass absl::string_views or std::string_views directly. + Matcher(internal::StringView s); // NOLINT +}; +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + +// Prints a matcher in a human-readable format. +template <typename T> +std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Matcher<T>& matcher) { + matcher.DescribeTo(&os); + return os; +} + +// The PolymorphicMatcher class template makes it easy to implement a +// polymorphic matcher (i.e. a matcher that can match values of more +// than one type, e.g. Eq(n) and NotNull()). +// +// To define a polymorphic matcher, a user should provide an Impl +// class that has a DescribeTo() method and a DescribeNegationTo() +// method, and define a member function (or member function template) +// +// bool MatchAndExplain(const Value& value, +// MatchResultListener* listener) const; +// +// See the definition of NotNull() for a complete example. +template <class Impl> +class PolymorphicMatcher { + public: + explicit PolymorphicMatcher(const Impl& an_impl) : impl_(an_impl) {} + + // Returns a mutable reference to the underlying matcher + // implementation object. + Impl& mutable_impl() { return impl_; } + + // Returns an immutable reference to the underlying matcher + // implementation object. + const Impl& impl() const { return impl_; } + + template <typename T> + operator Matcher<T>() const { + return Matcher<T>(new MonomorphicImpl<const T&>(impl_)); + } + + private: + template <typename T> + class MonomorphicImpl : public MatcherInterface<T> { + public: + explicit MonomorphicImpl(const Impl& impl) : impl_(impl) {} + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { impl_.DescribeTo(os); } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const override { + impl_.DescribeNegationTo(os); + } + + bool MatchAndExplain(T x, MatchResultListener* listener) const override { + return impl_.MatchAndExplain(x, listener); + } + + private: + const Impl impl_; + }; + + Impl impl_; +}; + +// Creates a matcher from its implementation. +// DEPRECATED: Especially in the generic code, prefer: +// Matcher<T>(new MyMatcherImpl<const T&>(...)); +// +// MakeMatcher may create a Matcher that accepts its argument by value, which +// leads to unnecessary copies & lack of support for non-copyable types. +template <typename T> +inline Matcher<T> MakeMatcher(const MatcherInterface<T>* impl) { + return Matcher<T>(impl); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher from its implementation. This is +// easier to use than the PolymorphicMatcher<Impl> constructor as it +// doesn't require you to explicitly write the template argument, e.g. +// +// MakePolymorphicMatcher(foo); +// vs +// PolymorphicMatcher<TypeOfFoo>(foo); +template <class Impl> +inline PolymorphicMatcher<Impl> MakePolymorphicMatcher(const Impl& impl) { + return PolymorphicMatcher<Impl>(impl); +} + +namespace internal { +// Implements a matcher that compares a given value with a +// pre-supplied value using one of the ==, <=, <, etc, operators. The +// two values being compared don't have to have the same type. +// +// The matcher defined here is polymorphic (for example, Eq(5) can be +// used to match an int, a short, a double, etc). Therefore we use +// a template type conversion operator in the implementation. +// +// The following template definition assumes that the Rhs parameter is +// a "bare" type (i.e. neither 'const T' nor 'T&'). +template <typename D, typename Rhs, typename Op> +class ComparisonBase { + public: + explicit ComparisonBase(const Rhs& rhs) : rhs_(rhs) {} + + using is_gtest_matcher = void; + + template <typename Lhs> + bool MatchAndExplain(const Lhs& lhs, std::ostream*) const { + return Op()(lhs, Unwrap(rhs_)); + } + void DescribeTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << D::Desc() << " "; + UniversalPrint(Unwrap(rhs_), os); + } + void DescribeNegationTo(std::ostream* os) const { + *os << D::NegatedDesc() << " "; + UniversalPrint(Unwrap(rhs_), os); + } + + private: + template <typename T> + static const T& Unwrap(const T& v) { + return v; + } + template <typename T> + static const T& Unwrap(std::reference_wrapper<T> v) { + return v; + } + + Rhs rhs_; +}; + +template <typename Rhs> +class EqMatcher : public ComparisonBase<EqMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyEq> { + public: + explicit EqMatcher(const Rhs& rhs) + : ComparisonBase<EqMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyEq>(rhs) { } + static const char* Desc() { return "is equal to"; } + static const char* NegatedDesc() { return "isn't equal to"; } +}; +template <typename Rhs> +class NeMatcher : public ComparisonBase<NeMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyNe> { + public: + explicit NeMatcher(const Rhs& rhs) + : ComparisonBase<NeMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyNe>(rhs) { } + static const char* Desc() { return "isn't equal to"; } + static const char* NegatedDesc() { return "is equal to"; } +}; +template <typename Rhs> +class LtMatcher : public ComparisonBase<LtMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyLt> { + public: + explicit LtMatcher(const Rhs& rhs) + : ComparisonBase<LtMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyLt>(rhs) { } + static const char* Desc() { return "is <"; } + static const char* NegatedDesc() { return "isn't <"; } +}; +template <typename Rhs> +class GtMatcher : public ComparisonBase<GtMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyGt> { + public: + explicit GtMatcher(const Rhs& rhs) + : ComparisonBase<GtMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyGt>(rhs) { } + static const char* Desc() { return "is >"; } + static const char* NegatedDesc() { return "isn't >"; } +}; +template <typename Rhs> +class LeMatcher : public ComparisonBase<LeMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyLe> { + public: + explicit LeMatcher(const Rhs& rhs) + : ComparisonBase<LeMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyLe>(rhs) { } + static const char* Desc() { return "is <="; } + static const char* NegatedDesc() { return "isn't <="; } +}; +template <typename Rhs> +class GeMatcher : public ComparisonBase<GeMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyGe> { + public: + explicit GeMatcher(const Rhs& rhs) + : ComparisonBase<GeMatcher<Rhs>, Rhs, AnyGe>(rhs) { } + static const char* Desc() { return "is >="; } + static const char* NegatedDesc() { return "isn't >="; } +}; + +template <typename T, typename = typename std::enable_if< + std::is_constructible<std::string, T>::value>::type> +using StringLike = T; + +// Implements polymorphic matchers MatchesRegex(regex) and +// ContainsRegex(regex), which can be used as a Matcher<T> as long as +// T can be converted to a string. +class MatchesRegexMatcher { + public: + MatchesRegexMatcher(const RE* regex, bool full_match) + : regex_(regex), full_match_(full_match) {} + +#if GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + bool MatchAndExplain(const internal::StringView& s, + MatchResultListener* listener) const { + return MatchAndExplain(std::string(s), listener); + } +#endif // GTEST_INTERNAL_HAS_STRING_VIEW + + // Accepts pointer types, particularly: + // const char* + // char* + // const wchar_t* + // wchar_t* + template <typename CharType> + bool MatchAndExplain(CharType* s, MatchResultListener* listener) const { + return s != nullptr && MatchAndExplain(std::string(s), listener); + } + + // Matches anything that can convert to std::string. + // + // This is a template, not just a plain function with const std::string&, + // because absl::string_view has some interfering non-explicit constructors. + template <class MatcheeStringType> + bool MatchAndExplain(const MatcheeStringType& s, + MatchResultListener* /* listener */) const { + const std::string& s2(s); + return full_match_ ? RE::FullMatch(s2, *regex_) + : RE::PartialMatch(s2, *regex_); + } + + void DescribeTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << (full_match_ ? "matches" : "contains") << " regular expression "; + UniversalPrinter<std::string>::Print(regex_->pattern(), os); + } + + void DescribeNegationTo(::std::ostream* os) const { + *os << "doesn't " << (full_match_ ? "match" : "contain") + << " regular expression "; + UniversalPrinter<std::string>::Print(regex_->pattern(), os); + } + + private: + const std::shared_ptr<const RE> regex_; + const bool full_match_; +}; +} // namespace internal + +// Matches a string that fully matches regular expression 'regex'. +// The matcher takes ownership of 'regex'. +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::MatchesRegexMatcher> MatchesRegex( + const internal::RE* regex) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::MatchesRegexMatcher(regex, true)); +} +template <typename T = std::string> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::MatchesRegexMatcher> MatchesRegex( + const internal::StringLike<T>& regex) { + return MatchesRegex(new internal::RE(std::string(regex))); +} + +// Matches a string that contains regular expression 'regex'. +// The matcher takes ownership of 'regex'. +inline PolymorphicMatcher<internal::MatchesRegexMatcher> ContainsRegex( + const internal::RE* regex) { + return MakePolymorphicMatcher(internal::MatchesRegexMatcher(regex, false)); +} +template <typename T = std::string> +PolymorphicMatcher<internal::MatchesRegexMatcher> ContainsRegex( + const internal::StringLike<T>& regex) { + return ContainsRegex(new internal::RE(std::string(regex))); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything equal to x. +// Note: if the parameter of Eq() were declared as const T&, Eq("foo") +// wouldn't compile. +template <typename T> +inline internal::EqMatcher<T> Eq(T x) { return internal::EqMatcher<T>(x); } + +// Constructs a Matcher<T> from a 'value' of type T. The constructed +// matcher matches any value that's equal to 'value'. +template <typename T> +Matcher<T>::Matcher(T value) { *this = Eq(value); } + +// Creates a monomorphic matcher that matches anything with type Lhs +// and equal to rhs. A user may need to use this instead of Eq(...) +// in order to resolve an overloading ambiguity. +// +// TypedEq<T>(x) is just a convenient short-hand for Matcher<T>(Eq(x)) +// or Matcher<T>(x), but more readable than the latter. +// +// We could define similar monomorphic matchers for other comparison +// operations (e.g. TypedLt, TypedGe, and etc), but decided not to do +// it yet as those are used much less than Eq() in practice. A user +// can always write Matcher<T>(Lt(5)) to be explicit about the type, +// for example. +template <typename Lhs, typename Rhs> +inline Matcher<Lhs> TypedEq(const Rhs& rhs) { return Eq(rhs); } + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything >= x. +template <typename Rhs> +inline internal::GeMatcher<Rhs> Ge(Rhs x) { + return internal::GeMatcher<Rhs>(x); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything > x. +template <typename Rhs> +inline internal::GtMatcher<Rhs> Gt(Rhs x) { + return internal::GtMatcher<Rhs>(x); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything <= x. +template <typename Rhs> +inline internal::LeMatcher<Rhs> Le(Rhs x) { + return internal::LeMatcher<Rhs>(x); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything < x. +template <typename Rhs> +inline internal::LtMatcher<Rhs> Lt(Rhs x) { + return internal::LtMatcher<Rhs>(x); +} + +// Creates a polymorphic matcher that matches anything != x. +template <typename Rhs> +inline internal::NeMatcher<Rhs> Ne(Rhs x) { + return internal::NeMatcher<Rhs>(x); +} +} // namespace testing + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 5046 + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_MATCHERS_H_ + +#include <stdio.h> +#include <memory> + +namespace testing { +namespace internal { + +GTEST_DECLARE_string_(internal_run_death_test); + +// Names of the flags (needed for parsing Google Test flags). +const char kDeathTestStyleFlag[] = "death_test_style"; +const char kDeathTestUseFork[] = "death_test_use_fork"; +const char kInternalRunDeathTestFlag[] = "internal_run_death_test"; + +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) + +// DeathTest is a class that hides much of the complexity of the +// GTEST_DEATH_TEST_ macro. It is abstract; its static Create method +// returns a concrete class that depends on the prevailing death test +// style, as defined by the --gtest_death_test_style and/or +// --gtest_internal_run_death_test flags. + +// In describing the results of death tests, these terms are used with +// the corresponding definitions: +// +// exit status: The integer exit information in the format specified +// by wait(2) +// exit code: The integer code passed to exit(3), _exit(2), or +// returned from main() +class GTEST_API_ DeathTest { + public: + // Create returns false if there was an error determining the + // appropriate action to take for the current death test; for example, + // if the gtest_death_test_style flag is set to an invalid value. + // The LastMessage method will return a more detailed message in that + // case. Otherwise, the DeathTest pointer pointed to by the "test" + // argument is set. If the death test should be skipped, the pointer + // is set to NULL; otherwise, it is set to the address of a new concrete + // DeathTest object that controls the execution of the current test. + static bool Create(const char* statement, Matcher<const std::string&> matcher, + const char* file, int line, DeathTest** test); + DeathTest(); + virtual ~DeathTest() { } + + // A helper class that aborts a death test when it's deleted. + class ReturnSentinel { + public: + explicit ReturnSentinel(DeathTest* test) : test_(test) { } + ~ReturnSentinel() { test_->Abort(TEST_ENCOUNTERED_RETURN_STATEMENT); } + private: + DeathTest* const test_; + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ReturnSentinel); + } GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; + + // An enumeration of possible roles that may be taken when a death + // test is encountered. EXECUTE means that the death test logic should + // be executed immediately. OVERSEE means that the program should prepare + // the appropriate environment for a child process to execute the death + // test, then wait for it to complete. + enum TestRole { OVERSEE_TEST, EXECUTE_TEST }; + + // An enumeration of the three reasons that a test might be aborted. + enum AbortReason { + TEST_ENCOUNTERED_RETURN_STATEMENT, + TEST_THREW_EXCEPTION, + TEST_DID_NOT_DIE + }; + + // Assumes one of the above roles. + virtual TestRole AssumeRole() = 0; + + // Waits for the death test to finish and returns its status. + virtual int Wait() = 0; + + // Returns true if the death test passed; that is, the test process + // exited during the test, its exit status matches a user-supplied + // predicate, and its stderr output matches a user-supplied regular + // expression. + // The user-supplied predicate may be a macro expression rather + // than a function pointer or functor, or else Wait and Passed could + // be combined. + virtual bool Passed(bool exit_status_ok) = 0; + + // Signals that the death test did not die as expected. + virtual void Abort(AbortReason reason) = 0; + + // Returns a human-readable outcome message regarding the outcome of + // the last death test. + static const char* LastMessage(); + + static void set_last_death_test_message(const std::string& message); + + private: + // A string containing a description of the outcome of the last death test. + static std::string last_death_test_message_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(DeathTest); +}; + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + +// Factory interface for death tests. May be mocked out for testing. +class DeathTestFactory { + public: + virtual ~DeathTestFactory() { } + virtual bool Create(const char* statement, + Matcher<const std::string&> matcher, const char* file, + int line, DeathTest** test) = 0; +}; + +// A concrete DeathTestFactory implementation for normal use. +class DefaultDeathTestFactory : public DeathTestFactory { + public: + bool Create(const char* statement, Matcher<const std::string&> matcher, + const char* file, int line, DeathTest** test) override; +}; + +// Returns true if exit_status describes a process that was terminated +// by a signal, or exited normally with a nonzero exit code. +GTEST_API_ bool ExitedUnsuccessfully(int exit_status); + +// A string passed to EXPECT_DEATH (etc.) is caught by one of these overloads +// and interpreted as a regex (rather than an Eq matcher) for legacy +// compatibility. +inline Matcher<const ::std::string&> MakeDeathTestMatcher( + ::testing::internal::RE regex) { + return ContainsRegex(regex.pattern()); +} +inline Matcher<const ::std::string&> MakeDeathTestMatcher(const char* regex) { + return ContainsRegex(regex); +} +inline Matcher<const ::std::string&> MakeDeathTestMatcher( + const ::std::string& regex) { + return ContainsRegex(regex); +} + +// If a Matcher<const ::std::string&> is passed to EXPECT_DEATH (etc.), it's +// used directly. +inline Matcher<const ::std::string&> MakeDeathTestMatcher( + Matcher<const ::std::string&> matcher) { + return matcher; +} + +// Traps C++ exceptions escaping statement and reports them as test +// failures. Note that trapping SEH exceptions is not implemented here. +# if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS +# define GTEST_EXECUTE_DEATH_TEST_STATEMENT_(statement, death_test) \ + try { \ + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ + } catch (const ::std::exception& gtest_exception) { \ + fprintf(\ + stderr, \ + "\n%s: Caught std::exception-derived exception escaping the " \ + "death test statement. Exception message: %s\n", \ + ::testing::internal::FormatFileLocation(__FILE__, __LINE__).c_str(), \ + gtest_exception.what()); \ + fflush(stderr); \ + death_test->Abort(::testing::internal::DeathTest::TEST_THREW_EXCEPTION); \ + } catch (...) { \ + death_test->Abort(::testing::internal::DeathTest::TEST_THREW_EXCEPTION); \ + } + +# else +# define GTEST_EXECUTE_DEATH_TEST_STATEMENT_(statement, death_test) \ + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement) + +# endif + +// This macro is for implementing ASSERT_DEATH*, EXPECT_DEATH*, +// ASSERT_EXIT*, and EXPECT_EXIT*. +#define GTEST_DEATH_TEST_(statement, predicate, regex_or_matcher, fail) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ + ::testing::internal::DeathTest* gtest_dt; \ + if (!::testing::internal::DeathTest::Create( \ + #statement, \ + ::testing::internal::MakeDeathTestMatcher(regex_or_matcher), \ + __FILE__, __LINE__, >est_dt)) { \ + goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_, __LINE__); \ + } \ + if (gtest_dt != nullptr) { \ + std::unique_ptr< ::testing::internal::DeathTest> gtest_dt_ptr(gtest_dt); \ + switch (gtest_dt->AssumeRole()) { \ + case ::testing::internal::DeathTest::OVERSEE_TEST: \ + if (!gtest_dt->Passed(predicate(gtest_dt->Wait()))) { \ + goto GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_, __LINE__); \ + } \ + break; \ + case ::testing::internal::DeathTest::EXECUTE_TEST: { \ + ::testing::internal::DeathTest::ReturnSentinel gtest_sentinel( \ + gtest_dt); \ + GTEST_EXECUTE_DEATH_TEST_STATEMENT_(statement, gtest_dt); \ + gtest_dt->Abort(::testing::internal::DeathTest::TEST_DID_NOT_DIE); \ + break; \ + } \ + default: \ + break; \ + } \ + } \ + } else \ + GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_label_, __LINE__) \ + : fail(::testing::internal::DeathTest::LastMessage()) +// The symbol "fail" here expands to something into which a message +// can be streamed. + +// This macro is for implementing ASSERT/EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH when compiled in +// NDEBUG mode. In this case we need the statements to be executed and the macro +// must accept a streamed message even though the message is never printed. +// The regex object is not evaluated, but it is used to prevent "unused" +// warnings and to avoid an expression that doesn't compile in debug mode. +#define GTEST_EXECUTE_STATEMENT_(statement, regex_or_matcher) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ + } else if (!::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ + ::testing::internal::MakeDeathTestMatcher(regex_or_matcher); \ + } else \ + ::testing::Message() + +// A class representing the parsed contents of the +// --gtest_internal_run_death_test flag, as it existed when +// RUN_ALL_TESTS was called. +class InternalRunDeathTestFlag { + public: + InternalRunDeathTestFlag(const std::string& a_file, + int a_line, + int an_index, + int a_write_fd) + : file_(a_file), line_(a_line), index_(an_index), + write_fd_(a_write_fd) {} + + ~InternalRunDeathTestFlag() { + if (write_fd_ >= 0) + posix::Close(write_fd_); + } + + const std::string& file() const { return file_; } + int line() const { return line_; } + int index() const { return index_; } + int write_fd() const { return write_fd_; } + + private: + std::string file_; + int line_; + int index_; + int write_fd_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(InternalRunDeathTestFlag); +}; + +// Returns a newly created InternalRunDeathTestFlag object with fields +// initialized from the GTEST_FLAG(internal_run_death_test) flag if +// the flag is specified; otherwise returns NULL. +InternalRunDeathTestFlag* ParseInternalRunDeathTestFlag(); + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST + +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_INTERNAL_H_ + +namespace testing { + +// This flag controls the style of death tests. Valid values are "threadsafe", +// meaning that the death test child process will re-execute the test binary +// from the start, running only a single death test, or "fast", +// meaning that the child process will execute the test logic immediately +// after forking. +GTEST_DECLARE_string_(death_test_style); + +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST + +namespace internal { + +// Returns a Boolean value indicating whether the caller is currently +// executing in the context of the death test child process. Tools such as +// Valgrind heap checkers may need this to modify their behavior in death +// tests. IMPORTANT: This is an internal utility. Using it may break the +// implementation of death tests. User code MUST NOT use it. +GTEST_API_ bool InDeathTestChild(); + +} // namespace internal + +// The following macros are useful for writing death tests. + +// Here's what happens when an ASSERT_DEATH* or EXPECT_DEATH* is +// executed: +// +// 1. It generates a warning if there is more than one active +// thread. This is because it's safe to fork() or clone() only +// when there is a single thread. +// +// 2. The parent process clone()s a sub-process and runs the death +// test in it; the sub-process exits with code 0 at the end of the +// death test, if it hasn't exited already. +// +// 3. The parent process waits for the sub-process to terminate. +// +// 4. The parent process checks the exit code and error message of +// the sub-process. +// +// Examples: +// +// ASSERT_DEATH(server.SendMessage(56, "Hello"), "Invalid port number"); +// for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { +// EXPECT_DEATH(server.ProcessRequest(i), +// "Invalid request .* in ProcessRequest()") +// << "Failed to die on request " << i; +// } +// +// ASSERT_EXIT(server.ExitNow(), ::testing::ExitedWithCode(0), "Exiting"); +// +// bool KilledBySIGHUP(int exit_code) { +// return WIFSIGNALED(exit_code) && WTERMSIG(exit_code) == SIGHUP; +// } +// +// ASSERT_EXIT(client.HangUpServer(), KilledBySIGHUP, "Hanging up!"); +// +// On the regular expressions used in death tests: +// +// GOOGLETEST_CM0005 DO NOT DELETE +// On POSIX-compliant systems (*nix), we use the <regex.h> library, +// which uses the POSIX extended regex syntax. +// +// On other platforms (e.g. Windows or Mac), we only support a simple regex +// syntax implemented as part of Google Test. This limited +// implementation should be enough most of the time when writing +// death tests; though it lacks many features you can find in PCRE +// or POSIX extended regex syntax. For example, we don't support +// union ("x|y"), grouping ("(xy)"), brackets ("[xy]"), and +// repetition count ("x{5,7}"), among others. +// +// Below is the syntax that we do support. We chose it to be a +// subset of both PCRE and POSIX extended regex, so it's easy to +// learn wherever you come from. In the following: 'A' denotes a +// literal character, period (.), or a single \\ escape sequence; +// 'x' and 'y' denote regular expressions; 'm' and 'n' are for +// natural numbers. +// +// c matches any literal character c +// \\d matches any decimal digit +// \\D matches any character that's not a decimal digit +// \\f matches \f +// \\n matches \n +// \\r matches \r +// \\s matches any ASCII whitespace, including \n +// \\S matches any character that's not a whitespace +// \\t matches \t +// \\v matches \v +// \\w matches any letter, _, or decimal digit +// \\W matches any character that \\w doesn't match +// \\c matches any literal character c, which must be a punctuation +// . matches any single character except \n +// A? matches 0 or 1 occurrences of A +// A* matches 0 or many occurrences of A +// A+ matches 1 or many occurrences of A +// ^ matches the beginning of a string (not that of each line) +// $ matches the end of a string (not that of each line) +// xy matches x followed by y +// +// If you accidentally use PCRE or POSIX extended regex features +// not implemented by us, you will get a run-time failure. In that +// case, please try to rewrite your regular expression within the +// above syntax. +// +// This implementation is *not* meant to be as highly tuned or robust +// as a compiled regex library, but should perform well enough for a +// death test, which already incurs significant overhead by launching +// a child process. +// +// Known caveats: +// +// A "threadsafe" style death test obtains the path to the test +// program from argv[0] and re-executes it in the sub-process. For +// simplicity, the current implementation doesn't search the PATH +// when launching the sub-process. This means that the user must +// invoke the test program via a path that contains at least one +// path separator (e.g. path/to/foo_test and +// /absolute/path/to/bar_test are fine, but foo_test is not). This +// is rarely a problem as people usually don't put the test binary +// directory in PATH. +// + +// Asserts that a given statement causes the program to exit, with an +// integer exit status that satisfies predicate, and emitting error output +// that matches regex. +# define ASSERT_EXIT(statement, predicate, regex) \ + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_(statement, predicate, regex, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) + +// Like ASSERT_EXIT, but continues on to successive tests in the +// test suite, if any: +# define EXPECT_EXIT(statement, predicate, regex) \ + GTEST_DEATH_TEST_(statement, predicate, regex, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) + +// Asserts that a given statement causes the program to exit, either by +// explicitly exiting with a nonzero exit code or being killed by a +// signal, and emitting error output that matches regex. +# define ASSERT_DEATH(statement, regex) \ + ASSERT_EXIT(statement, ::testing::internal::ExitedUnsuccessfully, regex) + +// Like ASSERT_DEATH, but continues on to successive tests in the +// test suite, if any: +# define EXPECT_DEATH(statement, regex) \ + EXPECT_EXIT(statement, ::testing::internal::ExitedUnsuccessfully, regex) + +// Two predicate classes that can be used in {ASSERT,EXPECT}_EXIT*: + +// Tests that an exit code describes a normal exit with a given exit code. +class GTEST_API_ ExitedWithCode { + public: + explicit ExitedWithCode(int exit_code); + ExitedWithCode(const ExitedWithCode&) = default; + void operator=(const ExitedWithCode& other) = delete; + bool operator()(int exit_status) const; + private: + const int exit_code_; +}; + +# if !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS && !GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA +// Tests that an exit code describes an exit due to termination by a +// given signal. +// GOOGLETEST_CM0006 DO NOT DELETE +class GTEST_API_ KilledBySignal { + public: + explicit KilledBySignal(int signum); + bool operator()(int exit_status) const; + private: + const int signum_; +}; +# endif // !GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +// EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH asserts that the given statements die in debug mode. +// The death testing framework causes this to have interesting semantics, +// since the sideeffects of the call are only visible in opt mode, and not +// in debug mode. +// +// In practice, this can be used to test functions that utilize the +// LOG(DFATAL) macro using the following style: +// +// int DieInDebugOr12(int* sideeffect) { +// if (sideeffect) { +// *sideeffect = 12; +// } +// LOG(DFATAL) << "death"; +// return 12; +// } +// +// TEST(TestSuite, TestDieOr12WorksInDgbAndOpt) { +// int sideeffect = 0; +// // Only asserts in dbg. +// EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH(DieInDebugOr12(&sideeffect), "death"); +// +// #ifdef NDEBUG +// // opt-mode has sideeffect visible. +// EXPECT_EQ(12, sideeffect); +// #else +// // dbg-mode no visible sideeffect. +// EXPECT_EQ(0, sideeffect); +// #endif +// } +// +// This will assert that DieInDebugReturn12InOpt() crashes in debug +// mode, usually due to a DCHECK or LOG(DFATAL), but returns the +// appropriate fallback value (12 in this case) in opt mode. If you +// need to test that a function has appropriate side-effects in opt +// mode, include assertions against the side-effects. A general +// pattern for this is: +// +// EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH({ +// // Side-effects here will have an effect after this statement in +// // opt mode, but none in debug mode. +// EXPECT_EQ(12, DieInDebugOr12(&sideeffect)); +// }, "death"); +// +# ifdef NDEBUG + +# define EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH(statement, regex) \ + GTEST_EXECUTE_STATEMENT_(statement, regex) + +# define ASSERT_DEBUG_DEATH(statement, regex) \ + GTEST_EXECUTE_STATEMENT_(statement, regex) + +# else + +# define EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH(statement, regex) \ + EXPECT_DEATH(statement, regex) + +# define ASSERT_DEBUG_DEATH(statement, regex) \ + ASSERT_DEATH(statement, regex) + +# endif // NDEBUG for EXPECT_DEBUG_DEATH +#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST + +// This macro is used for implementing macros such as +// EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED and ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED on systems where +// death tests are not supported. Those macros must compile on such systems +// if and only if EXPECT_DEATH and ASSERT_DEATH compile with the same parameters +// on systems that support death tests. This allows one to write such a macro on +// a system that does not support death tests and be sure that it will compile +// on a death-test supporting system. It is exposed publicly so that systems +// that have death-tests with stricter requirements than GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +// can write their own equivalent of EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED and +// ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED. +// +// Parameters: +// statement - A statement that a macro such as EXPECT_DEATH would test +// for program termination. This macro has to make sure this +// statement is compiled but not executed, to ensure that +// EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED compiles with a certain +// parameter if and only if EXPECT_DEATH compiles with it. +// regex - A regex that a macro such as EXPECT_DEATH would use to test +// the output of statement. This parameter has to be +// compiled but not evaluated by this macro, to ensure that +// this macro only accepts expressions that a macro such as +// EXPECT_DEATH would accept. +// terminator - Must be an empty statement for EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED +// and a return statement for ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED. +// This ensures that ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED will not +// compile inside functions where ASSERT_DEATH doesn't +// compile. +// +// The branch that has an always false condition is used to ensure that +// statement and regex are compiled (and thus syntactically correct) but +// never executed. The unreachable code macro protects the terminator +// statement from generating an 'unreachable code' warning in case +// statement unconditionally returns or throws. The Message constructor at +// the end allows the syntax of streaming additional messages into the +// macro, for compilational compatibility with EXPECT_DEATH/ASSERT_DEATH. +# define GTEST_UNSUPPORTED_DEATH_TEST(statement, regex, terminator) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (::testing::internal::AlwaysTrue()) { \ + GTEST_LOG_(WARNING) \ + << "Death tests are not supported on this platform.\n" \ + << "Statement '" #statement "' cannot be verified."; \ + } else if (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) { \ + ::testing::internal::RE::PartialMatch(".*", (regex)); \ + GTEST_SUPPRESS_UNREACHABLE_CODE_WARNING_BELOW_(statement); \ + terminator; \ + } else \ + ::testing::Message() + +// EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) and +// ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) expand to real death tests if +// death tests are supported; otherwise they just issue a warning. This is +// useful when you are combining death test assertions with normal test +// assertions in one test. +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST +# define EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) \ + EXPECT_DEATH(statement, regex) +# define ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) \ + ASSERT_DEATH(statement, regex) +#else +# define EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) \ + GTEST_UNSUPPORTED_DEATH_TEST(statement, regex, ) +# define ASSERT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED(statement, regex) \ + GTEST_UNSUPPORTED_DEATH_TEST(statement, regex, return) +#endif + +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_DEATH_TEST_H_ +// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// Macros and functions for implementing parameterized tests +// in Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) +// +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PARAM_TEST_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PARAM_TEST_H_ + +// Value-parameterized tests allow you to test your code with different +// parameters without writing multiple copies of the same test. +// +// Here is how you use value-parameterized tests: + +#if 0 + +// To write value-parameterized tests, first you should define a fixture +// class. It is usually derived from testing::TestWithParam<T> (see below for +// another inheritance scheme that's sometimes useful in more complicated +// class hierarchies), where the type of your parameter values. +// TestWithParam<T> is itself derived from testing::Test. T can be any +// copyable type. If it's a raw pointer, you are responsible for managing the +// lifespan of the pointed values. + +class FooTest : public ::testing::TestWithParam<const char*> { + // You can implement all the usual class fixture members here. +}; + +// Then, use the TEST_P macro to define as many parameterized tests +// for this fixture as you want. The _P suffix is for "parameterized" +// or "pattern", whichever you prefer to think. + +TEST_P(FooTest, DoesBlah) { + // Inside a test, access the test parameter with the GetParam() method + // of the TestWithParam<T> class: + EXPECT_TRUE(foo.Blah(GetParam())); + ... +} + +TEST_P(FooTest, HasBlahBlah) { + ... +} + +// Finally, you can use INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P to instantiate the test +// case with any set of parameters you want. Google Test defines a number +// of functions for generating test parameters. They return what we call +// (surprise!) parameter generators. Here is a summary of them, which +// are all in the testing namespace: +// +// +// Range(begin, end [, step]) - Yields values {begin, begin+step, +// begin+step+step, ...}. The values do not +// include end. step defaults to 1. +// Values(v1, v2, ..., vN) - Yields values {v1, v2, ..., vN}. +// ValuesIn(container) - Yields values from a C-style array, an STL +// ValuesIn(begin,end) container, or an iterator range [begin, end). +// Bool() - Yields sequence {false, true}. +// Combine(g1, g2, ..., gN) - Yields all combinations (the Cartesian product +// for the math savvy) of the values generated +// by the N generators. +// +// For more details, see comments at the definitions of these functions below +// in this file. +// +// The following statement will instantiate tests from the FooTest test suite +// each with parameter values "meeny", "miny", and "moe". + +INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(InstantiationName, + FooTest, + Values("meeny", "miny", "moe")); + +// To distinguish different instances of the pattern, (yes, you +// can instantiate it more than once) the first argument to the +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P macro is a prefix that will be added to the +// actual test suite name. Remember to pick unique prefixes for different +// instantiations. The tests from the instantiation above will have +// these names: +// +// * InstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/0 for "meeny" +// * InstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/1 for "miny" +// * InstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/2 for "moe" +// * InstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/0 for "meeny" +// * InstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/1 for "miny" +// * InstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/2 for "moe" +// +// You can use these names in --gtest_filter. +// +// This statement will instantiate all tests from FooTest again, each +// with parameter values "cat" and "dog": + +const char* pets[] = {"cat", "dog"}; +INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(AnotherInstantiationName, FooTest, ValuesIn(pets)); + +// The tests from the instantiation above will have these names: +// +// * AnotherInstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/0 for "cat" +// * AnotherInstantiationName/FooTest.DoesBlah/1 for "dog" +// * AnotherInstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/0 for "cat" +// * AnotherInstantiationName/FooTest.HasBlahBlah/1 for "dog" +// +// Please note that INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P will instantiate all tests +// in the given test suite, whether their definitions come before or +// AFTER the INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P statement. +// +// Please also note that generator expressions (including parameters to the +// generators) are evaluated in InitGoogleTest(), after main() has started. +// This allows the user on one hand, to adjust generator parameters in order +// to dynamically determine a set of tests to run and on the other hand, +// give the user a chance to inspect the generated tests with Google Test +// reflection API before RUN_ALL_TESTS() is executed. +// +// You can see samples/sample7_unittest.cc and samples/sample8_unittest.cc +// for more examples. +// +// In the future, we plan to publish the API for defining new parameter +// generators. But for now this interface remains part of the internal +// implementation and is subject to change. +// +// +// A parameterized test fixture must be derived from testing::Test and from +// testing::WithParamInterface<T>, where T is the type of the parameter +// values. Inheriting from TestWithParam<T> satisfies that requirement because +// TestWithParam<T> inherits from both Test and WithParamInterface. In more +// complicated hierarchies, however, it is occasionally useful to inherit +// separately from Test and WithParamInterface. For example: + +class BaseTest : public ::testing::Test { + // You can inherit all the usual members for a non-parameterized test + // fixture here. +}; + +class DerivedTest : public BaseTest, public ::testing::WithParamInterface<int> { + // The usual test fixture members go here too. +}; + +TEST_F(BaseTest, HasFoo) { + // This is an ordinary non-parameterized test. +} + +TEST_P(DerivedTest, DoesBlah) { + // GetParam works just the same here as if you inherit from TestWithParam. + EXPECT_TRUE(foo.Blah(GetParam())); +} + +#endif // 0 + +#include <iterator> +#include <utility> + +// Copyright 2008 Google Inc. +// All Rights Reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + + +// Type and function utilities for implementing parameterized tests. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PARAM_UTIL_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PARAM_UTIL_H_ + +#include <ctype.h> + +#include <cassert> +#include <iterator> +#include <memory> +#include <set> +#include <tuple> +#include <type_traits> +#include <utility> +#include <vector> + +// Copyright 2008, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. +// +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TEST_PART_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TEST_PART_H_ + +#include <iosfwd> +#include <vector> + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) + +namespace testing { + +// A copyable object representing the result of a test part (i.e. an +// assertion or an explicit FAIL(), ADD_FAILURE(), or SUCCESS()). +// +// Don't inherit from TestPartResult as its destructor is not virtual. +class GTEST_API_ TestPartResult { + public: + // The possible outcomes of a test part (i.e. an assertion or an + // explicit SUCCEED(), FAIL(), or ADD_FAILURE()). + enum Type { + kSuccess, // Succeeded. + kNonFatalFailure, // Failed but the test can continue. + kFatalFailure, // Failed and the test should be terminated. + kSkip // Skipped. + }; + + // C'tor. TestPartResult does NOT have a default constructor. + // Always use this constructor (with parameters) to create a + // TestPartResult object. + TestPartResult(Type a_type, const char* a_file_name, int a_line_number, + const char* a_message) + : type_(a_type), + file_name_(a_file_name == nullptr ? "" : a_file_name), + line_number_(a_line_number), + summary_(ExtractSummary(a_message)), + message_(a_message) {} + + // Gets the outcome of the test part. + Type type() const { return type_; } + + // Gets the name of the source file where the test part took place, or + // NULL if it's unknown. + const char* file_name() const { + return file_name_.empty() ? nullptr : file_name_.c_str(); + } + + // Gets the line in the source file where the test part took place, + // or -1 if it's unknown. + int line_number() const { return line_number_; } + + // Gets the summary of the failure message. + const char* summary() const { return summary_.c_str(); } + + // Gets the message associated with the test part. + const char* message() const { return message_.c_str(); } + + // Returns true if and only if the test part was skipped. + bool skipped() const { return type_ == kSkip; } + + // Returns true if and only if the test part passed. + bool passed() const { return type_ == kSuccess; } + + // Returns true if and only if the test part non-fatally failed. + bool nonfatally_failed() const { return type_ == kNonFatalFailure; } + + // Returns true if and only if the test part fatally failed. + bool fatally_failed() const { return type_ == kFatalFailure; } + + // Returns true if and only if the test part failed. + bool failed() const { return fatally_failed() || nonfatally_failed(); } + + private: + Type type_; + + // Gets the summary of the failure message by omitting the stack + // trace in it. + static std::string ExtractSummary(const char* message); + + // The name of the source file where the test part took place, or + // "" if the source file is unknown. + std::string file_name_; + // The line in the source file where the test part took place, or -1 + // if the line number is unknown. + int line_number_; + std::string summary_; // The test failure summary. + std::string message_; // The test failure message. +}; + +// Prints a TestPartResult object. +std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const TestPartResult& result); + +// An array of TestPartResult objects. +// +// Don't inherit from TestPartResultArray as its destructor is not +// virtual. +class GTEST_API_ TestPartResultArray { + public: + TestPartResultArray() {} + + // Appends the given TestPartResult to the array. + void Append(const TestPartResult& result); + + // Returns the TestPartResult at the given index (0-based). + const TestPartResult& GetTestPartResult(int index) const; + + // Returns the number of TestPartResult objects in the array. + int size() const; + + private: + std::vector<TestPartResult> array_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestPartResultArray); +}; + +// This interface knows how to report a test part result. +class GTEST_API_ TestPartResultReporterInterface { + public: + virtual ~TestPartResultReporterInterface() {} + + virtual void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) = 0; +}; + +namespace internal { + +// This helper class is used by {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NO_FATAL_FAILURE to check if a +// statement generates new fatal failures. To do so it registers itself as the +// current test part result reporter. Besides checking if fatal failures were +// reported, it only delegates the reporting to the former result reporter. +// The original result reporter is restored in the destructor. +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +class GTEST_API_ HasNewFatalFailureHelper + : public TestPartResultReporterInterface { + public: + HasNewFatalFailureHelper(); + ~HasNewFatalFailureHelper() override; + void ReportTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& result) override; + bool has_new_fatal_failure() const { return has_new_fatal_failure_; } + private: + bool has_new_fatal_failure_; + TestPartResultReporterInterface* original_reporter_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(HasNewFatalFailureHelper); +}; + +} // namespace internal + +} // namespace testing + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TEST_PART_H_ + +namespace testing { +// Input to a parameterized test name generator, describing a test parameter. +// Consists of the parameter value and the integer parameter index. +template <class ParamType> +struct TestParamInfo { + TestParamInfo(const ParamType& a_param, size_t an_index) : + param(a_param), + index(an_index) {} + ParamType param; + size_t index; +}; + +// A builtin parameterized test name generator which returns the result of +// testing::PrintToString. +struct PrintToStringParamName { + template <class ParamType> + std::string operator()(const TestParamInfo<ParamType>& info) const { + return PrintToString(info.param); + } +}; + +namespace internal { + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// Utility Functions + +// Outputs a message explaining invalid registration of different +// fixture class for the same test suite. This may happen when +// TEST_P macro is used to define two tests with the same name +// but in different namespaces. +GTEST_API_ void ReportInvalidTestSuiteType(const char* test_suite_name, + CodeLocation code_location); + +template <typename> class ParamGeneratorInterface; +template <typename> class ParamGenerator; + +// Interface for iterating over elements provided by an implementation +// of ParamGeneratorInterface<T>. +template <typename T> +class ParamIteratorInterface { + public: + virtual ~ParamIteratorInterface() {} + // A pointer to the base generator instance. + // Used only for the purposes of iterator comparison + // to make sure that two iterators belong to the same generator. + virtual const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* BaseGenerator() const = 0; + // Advances iterator to point to the next element + // provided by the generator. The caller is responsible + // for not calling Advance() on an iterator equal to + // BaseGenerator()->End(). + virtual void Advance() = 0; + // Clones the iterator object. Used for implementing copy semantics + // of ParamIterator<T>. + virtual ParamIteratorInterface* Clone() const = 0; + // Dereferences the current iterator and provides (read-only) access + // to the pointed value. It is the caller's responsibility not to call + // Current() on an iterator equal to BaseGenerator()->End(). + // Used for implementing ParamGenerator<T>::operator*(). + virtual const T* Current() const = 0; + // Determines whether the given iterator and other point to the same + // element in the sequence generated by the generator. + // Used for implementing ParamGenerator<T>::operator==(). + virtual bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface& other) const = 0; +}; + +// Class iterating over elements provided by an implementation of +// ParamGeneratorInterface<T>. It wraps ParamIteratorInterface<T> +// and implements the const forward iterator concept. +template <typename T> +class ParamIterator { + public: + typedef T value_type; + typedef const T& reference; + typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; + + // ParamIterator assumes ownership of the impl_ pointer. + ParamIterator(const ParamIterator& other) : impl_(other.impl_->Clone()) {} + ParamIterator& operator=(const ParamIterator& other) { + if (this != &other) + impl_.reset(other.impl_->Clone()); + return *this; + } + + const T& operator*() const { return *impl_->Current(); } + const T* operator->() const { return impl_->Current(); } + // Prefix version of operator++. + ParamIterator& operator++() { + impl_->Advance(); + return *this; + } + // Postfix version of operator++. + ParamIterator operator++(int /*unused*/) { + ParamIteratorInterface<T>* clone = impl_->Clone(); + impl_->Advance(); + return ParamIterator(clone); + } + bool operator==(const ParamIterator& other) const { + return impl_.get() == other.impl_.get() || impl_->Equals(*other.impl_); + } + bool operator!=(const ParamIterator& other) const { + return !(*this == other); + } + + private: + friend class ParamGenerator<T>; + explicit ParamIterator(ParamIteratorInterface<T>* impl) : impl_(impl) {} + std::unique_ptr<ParamIteratorInterface<T> > impl_; +}; + +// ParamGeneratorInterface<T> is the binary interface to access generators +// defined in other translation units. +template <typename T> +class ParamGeneratorInterface { + public: + typedef T ParamType; + + virtual ~ParamGeneratorInterface() {} + + // Generator interface definition + virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Begin() const = 0; + virtual ParamIteratorInterface<T>* End() const = 0; +}; + +// Wraps ParamGeneratorInterface<T> and provides general generator syntax +// compatible with the STL Container concept. +// This class implements copy initialization semantics and the contained +// ParamGeneratorInterface<T> instance is shared among all copies +// of the original object. This is possible because that instance is immutable. +template<typename T> +class ParamGenerator { + public: + typedef ParamIterator<T> iterator; + + explicit ParamGenerator(ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* impl) : impl_(impl) {} + ParamGenerator(const ParamGenerator& other) : impl_(other.impl_) {} + + ParamGenerator& operator=(const ParamGenerator& other) { + impl_ = other.impl_; + return *this; + } + + iterator begin() const { return iterator(impl_->Begin()); } + iterator end() const { return iterator(impl_->End()); } + + private: + std::shared_ptr<const ParamGeneratorInterface<T> > impl_; +}; + +// Generates values from a range of two comparable values. Can be used to +// generate sequences of user-defined types that implement operator+() and +// operator<(). +// This class is used in the Range() function. +template <typename T, typename IncrementT> +class RangeGenerator : public ParamGeneratorInterface<T> { + public: + RangeGenerator(T begin, T end, IncrementT step) + : begin_(begin), end_(end), + step_(step), end_index_(CalculateEndIndex(begin, end, step)) {} + ~RangeGenerator() override {} + + ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Begin() const override { + return new Iterator(this, begin_, 0, step_); + } + ParamIteratorInterface<T>* End() const override { + return new Iterator(this, end_, end_index_, step_); + } + + private: + class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<T> { + public: + Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* base, T value, int index, + IncrementT step) + : base_(base), value_(value), index_(index), step_(step) {} + ~Iterator() override {} + + const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* BaseGenerator() const override { + return base_; + } + void Advance() override { + value_ = static_cast<T>(value_ + step_); + index_++; + } + ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Clone() const override { + return new Iterator(*this); + } + const T* Current() const override { return &value_; } + bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<T>& other) const override { + // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other + // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. + GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) + << "The program attempted to compare iterators " + << "from different generators." << std::endl; + const int other_index = + CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other)->index_; + return index_ == other_index; + } + + private: + Iterator(const Iterator& other) + : ParamIteratorInterface<T>(), + base_(other.base_), value_(other.value_), index_(other.index_), + step_(other.step_) {} + + // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. + void operator=(const Iterator& other); + + const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* const base_; + T value_; + int index_; + const IncrementT step_; + }; // class RangeGenerator::Iterator + + static int CalculateEndIndex(const T& begin, + const T& end, + const IncrementT& step) { + int end_index = 0; + for (T i = begin; i < end; i = static_cast<T>(i + step)) + end_index++; + return end_index; + } + + // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. + void operator=(const RangeGenerator& other); + + const T begin_; + const T end_; + const IncrementT step_; + // The index for the end() iterator. All the elements in the generated + // sequence are indexed (0-based) to aid iterator comparison. + const int end_index_; +}; // class RangeGenerator + + +// Generates values from a pair of STL-style iterators. Used in the +// ValuesIn() function. The elements are copied from the source range +// since the source can be located on the stack, and the generator +// is likely to persist beyond that stack frame. +template <typename T> +class ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator : public ParamGeneratorInterface<T> { + public: + template <typename ForwardIterator> + ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator(ForwardIterator begin, ForwardIterator end) + : container_(begin, end) {} + ~ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator() override {} + + ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Begin() const override { + return new Iterator(this, container_.begin()); + } + ParamIteratorInterface<T>* End() const override { + return new Iterator(this, container_.end()); + } + + private: + typedef typename ::std::vector<T> ContainerType; + + class Iterator : public ParamIteratorInterface<T> { + public: + Iterator(const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* base, + typename ContainerType::const_iterator iterator) + : base_(base), iterator_(iterator) {} + ~Iterator() override {} + + const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* BaseGenerator() const override { + return base_; + } + void Advance() override { + ++iterator_; + value_.reset(); + } + ParamIteratorInterface<T>* Clone() const override { + return new Iterator(*this); + } + // We need to use cached value referenced by iterator_ because *iterator_ + // can return a temporary object (and of type other then T), so just + // having "return &*iterator_;" doesn't work. + // value_ is updated here and not in Advance() because Advance() + // can advance iterator_ beyond the end of the range, and we cannot + // detect that fact. The client code, on the other hand, is + // responsible for not calling Current() on an out-of-range iterator. + const T* Current() const override { + if (value_.get() == nullptr) value_.reset(new T(*iterator_)); + return value_.get(); + } + bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<T>& other) const override { + // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other + // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. + GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) + << "The program attempted to compare iterators " + << "from different generators." << std::endl; + return iterator_ == + CheckedDowncastToActualType<const Iterator>(&other)->iterator_; + } + + private: + Iterator(const Iterator& other) + // The explicit constructor call suppresses a false warning + // emitted by gcc when supplied with the -Wextra option. + : ParamIteratorInterface<T>(), + base_(other.base_), + iterator_(other.iterator_) {} + + const ParamGeneratorInterface<T>* const base_; + typename ContainerType::const_iterator iterator_; + // A cached value of *iterator_. We keep it here to allow access by + // pointer in the wrapping iterator's operator->(). + // value_ needs to be mutable to be accessed in Current(). + // Use of std::unique_ptr helps manage cached value's lifetime, + // which is bound by the lifespan of the iterator itself. + mutable std::unique_ptr<const T> value_; + }; // class ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator::Iterator + + // No implementation - assignment is unsupported. + void operator=(const ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator& other); + + const ContainerType container_; +}; // class ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// Default parameterized test name generator, returns a string containing the +// integer test parameter index. +template <class ParamType> +std::string DefaultParamName(const TestParamInfo<ParamType>& info) { + Message name_stream; + name_stream << info.index; + return name_stream.GetString(); +} + +template <typename T = int> +void TestNotEmpty() { + static_assert(sizeof(T) == 0, "Empty arguments are not allowed."); +} +template <typename T = int> +void TestNotEmpty(const T&) {} + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// Stores a parameter value and later creates tests parameterized with that +// value. +template <class TestClass> +class ParameterizedTestFactory : public TestFactoryBase { + public: + typedef typename TestClass::ParamType ParamType; + explicit ParameterizedTestFactory(ParamType parameter) : + parameter_(parameter) {} + Test* CreateTest() override { + TestClass::SetParam(¶meter_); + return new TestClass(); + } + + private: + const ParamType parameter_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ParameterizedTestFactory); +}; + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// TestMetaFactoryBase is a base class for meta-factories that create +// test factories for passing into MakeAndRegisterTestInfo function. +template <class ParamType> +class TestMetaFactoryBase { + public: + virtual ~TestMetaFactoryBase() {} + + virtual TestFactoryBase* CreateTestFactory(ParamType parameter) = 0; +}; + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// TestMetaFactory creates test factories for passing into +// MakeAndRegisterTestInfo function. Since MakeAndRegisterTestInfo receives +// ownership of test factory pointer, same factory object cannot be passed +// into that method twice. But ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo is going to call +// it for each Test/Parameter value combination. Thus it needs meta factory +// creator class. +template <class TestSuite> +class TestMetaFactory + : public TestMetaFactoryBase<typename TestSuite::ParamType> { + public: + using ParamType = typename TestSuite::ParamType; + + TestMetaFactory() {} + + TestFactoryBase* CreateTestFactory(ParamType parameter) override { + return new ParameterizedTestFactory<TestSuite>(parameter); + } + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestMetaFactory); +}; + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase is a generic interface +// to ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo classes. ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase +// accumulates test information provided by TEST_P macro invocations +// and generators provided by INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P macro invocations +// and uses that information to register all resulting test instances +// in RegisterTests method. The ParameterizeTestSuiteRegistry class holds +// a collection of pointers to the ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo objects +// and calls RegisterTests() on each of them when asked. +class ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase { + public: + virtual ~ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase() {} + + // Base part of test suite name for display purposes. + virtual const std::string& GetTestSuiteName() const = 0; + // Test suite id to verify identity. + virtual TypeId GetTestSuiteTypeId() const = 0; + // UnitTest class invokes this method to register tests in this + // test suite right before running them in RUN_ALL_TESTS macro. + // This method should not be called more than once on any single + // instance of a ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase derived class. + virtual void RegisterTests() = 0; + + protected: + ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase() {} + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase); +}; + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// Report a the name of a test_suit as safe to ignore +// as the side effect of construction of this type. +struct MarkAsIgnored { + explicit MarkAsIgnored(const char* test_suite); +}; + +GTEST_API_ void InsertSyntheticTestCase(const std::string& name, + CodeLocation location, bool has_test_p); + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo accumulates tests obtained from TEST_P +// macro invocations for a particular test suite and generators +// obtained from INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P macro invocations for that +// test suite. It registers tests with all values generated by all +// generators when asked. +template <class TestSuite> +class ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo : public ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase { + public: + // ParamType and GeneratorCreationFunc are private types but are required + // for declarations of public methods AddTestPattern() and + // AddTestSuiteInstantiation(). + using ParamType = typename TestSuite::ParamType; + // A function that returns an instance of appropriate generator type. + typedef ParamGenerator<ParamType>(GeneratorCreationFunc)(); + using ParamNameGeneratorFunc = std::string(const TestParamInfo<ParamType>&); + + explicit ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo(const char* name, + CodeLocation code_location) + : test_suite_name_(name), code_location_(code_location) {} + + // Test suite base name for display purposes. + const std::string& GetTestSuiteName() const override { + return test_suite_name_; + } + // Test suite id to verify identity. + TypeId GetTestSuiteTypeId() const override { return GetTypeId<TestSuite>(); } + // TEST_P macro uses AddTestPattern() to record information + // about a single test in a LocalTestInfo structure. + // test_suite_name is the base name of the test suite (without invocation + // prefix). test_base_name is the name of an individual test without + // parameter index. For the test SequenceA/FooTest.DoBar/1 FooTest is + // test suite base name and DoBar is test base name. + void AddTestPattern(const char* test_suite_name, const char* test_base_name, + TestMetaFactoryBase<ParamType>* meta_factory, + CodeLocation code_location) { + tests_.push_back(std::shared_ptr<TestInfo>(new TestInfo( + test_suite_name, test_base_name, meta_factory, code_location))); + } + // INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P macro uses AddGenerator() to record information + // about a generator. + int AddTestSuiteInstantiation(const std::string& instantiation_name, + GeneratorCreationFunc* func, + ParamNameGeneratorFunc* name_func, + const char* file, int line) { + instantiations_.push_back( + InstantiationInfo(instantiation_name, func, name_func, file, line)); + return 0; // Return value used only to run this method in namespace scope. + } + // UnitTest class invokes this method to register tests in this test suite + // right before running tests in RUN_ALL_TESTS macro. + // This method should not be called more than once on any single + // instance of a ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase derived class. + // UnitTest has a guard to prevent from calling this method more than once. + void RegisterTests() override { + bool generated_instantiations = false; + + for (typename TestInfoContainer::iterator test_it = tests_.begin(); + test_it != tests_.end(); ++test_it) { + std::shared_ptr<TestInfo> test_info = *test_it; + for (typename InstantiationContainer::iterator gen_it = + instantiations_.begin(); gen_it != instantiations_.end(); + ++gen_it) { + const std::string& instantiation_name = gen_it->name; + ParamGenerator<ParamType> generator((*gen_it->generator)()); + ParamNameGeneratorFunc* name_func = gen_it->name_func; + const char* file = gen_it->file; + int line = gen_it->line; + + std::string test_suite_name; + if ( !instantiation_name.empty() ) + test_suite_name = instantiation_name + "/"; + test_suite_name += test_info->test_suite_base_name; + + size_t i = 0; + std::set<std::string> test_param_names; + for (typename ParamGenerator<ParamType>::iterator param_it = + generator.begin(); + param_it != generator.end(); ++param_it, ++i) { + generated_instantiations = true; + + Message test_name_stream; + + std::string param_name = name_func( + TestParamInfo<ParamType>(*param_it, i)); + + GTEST_CHECK_(IsValidParamName(param_name)) + << "Parameterized test name '" << param_name + << "' is invalid, in " << file + << " line " << line << std::endl; + + GTEST_CHECK_(test_param_names.count(param_name) == 0) + << "Duplicate parameterized test name '" << param_name + << "', in " << file << " line " << line << std::endl; + + test_param_names.insert(param_name); + + if (!test_info->test_base_name.empty()) { + test_name_stream << test_info->test_base_name << "/"; + } + test_name_stream << param_name; + MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( + test_suite_name.c_str(), test_name_stream.GetString().c_str(), + nullptr, // No type parameter. + PrintToString(*param_it).c_str(), test_info->code_location, + GetTestSuiteTypeId(), + SuiteApiResolver<TestSuite>::GetSetUpCaseOrSuite(file, line), + SuiteApiResolver<TestSuite>::GetTearDownCaseOrSuite(file, line), + test_info->test_meta_factory->CreateTestFactory(*param_it)); + } // for param_it + } // for gen_it + } // for test_it + + if (!generated_instantiations) { + // There are no generaotrs, or they all generate nothing ... + InsertSyntheticTestCase(GetTestSuiteName(), code_location_, + !tests_.empty()); + } + } // RegisterTests + + private: + // LocalTestInfo structure keeps information about a single test registered + // with TEST_P macro. + struct TestInfo { + TestInfo(const char* a_test_suite_base_name, const char* a_test_base_name, + TestMetaFactoryBase<ParamType>* a_test_meta_factory, + CodeLocation a_code_location) + : test_suite_base_name(a_test_suite_base_name), + test_base_name(a_test_base_name), + test_meta_factory(a_test_meta_factory), + code_location(a_code_location) {} + + const std::string test_suite_base_name; + const std::string test_base_name; + const std::unique_ptr<TestMetaFactoryBase<ParamType> > test_meta_factory; + const CodeLocation code_location; + }; + using TestInfoContainer = ::std::vector<std::shared_ptr<TestInfo> >; + // Records data received from INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P macros: + // <Instantiation name, Sequence generator creation function, + // Name generator function, Source file, Source line> + struct InstantiationInfo { + InstantiationInfo(const std::string &name_in, + GeneratorCreationFunc* generator_in, + ParamNameGeneratorFunc* name_func_in, + const char* file_in, + int line_in) + : name(name_in), + generator(generator_in), + name_func(name_func_in), + file(file_in), + line(line_in) {} + + std::string name; + GeneratorCreationFunc* generator; + ParamNameGeneratorFunc* name_func; + const char* file; + int line; + }; + typedef ::std::vector<InstantiationInfo> InstantiationContainer; + + static bool IsValidParamName(const std::string& name) { + // Check for empty string + if (name.empty()) + return false; + + // Check for invalid characters + for (std::string::size_type index = 0; index < name.size(); ++index) { + if (!isalnum(name[index]) && name[index] != '_') + return false; + } + + return true; + } + + const std::string test_suite_name_; + CodeLocation code_location_; + TestInfoContainer tests_; + InstantiationContainer instantiations_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo); +}; // class ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +template <class TestCase> +using ParameterizedTestCaseInfo = ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo<TestCase>; +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry contains a map of +// ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase classes accessed by test suite names. TEST_P +// and INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P macros use it to locate their corresponding +// ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo descriptors. +class ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry { + public: + ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry() {} + ~ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry() { + for (auto& test_suite_info : test_suite_infos_) { + delete test_suite_info; + } + } + + // Looks up or creates and returns a structure containing information about + // tests and instantiations of a particular test suite. + template <class TestSuite> + ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo<TestSuite>* GetTestSuitePatternHolder( + const char* test_suite_name, CodeLocation code_location) { + ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo<TestSuite>* typed_test_info = nullptr; + for (auto& test_suite_info : test_suite_infos_) { + if (test_suite_info->GetTestSuiteName() == test_suite_name) { + if (test_suite_info->GetTestSuiteTypeId() != GetTypeId<TestSuite>()) { + // Complain about incorrect usage of Google Test facilities + // and terminate the program since we cannot guaranty correct + // test suite setup and tear-down in this case. + ReportInvalidTestSuiteType(test_suite_name, code_location); + posix::Abort(); + } else { + // At this point we are sure that the object we found is of the same + // type we are looking for, so we downcast it to that type + // without further checks. + typed_test_info = CheckedDowncastToActualType< + ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo<TestSuite> >(test_suite_info); + } + break; + } + } + if (typed_test_info == nullptr) { + typed_test_info = new ParameterizedTestSuiteInfo<TestSuite>( + test_suite_name, code_location); + test_suite_infos_.push_back(typed_test_info); + } + return typed_test_info; + } + void RegisterTests() { + for (auto& test_suite_info : test_suite_infos_) { + test_suite_info->RegisterTests(); + } + } +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + template <class TestCase> + ParameterizedTestCaseInfo<TestCase>* GetTestCasePatternHolder( + const char* test_case_name, CodeLocation code_location) { + return GetTestSuitePatternHolder<TestCase>(test_case_name, code_location); + } + +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + private: + using TestSuiteInfoContainer = ::std::vector<ParameterizedTestSuiteInfoBase*>; + + TestSuiteInfoContainer test_suite_infos_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry); +}; + +// Keep track of what type-parameterized test suite are defined and +// where as well as which are intatiated. This allows susequently +// identifying suits that are defined but never used. +class TypeParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry { + public: + // Add a suite definition + void RegisterTestSuite(const char* test_suite_name, + CodeLocation code_location); + + // Add an instantiation of a suit. + void RegisterInstantiation(const char* test_suite_name); + + // For each suit repored as defined but not reported as instantiation, + // emit a test that reports that fact (configurably, as an error). + void CheckForInstantiations(); + + private: + struct TypeParameterizedTestSuiteInfo { + explicit TypeParameterizedTestSuiteInfo(CodeLocation c) + : code_location(c), instantiated(false) {} + + CodeLocation code_location; + bool instantiated; + }; + + std::map<std::string, TypeParameterizedTestSuiteInfo> suites_; +}; + +} // namespace internal + +// Forward declarations of ValuesIn(), which is implemented in +// include/gtest/gtest-param-test.h. +template <class Container> +internal::ParamGenerator<typename Container::value_type> ValuesIn( + const Container& container); + +namespace internal { +// Used in the Values() function to provide polymorphic capabilities. + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +#pragma warning(push) +#pragma warning(disable : 4100) +#endif + +template <typename... Ts> +class ValueArray { + public: + explicit ValueArray(Ts... v) : v_(FlatTupleConstructTag{}, std::move(v)...) {} + + template <typename T> + operator ParamGenerator<T>() const { // NOLINT + return ValuesIn(MakeVector<T>(MakeIndexSequence<sizeof...(Ts)>())); + } + + private: + template <typename T, size_t... I> + std::vector<T> MakeVector(IndexSequence<I...>) const { + return std::vector<T>{static_cast<T>(v_.template Get<I>())...}; + } + + FlatTuple<Ts...> v_; +}; + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +#pragma warning(pop) +#endif + +template <typename... T> +class CartesianProductGenerator + : public ParamGeneratorInterface<::std::tuple<T...>> { + public: + typedef ::std::tuple<T...> ParamType; + + CartesianProductGenerator(const std::tuple<ParamGenerator<T>...>& g) + : generators_(g) {} + ~CartesianProductGenerator() override {} + + ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Begin() const override { + return new Iterator(this, generators_, false); + } + ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* End() const override { + return new Iterator(this, generators_, true); + } + + private: + template <class I> + class IteratorImpl; + template <size_t... I> + class IteratorImpl<IndexSequence<I...>> + : public ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType> { + public: + IteratorImpl(const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* base, + const std::tuple<ParamGenerator<T>...>& generators, bool is_end) + : base_(base), + begin_(std::get<I>(generators).begin()...), + end_(std::get<I>(generators).end()...), + current_(is_end ? end_ : begin_) { + ComputeCurrentValue(); + } + ~IteratorImpl() override {} + + const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* BaseGenerator() const override { + return base_; + } + // Advance should not be called on beyond-of-range iterators + // so no component iterators must be beyond end of range, either. + void Advance() override { + assert(!AtEnd()); + // Advance the last iterator. + ++std::get<sizeof...(T) - 1>(current_); + // if that reaches end, propagate that up. + AdvanceIfEnd<sizeof...(T) - 1>(); + ComputeCurrentValue(); + } + ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>* Clone() const override { + return new IteratorImpl(*this); + } + + const ParamType* Current() const override { return current_value_.get(); } + + bool Equals(const ParamIteratorInterface<ParamType>& other) const override { + // Having the same base generator guarantees that the other + // iterator is of the same type and we can downcast. + GTEST_CHECK_(BaseGenerator() == other.BaseGenerator()) + << "The program attempted to compare iterators " + << "from different generators." << std::endl; + const IteratorImpl* typed_other = + CheckedDowncastToActualType<const IteratorImpl>(&other); + + // We must report iterators equal if they both point beyond their + // respective ranges. That can happen in a variety of fashions, + // so we have to consult AtEnd(). + if (AtEnd() && typed_other->AtEnd()) return true; + + bool same = true; + bool dummy[] = { + (same = same && std::get<I>(current_) == + std::get<I>(typed_other->current_))...}; + (void)dummy; + return same; + } + + private: + template <size_t ThisI> + void AdvanceIfEnd() { + if (std::get<ThisI>(current_) != std::get<ThisI>(end_)) return; + + bool last = ThisI == 0; + if (last) { + // We are done. Nothing else to propagate. + return; + } + + constexpr size_t NextI = ThisI - (ThisI != 0); + std::get<ThisI>(current_) = std::get<ThisI>(begin_); + ++std::get<NextI>(current_); + AdvanceIfEnd<NextI>(); + } + + void ComputeCurrentValue() { + if (!AtEnd()) + current_value_ = std::make_shared<ParamType>(*std::get<I>(current_)...); + } + bool AtEnd() const { + bool at_end = false; + bool dummy[] = { + (at_end = at_end || std::get<I>(current_) == std::get<I>(end_))...}; + (void)dummy; + return at_end; + } + + const ParamGeneratorInterface<ParamType>* const base_; + std::tuple<typename ParamGenerator<T>::iterator...> begin_; + std::tuple<typename ParamGenerator<T>::iterator...> end_; + std::tuple<typename ParamGenerator<T>::iterator...> current_; + std::shared_ptr<ParamType> current_value_; + }; + + using Iterator = IteratorImpl<typename MakeIndexSequence<sizeof...(T)>::type>; + + std::tuple<ParamGenerator<T>...> generators_; +}; + +template <class... Gen> +class CartesianProductHolder { + public: + CartesianProductHolder(const Gen&... g) : generators_(g...) {} + template <typename... T> + operator ParamGenerator<::std::tuple<T...>>() const { + return ParamGenerator<::std::tuple<T...>>( + new CartesianProductGenerator<T...>(generators_)); + } + + private: + std::tuple<Gen...> generators_; +}; + +} // namespace internal +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PARAM_UTIL_H_ + +namespace testing { + +// Functions producing parameter generators. +// +// Google Test uses these generators to produce parameters for value- +// parameterized tests. When a parameterized test suite is instantiated +// with a particular generator, Google Test creates and runs tests +// for each element in the sequence produced by the generator. +// +// In the following sample, tests from test suite FooTest are instantiated +// each three times with parameter values 3, 5, and 8: +// +// class FooTest : public TestWithParam<int> { ... }; +// +// TEST_P(FooTest, TestThis) { +// } +// TEST_P(FooTest, TestThat) { +// } +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(TestSequence, FooTest, Values(3, 5, 8)); +// + +// Range() returns generators providing sequences of values in a range. +// +// Synopsis: +// Range(start, end) +// - returns a generator producing a sequence of values {start, start+1, +// start+2, ..., }. +// Range(start, end, step) +// - returns a generator producing a sequence of values {start, start+step, +// start+step+step, ..., }. +// Notes: +// * The generated sequences never include end. For example, Range(1, 5) +// returns a generator producing a sequence {1, 2, 3, 4}. Range(1, 9, 2) +// returns a generator producing {1, 3, 5, 7}. +// * start and end must have the same type. That type may be any integral or +// floating-point type or a user defined type satisfying these conditions: +// * It must be assignable (have operator=() defined). +// * It must have operator+() (operator+(int-compatible type) for +// two-operand version). +// * It must have operator<() defined. +// Elements in the resulting sequences will also have that type. +// * Condition start < end must be satisfied in order for resulting sequences +// to contain any elements. +// +template <typename T, typename IncrementT> +internal::ParamGenerator<T> Range(T start, T end, IncrementT step) { + return internal::ParamGenerator<T>( + new internal::RangeGenerator<T, IncrementT>(start, end, step)); +} + +template <typename T> +internal::ParamGenerator<T> Range(T start, T end) { + return Range(start, end, 1); +} + +// ValuesIn() function allows generation of tests with parameters coming from +// a container. +// +// Synopsis: +// ValuesIn(const T (&array)[N]) +// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements from +// a C-style array. +// ValuesIn(const Container& container) +// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements from +// an STL-style container. +// ValuesIn(Iterator begin, Iterator end) +// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements from +// a range [begin, end) defined by a pair of STL-style iterators. These +// iterators can also be plain C pointers. +// +// Please note that ValuesIn copies the values from the containers +// passed in and keeps them to generate tests in RUN_ALL_TESTS(). +// +// Examples: +// +// This instantiates tests from test suite StringTest +// each with C-string values of "foo", "bar", and "baz": +// +// const char* strings[] = {"foo", "bar", "baz"}; +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(StringSequence, StringTest, ValuesIn(strings)); +// +// This instantiates tests from test suite StlStringTest +// each with STL strings with values "a" and "b": +// +// ::std::vector< ::std::string> GetParameterStrings() { +// ::std::vector< ::std::string> v; +// v.push_back("a"); +// v.push_back("b"); +// return v; +// } +// +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(CharSequence, +// StlStringTest, +// ValuesIn(GetParameterStrings())); +// +// +// This will also instantiate tests from CharTest +// each with parameter values 'a' and 'b': +// +// ::std::list<char> GetParameterChars() { +// ::std::list<char> list; +// list.push_back('a'); +// list.push_back('b'); +// return list; +// } +// ::std::list<char> l = GetParameterChars(); +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(CharSequence2, +// CharTest, +// ValuesIn(l.begin(), l.end())); +// +template <typename ForwardIterator> +internal::ParamGenerator< + typename std::iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::value_type> +ValuesIn(ForwardIterator begin, ForwardIterator end) { + typedef typename std::iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::value_type ParamType; + return internal::ParamGenerator<ParamType>( + new internal::ValuesInIteratorRangeGenerator<ParamType>(begin, end)); +} + +template <typename T, size_t N> +internal::ParamGenerator<T> ValuesIn(const T (&array)[N]) { + return ValuesIn(array, array + N); +} + +template <class Container> +internal::ParamGenerator<typename Container::value_type> ValuesIn( + const Container& container) { + return ValuesIn(container.begin(), container.end()); +} + +// Values() allows generating tests from explicitly specified list of +// parameters. +// +// Synopsis: +// Values(T v1, T v2, ..., T vN) +// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements v1, v2, ..., vN. +// +// For example, this instantiates tests from test suite BarTest each +// with values "one", "two", and "three": +// +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(NumSequence, +// BarTest, +// Values("one", "two", "three")); +// +// This instantiates tests from test suite BazTest each with values 1, 2, 3.5. +// The exact type of values will depend on the type of parameter in BazTest. +// +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(FloatingNumbers, BazTest, Values(1, 2, 3.5)); +// +// +template <typename... T> +internal::ValueArray<T...> Values(T... v) { + return internal::ValueArray<T...>(std::move(v)...); +} + +// Bool() allows generating tests with parameters in a set of (false, true). +// +// Synopsis: +// Bool() +// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements {false, true}. +// +// It is useful when testing code that depends on Boolean flags. Combinations +// of multiple flags can be tested when several Bool()'s are combined using +// Combine() function. +// +// In the following example all tests in the test suite FlagDependentTest +// will be instantiated twice with parameters false and true. +// +// class FlagDependentTest : public testing::TestWithParam<bool> { +// virtual void SetUp() { +// external_flag = GetParam(); +// } +// } +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(BoolSequence, FlagDependentTest, Bool()); +// +inline internal::ParamGenerator<bool> Bool() { + return Values(false, true); +} + +// Combine() allows the user to combine two or more sequences to produce +// values of a Cartesian product of those sequences' elements. +// +// Synopsis: +// Combine(gen1, gen2, ..., genN) +// - returns a generator producing sequences with elements coming from +// the Cartesian product of elements from the sequences generated by +// gen1, gen2, ..., genN. The sequence elements will have a type of +// std::tuple<T1, T2, ..., TN> where T1, T2, ..., TN are the types +// of elements from sequences produces by gen1, gen2, ..., genN. +// +// Example: +// +// This will instantiate tests in test suite AnimalTest each one with +// the parameter values tuple("cat", BLACK), tuple("cat", WHITE), +// tuple("dog", BLACK), and tuple("dog", WHITE): +// +// enum Color { BLACK, GRAY, WHITE }; +// class AnimalTest +// : public testing::TestWithParam<std::tuple<const char*, Color> > {...}; +// +// TEST_P(AnimalTest, AnimalLooksNice) {...} +// +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(AnimalVariations, AnimalTest, +// Combine(Values("cat", "dog"), +// Values(BLACK, WHITE))); +// +// This will instantiate tests in FlagDependentTest with all variations of two +// Boolean flags: +// +// class FlagDependentTest +// : public testing::TestWithParam<std::tuple<bool, bool> > { +// virtual void SetUp() { +// // Assigns external_flag_1 and external_flag_2 values from the tuple. +// std::tie(external_flag_1, external_flag_2) = GetParam(); +// } +// }; +// +// TEST_P(FlagDependentTest, TestFeature1) { +// // Test your code using external_flag_1 and external_flag_2 here. +// } +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(TwoBoolSequence, FlagDependentTest, +// Combine(Bool(), Bool())); +// +template <typename... Generator> +internal::CartesianProductHolder<Generator...> Combine(const Generator&... g) { + return internal::CartesianProductHolder<Generator...>(g...); +} + +#define TEST_P(test_suite_name, test_name) \ + class GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, test_name) \ + : public test_suite_name { \ + public: \ + GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, test_name)() {} \ + void TestBody() override; \ + \ + private: \ + static int AddToRegistry() { \ + ::testing::UnitTest::GetInstance() \ + ->parameterized_test_registry() \ + .GetTestSuitePatternHolder<test_suite_name>( \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(test_suite_name), \ + ::testing::internal::CodeLocation(__FILE__, __LINE__)) \ + ->AddTestPattern( \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(test_suite_name), GTEST_STRINGIFY_(test_name), \ + new ::testing::internal::TestMetaFactory<GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_( \ + test_suite_name, test_name)>(), \ + ::testing::internal::CodeLocation(__FILE__, __LINE__)); \ + return 0; \ + } \ + static int gtest_registering_dummy_ GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; \ + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, \ + test_name)); \ + }; \ + int GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, \ + test_name)::gtest_registering_dummy_ = \ + GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, test_name)::AddToRegistry(); \ + void GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_suite_name, test_name)::TestBody() + +// The last argument to INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P allows the user to specify +// generator and an optional function or functor that generates custom test name +// suffixes based on the test parameters. Such a function or functor should +// accept one argument of type testing::TestParamInfo<class ParamType>, and +// return std::string. +// +// testing::PrintToStringParamName is a builtin test suffix generator that +// returns the value of testing::PrintToString(GetParam()). +// +// Note: test names must be non-empty, unique, and may only contain ASCII +// alphanumeric characters or underscore. Because PrintToString adds quotes +// to std::string and C strings, it won't work for these types. + +#define GTEST_EXPAND_(arg) arg +#define GTEST_GET_FIRST_(first, ...) first +#define GTEST_GET_SECOND_(first, second, ...) second + +#define INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(prefix, test_suite_name, ...) \ + static ::testing::internal::ParamGenerator<test_suite_name::ParamType> \ + gtest_##prefix##test_suite_name##_EvalGenerator_() { \ + return GTEST_EXPAND_(GTEST_GET_FIRST_(__VA_ARGS__, DUMMY_PARAM_)); \ + } \ + static ::std::string gtest_##prefix##test_suite_name##_EvalGenerateName_( \ + const ::testing::TestParamInfo<test_suite_name::ParamType>& info) { \ + if (::testing::internal::AlwaysFalse()) { \ + ::testing::internal::TestNotEmpty(GTEST_EXPAND_(GTEST_GET_SECOND_( \ + __VA_ARGS__, \ + ::testing::internal::DefaultParamName<test_suite_name::ParamType>, \ + DUMMY_PARAM_))); \ + auto t = std::make_tuple(__VA_ARGS__); \ + static_assert(std::tuple_size<decltype(t)>::value <= 2, \ + "Too Many Args!"); \ + } \ + return ((GTEST_EXPAND_(GTEST_GET_SECOND_( \ + __VA_ARGS__, \ + ::testing::internal::DefaultParamName<test_suite_name::ParamType>, \ + DUMMY_PARAM_))))(info); \ + } \ + static int gtest_##prefix##test_suite_name##_dummy_ \ + GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ = \ + ::testing::UnitTest::GetInstance() \ + ->parameterized_test_registry() \ + .GetTestSuitePatternHolder<test_suite_name>( \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(test_suite_name), \ + ::testing::internal::CodeLocation(__FILE__, __LINE__)) \ + ->AddTestSuiteInstantiation( \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(prefix), \ + >est_##prefix##test_suite_name##_EvalGenerator_, \ + >est_##prefix##test_suite_name##_EvalGenerateName_, \ + __FILE__, __LINE__) + + +// Allow Marking a Parameterized test class as not needing to be instantiated. +#define GTEST_ALLOW_UNINSTANTIATED_PARAMETERIZED_TEST(T) \ + namespace gtest_do_not_use_outside_namespace_scope {} \ + static const ::testing::internal::MarkAsIgnored gtest_allow_ignore_##T( \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(T)) + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +#define INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P \ + static_assert(::testing::internal::InstantiateTestCase_P_IsDeprecated(), \ + ""); \ + INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PARAM_TEST_H_ +// Copyright 2006, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// +// Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework definitions useful in production code. +// GOOGLETEST_CM0003 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PROD_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PROD_H_ + +// When you need to test the private or protected members of a class, +// use the FRIEND_TEST macro to declare your tests as friends of the +// class. For example: +// +// class MyClass { +// private: +// void PrivateMethod(); +// FRIEND_TEST(MyClassTest, PrivateMethodWorks); +// }; +// +// class MyClassTest : public testing::Test { +// // ... +// }; +// +// TEST_F(MyClassTest, PrivateMethodWorks) { +// // Can call MyClass::PrivateMethod() here. +// } +// +// Note: The test class must be in the same namespace as the class being tested. +// For example, putting MyClassTest in an anonymous namespace will not work. + +#define FRIEND_TEST(test_case_name, test_name)\ +friend class test_case_name##_##test_name##_Test + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PROD_H_ +// Copyright 2008 Google Inc. +// All Rights Reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TYPED_TEST_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TYPED_TEST_H_ + +// This header implements typed tests and type-parameterized tests. + +// Typed (aka type-driven) tests repeat the same test for types in a +// list. You must know which types you want to test with when writing +// typed tests. Here's how you do it: + +#if 0 + +// First, define a fixture class template. It should be parameterized +// by a type. Remember to derive it from testing::Test. +template <typename T> +class FooTest : public testing::Test { + public: + ... + typedef std::list<T> List; + static T shared_; + T value_; +}; + +// Next, associate a list of types with the test suite, which will be +// repeated for each type in the list. The typedef is necessary for +// the macro to parse correctly. +typedef testing::Types<char, int, unsigned int> MyTypes; +TYPED_TEST_SUITE(FooTest, MyTypes); + +// If the type list contains only one type, you can write that type +// directly without Types<...>: +// TYPED_TEST_SUITE(FooTest, int); + +// Then, use TYPED_TEST() instead of TEST_F() to define as many typed +// tests for this test suite as you want. +TYPED_TEST(FooTest, DoesBlah) { + // Inside a test, refer to the special name TypeParam to get the type + // parameter. Since we are inside a derived class template, C++ requires + // us to visit the members of FooTest via 'this'. + TypeParam n = this->value_; + + // To visit static members of the fixture, add the TestFixture:: + // prefix. + n += TestFixture::shared_; + + // To refer to typedefs in the fixture, add the "typename + // TestFixture::" prefix. + typename TestFixture::List values; + values.push_back(n); + ... +} + +TYPED_TEST(FooTest, HasPropertyA) { ... } + +// TYPED_TEST_SUITE takes an optional third argument which allows to specify a +// class that generates custom test name suffixes based on the type. This should +// be a class which has a static template function GetName(int index) returning +// a string for each type. The provided integer index equals the index of the +// type in the provided type list. In many cases the index can be ignored. +// +// For example: +// class MyTypeNames { +// public: +// template <typename T> +// static std::string GetName(int) { +// if (std::is_same<T, char>()) return "char"; +// if (std::is_same<T, int>()) return "int"; +// if (std::is_same<T, unsigned int>()) return "unsignedInt"; +// } +// }; +// TYPED_TEST_SUITE(FooTest, MyTypes, MyTypeNames); + +#endif // 0 + +// Type-parameterized tests are abstract test patterns parameterized +// by a type. Compared with typed tests, type-parameterized tests +// allow you to define the test pattern without knowing what the type +// parameters are. The defined pattern can be instantiated with +// different types any number of times, in any number of translation +// units. +// +// If you are designing an interface or concept, you can define a +// suite of type-parameterized tests to verify properties that any +// valid implementation of the interface/concept should have. Then, +// each implementation can easily instantiate the test suite to verify +// that it conforms to the requirements, without having to write +// similar tests repeatedly. Here's an example: + +#if 0 + +// First, define a fixture class template. It should be parameterized +// by a type. Remember to derive it from testing::Test. +template <typename T> +class FooTest : public testing::Test { + ... +}; + +// Next, declare that you will define a type-parameterized test suite +// (the _P suffix is for "parameterized" or "pattern", whichever you +// prefer): +TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(FooTest); + +// Then, use TYPED_TEST_P() to define as many type-parameterized tests +// for this type-parameterized test suite as you want. +TYPED_TEST_P(FooTest, DoesBlah) { + // Inside a test, refer to TypeParam to get the type parameter. + TypeParam n = 0; + ... +} + +TYPED_TEST_P(FooTest, HasPropertyA) { ... } + +// Now the tricky part: you need to register all test patterns before +// you can instantiate them. The first argument of the macro is the +// test suite name; the rest are the names of the tests in this test +// case. +REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(FooTest, + DoesBlah, HasPropertyA); + +// Finally, you are free to instantiate the pattern with the types you +// want. If you put the above code in a header file, you can #include +// it in multiple C++ source files and instantiate it multiple times. +// +// To distinguish different instances of the pattern, the first +// argument to the INSTANTIATE_* macro is a prefix that will be added +// to the actual test suite name. Remember to pick unique prefixes for +// different instances. +typedef testing::Types<char, int, unsigned int> MyTypes; +INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(My, FooTest, MyTypes); + +// If the type list contains only one type, you can write that type +// directly without Types<...>: +// INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(My, FooTest, int); +// +// Similar to the optional argument of TYPED_TEST_SUITE above, +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P takes an optional fourth argument which allows to +// generate custom names. +// INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(My, FooTest, MyTypes, MyTypeNames); + +#endif // 0 + + +// Implements typed tests. + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// Expands to the name of the typedef for the type parameters of the +// given test suite. +#define GTEST_TYPE_PARAMS_(TestSuiteName) gtest_type_params_##TestSuiteName##_ + +// Expands to the name of the typedef for the NameGenerator, responsible for +// creating the suffixes of the name. +#define GTEST_NAME_GENERATOR_(TestSuiteName) \ + gtest_type_params_##TestSuiteName##_NameGenerator + +#define TYPED_TEST_SUITE(CaseName, Types, ...) \ + typedef ::testing::internal::GenerateTypeList<Types>::type \ + GTEST_TYPE_PARAMS_(CaseName); \ + typedef ::testing::internal::NameGeneratorSelector<__VA_ARGS__>::type \ + GTEST_NAME_GENERATOR_(CaseName) + +#define TYPED_TEST(CaseName, TestName) \ + static_assert(sizeof(GTEST_STRINGIFY_(TestName)) > 1, \ + "test-name must not be empty"); \ + template <typename gtest_TypeParam_> \ + class GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(CaseName, TestName) \ + : public CaseName<gtest_TypeParam_> { \ + private: \ + typedef CaseName<gtest_TypeParam_> TestFixture; \ + typedef gtest_TypeParam_ TypeParam; \ + void TestBody() override; \ + }; \ + static bool gtest_##CaseName##_##TestName##_registered_ \ + GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ = ::testing::internal::TypeParameterizedTest< \ + CaseName, \ + ::testing::internal::TemplateSel<GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(CaseName, \ + TestName)>, \ + GTEST_TYPE_PARAMS_( \ + CaseName)>::Register("", \ + ::testing::internal::CodeLocation( \ + __FILE__, __LINE__), \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(CaseName), \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(TestName), 0, \ + ::testing::internal::GenerateNames< \ + GTEST_NAME_GENERATOR_(CaseName), \ + GTEST_TYPE_PARAMS_(CaseName)>()); \ + template <typename gtest_TypeParam_> \ + void GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(CaseName, \ + TestName)<gtest_TypeParam_>::TestBody() + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +#define TYPED_TEST_CASE \ + static_assert(::testing::internal::TypedTestCaseIsDeprecated(), ""); \ + TYPED_TEST_SUITE +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + +// Implements type-parameterized tests. + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// Expands to the namespace name that the type-parameterized tests for +// the given type-parameterized test suite are defined in. The exact +// name of the namespace is subject to change without notice. +#define GTEST_SUITE_NAMESPACE_(TestSuiteName) gtest_suite_##TestSuiteName##_ + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// +// Expands to the name of the variable used to remember the names of +// the defined tests in the given test suite. +#define GTEST_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P_STATE_(TestSuiteName) \ + gtest_typed_test_suite_p_state_##TestSuiteName##_ + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE DIRECTLY. +// +// Expands to the name of the variable used to remember the names of +// the registered tests in the given test suite. +#define GTEST_REGISTERED_TEST_NAMES_(TestSuiteName) \ + gtest_registered_test_names_##TestSuiteName##_ + +// The variables defined in the type-parameterized test macros are +// static as typically these macros are used in a .h file that can be +// #included in multiple translation units linked together. +#define TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(SuiteName) \ + static ::testing::internal::TypedTestSuitePState \ + GTEST_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P_STATE_(SuiteName) + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +#define TYPED_TEST_CASE_P \ + static_assert(::testing::internal::TypedTestCase_P_IsDeprecated(), ""); \ + TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + +#define TYPED_TEST_P(SuiteName, TestName) \ + namespace GTEST_SUITE_NAMESPACE_(SuiteName) { \ + template <typename gtest_TypeParam_> \ + class TestName : public SuiteName<gtest_TypeParam_> { \ + private: \ + typedef SuiteName<gtest_TypeParam_> TestFixture; \ + typedef gtest_TypeParam_ TypeParam; \ + void TestBody() override; \ + }; \ + static bool gtest_##TestName##_defined_ GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ = \ + GTEST_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P_STATE_(SuiteName).AddTestName( \ + __FILE__, __LINE__, GTEST_STRINGIFY_(SuiteName), \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(TestName)); \ + } \ + template <typename gtest_TypeParam_> \ + void GTEST_SUITE_NAMESPACE_( \ + SuiteName)::TestName<gtest_TypeParam_>::TestBody() + +// Note: this won't work correctly if the trailing arguments are macros. +#define REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(SuiteName, ...) \ + namespace GTEST_SUITE_NAMESPACE_(SuiteName) { \ + typedef ::testing::internal::Templates<__VA_ARGS__> gtest_AllTests_; \ + } \ + static const char* const GTEST_REGISTERED_TEST_NAMES_( \ + SuiteName) GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ = \ + GTEST_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P_STATE_(SuiteName).VerifyRegisteredTestNames( \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(SuiteName), __FILE__, __LINE__, #__VA_ARGS__) + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +#define REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P \ + static_assert(::testing::internal::RegisterTypedTestCase_P_IsDeprecated(), \ + ""); \ + REGISTER_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + +#define INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(Prefix, SuiteName, Types, ...) \ + static_assert(sizeof(GTEST_STRINGIFY_(Prefix)) > 1, \ + "test-suit-prefix must not be empty"); \ + static bool gtest_##Prefix##_##SuiteName GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_ = \ + ::testing::internal::TypeParameterizedTestSuite< \ + SuiteName, GTEST_SUITE_NAMESPACE_(SuiteName)::gtest_AllTests_, \ + ::testing::internal::GenerateTypeList<Types>::type>:: \ + Register(GTEST_STRINGIFY_(Prefix), \ + ::testing::internal::CodeLocation(__FILE__, __LINE__), \ + >EST_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P_STATE_(SuiteName), \ + GTEST_STRINGIFY_(SuiteName), \ + GTEST_REGISTERED_TEST_NAMES_(SuiteName), \ + ::testing::internal::GenerateNames< \ + ::testing::internal::NameGeneratorSelector< \ + __VA_ARGS__>::type, \ + ::testing::internal::GenerateTypeList<Types>::type>()) + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +#define INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_CASE_P \ + static_assert( \ + ::testing::internal::InstantiateTypedTestCase_P_IsDeprecated(), ""); \ + INSTANTIATE_TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_TYPED_TEST_H_ + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4251 \ +/* class A needs to have dll-interface to be used by clients of class B */) + +namespace testing { + +// Silence C4100 (unreferenced formal parameter) and 4805 +// unsafe mix of type 'const int' and type 'const bool' +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(push) +# pragma warning(disable:4805) +# pragma warning(disable:4100) +#endif + + +// Declares the flags. + +// This flag temporary enables the disabled tests. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(also_run_disabled_tests); + +// This flag brings the debugger on an assertion failure. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(break_on_failure); + +// This flag controls whether Google Test catches all test-thrown exceptions +// and logs them as failures. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(catch_exceptions); + +// This flag enables using colors in terminal output. Available values are +// "yes" to enable colors, "no" (disable colors), or "auto" (the default) +// to let Google Test decide. +GTEST_DECLARE_string_(color); + +// This flag controls whether the test runner should continue execution past +// first failure. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(fail_fast); + +// This flag sets up the filter to select by name using a glob pattern +// the tests to run. If the filter is not given all tests are executed. +GTEST_DECLARE_string_(filter); + +// This flag controls whether Google Test installs a signal handler that dumps +// debugging information when fatal signals are raised. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(install_failure_signal_handler); + +// This flag causes the Google Test to list tests. None of the tests listed +// are actually run if the flag is provided. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(list_tests); + +// This flag controls whether Google Test emits a detailed XML report to a file +// in addition to its normal textual output. +GTEST_DECLARE_string_(output); + +// This flags control whether Google Test prints only test failures. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(brief); + +// This flags control whether Google Test prints the elapsed time for each +// test. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(print_time); + +// This flags control whether Google Test prints UTF8 characters as text. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(print_utf8); + +// This flag specifies the random number seed. +GTEST_DECLARE_int32_(random_seed); + +// This flag sets how many times the tests are repeated. The default value +// is 1. If the value is -1 the tests are repeating forever. +GTEST_DECLARE_int32_(repeat); + +// This flag controls whether Google Test includes Google Test internal +// stack frames in failure stack traces. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(show_internal_stack_frames); + +// When this flag is specified, tests' order is randomized on every iteration. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(shuffle); + +// This flag specifies the maximum number of stack frames to be +// printed in a failure message. +GTEST_DECLARE_int32_(stack_trace_depth); + +// When this flag is specified, a failed assertion will throw an +// exception if exceptions are enabled, or exit the program with a +// non-zero code otherwise. For use with an external test framework. +GTEST_DECLARE_bool_(throw_on_failure); + +// When this flag is set with a "host:port" string, on supported +// platforms test results are streamed to the specified port on +// the specified host machine. +GTEST_DECLARE_string_(stream_result_to); + +#if GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_ +GTEST_DECLARE_string_(flagfile); +#endif // GTEST_USE_OWN_FLAGFILE_FLAG_ + +// The upper limit for valid stack trace depths. +const int kMaxStackTraceDepth = 100; + +namespace internal { + +class AssertHelper; +class DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter; +class ExecDeathTest; +class NoExecDeathTest; +class FinalSuccessChecker; +class GTestFlagSaver; +class StreamingListenerTest; +class TestResultAccessor; +class TestEventListenersAccessor; +class TestEventRepeater; +class UnitTestRecordPropertyTestHelper; +class WindowsDeathTest; +class FuchsiaDeathTest; +class UnitTestImpl* GetUnitTestImpl(); +void ReportFailureInUnknownLocation(TestPartResult::Type result_type, + const std::string& message); +std::set<std::string>* GetIgnoredParameterizedTestSuites(); + +} // namespace internal + +// The friend relationship of some of these classes is cyclic. +// If we don't forward declare them the compiler might confuse the classes +// in friendship clauses with same named classes on the scope. +class Test; +class TestSuite; + +// Old API is still available but deprecated +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ +using TestCase = TestSuite; +#endif +class TestInfo; +class UnitTest; + +// A class for indicating whether an assertion was successful. When +// the assertion wasn't successful, the AssertionResult object +// remembers a non-empty message that describes how it failed. +// +// To create an instance of this class, use one of the factory functions +// (AssertionSuccess() and AssertionFailure()). +// +// This class is useful for two purposes: +// 1. Defining predicate functions to be used with Boolean test assertions +// EXPECT_TRUE/EXPECT_FALSE and their ASSERT_ counterparts +// 2. Defining predicate-format functions to be +// used with predicate assertions (ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT*, etc). +// +// For example, if you define IsEven predicate: +// +// testing::AssertionResult IsEven(int n) { +// if ((n % 2) == 0) +// return testing::AssertionSuccess(); +// else +// return testing::AssertionFailure() << n << " is odd"; +// } +// +// Then the failed expectation EXPECT_TRUE(IsEven(Fib(5))) +// will print the message +// +// Value of: IsEven(Fib(5)) +// Actual: false (5 is odd) +// Expected: true +// +// instead of a more opaque +// +// Value of: IsEven(Fib(5)) +// Actual: false +// Expected: true +// +// in case IsEven is a simple Boolean predicate. +// +// If you expect your predicate to be reused and want to support informative +// messages in EXPECT_FALSE and ASSERT_FALSE (negative assertions show up +// about half as often as positive ones in our tests), supply messages for +// both success and failure cases: +// +// testing::AssertionResult IsEven(int n) { +// if ((n % 2) == 0) +// return testing::AssertionSuccess() << n << " is even"; +// else +// return testing::AssertionFailure() << n << " is odd"; +// } +// +// Then a statement EXPECT_FALSE(IsEven(Fib(6))) will print +// +// Value of: IsEven(Fib(6)) +// Actual: true (8 is even) +// Expected: false +// +// NB: Predicates that support negative Boolean assertions have reduced +// performance in positive ones so be careful not to use them in tests +// that have lots (tens of thousands) of positive Boolean assertions. +// +// To use this class with EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT assertions such as: +// +// // Verifies that Foo() returns an even number. +// EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(IsEven, Foo()); +// +// you need to define: +// +// testing::AssertionResult IsEven(const char* expr, int n) { +// if ((n % 2) == 0) +// return testing::AssertionSuccess(); +// else +// return testing::AssertionFailure() +// << "Expected: " << expr << " is even\n Actual: it's " << n; +// } +// +// If Foo() returns 5, you will see the following message: +// +// Expected: Foo() is even +// Actual: it's 5 +// +class GTEST_API_ AssertionResult { + public: + // Copy constructor. + // Used in EXPECT_TRUE/FALSE(assertion_result). + AssertionResult(const AssertionResult& other); + +// C4800 is a level 3 warning in Visual Studio 2015 and earlier. +// This warning is not emitted in Visual Studio 2017. +// This warning is off by default starting in Visual Studio 2019 but can be +// enabled with command-line options. +#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER < 1910 || _MSC_VER >= 1920) + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4800 /* forcing value to bool */) +#endif + + // Used in the EXPECT_TRUE/FALSE(bool_expression). + // + // T must be contextually convertible to bool. + // + // The second parameter prevents this overload from being considered if + // the argument is implicitly convertible to AssertionResult. In that case + // we want AssertionResult's copy constructor to be used. + template <typename T> + explicit AssertionResult( + const T& success, + typename std::enable_if< + !std::is_convertible<T, AssertionResult>::value>::type* + /*enabler*/ + = nullptr) + : success_(success) {} + +#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER < 1910 || _MSC_VER >= 1920) + GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() +#endif + + // Assignment operator. + AssertionResult& operator=(AssertionResult other) { + swap(other); + return *this; + } + + // Returns true if and only if the assertion succeeded. + operator bool() const { return success_; } // NOLINT + + // Returns the assertion's negation. Used with EXPECT/ASSERT_FALSE. + AssertionResult operator!() const; + + // Returns the text streamed into this AssertionResult. Test assertions + // use it when they fail (i.e., the predicate's outcome doesn't match the + // assertion's expectation). When nothing has been streamed into the + // object, returns an empty string. + const char* message() const { + return message_.get() != nullptr ? message_->c_str() : ""; + } + // Deprecated; please use message() instead. + const char* failure_message() const { return message(); } + + // Streams a custom failure message into this object. + template <typename T> AssertionResult& operator<<(const T& value) { + AppendMessage(Message() << value); + return *this; + } + + // Allows streaming basic output manipulators such as endl or flush into + // this object. + AssertionResult& operator<<( + ::std::ostream& (*basic_manipulator)(::std::ostream& stream)) { + AppendMessage(Message() << basic_manipulator); + return *this; + } + + private: + // Appends the contents of message to message_. + void AppendMessage(const Message& a_message) { + if (message_.get() == nullptr) message_.reset(new ::std::string); + message_->append(a_message.GetString().c_str()); + } + + // Swap the contents of this AssertionResult with other. + void swap(AssertionResult& other); + + // Stores result of the assertion predicate. + bool success_; + // Stores the message describing the condition in case the expectation + // construct is not satisfied with the predicate's outcome. + // Referenced via a pointer to avoid taking too much stack frame space + // with test assertions. + std::unique_ptr< ::std::string> message_; +}; + +// Makes a successful assertion result. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult AssertionSuccess(); + +// Makes a failed assertion result. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult AssertionFailure(); + +// Makes a failed assertion result with the given failure message. +// Deprecated; use AssertionFailure() << msg. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult AssertionFailure(const Message& msg); + +} // namespace testing + +// Includes the auto-generated header that implements a family of generic +// predicate assertion macros. This include comes late because it relies on +// APIs declared above. +// Copyright 2006, Google Inc. +// All rights reserved. +// +// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without +// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are +// met: +// +// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright +// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. +// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above +// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer +// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the +// distribution. +// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its +// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from +// this software without specific prior written permission. +// +// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS +// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR +// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT +// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, +// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT +// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, +// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY +// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT +// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE +// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. + +// This file is AUTOMATICALLY GENERATED on 01/02/2019 by command +// 'gen_gtest_pred_impl.py 5'. DO NOT EDIT BY HAND! +// +// Implements a family of generic predicate assertion macros. +// GOOGLETEST_CM0001 DO NOT DELETE + +#ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRED_IMPL_H_ +#define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRED_IMPL_H_ + + +namespace testing { + +// This header implements a family of generic predicate assertion +// macros: +// +// ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(pred_format, v1) +// ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(pred_format, v1, v2) +// ... +// +// where pred_format is a function or functor that takes n (in the +// case of ASSERT_PRED_FORMATn) values and their source expression +// text, and returns a testing::AssertionResult. See the definition +// of ASSERT_EQ in gtest.h for an example. +// +// If you don't care about formatting, you can use the more +// restrictive version: +// +// ASSERT_PRED1(pred, v1) +// ASSERT_PRED2(pred, v1, v2) +// ... +// +// where pred is an n-ary function or functor that returns bool, +// and the values v1, v2, ..., must support the << operator for +// streaming to std::ostream. +// +// We also define the EXPECT_* variations. +// +// For now we only support predicates whose arity is at most 5. +// Please email googletestframework@googlegroups.com if you need +// support for higher arities. + +// GTEST_ASSERT_ is the basic statement to which all of the assertions +// in this file reduce. Don't use this in your code. + +#define GTEST_ASSERT_(expression, on_failure) \ + GTEST_AMBIGUOUS_ELSE_BLOCKER_ \ + if (const ::testing::AssertionResult gtest_ar = (expression)) \ + ; \ + else \ + on_failure(gtest_ar.failure_message()) + + +// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED1. Don't use +// this in your code. +template <typename Pred, + typename T1> +AssertionResult AssertPred1Helper(const char* pred_text, + const char* e1, + Pred pred, + const T1& v1) { + if (pred(v1)) return AssertionSuccess(); + + return AssertionFailure() + << pred_text << "(" << e1 << ") evaluates to false, where" + << "\n" + << e1 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v1); +} + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT1. +// Don't use this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT1_(pred_format, v1, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, v1), \ + on_failure) + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED1. Don't use +// this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED1_(pred, v1, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred1Helper(#pred, \ + #v1, \ + pred, \ + v1), on_failure) + +// Unary predicate assertion macros. +#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(pred_format, v1) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT1_(pred_format, v1, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define EXPECT_PRED1(pred, v1) \ + GTEST_PRED1_(pred, v1, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(pred_format, v1) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT1_(pred_format, v1, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED1(pred, v1) \ + GTEST_PRED1_(pred, v1, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) + + + +// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED2. Don't use +// this in your code. +template <typename Pred, + typename T1, + typename T2> +AssertionResult AssertPred2Helper(const char* pred_text, + const char* e1, + const char* e2, + Pred pred, + const T1& v1, + const T2& v2) { + if (pred(v1, v2)) return AssertionSuccess(); + + return AssertionFailure() + << pred_text << "(" << e1 << ", " << e2 + << ") evaluates to false, where" + << "\n" + << e1 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v1) << "\n" + << e2 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v2); +} + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT2. +// Don't use this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT2_(pred_format, v1, v2, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, #v2, v1, v2), \ + on_failure) + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED2. Don't use +// this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED2_(pred, v1, v2, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred2Helper(#pred, \ + #v1, \ + #v2, \ + pred, \ + v1, \ + v2), on_failure) + +// Binary predicate assertion macros. +#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(pred_format, v1, v2) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT2_(pred_format, v1, v2, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define EXPECT_PRED2(pred, v1, v2) \ + GTEST_PRED2_(pred, v1, v2, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(pred_format, v1, v2) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT2_(pred_format, v1, v2, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED2(pred, v1, v2) \ + GTEST_PRED2_(pred, v1, v2, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) + + + +// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED3. Don't use +// this in your code. +template <typename Pred, + typename T1, + typename T2, + typename T3> +AssertionResult AssertPred3Helper(const char* pred_text, + const char* e1, + const char* e2, + const char* e3, + Pred pred, + const T1& v1, + const T2& v2, + const T3& v3) { + if (pred(v1, v2, v3)) return AssertionSuccess(); + + return AssertionFailure() + << pred_text << "(" << e1 << ", " << e2 << ", " << e3 + << ") evaluates to false, where" + << "\n" + << e1 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v1) << "\n" + << e2 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v2) << "\n" + << e3 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v3); +} + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT3. +// Don't use this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT3_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, #v2, #v3, v1, v2, v3), \ + on_failure) + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED3. Don't use +// this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED3_(pred, v1, v2, v3, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred3Helper(#pred, \ + #v1, \ + #v2, \ + #v3, \ + pred, \ + v1, \ + v2, \ + v3), on_failure) + +// Ternary predicate assertion macros. +#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT3(pred_format, v1, v2, v3) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT3_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define EXPECT_PRED3(pred, v1, v2, v3) \ + GTEST_PRED3_(pred, v1, v2, v3, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT3(pred_format, v1, v2, v3) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT3_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED3(pred, v1, v2, v3) \ + GTEST_PRED3_(pred, v1, v2, v3, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) + + + +// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED4. Don't use +// this in your code. +template <typename Pred, + typename T1, + typename T2, + typename T3, + typename T4> +AssertionResult AssertPred4Helper(const char* pred_text, + const char* e1, + const char* e2, + const char* e3, + const char* e4, + Pred pred, + const T1& v1, + const T2& v2, + const T3& v3, + const T4& v4) { + if (pred(v1, v2, v3, v4)) return AssertionSuccess(); + + return AssertionFailure() + << pred_text << "(" << e1 << ", " << e2 << ", " << e3 << ", " << e4 + << ") evaluates to false, where" + << "\n" + << e1 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v1) << "\n" + << e2 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v2) << "\n" + << e3 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v3) << "\n" + << e4 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v4); +} + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT4. +// Don't use this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT4_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, #v2, #v3, #v4, v1, v2, v3, v4), \ + on_failure) + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED4. Don't use +// this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED4_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred4Helper(#pred, \ + #v1, \ + #v2, \ + #v3, \ + #v4, \ + pred, \ + v1, \ + v2, \ + v3, \ + v4), on_failure) + +// 4-ary predicate assertion macros. +#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT4(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT4_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define EXPECT_PRED4(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4) \ + GTEST_PRED4_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT4(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT4_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED4(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4) \ + GTEST_PRED4_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) + + + +// Helper function for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED5. Don't use +// this in your code. +template <typename Pred, + typename T1, + typename T2, + typename T3, + typename T4, + typename T5> +AssertionResult AssertPred5Helper(const char* pred_text, + const char* e1, + const char* e2, + const char* e3, + const char* e4, + const char* e5, + Pred pred, + const T1& v1, + const T2& v2, + const T3& v3, + const T4& v4, + const T5& v5) { + if (pred(v1, v2, v3, v4, v5)) return AssertionSuccess(); + + return AssertionFailure() + << pred_text << "(" << e1 << ", " << e2 << ", " << e3 << ", " << e4 + << ", " << e5 << ") evaluates to false, where" + << "\n" + << e1 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v1) << "\n" + << e2 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v2) << "\n" + << e3 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v3) << "\n" + << e4 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v4) << "\n" + << e5 << " evaluates to " << ::testing::PrintToString(v5); +} + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT5. +// Don't use this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED_FORMAT5_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(pred_format(#v1, #v2, #v3, #v4, #v5, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5), \ + on_failure) + +// Internal macro for implementing {EXPECT|ASSERT}_PRED5. Don't use +// this in your code. +#define GTEST_PRED5_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, on_failure)\ + GTEST_ASSERT_(::testing::AssertPred5Helper(#pred, \ + #v1, \ + #v2, \ + #v3, \ + #v4, \ + #v5, \ + pred, \ + v1, \ + v2, \ + v3, \ + v4, \ + v5), on_failure) + +// 5-ary predicate assertion macros. +#define EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT5(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT5_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define EXPECT_PRED5(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5) \ + GTEST_PRED5_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT5(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5) \ + GTEST_PRED_FORMAT5_(pred_format, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_PRED5(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5) \ + GTEST_PRED5_(pred, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) + + + +} // namespace testing + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_PRED_IMPL_H_ + +namespace testing { + +// The abstract class that all tests inherit from. +// +// In Google Test, a unit test program contains one or many TestSuites, and +// each TestSuite contains one or many Tests. +// +// When you define a test using the TEST macro, you don't need to +// explicitly derive from Test - the TEST macro automatically does +// this for you. +// +// The only time you derive from Test is when defining a test fixture +// to be used in a TEST_F. For example: +// +// class FooTest : public testing::Test { +// protected: +// void SetUp() override { ... } +// void TearDown() override { ... } +// ... +// }; +// +// TEST_F(FooTest, Bar) { ... } +// TEST_F(FooTest, Baz) { ... } +// +// Test is not copyable. +class GTEST_API_ Test { + public: + friend class TestInfo; + + // The d'tor is virtual as we intend to inherit from Test. + virtual ~Test(); + + // Sets up the stuff shared by all tests in this test suite. + // + // Google Test will call Foo::SetUpTestSuite() before running the first + // test in test suite Foo. Hence a sub-class can define its own + // SetUpTestSuite() method to shadow the one defined in the super + // class. + static void SetUpTestSuite() {} + + // Tears down the stuff shared by all tests in this test suite. + // + // Google Test will call Foo::TearDownTestSuite() after running the last + // test in test suite Foo. Hence a sub-class can define its own + // TearDownTestSuite() method to shadow the one defined in the super + // class. + static void TearDownTestSuite() {} + + // Legacy API is deprecated but still available. Use SetUpTestSuite and + // TearDownTestSuite instead. +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + static void TearDownTestCase() {} + static void SetUpTestCase() {} +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + // Returns true if and only if the current test has a fatal failure. + static bool HasFatalFailure(); + + // Returns true if and only if the current test has a non-fatal failure. + static bool HasNonfatalFailure(); + + // Returns true if and only if the current test was skipped. + static bool IsSkipped(); + + // Returns true if and only if the current test has a (either fatal or + // non-fatal) failure. + static bool HasFailure() { return HasFatalFailure() || HasNonfatalFailure(); } + + // Logs a property for the current test, test suite, or for the entire + // invocation of the test program when used outside of the context of a + // test suite. Only the last value for a given key is remembered. These + // are public static so they can be called from utility functions that are + // not members of the test fixture. Calls to RecordProperty made during + // lifespan of the test (from the moment its constructor starts to the + // moment its destructor finishes) will be output in XML as attributes of + // the <testcase> element. Properties recorded from fixture's + // SetUpTestSuite or TearDownTestSuite are logged as attributes of the + // corresponding <testsuite> element. Calls to RecordProperty made in the + // global context (before or after invocation of RUN_ALL_TESTS and from + // SetUp/TearDown method of Environment objects registered with Google + // Test) will be output as attributes of the <testsuites> element. + static void RecordProperty(const std::string& key, const std::string& value); + static void RecordProperty(const std::string& key, int value); + + protected: + // Creates a Test object. + Test(); + + // Sets up the test fixture. + virtual void SetUp(); + + // Tears down the test fixture. + virtual void TearDown(); + + private: + // Returns true if and only if the current test has the same fixture class + // as the first test in the current test suite. + static bool HasSameFixtureClass(); + + // Runs the test after the test fixture has been set up. + // + // A sub-class must implement this to define the test logic. + // + // DO NOT OVERRIDE THIS FUNCTION DIRECTLY IN A USER PROGRAM. + // Instead, use the TEST or TEST_F macro. + virtual void TestBody() = 0; + + // Sets up, executes, and tears down the test. + void Run(); + + // Deletes self. We deliberately pick an unusual name for this + // internal method to avoid clashing with names used in user TESTs. + void DeleteSelf_() { delete this; } + + const std::unique_ptr<GTEST_FLAG_SAVER_> gtest_flag_saver_; + + // Often a user misspells SetUp() as Setup() and spends a long time + // wondering why it is never called by Google Test. The declaration of + // the following method is solely for catching such an error at + // compile time: + // + // - The return type is deliberately chosen to be not void, so it + // will be a conflict if void Setup() is declared in the user's + // test fixture. + // + // - This method is private, so it will be another compiler error + // if the method is called from the user's test fixture. + // + // DO NOT OVERRIDE THIS FUNCTION. + // + // If you see an error about overriding the following function or + // about it being private, you have mis-spelled SetUp() as Setup(). + struct Setup_should_be_spelled_SetUp {}; + virtual Setup_should_be_spelled_SetUp* Setup() { return nullptr; } + + // We disallow copying Tests. + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(Test); +}; + +typedef internal::TimeInMillis TimeInMillis; + +// A copyable object representing a user specified test property which can be +// output as a key/value string pair. +// +// Don't inherit from TestProperty as its destructor is not virtual. +class TestProperty { + public: + // C'tor. TestProperty does NOT have a default constructor. + // Always use this constructor (with parameters) to create a + // TestProperty object. + TestProperty(const std::string& a_key, const std::string& a_value) : + key_(a_key), value_(a_value) { + } + + // Gets the user supplied key. + const char* key() const { + return key_.c_str(); + } + + // Gets the user supplied value. + const char* value() const { + return value_.c_str(); + } + + // Sets a new value, overriding the one supplied in the constructor. + void SetValue(const std::string& new_value) { + value_ = new_value; + } + + private: + // The key supplied by the user. + std::string key_; + // The value supplied by the user. + std::string value_; +}; + +// The result of a single Test. This includes a list of +// TestPartResults, a list of TestProperties, a count of how many +// death tests there are in the Test, and how much time it took to run +// the Test. +// +// TestResult is not copyable. +class GTEST_API_ TestResult { + public: + // Creates an empty TestResult. + TestResult(); + + // D'tor. Do not inherit from TestResult. + ~TestResult(); + + // Gets the number of all test parts. This is the sum of the number + // of successful test parts and the number of failed test parts. + int total_part_count() const; + + // Returns the number of the test properties. + int test_property_count() const; + + // Returns true if and only if the test passed (i.e. no test part failed). + bool Passed() const { return !Skipped() && !Failed(); } + + // Returns true if and only if the test was skipped. + bool Skipped() const; + + // Returns true if and only if the test failed. + bool Failed() const; + + // Returns true if and only if the test fatally failed. + bool HasFatalFailure() const; + + // Returns true if and only if the test has a non-fatal failure. + bool HasNonfatalFailure() const; + + // Returns the elapsed time, in milliseconds. + TimeInMillis elapsed_time() const { return elapsed_time_; } + + // Gets the time of the test case start, in ms from the start of the + // UNIX epoch. + TimeInMillis start_timestamp() const { return start_timestamp_; } + + // Returns the i-th test part result among all the results. i can range from 0 + // to total_part_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, aborts the program. + const TestPartResult& GetTestPartResult(int i) const; + + // Returns the i-th test property. i can range from 0 to + // test_property_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, aborts the + // program. + const TestProperty& GetTestProperty(int i) const; + + private: + friend class TestInfo; + friend class TestSuite; + friend class UnitTest; + friend class internal::DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter; + friend class internal::ExecDeathTest; + friend class internal::TestResultAccessor; + friend class internal::UnitTestImpl; + friend class internal::WindowsDeathTest; + friend class internal::FuchsiaDeathTest; + + // Gets the vector of TestPartResults. + const std::vector<TestPartResult>& test_part_results() const { + return test_part_results_; + } + + // Gets the vector of TestProperties. + const std::vector<TestProperty>& test_properties() const { + return test_properties_; + } + + // Sets the start time. + void set_start_timestamp(TimeInMillis start) { start_timestamp_ = start; } + + // Sets the elapsed time. + void set_elapsed_time(TimeInMillis elapsed) { elapsed_time_ = elapsed; } + + // Adds a test property to the list. The property is validated and may add + // a non-fatal failure if invalid (e.g., if it conflicts with reserved + // key names). If a property is already recorded for the same key, the + // value will be updated, rather than storing multiple values for the same + // key. xml_element specifies the element for which the property is being + // recorded and is used for validation. + void RecordProperty(const std::string& xml_element, + const TestProperty& test_property); + + // Adds a failure if the key is a reserved attribute of Google Test + // testsuite tags. Returns true if the property is valid. + // FIXME: Validate attribute names are legal and human readable. + static bool ValidateTestProperty(const std::string& xml_element, + const TestProperty& test_property); + + // Adds a test part result to the list. + void AddTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& test_part_result); + + // Returns the death test count. + int death_test_count() const { return death_test_count_; } + + // Increments the death test count, returning the new count. + int increment_death_test_count() { return ++death_test_count_; } + + // Clears the test part results. + void ClearTestPartResults(); + + // Clears the object. + void Clear(); + + // Protects mutable state of the property vector and of owned + // properties, whose values may be updated. + internal::Mutex test_properties_mutex_; + + // The vector of TestPartResults + std::vector<TestPartResult> test_part_results_; + // The vector of TestProperties + std::vector<TestProperty> test_properties_; + // Running count of death tests. + int death_test_count_; + // The start time, in milliseconds since UNIX Epoch. + TimeInMillis start_timestamp_; + // The elapsed time, in milliseconds. + TimeInMillis elapsed_time_; + + // We disallow copying TestResult. + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestResult); +}; // class TestResult + +// A TestInfo object stores the following information about a test: +// +// Test suite name +// Test name +// Whether the test should be run +// A function pointer that creates the test object when invoked +// Test result +// +// The constructor of TestInfo registers itself with the UnitTest +// singleton such that the RUN_ALL_TESTS() macro knows which tests to +// run. +class GTEST_API_ TestInfo { + public: + // Destructs a TestInfo object. This function is not virtual, so + // don't inherit from TestInfo. + ~TestInfo(); + + // Returns the test suite name. + const char* test_suite_name() const { return test_suite_name_.c_str(); } + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + const char* test_case_name() const { return test_suite_name(); } +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + // Returns the test name. + const char* name() const { return name_.c_str(); } + + // Returns the name of the parameter type, or NULL if this is not a typed + // or a type-parameterized test. + const char* type_param() const { + if (type_param_.get() != nullptr) return type_param_->c_str(); + return nullptr; + } + + // Returns the text representation of the value parameter, or NULL if this + // is not a value-parameterized test. + const char* value_param() const { + if (value_param_.get() != nullptr) return value_param_->c_str(); + return nullptr; + } + + // Returns the file name where this test is defined. + const char* file() const { return location_.file.c_str(); } + + // Returns the line where this test is defined. + int line() const { return location_.line; } + + // Return true if this test should not be run because it's in another shard. + bool is_in_another_shard() const { return is_in_another_shard_; } + + // Returns true if this test should run, that is if the test is not + // disabled (or it is disabled but the also_run_disabled_tests flag has + // been specified) and its full name matches the user-specified filter. + // + // Google Test allows the user to filter the tests by their full names. + // The full name of a test Bar in test suite Foo is defined as + // "Foo.Bar". Only the tests that match the filter will run. + // + // A filter is a colon-separated list of glob (not regex) patterns, + // optionally followed by a '-' and a colon-separated list of + // negative patterns (tests to exclude). A test is run if it + // matches one of the positive patterns and does not match any of + // the negative patterns. + // + // For example, *A*:Foo.* is a filter that matches any string that + // contains the character 'A' or starts with "Foo.". + bool should_run() const { return should_run_; } + + // Returns true if and only if this test will appear in the XML report. + bool is_reportable() const { + // The XML report includes tests matching the filter, excluding those + // run in other shards. + return matches_filter_ && !is_in_another_shard_; + } + + // Returns the result of the test. + const TestResult* result() const { return &result_; } + + private: +#if GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST + friend class internal::DefaultDeathTestFactory; +#endif // GTEST_HAS_DEATH_TEST + friend class Test; + friend class TestSuite; + friend class internal::UnitTestImpl; + friend class internal::StreamingListenerTest; + friend TestInfo* internal::MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( + const char* test_suite_name, const char* name, const char* type_param, + const char* value_param, internal::CodeLocation code_location, + internal::TypeId fixture_class_id, internal::SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc, + internal::TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc, + internal::TestFactoryBase* factory); + + // Constructs a TestInfo object. The newly constructed instance assumes + // ownership of the factory object. + TestInfo(const std::string& test_suite_name, const std::string& name, + const char* a_type_param, // NULL if not a type-parameterized test + const char* a_value_param, // NULL if not a value-parameterized test + internal::CodeLocation a_code_location, + internal::TypeId fixture_class_id, + internal::TestFactoryBase* factory); + + // Increments the number of death tests encountered in this test so + // far. + int increment_death_test_count() { + return result_.increment_death_test_count(); + } + + // Creates the test object, runs it, records its result, and then + // deletes it. + void Run(); + + // Skip and records the test result for this object. + void Skip(); + + static void ClearTestResult(TestInfo* test_info) { + test_info->result_.Clear(); + } + + // These fields are immutable properties of the test. + const std::string test_suite_name_; // test suite name + const std::string name_; // Test name + // Name of the parameter type, or NULL if this is not a typed or a + // type-parameterized test. + const std::unique_ptr<const ::std::string> type_param_; + // Text representation of the value parameter, or NULL if this is not a + // value-parameterized test. + const std::unique_ptr<const ::std::string> value_param_; + internal::CodeLocation location_; + const internal::TypeId fixture_class_id_; // ID of the test fixture class + bool should_run_; // True if and only if this test should run + bool is_disabled_; // True if and only if this test is disabled + bool matches_filter_; // True if this test matches the + // user-specified filter. + bool is_in_another_shard_; // Will be run in another shard. + internal::TestFactoryBase* const factory_; // The factory that creates + // the test object + + // This field is mutable and needs to be reset before running the + // test for the second time. + TestResult result_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestInfo); +}; + +// A test suite, which consists of a vector of TestInfos. +// +// TestSuite is not copyable. +class GTEST_API_ TestSuite { + public: + // Creates a TestSuite with the given name. + // + // TestSuite does NOT have a default constructor. Always use this + // constructor to create a TestSuite object. + // + // Arguments: + // + // name: name of the test suite + // a_type_param: the name of the test's type parameter, or NULL if + // this is not a type-parameterized test. + // set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test suite + // tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test suite + TestSuite(const char* name, const char* a_type_param, + internal::SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc, + internal::TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc); + + // Destructor of TestSuite. + virtual ~TestSuite(); + + // Gets the name of the TestSuite. + const char* name() const { return name_.c_str(); } + + // Returns the name of the parameter type, or NULL if this is not a + // type-parameterized test suite. + const char* type_param() const { + if (type_param_.get() != nullptr) return type_param_->c_str(); + return nullptr; + } + + // Returns true if any test in this test suite should run. + bool should_run() const { return should_run_; } + + // Gets the number of successful tests in this test suite. + int successful_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of skipped tests in this test suite. + int skipped_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of failed tests in this test suite. + int failed_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of disabled tests that will be reported in the XML report. + int reportable_disabled_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of disabled tests in this test suite. + int disabled_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of tests to be printed in the XML report. + int reportable_test_count() const; + + // Get the number of tests in this test suite that should run. + int test_to_run_count() const; + + // Gets the number of all tests in this test suite. + int total_test_count() const; + + // Returns true if and only if the test suite passed. + bool Passed() const { return !Failed(); } + + // Returns true if and only if the test suite failed. + bool Failed() const { + return failed_test_count() > 0 || ad_hoc_test_result().Failed(); + } + + // Returns the elapsed time, in milliseconds. + TimeInMillis elapsed_time() const { return elapsed_time_; } + + // Gets the time of the test suite start, in ms from the start of the + // UNIX epoch. + TimeInMillis start_timestamp() const { return start_timestamp_; } + + // Returns the i-th test among all the tests. i can range from 0 to + // total_test_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. + const TestInfo* GetTestInfo(int i) const; + + // Returns the TestResult that holds test properties recorded during + // execution of SetUpTestSuite and TearDownTestSuite. + const TestResult& ad_hoc_test_result() const { return ad_hoc_test_result_; } + + private: + friend class Test; + friend class internal::UnitTestImpl; + + // Gets the (mutable) vector of TestInfos in this TestSuite. + std::vector<TestInfo*>& test_info_list() { return test_info_list_; } + + // Gets the (immutable) vector of TestInfos in this TestSuite. + const std::vector<TestInfo*>& test_info_list() const { + return test_info_list_; + } + + // Returns the i-th test among all the tests. i can range from 0 to + // total_test_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. + TestInfo* GetMutableTestInfo(int i); + + // Sets the should_run member. + void set_should_run(bool should) { should_run_ = should; } + + // Adds a TestInfo to this test suite. Will delete the TestInfo upon + // destruction of the TestSuite object. + void AddTestInfo(TestInfo * test_info); + + // Clears the results of all tests in this test suite. + void ClearResult(); + + // Clears the results of all tests in the given test suite. + static void ClearTestSuiteResult(TestSuite* test_suite) { + test_suite->ClearResult(); + } + + // Runs every test in this TestSuite. + void Run(); + + // Skips the execution of tests under this TestSuite + void Skip(); + + // Runs SetUpTestSuite() for this TestSuite. This wrapper is needed + // for catching exceptions thrown from SetUpTestSuite(). + void RunSetUpTestSuite() { + if (set_up_tc_ != nullptr) { + (*set_up_tc_)(); + } + } + + // Runs TearDownTestSuite() for this TestSuite. This wrapper is + // needed for catching exceptions thrown from TearDownTestSuite(). + void RunTearDownTestSuite() { + if (tear_down_tc_ != nullptr) { + (*tear_down_tc_)(); + } + } + + // Returns true if and only if test passed. + static bool TestPassed(const TestInfo* test_info) { + return test_info->should_run() && test_info->result()->Passed(); + } + + // Returns true if and only if test skipped. + static bool TestSkipped(const TestInfo* test_info) { + return test_info->should_run() && test_info->result()->Skipped(); + } + + // Returns true if and only if test failed. + static bool TestFailed(const TestInfo* test_info) { + return test_info->should_run() && test_info->result()->Failed(); + } + + // Returns true if and only if the test is disabled and will be reported in + // the XML report. + static bool TestReportableDisabled(const TestInfo* test_info) { + return test_info->is_reportable() && test_info->is_disabled_; + } + + // Returns true if and only if test is disabled. + static bool TestDisabled(const TestInfo* test_info) { + return test_info->is_disabled_; + } + + // Returns true if and only if this test will appear in the XML report. + static bool TestReportable(const TestInfo* test_info) { + return test_info->is_reportable(); + } + + // Returns true if the given test should run. + static bool ShouldRunTest(const TestInfo* test_info) { + return test_info->should_run(); + } + + // Shuffles the tests in this test suite. + void ShuffleTests(internal::Random* random); + + // Restores the test order to before the first shuffle. + void UnshuffleTests(); + + // Name of the test suite. + std::string name_; + // Name of the parameter type, or NULL if this is not a typed or a + // type-parameterized test. + const std::unique_ptr<const ::std::string> type_param_; + // The vector of TestInfos in their original order. It owns the + // elements in the vector. + std::vector<TestInfo*> test_info_list_; + // Provides a level of indirection for the test list to allow easy + // shuffling and restoring the test order. The i-th element in this + // vector is the index of the i-th test in the shuffled test list. + std::vector<int> test_indices_; + // Pointer to the function that sets up the test suite. + internal::SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc_; + // Pointer to the function that tears down the test suite. + internal::TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc_; + // True if and only if any test in this test suite should run. + bool should_run_; + // The start time, in milliseconds since UNIX Epoch. + TimeInMillis start_timestamp_; + // Elapsed time, in milliseconds. + TimeInMillis elapsed_time_; + // Holds test properties recorded during execution of SetUpTestSuite and + // TearDownTestSuite. + TestResult ad_hoc_test_result_; + + // We disallow copying TestSuites. + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestSuite); +}; + +// An Environment object is capable of setting up and tearing down an +// environment. You should subclass this to define your own +// environment(s). +// +// An Environment object does the set-up and tear-down in virtual +// methods SetUp() and TearDown() instead of the constructor and the +// destructor, as: +// +// 1. You cannot safely throw from a destructor. This is a problem +// as in some cases Google Test is used where exceptions are enabled, and +// we may want to implement ASSERT_* using exceptions where they are +// available. +// 2. You cannot use ASSERT_* directly in a constructor or +// destructor. +class Environment { + public: + // The d'tor is virtual as we need to subclass Environment. + virtual ~Environment() {} + + // Override this to define how to set up the environment. + virtual void SetUp() {} + + // Override this to define how to tear down the environment. + virtual void TearDown() {} + private: + // If you see an error about overriding the following function or + // about it being private, you have mis-spelled SetUp() as Setup(). + struct Setup_should_be_spelled_SetUp {}; + virtual Setup_should_be_spelled_SetUp* Setup() { return nullptr; } +}; + +#if GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +// Exception which can be thrown from TestEventListener::OnTestPartResult. +class GTEST_API_ AssertionException + : public internal::GoogleTestFailureException { + public: + explicit AssertionException(const TestPartResult& result) + : GoogleTestFailureException(result) {} +}; + +#endif // GTEST_HAS_EXCEPTIONS + +// The interface for tracing execution of tests. The methods are organized in +// the order the corresponding events are fired. +class TestEventListener { + public: + virtual ~TestEventListener() {} + + // Fired before any test activity starts. + virtual void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; + + // Fired before each iteration of tests starts. There may be more than + // one iteration if GTEST_FLAG(repeat) is set. iteration is the iteration + // index, starting from 0. + virtual void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& unit_test, + int iteration) = 0; + + // Fired before environment set-up for each iteration of tests starts. + virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; + + // Fired after environment set-up for each iteration of tests ends. + virtual void OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; + + // Fired before the test suite starts. + virtual void OnTestSuiteStart(const TestSuite& /*test_suite*/) {} + + // Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + virtual void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& /*test_case*/) {} +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + // Fired before the test starts. + virtual void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& test_info) = 0; + + // Fired after a failed assertion or a SUCCEED() invocation. + // If you want to throw an exception from this function to skip to the next + // TEST, it must be AssertionException defined above, or inherited from it. + virtual void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& test_part_result) = 0; + + // Fired after the test ends. + virtual void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& test_info) = 0; + + // Fired after the test suite ends. + virtual void OnTestSuiteEnd(const TestSuite& /*test_suite*/) {} + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + virtual void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& /*test_case*/) {} +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + // Fired before environment tear-down for each iteration of tests starts. + virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; + + // Fired after environment tear-down for each iteration of tests ends. + virtual void OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; + + // Fired after each iteration of tests finishes. + virtual void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test, + int iteration) = 0; + + // Fired after all test activities have ended. + virtual void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& unit_test) = 0; +}; + +// The convenience class for users who need to override just one or two +// methods and are not concerned that a possible change to a signature of +// the methods they override will not be caught during the build. For +// comments about each method please see the definition of TestEventListener +// above. +class EmptyTestEventListener : public TestEventListener { + public: + void OnTestProgramStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnTestIterationStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/, + int /*iteration*/) override {} + void OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnTestSuiteStart(const TestSuite& /*test_suite*/) override {} +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestCaseStart(const TestCase& /*test_case*/) override {} +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + void OnTestStart(const TestInfo& /*test_info*/) override {} + void OnTestPartResult(const TestPartResult& /*test_part_result*/) override {} + void OnTestEnd(const TestInfo& /*test_info*/) override {} + void OnTestSuiteEnd(const TestSuite& /*test_suite*/) override {} +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + void OnTestCaseEnd(const TestCase& /*test_case*/) override {} +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + void OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} + void OnTestIterationEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/, + int /*iteration*/) override {} + void OnTestProgramEnd(const UnitTest& /*unit_test*/) override {} +}; + +// TestEventListeners lets users add listeners to track events in Google Test. +class GTEST_API_ TestEventListeners { + public: + TestEventListeners(); + ~TestEventListeners(); + + // Appends an event listener to the end of the list. Google Test assumes + // the ownership of the listener (i.e. it will delete the listener when + // the test program finishes). + void Append(TestEventListener* listener); + + // Removes the given event listener from the list and returns it. It then + // becomes the caller's responsibility to delete the listener. Returns + // NULL if the listener is not found in the list. + TestEventListener* Release(TestEventListener* listener); + + // Returns the standard listener responsible for the default console + // output. Can be removed from the listeners list to shut down default + // console output. Note that removing this object from the listener list + // with Release transfers its ownership to the caller and makes this + // function return NULL the next time. + TestEventListener* default_result_printer() const { + return default_result_printer_; + } + + // Returns the standard listener responsible for the default XML output + // controlled by the --gtest_output=xml flag. Can be removed from the + // listeners list by users who want to shut down the default XML output + // controlled by this flag and substitute it with custom one. Note that + // removing this object from the listener list with Release transfers its + // ownership to the caller and makes this function return NULL the next + // time. + TestEventListener* default_xml_generator() const { + return default_xml_generator_; + } + + private: + friend class TestSuite; + friend class TestInfo; + friend class internal::DefaultGlobalTestPartResultReporter; + friend class internal::NoExecDeathTest; + friend class internal::TestEventListenersAccessor; + friend class internal::UnitTestImpl; + + // Returns repeater that broadcasts the TestEventListener events to all + // subscribers. + TestEventListener* repeater(); + + // Sets the default_result_printer attribute to the provided listener. + // The listener is also added to the listener list and previous + // default_result_printer is removed from it and deleted. The listener can + // also be NULL in which case it will not be added to the list. Does + // nothing if the previous and the current listener objects are the same. + void SetDefaultResultPrinter(TestEventListener* listener); + + // Sets the default_xml_generator attribute to the provided listener. The + // listener is also added to the listener list and previous + // default_xml_generator is removed from it and deleted. The listener can + // also be NULL in which case it will not be added to the list. Does + // nothing if the previous and the current listener objects are the same. + void SetDefaultXmlGenerator(TestEventListener* listener); + + // Controls whether events will be forwarded by the repeater to the + // listeners in the list. + bool EventForwardingEnabled() const; + void SuppressEventForwarding(); + + // The actual list of listeners. + internal::TestEventRepeater* repeater_; + // Listener responsible for the standard result output. + TestEventListener* default_result_printer_; + // Listener responsible for the creation of the XML output file. + TestEventListener* default_xml_generator_; + + // We disallow copying TestEventListeners. + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(TestEventListeners); +}; + +// A UnitTest consists of a vector of TestSuites. +// +// This is a singleton class. The only instance of UnitTest is +// created when UnitTest::GetInstance() is first called. This +// instance is never deleted. +// +// UnitTest is not copyable. +// +// This class is thread-safe as long as the methods are called +// according to their specification. +class GTEST_API_ UnitTest { + public: + // Gets the singleton UnitTest object. The first time this method + // is called, a UnitTest object is constructed and returned. + // Consecutive calls will return the same object. + static UnitTest* GetInstance(); + + // Runs all tests in this UnitTest object and prints the result. + // Returns 0 if successful, or 1 otherwise. + // + // This method can only be called from the main thread. + // + // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. + int Run() GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_; + + // Returns the working directory when the first TEST() or TEST_F() + // was executed. The UnitTest object owns the string. + const char* original_working_dir() const; + + // Returns the TestSuite object for the test that's currently running, + // or NULL if no test is running. + const TestSuite* current_test_suite() const GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); + +// Legacy API is still available but deprecated +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + const TestCase* current_test_case() const GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); +#endif + + // Returns the TestInfo object for the test that's currently running, + // or NULL if no test is running. + const TestInfo* current_test_info() const + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); + + // Returns the random seed used at the start of the current test run. + int random_seed() const; + + // Returns the ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry object used to keep track of + // value-parameterized tests and instantiate and register them. + // + // INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. + internal::ParameterizedTestSuiteRegistry& parameterized_test_registry() + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); + + // Gets the number of successful test suites. + int successful_test_suite_count() const; + + // Gets the number of failed test suites. + int failed_test_suite_count() const; + + // Gets the number of all test suites. + int total_test_suite_count() const; + + // Gets the number of all test suites that contain at least one test + // that should run. + int test_suite_to_run_count() const; + + // Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + int successful_test_case_count() const; + int failed_test_case_count() const; + int total_test_case_count() const; + int test_case_to_run_count() const; +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + // Gets the number of successful tests. + int successful_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of skipped tests. + int skipped_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of failed tests. + int failed_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of disabled tests that will be reported in the XML report. + int reportable_disabled_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of disabled tests. + int disabled_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of tests to be printed in the XML report. + int reportable_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of all tests. + int total_test_count() const; + + // Gets the number of tests that should run. + int test_to_run_count() const; + + // Gets the time of the test program start, in ms from the start of the + // UNIX epoch. + TimeInMillis start_timestamp() const; + + // Gets the elapsed time, in milliseconds. + TimeInMillis elapsed_time() const; + + // Returns true if and only if the unit test passed (i.e. all test suites + // passed). + bool Passed() const; + + // Returns true if and only if the unit test failed (i.e. some test suite + // failed or something outside of all tests failed). + bool Failed() const; + + // Gets the i-th test suite among all the test suites. i can range from 0 to + // total_test_suite_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. + const TestSuite* GetTestSuite(int i) const; + +// Legacy API is deprecated but still available +#ifndef GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + const TestCase* GetTestCase(int i) const; +#endif // GTEST_REMOVE_LEGACY_TEST_CASEAPI_ + + // Returns the TestResult containing information on test failures and + // properties logged outside of individual test suites. + const TestResult& ad_hoc_test_result() const; + + // Returns the list of event listeners that can be used to track events + // inside Google Test. + TestEventListeners& listeners(); + + private: + // Registers and returns a global test environment. When a test + // program is run, all global test environments will be set-up in + // the order they were registered. After all tests in the program + // have finished, all global test environments will be torn-down in + // the *reverse* order they were registered. + // + // The UnitTest object takes ownership of the given environment. + // + // This method can only be called from the main thread. + Environment* AddEnvironment(Environment* env); + + // Adds a TestPartResult to the current TestResult object. All + // Google Test assertion macros (e.g. ASSERT_TRUE, EXPECT_EQ, etc) + // eventually call this to report their results. The user code + // should use the assertion macros instead of calling this directly. + void AddTestPartResult(TestPartResult::Type result_type, + const char* file_name, + int line_number, + const std::string& message, + const std::string& os_stack_trace) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); + + // Adds a TestProperty to the current TestResult object when invoked from + // inside a test, to current TestSuite's ad_hoc_test_result_ when invoked + // from SetUpTestSuite or TearDownTestSuite, or to the global property set + // when invoked elsewhere. If the result already contains a property with + // the same key, the value will be updated. + void RecordProperty(const std::string& key, const std::string& value); + + // Gets the i-th test suite among all the test suites. i can range from 0 to + // total_test_suite_count() - 1. If i is not in that range, returns NULL. + TestSuite* GetMutableTestSuite(int i); + + // Accessors for the implementation object. + internal::UnitTestImpl* impl() { return impl_; } + const internal::UnitTestImpl* impl() const { return impl_; } + + // These classes and functions are friends as they need to access private + // members of UnitTest. + friend class ScopedTrace; + friend class Test; + friend class internal::AssertHelper; + friend class internal::StreamingListenerTest; + friend class internal::UnitTestRecordPropertyTestHelper; + friend Environment* AddGlobalTestEnvironment(Environment* env); + friend std::set<std::string>* internal::GetIgnoredParameterizedTestSuites(); + friend internal::UnitTestImpl* internal::GetUnitTestImpl(); + friend void internal::ReportFailureInUnknownLocation( + TestPartResult::Type result_type, + const std::string& message); + + // Creates an empty UnitTest. + UnitTest(); + + // D'tor + virtual ~UnitTest(); + + // Pushes a trace defined by SCOPED_TRACE() on to the per-thread + // Google Test trace stack. + void PushGTestTrace(const internal::TraceInfo& trace) + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); + + // Pops a trace from the per-thread Google Test trace stack. + void PopGTestTrace() + GTEST_LOCK_EXCLUDED_(mutex_); + + // Protects mutable state in *impl_. This is mutable as some const + // methods need to lock it too. + mutable internal::Mutex mutex_; + + // Opaque implementation object. This field is never changed once + // the object is constructed. We don't mark it as const here, as + // doing so will cause a warning in the constructor of UnitTest. + // Mutable state in *impl_ is protected by mutex_. + internal::UnitTestImpl* impl_; + + // We disallow copying UnitTest. + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(UnitTest); +}; + +// A convenient wrapper for adding an environment for the test +// program. +// +// You should call this before RUN_ALL_TESTS() is called, probably in +// main(). If you use gtest_main, you need to call this before main() +// starts for it to take effect. For example, you can define a global +// variable like this: +// +// testing::Environment* const foo_env = +// testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(new FooEnvironment); +// +// However, we strongly recommend you to write your own main() and +// call AddGlobalTestEnvironment() there, as relying on initialization +// of global variables makes the code harder to read and may cause +// problems when you register multiple environments from different +// translation units and the environments have dependencies among them +// (remember that the compiler doesn't guarantee the order in which +// global variables from different translation units are initialized). +inline Environment* AddGlobalTestEnvironment(Environment* env) { + return UnitTest::GetInstance()->AddEnvironment(env); +} + +// Initializes Google Test. This must be called before calling +// RUN_ALL_TESTS(). In particular, it parses a command line for the +// flags that Google Test recognizes. Whenever a Google Test flag is +// seen, it is removed from argv, and *argc is decremented. +// +// No value is returned. Instead, the Google Test flag variables are +// updated. +// +// Calling the function for the second time has no user-visible effect. +GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleTest(int* argc, char** argv); + +// This overloaded version can be used in Windows programs compiled in +// UNICODE mode. +GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleTest(int* argc, wchar_t** argv); + +// This overloaded version can be used on Arduino/embedded platforms where +// there is no argc/argv. +GTEST_API_ void InitGoogleTest(); + +namespace internal { + +// Separate the error generating code from the code path to reduce the stack +// frame size of CmpHelperEQ. This helps reduce the overhead of some sanitizers +// when calling EXPECT_* in a tight loop. +template <typename T1, typename T2> +AssertionResult CmpHelperEQFailure(const char* lhs_expression, + const char* rhs_expression, + const T1& lhs, const T2& rhs) { + return EqFailure(lhs_expression, + rhs_expression, + FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(lhs, rhs), + FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(rhs, lhs), + false); +} + +// This block of code defines operator==/!= +// to block lexical scope lookup. +// It prevents using invalid operator==/!= defined at namespace scope. +struct faketype {}; +inline bool operator==(faketype, faketype) { return true; } +inline bool operator!=(faketype, faketype) { return false; } + +// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ. +template <typename T1, typename T2> +AssertionResult CmpHelperEQ(const char* lhs_expression, + const char* rhs_expression, + const T1& lhs, + const T2& rhs) { + if (lhs == rhs) { + return AssertionSuccess(); + } + + return CmpHelperEQFailure(lhs_expression, rhs_expression, lhs, rhs); +} + +class EqHelper { + public: + // This templatized version is for the general case. + template < + typename T1, typename T2, + // Disable this overload for cases where one argument is a pointer + // and the other is the null pointer constant. + typename std::enable_if<!std::is_integral<T1>::value || + !std::is_pointer<T2>::value>::type* = nullptr> + static AssertionResult Compare(const char* lhs_expression, + const char* rhs_expression, const T1& lhs, + const T2& rhs) { + return CmpHelperEQ(lhs_expression, rhs_expression, lhs, rhs); + } + + // With this overloaded version, we allow anonymous enums to be used + // in {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ when compiled with gcc 4, as anonymous + // enums can be implicitly cast to BiggestInt. + // + // Even though its body looks the same as the above version, we + // cannot merge the two, as it will make anonymous enums unhappy. + static AssertionResult Compare(const char* lhs_expression, + const char* rhs_expression, + BiggestInt lhs, + BiggestInt rhs) { + return CmpHelperEQ(lhs_expression, rhs_expression, lhs, rhs); + } + + template <typename T> + static AssertionResult Compare( + const char* lhs_expression, const char* rhs_expression, + // Handle cases where '0' is used as a null pointer literal. + std::nullptr_t /* lhs */, T* rhs) { + // We already know that 'lhs' is a null pointer. + return CmpHelperEQ(lhs_expression, rhs_expression, static_cast<T*>(nullptr), + rhs); + } +}; + +// Separate the error generating code from the code path to reduce the stack +// frame size of CmpHelperOP. This helps reduce the overhead of some sanitizers +// when calling EXPECT_OP in a tight loop. +template <typename T1, typename T2> +AssertionResult CmpHelperOpFailure(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, + const T1& val1, const T2& val2, + const char* op) { + return AssertionFailure() + << "Expected: (" << expr1 << ") " << op << " (" << expr2 + << "), actual: " << FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(val1, val2) + << " vs " << FormatForComparisonFailureMessage(val2, val1); +} + +// A macro for implementing the helper functions needed to implement +// ASSERT_?? and EXPECT_??. It is here just to avoid copy-and-paste +// of similar code. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. + +#define GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(op_name, op)\ +template <typename T1, typename T2>\ +AssertionResult CmpHelper##op_name(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, \ + const T1& val1, const T2& val2) {\ + if (val1 op val2) {\ + return AssertionSuccess();\ + } else {\ + return CmpHelperOpFailure(expr1, expr2, val1, val2, #op);\ + }\ +} + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. + +// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NE +GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(NE, !=) +// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LE +GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(LE, <=) +// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LT +GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(LT, <) +// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GE +GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(GE, >=) +// Implements the helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GT +GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_(GT, >) + +#undef GTEST_IMPL_CMP_HELPER_ + +// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STREQ. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTREQ(const char* s1_expression, + const char* s2_expression, + const char* s1, + const char* s2); + +// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASEEQ. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRCASEEQ(const char* s1_expression, + const char* s2_expression, + const char* s1, + const char* s2); + +// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRNE. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRNE(const char* s1_expression, + const char* s2_expression, + const char* s1, + const char* s2); + +// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASENE. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRCASENE(const char* s1_expression, + const char* s2_expression, + const char* s1, + const char* s2); + + +// Helper function for *_STREQ on wide strings. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTREQ(const char* s1_expression, + const char* s2_expression, + const wchar_t* s1, + const wchar_t* s2); + +// Helper function for *_STRNE on wide strings. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult CmpHelperSTRNE(const char* s1_expression, + const char* s2_expression, + const wchar_t* s1, + const wchar_t* s2); + +} // namespace internal + +// IsSubstring() and IsNotSubstring() are intended to be used as the +// first argument to {EXPECT,ASSERT}_PRED_FORMAT2(), not by +// themselves. They check whether needle is a substring of haystack +// (NULL is considered a substring of itself only), and return an +// appropriate error message when they fail. +// +// The {needle,haystack}_expr arguments are the stringified +// expressions that generated the two real arguments. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const char* needle, const char* haystack); +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const wchar_t* needle, const wchar_t* haystack); +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const char* needle, const char* haystack); +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const wchar_t* needle, const wchar_t* haystack); +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const ::std::string& needle, const ::std::string& haystack); +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const ::std::string& needle, const ::std::string& haystack); + +#if GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const ::std::wstring& needle, const ::std::wstring& haystack); +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult IsNotSubstring( + const char* needle_expr, const char* haystack_expr, + const ::std::wstring& needle, const ::std::wstring& haystack); +#endif // GTEST_HAS_STD_WSTRING + +namespace internal { + +// Helper template function for comparing floating-points. +// +// Template parameter: +// +// RawType: the raw floating-point type (either float or double) +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +template <typename RawType> +AssertionResult CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ(const char* lhs_expression, + const char* rhs_expression, + RawType lhs_value, + RawType rhs_value) { + const FloatingPoint<RawType> lhs(lhs_value), rhs(rhs_value); + + if (lhs.AlmostEquals(rhs)) { + return AssertionSuccess(); + } + + ::std::stringstream lhs_ss; + lhs_ss << std::setprecision(std::numeric_limits<RawType>::digits10 + 2) + << lhs_value; + + ::std::stringstream rhs_ss; + rhs_ss << std::setprecision(std::numeric_limits<RawType>::digits10 + 2) + << rhs_value; + + return EqFailure(lhs_expression, + rhs_expression, + StringStreamToString(&lhs_ss), + StringStreamToString(&rhs_ss), + false); +} + +// Helper function for implementing ASSERT_NEAR. +// +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN A USER PROGRAM. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult DoubleNearPredFormat(const char* expr1, + const char* expr2, + const char* abs_error_expr, + double val1, + double val2, + double abs_error); + +// INTERNAL IMPLEMENTATION - DO NOT USE IN USER CODE. +// A class that enables one to stream messages to assertion macros +class GTEST_API_ AssertHelper { + public: + // Constructor. + AssertHelper(TestPartResult::Type type, + const char* file, + int line, + const char* message); + ~AssertHelper(); + + // Message assignment is a semantic trick to enable assertion + // streaming; see the GTEST_MESSAGE_ macro below. + void operator=(const Message& message) const; + + private: + // We put our data in a struct so that the size of the AssertHelper class can + // be as small as possible. This is important because gcc is incapable of + // re-using stack space even for temporary variables, so every EXPECT_EQ + // reserves stack space for another AssertHelper. + struct AssertHelperData { + AssertHelperData(TestPartResult::Type t, + const char* srcfile, + int line_num, + const char* msg) + : type(t), file(srcfile), line(line_num), message(msg) { } + + TestPartResult::Type const type; + const char* const file; + int const line; + std::string const message; + + private: + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(AssertHelperData); + }; + + AssertHelperData* const data_; + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(AssertHelper); +}; + +} // namespace internal + +// The pure interface class that all value-parameterized tests inherit from. +// A value-parameterized class must inherit from both ::testing::Test and +// ::testing::WithParamInterface. In most cases that just means inheriting +// from ::testing::TestWithParam, but more complicated test hierarchies +// may need to inherit from Test and WithParamInterface at different levels. +// +// This interface has support for accessing the test parameter value via +// the GetParam() method. +// +// Use it with one of the parameter generator defining functions, like Range(), +// Values(), ValuesIn(), Bool(), and Combine(). +// +// class FooTest : public ::testing::TestWithParam<int> { +// protected: +// FooTest() { +// // Can use GetParam() here. +// } +// ~FooTest() override { +// // Can use GetParam() here. +// } +// void SetUp() override { +// // Can use GetParam() here. +// } +// void TearDown override { +// // Can use GetParam() here. +// } +// }; +// TEST_P(FooTest, DoesBar) { +// // Can use GetParam() method here. +// Foo foo; +// ASSERT_TRUE(foo.DoesBar(GetParam())); +// } +// INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P(OneToTenRange, FooTest, ::testing::Range(1, 10)); + +template <typename T> +class WithParamInterface { + public: + typedef T ParamType; + virtual ~WithParamInterface() {} + + // The current parameter value. Is also available in the test fixture's + // constructor. + static const ParamType& GetParam() { + GTEST_CHECK_(parameter_ != nullptr) + << "GetParam() can only be called inside a value-parameterized test " + << "-- did you intend to write TEST_P instead of TEST_F?"; + return *parameter_; + } + + private: + // Sets parameter value. The caller is responsible for making sure the value + // remains alive and unchanged throughout the current test. + static void SetParam(const ParamType* parameter) { + parameter_ = parameter; + } + + // Static value used for accessing parameter during a test lifetime. + static const ParamType* parameter_; + + // TestClass must be a subclass of WithParamInterface<T> and Test. + template <class TestClass> friend class internal::ParameterizedTestFactory; +}; + +template <typename T> +const T* WithParamInterface<T>::parameter_ = nullptr; + +// Most value-parameterized classes can ignore the existence of +// WithParamInterface, and can just inherit from ::testing::TestWithParam. + +template <typename T> +class TestWithParam : public Test, public WithParamInterface<T> { +}; + +// Macros for indicating success/failure in test code. + +// Skips test in runtime. +// Skipping test aborts current function. +// Skipped tests are neither successful nor failed. +#define GTEST_SKIP() GTEST_SKIP_("") + +// ADD_FAILURE unconditionally adds a failure to the current test. +// SUCCEED generates a success - it doesn't automatically make the +// current test successful, as a test is only successful when it has +// no failure. +// +// EXPECT_* verifies that a certain condition is satisfied. If not, +// it behaves like ADD_FAILURE. In particular: +// +// EXPECT_TRUE verifies that a Boolean condition is true. +// EXPECT_FALSE verifies that a Boolean condition is false. +// +// FAIL and ASSERT_* are similar to ADD_FAILURE and EXPECT_*, except +// that they will also abort the current function on failure. People +// usually want the fail-fast behavior of FAIL and ASSERT_*, but those +// writing data-driven tests often find themselves using ADD_FAILURE +// and EXPECT_* more. + +// Generates a nonfatal failure with a generic message. +#define ADD_FAILURE() GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_("Failed") + +// Generates a nonfatal failure at the given source file location with +// a generic message. +#define ADD_FAILURE_AT(file, line) \ + GTEST_MESSAGE_AT_(file, line, "Failed", \ + ::testing::TestPartResult::kNonFatalFailure) + +// Generates a fatal failure with a generic message. +#define GTEST_FAIL() GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_("Failed") + +// Like GTEST_FAIL(), but at the given source file location. +#define GTEST_FAIL_AT(file, line) \ + GTEST_MESSAGE_AT_(file, line, "Failed", \ + ::testing::TestPartResult::kFatalFailure) + +// Define this macro to 1 to omit the definition of FAIL(), which is a +// generic name and clashes with some other libraries. +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_FAIL +# define FAIL() GTEST_FAIL() +#endif + +// Generates a success with a generic message. +#define GTEST_SUCCEED() GTEST_SUCCESS_("Succeeded") + +// Define this macro to 1 to omit the definition of SUCCEED(), which +// is a generic name and clashes with some other libraries. +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_SUCCEED +# define SUCCEED() GTEST_SUCCEED() +#endif + +// Macros for testing exceptions. +// +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_THROW(statement, expected_exception): +// Tests that the statement throws the expected exception. +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NO_THROW(statement): +// Tests that the statement doesn't throw any exception. +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_ANY_THROW(statement): +// Tests that the statement throws an exception. + +#define EXPECT_THROW(statement, expected_exception) \ + GTEST_TEST_THROW_(statement, expected_exception, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define EXPECT_NO_THROW(statement) \ + GTEST_TEST_NO_THROW_(statement, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define EXPECT_ANY_THROW(statement) \ + GTEST_TEST_ANY_THROW_(statement, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_THROW(statement, expected_exception) \ + GTEST_TEST_THROW_(statement, expected_exception, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_NO_THROW(statement) \ + GTEST_TEST_NO_THROW_(statement, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) +#define ASSERT_ANY_THROW(statement) \ + GTEST_TEST_ANY_THROW_(statement, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) + +// Boolean assertions. Condition can be either a Boolean expression or an +// AssertionResult. For more information on how to use AssertionResult with +// these macros see comments on that class. +#define GTEST_EXPECT_TRUE(condition) \ + GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(condition, #condition, false, true, \ + GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define GTEST_EXPECT_FALSE(condition) \ + GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(!(condition), #condition, true, false, \ + GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) +#define GTEST_ASSERT_TRUE(condition) \ + GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(condition, #condition, false, true, \ + GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) +#define GTEST_ASSERT_FALSE(condition) \ + GTEST_TEST_BOOLEAN_(!(condition), #condition, true, false, \ + GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) + +// Define these macros to 1 to omit the definition of the corresponding +// EXPECT or ASSERT, which clashes with some users' own code. + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_EXPECT_TRUE +#define EXPECT_TRUE(condition) GTEST_EXPECT_TRUE(condition) +#endif + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_EXPECT_FALSE +#define EXPECT_FALSE(condition) GTEST_EXPECT_FALSE(condition) +#endif + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_TRUE +#define ASSERT_TRUE(condition) GTEST_ASSERT_TRUE(condition) +#endif + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_FALSE +#define ASSERT_FALSE(condition) GTEST_ASSERT_FALSE(condition) +#endif + +// Macros for testing equalities and inequalities. +// +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ(v1, v2): Tests that v1 == v2 +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NE(v1, v2): Tests that v1 != v2 +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LT(v1, v2): Tests that v1 < v2 +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_LE(v1, v2): Tests that v1 <= v2 +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GT(v1, v2): Tests that v1 > v2 +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_GE(v1, v2): Tests that v1 >= v2 +// +// When they are not, Google Test prints both the tested expressions and +// their actual values. The values must be compatible built-in types, +// or you will get a compiler error. By "compatible" we mean that the +// values can be compared by the respective operator. +// +// Note: +// +// 1. It is possible to make a user-defined type work with +// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_??(), but that requires overloading the +// comparison operators and is thus discouraged by the Google C++ +// Usage Guide. Therefore, you are advised to use the +// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_TRUE() macro to assert that two objects are +// equal. +// +// 2. The {ASSERT|EXPECT}_??() macros do pointer comparisons on +// pointers (in particular, C strings). Therefore, if you use it +// with two C strings, you are testing how their locations in memory +// are related, not how their content is related. To compare two C +// strings by content, use {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STR*(). +// +// 3. {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ(v1, v2) is preferred to +// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_TRUE(v1 == v2), as the former tells you +// what the actual value is when it fails, and similarly for the +// other comparisons. +// +// 4. Do not depend on the order in which {ASSERT|EXPECT}_??() +// evaluate their arguments, which is undefined. +// +// 5. These macros evaluate their arguments exactly once. +// +// Examples: +// +// EXPECT_NE(Foo(), 5); +// EXPECT_EQ(a_pointer, NULL); +// ASSERT_LT(i, array_size); +// ASSERT_GT(records.size(), 0) << "There is no record left."; + +#define EXPECT_EQ(val1, val2) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::EqHelper::Compare, val1, val2) +#define EXPECT_NE(val1, val2) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperNE, val1, val2) +#define EXPECT_LE(val1, val2) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperLE, val1, val2) +#define EXPECT_LT(val1, val2) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperLT, val1, val2) +#define EXPECT_GE(val1, val2) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperGE, val1, val2) +#define EXPECT_GT(val1, val2) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperGT, val1, val2) + +#define GTEST_ASSERT_EQ(val1, val2) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::EqHelper::Compare, val1, val2) +#define GTEST_ASSERT_NE(val1, val2) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperNE, val1, val2) +#define GTEST_ASSERT_LE(val1, val2) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperLE, val1, val2) +#define GTEST_ASSERT_LT(val1, val2) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperLT, val1, val2) +#define GTEST_ASSERT_GE(val1, val2) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperGE, val1, val2) +#define GTEST_ASSERT_GT(val1, val2) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperGT, val1, val2) + +// Define macro GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_XY to 1 to omit the definition of +// ASSERT_XY(), which clashes with some users' own code. + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_EQ +# define ASSERT_EQ(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_EQ(val1, val2) +#endif + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_NE +# define ASSERT_NE(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_NE(val1, val2) +#endif + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_LE +# define ASSERT_LE(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_LE(val1, val2) +#endif + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_LT +# define ASSERT_LT(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_LT(val1, val2) +#endif + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_GE +# define ASSERT_GE(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_GE(val1, val2) +#endif + +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_ASSERT_GT +# define ASSERT_GT(val1, val2) GTEST_ASSERT_GT(val1, val2) +#endif + +// C-string Comparisons. All tests treat NULL and any non-NULL string +// as different. Two NULLs are equal. +// +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STREQ(s1, s2): Tests that s1 == s2 +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRNE(s1, s2): Tests that s1 != s2 +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASEEQ(s1, s2): Tests that s1 == s2, ignoring case +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_STRCASENE(s1, s2): Tests that s1 != s2, ignoring case +// +// For wide or narrow string objects, you can use the +// {ASSERT|EXPECT}_??() macros. +// +// Don't depend on the order in which the arguments are evaluated, +// which is undefined. +// +// These macros evaluate their arguments exactly once. + +#define EXPECT_STREQ(s1, s2) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTREQ, s1, s2) +#define EXPECT_STRNE(s1, s2) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRNE, s1, s2) +#define EXPECT_STRCASEEQ(s1, s2) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRCASEEQ, s1, s2) +#define EXPECT_STRCASENE(s1, s2)\ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRCASENE, s1, s2) + +#define ASSERT_STREQ(s1, s2) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTREQ, s1, s2) +#define ASSERT_STRNE(s1, s2) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRNE, s1, s2) +#define ASSERT_STRCASEEQ(s1, s2) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRCASEEQ, s1, s2) +#define ASSERT_STRCASENE(s1, s2)\ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperSTRCASENE, s1, s2) + +// Macros for comparing floating-point numbers. +// +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_FLOAT_EQ(val1, val2): +// Tests that two float values are almost equal. +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_DOUBLE_EQ(val1, val2): +// Tests that two double values are almost equal. +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NEAR(v1, v2, abs_error): +// Tests that v1 and v2 are within the given distance to each other. +// +// Google Test uses ULP-based comparison to automatically pick a default +// error bound that is appropriate for the operands. See the +// FloatingPoint template class in gtest-internal.h if you are +// interested in the implementation details. + +#define EXPECT_FLOAT_EQ(val1, val2)\ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ<float>, \ + val1, val2) + +#define EXPECT_DOUBLE_EQ(val1, val2)\ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ<double>, \ + val1, val2) + +#define ASSERT_FLOAT_EQ(val1, val2)\ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ<float>, \ + val1, val2) + +#define ASSERT_DOUBLE_EQ(val1, val2)\ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal::CmpHelperFloatingPointEQ<double>, \ + val1, val2) + +#define EXPECT_NEAR(val1, val2, abs_error)\ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT3(::testing::internal::DoubleNearPredFormat, \ + val1, val2, abs_error) + +#define ASSERT_NEAR(val1, val2, abs_error)\ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT3(::testing::internal::DoubleNearPredFormat, \ + val1, val2, abs_error) + +// These predicate format functions work on floating-point values, and +// can be used in {ASSERT|EXPECT}_PRED_FORMAT2*(), e.g. +// +// EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT2(testing::DoubleLE, Foo(), 5.0); + +// Asserts that val1 is less than, or almost equal to, val2. Fails +// otherwise. In particular, it fails if either val1 or val2 is NaN. +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult FloatLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, + float val1, float val2); +GTEST_API_ AssertionResult DoubleLE(const char* expr1, const char* expr2, + double val1, double val2); + + +#if GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +// Macros that test for HRESULT failure and success, these are only useful +// on Windows, and rely on Windows SDK macros and APIs to compile. +// +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_HRESULT_{SUCCEEDED|FAILED}(expr) +// +// When expr unexpectedly fails or succeeds, Google Test prints the +// expected result and the actual result with both a human-readable +// string representation of the error, if available, as well as the +// hex result code. +# define EXPECT_HRESULT_SUCCEEDED(expr) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(::testing::internal::IsHRESULTSuccess, (expr)) + +# define ASSERT_HRESULT_SUCCEEDED(expr) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(::testing::internal::IsHRESULTSuccess, (expr)) + +# define EXPECT_HRESULT_FAILED(expr) \ + EXPECT_PRED_FORMAT1(::testing::internal::IsHRESULTFailure, (expr)) + +# define ASSERT_HRESULT_FAILED(expr) \ + ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT1(::testing::internal::IsHRESULTFailure, (expr)) + +#endif // GTEST_OS_WINDOWS + +// Macros that execute statement and check that it doesn't generate new fatal +// failures in the current thread. +// +// * {ASSERT|EXPECT}_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(statement); +// +// Examples: +// +// EXPECT_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(Process()); +// ASSERT_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(Process()) << "Process() failed"; +// +#define ASSERT_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(statement) \ + GTEST_TEST_NO_FATAL_FAILURE_(statement, GTEST_FATAL_FAILURE_) +#define EXPECT_NO_FATAL_FAILURE(statement) \ + GTEST_TEST_NO_FATAL_FAILURE_(statement, GTEST_NONFATAL_FAILURE_) + +// Causes a trace (including the given source file path and line number, +// and the given message) to be included in every test failure message generated +// by code in the scope of the lifetime of an instance of this class. The effect +// is undone with the destruction of the instance. +// +// The message argument can be anything streamable to std::ostream. +// +// Example: +// testing::ScopedTrace trace("file.cc", 123, "message"); +// +class GTEST_API_ ScopedTrace { + public: + // The c'tor pushes the given source file location and message onto + // a trace stack maintained by Google Test. + + // Template version. Uses Message() to convert the values into strings. + // Slow, but flexible. + template <typename T> + ScopedTrace(const char* file, int line, const T& message) { + PushTrace(file, line, (Message() << message).GetString()); + } + + // Optimize for some known types. + ScopedTrace(const char* file, int line, const char* message) { + PushTrace(file, line, message ? message : "(null)"); + } + + ScopedTrace(const char* file, int line, const std::string& message) { + PushTrace(file, line, message); + } + + // The d'tor pops the info pushed by the c'tor. + // + // Note that the d'tor is not virtual in order to be efficient. + // Don't inherit from ScopedTrace! + ~ScopedTrace(); + + private: + void PushTrace(const char* file, int line, std::string message); + + GTEST_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN_(ScopedTrace); +} GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_; // A ScopedTrace object does its job in its + // c'tor and d'tor. Therefore it doesn't + // need to be used otherwise. + +// Causes a trace (including the source file path, the current line +// number, and the given message) to be included in every test failure +// message generated by code in the current scope. The effect is +// undone when the control leaves the current scope. +// +// The message argument can be anything streamable to std::ostream. +// +// In the implementation, we include the current line number as part +// of the dummy variable name, thus allowing multiple SCOPED_TRACE()s +// to appear in the same block - as long as they are on different +// lines. +// +// Assuming that each thread maintains its own stack of traces. +// Therefore, a SCOPED_TRACE() would (correctly) only affect the +// assertions in its own thread. +#define SCOPED_TRACE(message) \ + ::testing::ScopedTrace GTEST_CONCAT_TOKEN_(gtest_trace_, __LINE__)(\ + __FILE__, __LINE__, (message)) + +// Compile-time assertion for type equality. +// StaticAssertTypeEq<type1, type2>() compiles if and only if type1 and type2 +// are the same type. The value it returns is not interesting. +// +// Instead of making StaticAssertTypeEq a class template, we make it a +// function template that invokes a helper class template. This +// prevents a user from misusing StaticAssertTypeEq<T1, T2> by +// defining objects of that type. +// +// CAVEAT: +// +// When used inside a method of a class template, +// StaticAssertTypeEq<T1, T2>() is effective ONLY IF the method is +// instantiated. For example, given: +// +// template <typename T> class Foo { +// public: +// void Bar() { testing::StaticAssertTypeEq<int, T>(); } +// }; +// +// the code: +// +// void Test1() { Foo<bool> foo; } +// +// will NOT generate a compiler error, as Foo<bool>::Bar() is never +// actually instantiated. Instead, you need: +// +// void Test2() { Foo<bool> foo; foo.Bar(); } +// +// to cause a compiler error. +template <typename T1, typename T2> +constexpr bool StaticAssertTypeEq() noexcept { + static_assert(std::is_same<T1, T2>::value, "T1 and T2 are not the same type"); + return true; +} + +// Defines a test. +// +// The first parameter is the name of the test suite, and the second +// parameter is the name of the test within the test suite. +// +// The convention is to end the test suite name with "Test". For +// example, a test suite for the Foo class can be named FooTest. +// +// Test code should appear between braces after an invocation of +// this macro. Example: +// +// TEST(FooTest, InitializesCorrectly) { +// Foo foo; +// EXPECT_TRUE(foo.StatusIsOK()); +// } + +// Note that we call GetTestTypeId() instead of GetTypeId< +// ::testing::Test>() here to get the type ID of testing::Test. This +// is to work around a suspected linker bug when using Google Test as +// a framework on Mac OS X. The bug causes GetTypeId< +// ::testing::Test>() to return different values depending on whether +// the call is from the Google Test framework itself or from user test +// code. GetTestTypeId() is guaranteed to always return the same +// value, as it always calls GetTypeId<>() from the Google Test +// framework. +#define GTEST_TEST(test_suite_name, test_name) \ + GTEST_TEST_(test_suite_name, test_name, ::testing::Test, \ + ::testing::internal::GetTestTypeId()) + +// Define this macro to 1 to omit the definition of TEST(), which +// is a generic name and clashes with some other libraries. +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_TEST +#define TEST(test_suite_name, test_name) GTEST_TEST(test_suite_name, test_name) +#endif + +// Defines a test that uses a test fixture. +// +// The first parameter is the name of the test fixture class, which +// also doubles as the test suite name. The second parameter is the +// name of the test within the test suite. +// +// A test fixture class must be declared earlier. The user should put +// the test code between braces after using this macro. Example: +// +// class FooTest : public testing::Test { +// protected: +// void SetUp() override { b_.AddElement(3); } +// +// Foo a_; +// Foo b_; +// }; +// +// TEST_F(FooTest, InitializesCorrectly) { +// EXPECT_TRUE(a_.StatusIsOK()); +// } +// +// TEST_F(FooTest, ReturnsElementCountCorrectly) { +// EXPECT_EQ(a_.size(), 0); +// EXPECT_EQ(b_.size(), 1); +// } +// +// GOOGLETEST_CM0011 DO NOT DELETE +#if !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_TEST +#define TEST_F(test_fixture, test_name)\ + GTEST_TEST_(test_fixture, test_name, test_fixture, \ + ::testing::internal::GetTypeId<test_fixture>()) +#endif // !GTEST_DONT_DEFINE_TEST + +// Returns a path to temporary directory. +// Tries to determine an appropriate directory for the platform. +GTEST_API_ std::string TempDir(); + +#ifdef _MSC_VER +# pragma warning(pop) +#endif + +// Dynamically registers a test with the framework. +// +// This is an advanced API only to be used when the `TEST` macros are +// insufficient. The macros should be preferred when possible, as they avoid +// most of the complexity of calling this function. +// +// The `factory` argument is a factory callable (move-constructible) object or +// function pointer that creates a new instance of the Test object. It +// handles ownership to the caller. The signature of the callable is +// `Fixture*()`, where `Fixture` is the test fixture class for the test. All +// tests registered with the same `test_suite_name` must return the same +// fixture type. This is checked at runtime. +// +// The framework will infer the fixture class from the factory and will call +// the `SetUpTestSuite` and `TearDownTestSuite` for it. +// +// Must be called before `RUN_ALL_TESTS()` is invoked, otherwise behavior is +// undefined. +// +// Use case example: +// +// class MyFixture : public ::testing::Test { +// public: +// // All of these optional, just like in regular macro usage. +// static void SetUpTestSuite() { ... } +// static void TearDownTestSuite() { ... } +// void SetUp() override { ... } +// void TearDown() override { ... } +// }; +// +// class MyTest : public MyFixture { +// public: +// explicit MyTest(int data) : data_(data) {} +// void TestBody() override { ... } +// +// private: +// int data_; +// }; +// +// void RegisterMyTests(const std::vector<int>& values) { +// for (int v : values) { +// ::testing::RegisterTest( +// "MyFixture", ("Test" + std::to_string(v)).c_str(), nullptr, +// std::to_string(v).c_str(), +// __FILE__, __LINE__, +// // Important to use the fixture type as the return type here. +// [=]() -> MyFixture* { return new MyTest(v); }); +// } +// } +// ... +// int main(int argc, char** argv) { +// std::vector<int> values_to_test = LoadValuesFromConfig(); +// RegisterMyTests(values_to_test); +// ... +// return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); +// } +// +template <int&... ExplicitParameterBarrier, typename Factory> +TestInfo* RegisterTest(const char* test_suite_name, const char* test_name, + const char* type_param, const char* value_param, + const char* file, int line, Factory factory) { + using TestT = typename std::remove_pointer<decltype(factory())>::type; + + class FactoryImpl : public internal::TestFactoryBase { + public: + explicit FactoryImpl(Factory f) : factory_(std::move(f)) {} + Test* CreateTest() override { return factory_(); } + + private: + Factory factory_; + }; + + return internal::MakeAndRegisterTestInfo( + test_suite_name, test_name, type_param, value_param, + internal::CodeLocation(file, line), internal::GetTypeId<TestT>(), + internal::SuiteApiResolver<TestT>::GetSetUpCaseOrSuite(file, line), + internal::SuiteApiResolver<TestT>::GetTearDownCaseOrSuite(file, line), + new FactoryImpl{std::move(factory)}); +} + +} // namespace testing + +// Use this function in main() to run all tests. It returns 0 if all +// tests are successful, or 1 otherwise. +// +// RUN_ALL_TESTS() should be invoked after the command line has been +// parsed by InitGoogleTest(). +// +// This function was formerly a macro; thus, it is in the global +// namespace and has an all-caps name. +int RUN_ALL_TESTS() GTEST_MUST_USE_RESULT_; + +inline int RUN_ALL_TESTS() { + return ::testing::UnitTest::GetInstance()->Run(); +} + +GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_() // 4251 + +#endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_GTEST_H_ diff --git a/test/header-only-test.cc b/test/header-only-test.cc index 674dab99..570f09a5 100644 --- a/test/header-only-test.cc +++ b/test/header-only-test.cc @@ -1,3 +1,11 @@ // Header-only configuration test #include "fmt/core.h" +#include "fmt/ostream.h" +#include "gtest/gtest.h" + +#ifndef FMT_HEADER_ONLY +# error "Not in the header-only mode." +#endif + +TEST(header_only_test, format) { EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("foo"), "foo"); } diff --git a/test/header-only-test2.cc b/test/header-only-test2.cc deleted file mode 100644 index ea90b604..00000000 --- a/test/header-only-test2.cc +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -// Additional translation unit for the header-only configuration test - -#include "fmt/core.h" diff --git a/test/locale-test.cc b/test/locale-test.cc deleted file mode 100644 index c7c30f2e..00000000 --- a/test/locale-test.cc +++ /dev/null @@ -1,160 +0,0 @@ -// Formatting library for C++ - locale tests -// -// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich -// All rights reserved. -// -// For the license information refer to format.h. - -#include "fmt/locale.h" - -#include <complex> - -#include "gmock.h" - -using fmt::detail::max_value; - -#ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR -template <typename Char> struct numpunct : std::numpunct<Char> { - protected: - Char do_decimal_point() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return '?'; } - std::string do_grouping() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return "\03"; } - Char do_thousands_sep() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return '~'; } -}; - -template <typename Char> struct no_grouping : std::numpunct<Char> { - protected: - Char do_decimal_point() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return '.'; } - std::string do_grouping() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return ""; } - Char do_thousands_sep() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return ','; } -}; - -template <typename Char> struct special_grouping : std::numpunct<Char> { - protected: - Char do_decimal_point() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return '.'; } - std::string do_grouping() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return "\03\02"; } - Char do_thousands_sep() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return ','; } -}; - -template <typename Char> struct small_grouping : std::numpunct<Char> { - protected: - Char do_decimal_point() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return '.'; } - std::string do_grouping() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return "\01"; } - Char do_thousands_sep() const FMT_OVERRIDE { return ','; } -}; - -TEST(LocaleTest, DoubleDecimalPoint) { - std::locale loc(std::locale(), new numpunct<char>()); - EXPECT_EQ("1?23", fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 1.23)); -} - -TEST(LocaleTest, Format) { - std::locale loc(std::locale(), new numpunct<char>()); - EXPECT_EQ("1234567", fmt::format(std::locale(), "{:L}", 1234567)); - EXPECT_EQ("1~234~567", fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 1234567)); - EXPECT_EQ("-1~234~567", fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", -1234567)); - EXPECT_EQ("-256", fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", -256)); - fmt::format_arg_store<fmt::format_context, int> as{1234567}; - EXPECT_EQ("1~234~567", fmt::vformat(loc, "{:L}", fmt::format_args(as))); - std::string s; - fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), loc, "{:L}", 1234567); - EXPECT_EQ("1~234~567", s); - - std::locale no_grouping_loc(std::locale(), new no_grouping<char>()); - EXPECT_EQ("1234567", fmt::format(no_grouping_loc, "{:L}", 1234567)); - - std::locale special_grouping_loc(std::locale(), new special_grouping<char>()); - EXPECT_EQ("1,23,45,678", fmt::format(special_grouping_loc, "{:L}", 12345678)); - EXPECT_EQ("12,345", fmt::format(special_grouping_loc, "{:L}", 12345)); - - std::locale small_grouping_loc(std::locale(), new small_grouping<char>()); - EXPECT_EQ("4,2,9,4,9,6,7,2,9,5", - fmt::format(small_grouping_loc, "{:L}", max_value<uint32_t>())); -} - -TEST(LocaleTest, FormatDetaultAlign) { - std::locale special_grouping_loc(std::locale(), new special_grouping<char>()); - EXPECT_EQ(" 12,345", fmt::format(special_grouping_loc, "{:8L}", 12345)); -} - -TEST(LocaleTest, WFormat) { - std::locale loc(std::locale(), new numpunct<wchar_t>()); - EXPECT_EQ(L"1234567", fmt::format(std::locale(), L"{:L}", 1234567)); - EXPECT_EQ(L"1~234~567", fmt::format(loc, L"{:L}", 1234567)); - fmt::format_arg_store<fmt::wformat_context, int> as{1234567}; - EXPECT_EQ(L"1~234~567", fmt::vformat(loc, L"{:L}", fmt::wformat_args(as))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"1234567", fmt::format(std::locale("C"), L"{:L}", 1234567)); - - std::locale no_grouping_loc(std::locale(), new no_grouping<wchar_t>()); - EXPECT_EQ(L"1234567", fmt::format(no_grouping_loc, L"{:L}", 1234567)); - - std::locale special_grouping_loc(std::locale(), - new special_grouping<wchar_t>()); - EXPECT_EQ(L"1,23,45,678", - fmt::format(special_grouping_loc, L"{:L}", 12345678)); - - std::locale small_grouping_loc(std::locale(), new small_grouping<wchar_t>()); - EXPECT_EQ(L"4,2,9,4,9,6,7,2,9,5", - fmt::format(small_grouping_loc, L"{:L}", max_value<uint32_t>())); -} - -TEST(LocaleTest, DoubleFormatter) { - auto loc = std::locale(std::locale(), new special_grouping<char>()); - auto f = fmt::formatter<int>(); - auto parse_ctx = fmt::format_parse_context("L"); - f.parse(parse_ctx); - char buf[10] = {}; - fmt::basic_format_context<char*, char> format_ctx( - buf, {}, fmt::detail::locale_ref(loc)); - *f.format(12345, format_ctx) = 0; - EXPECT_STREQ("12,345", buf); -} - -FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE -template <class charT> struct formatter<std::complex<double>, charT> { - private: - detail::dynamic_format_specs<char> specs_; - - public: - typename basic_format_parse_context<charT>::iterator parse( - basic_format_parse_context<charT>& ctx) { - using handler_type = - detail::dynamic_specs_handler<basic_format_parse_context<charT>>; - detail::specs_checker<handler_type> handler(handler_type(specs_, ctx), - detail::type::string_type); - auto it = parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), handler); - detail::parse_float_type_spec(specs_, ctx.error_handler()); - return it; - } - - template <class FormatContext> - typename FormatContext::iterator format(const std::complex<double>& c, - FormatContext& ctx) { - detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>( - specs_.precision, specs_.precision_ref, ctx); - auto format_specs = std::string(); - if (specs_.precision > 0) - format_specs = fmt::format(".{}", specs_.precision); - if (specs_.type) - format_specs += specs_.type; - auto real = fmt::format(ctx.locale().template get<std::locale>(), - "{:" + format_specs + "}", c.real()); - auto imag = fmt::format(ctx.locale().template get<std::locale>(), - "{:" + format_specs + "}", c.imag()); - auto fill_align_width = std::string(); - if (specs_.width > 0) - fill_align_width = fmt::format(">{}", specs_.width); - return format_to( - ctx.out(), "{:" + fill_align_width + "}", - fmt::format(c.real() != 0 ? "({0}+{1}i)" : "{1}i", real, imag)); - } -}; -FMT_END_NAMESPACE - -TEST(FormatTest, Complex) { - std::string s = fmt::format("{}", std::complex<double>(1, 2)); - EXPECT_EQ(s, "(1+2i)"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.2f}", std::complex<double>(1, 2)), "(1.00+2.00i)"); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:8}", std::complex<double>(1, 2)), " (1+2i)"); -} - -#endif // FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR diff --git a/test/mock-allocator.h b/test/mock-allocator.h index 513a62e8..dc4942f1 100644 --- a/test/mock-allocator.h +++ b/test/mock-allocator.h @@ -8,16 +8,20 @@ #ifndef FMT_MOCK_ALLOCATOR_H_ #define FMT_MOCK_ALLOCATOR_H_ -#include "fmt/format.h" -#include "gmock.h" +#include <assert.h> // assert +#include <stddef.h> // size_t + +#include <memory> // std::allocator_traits + +#include "gmock/gmock.h" template <typename T> class mock_allocator { public: mock_allocator() {} mock_allocator(const mock_allocator&) {} - typedef T value_type; - MOCK_METHOD1_T(allocate, T*(size_t n)); - MOCK_METHOD2_T(deallocate, void(T* p, size_t n)); + using value_type = T; + MOCK_METHOD(T*, allocate, (size_t)); + MOCK_METHOD(void, deallocate, (T*, size_t)); }; template <typename Allocator> class allocator_ref { @@ -30,7 +34,7 @@ template <typename Allocator> class allocator_ref { } public: - typedef typename Allocator::value_type value_type; + using value_type = typename Allocator::value_type; explicit allocator_ref(Allocator* alloc = nullptr) : alloc_(alloc) {} diff --git a/test/module-test.cc b/test/module-test.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..bd9624f9 --- /dev/null +++ b/test/module-test.cc @@ -0,0 +1,520 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - module tests +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. +// +// Copyright (c) 2021 - present, Daniela Engert +// All Rights Reserved +// {fmt} module. + +#ifdef _MSC_FULL_VER +// hide some implementation bugs in msvc +// that are not essential to users of the module. +# define FMT_HIDE_MODULE_BUGS +#endif + +#include <bit> +#include <chrono> +#include <exception> +#include <iterator> +#include <locale> +#include <memory> +#include <ostream> +#include <string> +#include <string_view> +#include <system_error> + +#if (__has_include(<fcntl.h>) || defined(__APPLE__) || \ + defined(__linux__)) && \ + (!defined(WINAPI_FAMILY) || (WINAPI_FAMILY == WINAPI_FAMILY_DESKTOP_APP)) +# include <fcntl.h> +# define FMT_USE_FCNTL 1 +#else +# define FMT_USE_FCNTL 0 +#endif +#if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__) +# define FMT_POSIX(call) _##call +#else +# define FMT_POSIX(call) call +#endif + +import fmt; + +// check for macros leaking from BMI +static bool macro_leaked = +#if defined(FMT_CORE_H_) || defined(FMT_FORMAT_H_) + true; +#else + false; +#endif + +#define FMT_OS_H_ // don't pull in os.h, neither directly nor indirectly +#include "gtest-extra.h" + +// an implicitly exported namespace must be visible [module.interface]/2.2 +TEST(module_test, namespace) { + using namespace fmt; + using namespace fmt::literals; + ASSERT_TRUE(true); +} + +namespace detail { +bool oops_detail_namespace_is_visible; +} + +namespace fmt { +bool namespace_detail_invisible() { +#if defined(FMT_HIDE_MODULE_BUGS) && defined(_MSC_FULL_VER) && \ + _MSC_FULL_VER <= 193700000 + // bug in msvc up to at least 17.7: + + // the namespace is visible even when it is neither + // implicitly nor explicitly exported + return true; +#else + using namespace detail; + // this fails to compile if fmt::detail is visible + return !oops_detail_namespace_is_visible; +#endif +} +} // namespace fmt + +// the non-exported namespace 'detail' must be invisible [module.interface]/2 +TEST(module_test, detail_namespace) { + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::namespace_detail_invisible()); +} + +// macros must not be imported from a *named* module [cpp.import]/5.1 +TEST(module_test, macros) { +#if defined(FMT_HIDE_MODULE_BUGS) && defined(_MSC_FULL_VER) && \ + _MSC_FULL_VER <= 192930130 + // bug in msvc up to 16.11-pre2: + // include-guard macros leak from BMI + // and even worse: they cannot be #undef-ined + macro_leaked = false; +#endif + EXPECT_FALSE(macro_leaked); +} + +// The following is less about functional testing (that's done elsewhere) +// but rather visibility of all client-facing overloads, reachability of +// non-exported entities, name lookup and overload resolution within +// template instantitions. +// Exercise all exported entities of the API at least once. +// Instantiate as many code paths as possible. + +TEST(module_test, to_string) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::to_string(42)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::to_string(42.0)); + + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::to_wstring(42)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::to_wstring(42.0)); +} + +TEST(module_test, format) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{:}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("-42", fmt::format("{0}", -42.0)); + + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(L"{:}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"-42", fmt::format(L"{0}", -42.0)); +} + +TEST(module_test, format_to) { + std::string s; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), "{}", 42); + EXPECT_EQ("42", s); + + char buffer[4] = {0}; + fmt::format_to(buffer, "{}", 42); + EXPECT_EQ("42", std::string_view(buffer)); + + fmt::memory_buffer mb; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(mb), "{}", 42); + EXPECT_EQ("42", std::string_view(buffer)); + + std::wstring w; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(w), L"{}", 42); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", w); + + wchar_t wbuffer[4] = {0}; + fmt::format_to(wbuffer, L"{}", 42); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", std::wstring_view(wbuffer)); + + fmt::wmemory_buffer wb; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(wb), L"{}", 42); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", std::wstring_view(wbuffer)); +} + +TEST(module_test, formatted_size) { + EXPECT_EQ(2u, fmt::formatted_size("{}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(2u, fmt::formatted_size(L"{}", 42)); +} + +TEST(module_test, format_to_n) { + std::string s; + auto result = fmt::format_to_n(std::back_inserter(s), 1, "{}", 42); + EXPECT_EQ(2u, result.size); + char buffer[4] = {0}; + fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, "{}", 12345); + + std::wstring w; + auto wresult = fmt::format_to_n(std::back_inserter(w), 1, L"{}", 42); + EXPECT_EQ(2u, wresult.size); + wchar_t wbuffer[4] = {0}; + fmt::format_to_n(wbuffer, 3, L"{}", 12345); +} + +TEST(module_test, format_args) { + auto no_args = fmt::format_args(); + EXPECT_FALSE(no_args.get(1)); + + fmt::basic_format_args args = fmt::make_format_args(42); + EXPECT_TRUE(args.max_size() > 0); + auto arg0 = args.get(0); + EXPECT_TRUE(arg0); + decltype(arg0) arg_none; + EXPECT_FALSE(arg_none); + EXPECT_TRUE(arg0.type() != arg_none.type()); +} + +TEST(module_test, wformat_args) { + auto no_args = fmt::wformat_args(); + EXPECT_FALSE(no_args.get(1)); + fmt::basic_format_args args = fmt::make_wformat_args(42); + EXPECT_TRUE(args.get(0)); +} + +TEST(module_test, dynamic_format_args) { + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> dyn_store; + dyn_store.push_back(fmt::arg("a42", 42)); + fmt::basic_format_args args = dyn_store; + EXPECT_FALSE(args.get(3)); + EXPECT_TRUE(args.get(fmt::string_view("a42"))); + + fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::wformat_context> wdyn_store; + wdyn_store.push_back(fmt::arg(L"a42", 42)); + fmt::basic_format_args wargs = wdyn_store; + EXPECT_FALSE(wargs.get(3)); + EXPECT_TRUE(wargs.get(fmt::wstring_view(L"a42"))); +} + +TEST(module_test, vformat) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::vformat("{}", fmt::make_format_args(42))); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", + fmt::vformat(fmt::wstring_view(L"{}"), fmt::make_wformat_args(42))); +} + +TEST(module_test, vformat_to) { + auto store = fmt::make_format_args(42); + std::string s; + fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(s), "{}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("42", s); + + char buffer[4] = {0}; + fmt::vformat_to(buffer, "{:}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("42", std::string_view(buffer)); + + auto wstore = fmt::make_wformat_args(42); + std::wstring w; + fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(w), L"{}", wstore); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", w); + + wchar_t wbuffer[4] = {0}; + fmt::vformat_to(wbuffer, L"{:}", wstore); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", std::wstring_view(wbuffer)); +} + +TEST(module_test, vformat_to_n) { + auto store = fmt::make_format_args(12345); + std::string s; + auto result = fmt::vformat_to_n(std::back_inserter(s), 1, "{}", store); + char buffer[4] = {0}; + fmt::vformat_to_n(buffer, 3, "{:}", store); + + auto wstore = fmt::make_wformat_args(12345); + std::wstring w; + auto wresult = fmt::vformat_to_n(std::back_inserter(w), 1, + fmt::wstring_view(L"{}"), wstore); + wchar_t wbuffer[4] = {0}; + fmt::vformat_to_n(wbuffer, 3, fmt::wstring_view(L"{:}"), wstore); +} + +std::string as_string(std::wstring_view text) { + return {reinterpret_cast<const char*>(text.data()), + text.size() * sizeof(text[0])}; +} + +TEST(module_test, print) { + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print("{}µ", 42), "42µ"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::print(stderr, "{}µ", 4.2), "4.2µ"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::print(L"{}µ", 42), as_string(L"42µ")); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::print(stderr, L"{}µ", 4.2), as_string(L"4.2µ")); +} + +TEST(module_test, vprint) { + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::vprint("{:}µ", fmt::make_format_args(42)), "42µ"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::vprint(stderr, "{}", fmt::make_format_args(4.2)), + "4.2"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::vprint(L"{:}µ", fmt::make_wformat_args(42)), + as_string(L"42µ")); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::vprint(stderr, L"{}", fmt::make_wformat_args(42)), + as_string(L"42")); +} + +TEST(module_test, named_args) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{answer}", fmt::arg("answer", 42))); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(L"{answer}", fmt::arg(L"answer", 42))); +} + +TEST(module_test, literals) { + using namespace fmt::literals; + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{answer}", "answer"_a = 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(L"{answer}", L"answer"_a = 42)); +} + +TEST(module_test, locale) { + auto store = fmt::make_format_args(4.2); + const auto classic = std::locale::classic(); + EXPECT_EQ("4.2", fmt::format(classic, "{:L}", 4.2)); + EXPECT_EQ("4.2", fmt::vformat(classic, "{:L}", store)); + std::string s; + fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(s), classic, "{:L}", store); + EXPECT_EQ("4.2", s); + EXPECT_EQ("4.2", fmt::format("{:L}", 4.2)); + + auto wstore = fmt::make_wformat_args(4.2); + EXPECT_EQ(L"4.2", fmt::format(classic, L"{:L}", 4.2)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"4.2", fmt::vformat(classic, L"{:L}", wstore)); + std::wstring w; + fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(w), classic, L"{:L}", wstore); + EXPECT_EQ(L"4.2", w); + EXPECT_EQ(L"4.2", fmt::format(L"{:L}", 4.2)); +} + +TEST(module_test, string_view) { + fmt::string_view nsv("fmt"); + EXPECT_EQ("fmt", nsv); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::string_view("fmt") == nsv); + + fmt::wstring_view wsv(L"fmt"); + EXPECT_EQ(L"fmt", wsv); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::wstring_view(L"fmt") == wsv); +} + +TEST(module_test, memory_buffer) { + fmt::basic_memory_buffer<char, fmt::inline_buffer_size> buffer; + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buffer), "{}", "42"); + EXPECT_EQ("42", to_string(buffer)); + fmt::memory_buffer nbuffer(std::move(buffer)); + EXPECT_EQ("42", to_string(nbuffer)); + buffer = std::move(nbuffer); + EXPECT_EQ("42", to_string(buffer)); + nbuffer.clear(); + EXPECT_EQ(0u, to_string(nbuffer).size()); + + fmt::wmemory_buffer wbuffer; + EXPECT_EQ(0u, to_string(wbuffer).size()); +} + +TEST(module_test, is_char) { + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::is_char<char>()); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::is_char<wchar_t>()); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::is_char<char8_t>()); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::is_char<char16_t>()); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::is_char<char32_t>()); + EXPECT_FALSE(fmt::is_char<signed char>()); +} + +TEST(module_test, ptr) { + uintptr_t answer = 42; + auto p = std::bit_cast<int*>(answer); + EXPECT_EQ("0x2a", fmt::to_string(fmt::ptr(p))); + std::unique_ptr<int> up(p); + EXPECT_EQ("0x2a", fmt::to_string(fmt::ptr(up))); + up.release(); + auto sp = std::make_shared<int>(0); + p = sp.get(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(fmt::ptr(p)), fmt::to_string(fmt::ptr(sp))); +} + +TEST(module_test, errors) { + auto store = fmt::make_format_args(42); + EXPECT_THROW(throw fmt::format_error("oops"), std::exception); + EXPECT_THROW(throw fmt::vsystem_error(0, "{}", store), std::system_error); + EXPECT_THROW(throw fmt::system_error(0, "{}", 42), std::system_error); + + fmt::memory_buffer buffer; + fmt::format_system_error(buffer, 0, "oops"); + auto oops = to_string(buffer); + EXPECT_TRUE(oops.size() > 0); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::report_system_error(0, "oops"), oops + '\n'); + +#ifdef _WIN32 + EXPECT_THROW(throw fmt::vwindows_error(0, "{}", store), std::system_error); + EXPECT_THROW(throw fmt::windows_error(0, "{}", 42), std::system_error); + output_redirect redirect(stderr); + fmt::report_windows_error(0, "oops"); + EXPECT_TRUE(redirect.restore_and_read().size() > 0); +#endif +} + +TEST(module_test, error_code) { + EXPECT_EQ("generic:42", + fmt::format("{0}", std::error_code(42, std::generic_category()))); + EXPECT_EQ("system:42", + fmt::format("{0}", std::error_code(42, fmt::system_category()))); + EXPECT_EQ(L"generic:42", + fmt::format(L"{0}", std::error_code(42, std::generic_category()))); +} + +TEST(module_test, format_int) { + fmt::format_int sanswer(42); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::string_view(sanswer.data(), sanswer.size())); + fmt::format_int uanswer(42u); + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::string_view(uanswer.data(), uanswer.size())); +} + +struct test_formatter : fmt::formatter<char> { + bool check() { return true; } +}; + +TEST(module_test, formatter) { EXPECT_TRUE(test_formatter{}.check()); } + +TEST(module_test, join) { + int arr[3] = {1, 2, 3}; + std::vector<double> vec{1.0, 2.0, 3.0}; + std::initializer_list<int> il{1, 2, 3}; + auto sep = fmt::string_view(", "); + EXPECT_EQ("1, 2, 3", to_string(fmt::join(arr + 0, arr + 3, sep))); + EXPECT_EQ("1, 2, 3", to_string(fmt::join(arr, sep))); + EXPECT_EQ("1, 2, 3", to_string(fmt::join(vec.begin(), vec.end(), sep))); + EXPECT_EQ("1, 2, 3", to_string(fmt::join(vec, sep))); + EXPECT_EQ("1, 2, 3", to_string(fmt::join(il, sep))); + + auto wsep = fmt::wstring_view(L", "); + EXPECT_EQ(L"1, 2, 3", fmt::format(L"{}", fmt::join(arr + 0, arr + 3, wsep))); + EXPECT_EQ(L"1, 2, 3", fmt::format(L"{}", fmt::join(arr, wsep))); + EXPECT_EQ(L"1, 2, 3", fmt::format(L"{}", fmt::join(il, wsep))); +} + +TEST(module_test, time) { + auto time_now = std::time(nullptr); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::localtime(time_now).tm_year > 120); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::gmtime(time_now).tm_year > 120); + auto chrono_now = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::gmtime(chrono_now).tm_year > 120); +} + +TEST(module_test, time_point) { + auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); + std::string_view past("2021-05-20 10:30:15"); + EXPECT_TRUE(past < fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", now)); + std::wstring_view wpast(L"2021-05-20 10:30:15"); + EXPECT_TRUE(wpast < fmt::format(L"{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", now)); +} + +TEST(module_test, time_duration) { + using us = std::chrono::duration<double, std::micro>; + EXPECT_EQ("42s", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::seconds{42})); + EXPECT_EQ("4.2µs", fmt::format("{:3.1}", us{4.234})); + EXPECT_EQ("4.2µs", fmt::format(std::locale::classic(), "{:L}", us{4.2})); + + EXPECT_EQ(L"42s", fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::seconds{42})); + EXPECT_EQ(L"4.2µs", fmt::format(L"{:3.1}", us{4.234})); + EXPECT_EQ(L"4.2µs", fmt::format(std::locale::classic(), L"{:L}", us{4.2})); +} + +TEST(module_test, weekday) { + EXPECT_EQ("Mon", fmt::format(std::locale::classic(), "{}", fmt::weekday(1))); +} + +TEST(module_test, printf) { + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::printf("%f", 42.123456), "42.123456"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::printf("%d", 42), "42"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::printf(L"%f", 42.123456), as_string(L"42.123456")); + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::printf(L"%d", 42), as_string(L"42")); +} + +TEST(module_test, fprintf) { + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::fprintf(stderr, "%d", 42), "42"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::fprintf(stderr, L"%d", 42), as_string(L"42")); +} + +TEST(module_test, sprintf) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::sprintf("%d", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::sprintf(L"%d", 42)); +} + +TEST(module_test, vprintf) { + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::vprintf("%d", fmt::make_printf_args(42)), "42"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::vprintf(L"%d", fmt::make_wprintf_args(42)), + as_string(L"42")); +} + +TEST(module_test, vfprintf) { + auto args = fmt::make_printf_args(42); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::vfprintf(stderr, "%d", args), "42"); + auto wargs = fmt::make_wprintf_args(42); + EXPECT_WRITE(stderr, fmt::vfprintf(stderr, L"%d", wargs), as_string(L"42")); +} + +TEST(module_test, vsprintf) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::vsprintf("%d", fmt::make_printf_args(42))); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::vsprintf(L"%d", fmt::make_wprintf_args(42))); +} + +TEST(module_test, color) { + auto fg_check = fg(fmt::rgb(255, 200, 30)); + auto bg_check = bg(fmt::color::dark_slate_gray) | fmt::emphasis::italic; + auto emphasis_check = fmt::emphasis::underline | fmt::emphasis::bold; + EXPECT_EQ("\x1B[30m42\x1B[0m", + fmt::format(fg(fmt::terminal_color::black), "{}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"\x1B[30m42\x1B[0m", + fmt::format(fg(fmt::terminal_color::black), L"{}", 42)); +} + +TEST(module_test, cstring_view) { + auto s = "fmt"; + EXPECT_EQ(s, fmt::cstring_view(s).c_str()); + auto w = L"fmt"; + EXPECT_EQ(w, fmt::wcstring_view(w).c_str()); +} + +TEST(module_test, buffered_file) { + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::buffered_file{}.get() == nullptr); +} + +TEST(module_test, output_file) { +#ifdef __clang__ + fmt::println("\033[0;33m[=disabled=] {}\033[0;0m", + "Clang 16.0 emits multiple copies of vtables"); +#else + fmt::ostream out = fmt::output_file("module-test", fmt::buffer_size = 1); + out.close(); +#endif +} + +struct custom_context { + using char_type = char; + using parse_context_type = fmt::format_parse_context; +}; + +TEST(module_test, custom_context) { + fmt::basic_format_arg<custom_context> custom_arg; + EXPECT_TRUE(!custom_arg); +} + +TEST(module_test, compile_format_string) { + using namespace fmt::literals; +#ifdef __clang__ + fmt::println("\033[0;33m[=disabled=] {}\033[0;0m", + "Clang 16.0 fails to import user-defined literals"); +#else + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{0:x}"_cf, 0x42)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(L"{:}"_cf, 42)); + EXPECT_EQ("4.2", fmt::format("{arg:3.1f}"_cf, "arg"_a = 4.2)); + EXPECT_EQ(L" 42", fmt::format(L"{arg:>3}"_cf, L"arg"_a = L"42")); +#endif +} diff --git a/test/noexception-test.cc b/test/noexception-test.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..bf3472fd --- /dev/null +++ b/test/noexception-test.cc @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - Noexception tests +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#include "fmt/args.h" +#include "fmt/chrono.h" +#include "fmt/color.h" +#include "fmt/compile.h" +#include "fmt/core.h" +#include "fmt/format.h" +#include "fmt/os.h" +#include "fmt/ostream.h" +#include "fmt/printf.h" +#include "fmt/ranges.h" +#include "fmt/xchar.h" diff --git a/test/os-test.cc b/test/os-test.cc index 359b5ff8..1e6c7c4b 100644 --- a/test/os-test.cc +++ b/test/os-test.cc @@ -14,96 +14,49 @@ #include "gtest-extra.h" #include "util.h" -#ifdef fileno -# undef fileno -#endif - using fmt::buffered_file; -using fmt::error_code; +using testing::HasSubstr; +using wstring_view = fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t>; #ifdef _WIN32 # include <windows.h> -TEST(UtilTest, UTF16ToUTF8) { - std::string s = "ёжик"; - fmt::detail::utf16_to_utf8 u(L"\x0451\x0436\x0438\x043A"); - EXPECT_EQ(s, u.str()); - EXPECT_EQ(s.size(), u.size()); -} - -TEST(UtilTest, UTF16ToUTF8EmptyString) { - std::string s = ""; - fmt::detail::utf16_to_utf8 u(L""); - EXPECT_EQ(s, u.str()); - EXPECT_EQ(s.size(), u.size()); -} - -template <typename Converter, typename Char> -void check_utf_conversion_error( - const char* message, - fmt::basic_string_view<Char> str = fmt::basic_string_view<Char>(0, 1)) { - fmt::memory_buffer out; - fmt::detail::format_windows_error(out, ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER, message); - fmt::system_error error(0, ""); - try { - (Converter)(str); - } catch (const fmt::system_error& e) { - error = e; - } - EXPECT_EQ(ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER, error.error_code()); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(out), error.what()); -} - -TEST(UtilTest, UTF16ToUTF8Error) { - check_utf_conversion_error<fmt::detail::utf16_to_utf8, wchar_t>( - "cannot convert string from UTF-16 to UTF-8"); -} - -TEST(UtilTest, UTF16ToUTF8Convert) { - fmt::detail::utf16_to_utf8 u; - EXPECT_EQ(ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER, u.convert(fmt::wstring_view(0, 1))); - EXPECT_EQ(ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER, - u.convert(fmt::wstring_view(L"foo", INT_MAX + 1u))); -} - -TEST(UtilTest, FormatWindowsError) { - LPWSTR message = 0; - FormatMessageW(FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | - FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS, - 0, ERROR_FILE_EXISTS, - MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), - reinterpret_cast<LPWSTR>(&message), 0, 0); - fmt::detail::utf16_to_utf8 utf8_message(message); +TEST(os_test, format_windows_error) { + LPWSTR message = nullptr; + auto result = FormatMessageW( + FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | + FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS, + nullptr, ERROR_FILE_EXISTS, MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), + reinterpret_cast<LPWSTR>(&message), 0, nullptr); + auto utf8_message = + fmt::detail::to_utf8<wchar_t>(wstring_view(message, result - 2)); LocalFree(message); fmt::memory_buffer actual_message; fmt::detail::format_windows_error(actual_message, ERROR_FILE_EXISTS, "test"); EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("test: {}", utf8_message.str()), fmt::to_string(actual_message)); actual_message.resize(0); - auto max_size = fmt::detail::max_value<size_t>() / 2; - fmt::detail::format_windows_error(actual_message, ERROR_FILE_EXISTS, - fmt::string_view(nullptr, max_size)); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("error {}", ERROR_FILE_EXISTS), - fmt::to_string(actual_message)); } -TEST(UtilTest, FormatLongWindowsError) { - LPWSTR message = 0; +TEST(os_test, format_long_windows_error) { + LPWSTR message = nullptr; // this error code is not available on all Windows platforms and // Windows SDKs, so do not fail the test if the error string cannot // be retrieved. - const int provisioning_not_allowed = - 0x80284013L /*TBS_E_PROVISIONING_NOT_ALLOWED*/; - if (FormatMessageW(FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | - FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | - FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS, - 0, static_cast<DWORD>(provisioning_not_allowed), - MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), - reinterpret_cast<LPWSTR>(&message), 0, 0) == 0) { + int provisioning_not_allowed = 0x80284013L; // TBS_E_PROVISIONING_NOT_ALLOWED + auto result = FormatMessageW( + FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | + FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS, + nullptr, static_cast<DWORD>(provisioning_not_allowed), + MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), + reinterpret_cast<LPWSTR>(&message), 0, nullptr); + if (result == 0) { + LocalFree(message); return; } - fmt::detail::utf16_to_utf8 utf8_message(message); + auto utf8_message = + fmt::detail::to_utf8<wchar_t>(wstring_view(message, result - 2)); LocalFree(message); fmt::memory_buffer actual_message; fmt::detail::format_windows_error(actual_message, provisioning_not_allowed, @@ -112,20 +65,20 @@ TEST(UtilTest, FormatLongWindowsError) { fmt::to_string(actual_message)); } -TEST(UtilTest, WindowsError) { - fmt::system_error error(0, ""); +TEST(os_test, windows_error) { + auto error = std::system_error(std::error_code()); try { throw fmt::windows_error(ERROR_FILE_EXISTS, "test {}", "error"); - } catch (const fmt::system_error& e) { + } catch (const std::system_error& e) { error = e; } fmt::memory_buffer message; fmt::detail::format_windows_error(message, ERROR_FILE_EXISTS, "test error"); - EXPECT_EQ(to_string(message), error.what()); - EXPECT_EQ(ERROR_FILE_EXISTS, error.error_code()); + EXPECT_THAT(error.what(), HasSubstr(to_string(message))); + EXPECT_EQ(ERROR_FILE_EXISTS, error.code().value()); } -TEST(UtilTest, ReportWindowsError) { +TEST(os_test, report_windows_error) { fmt::memory_buffer out; fmt::detail::format_windows_error(out, ERROR_FILE_EXISTS, "test error"); out.push_back('\n'); @@ -134,36 +87,41 @@ TEST(UtilTest, ReportWindowsError) { fmt::to_string(out)); } +# if FMT_USE_FCNTL && !defined(__MINGW32__) +TEST(file_test, open_windows_file) { + using fmt::file; + file out = file::open_windows_file(L"test-file", + file::WRONLY | file::CREATE | file::TRUNC); + out.write("x", 1); + file in = file::open_windows_file(L"test-file", file::RDONLY); + EXPECT_READ(in, "x"); +} +# endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL && !defined(__MINGW32__) + #endif // _WIN32 #if FMT_USE_FCNTL using fmt::file; -// Checks if the file is open by reading one character from it. -static bool isopen(int fd) { +bool isclosed(int fd) { char buffer; - return FMT_POSIX(read(fd, &buffer, 1)) == 1; -} - -static bool isclosed(int fd) { - char buffer; - std::streamsize result = 0; + auto result = std::streamsize(); SUPPRESS_ASSERT(result = FMT_POSIX(read(fd, &buffer, 1))); return result == -1 && errno == EBADF; } // Opens a file for reading. -static file open_file() { +file open_file() { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); - write_end.write(FILE_CONTENT, std::strlen(FILE_CONTENT)); + write_end.write(file_content, std::strlen(file_content)); write_end.close(); return read_end; } // Attempts to write a string to a file. -static void write(file& f, fmt::string_view s) { +void write(file& f, fmt::string_view s) { size_t num_chars_left = s.size(); const char* ptr = s.data(); do { @@ -175,12 +133,12 @@ static void write(file& f, fmt::string_view s) { } while (num_chars_left != 0); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, DefaultCtor) { - buffered_file f; +TEST(buffered_file_test, default_ctor) { + auto f = buffered_file(); EXPECT_TRUE(f.get() == nullptr); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, MoveCtor) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, move_ctor) { buffered_file bf = open_buffered_file(); FILE* fp = bf.get(); EXPECT_TRUE(fp != nullptr); @@ -189,7 +147,7 @@ TEST(BufferedFileTest, MoveCtor) { EXPECT_TRUE(bf.get() == nullptr); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, MoveAssignment) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, move_assignment) { buffered_file bf = open_buffered_file(); FILE* fp = bf.get(); EXPECT_TRUE(fp != nullptr); @@ -199,45 +157,46 @@ TEST(BufferedFileTest, MoveAssignment) { EXPECT_TRUE(bf.get() == nullptr); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, MoveAssignmentClosesFile) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, move_assignment_closes_file) { buffered_file bf = open_buffered_file(); buffered_file bf2 = open_buffered_file(); - int old_fd = bf2.fileno(); + int old_fd = bf2.descriptor(); bf2 = std::move(bf); EXPECT_TRUE(isclosed(old_fd)); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, MoveFromTemporaryInCtor) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, move_from_temporary_in_ctor) { FILE* fp = nullptr; - buffered_file f(open_buffered_file(&fp)); + buffered_file f = open_buffered_file(&fp); EXPECT_EQ(fp, f.get()); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, MoveFromTemporaryInAssignment) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, move_from_temporary_in_assignment) { FILE* fp = nullptr; - buffered_file f; + auto f = buffered_file(); f = open_buffered_file(&fp); EXPECT_EQ(fp, f.get()); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, MoveFromTemporaryInAssignmentClosesFile) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, move_from_temporary_in_assignment_closes_file) { buffered_file f = open_buffered_file(); - int old_fd = f.fileno(); + int old_fd = f.descriptor(); f = open_buffered_file(); EXPECT_TRUE(isclosed(old_fd)); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, CloseFileInDtor) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, close_file_in_dtor) { int fd = 0; { buffered_file f = open_buffered_file(); - fd = f.fileno(); + fd = f.descriptor(); } EXPECT_TRUE(isclosed(fd)); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, CloseErrorInDtor) { - std::unique_ptr<buffered_file> f(new buffered_file(open_buffered_file())); +TEST(buffered_file_test, close_error_in_dtor) { + auto f = + std::unique_ptr<buffered_file>(new buffered_file(open_buffered_file())); EXPECT_WRITE( stderr, { @@ -245,63 +204,63 @@ TEST(BufferedFileTest, CloseErrorInDtor) { // otherwise the system may recycle closed file descriptor when // redirecting the output in EXPECT_STDERR and the second close // will break output redirection. - FMT_POSIX(close(f->fileno())); + FMT_POSIX(close(f->descriptor())); SUPPRESS_ASSERT(f.reset(nullptr)); }, - format_system_error(EBADF, "cannot close file") + "\n"); + system_error_message(EBADF, "cannot close file") + "\n"); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, Close) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, close) { buffered_file f = open_buffered_file(); - int fd = f.fileno(); + int fd = f.descriptor(); f.close(); EXPECT_TRUE(f.get() == nullptr); EXPECT_TRUE(isclosed(fd)); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, CloseError) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, close_error) { buffered_file f = open_buffered_file(); - FMT_POSIX(close(f.fileno())); + FMT_POSIX(close(f.descriptor())); EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR_NOASSERT(f.close(), EBADF, "cannot close file"); EXPECT_TRUE(f.get() == nullptr); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, Fileno) { - buffered_file f; -# ifndef __COVERITY__ - // fileno on a null FILE pointer either crashes or returns an error. - // Disable Coverity because this is intentional. - EXPECT_DEATH_IF_SUPPORTED( - { - try { - f.fileno(); - } catch (const fmt::system_error&) { - std::exit(1); - } - }, - ""); -# endif - f = open_buffered_file(); - EXPECT_TRUE(f.fileno() != -1); - file copy = file::dup(f.fileno()); - EXPECT_READ(copy, FILE_CONTENT); +TEST(buffered_file_test, descriptor) { + auto f = open_buffered_file(); + EXPECT_TRUE(f.descriptor() != -1); + file copy = file::dup(f.descriptor()); + EXPECT_READ(copy, file_content); } -TEST(OStreamTest, Move) { +TEST(ostream_test, move) { fmt::ostream out = fmt::output_file("test-file"); fmt::ostream moved(std::move(out)); moved.print("hello"); } -TEST(OStreamTest, Print) { +TEST(ostream_test, move_while_holding_data) { + { + fmt::ostream out = fmt::output_file("test-file"); + out.print("Hello, "); + fmt::ostream moved(std::move(out)); + moved.print("world!\n"); + } + { + file in("test-file", file::RDONLY); + EXPECT_READ(in, "Hello, world!\n"); + } +} + +TEST(ostream_test, print) { fmt::ostream out = fmt::output_file("test-file"); - out.print("The answer is {}.\n", 42); + out.print("The answer is {}.\n", + fmt::join(std::initializer_list<int>{42}, ", ")); out.close(); file in("test-file", file::RDONLY); EXPECT_READ(in, "The answer is 42.\n"); } -TEST(OStreamTest, BufferBoundary) { +TEST(ostream_test, buffer_boundary) { auto str = std::string(4096, 'x'); fmt::ostream out = fmt::output_file("test-file"); out.print("{}", str); @@ -311,33 +270,57 @@ TEST(OStreamTest, BufferBoundary) { EXPECT_READ(in, str + str); } -TEST(OStreamTest, BufferSize) { - fmt::ostream out = fmt::output_file("test-file", fmt::buffer_size=1); +TEST(ostream_test, buffer_size) { + fmt::ostream out = fmt::output_file("test-file", fmt::buffer_size = 1); out.print("{}", "foo"); out.close(); file in("test-file", file::RDONLY); EXPECT_READ(in, "foo"); } -TEST(FileTest, DefaultCtor) { +TEST(ostream_test, truncate) { + { + fmt::ostream out = fmt::output_file("test-file"); + out.print("0123456789"); + } + { + fmt::ostream out = fmt::output_file("test-file"); + out.print("foo"); + } + file in("test-file", file::RDONLY); + EXPECT_EQ("foo", read(in, 4)); +} + +TEST(ostream_test, flush) { + auto out = fmt::output_file("test-file"); + out.print("x"); + out.flush(); + auto in = fmt::file("test-file", file::RDONLY); + EXPECT_READ(in, "x"); +} + +TEST(file_test, default_ctor) { file f; EXPECT_EQ(-1, f.descriptor()); } -TEST(FileTest, OpenBufferedFileInCtor) { +TEST(file_test, open_buffered_file_in_ctor) { FILE* fp = safe_fopen("test-file", "w"); - std::fputs(FILE_CONTENT, fp); + std::fputs(file_content, fp); std::fclose(fp); file f("test-file", file::RDONLY); - ASSERT_TRUE(isopen(f.descriptor())); + // Check if the file is open by reading one character from it. + char buffer; + bool isopen = FMT_POSIX(read(f.descriptor(), &buffer, 1)) == 1; + ASSERT_TRUE(isopen); } -TEST(FileTest, OpenBufferedFileError) { +TEST(file_test, open_buffered_file_error) { EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(file("nonexistent", file::RDONLY), ENOENT, "cannot open file nonexistent"); } -TEST(FileTest, MoveCtor) { +TEST(file_test, move_ctor) { file f = open_file(); int fd = f.descriptor(); EXPECT_NE(-1, fd); @@ -346,7 +329,7 @@ TEST(FileTest, MoveCtor) { EXPECT_EQ(-1, f.descriptor()); } -TEST(FileTest, MoveAssignment) { +TEST(file_test, move_assignment) { file f = open_file(); int fd = f.descriptor(); EXPECT_NE(-1, fd); @@ -356,7 +339,7 @@ TEST(FileTest, MoveAssignment) { EXPECT_EQ(-1, f.descriptor()); } -TEST(FileTest, MoveAssignmentClosesFile) { +TEST(file_test, move_assignment_closes_file) { file f = open_file(); file f2 = open_file(); int old_fd = f2.descriptor(); @@ -364,34 +347,34 @@ TEST(FileTest, MoveAssignmentClosesFile) { EXPECT_TRUE(isclosed(old_fd)); } -static file OpenBufferedFile(int& fd) { +file open_buffered_file(int& fd) { file f = open_file(); fd = f.descriptor(); return f; } -TEST(FileTest, MoveFromTemporaryInCtor) { +TEST(file_test, move_from_temporary_in_ctor) { int fd = 0xdead; - file f(OpenBufferedFile(fd)); + file f(open_buffered_file(fd)); EXPECT_EQ(fd, f.descriptor()); } -TEST(FileTest, MoveFromTemporaryInAssignment) { +TEST(file_test, move_from_temporary_in_assignment) { int fd = 0xdead; file f; - f = OpenBufferedFile(fd); + f = open_buffered_file(fd); EXPECT_EQ(fd, f.descriptor()); } -TEST(FileTest, MoveFromTemporaryInAssignmentClosesFile) { +TEST(file_test, move_from_temporary_in_assignment_closes_file) { int fd = 0xdead; file f = open_file(); int old_fd = f.descriptor(); - f = OpenBufferedFile(fd); + f = open_buffered_file(fd); EXPECT_TRUE(isclosed(old_fd)); } -TEST(FileTest, CloseFileInDtor) { +TEST(file_test, close_file_in_dtor) { int fd = 0; { file f = open_file(); @@ -400,7 +383,7 @@ TEST(FileTest, CloseFileInDtor) { EXPECT_TRUE(isclosed(fd)); } -TEST(FileTest, CloseErrorInDtor) { +TEST(file_test, close_error_in_dtor) { std::unique_ptr<file> f(new file(open_file())); EXPECT_WRITE( stderr, @@ -412,10 +395,10 @@ TEST(FileTest, CloseErrorInDtor) { FMT_POSIX(close(f->descriptor())); SUPPRESS_ASSERT(f.reset(nullptr)); }, - format_system_error(EBADF, "cannot close file") + "\n"); + system_error_message(EBADF, "cannot close file") + "\n"); } -TEST(FileTest, Close) { +TEST(file_test, close) { file f = open_file(); int fd = f.descriptor(); f.close(); @@ -423,19 +406,19 @@ TEST(FileTest, Close) { EXPECT_TRUE(isclosed(fd)); } -TEST(FileTest, CloseError) { +TEST(file_test, close_error) { file f = open_file(); FMT_POSIX(close(f.descriptor())); EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR_NOASSERT(f.close(), EBADF, "cannot close file"); EXPECT_EQ(-1, f.descriptor()); } -TEST(FileTest, Read) { +TEST(file_test, read) { file f = open_file(); - EXPECT_READ(f, FILE_CONTENT); + EXPECT_READ(f, file_content); } -TEST(FileTest, ReadError) { +TEST(file_test, read_error) { file f("test-file", file::WRONLY); char buf; // We intentionally read from a file opened in the write-only mode to @@ -443,7 +426,7 @@ TEST(FileTest, ReadError) { EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(f.read(&buf, 1), EBADF, "cannot read from file"); } -TEST(FileTest, Write) { +TEST(file_test, write) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); write(write_end, "test"); @@ -451,61 +434,61 @@ TEST(FileTest, Write) { EXPECT_READ(read_end, "test"); } -TEST(FileTest, WriteError) { +TEST(file_test, write_error) { file f("test-file", file::RDONLY); // We intentionally write to a file opened in the read-only mode to // cause error. EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(f.write(" ", 1), EBADF, "cannot write to file"); } -TEST(FileTest, Dup) { +TEST(file_test, dup) { file f = open_file(); file copy = file::dup(f.descriptor()); EXPECT_NE(f.descriptor(), copy.descriptor()); - EXPECT_EQ(FILE_CONTENT, read(copy, std::strlen(FILE_CONTENT))); + EXPECT_EQ(file_content, read(copy, std::strlen(file_content))); } # ifndef __COVERITY__ -TEST(FileTest, DupError) { +TEST(file_test, dup_error) { int value = -1; EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR_NOASSERT(file::dup(value), EBADF, "cannot duplicate file descriptor -1"); } # endif -TEST(FileTest, Dup2) { +TEST(file_test, dup2) { file f = open_file(); file copy = open_file(); f.dup2(copy.descriptor()); EXPECT_NE(f.descriptor(), copy.descriptor()); - EXPECT_READ(copy, FILE_CONTENT); + EXPECT_READ(copy, file_content); } -TEST(FileTest, Dup2Error) { +TEST(file_test, dup2_error) { file f = open_file(); EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR_NOASSERT( f.dup2(-1), EBADF, fmt::format("cannot duplicate file descriptor {} to -1", f.descriptor())); } -TEST(FileTest, Dup2NoExcept) { +TEST(file_test, dup2_noexcept) { file f = open_file(); file copy = open_file(); - error_code ec; + std::error_code ec; f.dup2(copy.descriptor(), ec); - EXPECT_EQ(ec.get(), 0); + EXPECT_EQ(ec.value(), 0); EXPECT_NE(f.descriptor(), copy.descriptor()); - EXPECT_READ(copy, FILE_CONTENT); + EXPECT_READ(copy, file_content); } -TEST(FileTest, Dup2NoExceptError) { +TEST(file_test, dup2_noexcept_error) { file f = open_file(); - error_code ec; + std::error_code ec; SUPPRESS_ASSERT(f.dup2(-1, ec)); - EXPECT_EQ(EBADF, ec.get()); + EXPECT_EQ(EBADF, ec.value()); } -TEST(FileTest, Pipe) { +TEST(file_test, pipe) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); EXPECT_NE(-1, read_end.descriptor()); @@ -514,19 +497,10 @@ TEST(FileTest, Pipe) { EXPECT_READ(read_end, "test"); } -TEST(FileTest, Fdopen) { +TEST(file_test, fdopen) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); int read_fd = read_end.descriptor(); EXPECT_EQ(read_fd, FMT_POSIX(fileno(read_end.fdopen("r").get()))); } - -# ifdef FMT_LOCALE -TEST(LocaleTest, Strtod) { - fmt::locale loc; - const char *start = "4.2", *ptr = start; - EXPECT_EQ(4.2, loc.strtod(ptr)); - EXPECT_EQ(start + 3, ptr); -} -# endif #endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL diff --git a/test/ostream-test.cc b/test/ostream-test.cc index 4f432fb9..b2d15466 100644 --- a/test/ostream-test.cc +++ b/test/ostream-test.cc @@ -5,16 +5,19 @@ // // For the license information refer to format.h. +#include <fstream> + #include "fmt/format.h" +using fmt::runtime; + struct test {}; // Test that there is no issues with specializations when fmt/ostream.h is // included after fmt/format.h. namespace fmt { template <> struct formatter<test> : formatter<int> { - template <typename FormatContext> - typename FormatContext::iterator format(const test&, FormatContext& ctx) { + auto format(const test&, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { return formatter<int>::format(42, ctx); } }; @@ -22,21 +25,19 @@ template <> struct formatter<test> : formatter<int> { #include <sstream> +#include "fmt/compile.h" #include "fmt/ostream.h" #include "fmt/ranges.h" -#include "gmock.h" +#include "gmock/gmock.h" #include "gtest-extra.h" #include "util.h" -using fmt::format; -using fmt::format_error; - -static std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Date& d) { +auto operator<<(std::ostream& os, const date& d) -> std::ostream& { os << d.year() << '-' << d.month() << '-' << d.day(); return os; } -static std::wostream& operator<<(std::wostream& os, const Date& d) { +auto operator<<(std::wostream& os, const date& d) -> std::wostream& { os << d.year() << L'-' << d.month() << L'-' << d.day(); return os; } @@ -44,99 +45,81 @@ static std::wostream& operator<<(std::wostream& os, const Date& d) { // Make sure that overloaded comma operators do no harm to is_streamable. struct type_with_comma_op {}; template <typename T> void operator,(type_with_comma_op, const T&); -template <typename T> type_with_comma_op operator<<(T&, const Date&); +template <typename T> type_with_comma_op operator<<(T&, const date&); enum streamable_enum {}; -static std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, streamable_enum) { - return os << "streamable_enum"; -} -static std::wostream& operator<<(std::wostream& os, streamable_enum) { - return os << L"streamable_enum"; +auto operator<<(std::ostream& os, streamable_enum) -> std::ostream& { + return os << "streamable_enum"; } enum unstreamable_enum {}; +auto format_as(unstreamable_enum e) -> int { return e; } -TEST(OStreamTest, Enum) { - EXPECT_EQ("streamable_enum", fmt::format("{}", streamable_enum())); - EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{}", unstreamable_enum())); - EXPECT_EQ(L"streamable_enum", fmt::format(L"{}", streamable_enum())); - EXPECT_EQ(L"0", fmt::format(L"{}", unstreamable_enum())); +struct empty_test {}; +auto operator<<(std::ostream& os, empty_test) -> std::ostream& { + return os << ""; } -struct test_arg_formatter - : fmt::detail::arg_formatter<fmt::format_context::iterator, char> { - fmt::format_parse_context parse_ctx; - test_arg_formatter(fmt::format_context& ctx, fmt::format_specs& s) - : fmt::detail::arg_formatter<fmt::format_context::iterator, char>( - ctx, &parse_ctx, &s), - parse_ctx("") {} -}; +namespace fmt { +template <> struct formatter<test_string> : ostream_formatter {}; +template <> struct formatter<date> : ostream_formatter {}; +template <> struct formatter<streamable_enum> : ostream_formatter {}; +template <> struct formatter<empty_test> : ostream_formatter {}; +} // namespace fmt -TEST(OStreamTest, CustomArg) { - fmt::memory_buffer buffer; - fmt::format_context ctx(fmt::detail::buffer_appender<char>{buffer}, - fmt::format_args()); - fmt::format_specs spec; - test_arg_formatter af(ctx, spec); - fmt::visit_format_arg( - af, fmt::detail::make_arg<fmt::format_context>(streamable_enum())); - EXPECT_EQ("streamable_enum", std::string(buffer.data(), buffer.size())); +TEST(ostream_test, enum) { + EXPECT_EQ("streamable_enum", fmt::format("{}", streamable_enum())); + EXPECT_EQ("0", fmt::format("{}", unstreamable_enum())); } -TEST(OStreamTest, Format) { - EXPECT_EQ("a string", format("{0}", TestString("a string"))); - std::string s = format("The date is {0}", Date(2012, 12, 9)); - EXPECT_EQ("The date is 2012-12-9", s); - Date date(2012, 12, 9); - EXPECT_EQ(L"The date is 2012-12-9", - format(L"The date is {0}", Date(2012, 12, 9))); +TEST(ostream_test, format) { + EXPECT_EQ("a string", fmt::format("{0}", test_string("a string"))); + EXPECT_EQ("The date is 2012-12-9", + fmt::format("The date is {0}", date(2012, 12, 9))); } -TEST(OStreamTest, FormatSpecs) { - EXPECT_EQ("def ", format("{0:<5}", TestString("def"))); - EXPECT_EQ(" def", format("{0:>5}", TestString("def"))); -#if FMT_DEPRECATED_NUMERIC_ALIGN - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:=5}", TestString("def")), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); -#endif - EXPECT_EQ(" def ", format("{0:^5}", TestString("def"))); - EXPECT_EQ("def**", format("{0:*<5}", TestString("def"))); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:+}", TestString()), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:-}", TestString()), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0: }", TestString()), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:#}", TestString()), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(format("{0:05}", TestString()), format_error, - "format specifier requires numeric argument"); - EXPECT_EQ("test ", format("{0:13}", TestString("test"))); - EXPECT_EQ("test ", format("{0:{1}}", TestString("test"), 13)); - EXPECT_EQ("te", format("{0:.2}", TestString("test"))); - EXPECT_EQ("te", format("{0:.{1}}", TestString("test"), 2)); +TEST(ostream_test, format_specs) { + using fmt::format_error; + EXPECT_EQ("def ", fmt::format("{0:<5}", test_string("def"))); + EXPECT_EQ(" def", fmt::format("{0:>5}", test_string("def"))); + EXPECT_EQ(" def ", fmt::format("{0:^5}", test_string("def"))); + EXPECT_EQ("def**", fmt::format("{0:*<5}", test_string("def"))); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:+}"), test_string()), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:-}"), test_string()), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0: }"), test_string()), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:#}"), test_string()), + format_error, "invalid format specifier"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format(runtime("{0:05}"), test_string()), + format_error, "format specifier requires numeric argument"); + EXPECT_EQ("test ", fmt::format("{0:13}", test_string("test"))); + EXPECT_EQ("test ", fmt::format("{0:{1}}", test_string("test"), 13)); + EXPECT_EQ("te", fmt::format("{0:.2}", test_string("test"))); + EXPECT_EQ("te", fmt::format("{0:.{1}}", test_string("test"), 2)); } -struct EmptyTest {}; -static std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, EmptyTest) { - return os << ""; +TEST(ostream_test, empty_custom_output) { + EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format("{}", empty_test())); } -TEST(OStreamTest, EmptyCustomOutput) { - EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format("{}", EmptyTest())); -} +TEST(ostream_test, print) { + { + std::ostringstream os; + fmt::print(os, "Don't {}!", "panic"); + EXPECT_EQ("Don't panic!", os.str()); + } -TEST(OStreamTest, Print) { - std::ostringstream os; - fmt::print(os, "Don't {}!", "panic"); - EXPECT_EQ("Don't panic!", os.str()); - std::wostringstream wos; - fmt::print(wos, L"Don't {}!", L"panic"); - EXPECT_EQ(L"Don't panic!", wos.str()); + { + std::ostringstream os; + fmt::println(os, "Don't {}!", "panic"); + EXPECT_EQ("Don't panic!\n", os.str()); + } } -TEST(OStreamTest, WriteToOStream) { +TEST(ostream_test, write_to_ostream) { std::ostringstream os; fmt::memory_buffer buffer; const char* foo = "foo"; @@ -145,32 +128,33 @@ TEST(OStreamTest, WriteToOStream) { EXPECT_EQ("foo", os.str()); } -TEST(OStreamTest, WriteToOStreamMaxSize) { - size_t max_size = fmt::detail::max_value<size_t>(); - std::streamsize max_streamsize = fmt::detail::max_value<std::streamsize>(); +TEST(ostream_test, write_to_ostream_max_size) { + auto max_size = fmt::detail::max_value<size_t>(); + auto max_streamsize = fmt::detail::max_value<std::streamsize>(); if (max_size <= fmt::detail::to_unsigned(max_streamsize)) return; struct test_buffer final : fmt::detail::buffer<char> { explicit test_buffer(size_t size) - : fmt::detail::buffer<char>(nullptr, size, size) {} - void grow(size_t) {} + : fmt::detail::buffer<char>(nullptr, size, size) {} + void grow(size_t) override {} } buffer(max_size); struct mock_streambuf : std::streambuf { - MOCK_METHOD2(xsputn, std::streamsize(const void* s, std::streamsize n)); - std::streamsize xsputn(const char* s, std::streamsize n) { + MOCK_METHOD(std::streamsize, xsputn, (const void*, std::streamsize)); + auto xsputn(const char* s, std::streamsize n) -> std::streamsize override { const void* v = s; return xsputn(v, n); } } streambuf; struct test_ostream : std::ostream { - explicit test_ostream(mock_streambuf& buffer) : std::ostream(&buffer) {} + explicit test_ostream(mock_streambuf& output_buffer) + : std::ostream(&output_buffer) {} } os(streambuf); testing::InSequence sequence; const char* data = nullptr; - typedef std::make_unsigned<std::streamsize>::type ustreamsize; + using ustreamsize = std::make_unsigned<std::streamsize>::type; ustreamsize size = max_size; do { auto n = std::min(size, fmt::detail::to_unsigned(max_streamsize)); @@ -182,149 +166,126 @@ TEST(OStreamTest, WriteToOStreamMaxSize) { fmt::detail::write_buffer(os, buffer); } -TEST(OStreamTest, Join) { +TEST(ostream_test, join) { int v[3] = {1, 2, 3}; EXPECT_EQ("1, 2, 3", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(v, v + 3, ", "))); } +TEST(ostream_test, join_fallback_formatter) { + auto strs = std::vector<test_string>{test_string("foo"), test_string("bar")}; + EXPECT_EQ("foo, bar", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(strs, ", "))); +} + #if FMT_USE_CONSTEXPR -TEST(OStreamTest, ConstexprString) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", format(FMT_STRING("{}"), std::string("42"))); - EXPECT_EQ("a string", format(FMT_STRING("{0}"), TestString("a string"))); +TEST(ostream_test, constexpr_string) { + EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), std::string("42"))); + EXPECT_EQ("a string", + fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{0}"), test_string("a string"))); } #endif namespace fmt_test { -struct ABC {}; +struct abc {}; -template <typename Output> Output& operator<<(Output& out, ABC) { - out << "ABC"; - return out; +template <typename Output> auto operator<<(Output& out, abc) -> Output& { + return out << "abc"; } } // namespace fmt_test -template <typename T> struct TestTemplate {}; +template <typename T> struct test_template {}; template <typename T> -std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, TestTemplate<T>) { +auto operator<<(std::ostream& os, test_template<T>) -> std::ostream& { return os << 1; } namespace fmt { -template <typename T> struct formatter<TestTemplate<T>> : formatter<int> { - template <typename FormatContext> - typename FormatContext::iterator format(TestTemplate<T>, FormatContext& ctx) { +template <typename T> struct formatter<test_template<T>> : formatter<int> { + auto format(test_template<T>, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) { return formatter<int>::format(2, ctx); } }; + +template <> struct formatter<fmt_test::abc> : ostream_formatter {}; } // namespace fmt -#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 407 -TEST(OStreamTest, Template) { - EXPECT_EQ("2", fmt::format("{}", TestTemplate<int>())); +TEST(ostream_test, template) { + EXPECT_EQ("2", fmt::format("{}", test_template<int>())); } -TEST(FormatTest, FormatToN) { +TEST(ostream_test, format_to_n) { char buffer[4]; buffer[3] = 'x'; - auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, "{}", fmt_test::ABC()); + auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, "{}", fmt_test::abc()); EXPECT_EQ(3u, result.size); EXPECT_EQ(buffer + 3, result.out); - EXPECT_EQ("ABCx", fmt::string_view(buffer, 4)); - result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, "x{}y", fmt_test::ABC()); + EXPECT_EQ("abcx", fmt::string_view(buffer, 4)); + result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, "x{}y", fmt_test::abc()); EXPECT_EQ(5u, result.size); EXPECT_EQ(buffer + 3, result.out); - EXPECT_EQ("xABx", fmt::string_view(buffer, 4)); + EXPECT_EQ("xabx", fmt::string_view(buffer, 4)); } -#endif -#if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS -TEST(FormatTest, UDL) { - using namespace fmt::literals; - EXPECT_EQ("{}"_format("test"), "test"); +struct copyfmt_test {}; + +std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, copyfmt_test) { + std::ios ios(nullptr); + ios.copyfmt(os); + return os << "foo"; } -#endif -template <typename T> struct convertible { - T value; - explicit convertible(const T& val) : value(val) {} - operator T() const { return value; } -}; +namespace fmt { +template <> struct formatter<copyfmt_test> : ostream_formatter {}; +} // namespace fmt -TEST(OStreamTest, DisableBuiltinOStreamOperators) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{:d}", convertible<unsigned short>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(L"{:d}", convertible<unsigned short>(42))); - EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format("{}", convertible<const char*>("foo"))); +TEST(ostream_test, copyfmt) { + EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format("{}", copyfmt_test())); } -struct explicitly_convertible_to_string_like { - template <typename String, - typename = typename std::enable_if<std::is_constructible< - String, const char*, size_t>::value>::type> - explicit operator String() const { - return String("foo", 3u); - } -}; - -std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, - explicitly_convertible_to_string_like) { - return os << "bar"; +TEST(ostream_test, to_string) { + EXPECT_EQ("abc", fmt::to_string(fmt_test::abc())); } -TEST(OStreamTest, FormatExplicitlyConvertibleToStringLike) { - EXPECT_EQ("bar", fmt::format("{}", explicitly_convertible_to_string_like())); +TEST(ostream_test, range) { + auto strs = std::vector<test_string>{test_string("foo"), test_string("bar")}; + EXPECT_EQ("[foo, bar]", fmt::format("{}", strs)); } -#ifdef FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW -struct explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view { - explicit operator fmt::detail::std_string_view<char>() const { - return {"foo", 3u}; +struct abstract { + virtual ~abstract() = default; + virtual void f() = 0; + friend auto operator<<(std::ostream& os, const abstract&) -> std::ostream& { + return os; } }; -std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, - explicitly_convertible_to_std_string_view) { - return os << "bar"; -} - -TEST(OStreamTest, FormatExplicitlyConvertibleToStdStringView) { - EXPECT_EQ("bar", fmt::format("{}", explicitly_convertible_to_string_like())); -} -#endif // FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW - -struct streamable_and_convertible_to_bool { - operator bool() const { return true; } -}; +namespace fmt { +template <> struct formatter<abstract> : ostream_formatter {}; +} // namespace fmt -std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, streamable_and_convertible_to_bool) { - return os << "foo"; +void format_abstract_compiles(const abstract& a) { + fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), a); } -TEST(OStreamTest, FormatConvertibleToBool) { - EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format("{}", streamable_and_convertible_to_bool())); +TEST(ostream_test, is_formattable) { + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::is_formattable<std::string>()); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::is_formattable<fmt::detail::std_string_view<char>>()); } -struct copyfmt_test {}; +struct streamable_and_unformattable {}; -std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, copyfmt_test) { - std::ios ios(nullptr); - ios.copyfmt(os); +auto operator<<(std::ostream& os, streamable_and_unformattable) + -> std::ostream& { return os << "foo"; } -TEST(OStreamTest, CopyFmt) { - EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format("{}", copyfmt_test())); -} - -TEST(OStreamTest, CompileTimeString) { - EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), 42)); +TEST(ostream_test, streamed) { + EXPECT_FALSE(fmt::is_formattable<streamable_and_unformattable>()); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::streamed(streamable_and_unformattable())), + "foo"); } -TEST(OStreamTest, ToString) { - EXPECT_EQ("ABC", fmt::to_string(fmt_test::ABC())); +TEST(ostream_test, closed_ofstream) { + std::ofstream ofs; + fmt::print(ofs, "discard"); } - -TEST(OStreamTest, Range) { - auto strs = std::vector<TestString>{TestString("foo"), TestString("bar")}; - EXPECT_EQ("{foo, bar}", format("{}", strs)); -}
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/test/posix-mock-test.cc b/test/posix-mock-test.cc index eb85756d..32078bf8 100644 --- a/test/posix-mock-test.cc +++ b/test/posix-mock-test.cc @@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ // For the license information refer to format.h. // Disable bogus MSVC warnings. -#ifndef _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS +#if !defined(_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS) && defined(_MSC_VER) # define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #endif @@ -23,20 +23,23 @@ #ifdef _WIN32 # include <io.h> # undef max -# undef ERROR #endif -#include "gmock.h" +#include "gmock/gmock.h" #include "gtest-extra.h" #include "util.h" using fmt::buffered_file; -using fmt::error_code; using testing::_; using testing::Return; using testing::StrEq; +template <typename Mock> struct scoped_mock : testing::StrictMock<Mock> { + scoped_mock() { Mock::instance = this; } + ~scoped_mock() { Mock::instance = nullptr; } +}; + namespace { int open_count; int close_count; @@ -53,7 +56,7 @@ size_t read_nbyte; size_t write_nbyte; bool sysconf_error; -enum { NONE, MAX_SIZE, ERROR } fstat_sim; +enum { none, max_size, error } fstat_sim; } // namespace #define EMULATE_EINTR(func, error_result) \ @@ -69,12 +72,6 @@ int test::open(const char* path, int oflag, int mode) { EMULATE_EINTR(open, -1); return ::open(path, oflag, mode); } -#else -errno_t test::sopen_s(int* pfh, const char* filename, int oflag, int shflag, - int pmode) { - EMULATE_EINTR(open, EINTR); - return _sopen_s(pfh, filename, oflag, shflag, pmode); -} #endif #ifndef _WIN32 @@ -91,7 +88,7 @@ static off_t max_file_size() { return std::numeric_limits<off_t>::max(); } int test::fstat(int fd, struct stat* buf) { int result = ::fstat(fd, buf); - if (fstat_sim == MAX_SIZE) buf->st_size = max_file_size(); + if (fstat_sim == max_size) buf->st_size = max_file_size(); return result; } @@ -100,11 +97,11 @@ int test::fstat(int fd, struct stat* buf) { static LONGLONG max_file_size() { return std::numeric_limits<LONGLONG>::max(); } DWORD test::GetFileSize(HANDLE hFile, LPDWORD lpFileSizeHigh) { - if (fstat_sim == ERROR) { + if (fstat_sim == error) { SetLastError(ERROR_ACCESS_DENIED); return INVALID_FILE_SIZE; } - if (fstat_sim == MAX_SIZE) { + if (fstat_sim == max_size) { DWORD max = std::numeric_limits<DWORD>::max(); *lpFileSizeHigh = max >> 1; return max; @@ -194,15 +191,15 @@ int(test::fileno)(FILE* stream) { # define EXPECT_EQ_POSIX(expected, actual) #endif -static void write_file(fmt::cstring_view filename, fmt::string_view content) { +#if FMT_USE_FCNTL +void write_file(fmt::cstring_view filename, fmt::string_view content) { fmt::buffered_file f(filename, "w"); f.print("{}", content); } -#if FMT_USE_FCNTL using fmt::file; -TEST(UtilTest, GetPageSize) { +TEST(os_test, getpagesize) { # ifdef _WIN32 SYSTEM_INFO si = {}; GetSystemInfo(&si); @@ -216,18 +213,18 @@ TEST(UtilTest, GetPageSize) { # endif } -TEST(FileTest, OpenRetry) { +TEST(file_test, open_retry) { +# ifndef _WIN32 write_file("temp", "there must be something here"); std::unique_ptr<file> f{nullptr}; EXPECT_RETRY(f.reset(new file("temp", file::RDONLY)), open, "cannot open file temp"); -# ifndef _WIN32 char c = 0; f->read(&c, 1); # endif } -TEST(FileTest, CloseNoRetryInDtor) { +TEST(file_test, close_no_retry_in_dtor) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); std::unique_ptr<file> f(new file(std::move(read_end))); @@ -240,11 +237,11 @@ TEST(FileTest, CloseNoRetryInDtor) { saved_close_count = close_count; close_count = 0; }, - format_system_error(EINTR, "cannot close file") + "\n"); + system_error_message(EINTR, "cannot close file") + "\n"); EXPECT_EQ(2, saved_close_count); } -TEST(FileTest, CloseNoRetry) { +TEST(file_test, close_no_retry) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); close_count = 1; @@ -253,35 +250,39 @@ TEST(FileTest, CloseNoRetry) { close_count = 0; } -TEST(FileTest, Size) { +TEST(file_test, size) { std::string content = "top secret, destroy before reading"; write_file("temp", content); file f("temp", file::RDONLY); EXPECT_GE(f.size(), 0); EXPECT_EQ(content.size(), static_cast<unsigned long long>(f.size())); # ifdef _WIN32 - fmt::memory_buffer message; - fmt::detail::format_windows_error(message, ERROR_ACCESS_DENIED, - "cannot get file size"); - fstat_sim = ERROR; - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(f.size(), fmt::windows_error, fmt::to_string(message)); - fstat_sim = NONE; + auto error_code = std::error_code(); + fstat_sim = error; + try { + f.size(); + } catch (const std::system_error& e) { + error_code = e.code(); + } + fstat_sim = none; + EXPECT_EQ(error_code, + std::error_code(ERROR_ACCESS_DENIED, fmt::system_category())); # else f.close(); EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(f.size(), EBADF, "cannot get file attributes"); # endif } -TEST(FileTest, MaxSize) { +TEST(file_test, max_size) { write_file("temp", ""); file f("temp", file::RDONLY); - fstat_sim = MAX_SIZE; + fstat_sim = max_size; EXPECT_GE(f.size(), 0); EXPECT_EQ(max_file_size(), f.size()); - fstat_sim = NONE; + fstat_sim = none; } -TEST(FileTest, ReadRetry) { +TEST(file_test, read_retry) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); enum { SIZE = 4 }; @@ -294,7 +295,7 @@ TEST(FileTest, ReadRetry) { EXPECT_EQ_POSIX(static_cast<std::streamsize>(SIZE), count); } -TEST(FileTest, WriteRetry) { +TEST(file_test, write_retry) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); enum { SIZE = 4 }; @@ -312,7 +313,7 @@ TEST(FileTest, WriteRetry) { } # ifdef _WIN32 -TEST(FileTest, ConvertReadCount) { +TEST(file_test, convert_read_count) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); char c; @@ -320,12 +321,12 @@ TEST(FileTest, ConvertReadCount) { if (sizeof(unsigned) != sizeof(size_t)) ++size; read_count = 1; read_nbyte = 0; - EXPECT_THROW(read_end.read(&c, size), fmt::system_error); + EXPECT_THROW(read_end.read(&c, size), std::system_error); read_count = 0; EXPECT_EQ(UINT_MAX, read_nbyte); } -TEST(FileTest, ConvertWriteCount) { +TEST(file_test, convert_write_count) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); char c; @@ -333,13 +334,13 @@ TEST(FileTest, ConvertWriteCount) { if (sizeof(unsigned) != sizeof(size_t)) ++size; write_count = 1; write_nbyte = 0; - EXPECT_THROW(write_end.write(&c, size), fmt::system_error); + EXPECT_THROW(write_end.write(&c, size), std::system_error); write_count = 0; EXPECT_EQ(UINT_MAX, write_nbyte); } # endif -TEST(FileTest, DupNoRetry) { +TEST(file_test, dup_no_retry) { int stdout_fd = FMT_POSIX(fileno(stdout)); dup_count = 1; EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR( @@ -348,7 +349,7 @@ TEST(FileTest, DupNoRetry) { dup_count = 0; } -TEST(FileTest, Dup2Retry) { +TEST(file_test, dup2_retry) { int stdout_fd = FMT_POSIX(fileno(stdout)); file f1 = file::dup(stdout_fd), f2 = file::dup(stdout_fd); EXPECT_RETRY(f1.dup2(f2.descriptor()), dup2, @@ -356,21 +357,21 @@ TEST(FileTest, Dup2Retry) { f1.descriptor(), f2.descriptor())); } -TEST(FileTest, Dup2NoExceptRetry) { +TEST(file_test, dup2_no_except_retry) { int stdout_fd = FMT_POSIX(fileno(stdout)); file f1 = file::dup(stdout_fd), f2 = file::dup(stdout_fd); - error_code ec; + std::error_code ec; dup2_count = 1; f1.dup2(f2.descriptor(), ec); # ifndef _WIN32 EXPECT_EQ(4, dup2_count); # else - EXPECT_EQ(EINTR, ec.get()); + EXPECT_EQ(EINTR, ec.value()); # endif dup2_count = 0; } -TEST(FileTest, PipeNoRetry) { +TEST(file_test, pipe_no_retry) { file read_end, write_end; pipe_count = 1; EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR(file::pipe(read_end, write_end), EINTR, @@ -378,7 +379,7 @@ TEST(FileTest, PipeNoRetry) { pipe_count = 0; } -TEST(FileTest, FdopenNoRetry) { +TEST(file_test, fdopen_no_retry) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); fdopen_count = 1; @@ -387,7 +388,7 @@ TEST(FileTest, FdopenNoRetry) { fdopen_count = 0; } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, OpenRetry) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, open_retry) { write_file("temp", "there must be something here"); std::unique_ptr<buffered_file> f{nullptr}; EXPECT_RETRY(f.reset(new buffered_file("temp", "r")), fopen, @@ -399,7 +400,7 @@ TEST(BufferedFileTest, OpenRetry) { # endif } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, CloseNoRetryInDtor) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, close_no_retry_in_dtor) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); std::unique_ptr<buffered_file> f(new buffered_file(read_end.fdopen("r"))); @@ -412,11 +413,11 @@ TEST(BufferedFileTest, CloseNoRetryInDtor) { saved_fclose_count = fclose_count; fclose_count = 0; }, - format_system_error(EINTR, "cannot close file") + "\n"); + system_error_message(EINTR, "cannot close file") + "\n"); EXPECT_EQ(2, saved_fclose_count); } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, CloseNoRetry) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, close_no_retry) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); buffered_file f = read_end.fdopen("r"); @@ -426,12 +427,12 @@ TEST(BufferedFileTest, CloseNoRetry) { fclose_count = 0; } -TEST(BufferedFileTest, FilenoNoRetry) { +TEST(buffered_file_test, fileno_no_retry) { file read_end, write_end; file::pipe(read_end, write_end); buffered_file f = read_end.fdopen("r"); fileno_count = 1; - EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR((f.fileno)(), EINTR, "cannot get file descriptor"); + EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR((f.descriptor)(), EINTR, "cannot get file descriptor"); EXPECT_EQ(2, fileno_count); fileno_count = 0; } @@ -441,118 +442,12 @@ struct test_mock { static test_mock* instance; } * test_mock::instance; -TEST(ScopedMock, Scope) { +TEST(scoped_mock, scope) { { - ScopedMock<test_mock> mock; + scoped_mock<test_mock> mock; EXPECT_EQ(&mock, test_mock::instance); test_mock& copy = mock; static_cast<void>(copy); } EXPECT_EQ(nullptr, test_mock::instance); } - -#ifdef FMT_LOCALE - -typedef fmt::locale::type locale_type; - -struct locale_mock { - static locale_mock* instance; - MOCK_METHOD3(newlocale, locale_type(int category_mask, const char* locale, - locale_type base)); - MOCK_METHOD1(freelocale, void(locale_type locale)); - - MOCK_METHOD3(strtod_l, - double(const char* nptr, char** endptr, locale_type locale)); -} * locale_mock::instance; - -# ifdef _MSC_VER -# pragma warning(push) -# pragma warning(disable : 4273) -# ifdef __clang__ -# pragma clang diagnostic push -# pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Winconsistent-dllimport" -# endif - -_locale_t _create_locale(int category, const char* locale) { - return locale_mock::instance->newlocale(category, locale, 0); -} - -void _free_locale(_locale_t locale) { - locale_mock::instance->freelocale(locale); -} - -double _strtod_l(const char* nptr, char** endptr, _locale_t locale) { - return locale_mock::instance->strtod_l(nptr, endptr, locale); -} -# ifdef __clang__ -# pragma clang diagnostic pop -# endif -# pragma warning(pop) -# endif - -# if defined(__THROW) && FMT_GCC_VERSION > 0 && FMT_GCC_VERSION <= 408 -# define FMT_LOCALE_THROW __THROW -# else -# define FMT_LOCALE_THROW -# endif - -# if defined(__APPLE__) || \ - (defined(__FreeBSD__) && __FreeBSD_version < 1200002) -typedef int FreeLocaleResult; -# else -typedef void FreeLocaleResult; -# endif - -FreeLocaleResult freelocale(locale_type locale) FMT_LOCALE_THROW { - locale_mock::instance->freelocale(locale); - return FreeLocaleResult(); -} - -double strtod_l(const char* nptr, char** endptr, - locale_type locale) FMT_LOCALE_THROW { - return locale_mock::instance->strtod_l(nptr, endptr, locale); -} - -# undef FMT_LOCALE_THROW - -# ifndef _WIN32 -locale_t test::newlocale(int category_mask, const char* locale, locale_t base) { - return locale_mock::instance->newlocale(category_mask, locale, base); -} - -TEST(LocaleTest, LocaleMock) { - ScopedMock<locale_mock> mock; - locale_type locale = reinterpret_cast<locale_type>(11); - EXPECT_CALL(mock, newlocale(222, StrEq("foo"), locale)); - FMT_SYSTEM(newlocale(222, "foo", locale)); -} -# endif - -TEST(LocaleTest, Locale) { -# ifndef LC_NUMERIC_MASK - enum { LC_NUMERIC_MASK = LC_NUMERIC }; -# endif - ScopedMock<locale_mock> mock; - locale_type impl = reinterpret_cast<locale_type>(42); - EXPECT_CALL(mock, newlocale(LC_NUMERIC_MASK, StrEq("C"), nullptr)) - .WillOnce(Return(impl)); - EXPECT_CALL(mock, freelocale(impl)); - fmt::locale loc; - EXPECT_EQ(impl, loc.get()); -} - -TEST(LocaleTest, Strtod) { - ScopedMock<locale_mock> mock; - EXPECT_CALL(mock, newlocale(_, _, _)) - .WillOnce(Return(reinterpret_cast<locale_type>(42))); - EXPECT_CALL(mock, freelocale(_)); - fmt::locale loc; - const char* str = "4.2"; - char end = 'x'; - EXPECT_CALL(mock, strtod_l(str, _, loc.get())) - .WillOnce(testing::DoAll(testing::SetArgPointee<1>(&end), Return(777))); - EXPECT_EQ(777, loc.strtod(str)); - EXPECT_EQ(&end, str); -} - -#endif // FMT_LOCALE diff --git a/test/posix-mock.h b/test/posix-mock.h index e76af700..4f2a42c1 100644 --- a/test/posix-mock.h +++ b/test/posix-mock.h @@ -37,8 +37,6 @@ int fstat(int fd, struct stat* buf); #else typedef unsigned size_t; typedef int ssize_t; -errno_t sopen_s(int* pfh, const char* filename, int oflag, int shflag, - int pmode); #endif #ifndef _WIN32 diff --git a/test/printf-test.cc b/test/printf-test.cc index ccd72dcd..81db9b23 100644 --- a/test/printf-test.cc +++ b/test/printf-test.cc @@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ #include <climits> #include <cstring> -#include "fmt/core.h" +#include "fmt/xchar.h" #include "gtest-extra.h" #include "util.h" @@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ using fmt::format; using fmt::format_error; using fmt::detail::max_value; -const unsigned BIG_NUM = INT_MAX + 1u; +const unsigned big_num = INT_MAX + 1u; // Makes format string argument positional. static std::string make_positional(fmt::string_view format) { @@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ static std::string make_positional(fmt::string_view format) { return s; } -static std::wstring make_positional(fmt::wstring_view format) { +static std::wstring make_positional(fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t> format) { std::wstring s(format.data(), format.size()); s.replace(s.find(L'%'), 1, L"%1$"); return s; @@ -41,7 +41,8 @@ std::string test_sprintf(fmt::string_view format, const Args&... args) { return fmt::sprintf(format, args...); } template <typename... Args> -std::wstring test_sprintf(fmt::wstring_view format, const Args&... args) { +std::wstring test_sprintf(fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t> format, + const Args&... args) { return fmt::sprintf(format, args...); } @@ -50,12 +51,12 @@ std::wstring test_sprintf(fmt::wstring_view format, const Args&... args) { << "format: " << format; \ EXPECT_EQ(expected_output, fmt::sprintf(make_positional(format), arg)) -TEST(PrintfTest, NoArgs) { +TEST(printf_test, no_args) { EXPECT_EQ("test", test_sprintf("test")); EXPECT_EQ(L"test", fmt::sprintf(L"test")); } -TEST(PrintfTest, Escape) { +TEST(printf_test, escape) { EXPECT_EQ("%", test_sprintf("%%")); EXPECT_EQ("before %", test_sprintf("before %%")); EXPECT_EQ("% after", test_sprintf("%% after")); @@ -68,7 +69,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, Escape) { EXPECT_EQ(L"%s", fmt::sprintf(L"%%s")); } -TEST(PrintfTest, PositionalArgs) { +TEST(printf_test, positional_args) { EXPECT_EQ("42", test_sprintf("%1$d", 42)); EXPECT_EQ("before 42", test_sprintf("before %1$d", 42)); EXPECT_EQ("42 after", test_sprintf("%1$d after", 42)); @@ -78,40 +79,40 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, PositionalArgs) { EXPECT_EQ("abracadabra", test_sprintf("%1$s%2$s%1$s", "abra", "cad")); } -TEST(PrintfTest, AutomaticArgIndexing) { +TEST(printf_test, automatic_arg_indexing) { EXPECT_EQ("abc", test_sprintf("%c%c%c", 'a', 'b', 'c')); } -TEST(PrintfTest, NumberIsTooBigInArgIndex) { - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%{}$", BIG_NUM)), format_error, - "number is too big"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%{}$d", BIG_NUM)), format_error, - "number is too big"); +TEST(printf_test, number_is_too_big_in_arg_index) { + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%{}$", big_num)), format_error, + "argument not found"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%{}$d", big_num)), format_error, + "argument not found"); } -TEST(PrintfTest, SwitchArgIndexing) { +TEST(printf_test, switch_arg_indexing) { EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%1$d%", 1, 2), format_error, "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%1$d%{}d", BIG_NUM), 1, 2), + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%1$d%{}d", big_num), 1, 2), format_error, "number is too big"); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%1$d%d", 1, 2), format_error, "cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing"); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%d%1$", 1, 2), format_error, "cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%d%{}$d", BIG_NUM), 1, 2), format_error, - "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%d%{}$d", big_num), 1, 2), format_error, + "cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing"); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%d%1$d", 1, 2), format_error, "cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing"); // Indexing errors override width errors. - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%d%1${}d", BIG_NUM), 1, 2), + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%d%1${}d", big_num), 1, 2), format_error, "number is too big"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%1$d%{}d", BIG_NUM), 1, 2), + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%1$d%{}d", big_num), 1, 2), format_error, "number is too big"); } -TEST(PrintfTest, InvalidArgIndex) { +TEST(printf_test, invalid_arg_index) { EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%0$d", 42), format_error, "argument not found"); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%2$d", 42), format_error, @@ -120,16 +121,16 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, InvalidArgIndex) { "argument not found"); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%2$", 42), format_error, "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%{}$d", BIG_NUM), 42), format_error, - "number is too big"); + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%{}$d", big_num), 42), format_error, + "argument not found"); } -TEST(PrintfTest, DefaultAlignRight) { +TEST(printf_test, default_align_right) { EXPECT_PRINTF(" 42", "%5d", 42); EXPECT_PRINTF(" abc", "%5s", "abc"); } -TEST(PrintfTest, ZeroFlag) { +TEST(printf_test, zero_flag) { EXPECT_PRINTF("00042", "%05d", 42); EXPECT_PRINTF("-0042", "%05d", -42); @@ -146,7 +147,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, ZeroFlag) { EXPECT_PRINTF(" x", "%05c", 'x'); } -TEST(PrintfTest, PlusFlag) { +TEST(printf_test, plus_flag) { EXPECT_PRINTF("+42", "%+d", 42); EXPECT_PRINTF("-42", "%+d", -42); EXPECT_PRINTF("+0042", "%+05d", 42); @@ -168,7 +169,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, PlusFlag) { EXPECT_PRINTF("x", "% +c", 'x'); } -TEST(PrintfTest, MinusFlag) { +TEST(printf_test, minus_flag) { EXPECT_PRINTF("abc ", "%-5s", "abc"); EXPECT_PRINTF("abc ", "%0--5s", "abc"); @@ -188,7 +189,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, MinusFlag) { EXPECT_PRINTF(" 42", "%- d", 42); } -TEST(PrintfTest, SpaceFlag) { +TEST(printf_test, space_flag) { EXPECT_PRINTF(" 42", "% d", 42); EXPECT_PRINTF("-42", "% d", -42); EXPECT_PRINTF(" 0042", "% 05d", 42); @@ -198,7 +199,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, SpaceFlag) { EXPECT_PRINTF("x", "% c", 'x'); } -TEST(PrintfTest, HashFlag) { +TEST(printf_test, hash_flag) { EXPECT_PRINTF("042", "%#o", 042); EXPECT_PRINTF(fmt::format("0{:o}", static_cast<unsigned>(-042)), "%#o", -042); EXPECT_PRINTF("0", "%#o", 0); @@ -215,7 +216,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, HashFlag) { EXPECT_PRINTF("-42.000000", "%#f", -42.0); EXPECT_PRINTF("-42.000000", "%#F", -42.0); - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; + char buffer[256]; safe_sprintf(buffer, "%#e", -42.0); EXPECT_PRINTF(buffer, "%#e", -42.0); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%#E", -42.0); @@ -224,39 +225,37 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, HashFlag) { EXPECT_PRINTF("-42.0000", "%#g", -42.0); EXPECT_PRINTF("-42.0000", "%#G", -42.0); - safe_sprintf(buffer, "%#a", 16.0); - EXPECT_PRINTF(buffer, "%#a", 16.0); - safe_sprintf(buffer, "%#A", 16.0); - EXPECT_PRINTF(buffer, "%#A", 16.0); + EXPECT_PRINTF("0x1.p+4", "%#a", 16.0); + EXPECT_PRINTF("0X1.P+4", "%#A", 16.0); // '#' flag is ignored for non-numeric types. EXPECT_PRINTF("x", "%#c", 'x'); } -TEST(PrintfTest, Width) { +TEST(printf_test, width) { EXPECT_PRINTF(" abc", "%5s", "abc"); // Width cannot be specified twice. EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%5-5d", 42), format_error, - "invalid type specifier"); + "invalid format specifier"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%{}d", BIG_NUM), 42), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%{}d", big_num), 42), format_error, "number is too big"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%1${}d", BIG_NUM), 42), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf(format("%1${}d", big_num), 42), format_error, "number is too big"); } -TEST(PrintfTest, DynamicWidth) { +TEST(printf_test, dynamic_width) { EXPECT_EQ(" 42", test_sprintf("%*d", 5, 42)); EXPECT_EQ("42 ", test_sprintf("%*d", -5, 42)); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%*d", 5.0, 42), format_error, "width is not integer"); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%*d"), format_error, "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%*d", BIG_NUM, 42), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%*d", big_num, 42), format_error, "number is too big"); } -TEST(PrintfTest, IntPrecision) { +TEST(printf_test, int_precision) { EXPECT_PRINTF("00042", "%.5d", 42); EXPECT_PRINTF("-00042", "%.5d", -42); EXPECT_PRINTF("00042", "%.5x", 0x42); @@ -277,8 +276,8 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, IntPrecision) { EXPECT_PRINTF("00042 ", "%-#10.5o", 042); } -TEST(PrintfTest, FloatPrecision) { - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; +TEST(printf_test, float_precision) { + char buffer[256]; safe_sprintf(buffer, "%.3e", 1234.5678); EXPECT_PRINTF(buffer, "%.3e", 1234.5678); EXPECT_PRINTF("1234.568", "%.3f", 1234.5678); @@ -287,22 +286,22 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, FloatPrecision) { EXPECT_PRINTF(buffer, "%.3a", 1234.5678); } -TEST(PrintfTest, StringPrecision) { +TEST(printf_test, string_precision) { char test[] = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}; EXPECT_EQ(fmt::sprintf("%.4s", test), "Hell"); } -TEST(PrintfTest, IgnorePrecisionForNonNumericArg) { +TEST(printf_test, ignore_precision_for_non_numeric_arg) { EXPECT_PRINTF("abc", "%.5s", "abc"); } -TEST(PrintfTest, DynamicPrecision) { +TEST(printf_test, dynamic_precision) { EXPECT_EQ("00042", test_sprintf("%.*d", 5, 42)); EXPECT_EQ("42", test_sprintf("%.*d", -5, 42)); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%.*d", 5.0, 42), format_error, "precision is not integer"); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%.*d"), format_error, "argument not found"); - EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%.*d", BIG_NUM, 42), format_error, + EXPECT_THROW_MSG(test_sprintf("%.*d", big_num, 42), format_error, "number is too big"); if (sizeof(long long) != sizeof(int)) { long long prec = static_cast<long long>(INT_MIN) - 1; @@ -325,7 +324,7 @@ SPECIALIZE_MAKE_SIGNED(unsigned long long, long long); // Test length format specifier ``length_spec``. template <typename T, typename U> -void TestLength(const char* length_spec, U value) { +void test_length(const char* length_spec, U value) { long long signed_value = 0; unsigned long long unsigned_value = 0; // Apply integer promotion to the argument. @@ -364,54 +363,51 @@ void TestLength(const char* length_spec, U value) { EXPECT_PRINTF(os.str(), fmt::format("%{}X", length_spec), value); } -template <typename T> void TestLength(const char* length_spec) { +template <typename T> void test_length(const char* length_spec) { T min = std::numeric_limits<T>::min(), max = max_value<T>(); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, 42); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, -42); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, min); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, max); + test_length<T>(length_spec, 42); + test_length<T>(length_spec, -42); + test_length<T>(length_spec, min); + test_length<T>(length_spec, max); long long long_long_min = std::numeric_limits<long long>::min(); if (static_cast<long long>(min) > long_long_min) - TestLength<T>(length_spec, static_cast<long long>(min) - 1); + test_length<T>(length_spec, static_cast<long long>(min) - 1); unsigned long long long_long_max = max_value<long long>(); if (static_cast<unsigned long long>(max) < long_long_max) - TestLength<T>(length_spec, static_cast<long long>(max) + 1); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<short>::min()); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, max_value<unsigned short>()); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<int>::min()); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, max_value<int>()); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<unsigned>::min()); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, max_value<unsigned>()); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<long long>::min()); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, max_value<long long>()); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::min()); - TestLength<T>(length_spec, max_value<unsigned long long>()); -} - -TEST(PrintfTest, Length) { - TestLength<char>("hh"); - TestLength<signed char>("hh"); - TestLength<unsigned char>("hh"); - TestLength<short>("h"); - TestLength<unsigned short>("h"); - TestLength<long>("l"); - TestLength<unsigned long>("l"); - TestLength<long long>("ll"); - TestLength<unsigned long long>("ll"); - TestLength<intmax_t>("j"); - TestLength<size_t>("z"); - TestLength<std::ptrdiff_t>("t"); + test_length<T>(length_spec, static_cast<long long>(max) + 1); + test_length<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<short>::min()); + test_length<T>(length_spec, max_value<unsigned short>()); + test_length<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<int>::min()); + test_length<T>(length_spec, max_value<int>()); + test_length<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<unsigned>::min()); + test_length<T>(length_spec, max_value<unsigned>()); + test_length<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<long long>::min()); + test_length<T>(length_spec, max_value<long long>()); + test_length<T>(length_spec, std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::min()); + test_length<T>(length_spec, max_value<unsigned long long>()); +} + +TEST(printf_test, length) { + test_length<char>("hh"); + test_length<signed char>("hh"); + test_length<unsigned char>("hh"); + test_length<short>("h"); + test_length<unsigned short>("h"); + test_length<long>("l"); + test_length<unsigned long>("l"); + test_length<long long>("ll"); + test_length<unsigned long long>("ll"); + test_length<intmax_t>("j"); + test_length<size_t>("z"); + test_length<std::ptrdiff_t>("t"); long double max = max_value<long double>(); EXPECT_PRINTF(fmt::format("{:.6}", max), "%g", max); EXPECT_PRINTF(fmt::format("{:.6}", max), "%Lg", max); } -TEST(PrintfTest, Bool) { - EXPECT_PRINTF("1", "%d", true); - EXPECT_PRINTF("true", "%s", true); -} +TEST(printf_test, bool) { EXPECT_PRINTF("1", "%d", true); } -TEST(PrintfTest, Int) { +TEST(printf_test, int) { EXPECT_PRINTF("-42", "%d", -42); EXPECT_PRINTF("-42", "%i", -42); unsigned u = 0 - 42u; @@ -421,20 +417,20 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, Int) { EXPECT_PRINTF(fmt::format("{:X}", u), "%X", -42); } -TEST(PrintfTest, long_long) { +TEST(printf_test, long_long) { // fmt::printf allows passing long long arguments to %d without length // specifiers. long long max = max_value<long long>(); EXPECT_PRINTF(fmt::format("{}", max), "%d", max); } -TEST(PrintfTest, Float) { +TEST(printf_test, float) { EXPECT_PRINTF("392.650000", "%f", 392.65); EXPECT_PRINTF("392.65", "%.2f", 392.65); EXPECT_PRINTF("392.6", "%.1f", 392.65); EXPECT_PRINTF("393", "%.f", 392.65); EXPECT_PRINTF("392.650000", "%F", 392.65); - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; + char buffer[256]; safe_sprintf(buffer, "%e", 392.65); EXPECT_PRINTF(buffer, "%e", 392.65); safe_sprintf(buffer, "%E", 392.65); @@ -450,7 +446,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, Float) { EXPECT_EQ(buffer, format("{:A}", -392.65)); } -TEST(PrintfTest, Inf) { +TEST(printf_test, inf) { double inf = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); for (const char* type = "fega"; *type; ++type) { EXPECT_PRINTF("inf", fmt::format("%{}", *type), inf); @@ -459,7 +455,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, Inf) { } } -TEST(PrintfTest, Char) { +TEST(printf_test, char) { EXPECT_PRINTF("x", "%c", 'x'); int max = max_value<int>(); EXPECT_PRINTF(fmt::format("{}", static_cast<char>(max)), "%c", max); @@ -468,7 +464,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, Char) { EXPECT_PRINTF(fmt::format(L"{}", static_cast<wchar_t>(max)), L"%c", max); } -TEST(PrintfTest, String) { +TEST(printf_test, string) { EXPECT_PRINTF("abc", "%s", "abc"); const char* null_str = nullptr; EXPECT_PRINTF("(null)", "%s", null_str); @@ -479,13 +475,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, String) { EXPECT_PRINTF(L" (null)", L"%10s", null_wstr); } -TEST(PrintfTest, UCharString) { - unsigned char str[] = "test"; - unsigned char* pstr = str; - EXPECT_EQ("test", fmt::sprintf("%s", pstr)); -} - -TEST(PrintfTest, Pointer) { +TEST(printf_test, pointer) { int n; void* p = &n; EXPECT_PRINTF(fmt::format("{}", p), "%p", p); @@ -508,20 +498,17 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, Pointer) { EXPECT_PRINTF(L"(nil)", L"%p", null_wstr); } -TEST(PrintfTest, Location) { - // TODO: test %n -} - enum test_enum { answer = 42 }; +auto format_as(test_enum e) -> int { return e; } -TEST(PrintfTest, Enum) { +TEST(printf_test, enum) { EXPECT_PRINTF("42", "%d", answer); volatile test_enum volatile_enum = answer; EXPECT_PRINTF("42", "%d", volatile_enum); } #if FMT_USE_FCNTL -TEST(PrintfTest, Examples) { +TEST(printf_test, examples) { const char* weekday = "Thursday"; const char* month = "August"; int day = 21; @@ -529,7 +516,7 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, Examples) { "Thursday, 21 August"); } -TEST(PrintfTest, PrintfError) { +TEST(printf_test, printf_error) { fmt::file read_end, write_end; fmt::file::pipe(read_end, write_end); int result = fmt::fprintf(read_end.fdopen("r").get(), "test"); @@ -537,26 +524,17 @@ TEST(PrintfTest, PrintfError) { } #endif -TEST(PrintfTest, WideString) { EXPECT_EQ(L"abc", fmt::sprintf(L"%s", L"abc")); } - -TEST(PrintfTest, PrintfCustom) { - EXPECT_EQ("abc", test_sprintf("%s", TestString("abc"))); +TEST(printf_test, wide_string) { + EXPECT_EQ(L"abc", fmt::sprintf(L"%s", L"abc")); } -TEST(PrintfTest, OStream) { - std::ostringstream os; - int ret = fmt::fprintf(os, "Don't %s!", "panic"); - EXPECT_EQ("Don't panic!", os.str()); - EXPECT_EQ(12, ret); -} - -TEST(PrintfTest, VPrintf) { - fmt::format_arg_store<fmt::printf_context, int> as{42}; - fmt::basic_format_args<fmt::printf_context> args(as); - EXPECT_EQ(fmt::vsprintf("%d", args), "42"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::vprintf("%d", args), "42"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::vfprintf(stdout, "%d", args), "42"); - EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::vfprintf(std::cout, "%d", args), "42"); +TEST(printf_test, vprintf) { + int n = 42; + auto store = fmt::format_arg_store<fmt::printf_context, int>(n); + auto args = fmt::basic_format_args<fmt::printf_context>(store); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::vsprintf(fmt::string_view("%d"), args), "42"); + EXPECT_WRITE(stdout, fmt::vfprintf(stdout, fmt::string_view("%d"), args), + "42"); } template <typename... Args> @@ -564,65 +542,19 @@ void check_format_string_regression(fmt::string_view s, const Args&... args) { fmt::sprintf(s, args...); } -TEST(PrintfTest, CheckFormatStringRegression) { +TEST(printf_test, check_format_string_regression) { check_format_string_regression("%c%s", 'x', ""); } -TEST(PrintfTest, FixedLargeExponent) { +TEST(printf_test, fixed_large_exponent) { EXPECT_EQ("1000000000000000000000", fmt::sprintf("%.*f", -13, 1e21)); } -TEST(PrintfTest, VSPrintfMakeArgsExample) { - fmt::format_arg_store<fmt::printf_context, int, const char*> as{42, - "something"}; - fmt::basic_format_args<fmt::printf_context> args(as); - EXPECT_EQ("[42] something happened", fmt::vsprintf("[%d] %s happened", args)); - auto as2 = fmt::make_printf_args(42, "something"); - fmt::basic_format_args<fmt::printf_context> args2(as2); +TEST(printf_test, make_printf_args) { EXPECT_EQ("[42] something happened", - fmt::vsprintf("[%d] %s happened", args2)); - // The older gcc versions can't cast the return value. -#if !defined(__GNUC__) || (__GNUC__ > 4) - EXPECT_EQ("[42] something happened", - fmt::vsprintf("[%d] %s happened", + fmt::vsprintf(fmt::string_view("[%d] %s happened"), {fmt::make_printf_args(42, "something")})); -#endif -} - -TEST(PrintfTest, VSPrintfMakeWArgsExample) { - fmt::format_arg_store<fmt::wprintf_context, int, const wchar_t*> as{ - 42, L"something"}; - fmt::basic_format_args<fmt::wprintf_context> args(as); - EXPECT_EQ(L"[42] something happened", - fmt::vsprintf(L"[%d] %s happened", args)); - auto as2 = fmt::make_wprintf_args(42, L"something"); - fmt::basic_format_args<fmt::wprintf_context> args2(as2); EXPECT_EQ(L"[42] something happened", - fmt::vsprintf(L"[%d] %s happened", args2)); - // the older gcc versions can't cast the return value -#if !defined(__GNUC__) || (__GNUC__ > 4) - EXPECT_EQ(L"[42] something happened", - fmt::vsprintf(L"[%d] %s happened", + fmt::vsprintf(fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t>(L"[%d] %s happened"), {fmt::make_wprintf_args(42, L"something")})); -#endif -} - -TEST(PrintfTest, PrintfDetermineOutputSize) { - using backit = std::back_insert_iterator<std::vector<char>>; - using truncated_printf_context = - fmt::basic_printf_context<fmt::detail::truncating_iterator<backit>, char>; - - auto v = std::vector<char>{}; - auto it = std::back_inserter(v); - - const auto format_string = "%s"; - const auto format_arg = "Hello"; - const auto expected_size = fmt::sprintf(format_string, format_arg).size(); - - EXPECT_EQ((truncated_printf_context( - fmt::detail::truncating_iterator<backit>(it, 0), format_string, - fmt::make_format_args<truncated_printf_context>(format_arg)) - .format() - .count()), - expected_size); } diff --git a/test/ranges-odr-test.cc b/test/ranges-odr-test.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..031354d3 --- /dev/null +++ b/test/ranges-odr-test.cc @@ -0,0 +1,17 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - the core API +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#include <vector> + +#include "fmt/ranges.h" +#include "gtest/gtest.h" + +// call fmt::format from another translation unit to test ODR +TEST(ranges_odr_test, format_vector) { + auto v = std::vector<int>{1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v), "[1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11]"); +} diff --git a/test/ranges-test.cc b/test/ranges-test.cc index 63f9e6e6..ba5c464d 100644 --- a/test/ranges-test.cc +++ b/test/ranges-test.cc @@ -1,166 +1,235 @@ -// Formatting library for C++ - the core API +// Formatting library for C++ - ranges tests // -// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich and {fmt} contributors // All rights reserved. // // For the license information refer to format.h. -// -// Copyright (c) 2018 - present, Remotion (Igor Schulz) -// All Rights Reserved -// {fmt} support for ranges, containers and types tuple interface. #include "fmt/ranges.h" -#include "gtest.h" +#include <map> +#include <queue> +#include <stack> +#include <string> +#include <utility> +#include <vector> + +#include "gtest/gtest.h" -// Check if 'if constexpr' is supported. -#if (__cplusplus > 201402L) || \ - (defined(_MSVC_LANG) && _MSVC_LANG > 201402L && _MSC_VER >= 1910) +#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 601 +# define FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_C_STYLE_ARRAY +#endif -# include <array> -# include <map> -# include <string> -# include <vector> +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION > 1910 +# define FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_JOIN +# define FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_FORMAT_STRUCT +#endif -TEST(RangesTest, FormatVector) { - std::vector<int32_t> iv{1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11}; - auto ivf = fmt::format("{}", iv); - EXPECT_EQ("{1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11}", ivf); +#ifdef FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_C_STYLE_ARRAY +TEST(ranges_test, format_array) { + int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", arr), "[1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11]"); } -TEST(RangesTest, FormatVector2) { - std::vector<std::vector<int32_t>> ivv{{1, 2}, {3, 5}, {7, 11}}; - auto ivf = fmt::format("{}", ivv); - EXPECT_EQ("{{1, 2}, {3, 5}, {7, 11}}", ivf); +TEST(ranges_test, format_2d_array) { + int arr[][2] = {{1, 2}, {3, 5}, {7, 11}}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", arr), "[[1, 2], [3, 5], [7, 11]]"); } -TEST(RangesTest, FormatMap) { - std::map<std::string, int32_t> simap{{"one", 1}, {"two", 2}}; - EXPECT_EQ("{(\"one\", 1), (\"two\", 2)}", fmt::format("{}", simap)); +TEST(ranges_test, format_array_of_literals) { + const char* arr[] = {"1234", "abcd"}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", arr), "[\"1234\", \"abcd\"]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n}", arr), "\"1234\", \"abcd\""); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n:}", arr), "1234, abcd"); +} +#endif // FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_C_STYLE_ARRAY + +TEST(ranges_test, format_vector) { + auto v = std::vector<int>{1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v), "[1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{::#x}", v), "[0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x5, 0x7, 0xb]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n:#x}", v), "0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x5, 0x7, 0xb"); + + auto vc = std::vector<char>{'a', 'b', 'c'}; + auto vvc = std::vector<std::vector<char>>{vc, vc}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vc), "['a', 'b', 'c']"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vvc), "[['a', 'b', 'c'], ['a', 'b', 'c']]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n}", vvc), "['a', 'b', 'c'], ['a', 'b', 'c']"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n:n}", vvc), "'a', 'b', 'c', 'a', 'b', 'c'"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n:n:}", vvc), "a, b, c, a, b, c"); } -TEST(RangesTest, FormatPair) { - std::pair<int64_t, float> pa1{42, 1.5f}; - EXPECT_EQ("(42, 1.5)", fmt::format("{}", pa1)); +TEST(ranges_test, format_nested_vector) { + auto v = std::vector<std::vector<int>>{{1, 2}, {3, 5}, {7, 11}}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v), "[[1, 2], [3, 5], [7, 11]]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:::#x}", v), "[[0x1, 0x2], [0x3, 0x5], [0x7, 0xb]]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n:n:#x}", v), "0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x5, 0x7, 0xb"); } -TEST(RangesTest, FormatTuple) { - std::tuple<int64_t, float, std::string, char> t{42, 1.5f, "this is tuple", - 'i'}; - EXPECT_EQ("(42, 1.5, \"this is tuple\", 'i')", fmt::format("{}", t)); - EXPECT_EQ("()", fmt::format("{}", std::tuple<>())); +TEST(ranges_test, to_string_vector) { + auto v = std::vector<std::string>{"a", "b", "c"}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(v), "[\"a\", \"b\", \"c\"]"); } -TEST(RangesTest, JoinTuple) { - // Value tuple args - std::tuple<char, int, float> t1 = std::make_tuple('a', 1, 2.0f); - EXPECT_EQ("(a, 1, 2)", fmt::format("({})", fmt::join(t1, ", "))); +TEST(ranges_test, format_map) { + auto m = std::map<std::string, int>{{"one", 1}, {"two", 2}}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", m), "{\"one\": 1, \"two\": 2}"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n}", m), "\"one\": 1, \"two\": 2"); +} - // Testing lvalue tuple args - int x = 4; - std::tuple<char, int&> t2{'b', x}; - EXPECT_EQ("b + 4", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(t2, " + "))); +TEST(ranges_test, format_set) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::set<std::string>{"one", "two"}), + "{\"one\", \"two\"}"); +} - // Empty tuple - std::tuple<> t3; - EXPECT_EQ("", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(t3, "|"))); +// Models std::flat_set close enough to test if no ambiguous lookup of a +// formatter happens due to the flat_set type matching is_set and +// is_container_adaptor_like. +template <typename T> class flat_set { + public: + using key_type = T; + using container_type = std::vector<T>; - // Single element tuple - std::tuple<float> t4{4.0f}; - EXPECT_EQ("4", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(t4, "/"))); -} + using iterator = typename std::vector<T>::iterator; + using const_iterator = typename std::vector<T>::const_iterator; -TEST(RangesTest, JoinInitializerList) { - EXPECT_EQ("1, 2, 3", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join({1, 2, 3}, ", "))); - EXPECT_EQ("fmt rocks !", - fmt::format("{}", fmt::join({"fmt", "rocks", "!"}, " "))); -} + template <typename... Ts> + explicit flat_set(Ts&&... args) : c{std::forward<Ts>(args)...} {} -struct my_struct { - int32_t i; - std::string str; // can throw - template <size_t N> decltype(auto) get() const noexcept { - if constexpr (N == 0) - return i; - else if constexpr (N == 1) - return fmt::string_view{str}; - } + auto begin() -> iterator { return c.begin(); } + auto end() -> iterator { return c.end(); } + + auto begin() const -> const_iterator { return c.begin(); } + auto end() const -> const_iterator { return c.end(); } + + private: + std::vector<T> c; }; -template <size_t N> decltype(auto) get(const my_struct& s) noexcept { - return s.get<N>(); +TEST(ranges_test, format_flat_set) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", flat_set<std::string>{"one", "two"}), + "{\"one\", \"two\"}"); } -namespace std { +namespace adl { +struct box { + int value; +}; -template <> struct tuple_size<my_struct> : std::integral_constant<size_t, 2> {}; +auto begin(const box& b) -> const int* { return &b.value; } +auto end(const box& b) -> const int* { return &b.value + 1; } +} // namespace adl -template <size_t N> struct tuple_element<N, my_struct> { - using type = decltype(std::declval<my_struct>().get<N>()); -}; +TEST(ranges_test, format_adl_begin_end) { + auto b = adl::box{42}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", b), "[42]"); +} -} // namespace std +TEST(ranges_test, format_pair) { + auto p = std::pair<int, float>(42, 1.5f); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", p), "(42, 1.5)"); +} -TEST(RangesTest, FormatStruct) { - my_struct mst{13, "my struct"}; - EXPECT_EQ("(13, \"my struct\")", fmt::format("{}", mst)); +struct unformattable {}; + +TEST(ranges_test, format_tuple) { + auto t = + std::tuple<int, float, std::string, char>(42, 1.5f, "this is tuple", 'i'); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", t), "(42, 1.5, \"this is tuple\", 'i')"); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::tuple<>()), "()"); + + EXPECT_TRUE((fmt::is_formattable<std::tuple<>>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<unformattable>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<std::tuple<unformattable>>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<std::tuple<unformattable, int>>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<std::tuple<int, unformattable>>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE( + (fmt::is_formattable<std::tuple<unformattable, unformattable>>::value)); + EXPECT_TRUE((fmt::is_formattable<std::tuple<int, float>>::value)); } -TEST(RangesTest, FormatTo) { - char buf[10]; - auto end = fmt::format_to(buf, "{}", std::vector{1, 2, 3}); - *end = '\0'; - EXPECT_STREQ(buf, "{1, 2, 3}"); +struct not_default_formattable {}; +struct bad_format {}; + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct formatter<not_default_formattable> { + auto parse(format_parse_context&) -> const char* { throw bad_format(); } + auto format(not_default_formattable, format_context& ctx) + -> format_context::iterator { + return ctx.out(); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(ranges_test, tuple_parse_calls_element_parse) { + auto f = fmt::formatter<std::tuple<not_default_formattable>>(); + auto ctx = fmt::format_parse_context(""); + EXPECT_THROW(f.parse(ctx), bad_format); } -struct path_like { - const path_like* begin() const; - const path_like* end() const; +#ifdef FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_FORMAT_STRUCT +struct tuple_like { + int i; + std::string str; - operator std::string() const; + template <size_t N> + auto get() const noexcept -> fmt::enable_if_t<N == 0, int> { + return i; + } + template <size_t N> + auto get() const noexcept -> fmt::enable_if_t<N == 1, fmt::string_view> { + return str; + } }; -TEST(RangesTest, PathLike) { - EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_range<path_like, char>::value)); +template <size_t N> +auto get(const tuple_like& t) noexcept -> decltype(t.get<N>()) { + return t.get<N>(); } -#endif // (__cplusplus > 201402L) || (defined(_MSVC_LANG) && _MSVC_LANG > - // 201402L && _MSC_VER >= 1910) +namespace std { +template <> +struct tuple_size<tuple_like> : std::integral_constant<size_t, 2> {}; -#ifdef FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW -struct string_like { - const char* begin(); - const char* end(); - explicit operator fmt::string_view() const { return "foo"; } - explicit operator std::string_view() const { return "foo"; } +template <size_t N> struct tuple_element<N, tuple_like> { + using type = decltype(std::declval<tuple_like>().get<N>()); }; +} // namespace std -TEST(RangesTest, FormatStringLike) { - EXPECT_EQ("foo", fmt::format("{}", string_like())); +TEST(ranges_test, format_struct) { + auto t = tuple_like{42, "foo"}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", t), "(42, \"foo\")"); } -#endif // FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW +#endif // FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_FORMAT_STRUCT -struct zstring_sentinel {}; +TEST(ranges_test, format_to) { + char buf[10]; + auto end = fmt::format_to(buf, "{}", std::vector<int>{1, 2, 3}); + *end = '\0'; + EXPECT_STREQ(buf, "[1, 2, 3]"); +} -bool operator==(const char* p, zstring_sentinel) { return *p == '\0'; } -bool operator!=(const char* p, zstring_sentinel) { return *p != '\0'; } +template <typename Char> struct path_like { + auto begin() const -> const path_like*; + auto end() const -> const path_like*; -struct zstring { - const char* p; - const char* begin() const { return p; } - zstring_sentinel end() const { return {}; } + operator std::basic_string<Char>() const; }; -TEST(RangesTest, JoinSentinel) { - zstring hello{"hello"}; - EXPECT_EQ("{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}", fmt::format("{}", hello)); - EXPECT_EQ("h_e_l_l_o", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(hello, "_"))); +TEST(ranges_test, disabled_range_formatting_of_path) { + // Range formatting of path is disabled because of infinite recursion + // (path element is itself a path). + EXPECT_EQ((fmt::range_format_kind<path_like<char>, char>::value), + fmt::range_format::disabled); + EXPECT_EQ((fmt::range_format_kind<path_like<wchar_t>, char>::value), + fmt::range_format::disabled); } -// A range that provides non-const only begin()/end() to test fmt::join handles -// that +// A range that provides non-const only begin()/end() to test fmt::join +// handles that. // -// Some ranges (eg those produced by range-v3's views::filter()) can cache +// Some ranges (e.g. those produced by range-v3's views::filter()) can cache // information during iteration so they only provide non-const begin()/end(). template <typename T> class non_const_only_range { private: @@ -171,33 +240,291 @@ template <typename T> class non_const_only_range { template <typename... Args> explicit non_const_only_range(Args&&... args) - : vec(::std::forward<Args>(args)...) {} + : vec(std::forward<Args>(args)...) {} - const_iterator begin() { return vec.begin(); } - const_iterator end() { return vec.end(); } + auto begin() -> const_iterator{ return vec.begin(); } + auto end() -> const_iterator { return vec.end(); } }; -TEST(RangesTest, JoinRange) { - non_const_only_range<int> x(3u, 0); - EXPECT_EQ("0,0,0", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(x, ","))); - EXPECT_EQ( - "0,0,0", - fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(non_const_only_range<int>(3u, 0), ","))); +template <typename T> class noncopyable_range { + private: + std::vector<T> vec; + + public: + using iterator = typename ::std::vector<T>::iterator; + + template <typename... Args> + explicit noncopyable_range(Args&&... args) + : vec(std::forward<Args>(args)...) {} + + noncopyable_range(noncopyable_range const&) = delete; + noncopyable_range(noncopyable_range&) = delete; - std::vector<int> y(3u, 0); - EXPECT_EQ("0,0,0", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(y, ","))); - EXPECT_EQ("0,0,0", - fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(std::vector<int>(3u, 0), ","))); + auto begin() -> iterator { return vec.begin(); } + auto end() -> iterator { return vec.end(); } +}; + +TEST(ranges_test, range) { + auto&& w = noncopyable_range<int>(3u, 0); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", w), "[0, 0, 0]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", noncopyable_range<int>(3u, 0)), "[0, 0, 0]"); + + auto x = non_const_only_range<int>(3u, 0); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", x), "[0, 0, 0]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", non_const_only_range<int>(3u, 0)), "[0, 0, 0]"); + + auto y = std::vector<int>(3u, 0); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", y), "[0, 0, 0]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::vector<int>(3u, 0)), "[0, 0, 0]"); - const std::vector<int> z(3u, 0); - EXPECT_EQ("0,0,0", fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(z, ","))); + const auto z = std::vector<int>(3u, 0); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", z), "[0, 0, 0]"); } -#if !FMT_MSC_VER || FMT_MSC_VER >= 1927 -struct unformattable {}; +enum test_enum { foo }; +auto format_as(test_enum e) -> int { return e; } + +TEST(ranges_test, enum_range) { + auto v = std::vector<test_enum>{test_enum::foo}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v), "[0]"); +} -TEST(RangesTest, UnformattableRange) { +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION +TEST(ranges_test, unformattable_range) { EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::has_formatter<std::vector<unformattable>, fmt::format_context>::value)); } #endif + +#ifdef FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_JOIN +TEST(ranges_test, join_tuple) { + // Value tuple args. + auto t1 = std::tuple<char, int, float>('a', 1, 2.0f); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("({})", fmt::join(t1, ", ")), "(a, 1, 2)"); + + // Testing lvalue tuple args. + int x = 4; + auto t2 = std::tuple<char, int&>('b', x); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(t2, " + ")), "b + 4"); + + // Empty tuple. + auto t3 = std::tuple<>(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(t3, "|")), ""); + + // Single element tuple. + auto t4 = std::tuple<float>(4.0f); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(t4, "/")), "4"); + +# if FMT_TUPLE_JOIN_SPECIFIERS + // Specs applied to each element. + auto t5 = std::tuple<int, int, long>(-3, 100, 1); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:+03}", fmt::join(t5, ", ")), "-03, +100, +01"); + + auto t6 = std::tuple<float, double, long double>(3, 3.14, 3.1415); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:5.5f}", fmt::join(t6, ", ")), + "3.00000, 3.14000, 3.14150"); + + // Testing lvalue tuple args. + int y = -1; + auto t7 = std::tuple<int, int&, const int&>(3, y, y); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:03}", fmt::join(t7, ", ")), "003, -01, -01"); +# endif +} + +TEST(ranges_test, join_initializer_list) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join({1, 2, 3}, ", ")), "1, 2, 3"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join({"fmt", "rocks", "!"}, " ")), + "fmt rocks !"); +} + +struct zstring_sentinel {}; + +bool operator==(const char* p, zstring_sentinel) { return *p == '\0'; } +bool operator!=(const char* p, zstring_sentinel) { return *p != '\0'; } + +struct zstring { + const char* p; + auto begin() const -> const char* { return p; } + auto end() const -> zstring_sentinel { return {}; } +}; + +# ifdef __cpp_lib_ranges +struct cpp20_only_range { + struct iterator { + int val = 0; + + using value_type = int; + using difference_type = std::ptrdiff_t; + using iterator_concept = std::input_iterator_tag; + + iterator() = default; + iterator(int i) : val(i) {} + auto operator*() const -> int { return val; } + auto operator++() -> iterator&{ + ++val; + return *this; + } + void operator++(int) { ++*this; } + auto operator==(const iterator& rhs) const -> bool { + return val == rhs.val; + } + }; + + int lo; + int hi; + + auto begin() const -> iterator { return iterator(lo); } + auto end() const -> iterator { return iterator(hi); } +}; + +static_assert(std::input_iterator<cpp20_only_range::iterator>); +# endif + +TEST(ranges_test, join_sentinel) { + auto hello = zstring{"hello"}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", hello), "['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{::}", hello), "[h, e, l, l, o]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(hello, "_")), "h_e_l_l_o"); +} + +TEST(ranges_test, join_range) { + auto&& w = noncopyable_range<int>(3u, 0); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(w, ",")), "0,0,0"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(noncopyable_range<int>(3u, 0), ",")), + "0,0,0"); + + auto x = non_const_only_range<int>(3u, 0); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(x, ",")), "0,0,0"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(non_const_only_range<int>(3u, 0), ",")), + "0,0,0"); + + auto y = std::vector<int>(3u, 0); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(y, ",")), "0,0,0"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(std::vector<int>(3u, 0), ",")), + "0,0,0"); + + const auto z = std::vector<int>(3u, 0); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(z, ",")), "0,0,0"); + +# ifdef __cpp_lib_ranges + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", cpp20_only_range{.lo = 0, .hi = 5}), + "[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]"); + EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(cpp20_only_range{.lo = 0, .hi = 5}, ",")), + "0,1,2,3,4"); +# endif +} +#endif // FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_JOIN + +TEST(ranges_test, is_printable) { + using fmt::detail::is_printable; + EXPECT_TRUE(is_printable(0x0323)); + EXPECT_FALSE(is_printable(0x0378)); + EXPECT_FALSE(is_printable(0x110000)); +} + +TEST(ranges_test, escape) { + using vec = std::vector<std::string>; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"\n\r\t\"\\"}), "[\"\\n\\r\\t\\\"\\\\\"]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"\x07"}), "[\"\\x07\"]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"\x7f"}), "[\"\\x7f\"]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"n\xcc\x83"}), "[\"n\xcc\x83\"]"); + + if (fmt::detail::is_utf8()) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"\xcd\xb8"}), "[\"\\u0378\"]"); + // Unassigned Unicode code points. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"\xf0\xaa\x9b\x9e"}), "[\"\\U0002a6de\"]"); + // Broken utf-8. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"\xf4\x8f\xbf\xc0"}), + "[\"\\xf4\\x8f\\xbf\\xc0\"]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"\xf0\x28"}), "[\"\\xf0(\"]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"\xe1\x28"}), "[\"\\xe1(\"]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{std::string("\xf0\x28\0\0anything", 12)}), + "[\"\\xf0(\\x00\\x00anything\"]"); + + // Correct utf-8. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec{"🦄"}), "[\"🦄\"]"); + } + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::vector<std::vector<char>>{{'x'}}), + "[['x']]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::tuple<std::vector<char>>{{'x'}}), "(['x'])"); +} + +template <typename R> struct fmt_ref_view { + R* r; + + auto begin() const -> decltype(r->begin()) { return r->begin(); } + auto end() const -> decltype(r->end()) { return r->end(); } +}; + +TEST(ranges_test, range_of_range_of_mixed_const) { + auto v = std::vector<std::vector<int>>{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5}}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v), "[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]"); + + auto r = fmt_ref_view<decltype(v)>{&v}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", r), "[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]"); +} + +TEST(ranges_test, vector_char) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::vector<char>{'a', 'b'}), "['a', 'b']"); +} + +TEST(ranges_test, container_adaptor) { + { + using fmt::detail::is_container_adaptor_like; + using T = std::nullptr_t; + static_assert(is_container_adaptor_like<std::stack<T>>::value, ""); + static_assert(is_container_adaptor_like<std::queue<T>>::value, ""); + static_assert(is_container_adaptor_like<std::priority_queue<T>>::value, ""); + static_assert(!is_container_adaptor_like<std::vector<T>>::value, ""); + } + + { + auto s = std::stack<int>(); + s.push(1); + s.push(2); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", s), "[1, 2]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", const_cast<const decltype(s)&>(s)), "[1, 2]"); + } + + { + auto q = std::queue<int>(); + q.push(1); + q.push(2); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", q), "[1, 2]"); + } + + { + auto q = std::priority_queue<int>(); + q.push(3); + q.push(1); + q.push(2); + q.push(4); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", q), "[4, 3, 2, 1]"); + } + + { + auto s = std::stack<char, std::string>(); + s.push('a'); + s.push('b'); + // See https://cplusplus.github.io/LWG/issue3881. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", s), "['a', 'b']"); + } + + { + struct my_container_adaptor { + using value_type = int; + using container_type = std::vector<value_type>; + void push(const value_type& v) { c.push_back(v); } + + protected: + container_type c; + }; + + auto m = my_container_adaptor(); + m.push(1); + m.push(2); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", m), "[1, 2]"); + } +} diff --git a/test/scan-test.cc b/test/scan-test.cc index 962de54c..bec54134 100644 --- a/test/scan-test.cc +++ b/test/scan-test.cc @@ -11,25 +11,25 @@ #include <climits> -#include "gmock.h" +#include "gmock/gmock.h" #include "gtest-extra.h" -TEST(ScanTest, ReadText) { - fmt::string_view s = "foo"; +TEST(scan_test, read_text) { + auto s = fmt::string_view("foo"); auto end = fmt::scan(s, "foo"); EXPECT_EQ(end, s.end()); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::scan("fob", "foo"), fmt::format_error, "invalid input"); } -TEST(ScanTest, ReadInt) { - int n = 0; +TEST(scan_test, read_int) { + auto n = int(); fmt::scan("42", "{}", n); EXPECT_EQ(n, 42); fmt::scan("-42", "{}", n); EXPECT_EQ(n, -42); } -TEST(ScanTest, ReadLongLong) { +TEST(scan_test, read_longlong) { long long n = 0; fmt::scan("42", "{}", n); EXPECT_EQ(n, 42); @@ -37,15 +37,15 @@ TEST(ScanTest, ReadLongLong) { EXPECT_EQ(n, -42); } -TEST(ScanTest, ReadUInt) { - unsigned n = 0; +TEST(scan_test, read_uint) { + auto n = unsigned(); fmt::scan("42", "{}", n); EXPECT_EQ(n, 42); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::scan("-42", "{}", n), fmt::format_error, "invalid input"); } -TEST(ScanTest, ReadULongLong) { +TEST(scan_test, read_ulonglong) { unsigned long long n = 0; fmt::scan("42", "{}", n); EXPECT_EQ(n, 42); @@ -53,19 +53,19 @@ TEST(ScanTest, ReadULongLong) { "invalid input"); } -TEST(ScanTest, ReadString) { - std::string s; +TEST(scan_test, read_string) { + auto s = std::string(); fmt::scan("foo", "{}", s); EXPECT_EQ(s, "foo"); } -TEST(ScanTest, ReadStringView) { - fmt::string_view s; +TEST(scan_test, read_string_view) { + auto s = fmt::string_view(); fmt::scan("foo", "{}", s); EXPECT_EQ(s, "foo"); } -#ifndef _WIN32 +#ifdef FMT_HAVE_STRPTIME namespace fmt { template <> struct scanner<tm> { std::string format; @@ -90,8 +90,8 @@ template <> struct scanner<tm> { }; } // namespace fmt -TEST(ScanTest, ReadCustom) { - const char* input = "Date: 1985-10-25"; +TEST(scan_test, read_custom) { + auto input = "Date: 1985-10-25"; auto t = tm(); fmt::scan(input, "Date: {0:%Y-%m-%d}", t); EXPECT_EQ(t.tm_year, 85); @@ -100,16 +100,16 @@ TEST(ScanTest, ReadCustom) { } #endif -TEST(ScanTest, InvalidFormat) { +TEST(scan_test, invalid_format) { EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::scan("", "{}"), fmt::format_error, "argument index out of range"); EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::scan("", "{"), fmt::format_error, "invalid format string"); } -TEST(ScanTest, Example) { - std::string key; - int value; +TEST(scan_test, example) { + auto key = std::string(); + auto value = int(); fmt::scan("answer = 42", "{} = {}", key, value); EXPECT_EQ(key, "answer"); EXPECT_EQ(value, 42); diff --git a/test/scan.h b/test/scan.h index de82067a..a2cb2aa6 100644 --- a/test/scan.h +++ b/test/scan.h @@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ struct scan_context { public: using iterator = const char*; - explicit scan_context(string_view input) : input_(input) {} + explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_context(string_view input) : input_(input) {} iterator begin() const { return input_.data(); } iterator end() const { return begin() + input_.size(); } @@ -83,17 +83,21 @@ class scan_arg { // TODO: more types }; - scan_arg() : type(scan_type::none_type) {} - scan_arg(int& value) : type(scan_type::int_type), int_value(&value) {} - scan_arg(unsigned& value) : type(scan_type::uint_type), uint_value(&value) {} - scan_arg(long long& value) + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg() : type(scan_type::none_type), int_value(nullptr) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(int& value) + : type(scan_type::int_type), int_value(&value) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(unsigned& value) + : type(scan_type::uint_type), uint_value(&value) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(long long& value) : type(scan_type::long_long_type), long_long_value(&value) {} - scan_arg(unsigned long long& value) + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(unsigned long long& value) : type(scan_type::ulong_long_type), ulong_long_value(&value) {} - scan_arg(std::string& value) : type(scan_type::string_type), string(&value) {} - scan_arg(fmt::string_view& value) + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(std::string& value) + : type(scan_type::string_type), string(&value) {} + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(fmt::string_view& value) : type(scan_type::string_view_type), string_view(&value) {} - template <typename T> scan_arg(T& value) : type(scan_type::custom_type) { + template <typename T> + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(T& value) : type(scan_type::custom_type) { custom.value = &value; custom.scan = scan_custom_arg<T>; } @@ -114,7 +118,7 @@ struct scan_args { const detail::scan_arg* data; template <size_t N> - scan_args(const std::array<detail::scan_arg, N>& store) + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_args(const std::array<detail::scan_arg, N>& store) : size(N), data(store.data()) { static_assert(N < INT_MAX, "too many arguments"); } @@ -154,7 +158,8 @@ struct scan_handler : error_handler { } public: - scan_handler(string_view format, string_view input, scan_args args) + FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_handler(string_view format, string_view input, + scan_args args) : parse_ctx_(format), scan_ctx_(input), args_(args), next_arg_id_(0) {} const char* pos() const { return scan_ctx_.begin(); } @@ -162,20 +167,21 @@ struct scan_handler : error_handler { void on_text(const char* begin, const char* end) { auto size = to_unsigned(end - begin); auto it = scan_ctx_.begin(); - if (it + size > scan_ctx_.end() || - !std::equal(begin, end, make_checked(it, size))) { + if (it + size > scan_ctx_.end() || !std::equal(begin, end, it)) on_error("invalid input"); - } scan_ctx_.advance_to(it + size); } - int on_arg_id() { return on_arg_id(next_arg_id_++); } - int on_arg_id(int id) { + FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id() { return on_arg_id(next_arg_id_++); } + FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(int id) { if (id >= args_.size) on_error("argument index out of range"); arg_ = args_.data[id]; return id; } - int on_arg_id(string_view) { return on_error("invalid format"), 0; } + FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(string_view id) { + if (id.data()) on_error("invalid format"); + return 0; + } void on_replacement_field(int, const char*) { auto it = scan_ctx_.begin(), end = scan_ctx_.end(); diff --git a/test/static-export-test/CMakeLists.txt b/test/static-export-test/CMakeLists.txt new file mode 100644 index 00000000..492194f9 --- /dev/null +++ b/test/static-export-test/CMakeLists.txt @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ +cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8...3.25) + +project(fmt-link CXX) + +set(BUILD_SHARED_LIBS OFF) +set(CMAKE_VISIBILITY_INLINES_HIDDEN TRUE) +set(CMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET "hidden") + +# Broken LTO on GCC 4 +if (CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX AND CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 5) + set(BROKEN_LTO ON) +endif () + +if (NOT BROKEN_LTO AND CMAKE_VERSION VERSION_GREATER "3.8") + # CMake 3.9+ + include(CheckIPOSupported) + check_ipo_supported(RESULT HAVE_IPO) + if (HAVE_IPO) + set(CMAKE_INTERPROCEDURAL_OPTIMIZATION TRUE) + endif () +endif () + +add_subdirectory(../.. fmt) +set_property(TARGET fmt PROPERTY POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE ON) + +add_library(library-test SHARED library.cc) +target_link_libraries(library-test PRIVATE fmt::fmt) + +add_executable(exe-test main.cc) +target_link_libraries(exe-test PRIVATE library-test) diff --git a/test/static-export-test/library.cc b/test/static-export-test/library.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..fe4801ba --- /dev/null +++ b/test/static-export-test/library.cc @@ -0,0 +1,5 @@ +#include <fmt/compile.h> + +__attribute__((visibility("default"))) std::string foo() { + return fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("foo bar {}"), 4242); +} diff --git a/test/static-export-test/main.cc b/test/static-export-test/main.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..38f7999e --- /dev/null +++ b/test/static-export-test/main.cc @@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ +#include <iostream> +#include <string> + +extern std::string foo(); + +int main() { std::cout << foo() << std::endl; } diff --git a/test/std-format-test.cc b/test/std-format-test.cc deleted file mode 100644 index 8bf4b6d1..00000000 --- a/test/std-format-test.cc +++ /dev/null @@ -1,157 +0,0 @@ -#include <format> - -#include "gtest.h" - -TEST(StdFormatTest, Escaping) { - using namespace std; - string s = format("{0}-{{", 8); // s == "8-{" - EXPECT_EQ(s, "8-{"); -} - -TEST(StdFormatTest, Indexing) { - using namespace std; - string s0 = format("{} to {}", "a", "b"); // OK: automatic indexing - string s1 = format("{1} to {0}", "a", "b"); // OK: manual indexing - EXPECT_EQ(s0, "a to b"); - EXPECT_EQ(s1, "b to a"); - // Error: mixing automatic and manual indexing - EXPECT_THROW(string s2 = format("{0} to {}", "a", "b"), std::format_error); - // Error: mixing automatic and manual indexing - EXPECT_THROW(string s3 = format("{} to {1}", "a", "b"), std::format_error); -} - -TEST(StdFormatTest, Alignment) { - using namespace std; - char c = 120; - string s0 = format("{:6}", 42); // s0 == " 42" - string s1 = format("{:6}", 'x'); // s1 == "x " - string s2 = format("{:*<6}", 'x'); // s2 == "x*****" - string s3 = format("{:*>6}", 'x'); // s3 == "*****x" - string s4 = format("{:*^6}", 'x'); // s4 == "**x***" - // Error: '=' with charT and no integer presentation type - EXPECT_THROW(string s5 = format("{:=6}", 'x'), std::format_error); - string s6 = format("{:6d}", c); // s6 == " 120" - string s7 = format("{:6}", true); // s9 == "true " - EXPECT_EQ(s0, " 42"); - EXPECT_EQ(s1, "x "); - EXPECT_EQ(s2, "x*****"); - EXPECT_EQ(s3, "*****x"); - EXPECT_EQ(s4, "**x***"); - EXPECT_EQ(s6, " 120"); - EXPECT_EQ(s7, "true "); -} - -TEST(StdFormatTest, Float) { - using namespace std; - double inf = numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); - double nan = numeric_limits<double>::quiet_NaN(); - string s0 = format("{0:} {0:+} {0:-} {0: }", 1); // s0 == "1 +1 1 1" - string s1 = format("{0:} {0:+} {0:-} {0: }", -1); // s1 == "-1 -1 -1 -1" - string s2 = - format("{0:} {0:+} {0:-} {0: }", inf); // s2 == "inf +inf inf inf" - string s3 = - format("{0:} {0:+} {0:-} {0: }", nan); // s3 == "nan +nan nan nan" - EXPECT_EQ(s0, "1 +1 1 1"); - EXPECT_EQ(s1, "-1 -1 -1 -1"); - EXPECT_EQ(s2, "inf +inf inf inf"); - EXPECT_EQ(s3, "nan +nan nan nan"); -} - -TEST(StdFormatTest, Int) { - using namespace std; - string s0 = format("{}", 42); // s0 == "42" - string s1 = format("{0:b} {0:d} {0:o} {0:x}", 42); // s1 == "101010 42 52 2a" - string s2 = format("{0:#x} {0:#X}", 42); // s2 == "0x2a 0X2A" - string s3 = format("{:L}", 1234); // s3 == "1234" (depends on the locale) - EXPECT_EQ(s0, "42"); - EXPECT_EQ(s1, "101010 42 52 2a"); - EXPECT_EQ(s2, "0x2a 0X2A"); - EXPECT_EQ(s3, "1234"); -} - -#include <format> - -enum color { red, green, blue }; - -const char* color_names[] = {"red", "green", "blue"}; - -template <> struct std::formatter<color> : std::formatter<const char*> { - auto format(color c, format_context& ctx) { - return formatter<const char*>::format(color_names[c], ctx); - } -}; - -struct err {}; - -TEST(StdFormatTest, Formatter) { - std::string s0 = std::format("{}", 42); // OK: library-provided formatter - // std::string s1 = std::format("{}", L"foo"); // Ill-formed: disabled - // formatter - std::string s2 = std::format("{}", red); // OK: user-provided formatter - // std::string s3 = std::format("{}", err{}); // Ill-formed: disabled - // formatter - EXPECT_EQ(s0, "42"); - EXPECT_EQ(s2, "red"); -} - -struct S { - int value; -}; - -template <> struct std::formatter<S> { - size_t width_arg_id = 0; - - // Parses a width argument id in the format { <digit> }. - constexpr auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) { - auto iter = ctx.begin(); - // auto get_char = [&]() { return iter != ctx.end() ? *iter : 0; }; - auto get_char = [&]() { return iter != ctx.end() ? *iter : '\0'; }; - if (get_char() != '{') return iter; - ++iter; - char c = get_char(); - if (!isdigit(c) || (++iter, get_char()) != '}') - throw format_error("invalid format"); - width_arg_id = c - '0'; - ctx.check_arg_id(width_arg_id); - return ++iter; - } - - // Formats S with width given by the argument width_arg_id. - auto format(S s, format_context& ctx) { - int width = visit_format_arg( - [](auto value) -> int { - using type = decltype(value); - if constexpr (!is_integral_v<type> || is_same_v<type, bool>) - throw format_error("width is not integral"); - // else if (value < 0 || value > numeric_limits<int>::max()) - else if (fmt::detail::is_negative(value) || - value > numeric_limits<int>::max()) - throw format_error("invalid width"); - else - return static_cast<int>(value); - }, - ctx.arg(width_arg_id)); - return format_to(ctx.out(), "{0:{1}}", s.value, width); - } -}; - -TEST(StdFormatTest, Parsing) { - std::string s = std::format("{0:{1}}", S{42}, 10); // s == " 42" - EXPECT_EQ(s, " 42"); -} - -#if FMT_USE_INT128 -template <> struct std::formatter<__int128_t> : std::formatter<long long> { - auto format(__int128_t n, format_context& ctx) { - // Format as a long long since we only want to check if it is possible to - // specialize formatter for __int128_t. - return formatter<long long>::format(static_cast<long long>(n), ctx); - } -}; - -TEST(StdFormatTest, Int128) { - __int128_t n = 42; - auto s = std::format("{}", n); - EXPECT_EQ(s, "42"); -} -#endif // FMT_USE_INT128 diff --git a/test/std-test.cc b/test/std-test.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..41183dbf --- /dev/null +++ b/test/std-test.cc @@ -0,0 +1,264 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - tests of formatters for standard library types +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#include "fmt/std.h" + +#include <bitset> +#include <stdexcept> +#include <string> +#include <vector> + +#include "fmt/os.h" // fmt::system_category +#include "fmt/ranges.h" +#include "gtest-extra.h" // StartsWith + +#ifdef __cpp_lib_filesystem +TEST(std_test, path) { + using std::filesystem::path; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", path("/usr/bin")), "/usr/bin"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:?}", path("/usr/bin")), "\"/usr/bin\""); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:8}", path("foo")), "foo "); + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", path("foo\"bar")), "foo\"bar"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:?}", path("foo\"bar")), "\"foo\\\"bar\""); + +# ifdef _WIN32 + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", path( + L"\x0428\x0447\x0443\x0447\x044B\x043D\x0448" + L"\x0447\x044B\x043D\x0430")), + "Шчучыншчына"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", path(L"\xd800")), "�"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:?}", path(L"\xd800")), "\"\\ud800\""); +# endif +} + +// Test ambiguity problem described in #2954. +TEST(ranges_std_test, format_vector_path) { + auto p = std::filesystem::path("foo/bar.txt"); + auto c = std::vector<std::string>{"abc", "def"}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("path={}, range={}", p, c), + "path=foo/bar.txt, range=[\"abc\", \"def\"]"); +} + +// Test that path is not escaped twice in the debug mode. +TEST(ranges_std_test, format_quote_path) { + auto vec = + std::vector<std::filesystem::path>{"path1/file1.txt", "path2/file2.txt"}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", vec), + "[\"path1/file1.txt\", \"path2/file2.txt\"]"); +# ifdef __cpp_lib_optional + auto o = std::optional<std::filesystem::path>("path/file.txt"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", o), "optional(\"path/file.txt\")"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:?}", o), "optional(\"path/file.txt\")"); +# endif +} +#endif + +TEST(std_test, thread_id) { + EXPECT_FALSE(fmt::format("{}", std::this_thread::get_id()).empty()); +} + +TEST(std_test, optional) { +#ifdef __cpp_lib_optional + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::optional<int>{}), "none"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::pair{1, "second"}), "(1, \"second\")"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::vector{std::optional{1}, std::optional{2}, + std::optional{3}}), + "[optional(1), optional(2), optional(3)]"); + EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format("{}", std::optional<std::optional<const char*>>{{"nested"}}), + "optional(optional(\"nested\"))"); + EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format("{:<{}}", std::optional{std::string{"left aligned"}}, 30), + "optional(\"left aligned\" )"); + EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format("{::d}", std::optional{std::vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}}), + "optional([104, 101, 108, 108, 111])"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::optional{std::string{"string"}}), + "optional(\"string\")"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::optional{'C'}), "optional(\'C\')"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.{}f}", std::optional{3.14}, 1), "optional(3.1)"); + + struct unformattable {}; + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<unformattable>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<std::optional<unformattable>>::value)); + EXPECT_TRUE((fmt::is_formattable<std::optional<int>>::value)); +#endif +} + +struct throws_on_move { + throws_on_move() = default; + + [[noreturn]] throws_on_move(throws_on_move&&) { + throw std::runtime_error("Thrown by throws_on_move"); + } + + throws_on_move(const throws_on_move&) = default; +}; + +namespace fmt { +template <> struct formatter<throws_on_move> : formatter<string_view> { + auto format(const throws_on_move&, format_context& ctx) const + -> decltype(ctx.out()) { + string_view str("<throws_on_move>"); + return formatter<string_view>::format(str, ctx); + } +}; +} // namespace fmt + +TEST(std_test, variant) { +#ifdef __cpp_lib_variant + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::monostate{}), "monostate"); + using V0 = std::variant<int, float, std::string, char>; + V0 v0(42); + V0 v1(1.5f); + V0 v2("hello"); + V0 v3('i'); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v0), "variant(42)"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v1), "variant(1.5)"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v2), "variant(\"hello\")"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v3), "variant('i')"); + + struct unformattable {}; + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<unformattable>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<std::variant<unformattable>>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<std::variant<unformattable, int>>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE((fmt::is_formattable<std::variant<int, unformattable>>::value)); + EXPECT_FALSE( + (fmt::is_formattable<std::variant<unformattable, unformattable>>::value)); + EXPECT_TRUE((fmt::is_formattable<std::variant<int, float>>::value)); + + using V1 = std::variant<std::monostate, std::string, std::string>; + V1 v4{}; + V1 v5{std::in_place_index<1>, "yes, this is variant"}; + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v4), "variant(monostate)"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v5), "variant(\"yes, this is variant\")"); + + volatile int i = 42; // Test compile error before GCC 11 described in #3068. + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", i), "42"); + + std::variant<std::monostate, throws_on_move> v6; + + try { + throws_on_move thrower; + v6.emplace<throws_on_move>(std::move(thrower)); + } catch (const std::runtime_error&) { + } + // v6 is now valueless by exception + + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v6), "variant(valueless by exception)"); + +#endif +} + +TEST(std_test, error_code) { + EXPECT_EQ("generic:42", + fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{0}"), + std::error_code(42, std::generic_category()))); + EXPECT_EQ("system:42", + fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{0}"), + std::error_code(42, fmt::system_category()))); + EXPECT_EQ("system:-42", + fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{0}"), + std::error_code(-42, fmt::system_category()))); +} + +template <typename Catch> void exception_test() { + try { + throw std::runtime_error("Test Exception"); + } catch (const Catch& ex) { + EXPECT_EQ("Test Exception", fmt::format("{}", ex)); + EXPECT_EQ("std::runtime_error: Test Exception", fmt::format("{:t}", ex)); + } +} + +namespace my_ns1 { +namespace my_ns2 { +struct my_exception : public std::exception { + private: + std::string msg; + + public: + my_exception(const std::string& s) : msg(s) {} + const char* what() const noexcept override; +}; +const char* my_exception::what() const noexcept { return msg.c_str(); } +} // namespace my_ns2 +} // namespace my_ns1 + +TEST(std_test, exception) { + using testing::StartsWith; + exception_test<std::exception>(); + exception_test<std::runtime_error>(); + + try { + using namespace my_ns1::my_ns2; + throw my_exception("My Exception"); + } catch (const std::exception& ex) { + EXPECT_EQ("my_ns1::my_ns2::my_exception: My Exception", + fmt::format("{:t}", ex)); + EXPECT_EQ("My Exception", fmt::format("{:}", ex)); + } + + try { + throw std::system_error(std::error_code(), "message"); + } catch (const std::system_error& ex) { + EXPECT_THAT(fmt::format("{:t}", ex), StartsWith("std::system_error: ")); + } + +#ifdef __cpp_lib_filesystem + // Tests that the inline namespace is stripped out, e.g. + // std::filesystem::__cxx11::* -> std::filesystem::*. + try { + throw std::filesystem::filesystem_error("message", std::error_code()); + } catch (const std::filesystem::filesystem_error& ex) { + EXPECT_THAT(fmt::format("{:t}", ex), + StartsWith("std::filesystem::filesystem_error: ")); + } +#endif +} + +TEST(std_test, format_bit_reference) { + std::bitset<2> bs(1); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{} {}", bs[0], bs[1]), "true false"); + std::vector<bool> v = {true, false}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{} {}", v[0], v[1]), "true false"); +} + +TEST(std_test, format_const_bit_reference) { + const std::bitset<2> bs(1); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{} {}", bs[0], bs[1]), "true false"); + const std::vector<bool> v = {true, false}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{} {}", v[0], v[1]), "true false"); +} + +TEST(std_test, format_bitset) { + auto bs = std::bitset<6>(42); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", bs), "101010"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:0>8}", bs), "00101010"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:-^12}", bs), "---101010---"); +} + +TEST(std_test, format_atomic) { + std::atomic<bool> b(false); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", b), "false"); + + const std::atomic<bool> cb(true); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", cb), "true"); +} + +#ifdef __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test +TEST(std_test, format_atomic_flag) { + std::atomic_flag f = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT; + (void) f.test_and_set(); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", f), "true"); + + const std::atomic_flag cf = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", cf), "false"); +} +#endif // __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test diff --git a/test/test-assert.h b/test/test-assert.h index f613722f..ab7b2bf7 100644 --- a/test/test-assert.h +++ b/test/test-assert.h @@ -10,7 +10,11 @@ #include <stdexcept> -#include "gtest.h" +void throw_assertion_failure(const char* message); +#define FMT_ASSERT(condition, message) \ + if (!(condition)) throw_assertion_failure(message); + +#include "gtest/gtest.h" class assertion_failure : public std::logic_error { public: @@ -22,8 +26,11 @@ class assertion_failure : public std::logic_error { void assertion_failure::avoid_weak_vtable() {} -#define FMT_ASSERT(condition, message) \ - if (!(condition)) throw assertion_failure(message); +// We use a separate function (rather than throw directly from FMT_ASSERT) to +// avoid GCC's -Wterminate warning when FMT_ASSERT is used in a destructor. +inline void throw_assertion_failure(const char* message) { + throw assertion_failure(message); +} // Expects an assertion failure. #define EXPECT_ASSERT(stmt, message) \ diff --git a/test/test-main.cc b/test/test-main.cc index 8db257d6..39d2789d 100644 --- a/test/test-main.cc +++ b/test/test-main.cc @@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ #include <cstdlib> -#include "gtest.h" +#include "gtest/gtest.h" #ifdef _WIN32 # include <windows.h> @@ -15,9 +15,6 @@ #ifdef _MSC_VER # include <crtdbg.h> -#else -# define _CrtSetReportFile(a, b) -# define _CrtSetReportMode(a, b) #endif int main(int argc, char** argv) { @@ -28,13 +25,16 @@ int main(int argc, char** argv) { SetErrorMode(SEM_FAILCRITICALERRORS | SEM_NOGPFAULTERRORBOX | SEM_NOOPENFILEERRORBOX); #endif +#ifdef _MSC_VER // Disable message boxes on assertion failures. _CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_ERROR, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE | _CRTDBG_MODE_DEBUG); _CrtSetReportFile(_CRT_ERROR, _CRTDBG_FILE_STDERR); _CrtSetReportMode(_CRT_ASSERT, _CRTDBG_MODE_FILE | _CRTDBG_MODE_DEBUG); _CrtSetReportFile(_CRT_ASSERT, _CRTDBG_FILE_STDERR); +#endif try { testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); + testing::FLAGS_gtest_death_test_style = "threadsafe"; return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); } catch (...) { // Catch all exceptions to make Coverity happy. diff --git a/test/unicode-test.cc b/test/unicode-test.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..e9ea5e5e --- /dev/null +++ b/test/unicode-test.cc @@ -0,0 +1,48 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - Unicode tests +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#include <iomanip> +#include <locale> +#include <vector> + +#include "fmt/chrono.h" +#include "gmock/gmock.h" +#include "util.h" // get_locale + +using testing::Contains; + +TEST(unicode_test, is_utf8) { EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_utf8()); } + +TEST(unicode_test, legacy_locale) { + auto loc = get_locale("be_BY.CP1251", "Belarusian_Belarus.1251"); + if (loc == std::locale::classic()) return; + + auto s = std::string(); + try { + s = fmt::format(loc, "Дзень тыдня: {:L}", fmt::weekday(1)); + } catch (const fmt::format_error& e) { + // Formatting can fail due to an unsupported encoding. + fmt::print("Format error: {}\n", e.what()); + return; + } + +#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 500 + auto&& os = std::ostringstream(); + os.imbue(loc); + auto tm = std::tm(); + tm.tm_wday = 1; + os << std::put_time(&tm, "%a"); + auto wd = os.str(); + if (wd == "??") { + EXPECT_EQ(s, "Дзень тыдня: ??"); + fmt::print("std::locale gives ?? as a weekday.\n"); + return; + } +#endif + EXPECT_THAT((std::vector<std::string>{"Дзень тыдня: пн", "Дзень тыдня: Пан"}), + Contains(s)); +} diff --git a/test/util.cc b/test/util.cc index d08dcbdc..4ff34a91 100644 --- a/test/util.cc +++ b/test/util.cc @@ -9,42 +9,37 @@ #include <cstring> -void increment(char* s) { - for (int i = static_cast<int>(std::strlen(s)) - 1; i >= 0; --i) { - if (s[i] != '9') { - ++s[i]; - break; - } - s[i] = '0'; - } -} - -std::string get_system_error(int error_code) { -#if defined(__MINGW32__) || !defined(_WIN32) - return strerror(error_code); -#else - enum { BUFFER_SIZE = 200 }; - char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; - if (strerror_s(buffer, BUFFER_SIZE, error_code)) - throw std::exception("strerror_s failed"); - return buffer; -#endif -} - -const char* const FILE_CONTENT = "Don't panic!"; +const char* const file_content = "Don't panic!"; fmt::buffered_file open_buffered_file(FILE** fp) { #if FMT_USE_FCNTL fmt::file read_end, write_end; fmt::file::pipe(read_end, write_end); - write_end.write(FILE_CONTENT, std::strlen(FILE_CONTENT)); + write_end.write(file_content, std::strlen(file_content)); write_end.close(); fmt::buffered_file f = read_end.fdopen("r"); if (fp) *fp = f.get(); #else fmt::buffered_file f("test-file", "w"); - fputs(FILE_CONTENT, f.get()); + fputs(file_content, f.get()); if (fp) *fp = f.get(); #endif return f; } + +std::locale do_get_locale(const char* name) { + try { + return std::locale(name); + } catch (const std::runtime_error&) { + } + return std::locale::classic(); +} + +std::locale get_locale(const char* name, const char* alt_name) { + auto loc = do_get_locale(name); + if (loc == std::locale::classic() && alt_name) + loc = do_get_locale(alt_name); + if (loc == std::locale::classic()) + fmt::print(stderr, "{} locale is missing.\n", name); + return loc; +} diff --git a/test/util.h b/test/util.h index 24a5f4e3..9120e22e 100644 --- a/test/util.h +++ b/test/util.h @@ -7,12 +7,11 @@ #include <cstdarg> #include <cstdio> +#include <locale> #include <string> #include "fmt/os.h" -enum { BUFFER_SIZE = 256 }; - #ifdef _MSC_VER # define FMT_VSNPRINTF vsprintf_s #else @@ -27,12 +26,7 @@ void safe_sprintf(char (&buffer)[SIZE], const char* format, ...) { va_end(args); } -// Increment a number in a string. -void increment(char* s); - -std::string get_system_error(int error_code); - -extern const char* const FILE_CONTENT; +extern const char* const file_content; // Opens a buffered file for reading. fmt::buffered_file open_buffered_file(FILE** fp = nullptr); @@ -40,7 +34,7 @@ fmt::buffered_file open_buffered_file(FILE** fp = nullptr); inline FILE* safe_fopen(const char* filename, const char* mode) { #if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__) // Fix MSVC warning about "unsafe" fopen. - FILE* f = 0; + FILE* f = nullptr; errno = fopen_s(&f, filename, mode); return f; #else @@ -48,37 +42,40 @@ inline FILE* safe_fopen(const char* filename, const char* mode) { #endif } -template <typename Char> class BasicTestString { +template <typename Char> class basic_test_string { private: std::basic_string<Char> value_; - static const Char EMPTY[]; + static const Char empty[]; public: - explicit BasicTestString(const Char* value = EMPTY) : value_(value) {} + explicit basic_test_string(const Char* value = empty) : value_(value) {} const std::basic_string<Char>& value() const { return value_; } }; -template <typename Char> const Char BasicTestString<Char>::EMPTY[] = {0}; +template <typename Char> const Char basic_test_string<Char>::empty[] = {0}; -typedef BasicTestString<char> TestString; -typedef BasicTestString<wchar_t> TestWString; +typedef basic_test_string<char> test_string; +typedef basic_test_string<wchar_t> test_wstring; template <typename Char> std::basic_ostream<Char>& operator<<(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, - const BasicTestString<Char>& s) { + const basic_test_string<Char>& s) { os << s.value(); return os; } -class Date { +class date { int year_, month_, day_; public: - Date(int year, int month, int day) : year_(year), month_(month), day_(day) {} + date(int year, int month, int day) : year_(year), month_(month), day_(day) {} int year() const { return year_; } int month() const { return month_; } int day() const { return day_; } }; + +// Returns a locale with the given name if available or classic locale otherwise. +std::locale get_locale(const char* name, const char* alt_name = nullptr); diff --git a/test/xchar-test.cc b/test/xchar-test.cc new file mode 100644 index 00000000..f72e94dc --- /dev/null +++ b/test/xchar-test.cc @@ -0,0 +1,641 @@ +// Formatting library for C++ - formatting library tests +// +// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich +// All rights reserved. +// +// For the license information refer to format.h. + +#include "fmt/xchar.h" + +#include <algorithm> +#include <complex> +#include <cwchar> +#include <vector> + +#include "fmt/chrono.h" +#include "fmt/color.h" +#include "fmt/ostream.h" +#include "fmt/ranges.h" +#include "fmt/std.h" +#include "gtest-extra.h" // Contains +#include "util.h" // get_locale + +using fmt::detail::max_value; +using testing::Contains; + +#if defined(__MINGW32__) && !defined(_UCRT) +// Only C89 conversion specifiers when using MSVCRT instead of UCRT +# define FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME 0 +#else +# define FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME 1 +#endif + +struct non_string {}; + +template <typename T> class is_string_test : public testing::Test {}; + +using string_char_types = testing::Types<char, wchar_t, char16_t, char32_t>; +TYPED_TEST_SUITE(is_string_test, string_char_types); + +template <typename Char> +struct derived_from_string_view : fmt::basic_string_view<Char> {}; + +TYPED_TEST(is_string_test, is_string) { + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<TypeParam*>::value); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<const TypeParam*>::value); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<TypeParam[2]>::value); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<const TypeParam[2]>::value); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<std::basic_string<TypeParam>>::value); + EXPECT_TRUE(fmt::detail::is_string<fmt::basic_string_view<TypeParam>>::value); + EXPECT_TRUE( + fmt::detail::is_string<derived_from_string_view<TypeParam>>::value); + using fmt_string_view = fmt::detail::std_string_view<TypeParam>; + EXPECT_TRUE(std::is_empty<fmt_string_view>::value != + fmt::detail::is_string<fmt_string_view>::value); + EXPECT_FALSE(fmt::detail::is_string<non_string>::value); +} + +// std::is_constructible is broken in MSVC until version 2015. +#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1900 +struct explicitly_convertible_to_wstring_view { + explicit operator fmt::wstring_view() const { return L"foo"; } +}; + +TEST(xchar_test, format_explicitly_convertible_to_wstring_view) { + // Types explicitly convertible to wstring_view are not formattable by + // default because it may introduce ODR violations. + static_assert( + !fmt::is_formattable<explicitly_convertible_to_wstring_view>::value, ""); +} +#endif + +TEST(xchar_test, format) { + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::format(L"{}", 42)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"4.2", fmt::format(L"{}", 4.2)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"abc", fmt::format(L"{}", L"abc")); + EXPECT_EQ(L"z", fmt::format(L"{}", L'z')); + EXPECT_THROW(fmt::format(fmt::runtime(L"{:*\x343E}"), 42), fmt::format_error); + EXPECT_EQ(L"true", fmt::format(L"{}", true)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"a", fmt::format(L"{0}", 'a')); + EXPECT_EQ(L"a", fmt::format(L"{0}", L'a')); + EXPECT_EQ(L"Cyrillic letter \x42e", + fmt::format(L"Cyrillic letter {}", L'\x42e')); + EXPECT_EQ(L"abc1", fmt::format(L"{}c{}", L"ab", 1)); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, is_formattable) { + static_assert(!fmt::is_formattable<const wchar_t*>::value, ""); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, compile_time_string) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fmt::wformat_string<int>(L"{}"), 42), L"42"); +#if defined(FMT_USE_STRING_VIEW) && FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(FMT_STRING(std::wstring_view(L"{}")), 42), L"42"); +#endif +} + +#if FMT_CPLUSPLUS > 201103L +struct custom_char { + int value; + custom_char() = default; + + template <typename T> + constexpr custom_char(T val) : value(static_cast<int>(val)) {} + + constexpr operator char() const { + return value <= 0xff ? static_cast<char>(value) : '\0'; + } + constexpr bool operator<(custom_char c) const { return value < c.value; } +}; + +namespace std { + +template <> struct char_traits<custom_char> { + using char_type = custom_char; + using int_type = int; + using off_type = streamoff; + using pos_type = streampos; + using state_type = mbstate_t; + + static constexpr void assign(char_type& r, const char_type& a) { r = a; } + static constexpr bool eq(char_type a, char_type b) { return a == b; } + static constexpr bool lt(char_type a, char_type b) { return a < b; } + static FMT_CONSTEXPR int compare(const char_type* s1, const char_type* s2, + size_t count) { + for (; count; count--, s1++, s2++) { + if (lt(*s1, *s2)) return -1; + if (lt(*s2, *s1)) return 1; + } + return 0; + } + static FMT_CONSTEXPR size_t length(const char_type* s) { + size_t count = 0; + while (!eq(*s++, custom_char(0))) count++; + return count; + } + static const char_type* find(const char_type*, size_t, const char_type&); + static FMT_CONSTEXPR char_type* move(char_type* dest, const char_type* src, + size_t count) { + if (count == 0) return dest; + char_type* ret = dest; + if (src < dest) { + dest += count; + src += count; + for (; count; count--) assign(*--dest, *--src); + } else if (src > dest) + copy(dest, src, count); + return ret; + } + static FMT_CONSTEXPR char_type* copy(char_type* dest, const char_type* src, + size_t count) { + char_type* ret = dest; + for (; count; count--) assign(*dest++, *src++); + return ret; + } + static FMT_CONSTEXPR char_type* assign(char_type* dest, std::size_t count, + char_type a) { + char_type* ret = dest; + for (; count; count--) assign(*dest++, a); + return ret; + } + static int_type not_eof(int_type); + static char_type to_char_type(int_type); + static int_type to_int_type(char_type); + static bool eq_int_type(int_type, int_type); + static int_type eof(); +}; + +} // namespace std + +auto to_ascii(custom_char c) -> char { return c; } + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <> struct is_char<custom_char> : std::true_type {}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(xchar_test, format_custom_char) { + const custom_char format[] = {'{', '}', 0}; + auto result = fmt::format(format, custom_char('x')); + EXPECT_EQ(result.size(), 1); + EXPECT_EQ(result[0], custom_char('x')); +} +#endif + +// Convert a char8_t string to std::string. Otherwise GTest will insist on +// inserting `char8_t` NTBS into a `char` stream which is disabled by P1423. +template <typename S> std::string from_u8str(const S& str) { + return std::string(str.begin(), str.end()); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, format_utf8_precision) { + using str_type = std::basic_string<fmt::detail::char8_type>; + auto format = + str_type(reinterpret_cast<const fmt::detail::char8_type*>(u8"{:.4}")); + auto str = str_type(reinterpret_cast<const fmt::detail::char8_type*>( + u8"caf\u00e9s")); // cafés + auto result = fmt::format(format, str); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::compute_width(result), 4); + EXPECT_EQ(result.size(), 5); + EXPECT_EQ(from_u8str(result), from_u8str(str.substr(0, 5))); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, format_to) { + auto buf = std::vector<wchar_t>(); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), L"{}{}", 42, L'\0'); + EXPECT_STREQ(buf.data(), L"42"); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, vformat_to) { + auto args = fmt::make_wformat_args(42); + auto w = std::wstring(); + fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(w), L"{}", args); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42", w); +} + +namespace test { +struct struct_as_wstring_view {}; +auto format_as(struct_as_wstring_view) -> fmt::wstring_view { return L"foo"; } +} // namespace test + +TEST(xchar_test, format_as) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", test::struct_as_wstring_view()), L"foo"); +} + +TEST(format_test, wide_format_to_n) { + wchar_t buffer[4]; + buffer[3] = L'x'; + auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, L"{}", 12345); + EXPECT_EQ(5u, result.size); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer + 3, result.out); + EXPECT_EQ(L"123x", fmt::wstring_view(buffer, 4)); + buffer[0] = L'x'; + buffer[1] = L'x'; + buffer[2] = L'x'; + result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, L"{}", L'A'); + EXPECT_EQ(1u, result.size); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer + 1, result.out); + EXPECT_EQ(L"Axxx", fmt::wstring_view(buffer, 4)); + result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, 3, L"{}{} ", L'B', L'C'); + EXPECT_EQ(3u, result.size); + EXPECT_EQ(buffer + 3, result.out); + EXPECT_EQ(L"BC x", fmt::wstring_view(buffer, 4)); +} + +#if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS +TEST(xchar_test, named_arg_udl) { + using namespace fmt::literals; + auto udl_a = + fmt::format(L"{first}{second}{first}{third}", L"first"_a = L"abra", + L"second"_a = L"cad", L"third"_a = 99); + EXPECT_EQ( + fmt::format(L"{first}{second}{first}{third}", fmt::arg(L"first", L"abra"), + fmt::arg(L"second", L"cad"), fmt::arg(L"third", 99)), + udl_a); +} +#endif // FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS + +TEST(xchar_test, print) { + // Check that the wide print overload compiles. + if (fmt::detail::const_check(false)) { + fmt::print(L"test"); + fmt::println(L"test"); + } +} + +TEST(xchar_test, join) { + int v[3] = {1, 2, 3}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"({})", fmt::join(v, v + 3, L", ")), L"(1, 2, 3)"); + auto t = std::tuple<wchar_t, int, float>('a', 1, 2.0f); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"({})", fmt::join(t, L", ")), L"(a, 1, 2)"); +} + +enum streamable_enum {}; + +std::wostream& operator<<(std::wostream& os, streamable_enum) { + return os << L"streamable_enum"; +} + +namespace fmt { +template <> +struct formatter<streamable_enum, wchar_t> : basic_ostream_formatter<wchar_t> { +}; +} // namespace fmt + +enum unstreamable_enum {}; +auto format_as(unstreamable_enum e) -> int { return e; } + +TEST(xchar_test, enum) { + EXPECT_EQ(L"streamable_enum", fmt::format(L"{}", streamable_enum())); + EXPECT_EQ(L"0", fmt::format(L"{}", unstreamable_enum())); +} + +struct streamable_and_unformattable {}; + +auto operator<<(std::wostream& os, streamable_and_unformattable) + -> std::wostream& { + return os << L"foo"; +} + +TEST(xchar_test, streamed) { + EXPECT_FALSE(fmt::is_formattable<streamable_and_unformattable>()); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", fmt::streamed(streamable_and_unformattable())), + L"foo"); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, sign_not_truncated) { + wchar_t format_str[] = { + L'{', L':', + '+' | static_cast<wchar_t>(1 << fmt::detail::num_bits<char>()), L'}', 0}; + EXPECT_THROW(fmt::format(fmt::runtime(format_str), 42), fmt::format_error); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, chrono) { + auto tm = std::tm(); + tm.tm_year = 116; + tm.tm_mon = 3; + tm.tm_mday = 25; + tm.tm_hour = 11; + tm.tm_min = 22; + tm.tm_sec = 33; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}.", tm), + "The date is 2016-04-25 11:22:33."); + EXPECT_EQ(L"42s", fmt::format(L"{}", std::chrono::seconds(42))); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{:%F}", tm), L"2016-04-25"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{:%T}", tm), L"11:22:33"); +} + +std::wstring system_wcsftime(const std::wstring& format, const std::tm* timeptr, + std::locale* locptr = nullptr) { + auto loc = locptr ? *locptr : std::locale::classic(); + auto& facet = std::use_facet<std::time_put<wchar_t>>(loc); + std::wostringstream os; + os.imbue(loc); + facet.put(os, os, L' ', timeptr, format.c_str(), + format.c_str() + format.size()); +#ifdef _WIN32 + // Workaround a bug in older versions of Universal CRT. + auto str = os.str(); + if (str == L"-0000") str = L"+0000"; + return str; +#else + return os.str(); +#endif +} + +TEST(chrono_test_wchar, time_point) { + auto t1 = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>( + std::chrono::system_clock::now()); + + std::vector<std::wstring> spec_list = { + L"%%", L"%n", L"%t", L"%Y", L"%EY", L"%y", L"%Oy", L"%Ey", L"%C", + L"%EC", L"%G", L"%g", L"%b", L"%h", L"%B", L"%m", L"%Om", L"%U", + L"%OU", L"%W", L"%OW", L"%V", L"%OV", L"%j", L"%d", L"%Od", L"%e", + L"%Oe", L"%a", L"%A", L"%w", L"%Ow", L"%u", L"%Ou", L"%H", L"%OH", + L"%I", L"%OI", L"%M", L"%OM", L"%S", L"%OS", L"%x", L"%Ex", L"%X", + L"%EX", L"%D", L"%F", L"%R", L"%T", L"%p"}; +#ifndef _WIN32 + // Disabled on Windows, because these formats is not consistent among + // platforms. + spec_list.insert(spec_list.end(), {L"%c", L"%Ec", L"%r"}); +#elif !FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME + // Only C89 conversion specifiers when using MSVCRT instead of UCRT + spec_list = {L"%%", L"%Y", L"%y", L"%b", L"%B", L"%m", L"%U", + L"%W", L"%j", L"%d", L"%a", L"%A", L"%w", L"%H", + L"%I", L"%M", L"%S", L"%x", L"%X", L"%p"}; +#endif + spec_list.push_back(L"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"); + + for (const auto& spec : spec_list) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(t1); + auto tm = *std::gmtime(&t); + + auto sys_output = system_wcsftime(spec, &tm); + + auto fmt_spec = fmt::format(L"{{:{}}}", spec); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), tm)); + } + + // Timezone formatters tests makes sense for localtime. +#if FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME + spec_list = {L"%z", L"%Z"}; +#else + spec_list = {L"%Z"}; +#endif + for (const auto& spec : spec_list) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(t1); + auto tm = *std::localtime(&t); + + auto sys_output = system_wcsftime(spec, &tm); + + auto fmt_spec = fmt::format(L"{{:{}}}", spec); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(fmt::runtime(fmt_spec), tm)); + + if (spec == L"%z") { + sys_output.insert(sys_output.end() - 2, 1, L':'); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(L"{:%Ez}", tm)); + EXPECT_EQ(sys_output, fmt::format(L"{:%Oz}", tm)); + } + } + + // Separate tests for UTC, since std::time_put can use local time and ignoring + // the timezone in std::tm (if it presents on platform). + if (fmt::detail::has_member_data_tm_zone<std::tm>::value) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(t1); + auto tm = *std::gmtime(&t); + + std::vector<std::wstring> tz_names = {L"GMT", L"UTC"}; + EXPECT_THAT(tz_names, Contains(fmt::format(L"{:%Z}", t1))); + EXPECT_THAT(tz_names, Contains(fmt::format(L"{:%Z}", tm))); + } + + if (fmt::detail::has_member_data_tm_gmtoff<std::tm>::value) { + auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(t1); + auto tm = *std::gmtime(&t); + + EXPECT_EQ(L"+0000", fmt::format(L"{:%z}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"+0000", fmt::format(L"{:%z}", tm)); + + EXPECT_EQ(L"+00:00", fmt::format(L"{:%Ez}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"+00:00", fmt::format(L"{:%Ez}", tm)); + + EXPECT_EQ(L"+00:00", fmt::format(L"{:%Oz}", t1)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"+00:00", fmt::format(L"{:%Oz}", tm)); + } +} + +TEST(xchar_test, color) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(fg(fmt::rgb(255, 20, 30)), L"rgb(255,20,30) wide"), + L"\x1b[38;2;255;020;030mrgb(255,20,30) wide\x1b[0m"); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, ostream) { +#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 409 + { + std::wostringstream wos; + fmt::print(wos, L"Don't {}!", L"panic"); + EXPECT_EQ(wos.str(), L"Don't panic!"); + } + + { + std::wostringstream wos; + fmt::println(wos, L"Don't {}!", L"panic"); + EXPECT_EQ(wos.str(), L"Don't panic!\n"); + } +#endif +} + +TEST(xchar_test, format_map) { + auto m = std::map<std::wstring, int>{{L"one", 1}, {L"t\"wo", 2}}; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", m), L"{\"one\": 1, \"t\\\"wo\": 2}"); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, escape_string) { + using vec = std::vector<std::wstring>; + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", vec{L"\n\r\t\"\\"}), L"[\"\\n\\r\\t\\\"\\\\\"]"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", vec{L"понедельник"}), L"[\"понедельник\"]"); +} + +TEST(xchar_test, to_wstring) { EXPECT_EQ(L"42", fmt::to_wstring(42)); } + +#ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR + +template <typename Char> struct numpunct : std::numpunct<Char> { + protected: + Char do_decimal_point() const override { return '?'; } + std::string do_grouping() const override { return "\03"; } + Char do_thousands_sep() const override { return '~'; } +}; + +template <typename Char> struct no_grouping : std::numpunct<Char> { + protected: + Char do_decimal_point() const override { return '.'; } + std::string do_grouping() const override { return ""; } + Char do_thousands_sep() const override { return ','; } +}; + +template <typename Char> struct special_grouping : std::numpunct<Char> { + protected: + Char do_decimal_point() const override { return '.'; } + std::string do_grouping() const override { return "\03\02"; } + Char do_thousands_sep() const override { return ','; } +}; + +template <typename Char> struct small_grouping : std::numpunct<Char> { + protected: + Char do_decimal_point() const override { return '.'; } + std::string do_grouping() const override { return "\01"; } + Char do_thousands_sep() const override { return ','; } +}; + +TEST(locale_test, localized_double) { + auto loc = std::locale(std::locale(), new numpunct<char>()); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 1.23), "1?23"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:Lf}", 1.23), "1?230000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 1234.5), "1~234?5"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 12000.0), "12~000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:8L}", 1230.0), " 1~230"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:15.6Lf}", 0.1), " 0?100000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:15.6Lf}", 1.0), " 1?000000"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{:15.6Lf}", 1e3), " 1~000?000000"); +} + +TEST(locale_test, format) { + auto loc = std::locale(std::locale(), new numpunct<char>()); + EXPECT_EQ("1234567", fmt::format(std::locale(), "{:L}", 1234567)); + EXPECT_EQ("1~234~567", fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", 1234567)); + EXPECT_EQ("-1~234~567", fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", -1234567)); + EXPECT_EQ("-256", fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", -256)); + auto n = 1234567; + EXPECT_EQ("1~234~567", fmt::vformat(loc, "{:L}", fmt::make_format_args(n))); + auto s = std::string(); + fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(s), loc, "{:L}", 1234567); + EXPECT_EQ("1~234~567", s); + + auto no_grouping_loc = std::locale(std::locale(), new no_grouping<char>()); + EXPECT_EQ("1234567", fmt::format(no_grouping_loc, "{:L}", 1234567)); + + auto special_grouping_loc = + std::locale(std::locale(), new special_grouping<char>()); + EXPECT_EQ("1,23,45,678", fmt::format(special_grouping_loc, "{:L}", 12345678)); + EXPECT_EQ("12,345", fmt::format(special_grouping_loc, "{:L}", 12345)); + + auto small_grouping_loc = + std::locale(std::locale(), new small_grouping<char>()); + EXPECT_EQ("4,2,9,4,9,6,7,2,9,5", + fmt::format(small_grouping_loc, "{:L}", max_value<uint32_t>())); +} + +TEST(locale_test, format_detault_align) { + auto loc = std::locale({}, new special_grouping<char>()); + EXPECT_EQ(" 12,345", fmt::format(loc, "{:8L}", 12345)); +} + +TEST(locale_test, format_plus) { + auto loc = std::locale({}, new special_grouping<char>()); + EXPECT_EQ("+100", fmt::format(loc, "{:+L}", 100)); +} + +TEST(locale_test, wformat) { + auto loc = std::locale(std::locale(), new numpunct<wchar_t>()); + EXPECT_EQ(L"1234567", fmt::format(std::locale(), L"{:L}", 1234567)); + EXPECT_EQ(L"1~234~567", fmt::format(loc, L"{:L}", 1234567)); + int n = 1234567; + EXPECT_EQ(L"1~234~567", + fmt::vformat(loc, L"{:L}", fmt::make_wformat_args(n))); + EXPECT_EQ(L"1234567", fmt::format(std::locale("C"), L"{:L}", 1234567)); + + auto no_grouping_loc = std::locale(std::locale(), new no_grouping<wchar_t>()); + EXPECT_EQ(L"1234567", fmt::format(no_grouping_loc, L"{:L}", 1234567)); + + auto special_grouping_loc = + std::locale(std::locale(), new special_grouping<wchar_t>()); + EXPECT_EQ(L"1,23,45,678", + fmt::format(special_grouping_loc, L"{:L}", 12345678)); + + auto small_grouping_loc = + std::locale(std::locale(), new small_grouping<wchar_t>()); + EXPECT_EQ(L"4,2,9,4,9,6,7,2,9,5", + fmt::format(small_grouping_loc, L"{:L}", max_value<uint32_t>())); +} + +TEST(locale_test, int_formatter) { + auto loc = std::locale(std::locale(), new special_grouping<char>()); + auto f = fmt::formatter<int>(); + auto parse_ctx = fmt::format_parse_context("L"); + f.parse(parse_ctx); + auto buf = fmt::memory_buffer(); + fmt::basic_format_context<fmt::appender, char> format_ctx( + fmt::appender(buf), {}, fmt::detail::locale_ref(loc)); + f.format(12345, format_ctx); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(buf), "12,345"); +} + +FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE +template <class charT> struct formatter<std::complex<double>, charT> { + private: + detail::dynamic_format_specs<char> specs_; + + public: + FMT_CONSTEXPR typename basic_format_parse_context<charT>::iterator parse( + basic_format_parse_context<charT>& ctx) { + auto end = parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), specs_, ctx, + detail::type::float_type); + detail::parse_float_type_spec(specs_, detail::error_handler()); + return end; + } + + template <class FormatContext> + typename FormatContext::iterator format(const std::complex<double>& c, + FormatContext& ctx) { + detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>( + specs_.precision, specs_.precision_ref, ctx); + auto specs = std::string(); + if (specs_.precision > 0) specs = fmt::format(".{}", specs_.precision); + if (specs_.type == presentation_type::fixed_lower) specs += 'f'; + auto real = fmt::format(ctx.locale().template get<std::locale>(), + fmt::runtime("{:" + specs + "}"), c.real()); + auto imag = fmt::format(ctx.locale().template get<std::locale>(), + fmt::runtime("{:" + specs + "}"), c.imag()); + auto fill_align_width = std::string(); + if (specs_.width > 0) fill_align_width = fmt::format(">{}", specs_.width); + return format_to(ctx.out(), runtime("{:" + fill_align_width + "}"), + c.real() != 0 ? fmt::format("({}+{}i)", real, imag) + : fmt::format("{}i", imag)); + } +}; +FMT_END_NAMESPACE + +TEST(locale_test, complex) { + std::string s = fmt::format("{}", std::complex<double>(1, 2)); + EXPECT_EQ(s, "(1+2i)"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.2f}", std::complex<double>(1, 2)), "(1.00+2.00i)"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:8}", std::complex<double>(1, 2)), " (1+2i)"); +} + +TEST(locale_test, chrono_weekday) { + auto loc = get_locale("es_ES.UTF-8", "Spanish_Spain.1252"); + auto loc_old = std::locale::global(loc); + auto sat = fmt::weekday(6); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", sat), L"Sat"); + if (loc != std::locale::classic()) { + // L'\xE1' is 'á'. + auto saturdays = std::vector<std::wstring>{L"s\xE1""b", L"s\xE1."}; + EXPECT_THAT(saturdays, Contains(fmt::format(loc, L"{:L}", sat))); + } + std::locale::global(loc_old); +} + +TEST(locale_test, sign) { + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(std::locale(), L"{:L}", -50), L"-50"); +} + +TEST(std_test_xchar, optional) { +# ifdef __cpp_lib_optional + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", std::optional{L'C'}), L"optional(\'C\')"); + EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", std::optional{std::wstring{L"wide string"}}), + L"optional(\"wide string\")"); +# endif +} + +#endif // FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR |
